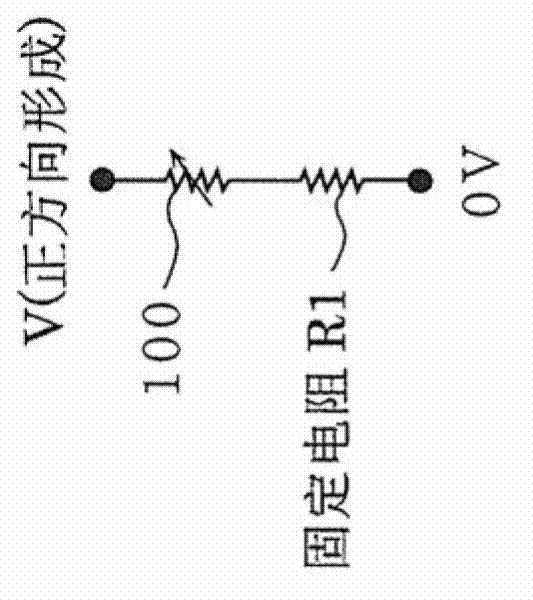
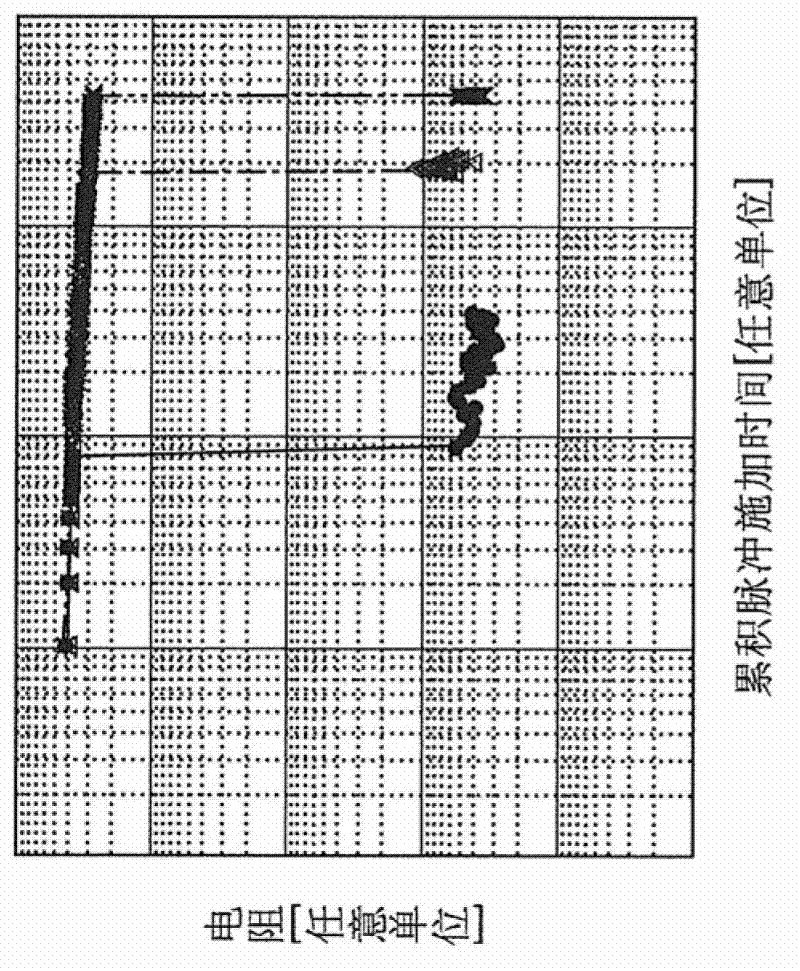
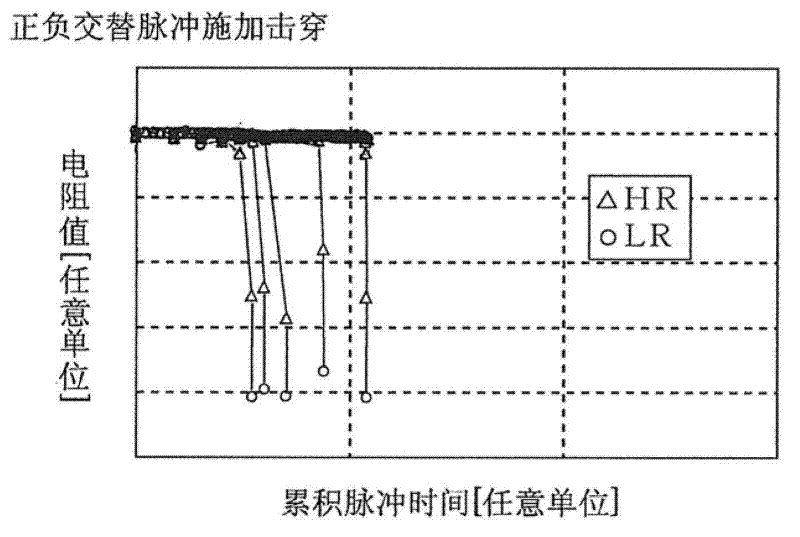
Forming method of performing forming on variable resistance nonvolatile memory element, and variable resistance nonvolatile memory device
A non-volatile storage, resistance change technology, applied in electrical components, information storage, static memory, etc., can solve the problems of reduced cell current, uneven voltage formed by resistance change elements, and increased voltage formed by resistance change elements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0284] Next, the description implements Figure 16 An example of the nonvolatile memory device of the formation flow is taken as the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0285] (Nonvolatile memory device according to the second embodiment)
[0286] Figure 19It is a block diagram showing an example of the configuration of the variable resistance nonvolatile memory device 200 (hereinafter, simply referred to as the nonvolatile memory device 200 ) according to the second embodiment of the present invention. and, Figure 20 is showing Figure 19 A perspective view of the structure of part A (the structure of the 4-bit part) in .
[0287] like Figure 19 It is shown that the nonvolatile memory device 200 according to this embodiment includes a memory main body 201 on a semiconductor substrate, and the memory main body 201 includes: a memory cell array 202; a row selection circuit / driver 203; a column selection circuit / driver 204; The writing circuit 205 is used to w...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0370] Next, the third embodiment of the present invention will describe a case in which the automatic formation control circuit 211 and the automatic formation circuit 210 in the nonvolatile memory device described in the second embodiment are not provided in the device, and from The outside of the nonvolatile memory device is controlled and implemented.
[0371] (Nonvolatile memory device according to the third embodiment)
[0372] Figure 26 It is a block diagram showing an example of the configuration of the variable resistance nonvolatile memory device 400 (hereinafter, simply referred to as the nonvolatile memory device 400 ) according to the embodiment of the present invention.
[0373] like Figure 26 As shown, the nonvolatile memory device 400 according to this embodiment includes a memory main body 401 on a semiconductor substrate, and the memory main body 401 includes a memory cell array 402 for Figure 39 The illustrated upper electrode 100c utilizes 1T1R type m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Film thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Film thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Film thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com