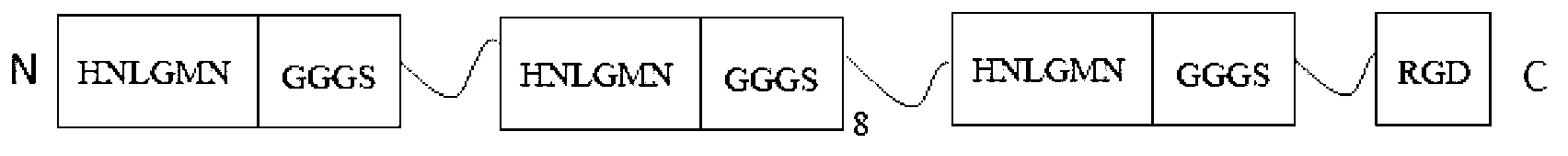Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93 results about "Adhesion protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods and compositions based on inhibition of cell invasion and fibrosis by anionic polymers
Owner:TRIAD
Adhesive compounds and methods use for hernia repair
ActiveUS20120116424A1Inhibits and reduces growth of biofilmImprove cohesionSurgical adhesivesPolyether adhesivesMedicinal chemistryAdhesive proteins
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
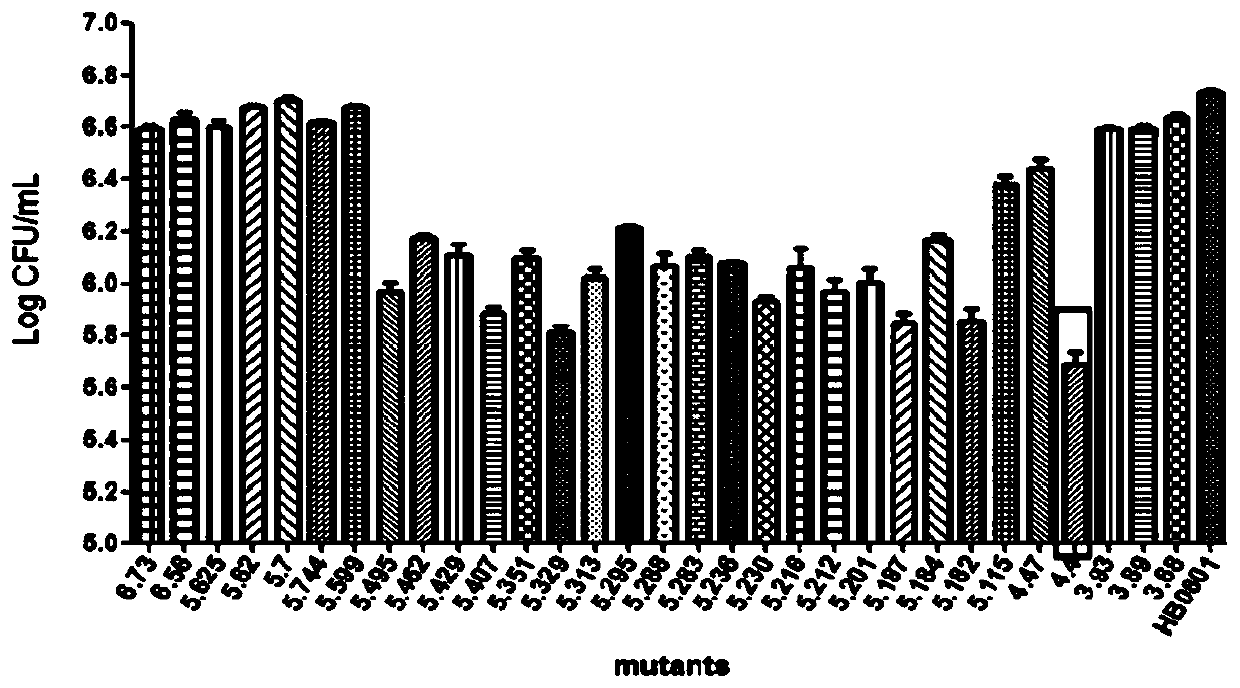
Mycoplasma bovis gene mutation strain having reduced adhesion capacity and adhesion protein
ActiveCN109837226AReduce adhesionDemonstrated adhesionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the technical field of prevention and treatment of animal borne diseases, and relates to a mycoplasma bovis gene mutation strain having reduced adhesion capacity and adhesionprotein. The protein gene Mbov_0503 is cloned from a mycoplasma bovis HB0801 genome. According to the partiality properties of escherichia coli to codons, the Mbov_0503 gene is modified, and mycoplasma bovis tryptophan codons UGA are mutated into codons UGG for coding tryptophan in the escherichia coli, so that recombination protein Mbov0503 is obtained. The nucleotide sequence of the protein geneis shown as SEQID NO:13, and the coded protein sequence is shown as SEQID NO:14. The mutation strain is the adhesion defect strain screened from a mutant library. Compared with wild strains, the mutation stain has the advantages that the adhesion capacity to host EBL cells, the cross-membrane transmission capacity to MDBK cells and destructivity to tight connection between cells of the mutation strain are notably reduced. The mycoplasma bovis gene mutation strain can be used for prevention and treatment of mycoplasma bovis diseases.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Fish and shrimp phagostimulant of famented product adhesion protein and its prepn process
InactiveCN101088362AImprove immunity and disease resistanceMaintain metabolismClimate change adaptationMicroorganism/unicellular-algae proteins working-upMetaboliteAntioxidant
The fish and shrimp phagostimulant of fermented product and adsorbed protein is prepared through screening beneficial bacteria seed from cultivated animal body, culturing in composite culture medium to proliferate, concentrating and adding plant protein with phagostimulant effect. It is added into fish and shrimp feed to raise their feed intake and improve their digesting function. The production process has combined beneficial microbe fermenting technology and low temperature drying technology to ensure the fast growth of beneficial bacteria, the well preservation of metabolic product and the special cultivating function. The fish and shrimp phagostimulant is one kind of green product capable of replacing traditional phagostimulant and antioxidant.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHUANGBO ECOLOGICAL ENG
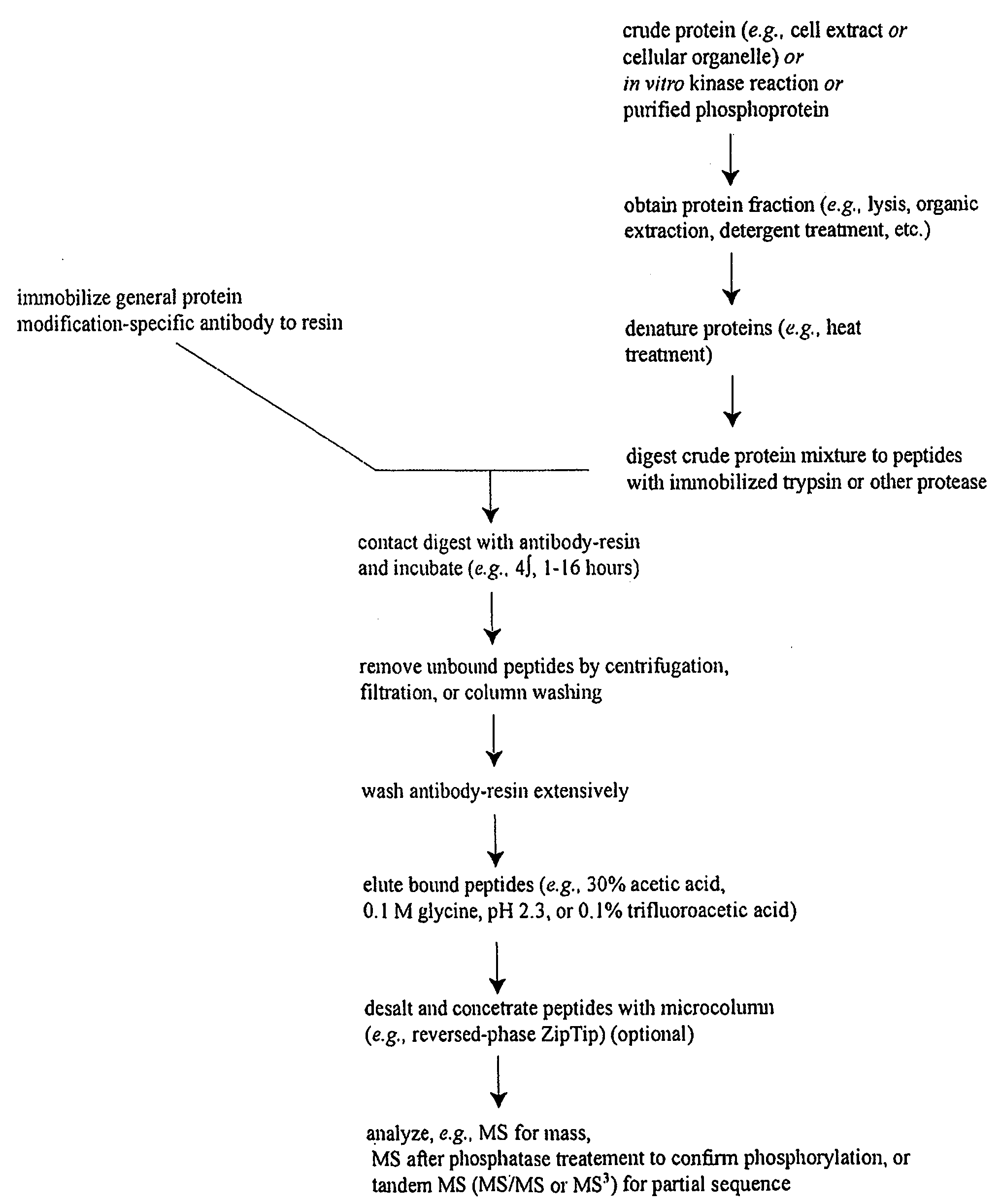
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090258442A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationPhospholipaseADAMTS Proteins
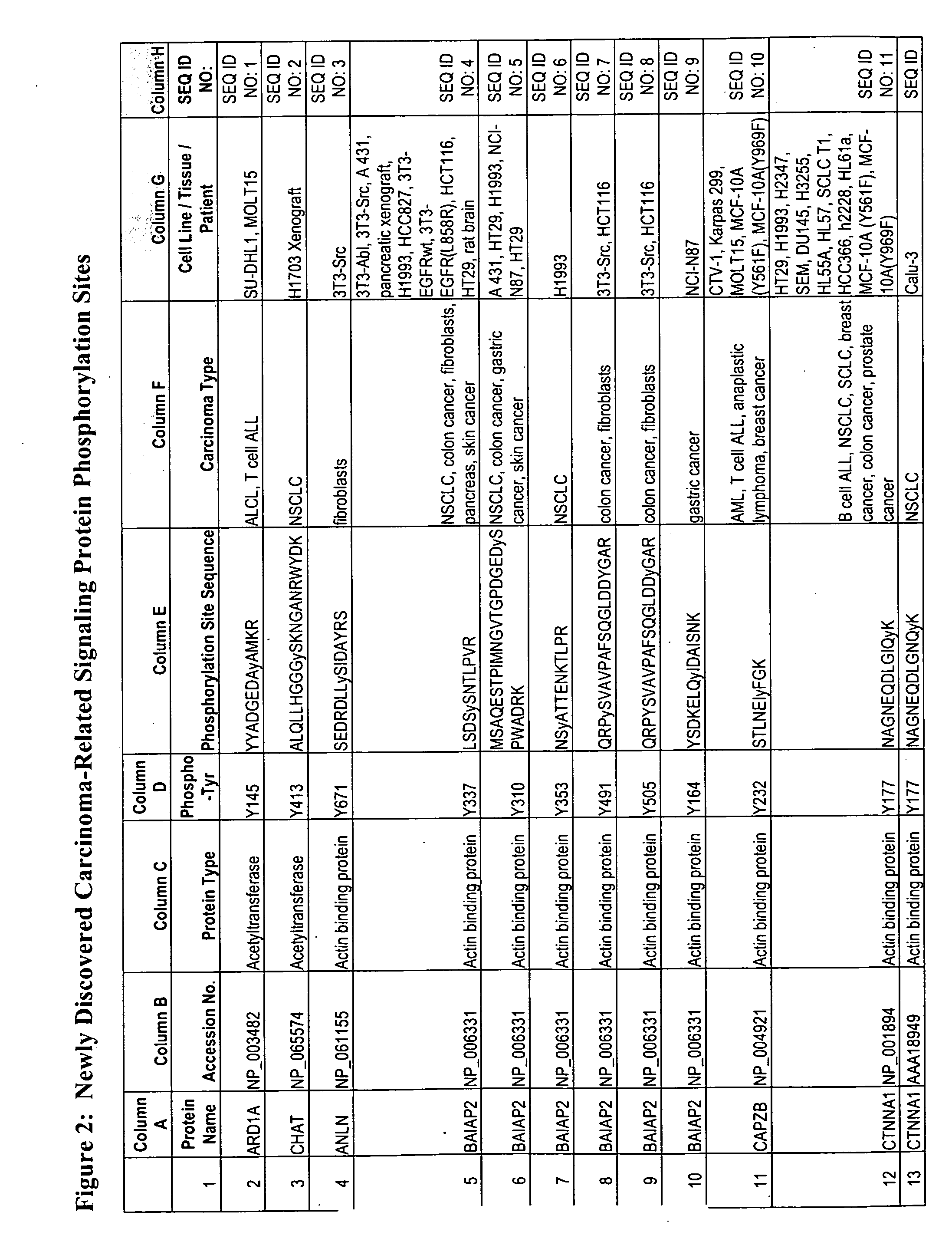
The invention discloses nearly 474 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Kinase, Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Phosphatase, G protein Regulator / Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors / GTPase Activating Proteins, Cytoskeleton Proteins, DNA Binding Proteins, Phospholipase, Receptor Proteins, Enzymes, DNA Repair / Replication Proteins, Adhesion Proteins, and Proteases, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
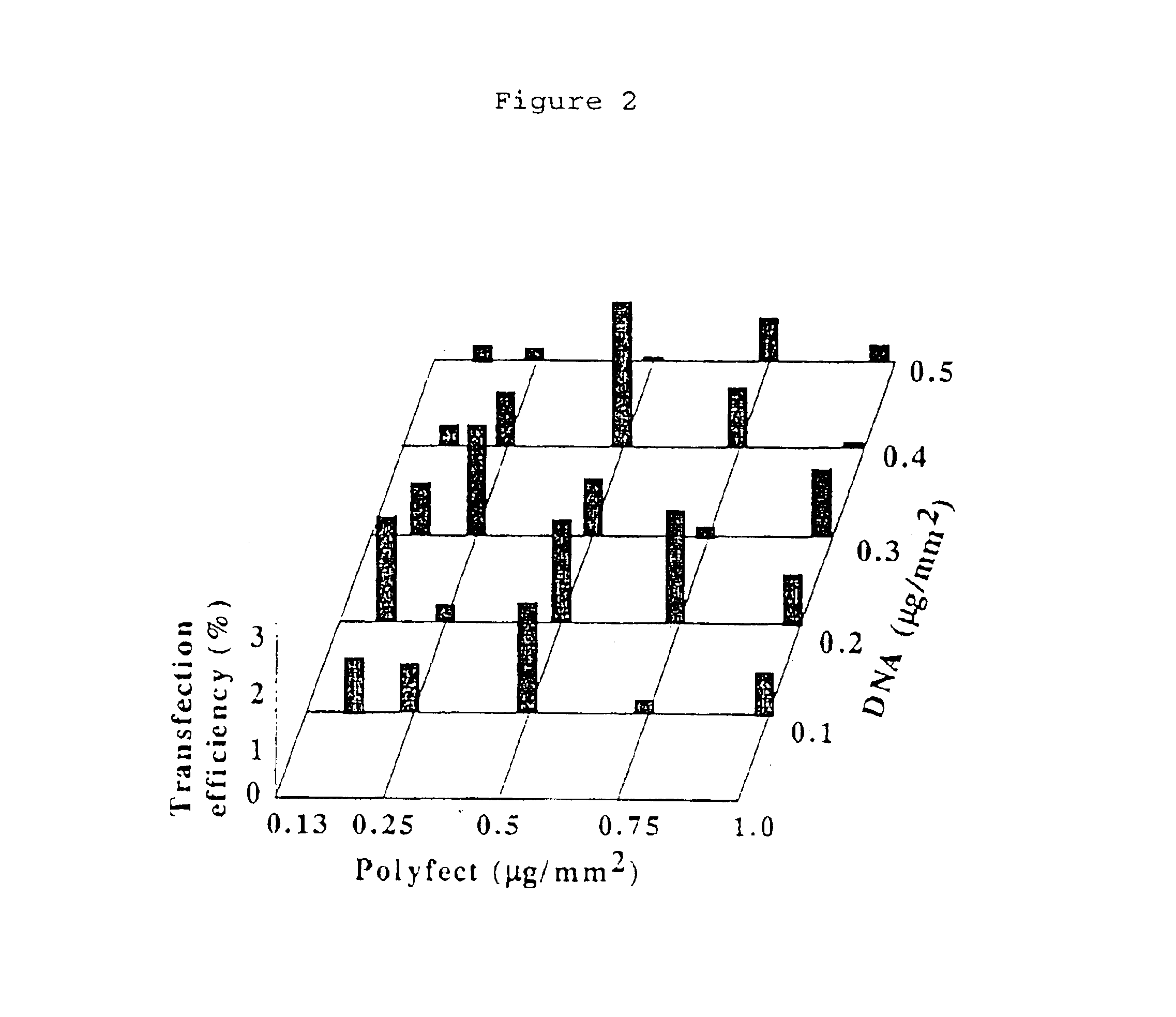
DNA array for high throughput solid-phase transfection and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6905878B2High transfection efficiencyReduce cross contaminationMicroencapsulation basedMicrobiological testing/measurementSolid phasesSolid base
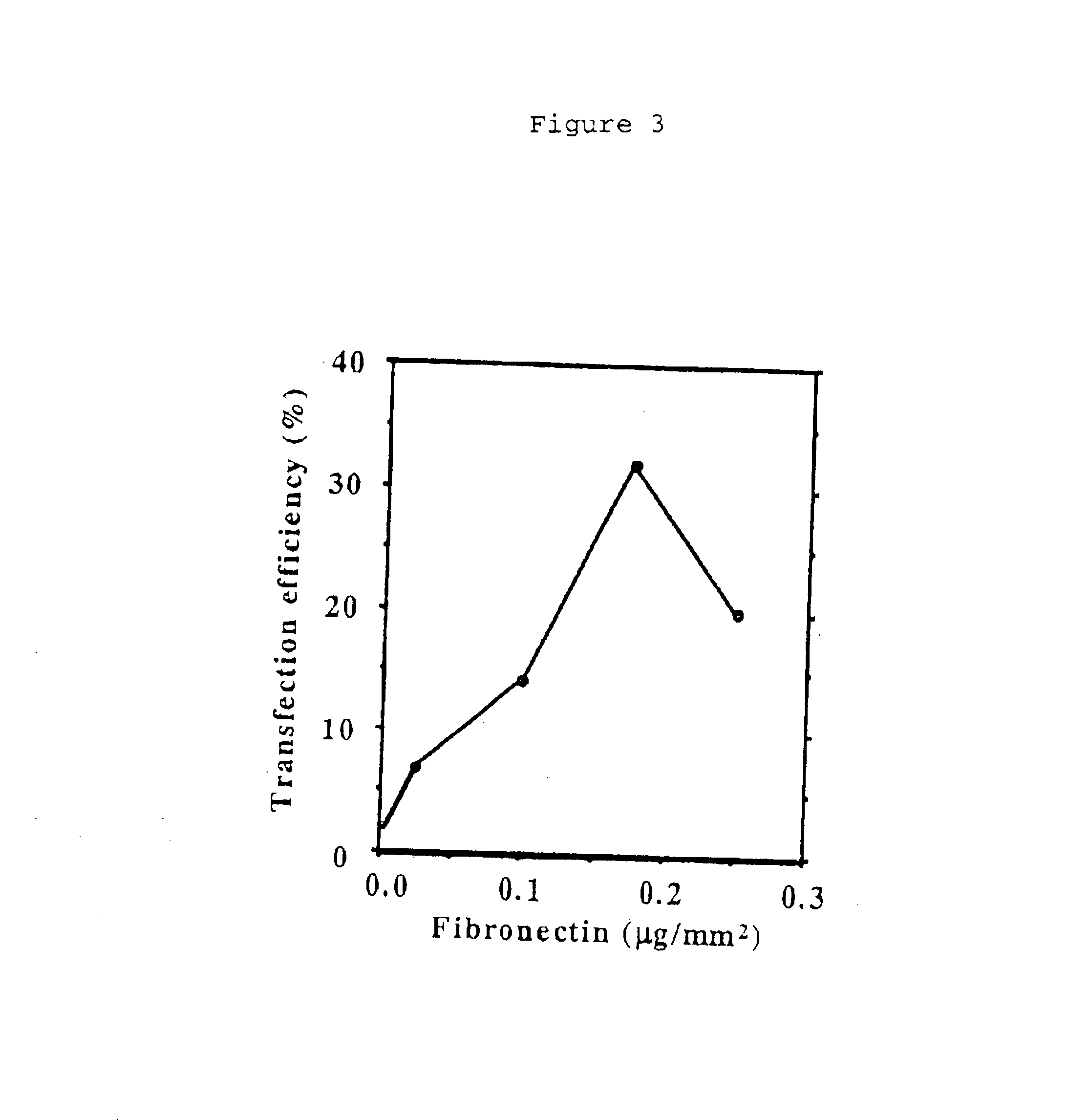
The present invention relates to a DNA array for high throughput and highly efficient solid-based transfection which comprises a plurality of dried spots on a solid support, said dried spot comprises (1) a plasmid DNA to be introduced into cells, (2) a transfection reagent and (3) a cell-adhesion protein and to a high throughput and highly efficient solid-based transfection method to introduce plasmid DNA into cells, using the same.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Immobilization of biomolecules on substrates by attaching them to adsorbed bridging biomolecules
InactiveUS20040029156A1Expensive productSimple taskBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyAdhesive proteinsChemistry
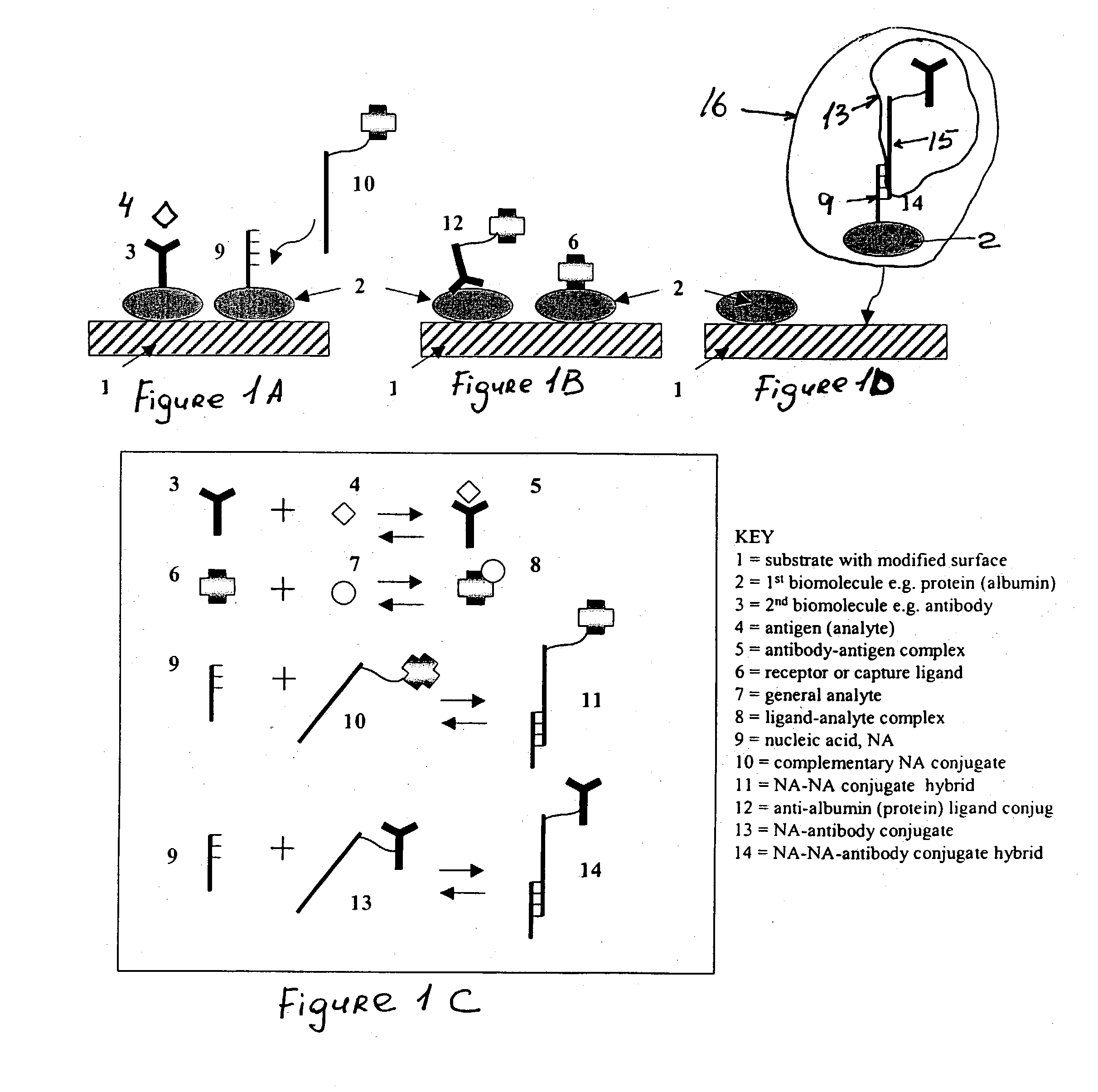
An assay article for detection first biomolecules contained in a sample is described. The assay article includes a substrate having a modified surface and a first biomolecule directly adsorbed and immobilized on the modified surface of the substrate without linking moieties. A second biomolecule is bound to or adsorbed on the first biomolecule. Also disclosed is a method of making the assay article. A first biomolecule (other than an adhesive protein) is contacted with a modified surface of a substrate. The substrate is dried to directly adsorb the first biomolecule and immobilize it on the modified surface of the substrate without additional fixing steps to form an activated substrate. Then, a second biomolecule is contacted with the activated substrate under conditions sufficient for the first biomolecule to bind the second biomolecule.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Establishment and expression of fusion protein having function of adsorbing heavy metal ions, and application fusion protein in bioremediation
The invention discloses a preparation method of a fusion protein (SEQ ID No: 4) of a decamer containing a metal binding polypeptide and a connecting peptide, and a skin cell adhesion tripeptide, and an application of the fusion protein, especially an application of the fusion protein in the field of cosmetics. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is characterized by comprising the following steps of: obtaining a DNA sequence (SEQ ID No: 8) for coding the fusion protein of the decamer containing the metal binding polypeptide and the connecting peptide, and the skin cell adhesion tripeptide by virtue of a gene engineering technique, and then performing recombination expression by a surface display method in lactic acid bacteria. As the metal binding polypeptide and the skin cell adhesion protein have the abilities of binding harmful heavy metal ions and increasing the adhesive skin of an expression host, respectively, the cosmetics prepared from lactic acid engineering bacteria of the fusion protein of the decamer containing the metal binding polypeptide and the connecting peptide and the skin cell adhesion tripeptide expressed by the surface display method are capable of effectively reducing accumulation of toxic heavy metals in skin; and therefore, the effect of bioremediation is achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BIO ZONE BIOTECH +1
Method for preparing novel mixing artificial blood vessel
The present invention discloses a method for preparing a novel mixing artificial blood vessel, which relates to a surface treatment of artificial blood vessel materials, and the object is to improve the adhesiveness of vascular smooth muscle cells and vascular endothelial cells. According to the present researches, the endothelialization of artificial blood vessel is considered a new direction for researching, but the monolayer endothelial cells on the inner surface of the artificial blood vessel are easy to partly lose under shearing force. According to the invention, 75% medical alcohol is instilled to increase the permeability of the artificial blood vessel and 0.01% fiber adhesion protein coating is used to increase the adhesiveness, in order to increase the adhesiveness of the blood vessel endothelial cells and the surface of the artificial blood vessel. Besides, blood vessel smooth muscle cells and blood vessel endothelial cells are respectively inoculated on the inner surface of the artificial blood vessel to construct an artificial blood vessel with better organism simulation. The method for preparing a novel mixing artificial blood vessel provided by the invention establishes the foundation for the subsequent development and exploitation of organization engineering artificial blood vessel having compositions and functions similar to a physiological artery.
Owner:THE STOMATOLOGIAL HOSPITAL OF ZHEJIANG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
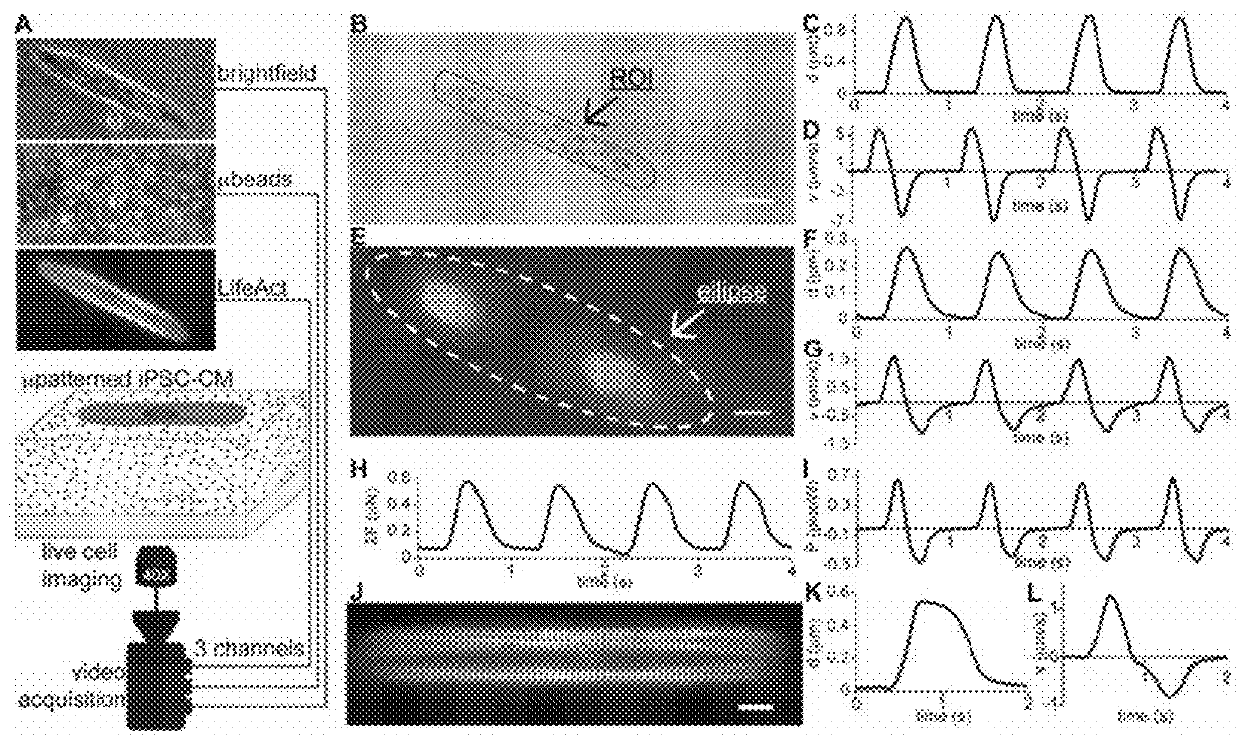
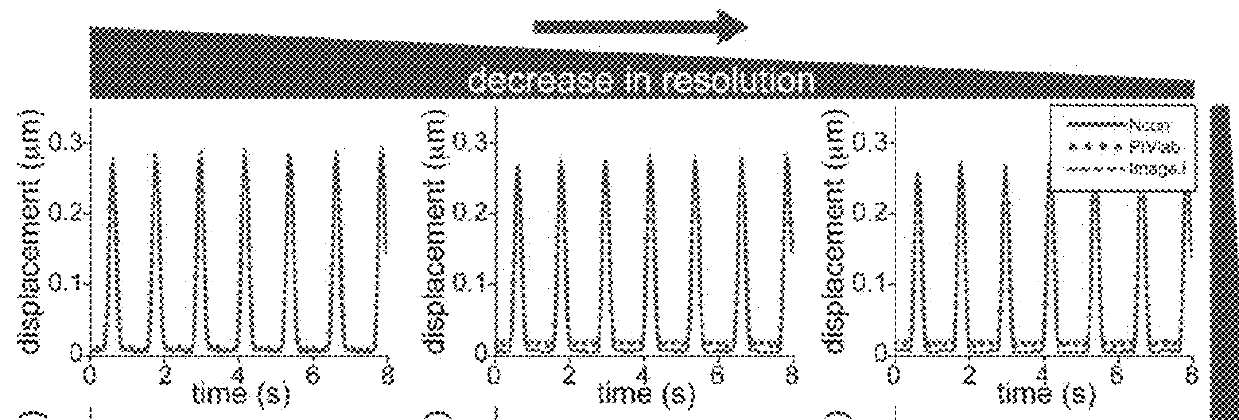
High throughput cardiotoxicity screening platform
InactiveUS20180106782A1Analyze loss of synchronicity of beatingEasy to holdUnknown materialsBiological testingHipsc cmsTraction force microscopy
Systems for assaying human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) are provided. Aspects of the systems include a traction force microscopy substrate, such as a traction force microscopy hydrogel (TFM-hydrogel), having an adhesion protein domain on a surface thereof; a video imager configured to obtain video data from an hiPSC-CM present on the adhesion protein domain; and a processing module configured to receive the video data and derive a parameter of the hiPSC-CM therefrom. Also provided are methods of using the systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Blocking the migration or metastasis of cancer cells by affecting adhesion proteins and the uses of new compounds thereof
This invention provides methods, processes, compounds and compositions for modulating the gene expression and modulating the secretion, expression, or synthesis of adhesion proteins or their receptors to cure disease, wherein the modulating comprises positive and negative regulating; wherein comprises inhibiting cancer growth, wherein the adhesion proteins or receptors comprise fibronectin, integrins family, Myosin, vitronectin, collagen, laminin, Glycosylation cell surface proteins, polyglycans, cadherin, heparin, tenascin, CD 54, CAM, elastin and FAK; wherein the methods, processes, compounds and compositions are also for anti-angiogenesis; wherein the cancers comprise breast cancer, leukocyte cancer, liver cancer, ovarian cancer, bladder cancer, prostate cancer, skin cancer, bone cancer, brain cancer, leukemia cancer, lung cancer, colon cancer, CNS cancer, melanoma cancer, renal cancer or cervix cancer.
Owner:PACIFIC ARROW
Highly bioactive extracellular matrix material and preparation method and application thereof
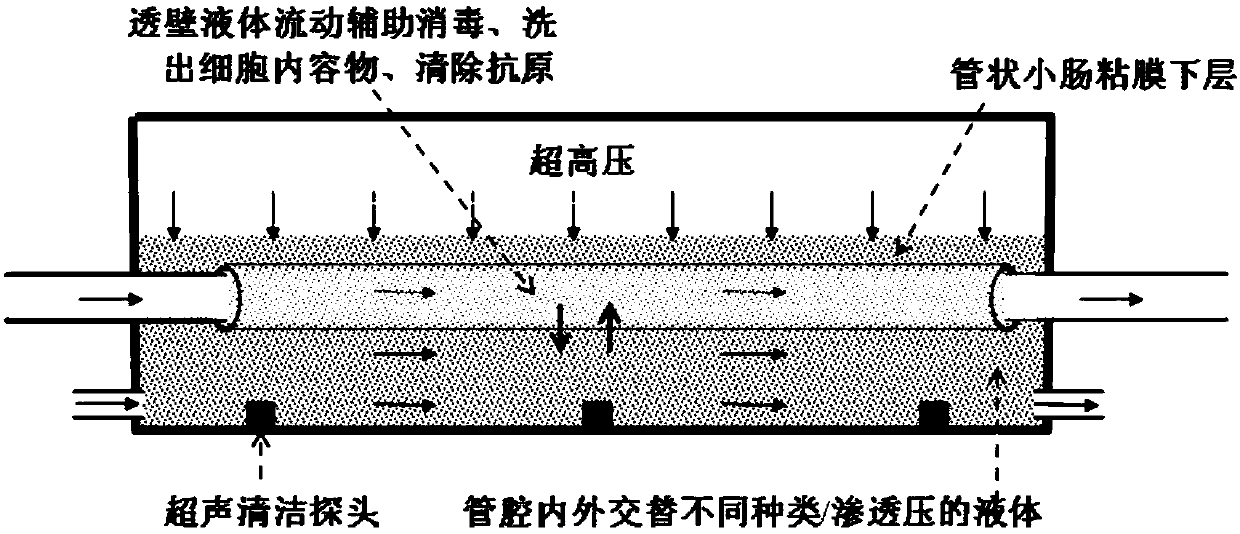
ActiveCN107823710AIn line with the law of regenerationAchieving functional restorationTissue regenerationProsthesisUltra high pressureCell-Extracellular Matrix
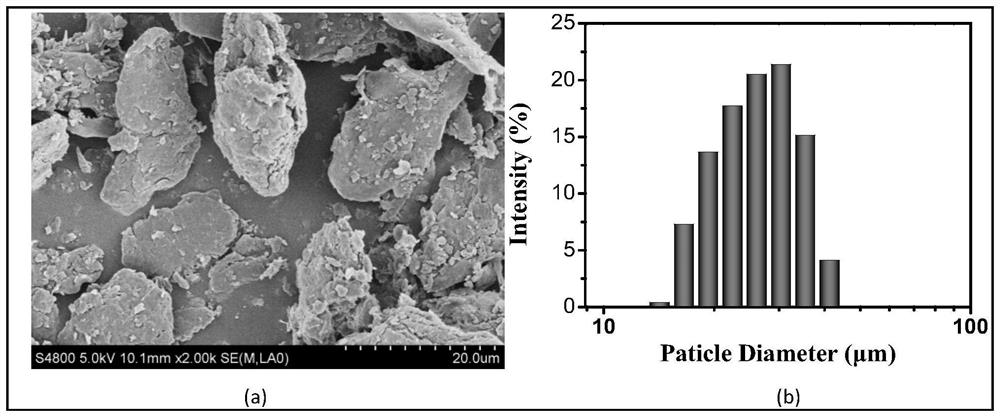
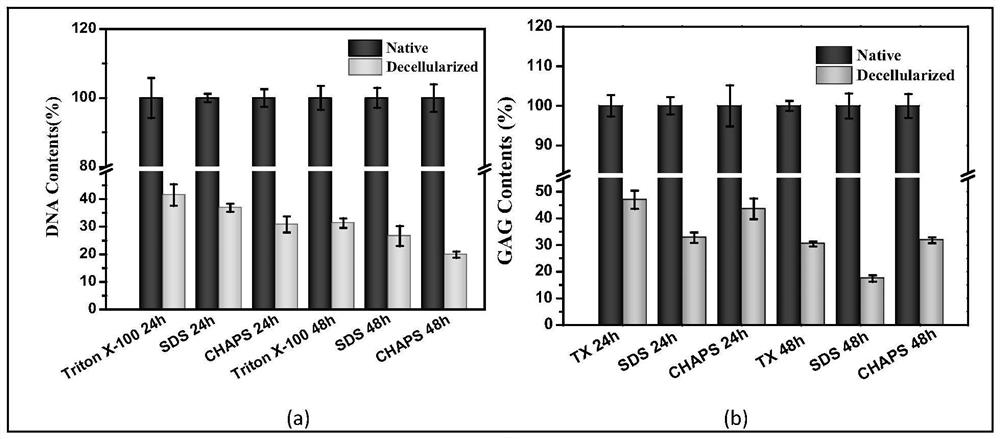
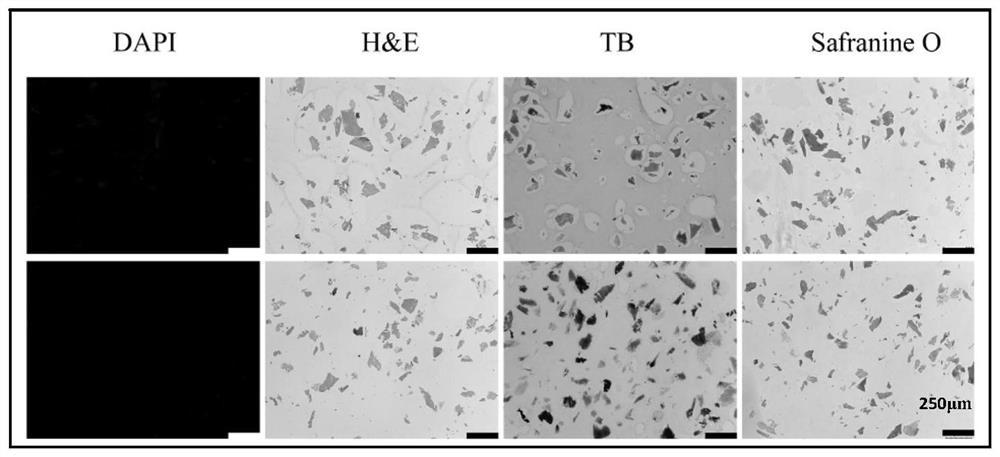
The invention relates to a highly bioactive extracellular matrix material and a preparation method and an application thereof. The material is prepared from raw materials with combined use of ultra-high pressure and cavity internal and external perfusion. The preparation method mainly includes the steps: raw material obtaining and preparation, and pretreatment; extracellular matrix mechanical separation; ultra-high pressure crushing and decellularizing; cell content elution and antigen elimination; and ultimately disinfection, sterilization and preservation. Compared with an extracellular matrix obtained by decellularizing through a mechanical oscillation method and a chemical reagent or biological reagent method, the extracellular matrix obtained by the preparation method has the retention amount of adhesion proteins, growth factors, proteoglycans, glycoproteins, glycosaminoglycans and other bioactive components significantly improved; at the same time, the mechanical strength is wellretained, the decellularizing is thorough, and viruses and other biological supporters are removed cleanly and industrialized production is convenient.
Owner:EXCELLENCE MEDICAL TECH SUZHOU CO LTD +2
Carbocyclic hydrazino inhibitors of copper-containing amine oxidases
InactiveUS6982286B2Inhibits adhesion of leukocyteUseful in treatmentBiocideNervous disorderHydrazine compoundOxidative enzyme
The present invention is directed to carbocyclic hydrazino compounds that function as inhibitors of copper-containing amine oxidases commonly known as semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidases (SSAO), including the human SSAO known as Vascular Adhesion Protein-I (VAP-1). These SSAO inhibitors have therapeutic utility as drugs to treat conditions and diseases including, but not limited to, a number of inflammatory conditions and diseases (in particular chronic inflammatory conditions such as chronic arthritis, inflammatory bowel diseases, and chronic skin dermatoses), diseases related to carbohydrate metabolism and to aberrations in adipocyte differentiation or function and smooth muscle cell function, and vascular diseases. The novel compounds have the general formula: or a pharmaceutically acceptable solvate, hydrate, or salt thereof wherein R1 to R11 are as defined herein.
Owner:BIOTIE THERAPIES CORP
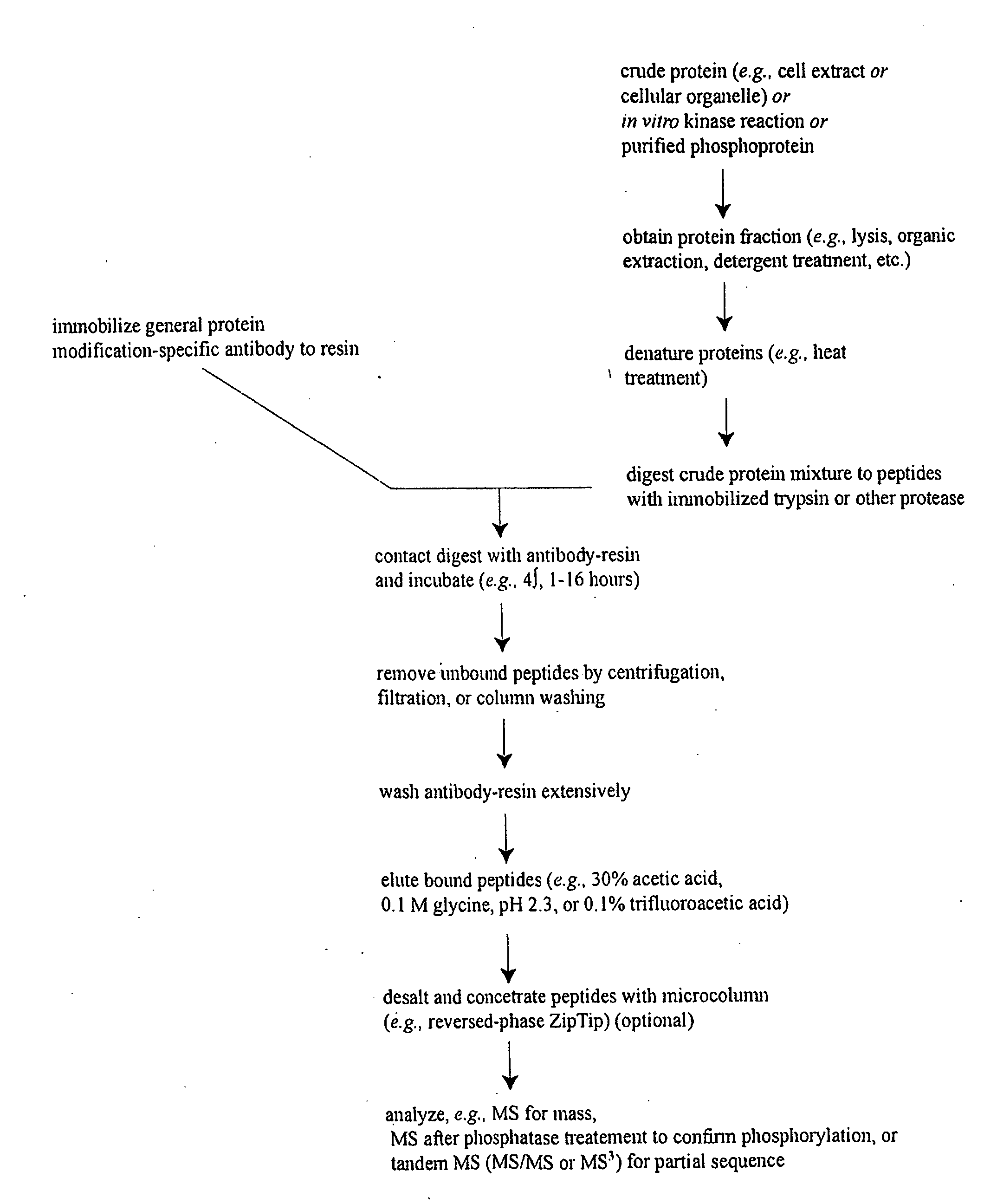
Method for screening and identifying adhesion proteins
InactiveCN101881751AImprove screening efficiencyLow costMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMagnetic beadThroughput
The invention provides a method for screening and identifying adhesion proteins. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: carboxylating superficial magnetic beads; processing the carboxylated magnetic beads by using carbodiimide and sulfo-hydroxysuccinimide; covalently coupling the magnetic beads with enterocyte debris to form amido bonds; after cleaning the magnetic beads, incubating the magnetic beads and probiotic surface protein solution together for one hour; washing the magnetic beads by using PBS buffer solution for three times to remove non-adhesion surface proteins; eluting the adhesion proteins by using 50 mM of glycine hydrochloric acid buffer solution of which the pH value is 2.3; and after SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, sequencing by mass spectrometry to identify the adhesion proteins. The method for screening and identifying the adhesion proteins has the advantages that: a magnetic bead method makes use of the characteristic that the adhesion proteins can adhere enterocyte to combine the function and separation into one step, so that the efficiency of screening the adhesion proteins is greatly improved, and the adhesion proteins can be efficiently screened and identified in a high-throughput mode; and compared with the conventional chromatography method, the method has the advantages of low cost, time saving, labor saving, and capacity of screening and identifying a plurality of adhesion proteins in one step.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Macrophage vesicle entrapped nano-drug preparation and application thereof in treating arthritis
InactiveCN111346070AGood treatment effectOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticImmunosuppressive drugArthritis
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, relates to preparation of bionic nano-carriers and targeted treatment of arthritis, and particularly relates to a macrophage vesicle entrappednano-drug preparation and application thereof in treating arthritis. The nano-drug preparation targets an arthritis part through adhesive protein on the surface of a macrophage vesicle, and an immunosuppressive drug is delivered for targeted treatment of arthritis. Furthermore, a new strategy for targeted treatment of arthritis is provided for clinical practice, and the strategy comprises the steps of fusing an artificial drug carrier and the natural macrophage vesicle, and constructing the stable macrophage vesicle entrapped nano-drug preparation, thereby improving the targeted treatment effect of arthritis.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Preparation method of cartilage acellular matrix composite scaffold and application thereof
ActiveCN111840642ADesign scienceImprove controllabilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationCartilage cellsAcellular matrix
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical materials, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a cartilage acellular matrix composite scaffold and an application thereof. The structure of the cartilage acellular matrix composite scaffold is shown as a formula I, and the cartilage acellular matrix composite scaffold is a natural polymer or a derivative thereof and is a digested cartilage acellular matrix; wherein the mass percentage of the natural polymer or the derivative thereof is 25-75%, preferably 25-50%; wherein the mass percentage of the digested cartilage acellular matrix is 25-75%, preferably 50-75%. The invention discloses an acellular matrix / natural polymer composite material, after being implanted into a body, natural macromolecules or derivatives thereof are gradually degraded and absorbed in vivo, adhesion protein, growth factors and the like in acellular matrixes promote mesenchymal stem cells in bone marrow blood to differentiate into cartilage cells andmaintain the phenotype of the cartilage cells, the cartilage healing effect is effectively improved, a good operation curative effect is achieved, and the clinical application prospect is good.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Macroporous bioengineered scaffolds for cell transplantation
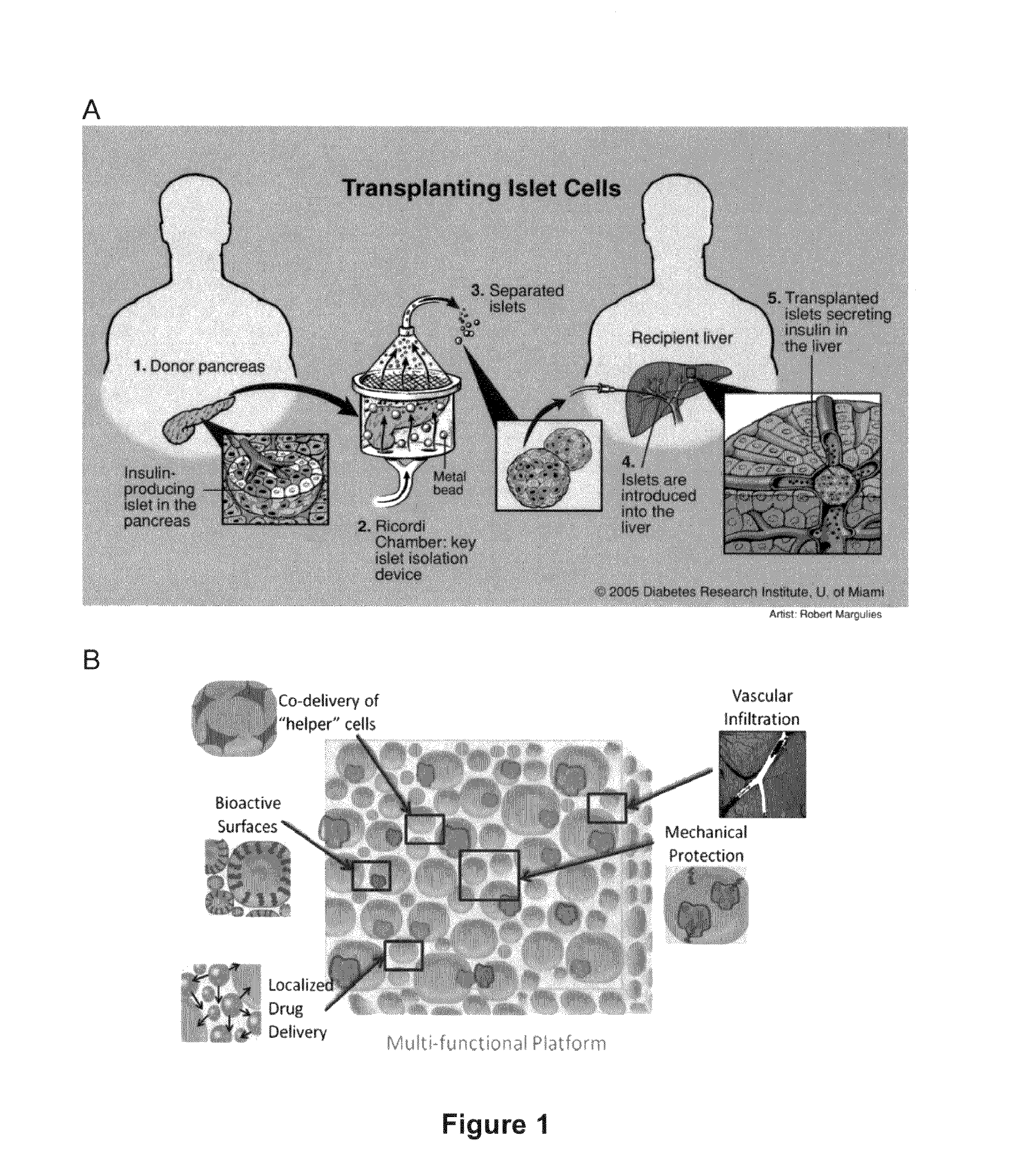
InactiveUS20130089594A1Hindering nutrient deliveryImprove viabilityBiocidePancreatic cellsCell adhesionInsulin producing cell
The present invention provides highly porous, biocompatible and biostable scaffold constructs for improving overall cell engraftment, survival, function and long-term viability. These scaffolds can provide mechanical protection to implanted cells, afford retrievability from a subject, and allow for both intra-device vascularization and a means to spatially distribute the cells within the device. The scaffold surface or material may be modified with one or more different adhesion proteins and optionally other biological factors for enhanced cell adherence and viability. Further, the scaffold surface or material may be modified with one or more agents with slow / sustained release characteristics to aid engraftment, survival, function or long-term viability. Implanted cells of the invention may be insulin-producing cells such as islets.
Owner:CONVERGE BIOTECH INC +1
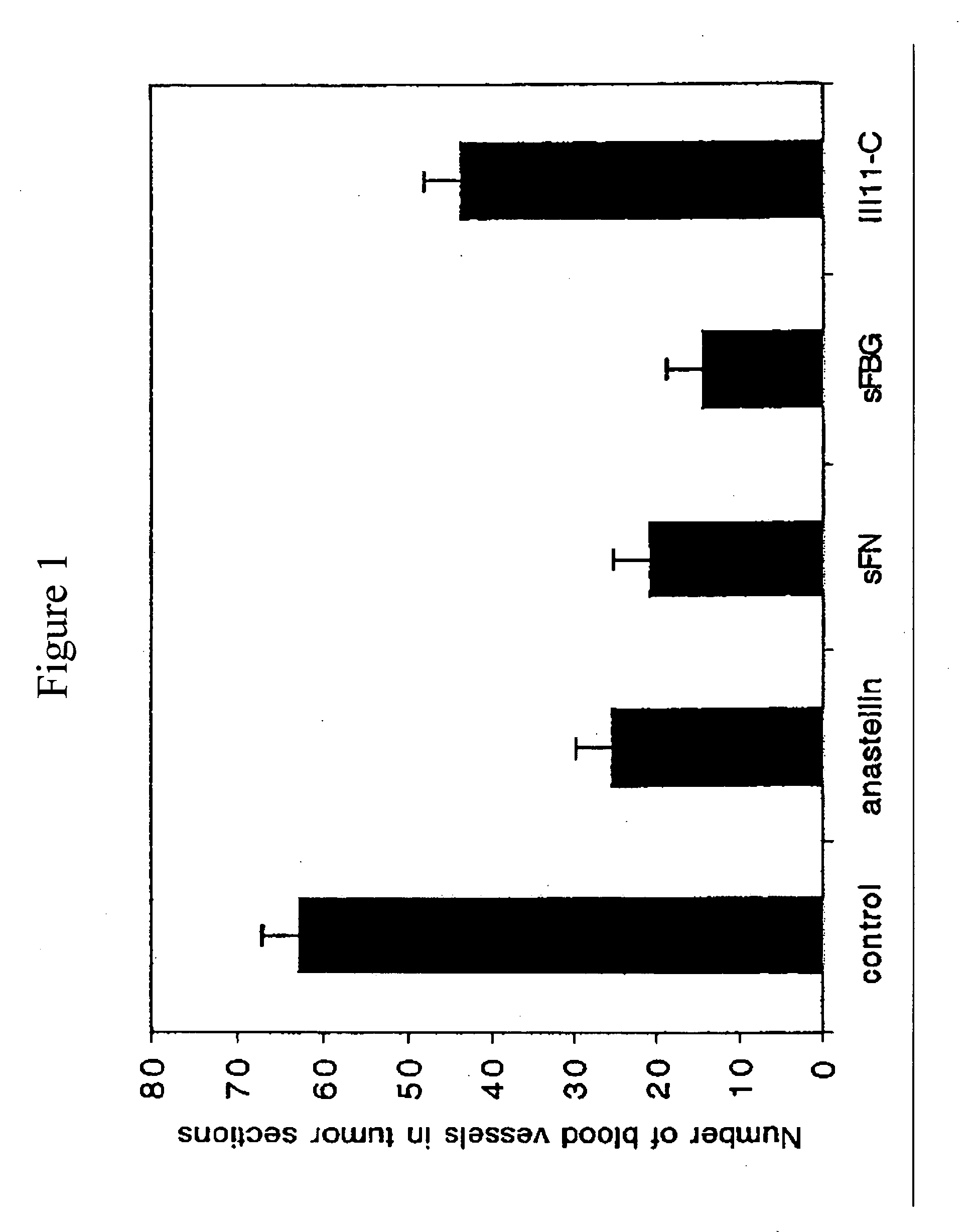
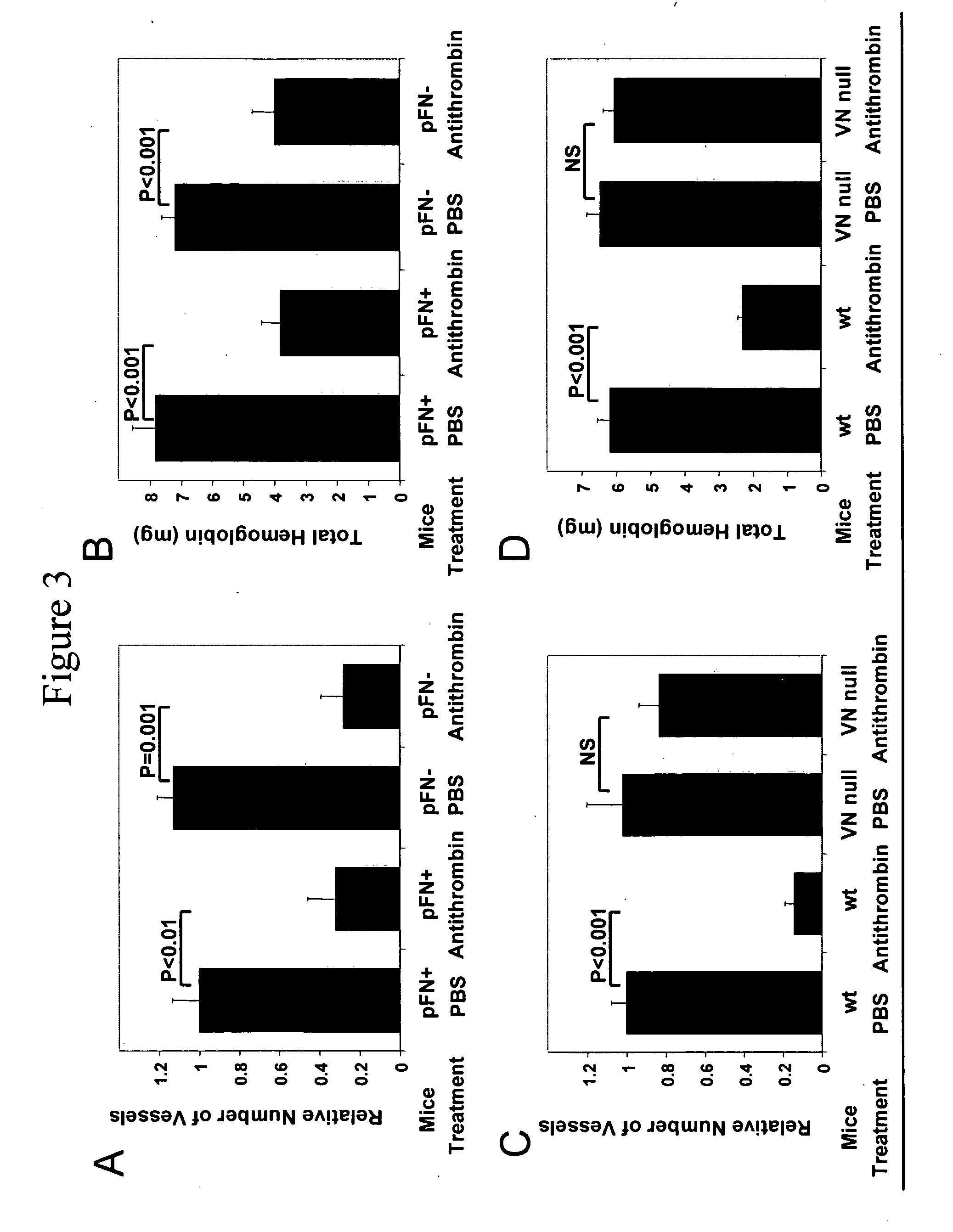
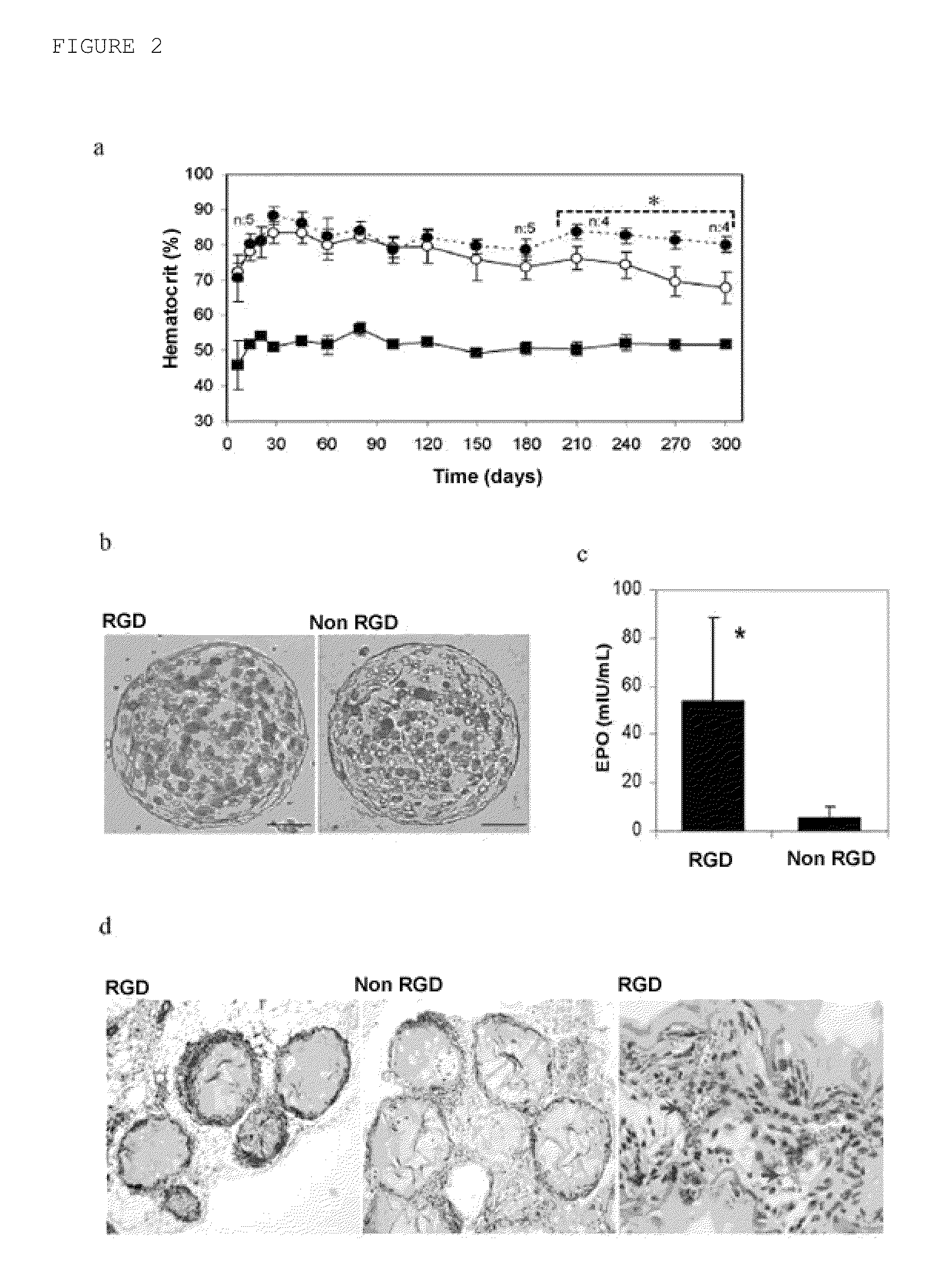
Methods and compositions for inhibiting tumor growth and angiogenesis
InactiveUS20070015708A1Connective tissue peptidesCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsLymphatic SpreadAngiogenesis growth factor
The invention provides compositions comprising angiogenesis inhibitors and RGD-containing plasma adhesion proteins in a pharmaceutical carrier. This invention also provides methods of inhibiting angiogenesis, tumor growth and metastasis by administering angiogenesis inhibitors in combination with RGD-containing plasma adhesion proteins in a pharmaceutical carrier.
Owner:RUSHTI ERKKI
Method for separating and purifying mussel adhesive protein
InactiveUS20200062809A1High purityLow production costAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptide preparation methodsInsoluble proteinOrganic solvent
Provided is a method for separating and purifying a mussel adhesive protein, including the steps of: (1) crushing cells containing a mussel adhesive protein; (2) centrifuging the crushed cells to obtain an insoluble protein aggregate including the mussel adhesive protein; (3) treating the insoluble protein aggregate with an acidic organic solvent to obtain a low-purity mussel adhesive protein solution; (4) selectively precipitating the mussel adhesive protein by controlling the acidity of the low-purity mussel adhesive protein solution; and (5) treating the precipitate with a surfactant to remove endotoxins from the mussel adhesive protein. The method of the subject matter can purify a large amount of mussel adhesive proteins of high purity with a simple process. In particular, the subject matter can be applied effectively to the development of novel uses of mussel adhesive proteins by significantly reducing production costs through economical production of the mussel adhesive protein.
Owner:KOLLODIS BIOSCI
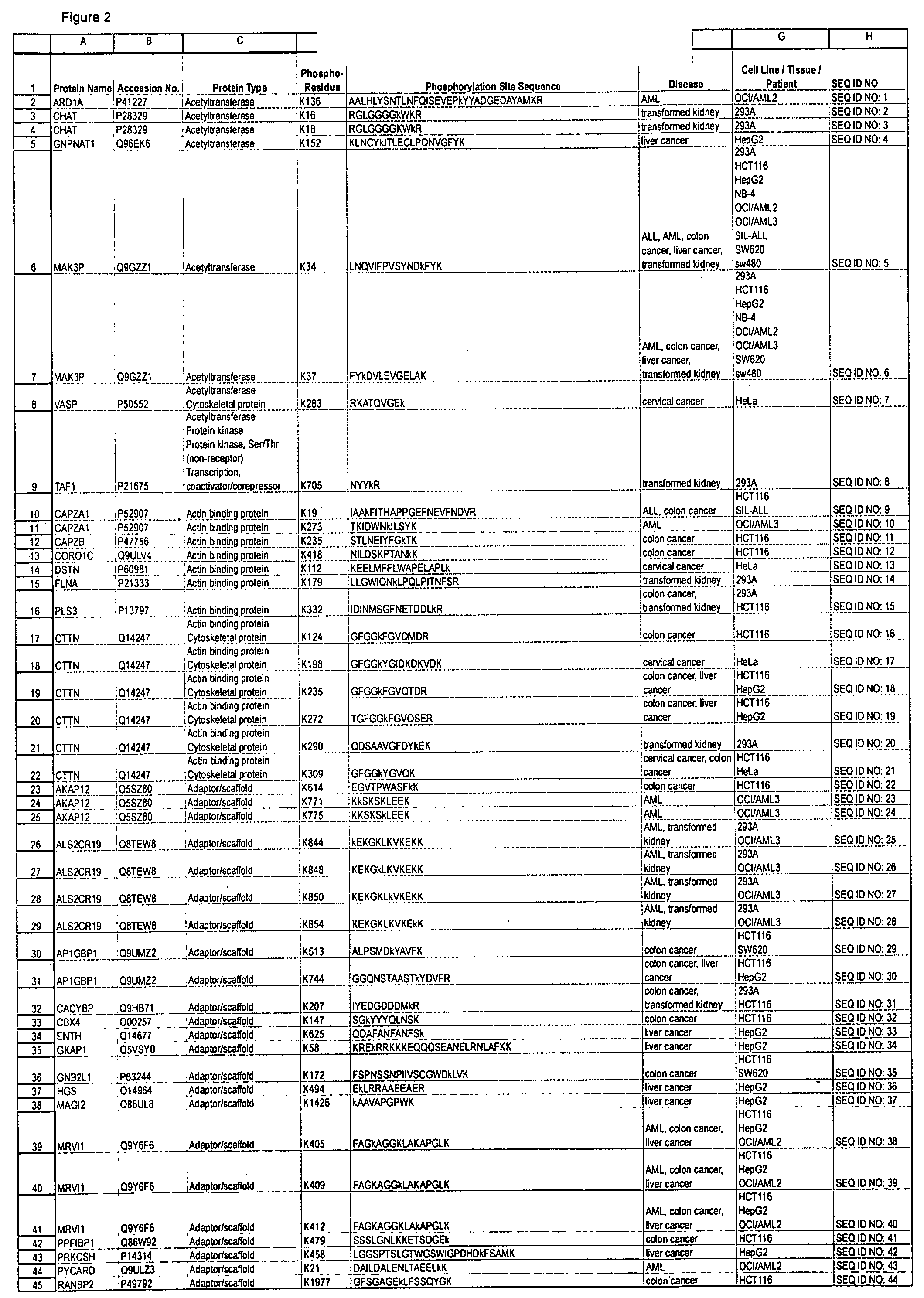
Reagens for the Detection of Protein Acetylation Signaling Pathways
InactiveUS20090124023A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingCell Surface ProteinsMetabolic enzymes
The invention discloses 432 novel acetylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human protein acetylation signaling pathways, and provides acetylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these acetylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the acetylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Acetyltransferases, Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Actin binding proteins, Adhesion proteins, Apoptosis proteins, Calcium-binding proteins, Cell Cycle Regulation proteins, Cell Surface proteins, DNA binding proteins, DNA replication proteins, Channel proteins, Chaperone proteins, Cellular Metabolism enzymes, Cytoskeletal proteins, DNA repair proteins, Endoplasmic reticulum proteins, Enzyme proteins, G protein and GTPase Activating proteins, Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors, Helicase proteins, Isomerase proteins, Extracelluar matrix proteins, Hydrolases, Ligase proteins, Lipid kinases, Inhibtor proteins, Lipid Binding proteins and Lyases.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Rgd-modified alginate microparticles as a drug release system
The object of the present invention is to provide particles of a polymeric material containing cells therein, wherein said particles have a strength that is substantially greater than the microcapsules known in the state of the art. Said strength is achieved by means of functionalizing the polymeric material forming the microcapsule with a peptide which can bind to the adhesion proteins of the cell membrane, such that the cells act as cross-linking agents of the matrix resulting in an improvement of the mechanical properties of the matrixes
Owner:UNIV DEL PAIS VASCO EUSKAL HERRIKO UNIBERTSITATEA
Mussel adhesive protein product and applications thereof in suppression of skin inflammations
ActiveUS10568938B2Keep for a long timeImprove permeabilityCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsEczematous rashDrug eruption
Disclosed are applications of a mussel adhesive protein or preparations thereof in suppression of skin inflammations. Specifically disclosed are applications of a mussel adhesive protein, preparations thereof and applications thereof in dermatitis, eczema, skin ulcer, technologies related to burns (comprising skin grafting), perniones, surgical incisions, herpes, abrasions, scars, psoriasis, erythema multiforme, skin damage after radiotherapy, skin cancers, folliculitis, urticaria and drug eruption, and applications in sunburn, polymorphous light eruption, pathological alopecia (comprising hair transplant), acne vulgaris, rosacea (that is, acne rosacea), and the like, and applications in the treatment of otitis externa.
Owner:BENGT I SAMUELSSON INST OF LIFE SCI CO LTD
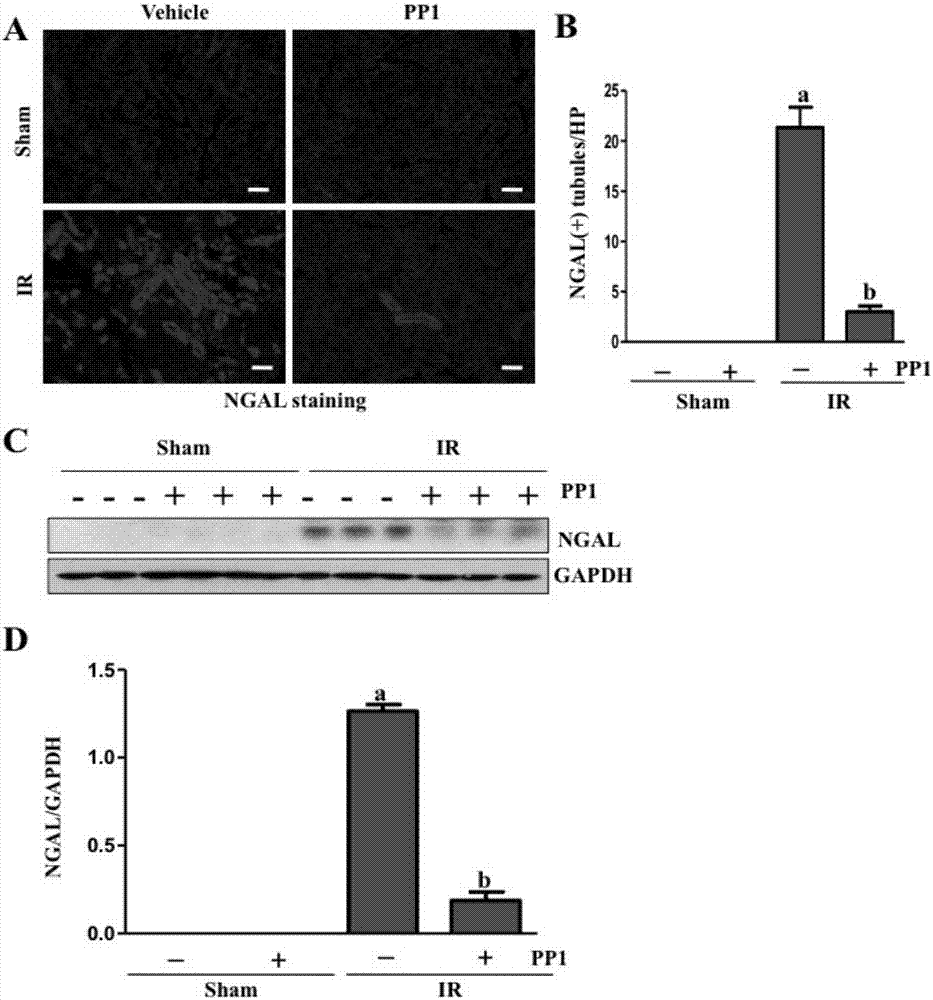
Application of Src kinase inhibitor in preparing medicaments for treating acute kidney injury
InactiveCN106924263AInhibit apoptosisSuppress deathOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderTyrosine-kinase inhibitorApoptosis
The invention provides application of Src kinase inhibitor in preparing medicaments for treating acute kidney injury. Further, the acute kidney injury is caused by renal ischemia. Further, the Src kinase inhibitor is PP1 (4-Amino-5-(methylphenyl)-7-(t-butyl)pyrazolo-(3,4-d)pyrimidine). The invention proves that PP1 inhibition of Src can relieve the pathobiological change of kidney after I / R, so as to improve kidney function. The treatment mechanism of the Src kinase inhibitor includes procedures of inhibiting apoptosis of renal tubule cells, protecting multiple connexins and adhesive proteins, and inhibiting cell death and inflammation signal pathway.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL
High adhesion clostridium butyricum and its preparation method
InactiveCN103911337AImprove adhesionBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsLactobacillusMicrobiology
The invention discloses high adhesion clostridium butyricum and its preparation method, and belongs to the field of gene recombination. The invention provides the high adhesion clostridium butyricum and its preparation method to solve the technical problem, the main points of the technical proposal are that lactobacillus adhesion protein gene is obtained by cloning, and a lactobacillus adhesion protein gene-containing recombinant plasmid is converted into clostridium butyricum by use of a gene recombination method to obtain a clostridium butyricum recombinant strain. Through gene expression, the clostridium butyricum is capable of autologous production of a protein with the adhesion function, the adhesion ability is greatly improved, and the efficacy of the treatment of the clostridium butyricum is further improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Mussel adhesive protein product and use thereof for treating mucosal inflammation
ActiveUS20200101135A1Keep for a long timeImprove permeabilityCosmetic preparationsAntipyreticMucosal inflammationStomach cancer
The invention relates to a mussel adhesive protein (MAP) and an application thereof in inhibiting catarrh, and specifically, to applications of a MAP or a product thereof in oral mucositis, rhinitis, otitis media, pharyngitis, laryngitis, bronchitis, esophagitis, gastritis, enteritis, cervicitis, endomyometritis, inflammation resulting from inhalation injury, and oral cavity cancer, nasopharyngeal cancer, carcinoma of middle ear, conjunctival cancer, laryngeal cancer, lung cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, bowel cancer, cervical cancer, endometrial cancer, and other cancers resulting from the inflammation. The MAP can inhibit symptoms such as flush, fever, swell, and pain owing to catarrh, facilitating healing, relieving itch and pain, and having broad applications in the fields of medicines, cosmetics, medical products, disinfection products, healthcare products, foods, and household goods.
Owner:BENGT I SAMUELSSON INST OF LIFE SCI CO LTD
Coacervate having an ionic polymer mixed with the adhesive protein of a mussel or of a species of the variome thereof
ActiveUS8673986B2Improve adhesion strengthEffectively used as adhesiveBiocideNervous disorderPolymer scienceAnionic polymers
The present invention relates to a coacervate comprising a mussel adhesive protein and an anionic polymer, and more particularly, to a coacervate prepared by mixing a mussel adhesive protein with an anionic polymer, and a novel use thereof. In the present invention, a coacervate prepared by mixing a mussel adhesive protein and an anionic polymer shows a very excellent adhesive strength to various substrates such as cells or metals, and is able to maintain its adhesive strength in the presence of water or under water, thereby being effectively used as an adhesive. Moreover, it has an activity capable of encapsulating bioactive materials, thereby being effectively used as an active component of a composition for delivering bioactive materials.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in carcinoma signaling pathways
The invention discloses nearly 443 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human carcinoma, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Protein kinases (including Serine / Threonine dual specificity, and Tyrosine kinases), Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Transcription factors, Phospoatases, Tumor supressors, Ubiquitin conjugating system proteins, Translation initiation complex proteins, RNA binding proteins, Apoptosis proteins, Adhesion proteins, G protein regulators / GTPase activating protein / Guanine nucleotide exchange factor proteins, and DNA binding / replication / repair proteins, as well as other protein types.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
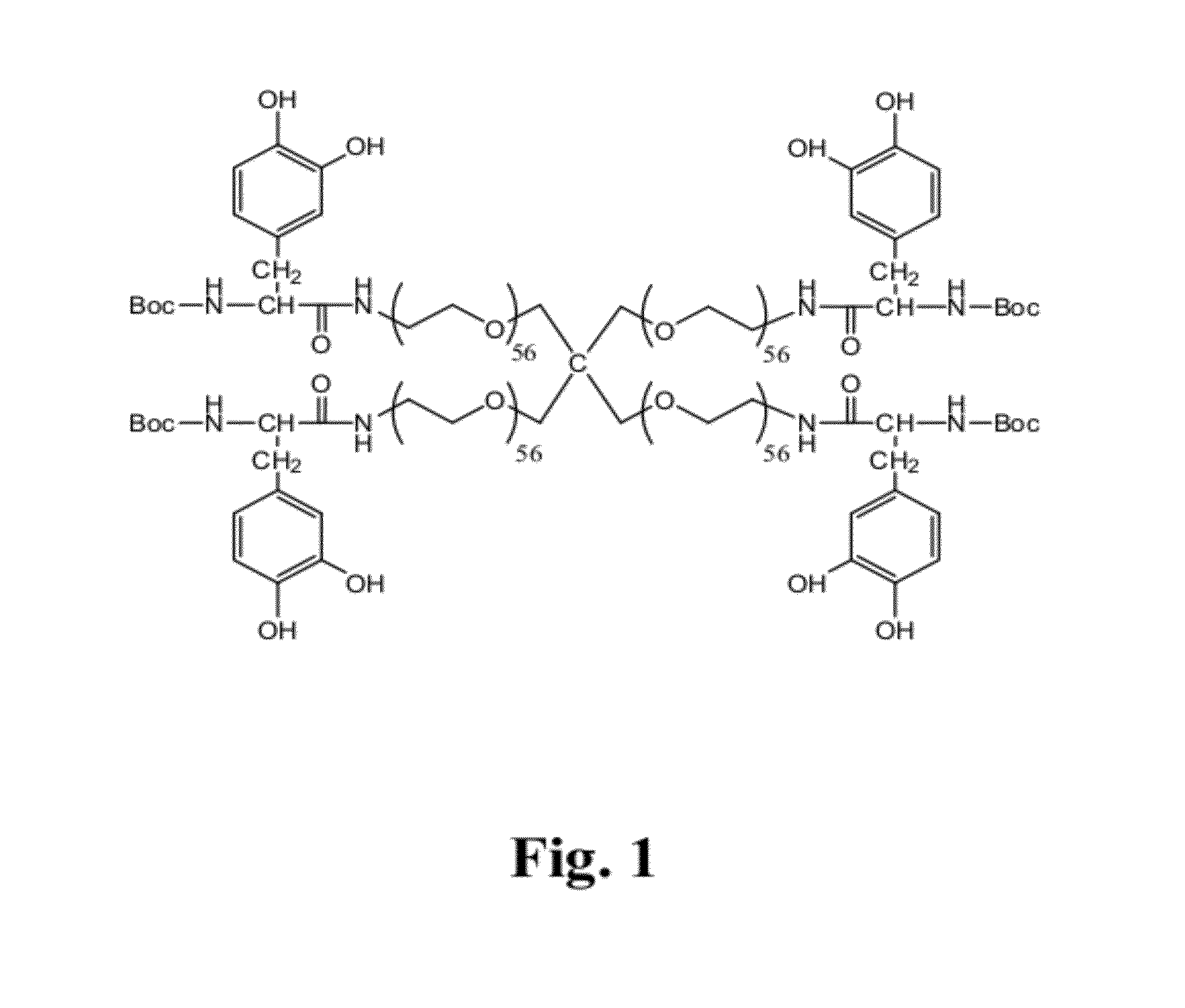
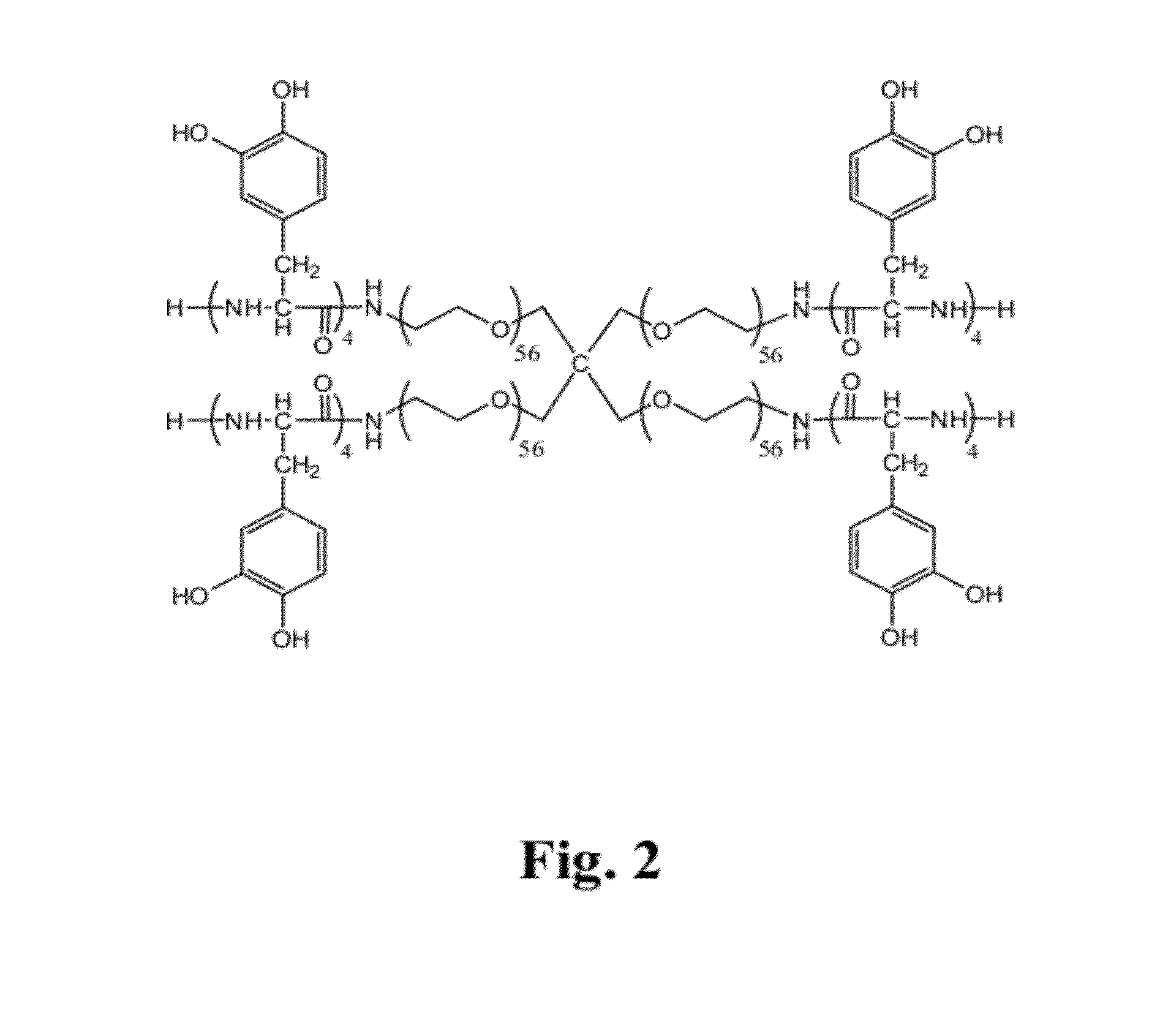
Multi-linked star-shaped polymers and synthetic methods therfor
InactiveUS20110318394A1Inhibits and reduces growth of biofilmControl bleedingAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPolymer scienceSynthesis methods
Owner:KNC NER ACQUISITION SUB
Diblock fusion protein with adhesion-antifreeze dual functions, and synthesis method and application thereof
ActiveCN110776569AGrowth impactGentle and efficient processAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHybrid peptidesEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
The invention relates to a diblock fusion protein with adhesion-antifreeze dual functions, and a synthesis method and application thereof. By taking genetic engineering as a technological means, a gene expression vector simultaneously containing antifreeze protein genes and adhesion protein genes is prepared and converted into a host cell, through an inducer, the host cell overexpresses the protein, and thus the fusion protein is obtained by separation and purification. The amino acid sequence of the fusion protein is SEQ ID NO.3, and the nucleotide sequence of the fusion protein is SEQ ID NO.4. The mussel adhesion protein and the antifreeze protein are fused on the gene level, and thus the diblock fusion protein with the adhesion-antifreeze dual functions is constructed; and the fusion protein is expressed through fermentation of escherichia coli, supernatant protein is purified through an affinity chromatogram, an inclusion body is purified through acetic acid, a high-purity separation and purification method is constructed, the fusion protein is synthesized through a microbial one-step method, the process is mild and efficient, the cost is low, the equipment requirement degree is low, and expanded production at the later period is easy.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Haemophilus adhesion proteins
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com