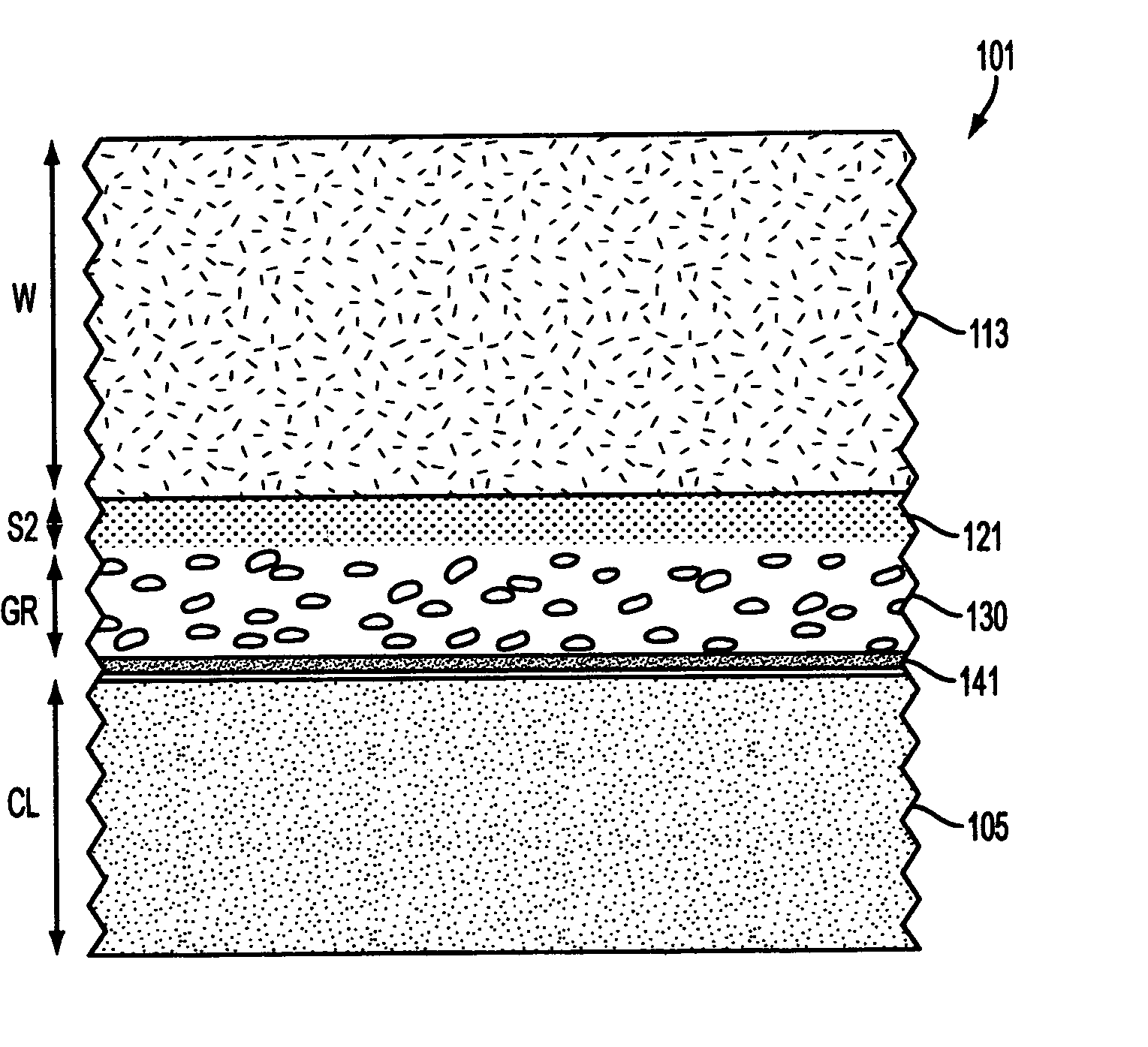
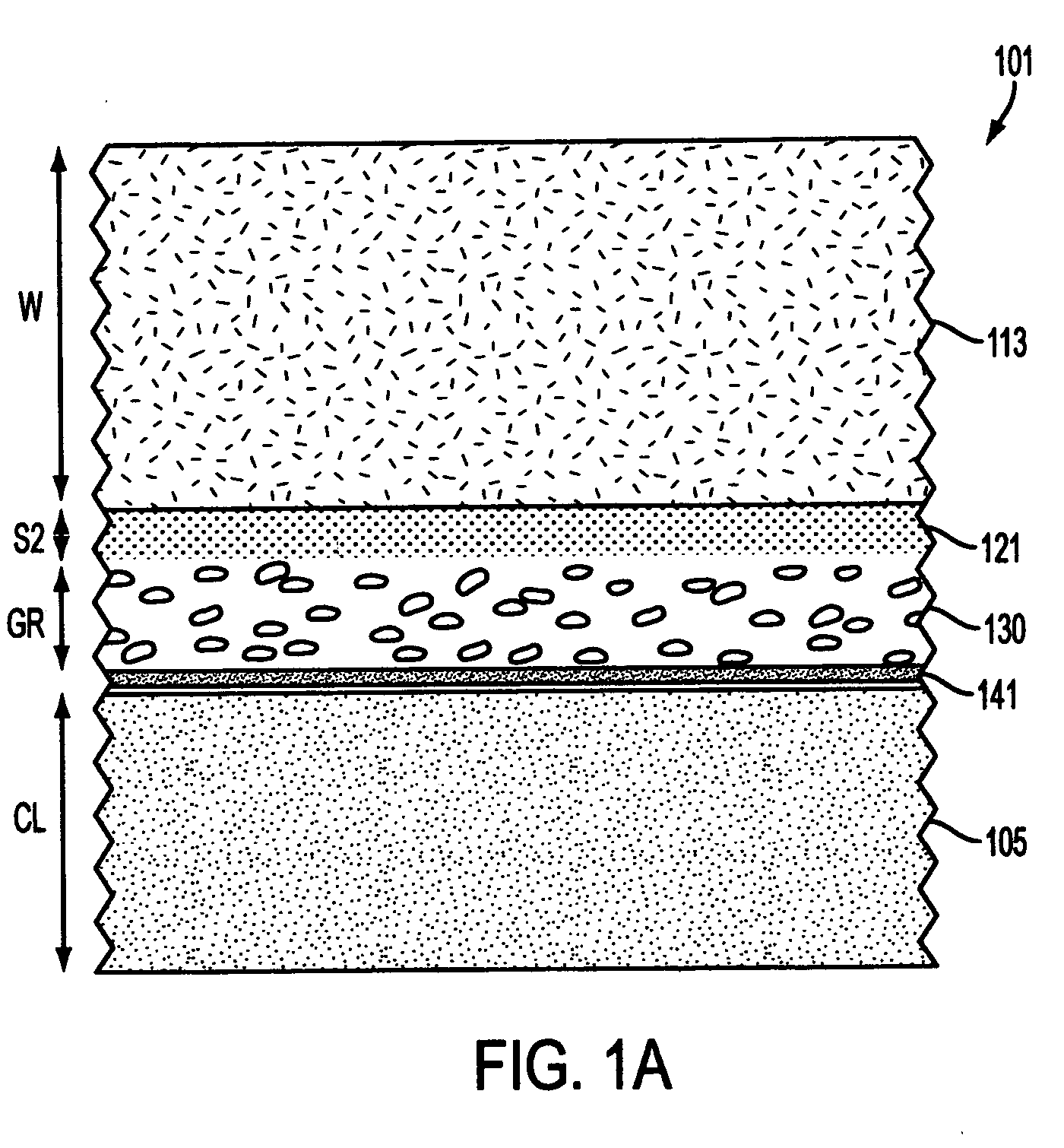
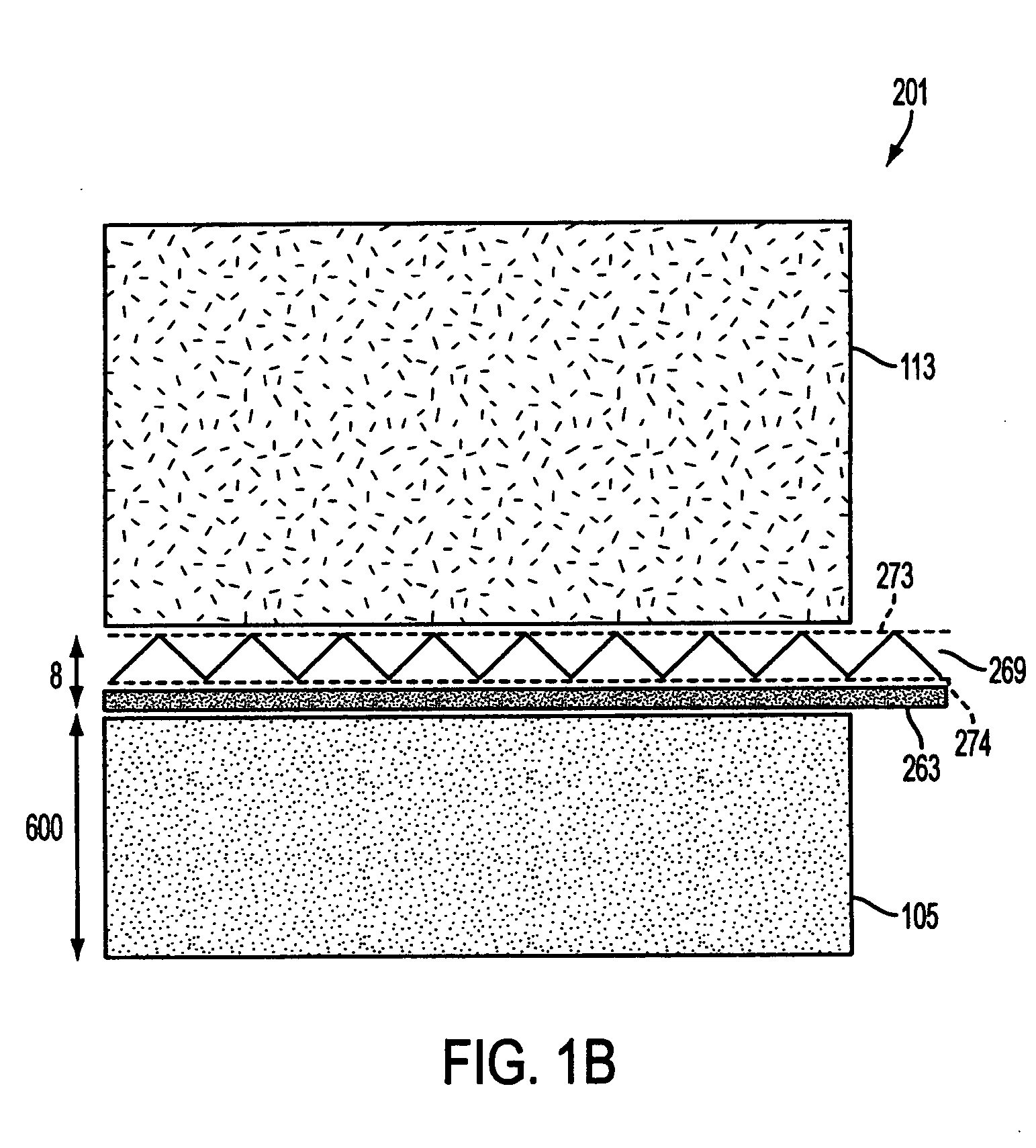
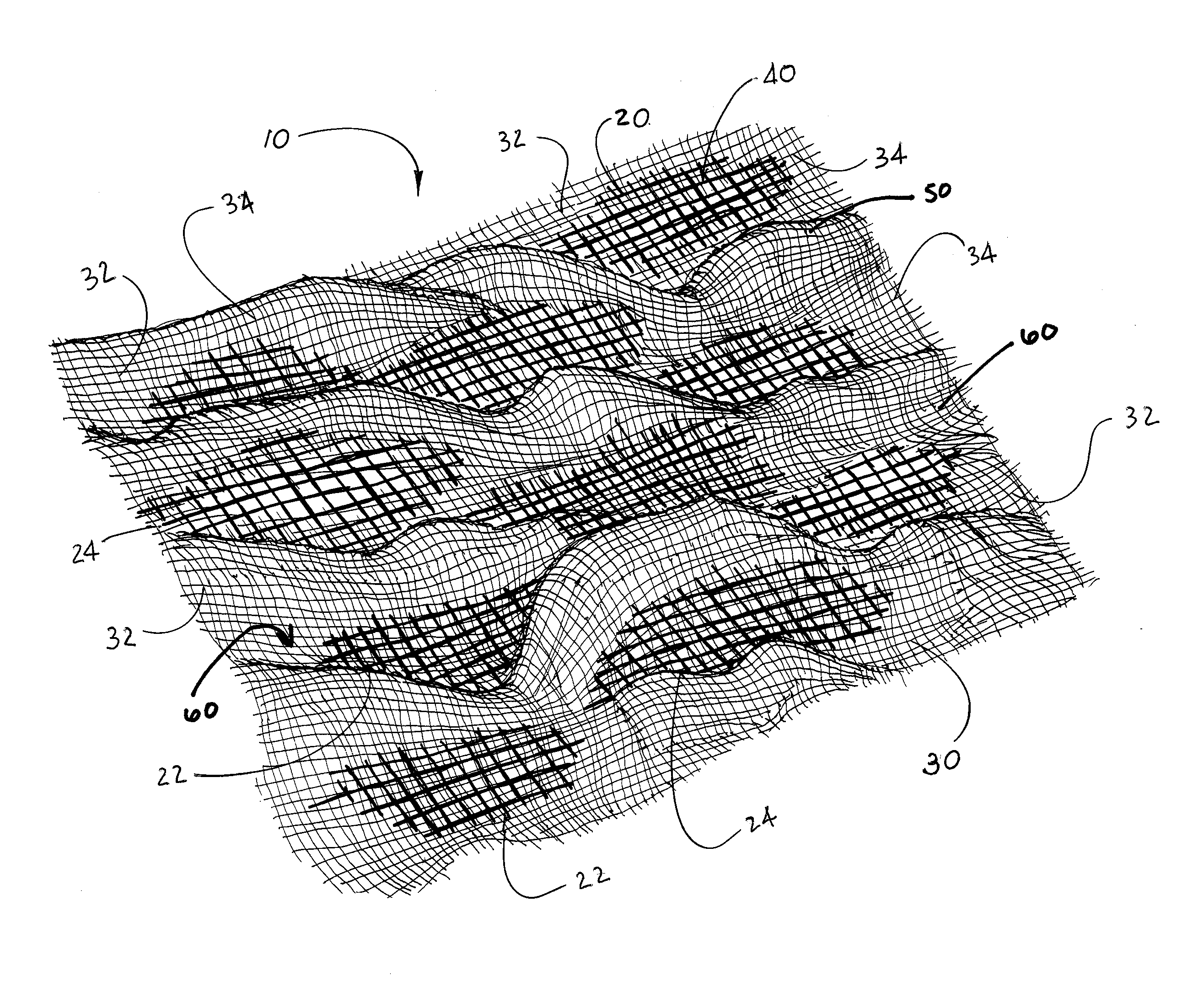
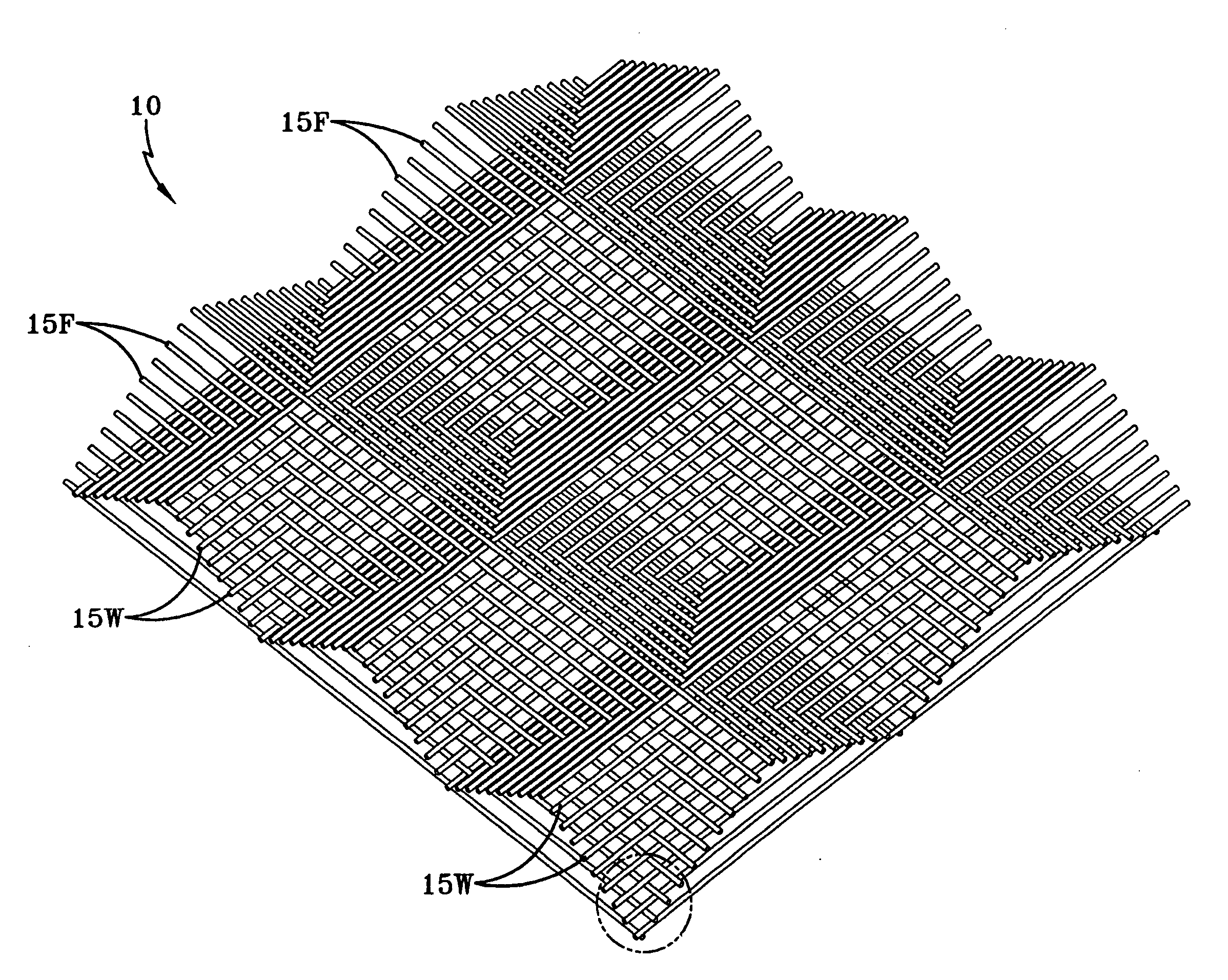
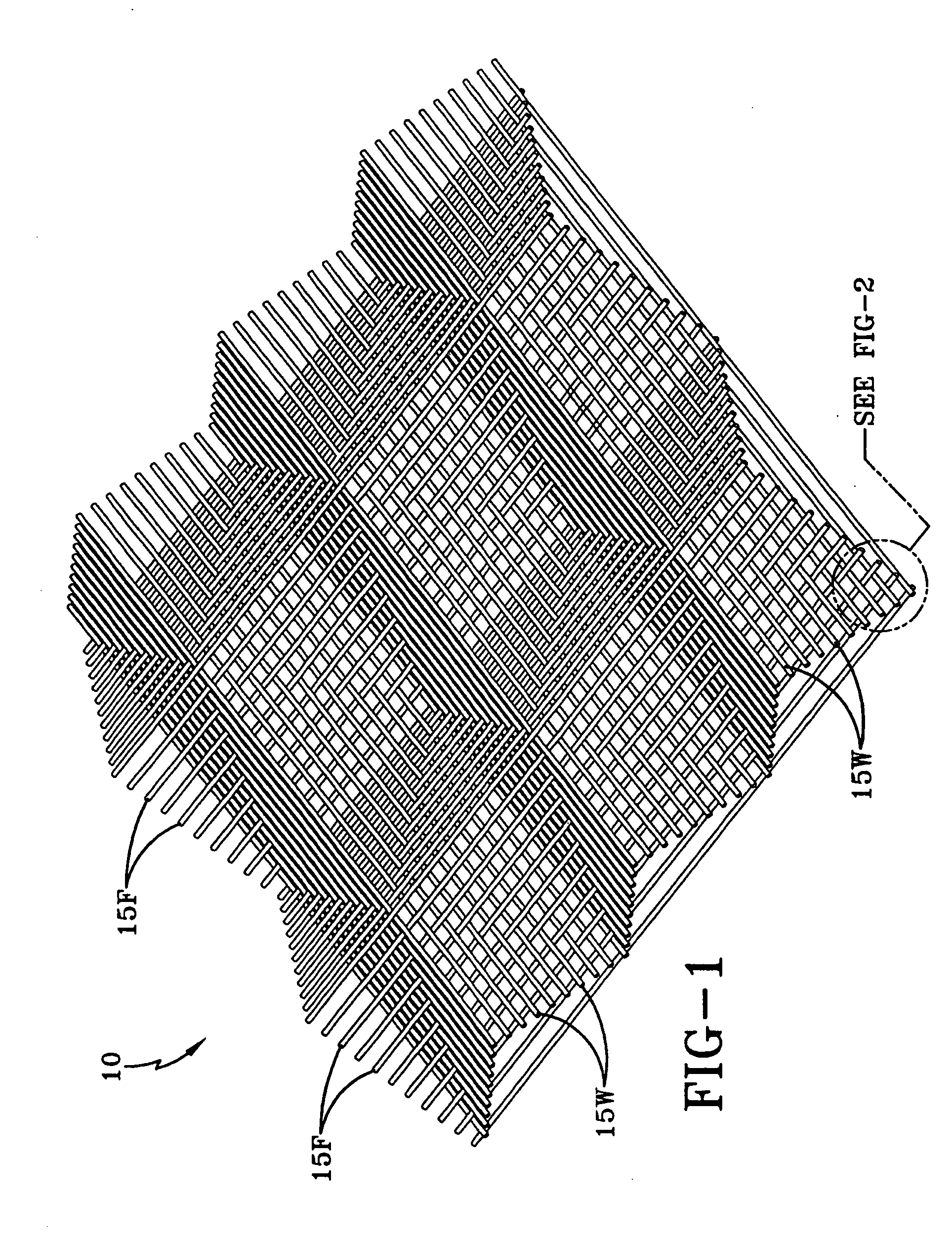
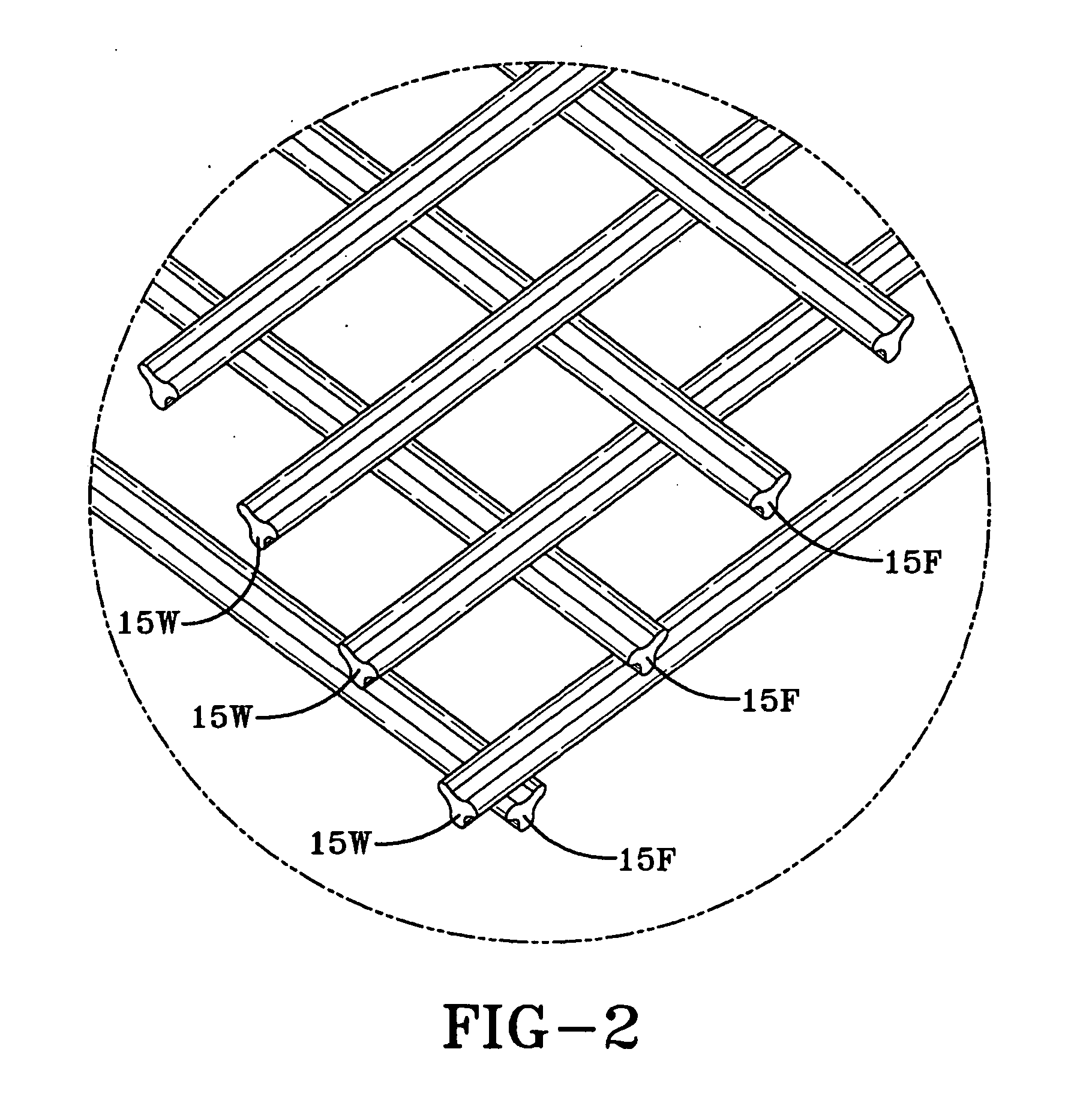
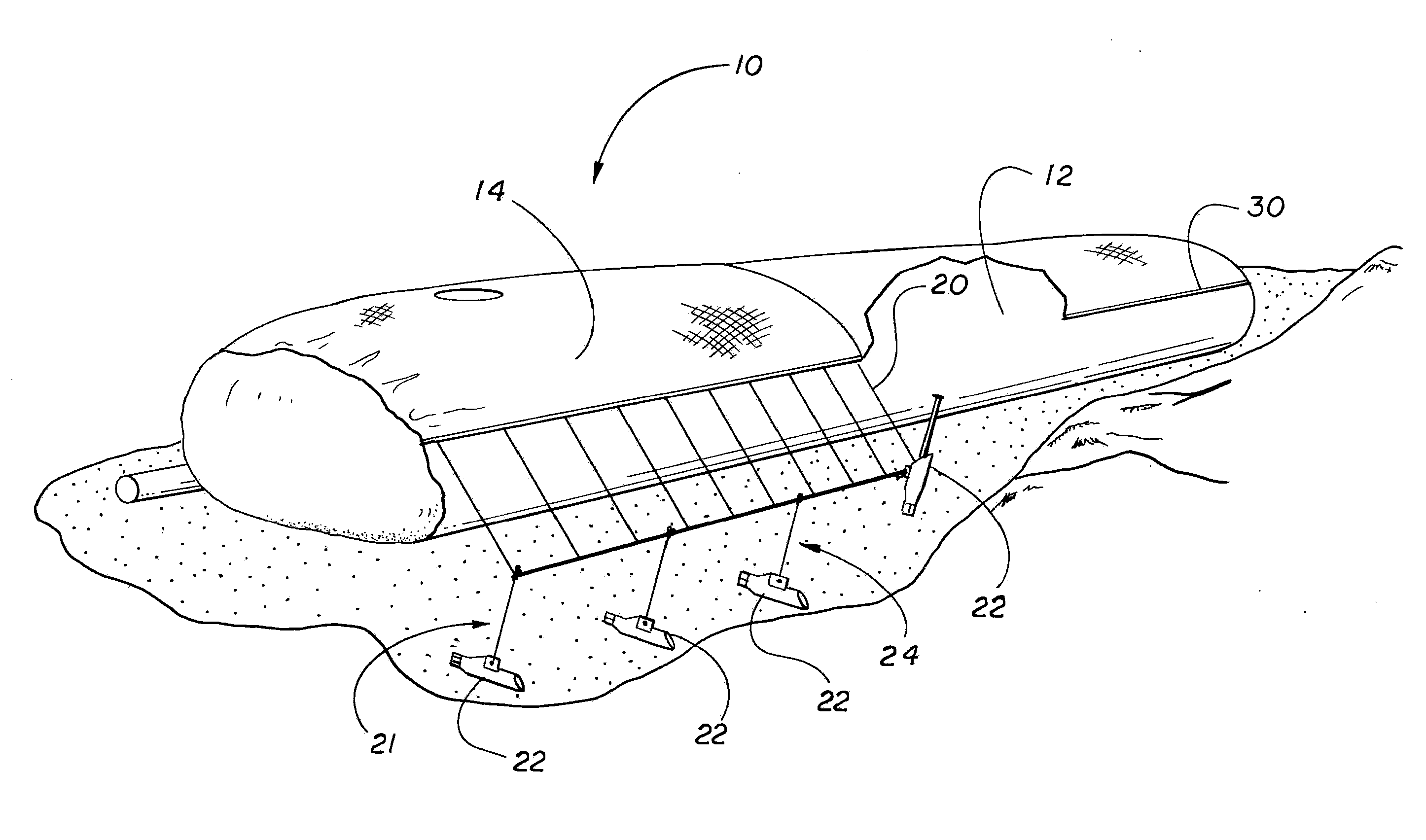
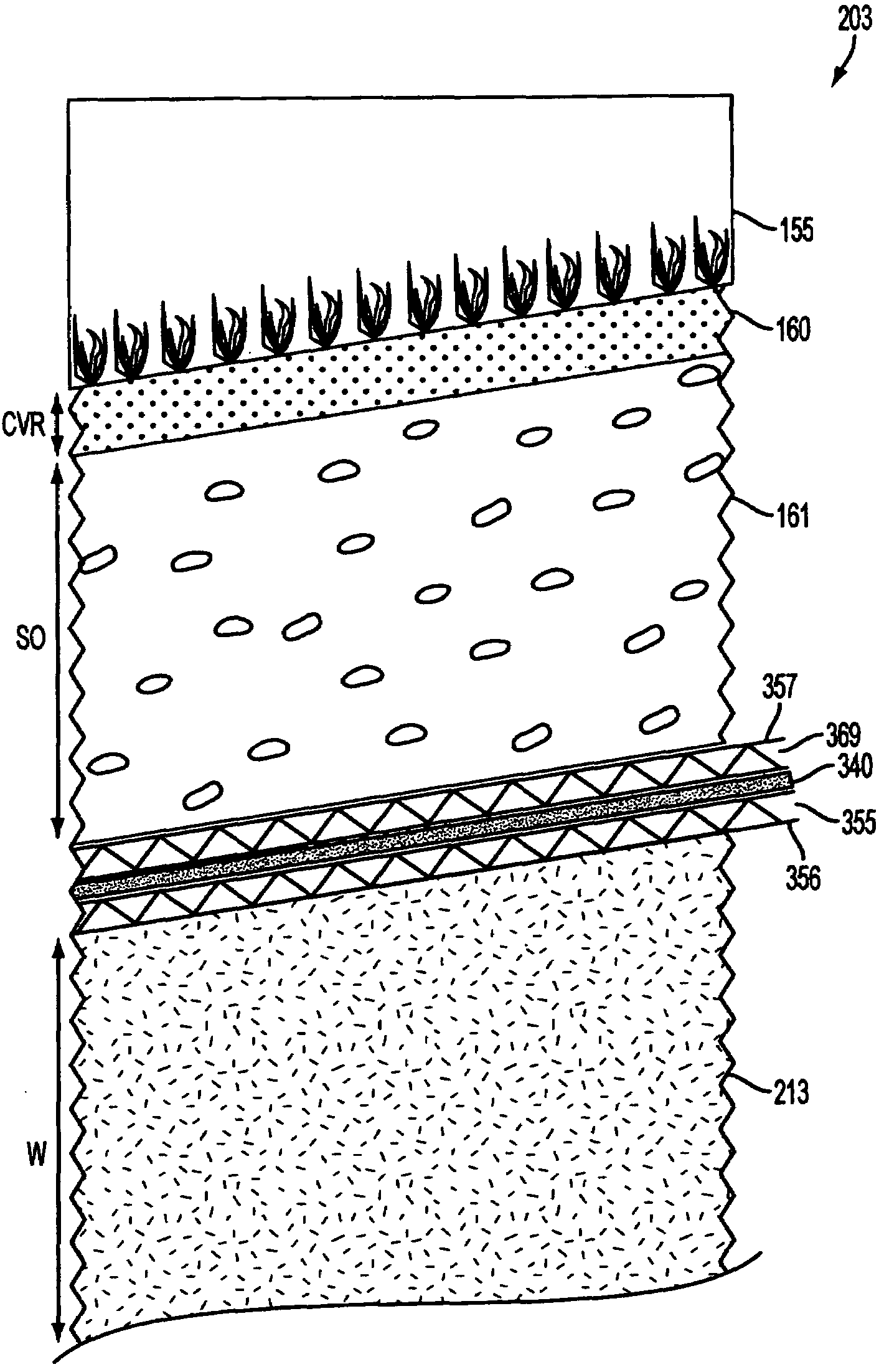
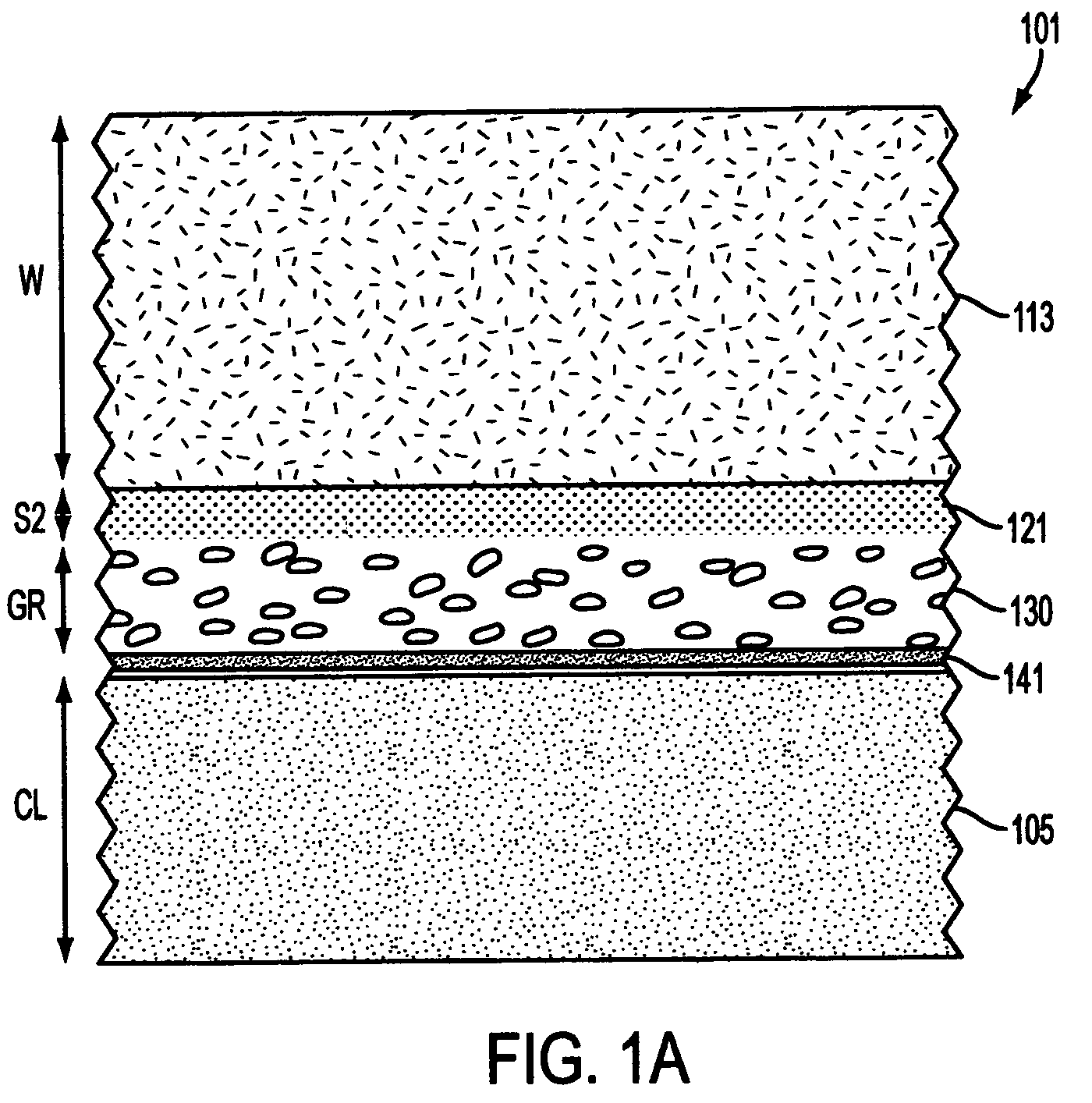
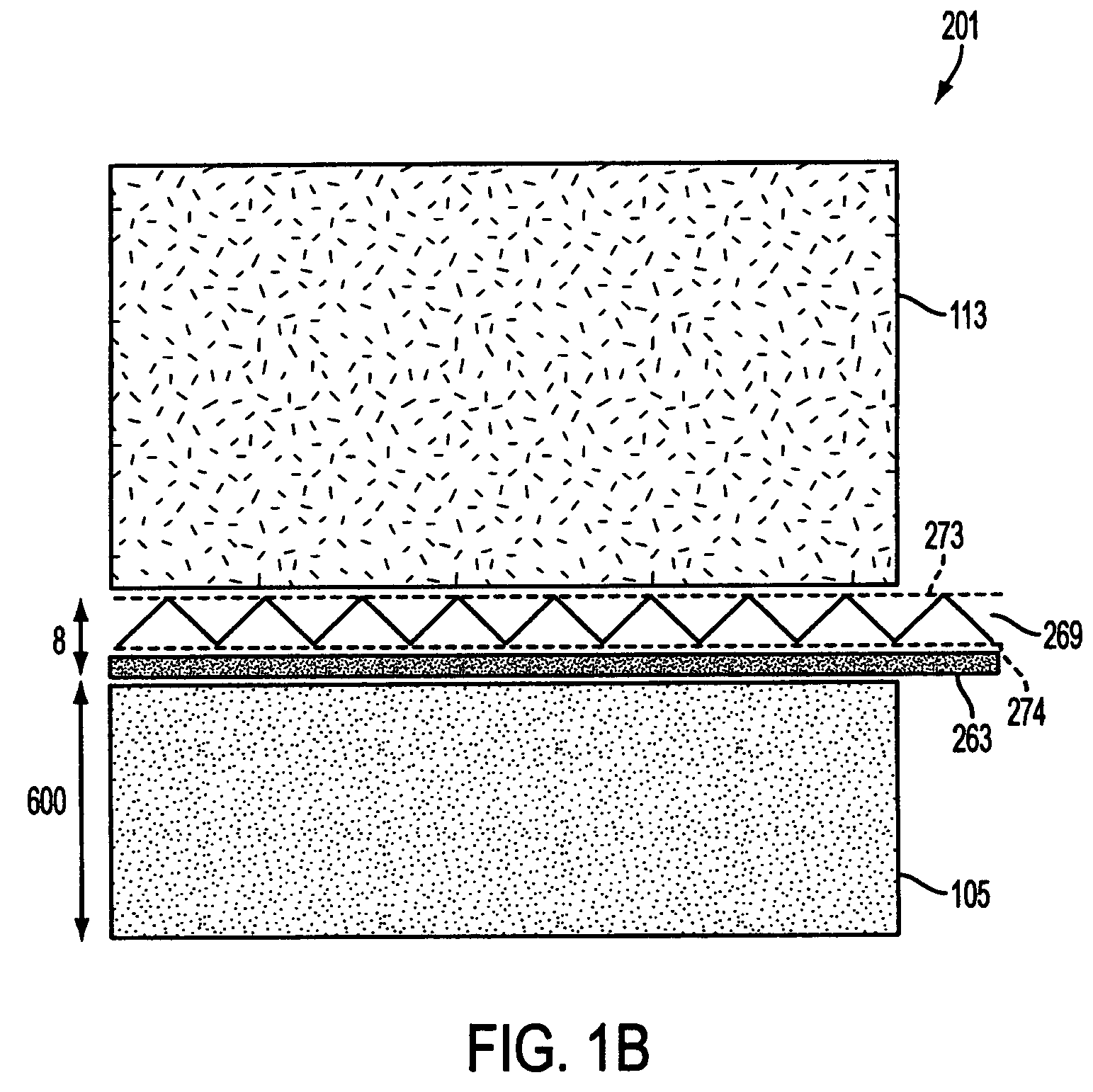
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
549results about "Geotextiles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
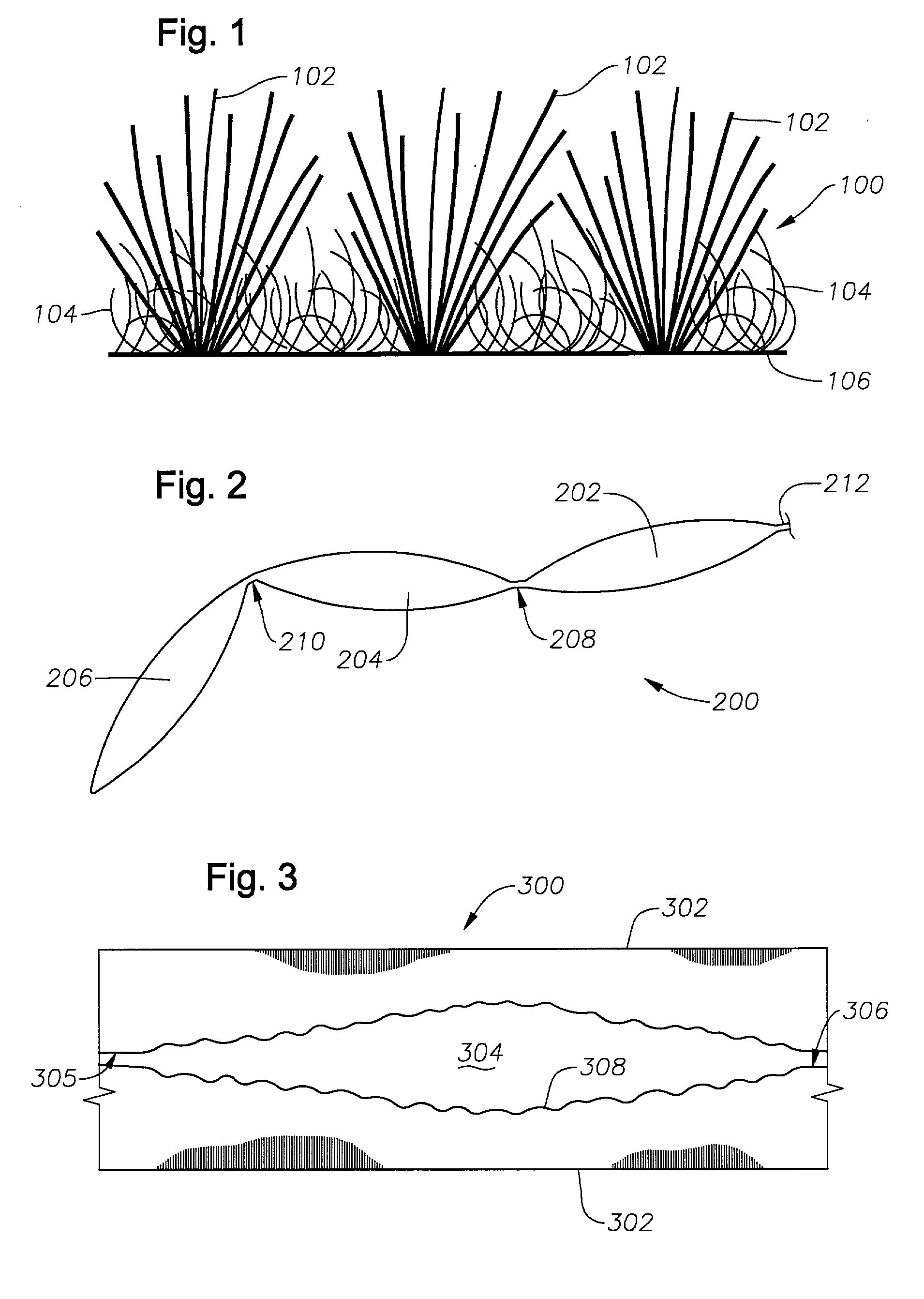
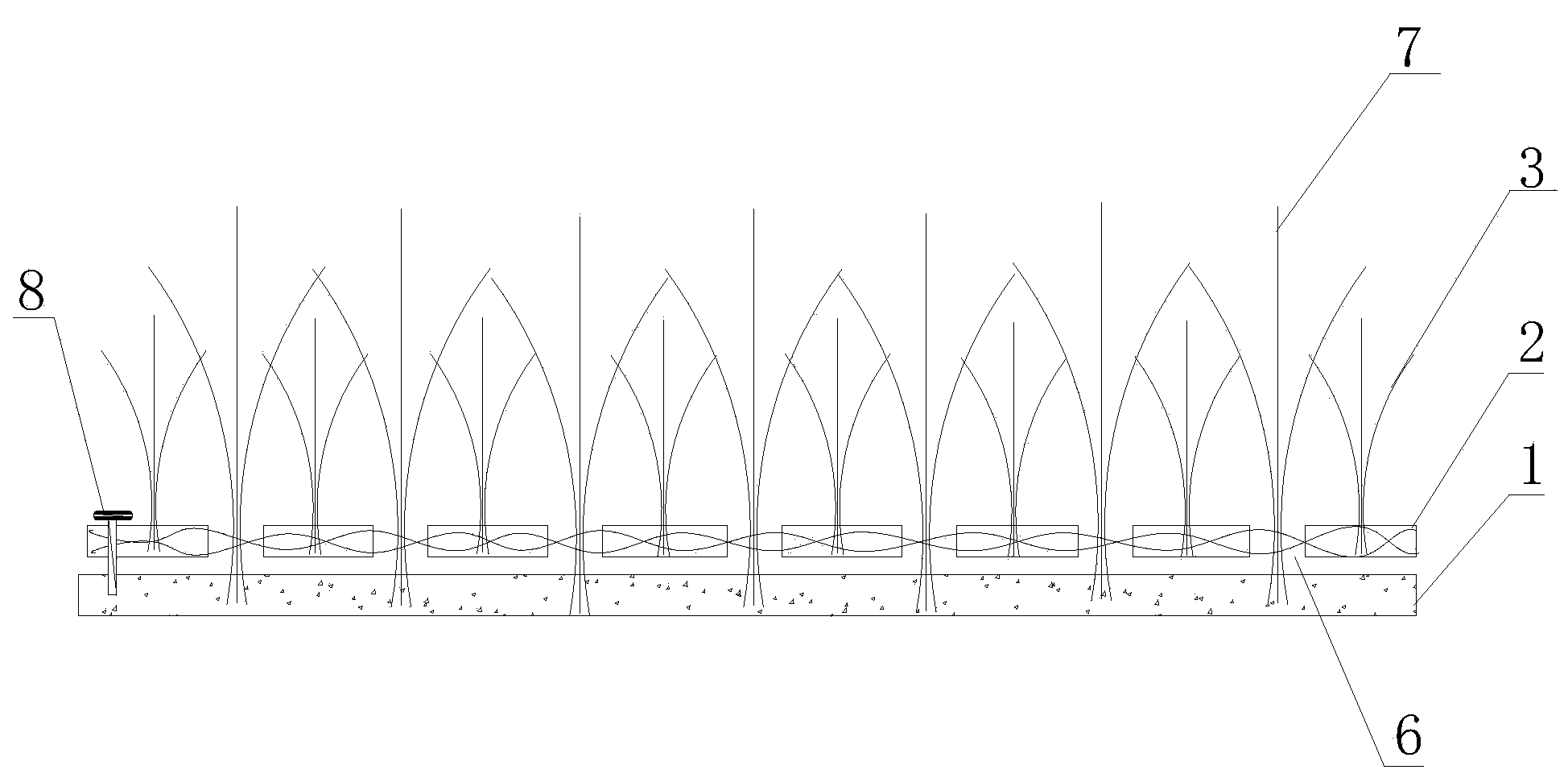
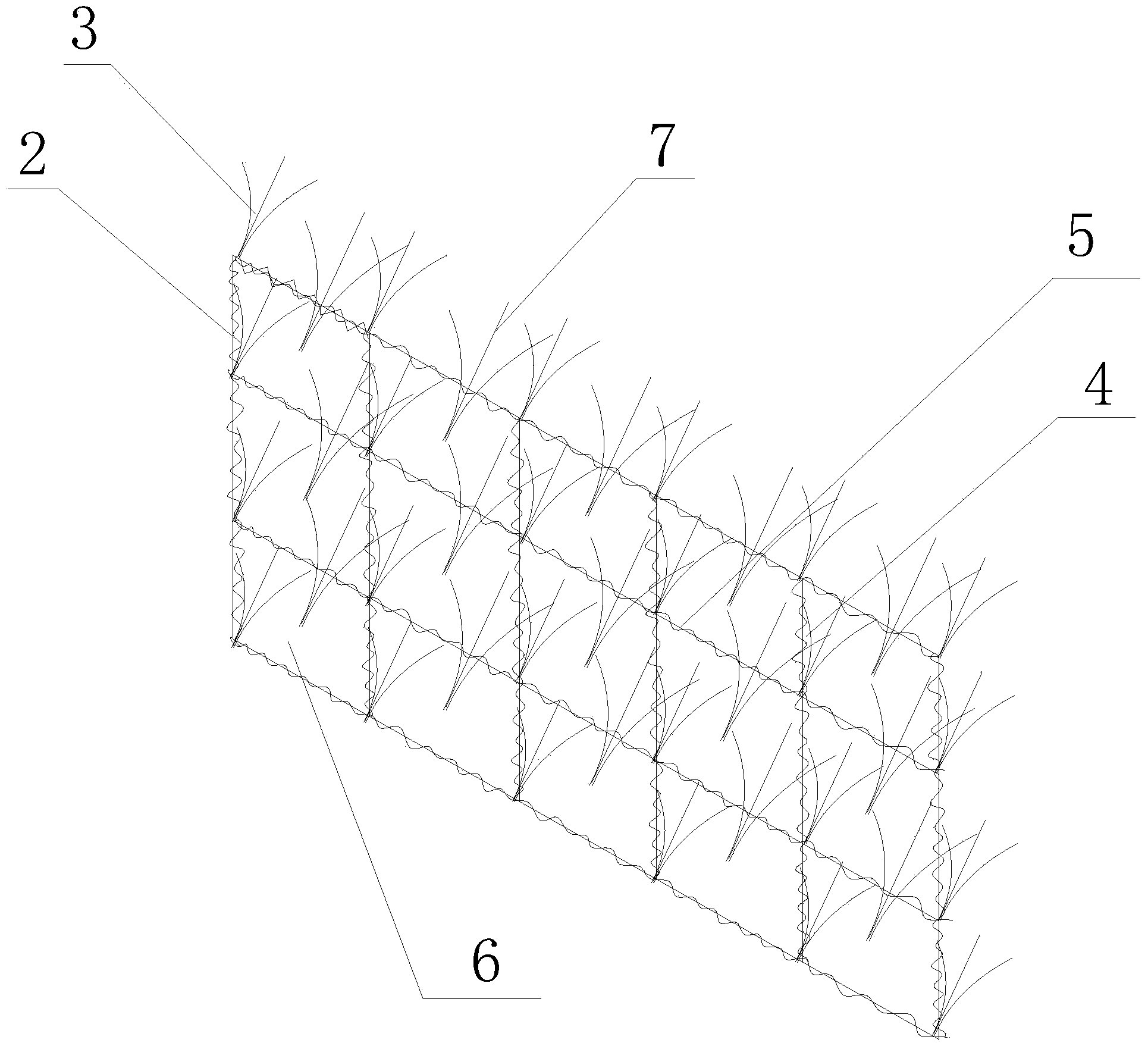
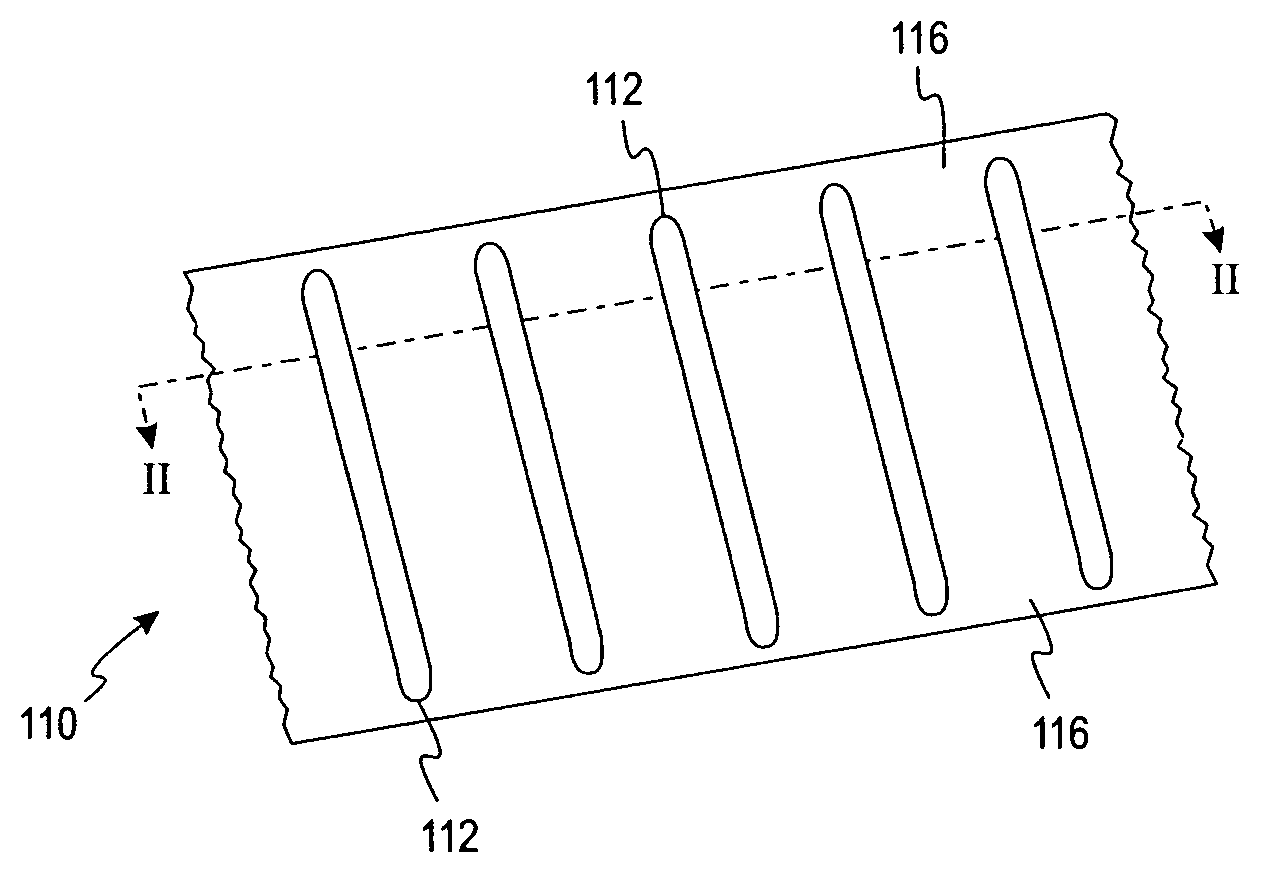
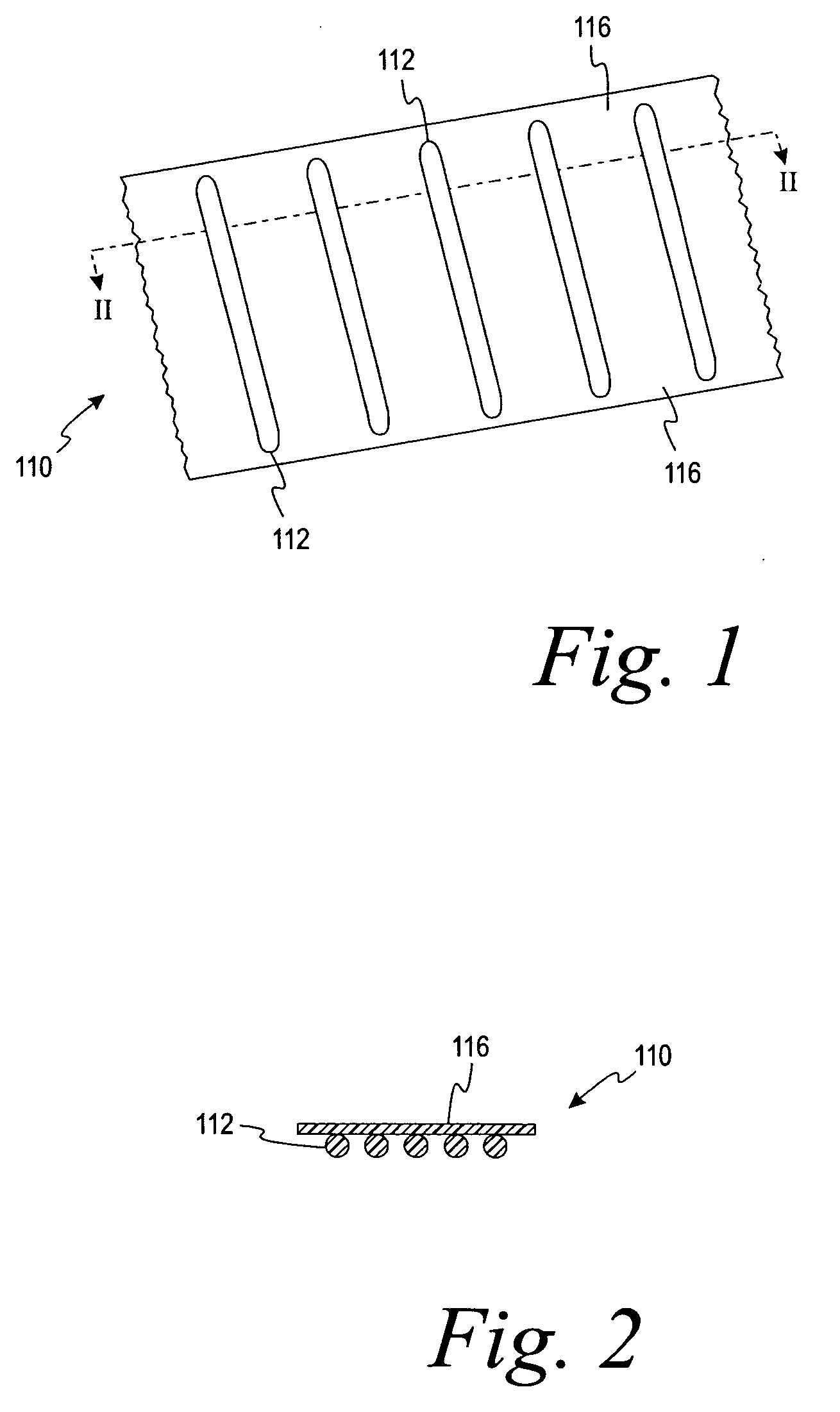
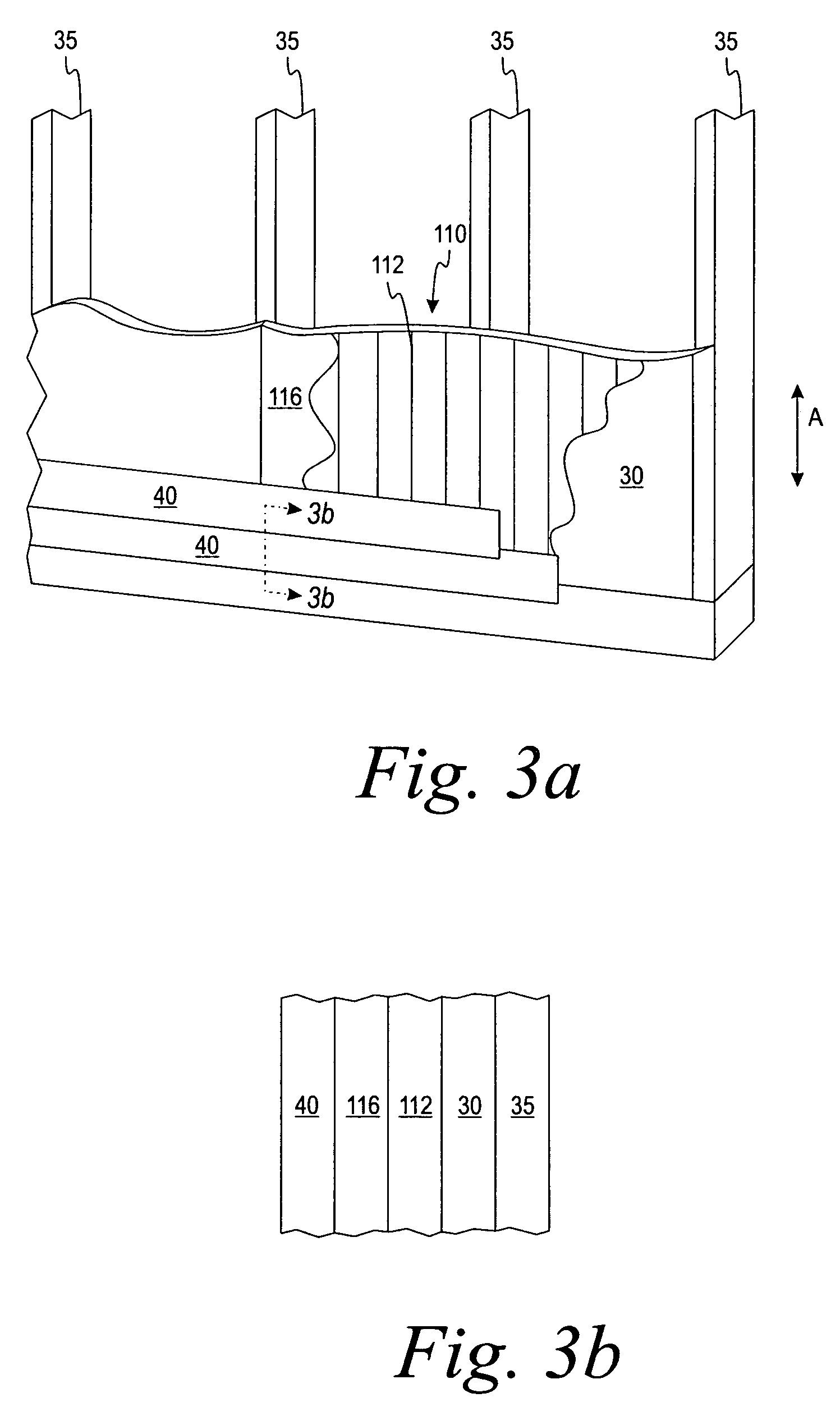
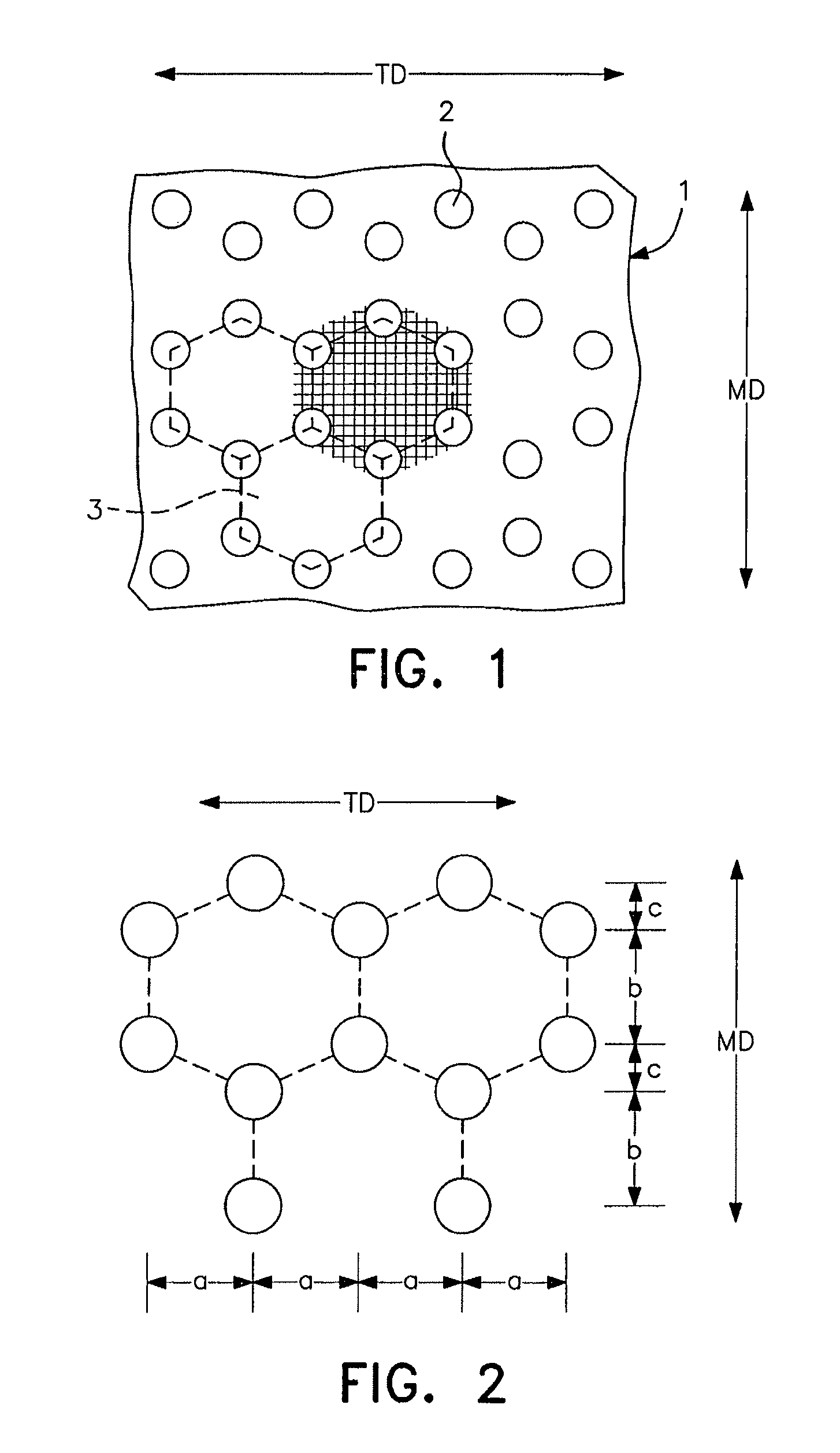
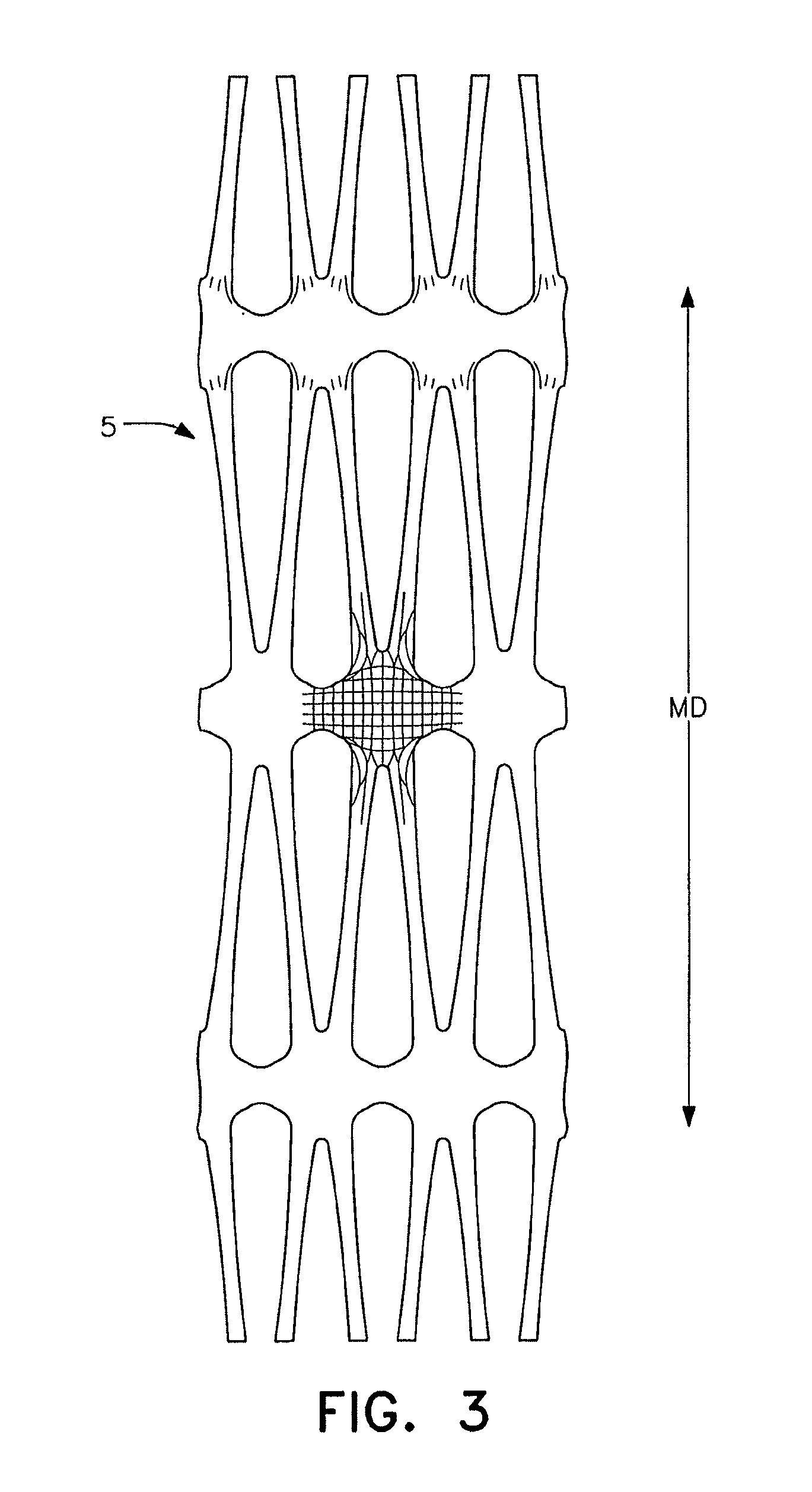
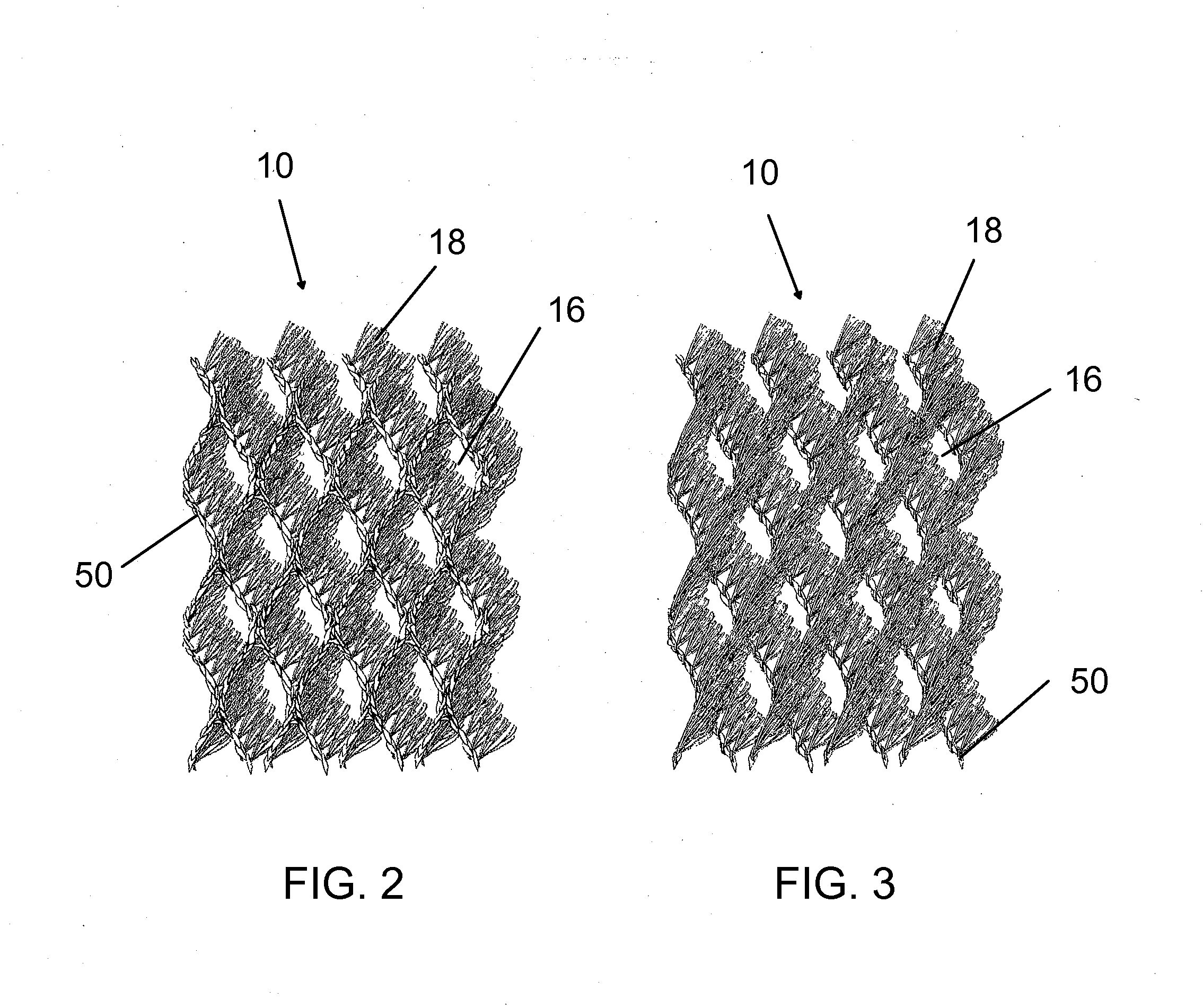
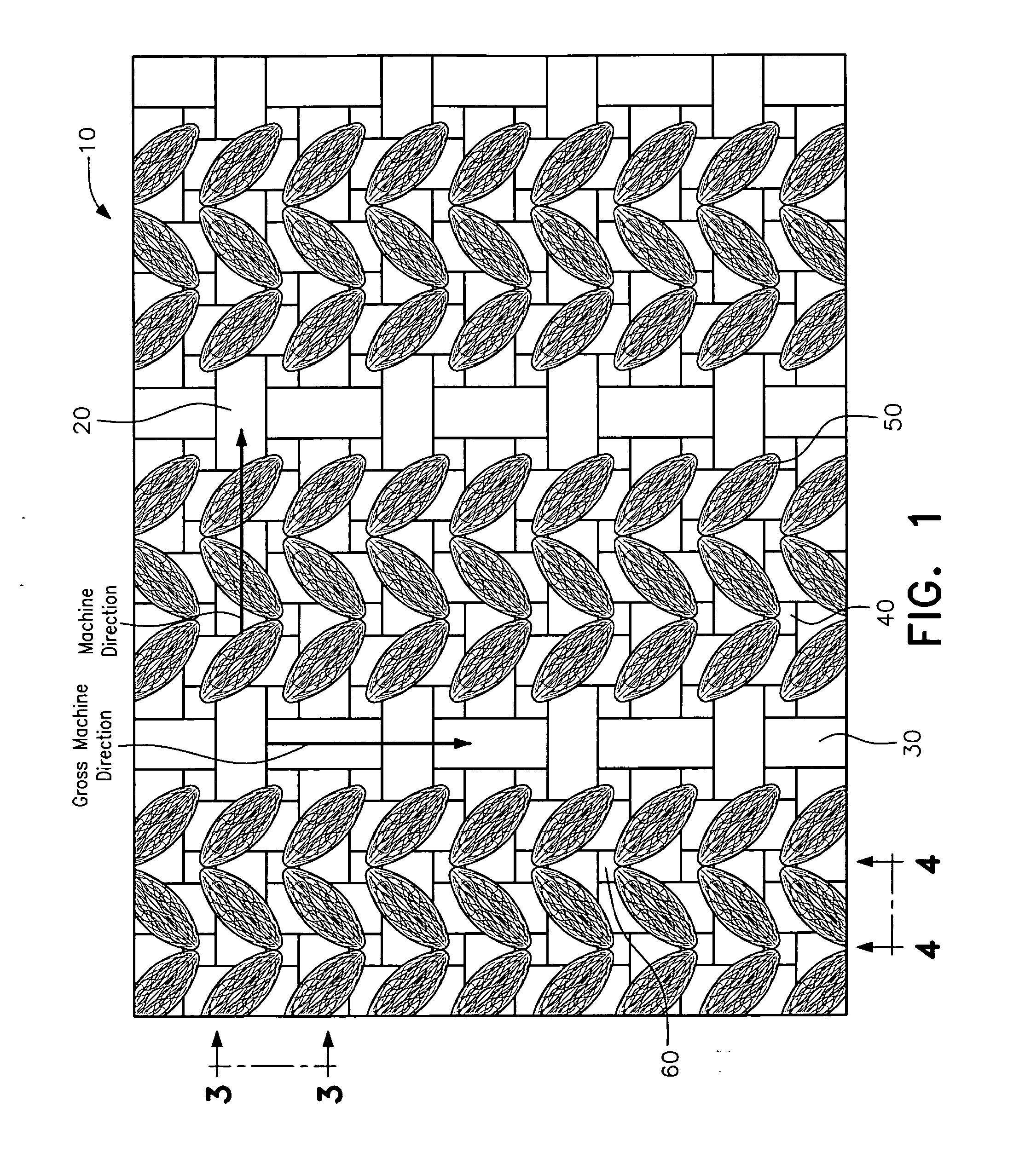
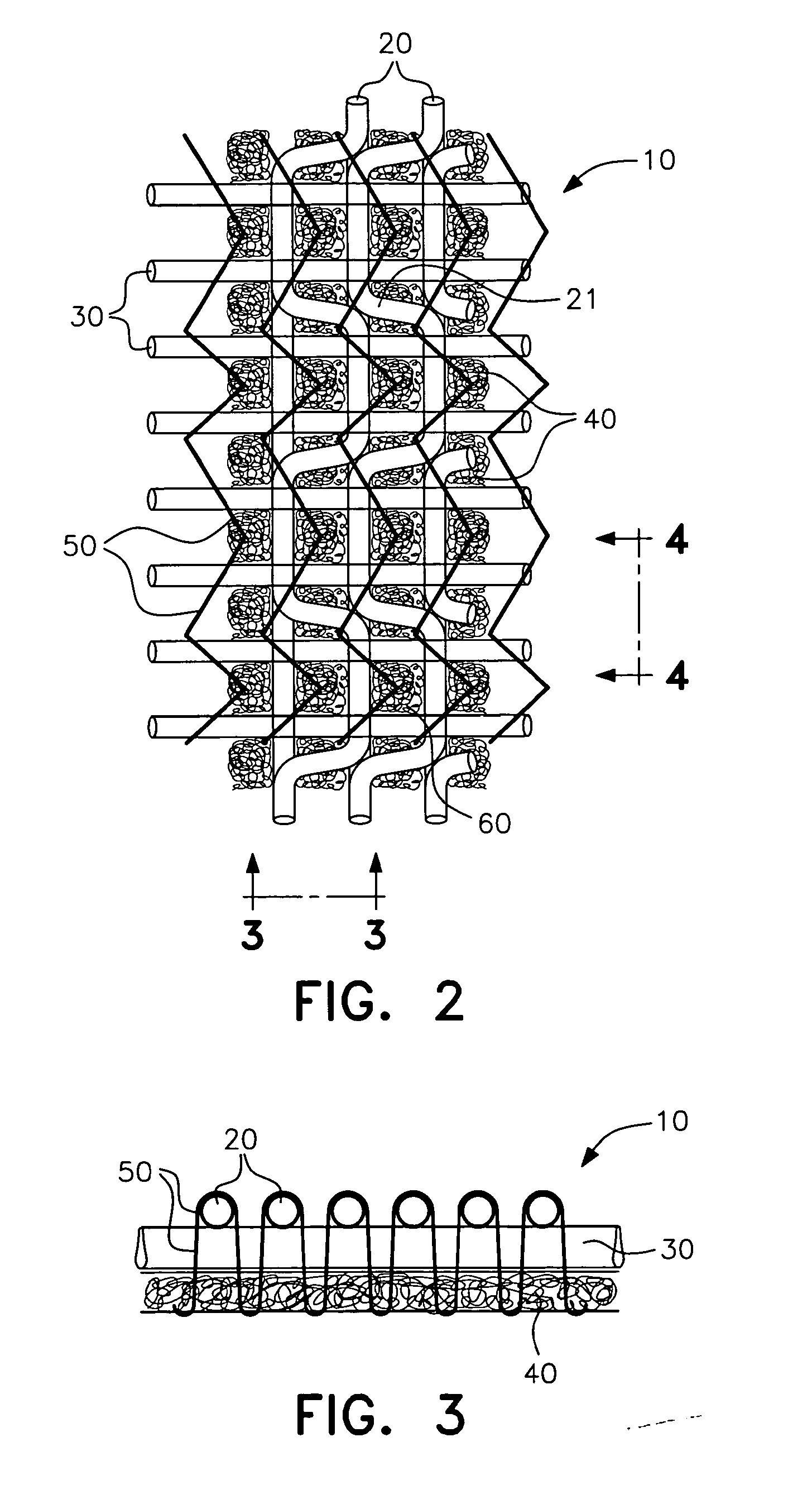
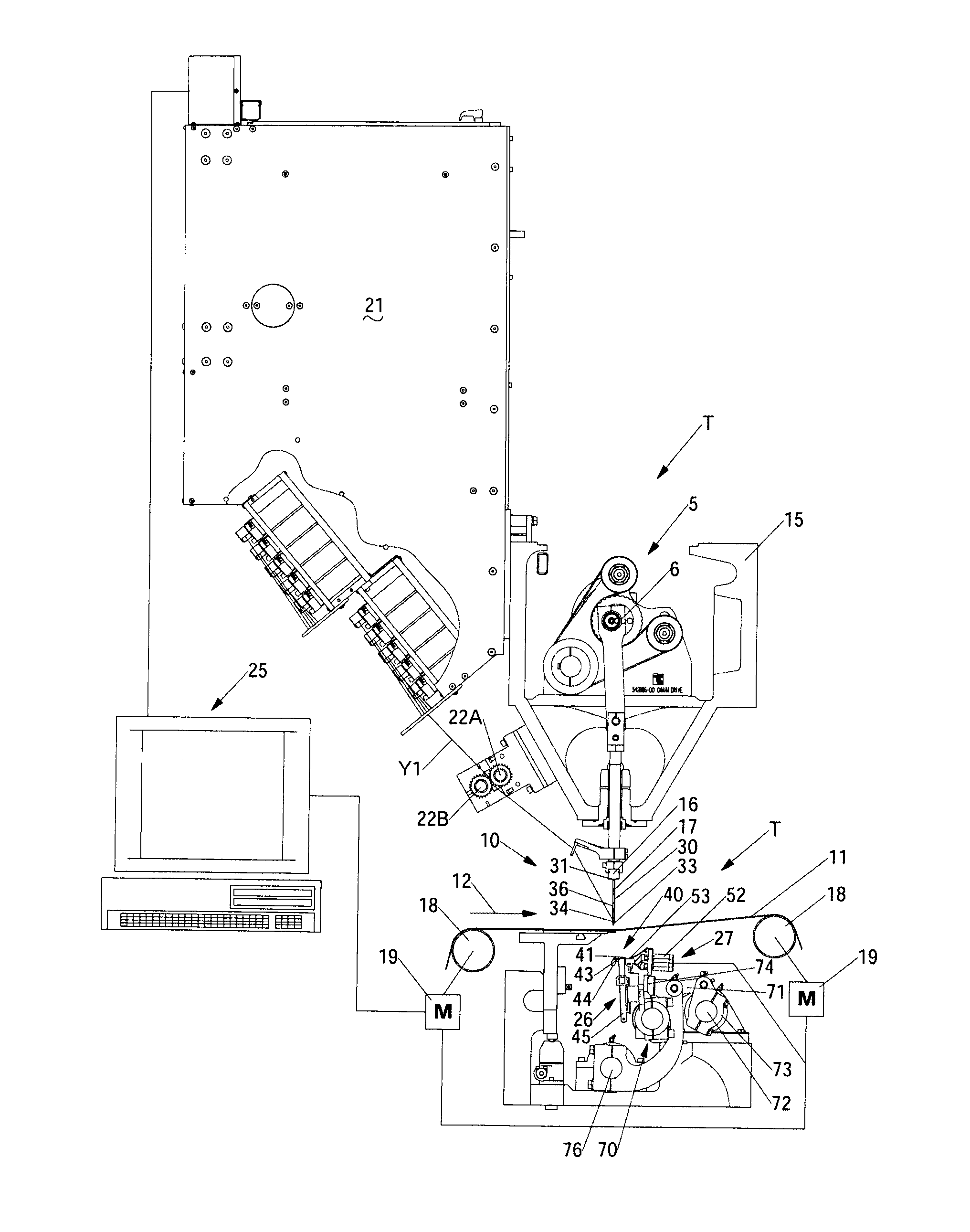
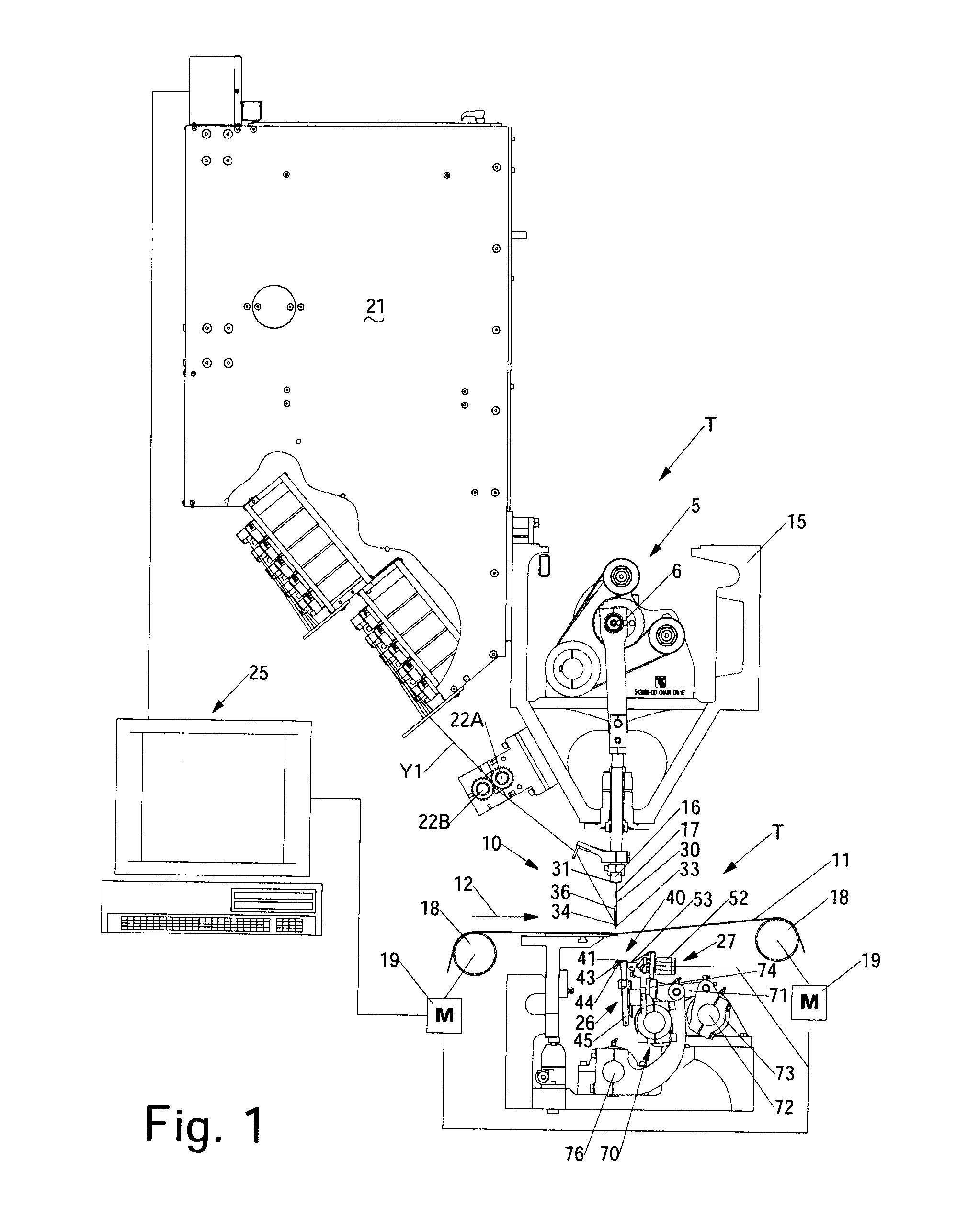
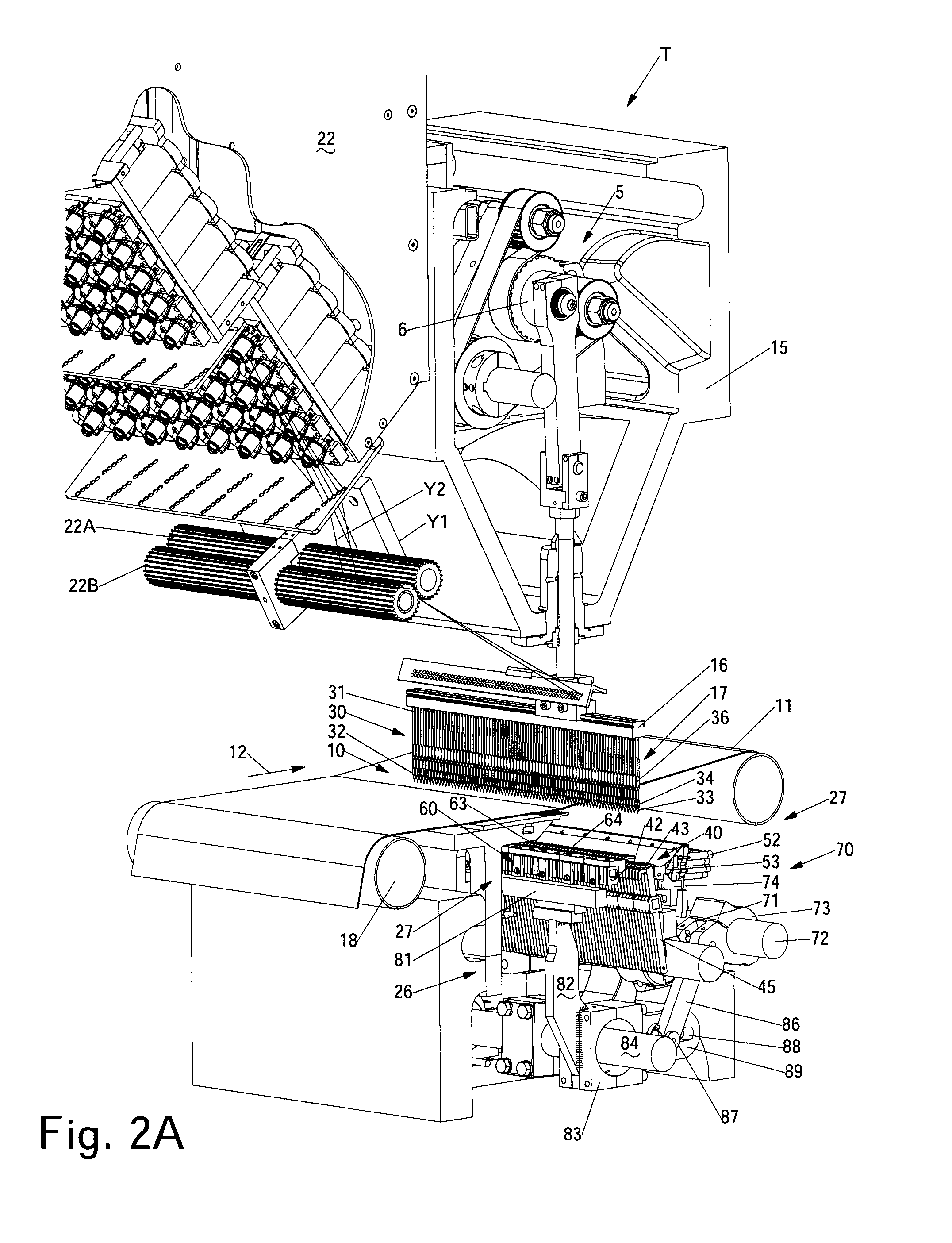
Artificial turf system
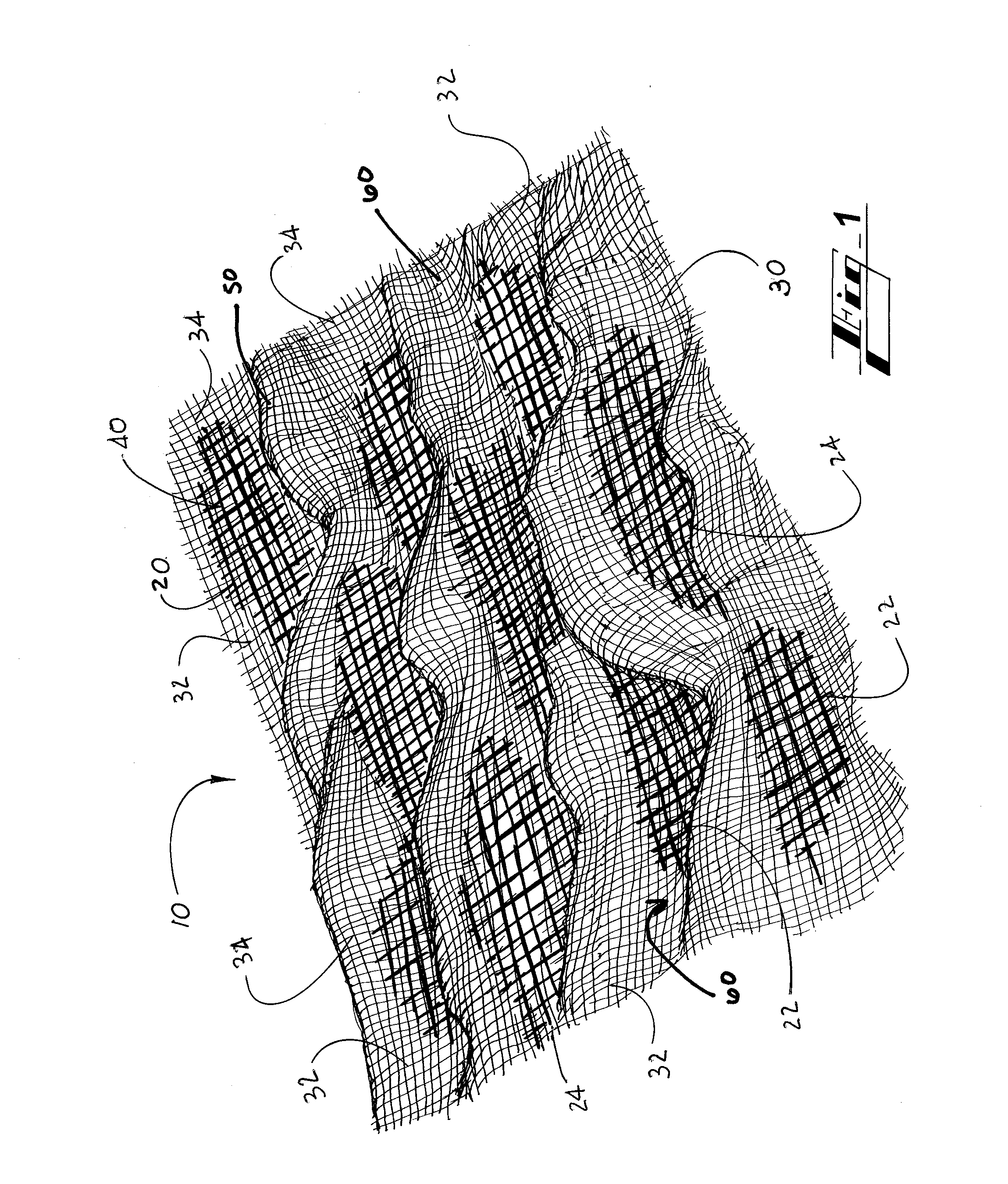
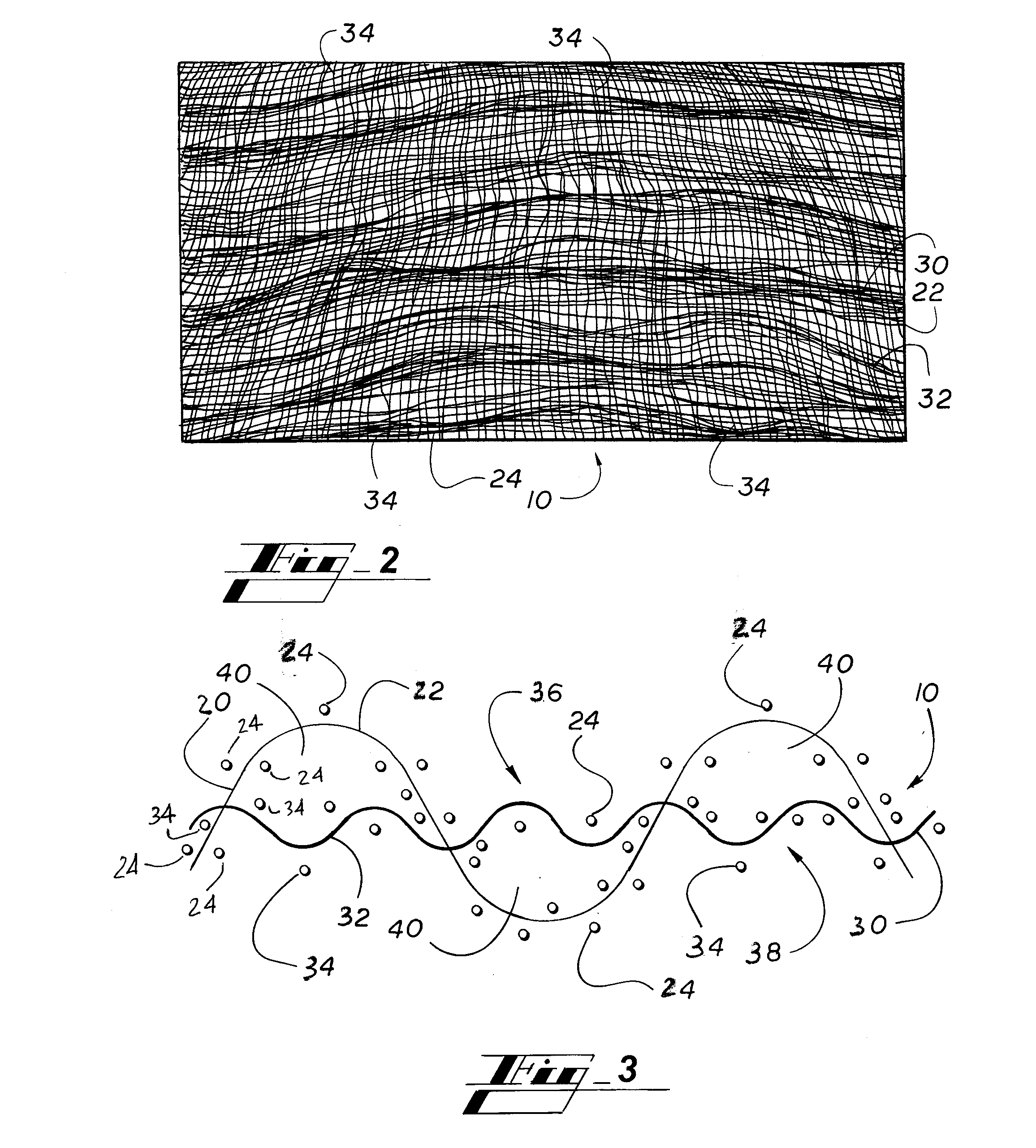
An artificial turf that includes a first face yarn, a second face yarn, and a stitch-in yarn. The second face yarn is textured in some embodiments, for at least the reason of creating a zone such as a textured zone. A knot is formed by knitting the first face yarn, the second face yarn, and the stitch-in yarn together. A row of knots is also formed in this manner. A backing is formed when a lay-in yarn is extended between at least two rows of the knots and knitted to hold the at least two rows of knots together. A coating is coupled to the backing to prevent, among other things, detachment of the yarns after extended use of the artificial turf. An underlayment is positioned beneath the backing such that a stable base is provided for the artificial turf.
Owner:APT ADVANCED POLYMER TECH CORP
Speaker for mobile terminals and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050220320A1Thin structureWide frequency characteristicTransducer detailsGeotextilesEngineeringSound quality
Disclosed herein are a speaker for mobile terminals which has a slim structure and has a wide frequency characteristic and an excellent high frequency distortion characteristic, thus accomplishing an excellent sound quality, and a method of manufacturing the speaker.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Geogrid composed of fiber-reinforced polymeric strip and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20060116040A1Increase resistance against vertical loadIncrease friction forceWarp knittingWelding/cutting auxillary devicesTensile strainGeogrid
A geogrid using fiber-reinforced polymeric strips and its producing method are disclosed. The geogrid of a lattice shape includes plural longitudinal fiber-reinforced polymeric strips longitudinally arranged in parallel at regular intervals and formed by reinforcing fiber in a thermoplastic polymer resin, and plural lateral fiber-reinforced polymer strip laterally arranged in parallel at regular intervals and formed by reinforcing fiber in a thermoplastic polymer resin. Each longitudinal fiber-reinforced polymer strip has at lease one first contact point crossed with the lateral fiber-reinforced polymer strip on the upper surface and at least one second contact point crossed with the lateral fiber-reinforced polymer strips on the lower surface. The contact points are fixed by welding the longitudinal and lateral fiber-reinforced polymer strips. The geogrid is excellent in installation capacity, frictional feature and shape stabilisation and shows high tensile strength and low tensile strain and low creep deformation.
Owner:SAMSANG CORP
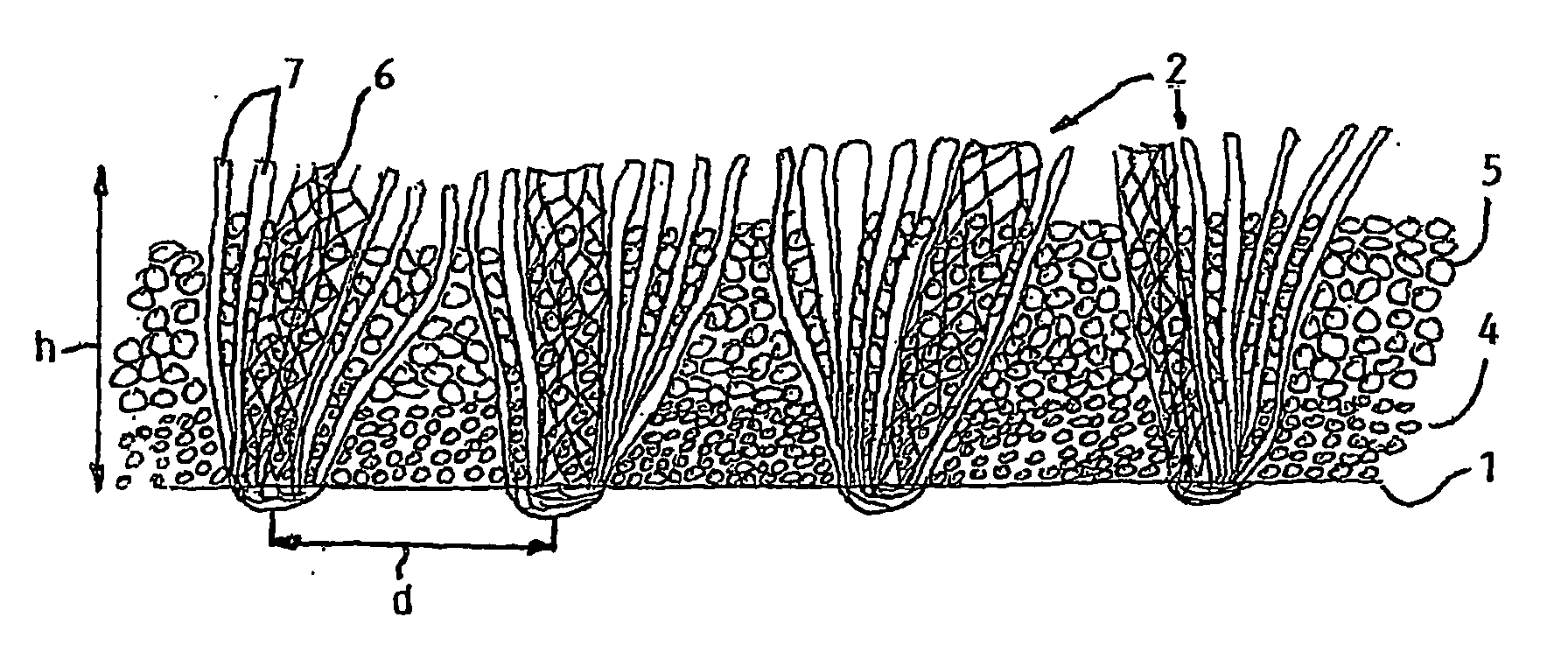
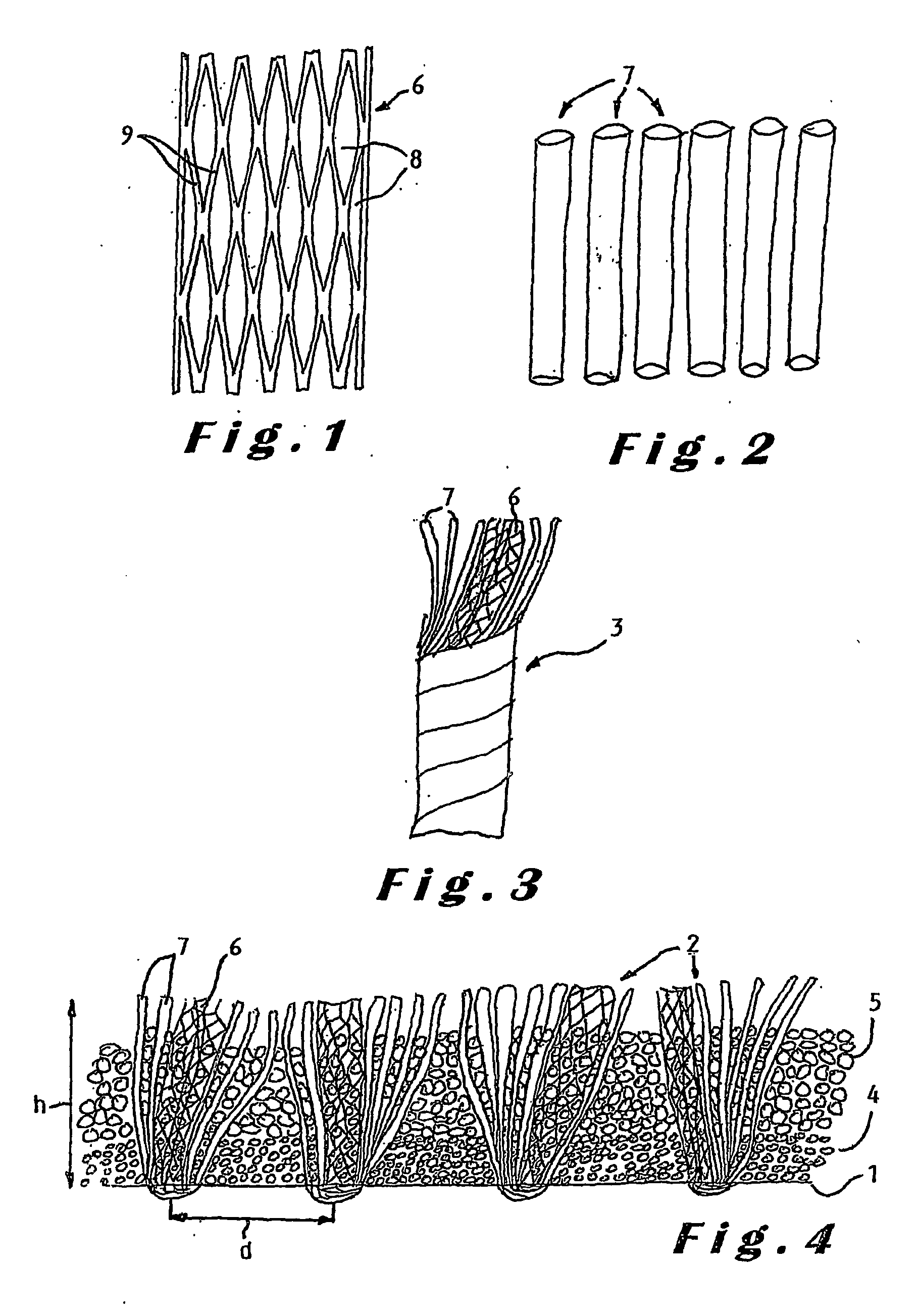
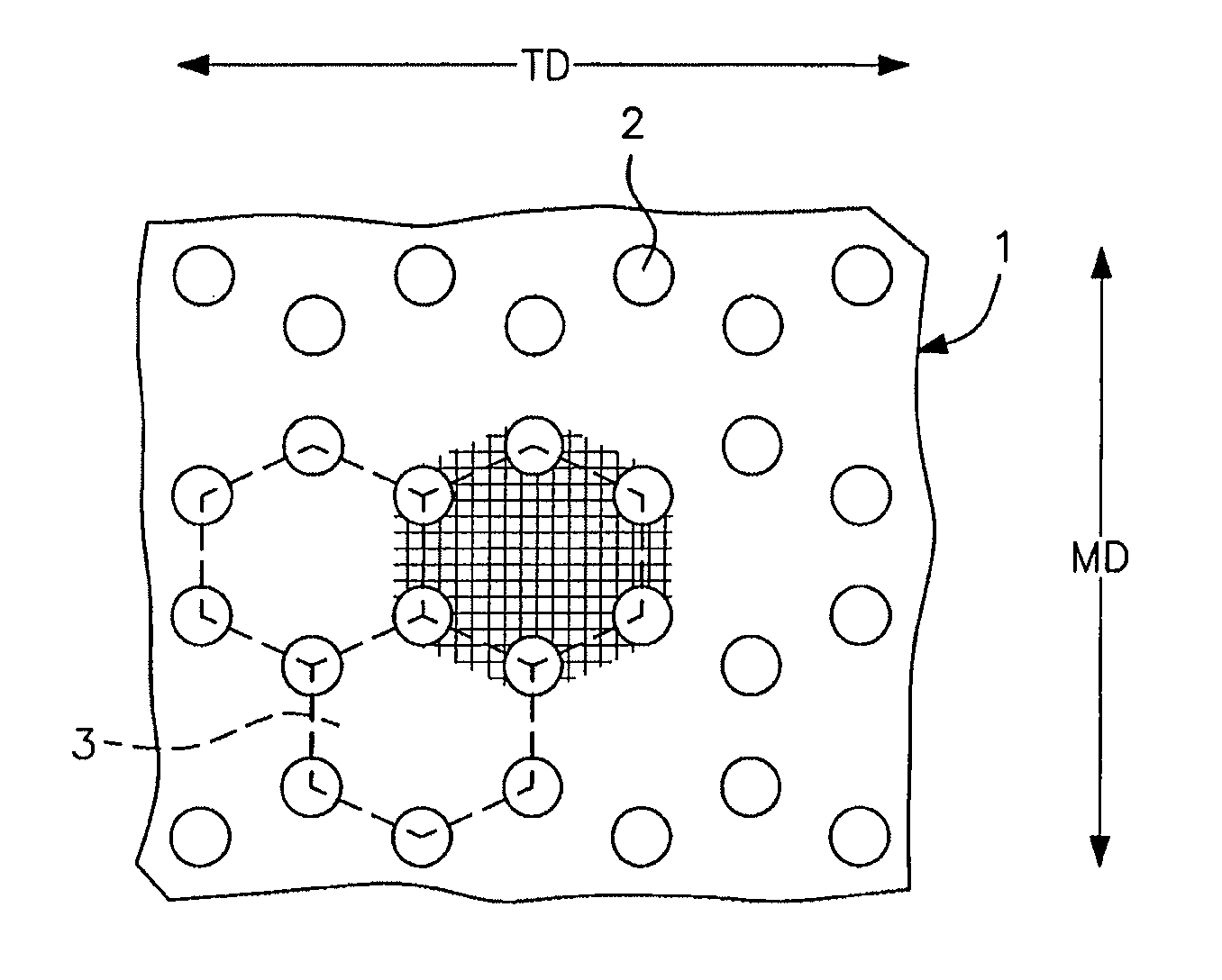
Synthetic turf
InactiveUS20060093783A1Increase elasticityEasy to recycleDead plant preservationArtificial flowers and garlandsInfillWear pattern
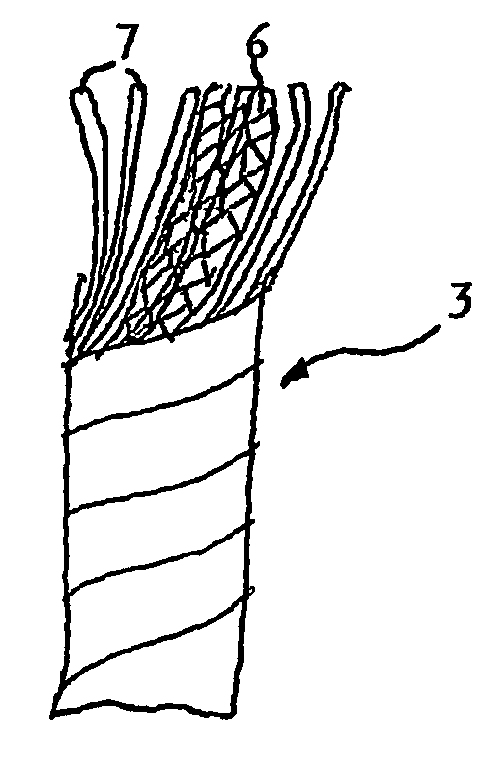
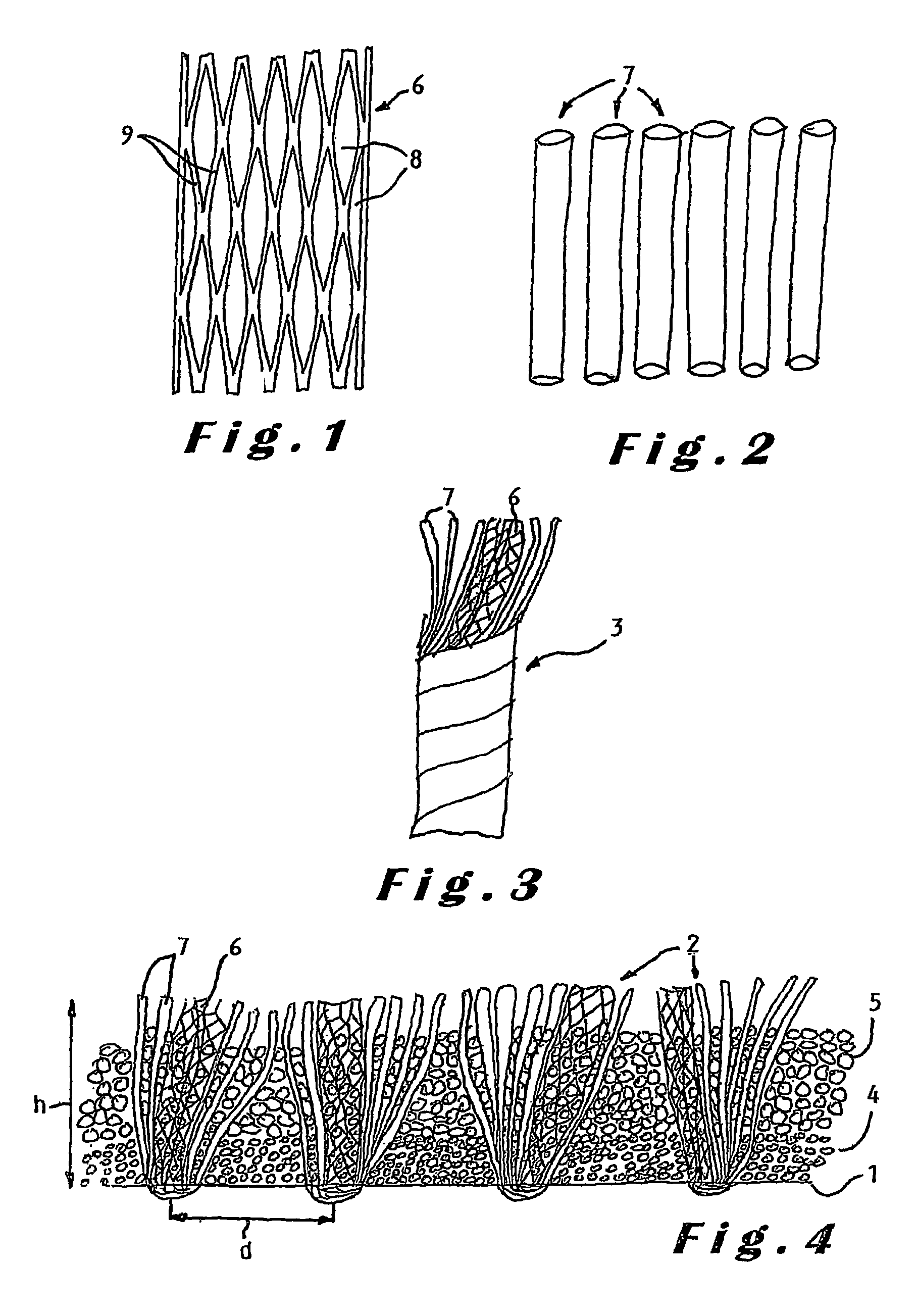
The present invention provides new types of synthetic turf. The synthetic turf includes a pile fabric having a backing (1) and tufts (2) projecting therefrom. In one embodiment, at least a number of the tufts are made of a composite yarn formed by at least one fibrillated yarn (6) together with a number of individual filament yarns (7), in particular with so-called monofilament or monotape yarns. The fibrillated yarn and the individual filament yarns are preferably made of polyethylene so that the synthetic turf is sliding-friendly. In another embodiment, at least a number of the tufts are made of a composite yarn formed by monotape yarns twisted together with a number of the monofilament yarns. The monofilament and monotape yarns are preferably made of polyethylene so that the synthetic turf is sliding-friendly. The combination of a fibrillated yarn and individual filament yarns or the combination of monofilament and monotape yarns in a composite yarn allows immediate achievement of the look of natural grass, that is, without post-fibrillation, and avoids any visible difference in wear pattern between the different types of yarns. In another embodiment, the invention also provides improved particulate material for use as infill material for top-dressing a synthetic turf.
Owner:DOMO ZELE
Reinforcement Element With Sensor Fiber, Monitoring System, And Monitoring Method
A reinforcement element, comprises at least one sensor fiber adapted for strain measurements based on stimulated Brillouin scattering within said sensor fiber. Furthermore, a system for monitoring strain within a structure comprises a reinforcement element comprising at least one sensor fiber adapted for strain measurements based on stimulated Brillouin scattering within said sensor fiber, a pump laser for coupling in laser radiation of a pump frequency into said at least one sensor fiber, a Stokes laser for coupling in laser radiation of a Stokes laser radiation into said at least one sensor fiber, wherein the pump frequency and the Stokes frequency are different from one another and wherein the frequency difference between the pump and Stokes frequencies is within the range of acoustical phonons within said sensor fiber, a sensor adapted to obtain a stimulated Brillouin backscattering signal, and a network analyzer adapted for determining the complex transfer function of the sensor fiber to determine a spatially resolved strain measurement.
Owner:GLOTZL GES FUR BAUMESSTECHN +2
System and method for providing a personal broadcasting service using a mobile communication terminal
ActiveUS20060195872A1Broadcast-related systemsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsService provisionComputer science
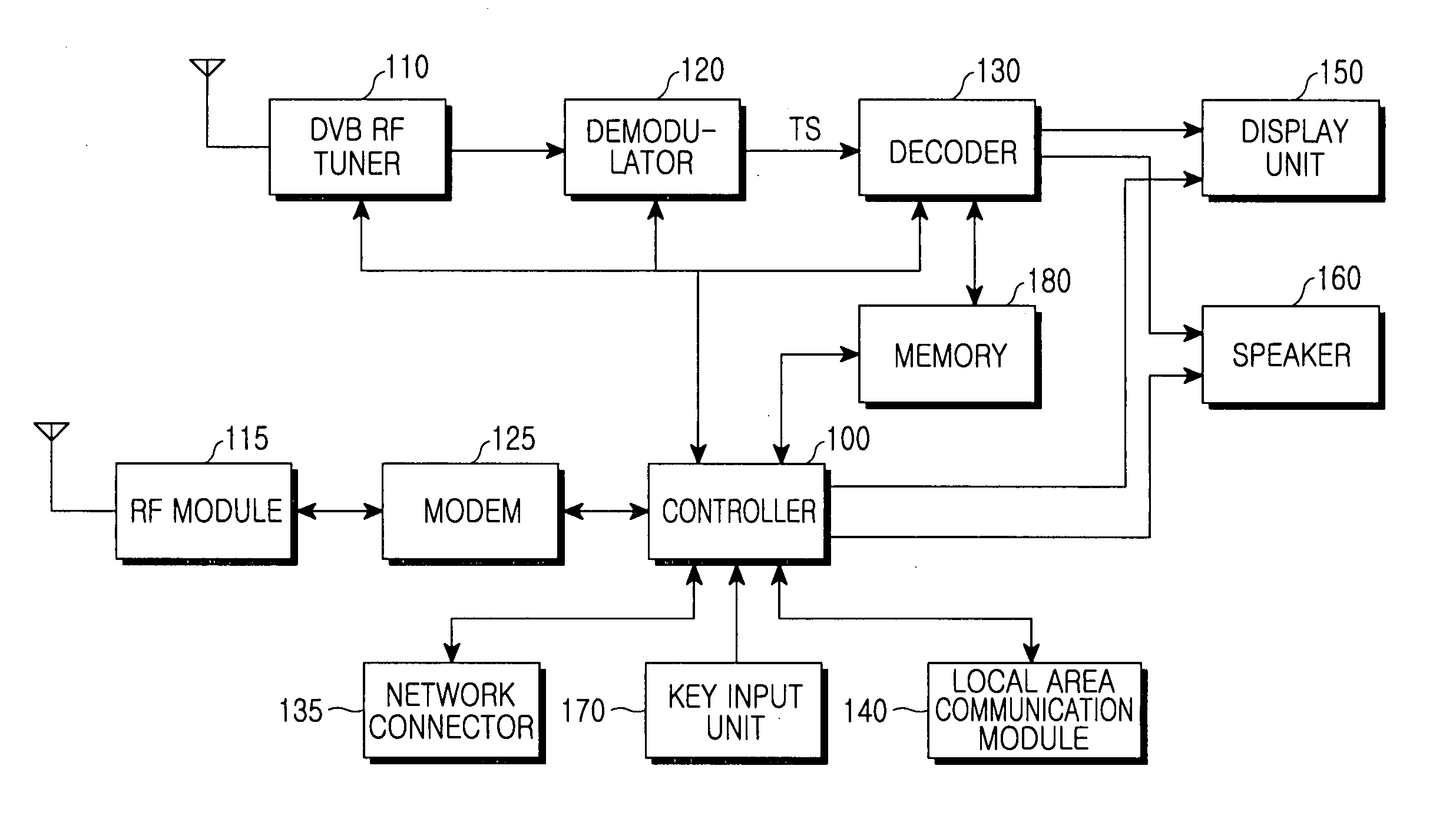
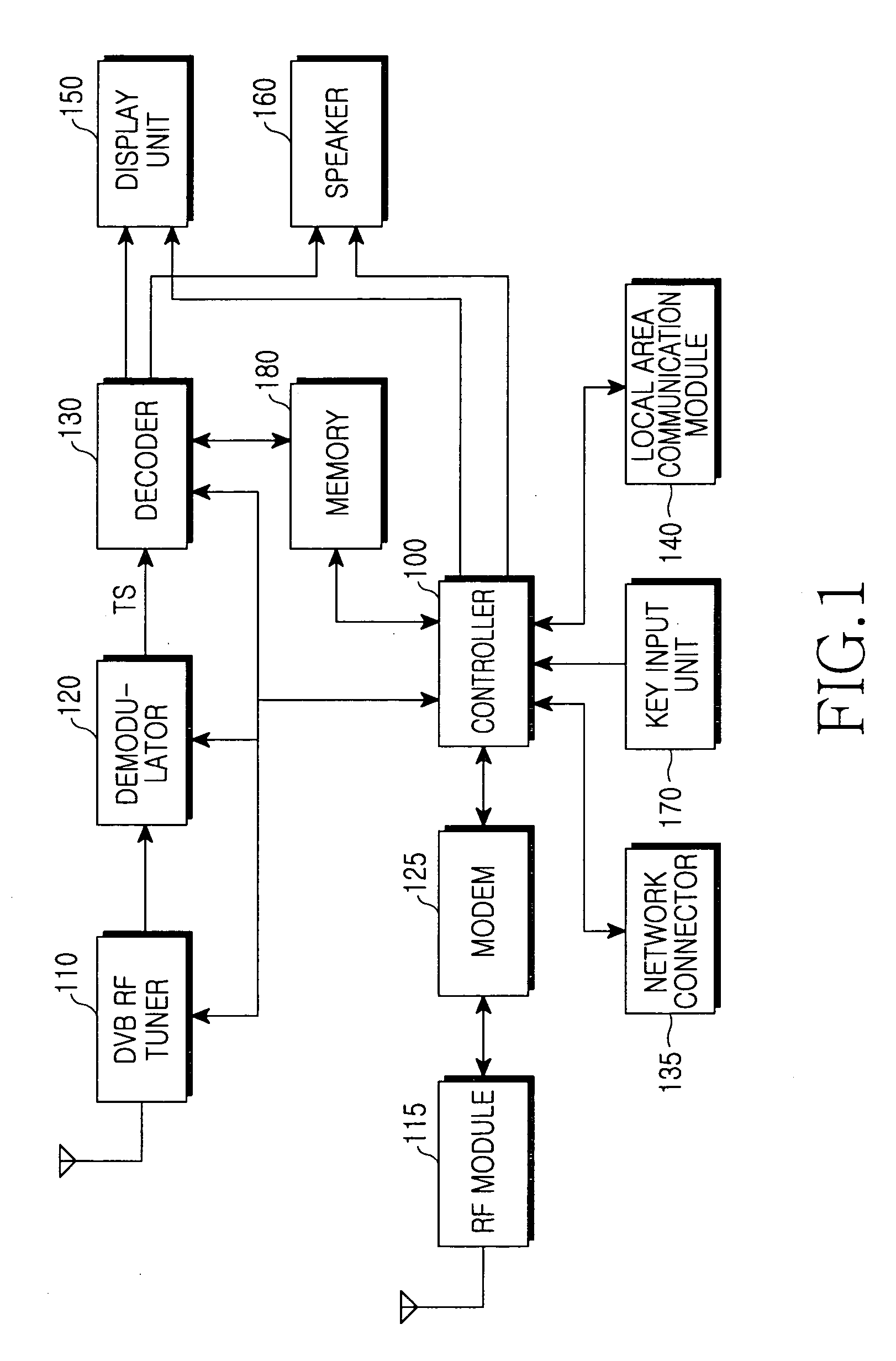
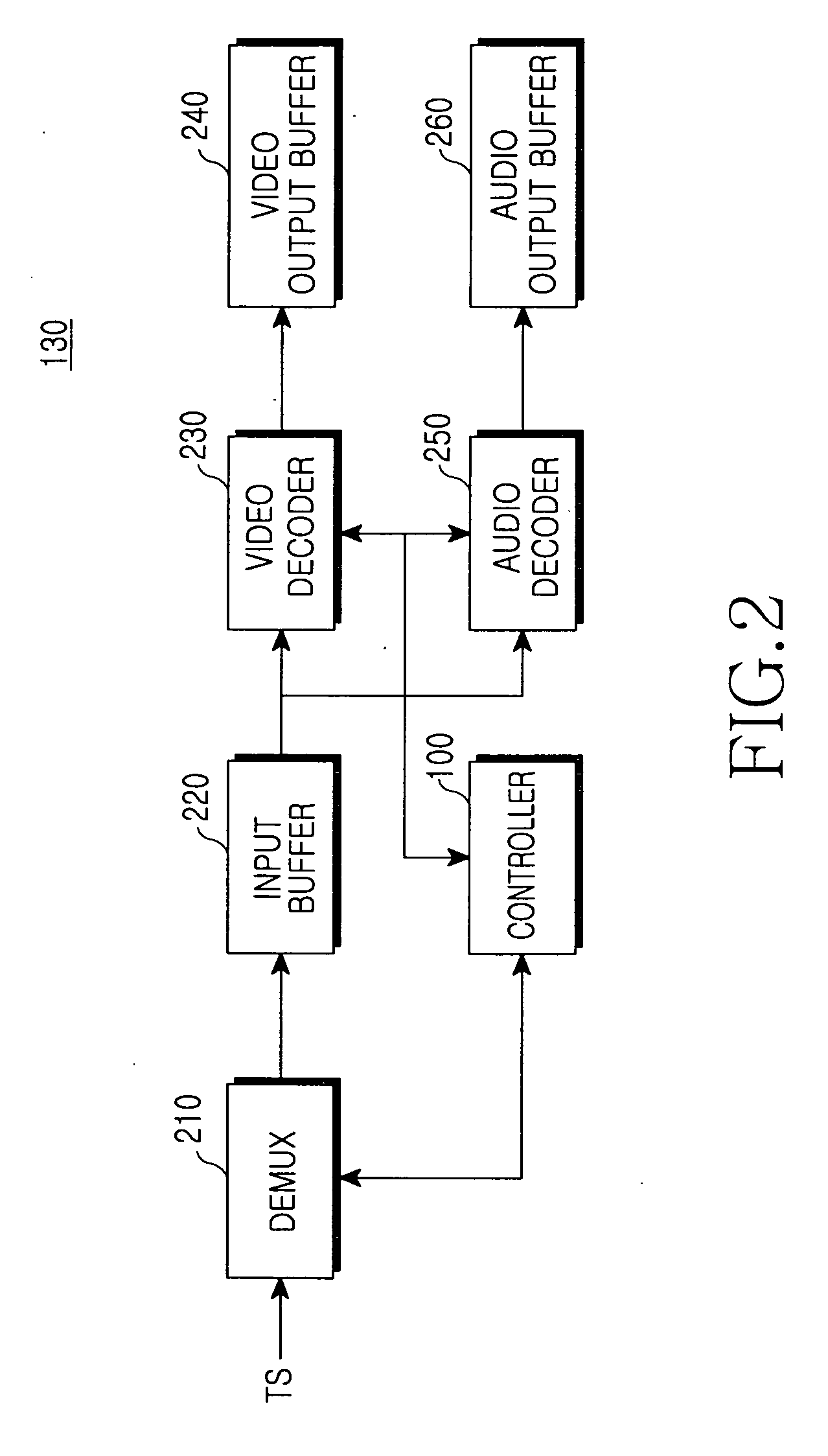
A system and method for providing a personal broadcasting service using a mobile communication terminal with a multimedia broadcasting module are provided. A broadcasting service provider provides multimedia broadcasting content. A multimedia broadcasting terminal sends a channel selection signal to the broadcasting service provider, receives multimedia broadcasting content of a selected channel, and opens personal broadcasting. A normal terminal sends a multimedia broadcasting content request to the multimedia broadcasting terminal opening the personal broadcasting, and receives the multimedia broadcasting content from the multimedia broadcasting terminal opening the personal broadcasting.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Void-maintaining synthetic drainable base courses in landfills and other large structures, and methods for controlling the flow and evacuation of fluids from landifills
Numerous embodiments of one or more layers of void-maintaining synthetic drainable base courses (“VMSDBC's”) are provided as incorporated into landfills and other waste containment facilities. Key advantages of landfills and methods according to the invention include a substantial decrease in the necessity for conventional gravel and sand layers, and an increase in the effective volume of a landfill or similar facility. Moreover, the invention decreases the cost attendant to locating, transporting, and forming conventional rock, sand and gravel materials into discreet layers.
Owner:ADVANCED GEOTECH SYST
Turf reinforcement erosion control mat
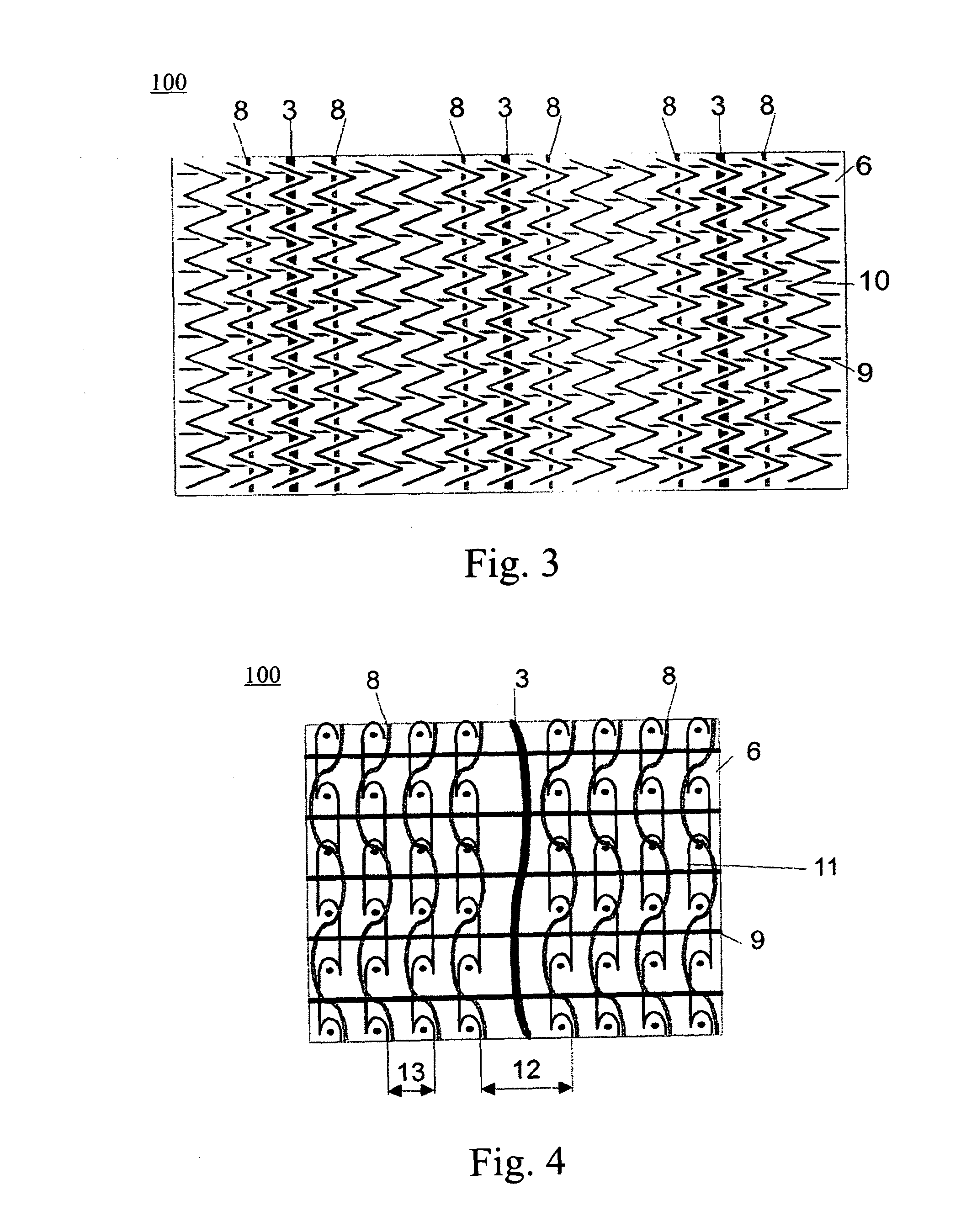
A bi-layer, woven geotextile fabric has interwoven first and second layers. The first layer is over and under woven through the second layer in a pre-determined pattern so that the first layer has portions which face a first side of the second layer and portions which face a second side of the second layer. Monofilaments in the warp direction of the first layer have a pre-determined differential heat shrinkage characteristic that is greater than the monofilaments in the warp direction of the second layer. Closed cells defined by the pattern of the over and under weave are disposed on the first and second sides of the second layer. Shrinkage of the monofilaments in the warp direction of the first layer provide for a separation of a portion of the second layer from the first layer at the cells.
Owner:NICOLON CORP
Combined and stabilized turf for an athletic field
InactiveUS6372310B2Low costFirmly connectedDead plant preservationArtificial flowers and garlandsFiberEngineering
Owner:APT ADVANCED POLYMER TECH CORP
Speaker for mobile terminals and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN1678131ACompact structureWith broadband characteristicsTransducer detailsGeotextilesSound qualityEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Mats for use in paved surfaces
A method of repairing a paved surface utilizes a nonwoven or woven fibrous mat made from fibers including polymer fibers, the polymer fibers having a melting point greater than about 320° F. (160° C.). The mat has a load-elongation behavior such that when the mat is subject to tensile stress, the mat achieves at least 90% of its ultimate load at an elongation not greater than 5% of the specimen length in the direction of applied stress. Another mat comprises a nonwoven or woven fibrous mat made from fibers selected from the group consisting of mineral fibers, polymer fibers, natural fibers, and mixtures thereof, and a rubbery binder. Another mat comprises a nonwoven or woven fibrous mat made from a blend of high melt polymer fibers having a melting point of at least 350° F. (177° C.) and low melt polymer fibers having a melting point of less than 350° F. (177° C.).
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
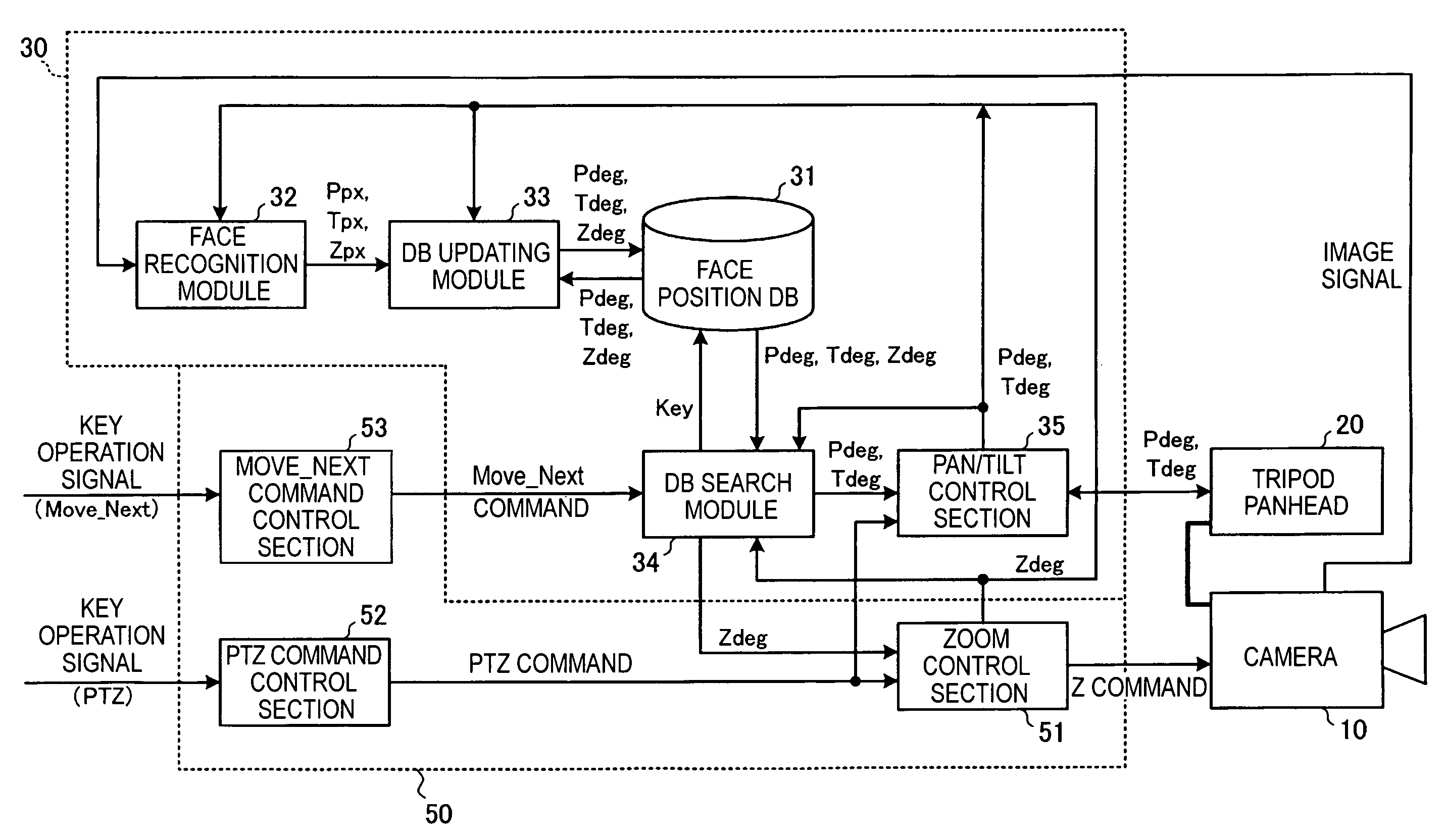
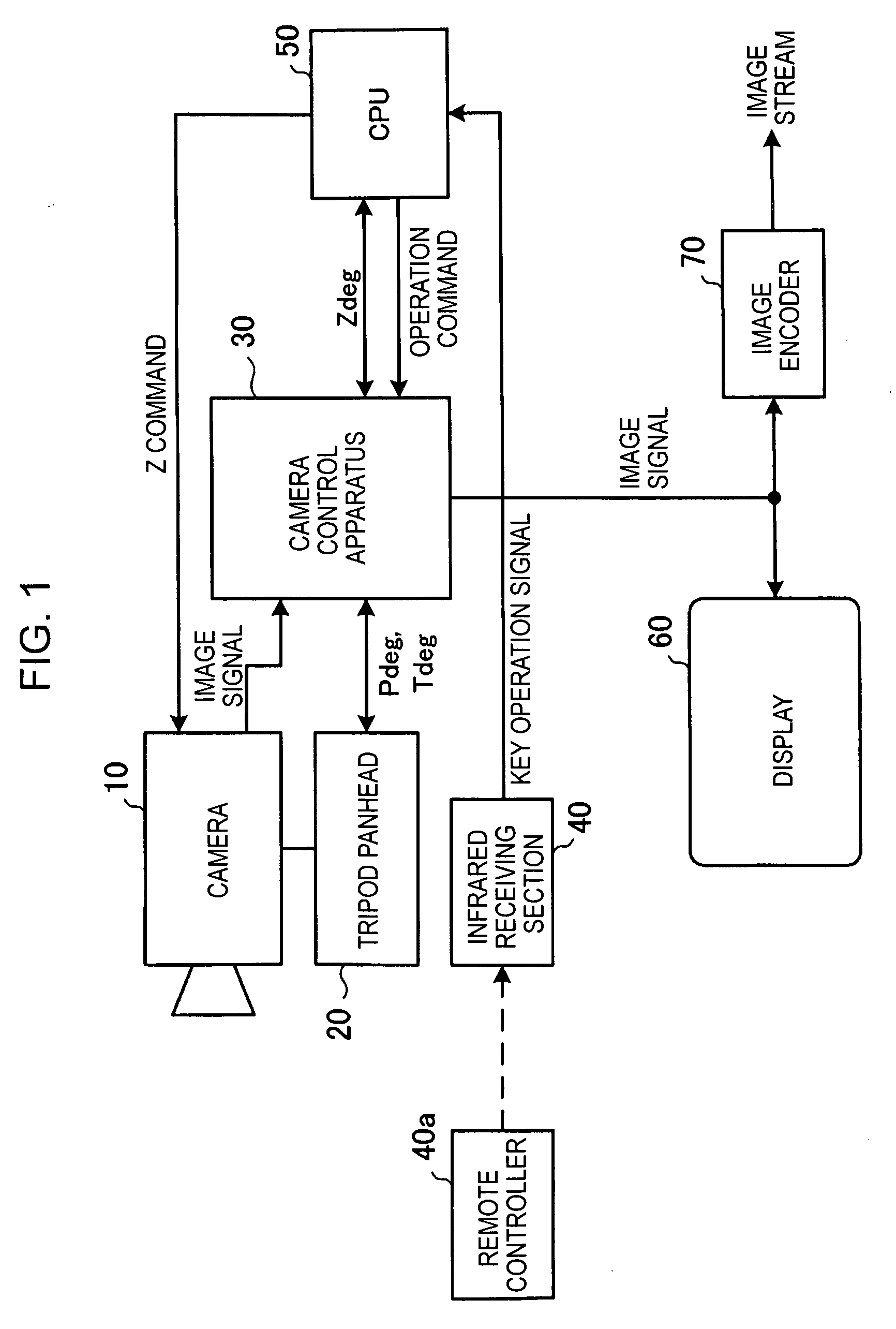
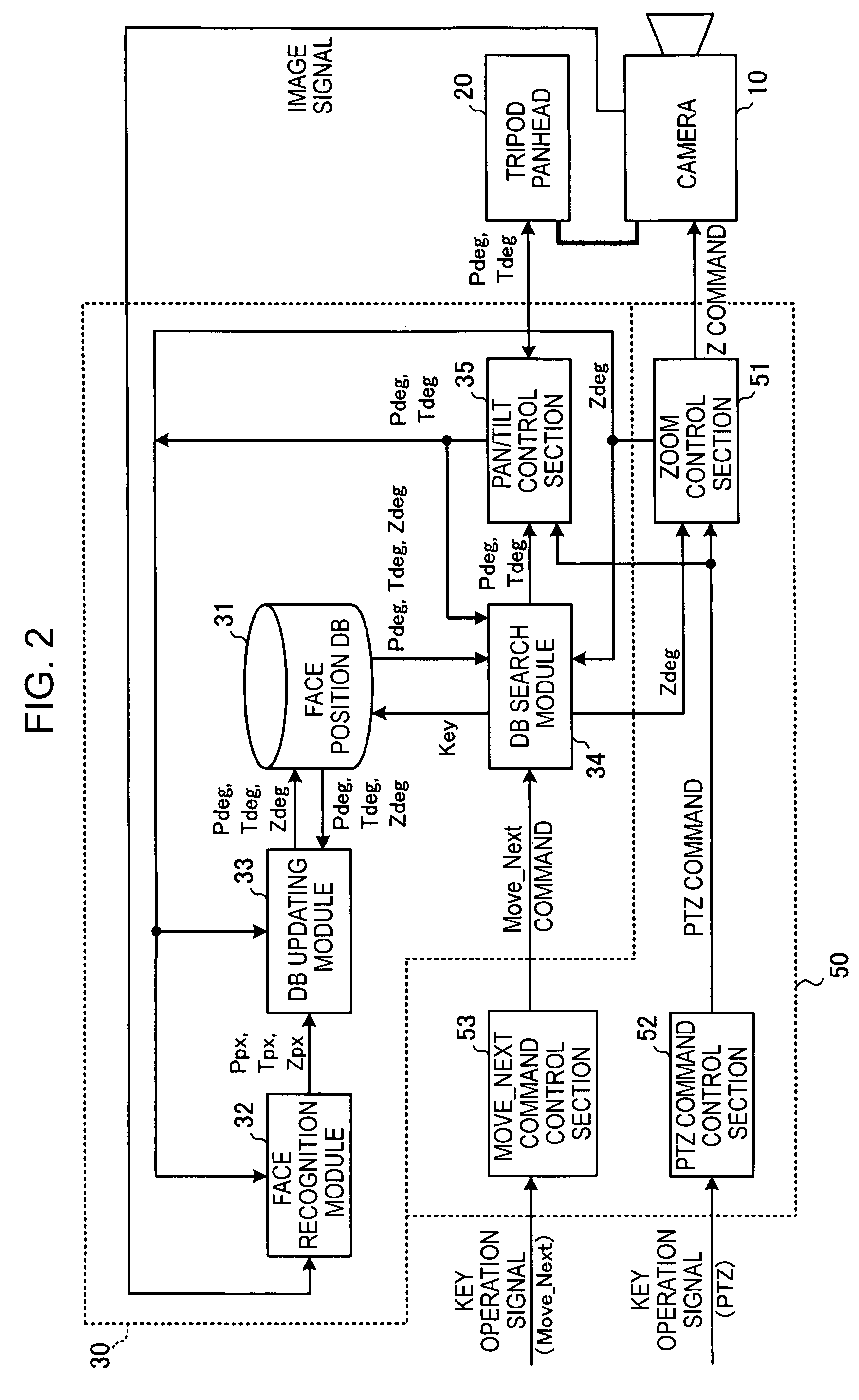
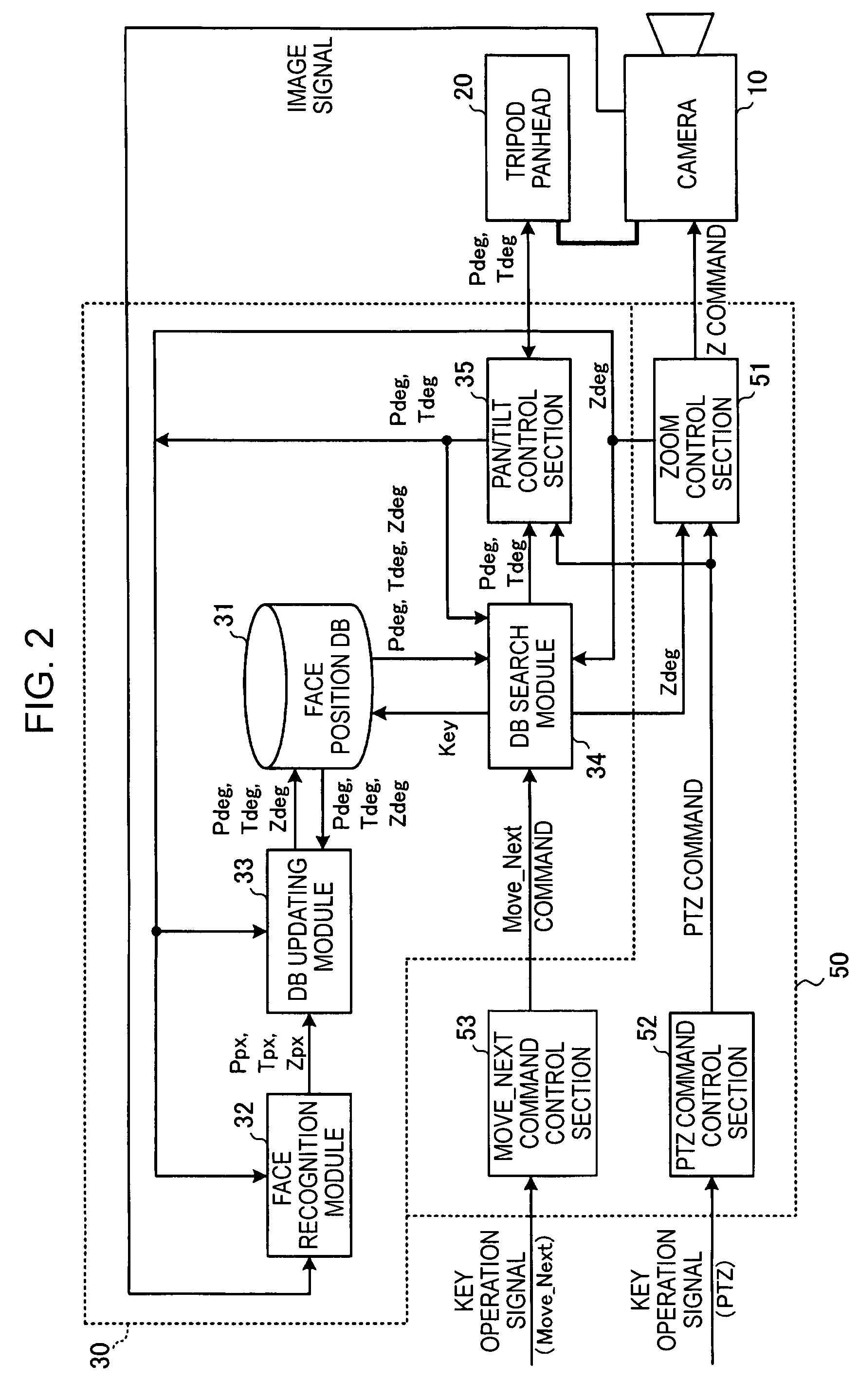
Camera control apparatus, camera system, electronic conference system, and camera control method
InactiveUS20060187306A1Reliably photographing one personEasy to operateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera controlLocation detection
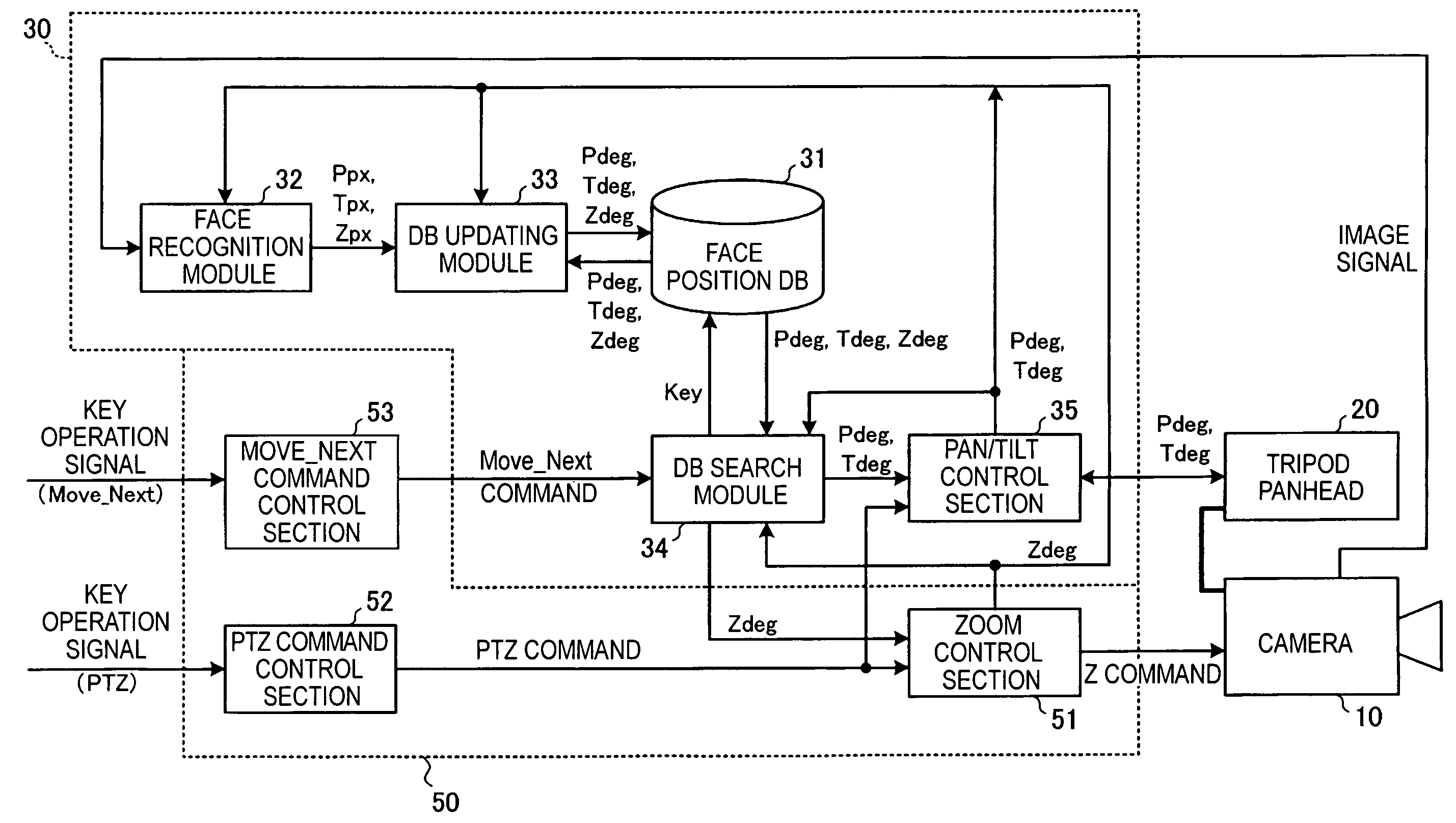
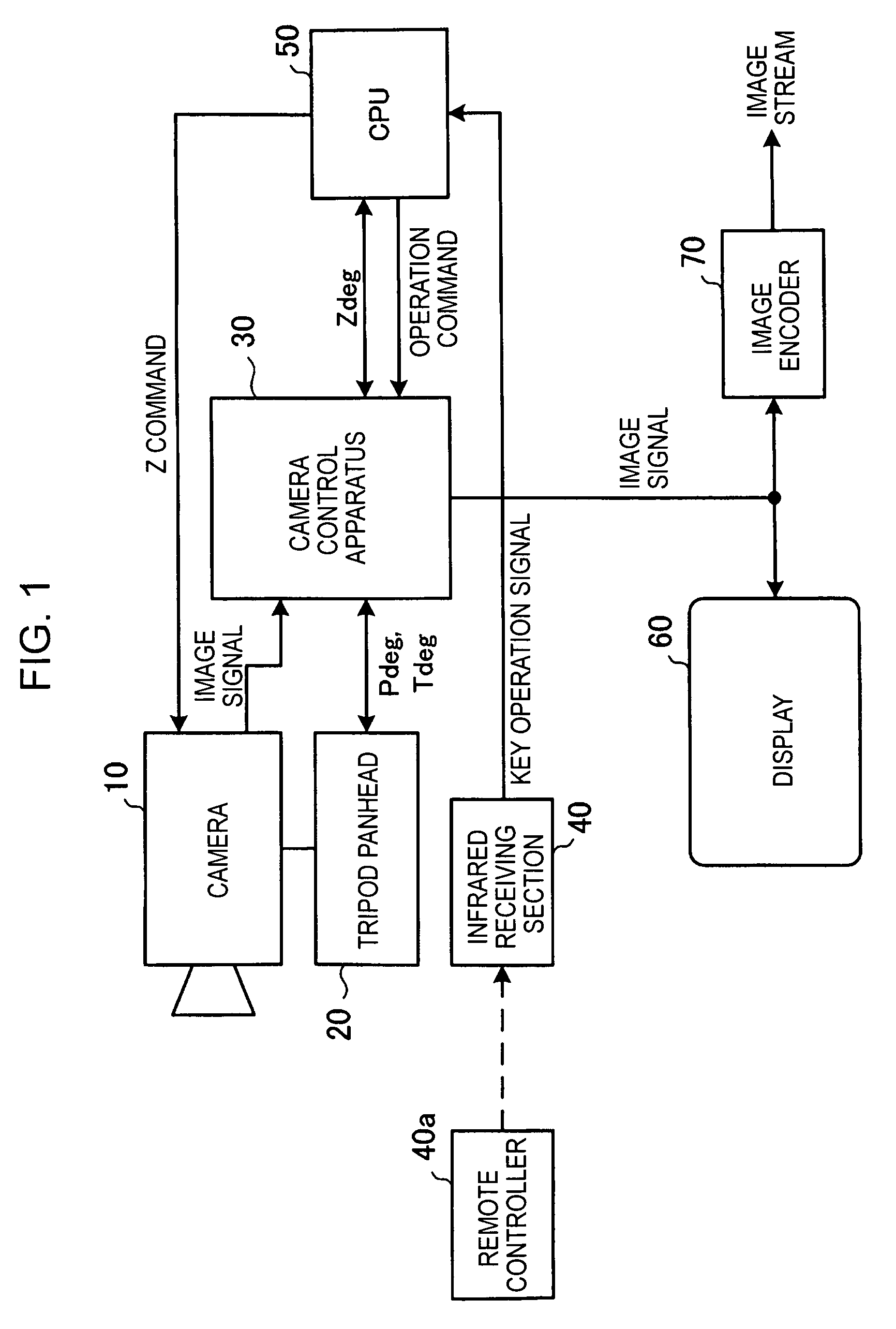
A camera control apparatus includes a storage section storing, for each person to be photographed, face direction information when each face of a plurality of persons to be photographed by a camera is positioned in the central portion of a photographing range by the camera; a face position detection section detecting a position of a face of a person from a photographed image signal of the camera; a registration section computing face direction information on the basis of a detection result by the face position detection section and information indicating a current photographing direction of the camera and registering the face direction information in the storage section; and a driving control section reading face direction information corresponding to a person specified by an operation input from a user and controlling the driving apparatus in accordance with the face direction information in order to change the photographing direction of the camera.
Owner:SONY CORP
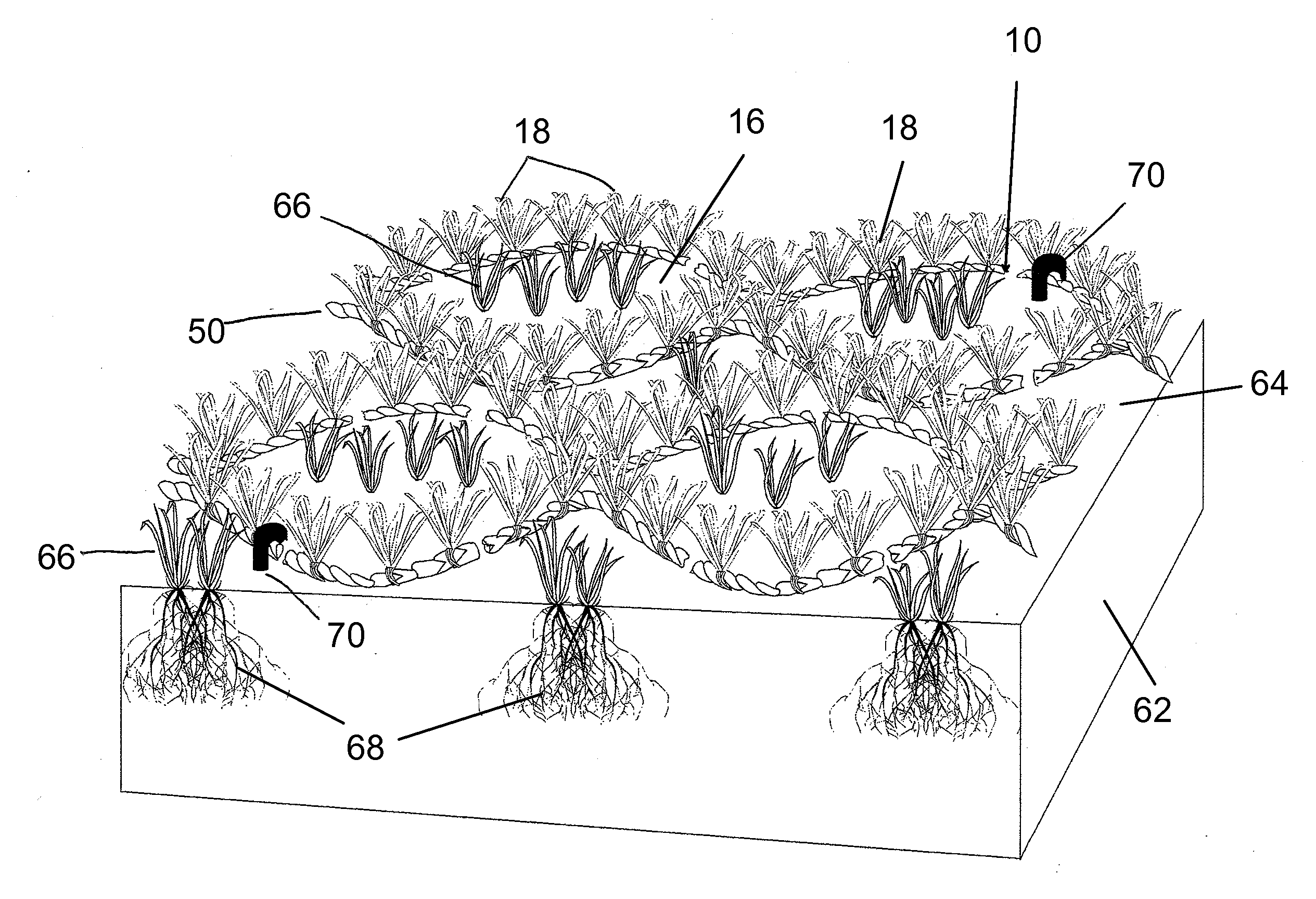
Artificial lawn and fabrication process thereof
The invention discloses an artificial lawn and a fabrication process thereof. The lawn comprises a soil basal layer, a warp knitting grid net paved above the soil basal layer, and fiber grass clusters knitted on the warp knitting grid net, wherein the warp knitting grid net is in a grid structure which is formed by interlacing warps and wefts, natural grass is inserted into grids by the warp knitting grid net, and grass roots of the natural grass are planted in the soil basal layer; the warps and the wefts are all grass silk yarn harnesses knitted and twined by fiber grass yarns, and the grass roots of the fiber grass clusters are knitted in the grass silk yarn harnesses. The process comprises the steps: producing the fiber grass yarns; arraying a plurality of fiber grass yarns side by side, then, knitting the grass yarns into a fried dough twist grass yarn harnesses, and knitting the grass yarn harnesses into the warp knitting grid net; building the soil basal layer on the ground; paving the knitted warp knitting grid net above the soil basal layer; inserting or planting the natural grass in the warp knitting grid net. The artificial lawn and the fabrication process thereof have the benefits that materials, such as base fabrics and mucilage glue, are not needed, so that the economic cost is reduced; the natural grass is planted in the grid, so that the artificial lawn and the fabrication process thereof are more real and have strong flexibility.
Owner:江蘇聯創人造草坪股ふん有限公司
Facing material with controlled porosity for construction boards
InactiveUS20060065342A1Prevent penetrationHigh strengthConstruction materialSynthetic resin layered productsPorosityWater vapor
This invention provides facing materials for cementitious boards such as those including Portland cement or gypsum cores. The preferred facing material includes, in a first embodiment, a facing layer having an areal weight of about 300 grams / M2, and an air permeability rating of no greater than about 300 CFM / ft2 (FG 436-910 test method). The facing layer reduces the penetration of a slurry of cementitious material during the manufacture of a cementitious board, while permitting the water vapor from the slurry to pass therethrough. The facing materials of this invention can be designed to substantially eliminate the fouling of rolls used in continuous processing of such boards without the use, or with greatly reduced use, of costly viscosity control agents in the slurry. In addition, further embodiments of this invention can include binders, coatings or saturants which are designed to decrease pore size, increase or decrease the contact angle of liquids, or promote greater adhesion to cementitious cores, greater adhesion to other layers in the facing material, or greater adhesion or affinity to various types of adhesive compositions used to join cementitious boards to insulation and exterior finishing systems (EIS or EIFS).
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN ADFORS CANADA LTD
Contaminant-reactive geocomposite mat and method of manufacture and use
Reactive geocomposite mats, and their method of manufacture, for treating contaminants in soil or water that allow the passage of essentially non-contaminated water therethrough. The geocomposite mat includes a pre-formed woven or non-woven geotextile, having a thickness of about 6 mm to about 200 mm, and having, a porosity sufficient to receive a powdered or granular contaminant-reactive material, contaminant-sorptive material, or a contaminant-neutralizing material (hereinafter collectively referred to as “contaminant-reactant material” or “contaminant-reactive material”) throughout its thickness, or in any portion of the thickness across its entire major surface(s). The powdered or granular contaminant-reactive material is disposed within the pores of the previously formed, high loft geotextile mat to surround the fibers, e.g., by vacuum or vibrating the high loft mat while in contact with the contaminant-reactive material to allow the powdered or granular contaminant-reactive material to flow by gravity into the pores of the previously formed geotextile and vibrational forces. Liquid-permeable cover sheets are adhered to the upper and lower major surfaces of the filled geotextile to prevent the powdered or granular material from escaping from the geotextile during transportation and installation.
Owner:AMCOL INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Pyramidal fabrics having multi-lobe filament yarns and method for erosion control
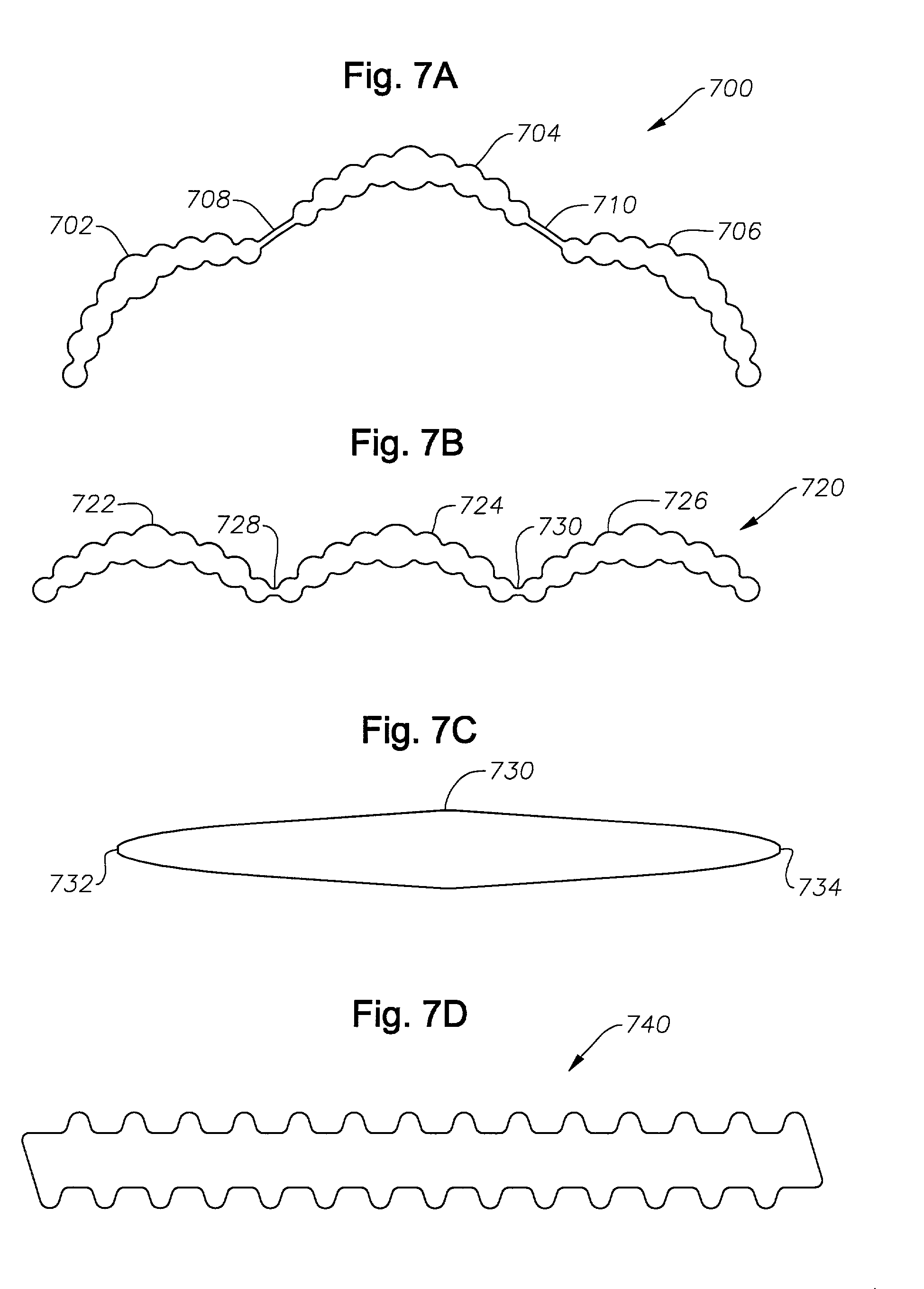
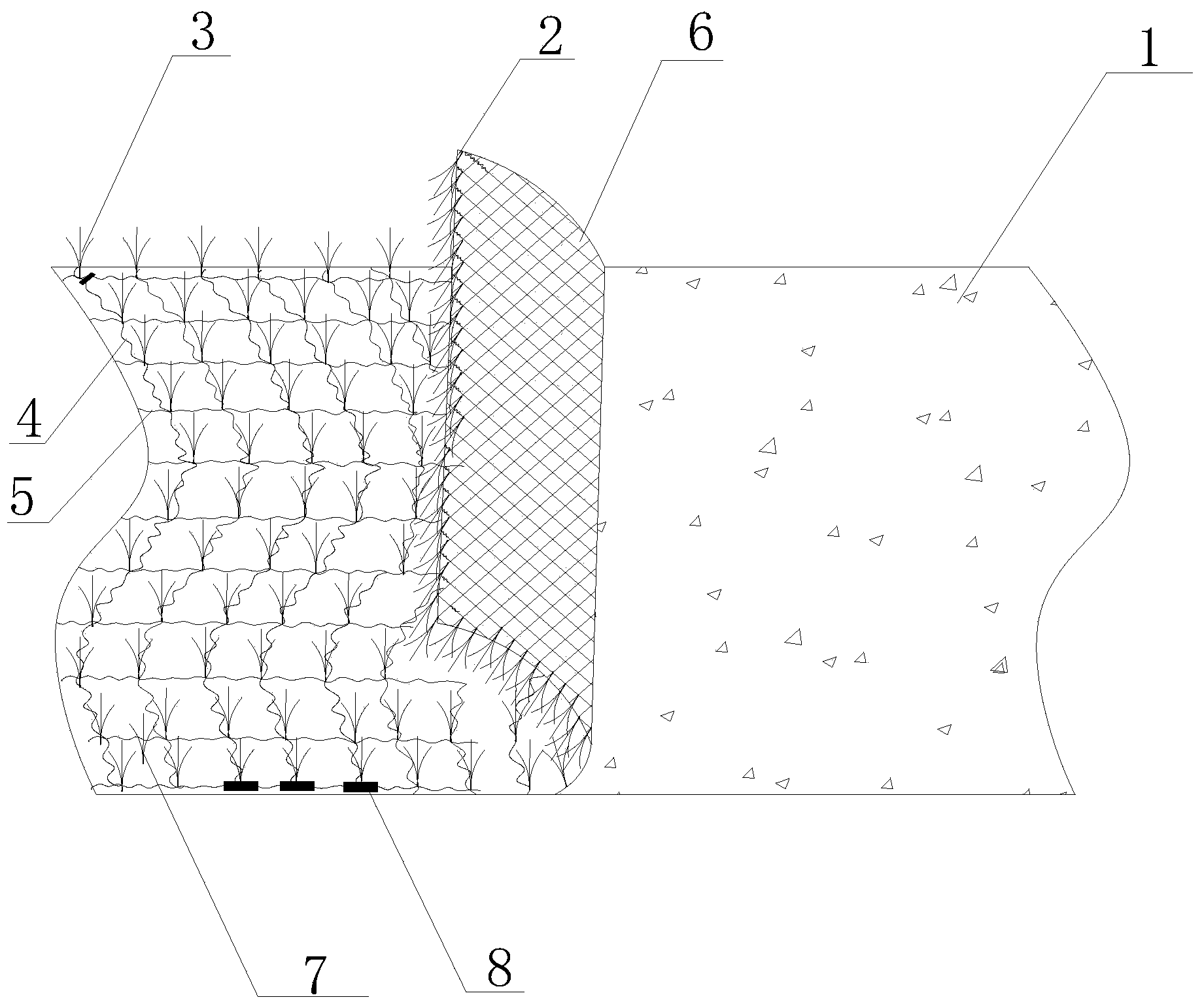
InactiveUS20050287343A1Avoid erosionImprove water qualityLayered productsGeotextilesErosion controlPerpendicular direction
A pyramidal geotextile fabric comprising two sets of multi-lobe filament yarns interwoven in substantially perpendicular direction to each other, each of the multi-lobe filament yarns having pre-determined, different heat shrinkage characteristics such that, upon heating, the fabric forms a three-dimensional, cuspated profile. A method of stabilizing soil and reinforcing vegetation comprises the steps of placing a three-dimensional, high-profile woven fabric into soil, wherein the fabric comprises two sets of multi-lobe filament yarns interwoven in substantially perpendicular direction to each other, each of the multi-lobe filament yarns having pre-determined, different heat shrinkage characteristics such that, upon heating, the fabric forms a three-dimensional, cuspated profile; securing the fabric to the ground; and, distributing soil and seed onto the fabric such that the section of ground is quickly revegetated and thereby protected from further erosion.
Owner:PROPEX CONCRETE SYST CORP
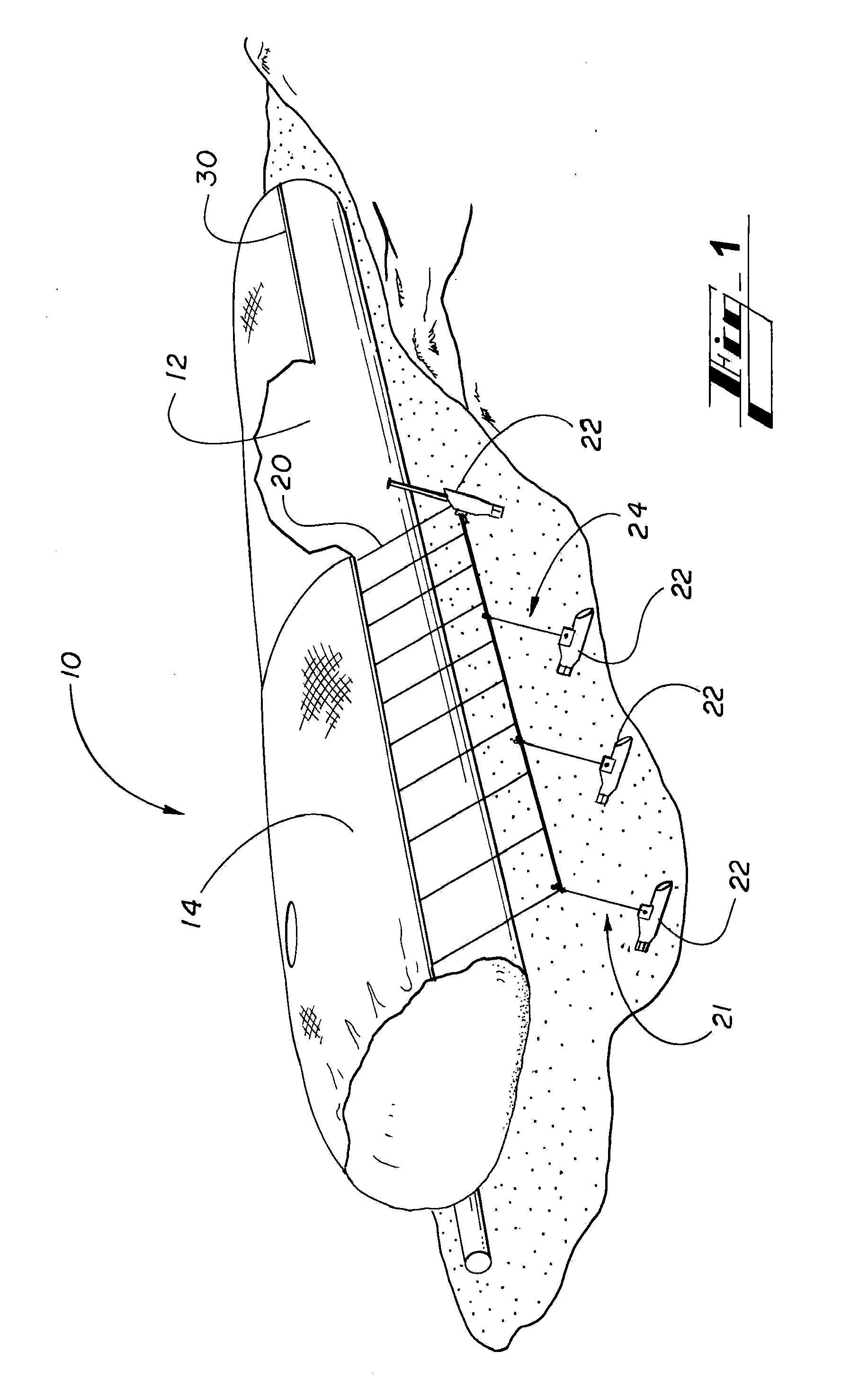
Debris shield for geocontainers, method of making, and method of use thereof
Described herein is a protected container 10 employed to prevent soil erosion. The protected container is a geotextile container having a debris shield disposed thereon. The debris shield protects the integrity of the geotextile container by providing a strike barrier which has air and water flow capabilities. The debris shield is a composite fabric comprising a woven protective layer having abrasion resistance and a woven three-dimensional layer which provides impact dampening and energy dissipation.
Owner:NICOLON CORP
Camera control apparatus, camera system, electronic conference system, and camera control method
InactiveUS7675539B2Reliably photographing one personEasy to operateTelevision system detailsTelevision conference systemsCamera controlLocation detection
A camera control apparatus includes a storage section storing, for each person to be photographed, face direction information when each face of a plurality of persons to be photographed by a camera is positioned in the central portion of a photographing range by the camera; a face position detection section detecting a position of a face of a person from a photographed image signal of the camera; a registration section computing face direction information on the basis of a detection result by the face position detection section and information indicating a current photographing direction of the camera and registering the face direction information in the storage section; and a driving control section reading face direction information corresponding to a person specified by an operation input from a user and controlling the driving apparatus in accordance with the face direction information in order to change the photographing direction of the camera.
Owner:SONY CORP
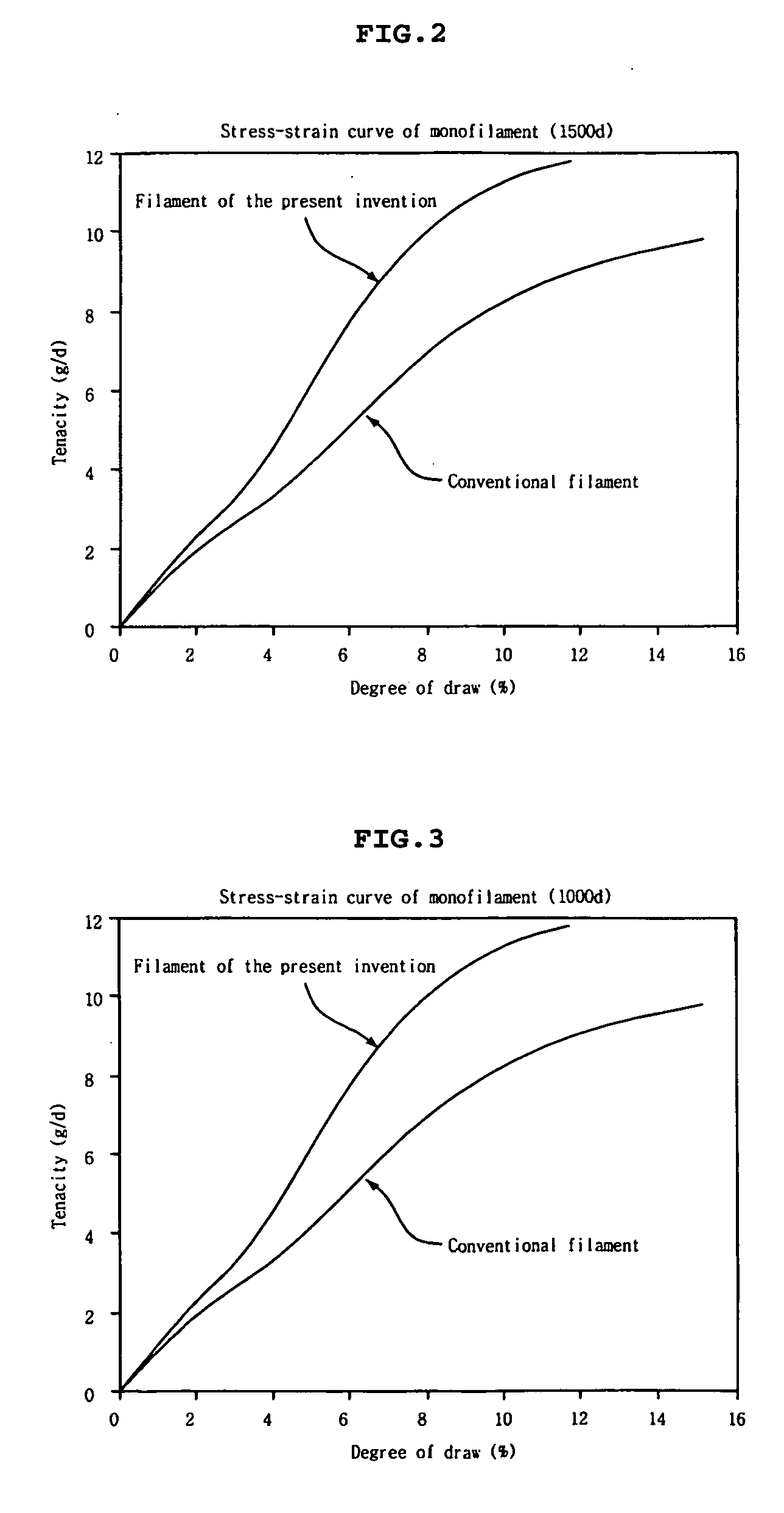
Polyethylene terephthalate filament having high tenacity for industrial use
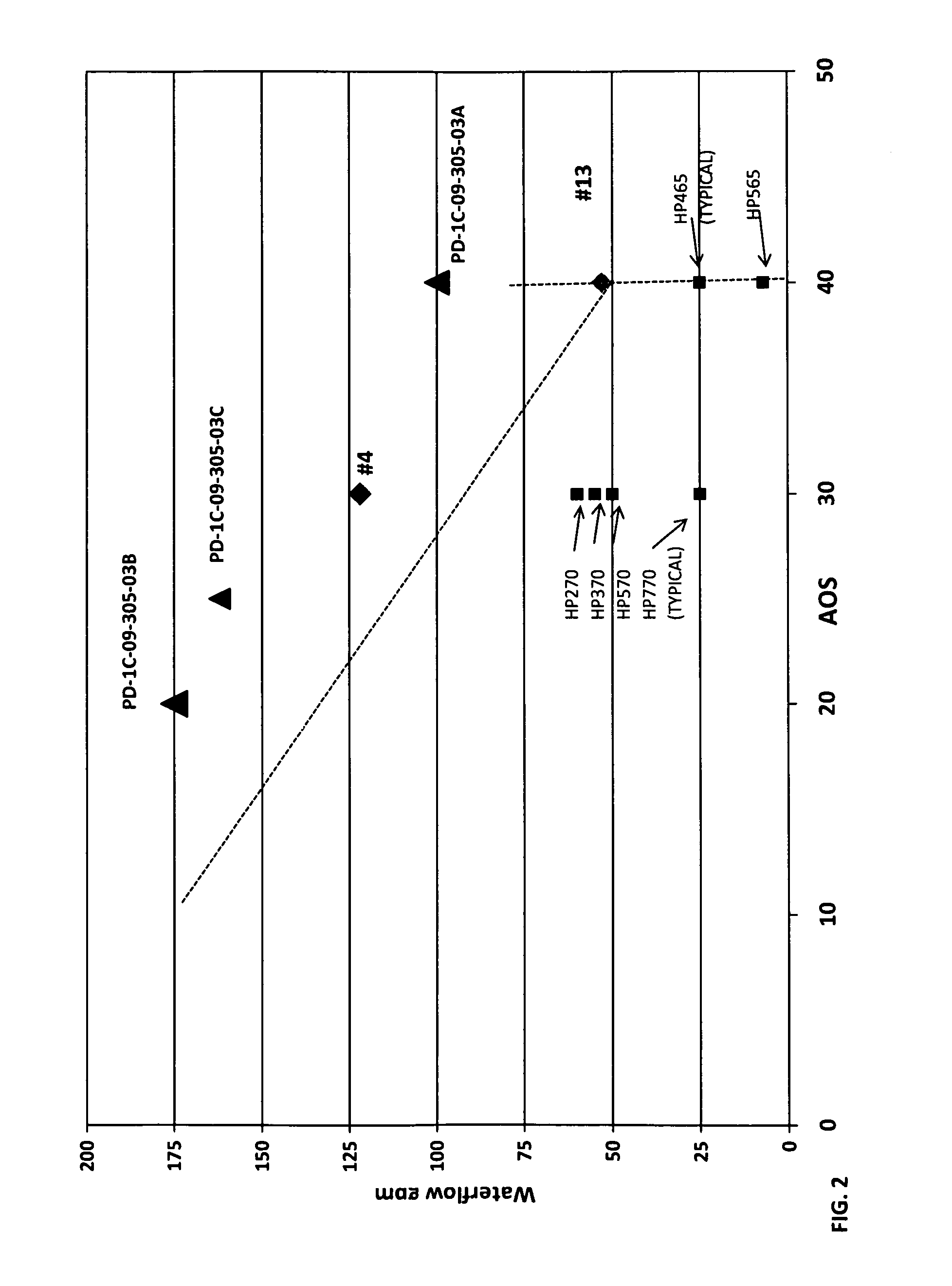
InactiveUS20070243378A1Raise the draw ratioGeotextilesYarnPolyethylene terephthalateStress–strain curve
A polyethylene terephthalate monofilament obtained by spinning a polyethylene terephthalate chip having an intrinsic viscosity of 0.8 to 1.3, which gives a stress-strain curve exhibiting an elongation of less than 2.5% at an initial stress of 2.0 g / d, with an initial modulus value of 80 to 160 g / d, an elongation of 7.5% or less in a stress range of from 2.0 g / d to 9.0 g / d, and an elongation of at least 2.0% or more in a stress range of from 10.0 g / d to the point of break, is provided.
Owner:HYOSUNG CORP
Fabric stimulating the plant structure for moisture management
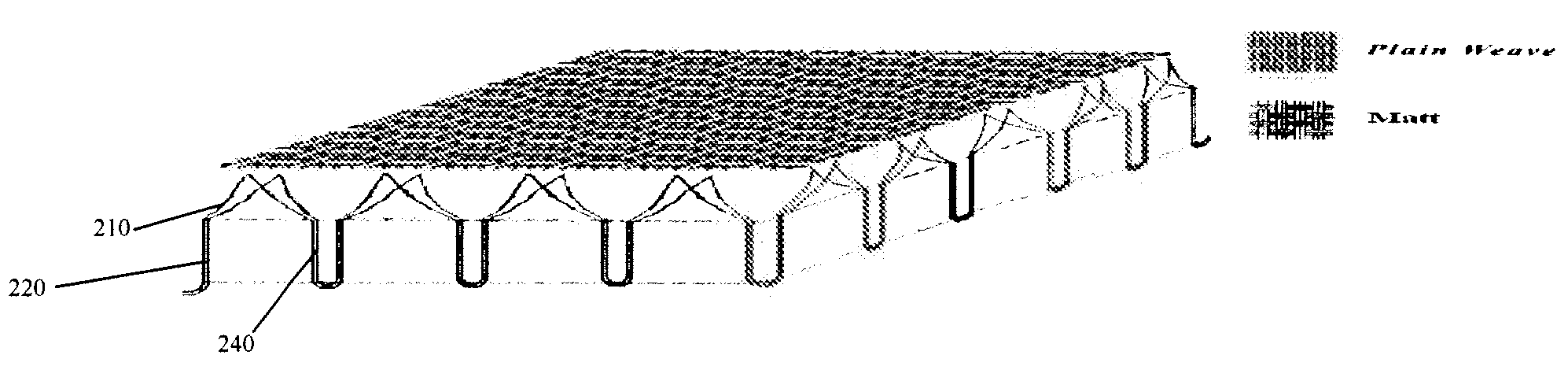
ActiveUS20080220185A1Excellent water transport propertyKeep coolGarment special featuresDead plant preservationPlant StructuresEngineering
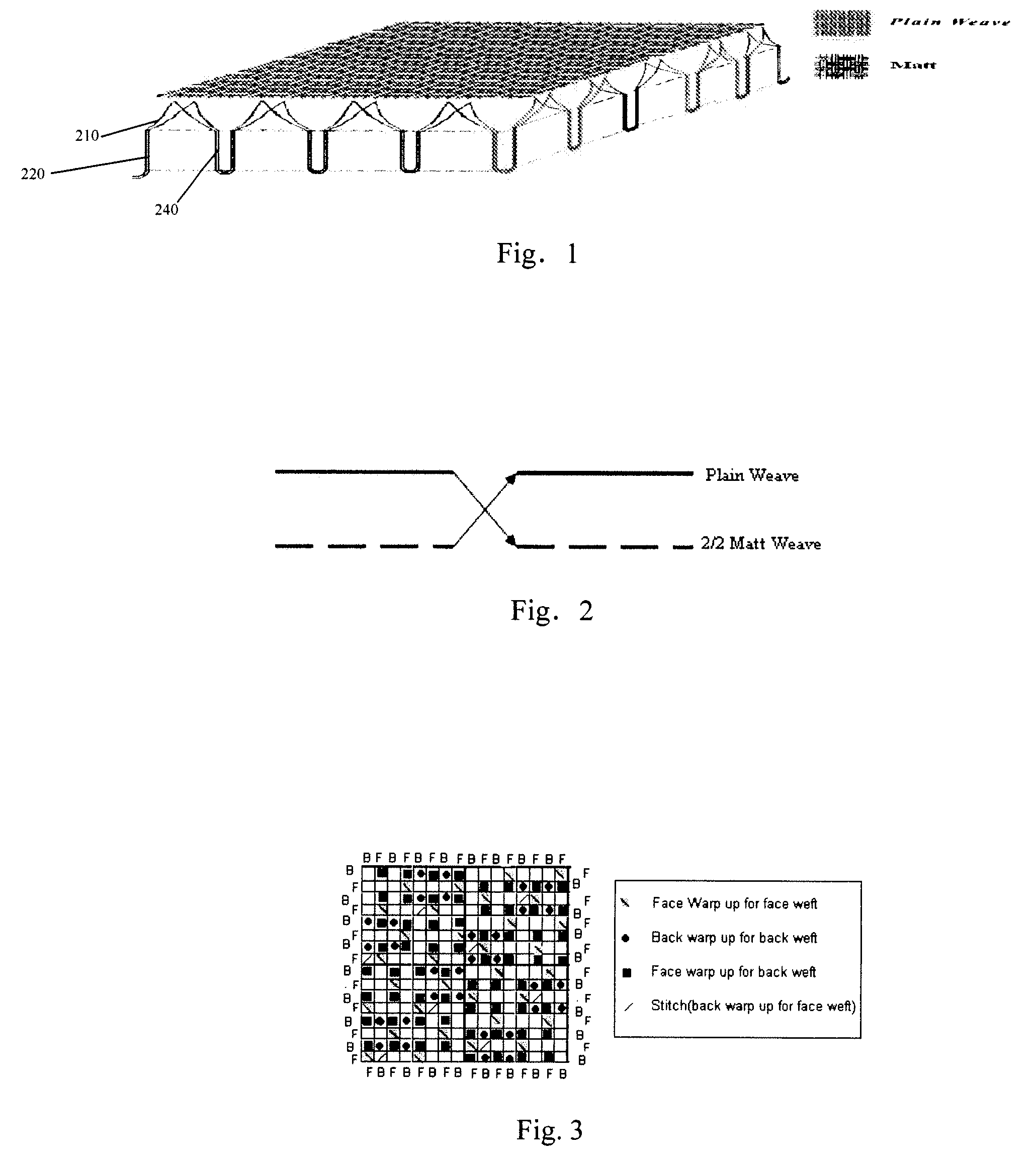
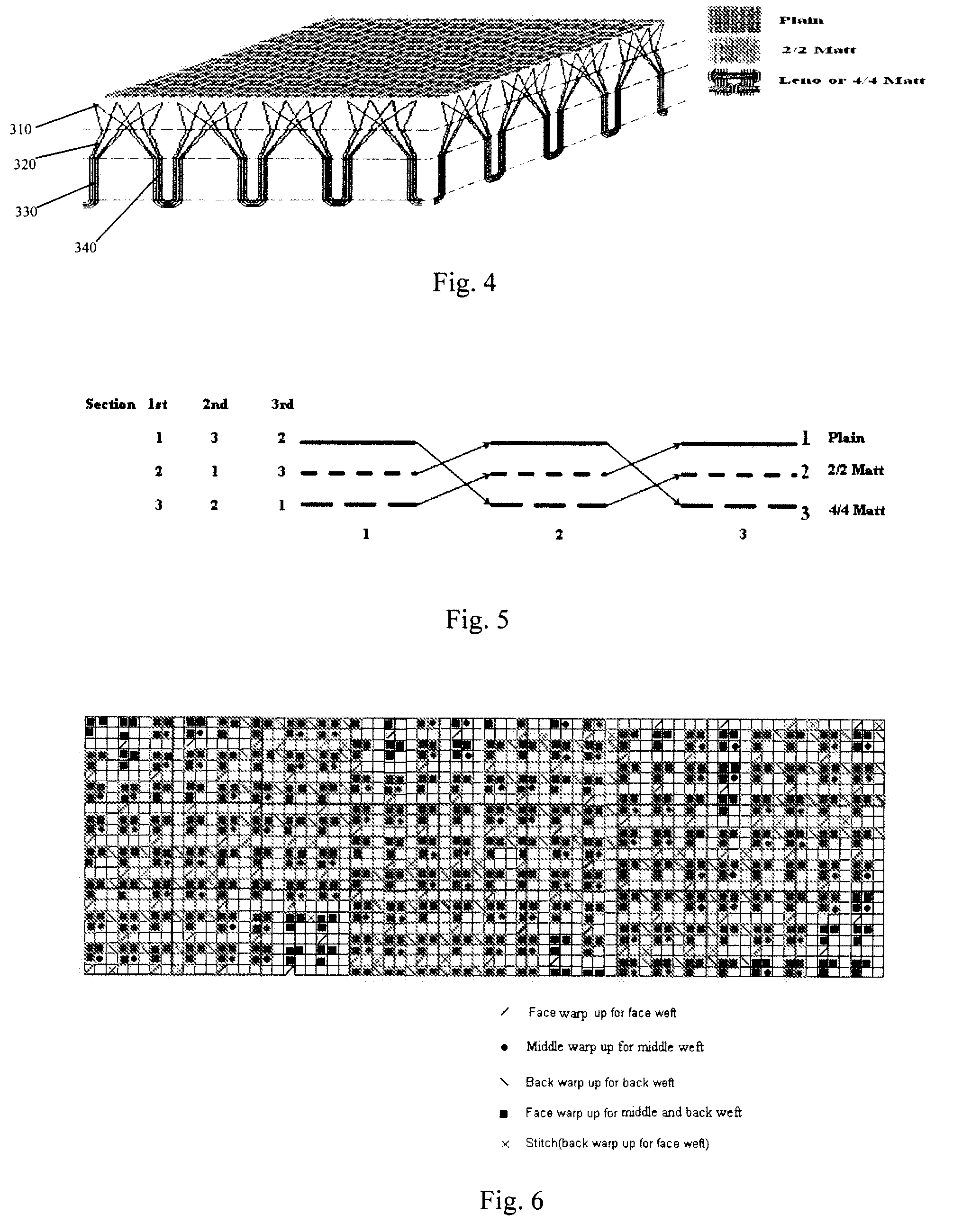
A fabric having moisture management function, which has a structure simulating plant structure and comprises at least two layers as follows: a bottom layer, which is of a leno or matt structure simulating main stem of plant, in which a number of yarns are grouped together to form a plurality of fabric units; said bottom layer can be adapted to be in contact with human skin; a top layer, which is of a plain weave structure, in which the yarns of said fabric unit further split in the top layer to form such a plain weave structure, simulating the branching in plant structure; wherein, in said fabric, water can be transported from the bottom layer to the middle layer and further to the top layer where it evaporates due to the improved capillarity of the yarns so as to provide better moisture management function.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Synthetic turf
InactiveUS7399514B2Less differenceSmall coefficient of frictionDead plant preservationArtificial flowers and garlandsInfillWear pattern
The present invention provides new types of synthetic turf. The synthetic turf includes a pile fabric having a backing (1) and tufts (2) projecting therefrom. In one embodiment, at least a number of the tufts are made of a composite yarn formed by at least one fibrillated yarn (6) together with a number of individual filament yarns (7), in particular with so-called monofilament or monotape yarns. The fibrillated yarn and the individual filament yarns are preferably made of polyethylene so that the synthetic turf is sliding-friendly. In another embodiment, at least a number of the tufts are made of a composite yarn formed by monotape yarns twisted together with a number of the monofilament yarns. The monofilament and monotape yarns are preferably made of polyethylene so that the synthetic turf is sliding-friendly. The combination of a fibrillated yarn and individual filament yarns or the combination of monofilament and monotape yarns in a composite yarn allows immediate achievement of the look of natural grass, that is, without post-fibrillation, and avoids any visible difference in wear pattern between the different types of yarns. In another embodiment, the invention also provides improved particulate material for use as infill material for top-dressing a synthetic turf.
Owner:DOMO ZELE
Protective drainage wraps
A protective drainage wrap comprises a polymeric spunbonded portion being adapted to allow water vapor to flow therethrough and a plurality of fibers, filaments, tapes or yarn being attached to the polymeric spunbonded portion. The plurality of fibers, filaments, tapes or yarn forms a plurality of channels to assist in forming a drainage path for draining liquid moisture from the protective drainage wrap.
Owner:PACTIV CORP
Multi-axial grid or mesh structures with high aspect ratio ribs
ActiveUS9556580B2Improve the immunityHigh aspect ratioPaving reinforcementsLayered productsEngineeringEngineering structures
Owner:TENSAR TECH
Removable support surface
InactiveUS20140250780A1Easy to drainEasy to installWeft knittingPattern makingArtificial turfEngineering
A removable support surface has knitted loops of yarn, and has piles extending from the knitted yarn to form an artificial turf, or to form a hybrid turf when combined with natural grass which grows between the knitted yarn. The piles may be hollow to retain liquid, and the dimensions of the yarn and the piles may be adjusted during fabrication. The removable support surface is fabricated by warp knitting, and the piles may be bent to have a crimped configuration. When used in a bunker with sand, the crimped configuration prevents sand from migrating. The removable support surface may also be placed on a seeded mat, on a dirt layer, or on existing natural grass. The removable support surface may be composed of biodegradable material.
Owner:EZ HYBRID TURF +2
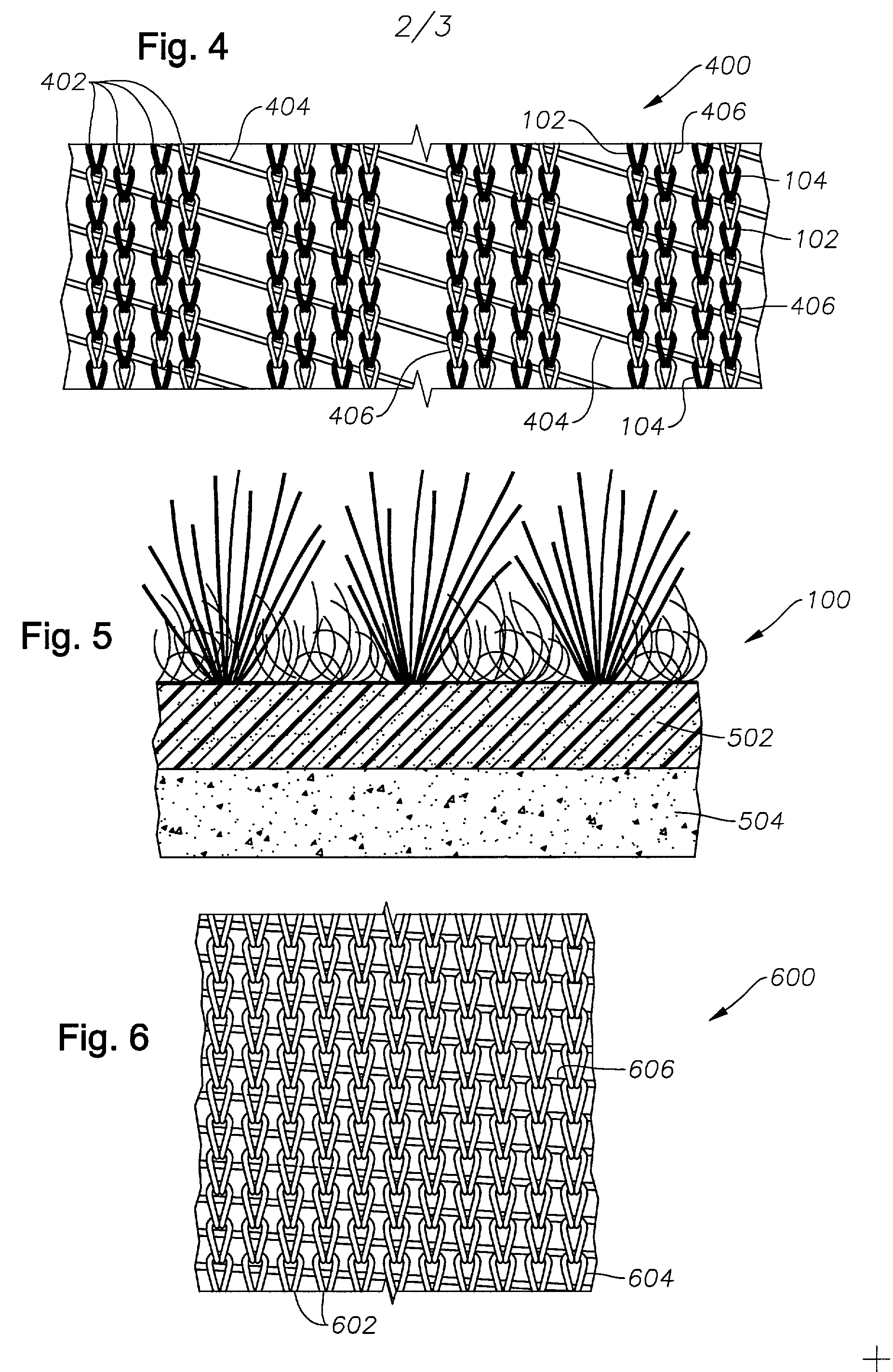
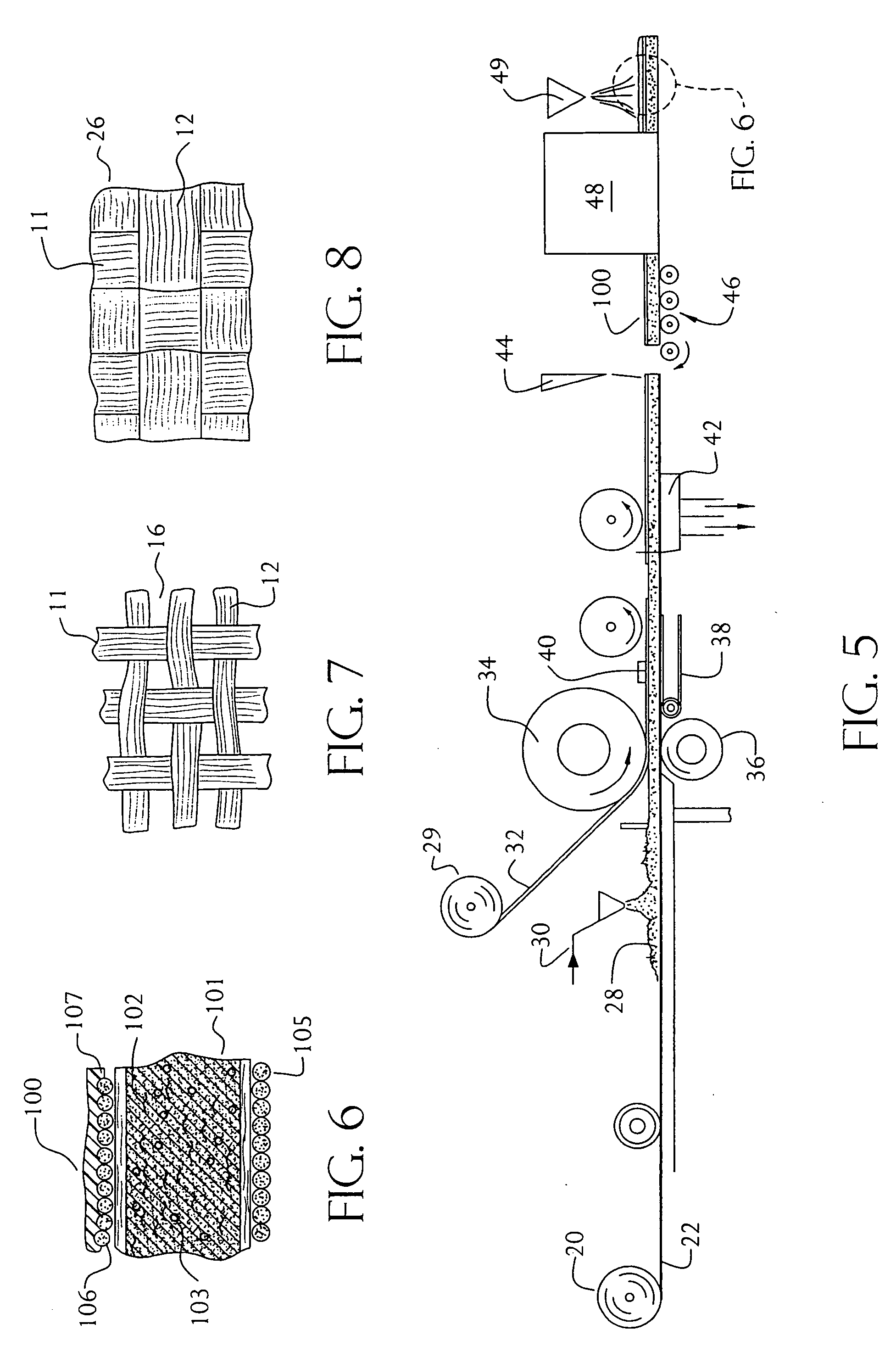
Woven geosynthetic fabric
A woven geosynthetic fabric is disclosed having a first weft yarn, a second weft yarn, and a stuffer pick woven in the weft direction of the fabric. A warp yarn interweaves the first and second weft yarns and the stuffer pick. The first weft yarn and the second weft yarn having different cross-sectional shapes. At least a portion of the fabric has a plurality of weft yarn sets with stuffer picks respectively disposed and woven between the weft yarn sets. Each weft yarn set has two first weft yarns and two second weft yarns. One of the two first weft yarns is adjacent one of the two second weft yarns and stacked on the other second weft yarn. The adjacent second weft yarn is stacked on the other first weft yarn.
Owner:NICOLON CORP
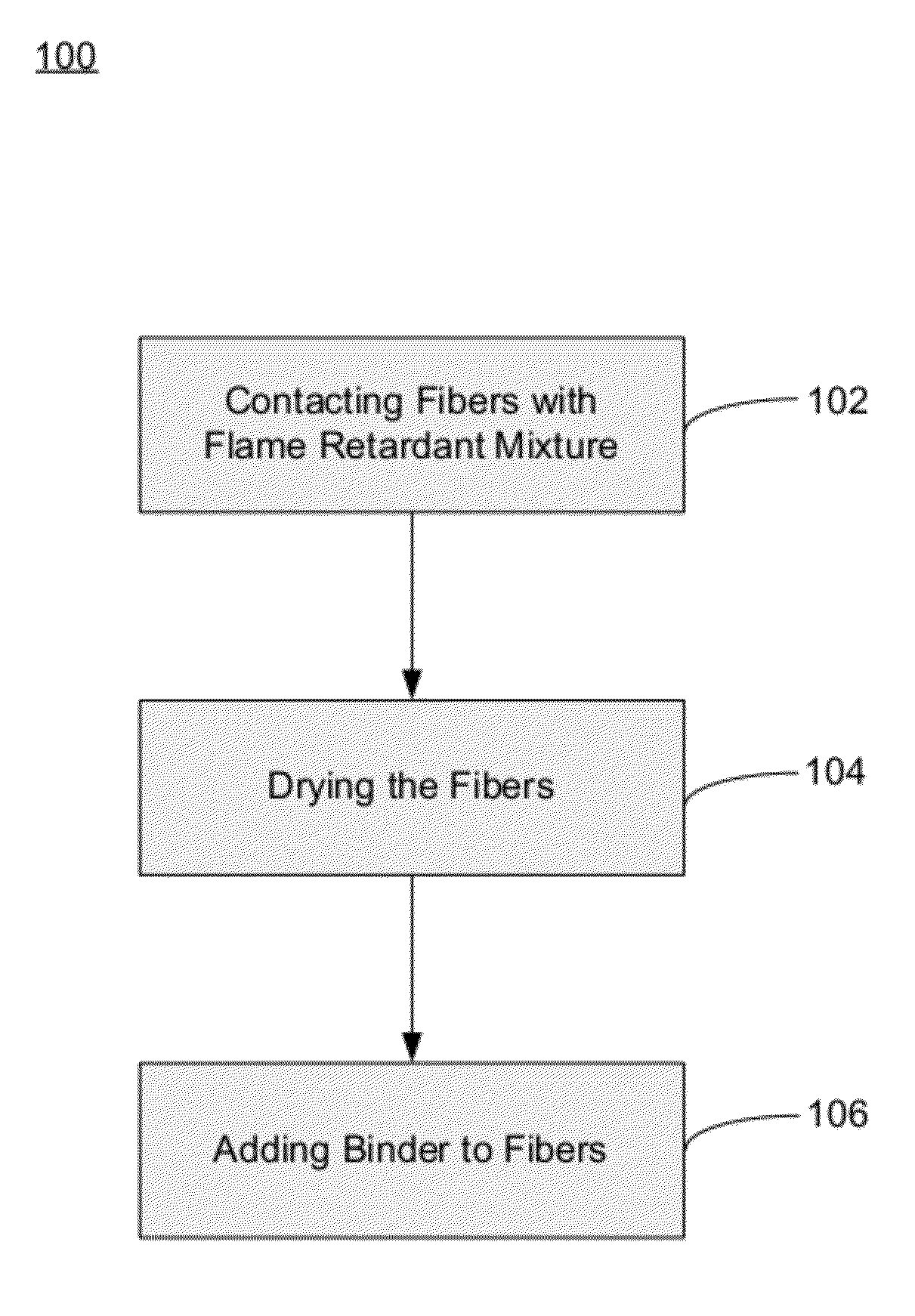
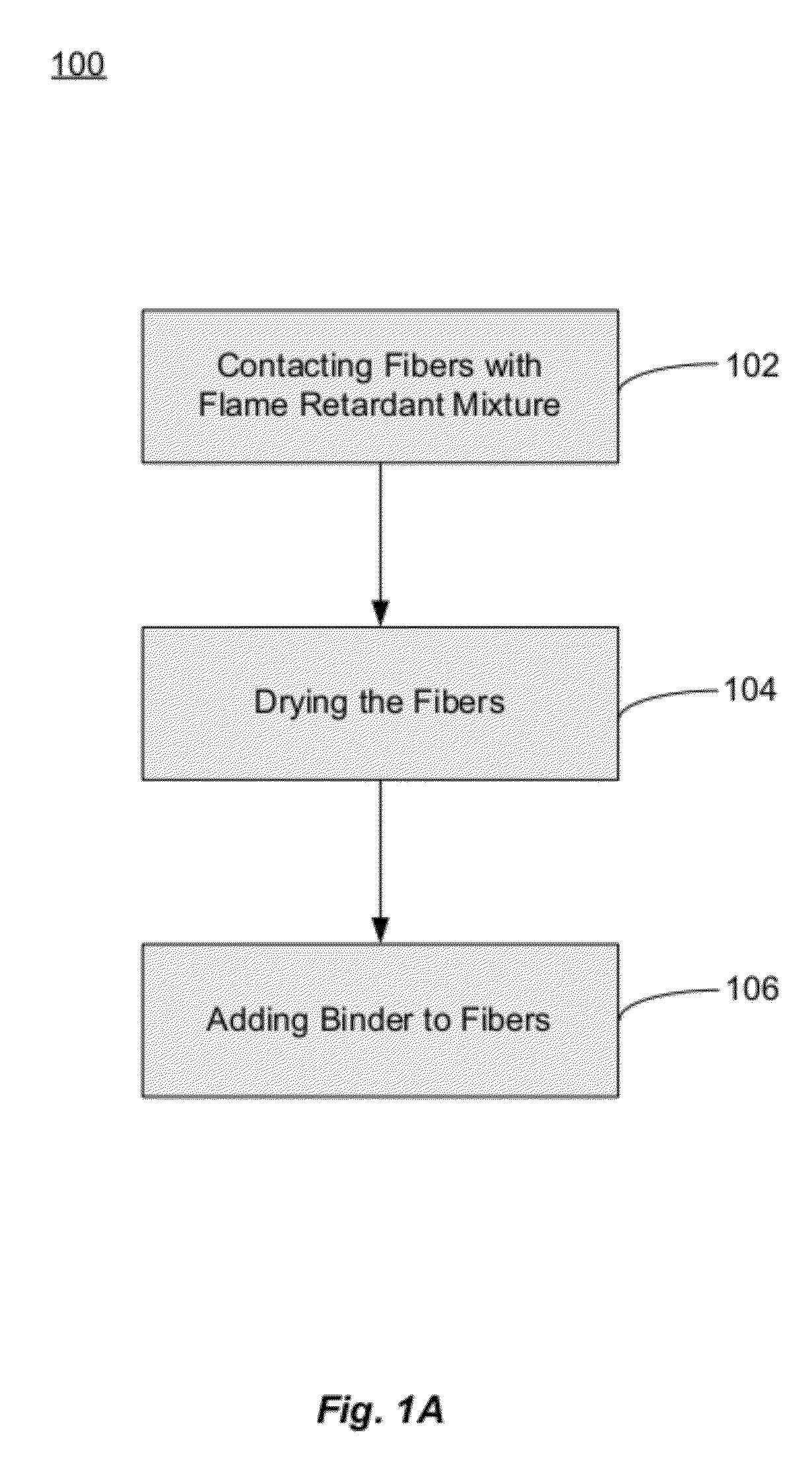
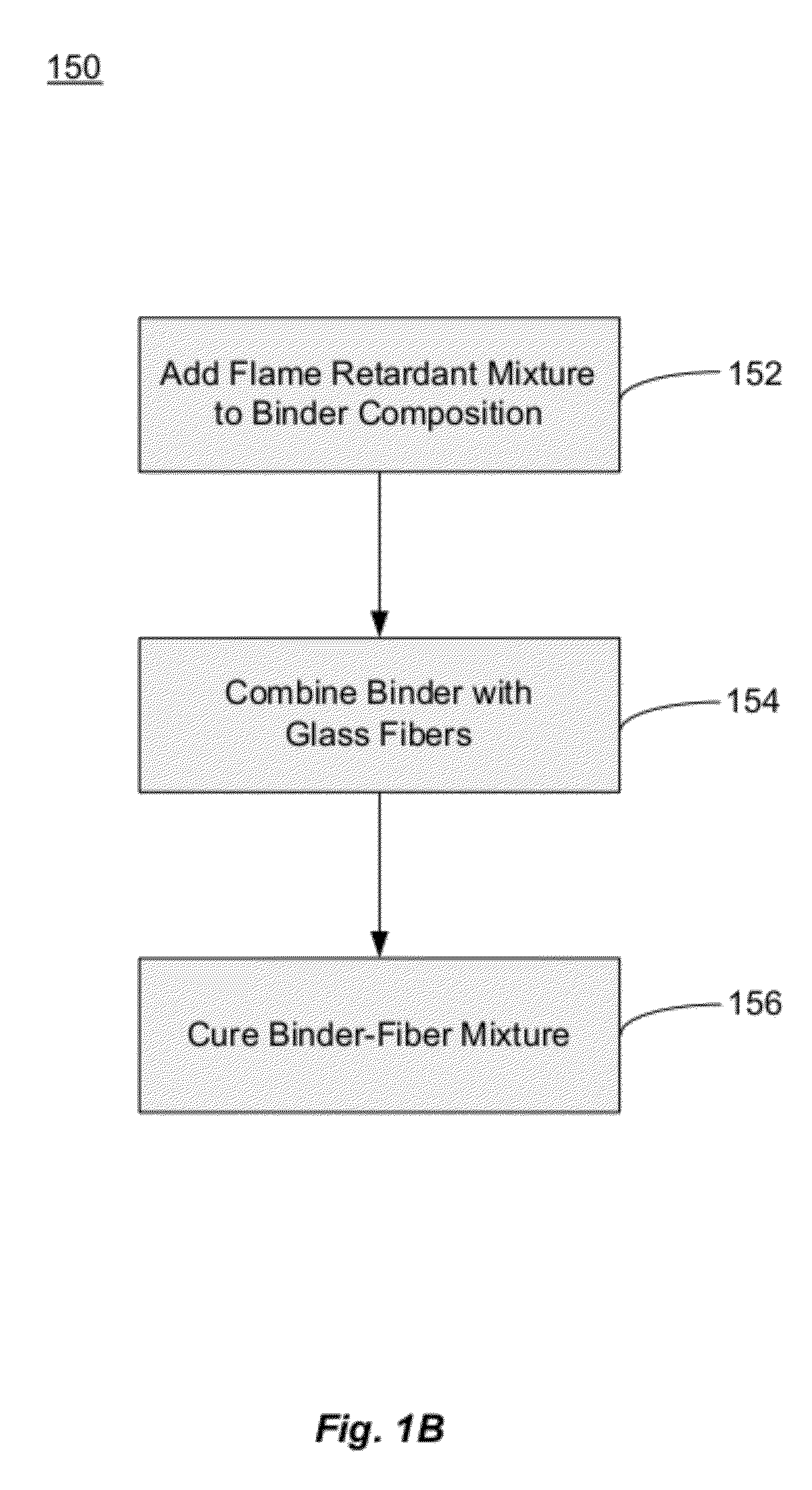
Fiberglass composites with improved flame resistance from phosphorous-containing materials and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20120315458A1Improve flame retardant performanceReduce meltingLayered productsPretreated surfacesGlass fiberOrganophosphorous compounds
Fiberglass products with increased flame resistance are described. The products may include fiberglass-containing thermal insulation that include a plurality of glass fibers coated with a phosphorous-containing flame retardant. The flame retardant may include an organophosphorous compound having a substituted or unsubstituted organophosphorous group bonded to a substituted or unsubstituted amide group by a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group. The fiberglass products may further include fiberglass composites that are about 50 wt. % to about 98 wt. % glass fibers, about 2 wt. % to about 50 wt. % of a binder; and a phosphorous-containing flame retardant. Also described are methods of making fiberglass products with increased flame resistance. These methods may include the steps of contacting glass fibers and / or fiberglass products with a flame retardant mixture that includes a phosphorous-containing compound.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
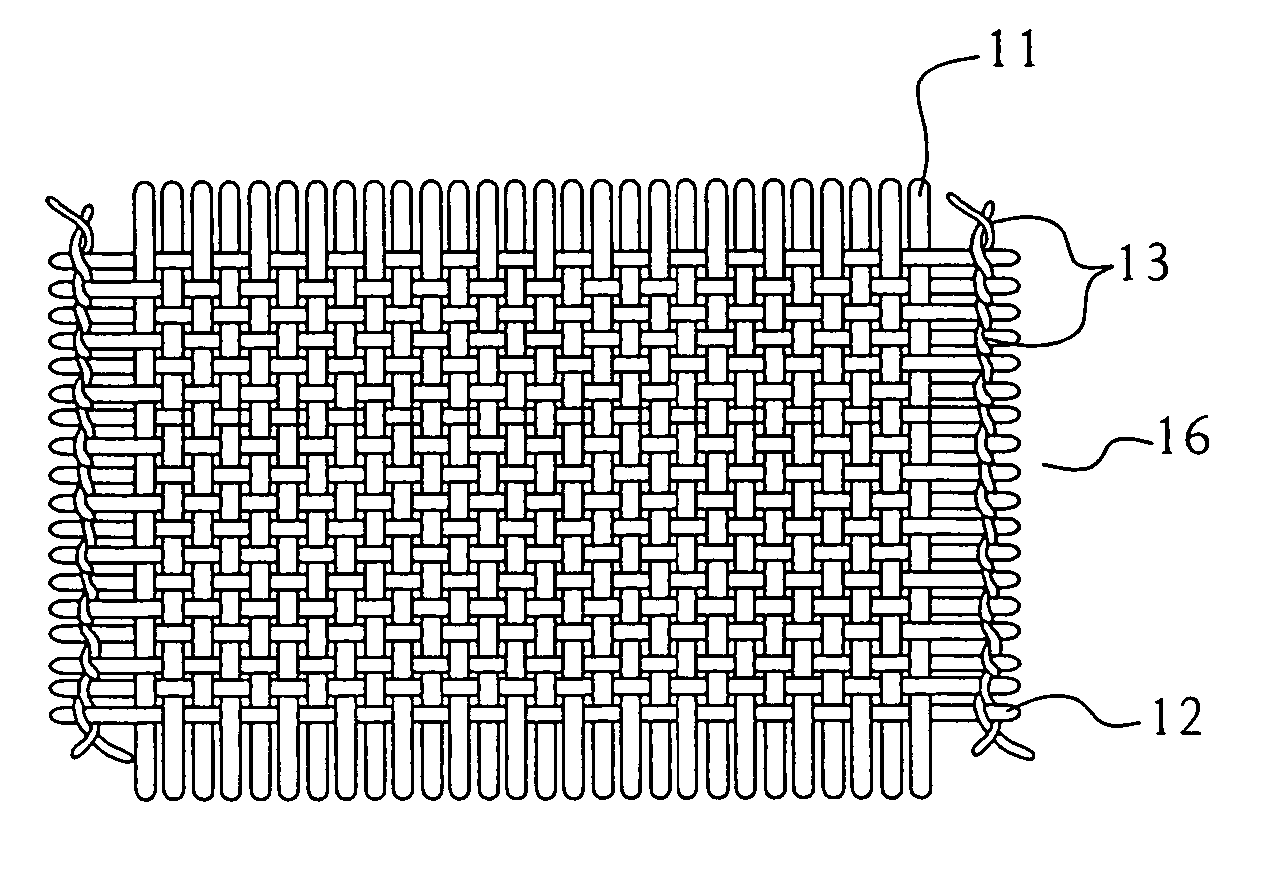
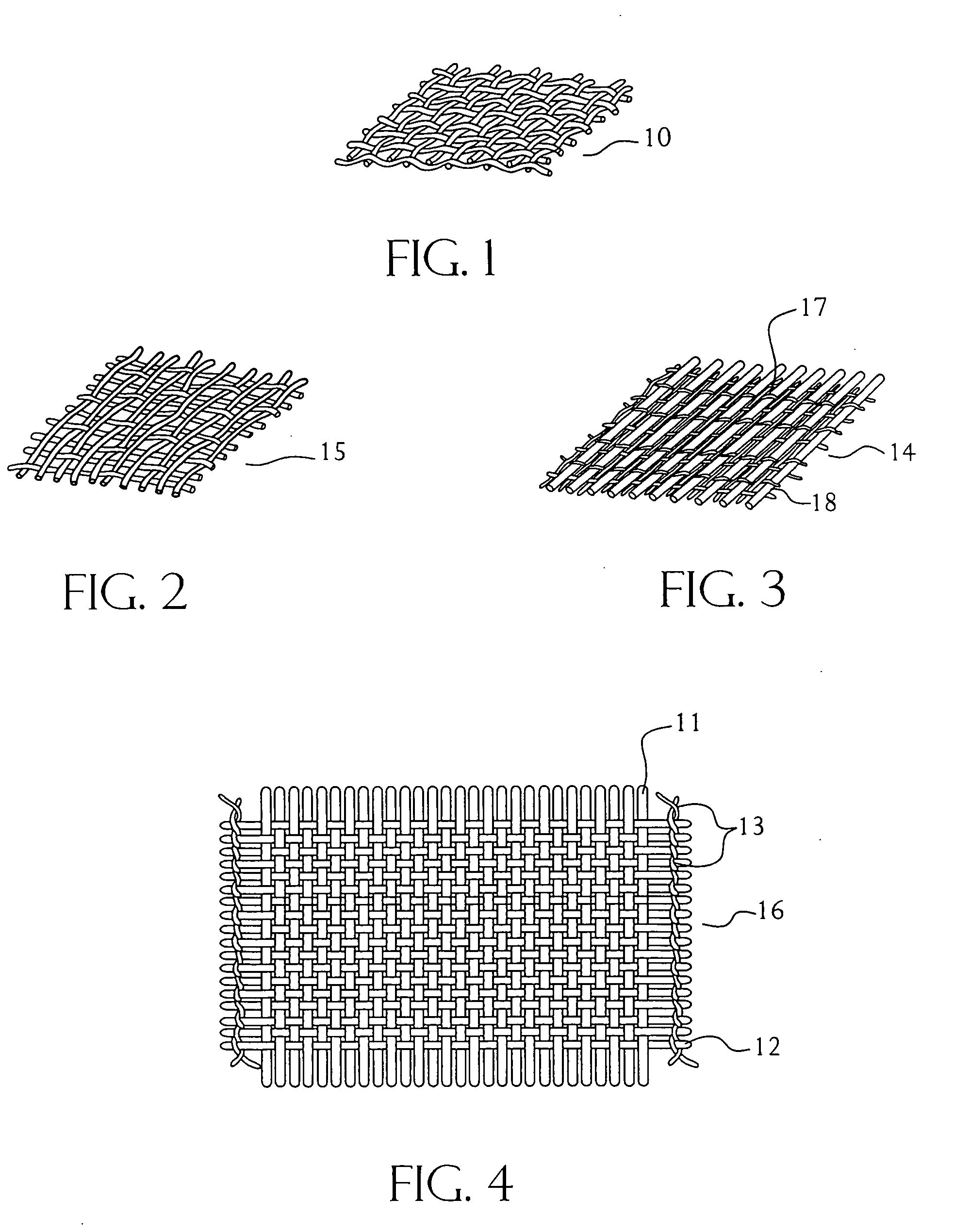
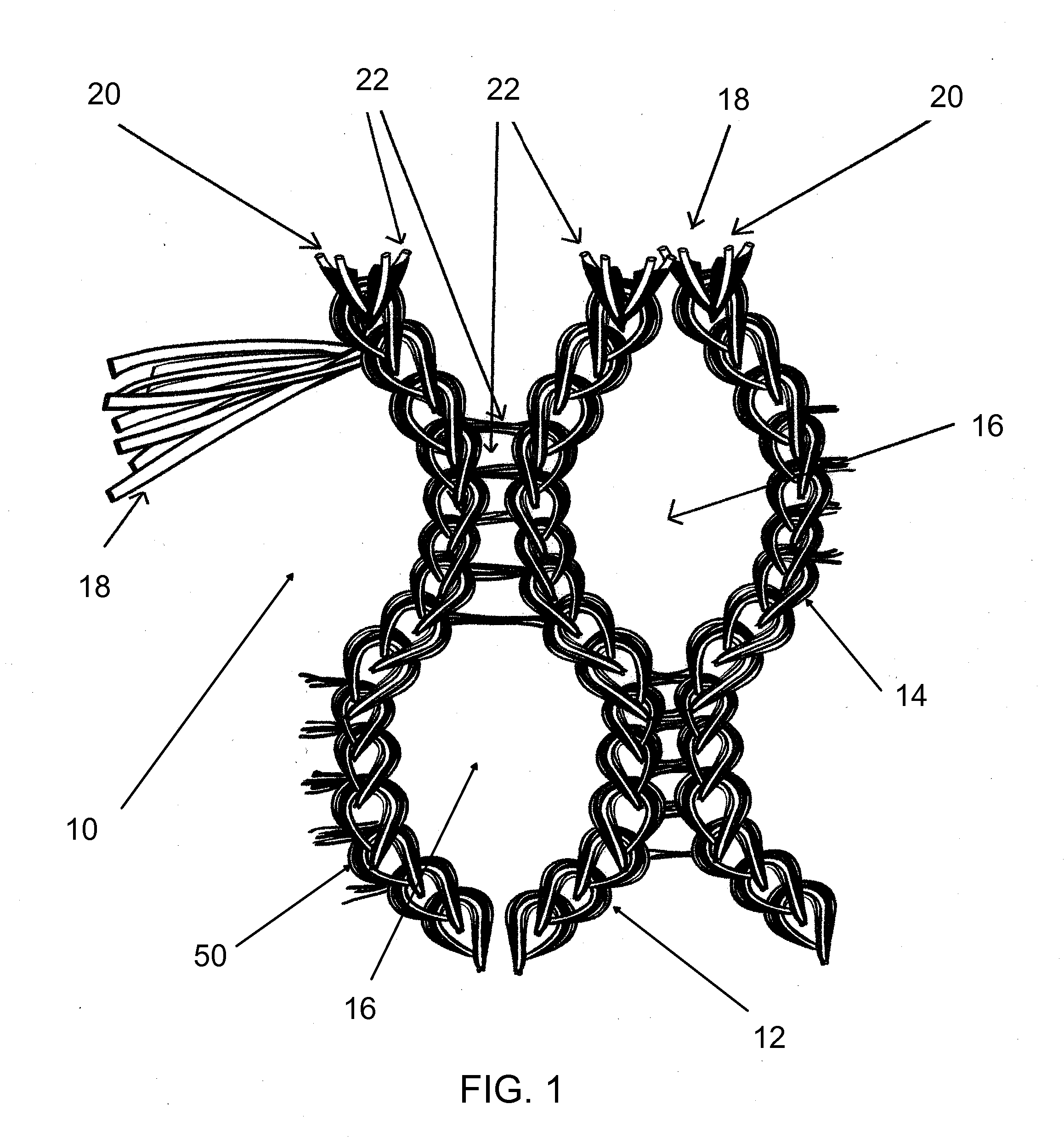
Knitted geotextile, and geotextile tube constructed thereof
InactiveUS20110262682A1Improve performanceReduce strainSludge treatmentOrnamental textile articlesFiberWater flow
A geotextile for sediment dewatering and containment has a pattern of oriented warp fibers positioned substantially parallel to each other, a pattern of oriented weft inserted fibers positioned substantially parallel to each other and substantially perpendicular to the oriented warp fibers, a nonwoven fleece, and oriented knitting fibers that interconnect the warp fibers, the weft fibers, and the nonwoven fleece as a knitted structure. Because of the knitted configuration, the load bearing warp fibers and weft fibers remain substantially straight rather than interlaced as in a woven product. Consequently, the load bearing warp fibers and weft fibers take up stress immediately, thereby giving higher performance at lower strain. Because the load bearing warp fibers and weft fibers are substantially straight, they also retain their permeability under loading. Since more water flows through and from the geotextile, even when fully loaded, the dewatering process is both faster and safer to complete
Owner:TENSAR INT CORP +1
Novel partial deep layer pressurizing type vacuum preloading soft soil foundation processing method
The invention relates to a novel partial deep layer pressurizing type vacuum preloading soft soil foundation processing method. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises a vertical drainage system, a transverse drainage system, vacuum extraction equipment, a pressurizing system, pressurizing equipment and a sealing system; a vertical drainage board adopts a novel anti-clogging drainage board, the vertical drainage board is divided into two parts to be driven, one part is driven into a soil body, and the other part is exposed out of the surface of the soil body. The technology enables a deep soil body to obtain higher air pressure, enables a larger pressure difference to be formed among the deep soil body, an upper soil body and the vertical drainage board, and enables the free water in the deep soil body to fast flow to the upper soil body and the drainage boards. In addition, the flow direction of airflow from a jet head obliquely upwards points to the drainage boards, therefore the seepage of the pore water in the deep soil body to the drainage boards can be accelerated, and the deep soil body can obtain better reinforcement effect.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
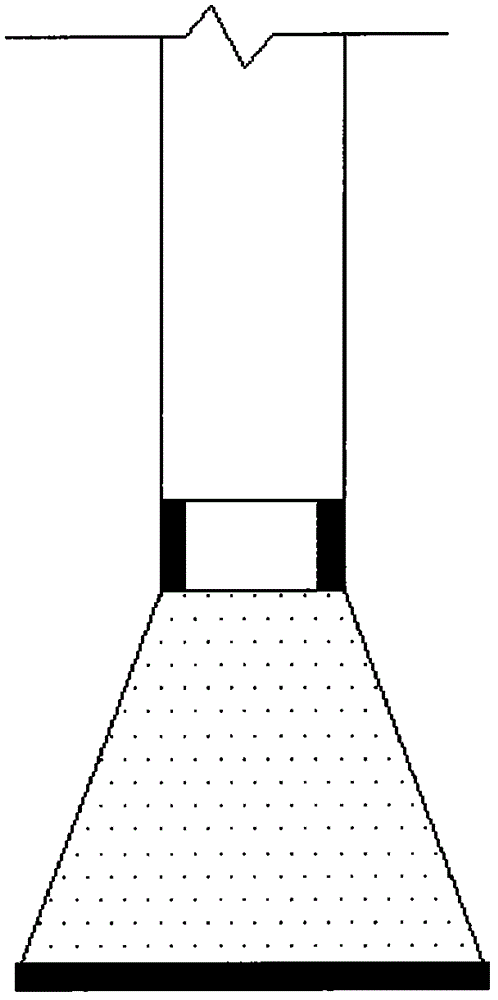
System and method for forming patterned artificial/synthetic sports turf fabrics
ActiveUS20140331906A1Reduce the amount requiredAdd supportTufting apparatusPattern makingYarnEngineering
A system and method for forming synthetic / artificial grass or turf products in which a series of tufts of artificial / synthetic grass filaments or yarns are formed in a backing material with various graphic pattern effects being formed therewith. The system generally will include at least one needle bar having at least one row of needles mounted along a tufting zone and reciprocated through the backing to a desired penetration depth, and will present a desired set or group of yarns to a series of pattern pixels or stitch areas. A series of level cut loop loopers or hooks will be aligned with and will engage the needles in order to form tufts of yarns in the backing material. Clips of the level cut loop loopers will be selectively controlled to control the retention of selected ones of the yarns presented at each pattern pixel. The remaining, non-selected yarns generally are not retained at the pattern pixels, and can be formed as lower pile tufts or removed from the backing material.
Owner:CARD MONROE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com