Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
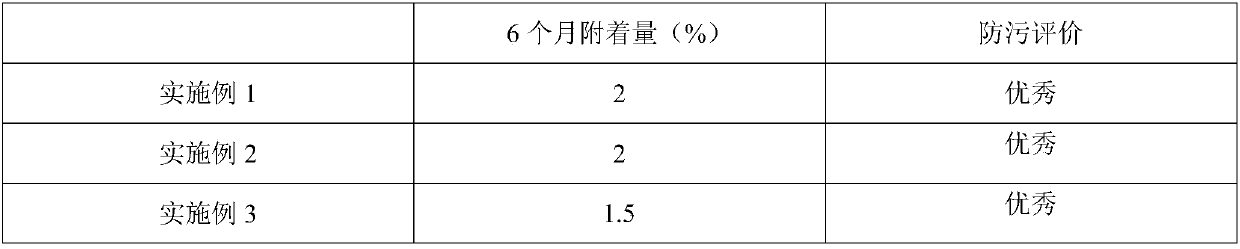
40 results about "2-n-Octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Antimicrobial Composition and Method
InactiveUS20080249136A1Improve performanceImprove securityAntibacterial agentsBiocideSodium PyrithioneNitrostyrol
An antimicrobial composition containing a cationic polymer having limited antimicrobial activity (such as a hydrophobically-modified quaternary ammonium cellulose ether) and an antimicrobial compound (such as one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of diiodomethyl-para-tolylsulfone, ortho-phenylphenol, sodium pyrithione, zinc pyrithione, 3-iodo-2-propynylbutylcarbamate, 2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 1,2-benzisothiazolin-3-one, 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 1-(3-chloroallyl)-3,5,7-triaza-1-azoniaadamantane chloride, 2-(4-thiazolyl)-benzimidazole, β-bromo-β-nitrostyrene, 2,4,4′-trichloro-2-hydroxyphenyl ether, chloroxylenol, chlorocresol, para-tert-amylphenol, N-(4-chlorophenyl)-N′-(3,4 dichlorophenyl)-urea, and para-hydroxybenzoic acid esters). The growth of microorganisms (such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa) can be inhibited by exposing the microorganism to such a composition.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Antifouling paint composition, antifouling paint films, and, ships, underwater underwater structures, fishing gear and fishing nets covered with the films
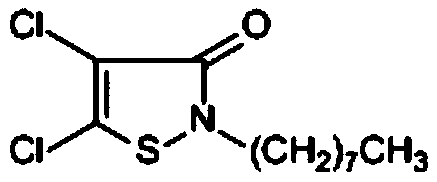
An antifouling coating composition substantially not containing cuprous oxide and organotins, characterized by comprising (A) a metal-containing copolymer obtained by copolymerization of a polymerizable unsaturated monomer (a1) containing a metal and an unsaturated monomer (a2) capable of radical polymerization containing no metals; (B) 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one; and (C) a metal pyrithione compound. There are provided an antifouling coating composition, antifouling coating film and, covered with the antifouling coating film, marine vessel, underwater structure and fishing gear or fishing net, which can reduce burdens on the environment, exhibiting excellent antifouling performance, and which excel in not only uniform wasting of coating film but also capability of maintaining antifouling performance of coating film for a prolonged period of time.
Owner:CHUGOKU MARINE PAINTS
Microbicidal composition
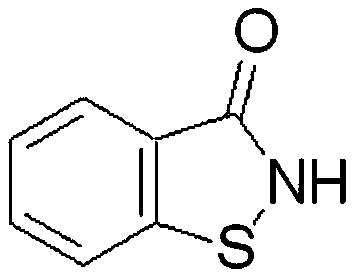
A microbicidal composition containing: (a) a stabilized hypochlorite and bromide composition; and (b) at least one microbicide selected from among 2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 5-choloro-2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 4,5-dichloro-2-N-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 1,2-benzisothiazolin-3-one, 3-bromo-1-chloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin, poly(hexamethylenebiguanide hydrochloride), alkyl-dimethyl-benzylammonium chloride, pentane-1,5-dial (glutaraldehyde), 5-bromo-2-nitro-1,3-propane-diol and 2,2-dibromo-3-nitrilopropionamide.
Owner:WILLIAMS TERRY MICHAEL
Antimicrobial composition and method
InactiveCN101291581AGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsSodium PyrithioneNitrostyrol
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
A marine antifouling coating
InactiveCN102277025AImprove antifouling performanceImprove durabilityAntifouling/underwater paintsRosin coatingsToxic materialCopper
The invention relates to a marine antifouling paint, which is composed of a film-forming base material, an antirust pigment, a diluent, a filler and a combined antifouling agent, characterized in that the combined antifouling agent is composed of A and B components, The weight ratio of the two components A and B is 1:3 to 1:20; wherein component A is oil-soluble nano-silver, and component B is an organic algicide; the organic algicide is selected from N, N-di Methyldichlorophenylurea, 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, N,N'-dimethyl-N'-phenyl-(N-fluoro Dichloromethylthio)sulfonamide has one or more of them mixed. The coating does not contain tin or copper and other toxic substances that are harmful to the environment. The antifouling agent is combined with nano silver and easily degradable organic algicide. The antifouling effect of the antifouling coating is efficient and durable, and the amount of antifouling agent added Low, is an environmentally friendly antifouling coating. The preparation method is simple and the cost is reasonable.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Antimicrobial composition containing N-(n-butyl)-1,2-benzisothiazolin-3-one
InactiveUS20050197366A1Broaden potential marketsReduce concentrationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsKetoneBiology
An antimicrobial composition comprising: (a) N-(n-butyl)-1,2-benzisothiazolin-3-one; and (b) 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one.
Owner:CHIA LI LIANG +1
Method for preparing solid wood particleboard of soybean protein adhesive
InactiveCN102896682ASimple processLow costNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesProtein adhesivesAdhesiveHydrogen-Ion Concentrations
The invention discloses a method for preparing a solid wood particleboard of a soybean protein adhesive and solves the problem that the emission of formaldehyde of existing solid wood particleboards exceeds standard. The method includes the following steps that the adhesive is firstly prepared, 100 parts by weight of defatted soybean powders are uniformly mixed with 1000 parts to 1500 parts by weight of water to obtain a mixture, the mixture is firstly dissolved by 30 parts to 35 parts by weight of alkali solution with hydroxide ion concentration of 2mol / L, then the dissolved mixture is sedimentated and purified by 25 parts to 30 parts by weight of acid solution with hydrogen ion concentration of 2mol / L to obtain isolated soybean protein, then the isolated soybean protein is subjected to union modification by 3 parts to 6 parts by weight of alkali or anionic surface active agent lauryl sodium sulfate, then 0.5% (v / v) of 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one is added to serve as an antiseptic to obtain the soybean protein adhesive, a wood raw material is subjected to chipping, flaking, drying and sorting, the adhesive is applied, and mat formation, prepressing, hot-pressing, cooling, edge sawing, sanding, grading and putting in storage are performed. The method for preparing the solid wood particleboard of the soybean protein adhesive is simple in process, low in cost and free of emission of formaldehyde.
Owner:湖北嘉聚宝森工有限责任公司
Modified antirust paint for egg turning rack of incubator
InactiveCN106118273AImprove thermal shock resistanceImprove stabilityAnti-corrosive paintsEpoxy resin coatingsEpoxyThermal shock
The invention relates to the field of antirust paint, in particular to modified antirust paint for an egg turning rack of an incubator. The modified antirust paint is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 36 to 40 parts of a styrene-acrylic emulsion, 14 to 20 parts of an epoxy resin emulsion, 3 to 5 parts of inositol hexaphosphate, 3 to 5 parts of tourmaline powder, 4 to 6 parts of a silane coupling agent, 1 to 2 parts of tris(2-ethylhexyl)acetyl citrate, 2 to 4 parts of bamboo charcoal fiber, 3 to 6 parts of basic calcium-zinc molybdate, 0.5 to 1 part of butylene terephthalate, 0.5 to 1 part of 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 1 to 2 parts of oxyethylene polyoxypropylene ether and 4 to 8 parts of modified nano graphene. The antirust paint is good in thermal shock resistance, can tolerate frequent change of temperature, is strong in adhesion to metal, free of cracking and spalling, and resistant to acid-alkali, salt spray and bacterium erosion, can also emit far infrared rays, has certain benefits on hatching eggs, is good in stability, very low in volatilization rate and non-toxic, and cannot cause influence on the hatching eggs.
Owner:BENGBU JIAAI ELECTRONICS
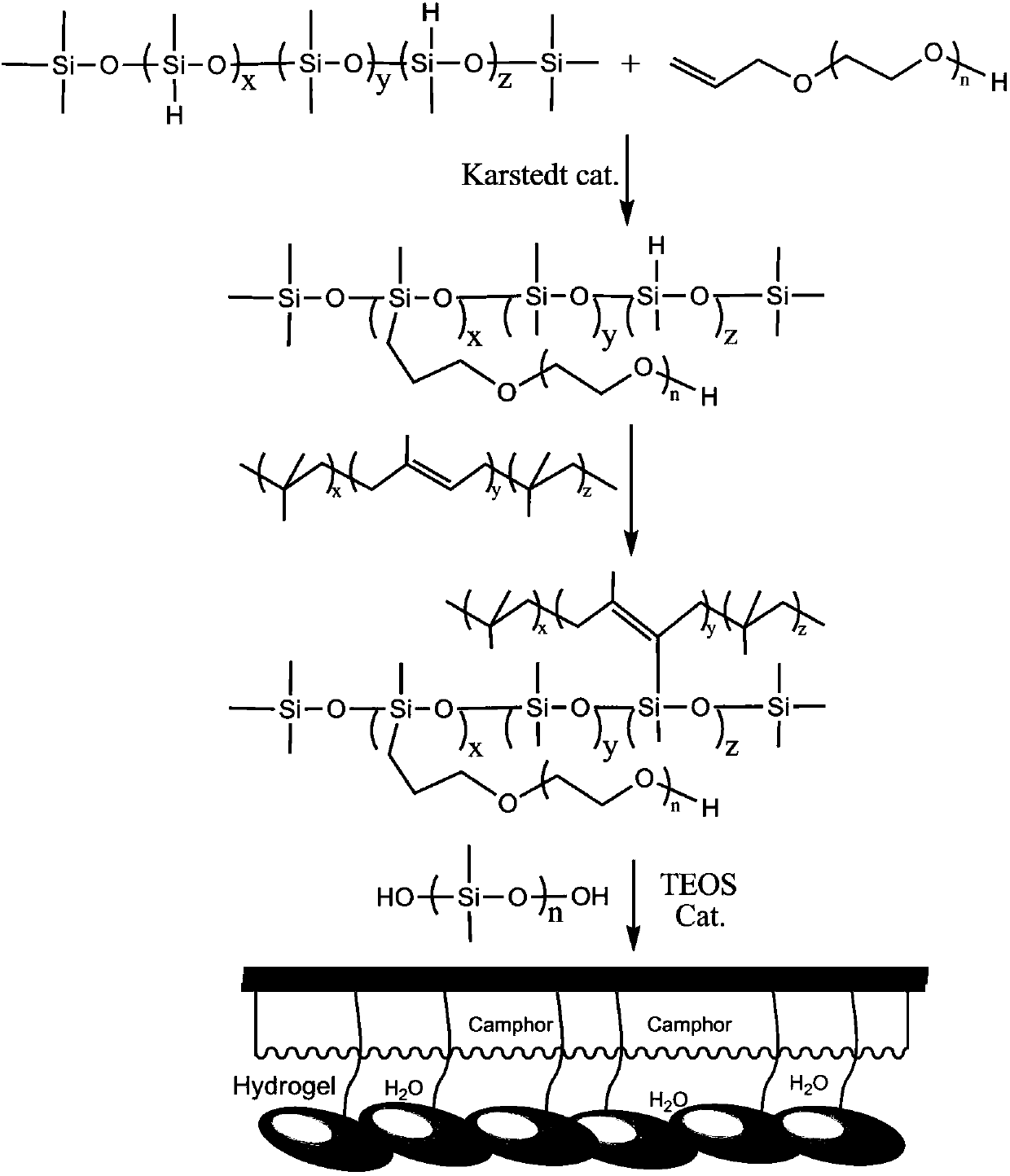
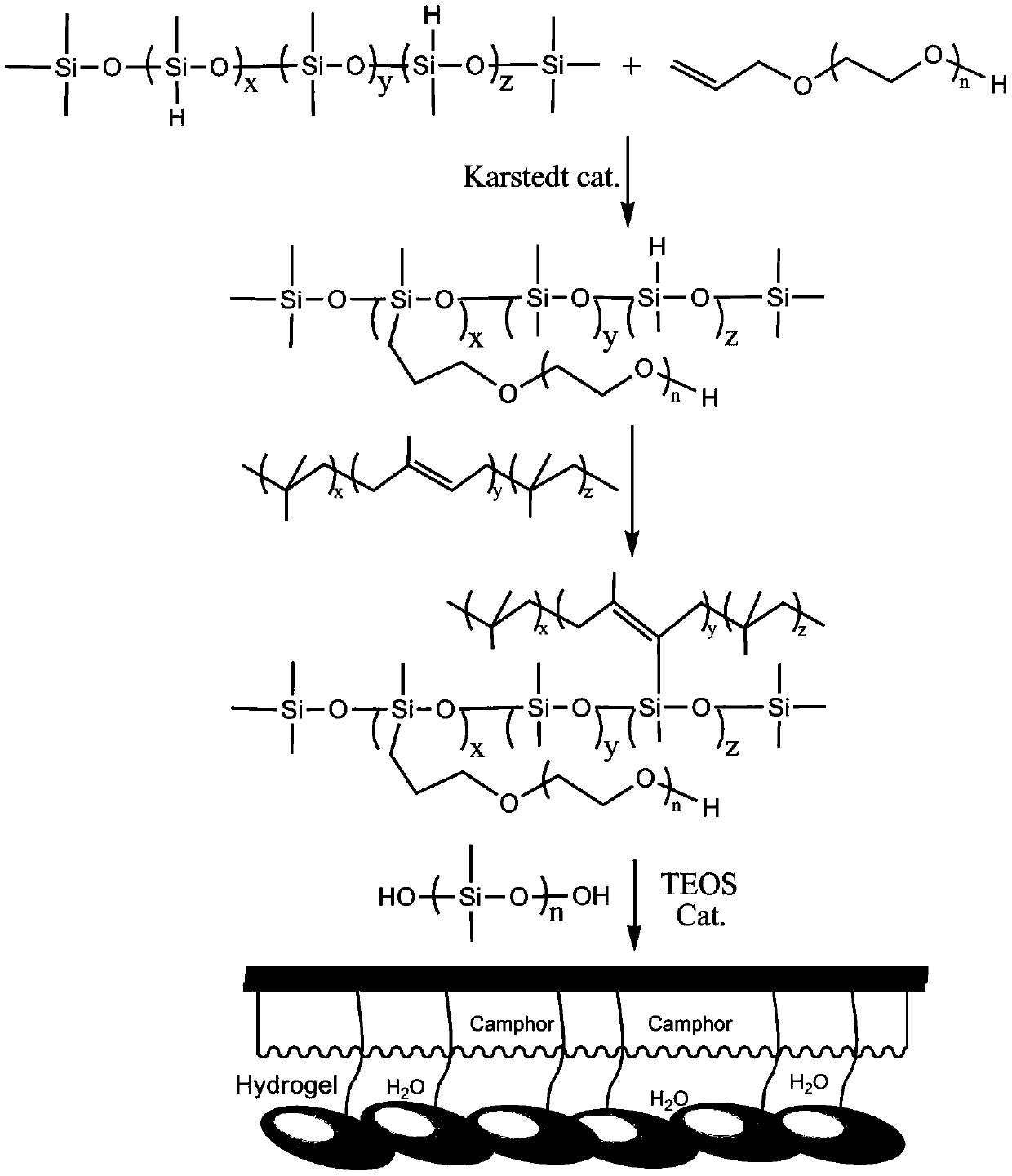
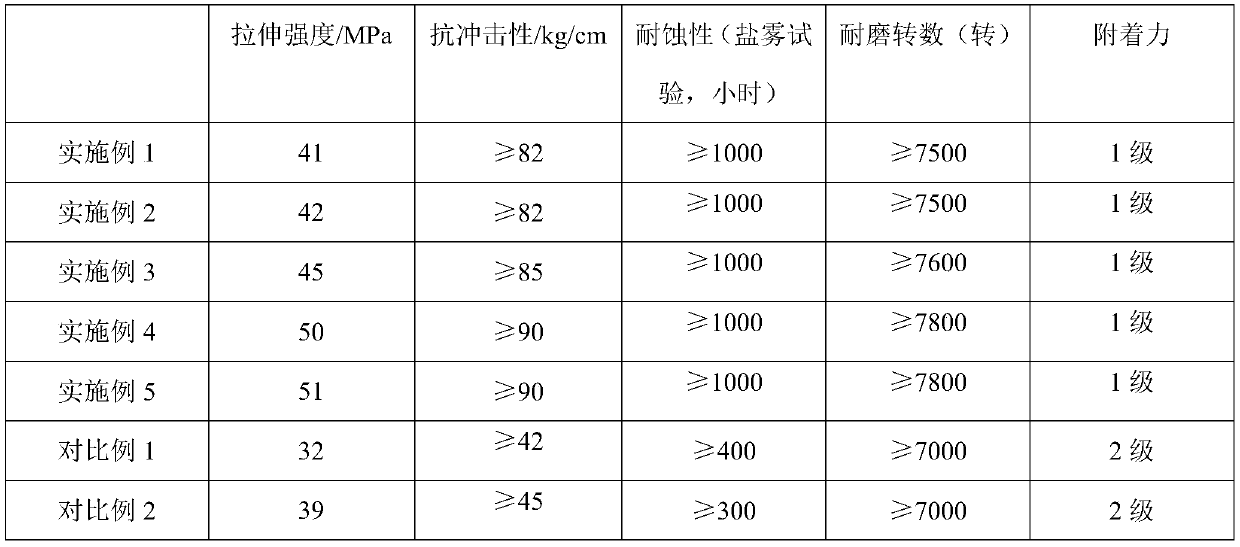
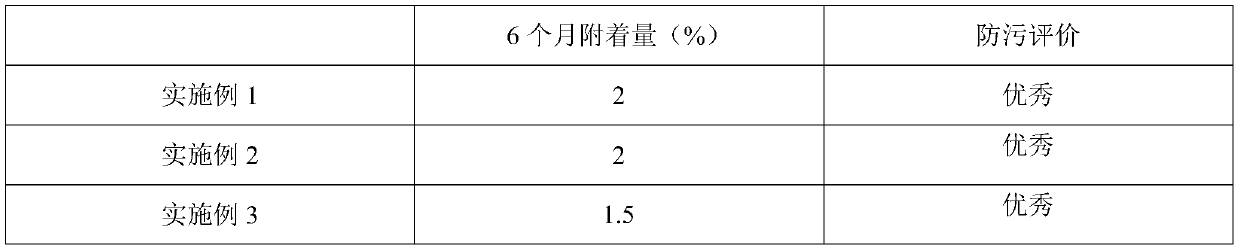
Environment-friendly anti-fouling material based on silicone hydrogel resin and natural anti-fouling agent
ActiveCN107652887AEnvironmentally friendlyImprove adhesionAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesCyclohexanonePolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a preparation method of an environment-friendly anti-fouling material based on silicone hydrogel resin and a natural anti-fouling agent. The preparation method includes: usingallyl polyglycol ether or 2-allyloxyethanol and hydrogen-containing silicone oil as the initial raw materials, heating to perform hydrogen silicification reaction, adding butyl rubber sufficiently swollen and dissolved in xylene, and continuing reaction to prepare silicone hydrogel resin; keeping reaction temperature unchanged, adding a thixotropic agent, hydroxyl silicone oil, diketen, 4, 5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, synthetic camphor and polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane, and performing stirring reaction to obtain a component A for standby; evenly mixing tetraethyl orthosilicate with di-n-butyltin dilaurate, methyl triethoxysilane, cyclohexanone, acetylacetone and xylene to obtain a component B; evenly mixing the component A and the component B according to the mass ratio of (7-9):1, and solidifying for 5-8 hours to obtain the anti-fouling material.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
Synergistic combination of flumetsulam or diclosulam with isothiazolones
InactiveUS20120115887A1High activityEffective controlOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBiologySynergistic combination
A synergistic antimicrobial composition containing flumetsulam and an isothiazolone biocide chosen from among 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one and N-n-butyl-1,2-benzisothiazolin-3-one. A synergistic antimicrobial composition containing diclosulam and an isothiazolone biocide chosen from 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one and 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Isothiazolinone type compound micro-emulsion type sterilization mildew preventive as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110037041ASolve insolubleGood chemical stabilityBiocideFungicidesEnvironmental resistanceIsothiazolinone
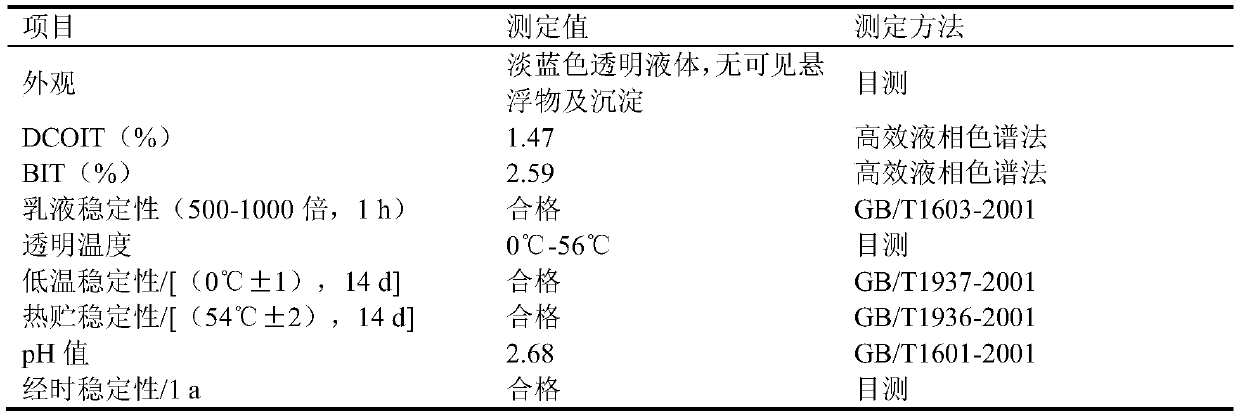
The embodiment of the invention relates to the field of industrial corrosion prevention and mildew prevention, particularly relates to an isothiazolinone type compound micro-emulsion type sterilization mildew preventive as well as a preparation method and application thereof and more particularly relates to a 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one (DCOIT) and 1,2-benzisothiazolin-3-one (BIT)compound micro-emulsion type sterilization mildew preventive as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The DCOIT and BIT compound micro-emulsion type sterilization mildew preventive provided by the embodiment of the invention is prepared from: DCOIT, BIT and auxiliary agents for a micro-emulsion preparation; the preparation method of the DCOIT and BIT compound micro-emulsion type sterilization mildew preventive comprises the following step: preparing the DCOIT, the BIT and the auxiliary agents for the micro-emulsion preparation into the DCOIT and BIT compound micro-emulsion typesterilization mildew preventive. The DCOIT and BIT compound micro-emulsion type sterilization mildew preventive provided by the embodiment of the invention is a stable, efficient and environment-friendly compound micro-emulsion type sterilization mildew preventive of slightly soluble fungicides including the DCOIT and the BIT, can be diluted randomly by water and is not separated out; respectiveadvantages of the DCOIT and the BIT in the aspects of sterilization, corrosion prevention and mildew prevention also can be sufficiently expressed; the DCOIT and BIT compound micro-emulsion type sterilization mildew preventive has high efficiency, low toxicity and high application value.
Owner:HEBEI HOFMANN NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Dinotefuran dispersible oil suspension agent and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a dinotefuran dispersible oil suspension agent. The dinotefuran dispersible oil suspension agent is prepared from 20-30% of dinotefuran, 4-6% of polyoxyethylene octylphenol ether, 4-6% of calcium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, 4-6% of phenethyl phenylpropyl phenol polyoxyethylene ether, 0.8-1.2% of organobentonite, 0.8-1.2% of white carbon black, 0.1-0.5% of citric acid, 0.1-0.5% of dihydrogenated tallow phthalic acid amide, 0.1-0.5% of tris(2,4-di-tert-butyl-pheny)phosphite, 0.1-0.5% of 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 0.1-0.5% of HT-508 organosilicone, 18-22% of soybean oil and the balance methyl oleate. The dinotefuran dispersible oil suspension agent is stable in performance, high in adhesion, good in spreading performance and high in rain wash resistance, has an obvious synergistic effect on target matter and contains no synergist, a medium can be degraded, dust is avoided in the production and use process, pollution is not likely to be caused to the environment and the human, the pesticide effect of dinotefuran can be fully exerted, the dose can be reduced, cost can be reduced, development of the resistance of pests to dinotefuran can be retarded, and the dinotefuran dispersible oil suspension agent has obvious economic and social benefits and good development prospects.
Owner:JIANGSU KESHENG CROP TECH
Resin immobilized biocide
The present invention relates to a composition comprising:(a) 85% to 99% by weight of a resin selected from the group consisting of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate-Carbon Monoxide; Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene; Styrene-Maleic Anhydride; Styrene-Methyl Methacrylate; Thermoplastic polyurethane; Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate and Acrylic Rubber; and mixtures thereof;(b) 1% to 15% by weight of a biocide selected from the group consisting of 4,5,-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolone-3-one biocide (DCIOT) and 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one (OIT).
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Antibacterial polyvinyl chloride tube material
InactiveCN105440489AAvoid decompositionImprove heat resistanceRigid pipesLow-density polyethylenePhosphate
The invention discloses an antibacterial polyvinyl chloride tube material. The antibacterial polyvinyl chloride tube material comprises polyvinyl chloride, sulfonated polyethersulfone, styrene-butadiene rubber, butadiene-acrylonitrile rubber, high density polyethylene, nanometer zinc oxide, modified nanometer titanium dioxide, attapulgite, nanometer montmorillonite, epoxidized butyl oleate, tri-isopropylphenyl phosphate, zinc stearate, zinc azelate, calcium pimelate, pentaerythritol, lanthanum 2-ethyloctoate, dimethyltin bis(isooctylmercaptoacetate), an anti-oxidant, 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one and p-tert-butylcatechol. A preparation method of the modified nanometer titanium dioxide comprises adding ferric nitrate and nanometer titanium dioxide into deionized water, stirring the solution at a room temperature for 50-60h, carrying out aging for 25-30h, carrying drying, carrying out grinding, carrying out calcination at a temperature of 450-500 DEG C for 2-3.5h and then cooling the product to the room temperature. The antibacterial polyvinyl chloride tube material has good bacterinertness, heat resistance and aging resistance.
Owner:安徽宁国市高新管业有限公司
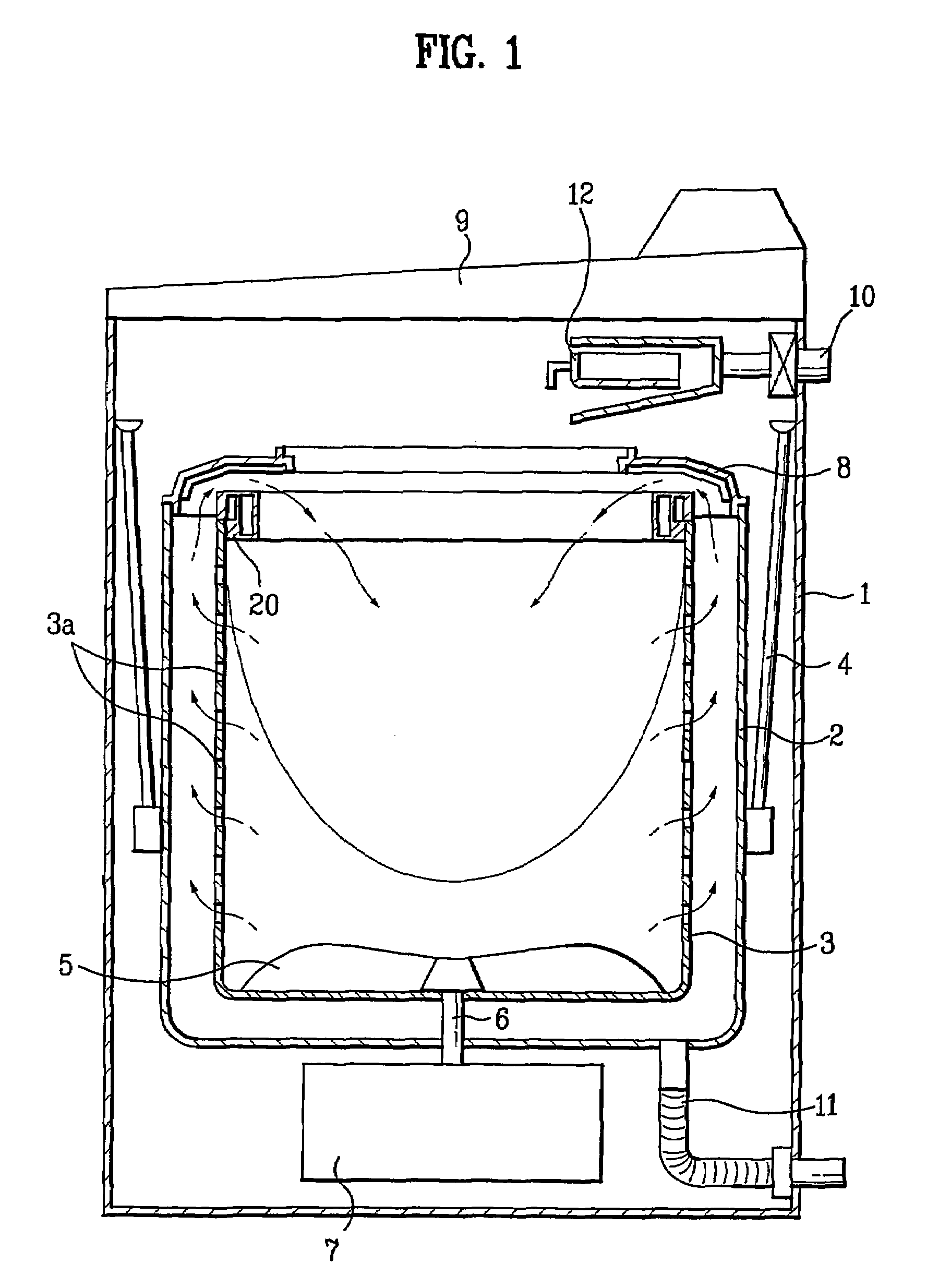
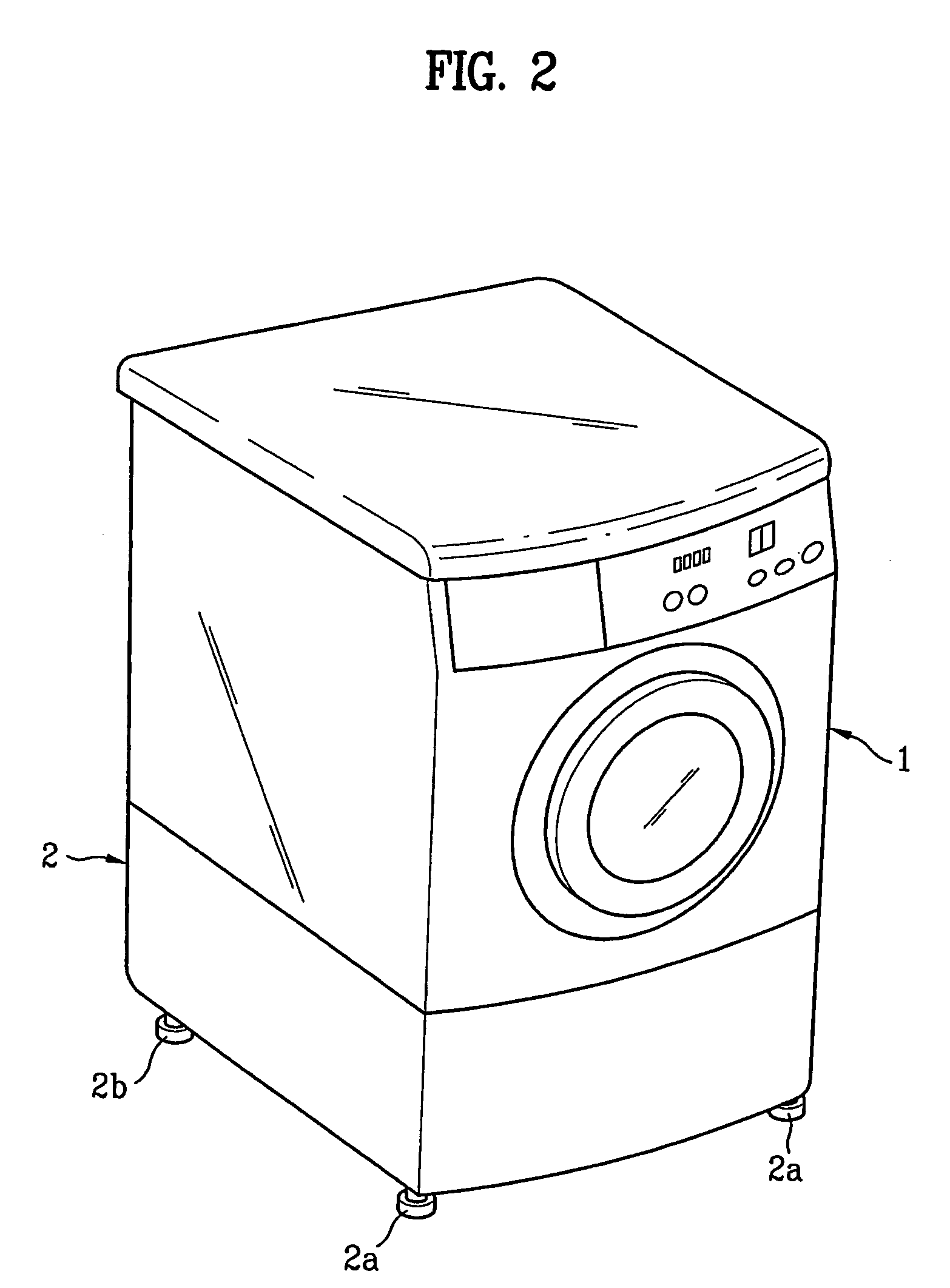
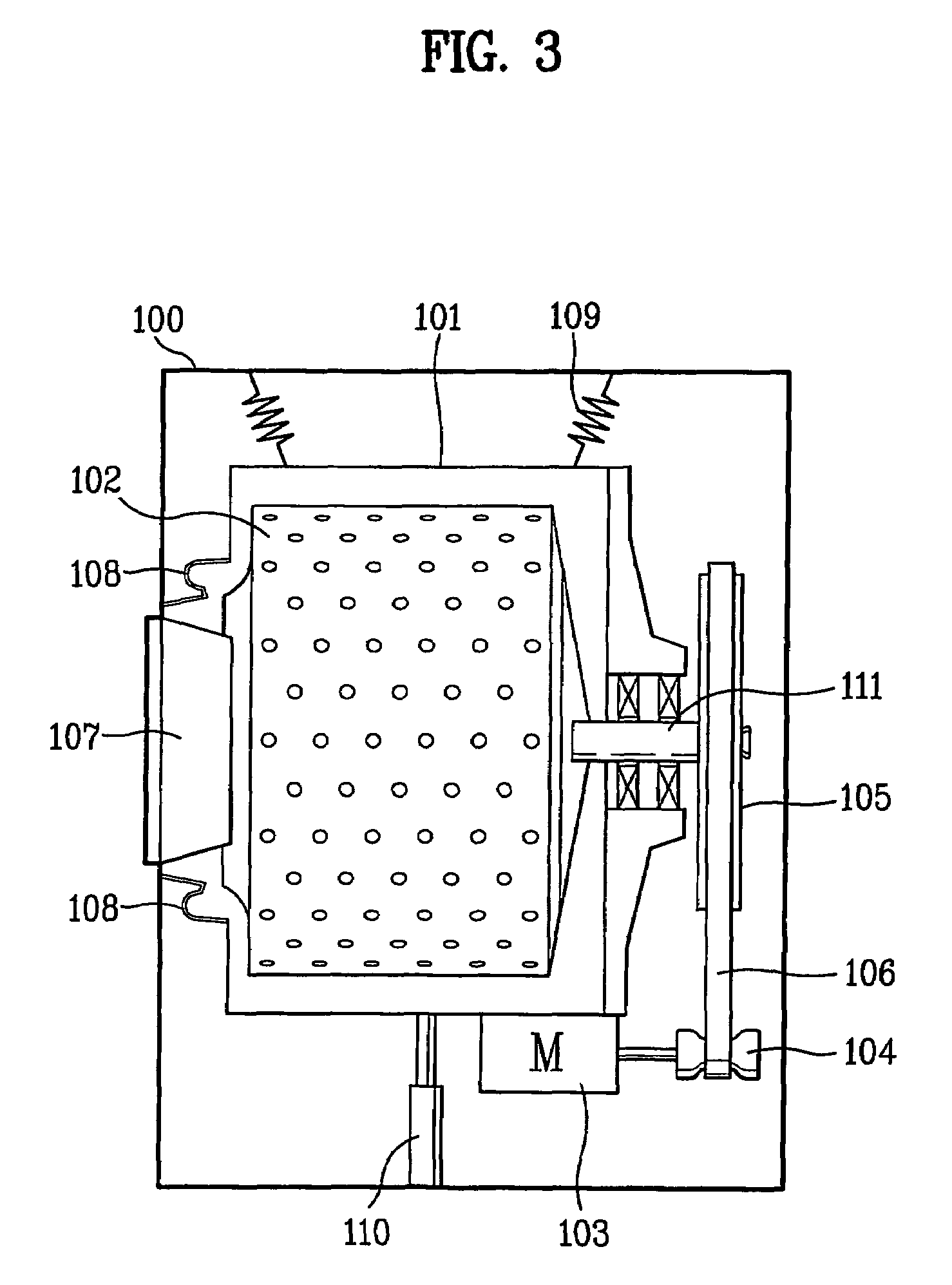
Anti-microbial plastic composition and washing machine comprising the parts manufactured by using the same
Disclosed are anti-microbial composition, a washing machine including parts manufactured by the same, and a drum washing machine including a stand manufactured by the same. The anti-microbial plastic composition includes 99.0-99.7% of polypropylene and 0.3-1.0% of an anti-microbial master batch, the anti-microbial mater batch having 90% of polypropylene and 5% of isothiazolin compound, and 5% of inorganic compound or 89% of polypropylene, 5% of isothiazolin compound, 5% of inorganic compound, and 1% of silver compound. The isothiazolin compound comprises 4,5-dichloro-2-N-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one of chemical formula 1 and 2-N-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one of chemical formula 2 at a ratio of 4:1. The inorganic compound is zinc oxide. The washing machine in accordance with the present invention includes the anti-microbial plastic composition, and parts manufactured by the same such that the germs and fungus are prevented from being generated thereof. The drum washing machine in accordance with the present invention includes a cabinet divided into two drawers at the stand thereof.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Bacteriostatic antirust oil
The invention discloses a bacteriostatic antirust oil. The bacteriostatic antirust oil is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 60 to 70 parts of de-waxed kerosene, 1 to 2 parts of hydroxyethyl ethylene bisstearamide, 0.7 to 1 part of 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 0.5 to 1 part of 3-mercaptopropionic acid, 0.1 to 0.2 part of myristyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride, 3 to 4 parts of polyglycerol fatty acid ester, 3 to 5 parts of calcium petroleum sulfonate, 0.3 to 1 part of dehydrated sorbitol fatty acid ester, 5 to 7 parts of an antirust aid and 0.3 to 1 part of an anti-oxidant 168. According to the invention, 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, myristyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride and like added into the antirust oil all have good bacteriostatic effects, so adsorption of bacteria can be reduced, damage to an oil film is mitigated, and the service life of the antirust oil is prolonged.
Owner:吴燕
Microbial resistant kraft facing for fiberglass insulation
InactiveUS20060105657A1Long life-timeUnpleasant odorBiocideSynthetic resin layered productsFungal microorganismsMicrobial composition
An insulation product that contains a Kraft paper facing treated with a combination of antimicrobial agents that imparts improved microbial resistance to the Kraft paper is provided. A preferred anti-microbial composition includes (1-[[2-(2,4-dichloropheyl)-4-propyl-1,3-diololan-2-yl]-methyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole, α-(2-(4-chlorphenyl)ethyl)-α-(1-1-dimethylethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-ethanol, and alkyl dimethylbenzyl ammonium saccharinate. The anti-microbial agents may each be present in the anti-microbial composition in an amount of from 50 to 1000 ppm. A biocide such as 2-(4-thiazolyl)benzimidazole may be added to the anti-microbial composition to impart additional microbial resistance. The Kraft paper may be adhered to the insulation by anti-microbially treated asphalt. The anti-microbial agent may be added to the asphalt in an amount of from 200-3000 ppm prior to applying the asphalt to the Kraft paper. In at least one exemplary embodiment, 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one is added to the asphalt. The insulation product formed is substantially free of bacteria, fungi, and molds.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Anti-microbiology composition for storing wood
The present invention provides a synergistic antimicrobial composition useful for preserving wood comprising: (a) monoethanolamine complex of copper(II); and (b) 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one or copper containing 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one and micronized copper, the activity of the composition is higher than the activity observed by each antimicrobial composition.
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 2 LLC
Synergistic combination of lenacil and one of dcoit or oit for dry film protection
A synergistic antimicrobial composition containing lenacil and one of 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one or 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one is provided. Also provided is a method of inhibiting the growth of or controlling the growth of microorganisms in a building material by adding such a synergistic antimicrobial composition. Also provided is a coating composition containing such a synergistic antimicrobial composition, and a dry film made from such a coating composition.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO +1
Reduction of antimicrobial compound levels during product dispensing
InactiveUS20100270241A1Lower Level RequirementsReduce compoundingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsHydroxybenzoatesHexetidine
A method for reducing antimicrobial compound levels in a liquid composition containing at least one antimicrobial compound. The method comprises contacting said liquid composition with a functionalized resin. Antimicrobial compounds that may be removed by this method include isothiazolin-3-ones, e.g., 2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one; 5-chloro-2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one; 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one; 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one; 1,2-benzisothiazolin-3-one and N-alkyl derivatives thereof, especially N-methyl and N-n-butyl; 2,2-dibromo-3-nitrilopropionamide (DBNPA); 2-bromo-2-nitropropanediol (BNPD); dithio-2,2′-bis(benzmethylamide) (DTBMA); hexetidine; chlorphenesin, C1-C4 alkyl-4-hydroxybenzoates (alkyl parabens); 3-iodopropynylbutylcarbamate (IPBC); formaldehyde releasers and mixtures thereof.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Synergistic combination of zoxamide and one of dcoit or oit for dry film protection
A synergistic antimicrobial composition containing zoxamide and one of 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one or 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one is provided. Also provided is a method of inhibiting the growth of or controlling the growth of microorganisms in a building material by adding such a synergistic antimicrobial composition. Also provided is a coating composition containing such a synergistic antimicrobial composition, and a dry film made from such a coating composition.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO +1
Method for reducing odor in latex paints
A method for reducing odor arising from surfaces coated with latex paints. The method comprises combining in a latex paint: (i) at least one stabilizer; (ii) at least isothiazolone one biocide comprising 2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one or 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one; and (iii) at least one thickener comprising a polyurethane, hydroxyethyl cellulose, carboxymethyl cellulose, an alkali soluble emulsion polymer, a hydrophobically modified alkali soluble emulsion polymer or a hydrophobically modified hydroxyethyl cellulose.
Owner:DDP SPECIALTY ELECTRONICS MATERIALS US 8 LLC
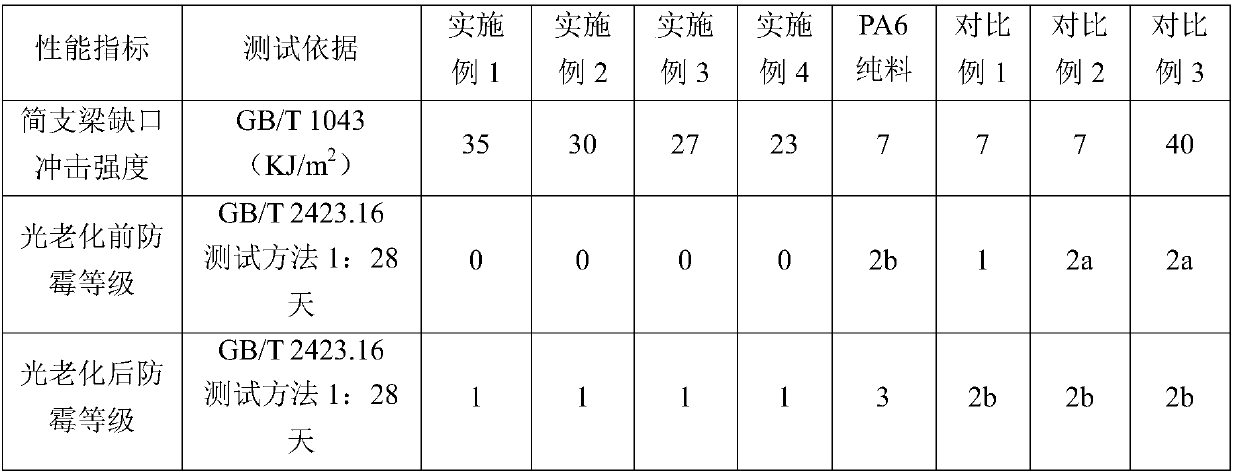
Impact-resistant mildew-proof nylon material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an impact-resistant mildew-proof nylon material and a preparation method thereof. The impact-resistant mildew-proof nylon material is prepared from the following components inparts by weight: 50-100 parts of PA, 3.15-10.3 parts of a mildew-proof agent, 0.5-1 part of an auxiliary agent and 0-40 parts of glass fibers, wherein the mildew-proof agent is prepared by compoundingchlorinated polyethylene, 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one and nanometer titanium dioxide according to a mass ratio of (6-10): 0.1: 0.2. The prepared nylon material is low in production cost, good in impact resistance and good in antibacterial and mildew-proof effect, and has both short-term efficient sterilization performance and long-term sterilization and mildew-proof performance.
Owner:HEFEI GENIUS NEW MATERIALS
Reduction of antimicrobial compound levels during product dispensing
InactiveUS8303821B2Reduce compoundingLower Level RequirementsCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsHydroxybenzoatesHexetidine
A method for reducing antimicrobial compound levels in a liquid composition containing at least one antimicrobial compound. The method comprises contacting said liquid composition with a functionalized resin. Antimicrobial compounds that may be removed by this method include isothiazolin-3-ones, e.g., 2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one; 5-chloro-2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one; 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one; 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one; 1,2-benzisothiazolin-3-one and N-alkyl derivatives thereof, especially N-methyl and N-n-butyl; 2,2-dibromo-3-nitrilopropionamide (DBNPA); 2-bromo-2-nitropropanediol (BNPD); dithio-2,2′-bis(benzmethylamide) (DTBMA); hexetidine; chlorphenesin, C1-C4 alkyl-4-hydroxybenzoates (alkyl parabens); 3-iodopropynylbutylcarbamate (IPBC); formaldehyde releasers and mixtures thereof.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Crude-fine fiber blended yarn
InactiveCN105506970AImprove mildew resistanceExcellent mothproofBiochemical fibre treatmentHeat resistant fibresYarnFiber
The invention discloses crude-fine fiber blended yarn. The crude-fine fiber blended yarn is subjected to dipping treatment, and the dipping treatment comprises steps as follows: 1), 1-2 parts by weight of glycerol monostearate, 1.4 parts by weight of hydroxy propyl cellulose, 0.4 parts by weight of zinc sulfate and 1.2 parts by weight of trichloracetic aldehyde are added to 12.7 parts by weight of deionized water, and the materials are stirred uniformly; 2), 0.7 parts by weight of vinyltriethoxysilane, 0.4 parts by weight of potassium peroxodisulfate, 0.8 parts by weight of 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one and 0.9 parts by weight of dimethyl octadecyl hydroxyethyl ammonium nitrate are added simultaneously and slowly, the materials are stirred continuously until the materials are mixed sufficiently and uniformly, and a finishing liquid is prepared; 3), blended yarn is subjected to dipping treatment in the finishing liquid, and then is taken out for drying at the constant temperature. The crude-fine fiber blended yarn has excellent mould-proof, mothproof, anti-bacterial, anti-flaming and anti-static performance.
Owner:常熟市明达腈纺有限公司
Environmentally friendly antifouling materials based on silicone hydrogel resins and natural antifouling agents
ActiveCN107652887BEnvironmentally friendlyImprove adhesionAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesCyclohexanonePolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a preparation method of an environment-friendly anti-fouling material based on silicone hydrogel resin and a natural anti-fouling agent. The preparation method includes: usingallyl polyglycol ether or 2-allyloxyethanol and hydrogen-containing silicone oil as the initial raw materials, heating to perform hydrogen silicification reaction, adding butyl rubber sufficiently swollen and dissolved in xylene, and continuing reaction to prepare silicone hydrogel resin; keeping reaction temperature unchanged, adding a thixotropic agent, hydroxyl silicone oil, diketen, 4, 5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, synthetic camphor and polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane, and performing stirring reaction to obtain a component A for standby; evenly mixing tetraethyl orthosilicate with di-n-butyltin dilaurate, methyl triethoxysilane, cyclohexanone, acetylacetone and xylene to obtain a component B; evenly mixing the component A and the component B according to the mass ratio of (7-9):1, and solidifying for 5-8 hours to obtain the anti-fouling material.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
Environmental protection glass glue
InactiveCN106634819AFast dryingHigh viscosityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesOil/fat/wax adhesivesChemical industryBetaine
The present invention relates to an environmental protection glass glue, and belongs to the technical field of chemical industry materials, wherein the environmental protection glass glue is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 3-9 parts of silica sol, 1.3-1.9 parts of pine oil ester, 4-12 parts of sodium dodecyl sulfate, 3-11 parts of ammonia water, 0.3-0.5 part of N-(2-benzimidazolyl)-carbamate, 0.4-0.6 part of 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 1-3 parts of cocoamidopropyl betaine, 0.1-0.3 part of a wetting and dispersing agent, 5-8 parts of propylene glycol, and 2-5 parts of clove oil. The environmental protection glass glue of the present invention has advantages of fast drying, strong viscosity, sterilization, blackening resistance, cleaning, environmental protection and wide application scope, and is convenient for industrial production and life.
Owner:徐勤凤
Anti-microbiology composition for storing wood
The present invention provides a synergistic antimicrobial composition useful for preserving wood comprising: (a) monoethanolamine complex of copper(II); and (b) 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one or copper containing 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one and micronized copper, the activity of the composition is higher than the activity observed by each antimicrobial composition.
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 2 LLC
Method for preparing a stable isothiazolone formulation
A method for producing a stable microbicidal composition. The method comprises steps of: (a) combining a glycol solvent of formula R(OCH2CHR1)nH, wherein R is C1-C6 alkyl and n has a number average value from 2 to 5 and R1 is hydrogen or methyl; dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid in an amount from 0.3 to 1.8 wt % based on the entire microbicidal composition; and a copper (II) salt selected from the group consisting of copper (II) hydroxide, copper (II) carbonate and mixtures thereof to form an initial mixture; wherein a mole ratio of copper:dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid is from 1:0.25 to 1:1.95; (b) maintaining the initial mixture at 40 to 80° C. until an amount of copper ion in solution is stable; and (c) adding 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one to produce a final mixture.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Green and environment-friendly glass cement
InactiveCN107353868AFast dryingHigh viscosityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesCarbamateCocamidopropyl betaine
The invention discloses a green and environment-friendly glass cement, which is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 3-6 parts of silica sol, 1-1.5 parts of terpinyl ester, 4-8 parts of sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-2 parts of nano titanium dioxide, 3-8 parts of ammonia water, 0.3-0.5 part of N-(2-benzimidazolyl)-carbamate, 0.4-0.6 part of 2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 1-2 parts of nano silica, 1-2 parts of cocamidopropyl betaine, 0.1-0.3 part of a wetting dispersant, 5-10 parts of propylene glycol, and 2-5 parts of clove oil. The environment-friendly glass cement provided by the invention has fast drying speed and strong viscosity, and by adding trace nanoparticles, the glass cement can reach a degerming effect, and has the advantages of difficult blackening, cleanness, environmental protection, and wider application range, and is convenient for industrial production and life.
Owner:FOSHAN ZHENGLUE INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com