Bias voltage applying circuit and semiconductor memory device
一种偏置电压、偏置电路的技术,应用在读出技术领域,能够解决导通电阻变高、阻碍高速读出、过渡特性恶化等问题,达到高增益、实现高速读出的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0049] A first embodiment of a semiconductor memory device and a bias voltage applying circuit (hereinafter referred to as "the device of the present invention" and "the circuit of the present invention" as appropriate) according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
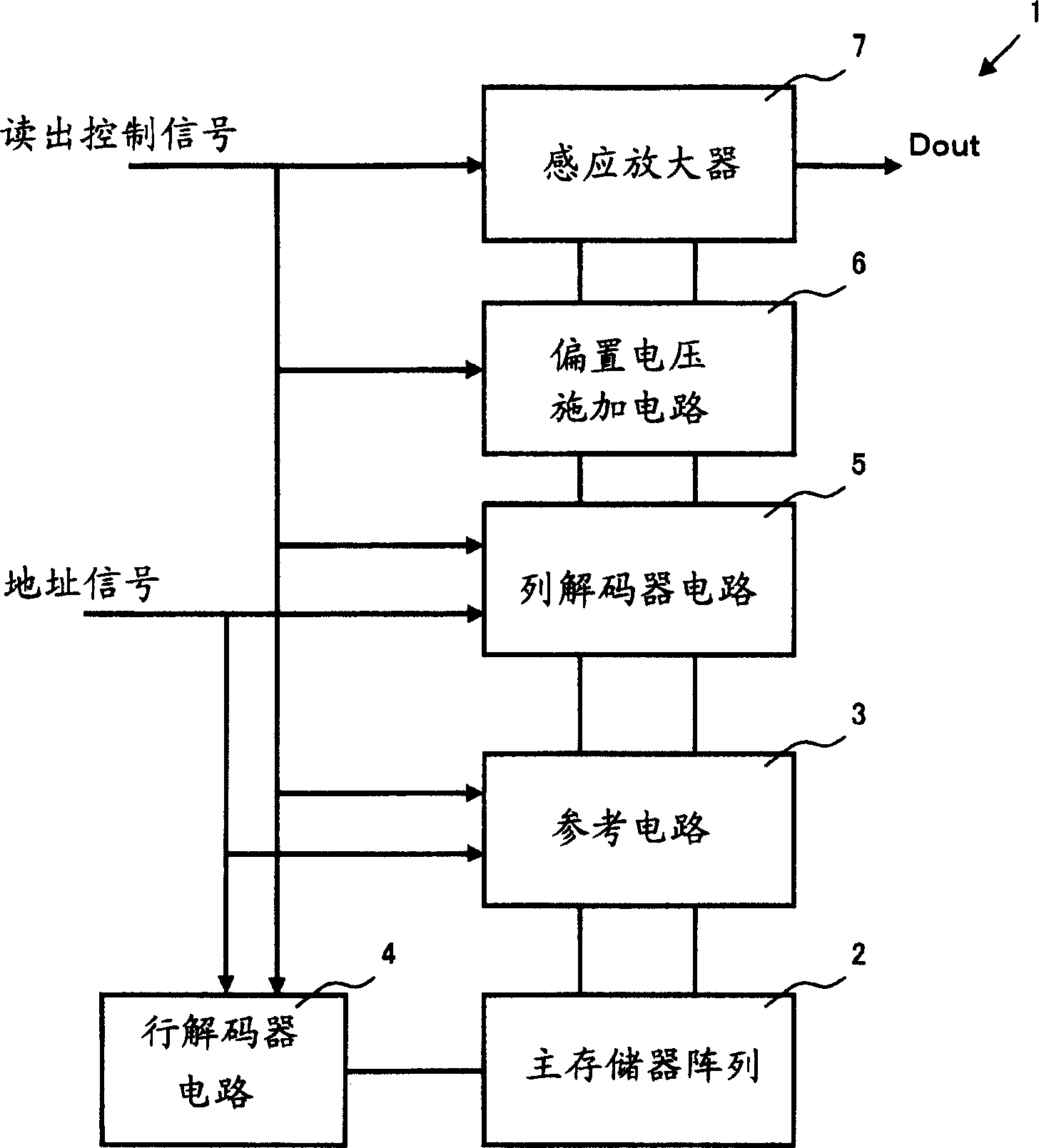
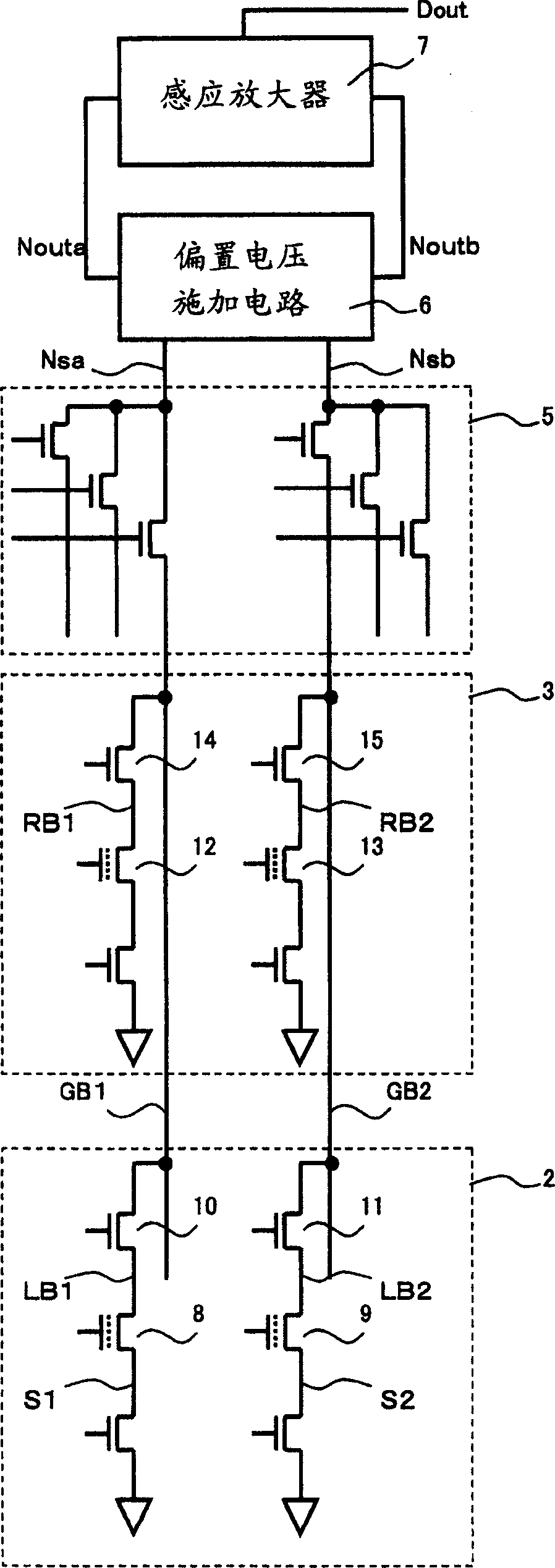
[0050] Such as figure 1 As shown, the device 1 of the present invention has: a main memory array 2, a reference circuit 3, a row decoder 4, a column decoder 5, a bias voltage applying circuit 6 involved in the present invention, a sense amplifier 7, and the like. Also, although not shown, necessary address signals and read control signals (chip enable signal, output enable signal, etc.) are separately supplied to each part via respective input circuits. In addition, the output Dout of the sense amplifier 7 is output to the outside via a predetermined output circuit.
[0051] The main memory array 2 is configured by arranging a plurality of memory cells to be read in an arra...
no. 2 approach
[0071] Next, the circuit configuration and circuit operation of the second embodiment of the semiconductor memory device according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
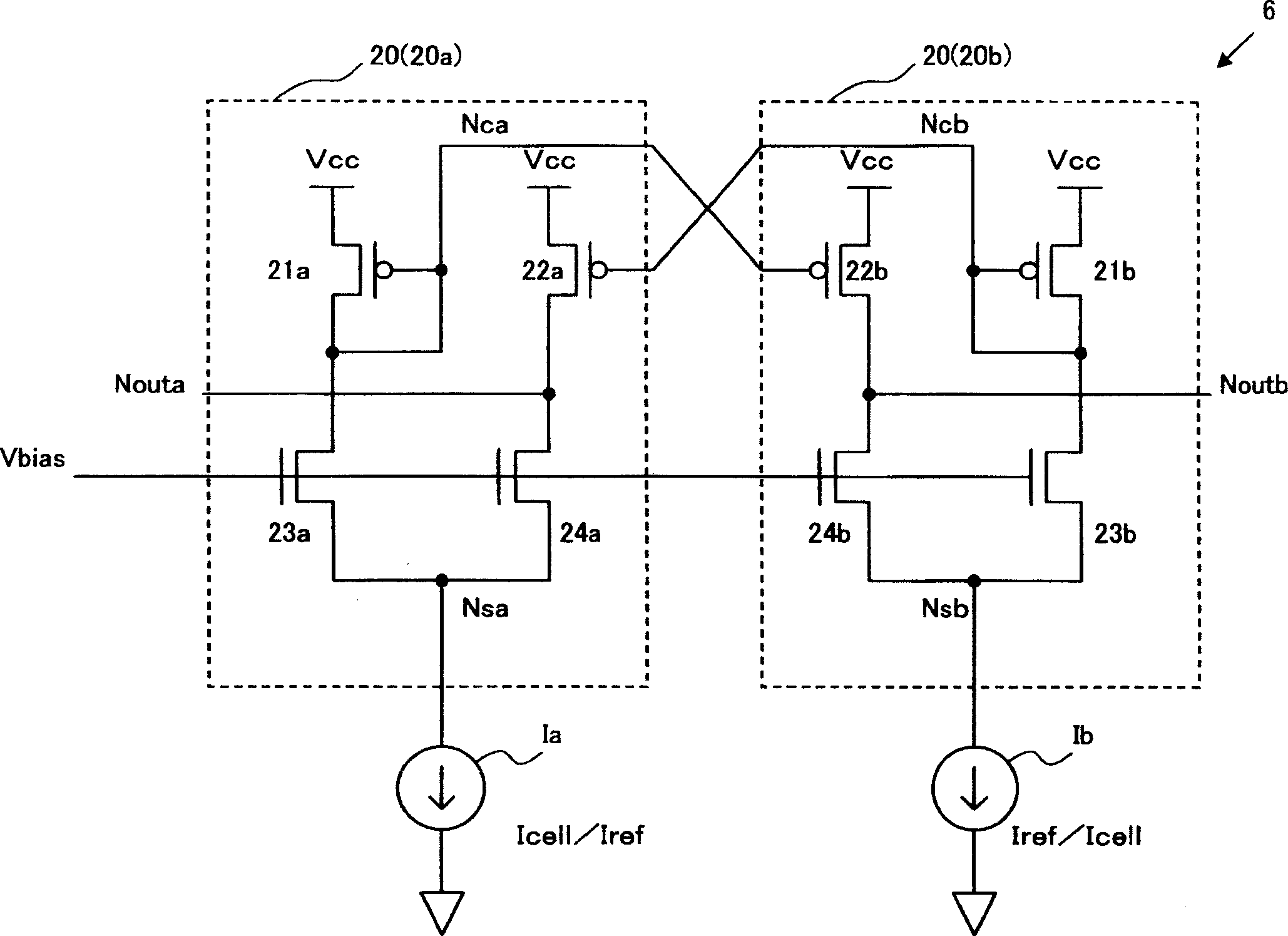
[0072] As shown in FIG. 11 , the inventive circuit 6 of this embodiment has two completely equivalent bias circuits 30 . As in the first embodiment, one is called a first bias circuit 30a, and the other is called a second bias circuit 30b. In addition, in the figure, the two current sources Ia and Ib are the same as those in the first embodiment, one of which represents the memory cell current Icell of the selected memory cell, and the other represents the reference cell current Iref of the reference memory cell. The memory cell current Icell of the selected memory cell varies according to the threshold voltage corresponding to the stored information.
[0073] The bias circuits 30a ( 30b ) of this embodiment are each composed of active elements including six MOSFETs. The...
no. 3 approach
[0084] Next, the circuit configuration and circuit operation of the third embodiment of the semiconductor memory device according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. In the second embodiment, the current path is divided and the memory cell current Icell or the reference memory cell current Iref copied from the first active element to the third active element is used, but in this embodiment, the current path is not divided. , but copy the current from the first active element to the third active element and the fourth active element respectively.
[0085] As shown in FIG. 12 , the inventive circuit 6 of this embodiment has two completely equivalent bias circuits 40 . As in the first and second embodiments, one is called a first bias circuit 40a, and the other is called a second bias circuit 40b. In addition, in the figure, the two current sources Ia and Ib are the same as those in the first and second embodiments, one of which represents ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com