Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
139results about How to "Reduce share" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
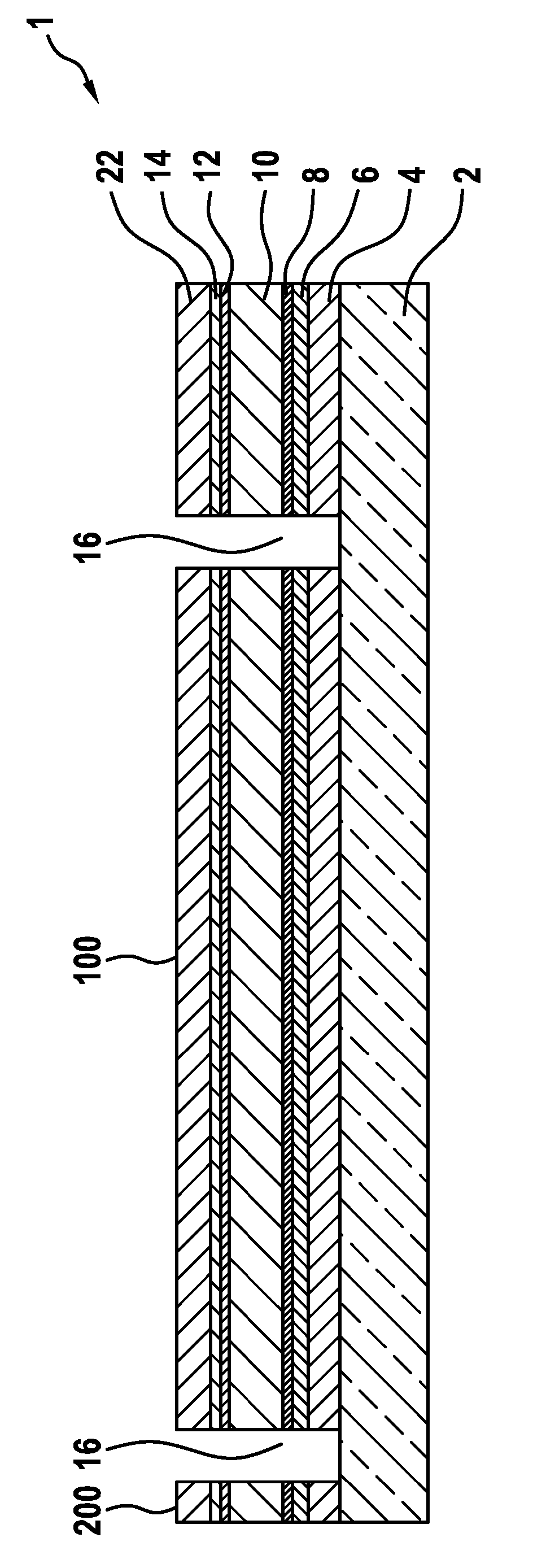
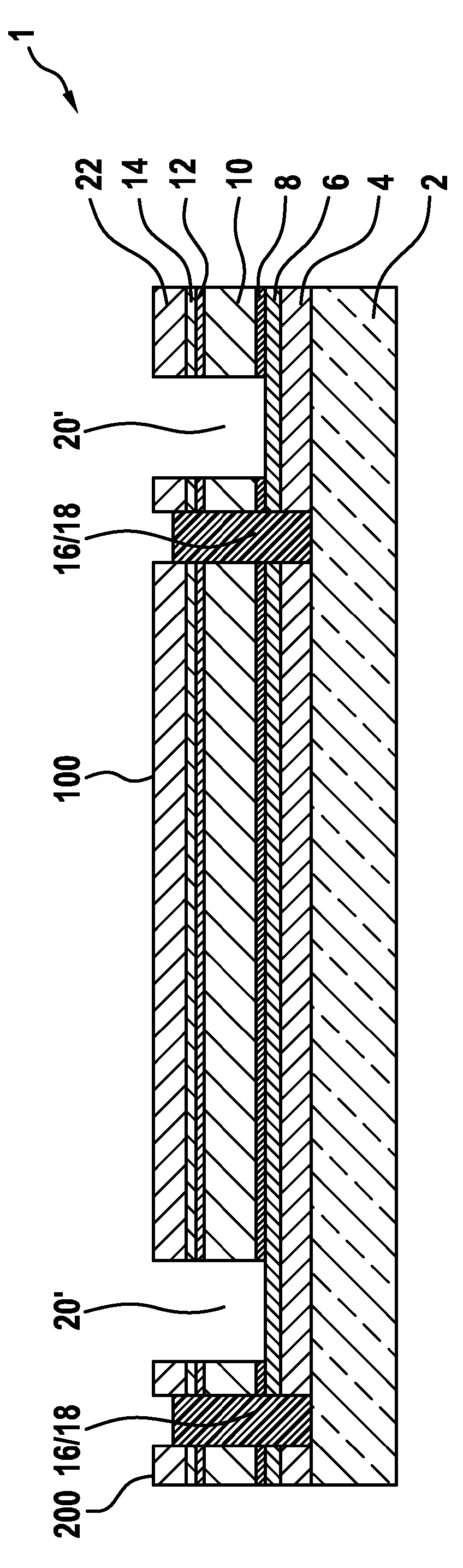
CPO regenerated lean NOx trap with no moving parts
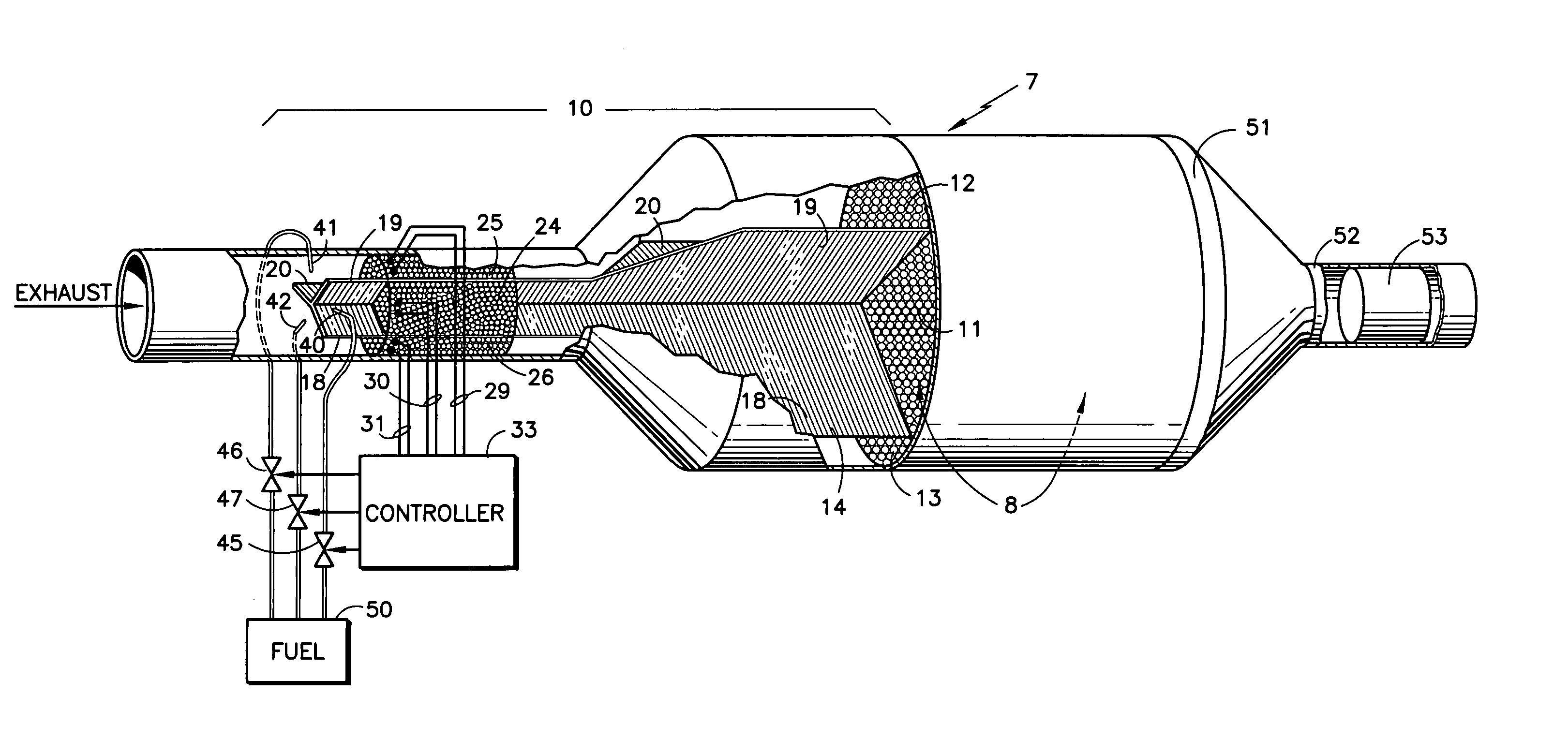
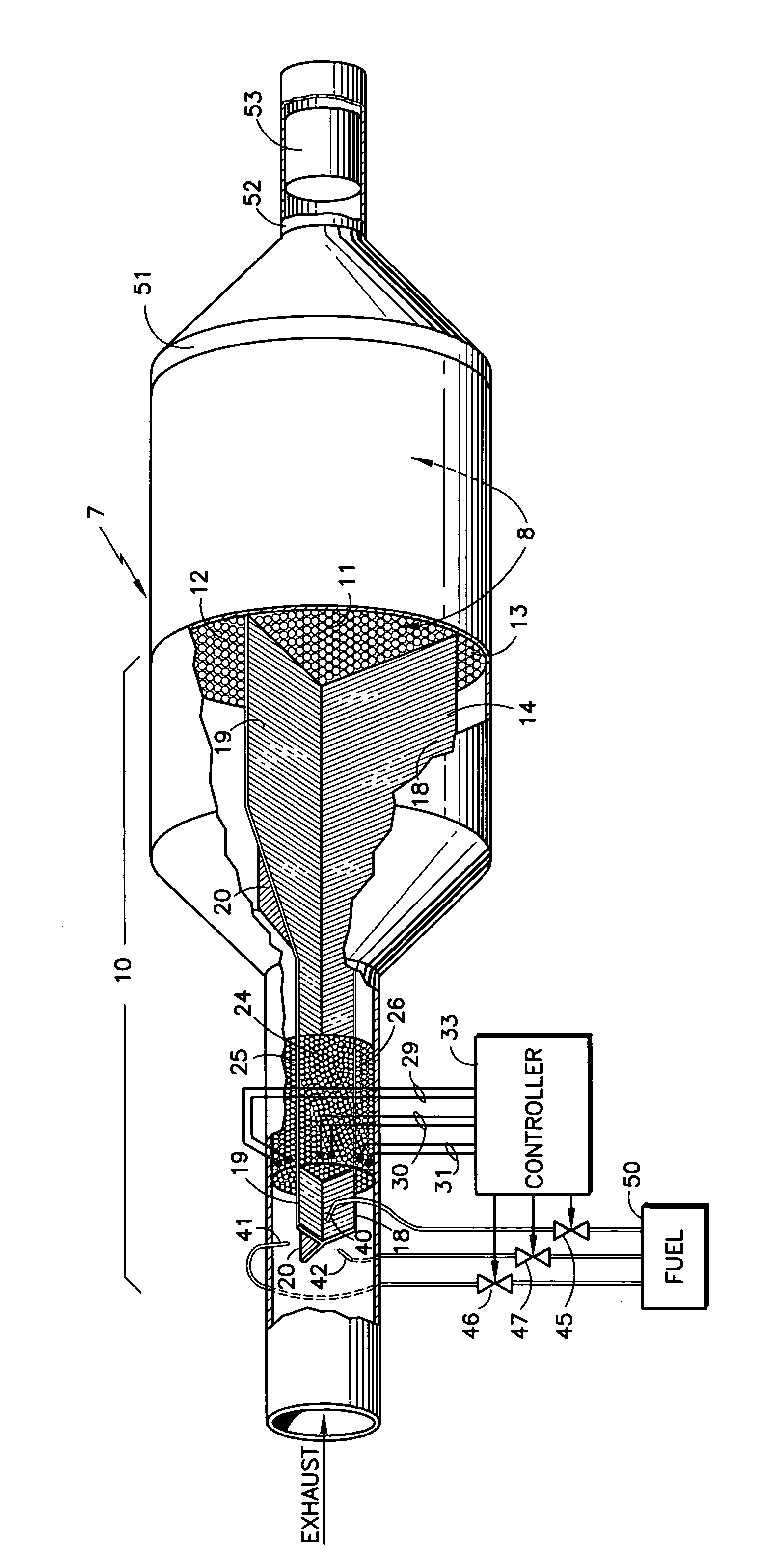
InactiveUS6955042B1Reduce additionalAvoid wastingInternal combustion piston enginesSilencing apparatusDiesel particulate filterInlet manifold
A single lean NOx trap (8) has an inlet manifold (10) with baffles (18–20) to divide the inlet manifold into three flow paths (11–13). Each flow path has a thermal reformer (24–26; CPO, (POX, or ATR) with an electric heater provided electric power by related lines (29–31). Fuel from a source (50) is controlled (45–46) to apply pulses of fuel through nozzles (40–42) into each corresponding path (11–13) in turn. A plurality of diesel particulate filters (14) are disposed in the flow paths (11–13) upstream of the lean NOx trap (8). A diesel oxidation catalyst (53) is disposed downstream of the lean NOx trap.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Measuring device with a reduced share of stray light
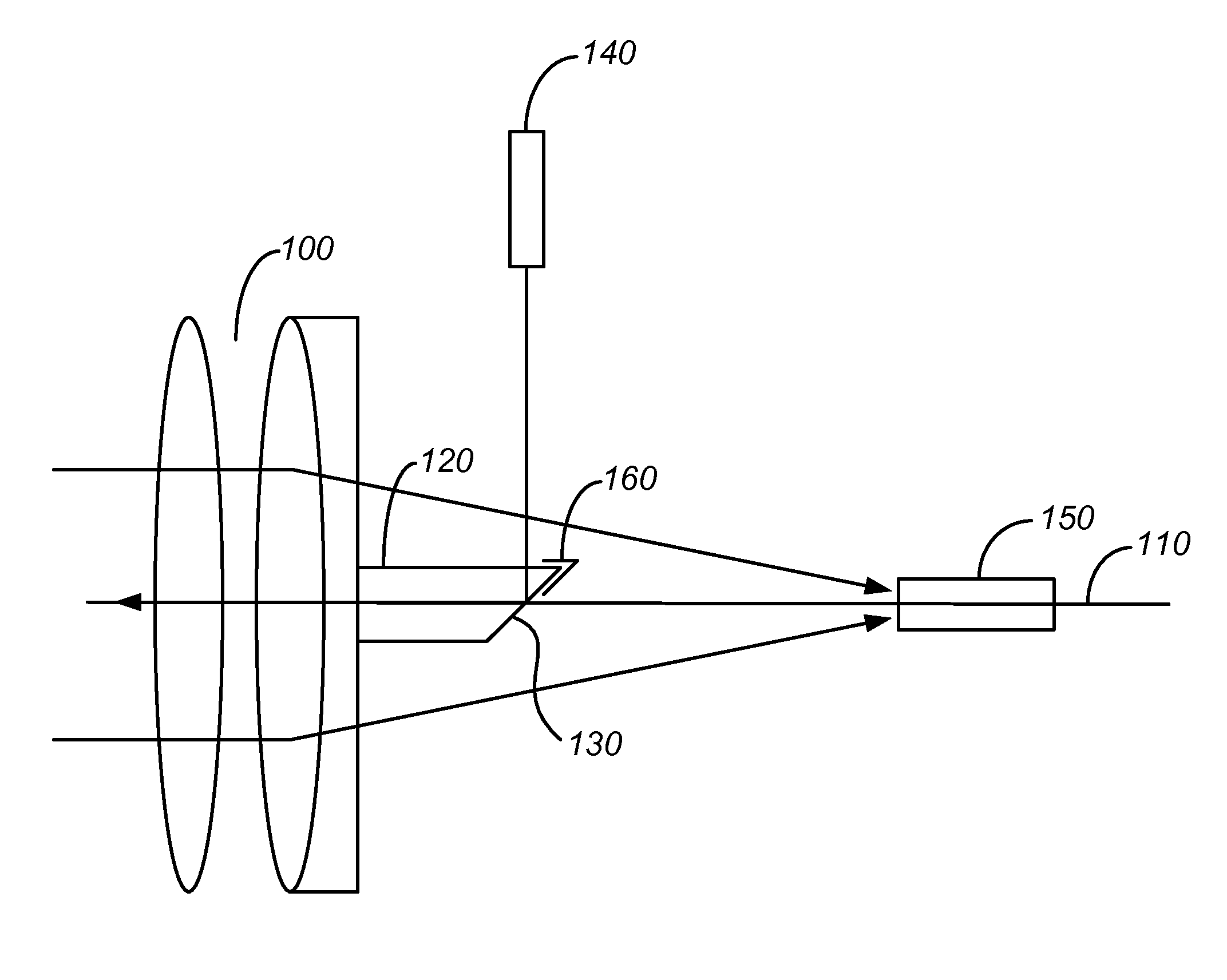
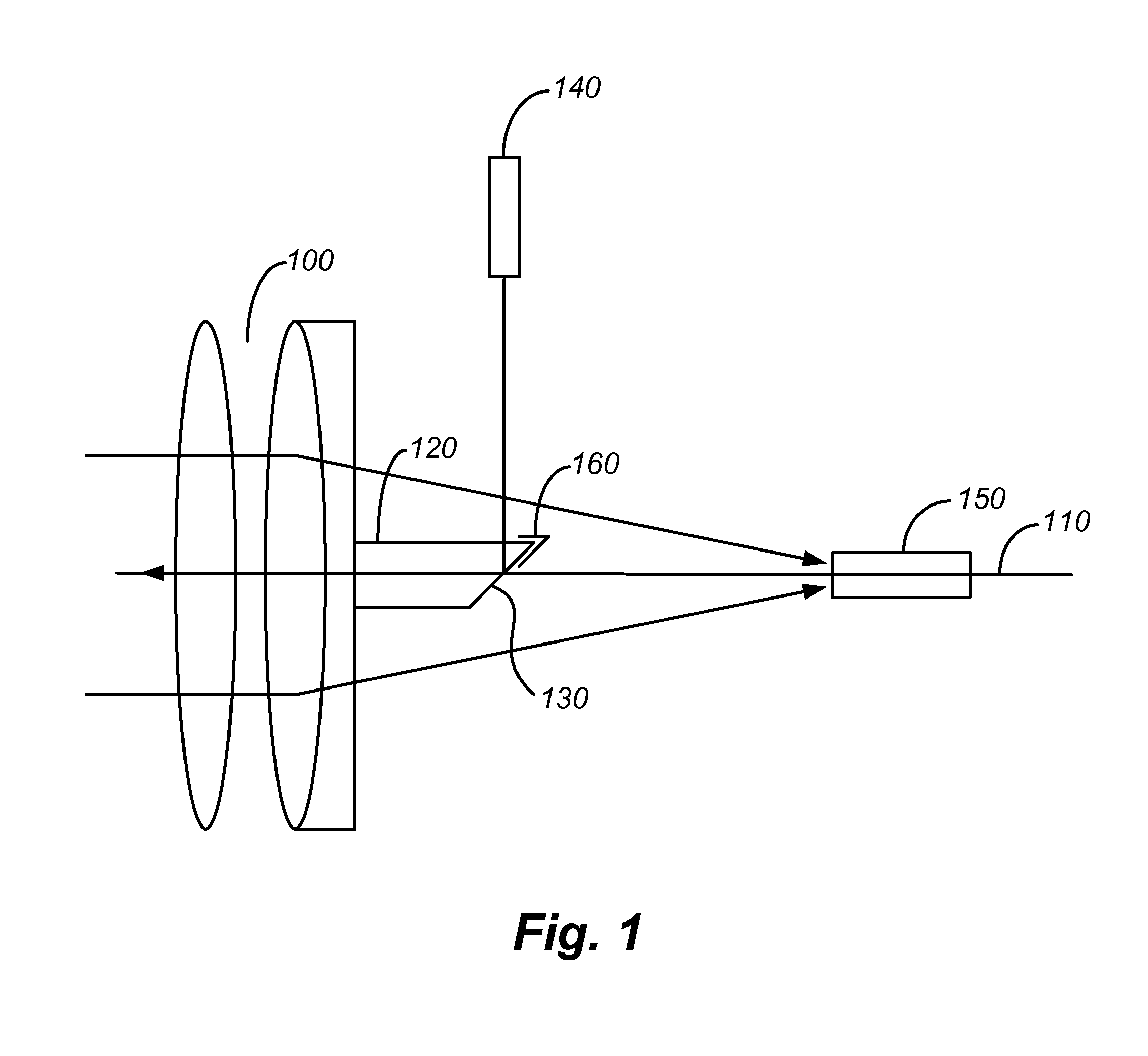
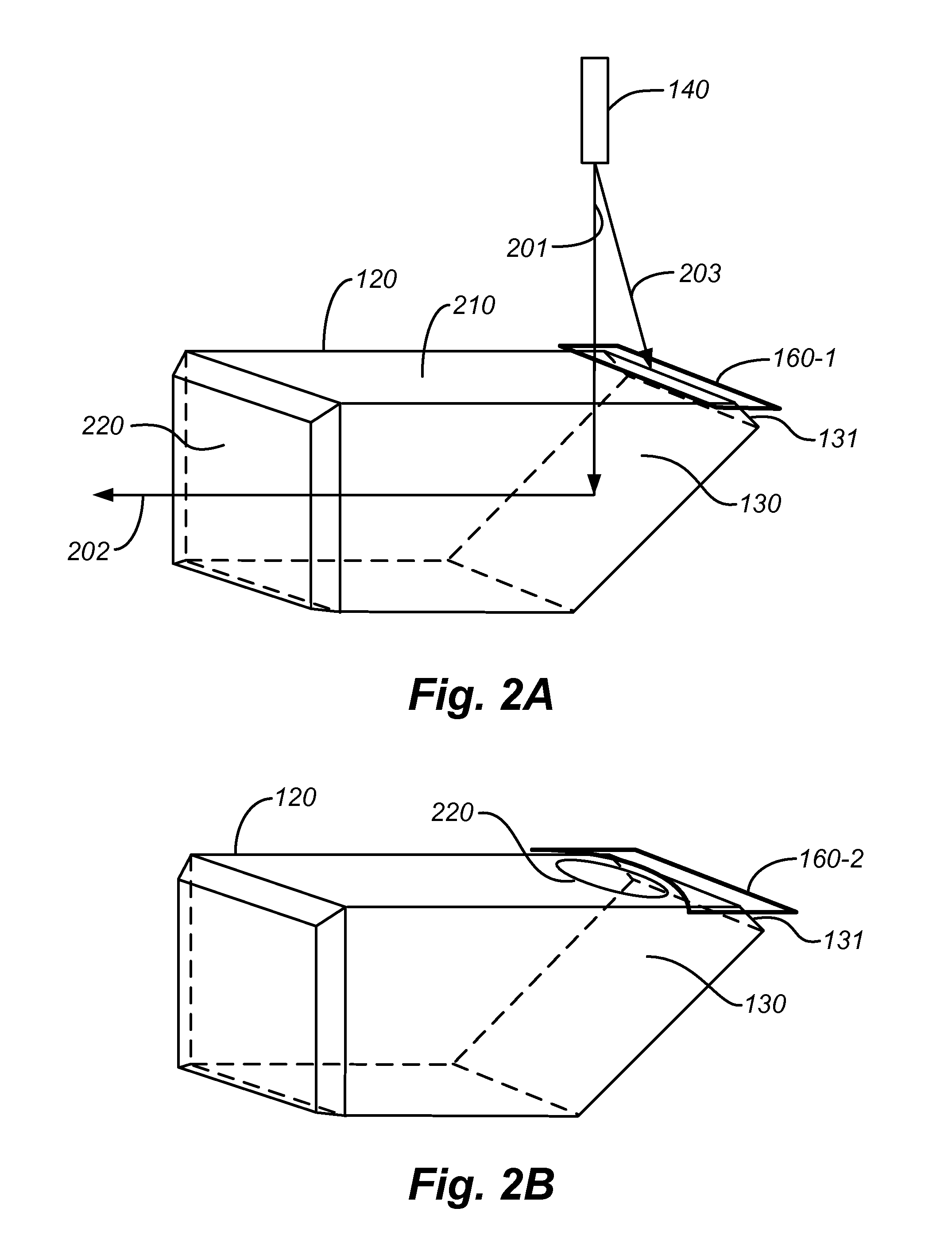
ActiveUS20110188121A1Improve dynamic rangeReduce sharePrismsWave based measurement systemsMeasurement deviceOptical axis
A device for measurement by means of a light ray is equipped with a covering device for reducing stray light. The device comprises an array of lenses along an optical axis; a prism attached to one of the lenses with a slanted surface for coupling of the light ray incident from a light source placed lateral to the optical axis, onto the optical axis, so that the light ray can pass through the array of lenses along the optical axis; a receiver for receipt of a share of the light ray reflected by an object; and a covering device for at least one area of the prism that scatters a share of the light ray as stray light to the receiver.
Owner:TRIMBLE JENA
Processing wireless resources in mobile AD hoc network
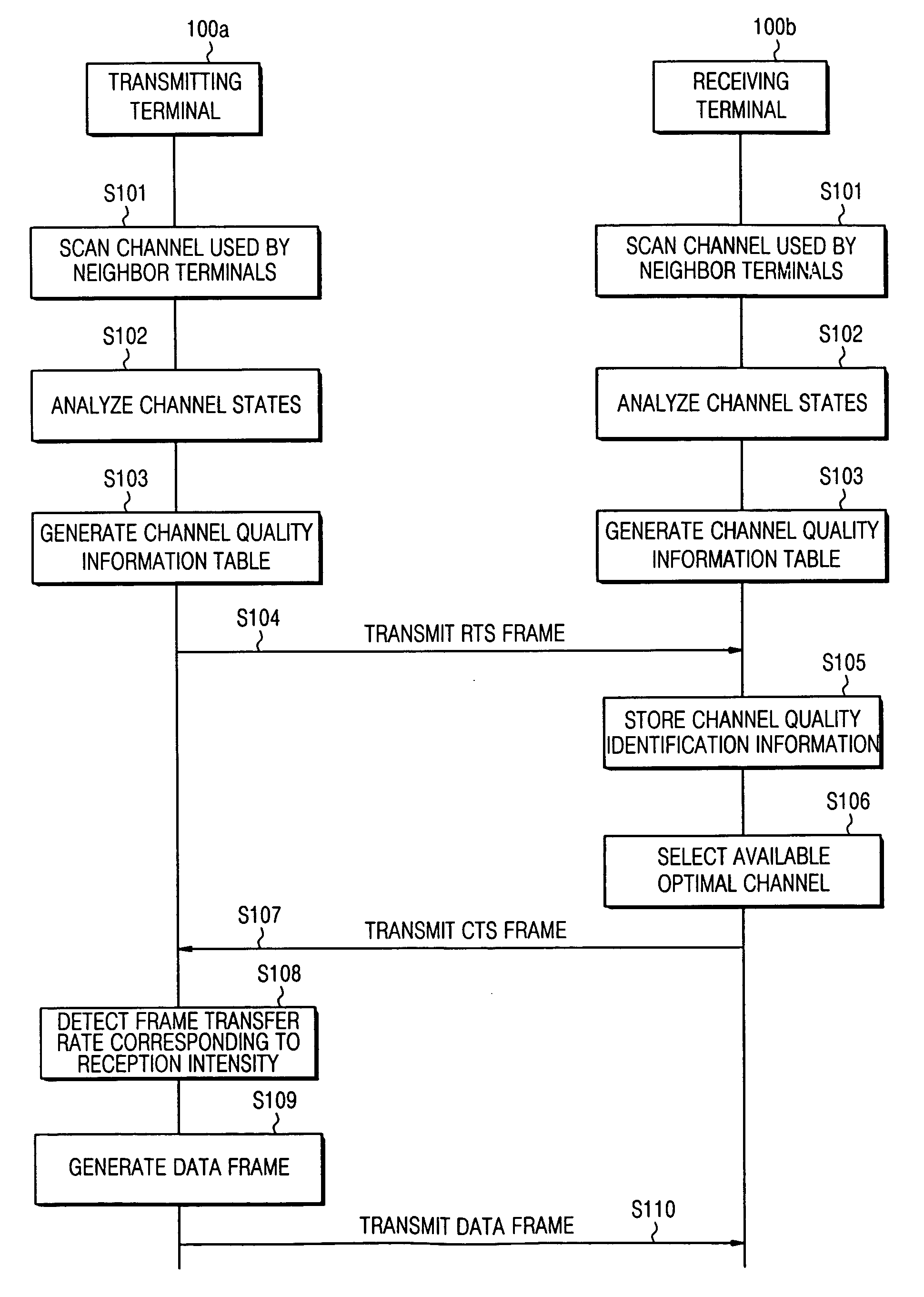
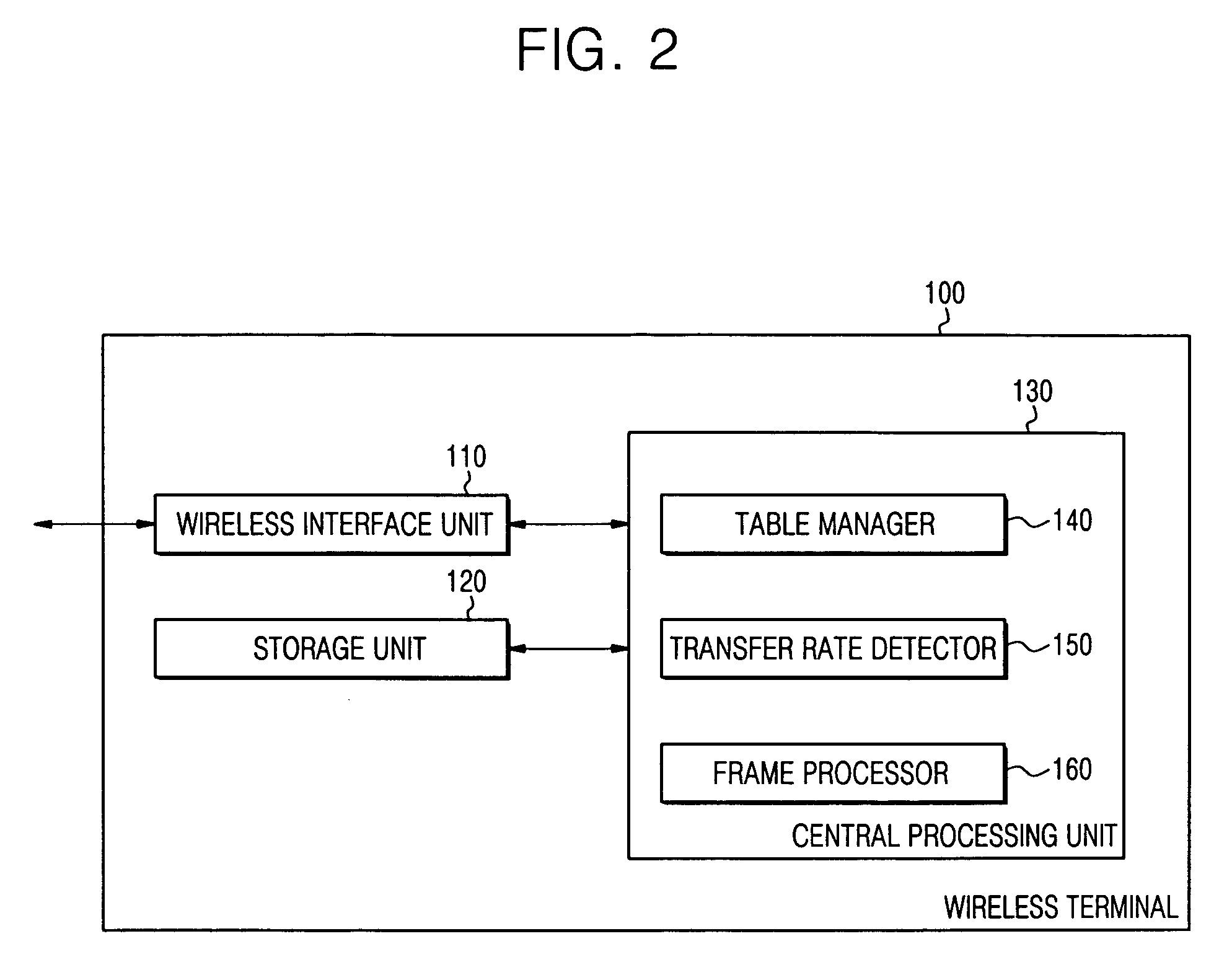
InactiveUS20070165587A1Easy to useHigh quality informationNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless ad hoc networkTransmission response
An apparatus and method to process wireless resources in a wireless Ad Hoc network includes: a first terminal to scan wireless resources in the network, to set quality information of each wireless resource in accordance with a state of each wireless resource, and to transmit a frame transmission request message containing quality identification information of each wireless resource in accordance with the quality information; and a second terminal to select wireless resource having a highest quality in accordance with the quality identification information of each wireless resource received from the first terminal and the quality information of each scanned wireless resource, and to transmit a frame transmission response message containing information on the selected wireless resource to the first terminal. Furthermore, the apparatus and method allow the receiving terminal to detect the frame transfer rate corresponding to the reception intensity of the frame transmission request message received from the transmitting terminal, and allow the transmitting and receiving terminals to transmit the data frame using the detected frame transfer rate, thereby transmitting the data frame at the highest transfer rate between the transmitting and receiving terminals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
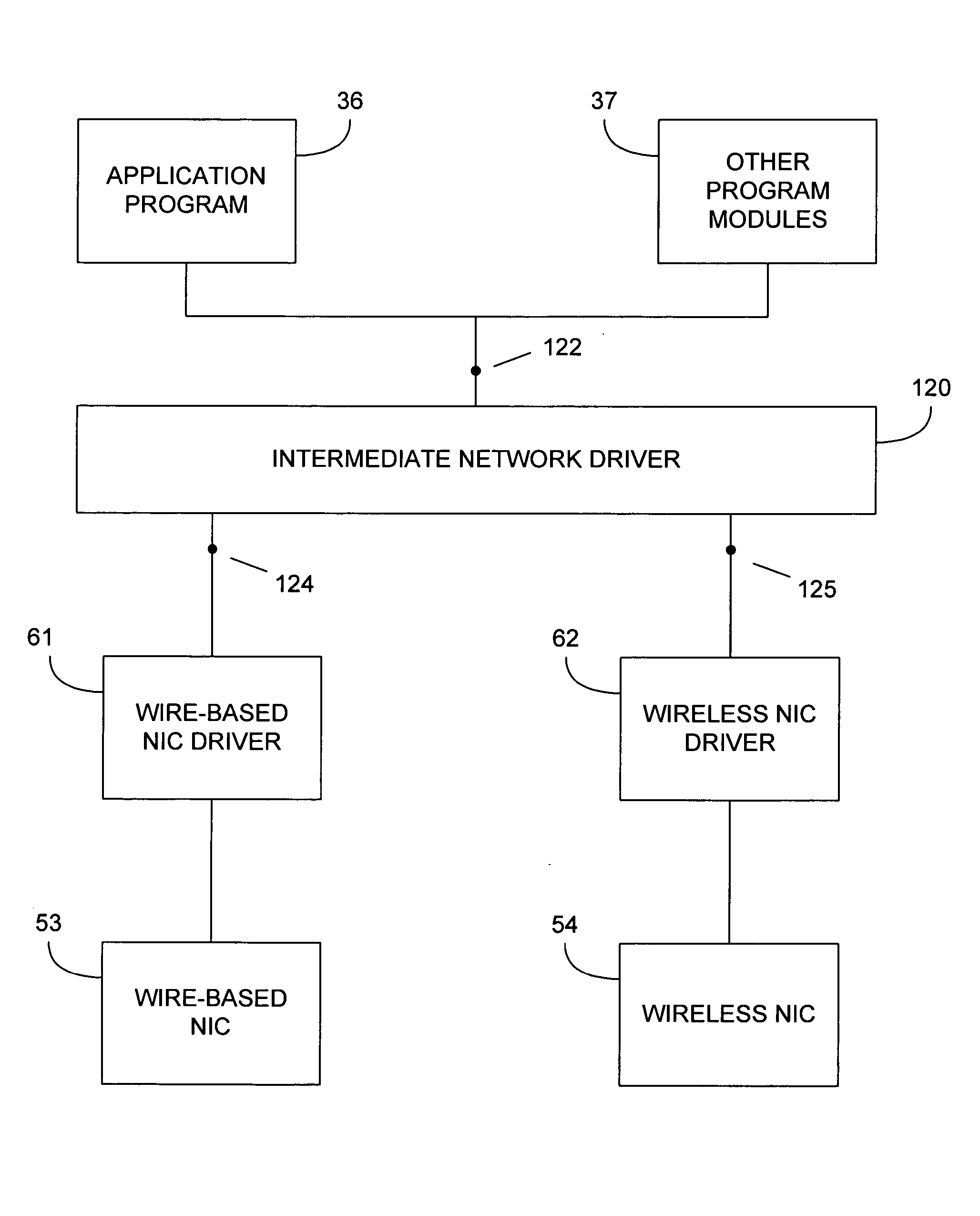
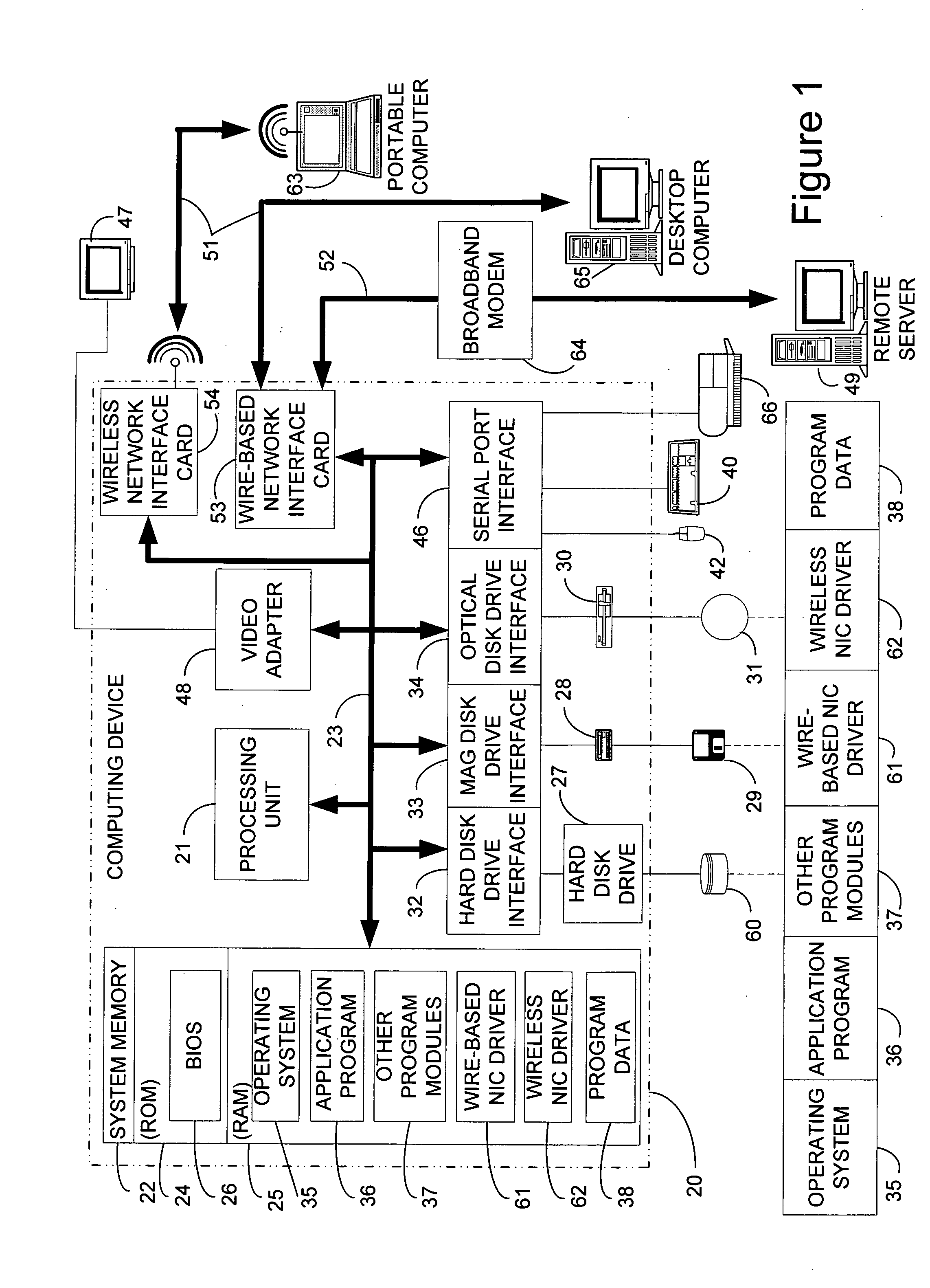
Exposing a bridged network as a single virtual segment
InactiveUS20060010253A1More buffer spaceConstant and efficient amount of timeMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksReal-time computingNetwork interface
A software network bridge is disclosed which allows the connected network segments to be presented as a single network unit to the host computer. The software bridge can be implemented as an intermediate network driver, abstracting multiple network segments into a single network interface for higher level protocols and applications. While the intermediate network driver acts as a software bridge implementing the Spanning Tree Algorithm, it also acts a network interface driver to higher level protocols, conglomerating information from the multiple underlying network interface cards and forwarding along commands from the higher level software to the appropriate network interface card. The intermediate network driver can also simultaneously send the same data packet through multiple network interfaces by creating multiple packet descriptors, each pointing to the same data, but each given individually to the underlying network interfaces to control during their transmission. Further efficiencies can also be achieved by the software bridge, implemented as an intermediate network driver, through the use of a dynamic allocation scheme which increases the size of the useable buffers of each network interface without increasing the overall memory consumption, and the use of a queuing scheme which preliminarily examines incoming data packets to determine if any processing needs to be performed, and queues the packets should they require processing. Additionally, a user interface is presented exposing this functionality of the intermediate network driver.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
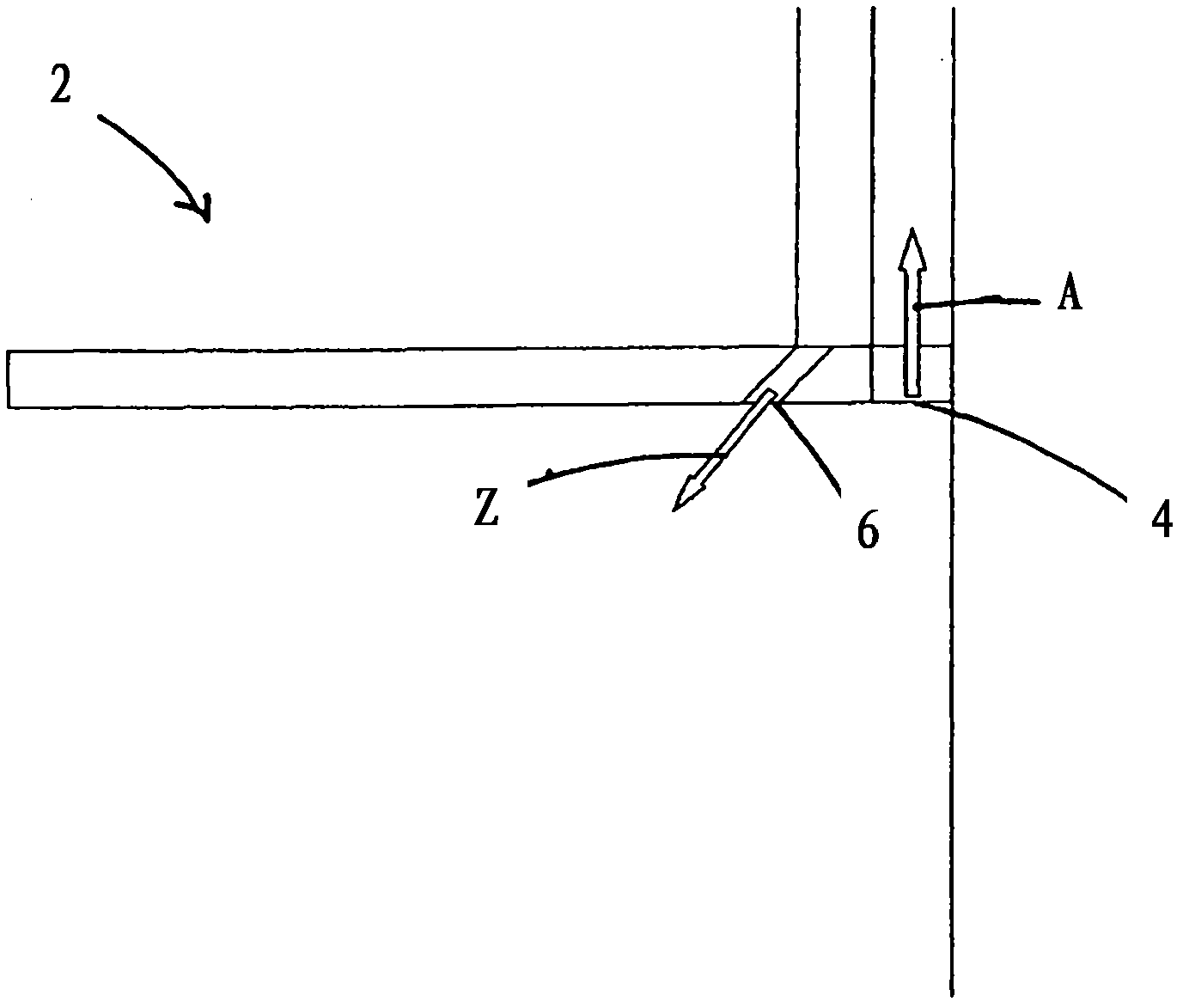
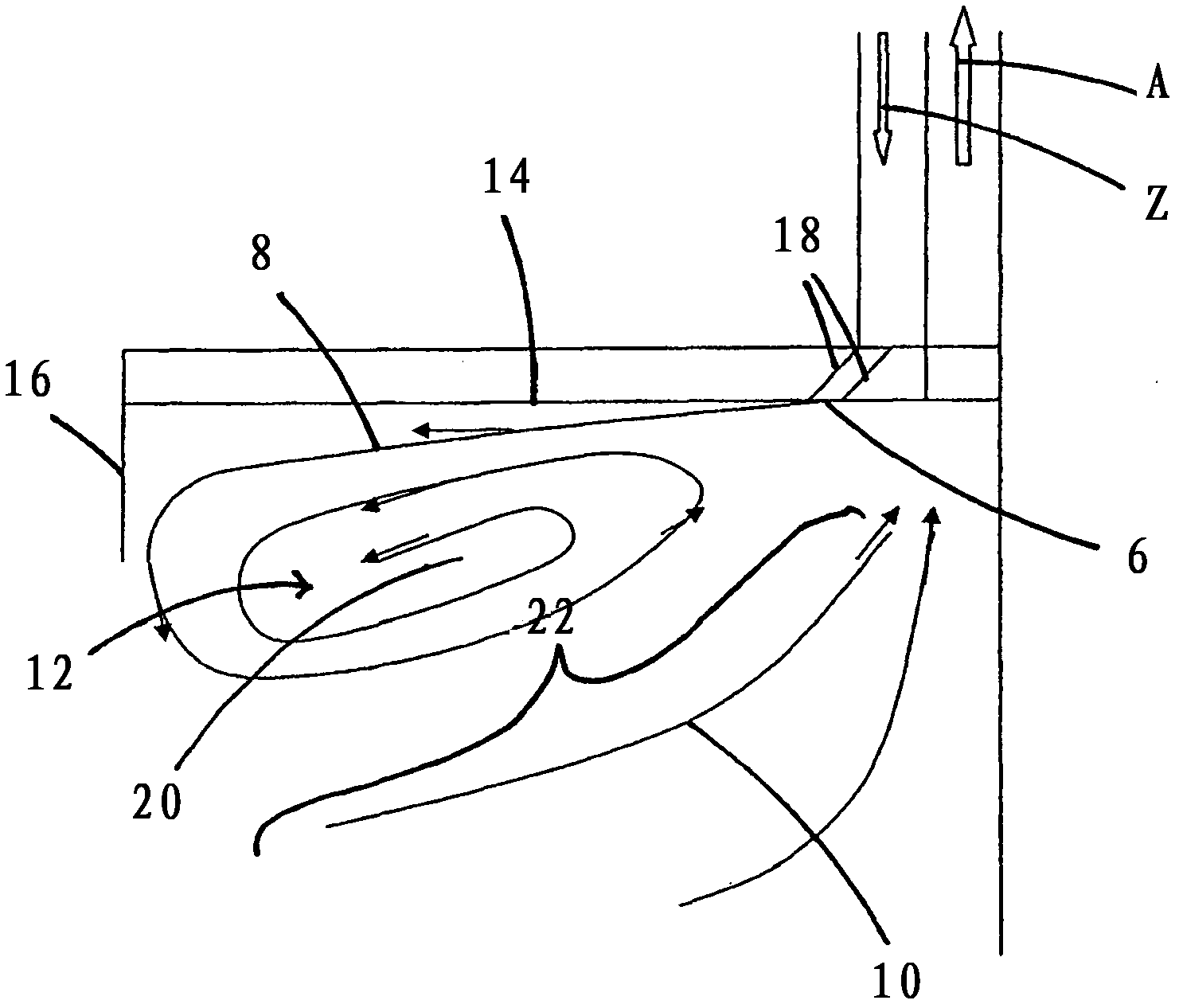
Fume Extraction Hood
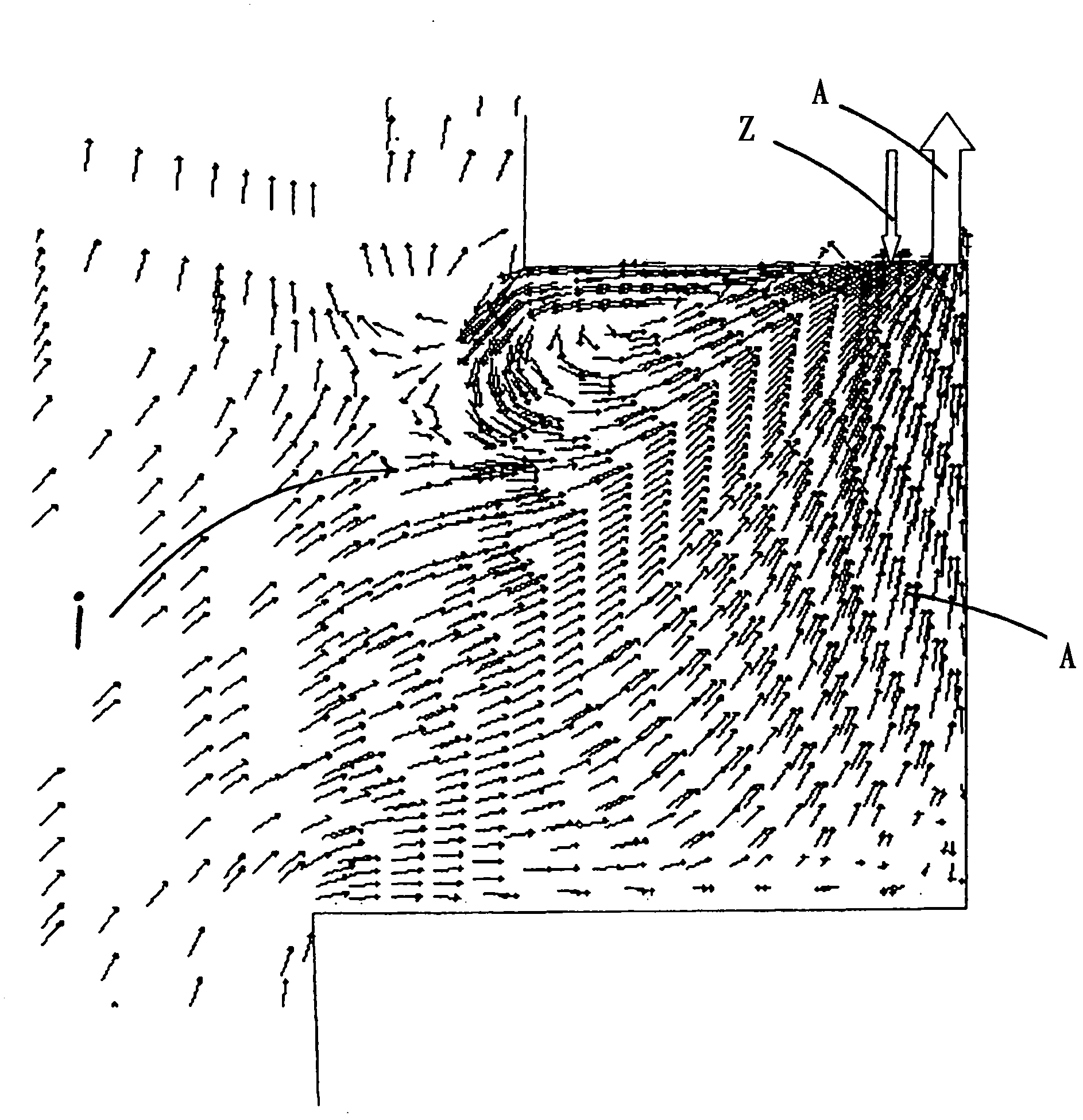
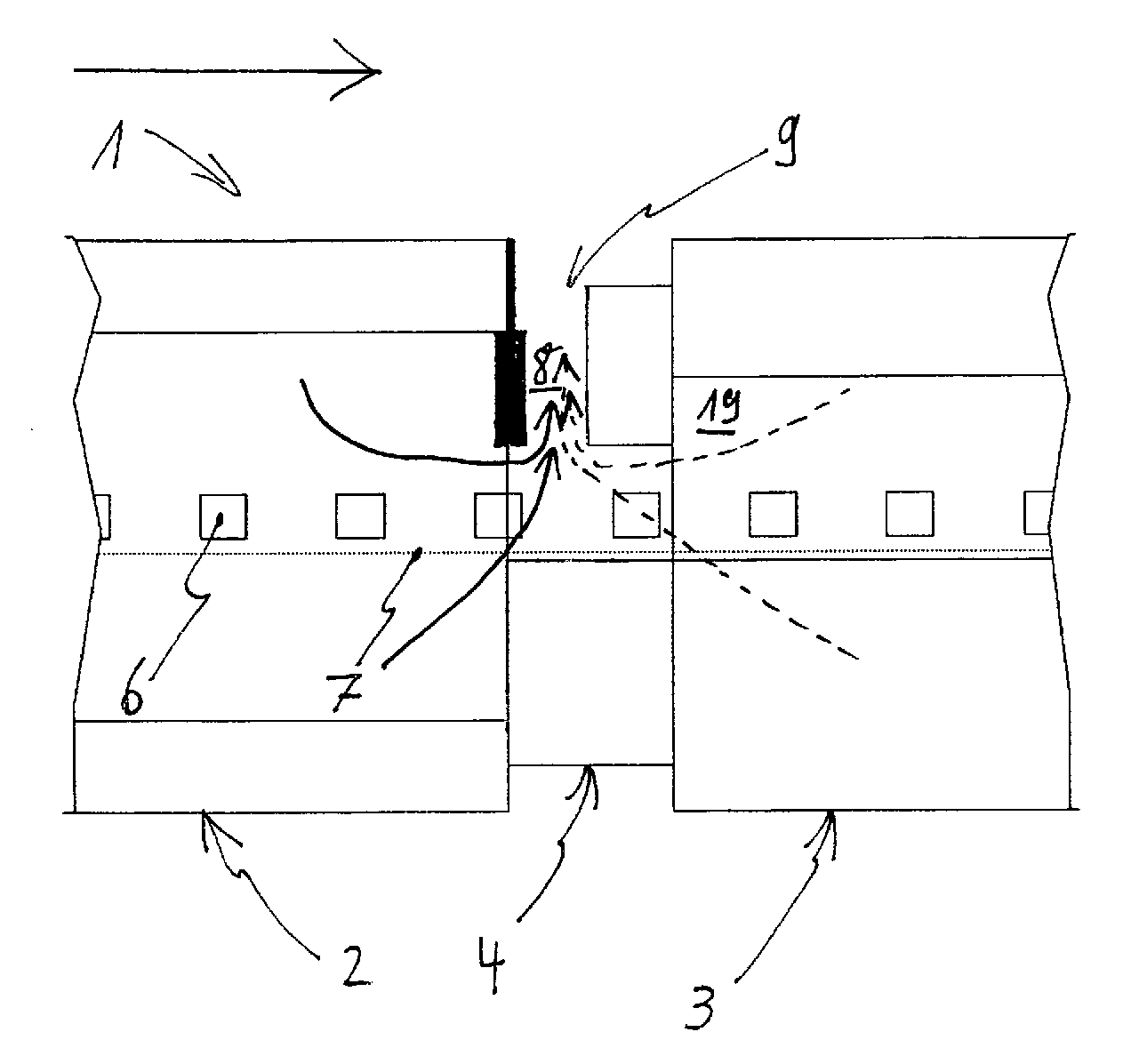
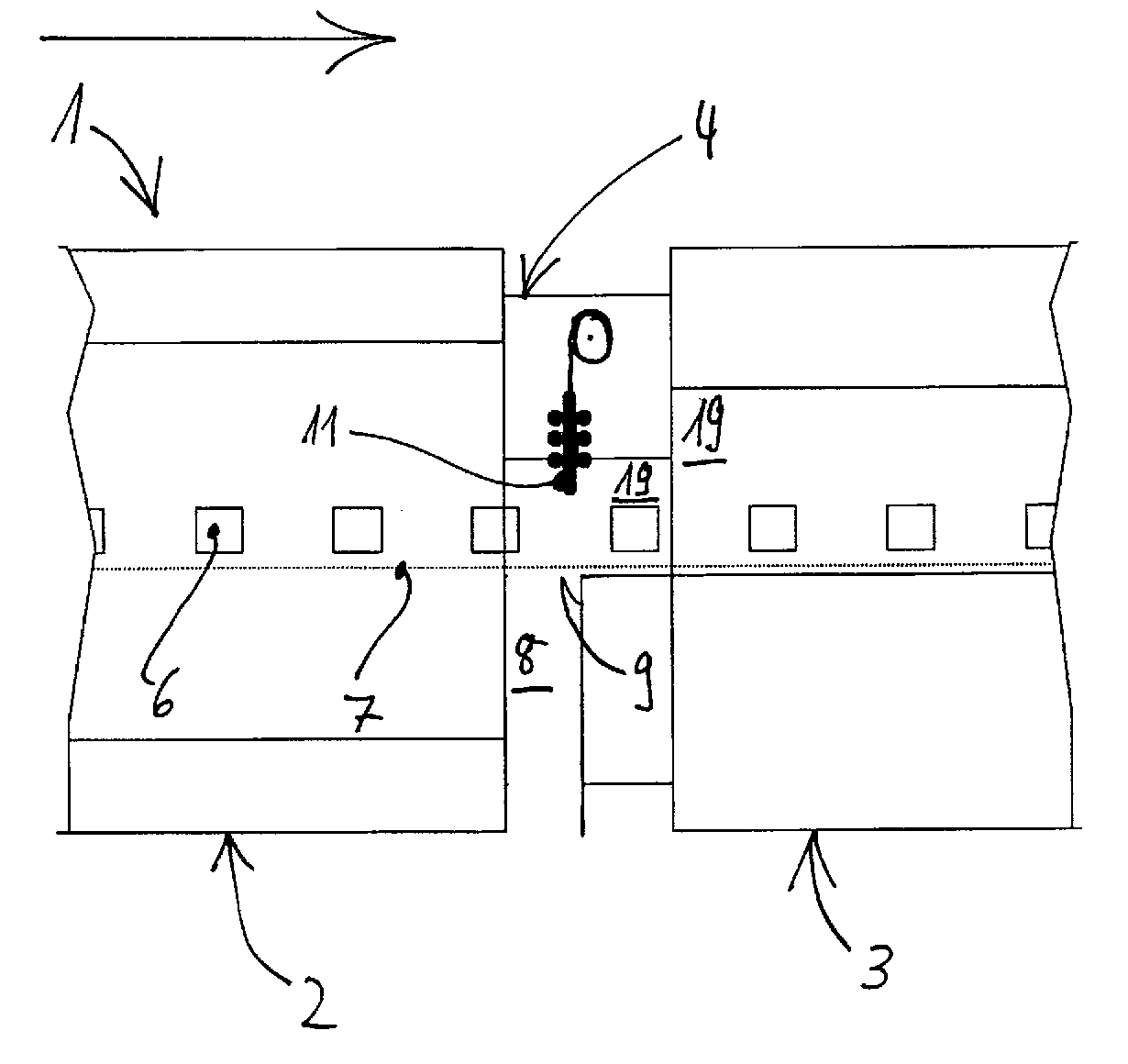
InactiveCN102483240AReduce lossReduced airflow effectDomestic stoves or rangesCooking fumes removalEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention relates to a fume extraction hood (2) having an exhaust opening (4) for leading away exhaust air (A) and an inlet opening (6) for feeding inlet air (Z), disposed adjacent to the exhaust opening (4). In order to achieve an inlet air guide, by means of which cooking vapors can be effectively captured and fed to the exhaust opening, the invention proposes that the inlet opening (6) is disposed and implemented so that the inlet air flow (8) flowing out of the inlet opening (6) in a direction oriented opposite to the flow direction of an exhaust gas flow (10) flowing into the exhaust opening (4), and the exhaust air flow (10) is deflected sideways via an extraction path (F).
Owner:BERLING
System and method for virtual attendance at special events
InactiveUS20060294012A1Reduce shareIncrease profitComputer security arrangementsMarketingNon profitService provision
A system and method that provides for “virtual attendance” in real-time, as well as provides for recording the event. The system generally includes at least one video camera, an interface with the Internet for transmission of real-time video, a server, and an optional recording device. The equipment is installed in the facilities of a non-profit or charitable organization by a service provider at no cost to the organization, and the service provider maintains and operates the system at no cost to the organization. The service provider then charges a fee to the person holding the event for use of the system. Revenues for providing the service are shared between the service provider and the organization providing the facilities for the event. Once the service provider recovers the cost of the equipment, the equipment is donated to the organization and, in addition, the organization receives a larger share of the revenues.
Owner:BEHOLD EVENT NETWORKS
Electric tool
ActiveUS20100263895A1Reduce the amplitudeReduce distractionsDrilling rodsConstructionsEngineeringPower tool
The invention relates to a hand-guided electric tool having a motor and a pulse width modulator for generating a pulse width modulated signal for operating the motor. A unit is provided for reducing the EMC interferences emitted by the electric tool.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
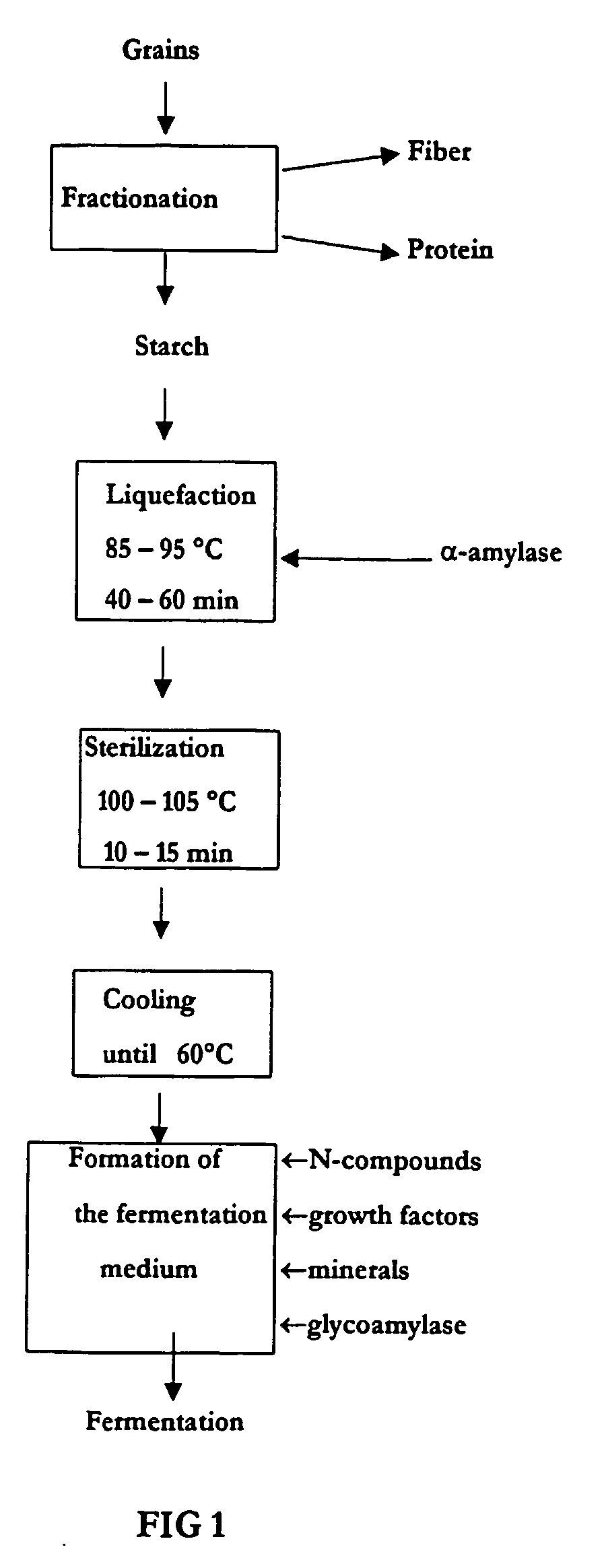
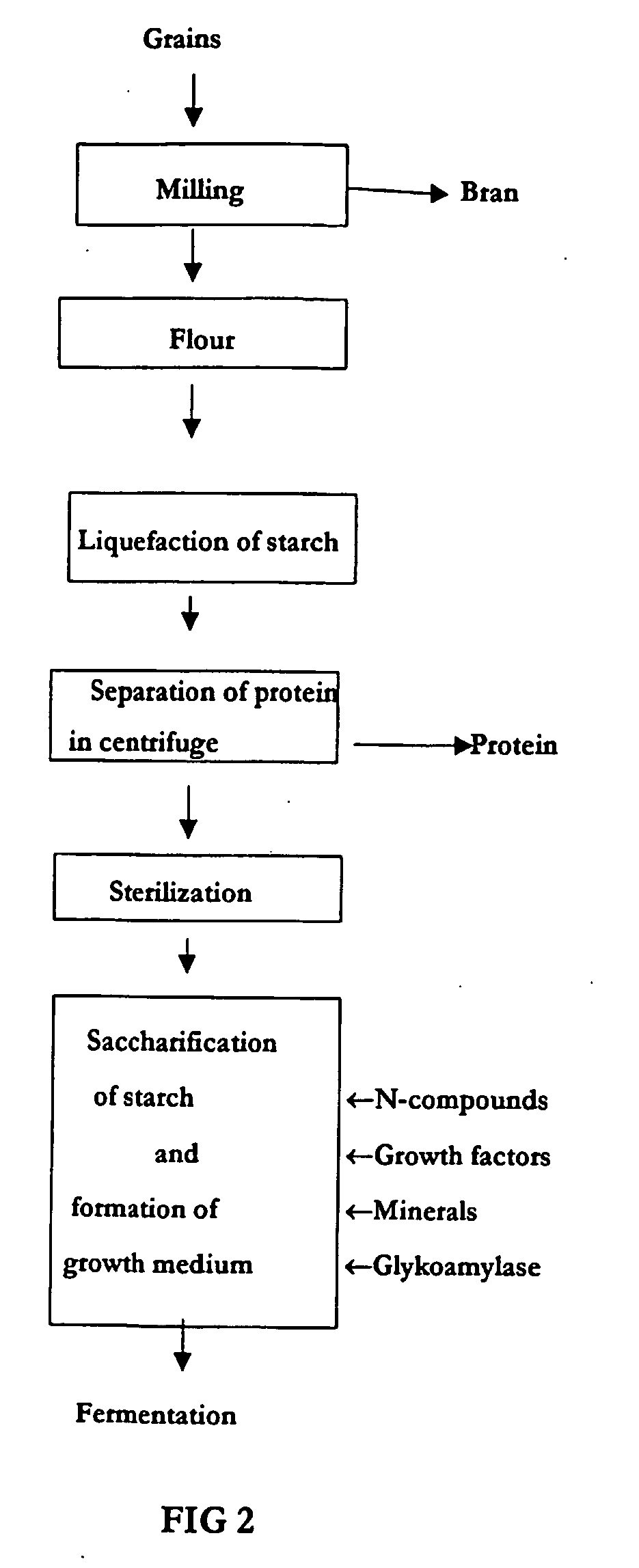
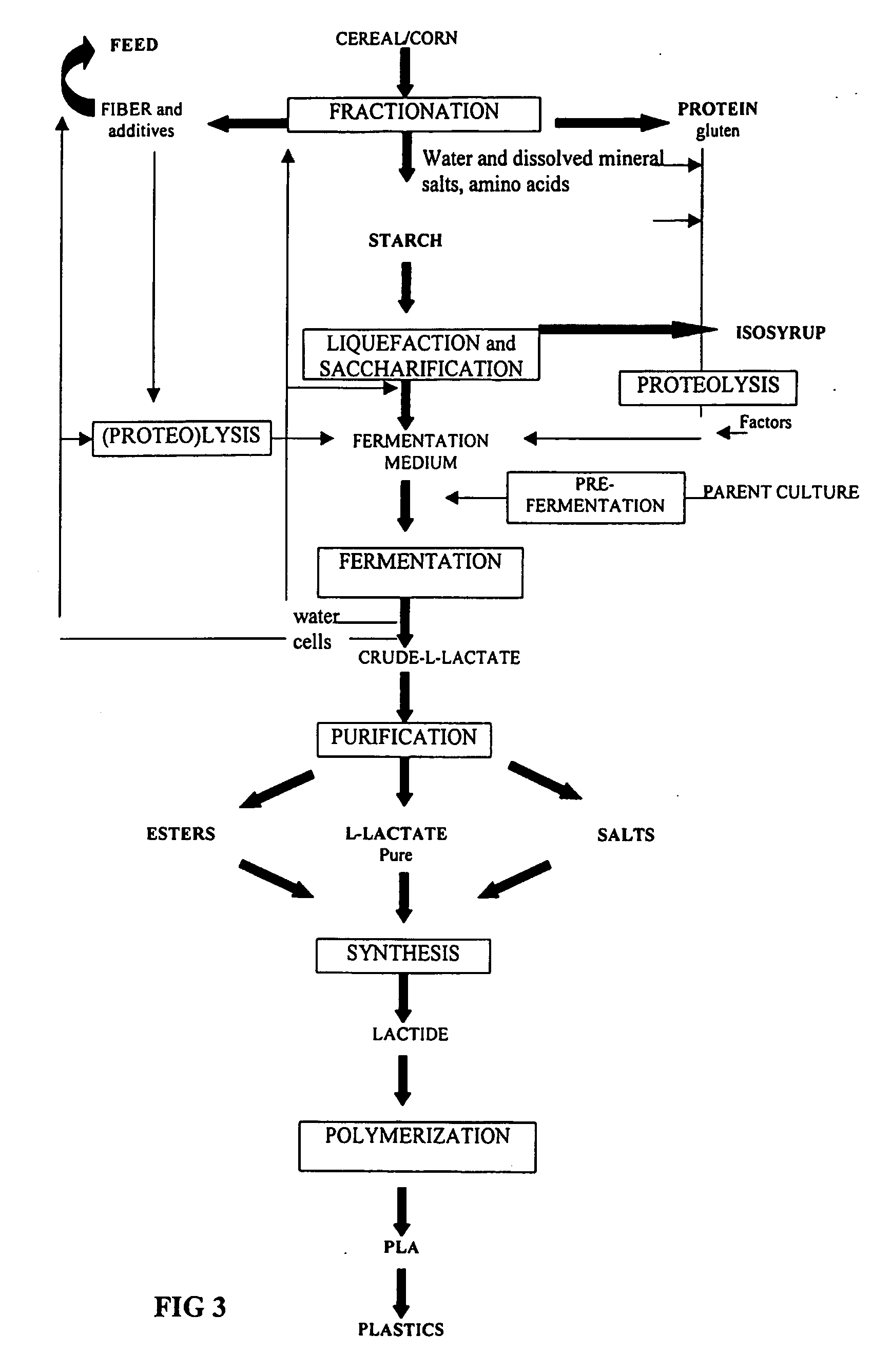
Method of production of biodegradable lactic acid polymers and the use of lactic acid polymers produced using such a method
InactiveUS20060154350A1Reduce shareSave resourcesFermentationFood preparationPolymer scienceFermentation
The invention relates to the use of lactic acid and its esters produced upon microbiological fermentation of organic substances, particularly cereal starch, for producing biodegradable lactic acid polymers and use of the biodegradable polymer produced using such a technique. The areas of application of the invention include food processing and chemical technology. The fields of usage of the invention include the production of starch, phytoprotein, lactic acid and its derivatives, including its salts, esters and biodegradable polymer (PLA).
Owner:MAILTEC
Dynamic mixer
ActiveCN103534017AShort structure lengthReduce shareLiquid surface applicatorsImpression capsCurve shapeEngineering
Owner:MEDMIX SWITZERLAND AG
Method of synchronous image sharing
A method is provided for synchronous sharing of a document between a first and a second terminal. The method includes: transmission of a message to the second terminal comprising the coordinates of at least one contact point defined on the basis of the document to be shared; upon the opening of a viewing time window defined by the intersection of a first and of a second time window defined respectively for the first and the second terminal and each being bounded by the receipt, originating from the terminal, of a sharing agreement message triggered by an action on the at least one contact point and the receipt of an abandonment message triggered by the stopping of the action on the at least one contact point, of transmission of the document and of a command to display the document to the second terminal; and transmission of a command to delete the document upon the closing of the viewing time window.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
Cleaning device for textile
ActiveCN106120220AAvoid quality lossReduce shareTextile treatment containersTextile treatment carriersDrive wheelDrive shaft
The invention discloses a cleaning device for textile. The cleaning device comprises an outer shell; the top of the outer shell is movably connected with a device door through a rotating shaft; the left side of the outer shell is fixedly connected with a controller; a position measuring device is arranged on each of the two sides of the inner wall of the outer shell; each position measuring device comprises a position measuring outer shell; the right side of the position measuring outer shell is movably connected with a rolling wheel through the rotating shaft; a position measuring button is fixedly mounted on the right side of the inner cavity of the position measuring outer shell. The cleaning device for the textile can clean a fabric repeatedly through the cooperation and use of a motor, a driving shaft, a driving wheel, a driven shaft, a driven wheel and cleaning equipment; the reduction of the quality of the fabric caused by incompletion of the cloth cleaning degree is avoided; the proportion of unqualified fabric is reduced; through the cooperation and use of the controller and the position measuring devices, a cleaning position can be regulated very well by controlling the motor to rotate through the controller; the automation degree of a cleaning operation is improved.
Owner:无锡惠山万邦科技有限公司
Method and Apparatus for Producing Fruit Leather from a Fruit Mass
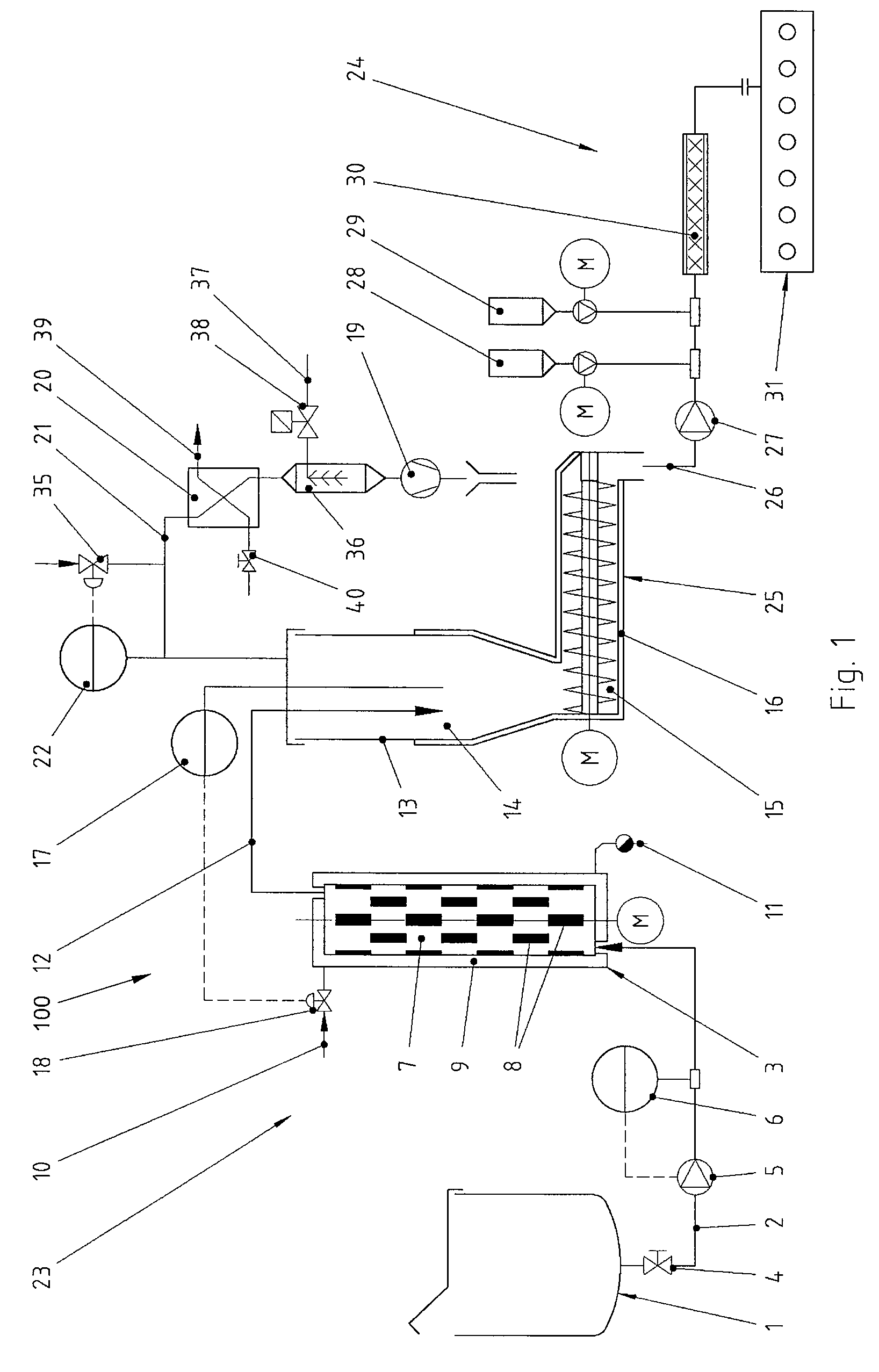
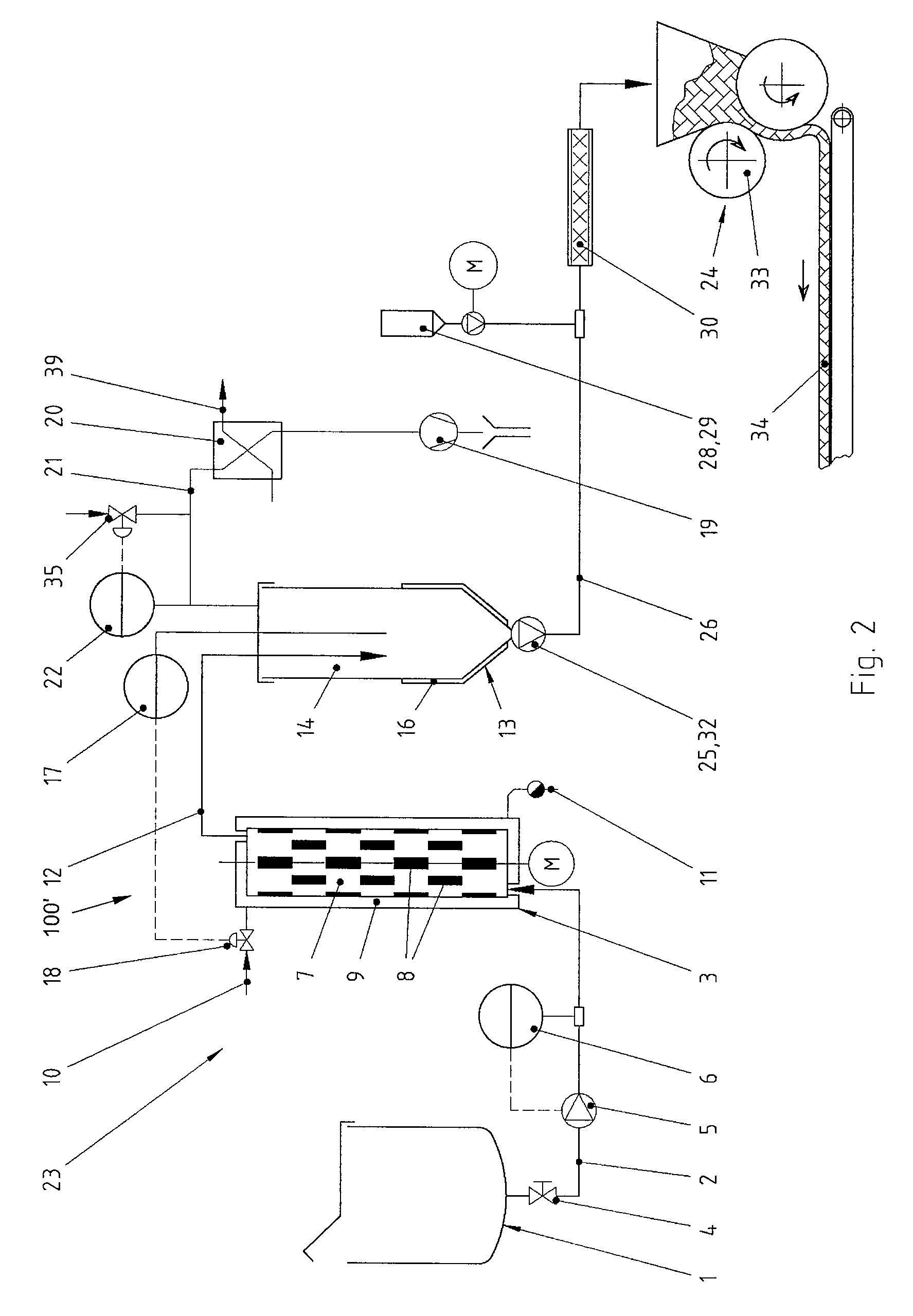
ActiveUS20090169694A1Reducing share of waterLow of filling materialDrying solid materials without heatConfectioneryAdded sugarFood science
A method and an apparatus (100, 100′) serve to continuously produce fruit leather from a fruit mass. The fruit leather does not include added sugar or fat. The fruit mass includes a share of dry substance of at least 50% and a share of water. The fruit mass exposed to vacuum is cooked for less than one minute in a way to reduce the share of water in the fruit mass to increase the share of dry substance in the fruit mass to approximately between 80% to 90%. The fruit mass is then formed to attain the fruit leather.
Owner:CHOCOTECH
Electric tool
ActiveUS8439126B2Reduce the amplitudeReduce distractionsDrilling rodsConstructionsEngineeringPower tool
The invention relates to a hand-guided electric tool having a motor and a pulse width modulator for generating a pulse width modulated signal for operating the motor. A unit is provided for reducing the EMC interferences emitted by the electric tool.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Gas turbine
ActiveCN101506474APrevent inflowEasy to cleanEngine fuctionsBlade accessoriesParticulatesProduct gas
An improved system for removing particulates from the cooling air in a gas turbine engine (10) has a separating element (60) set axially opposite to the air inlet (20) from the compressor (12) and comprising a circular sleeve fitted to the turbine housing. The cooling airstreams are ducted into the cooling air inlets (54, 55) via a non direct path. Particulates are prevented from blocking the air inlets and are taken into the burn chambers.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH CO & KG
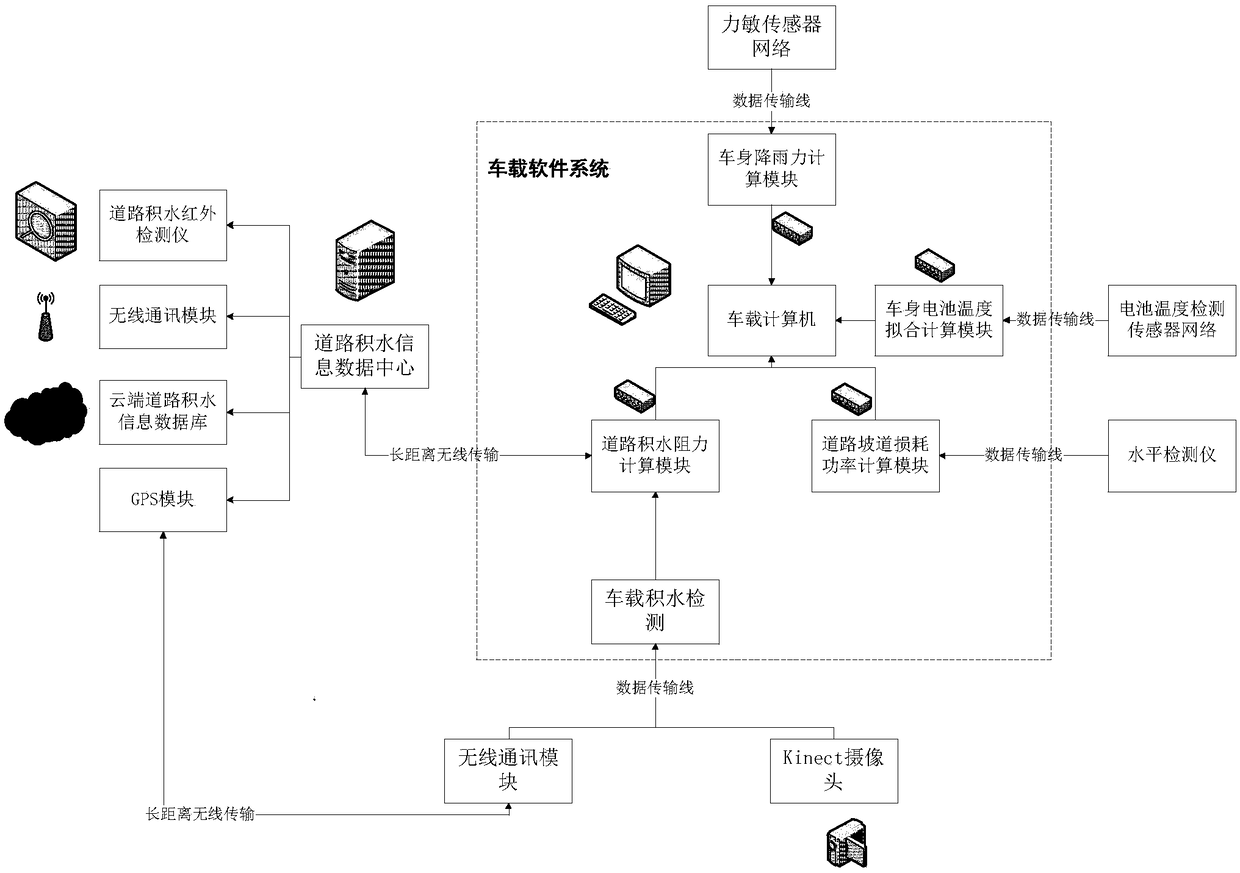
Battery capacity predication method and pre-warning system for unmanned vehicle on heavy rain road
ActiveCN108621844AAccurate real-time powerGuaranteed reliabilityOperating modesVehicular energy storageData informationGenetic algorithm
The invention discloses a battery capacity predication method and pre-warning system for an unmanned vehicle on a heavy rain road. According to the battery capacity predication method for the unmannedvehicle on the heavy rain road, by using a plurality of sensors to form a sensor network, multiple running environment factors of the unmanned vehicle on the heavy rain road can be comprehensively considered; rainfall resistance of a vehicle body is measured by using a force sensor; integrated data fusion is carried out by using a fusion coefficient; by using a genetic algorithm to carry out weighted coefficient optimization on collected data information, the influences of the different running environment factors on the vehicle battery capacity can be distinguished so that the obtained datastructure is more representative; the battery capacity of the unmanned vehicle under an extreme heavy rain environment is predicated in real time by using a two-layer neural network; and various quantitative and qualitative variable factors under a non-linear environment are sufficiently considered through the adoption of the the neural network. Compared with the common SOC battery capacity predication method, the battery capacity predication method for the unmanned vehicle on the heavy rain road has the advantages that the method is more intelligent, the obtained battery capacity predicationresult is more accurate, and a very good pre-warning function can also be realized.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for producing a piston ring
ActiveCN103154583AReduce plane moment of inertiaReduce radial pressurePiston ringsMachines/enginesButt jointMaterial removal
The invention relates to a method for producing a piston ring (1) provided with a butt joint (5), in that an annular metal main body is provided with at least one hard layer (2') at least in the area of the outer circumferential surface (2) of said main body, wherein after this coating the inner circumferential surface (3) of the piston ring is at least partially subjected to a wall-thickness-reducing material removal process.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL BURSCHEID
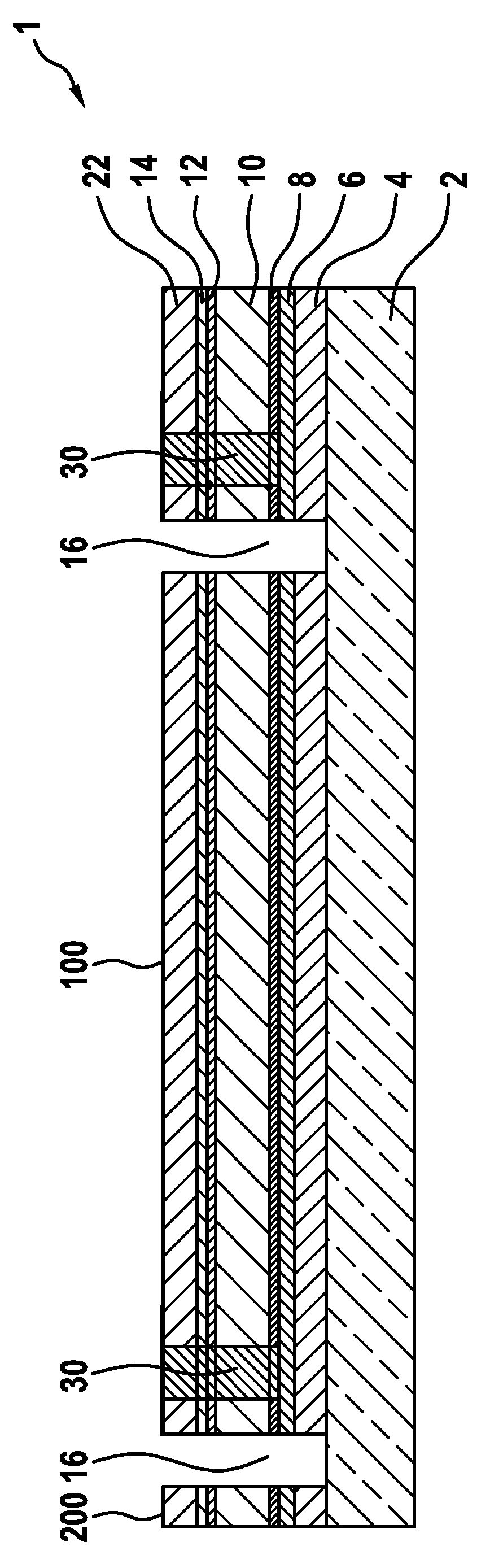
Photovoltaic thin-film solar modules and method for producing such thin-film solar modules
ActiveCN104335351AQuality improvementVolume expansion cannot be preventedFinal product manufactureDiodeElectrical batteryOhmic contact
The invention relates to photovoltaic thin-film solar modules, comprising in a first embodiment, particularly in the following order: at least one substrate layer; at least one rear electrode layer, particularly directly contacting the substrate layer; at least one conductive barrier layer, particularly directly contacting the rear electrode layer and / or the substrate layer; at least one contact layer, particularly an ohmic contact layer, particularly directly contacting the barrier layer; at least one semiconductor absorber layer, particularly a chalcopyrite or kesterite semiconductor absorber layer, particularly directly contacting the contact layer; optionally at least one first buffer layer, particularly directly contacting the semiconductor absorber layer and containing or substantially made of CdS or a CdS-free layer, particularly containing or made substantially of Zn(S, OH) or In2S3; and / or optionally at least one second buffer layer, particularly directly contacting the semiconductor absorber layer or the first buffer layer and containing or substantially made of intrinsic zinc oxide and / or high-resistance zinc oxide; and at least one transparent front electrode layer, particularly directly contacting the semiconductor absorber layer, the first buffer layer and / or the second buffer layer and particularly containing or substantially made of n-doped zinc oxide. Said thin-film solar modules further comprise: spaced-apart first structuring separation trenches filled with at least one insulating material, said trenches separating adjacent solar cells from one another down to the substrate layer; spaced-apart second structuring separation trenches filled or provided with at least one conductive material, said trenches extending to the contact layer or to the rear electrode layer or to the barrier layer, particularly to the barrier layer and each being adjacent to a filled first structuring separation trench; spaced-apart third structuring separation trenches, which extend to the contact layer or to the rear electrode layer or to the barrier layer, particularly to the barrier layer, and are each adjacent to a second structuring trench on the other side of the first structuring trench to which the second structuring trench is adjacent; and at least one conductive bridge from second structuring trenches filled with a conductive material or furnished with such a material to the front electrode layer of the adjacent solar cell, across adjacent first structuring separation trenches filled with insulating material. The invention further relates to a method for producing such thin-film solar modules.
Owner:NICE SOLAR ENERGY GMBH
Exposing multiple network interfaces as a single network interface to a higher level networking software
InactiveUS7080163B2Guaranteed normal transmissionImprove efficiencyMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksSoftware networkNetwork packet
A software network bridge is disclosed which allows the connected network segments to be presented as a single network unit to the host computer. The software bridge can be implemented as an intermediate network driver, abstracting multiple network segments into a single network interface for higher level protocols and applications. While the intermediate network driver acts as a software bridge implementing the Spanning Tree Algorithm, it also acts a network interface driver to higher level protocols, conglomerating information from the multiple underlying network interface cards and forwarding along commands from the higher level software to the appropriate network interface card. The intermediate network driver can also simultaneously send the same data packet through multiple network interfaces by creating multiple packet descriptors, each pointing to the same data, but each given individually to the underlying network interfaces to control during their transmission. Further efficiencies can also be achieved by the software bridge, implemented as an intermediate network driver, through the use of a dynamic allocation scheme which increases the size of the useable buffers of each network interface without increasing the overall memory consumption, and the use of a queuing scheme which preliminarily examines incoming data packets to determine if any processing needs to be performed, and queues the packets should they require processing. Additionally, a user interface is presented exposing this functionality of the intermediate network driver.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Econnoisseur identification method and device based on user behavior detection and electronic equipment
PendingCN110363540ARestrict permissionsReduce shareDiscounts/incentivesComputer scienceData combination
The invention provides an econnoisseur identification method and device based on user behavior detection, and an electronic device. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a user behaviorrelated data combination performed by a user for actuating a specific activity welfare; based on the user behavior related data combination, detecting econnoisseur attribute information correspondingto the user; and when it is detected that the econnoisseur attribute information conforms to or partially conforms to the abnormal strategy value, obtaining the specific activity welfare, and limiting the permission of the user to use the specific activity welfare. According to the invention, the partitioning of theeconnoisseur for promotion welfare can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI QIFU INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Method and device for controlling a drivetrain of a vehicle
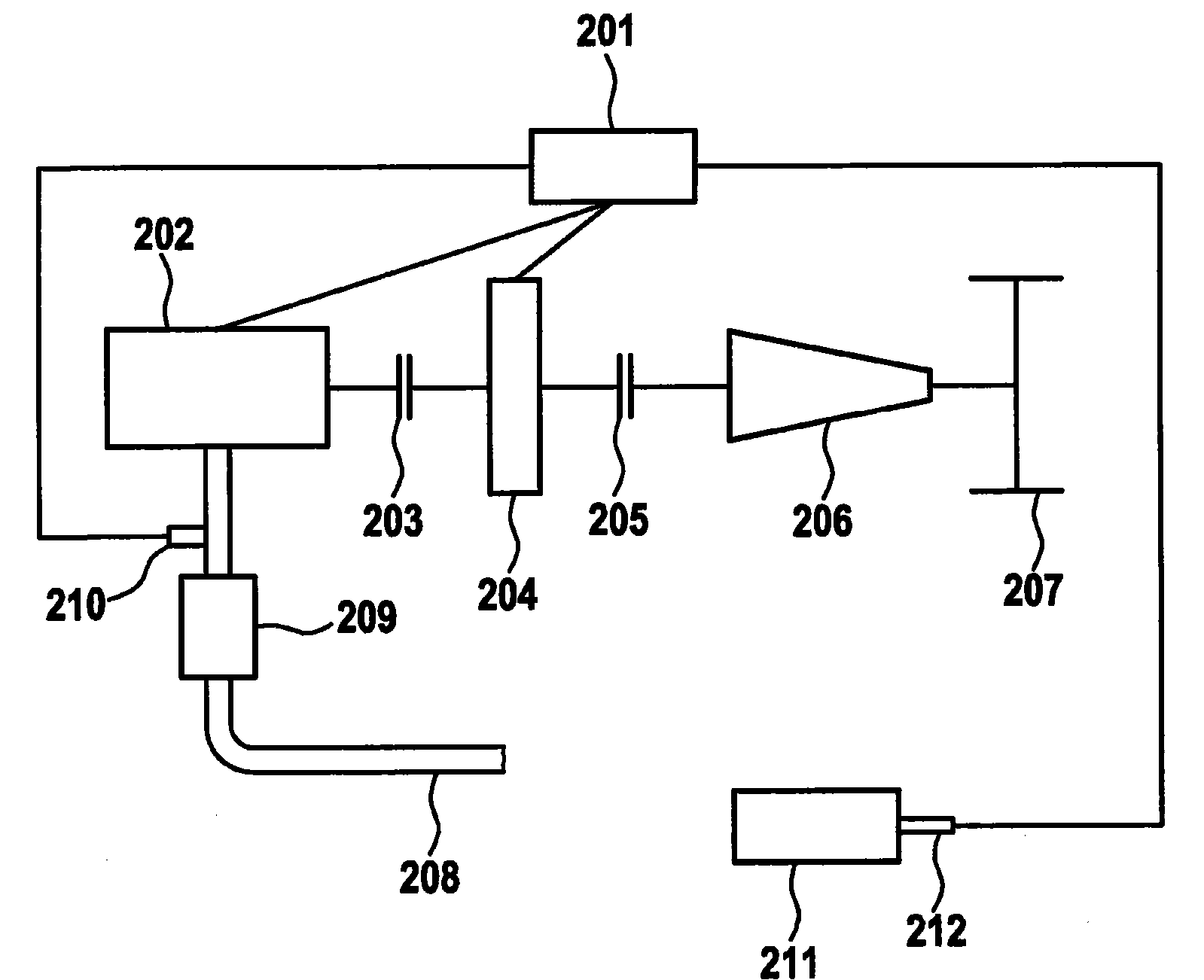
ActiveCN101946076AAvoid running at full capacityReduce torqueElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesDrivetrainInternal combustion engine
The invention relates to a method and a device for controlling a drivetrain of a vehicle, particularly a hybrid vehicle. The drivetrain comprises at least two drive units. One drive unit is an internal combustion engine (202), the other is another motor (204). A temperature value representing the exhaust gas temperature of the internal combustion engine is detected. The proportion for generating the drive torque by means of the another motor is set as a function of the exhaust gas temperature such that a greater proportion of the driving torque is generated by means of the another motor at higher exhaust gas temperatures than at lower exhaust gas temperatures.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Tower type solar energy temperature difference power station
A tower type solar energy temperature difference power station comprises a tower frame, a reflector field, a heat absorber and a generator, and further comprises a programmed switch type temperature difference engine. The programmed switch type temperature difference engine is installed on the tower frame. A heat absorber is installed on a focal spot of a reflector, a heater of the programmed switch type temperature difference engine is tightly connected with the heat absorber through heat conduction materials. The heater of the programmed switch type temperature difference engine is arranged perpendicular to the ground, and a cooler of the programmed switch type temperature difference engine is installed on the other side of a temperature difference engine and is parallel to the heater. The invention provides the tower type solar energy temperature difference power station, the heater of the temperature difference engine is heated by gathering light, power is generated by utilizing a temperature difference, and then an electromotor is driven to generate power output. By means of the tower type solar energy temperature difference power station, solar power generation cost is expected to be lowered by a large margin, and the popularization of solar power generation is facilitated.
Owner:上海领势新能源科技有限公司 +1
Device for controlling a power supply with DC DC splitting of the type including N interlaced paths
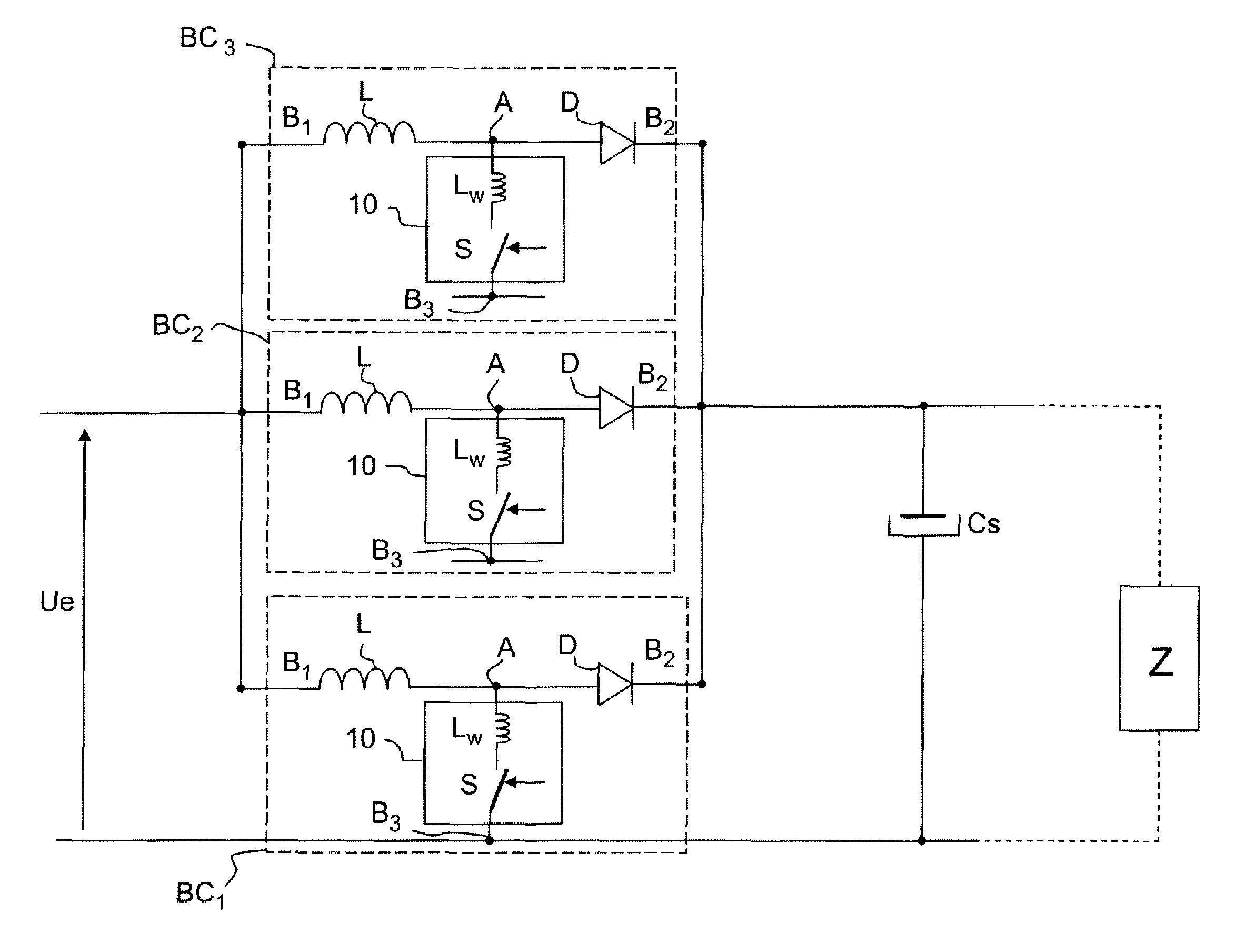
InactiveUS8519685B2Efficiency be degradeImprove power efficiencyFuel cell auxillariesDc-dc conversionElectrical current
In a power supply with n interlaced conversion cells, a control device activates m paths out of n paths, 1≦m≦n, as a function of the power or of the current handled by the power supply. The cell may have a boost, buck, buck / boost, Cuk, or SEPIC topology.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Sintering furnace with a gas removal device
InactiveCN104321605AFlexible connectionQuality improvementMaintainance of heating chambersCharge manipulationMetallurgy
A sintering furnace with a first zone, in particular a burn-off zone, and a second zone, in particular a sintering zone, and also a transitional zone arranged between the first zone and the second zone. The sintering furnace has at least one transporting mechanism for transporting bodies to be sintered on a transporting area. With this transporting mechanism, the bodies to be sintered can be transported from the first zone and through the transitional zone to the second zone. The sintering furnace also has at least one gas removal device with at least one gas removal device opening. Here, the gas removal device opening is at least partially arranged in the region of the transitional zone. Furthermore, a method by means of which gases can be removed from a sintering furnace is claimed.
Owner:GKN SINTER METALS GMBH & CO KG
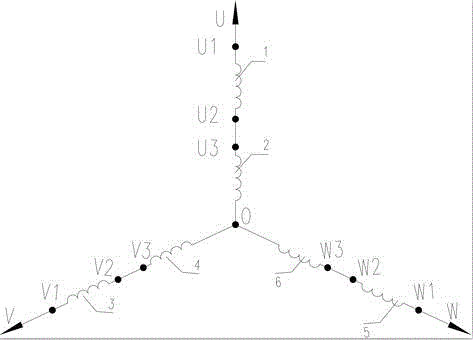
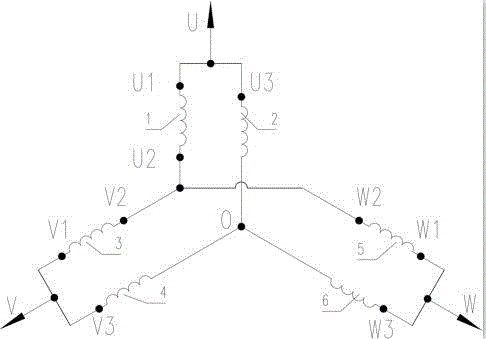
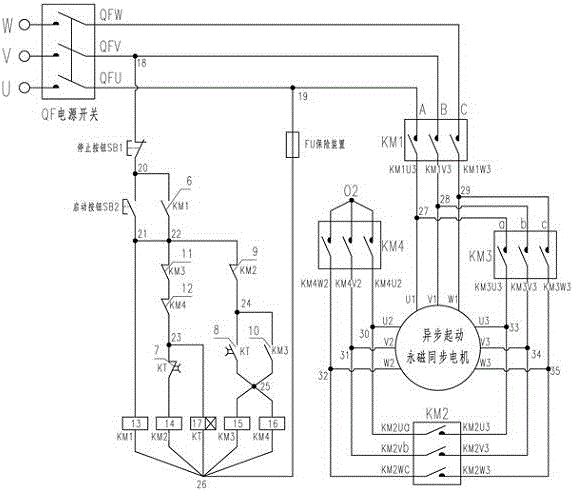
Starting structure set and method of asynchronous starting permanent-magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN106655920AIncrease the cross-sectional areaReduce shareStarter arrangementsSynchronous motorControl system
A starting set and method of an asynchronous starting permanent-magnet synchronous motor comprises an asynchronous starting permanent-magnet synchronous motor main body and a combined control system thereof and is characterized in that two groups of independent windings are arranged between phases of the asynchronous starting permanent-magnet synchronous motor and are led out by nine leading-out lines, a winding combination structure of the asynchronous starting permanent-magnet synchronous motor is changed under the setting of a combined structure of the control system, low-current starting stable speed rising is achieved by a three-step starting structure mode, the starting and the running are both in star-like winding connection method, the high-efficiency performance of the asynchronous starting permanent-magnet synchronous motor is ensured, and a demagnetization phenomenon of a permanent-magnet material caused by impact of a large current during instant starting of the asynchronous starting permanent-magnet synchronous motor is effectively prevented.
Owner:郭自刚
Composite connector for memory cards
InactiveCN101577381AReduce shareEasy to assembleCoupling device connectionsSensing record carriersMemory cardsComputer science
The invention provides a composite connector which reduces occupied portion of a substrate caused by a plurality of memory cards related to the carried substrate. The composite connector of the invention has at least a card insertion opening where a first and a second memory card (24, 25) can be plugged on a body (21). The body (21) has a first body (27) for connection and a second body (28) for connection connected with an edge of the first body (27) for connection. On the first body (27) for connection, a first card conductive cover (22) is covered by way of forming a first card insertion opening (45) and on the second body (28) for connection, a second card conductive cover (23) is covered by way of forming a second card insertion opening (53). Outer side surface of the first card conductive cover (22) is used as a slide surface of the second memory card (25) so that the slide surface faces the second card insertion opening (53).
Owner:SMK CO LTD
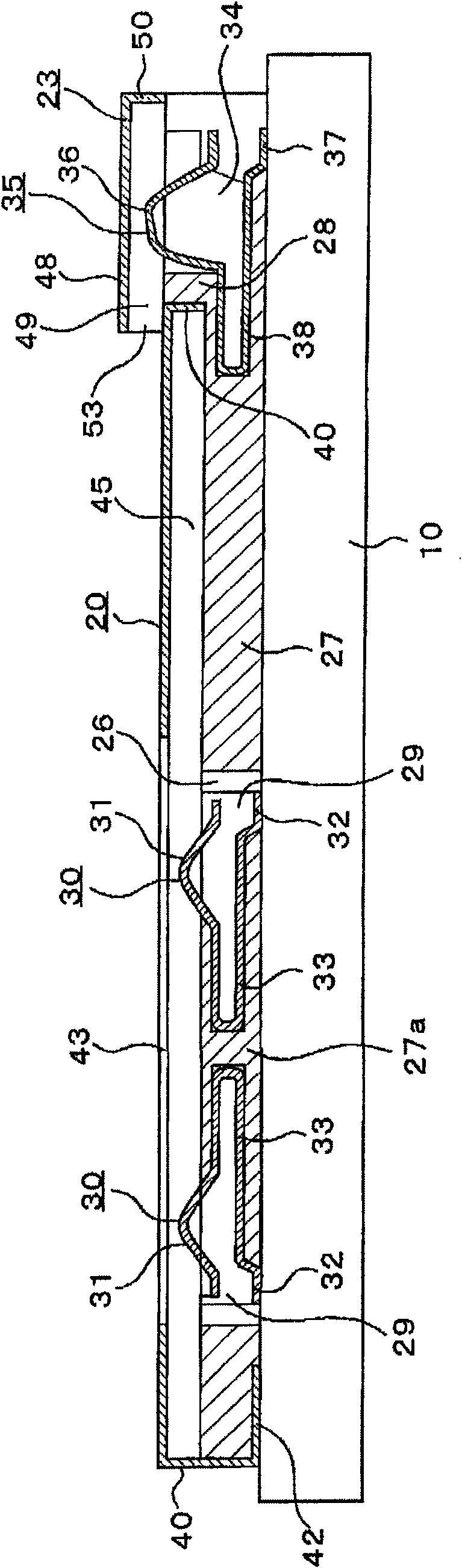
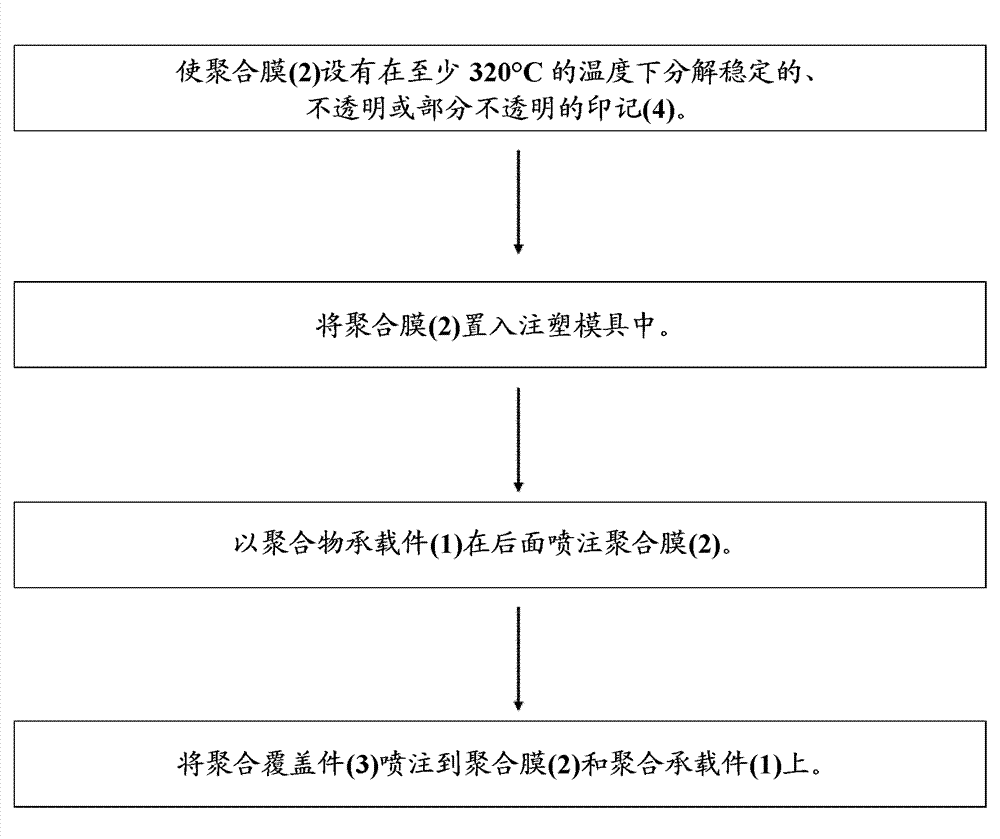
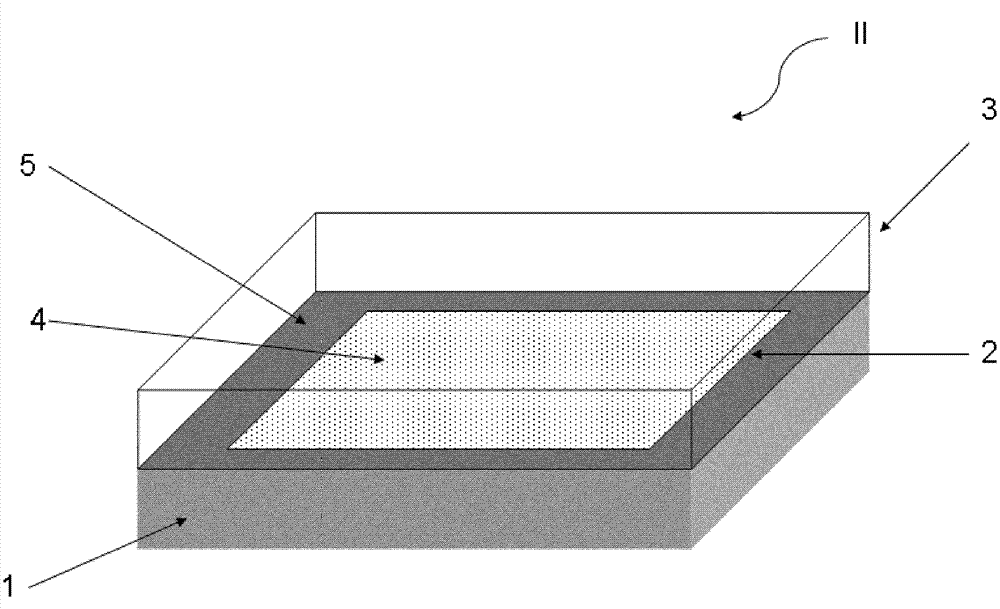
Method for producing a plastic trim part
InactiveCN103842146AImprove stabilityReduce shareLayered productsDomestic articlesPolymer scienceDecomposition
The invention relates to a method for producing a plastic trim part, wherein a. a polymer film (2) is laid in an injection die, wherein the polymer film (2) has an opaque or partially opaque imprint (4) or color pigmentation which is decomposition-stable at a temperature of at least 250 DEG C, b. the polymer film (2) is back-injected by a polymer carrier component (1) and c. a polymer cover component (3) is injected on the polymer film (2) and the polymer carrier component (1).
Owner:SAINT-GOBAIN GLASS FRANCE
Improved fragrant rice processing and production method
InactiveCN107042132AQuality impactImprove processing qualityGrain huskingGrain polishingBletilla striataBroken rice
The invention relates to the technical field of rice processing, in particular to an improved fragrant rice processing and production method. On the one hand, impurities and water mixed in unhulled rice are effectively removed; the adhesion strength between rice grains and hulls of the unhulled rice is reduced through drying treatment, and the rice hulls fall off advantageously; the influence on the quality of the rice from the impurities can be avoided through the impurity removal treatment, and the rice processing quality is improved; through the earlier-stage processing, hull removal of the unhulled rice is more technological, reduction of broken rice is facilitated, and the proportion of the broken rice is reduced; on the other hand, the taste of the rice is effectively improved through treatment in a storage bin and fumigating treatment in a fumigating bin, and as traditional Chinese medicine raw materials like Eucommia ulmoides and Bletilla striata are included in fumigation materials, dietary therapy for people who eat the rice is facilitated; and in addition, the safety quality of the fragrant rice is improved and the expiration date is prolonged through sterilization treatment, package and storage in the later stage.
Owner:灵武市桂林米业有限公司
Method and System for Producing Viscous Fruit Product
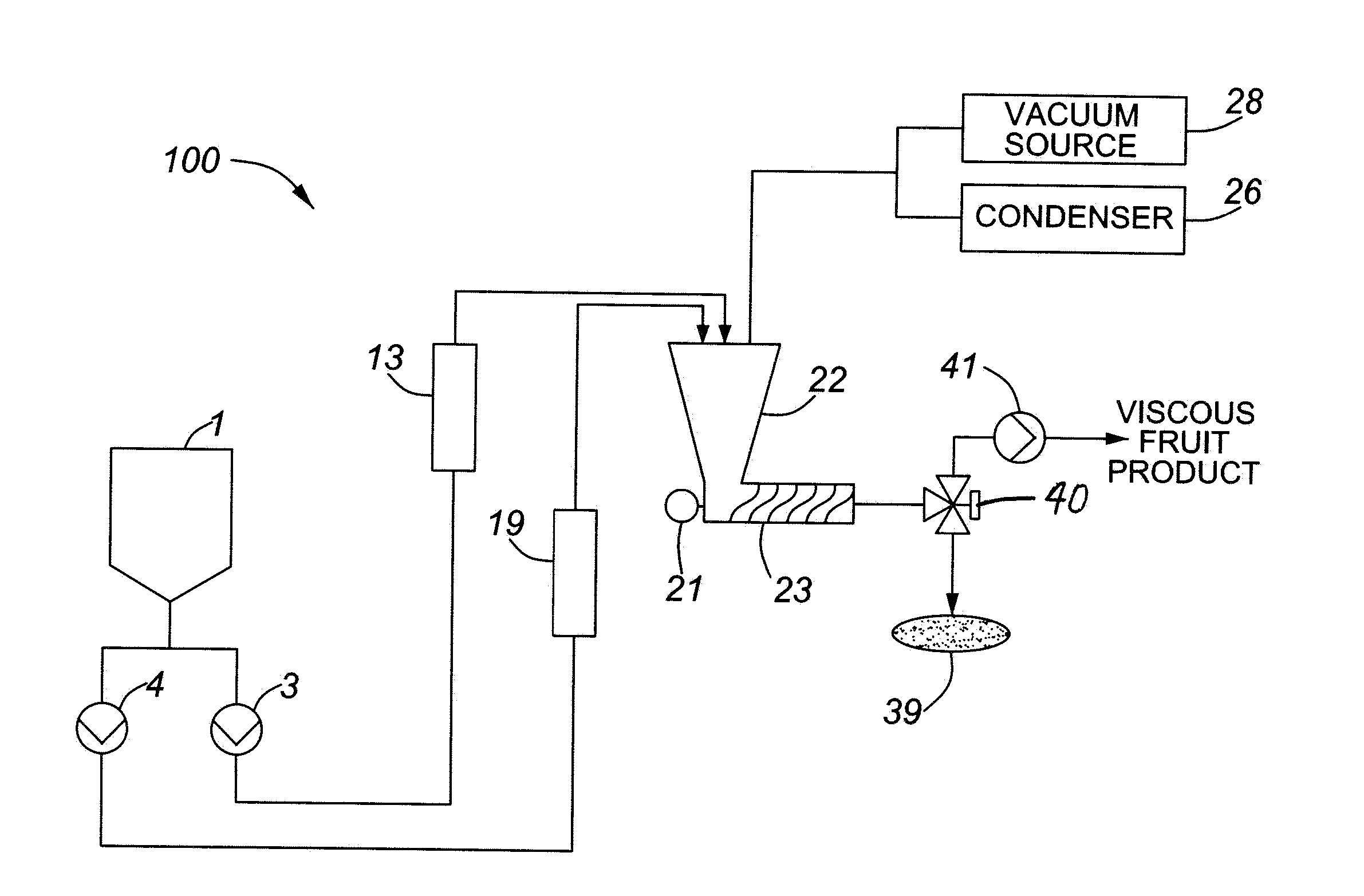
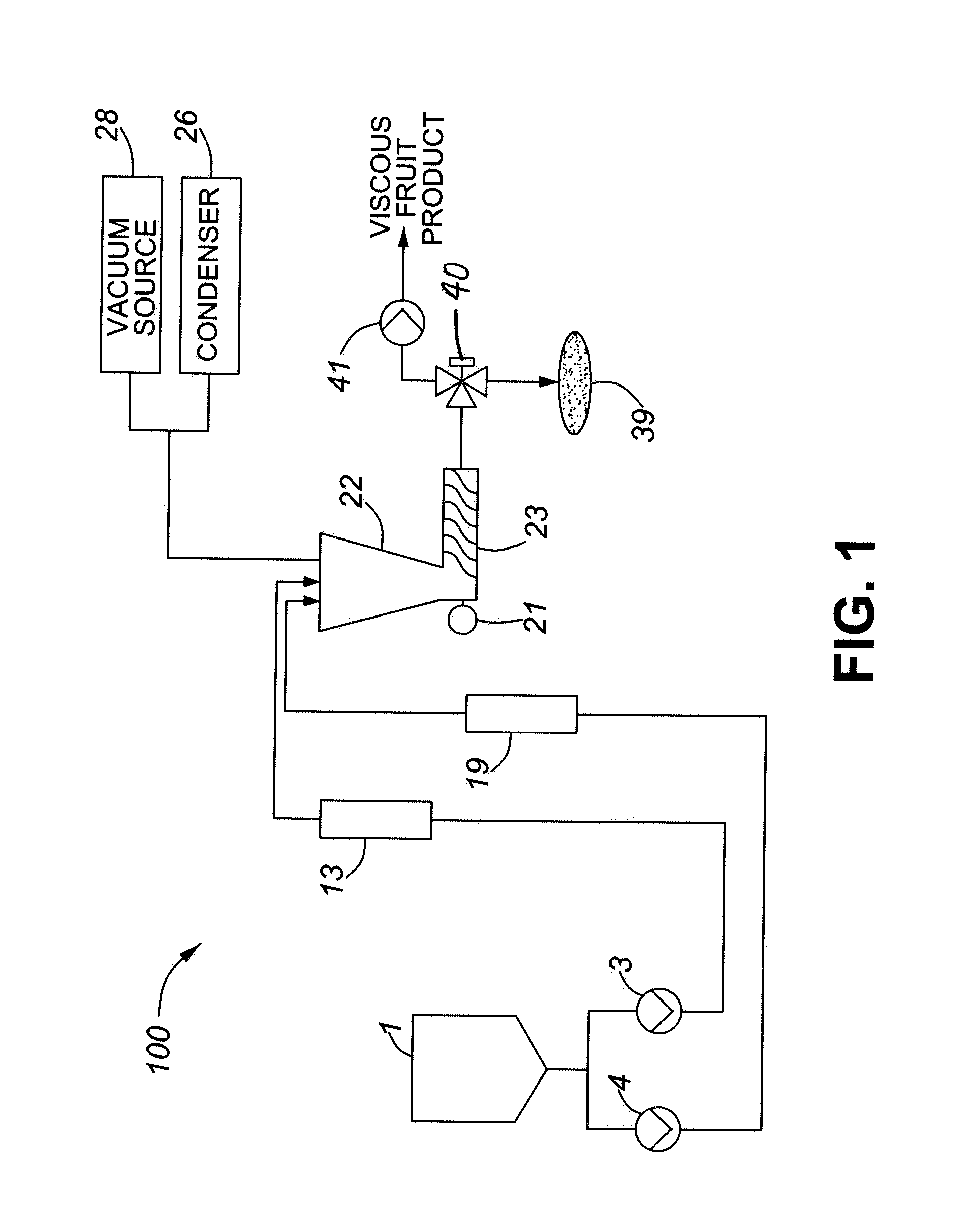
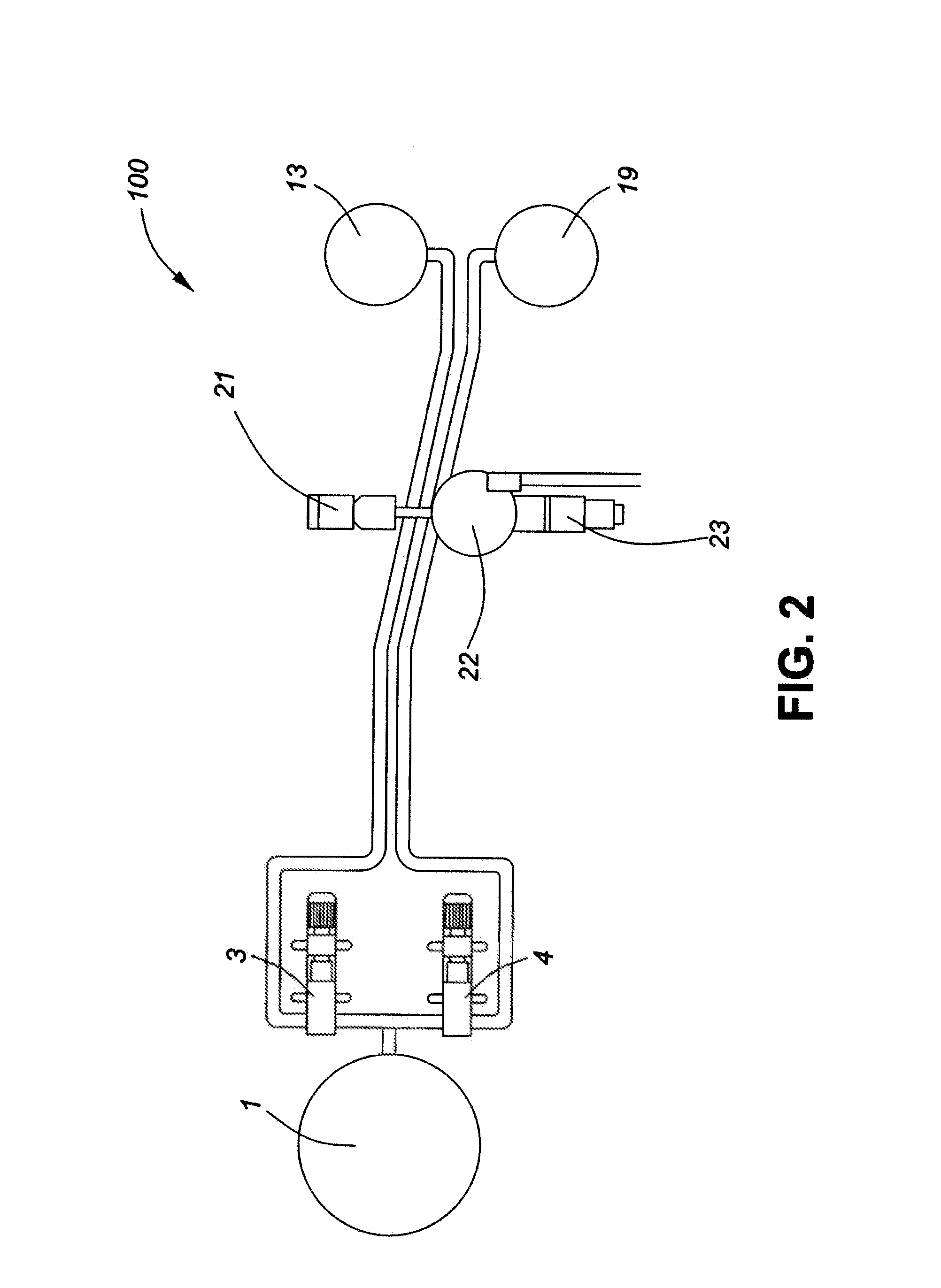
InactiveUS20100159112A1Reduce the total massReduce shareAnimal feeding stuffPackaging under vacuum/special atmosphereEvaporationSlurry
Described herein are a method and system for cooking viscous fruit product composed of a high proportion of fruit from a fruit based slurry. The method includes heating the slurry in a heat exchanger, and subjecting the slurry to a vacuum in a vacuum chamber. The vacuum removes moisture from the slurry. The system includes a heat exchanger for heating the slurry to promote evaporation, and a vacuum chamber fluidly coupled to the heat exchangers. The vacuum chamber generates a vacuum that removes moisture from the slurry. Using the described method and system, a viscous intermediate fruit product composed of a high proportion of fruit, as high as 100% fruit, can be made. The viscous intermediate fruit product can subsequently be formed into consumable end fruit products.
Owner:MADSEN JOHN ALAN +1
Block adaptive carton image compression method based on dictionary learning
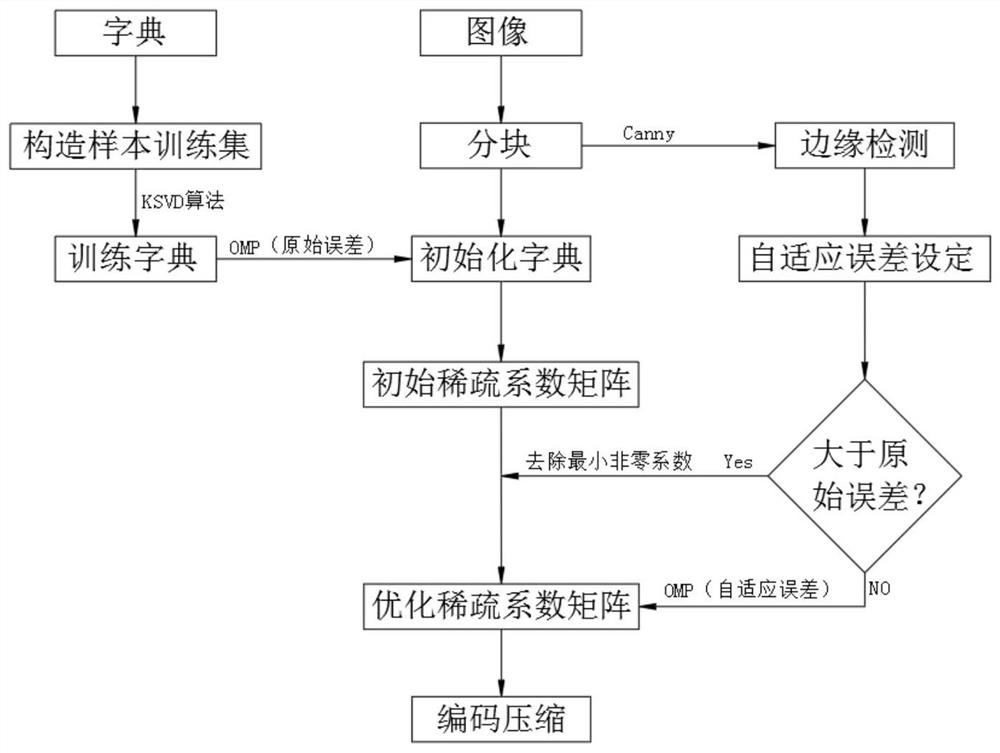
ActiveCN113112557AAchieve high compressionImprove compression qualityImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionSingular value decomposition
The invention relates to the technical field of image processing, and discloses a dictionary learning-based block adaptive carton image compression method, which comprises the following steps of: performing coding compression by using a learning dictionary, image segmentation, edge detection, adaptive error setting and a quadratic optimization sparse coefficient matrix; the method comprises the following steps: training an offline dictionary for a carton image sample set by using a K-SVD (K-Singular Value Decomposition) algorithm, carrying out improved Canny edge detection after image partitioning to obtain a contour area, determining the structural complexity of an image block, adaptively setting an error of a sparse representation model in a partitioning manner, calculating an initial sparse coefficient matrix of the image block under an original error by using an OMP (Orthogonal Matching Practice) algorithm, and carrying out sparse representation on the initial sparse coefficient matrix; the method comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting a sparse coefficient matrix according to a self-adaptive error, secondly, carrying out secondary optimization on the sparse coefficient matrix according to the self-adaptive error, finally extracting a non-zero value and an index of the non-zero value, and carrying out coding compression. Image data sparseness and reconstruction can be completed, computer storage resources occupied by image data are reduced, and the storage cost is reduced.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing moulded part and feeder insert for use in such method
ActiveCN111542405AAvoid damageImprove reliabilityFoundry mouldsFoundry coresManufacturing engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a method for producing a moulded part (26), having a feeder insert arranged therein and having an inlet for liquid metal, for a separable casting mould for metal casting, comprising the steps of: producing or providing a moulded part (26) equipped with a closed feeder insert (2) from a compressed moulding material (28), the closed feeder insert (2) being arranged stationary in the compressed moulding material (28) of the moulded part (26) and having a feeder opening (10) connected to regions of the mould cavity (30) to be formed, and opening the closed feeder insert (2) such that an inlet (32) for liquid metal is formed.
Owner:CHEMEX FOUNDRY SOLUTIONS GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com