Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "High speed readout" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
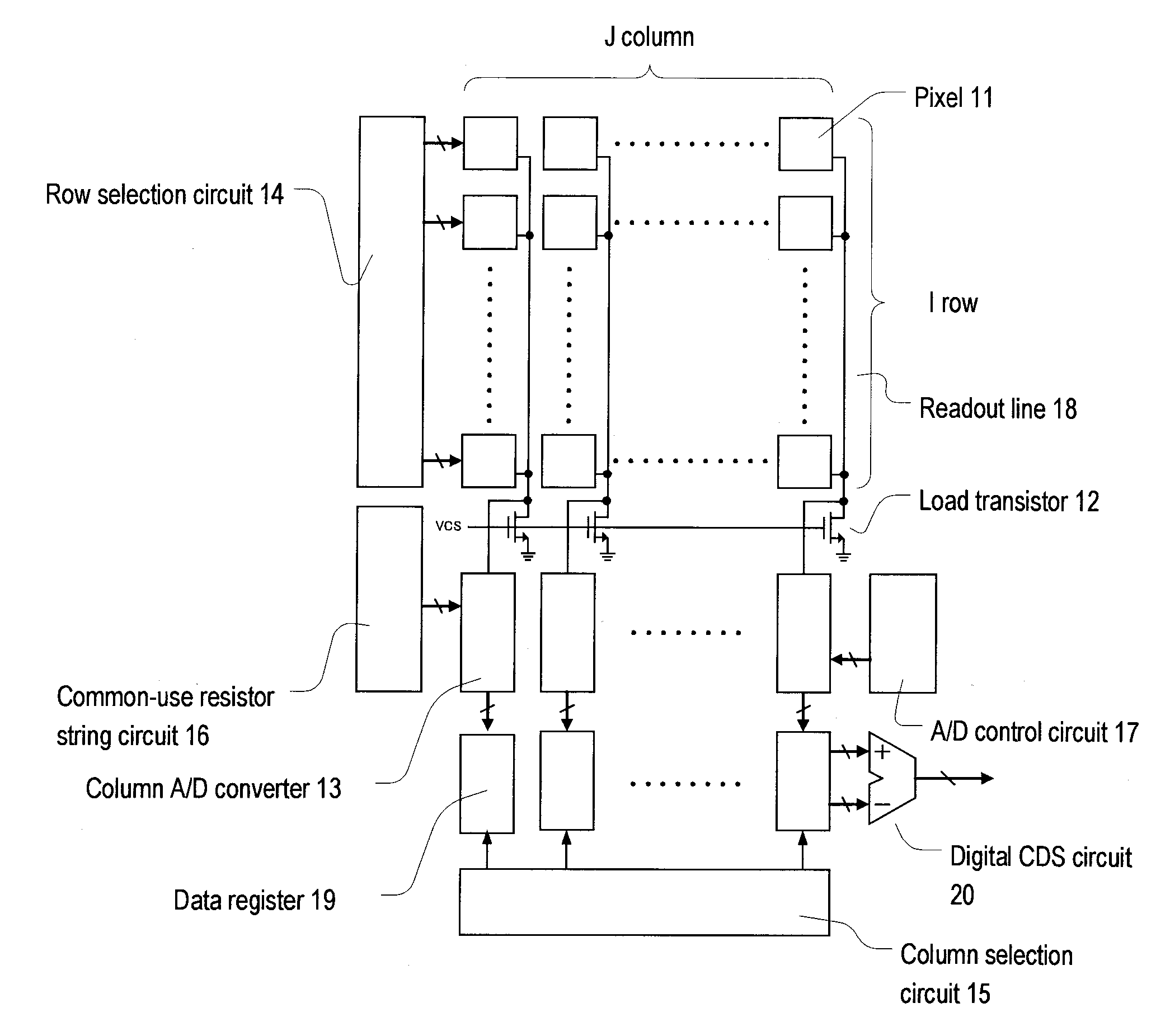
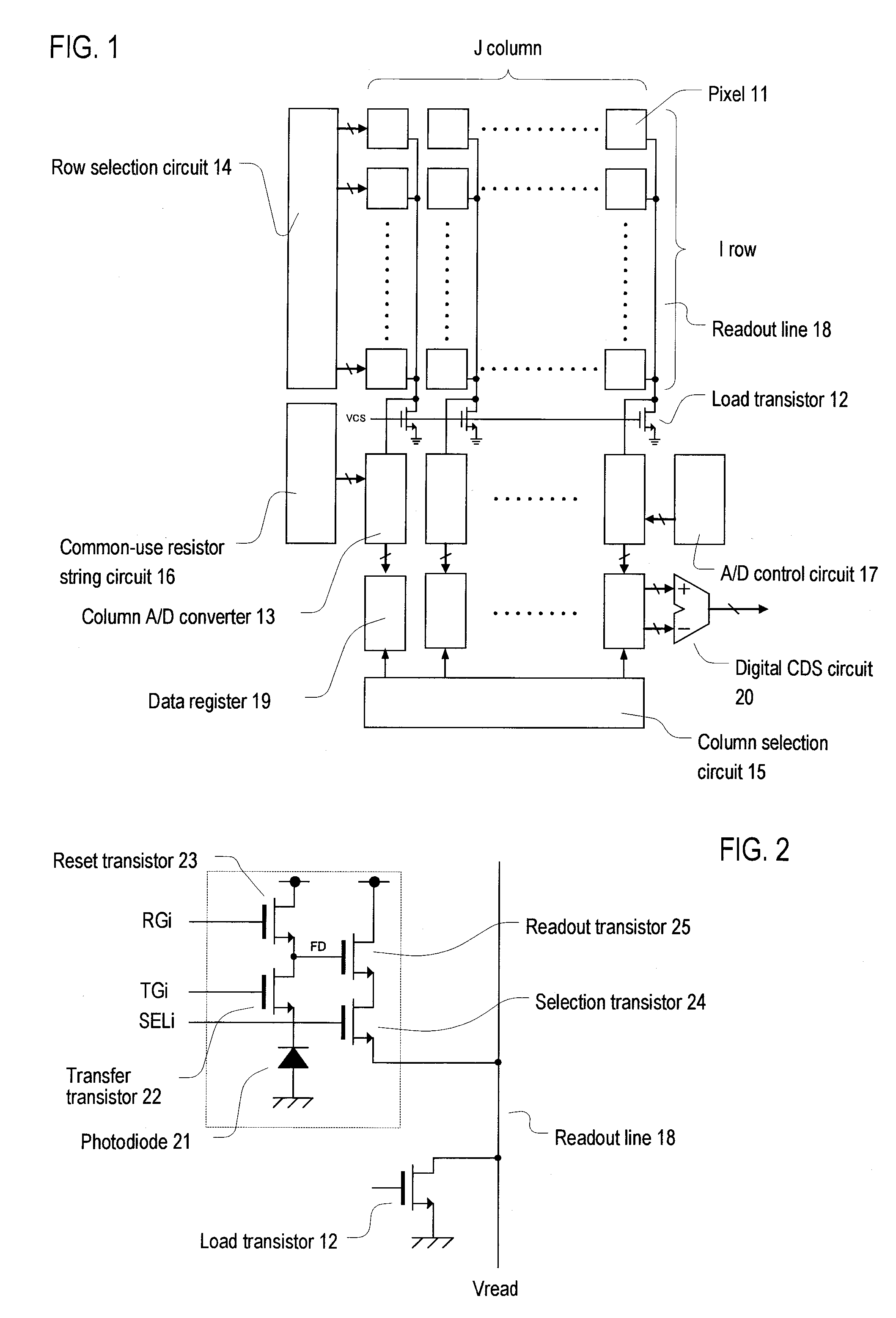
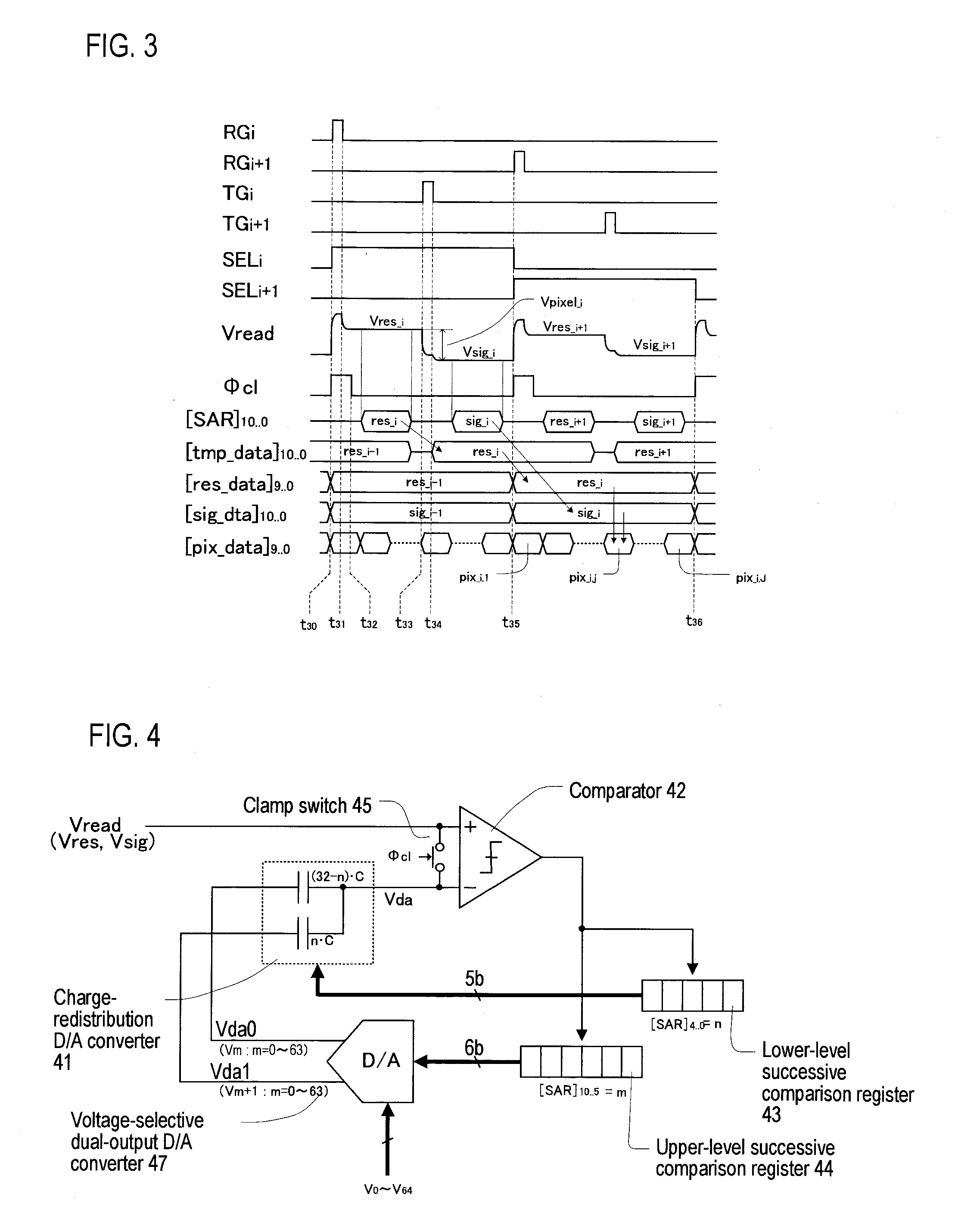
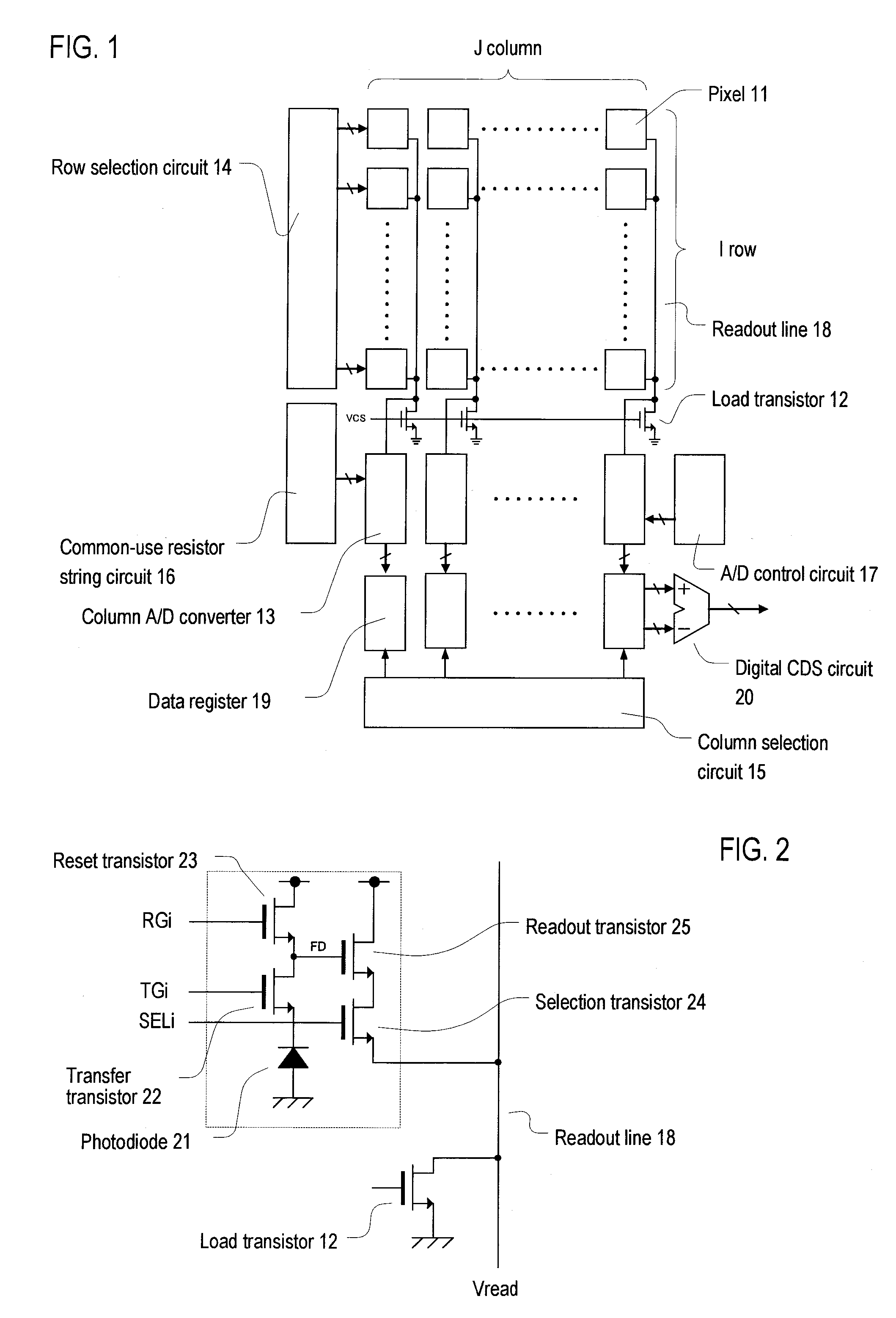
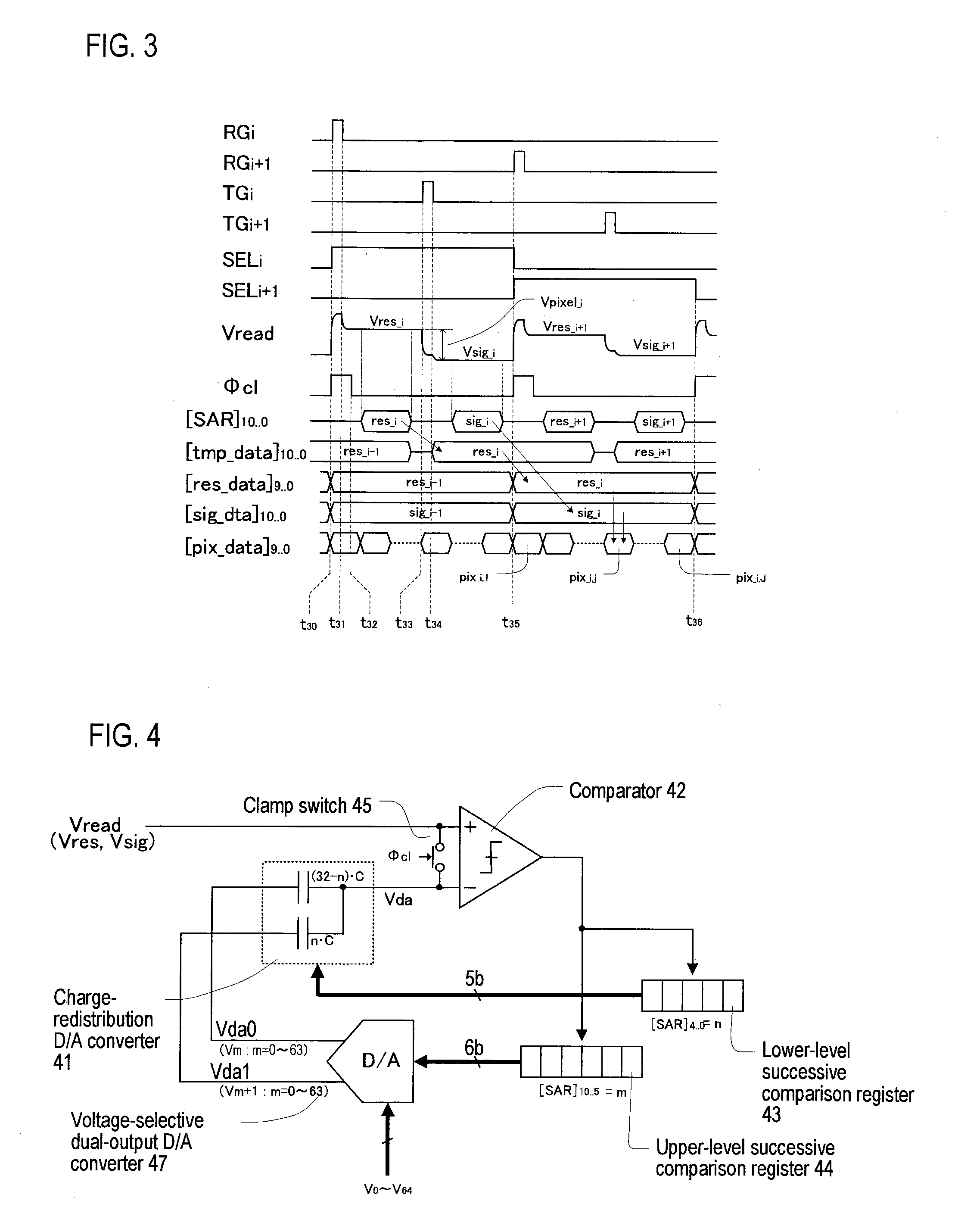
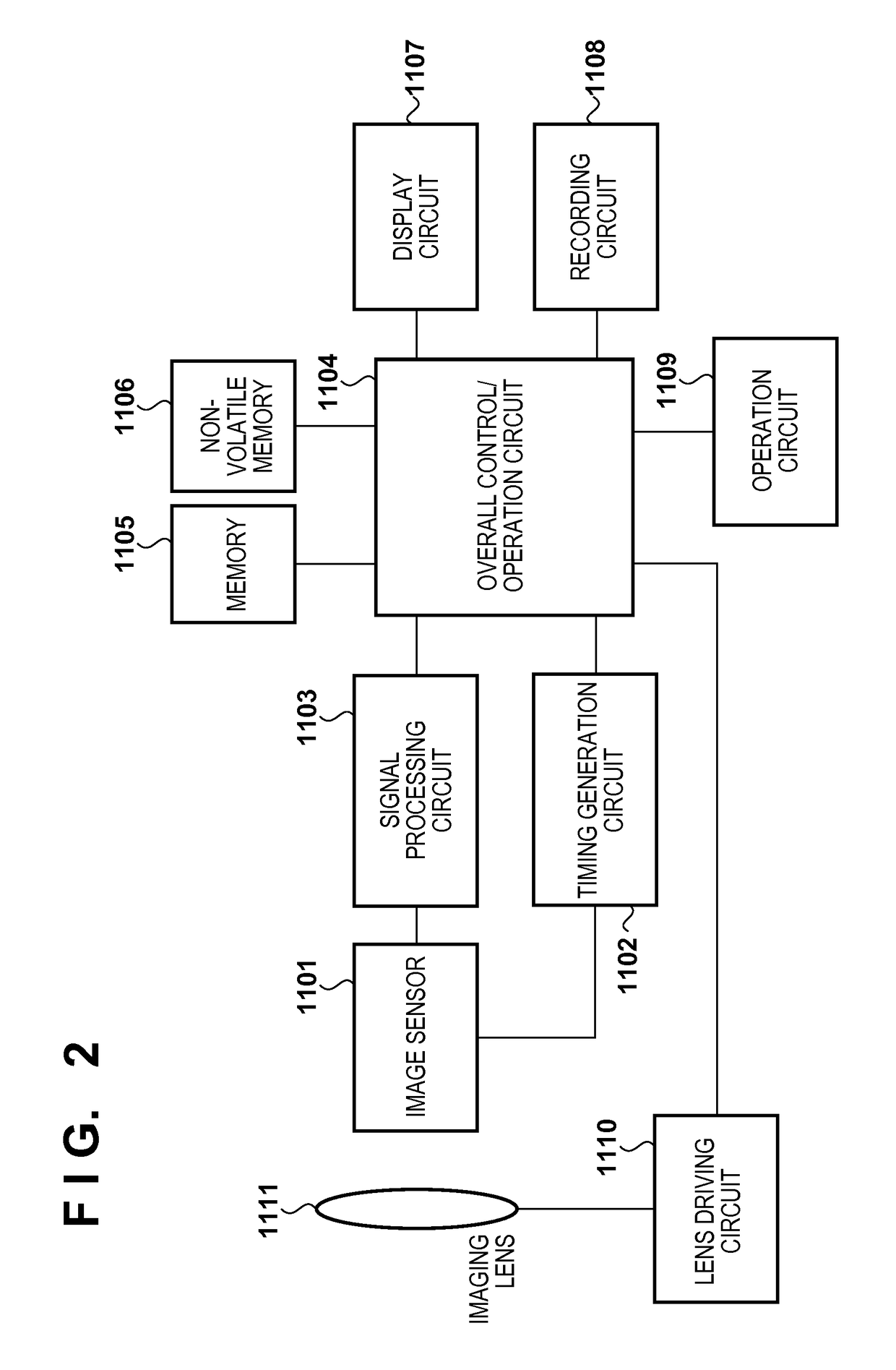
A/d converter unit for image sensor
InactiveUS20110025895A1Reduce in sizeSmall sizeTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsFull scaleVoltage reference
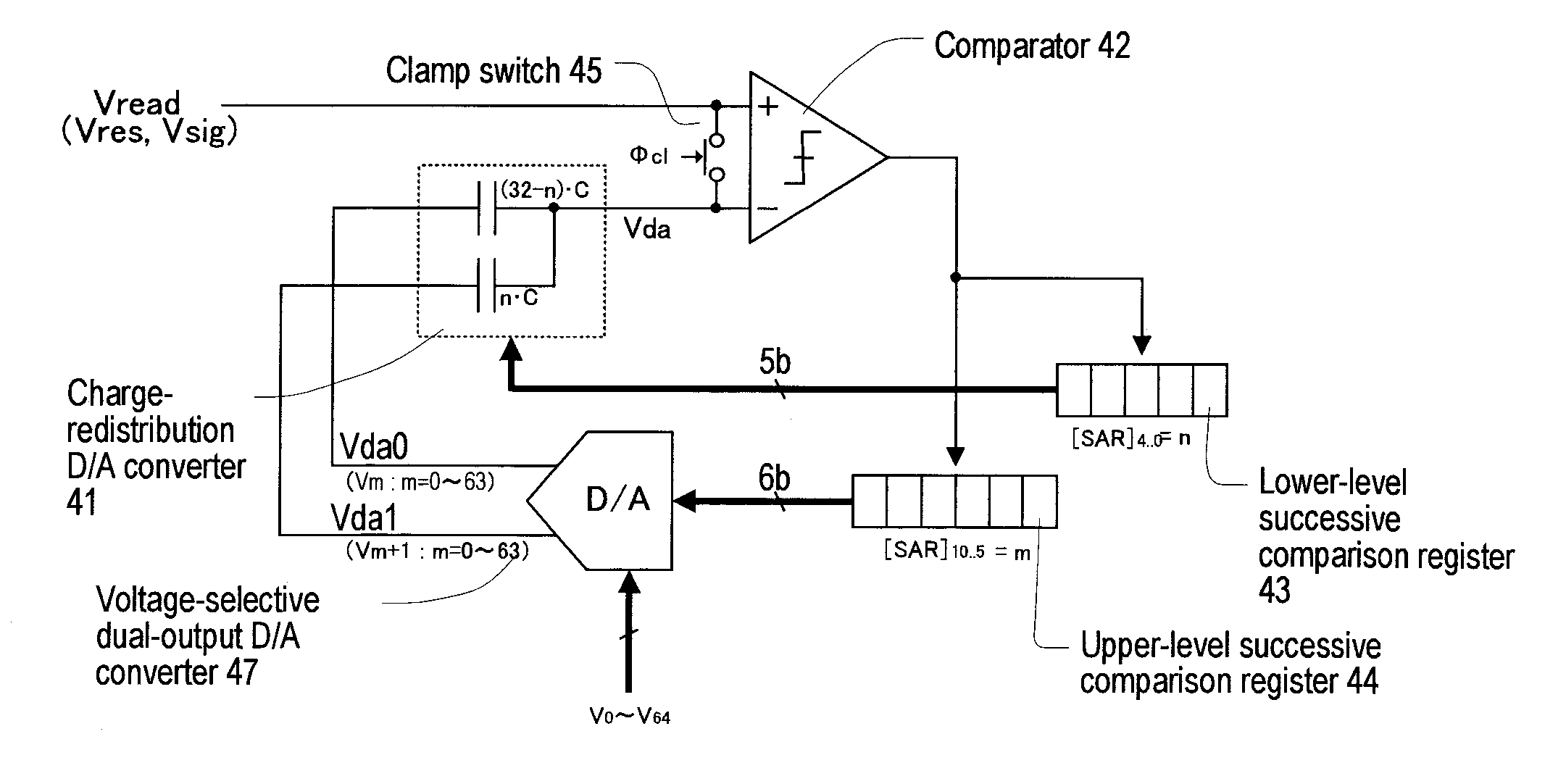
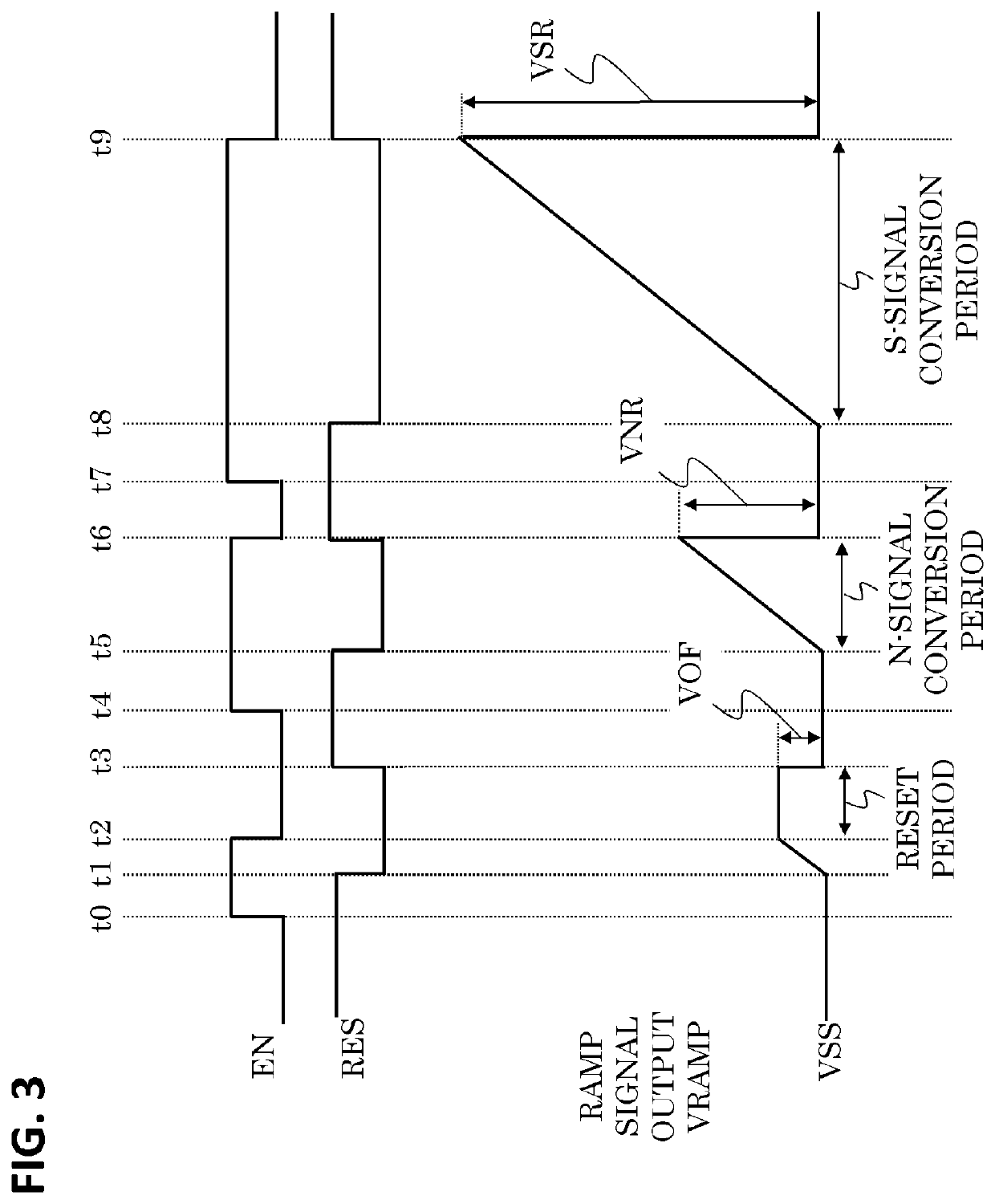
A high-speed, high-resolution column A / D converter having a noise reduction function to eliminate a fixed pattern noise etc. is provided with a small circuit scale. Each column A / D converter includes a dual-output D / A converter for selecting two reference voltages from among a reference voltage group supplied in common to each column A / D converter, so as to output the two reference voltages to sandwich each sensor signal voltage input to each column A / D converter, along with a charge-redistribution D / A converter having a full scale determined by the above two reference voltages. Thus, the high-speed, high-resolution column A / D converter is achieved with a small circuit scale. Further, by the utilization of high-speed conversion capability, noise reduction is performed through digital calculation after the A / D conversion.
Owner:CURIOUS CORP
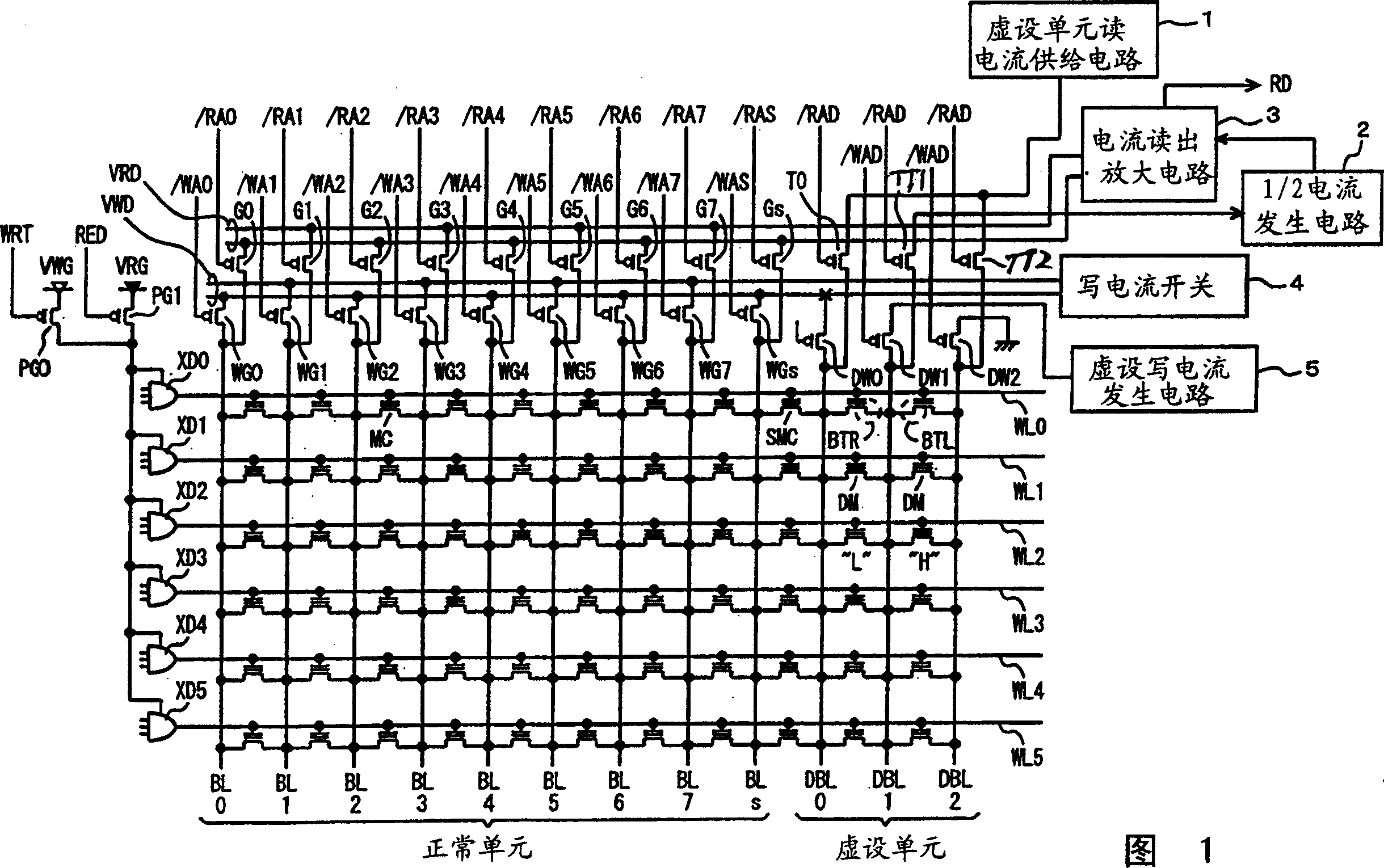
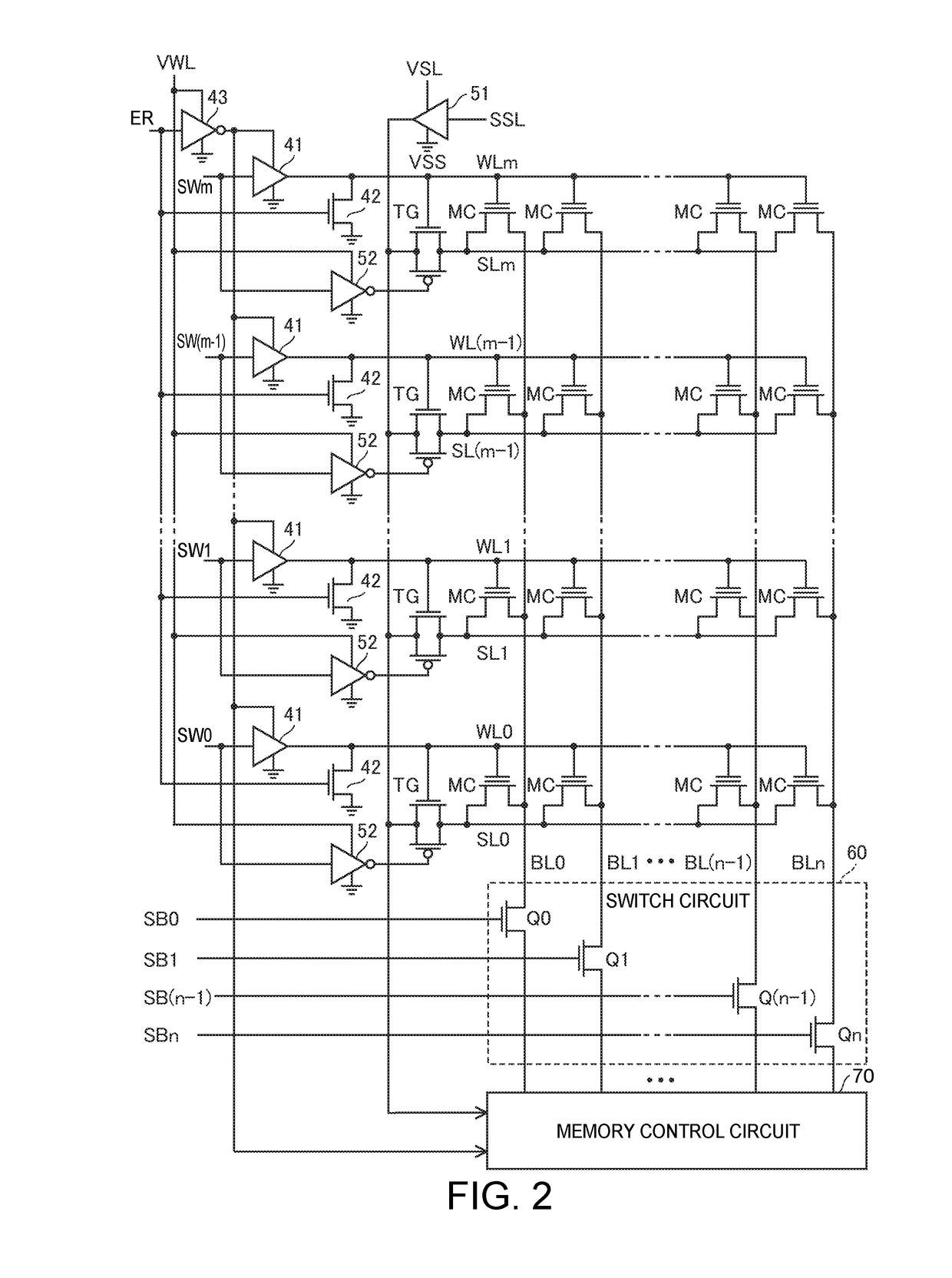
Nonvolatile memory for catching charges in isolative films
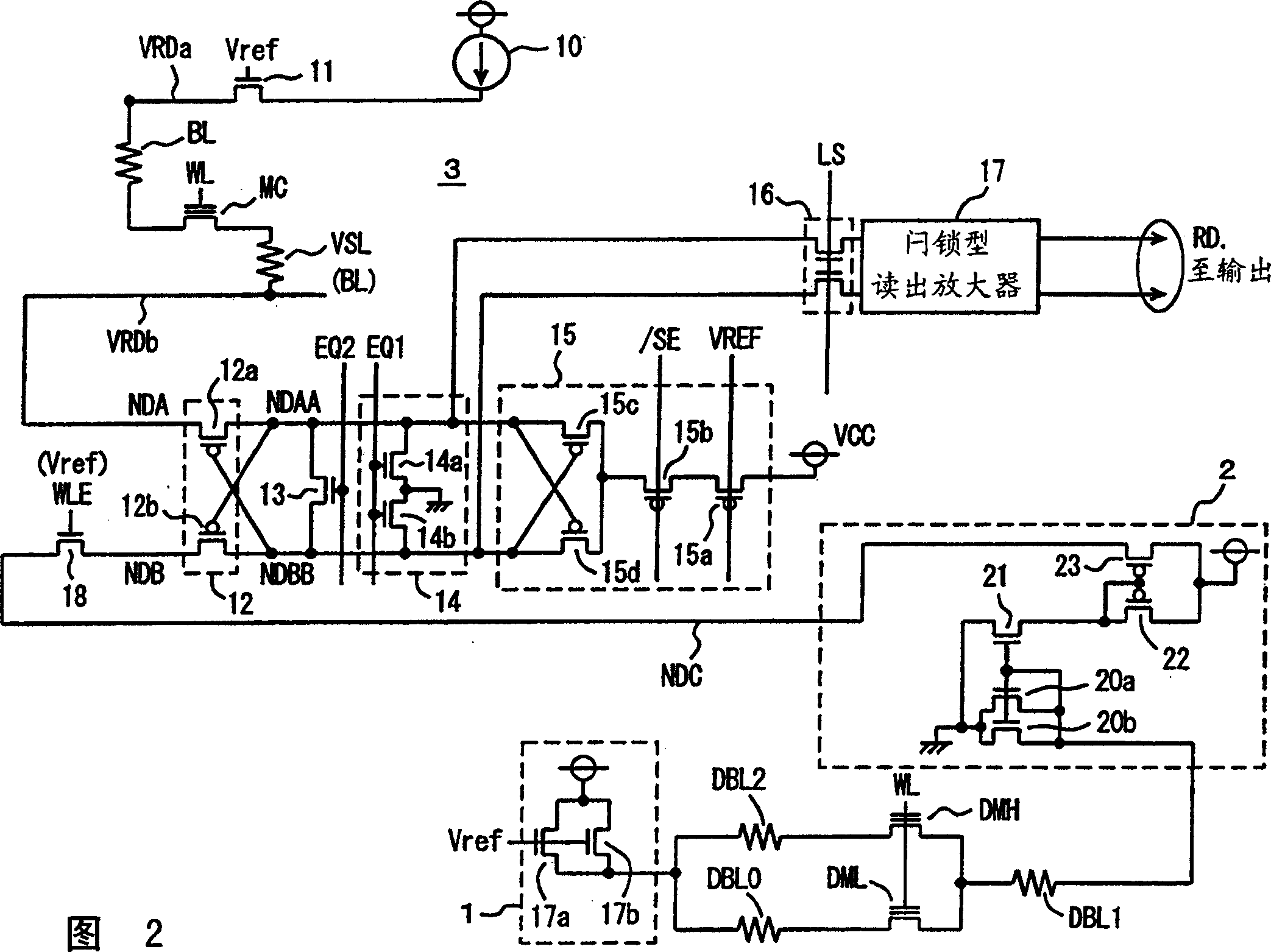
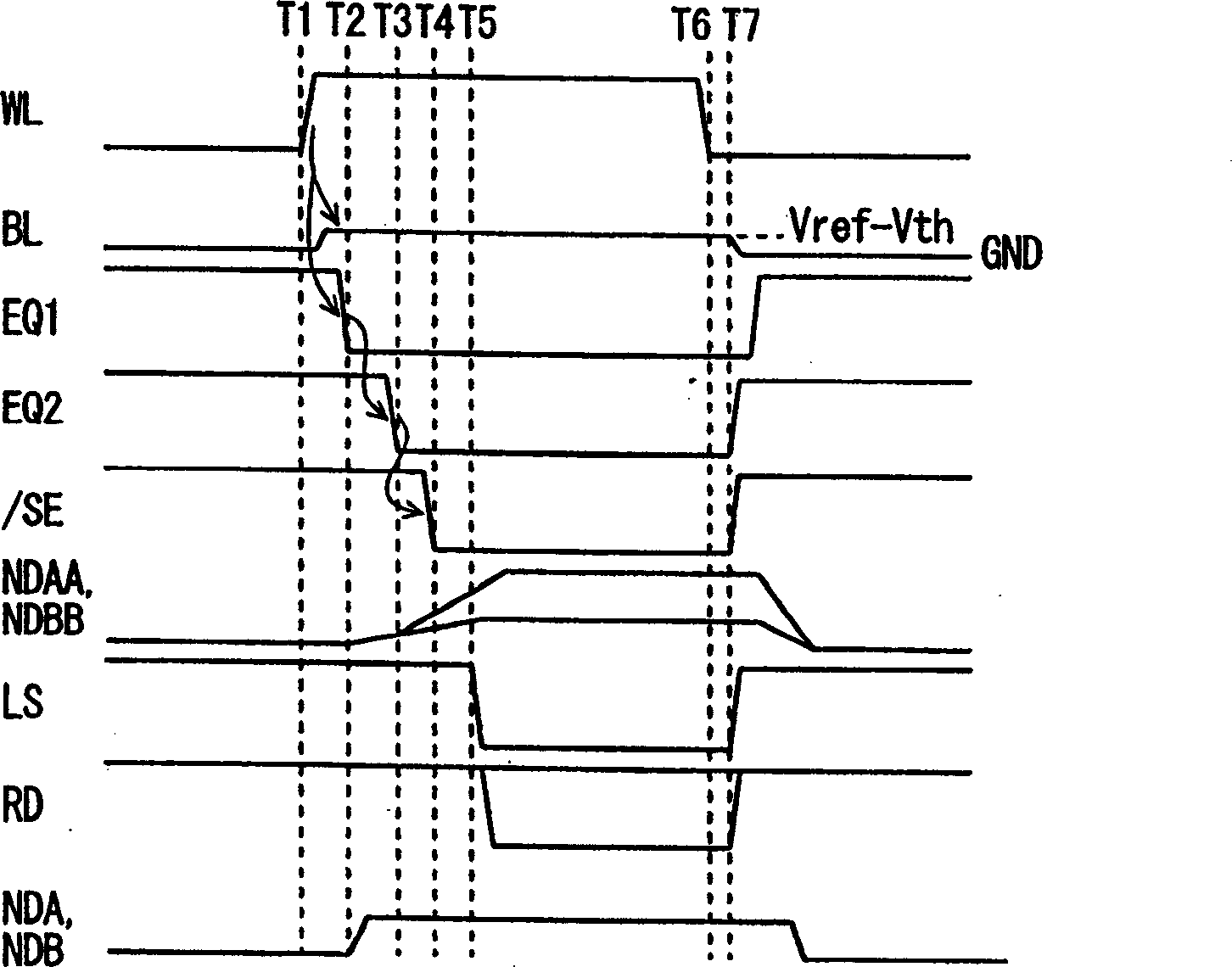
InactiveCN1440038AAccurate detectionHigh speed readoutTransistorSolid-state devicesAverage currentNormal cell
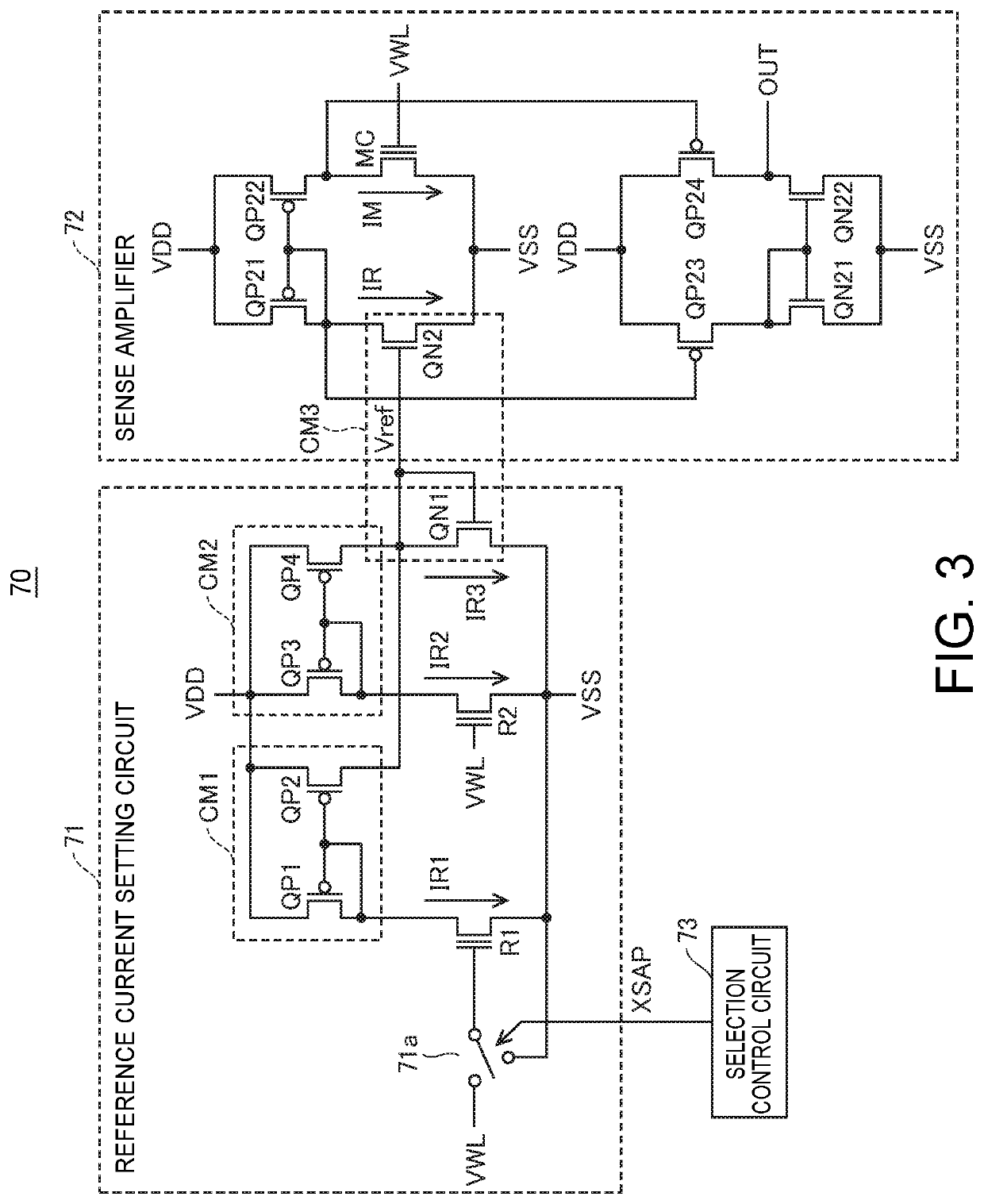
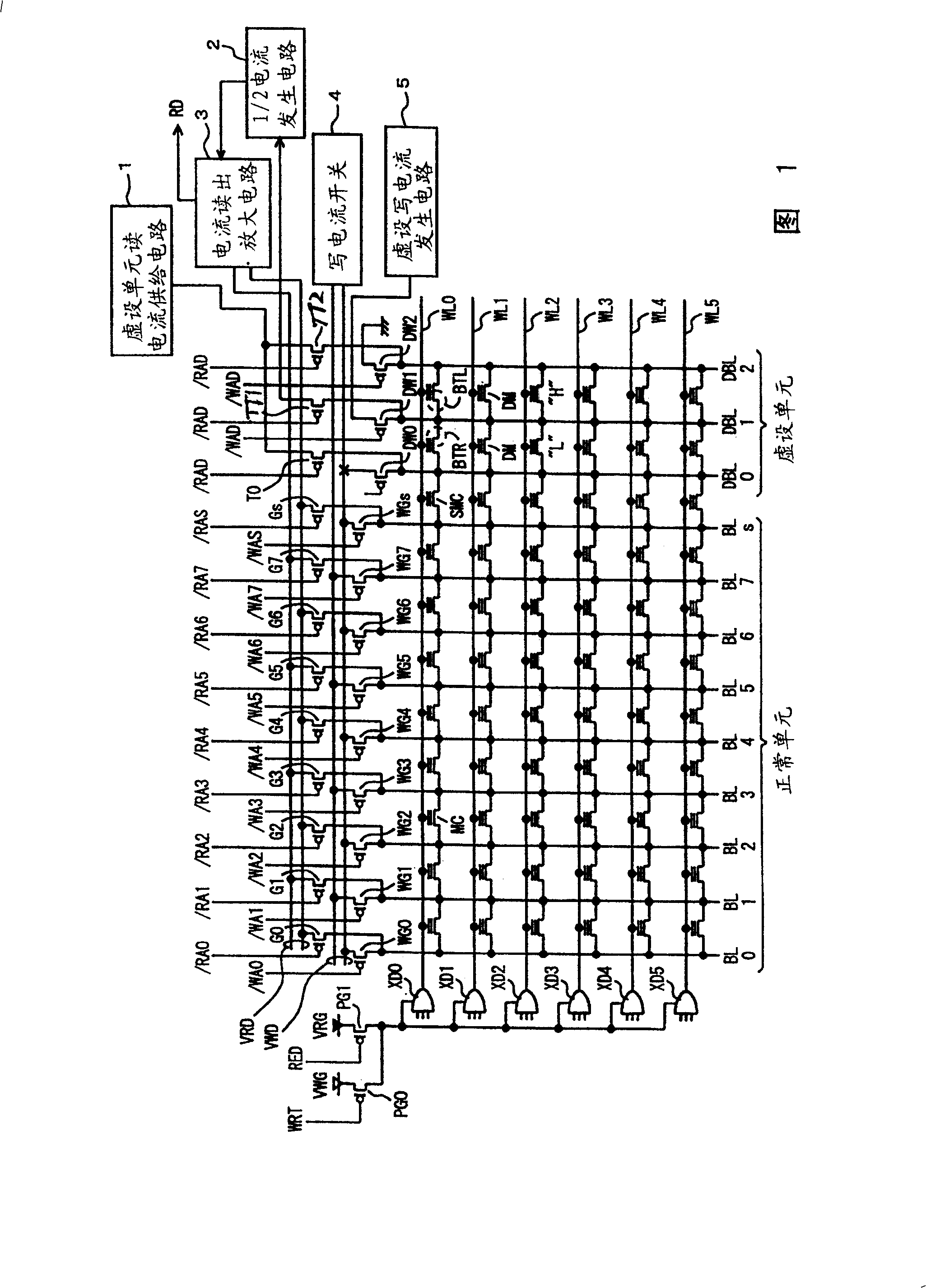
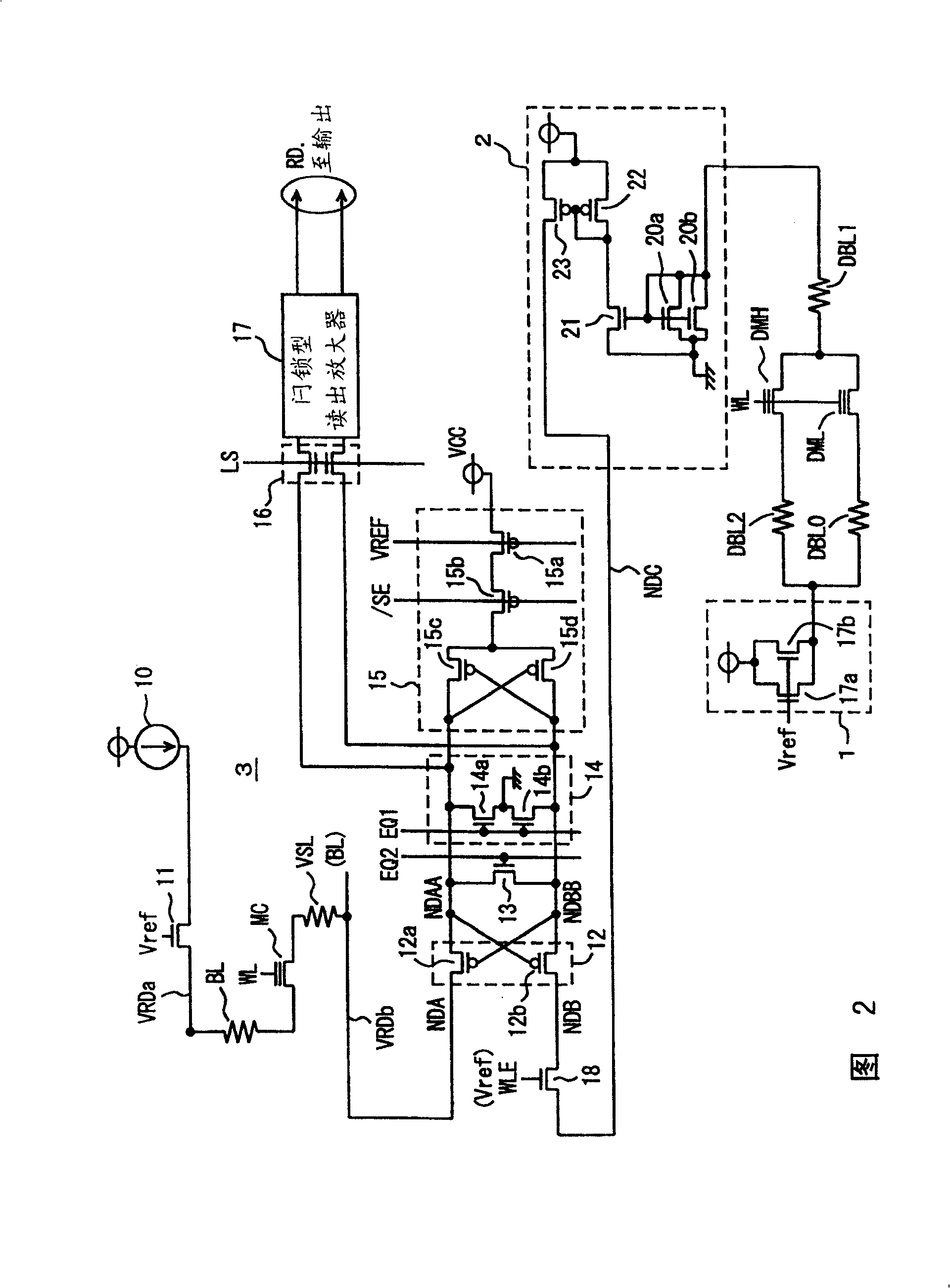
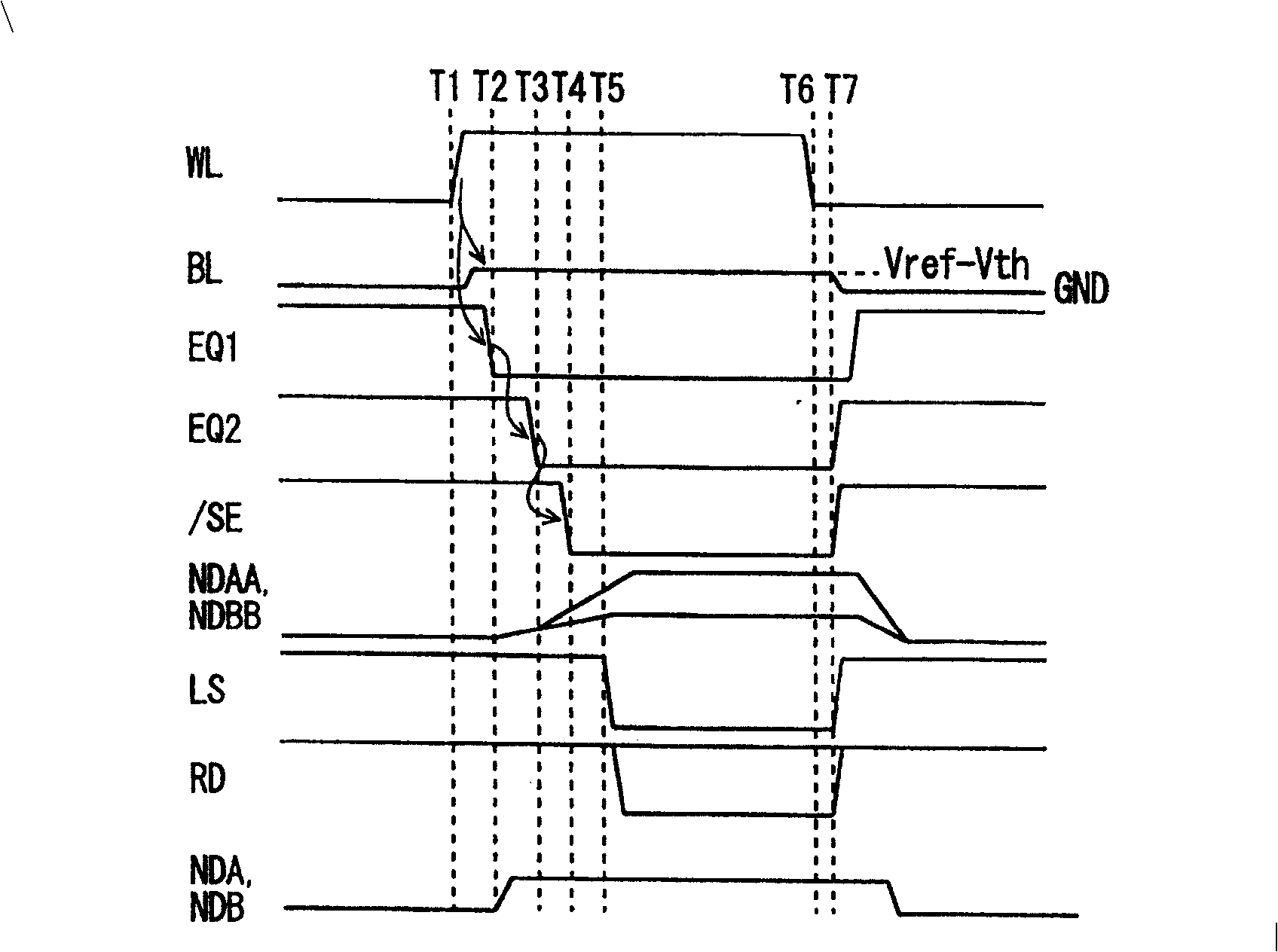
Dummy cells in an erased state and in a write state are used to generate a dummy current corresponding to the average current of currents flowing in the dummy cells using a 1 / 2 current generating circuit, and the dummy current is compared with a current corresponding to a memory cell current flowing in a selected normal cell using a current sense amplification circuit to generate internal read data according to a result of the comparison. With such a configuration, a non-volatile semiconductor memory device capable of reading data at high speed can be achieved.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
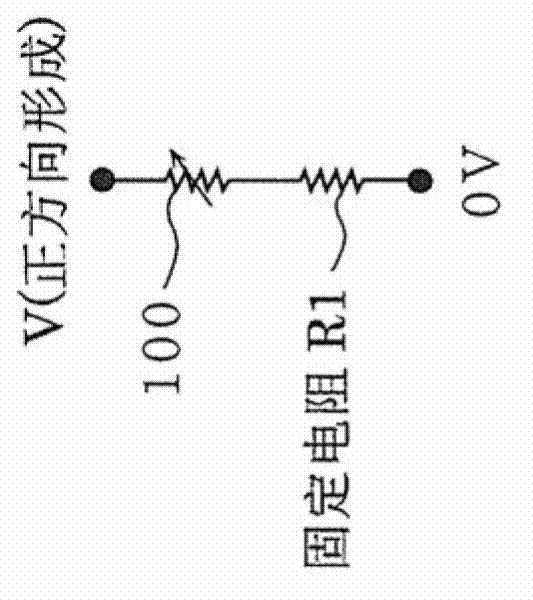
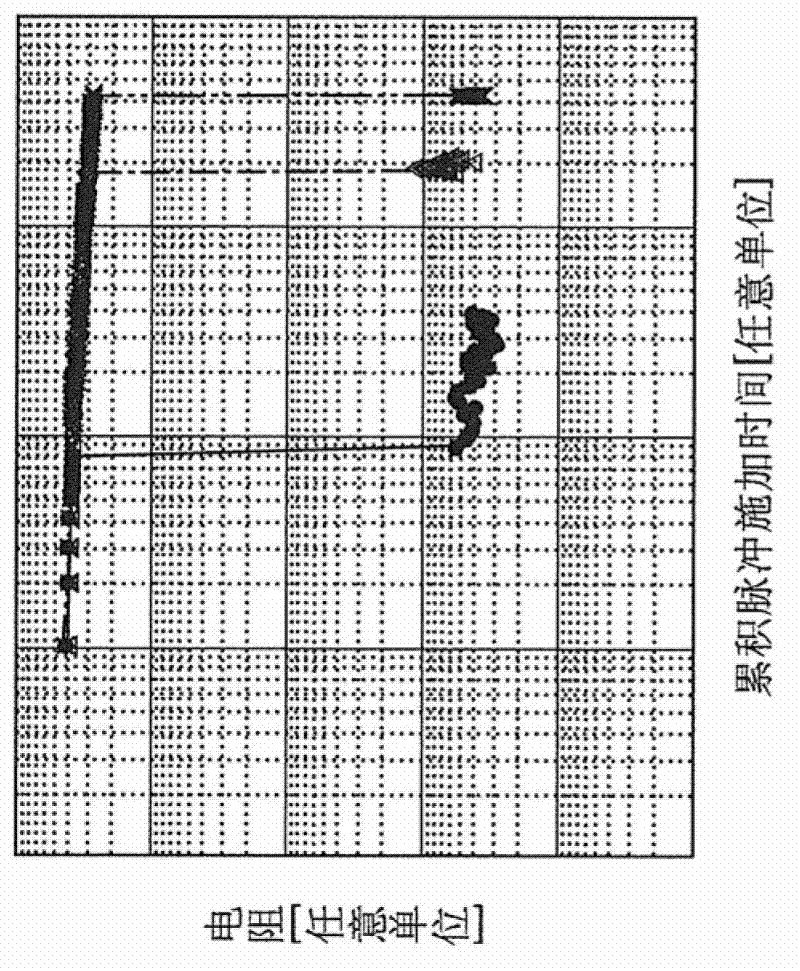
Forming method of performing forming on variable resistance nonvolatile memory element, and variable resistance nonvolatile memory device
ActiveCN102667947AForming high speedAvoid unevennessSolid-state devicesDigital storageElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
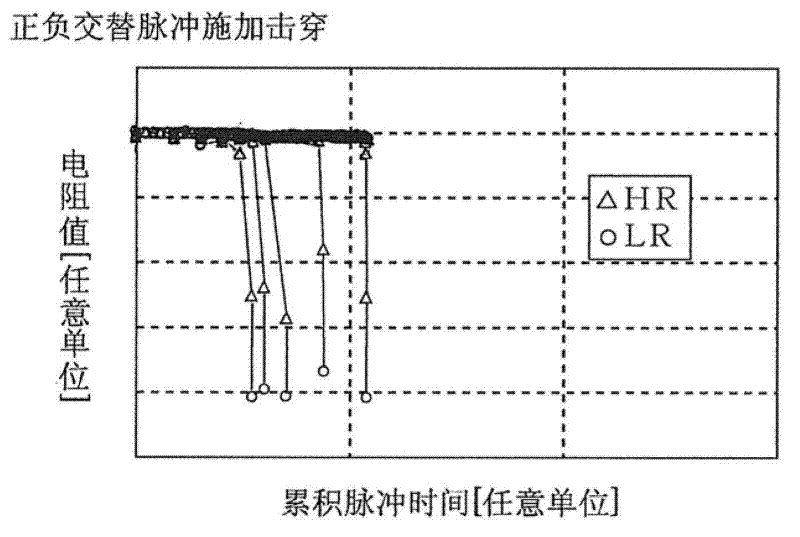
In forming, an automatic forming circuit (210) included in a nonvolatile memory device (200) causes a constant current IL to flow in a selected memory cell having a considerably high initial resistance. When the forming generates a filament path in the memory cell and thereby a resistance value is decreased, a potential of a node NBL and a potential of a node Nin are also decreased. If the potentials become lower than that of a reference voltage Vref, an output NO of a difference amplifier (303) for detecting forming success is activated, and a forming success signal Vfp is activated after a delay time depending on the number n of flip flops FF1 to FFn and a clock signal CLK. Thereby, a switch transistor (301) is in a non-conducting state and the forming on a variable resistance element is automatically terminated.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Nonvolatile memory device, semiconductor device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS10614893B2Improve current supply capabilityShorten the timeRead-only memoriesMemory cellDevice material
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
A/D converter unit for image sensor
InactiveUS8358361B2Small sizeHigh-speed readoutTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsImage resolutionBuck converter
A high-speed, high-resolution column A / D converter having a noise reduction function to eliminate a fixed pattern noise etc. is provided with a small circuit scale. Each column A / D converter includes a dual-output D / A converter for selecting two reference voltages from among a reference voltage group supplied in common to each column A / D converter, so as to output the two reference voltages to sandwich each sensor signal voltage input to each column A / D converter, along with a charge-redistribution D / A converter having a full scale determined by the above two reference voltages. Thus, the high-speed, high-resolution column A / D converter is achieved with a small circuit scale. Further, by the utilization of high-speed conversion capability, noise reduction is performed through digital calculation after the A / D conversion.
Owner:CURIOUS CORP
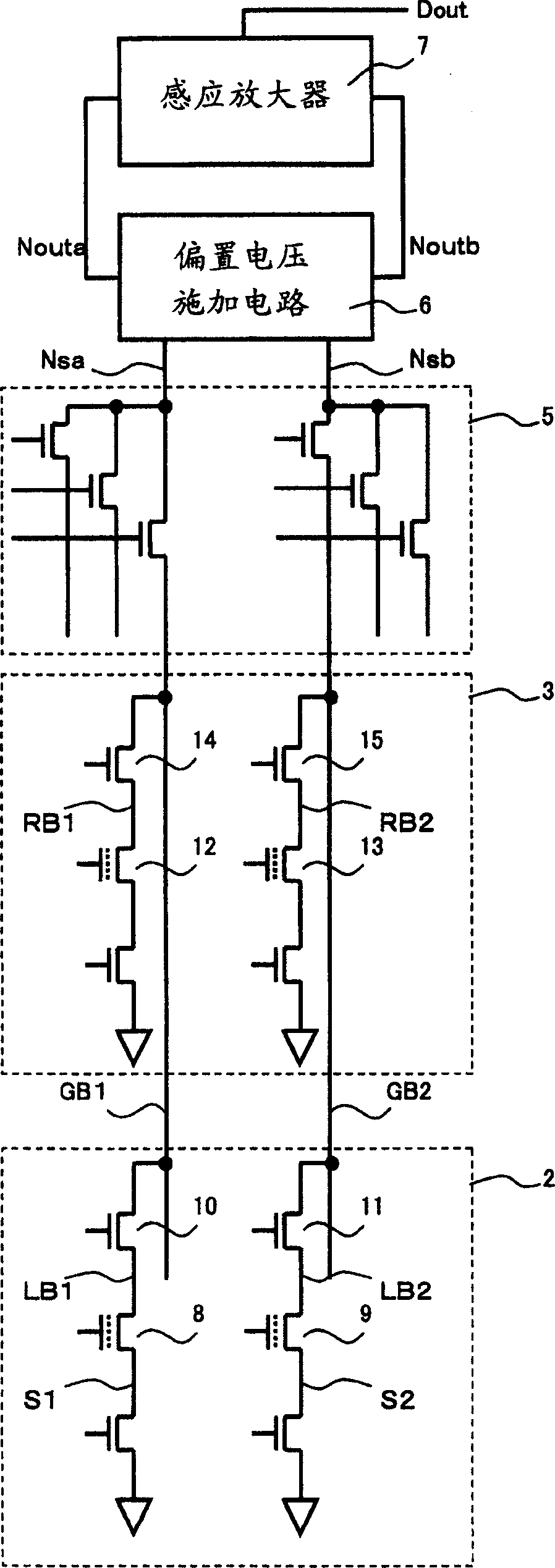
Bias voltage applying circuit and semiconductor memory device
InactiveCN1655281ASuppression DiscreteHigh speed readoutRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsEngineering
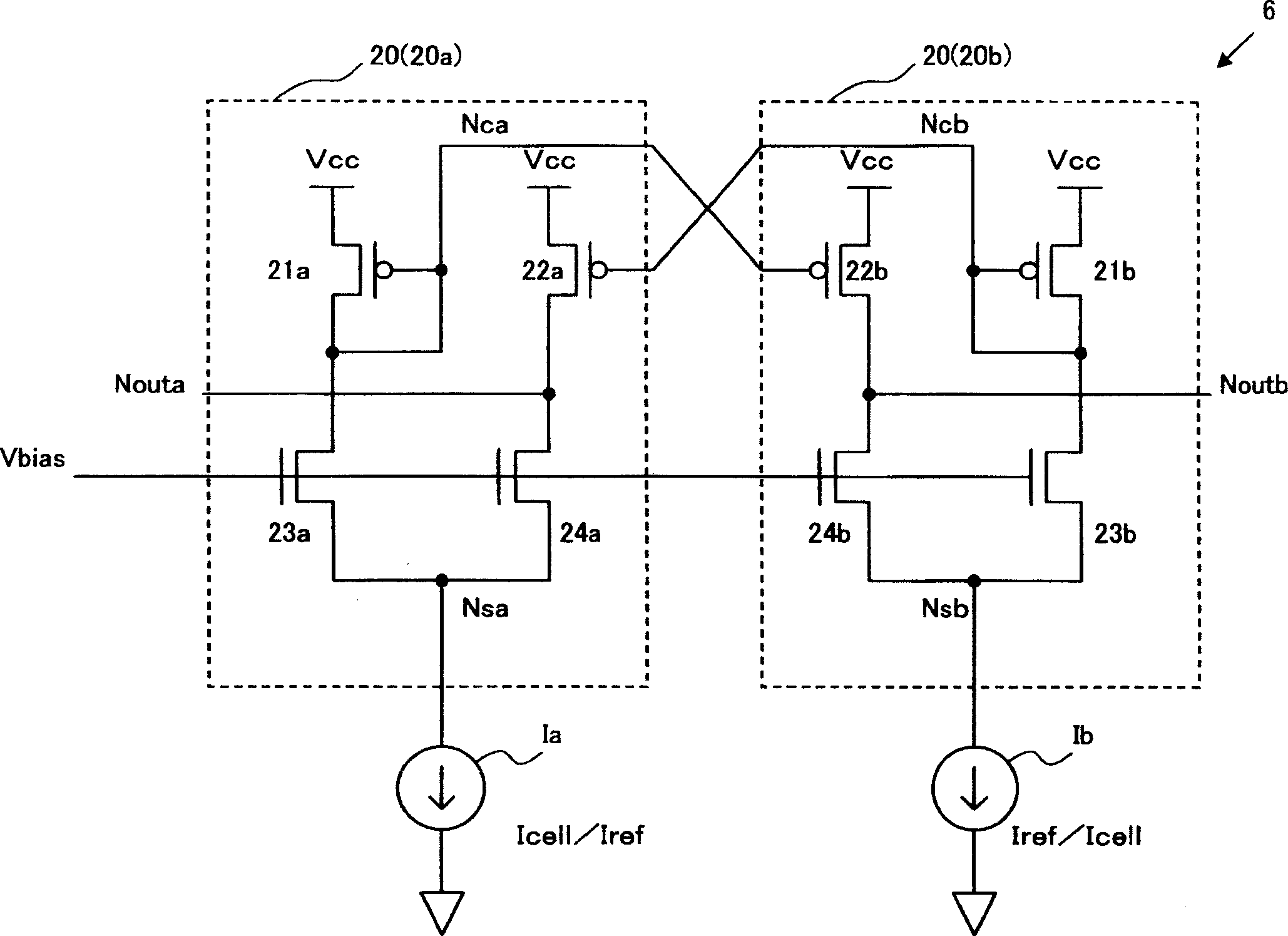
Two bias circuits (20) which supply a current to a selected memory cell and a reference memory cell have the same circuit constitution. Each bias circuit includes a first active element (21a, 21b) between a power supply node Vcc and a junction node (Nca, Ncb), where a current is controlled to prevent a voltage level at the junction node from fluctuating, a second active element (22a, 22b) between the power supply node and an output node (Nouta, Noutb), where a current is controlled such that a voltage level at the output node is changed in direction opposite to a voltage level at the junction node in other bias circuit, a third active element (23a, 23b) and a fourth active element (24a, 24b) between the junction node and a current supply node Nsa (Nsb) and between the output node and the current supply node, respectively, where a bias voltage is adjusted.
Owner:SHARP KK
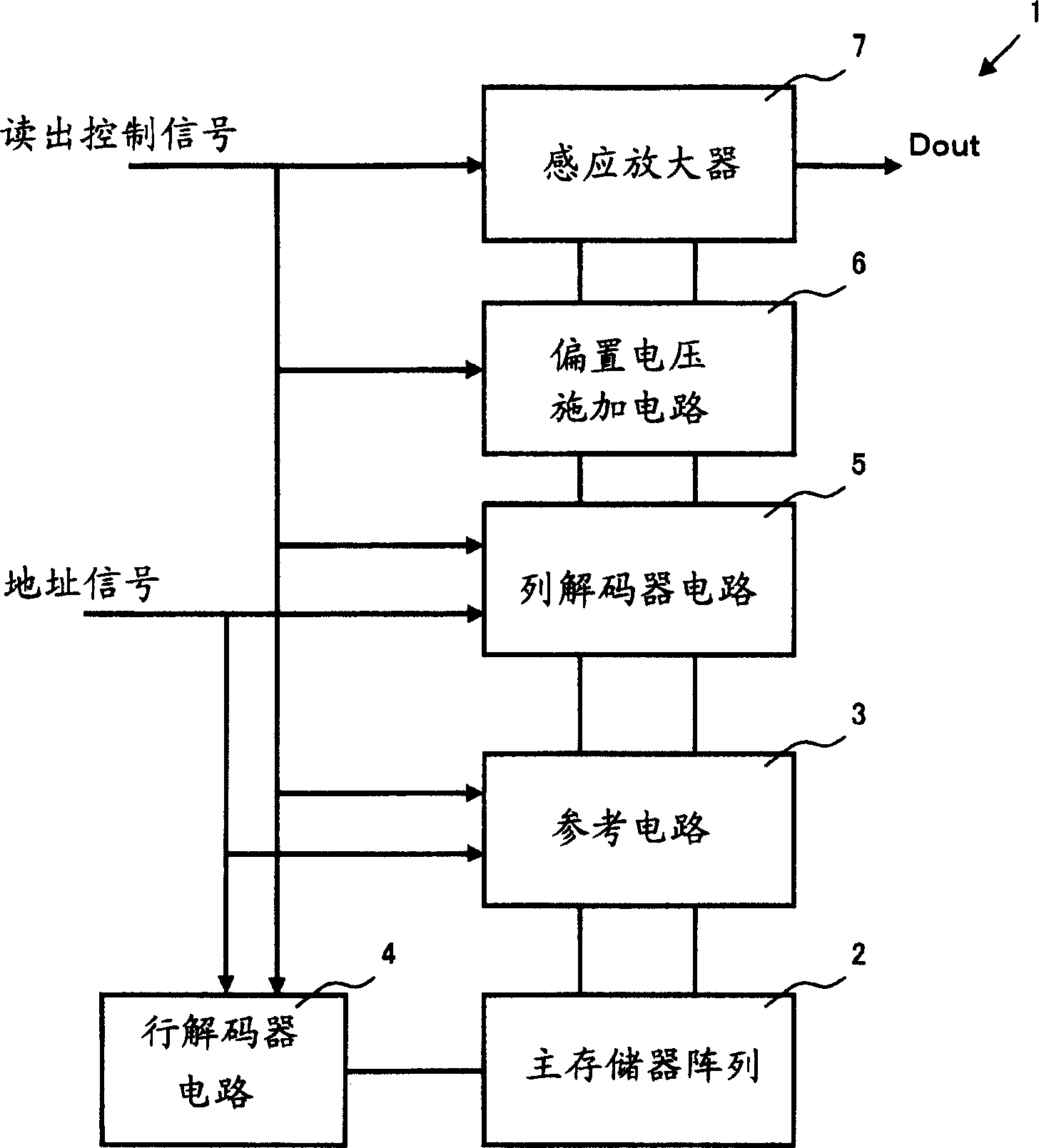
Readout circuit for semiconductor storage device
InactiveUS20060158945A1Reduce areaReduce consumptionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor storage devicesComputer science
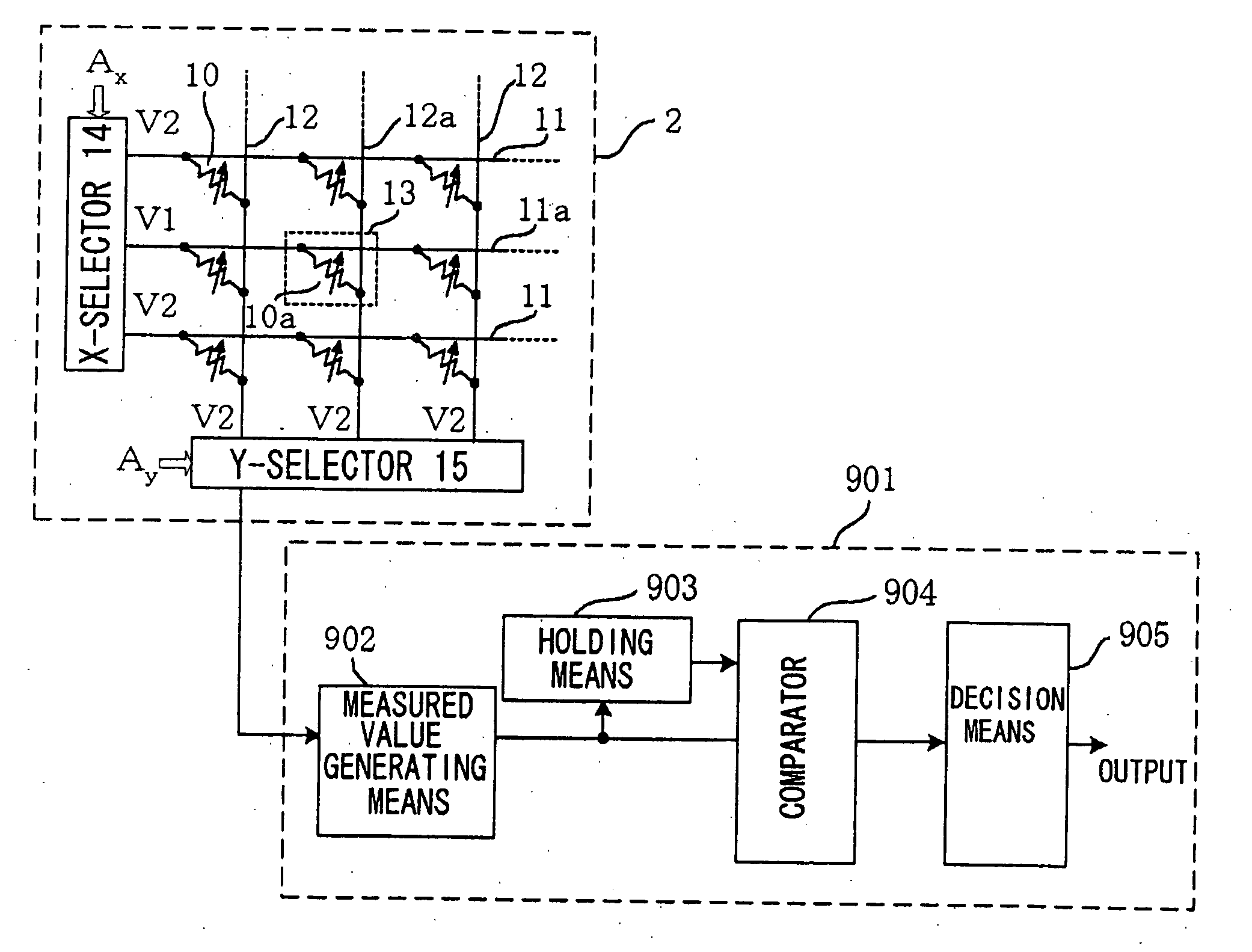
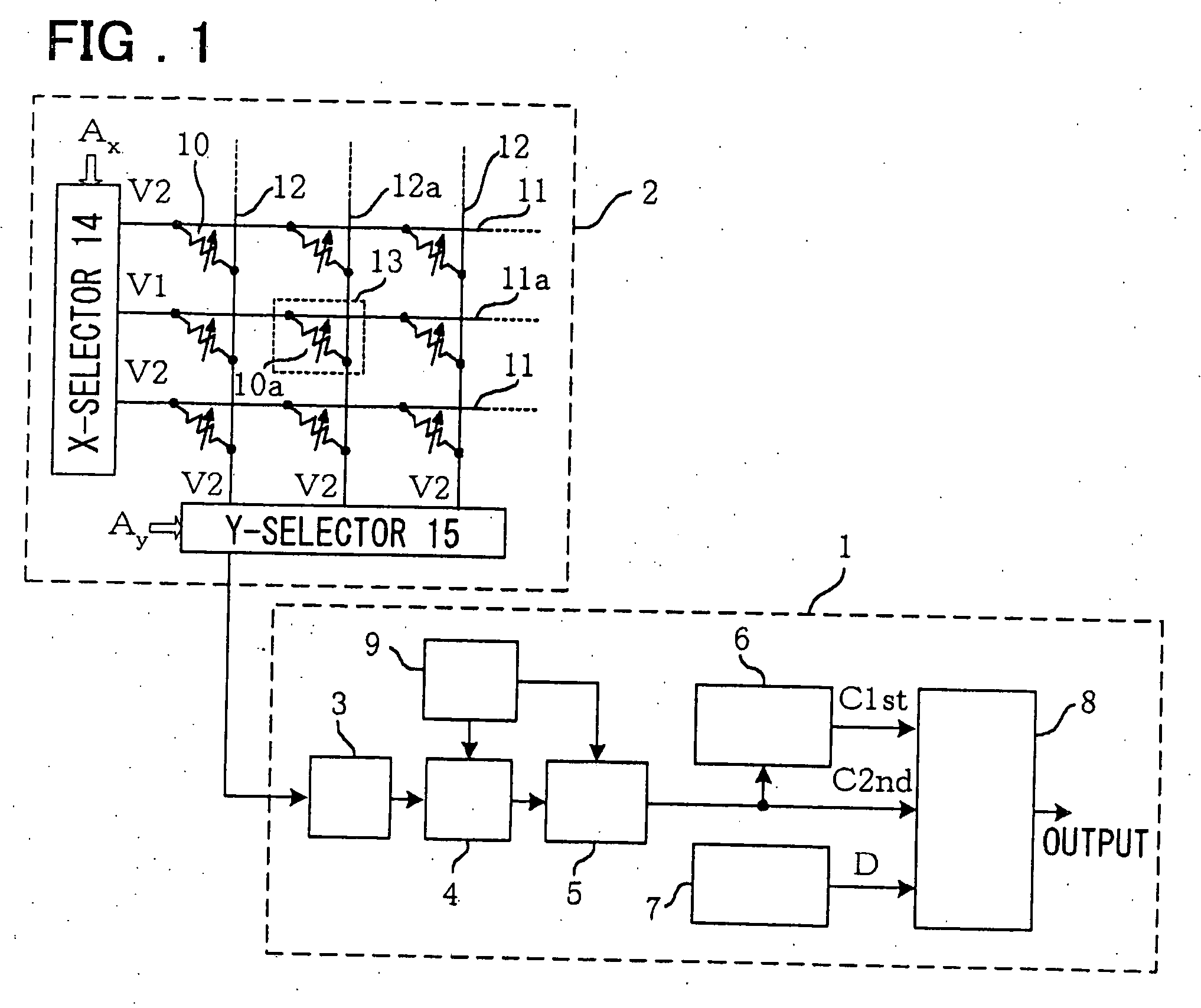
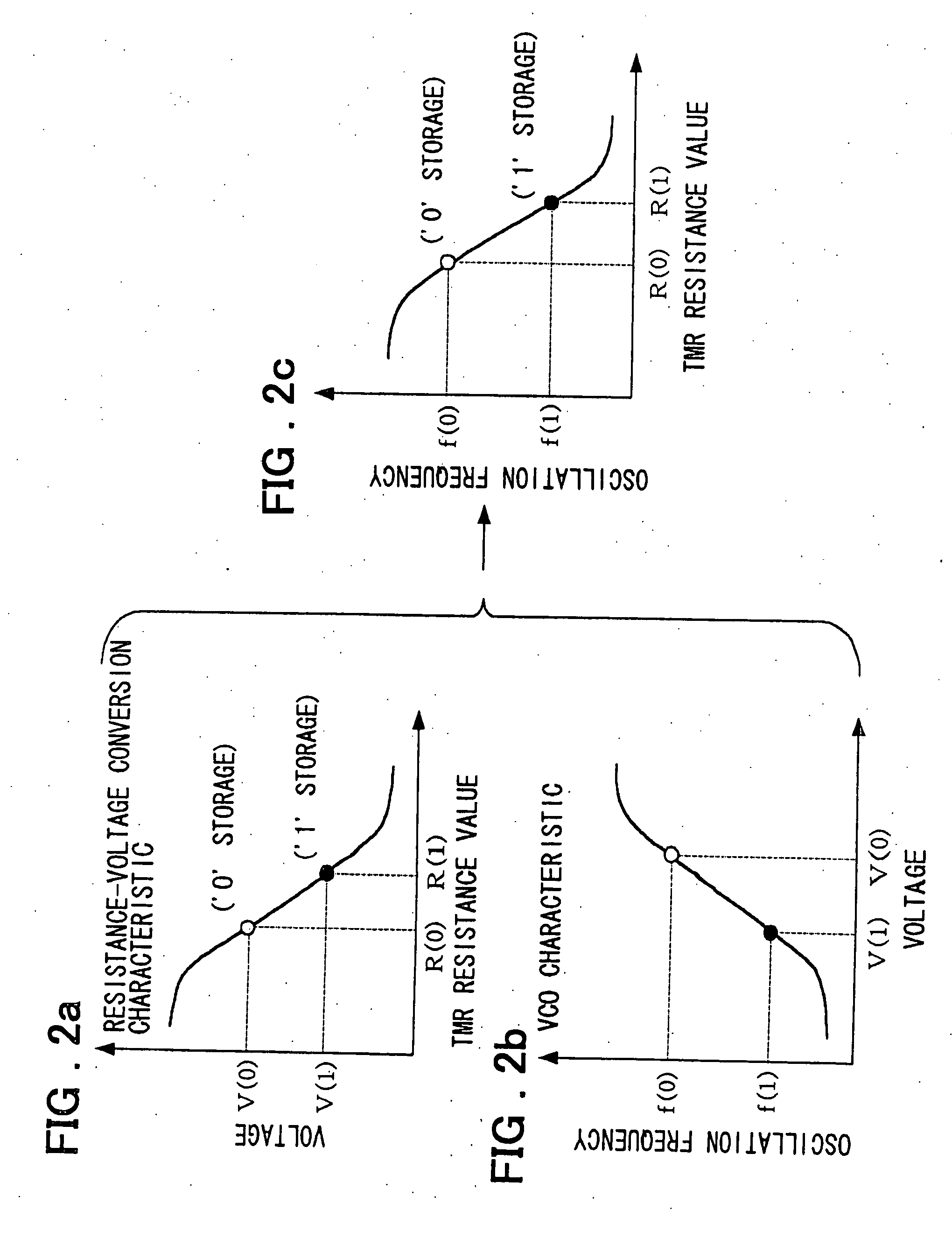
By first readout, the current input from a selected cell 13 is converted by a preamplifier 3 and a VCO 4 into pulses of a frequency inversely proportionate to the current value, and the number of the pulses within a preset time interval is counted by a counter 5 so as to be stored in a readout value register 6. A selected cell is then written to one of two storage states, and second readout is then carried out. The storage state of the selected cell is verified by comparing a count value of the counter for the second readout, a count value for the first readout as stored in a readout value register and a reference value stored in a reference value register 7 to one another. By the use of the VCO, the integrating capacitor for the current or reference pulse generating means, so far needed, may be eliminated to assure a small area, low power consumption and fast readout.
Owner:NEC CORP
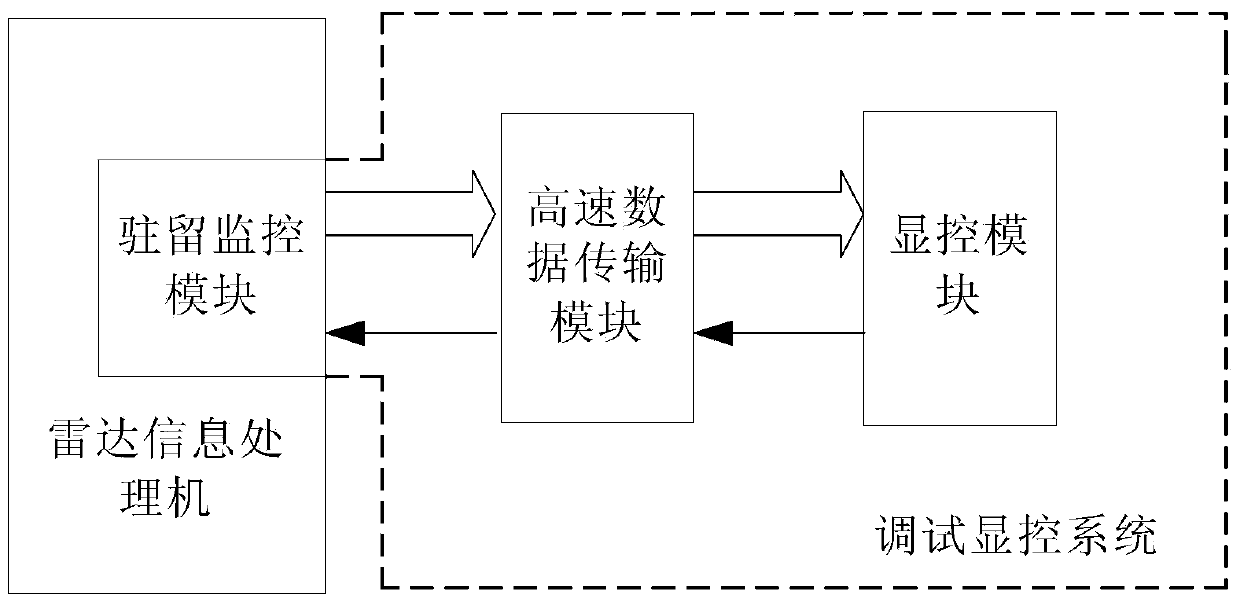
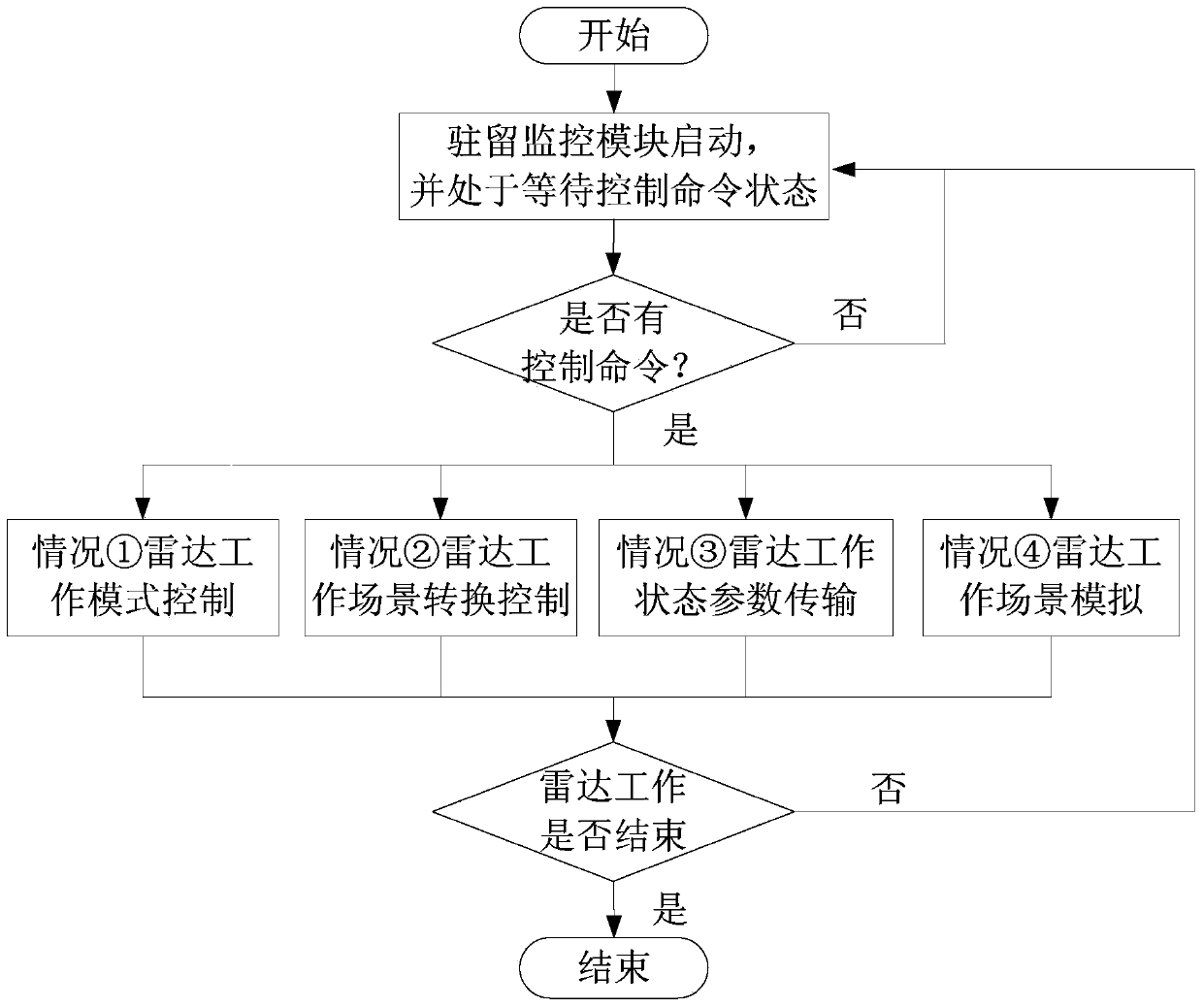
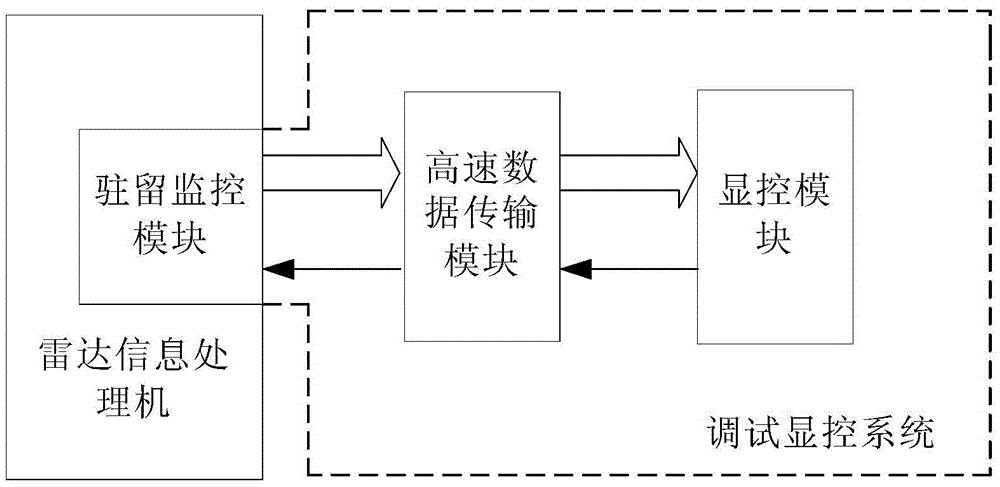
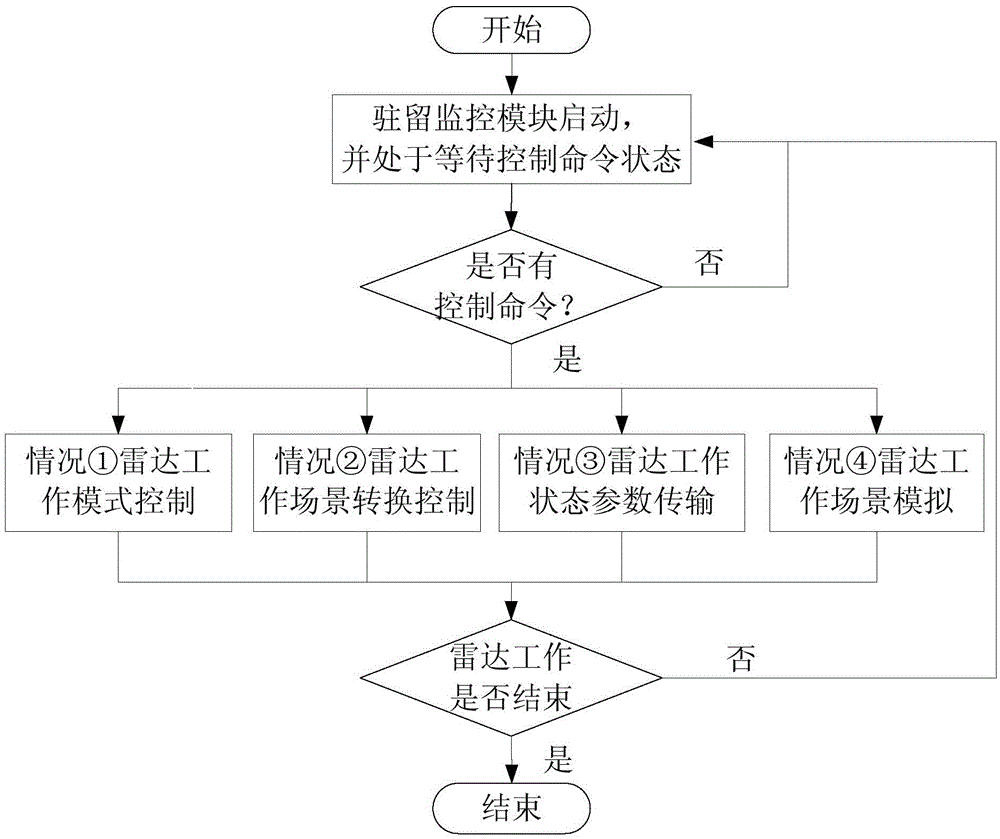
Debugging and display controlling system of radar information processor
ActiveCN103744315AEnable coherent debuggingRealize controlWave based measurement systemsProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersTest efficiencyControl system
The invention provides a debugging and display controlling system of a radar information processor. The debugging and display controlling system comprises a high-speed data transmission module, a display control module and a resident monitoring module, wherein the resident monitoring module is mounted on the radar information processor; the display control module is used for receiving external input task requirements and sending corresponding control commands, the control commands are transmitted to the resident monitoring module through the high-speed data transmission module, and the resident monitoring module responds to the control commands, carries out corresponding operations on the radar information processor and uploads operation results to the display control module through the high-speed data transmission module. According to the debugging and display controlling system, the coherence debugging and display controlling for the radar information processor can be realized, the real-time performance and coherence of the radar information processor are verified, and the test efficiency of the radar information processor is increased.
Owner:西安导引科技有限责任公司
Nonvolatile memory device, semiconductor device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20180336952A1Improve current supply capabilityShorten the timeRead-only memoriesElectrical batteryReference current
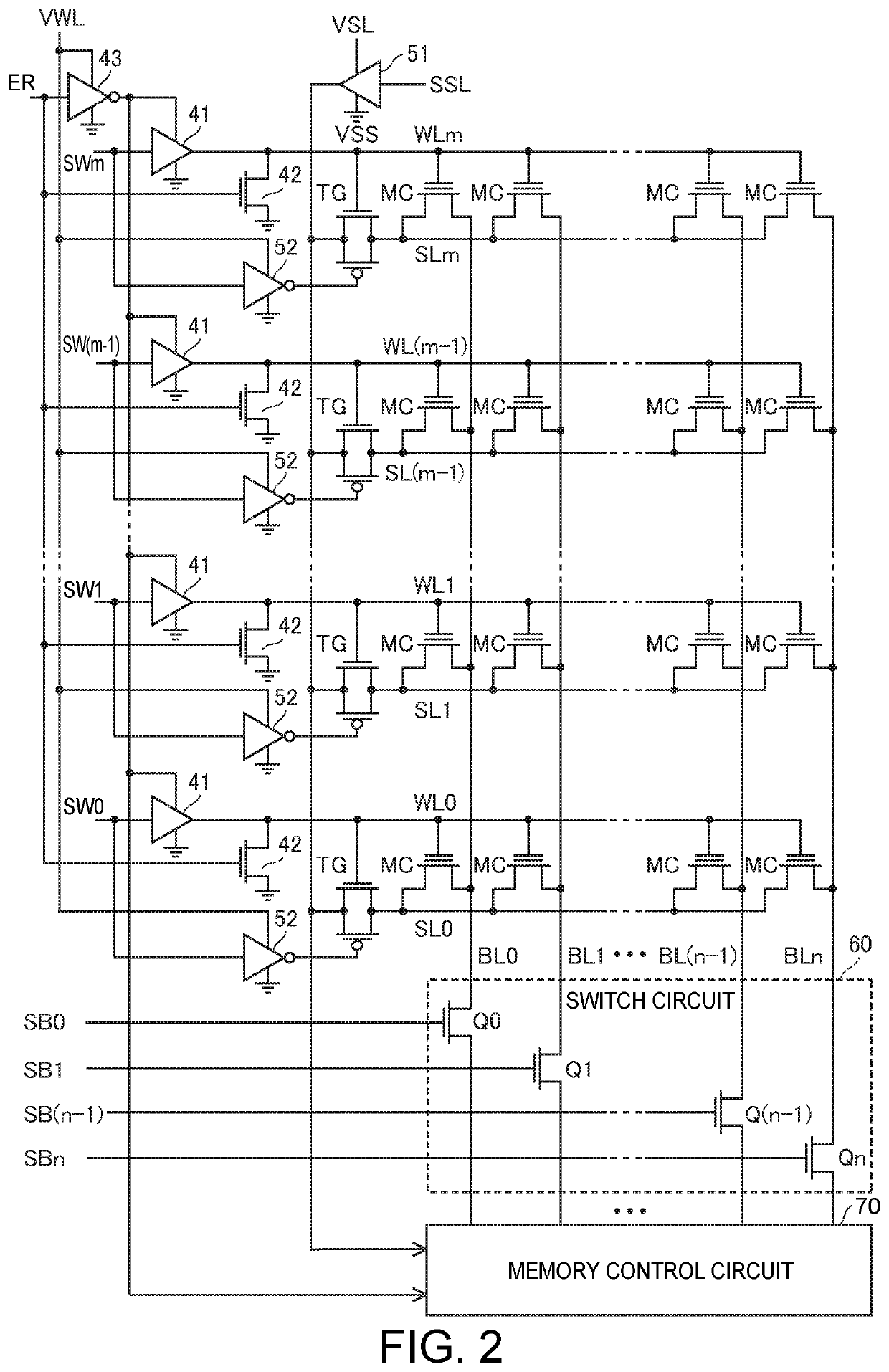
A nonvolatile memory device includes: a first reference cell; a second reference cell; a circuit that generates a first mirror current proportional to a current flowing through the first reference cell; a circuit that generates a second mirror current proportional to a current flowing through the second reference cell; a sense amplifier that reads out data by comparing a current flowing through a memory cell with a reference current; and a selection circuit that sets a selection state of the first reference cell and the second reference cell such that, in a readout mode, the reference current is generated based on at least the first mirror current, and in a verify mode, the reference current is generated based on the second mirror current.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Rapid reading out system and method of holographic data storage
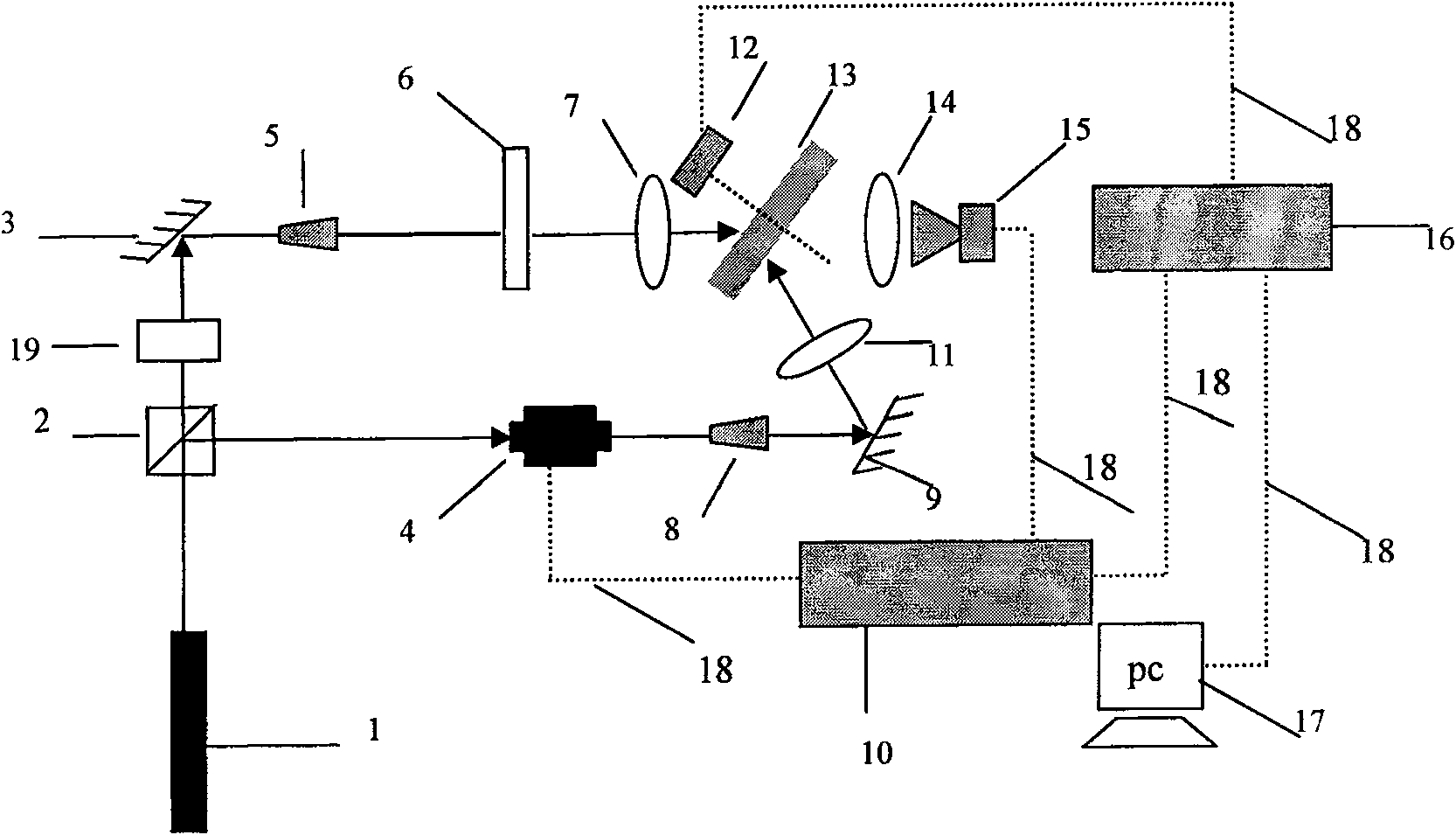
InactiveCN101290781AHigh speed readoutOptical beam guiding meansRecording/reproducing/erasing using optical interference patternsAcquisition apparatusOptical storage
The invention relates to a quick read out system and a method of holographic data storage, belonging to the optical storage technical field. The quick read out method is as follows: firstly, a plurality of holograms are recorded at intervals on a holographic medium; then, the high-speed read out of the holograms is realized by means of the synchronous working among precise addressing equipment, an electro-optical switch and high-speed image collection equipment in the state of high-speed motion of the holographic medium. Because the quick read out system of holographic data storage is designed by the method, and consists of a microdrive positioning controller, a pulse generator, high-speed precise addressing equipment, an electro-optical switch, high-speed image collection equipment, a laser and a necessary optical element, the holographic medium is in a high-speed motion state all the time during continuously reading out a plurality of holograms, thereby realizing continuous high-speed read out of the holograms.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
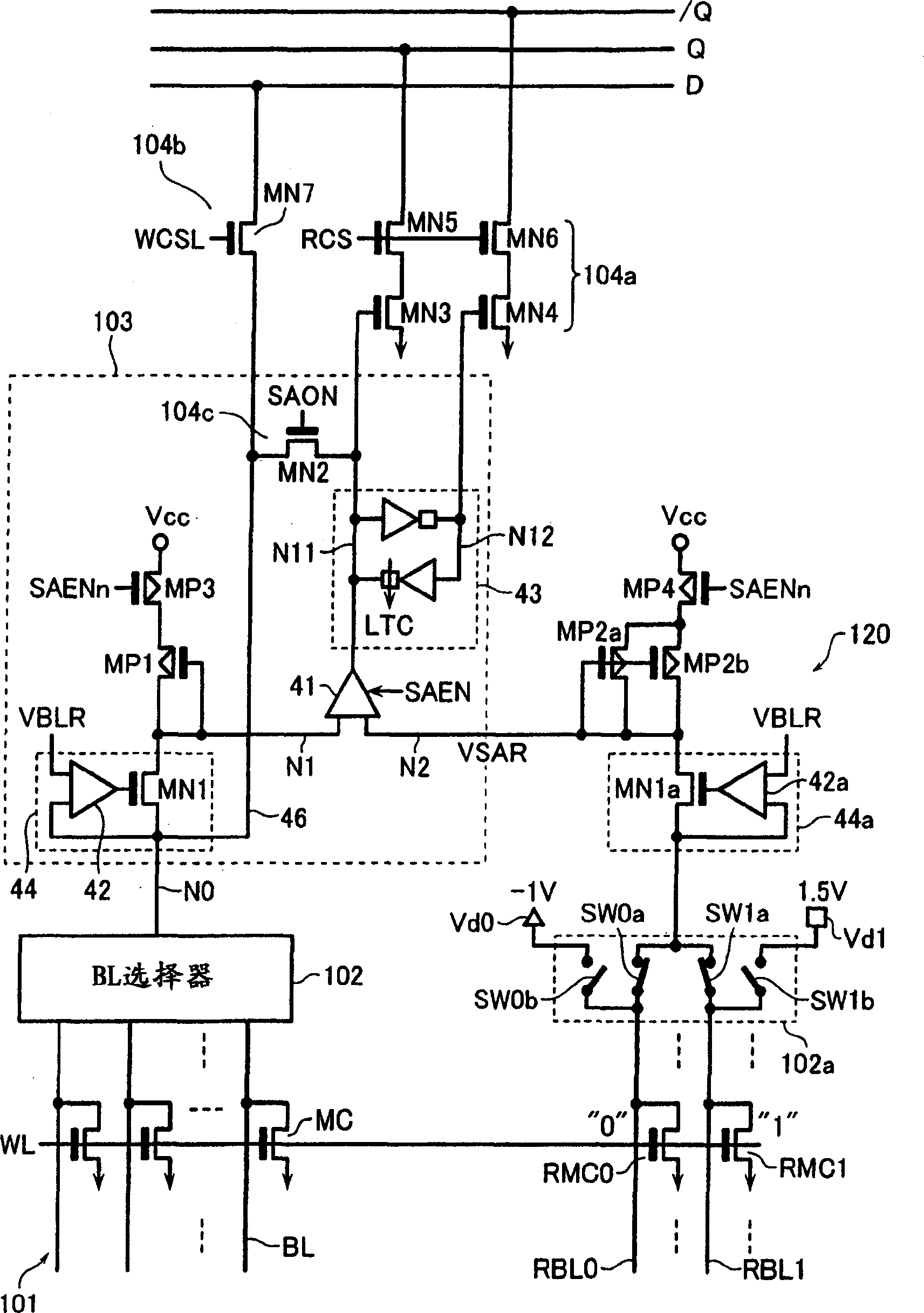
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveCN1551363AHigh speed readoutTransistorSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierUnit structure
A semiconductor memory device includes: a device substrate having a semiconductor layer separated by a dielectric layer from a base substrate; a memory cell array having a plurality of memory cells formed and arranged on the semiconductor layer of the device substrate, each the memory cell having a MOS transistor structure with a body in an electrically floating state to store data based on a majority carrier accumulation state of the body; and a sense amplifier circuit configured to read out data of a selected memory cell in the memory cell array to store the read data in a data latch, then transfer the read data to an output circuit and write back the read data into the selected memory cell.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device
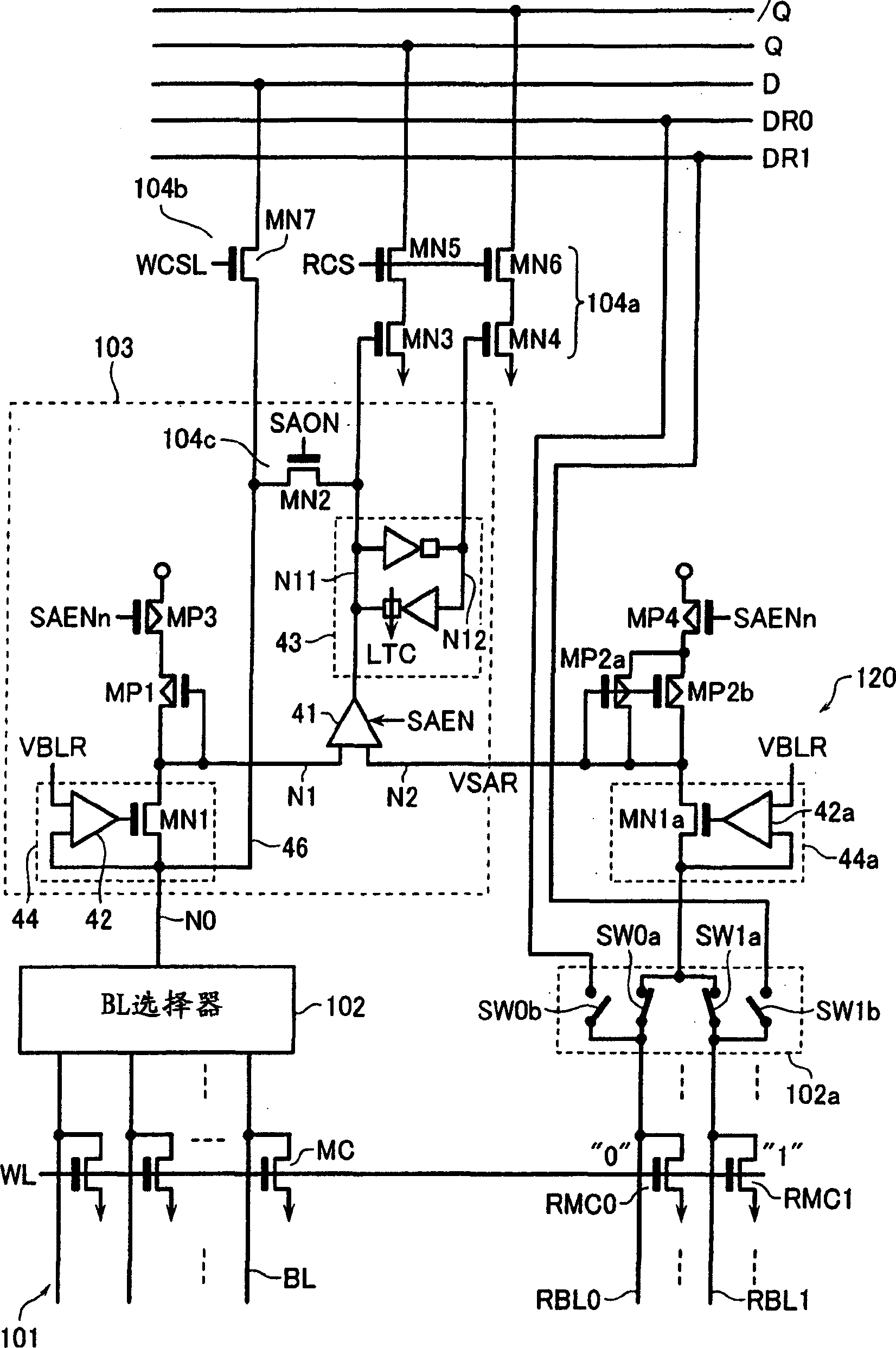
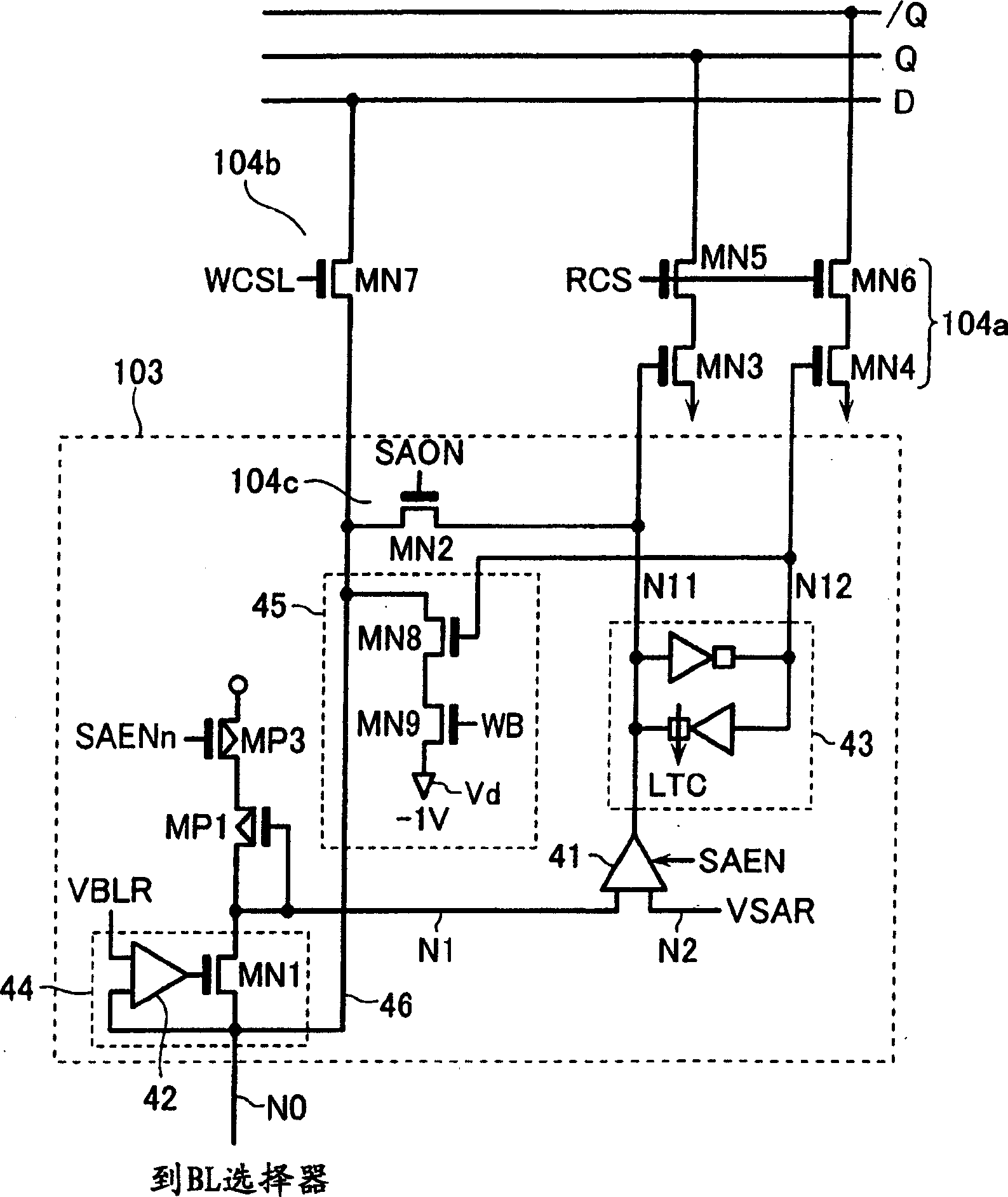
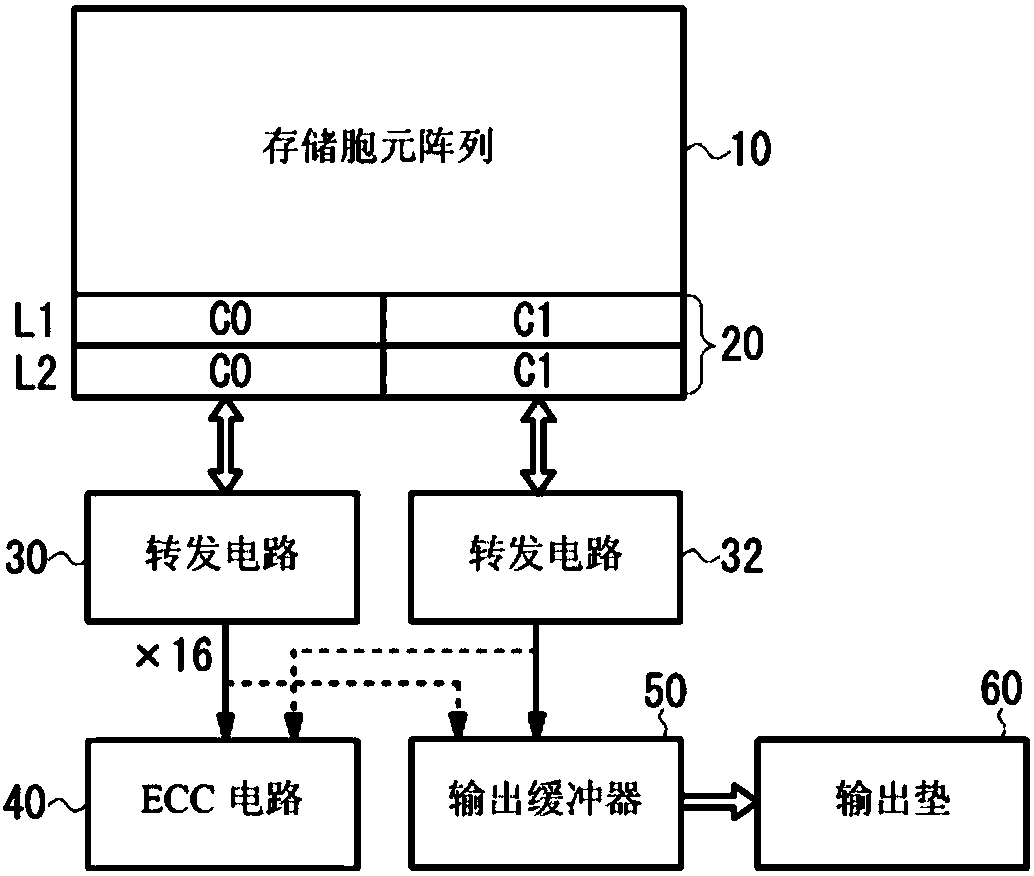
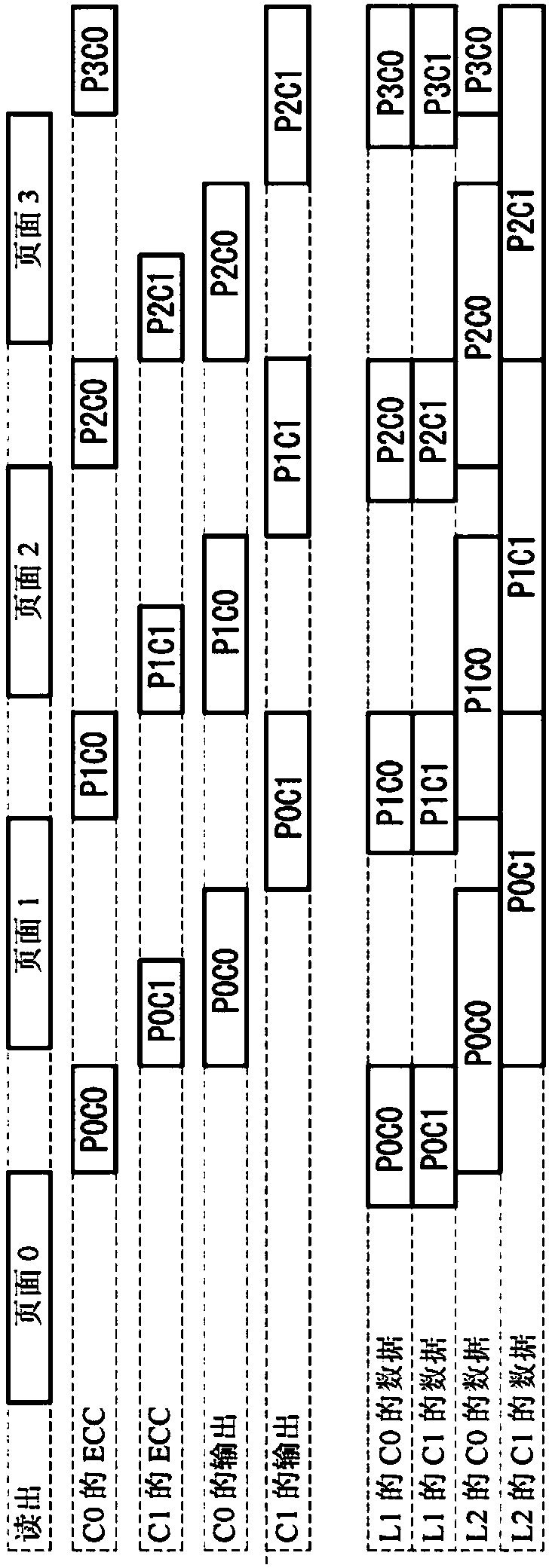
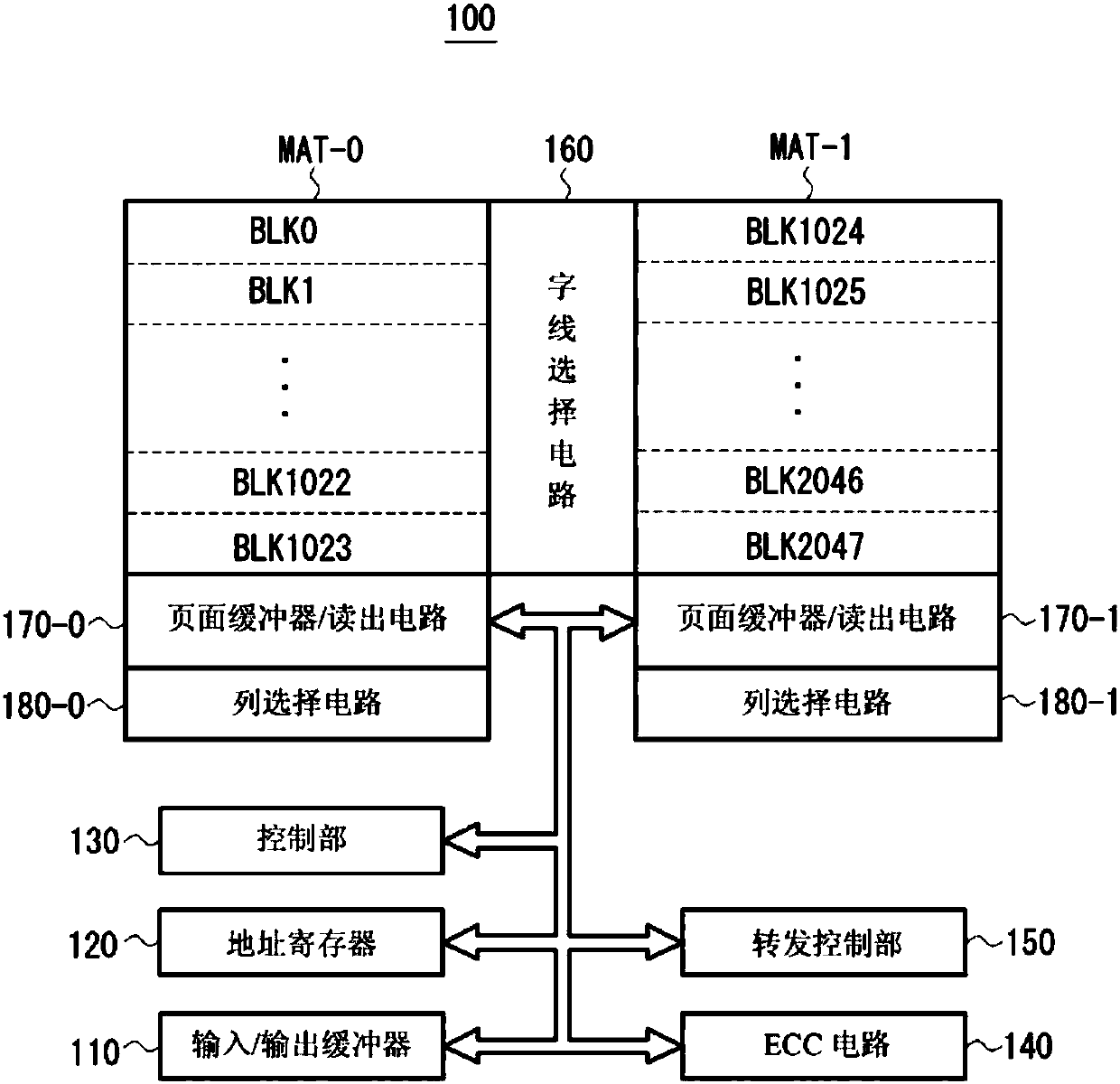
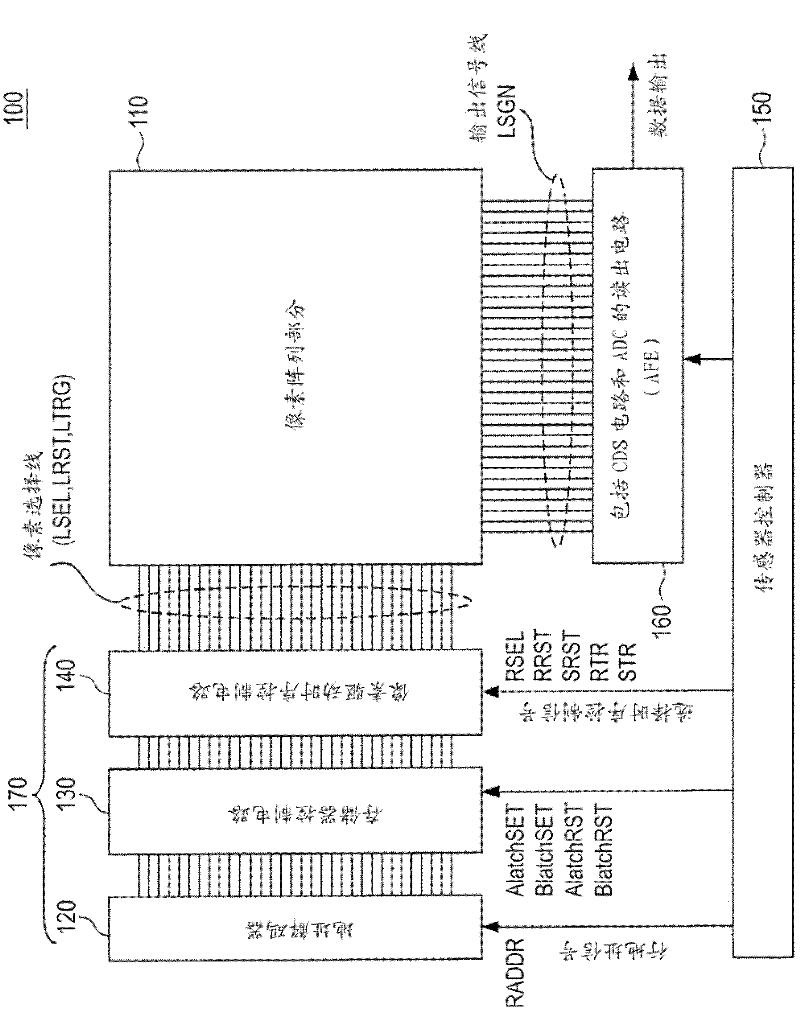
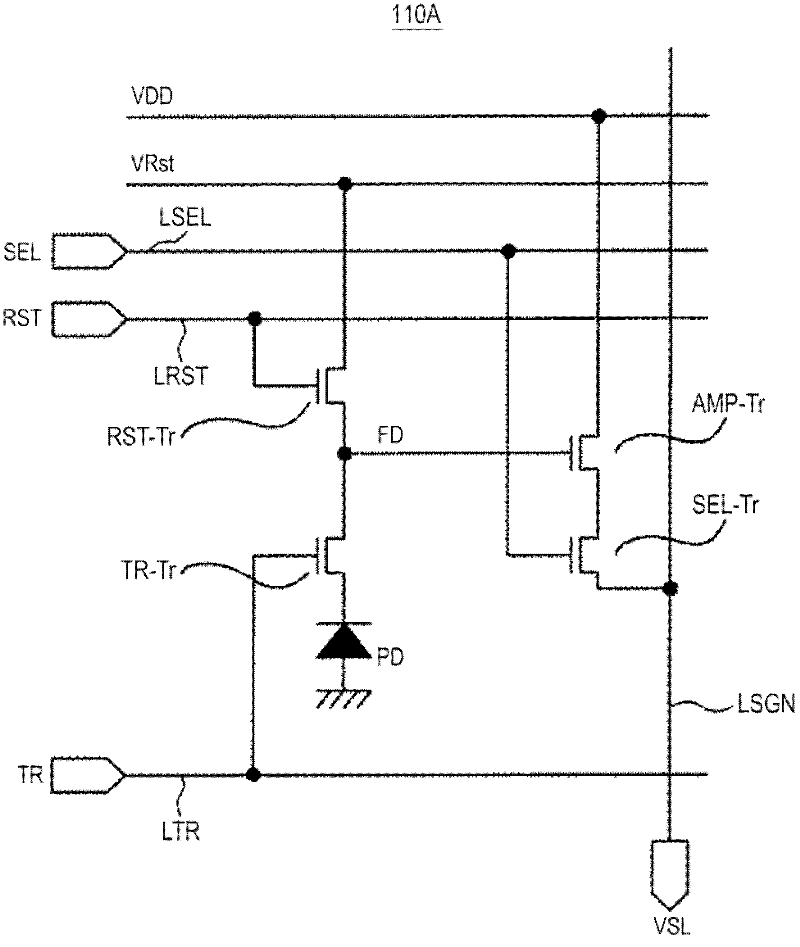
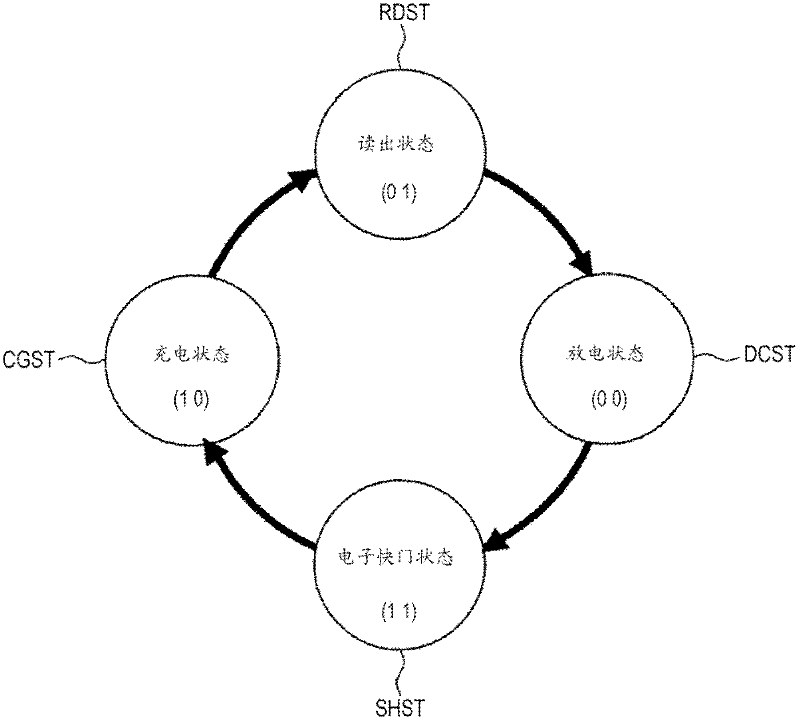
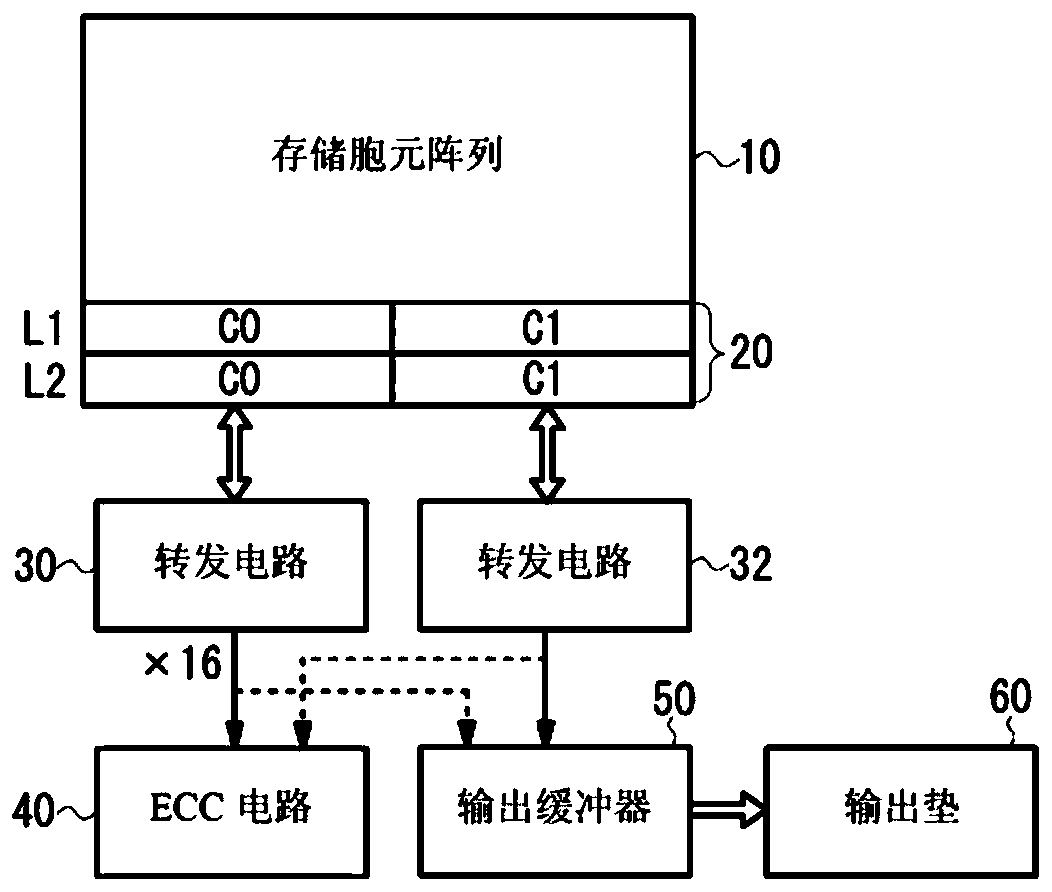
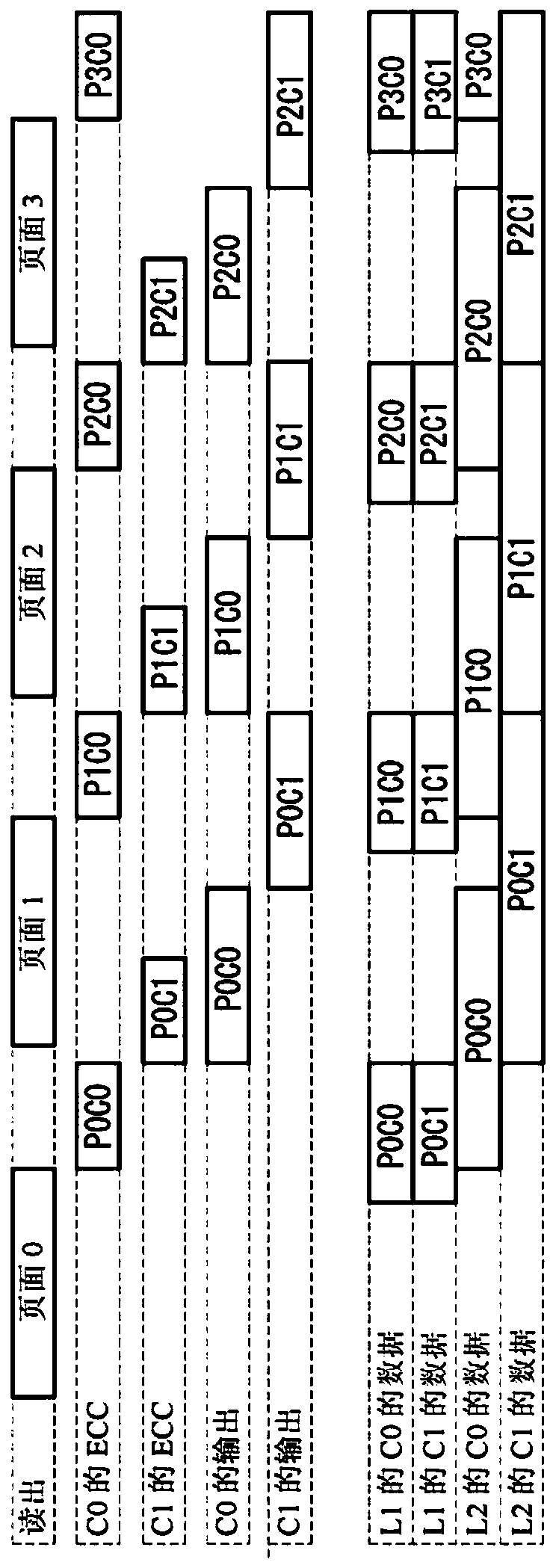
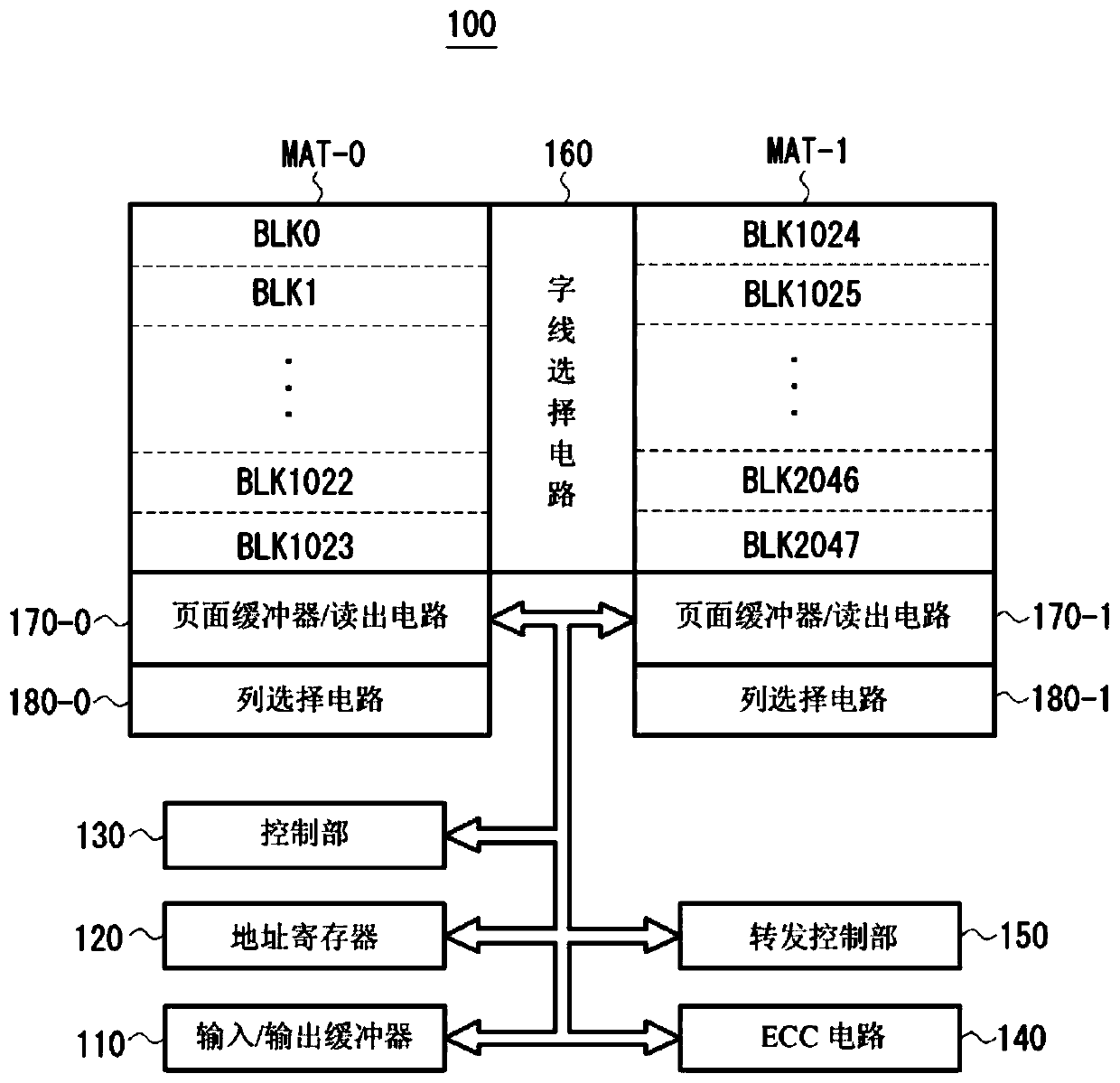
ActiveCN107833589AHigh speed readoutRead-only memoriesRedundant data error correctionData errorPage buffers
The invention provides a flash memory comprising a memory array comprising a memory mat MAT-0, MAT-1; a page buffer 170-0, holding data read from the memory mat MAT-0; a page buffer 170-1, holding data read from the memory mat MAT-1; an ECC circuit 140, performing data error checking and correction; an output buffer 110 for outputting data; and a transferring control element, controlling transferring of data between the page buffer 170-0, page buffer 170-1, ECC circuit 140 and output buffer 110. When the memory mat MAT-0 is selected, the transferring control element transfers data held by thepage buffer 170-0 to the page buffer 170-1 of the memory mat MAT-1.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Solid-state imaging device and camera system
InactiveCN102316286ASuppress blown highlightsSmall sizeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsElectronic shutterControl signal
Owner:SONY CORP
Frame data creation method and device, frame data creation program, and plotting method and device
InactiveCN101102900AHigh-speed generationHigh speed readoutOther printing apparatusPictoral communicationComputer scienceImaging data
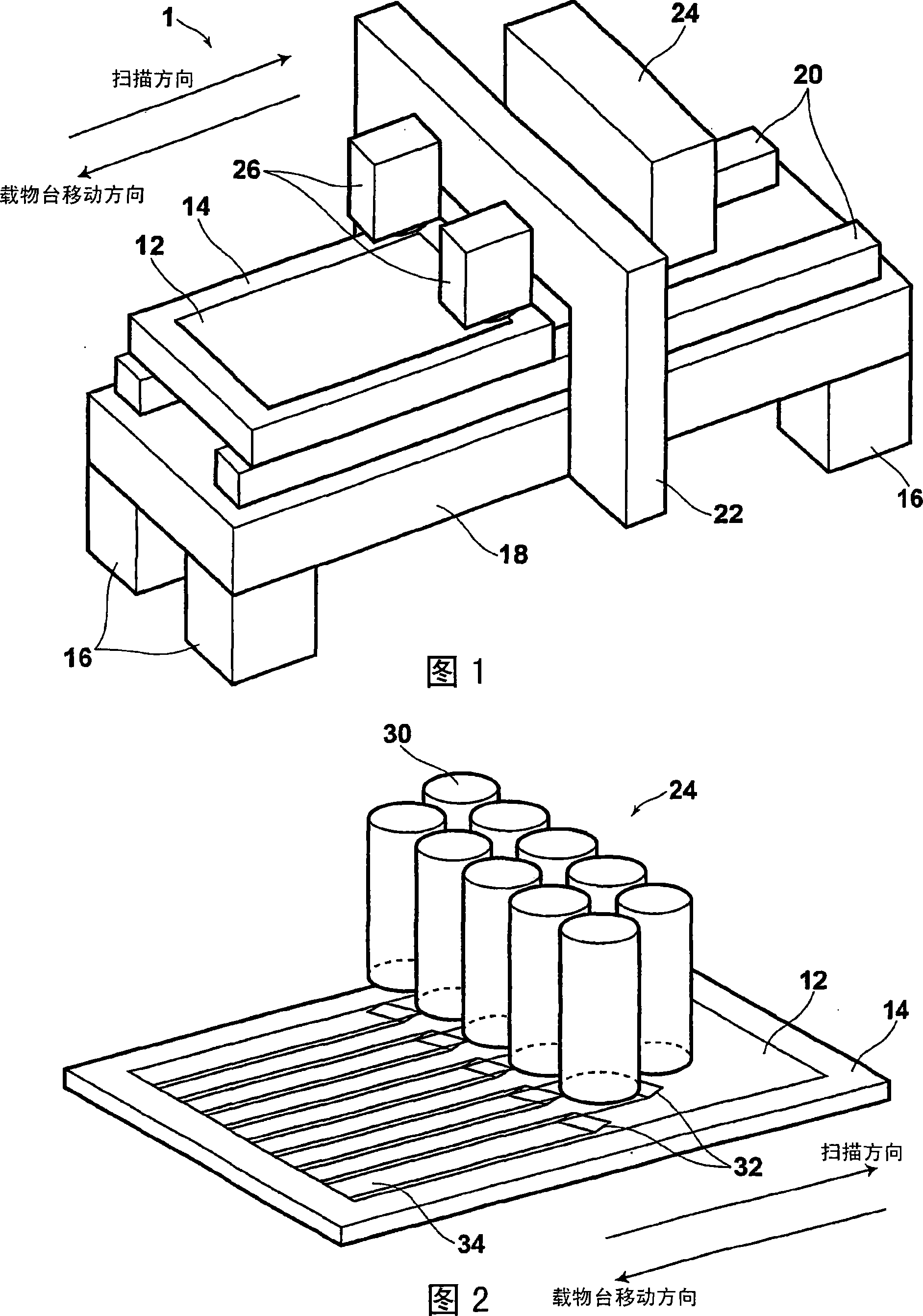
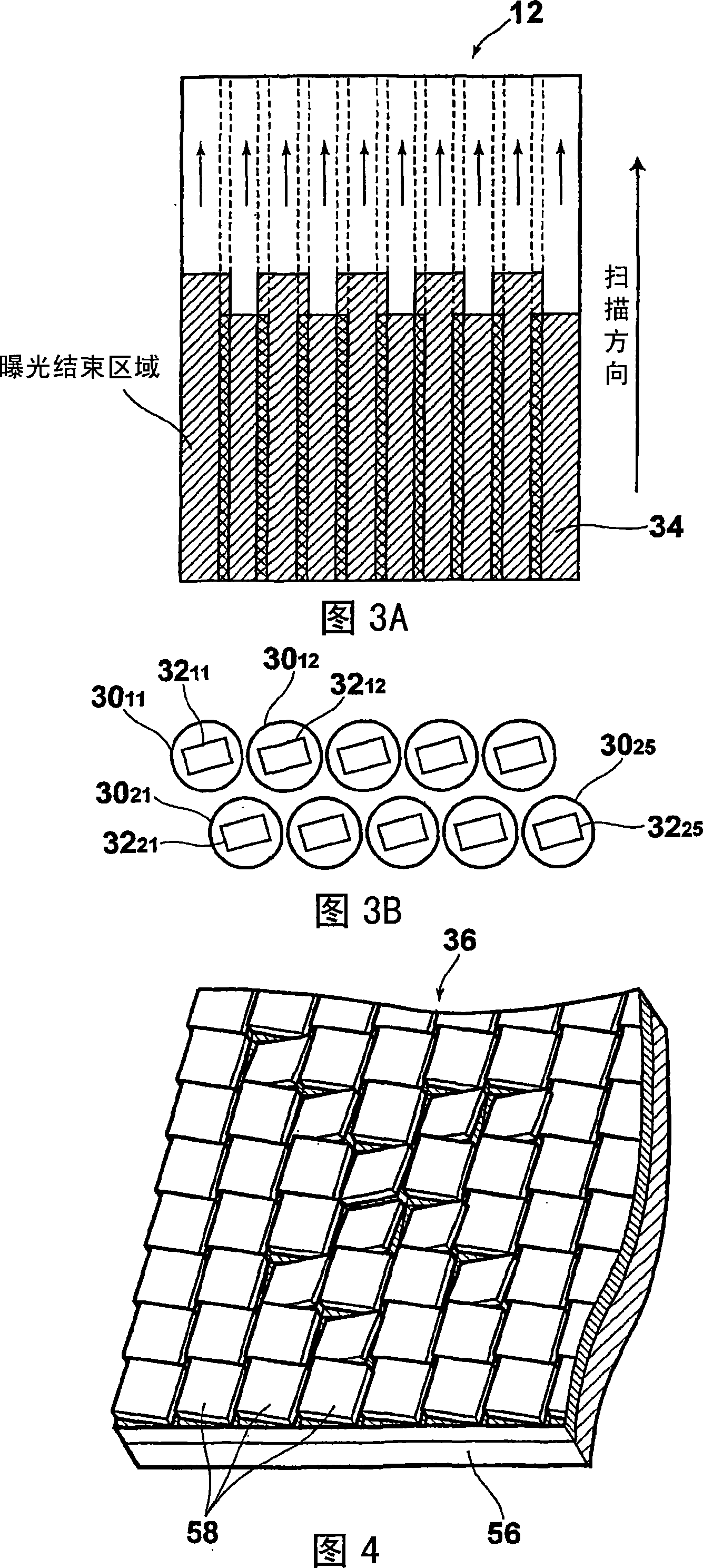
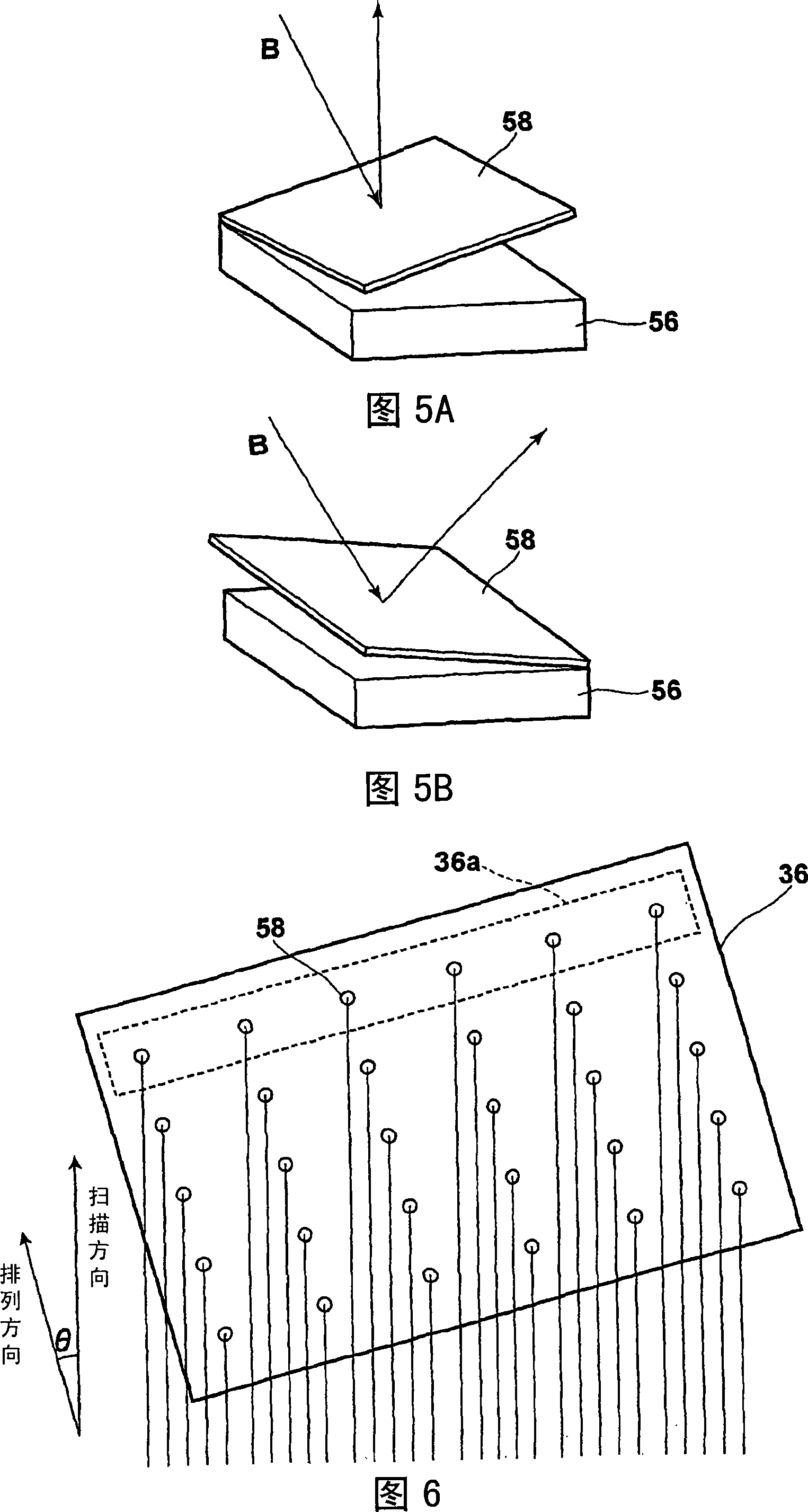
It is possible to rapidly create frame data used when moving a spatial light modulation element in a scan direction and forming an image by inputting the frame data into a spatial light modulation element in accordance with the movement in the scan direction. There is provided a method for creating the frame data used when moving the spatial light modulation element having a plurality of arranged plotting element groups in the scan direction defining an inclination angle against the arrangement direction of the plotting element groups and inputting the frame data into the spatial light modulation element to form an image in accordance with the movement. The frame data creation method creates frame data according to image data in which pixel data are two-dimensionally arranged in a sub-scan direction corresponding to the aforementioned scan direction and a main scan direction orthogonal to the sub-scan direction. The image data is subjected to deformation processing sot that the image data corresponding to the plotting element groups (circle 1 to circle 6) are arranged in the main scan direction and the frame data is created in accordance with the deformed image data.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic memory device
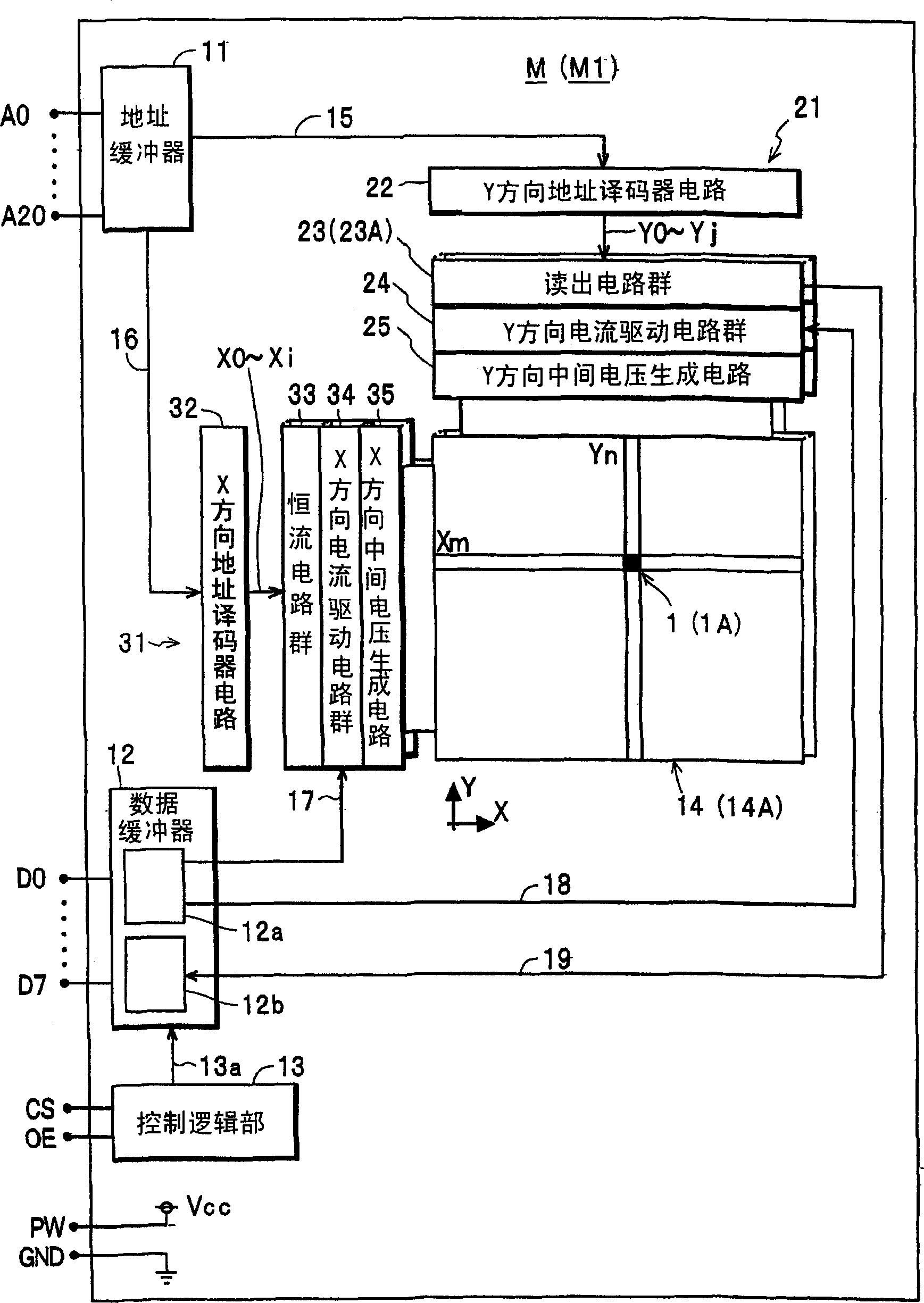
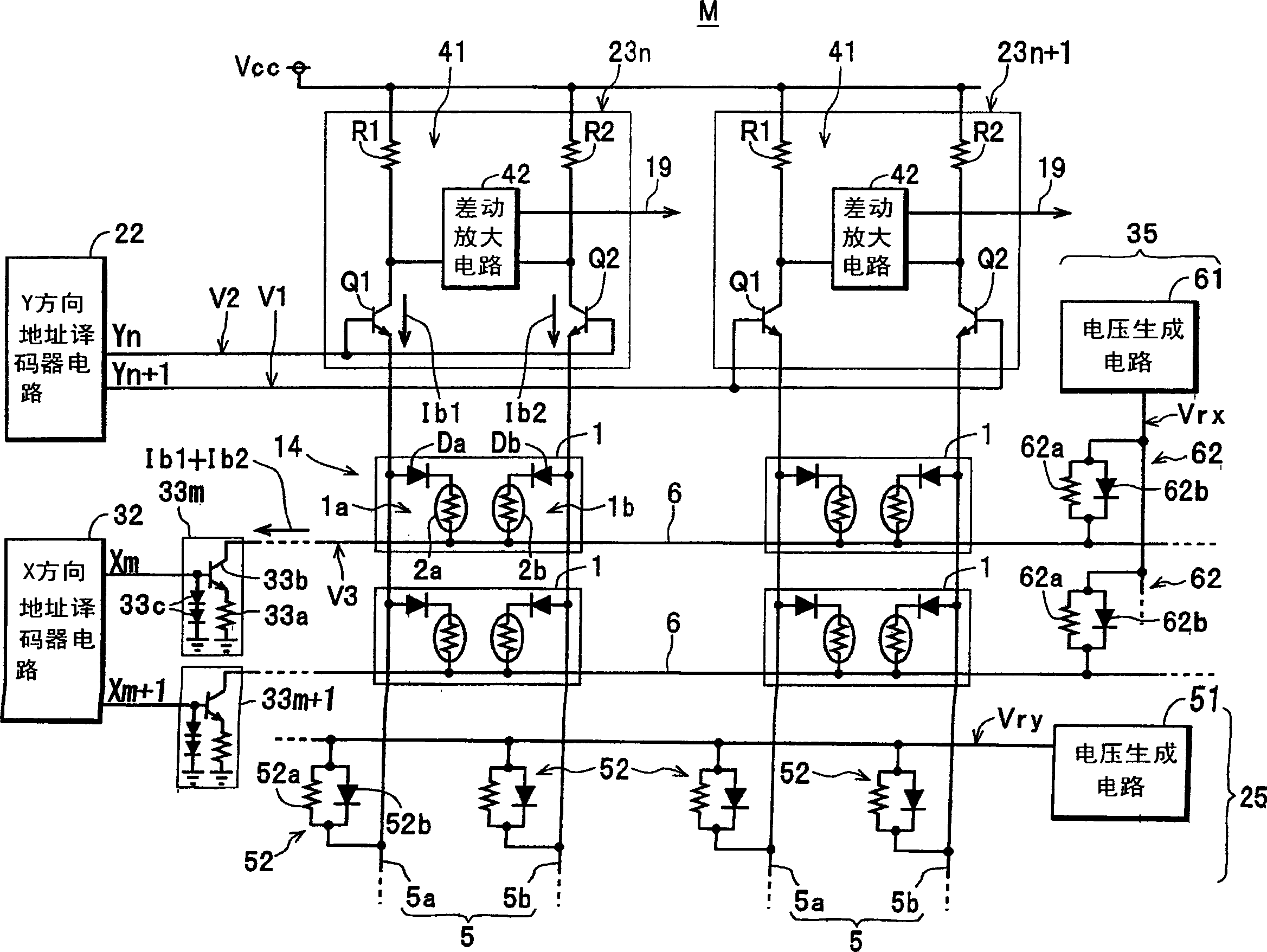
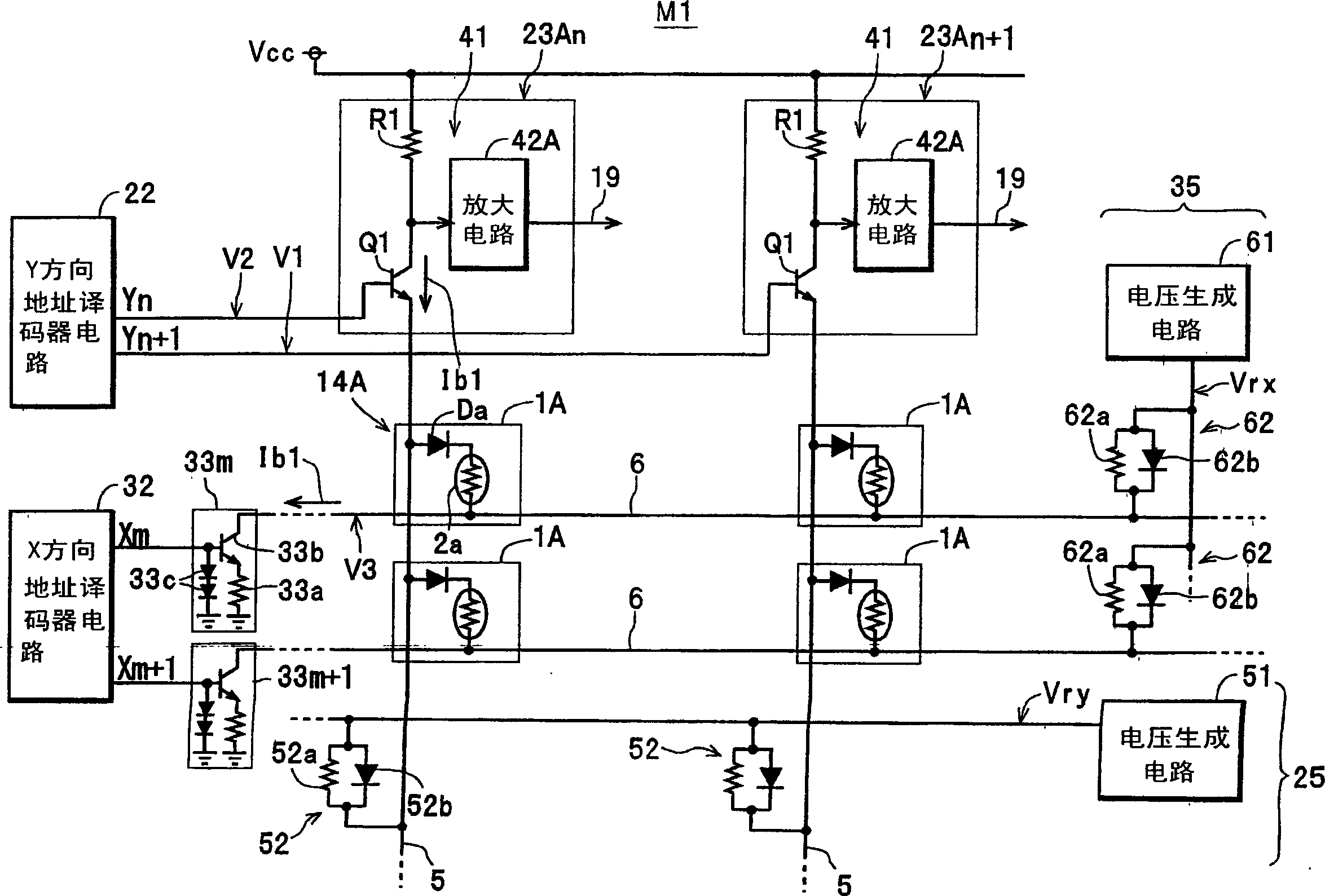
The invention provides a magnetic memory device capable of reading information at high speed. The device is equipped with a plurality of storage cells 1 arranged in two-dimensional array; a plurality of read bit lines 5 and a plurality of read word lines 6 for supplying read current Ib1, Ib2 for reading the information from first power supply (supply voltage Vcc) to each of the storage cells 1; a medium voltage generation circuit 25 of Y direction, connected to a part of the read bit line 5, for impressing the medium voltage Vry, lower than the supply voltage Vcc, to the read bit line 5; and a medium voltage generation circuit 35 of X direction, connected to the part of the read word line 6, for impressing the medium voltage Vrx, lower than supply voltage Vcc, to the read word line 6.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
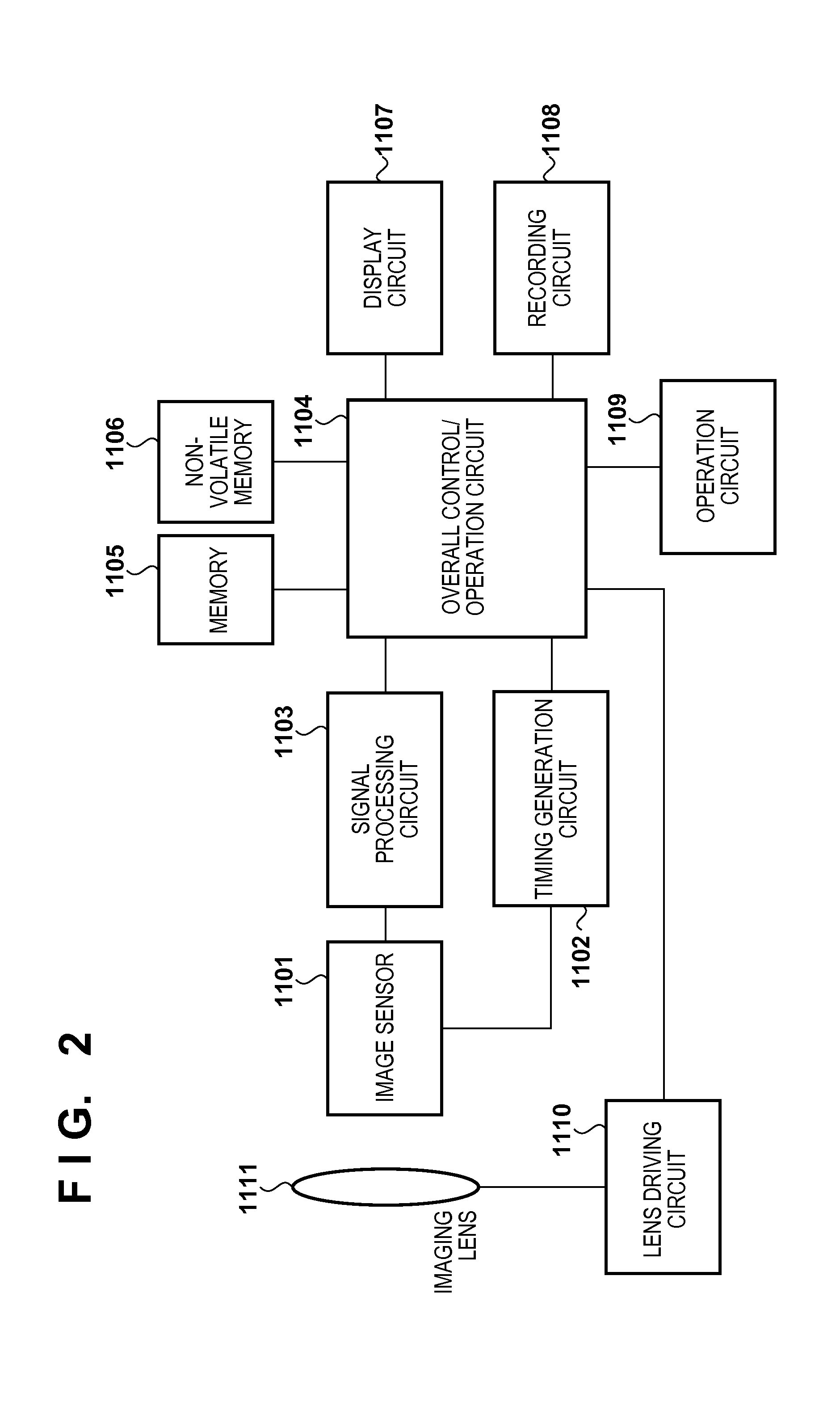
Image capturing apparatus and method of controlling image capturing apparatus
ActiveUS20160073008A1Prevent image degradationIncrease power consumptionTelevision system detailsPicture signal generatorsPhotoelectric conversionComputer science
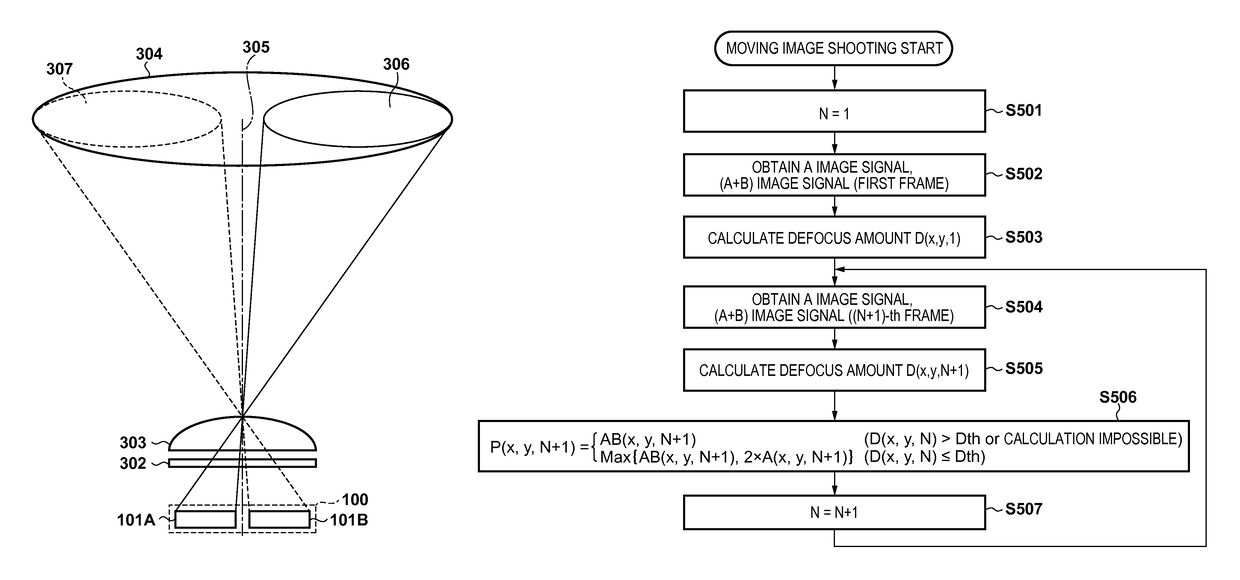
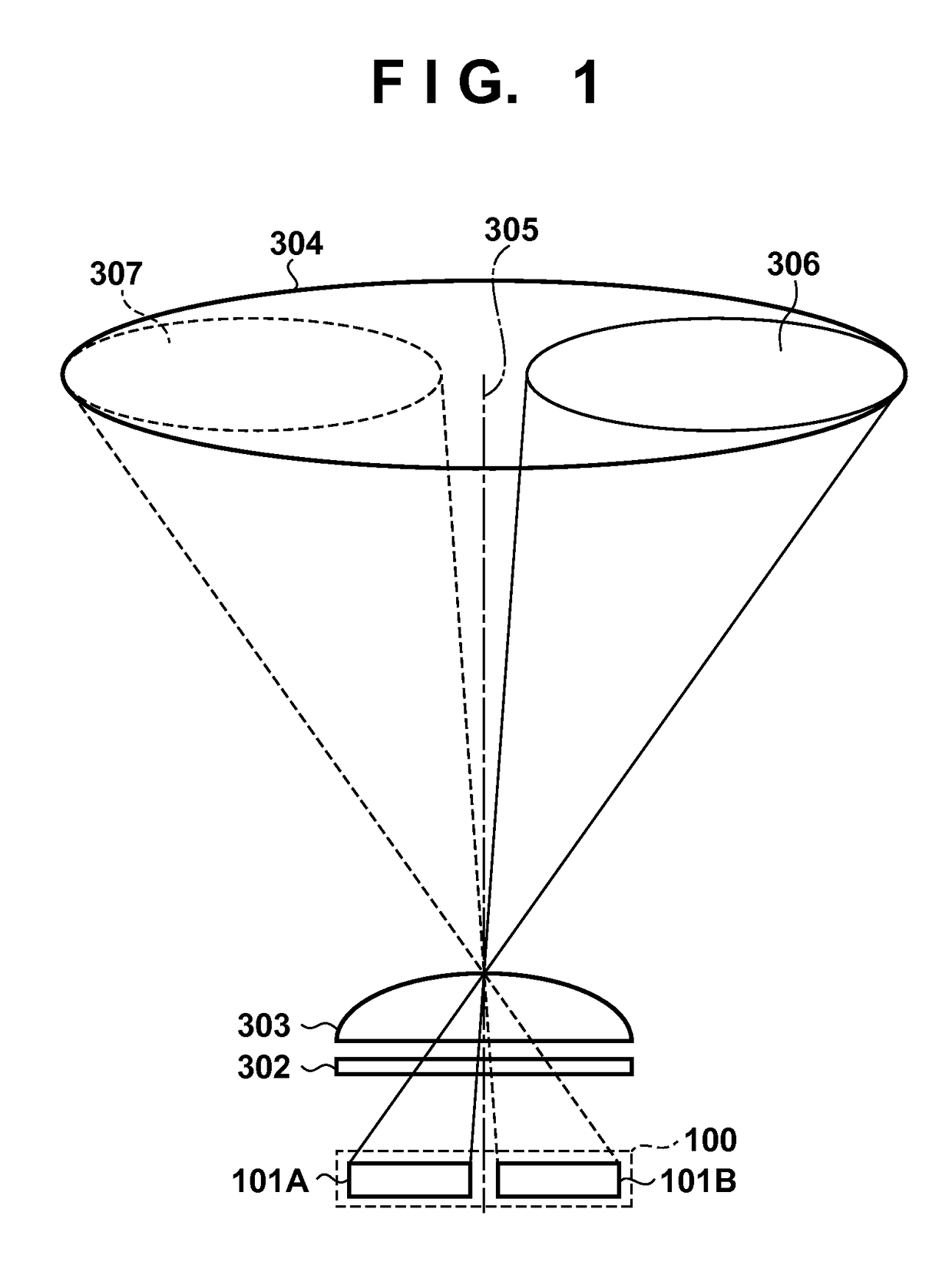
In an image capturing apparatus having an image sensor including a plurality of unit pixels each having a plurality of photoelectric conversion portions and a microlens, the image sensor can be scanned with a first scan method of adding and reading out signals from a portion of the photoelectric conversion portions by a predetermined number of unit pixels and with a second scan method of adding and reading out signals from the photoelectric conversion portions by the predetermined number of unit pixels. A pixel signal read out with the second scan method is selected if a defocus amount is larger than a threshold value and the larger of the pixel signal read out with the second scan method and a signal obtained by using the pixel signal read out with the first scan method is selected if the defocus amount is equal to the threshold value or less.
Owner:CANON KK
CMOS image sensor capable of improving frame frequency high-speed full-digital data reading
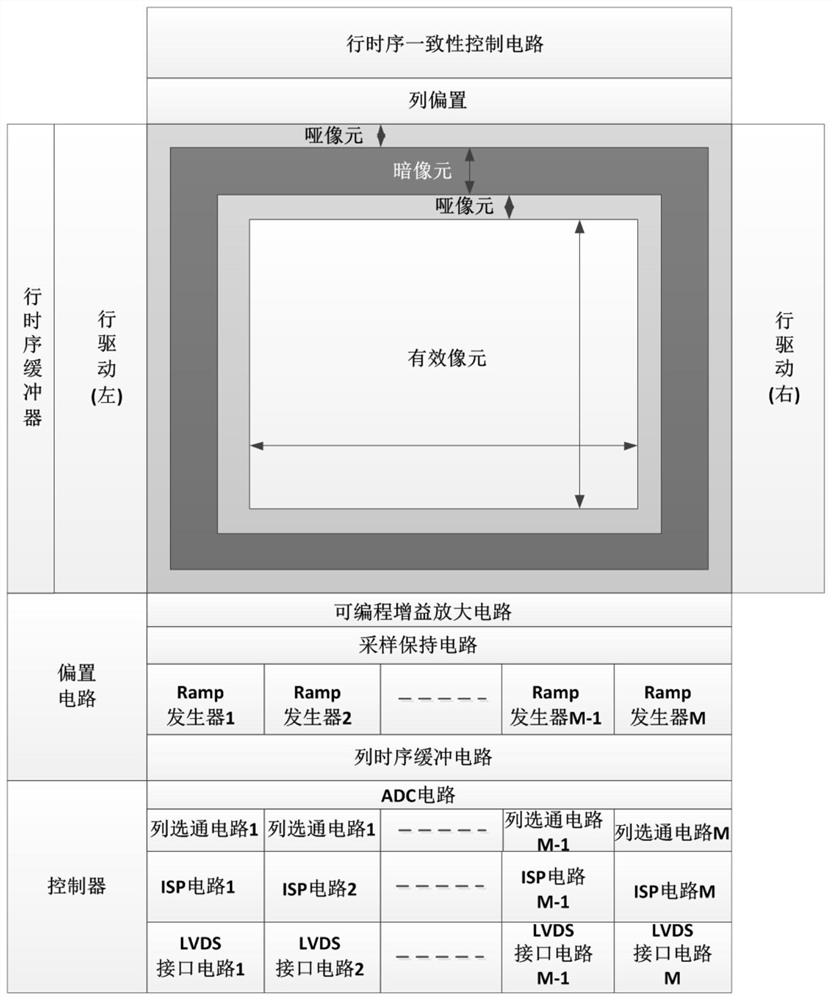
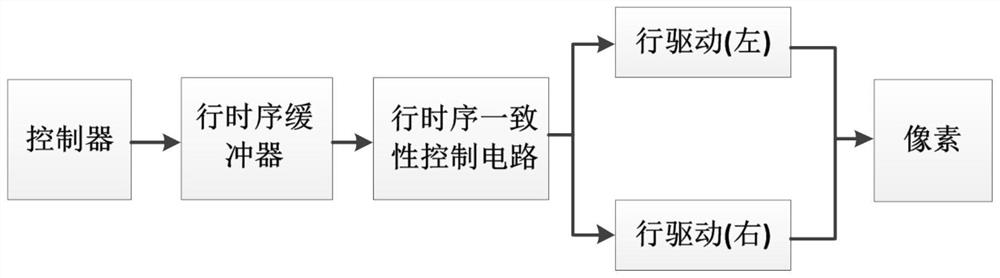
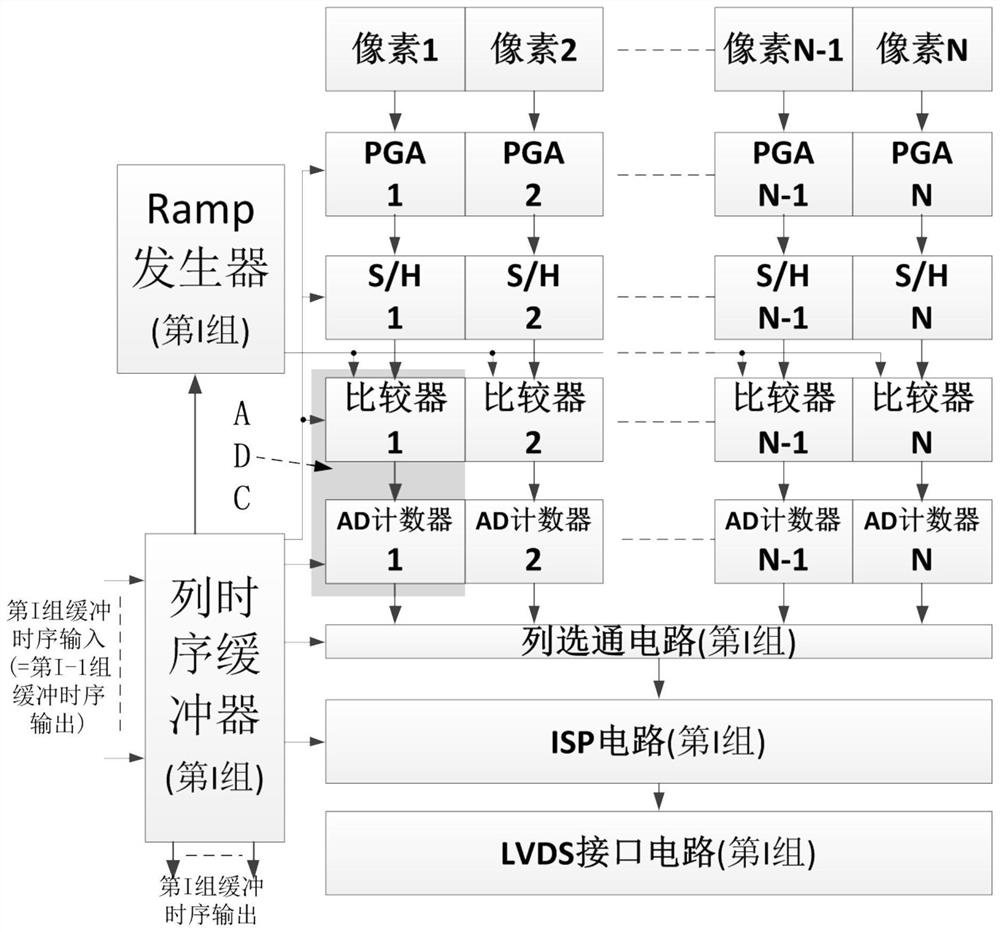
ActiveCN111669526AIncrease frame rateShort delay timeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsProgrammable-gain amplifierImage sensor
The invention belongs to the technical field of CMOS image sensors, in particular to a CMOS image sensor capable of improving frame frequency high-speed full-digital data reading. The CMOS image sensor comprises a photosensitive area array, a first row driver, a second row driver and a reading circuit; the reading circuit comprises a column reading circuit and a column time sequence buffer circuit, and the column reading circuit comprises a programmable gain amplifier, an ADC circuit, a Ramp generator, a column gating circuit, an ISP circuit and an LVDS interface circuit; the first row drive is arranged on the left side of the photosensitive area array, the row timing sequence buffer is arranged on the left side of the first drive, and the second row drive is arranged on the right side ofthe photosensitive area array. The controller is used for exposure and conversion of pixels, pixel row time sequence consistency control, PGA sampling and amplification, ADC conversion, column circuitgating and ISP processing time sequence control. According to the invention, the frame frequency of the super-large area array CMOS image sensor is improved, and digital image reading with extended dynamic range, low noise and high speed is realized.
Owner:THE 44TH INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Imaging apparatus, imaging system, movable object, and method for driving imaging apparatus
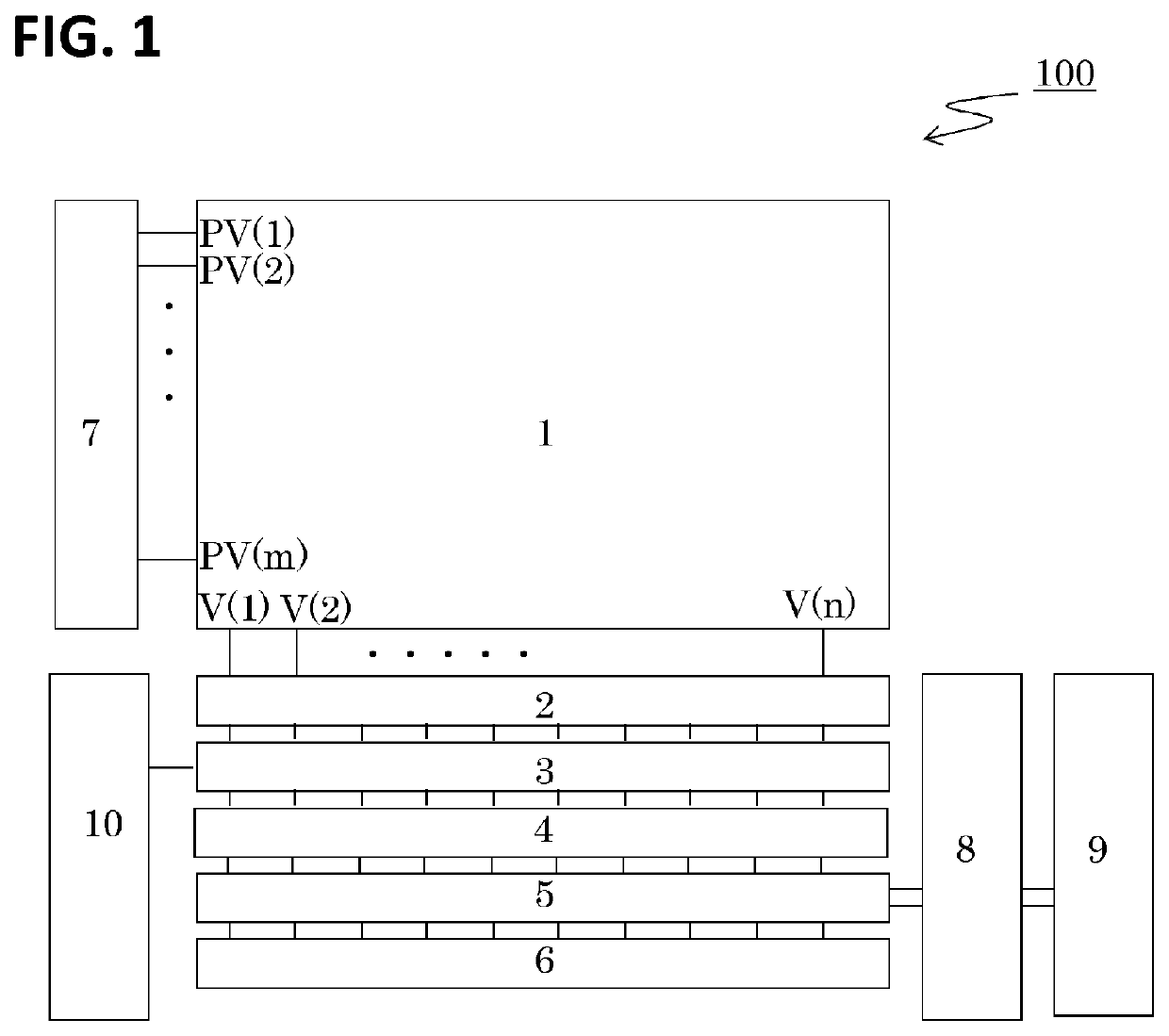
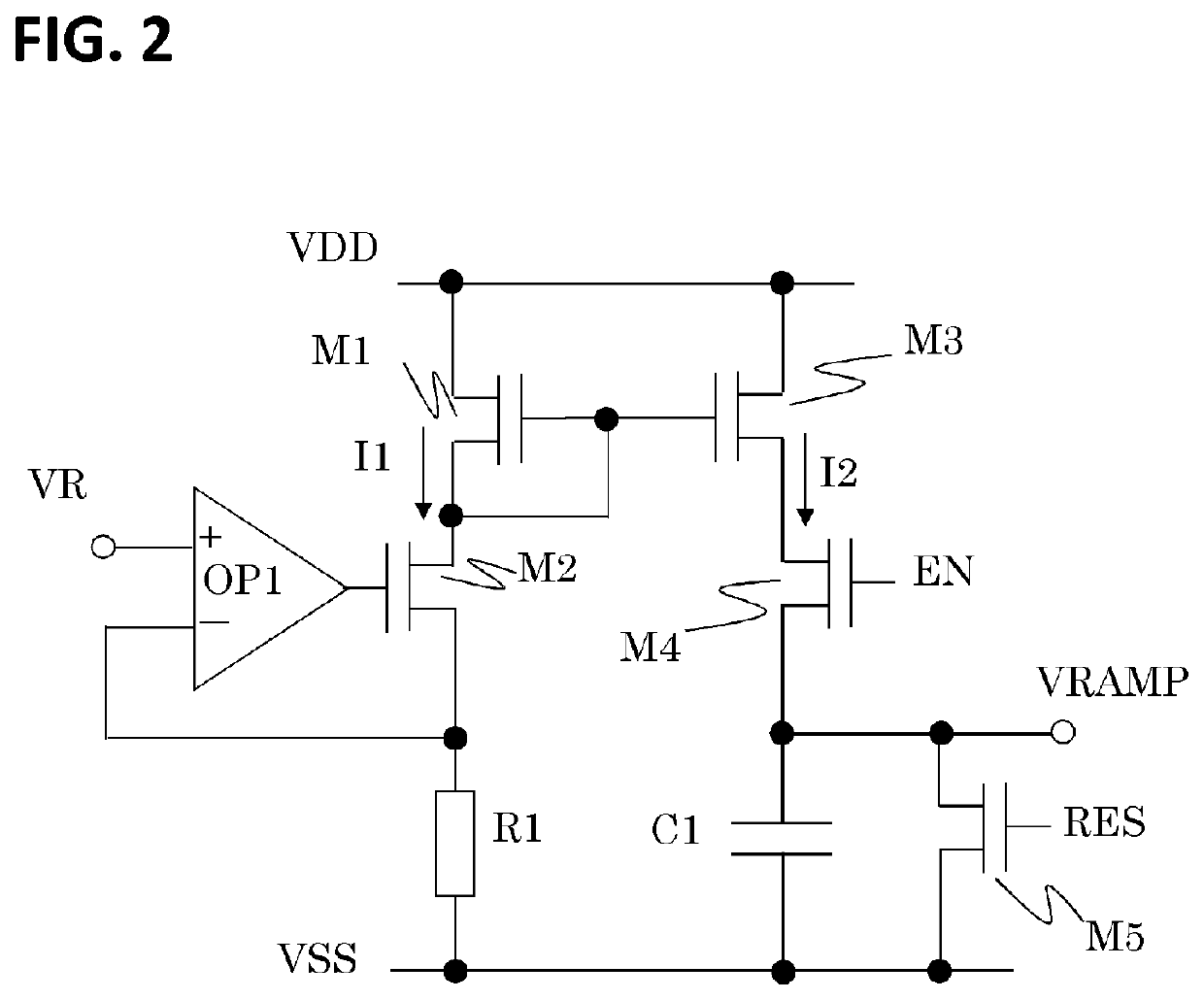
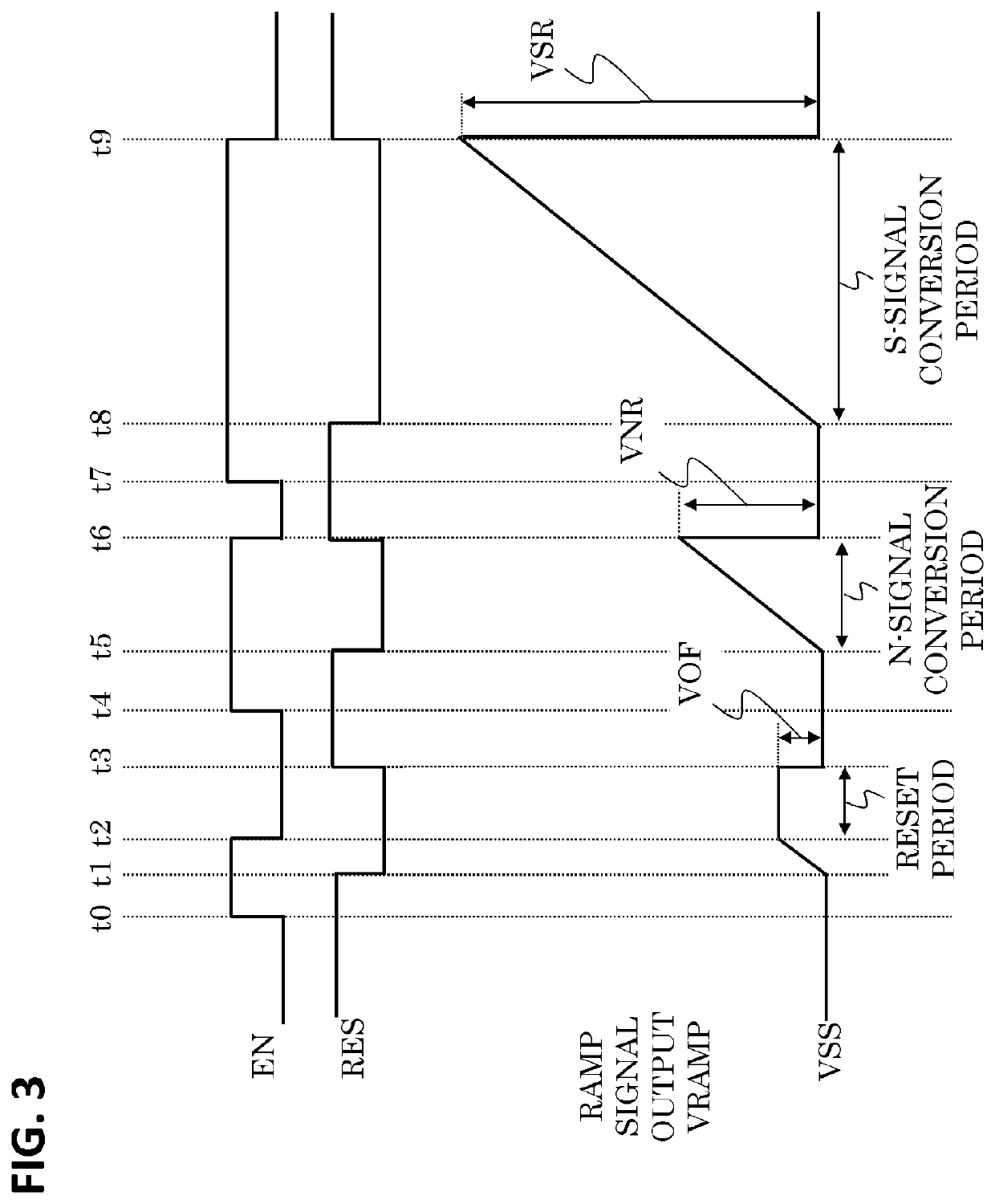
ActiveUS20210377480A1High-speed readoutHigh-quality image signalTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSoftware engineeringComparators circuits
An imaging apparatus including a ramp voltage generation circuit having a first period for outputting an offset voltage that sets a reference voltage for the comparator circuit, and a second period for outputting a reference voltage having a slope-shaped voltage waveform that varies with time, wherein the generation circuit has a first drive state in which a voltage change amount per unit time of the reference voltage in the second period is a first voltage amount, and a second drive state in which the voltage change amount per unit time of the reference voltage in the second period is a second voltage amount that is less than the first voltage amount, and wherein the offset voltage in the second drive state is less than a value obtained by multiplying the offset voltage in the first drive state by a ratio of the second voltage amount to the first voltage amount.
Owner:CANON KK
Forming method of performing forming on variable resistance nonvolatile memory element, and variable resistance nonvolatile memory device
ActiveCN102667947BForming high speedAvoid unevennessSolid-state devicesDigital storageEngineeringMaterials science
When the variable resistance nonvolatile memory element having a first electrode, a second electrode, and a transition metal oxide layer sandwiched between the first electrode and the second electrode is in an initial state, the first electrode A first forming voltage is applied between the first electrode and the second electrode until the first formation of the first operable state reversibly transitioned between the high resistance state and the low resistance state occurs, between the first electrode and the second electrode. Applying a second forming voltage between the second electrodes until it changes to a resistance value lower than the resistance value of the low resistance state in the first operable state after the first formation. Formation of the variable resistance nonvolatile memory element proceeds until the second formation of the second operable state of the resistance state is performed.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
A debug display and control system for radar information processor
ActiveCN103744315BWork mode controlWork scene controlWave based measurement systemsProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersControl systemEmbedded system
The invention provides a debugging and display controlling system of a radar information processor. The debugging and display controlling system comprises a high-speed data transmission module, a display control module and a resident monitoring module, wherein the resident monitoring module is mounted on the radar information processor; the display control module is used for receiving external input task requirements and sending corresponding control commands, the control commands are transmitted to the resident monitoring module through the high-speed data transmission module, and the resident monitoring module responds to the control commands, carries out corresponding operations on the radar information processor and uploads operation results to the display control module through the high-speed data transmission module. According to the debugging and display controlling system, the coherence debugging and display controlling for the radar information processor can be realized, the real-time performance and coherence of the radar information processor are verified, and the test efficiency of the radar information processor is increased.
Owner:西安导引科技有限责任公司
Information recording medium, apparatus and method for recording or reproducing recording medium
InactiveCN1228781CHigh speed readoutTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsStreaming dataRecording duration
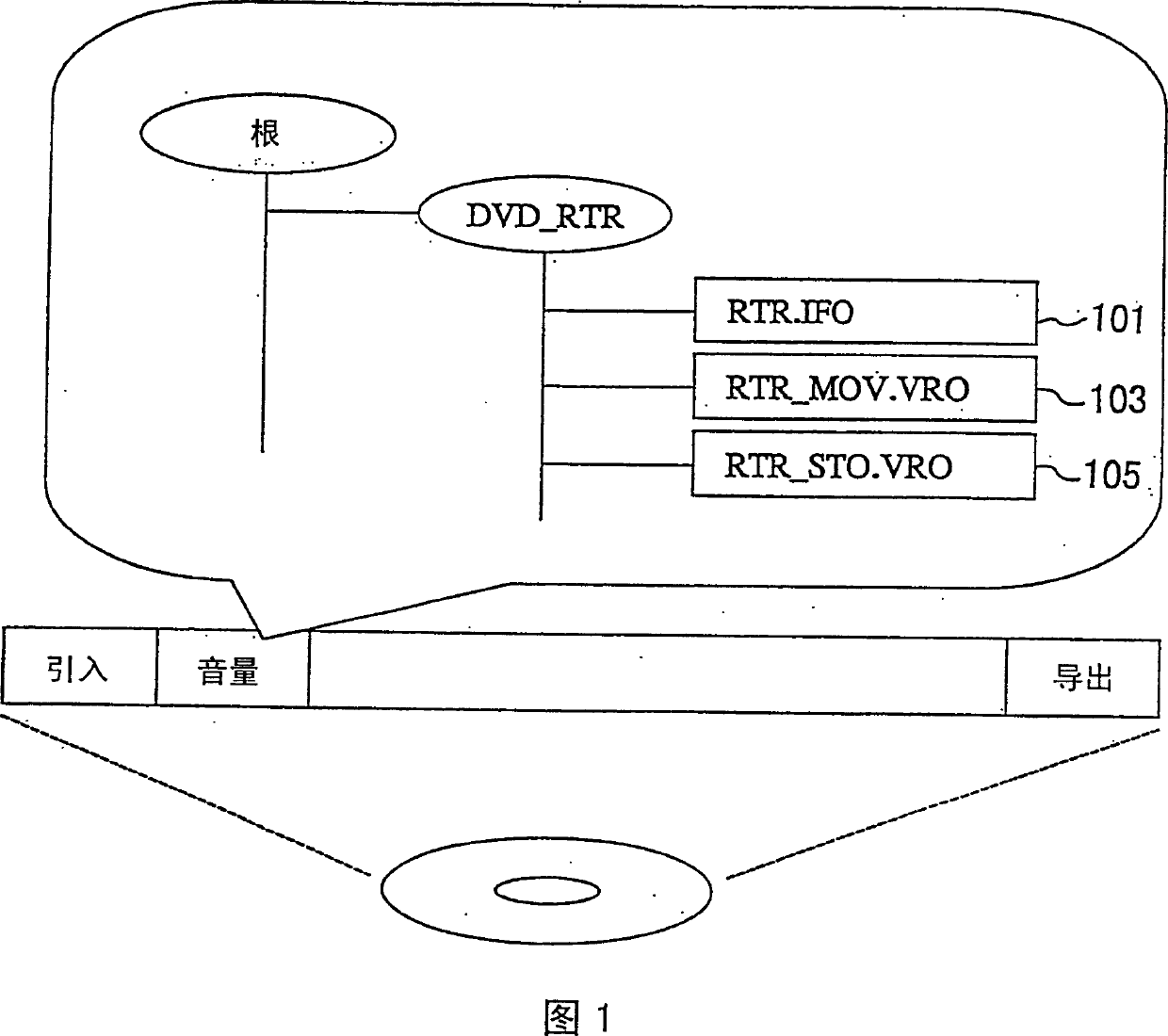
An information recording medium suitable for an optical disc such as DVD, which is capable of reading quickly the recording time information of the video data for displaying on the menu. The recording medium stores management information (RTR.IFO) for each stream data. The management information includes a recording time information (VOB_REC_TM) that has a date and time at which the head video frame of the stream data is recorded. The management information also has an error information (VOB_REC_TM_SUB) indicative of error or fraction of the recording time information which indicates a time less than 1 second and is generated on edit operations including partial deletion.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
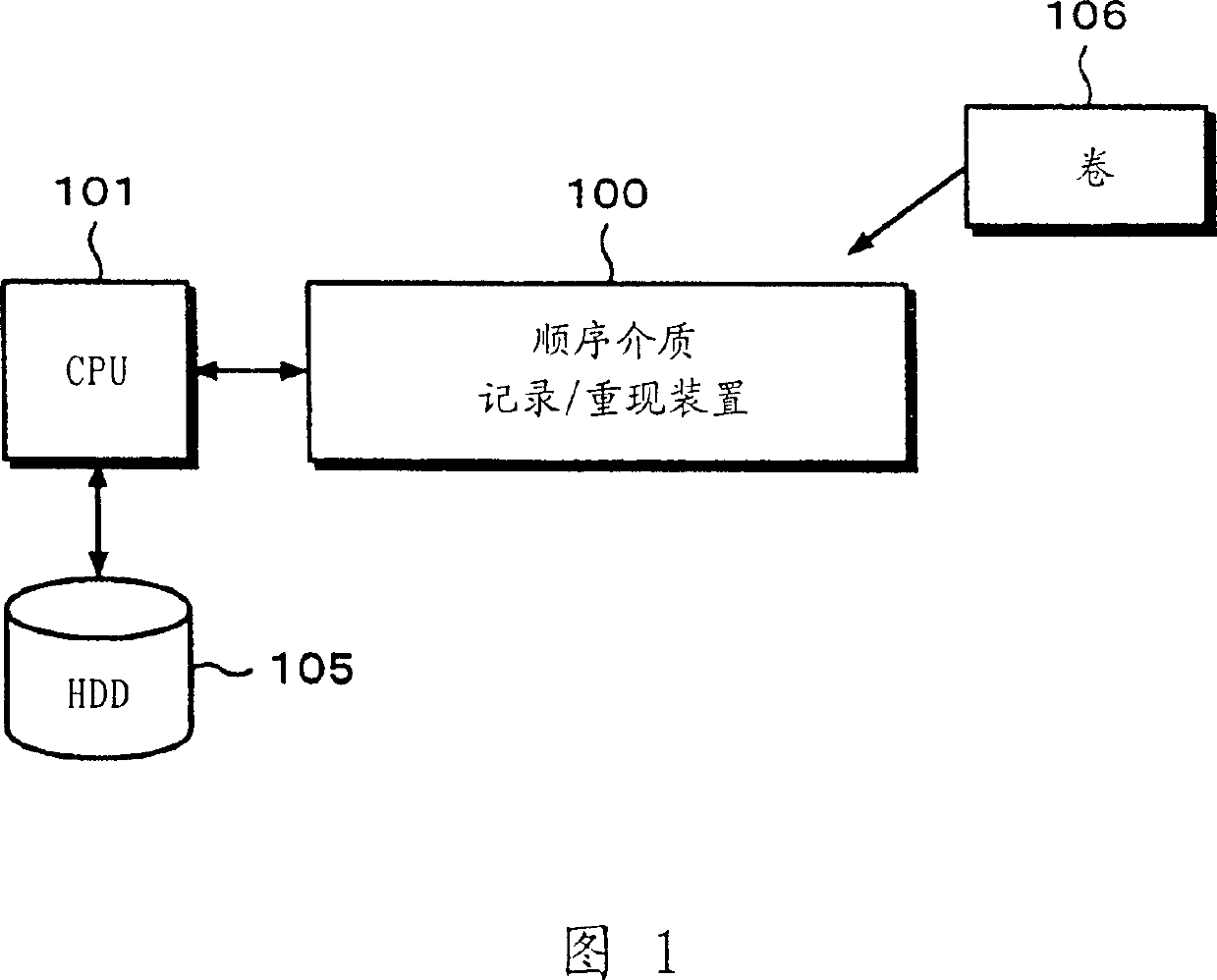
Magnetic tape drive device and method of magnetic tape medium mounting roll
InactiveCN1106644CHigh speed readoutImprove reliabilityFlat record carrier combinationsInput/output to record carriersMagnetic tapeComputer science
Owner:SONY CORP
Image capturing apparatus and method of controlling image capturing apparatus
ActiveUS9635241B2Prevent image degradationIncrease power consumptionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPhotoelectric conversionImage capture
In an image capturing apparatus having an image sensor including a plurality of unit pixels each having a plurality of photoelectric conversion portions and a microlens, the image sensor can be scanned with a first scan method of adding and reading out signals from a portion of the photoelectric conversion portions by a predetermined number of unit pixels and with a second scan method of adding and reading out signals from the photoelectric conversion portions by the predetermined number of unit pixels. A pixel signal read out with the second scan method is selected if a defocus amount is larger than a threshold value and the larger of the pixel signal read out with the second scan method and a signal obtained by using the pixel signal read out with the first scan method is selected if the defocus amount is equal to the threshold value or less.
Owner:CANON KK
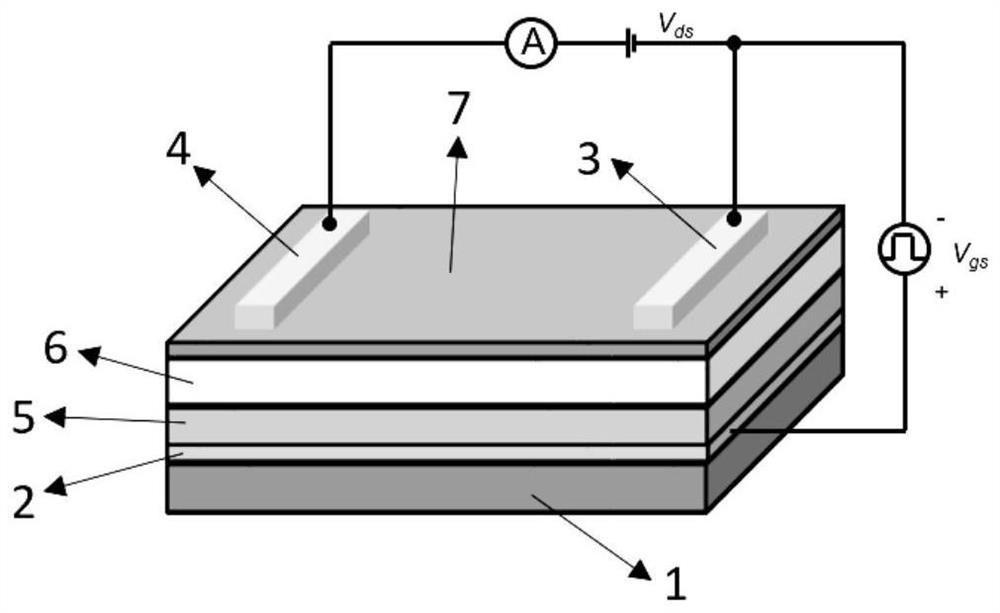
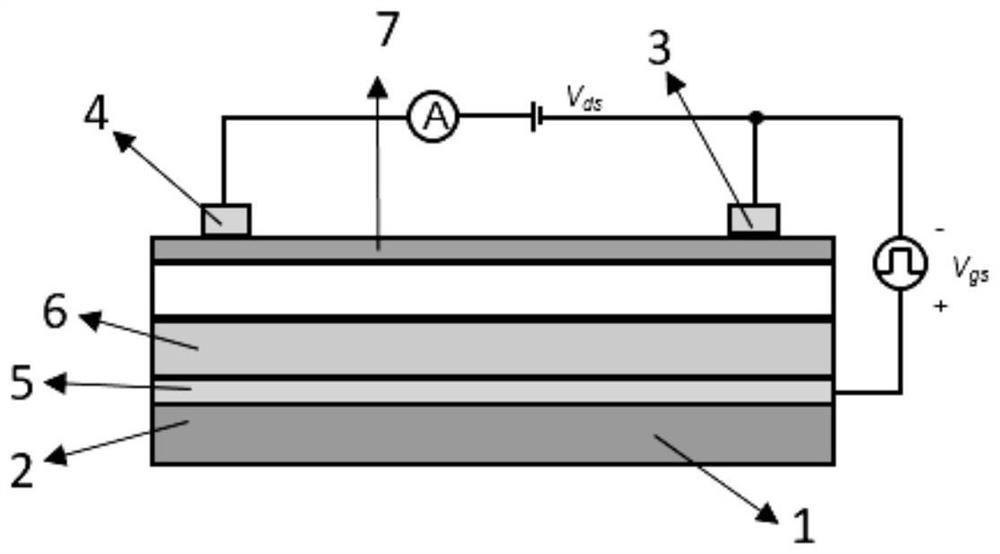
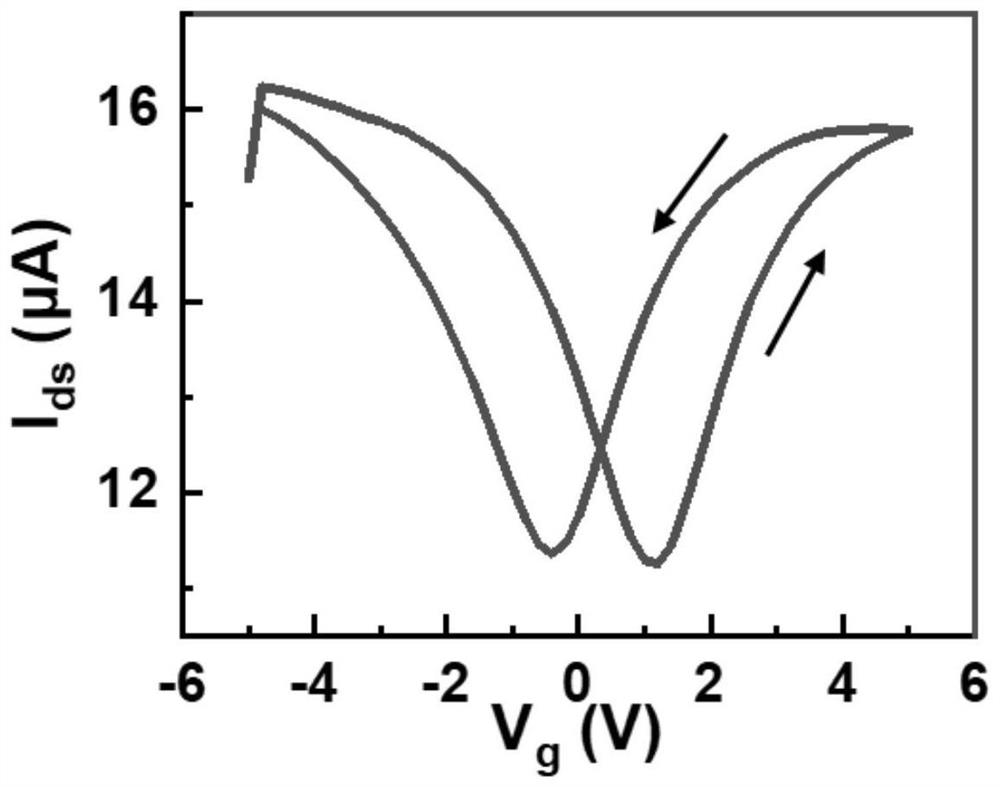
Multifunctional photosensitive synaptic device based on two-dimensional material and preparation method of multifunctional photosensitive synaptic device
PendingCN114497247ASimple structureThe working principle is simple and easy to understandPhysical realisationSemiconductor devicesHigh densityHexagonal boron nitride
The invention discloses a multifunctional photosensitive synapse device based on a two-dimensional material and a preparation method thereof, the device comprises a substrate, a grid electrode, a source electrode, a drain electrode and a stacking structure, the grid electrode, the source electrode, the drain electrode and the stacking structure are arranged on the substrate, the stacking structure comprises a first two-dimensional material layer, a second two-dimensional material layer and a third two-dimensional material layer, the grid electrode is arranged on the substrate, and the third two-dimensional material layer is arranged on the substrate. A first two-dimensional material layer, a second two-dimensional material layer and a third two-dimensional material layer are sequentially covered on the grid electrode, a source electrode and a drain electrode are respectively covered on the third two-dimensional material layer, and a channel is formed between the source electrode and the drain electrode. The second two-dimensional material layer comprises hexagonal boron nitride in a defect state, the first two-dimensional material layer serves as a light absorption layer, the second two-dimensional material layer serves as an isolation layer, and the third two-dimensional material layer serves as a readout layer. The device is simple in structure, simple and understandable in working principle, simple in preparation process and easy to master; based on vertical stacking of pure two-dimensional thin film materials, the size is small, and the requirements for high density and high integration level are met.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV HANGZHOU GLOBAL SCI & TECH INNOVATION CENT
Rapid reading out system and method of holographic data storage
InactiveCN100580778CHigh speed readoutOptical beam guiding meansRecording/reproducing/erasing using optical interference patternsComputer hardwareEngineering
The invention relates to a quick read out system and a method of holographic data storage, belonging to the optical storage technical field. The quick read out method is as follows: firstly, a plurality of holograms are recorded at intervals on a holographic medium; then, the high-speed read out of the holograms is realized by means of the synchronous working among precise addressing equipment, an electro-optical switch and high-speed image collection equipment in the state of high-speed motion of the holographic medium. Because the quick read out system of holographic data storage is designed by the method, and consists of a microdrive positioning controller, a pulse generator, high-speed precise addressing equipment, an electro-optical switch, high-speed image collection equipment, a laser and a necessary optical element, the holographic medium is in a high-speed motion state all the time during continuously reading out a plurality of holograms, thereby realizing continuous high-speed read out of the holograms.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
non-volatile semiconductor storage device
ActiveCN107833589BHigh speed readoutRead-only memoriesRedundant data error correctionSemiconductor storage devicesHemt circuits
The present invention provides a non-volatile semiconductor memory device, comprising: a memory array, including memory pads (MAT-0, MAT-1); a page buffer (170-0), which maintains the The data out; Page buffer (170-1), keeps the data read from storage pad (MAT-1); ECC circuit (140), carries out error detection and correction of data; Output buffer (110), outputs data and a forwarding control section, controlling data forwarding between the page buffer (170-0), the page buffer (170-1), the ECC circuit (140), and the output buffer (110). When the memory mat (MAT-0) is selected, the transfer control unit transfers the data held in the page buffer (170-0) to the page buffer (170-1) of the memory mat (MAT-1).
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Imaging element, method for controlling same, and camera
InactiveCN101836433AReduce noiseHigh speed readoutTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringTransistor
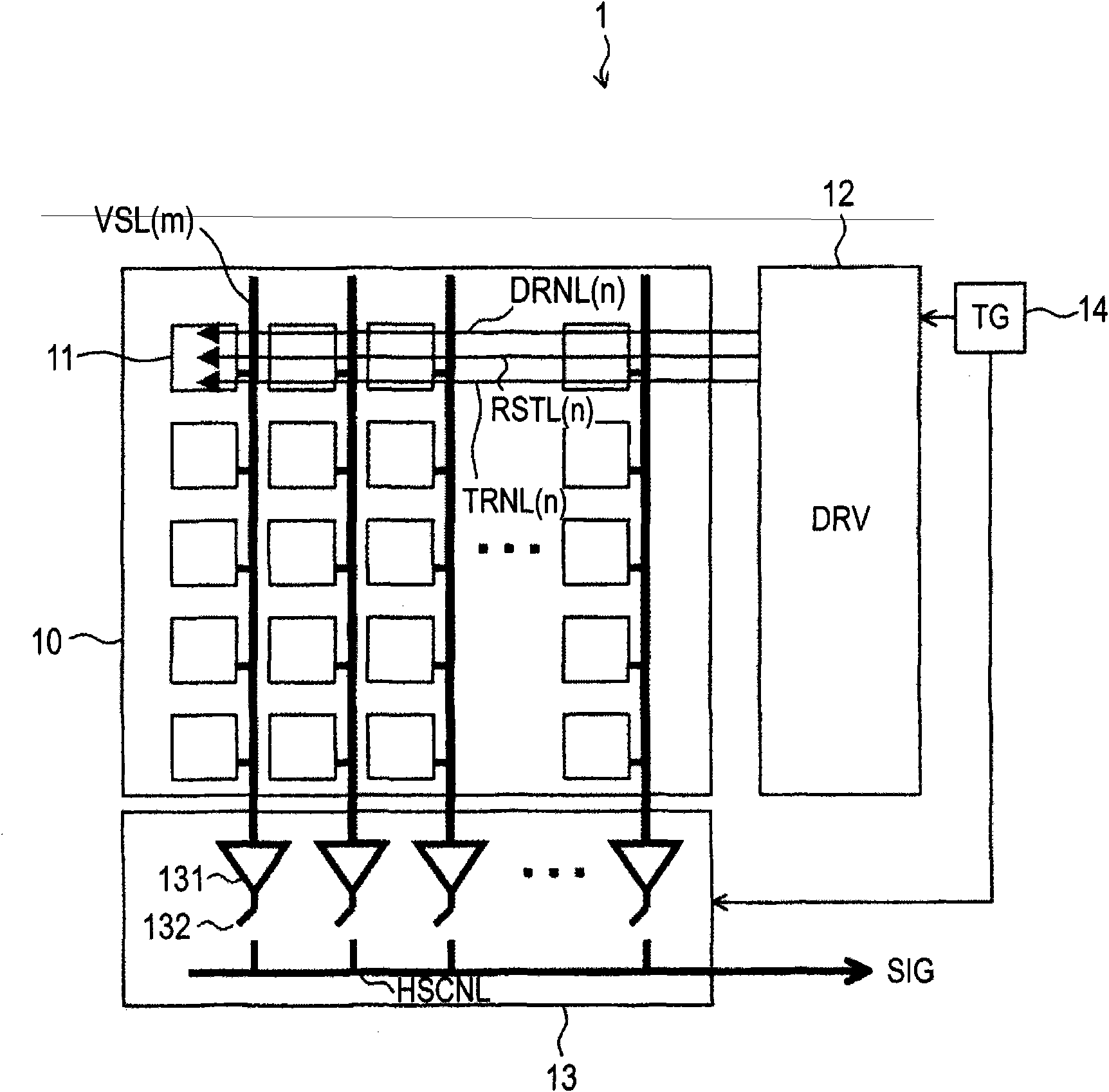
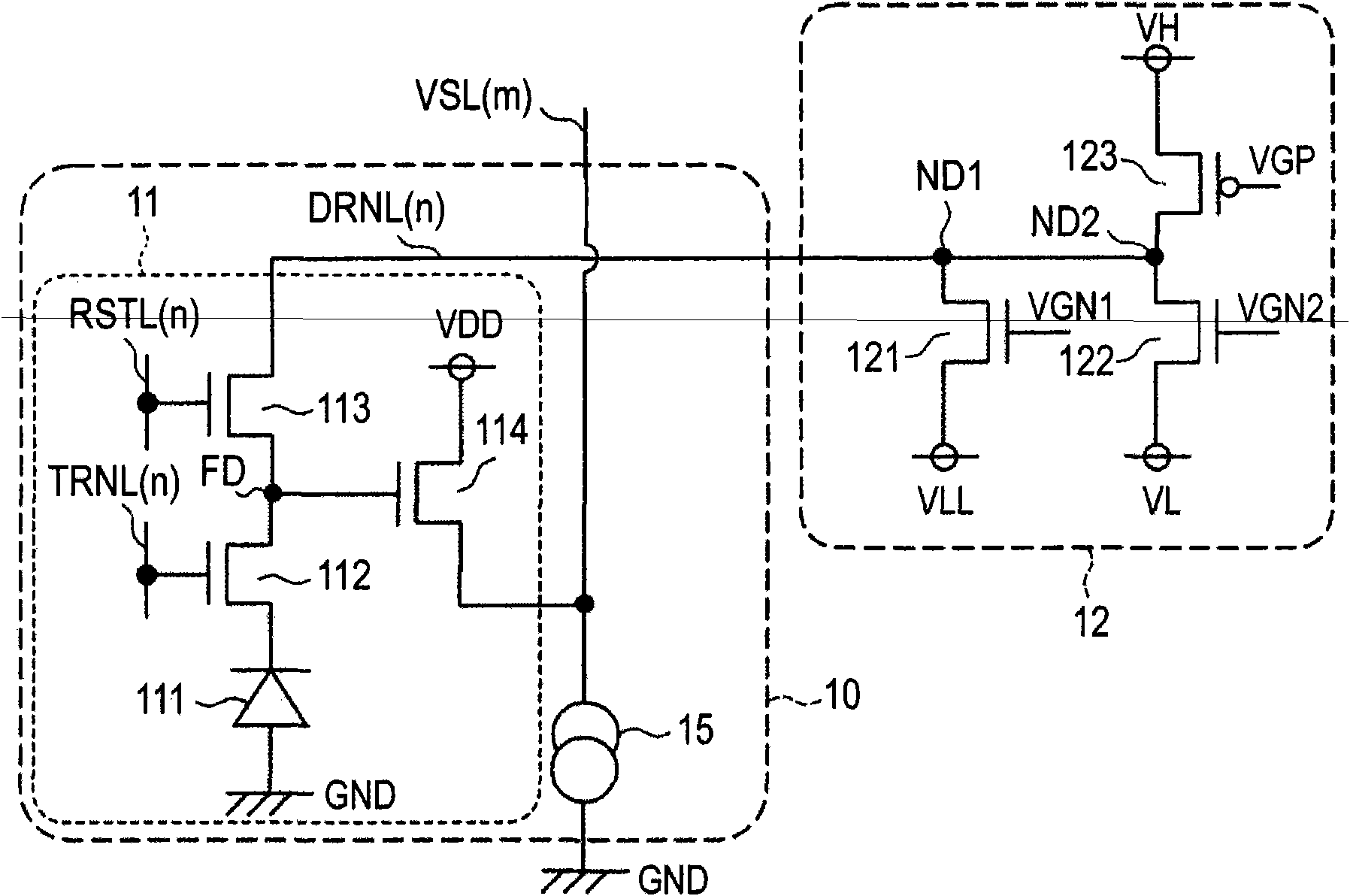
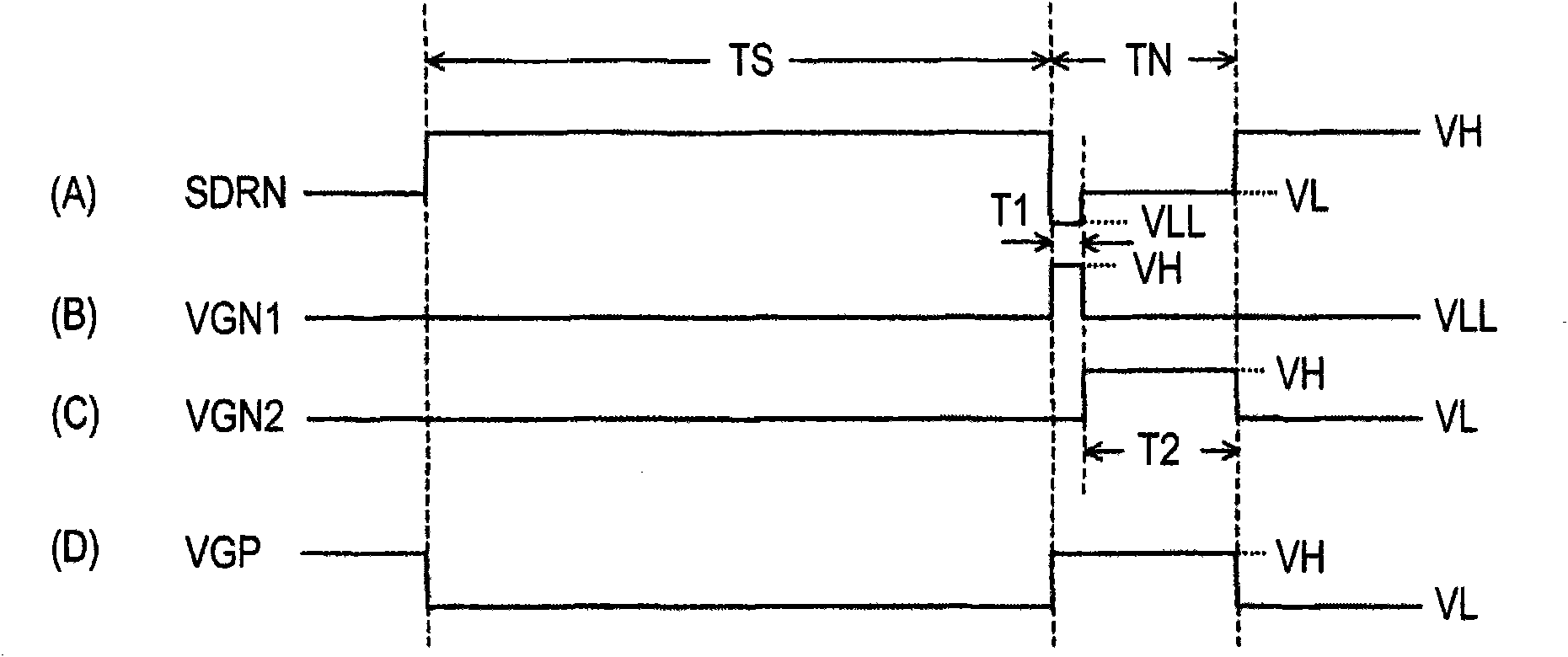
Provided are an imaging element capable of not only reducing noise such as shading but also executing high-speed pixel read-out, a method for controlling same, and a camera. In a three-transistor-driven pixel circuit (11), the drain of a reset transistor (113) is connected to a drive signal line DRNL (n), and the drain of an amplification transistor (114) is connected to a power supply voltage VDD. A row drive circuit (12a) rapidly switches the level of voltage to be applied to the drive signal line DRNL (n) from a high-level voltage VH to a lowest-level voltage VLL and slowly restores the voltage level from the lowest-level voltage VLL to the original high-level voltage VH through a low-level voltage VL.
Owner:SONY CORP
Recording apparatus and method
InactiveCN1558415AAvoid fragmentationHigh speed readoutTelevision system detailsMagneto-optical discsComputer hardwareComputer science
Before each content file is recorded first to a recording medium, a flag indicating a recording state of a content file is generated corresponding to a physical area where an index file can be continuously recorded. An index file is generated which associates attribute information with the generated flag added thereto with real data of each content file, and the generated index file is recorded to the recording medium. Since fragmentation of the physical area where the index file is recorded is restrained to a minimum level, a high-speed reading operation is realized.
Owner:SONY CORP
Imaging apparatus, imaging system, movable object, and method for driving imaging apparatus
ActiveUS11418745B2High-speed readoutHigh-quality image signalTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSoftware engineeringComparators circuits
An imaging apparatus including a ramp voltage generation circuit having a first period for outputting an offset voltage that sets a reference voltage for the comparator circuit, and a second period for outputting a reference voltage having a slope-shaped voltage waveform that varies with time, wherein the generation circuit has a first drive state in which a voltage change amount per unit time of the reference voltage in the second period is a first voltage amount, and a second drive state in which the voltage change amount per unit time of the reference voltage in the second period is a second voltage amount that is less than the first voltage amount, and wherein the offset voltage in the second drive state is less than a value obtained by multiplying the offset voltage in the first drive state by a ratio of the second voltage amount to the first voltage amount.
Owner:CANON KK
Nonvolatile memory for catching charges in isolative films
InactiveCN100416705CAccurate detectionHigh speed readoutTransistorSolid-state devicesAverage currentNormal cell
Dummy cells in an erased state and in a write state are used to generate a dummy current corresponding to the average current of currents flowing in the dummy cells using a 1 / 2 current generating circuit, and the dummy current is compared with a current corresponding to a memory cell current flowing in a selected normal cell using a current sense amplification circuit to generate internal read data according to a result of the comparison. With such a configuration, a non-volatile semiconductor memory device capable of reading data at high speed can be achieved.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com