Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
101results about "Pulping with halogen compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
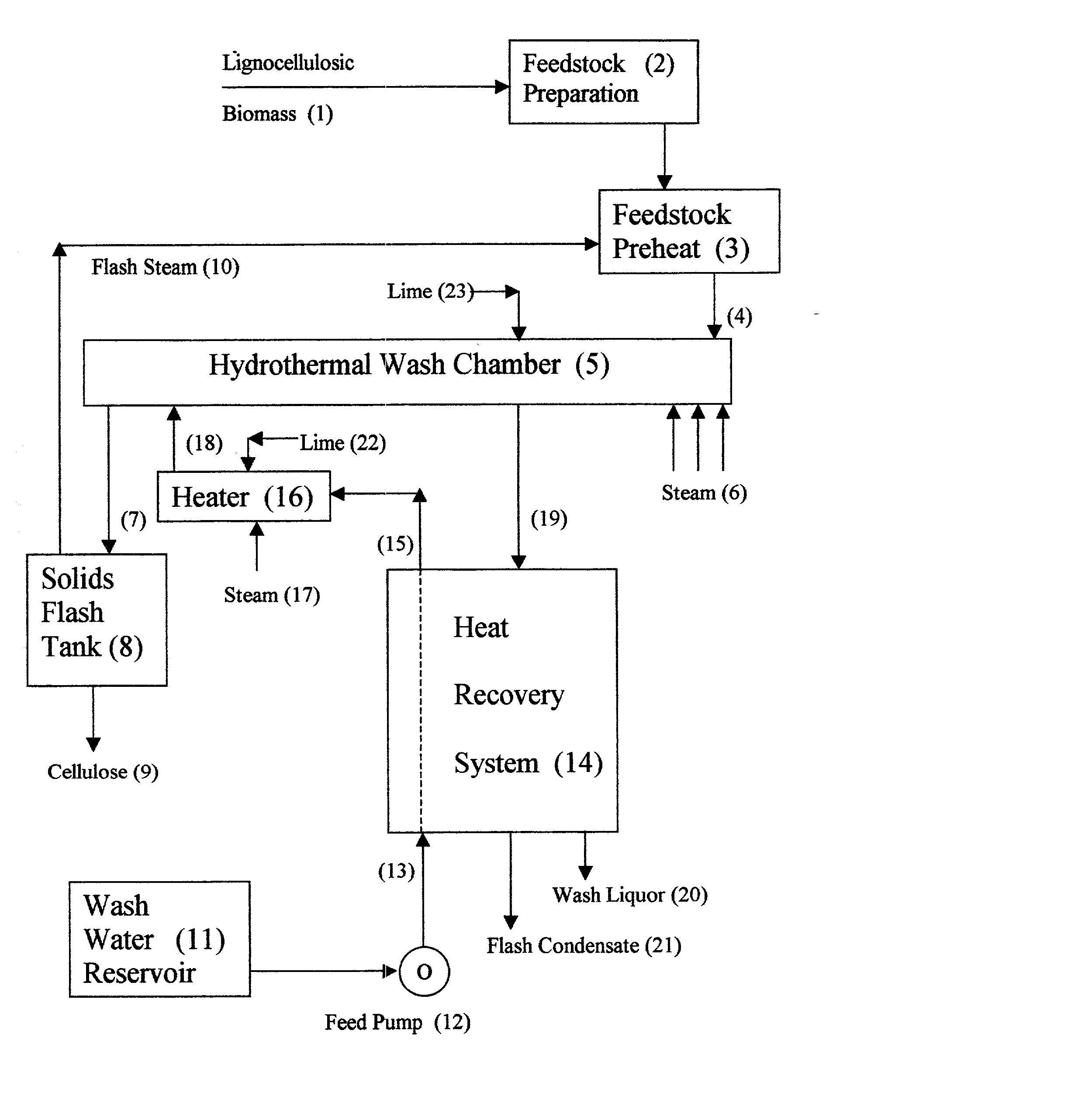
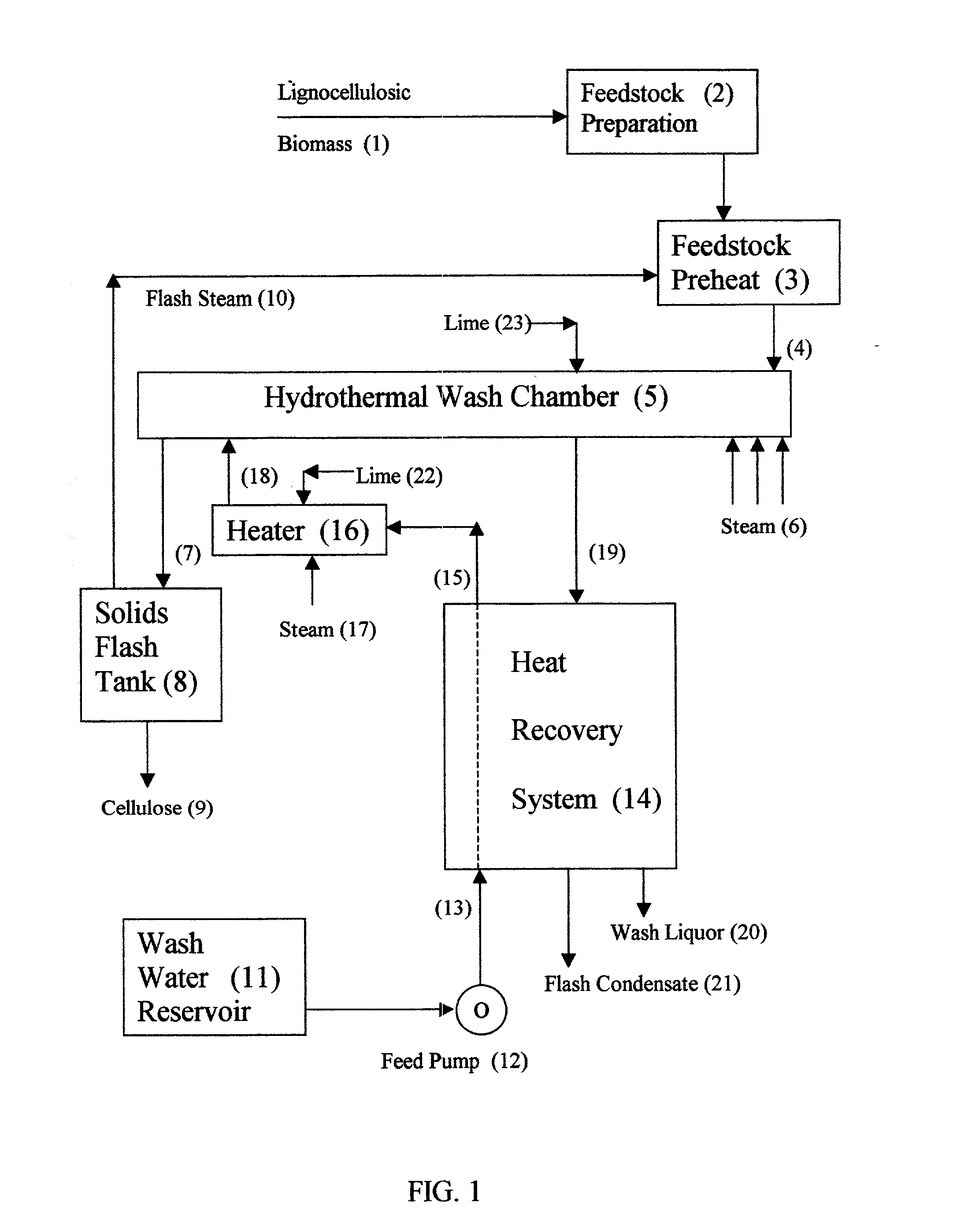
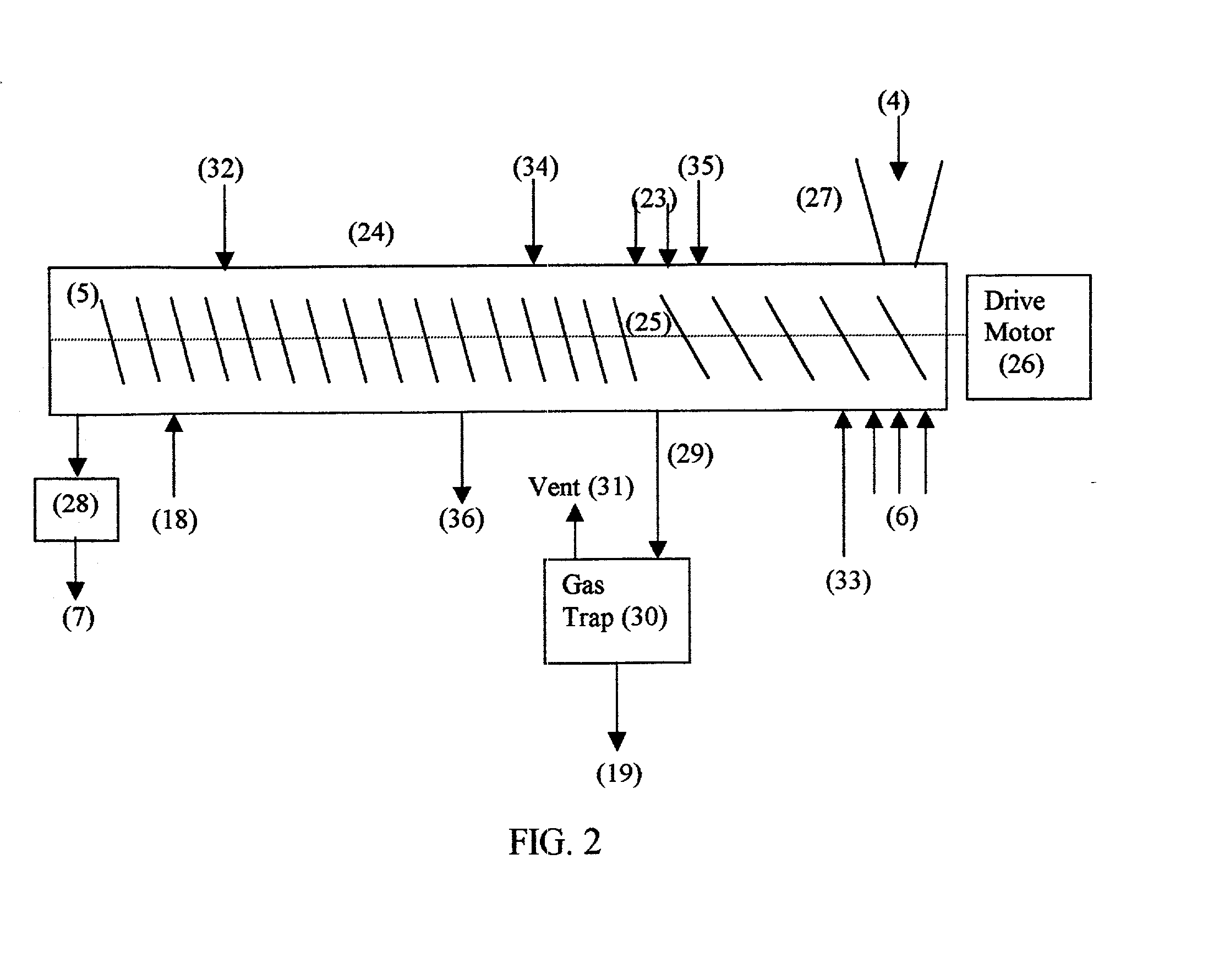
Ligno cellulosic materials and the products made therefrom
ActiveUS20060260773A1Reducing functional groupGood drainage propertyBiocidePaper after-treatmentCelluloseHypochlorite
A process comprising treating a lignocellulosic material preferably pulp in the presence of a transition metal catalyst with a oxidizing agent selected from a group consisting of hydrogen peroxide, hypochlorite, hypochlorous acid and any combination thereof to form a treated lignocellulosic material having a viscosity equal to or less than about 17 cp and having reducing functional groups selected from the group consisting of aldehyde and aldehyde type functional groups at the C6 and C1 positions but predominating at the C1 position.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Product and processes from an integrated forest biorefinery
ActiveUS20070079944A1Easy to optimizePretreatment with water/steamPulping with acid salts/anhydridesPulp and paper industrySugar
An omnibus process of pulping and bleaching lignocellulosic materials in which a charge of a lignocellulosic material is biopulped and / or water extracted prior to pulping and bleaching. The lignocellulosic material may be mechanically pulped and bleached in the presence of an enzyme that breaks lignin-carbohydrate complexes. The aqueous extract in embodiments including a water extract step is separated into acetic acid and hemicellulose sugar aqueous solutions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
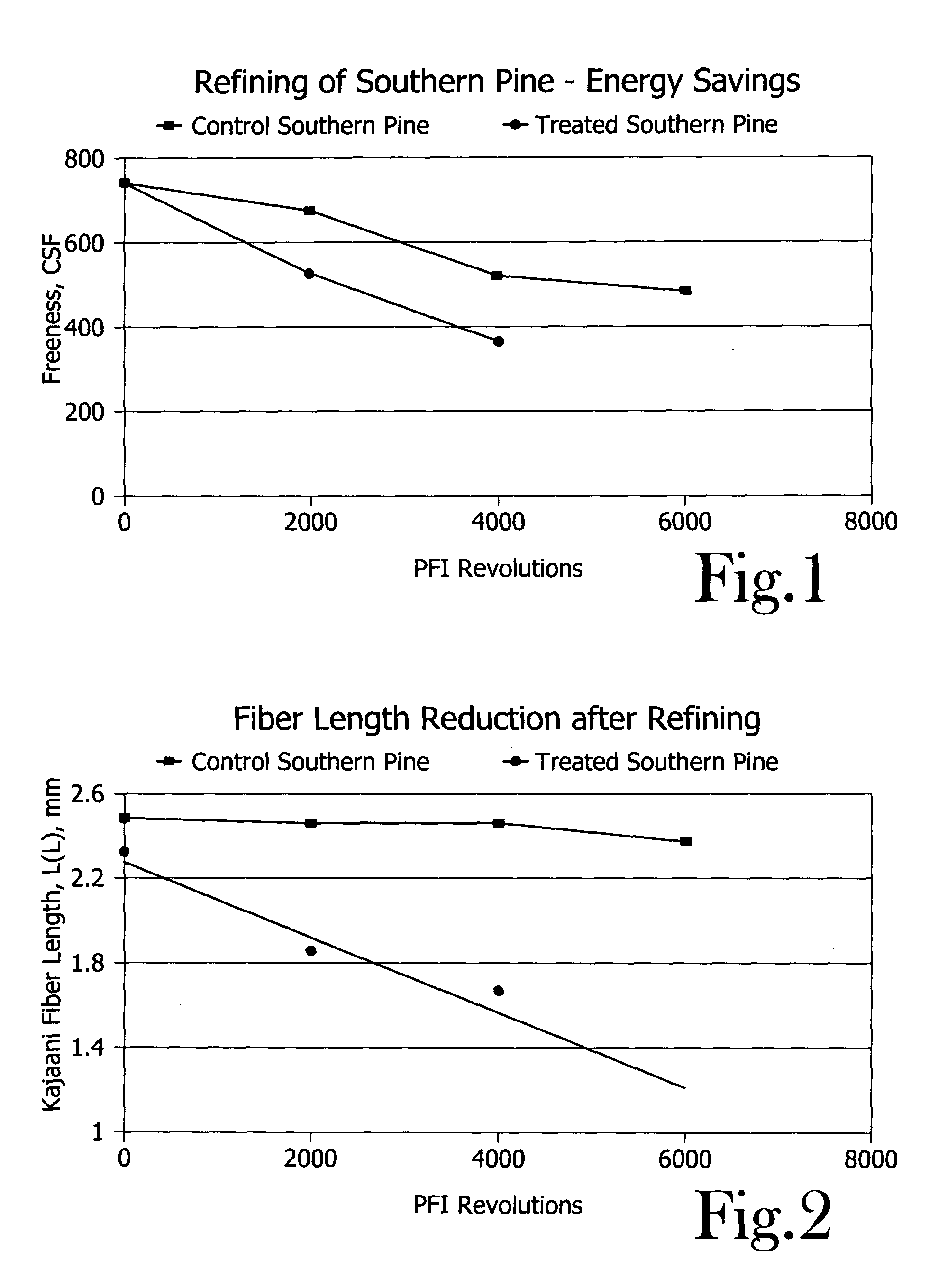
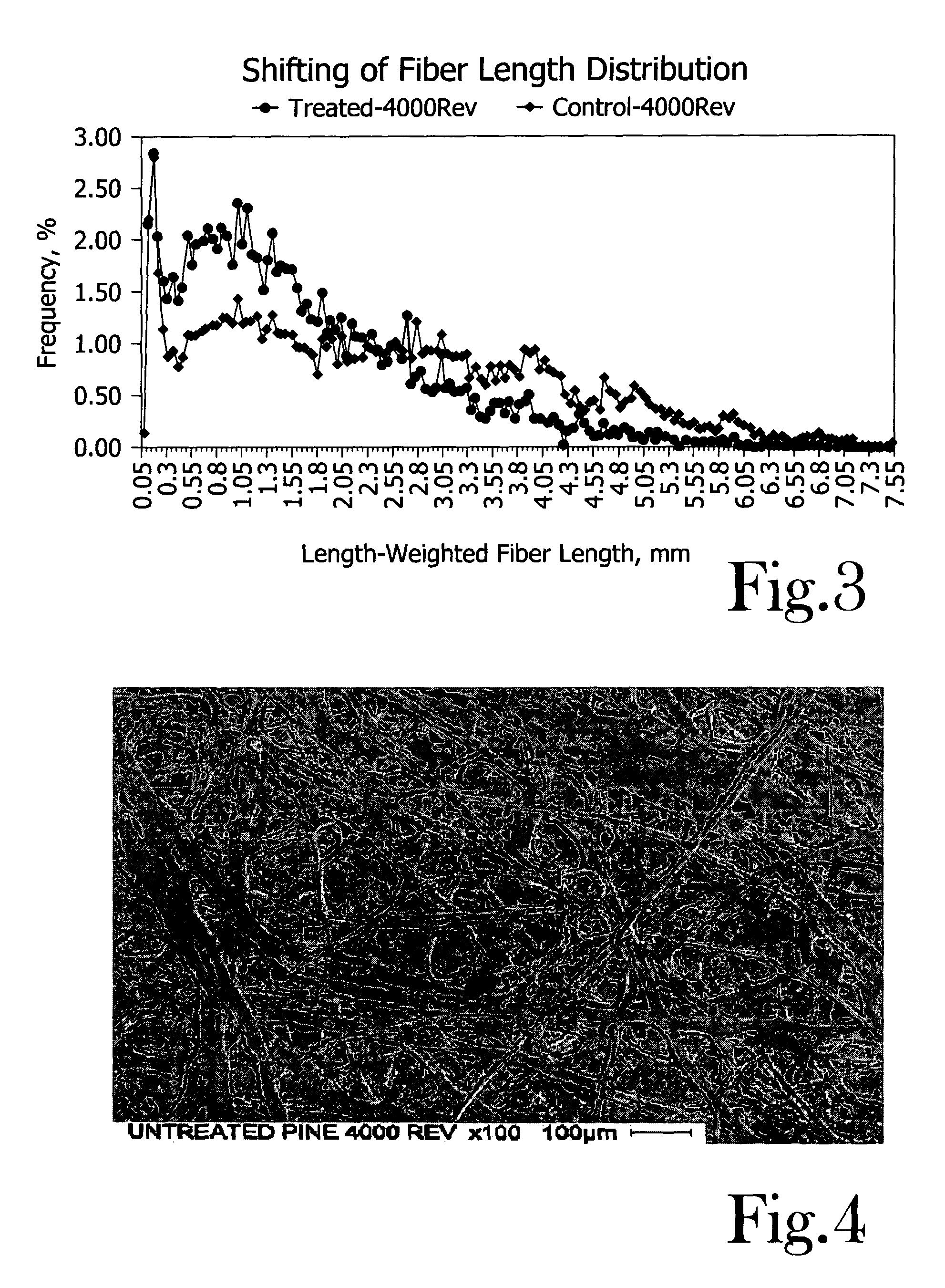
Chemical activation and refining of southern pine kraft fibers
InactiveUS20050061455A1Increase the pulp freenessEasy to drainPulp properties modificationPulp bleachingChemical treatmentCellulose fiber
A method for alteration of the morphology of cellulose fibers, particularly softwood fibers, by (a) subjecting the fibers to a metal ion-activated peroxide treatment carried out at a pH of between about 1 and about 9, preferably between 3 and 7, and (b) subjecting the treated fibers to a refining treatment thereby converts SW fibers to HW-like fibers in many respects. The metal ion-activated peroxide treatment has been noted to act on pulp cellulose and hemi-cellulose, causing oxidation and oxidative degradation of cellulose fibers. The chemical treatment of the pulp, taken alone, is not sufficient to attain the desired modification of the morphology of the fibers, however, subsequent refining or like mechanical treatment of the chemically-treated fibers to achieve a given degree of refinement of the fibers requires dramatically less refining energy to achieve a desired end point of refinement and to impart other desirable properties to the pulp. A pulp of modified SW fibers and a mixture of HW fibers and modified HW fibers are disclosed.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
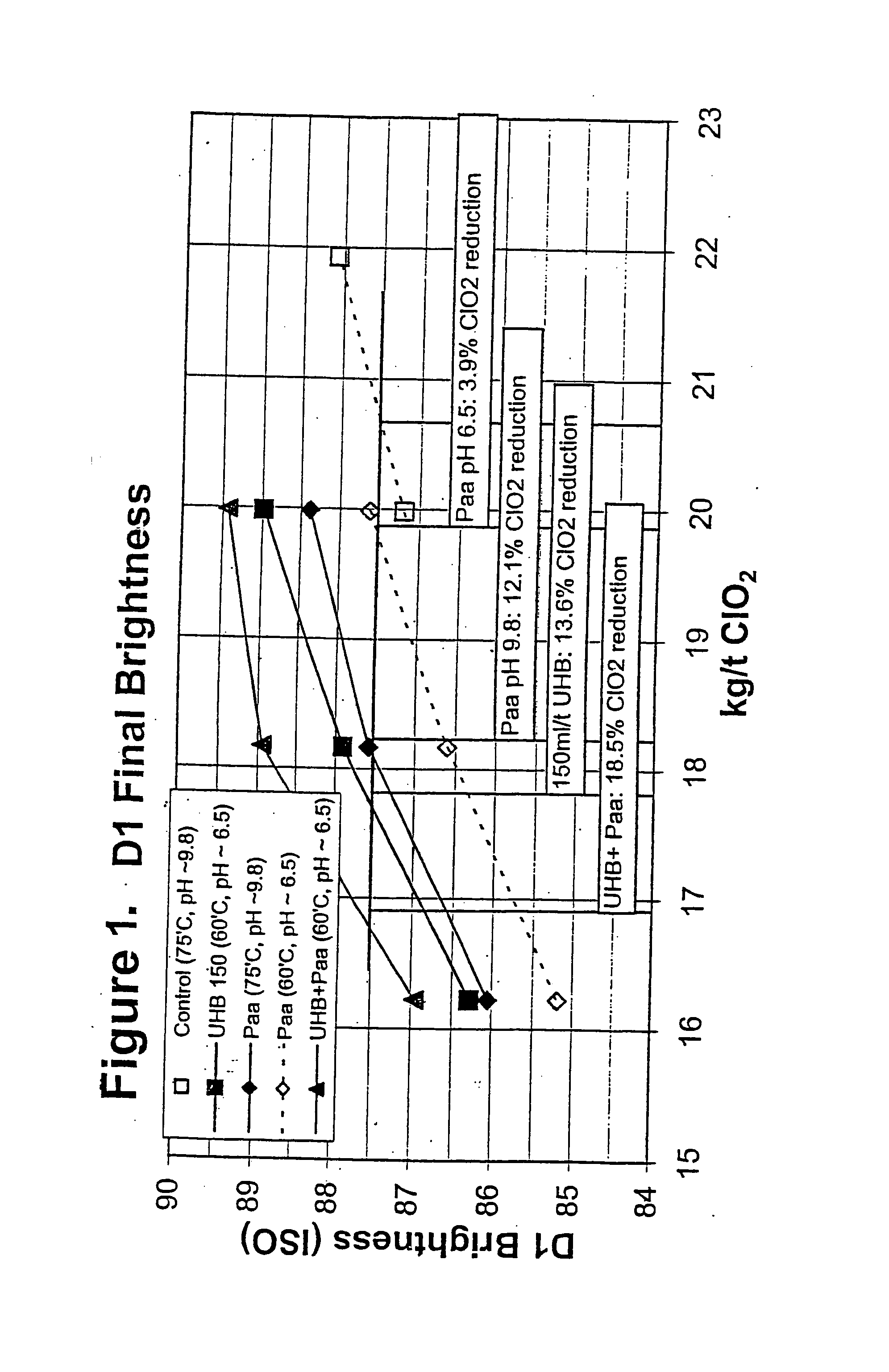
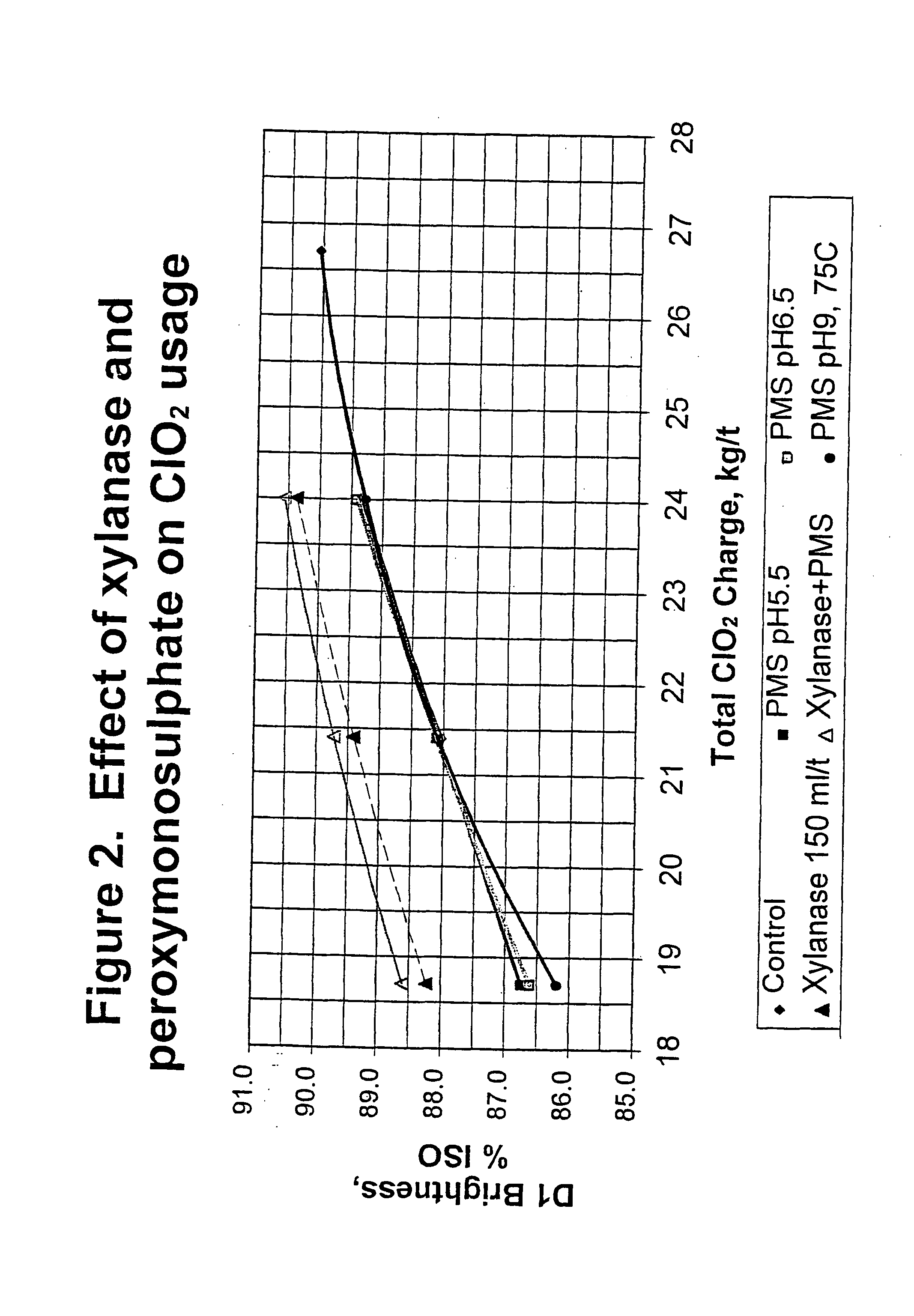
Bleaching stage using xylanase with hydrogen peroxide, peracids, or a combination thereof
InactiveUS20040112555A1Less-costly bleaching operationReduce usagePulp bleachingPulping with inorganic basesChlorine dioxideXylanase Y
The present invention discloses methods of bleaching chemical pulp that combine xylanase enzymes with hydrogen peroxide, peracids, or a mixture. The method comprises the steps of carrying out a chemical pulping operation, optionally followed by delignifying the pulp with oxygen, then combining xylanase enzymes with hydrogen peroxide, peracids, or a mixture to bleach the pulp. The method allows the mill to use both xylanase and peracids in a single bleaching tower to decrease the usage of chlorine dioxide and other bleaching chemicals. The pulp bleaching method of the present invention may be performed in a pulp mill as part of a complex pulp bleaching process.
Owner:IOGEN BIO PRODUCKTS CORP
Compositions and processes for paper production
ActiveUS20080017337A1Avoid brightness lossIncrease brightnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPaper productionPapermaking
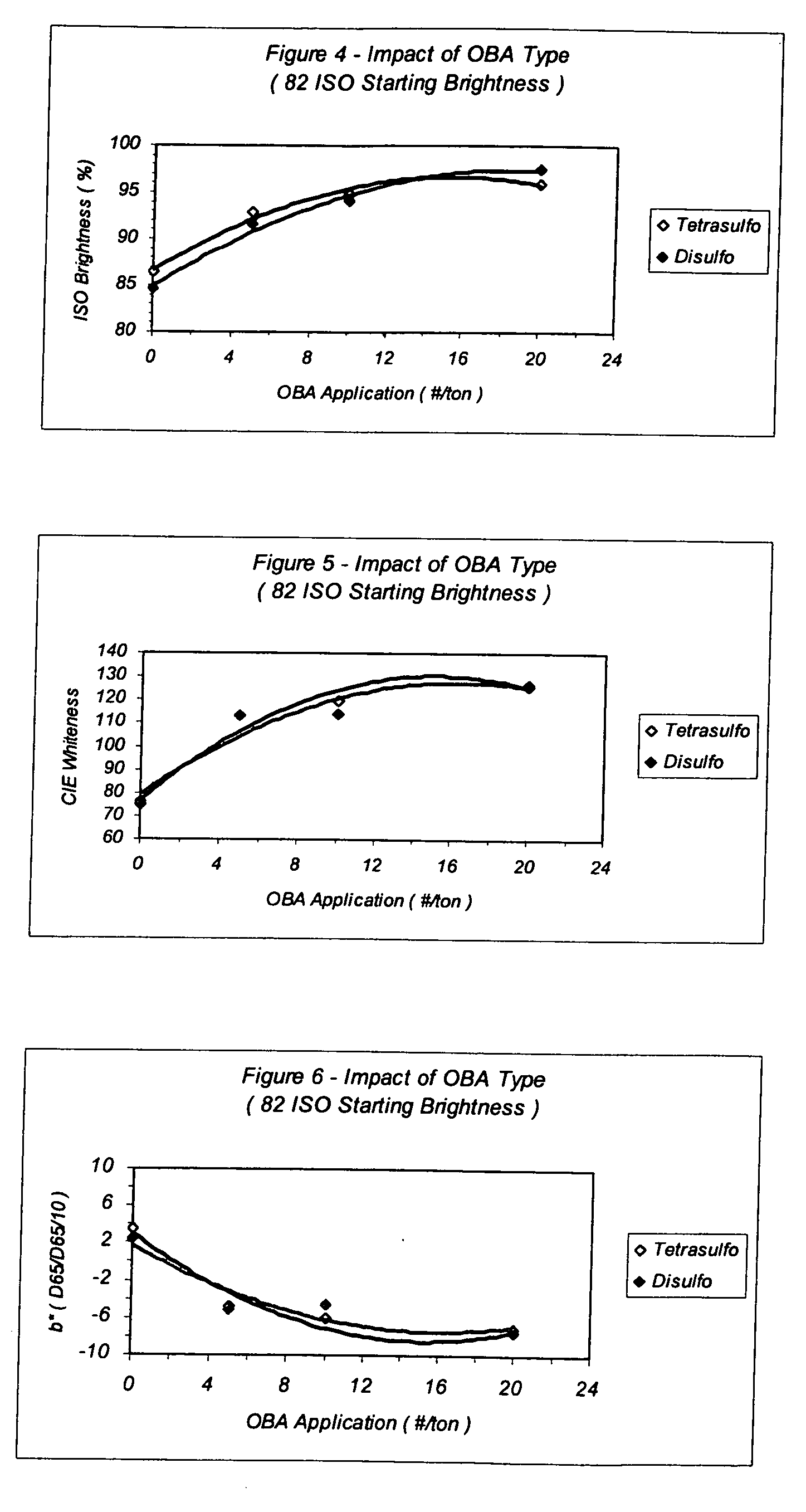
Oxidative compositions and processes that preserve and enhance the brightness and improve color of pulp or paper when applied during different stages of the papermaking process are identified. The oxidative composition and method maintains and / or enhances brightness, prevents yellowing, and enhances the performance of paper products. Used in combination with optical brighteners and / or chelants the oxidative agents produce a synergistic effect not previously identified in the paper process.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
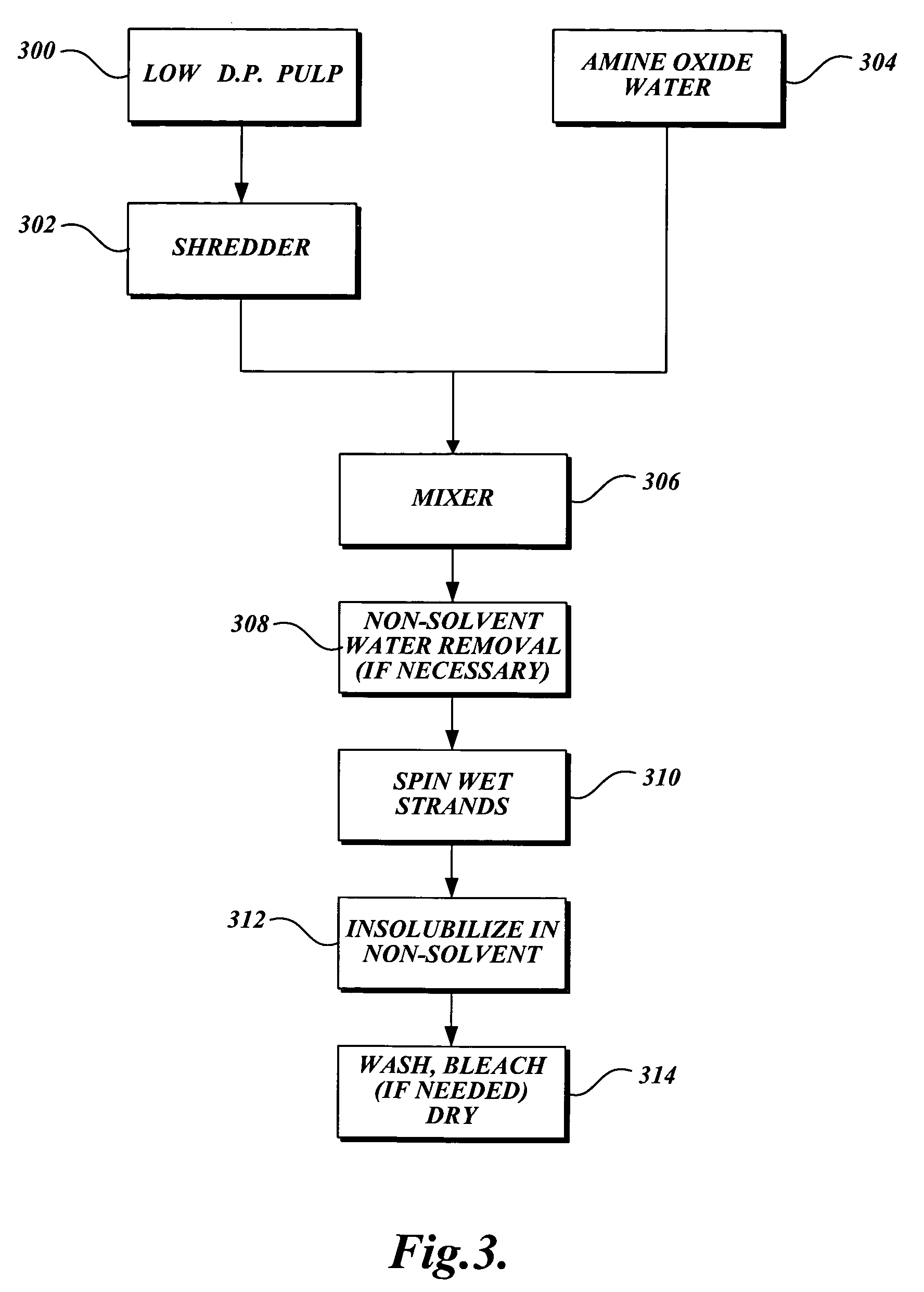
Low pH treatment of pulp in a bleach sequence to produce pulp having low D.P. and low copper number for use in lyocell manufacture
InactiveUS20060070711A1Reduce the degree of polymerizationIncreasing copper numberPulp properties modificationLayered productsBleachPulp mill
A high pH and a low pH process for reducing the degree of polymerization of a pulp having a hemicellulose content of at least 7%. The high pH is greater than 8, and the low pH process is 2 to 8. The high pH process reduces the degree of polymerization without substantially increasing the copper number. The low pH process requires a subsequent treatment with alkali to reduce the copper number of the pulp to less than 2. The process can be practiced in pulp mills with a bleaching sequence having one or more E or D stages. At the end of the bleach sequence, a pulp having a degree of polymerization of 200 to 1100, a copper number of less than 2, and a hemicellulose content of at least 7% is provided. The pulp can be used to make lyocell fibers.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
Cellulose production from lignocellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20020148575A1Low costHigh yieldPretreatment with water/steamPulp liquor regenerationEnergy recoveryCellulose fiber
A multi-function process is described for the separation of cellulose fibers from the other constituents of lignocellulosic biomass such as found in trees, grasses, agricultural waste, and waste paper with application in the preparation of feedstocks for use in the manufacture of paper, plastics, ethanol, and other chemicals. This process minimizes waste disposal problems since it uses only steam, water, and oxygen at elevated temperature in the range of 180° C. to 240° C. for 1 to 10 minutes plus a small amount of chemical reagents to maintain pH in the range 8 to 13. An energy recuperation function is important to the economic viability of the process.
Owner:PUREVISION TECH
Nanofiber sheet, process for producing the same, and fiber-reinforced composite material
ActiveUS20090264036A1High cellulose fiber crystallinityReduction factorFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPrinted circuit aspectsPolymer scienceYoung's modulus
Provided is a nanofiber sheet that sufficiently refined by fibrillation and has high crystallinity of cellulose fiber and can realize a fiber-reinforced composite material exhibiting high transparency, a high elastic modulus, a low coefficient of linear thermal expansion, and high heat resistance and being high in flatness and smoothness. This nanofiber sheet includes crystalline cellulose as the main component and a lignin in an amount of from 10 ppm to 10 wt %. When a fiber / resin composite material obtained by impregnating the nanofiber sheet with tricyclodecane dimethacrylate, subjecting the impregnated product to UV-curing at 20 J / cm2, and heating the cured product in vacuum at 160° C. for two hours includes 60 wt % of the cured tricyclodecane dimethacrylate and 40 wt % of nanofiber, the following physical characteristics (i) to (iii) are satisfied: (i) the parallel light transmittance of light of a wavelength of 600 nm at a sheet thickness of 100 μm is 70% or more; (ii) the Young's modulus is 5.0 GPa or more; and (iii) the coefficient of linear thermal expansion is 20 ppm / K or less.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD +1
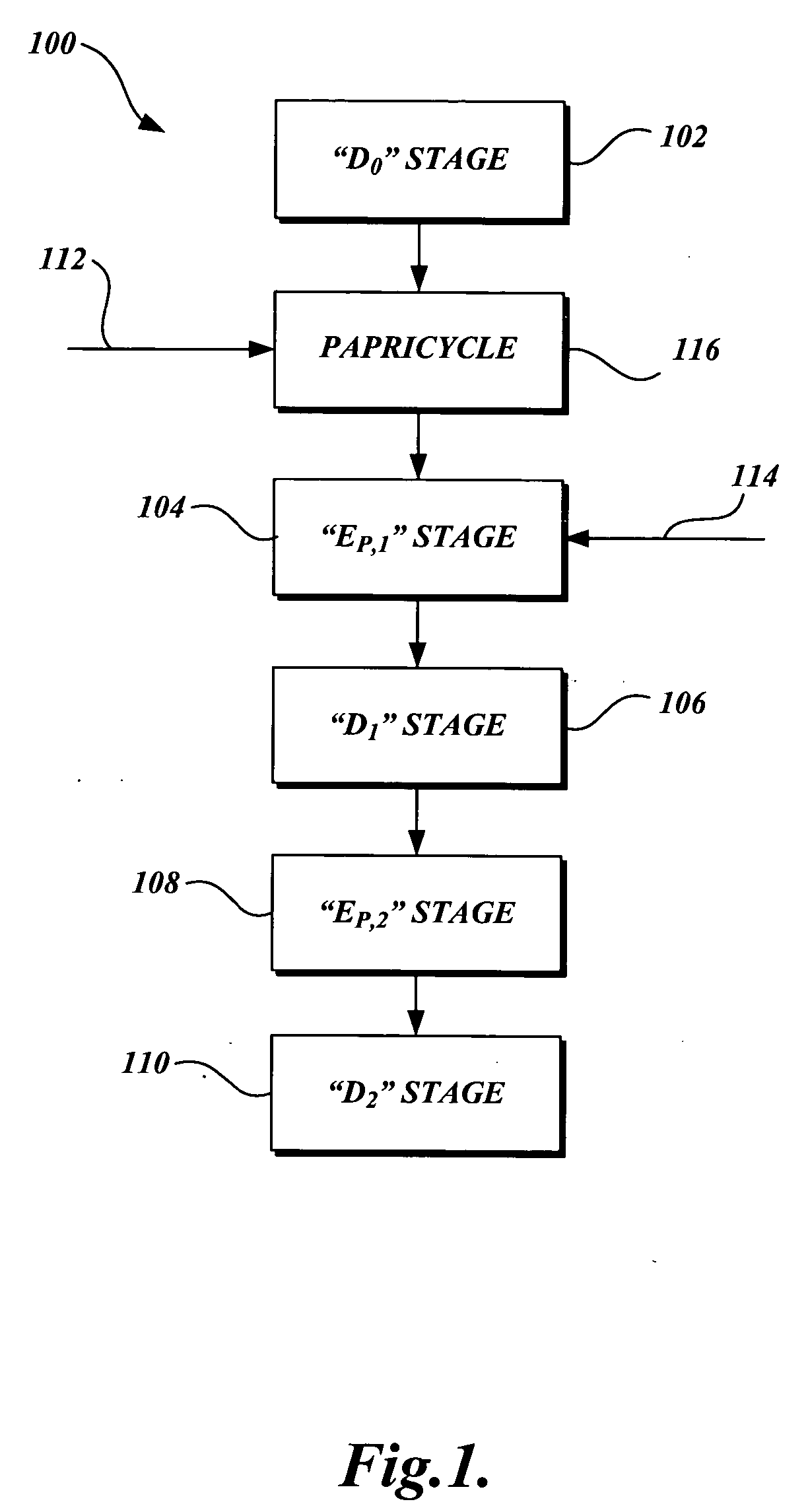
Xylanase treatment of chemical pulp
InactiveUS20050150619A1Reduce usageHigh strengthPulp bleachingPulping with organic solventsChlorine dioxidePulp mill
The present invention discloses methods of bleaching chemical pulp that use xylanase enzymes after chemical bleaching. The method comprises the steps of carrying out a chlorine dioxide stage to produce a partially bleached pulp, treating the partially bleached pulp with a xylanase enzyme, optionally in the presence of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, in a mild extraction stage, then bleaching the pulp with a second chlorine dioxide stage. The method allows the mill to decrease the usage of sodium hydroxide or other alkali, while decreasing the use of chlorine dioxide, and possibly improving the yield and strength of the pulp, while maintaining a similar level of bleached brightness of the pulp. The pulp bleaching method of the present invention may be performed in a pulp mill as part of a complex pulp bleaching process.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
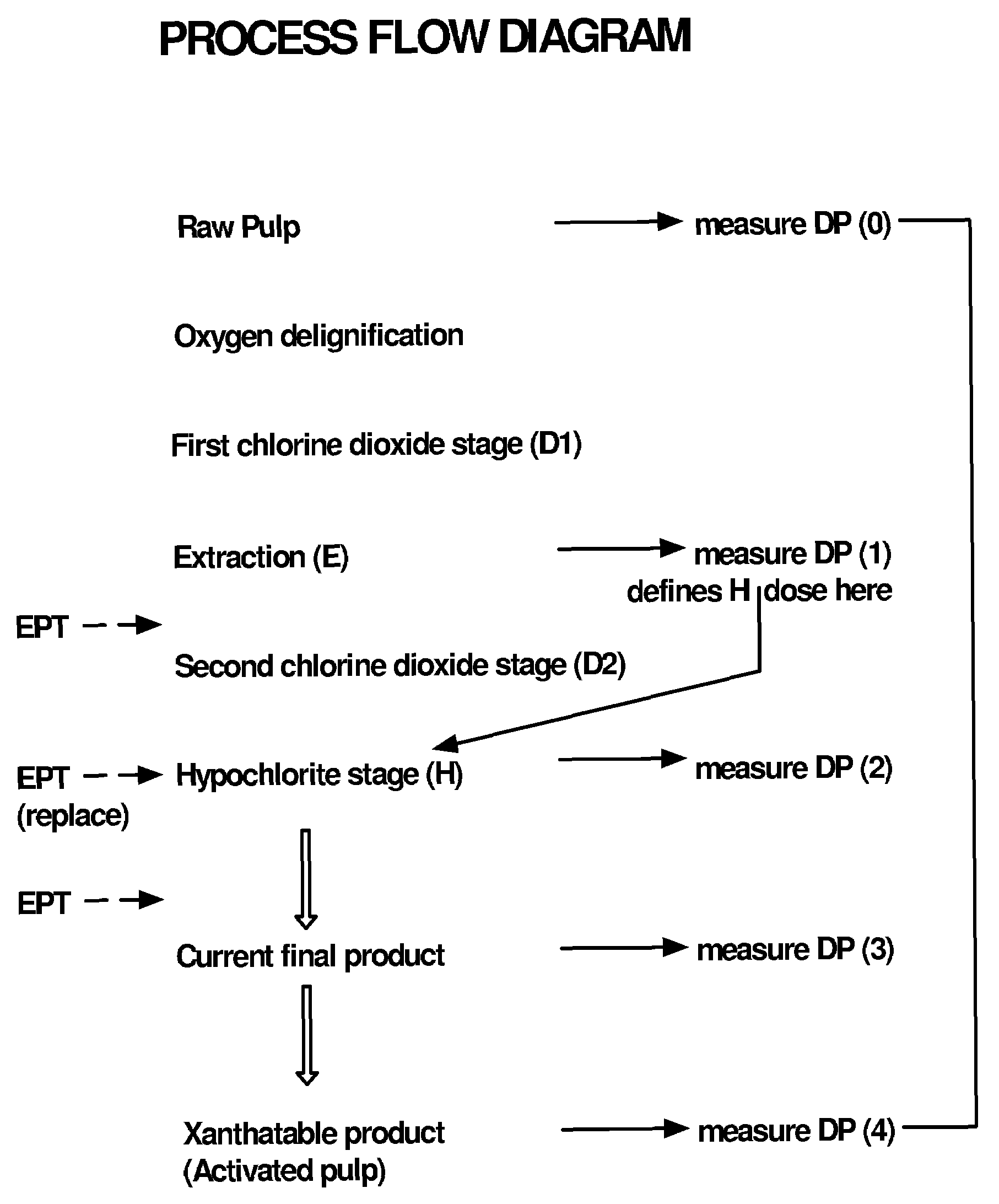
Pulp treatment and process
InactiveUS7267744B2Reduce stepsReduce in quantityElectrolysis componentsWood treatment detailsPulp treatmentCompound (substance)
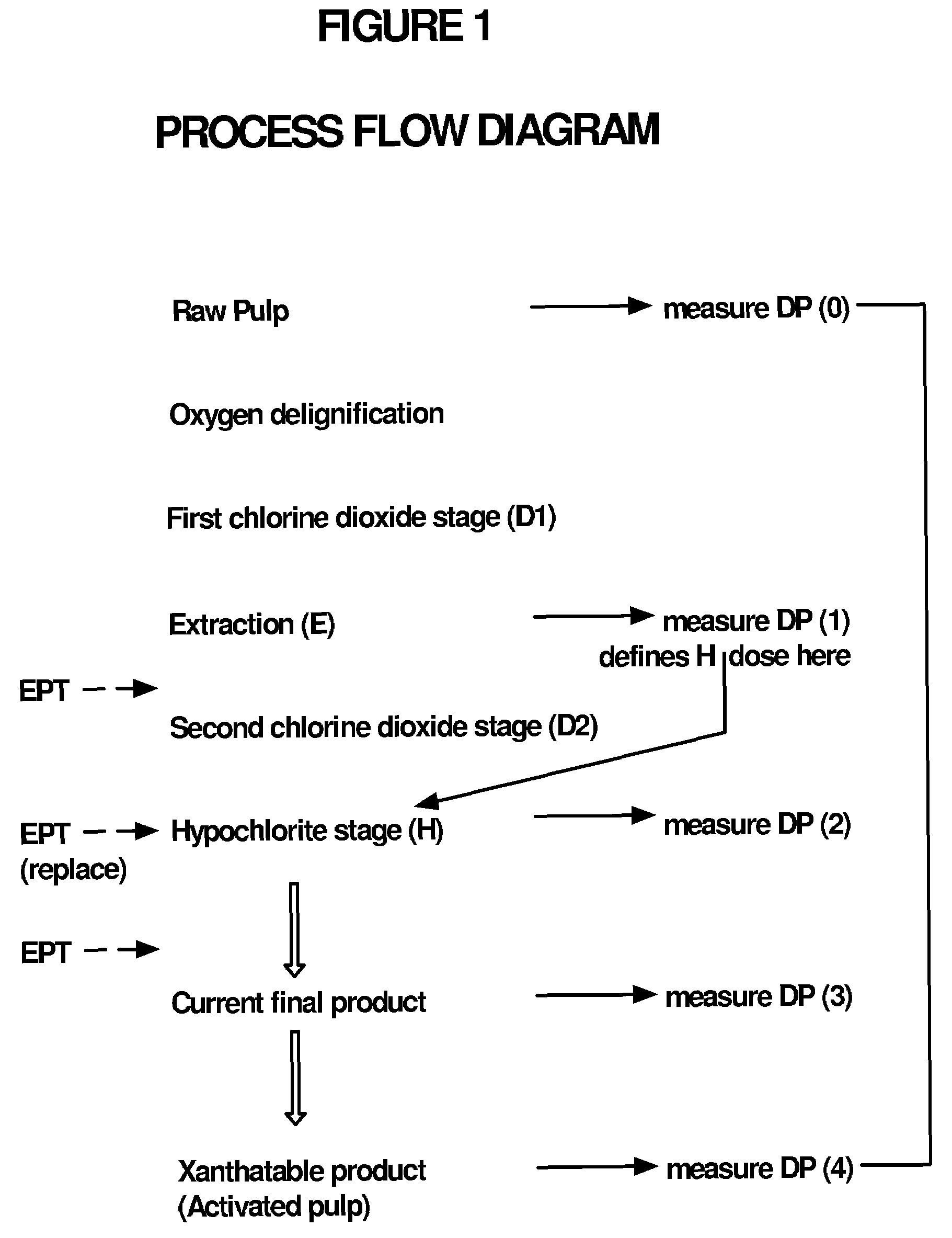
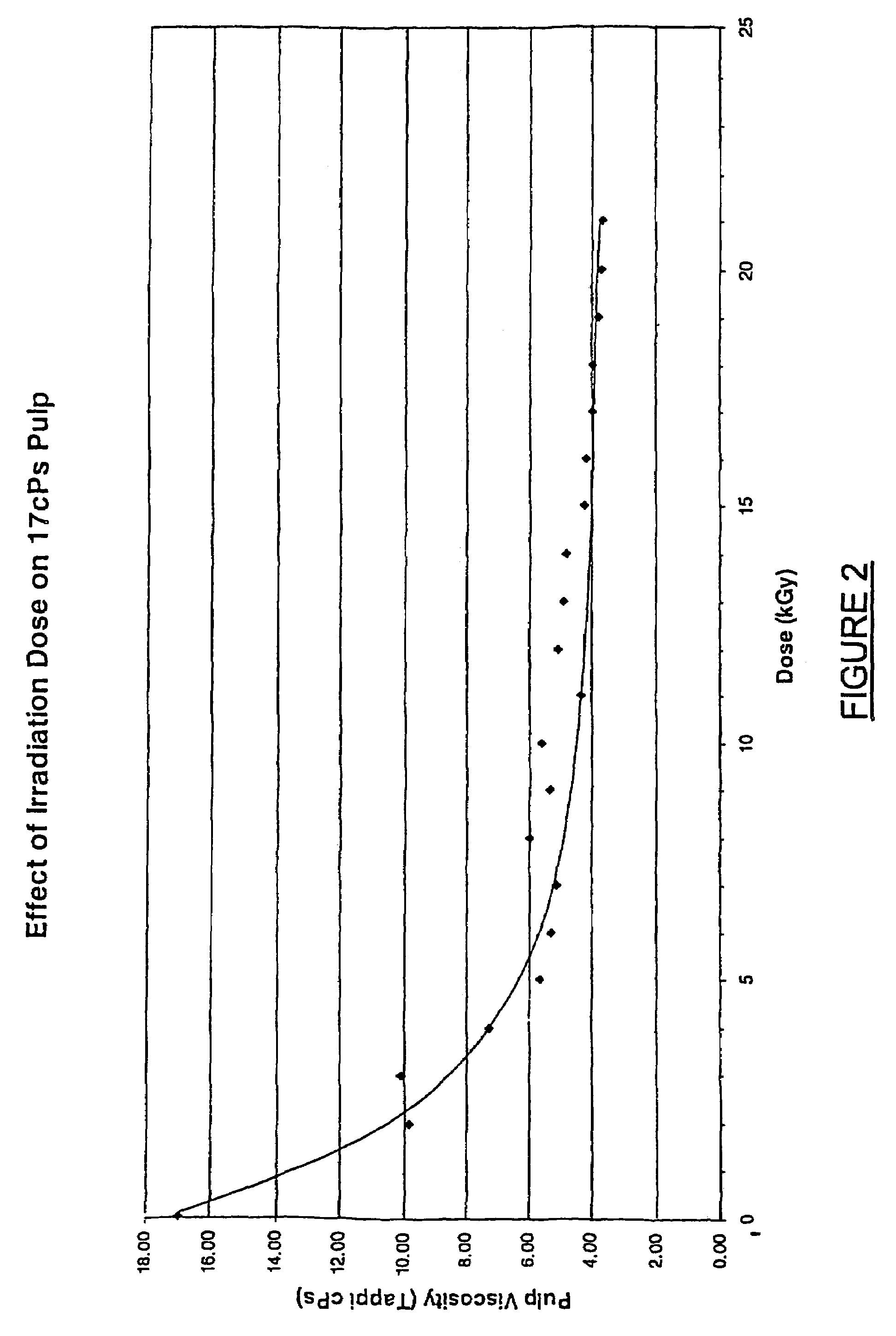
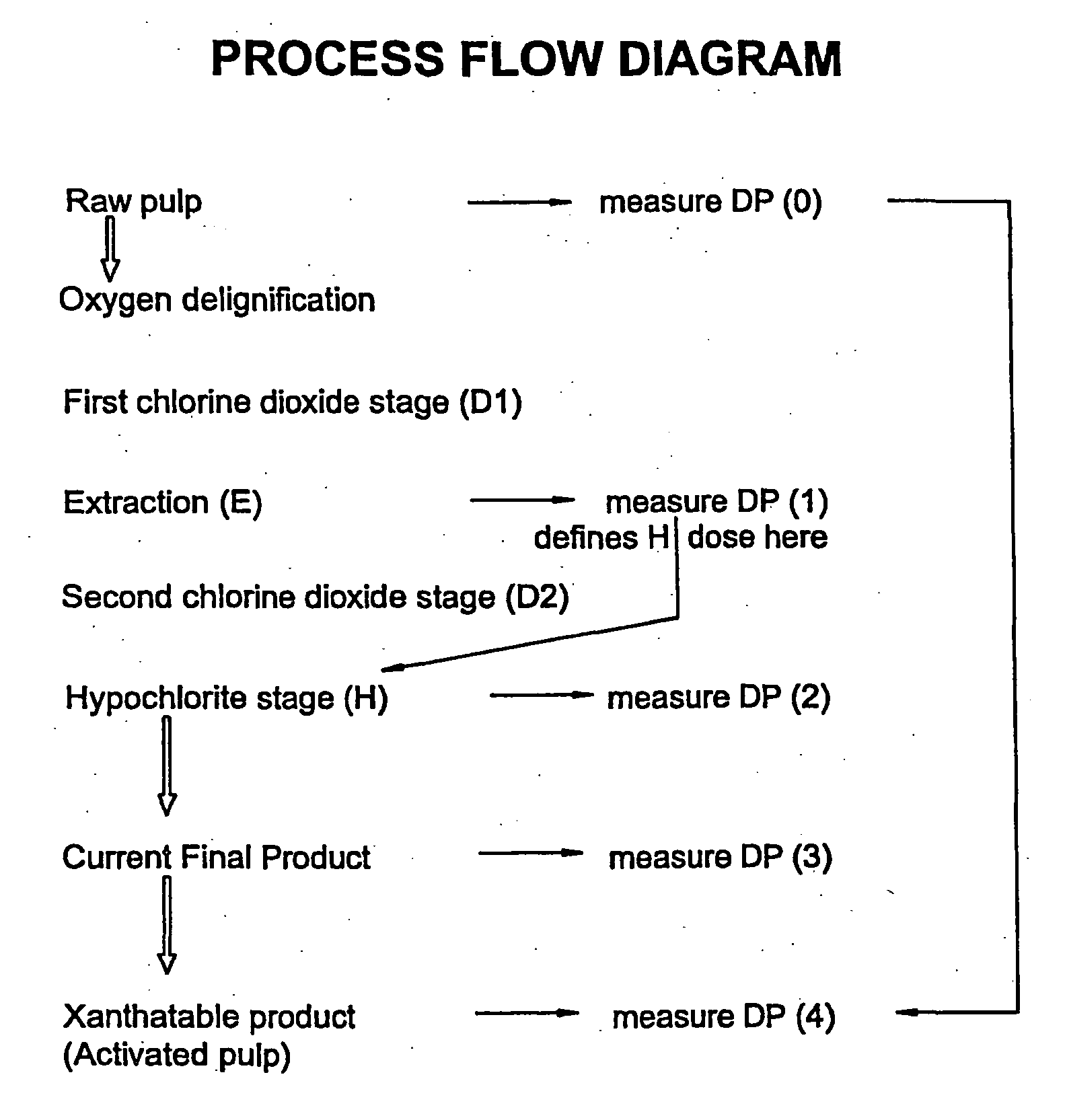
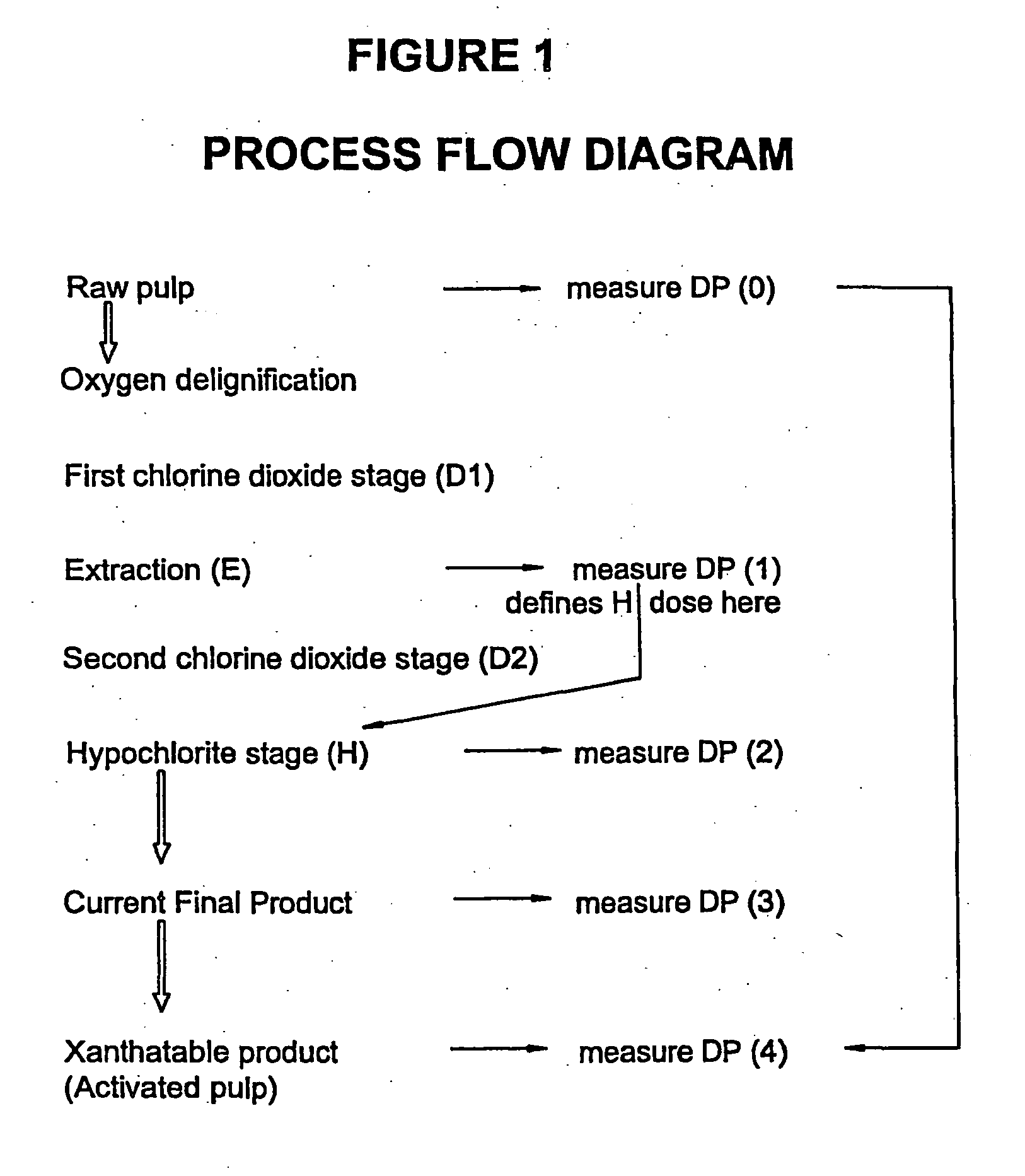
This invention provides a process for treating chemical woodpulp, or chemical cellulose including cotton linter, including the step of applying an electron processing technology (EPT) step to chemical woodpulp, or chemical cellulose, as the case may be, on an in-line basis to provide control of pulp viscosity or degree of polymerization (DP). The invention also provides a method of process control in treating the aforementioned woodpulp or cellulose, including the step of using radiation dose-viscosity relationship curve for applying an EPT step on an in-line basis. The in-line EPT step may, in one form of the invention, replace and hence eliminate a chemical DP reduction step.
Owner:SAPPI LTD
Pulp treatment and process
InactiveUS20040129394A1Reduce environmental problemsSmall DP rangeElectrolysis componentsWood treatment detailsPulp treatmentCompound (substance)
This invention provides a process for treating chemical woodpulp, or chemical cellulose including cotton linter, including the step of applying an electron processing technology (EPT) step to chemical woodpulp, or chemical cellulose, as the case may be, on an in-line basis to provide control of pulp viscosity or degree of polymerisation (DP). The invention also provides a method of process control in treating the aforementioned woodpulp or cellulose, including the step of using radiation dose-viscosity relationship curve for applying an EPT step on an in-line basis. The in-line EPT step may, in one form of the invention, replace and hence eliminate a chemical DP reduction step.
Owner:SAPPI LTD
Method for producing cellulose nanofibers
ActiveUS20140238626A1Low viscosityImprove liquidityPretreatment with water/steamPulp properties modificationHigh concentrationWater use
Provided is a method which is capable of producing a cellulose nanofiber dispersion liquid that has a low viscosity and excellent fluidity even at a high concentration, while exhibiting excellent transparency. In a method for producing cellulose nanofibers, wherein a cellulosic starting material is oxidized in water using an oxidant in the presence of an N-oxyl compound and a compound that is selected from the group consisting of a bromide, an iodide and a mixture thereof and the thus obtained oxidized cellulose is defibrated and dispersed, pulp which is obtained by carrying out kraft cooking after a hydrolysis process is used as the cellulosic starting material.
Owner:NIPPON PAPER IND CO LTD
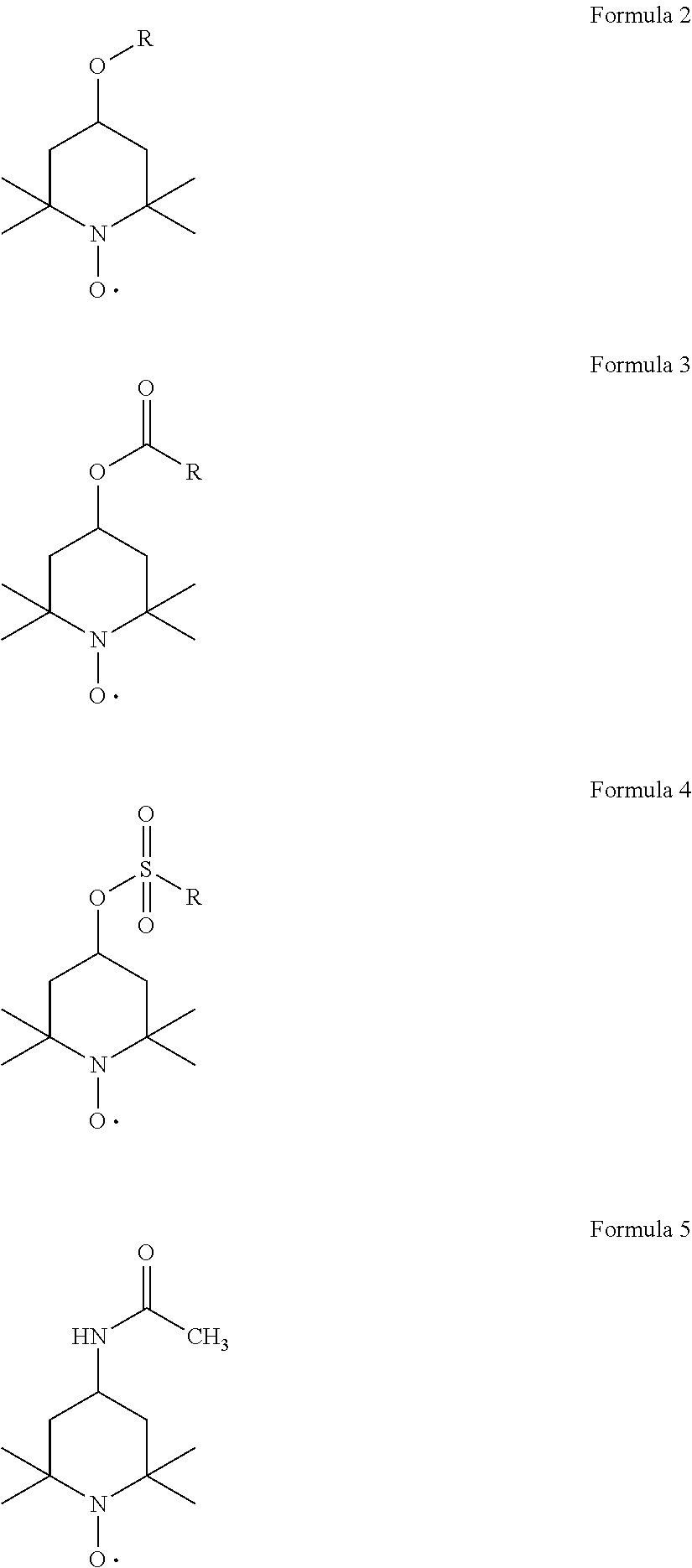
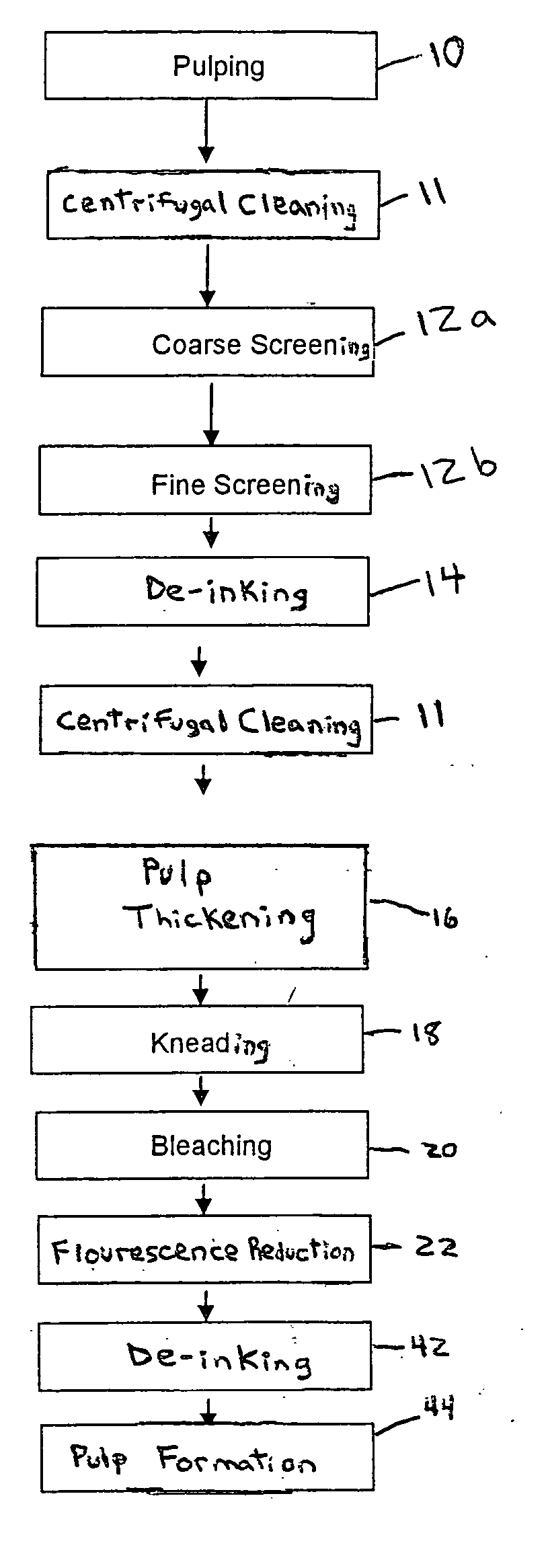
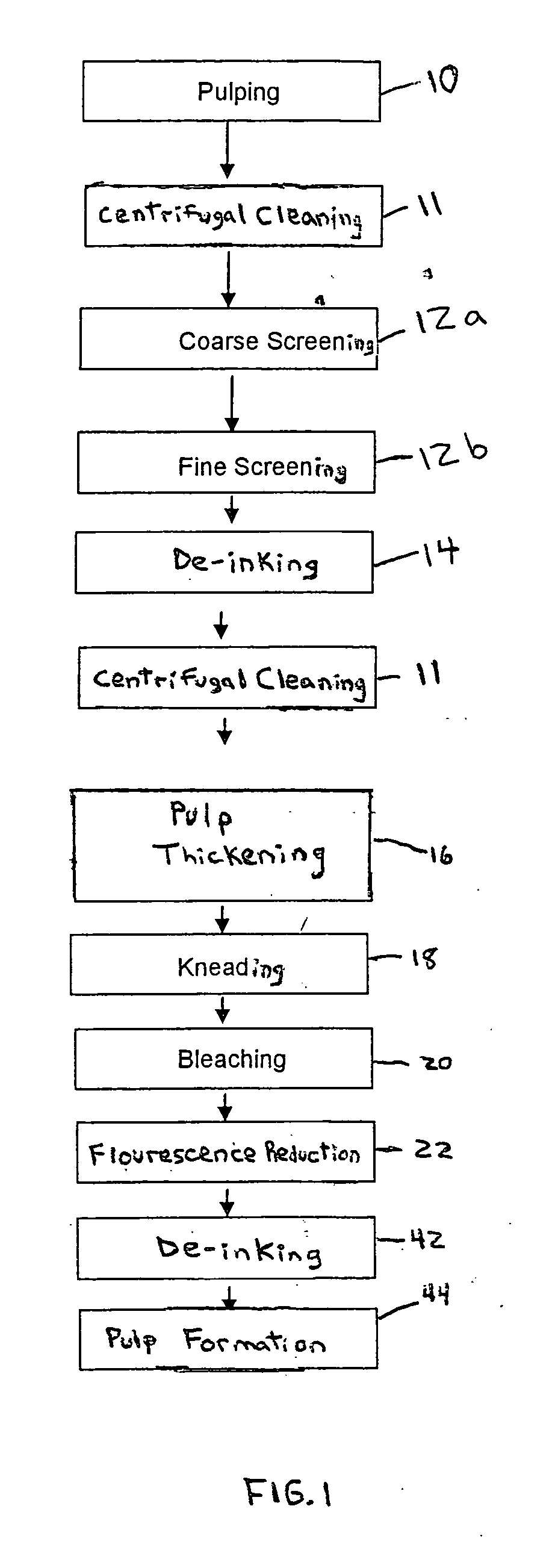
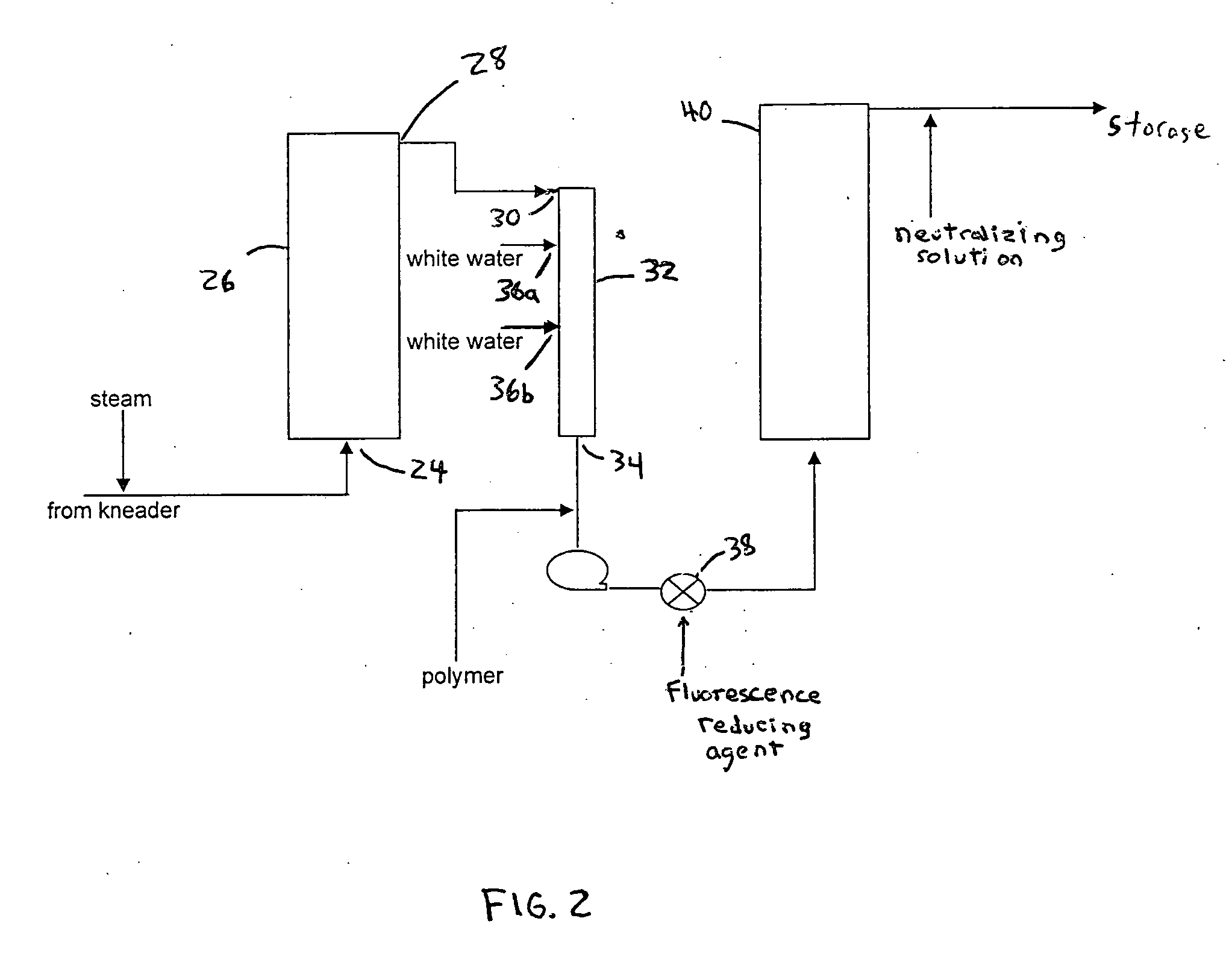
Methods for reducing fluorescence in pulp and paper
ActiveUS20050194110A1Reduce fluorescenceReduced activityNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperWhitening AgentsPulp and paper industry
Methods for reducing, and in some cases eliminating, fluorescence in pulp and paper, as well as the resulting articles, are provided. The methods destroy fluorescent activity of agents (e.g., whitening agents) which may be present in the pulp during processing. The methods are particularly applicable to recycling processes that use paper that includes fluorescent whitening agents. The methods may be used to produce recycled pulp and paper that, for example, may be suitably used in food grade applications which require no, or minimal, amount of fluorescence. In some cases, the methods also advantageously enable production of recycled pulp and paper that has reduced amounts of phosphorescence.
Owner:SUSTANA FIBER LLC
Control of development of biofilms in industrial process water
InactiveUS7189329B2Avoid developmentBiocideWater/sewage treatment by substance additionMicroorganismBiochemical engineering
Owner:A Y LAB LTD
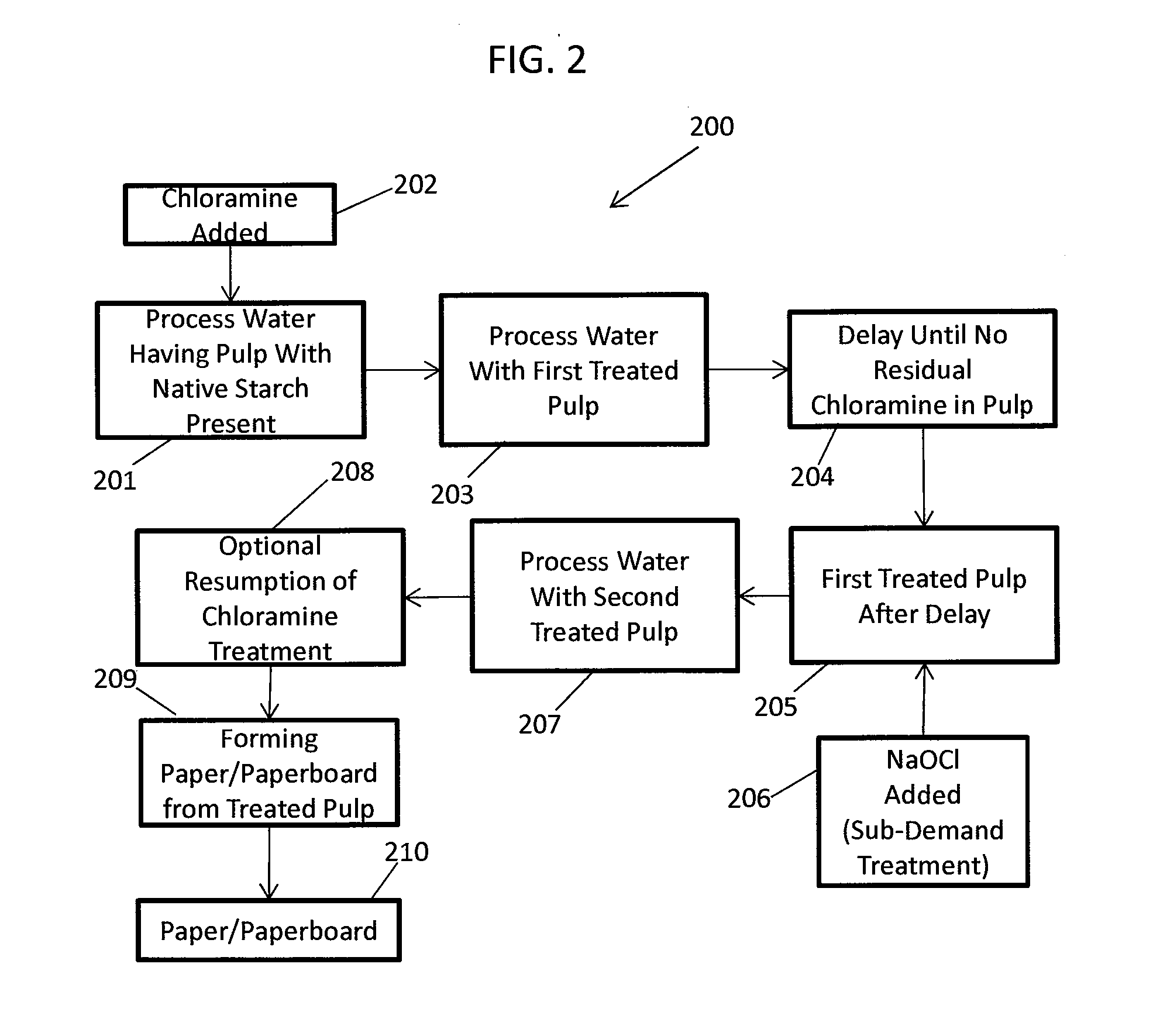
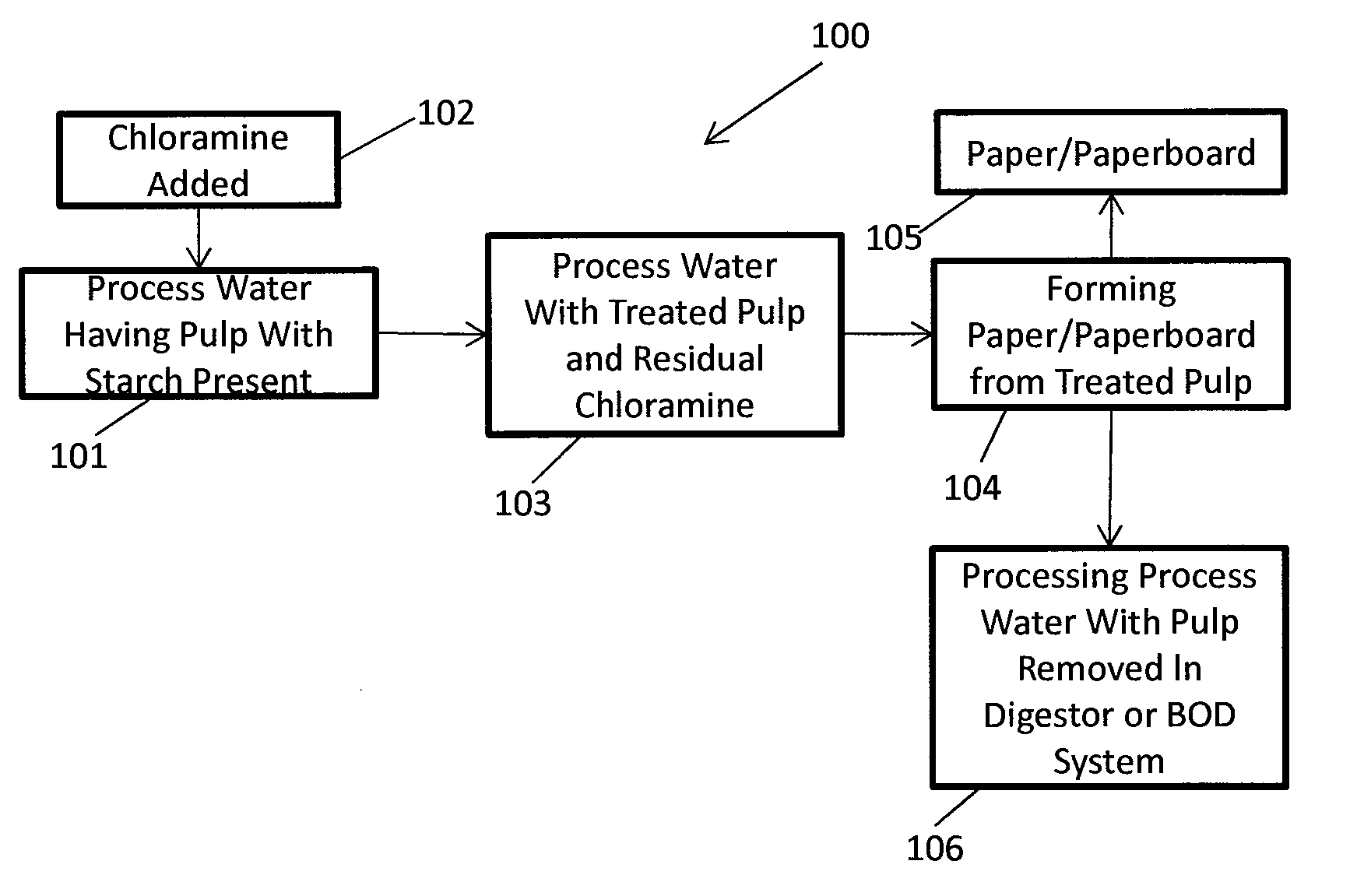
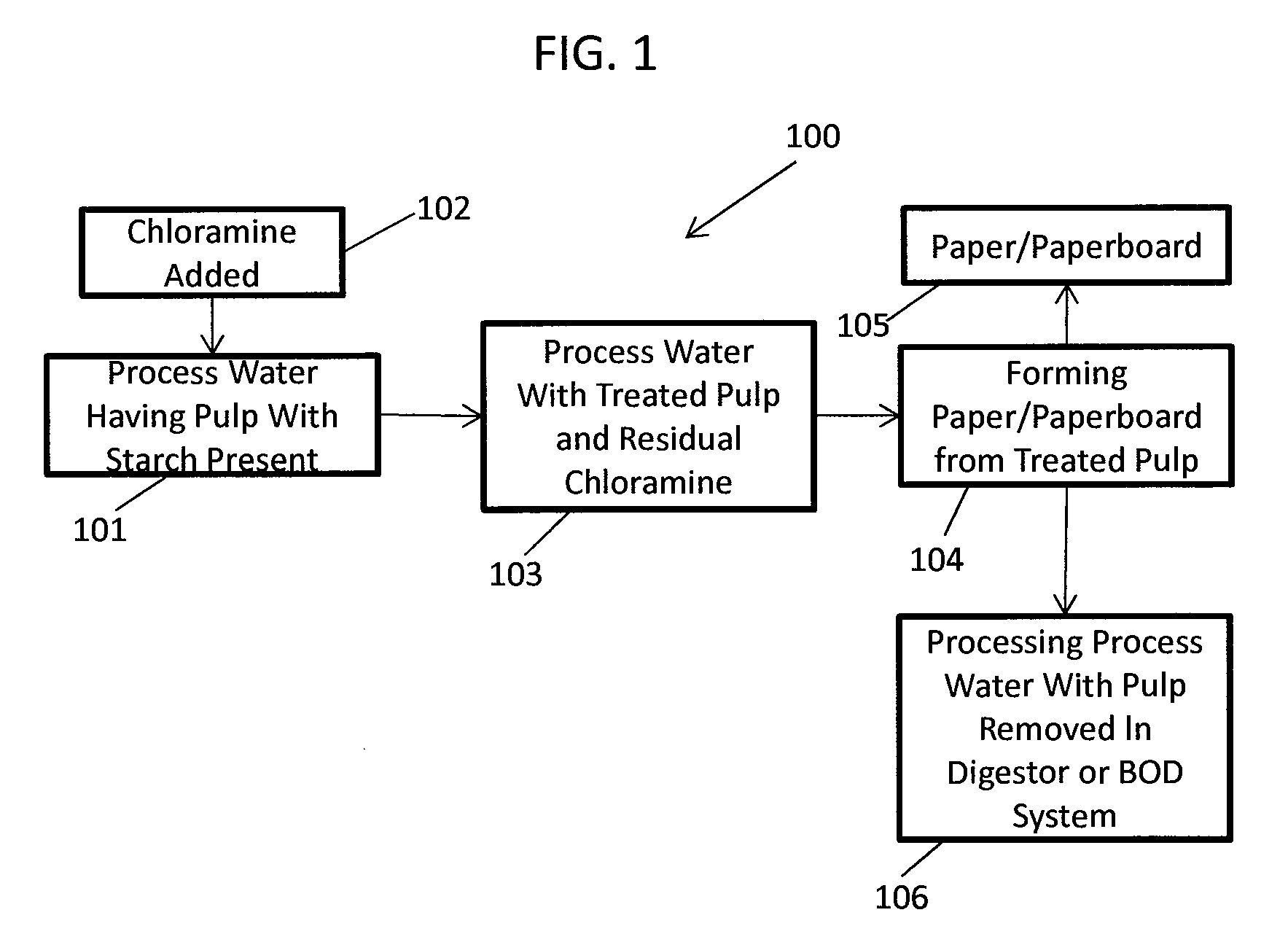
Methods Of Preserving Starch In Pulp And Controlling Calcium Precipitation And/Or Scaling
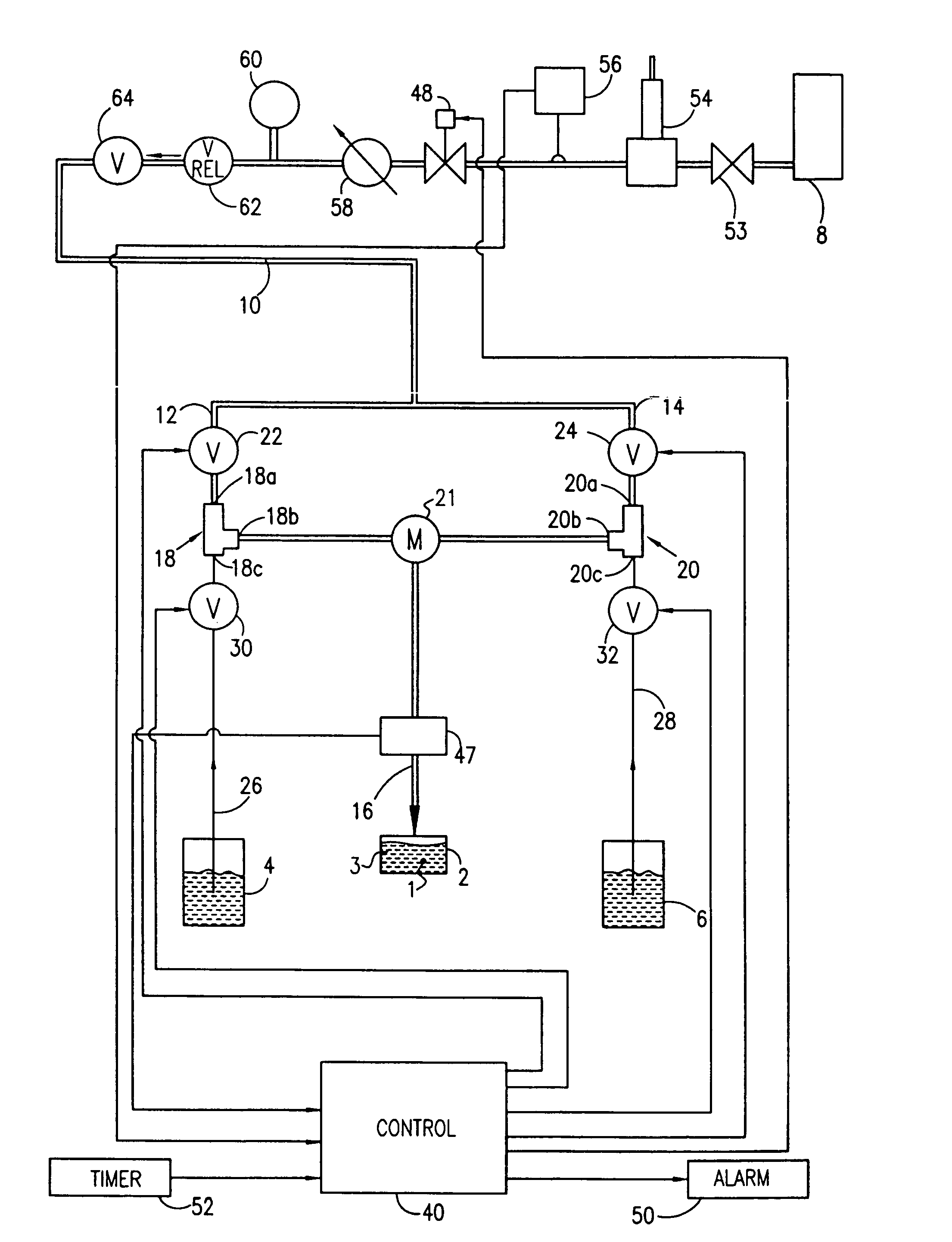
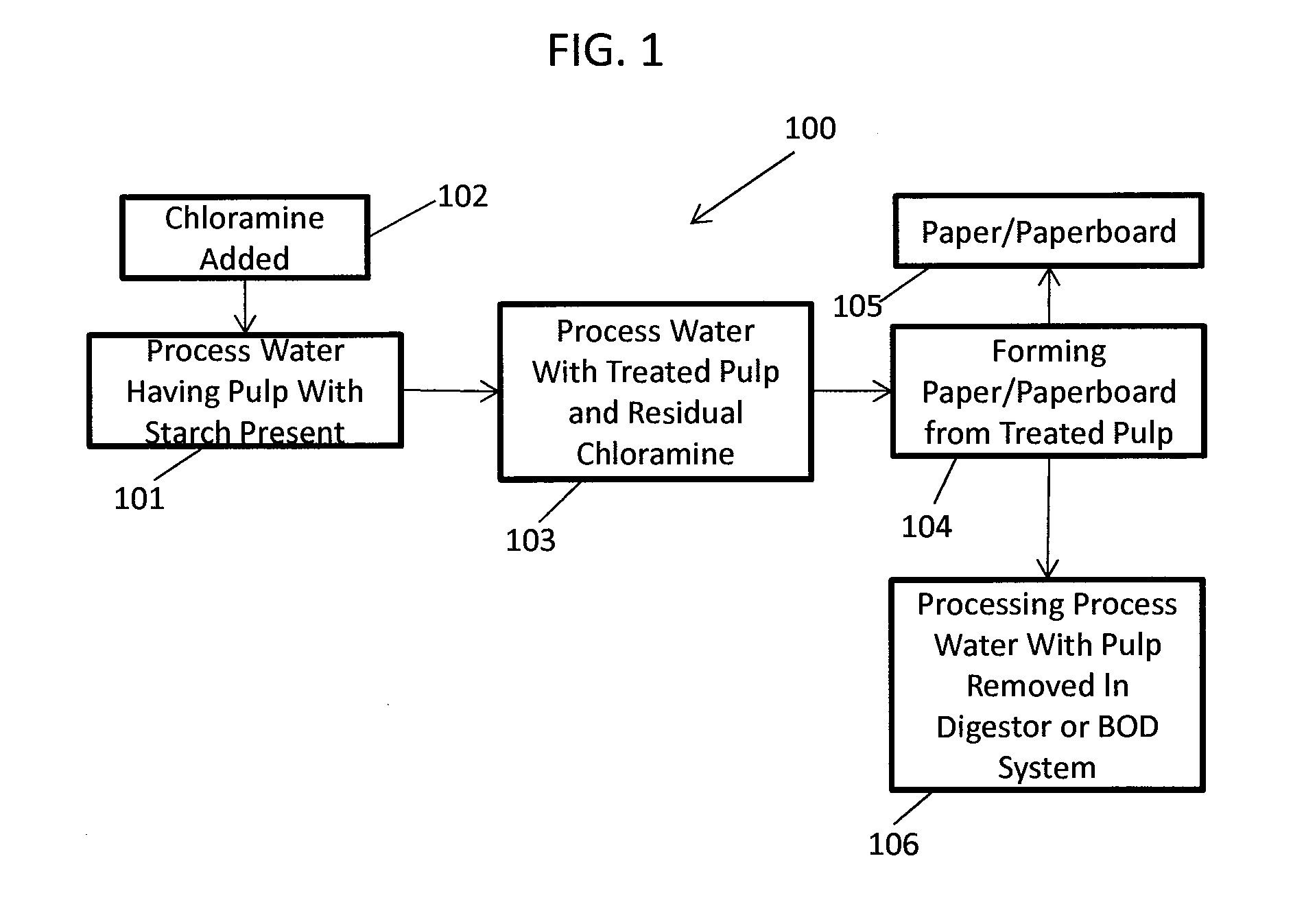
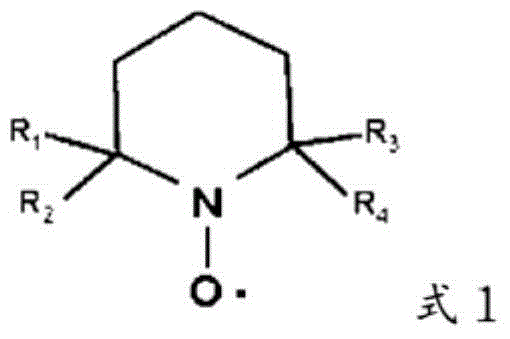
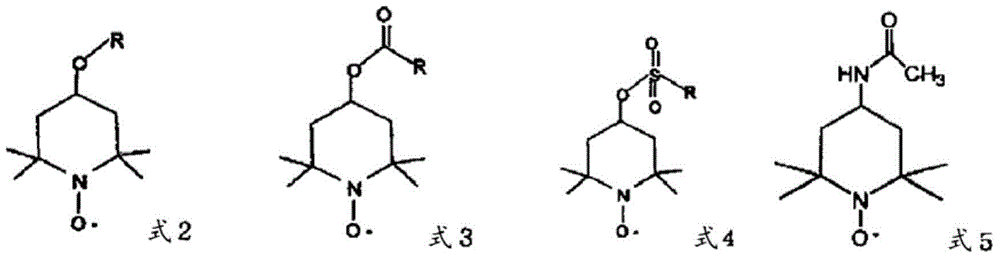
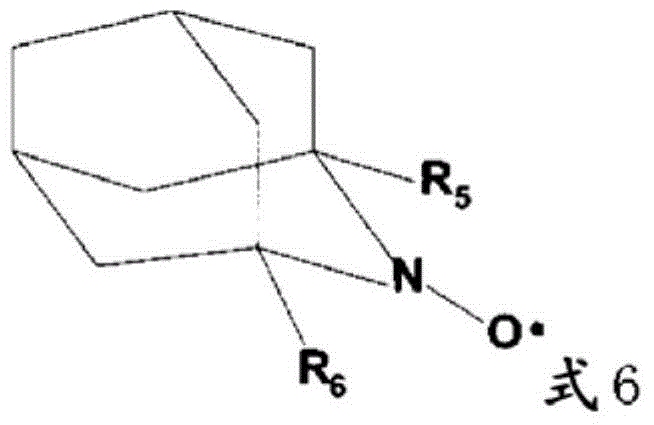
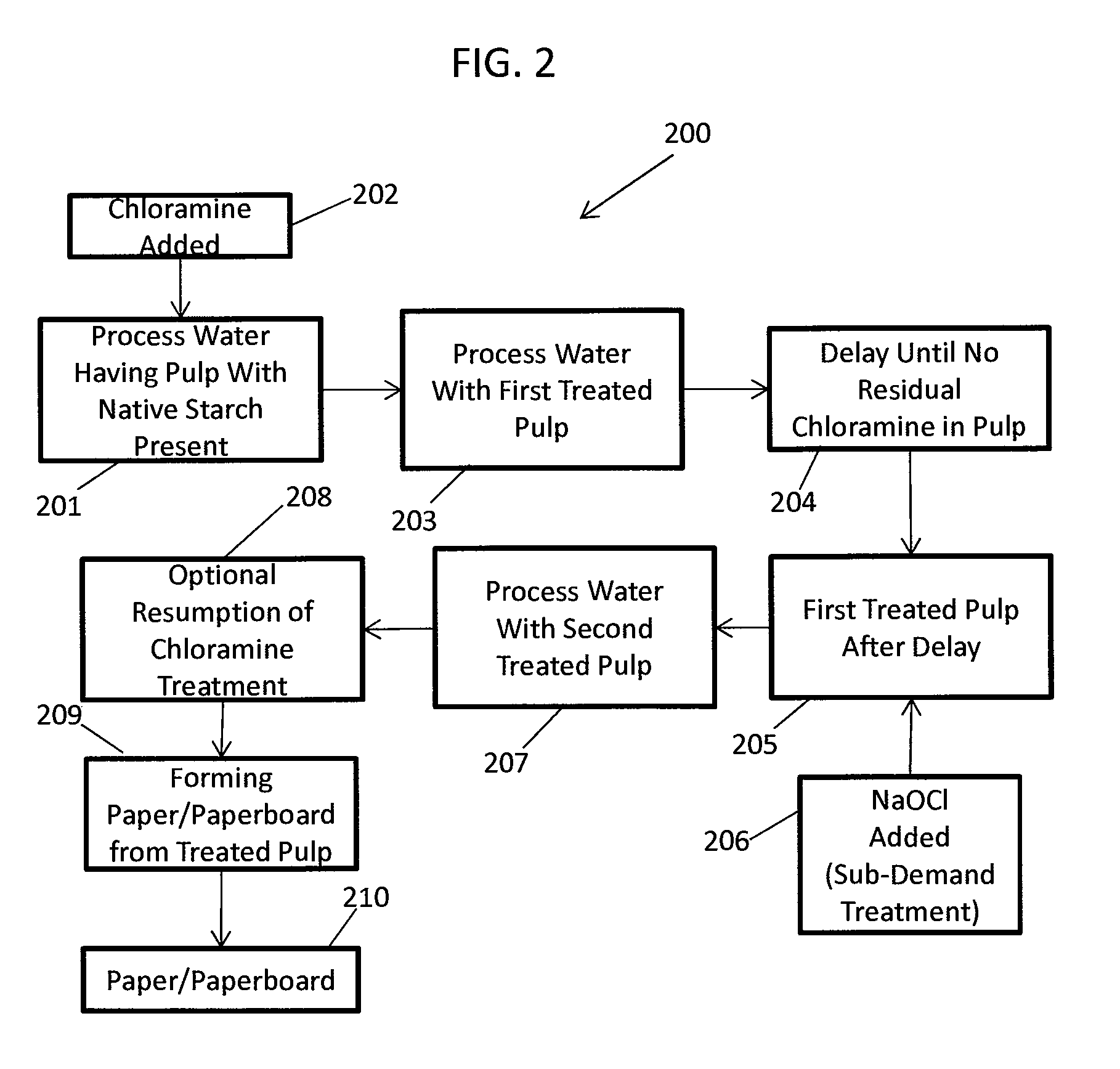
ActiveUS20130319627A1Improve the level ofHigh strengthBiocideNatural cellulose pulp/paperChloramine BChloramine
Methods to preserve starch present in pulp are provided and also methods to control calcium precipitation and / or scaling in digesters or BOD systems. The methods can be performed as part of a papermaking process. Process water containing pulp can be treated with a chloramine. Process water containing pulp with native starch can receive a double treatment with at least one biocide, such as chloramine, and at least one oxidant, such as sodium hypochlorite. The treatment can be performed in any suitable manner. The treatment can be performed at one or more stages or locations in a papermaking system. A target residual chloramine value or range can be achieved by the treatment. Packaging sheets / boards and other paper products manufactured using the methods provided exhibit superior strength and other desirable characteristics.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
Method for producing cellulose nanofibers
InactiveCN103827146AIncrease concentrationLow viscosityPretreatment with water/steamPulp properties modificationHigh concentrationFiber
Provided is a method which is capable of producing a cellulose nanofiber dispersion liquid that has a low viscosity and excellent fluidity even at a high concentration, while exhibiting excellent transparency. In a method for producing cellulose nanofibers, wherein a cellulose-based starting material is oxidized in water using an oxidant in the presence of an N-oxyl compound and a compound that is selected from the group consisting of a bromide, an iodide and a mixture of a bromide and an iodide and the thus-obtained oxidized cellulose is fibrillated and dispersed, pulp which is obtained by carrying out kraft cooking after a hydrolysis process is used as the cellulose-based starting material.
Owner:NIPPON PAPER IND CO LTD
Process for isolating cellulose from cellulosic biomass, isolated cellulose of type i and composite materials comprising same
InactiveUS20150361616A1Simpler and cheap and efficientLess waterPulp properties modificationWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsExternal energyCellulose pulp
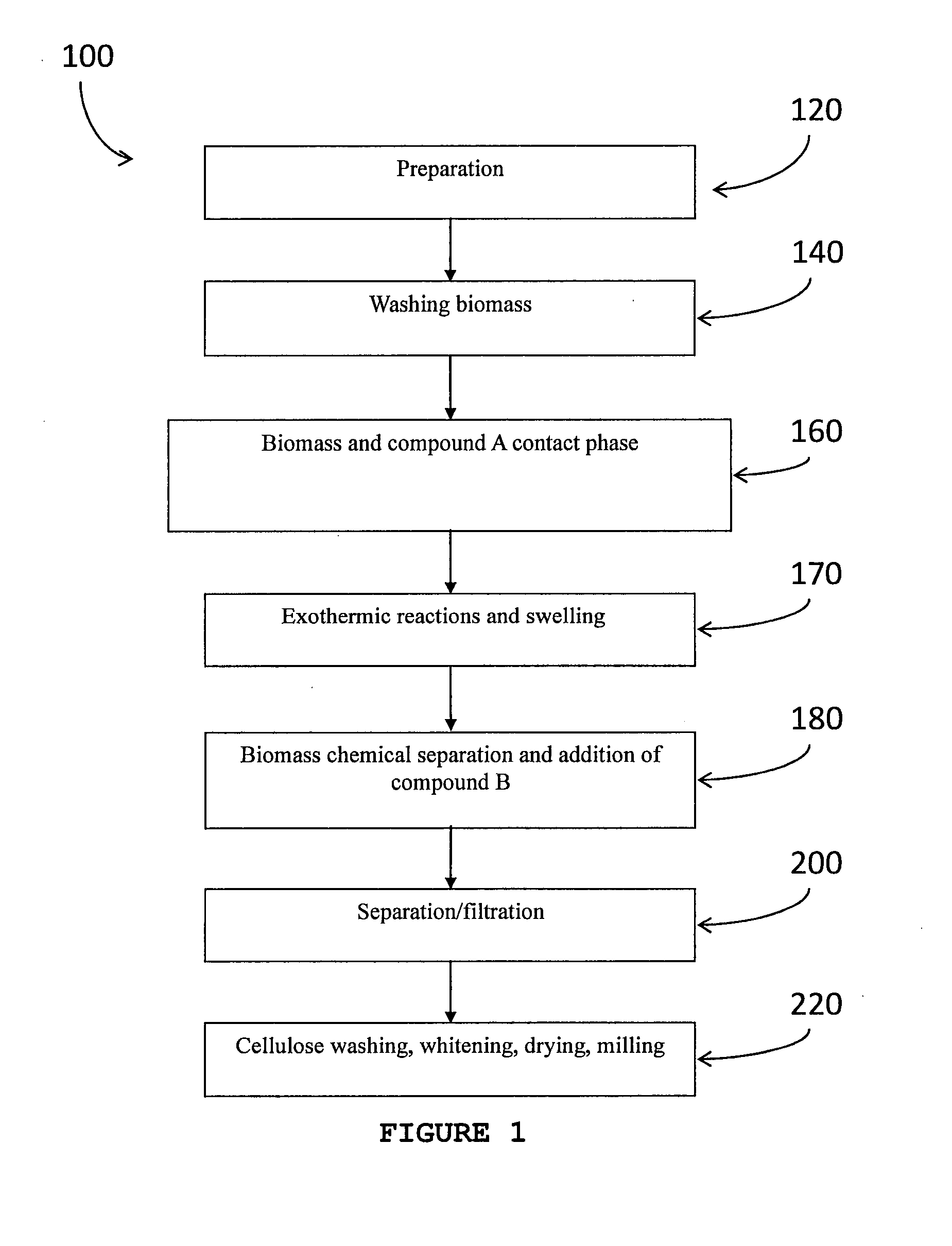
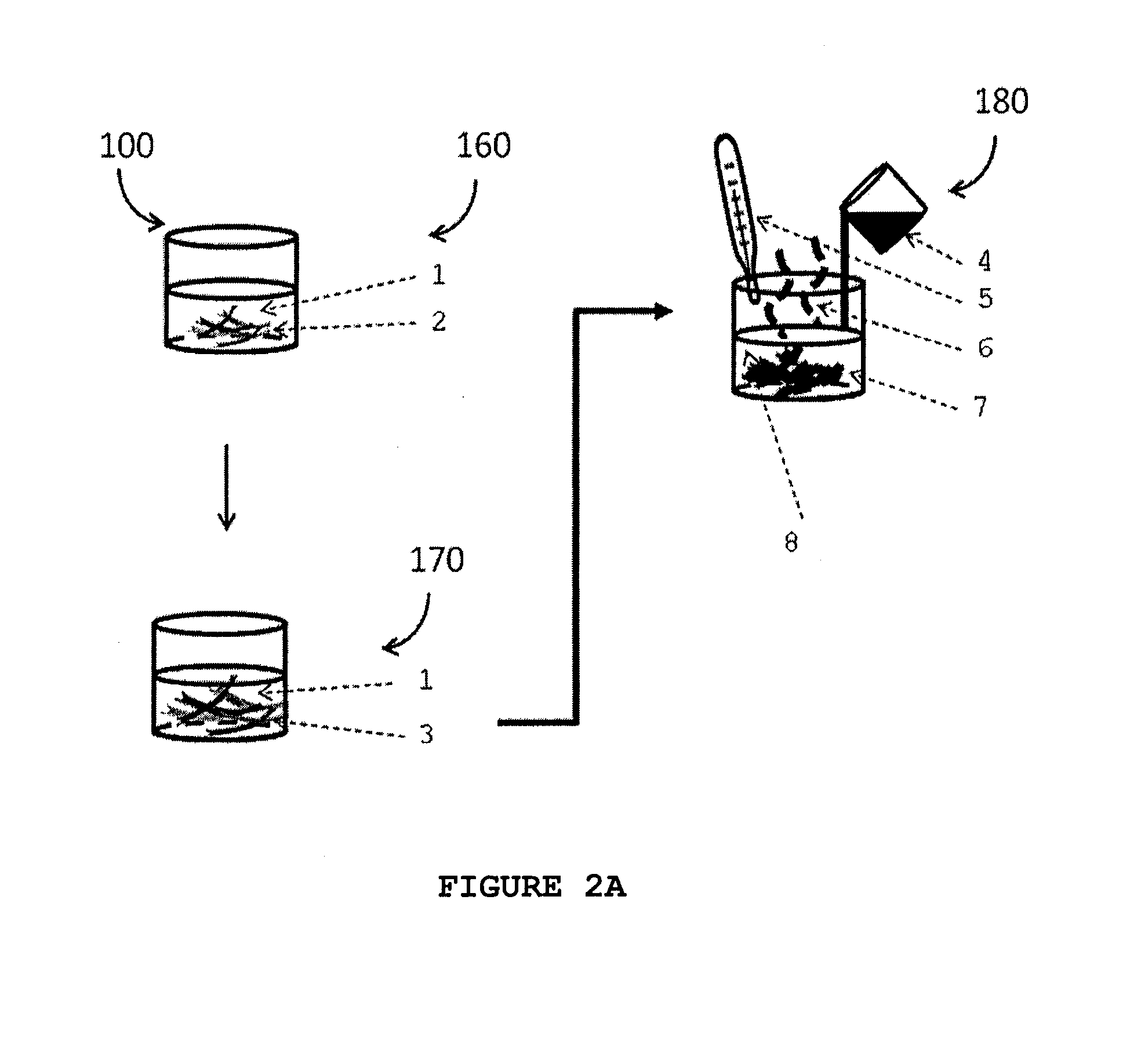
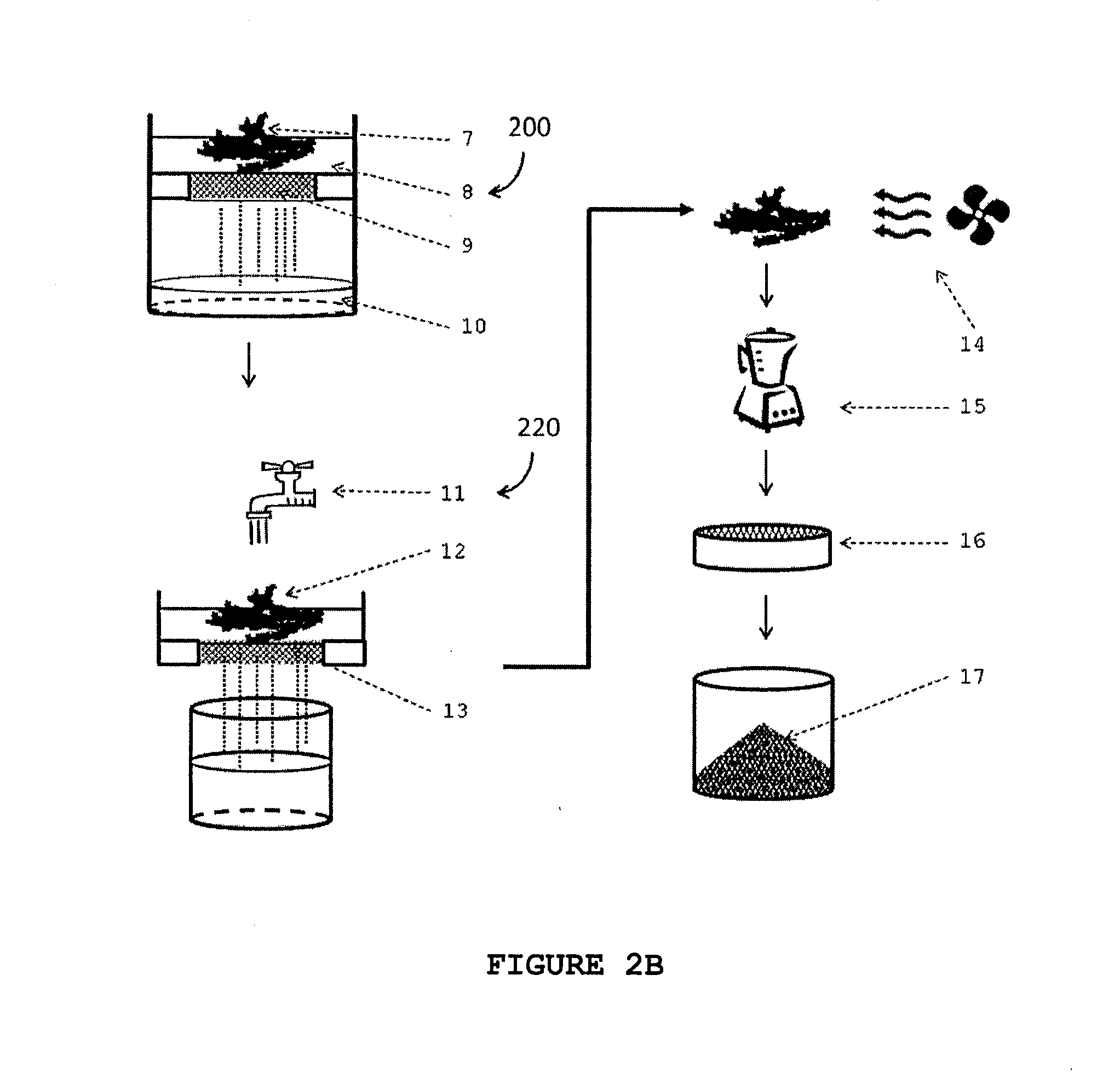
Described herein are processes for the production of a cellulose pulp and processes for isolating cellulose from cellulose-containing biomass. The processes of the invention comprises contacting the biomass with a source of anions and a source of cations, the source of anions and the source of cations being selected to react exothermically with the biomass and with each other. The processes of the invention have the particularity of generating exothermic reactions through enthalpies of reaction and mixture. Accordingly, the processes of the invention do not require any supply of external energy since the required energy is provided by chemical reagents that are already present in the biomass or added as needed. The invention also relates to isolated cellulose obtained from these processes and the use of same in various materials.
Owner:VENTIX ENVIRONNEMENT
Method for preparation of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils
A method for producing nanocellulose is described herein. The method includes contacting a cellulosic material with an oxidizing agent, and a compound selected from the group consisting of an alkali metal bromide, an alkali metal iodide, an alkali metal fluoride, an alkali metal chloride, or a combination thereof, in an aqueous solution to provide an oxidized cellulose mixture. The nanocellulose prepared according to the method is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Product and processes from an integrated forest biorefinery
An omnibus process of pulping and bleaching lignocellulosic materials in which a charge of a lignocellulosic material is biopulped and / or water extracted prior to pulping and bleaching. The lignocellulosic material may be mechanically pulped and bleached in the presence of an enzyme that breaks lignin-carbohydrate complexes. The aqueous extract in embodiments including a water extract step is separated into acetic acid and hemicellulose sugar aqueous solutions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method for improving fiber quality and process efficiency in mechanical pulping
ActiveUS8262852B2Reduce freenessReduce the amount requiredPulping with organic solventsFibrous raw materialsFiberHydrotrope
This invention provides a composition and method for improving a mechanical pulping process by decreasing freeness and amount of shives, providing energy and chemical savings, and enhancing brightness and mechanical strength of a paper product made from a pulp material in the process. The composition includes formulations, such as surfactants, chelants, hydrotropes, reductive and oxidative pulp modifiers, and pH-controlling chemicals. The method includes selectively introducing these formulations to the pulp material in the mechanical pulping process.
Owner:NALCO CO
Method for manufacturing nanofiber transparent paper from straw
InactiveCN105568747AIncrease electrostatic repulsionEasy to separatePulp bleachingPulping with halogen compoundsFiberPapermaking
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing nanofiber transparent paper from straw, belonging to the field of papermaking. According to the invention, with adoption of oxidized fiber of a 1,3-dihydroxyacetone oxidization system, the electrostatic repulsive force among nano-cellulose is enhanced, so that the cellulose can be separated from cell walls completely, and the transparent paper has higher transparency and excellent mechanical strength. Sodium hypochlorite can be used as an oxidizing agent, has a bleaching function due to strong oxidizing property, and can react with little lignin left in original fiber to remove the lignin so as to improve light transmission. The raw materials are readily available, and the transparent paper is biologically degradable and cheap.
Owner:梅庆波
Process for manufacturing pulp, paper and paperboard products
A process for bleaching mechanical wood pulp is provided comprising subjecting the wood pulp to at least one bleaching stage with one or more bleaching agents in the presence of one or more optical brightening agent, wherein the bleaching agents are selected from the group consisting of oxidative bleaching agents other than chlorine based bleaching agents such as chlorine dioxide, elemental chlorine or a combination thereof, reductive bleaching agents or any combination of two or more thereof.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
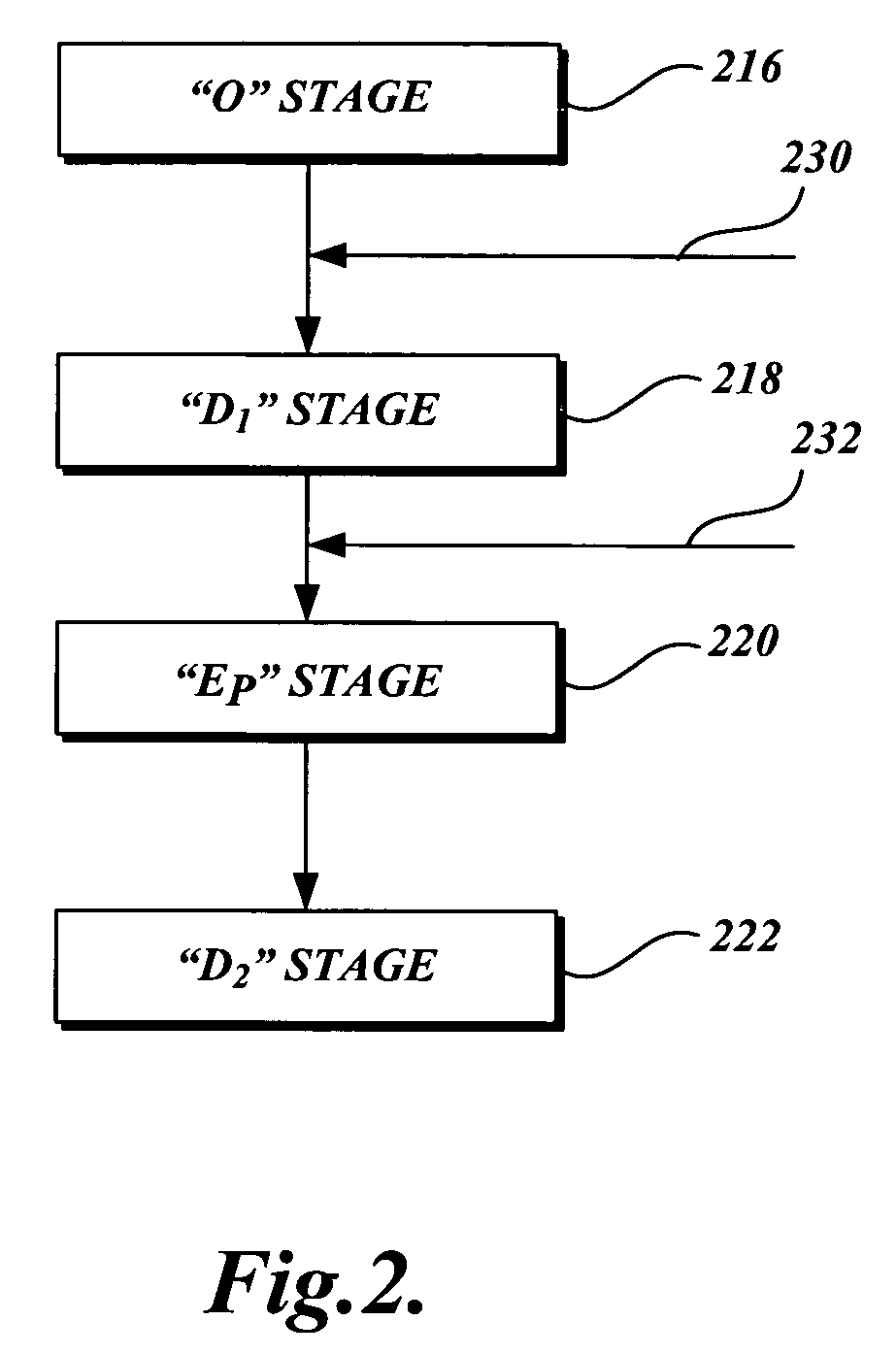
Method of bleaching cellulose pulp and bleaching line therefore
ActiveUS20040149404A1Washing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsPulp bleachingDistribution systemPulp and paper industry
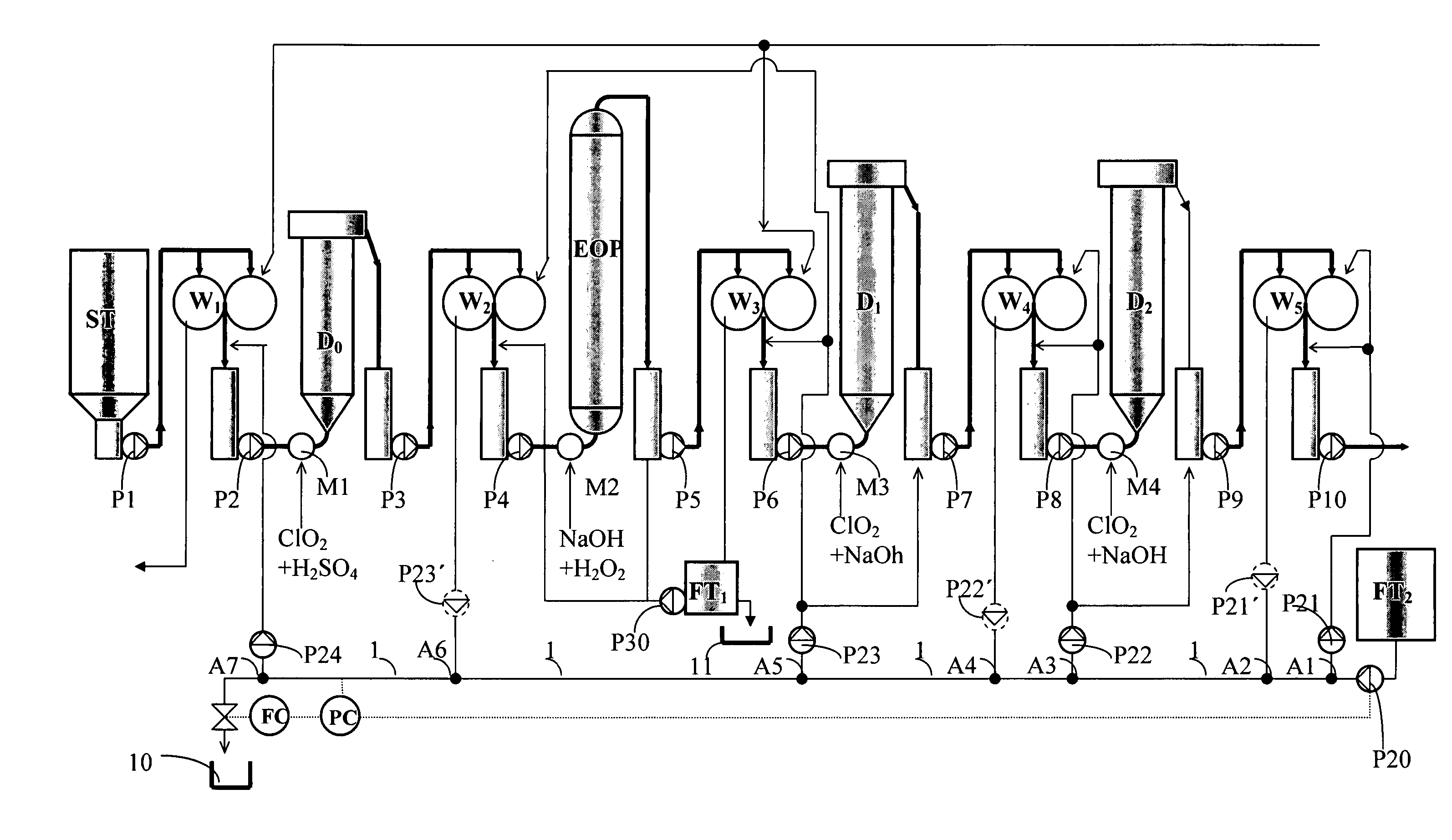
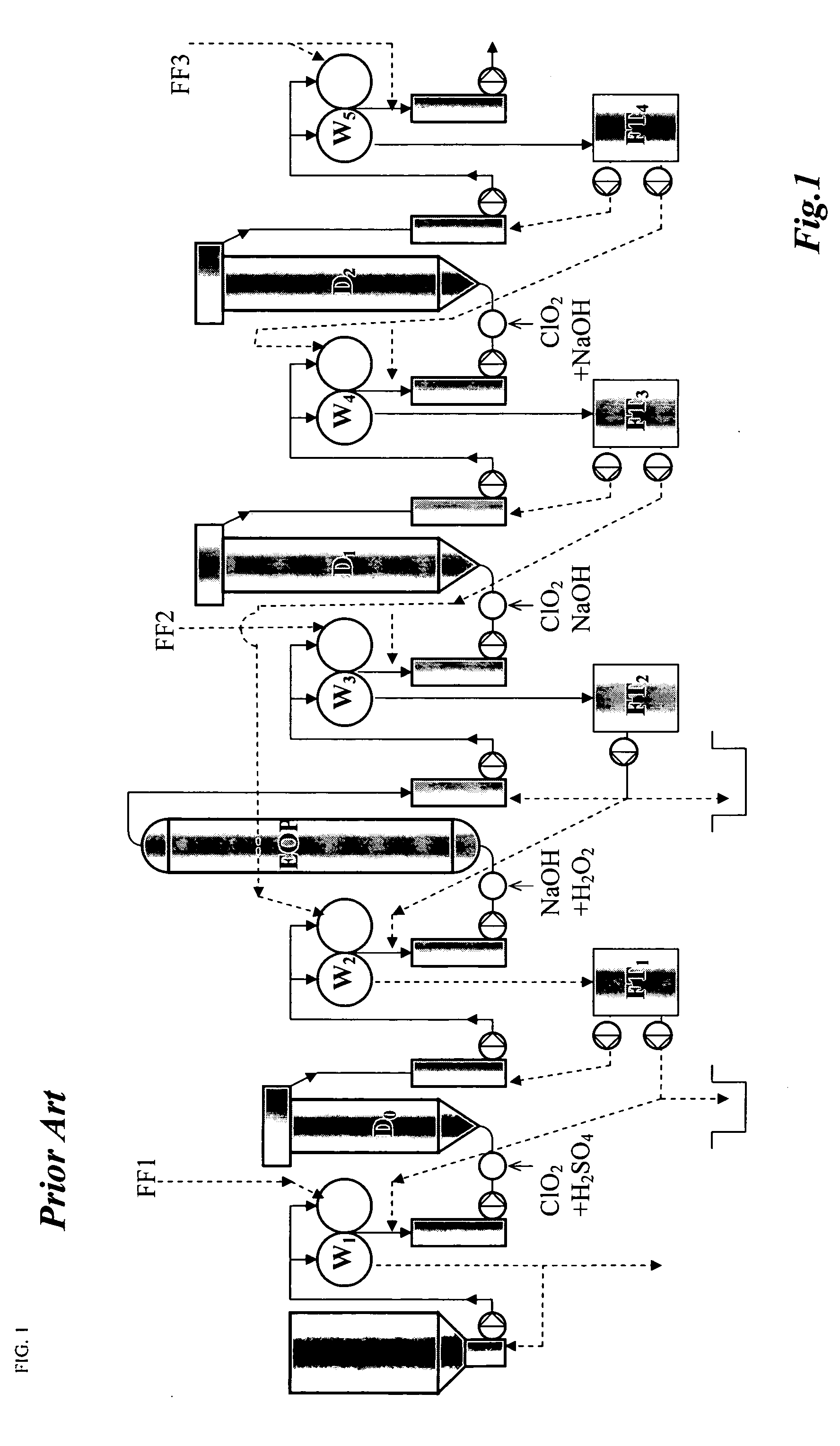
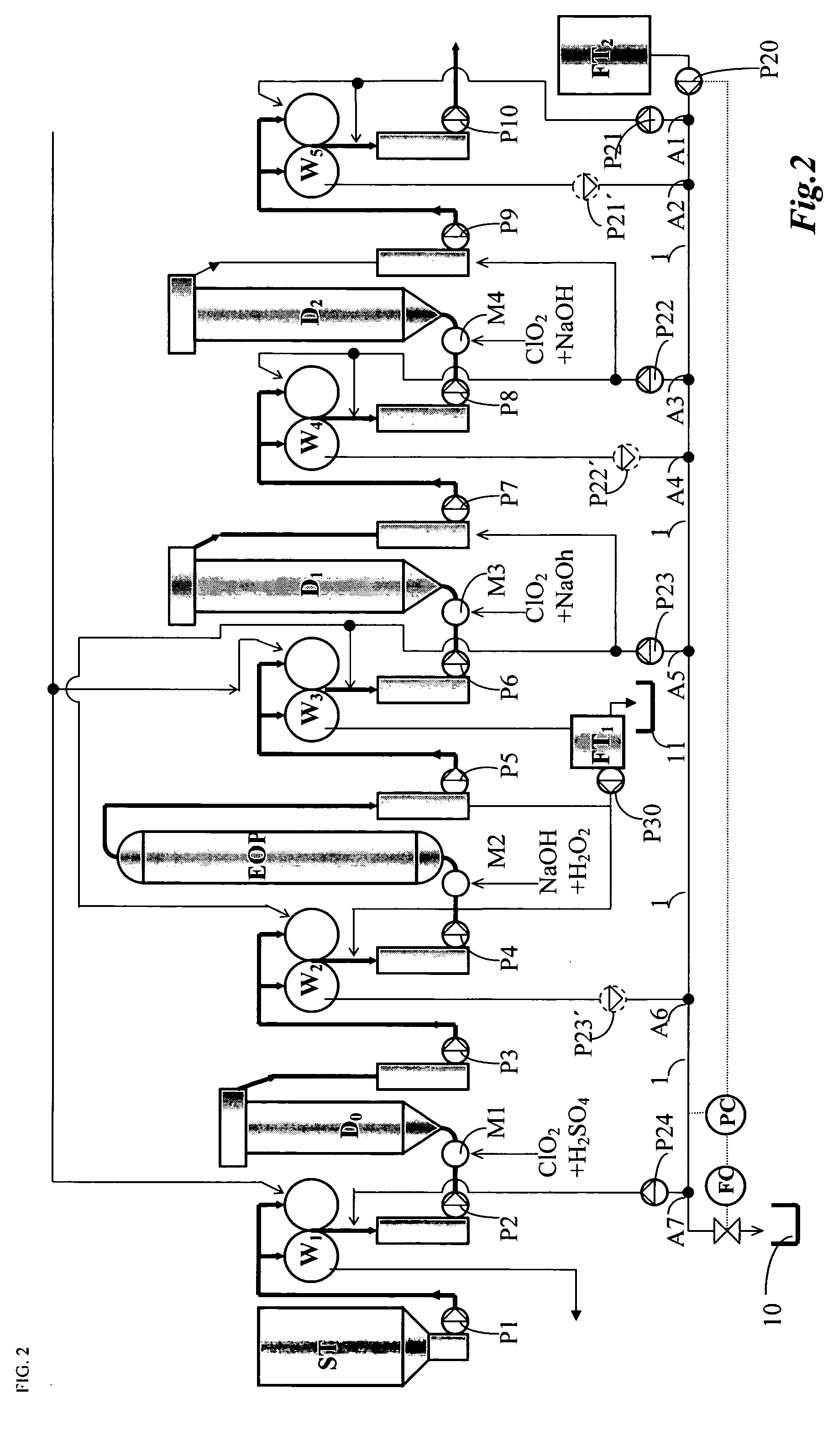
The invention relates to a method of bleaching cellulose pulp in a bleach line having at least two bleaching steps D1, D2 of alkaline or acidic type, and a bleaching line for the method, in which the filtrate distribution is led up through the bleaching line in counter-current to the flow of cellulose pulp established in the bleaching line. Instead of a conventional filtrate distribution including filtrate tanks, a single joint main conduit 1 is used for the bleaching steps of the same type. Wash filtrate obtained from the wash steps of the same type used after or before the bleaching step, is led to a branch point A2, A4, A6 on the main conduit 1, that is positioned after the branch point for drawing off of wash and / or dilution liquor for the wash step in question A1, A3, A5, A7. All branch points in the joint main conduit are in open communication with each other in the main conduit, at least as seen in a direction from the last bleaching step. Hereby, a simplified and improved filtrate distribution system with an improved runnability is obtained.
Owner:ANDRITZ AB
Compositions and processes for paper production
ActiveUS7914646B2Improve the immunityImproving and stabilizing brightnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPapermakingPaper production
Oxidative compositions and processes that preserve and enhance the brightness and improve color of pulp or paper when applied during different stages of the papermaking process are identified. The oxidative composition and method maintains and / or enhances brightness, prevents yellowing, and enhances the performance of paper products. Used in combination with optical brighteners and / or chelants the oxidative agents produce a synergistic effect not previously identified in the paper process.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Method of xylanase treatment in a chlorine dioxide bleaching sequence
InactiveUS7320741B2Enhances pulp bleachingEasily integrated into pulp bleaching processPulp bleachingBleaching apparatusChlorine dioxidePulp mill
A method of bleaching chemical pulp with xylanase after chemical bleaching is provided. The method comprises the steps of exposing chemical pulp to a chlorine dioxide bleaching stage to produce a partially bleached pulp, treating the partially bleached pulp with a xylanase in an enzyme treatment stage at a pH of about 3 to about 8, then carrying out an alkaline extraction of the pulp. The pulp bleaching method of the present invention may be performed in a pulp mill as part of a complex pulp bleaching process.
Owner:IOGEN BIO PRODUCKTS CORP
Method for catalytic oxidation of cellulose and method for making a cellulose product
ActiveUS20140110070A1Effectively and selectively oxidizing C-Reduce usageNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperCelluloseHypochlorite
In a method for catalytic oxidation of cellulose a heterocyclic nitroxyl radical is used as catalyst, hypochlorite is used as main oxidant acting as oxygen source, and a tertiary amine or chlorine dioxide as an activator of the heterocyclic nitroxyl radical.
Owner:UPM-KYMMENE OYJ
Method for utilizing straw and waste paper pulp to prepare high strength corrugated base paper
ActiveCN107881842ALow costHigh strengthPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsPulping with organic compoundsCelluloseChlorine dioxide
The invention discloses a method for utilizing straw and waste paper pulp to prepare high strength corrugated base paper, and relates to the field of utilizing cellulose to make paper. After the strawis dried, straw husk is removed to separate out straw medulla, the straw medulla is pulverized, the straw medulla powder is mixed with a NaOH and / or KOH solution of which the mass concentration is 1-10% till the mass concentration of the material is 0.5-5%, after being soaked, the material is washed to be neutral, and water is added to obtain straw medulla pulp, wherein the concentration of the straw medulla is 0.5-5%; then peroxyacetic acid is added into the straw medulla pulp till the mass concentration of peroxyacetic acid is 1-8%, or a hydrochloric acid solution is added into the straw medulla pulp to adjust the pH value of the straw medulla pulp to be 2 or below, then chlorine dioxide is added till the mass concentration of chlorine dioxide in the straw medulla pulp is 1-8%; then thestraw medulla pulp is stirred or oscillated, after being washed to be neutral, the straw medulla pulp is mixed with the waste paper pulp, the mass percentage of the straw medulla in mixed paper pulpis 10-30%, and the mixed paper pulp is utilized to make the corrugated base paper.
Owner:山东科迈生物制浆有限公司
Methods of preserving starch in pulp and controlling calcium precipitation and/or scaling
Methods to preserve starch present in pulp are provided and also methods to control calcium precipitation and / or scaling in digesters or BOD systems. The methods can be performed as part of a papermaking process. Process water containing pulp can be treated with a chloramine. Process water containing pulp with native starch can receive a double treatment with at least one biocide, such as chloramine, and at least one oxidant, such as sodium hypochlorite. The treatment can be performed in any suitable manner. The treatment can be performed at one or more stages or locations in a papermaking system. A target residual chloramine value or range can be achieved by the treatment. Packaging sheets / boards and other paper products manufactured using the methods provided exhibit superior strength and other desirable characteristics.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
Nanofiber sheet, process for producing the same, and fiber-reinforced composite material
ActiveUS9029275B2High crystallinityReduction factorPowder deliveryWood working apparatusPolymer scienceYoung's modulus
Owner:ROHM CO LTD +1
Processes and systems for the bleaching of lignocellulosic pulps following cooking with soda and anthraquinone
InactiveUS20090032208A1Washing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsPulping with inorganic basesCellulose pulpAnthraquinone process
Process for bleaching of pulps following cooking of the lignocellulosic material with soda and anthraquinone. The process may produce a whiteness on par with the bleaching of kraft pulp when using a similar bleaching sequence. In some instances, the bleaching sequence may be O-A-Do-Eop-D, O-A-ZDo-Eop-D, A-Do, or A-ZDO.
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com