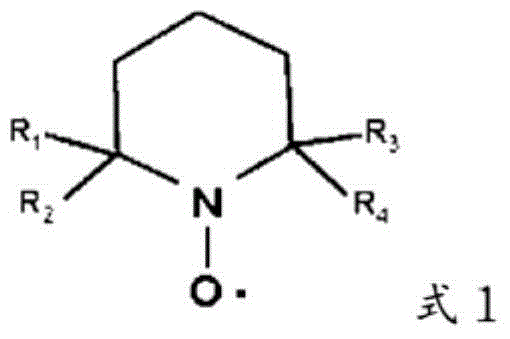
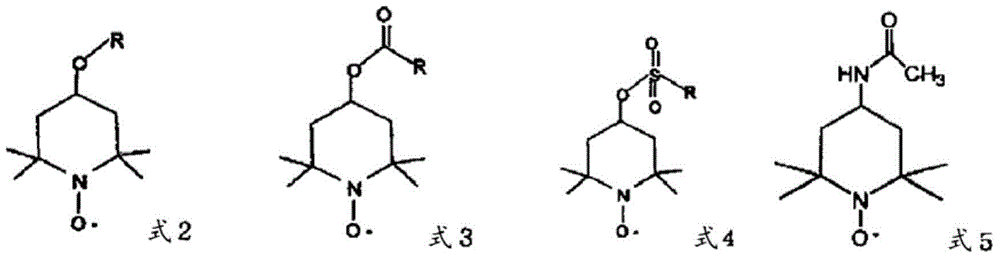
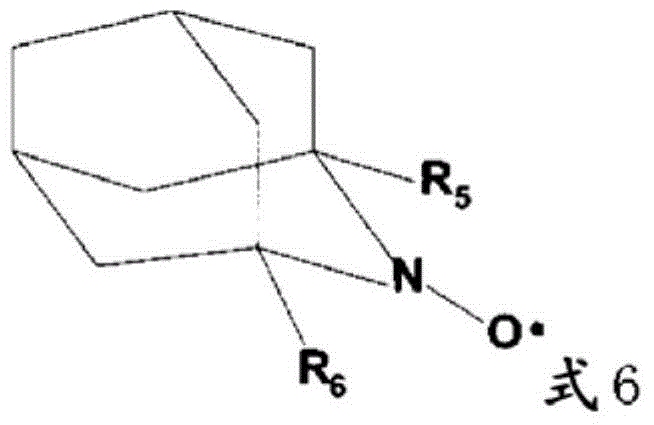
Method for producing cellulose nanofibers
一种纳米纤维、制造方法的技术,应用在纤维素纸浆后处理、纤维素纸浆后处理改性、纤维原料处理等方向,能够解决无法均匀混合、分散液粘度过高等问题,达到流动性和透明性优异的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0024] The type of plant material used in the preparation of DKP is not particularly limited, and wood chips of coniferous or broad-leaved trees generally used for pulp production, kenaf, hemp, rice, bagasse, bamboo, and the like can be used.
[0025] The DKP used in the present invention is characterized in that hydrolysis treatment is performed as a pretreatment of kraft cooking. As one of the hydrolysis treatment methods, there is a direct steam blowing method. In this method, it is considered that the organic acid in the plant material is liberated by high-temperature steam blown into the plant material, and then hydrolyzed by the action of the acid.
[0026] The conditions of the hydrolysis treatment are not particularly limited, for example, it can be carried out as follows, that is, using an autoclave or the like, the liquid phase or vapor phase of water or 2% by mass or less of an inorganic acid is contacted with a plant material such as wood chips, and the temperature...
Embodiment 1
[0110] To a rotary autoclave with a capacity of 2.4 L, 300 g of broad-leaved wood chips with an absolute dry mass were charged, and water was added so that the liquid ratio would be 2 L / kg. After holding at 170° C. for 30 minutes to carry out hydrolysis treatment, a neutralizing solution was added, and neutralization treatment was carried out at 155° C. for 15 minutes. The neutralizing solution is prepared by mixing sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide in the form of active alkali 11% (relative to sawdust mass), degree of sulfidation 25%, and liquid ratio 2.5L / kg. After the neutralization treatment, extract the liquid from the autoclave, add cooking liquid (prepared by mixing sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide in the form of active alkali 9% (relative to sawdust mass), degree of sulfidation 25%, and liquid ratio 2.5L / kg), in Cook at 160°C until the H factor becomes 830 (preparation of DKP).
[0111] After oxygen delignification of cooked green pulp, it was bleached in the seq...
Embodiment 2
[0122] Into a 2.4 L volume rotary autoclave, 300 g of coniferous wood chips in an absolute dry mass were charged, and water was added so that the liquid ratio was 3.2 L / kg. After maintaining at 170° C. for 30 minutes for hydrolysis treatment, a neutralizing solution was added and neutralized at 155° C. for 15 minutes. The neutralizing solution is prepared by mixing sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide in the form of active alkali 13% (relative to the mass of wood chips), sulfidation degree 25%, and liquid ratio 3.2L / kg. After the neutralization treatment, extract the liquid from the autoclave, add cooking liquid (prepared by mixing sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide in the form of active alkali 11% (relative to sawdust mass), degree of sulfidation 25%, and liquid ratio 3.2L / kg), in Cook at 170°C until the H factor becomes 1800 (preparation of DKP).
[0123] After oxygen delignification of the cooked green pulp, it is bleached in the order of D0-E / P-D1 as ECF bleaching. Oxyge...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| whiteness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| visible light transmittance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com