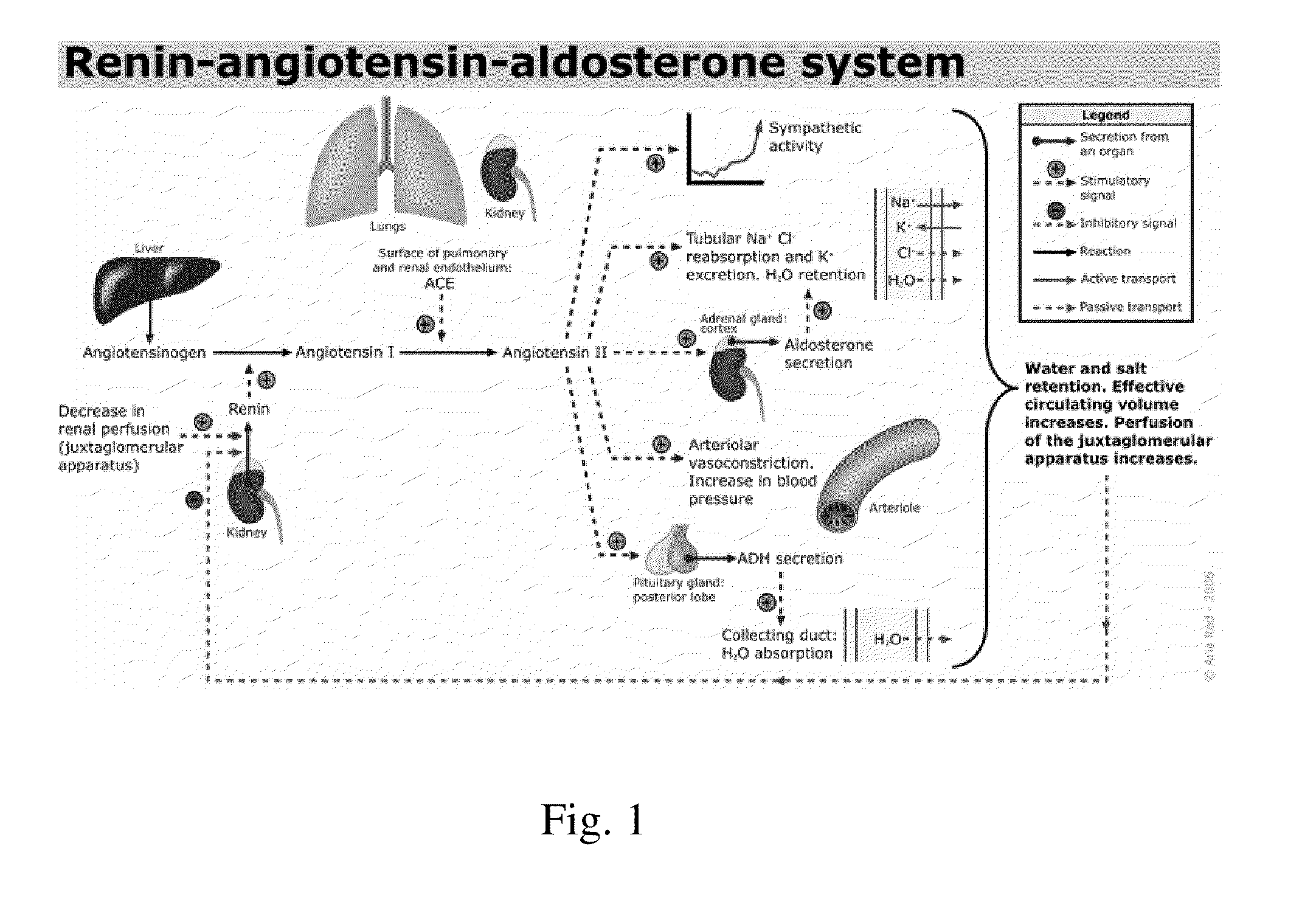
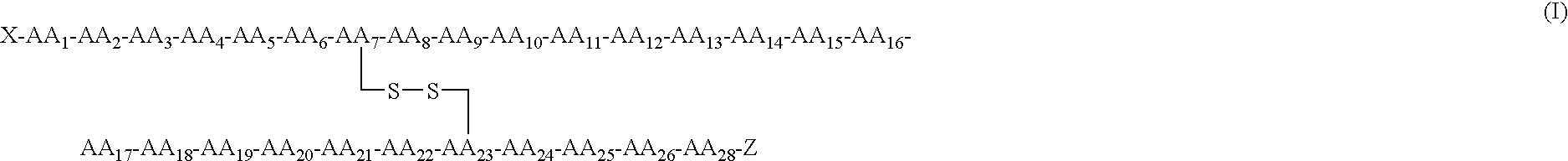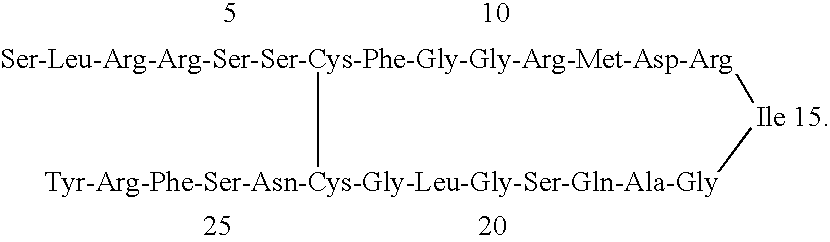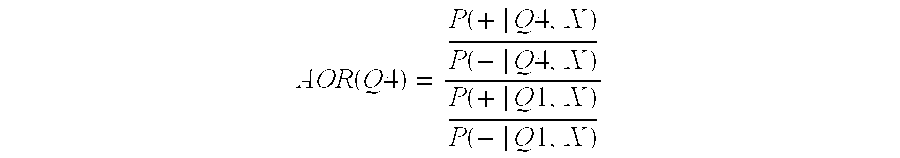Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
176 results about "Acute kidney injury" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An abrupt reduction in the ability of kidneys to filter waste products.
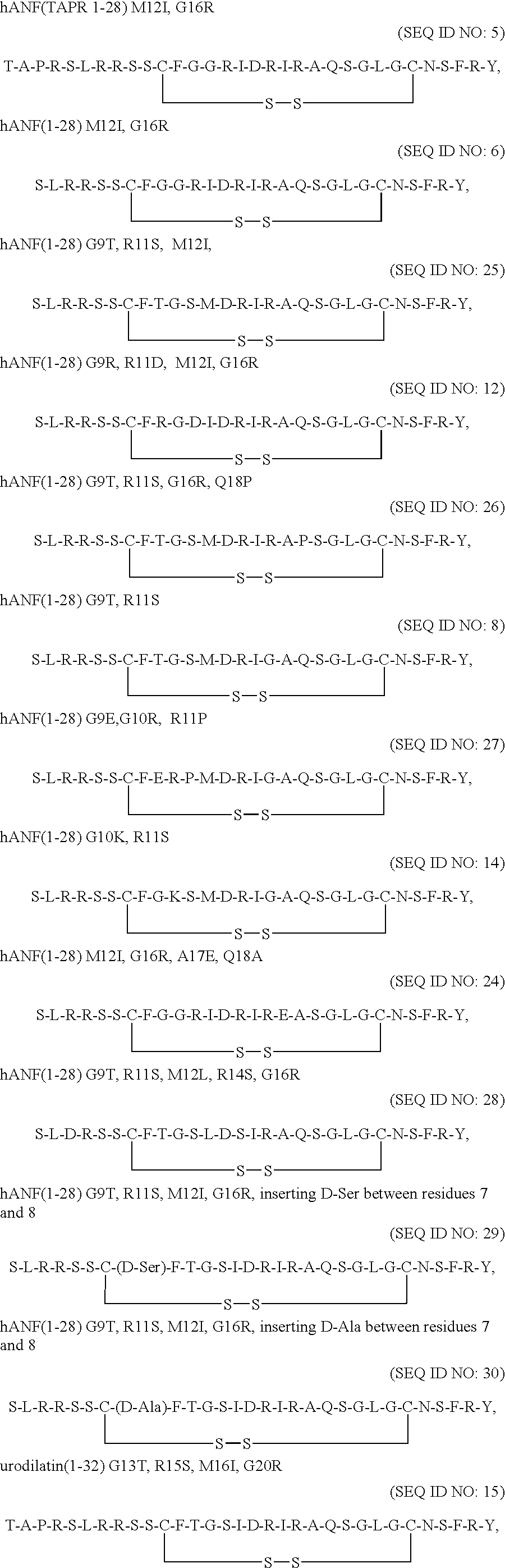
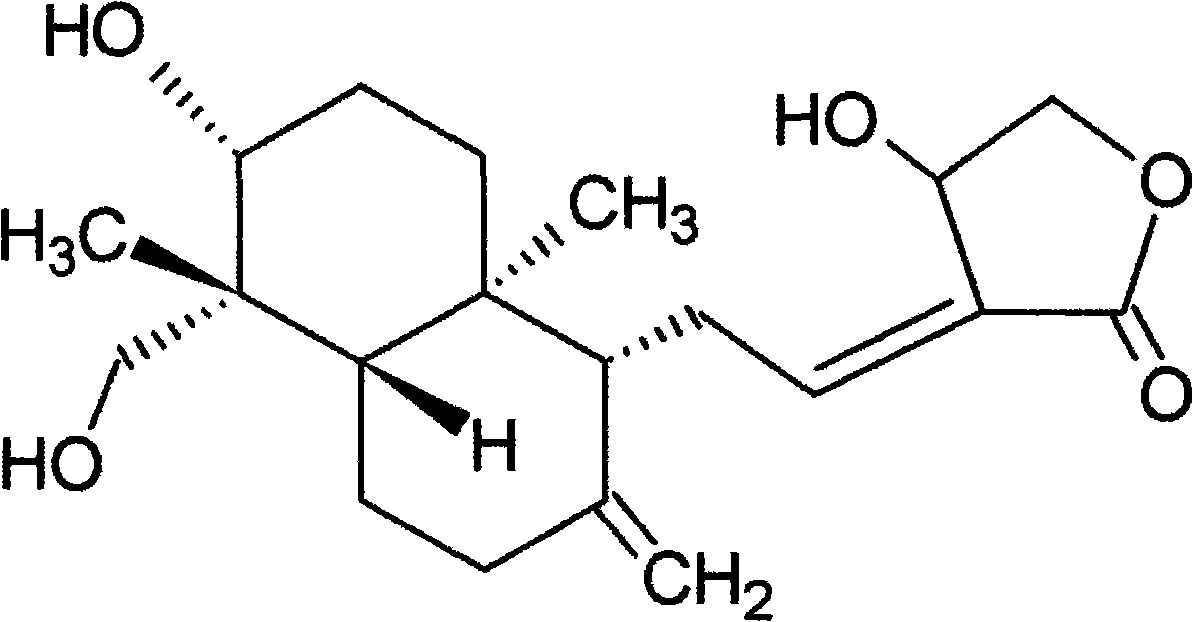
Receptor specific atrial natriuretic peptides
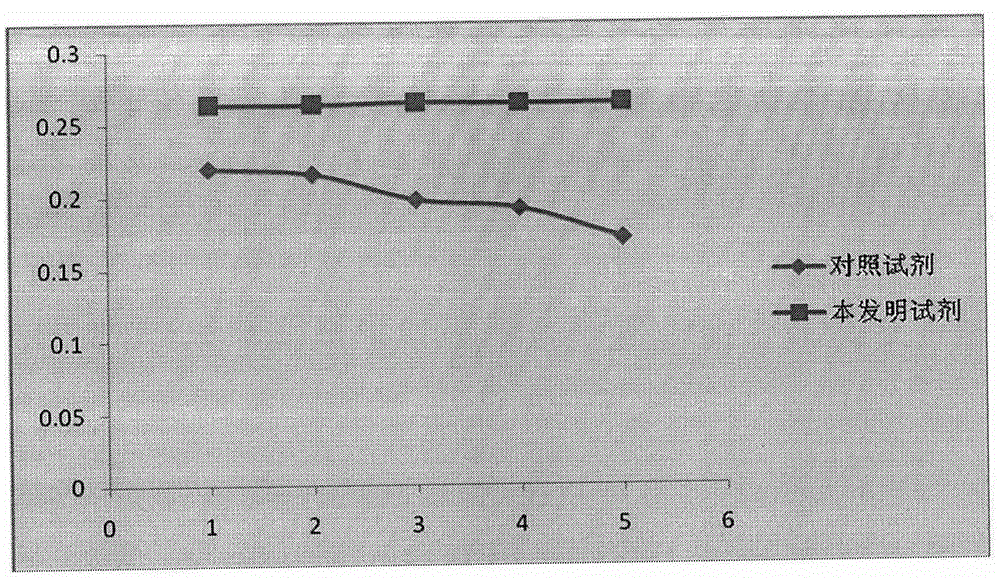
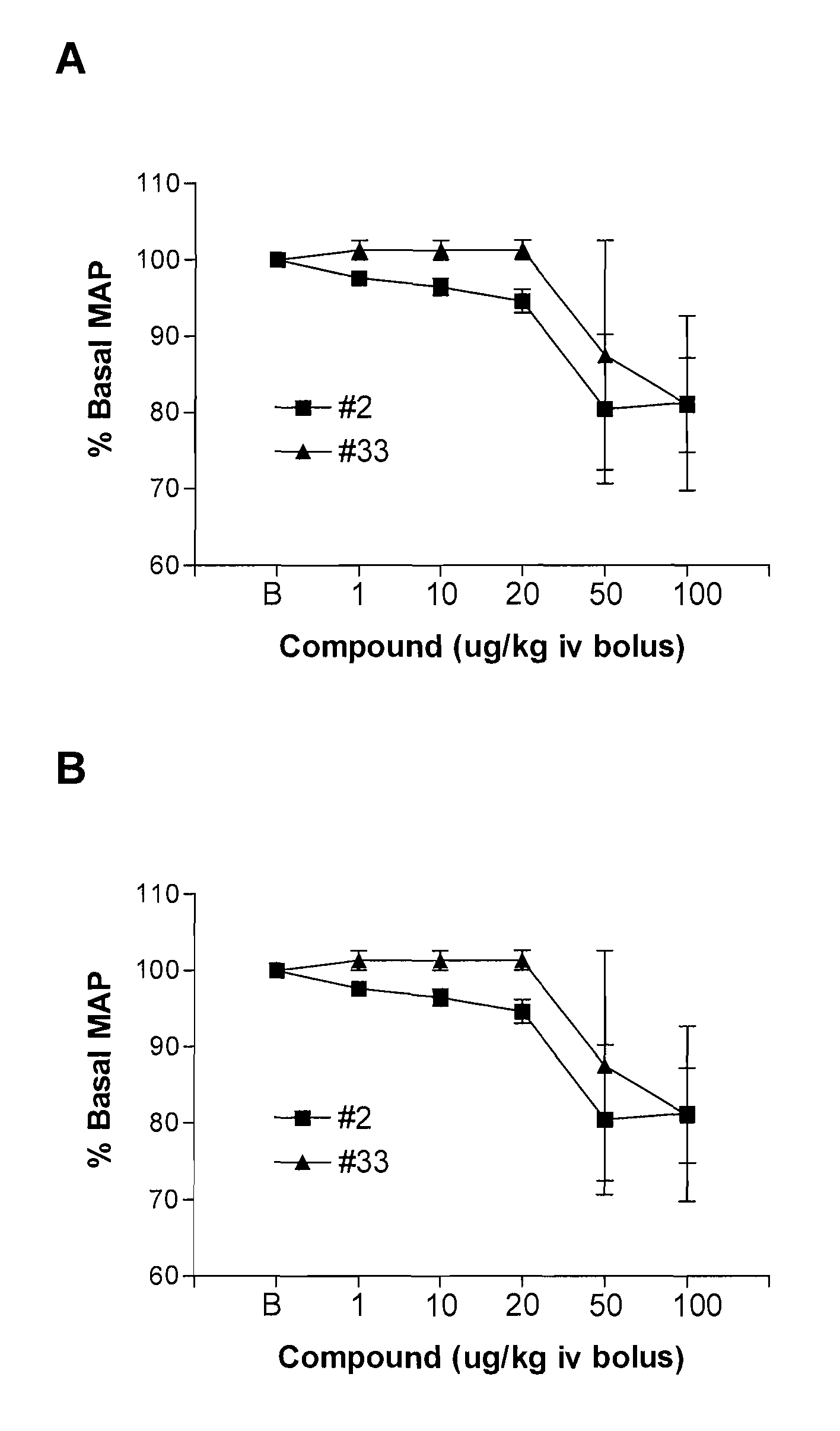
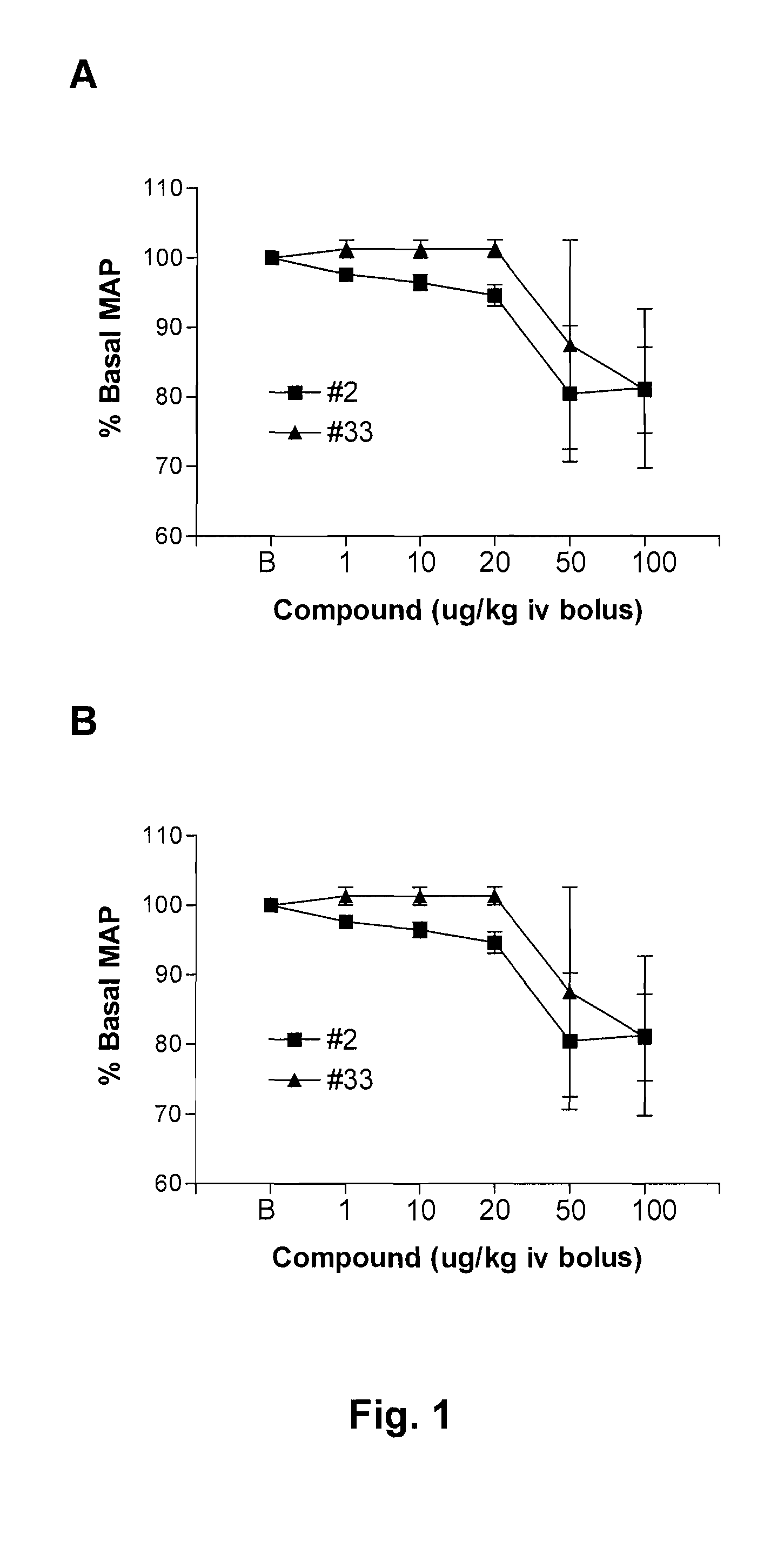
Human receptor selective atrial natriuretic factor variants containing various substitutions, especially G16R, show equal potency and binding affinity for the human A-receptor but have decreased affinity for the human clearance or C-receptor. These ANF variants have natriuretic, diuretic and vasorelaxant activity but have increased metabolic stability, making them suitable for treating congestive heart failure, acute kidney failure and renal hypertension.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
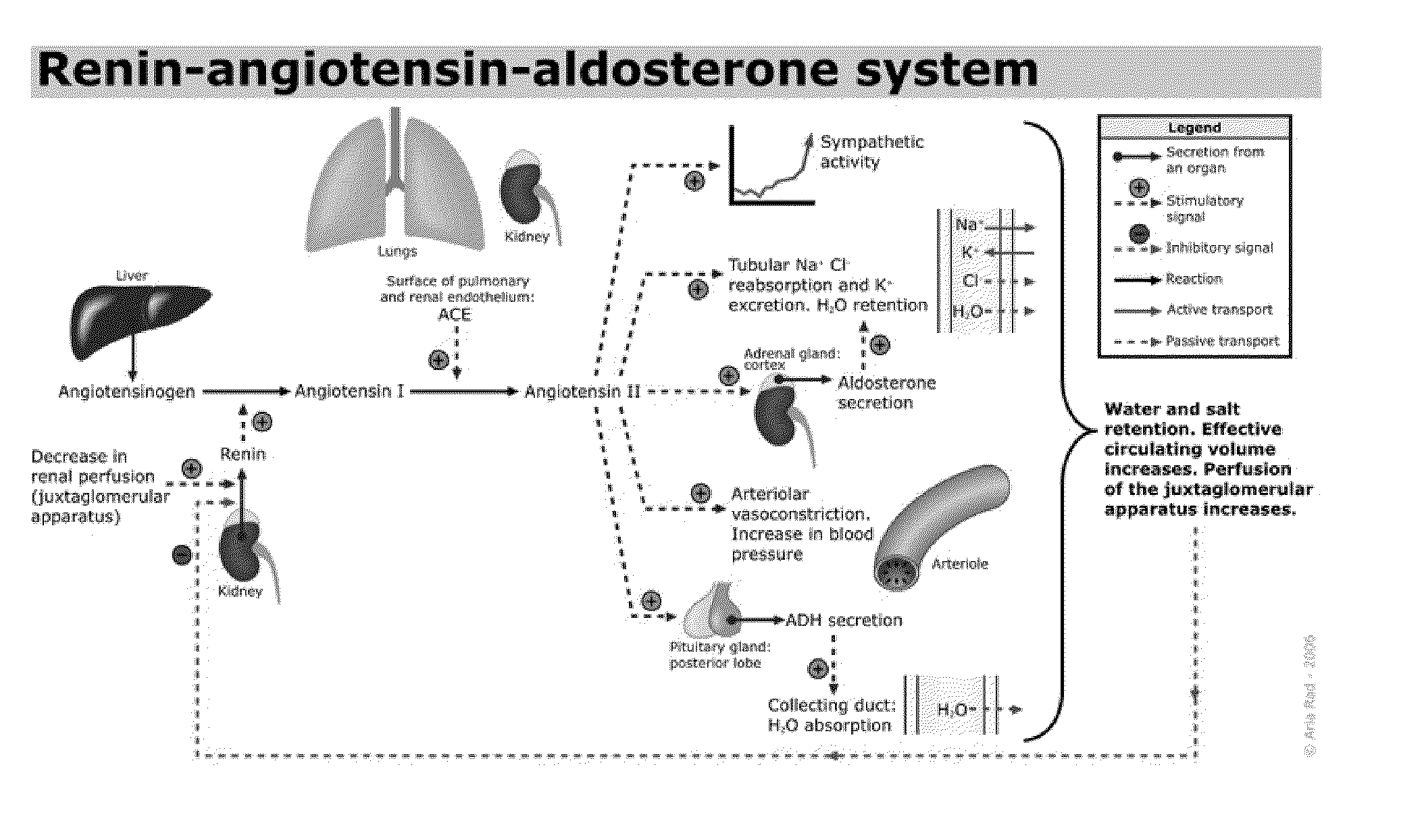
Method of Treating Low Blood Pressure
ActiveUS20110144026A1Lower blood pressurePeptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderCardiorespiratory arrestLow blood pressures
A method for treating a patient suffering from one of septic shock, acute kidney injury, severe hypotension, cardiac arrest, and refractory hypotension, but not from myocardial infarction, is provided. The method includes administering a therapeutically effective dose of Angiotensin II, or Ang II, to the patient.
Owner:THE GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIV A CONGRESSIONALLY CHARTERED NOT FOR PROFIT CORP
Health-care product composite with alcoholism relieving function and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102100803AGood liver protectionImprove metabolic abnormalitiesOrganic active ingredientsPre-extraction tea treatmentAlcoholismsSide effect
The invention relates to a health-care product composite with an alcoholism relieving function and a preparation method thereof, and discloses a health-care product composite with an alcoholism relieving function and a preparation method thereof. The composite is prepared from the following raw materials: pueraria flower, hovenia dulcis thumb, kudzuvine root, green tea and oligosaccharide, wherein plantain herb, chrysanthemum, lalang grass rhizome, liquoric root, tangerine peel and hawthorn fruit are also added into the raw materials of the composite. The health-care product composite is prepared by refining wild plants, does not have toxic or side effect, has excellent effects of relieving alcoholism and activating spleen and protecting liver and stomach, and can eliminate or relieve acute mild and moderate alcoholism, acute stomach injury, chronic gastritis and acute liver injury which are caused by drinking. The health-care product composite can be prepared into granules, tea bags and capsules.
Owner:湖北万松堂大健康医药集团有限公司
Bifunctional hormone and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090011997A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsTetrapeptide ingredientsDiseaseHormones regulation
A bifunctional hormone exhibiting an alpha-MSH activity and a natriuretic peptide activity is described. The bifunctional hormone comprises for example a first domain having alpha-MSH related hormonal activity covalently linked to a second domain having natriuretic peptide related hormonal activity. The bifunctional hormone of the present invention is useful for example for the prevention and / or treatment of renal related diseases or conditions, such as acute renal failure (ARF) or acute kidney injury (AKI).
Owner:THERATECHONOLGIES INC
Tibetan capillaris extract and preparation method, pharmaceutical composition and use thereof
ActiveCN102138966ATake advantage ofCan play a therapeutic rolePowder deliveryDigestive systemTriterpeneAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a Tibetan capillaris extract, which comprises components of secoiridoid, xanthone, triterpene and the like, wherein the total content of the three components is 20%-80% (by weight). The invention also provides a preparation method of the Tibetan capillaris extract, and a pharmaceutical composition containing the Tibetan capillaris extract. The Tibetan capillaris extract hasthe obvious function of benefiting the cholecyst, and has obvious functions of protecting and improving acute liver injury caused by chemicals and hypohepatia of obstructive jaundice.
Owner:TIANJIN INSTITUTE OF PHARMA RESEARCH
Use of human fat-derived mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of diseases in kidney and ocular fundus
The invention relates to the use of human fat-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of diseases in kidney and ocular fundus. The invention provides the use of the human fat-derived mesenchymal stem cells in cell preparation for treating diseases in kidney and / or ocular fundus, such as acute kidney injury, renal fibrosis, renal tubular epithelial cell damage, retinosis, diabetic retinopathy and retinal tear. The cell preparation can promote the repair of kidney structure and damaged eyeball pathologic structure with good effect.
Owner:微能生命科技集团有限公司
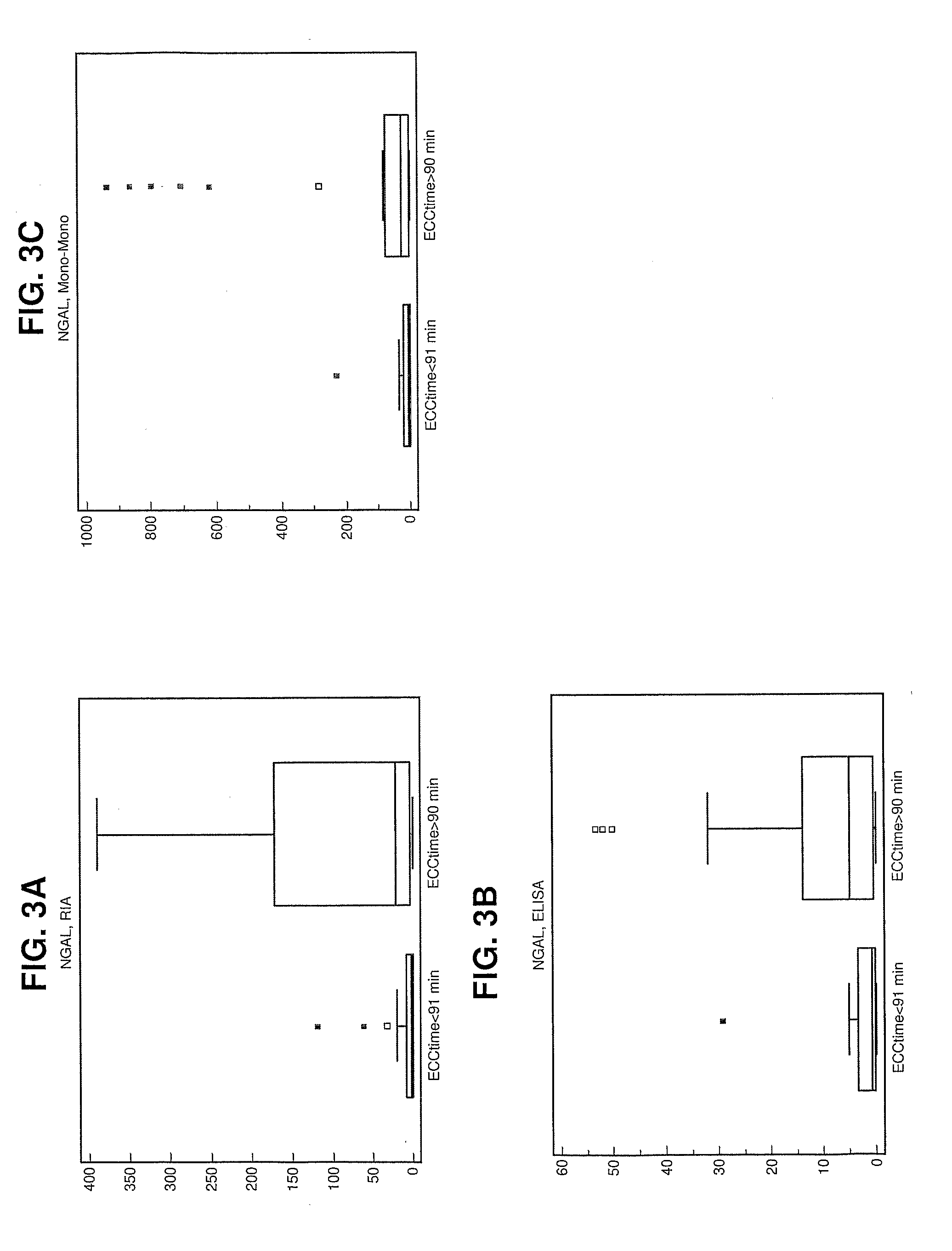
Methods, Devices and Kits for Detecting or Monitoring Acute Kidney Injury
ActiveUS20110287455A1High sensitivityEasy to detectPeptide librariesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceEpitopeGelatinase
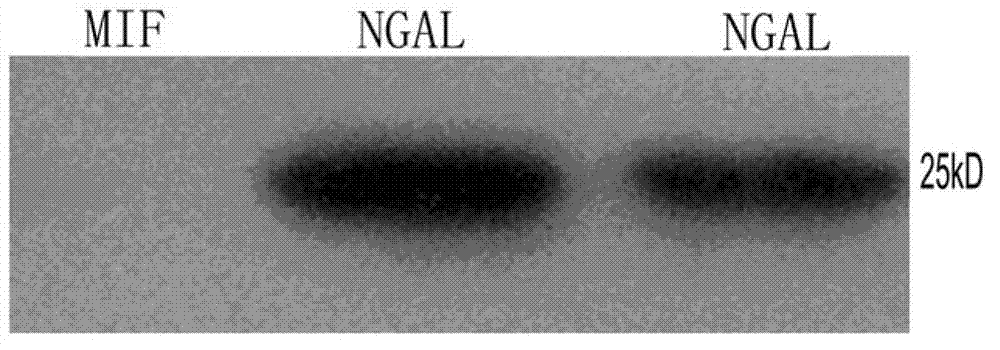
Methods for detecting acute kidney injury in an individual comprise (a) contacting a body fluid sample from the individual with an assay device including neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) antibody and a detectable label, to allow complexing of NGAL protein in the sample with NGAL antibody, and determining an amount of complex formed between NGAL protein from the sample and NGAL antibody in the assay device using the detectable label, wherein NGAL antibody in the device has binding capacity with more than two NGAL protein epitopes, and wherein the amount of the formed complex represents a level of acute kidney injury. Methods for determining an origin of NGAL protein in a sample from an individual include the step of determining relative amounts of monomeric, dimeric and heterodimeric forms of NGAL protein in the sample and allow improved diagnosis and therefore better targeted treatment.
Owner:FUTURE MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
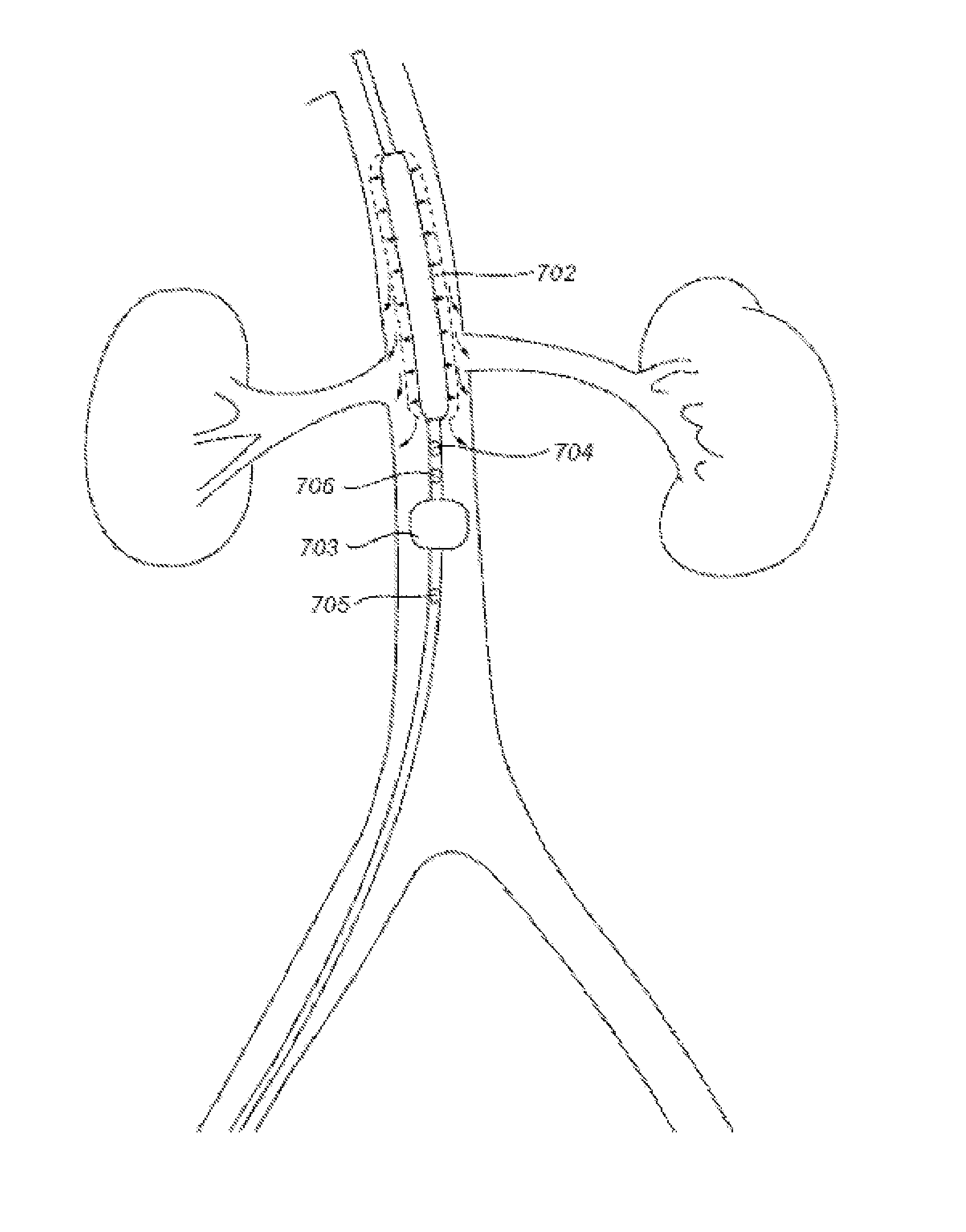
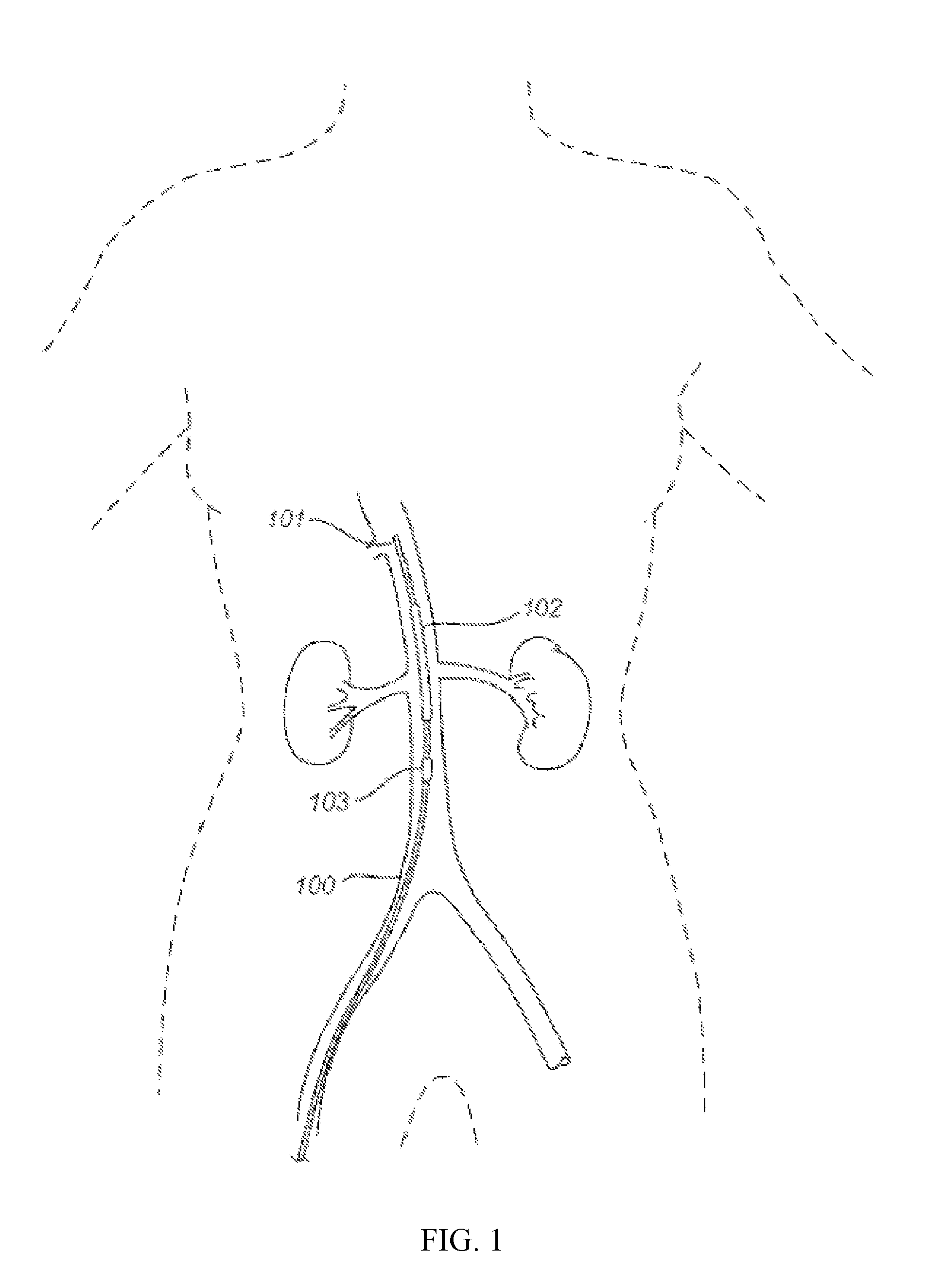
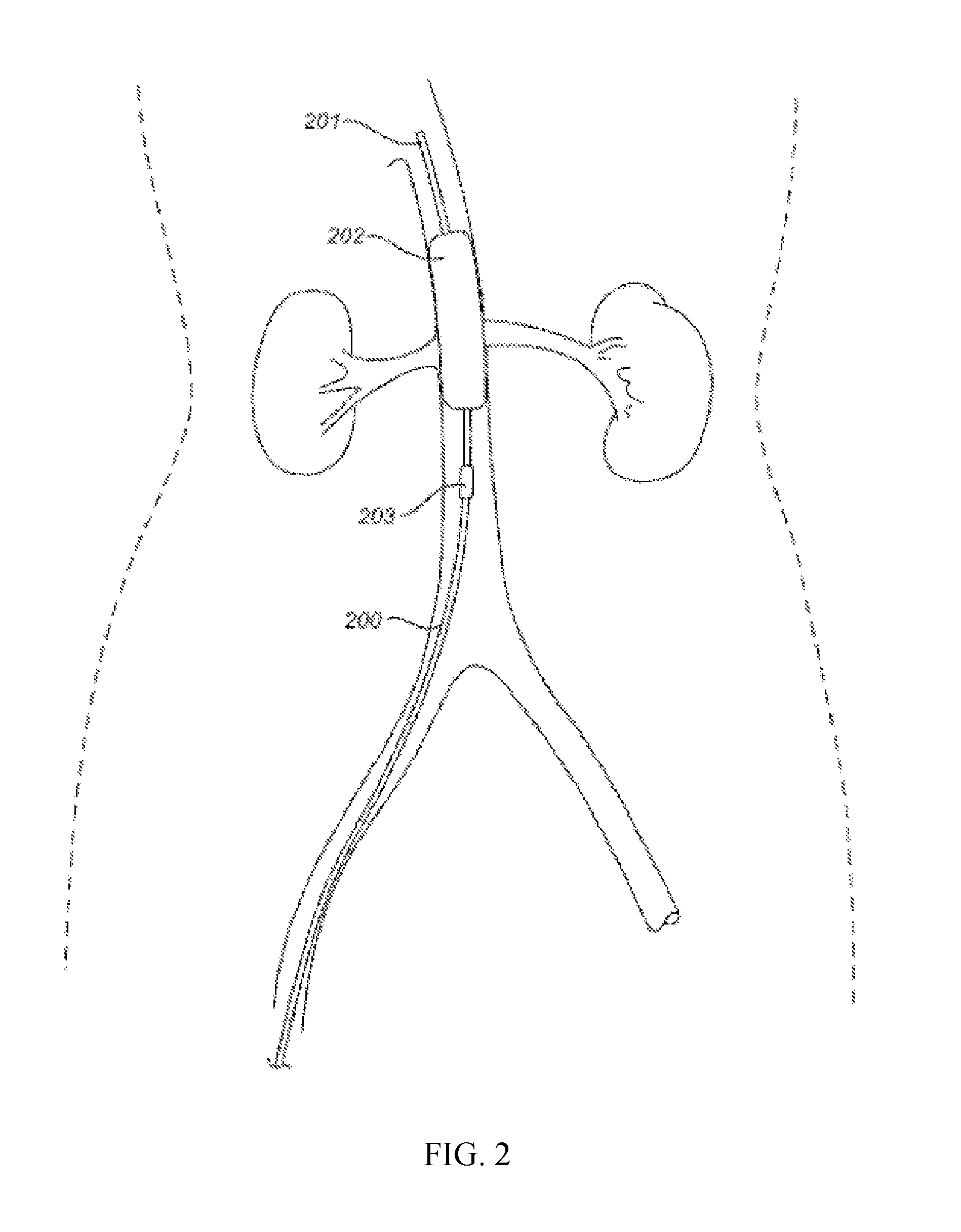
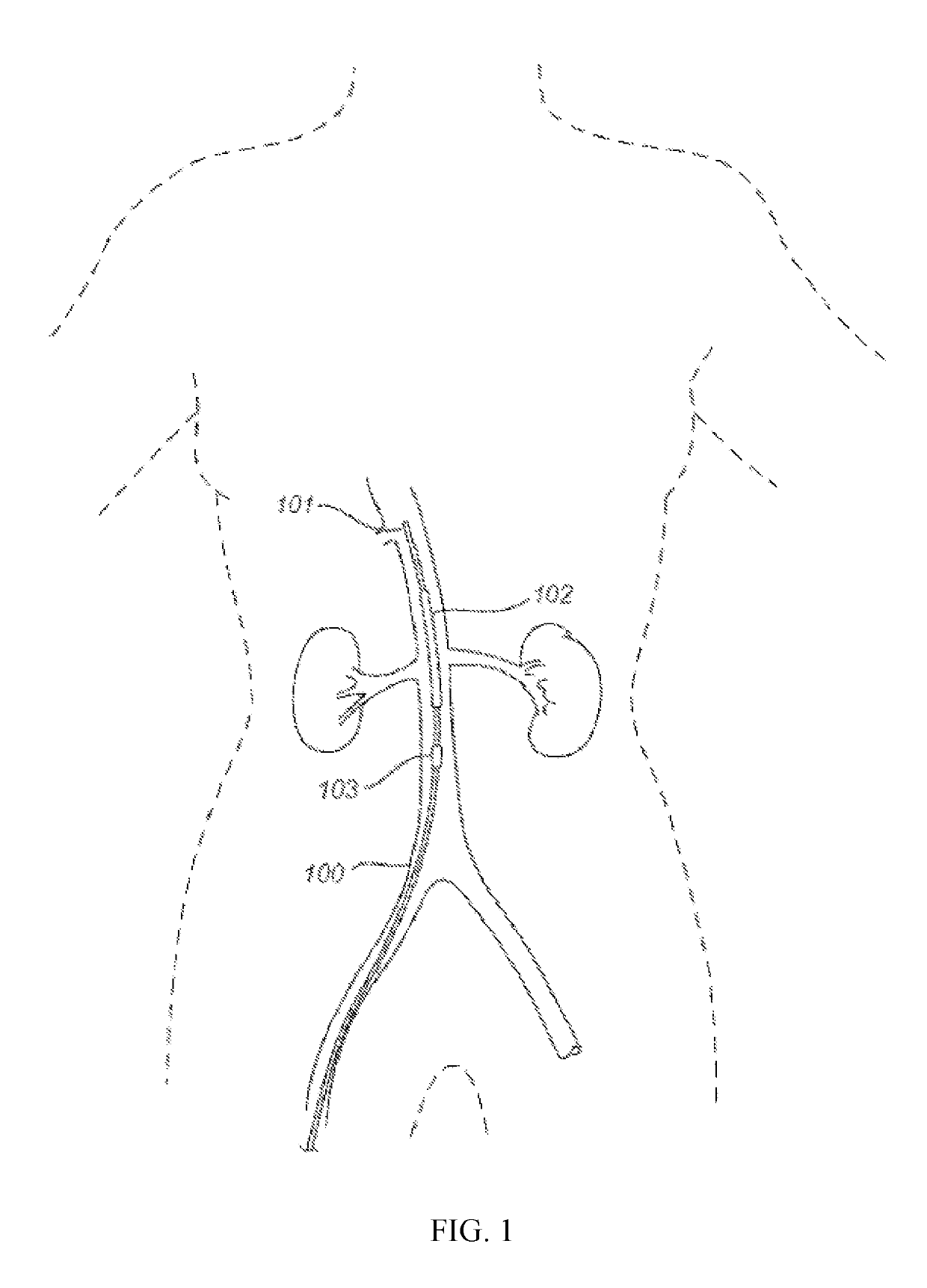
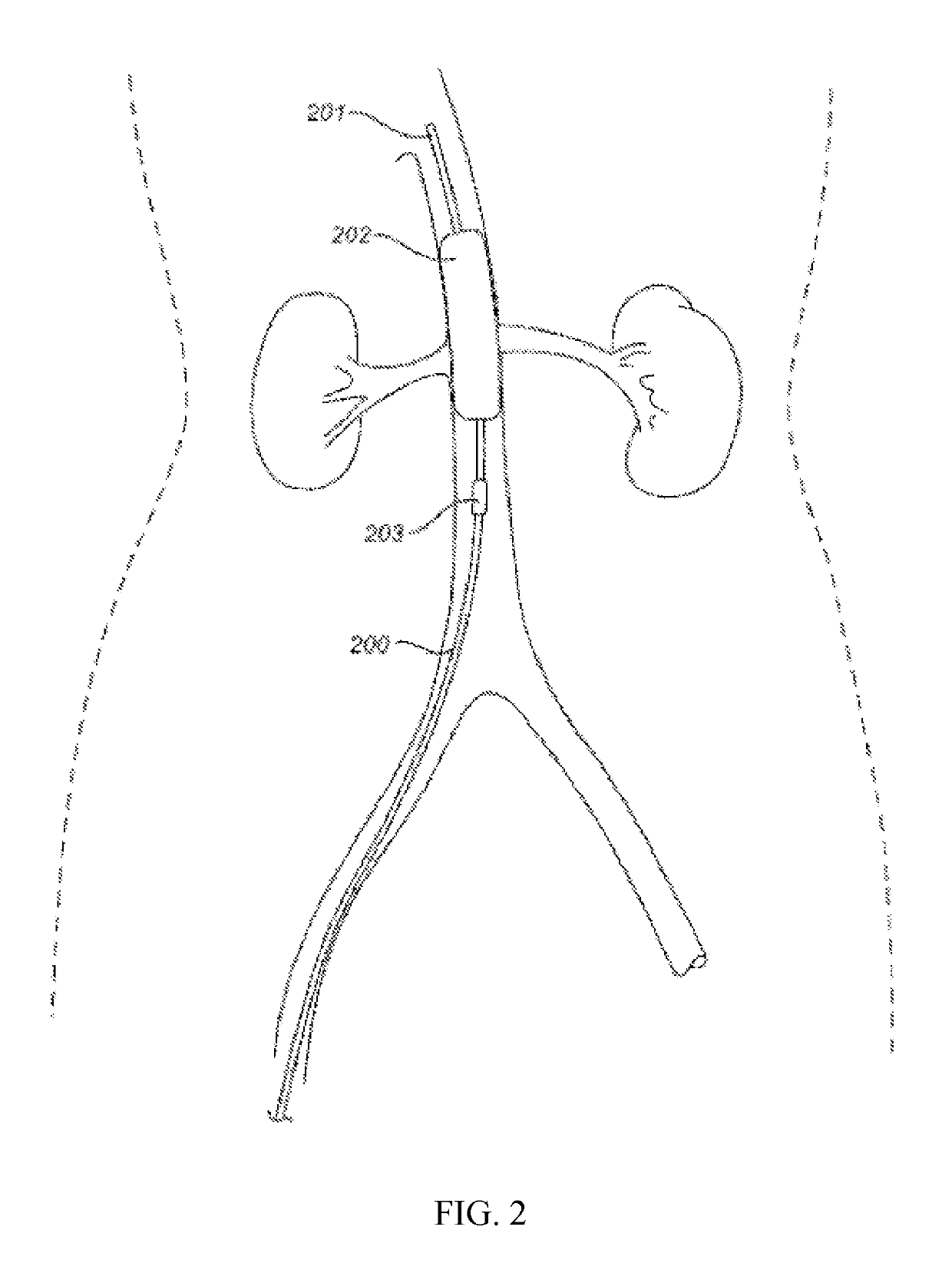
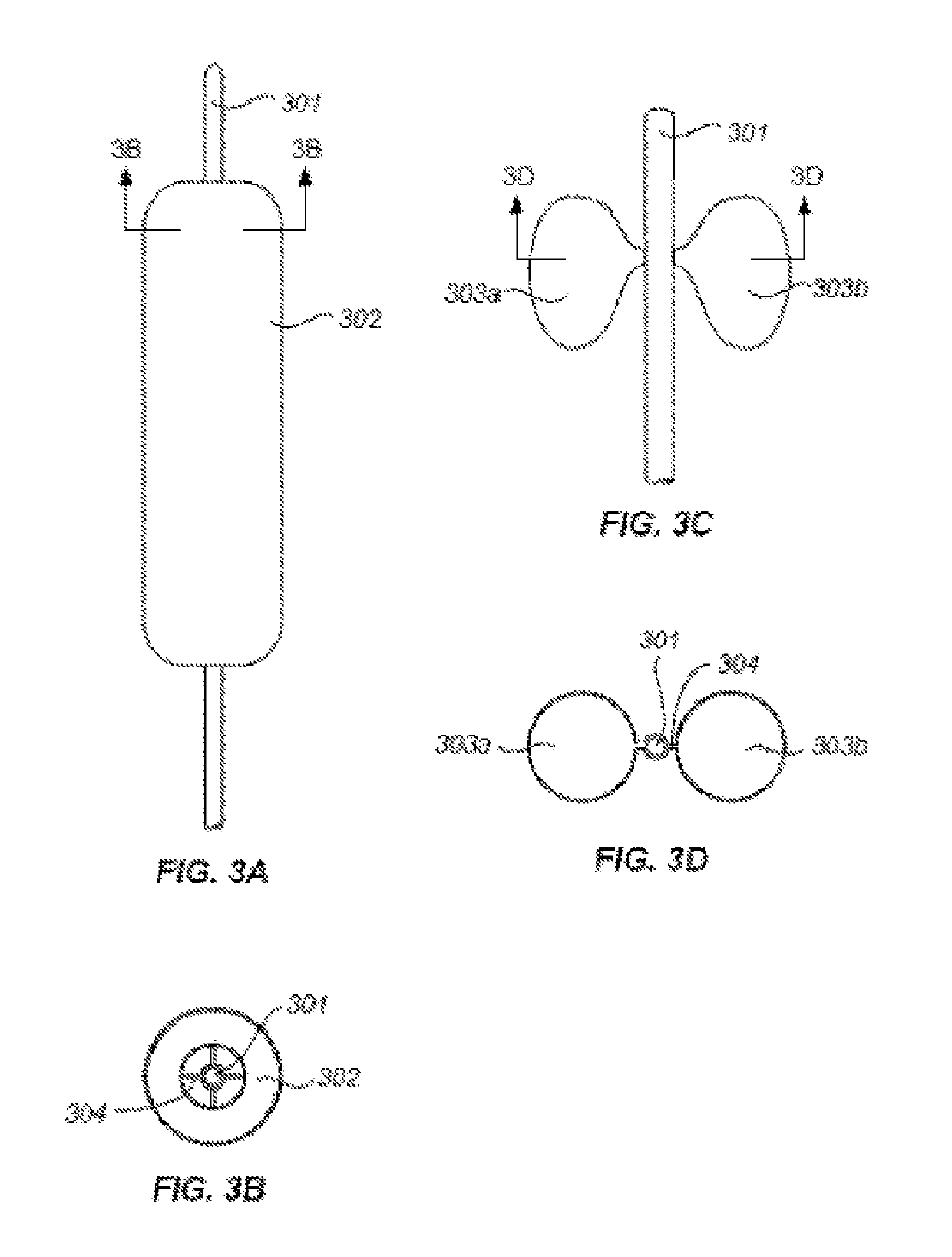
Devices and methods for treating acute kidney injury
A catheter devices / systems and methods therefrom are described herein for treating acute kidney injury, especially the contrast-induced acute kidney injury wherein the devices prevent the contrast dyes from entering into kidney and / or facilitate blood flow of kidney by said catheter system.
Owner:RENALPRO MEDICAL
Use of urinary ngal to distinguish kidney disease and predict mortality in subjects with cirrhosis
InactiveUS20100233740A1Increase opportunitiesLow chanceDisease diagnosisBiological testingMortality rateNGAL Protein
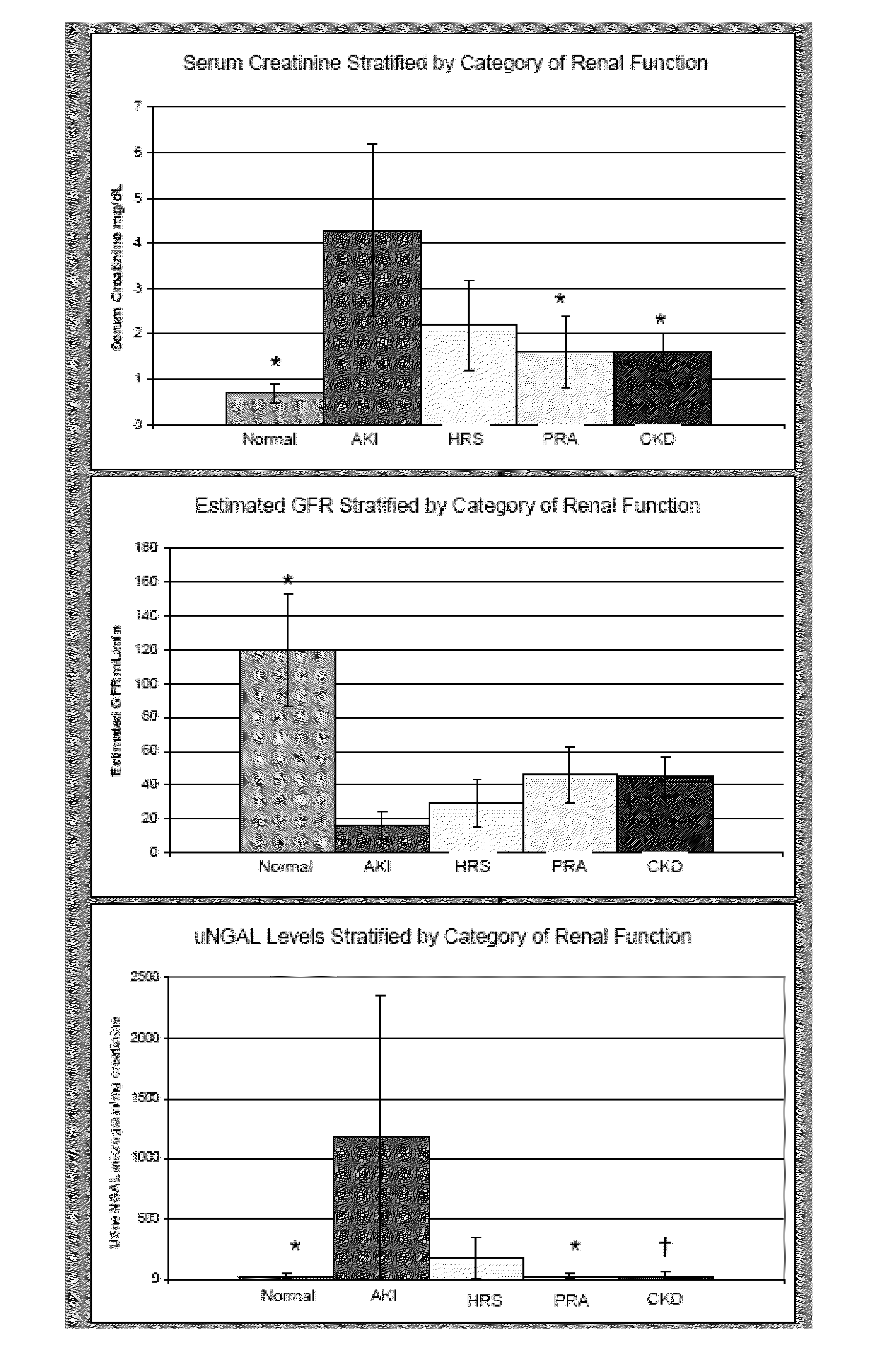
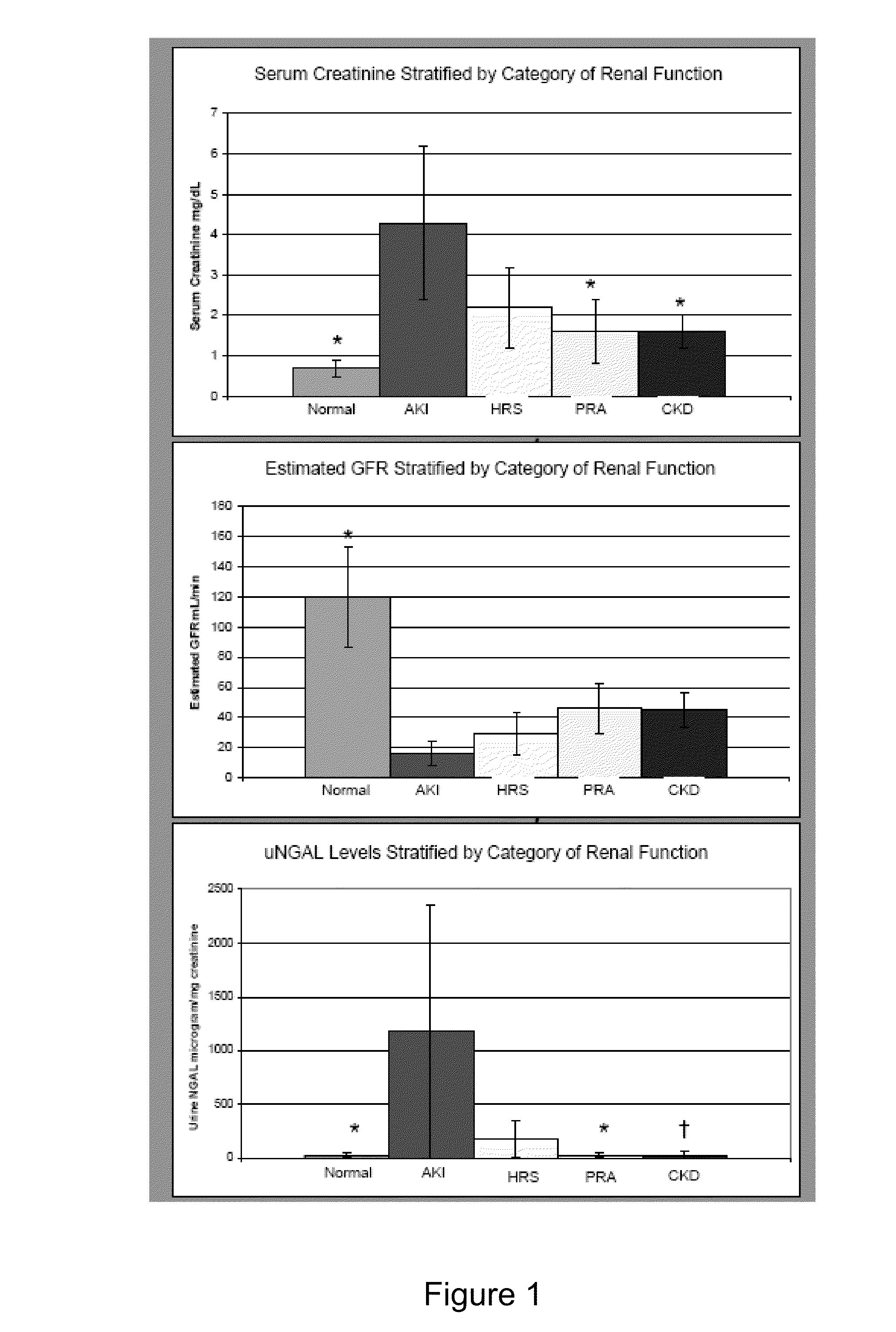
In one embodiment, the present invention is directed to methods for diagnosis of acute kidney injury (AKI) and hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) in cirrhosis patients, and to methods for distinguishing between AKI and / or HRS and / or other kidney diseases in cirrhosis subjects. In another embodiment, the present invention is directed to prognostic methods for predicting disease-specific mortality in cirrhosis patients. In some aspects, the diagnostic and prognostic methods of the invention are based on determining whether a bodily fluid sample, such as a urine sample, contains an amount of NGAL protein that exceeds or is less than a certain threshold level, or that falls within a certain range.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
ActiveUS10300108B2Easy to replaceImprovements in renal statusDisease diagnosisCyclic peptide ingredientsRenal FailuresSingle administration
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL +1
Method of treating low blood pressure
ActiveUS9572856B2Peptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderCardiorespiratory arrestLow blood pressures
A method for treating a patient suffering from one of septic shock, acute kidney injury, severe hypotension, cardiac arrest, and refractory hypotension, but not from myocardial infarction, is provided. The method includes administering a therapeutically effective dose of Angiotensin II, or Ang II, to the patient.
Owner:THE GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIV A CONGRESSIONALLY CHARTERED NOT FOR PROFIT CORP
Method of treating low blood pressure
ActiveUS20170095526A1Peptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderCardiorespiratory arrestLow blood pressures
Owner:THE GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIV A CONGRESSIONALLY CHARTERED NOT FOR PROFIT CORP
Application of andrographolidume to preparing medicine for treating acute liver injury
InactiveCN101947216ASuppress generationProtection from damageOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemApoptosisSemen
The invention discloses application of andrographolidume to preparing medicine for treating acute liver injury. The andrographolidume can remarkably inhibit liver injury induced by semen canavaliae A, the liver cell apoptosis induced by the ssemen canavaliae A and inflammatory response of liver, and can also be used for treating the liver injury induced by the semen canavaliae A. The invention firstly provides the evidence of the andrographolidume for treating the liver injury induced by the semen canavaliae A in an animal model, definitudes that the liver cell apoptosis caused by the semen canavaliae A is inhibited by inhibiting excessive active oxygen species caused by the semen canavaliae A, and prompts that the andrographolidume has the protection function on the acute liver injury in clinical.
Owner:宁光
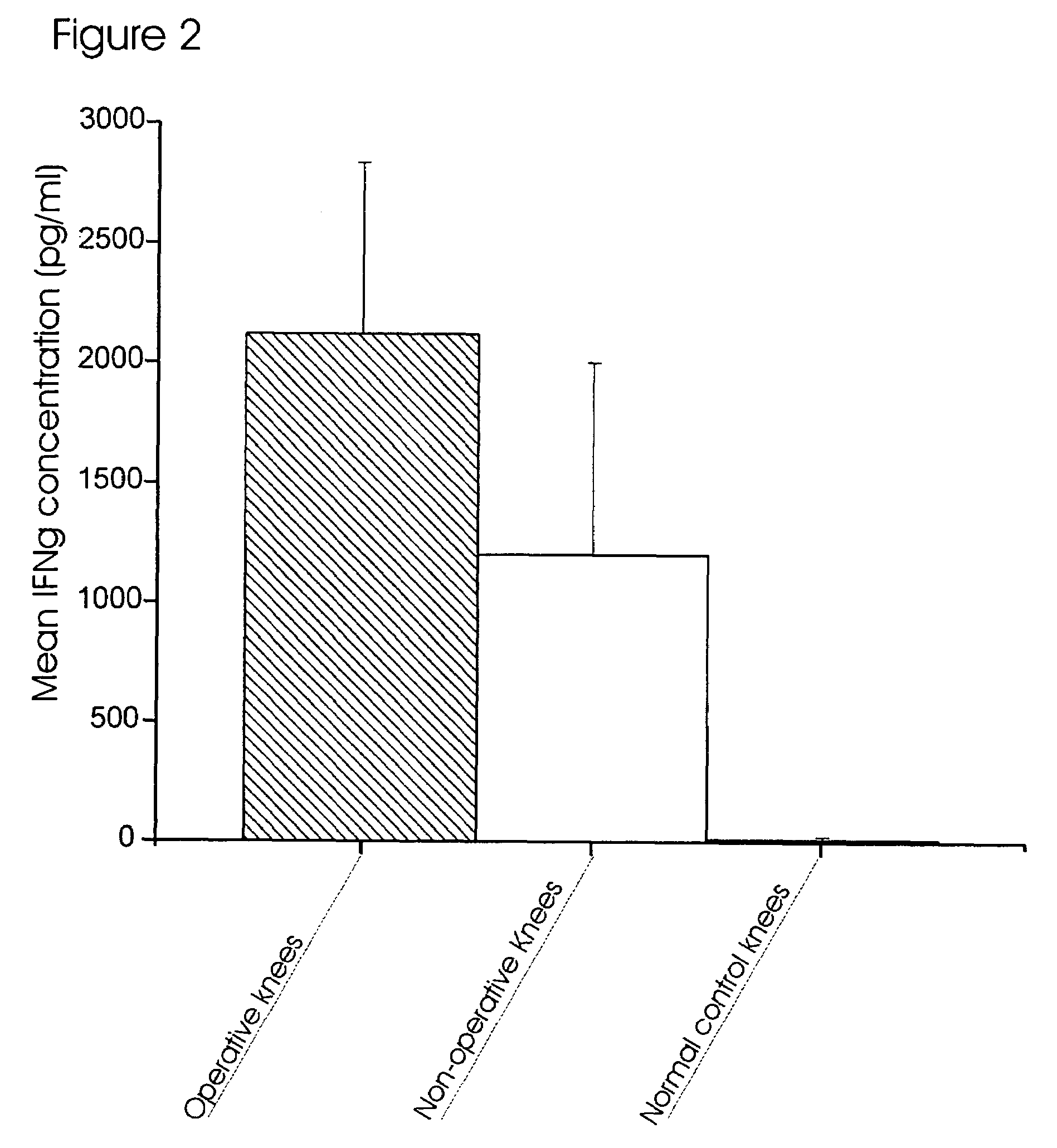
Method for diagnosing and treating acute joint injury
The present invention provides methods, reagents and kits for diagnosing and / or for the prognosis of non-autoimmune acute joint inflammation by detecting cytokine biomarkers in a sample obtained from an individual thought to be suffering from joint injury. The cytokine biomarkers used with the methods and kits of the present invention are IL-6, MIP-1β, MCP1 and IFNγ.
Owner:CYTONICS CORP
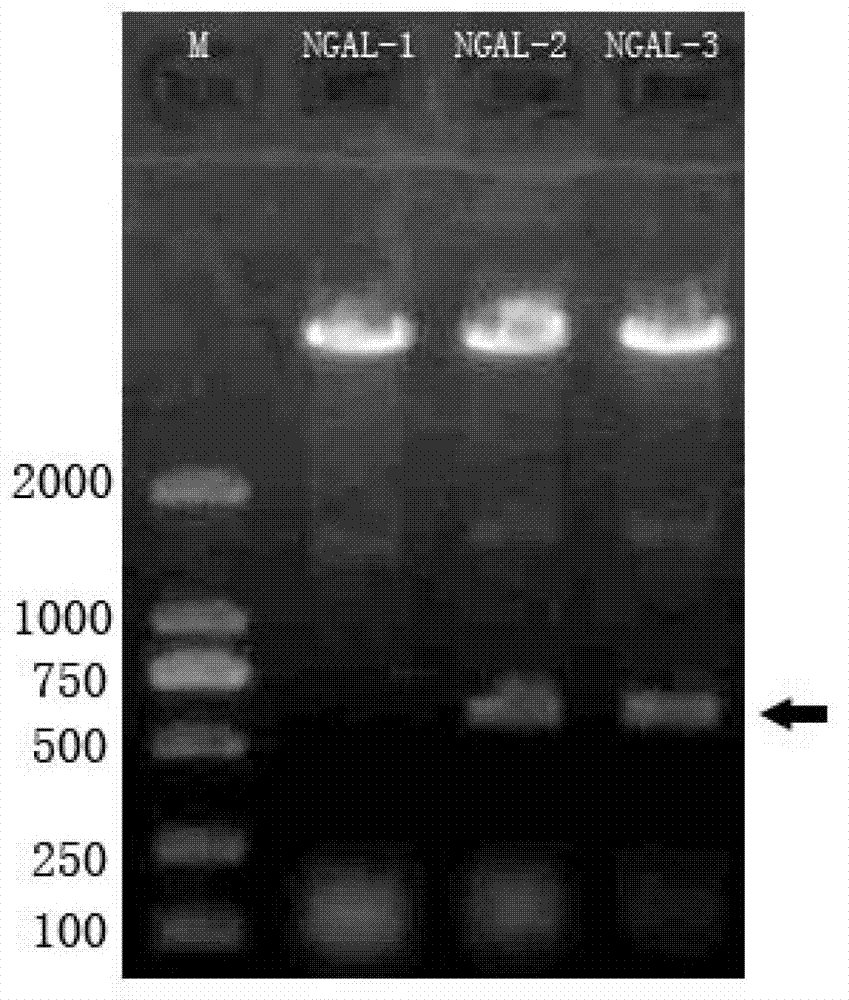
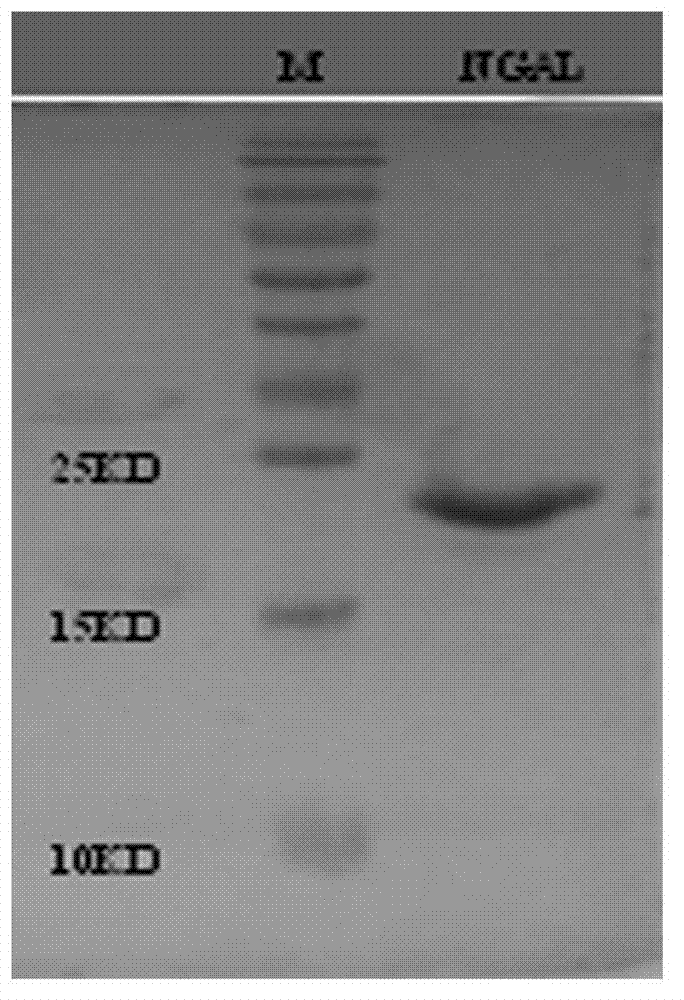
B cell epitope peptide of human neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin and application thereof
ActiveCN102775473AHigh purityHigh potencyImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMicroorganism based processesImmune complex depositionNGAL Protein
The invention belongs to the medical field and particularly relates to an acute kidney injury diagnosis technology, a B cell epitope peptide of human NGAL (Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin) and a hybridoma cell prepared by same, and an application of the B cell epitope peptide and a specific antibody thereof and an immune complex of the specific antibody in preparing diagnostic reagent for acute kidney injury. The B cell epitope peptide prepared by the invention immunizes a monoclonal antibody prepared by adopting a rat and has the advantages of high purity (The SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate)-PAGE (PolyAcrylamide Gel Electrophoresi) detection purity is more than 96 percent), high valence (the ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay) valence reaches 1:256000), good specificity, mass preparation and the like; and through the monoclonal antibody and a polyclonal antibody prepared by the B cell epitope peptide, the B cell epitope peptide can be used for detecting the content of the NGAL in the urine of a patient, for example, by adopting a double antibody sandwich ELISA reaction mode, a double antibody sandwich structure formed by an enzyme labeled human anti-NGAL monoclonal antibody, an enzyme labeled plate package anti-NGAL polyclonal antibody and a measured sample NGAL antigen is detected.
Owner:重庆业为基生物科技有限公司
Methods and compositions for assigning likelihood of acute kidney injury progression
InactiveUS20140315734A1Raise the possibilityImprovement of biomarker levelBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsObject basedCore domain
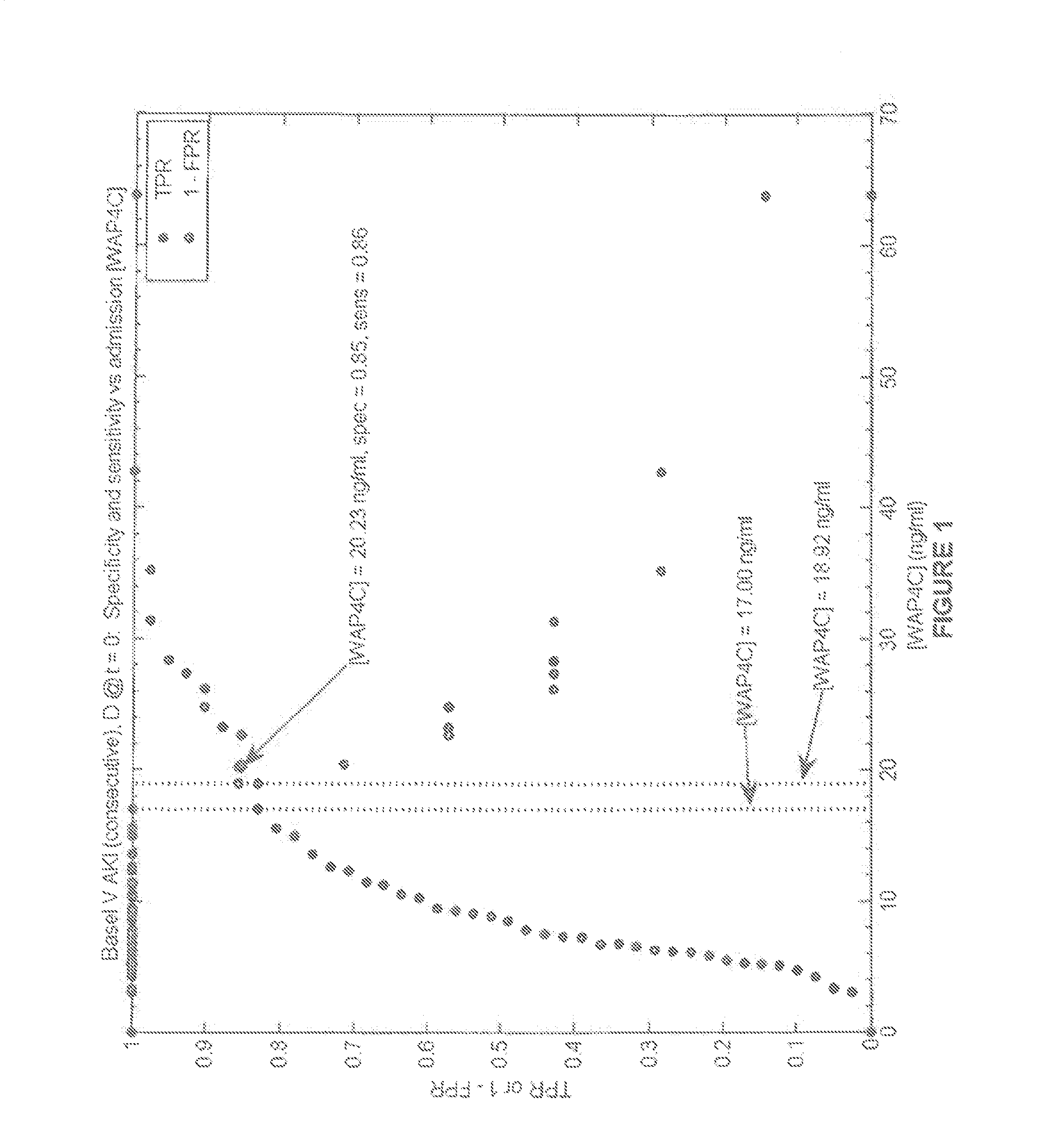
The invention encompasses diagnosis and prognosis in the context of heart or renal failure, particularly in subjects who exhibit a normal body fluid level of a natriuretic peptide. The invention also relates to methods of assigning an increased likelihood that a subject having AKI is susceptible to AKI progression. The invention relates in part to assigning a diagnosis of heart and / or renal failure, and / or an outcome risk (e.g., worsening cardiac and / or renal function or a mortality risk) to a subject based, at least in part, on the result(s) obtained from an assay that detects WAP four-disulfide core domain protein 2 performed on a body fluid sample obtained from a subject.
Owner:ALERE SAN DIEGO INC
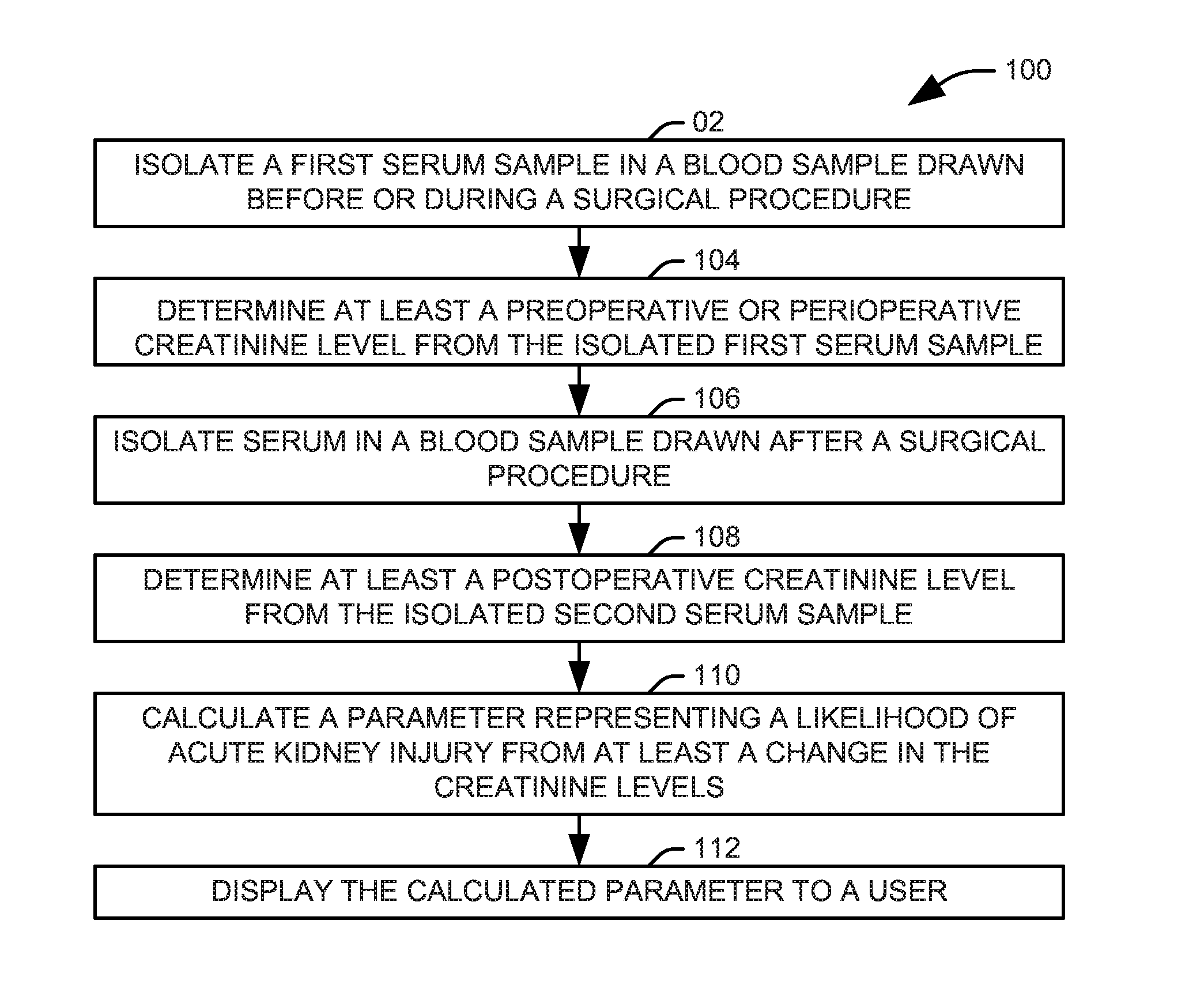
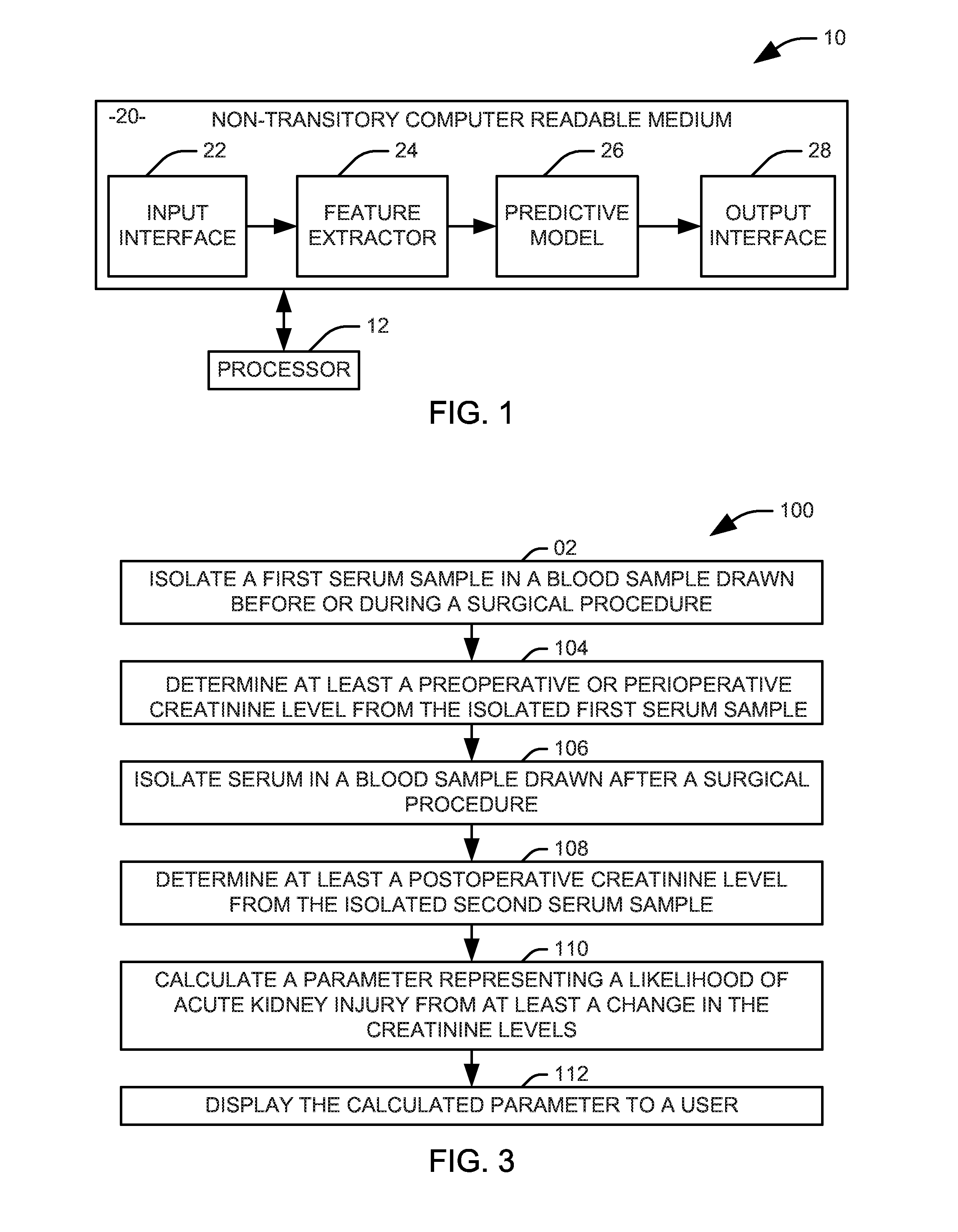
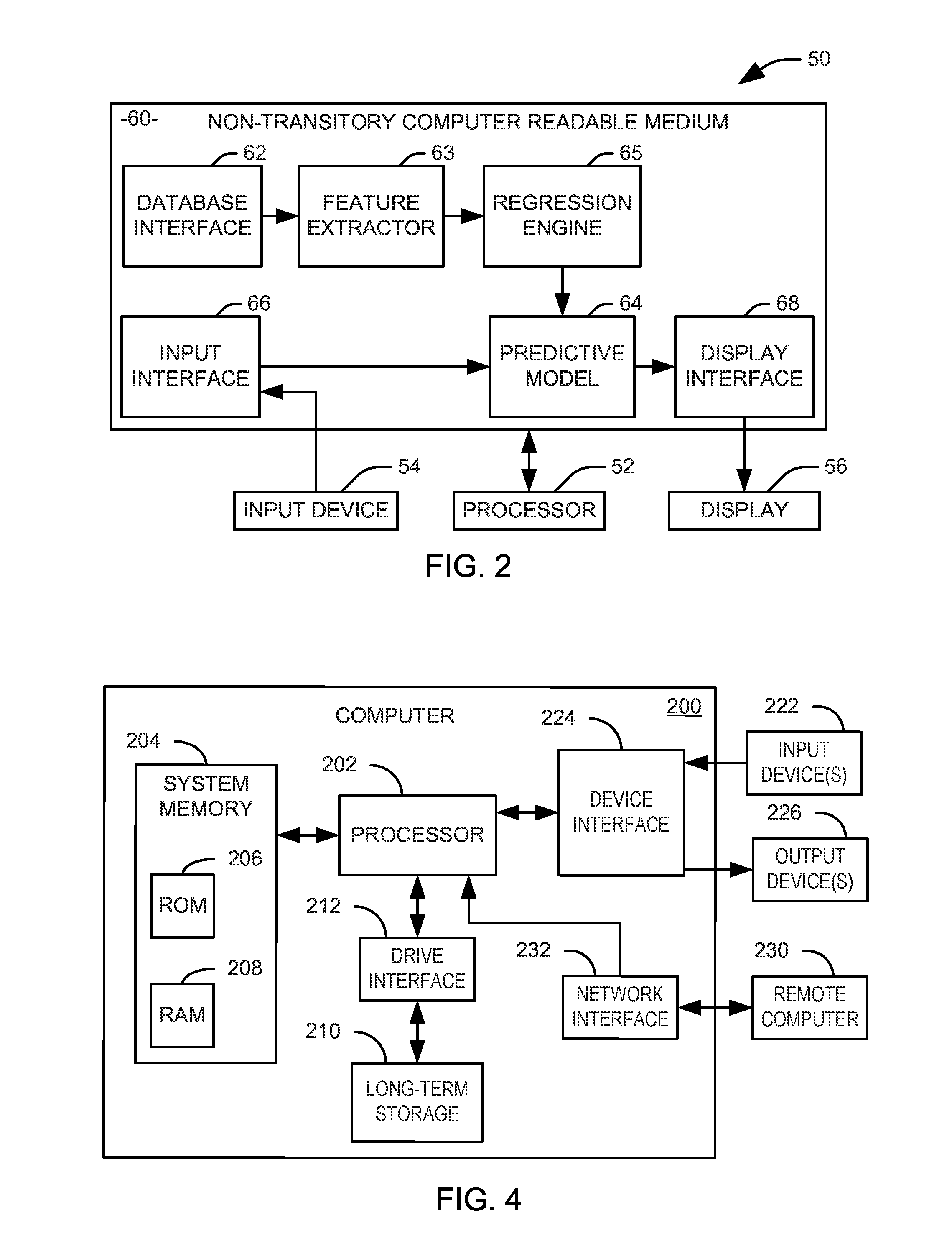
Prediction of acute kidney injury from a post-surgical metabolic blood panel
Systems and methods are provided for predicting the likelihood of acute kidney injury. An input interface is configured to receive a plurality of features derived from the results of a post-surgical metabolic blood panel and either a pre-surgical metabolic blood panel or a perisurgical metabolic blood panel. A predictive model is configured to calculate a parameter representing a likelihood of acute kidney injury from the plurality of features. A user interface is configured to provide the calculated parameter to a user in a human comprehensible form.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Hybridoma cell strain generating anti-human NGAL specific monoclonal antibody, monoclonal antibody generated by same and application
InactiveCN103074303AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMicroorganism based processesBALB/cNGAL Protein
The invention discloses a hybridoma cell strain generating an anti-human NGAL specific monoclonal antibody and a monoclonal antibody generated by the same. The hybridoma cell strain is generated in a way that after an amino acid sequence shown by SEQIDNO:1 immunizes a Balb / c rat, a spleen B lymph cell and a myeloma cell of the rat are fused for further cultivation. The antibody can be used for the immunity detection of the NGAL. Based on the invention, an immunity detection reagent for the NGAL can be developed and used for diagnosing and detecting acute kidney injury and other diseases.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Biomarker for the estimation of acute renal disorder and prognosis of the disorder, and use of the biomarker
Disclosed is a novel biomarker which is useful for the prediction of early onset of acute renal disorder, the estimation of prognosis associated with a renal function, and the diagnosis of acute renal disorder. Also disclosed is use of the novel biomarker. A midkine is used as the biomarker. The determination of the possibility of the onset of acute renal disorder, the estimation of prognosis associated with a renal function or the diagnosis of acute renal disorder can be achieved based on the results of the detection of a midkine in urine.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
ActiveUS20160303187A1Easy to replaceImprovements in renal statusDisease diagnosisCyclic peptide ingredientsRenal FailuresSingle administration
It is an object of the present invention to provide methods and compositions for protection of subjects from acute kidney injury by treating the subject with compounds that modulate the cell cycle. Modulating the cell cycle can comprise inducing G0 / G1 cell cycle arrest, and / or inducing cell cycle progression. As demonstrated below, even a single administration of a compound which induces G0 / G1 cell cycle arrest can protect subjects from AKI, and may be used prophylactically in advance of, or as a treatment following, various treatments or conditions that are known to be injurious to the kidney, followed optionally by release of the arrest. Once AKI is established, cell cycle progression can be induced to increase replacement of lost and damaged cells
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL +1
Colloidal gold immunocolorimetry kit for detecting retinol conjugated protein (RBP) and preparation method of kit
InactiveCN105891501AIncrease or decrease the ratioHigh sensitivityBiological testingAntigenVitamin A Retinol
The invention provides a colloidal gold immunocolorimetry kit for detecting retinol conjugated protein (RBP) and a preparation method of the kit and belongs to the field of in-vitro diagnostic reagents. The kit is used for judging whether the situation of individual acute kidney injury occurs or not. According to the method, colloidal gold particles are adopted as a carrier, a retinol conjugated protein (RBP for short) antibody and the colloidal gold particles are coupled, RBP protein in a sample makes contact with the coupled gold particles in a corresponding detection device, an antigen-antibody-gold compound is formed, the light absorbance of the gold particles under detection wavelength is changed, the change amount of the light absorbance is positively correlated with the concentration of RBP protein, and then the purpose of detecting RBP protein in the sample is achieved. The kit has high analysis sensitivity.
Owner:CHEMCLIN DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Molecular marker and kit for early diagnosis and prediction of septicopyemia complicated by acute kidney injury and application thereof
ActiveCN107541563AStrong molecular biology foundationMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMolecular markerPathology
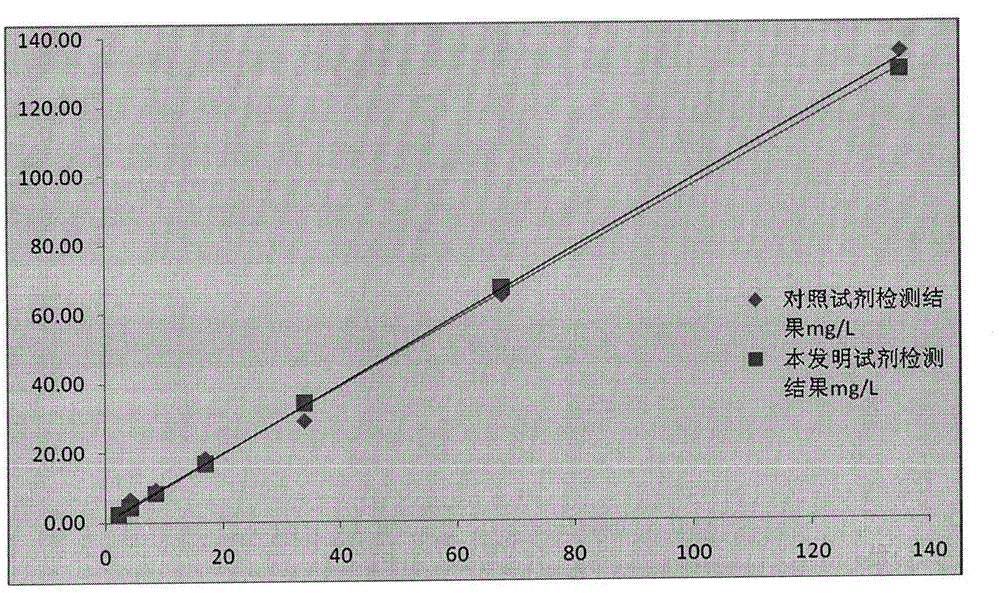
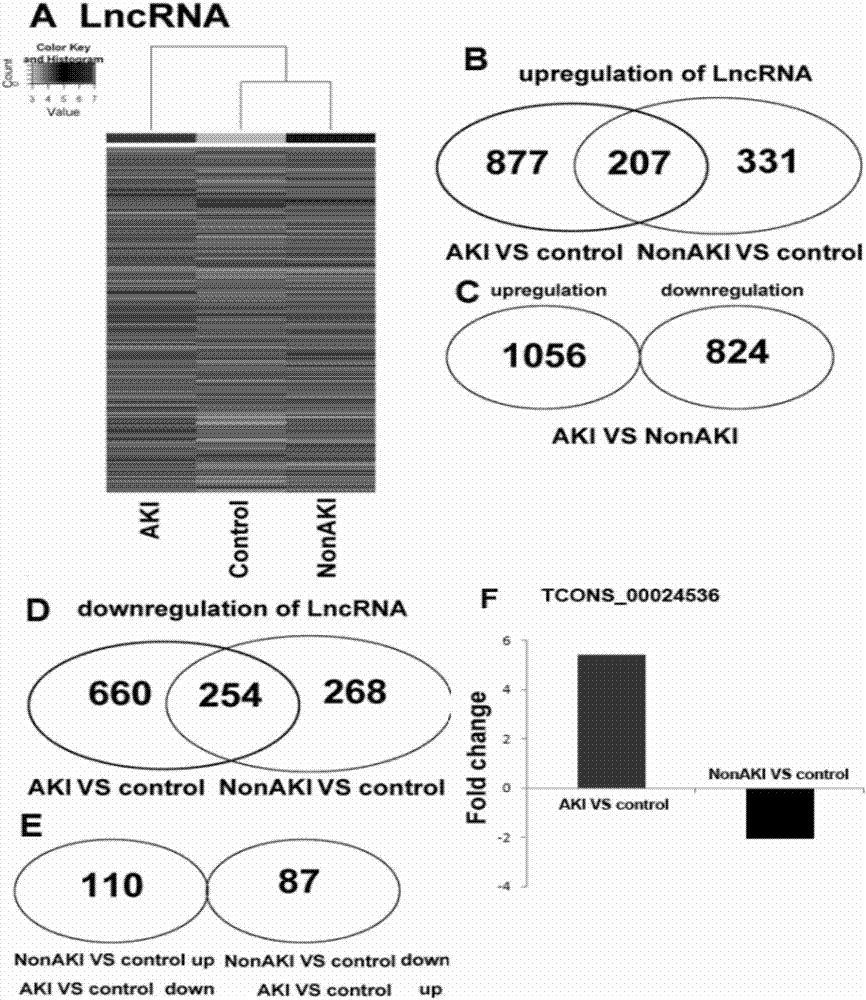
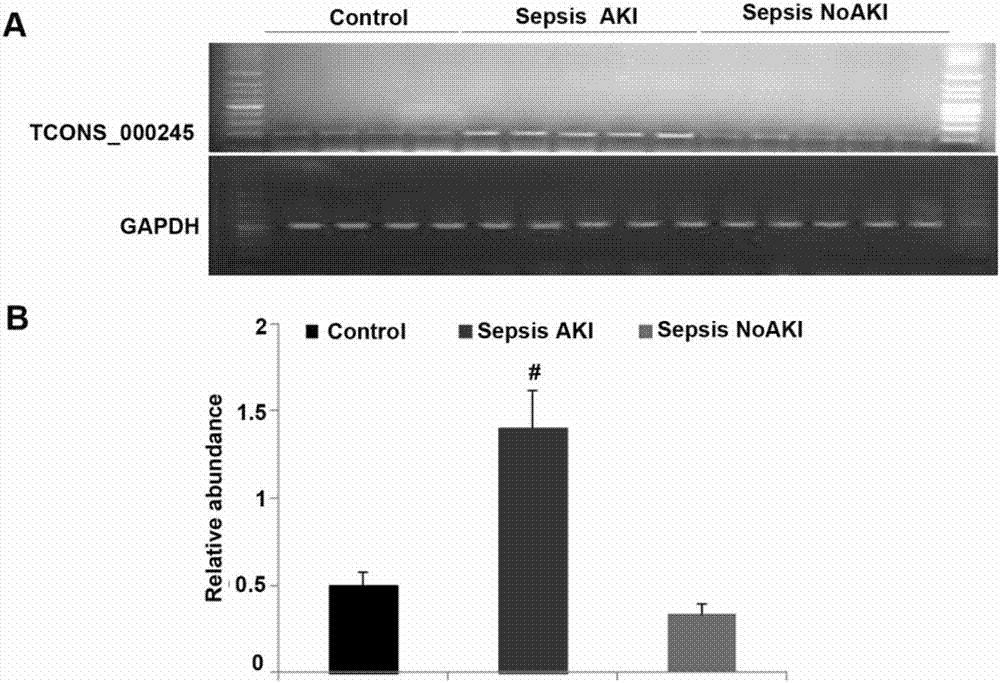
The invention discloses a molecular marker and kit for early diagnosis and prediction of septicopyemia complicated by acute kidney injury and application thereof. TCONS_00024536 is highly expressed inthe blood of the patient suffering from septicopyemia complicated by acute kidney injury and through detecting the expression level of TCONS_00024536 in the patient blood, septicopyemia complicated by acute kidney injury or the probability of septicopyemia complicated by acute kidney injury are determined. The molecular marker and kit have the great significance for specific and sensitive early diagnosis and prediction of septicopyemia complicated by acute kidney injury.
Owner:THE SECOND XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
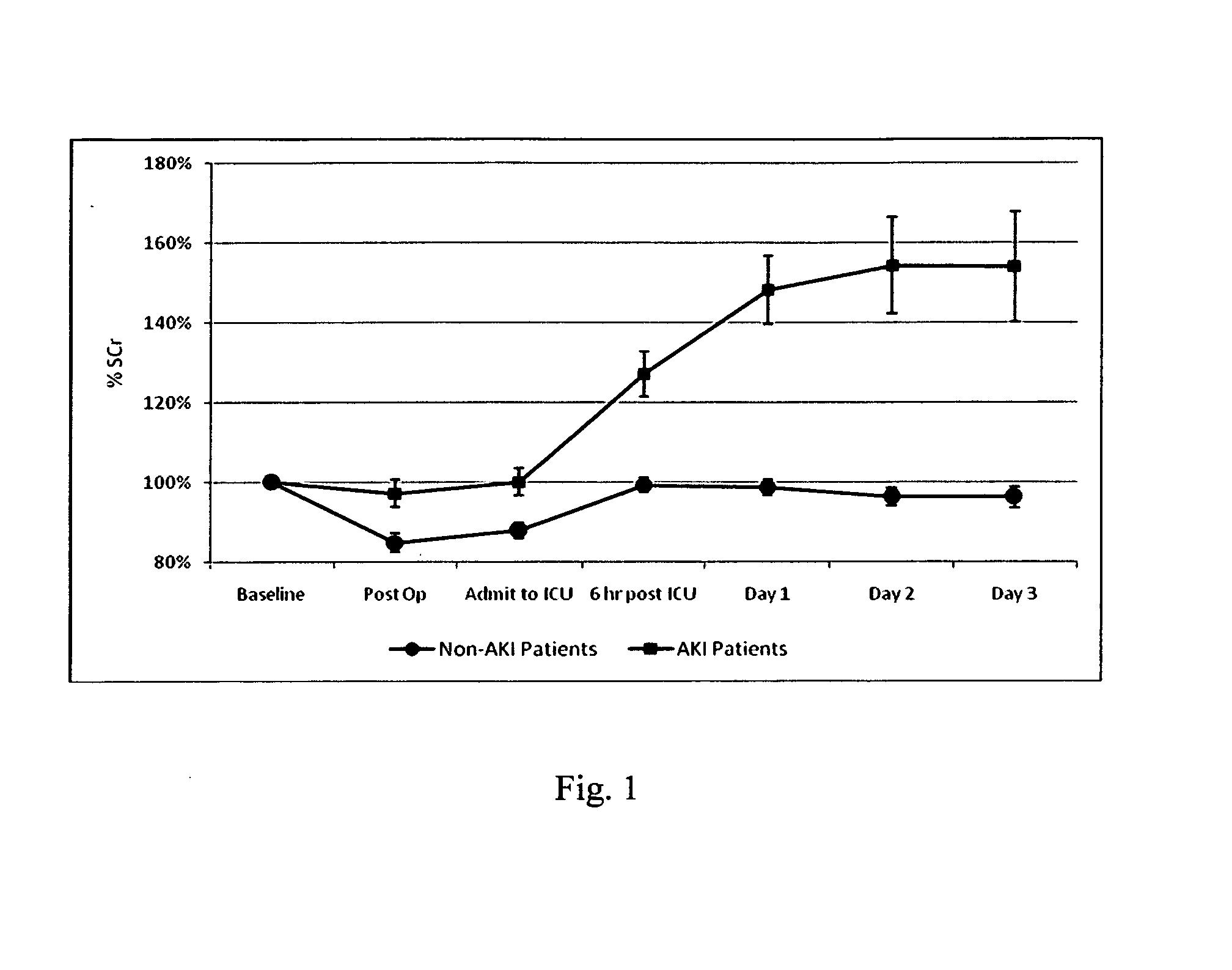
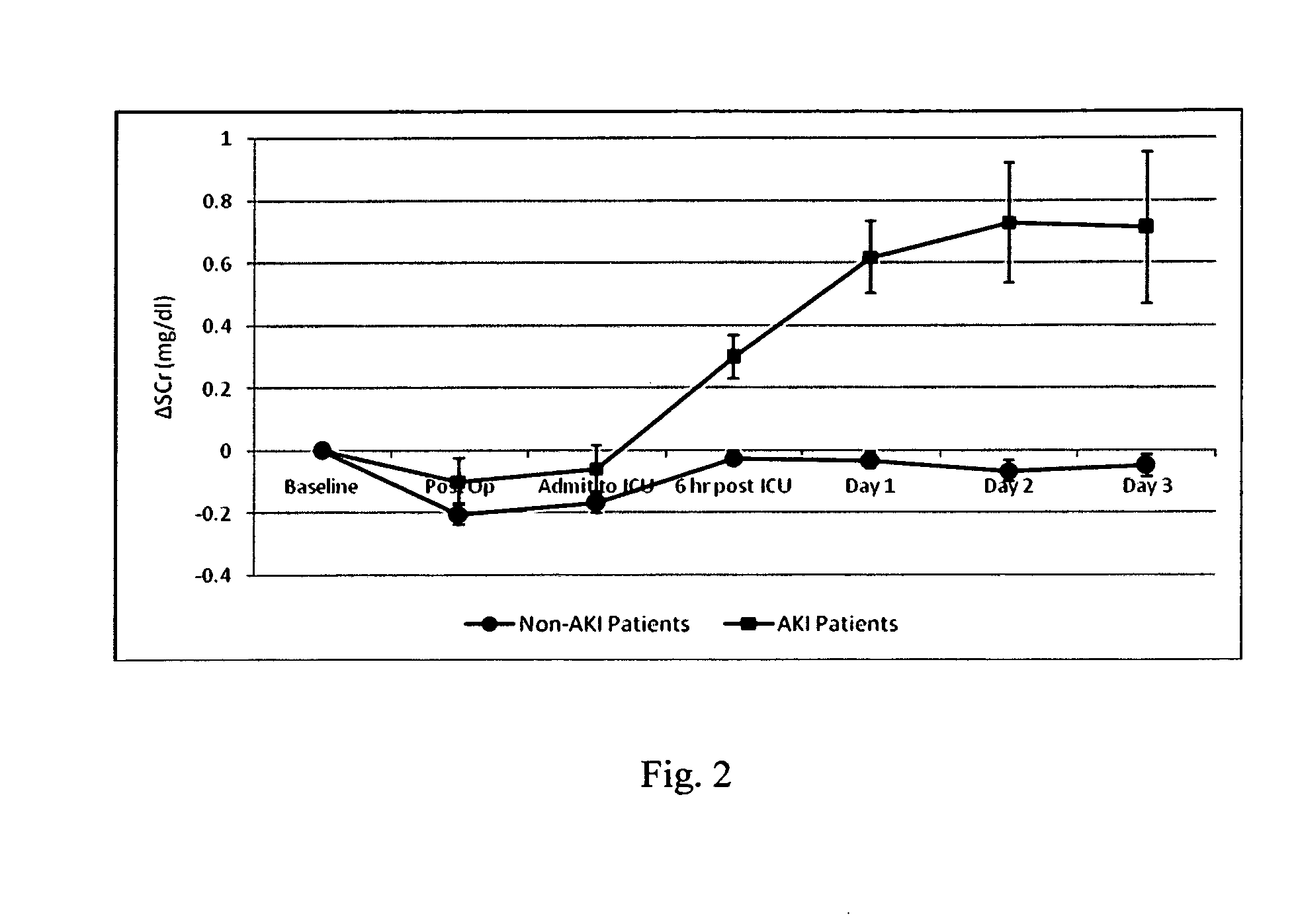
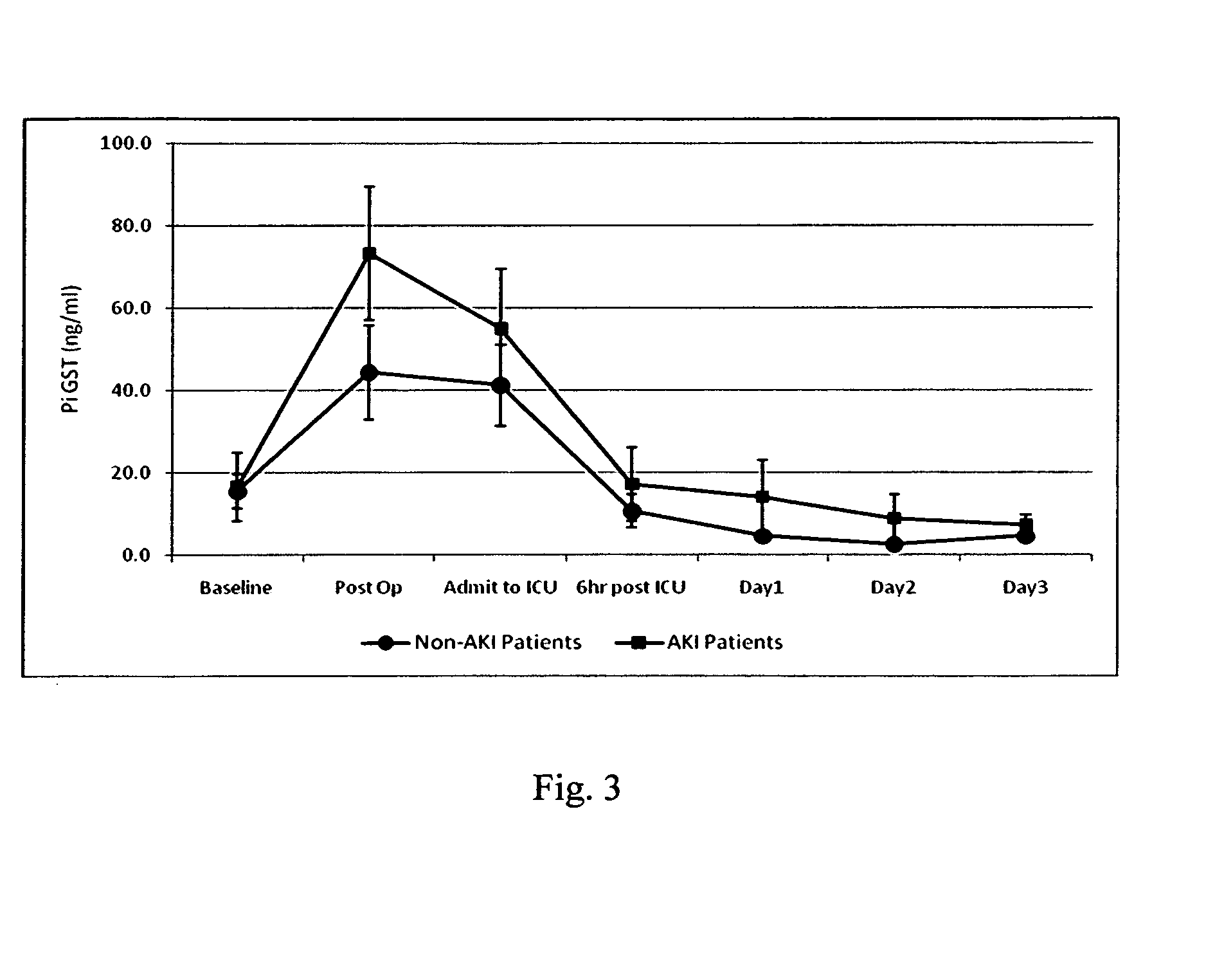
Method for the early indentification and prediction of an abrupt reduction in kidney function in a patient undergoing cardiothoracic surgery
InactiveUS20090238812A1Early detectionConvenient treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsDisease diagnosisRenal tubuleRecovery stage
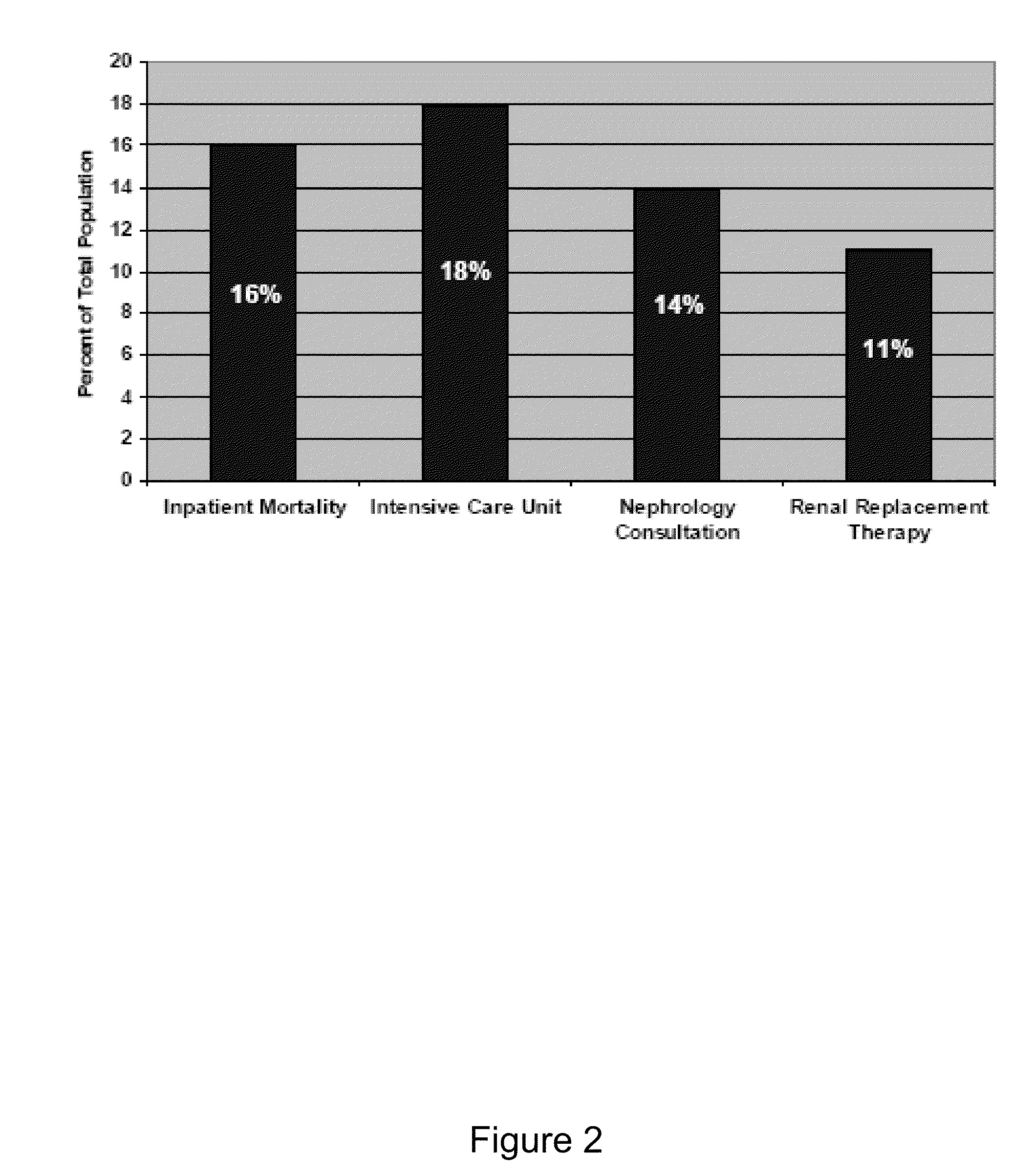
A method for the early identification and prediction of an abrupt reduction in kidney function in a patient undergoing cardiothoracic (CT) surgery, including Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB), comprises contacting a urine sample from the patient with a capture molecule for a biomarker, especially πGST, specific for the distal region of the renal tubule and which biomarker is released from said region when there is damage to said region indicative and predictive of an abrupt reduction in kidney function, the biomarker being detectable as early as intraoperatively or in the recovery stage post CT surgery, for example prior to transfer of the patient to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), allowing for immediate corrective medical intervention. The method can be used to detect Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) and a requirement for Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT) namely dialysis, earlier than two hours post CT surgery and as early as zero hours post or during CT surgery or CPB.
Owner:ARGUTUS INTPROP
Application of mPGES-2 as target in treatment or prevention of drug-induced acute liver injury
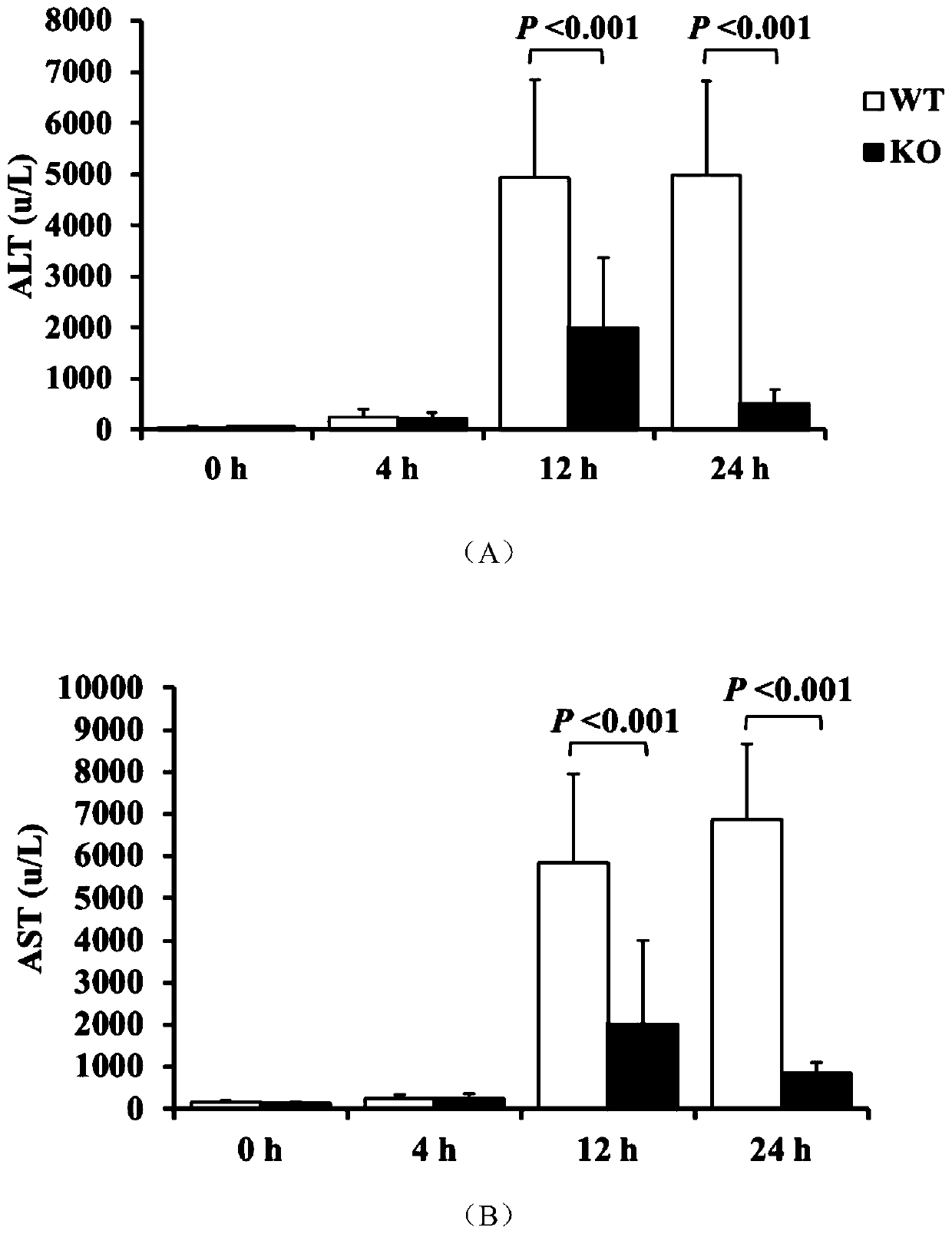
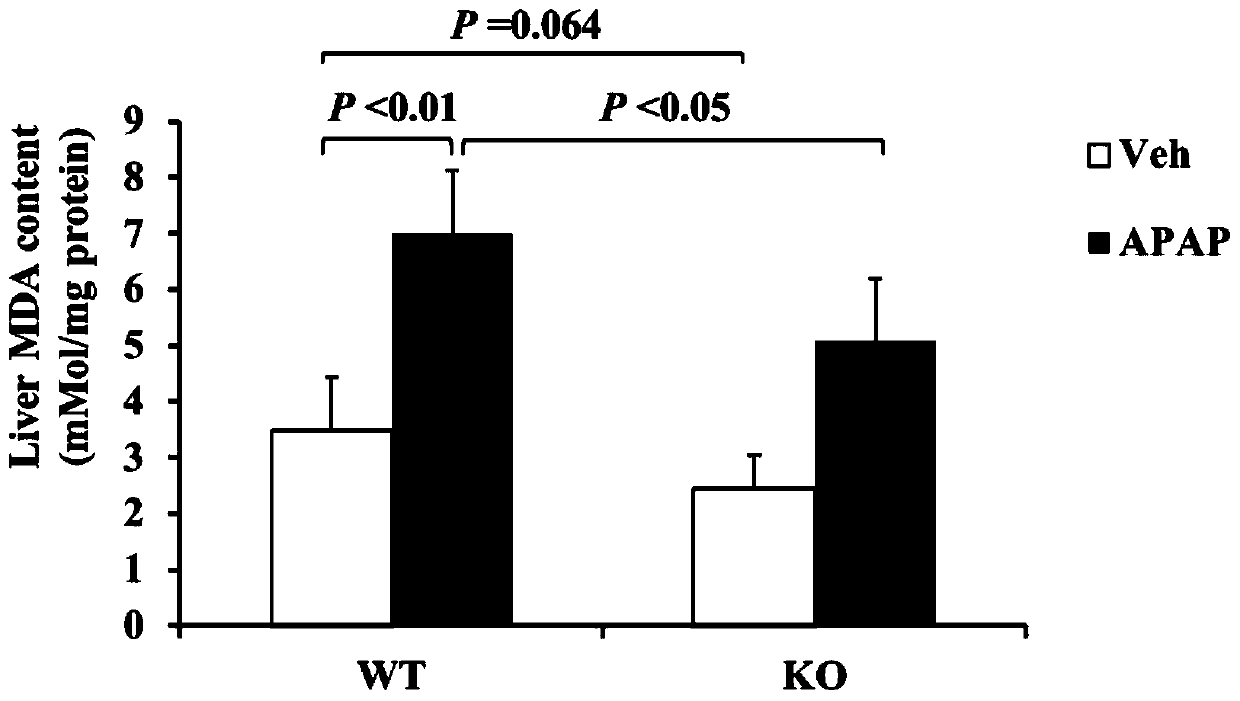
The present invention discloses the application of the mPGES-2 as a target in the treatment or prevention of drug-induced acute liver injury, and belongs to the field of biomedicine. Experiments haveshown that in an acetaminophen-induced mouse acute liver injury model, knockout of the mPGES-2 can significantly reduce ALT and AST levels in the serum, and overexpression of the mPGES-2 can increasethe ALT and AST levels in the serum. This indicates that the mPGES-2 has a regulatory effect on acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury, and the mPGES-2 can be used as a new target for the treatmentor prevention of drug-induced acute liver injury. Knockout of the mPGES-2 can reduce p-JNK and inflammatory responses by inhibiting the oxidative stress, so that acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury can be significantly reduced.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
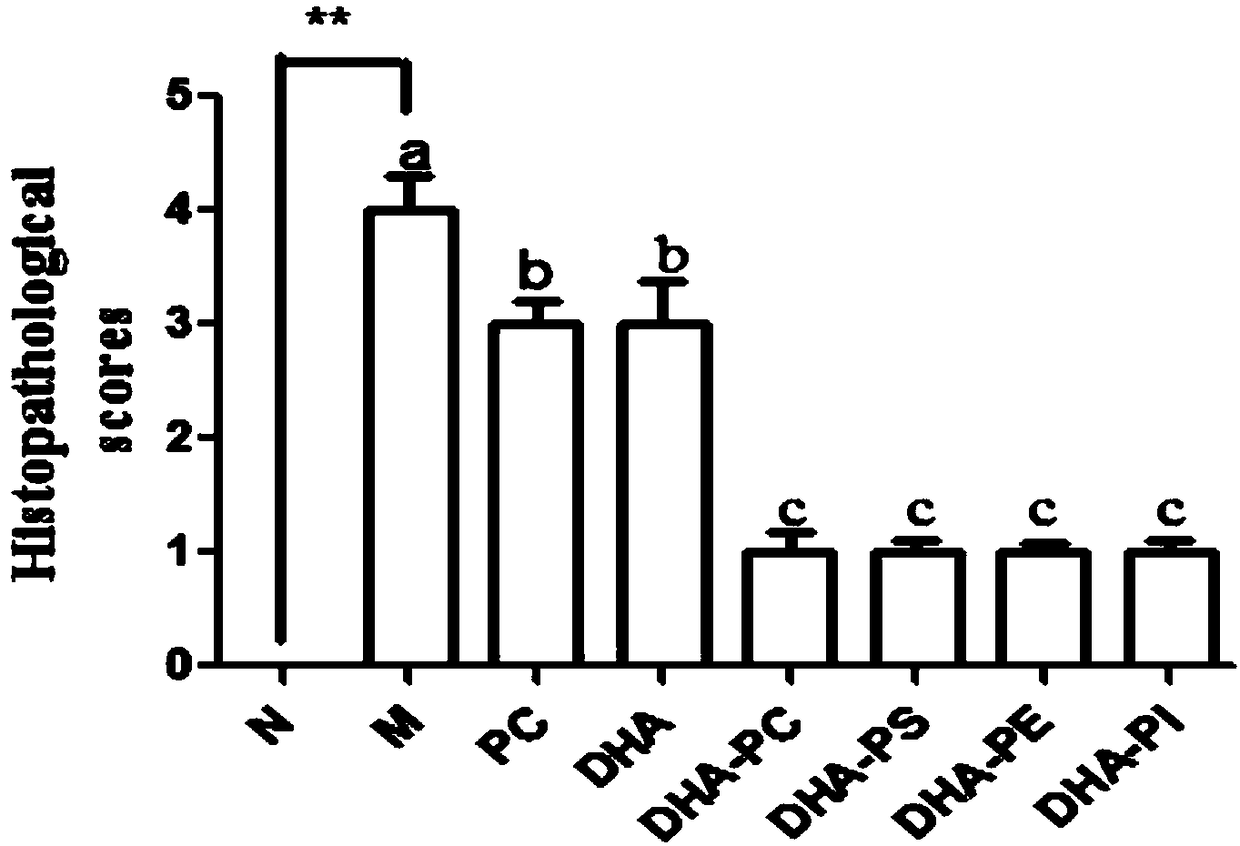
Application of phospholipid rich in DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) to product for improving acute kidney injury
InactiveCN108309991ALow costSimple stepsOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderDocosahexaenoic acidOrganic solvent
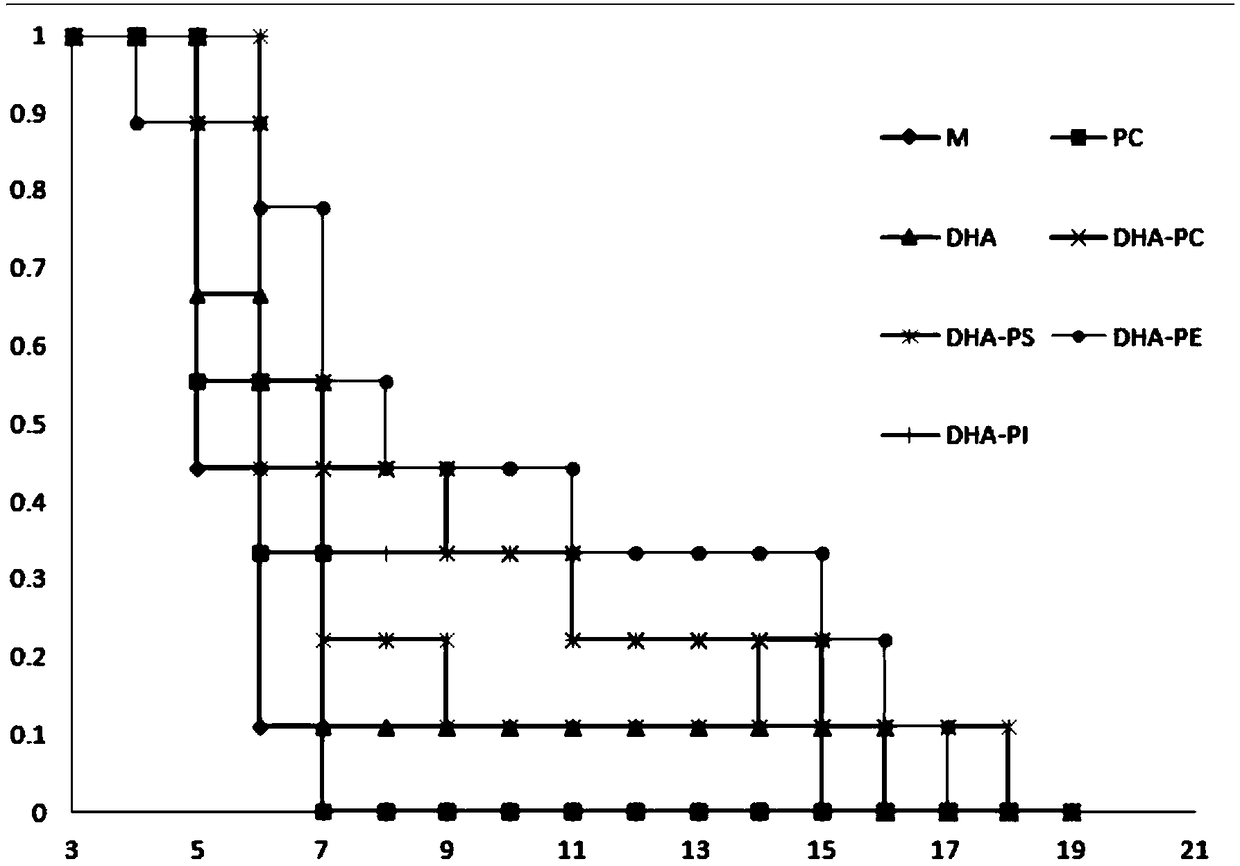
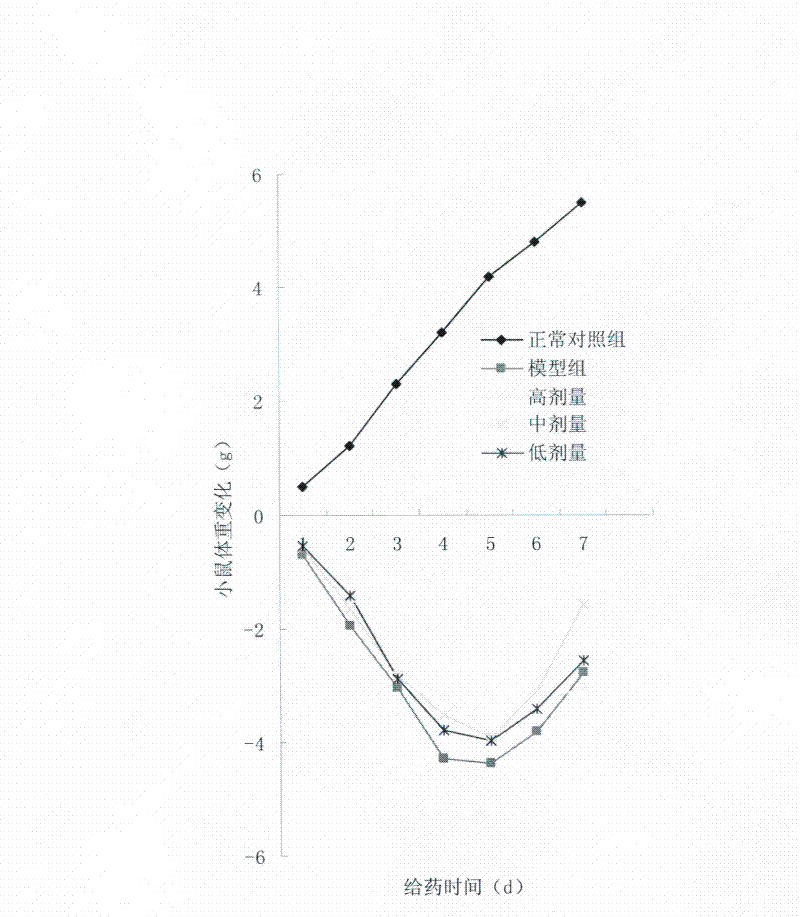
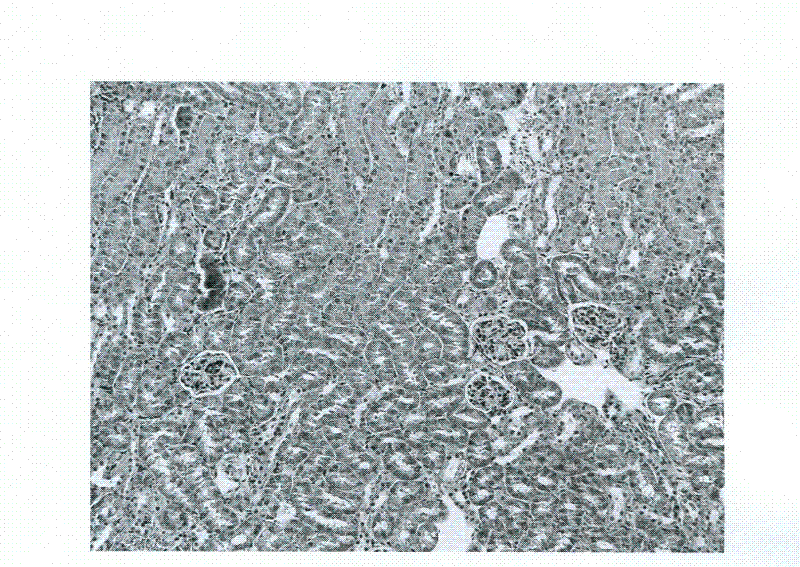
The invention discloses application of phospholipid rich in DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) to a product for improving the acute kidney injury. According to the invention, DHA phospholipid is prepared by using sleeve-fish roes as raw materials, separation and conversion are further carried out, and purity of the prepared phospholipid is all 90% or above. A preparation method of sleeve-fish phosphatidylcholine extract is low in cost and simple in step, uses a small volume of organic solvent, and generates little organic solvent pollution to the environment. Animal experiments prove that when a mousesuffering from the acute kidney injury is only supplemented and intervened with 200 to 400mg / kg DHA-rich phosphatidylcholine, life time of the mouse suffering from the acute kidney injury is obviously prolonged and the kidney tissue injury degree of the mouse is reduced, which proves that the phospholipid rich in DHA can be applied to the product for improving the acute kidney injury.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
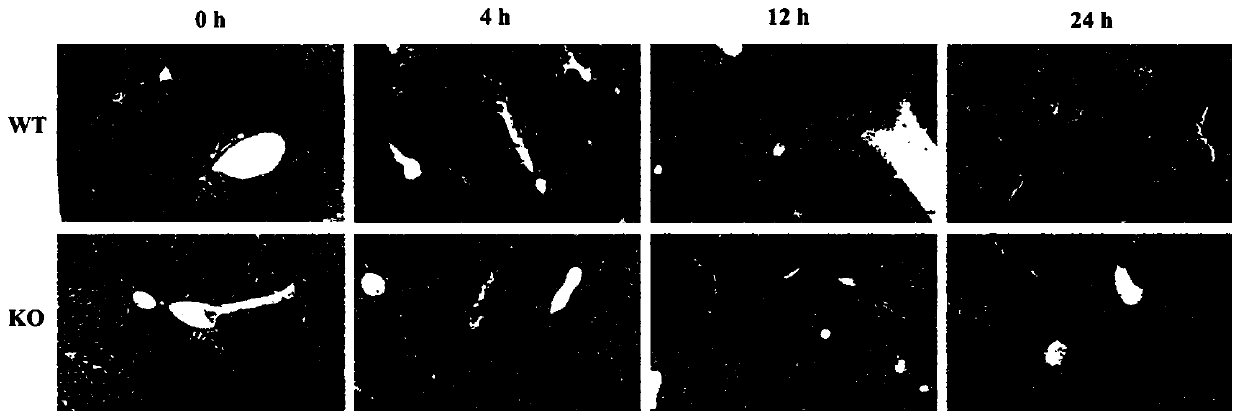
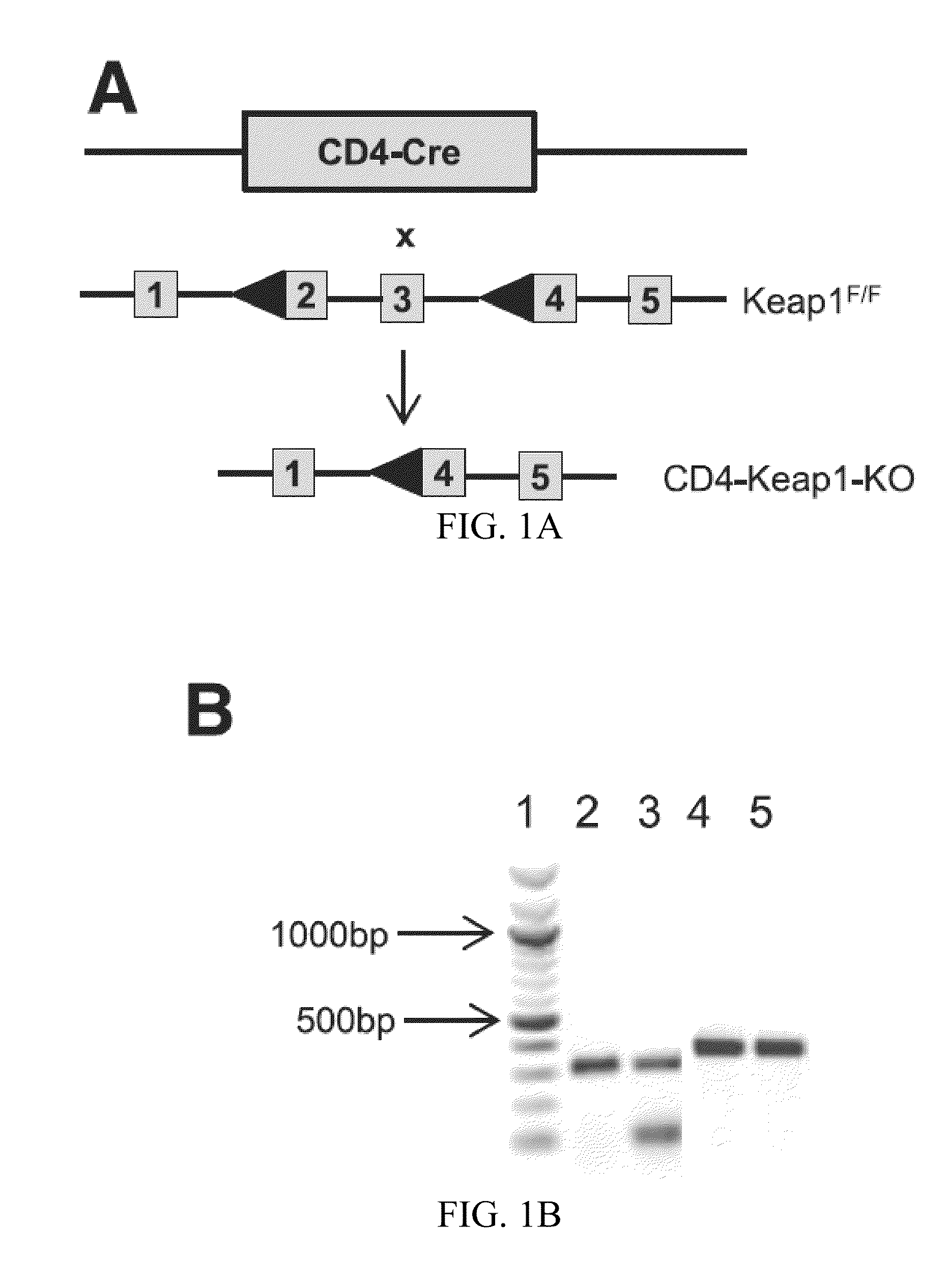
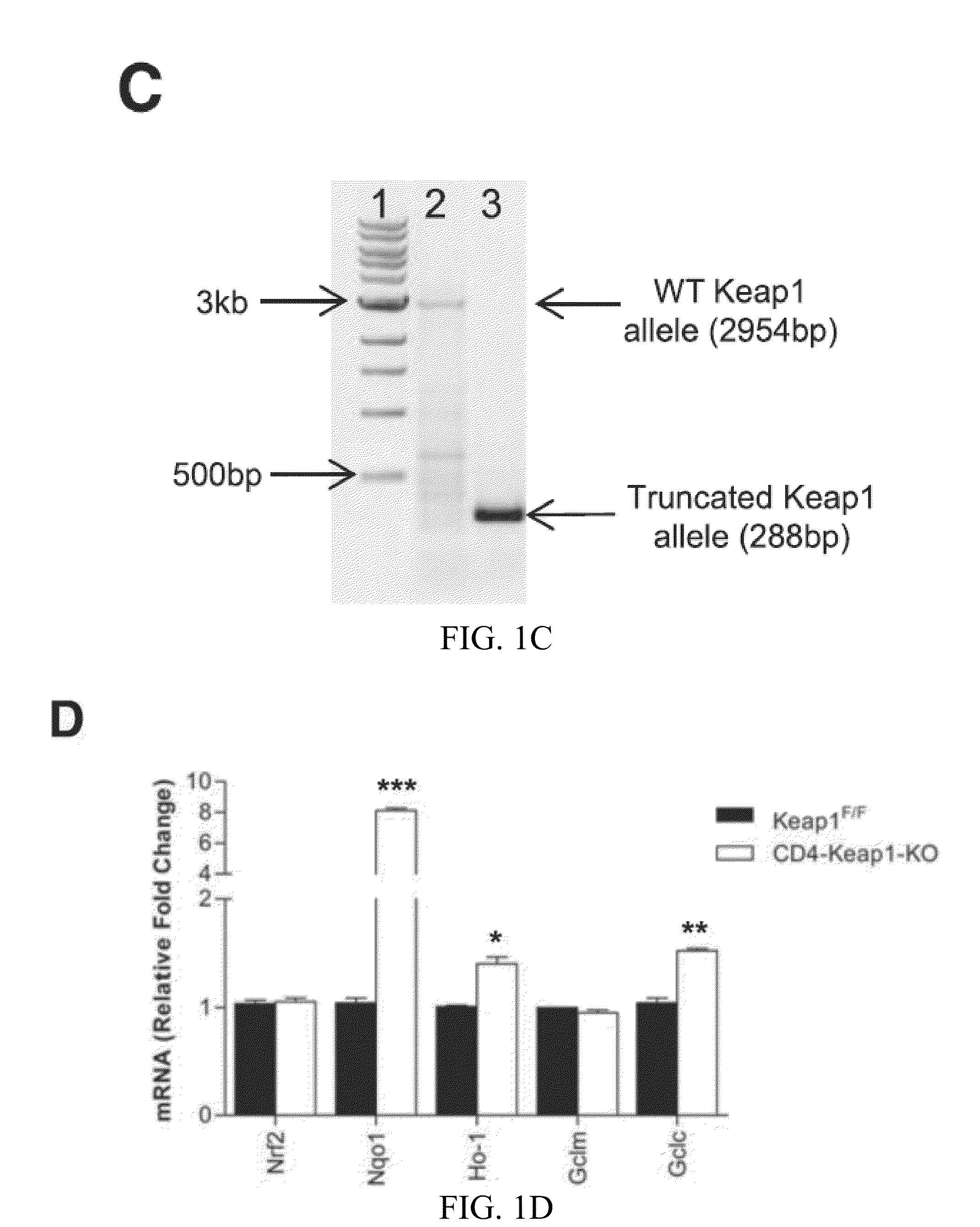
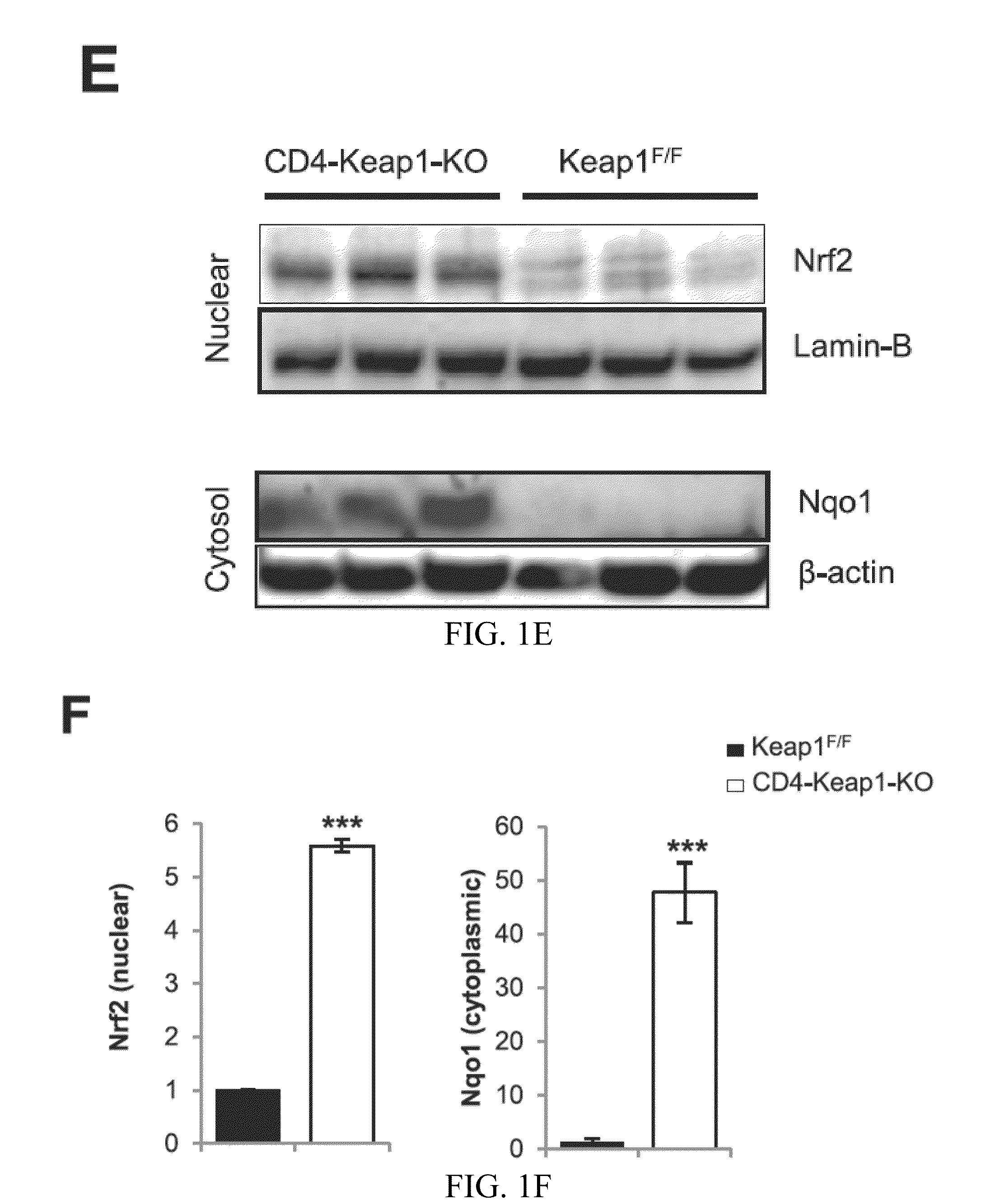
Compositions and methods for the study and treatment of acute kidney injury
InactiveUS20160120158A1Acute injuryNatural and tolerable treatmentBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsKnockout animalT cell
The present invention relates to the field of nephrology. More specifically, the present invention provides compositions and methods useful for the study and treatment of acute kidney injury. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a knockout animal whose genome comprises a deletion of exon 2 and exon 3 of kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) in T-cells. In another embodiment, a method for treating a subject diagnosed with AKI comprising the steps of (a) isolating T-cells from the subject; (b) activating Nrf2 expression in the isolated T-cells; and (c) administering the T-cells back to the subject.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Devices and methods for treating acute kidney injury
A catheter devices / systems and methods therefrom are described herein for treating acute kidney injury, especially the contrast-induced acute kidney injury wherein the devices prevent the contrast dyes from entering into kidney and / or facilitate blood flow of kidney by said catheter system.
Owner:RENALPRO MEDICAL
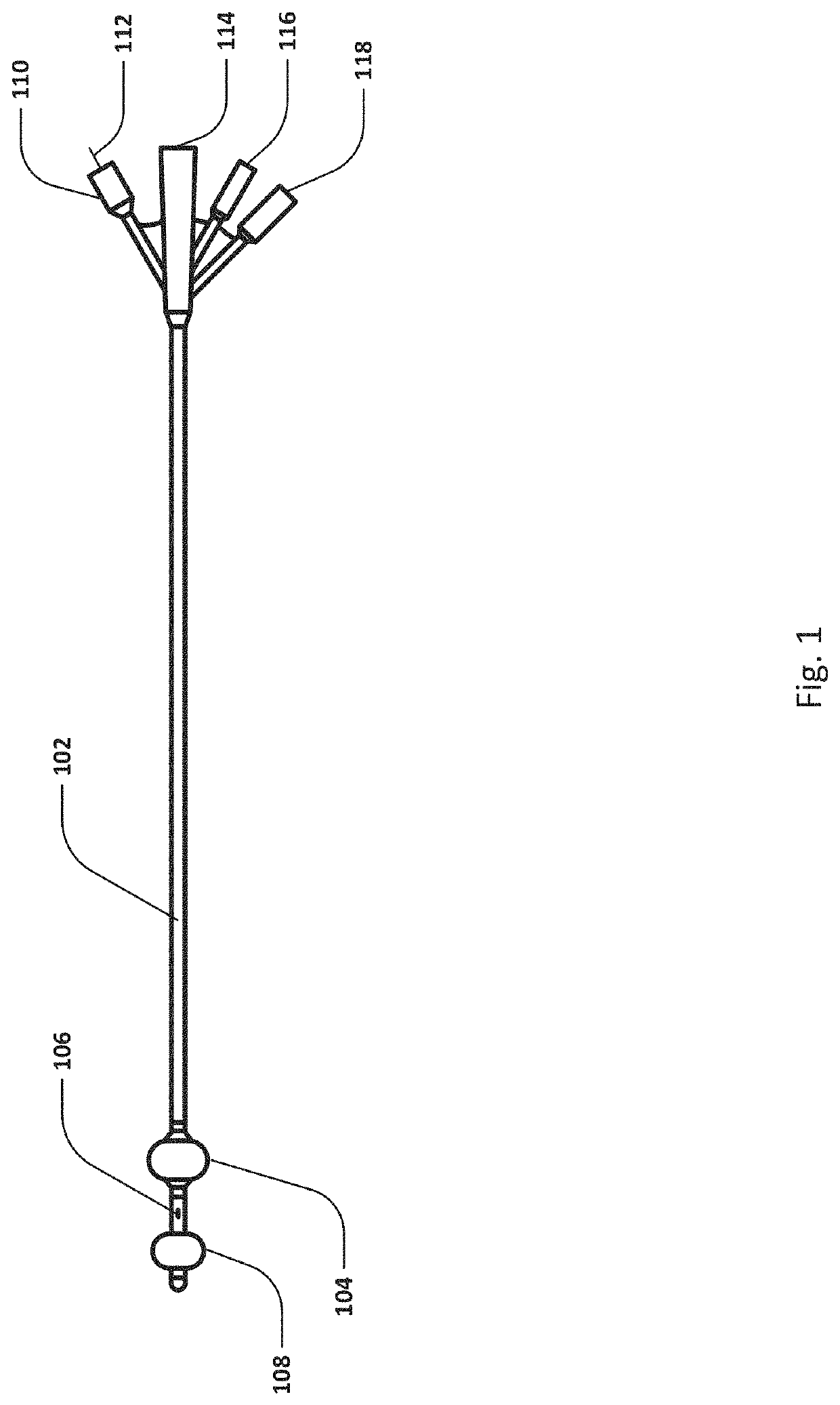
Systems, devices and methods for draining and analyzing bodily fluids and assessing health
PendingUS20210093243A1Low costEasily put in placeCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationEngineeringCatheter
Systems, devices and methods for draining and analyzing bodily fluids and assessing health are described and generally comprise a drainage tube in fluid communication with at least one opening near or at a distal end of a catheter, a pump in fluid communication with the drainage tube and configured to apply a negative pressure to the drainage tube, and a valve configured for unidirectional flow and in fluid communication with the drainage tube. A controller is configured to actuate the pump to apply the negative pressure for clearing an airlock and to monitor a urine output from the patient over a first predetermined period of time above a urine output threshold and over a second predetermined period of time below the urine output threshold. The controller may determine a risk of acute kidney injury if the urine output below the urine output threshold exceeds the second predetermined period of time.
Owner:POTRERO MEDICAL
Use of cat isaria mycelium
InactiveCN102228471AInanimate material medical ingredientsUrinary disorderCis-platinumAcute kidney injury
The invention discloses an application of a cat isaria mycelium in the preparation for a medicine treating acute kidney injury caused by cis-platinum. An experimental result displays that after mice are injected with cis-platinum and patients are chemo-treated by cis-platinum, the CRE and BUN levels in the serums thereof are obviously increased, meaning that the cis-platinum can cause an acute kidney injury to the mice and the chemo-treated patients; after the mice injected with cis-platinum are perfused with cat isaria mycelium dry powder and the patients chemo-treated by cis-platinum take cat isaria mycelium dry powder, the CRE and BUN levels in the serums thereof are obviously decreased, meaning that the cat isaria mycelium has a remarkable treatment function to the acute kidney injury caused by cis-platinum. The invention provides the application of the cat isaria mycelium in the preparation for a medicine treating acute kidney injury caused by cis-platinum, and the cat isaria mycelium can be further developed to be an assistant medicine in the cis-platinum chemotherapy.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Construction method of contrast agent induced acute kidney injury animal model
ActiveCN105106975AReduce distractionsExperimental results are reliableOrganic active ingredientsX-ray constrast preparationsCytologyAnimal model
The invention provides a construction method of a contrast agent induced acute kidney injury animal model. A clinically commonly used low permeability contrast agent is used in the construction method to make the stable CI-AKI model within a short time, so interferences of other confounding factors are effectively avoided, bases are provided for further researches of the pathologic and physiologic mechanisms, the molecular cytology and the molecular biology of the CI-AKI, and bases are provided for early prevention and treatment of CI-AKI of clinic patients.
Owner:陈纪言 +4
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com