Nonvolatile memory for catching charges in isolative films
A non-volatile storage and non-volatile technology, applied in the field of non-volatile semiconductor memory, can solve the problems of delay amplification circuit activation, unable to generate read data at high speed, unable to achieve high-speed access, etc., to achieve high-speed And the effect of accurate reading
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
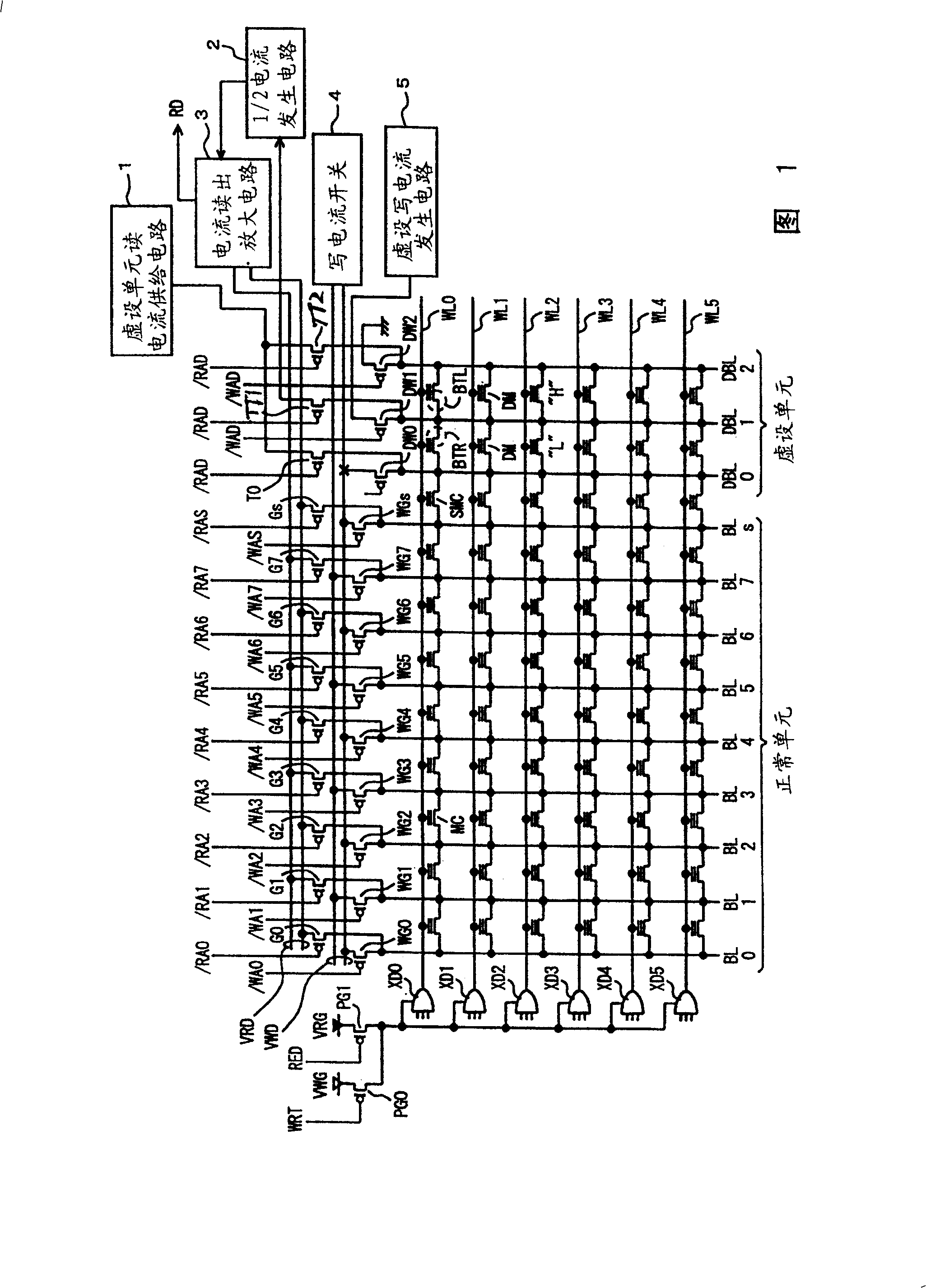
[0107] FIG. 1 is a diagram schematically showing the configuration of important parts of a nonvolatile semiconductor memory according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In FIG. 1 , the memory cell array includes normal memory cells (normal cells) MC arranged in rows and columns, and dummy cells DM arranged in line with the normal cells MC in the row direction. Word lines WL are arranged corresponding to each row of normal cells MC and dummy cells DM. In FIG. 1 , six word lines WL0 to WL5 are representatively shown.
[0108] Bit lines BL are arranged corresponding to each column of normal cells MC and shared by memory cells of adjacent columns. In FIG. 1 , normal bit lines BL0 to BL7 are representatively shown. The bit line BLs is arranged adjacent to the bit line BL7. Dummy bit lines DBL are arranged corresponding to each column of dummy cells DM. In FIG. 1, since dummy cells DM are arranged in two columns, three dummy bit lines DBL0 to DBL2 are shown.
[0109] Non-a...
Embodiment 2
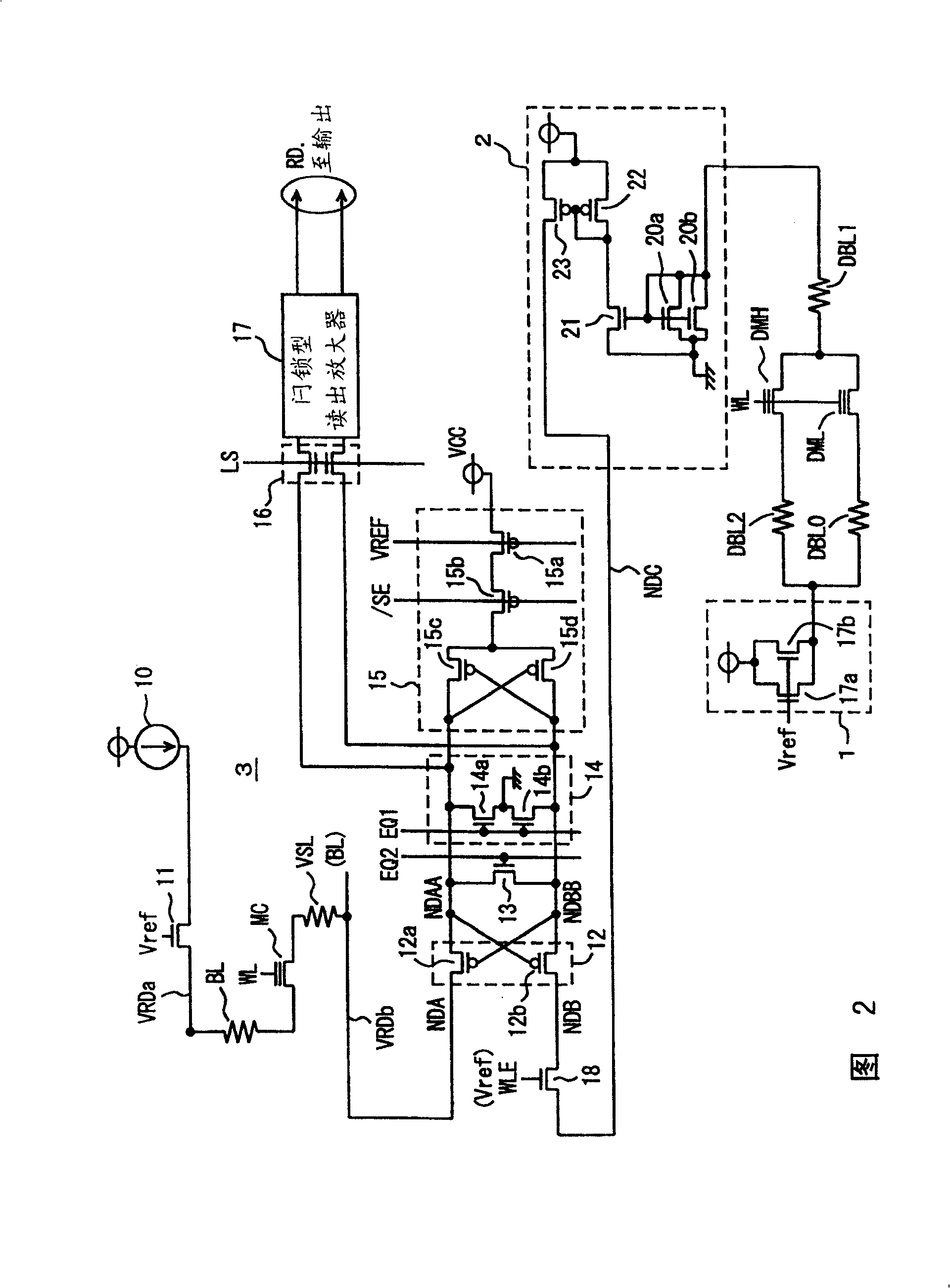
[0175] FIG. 5 is a diagram schematically showing the configuration of important parts of a nonvolatile semiconductor memory according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. The structure shown in FIG. 5 differs from the structure shown in FIG. 1 in the following points. That is, when data is read, a dummy read current i is supplied to dummy bit lines DBL0 and DBL2 , and a reference current generating circuit 30 that generates the average current and sends it to the current amplifier circuit 3 is provided. In addition, dummy bit line DBL1 is connected to the ground node through this read selection gate TT1 when data is read. The other structures are the same as those shown in FIG. 1, and the corresponding parts are denoted by the same reference numerals, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
[0176] In the configuration shown in FIG. 5, dummy bit line DBL1 is connected to the ground node when data is read. The reference current generating circuit 30 supplies a...
Embodiment 3
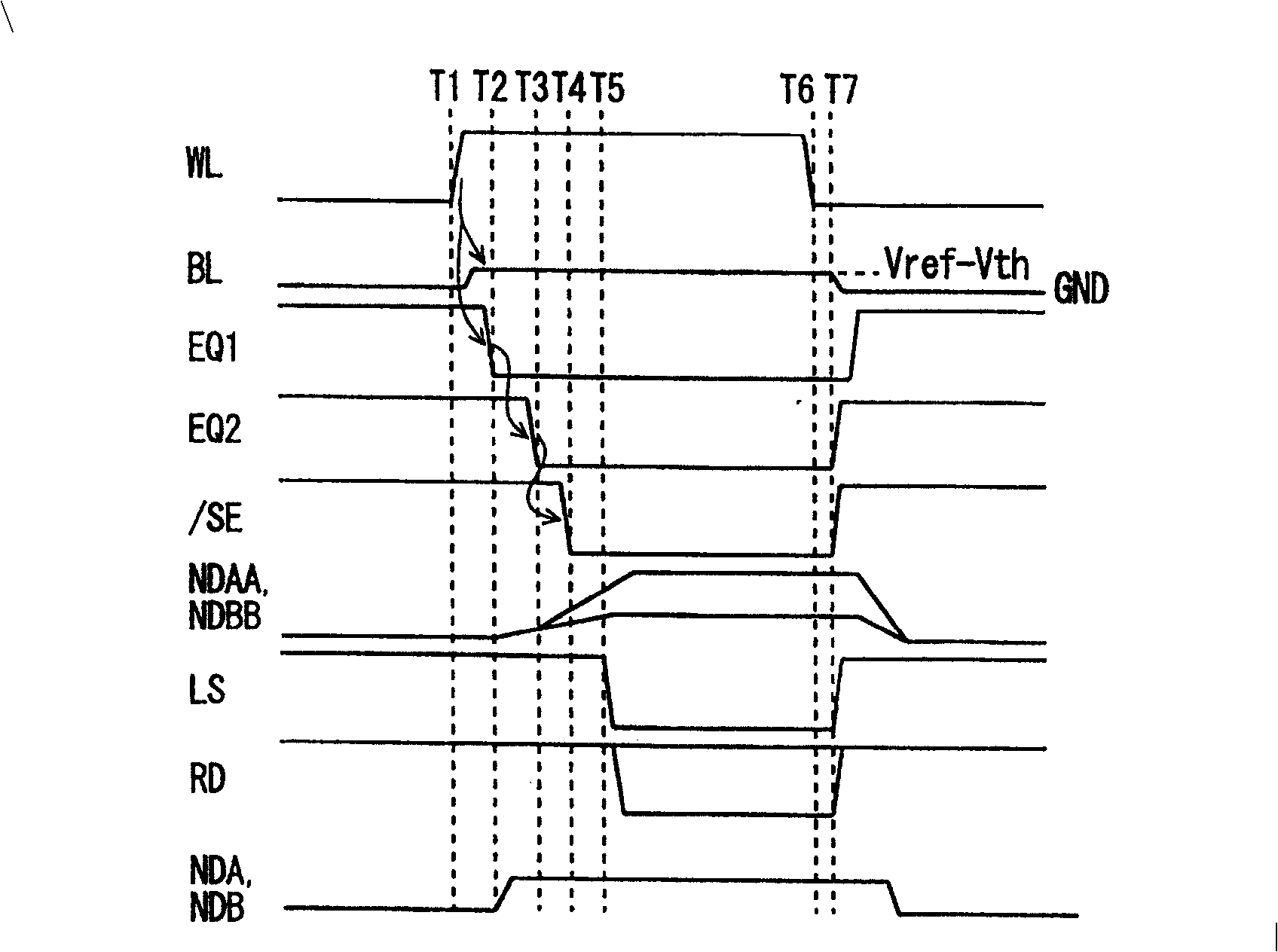
[0187] FIG. 7 is a structural diagram showing important parts of a nonvolatile semiconductor memory according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. In FIG. 7, the current sense / amplifier circuit 3 has the same structure as that of the first and second embodiments. However, this current read / amplifier circuit 3 compares the current flowing through the internal read data line VRDa with the current supplied from the subtraction circuit 45 , unlike the first and second embodiments described above. That is, in the configuration shown in FIG. 7 , the current sense / amplifier circuit 3 uses the current obtained by subtracting the current flowing through the memory cell from the reference current as a comparison object.
[0188] In this third embodiment, dummy cells DM and normal cells MC are arranged in a straight line within the same array. The structure of the memory cell array in Embodiment 3 is the same as that of the memory cell array shown in FIG. 1 or FIG. 5 .
[0189] In...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com