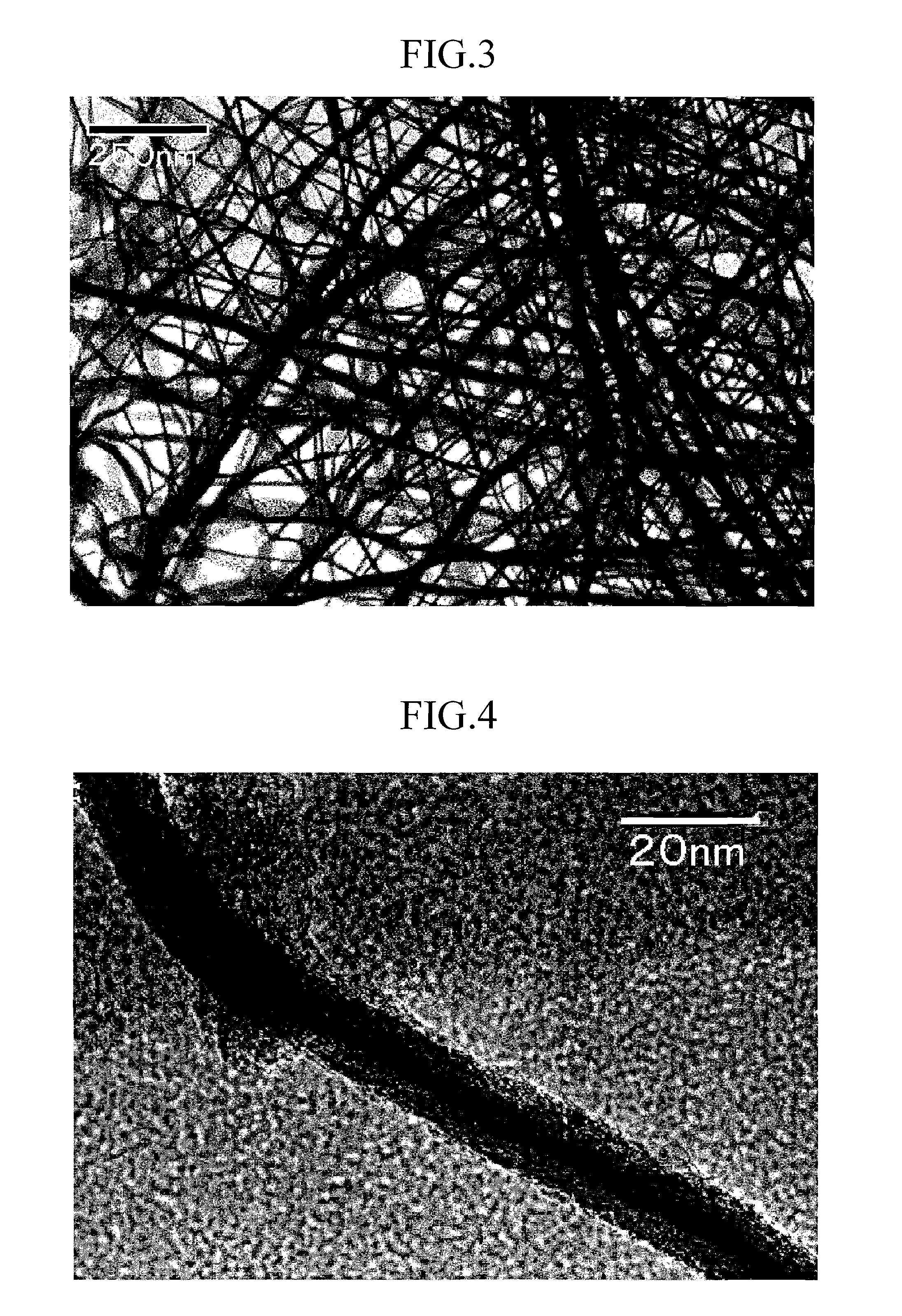
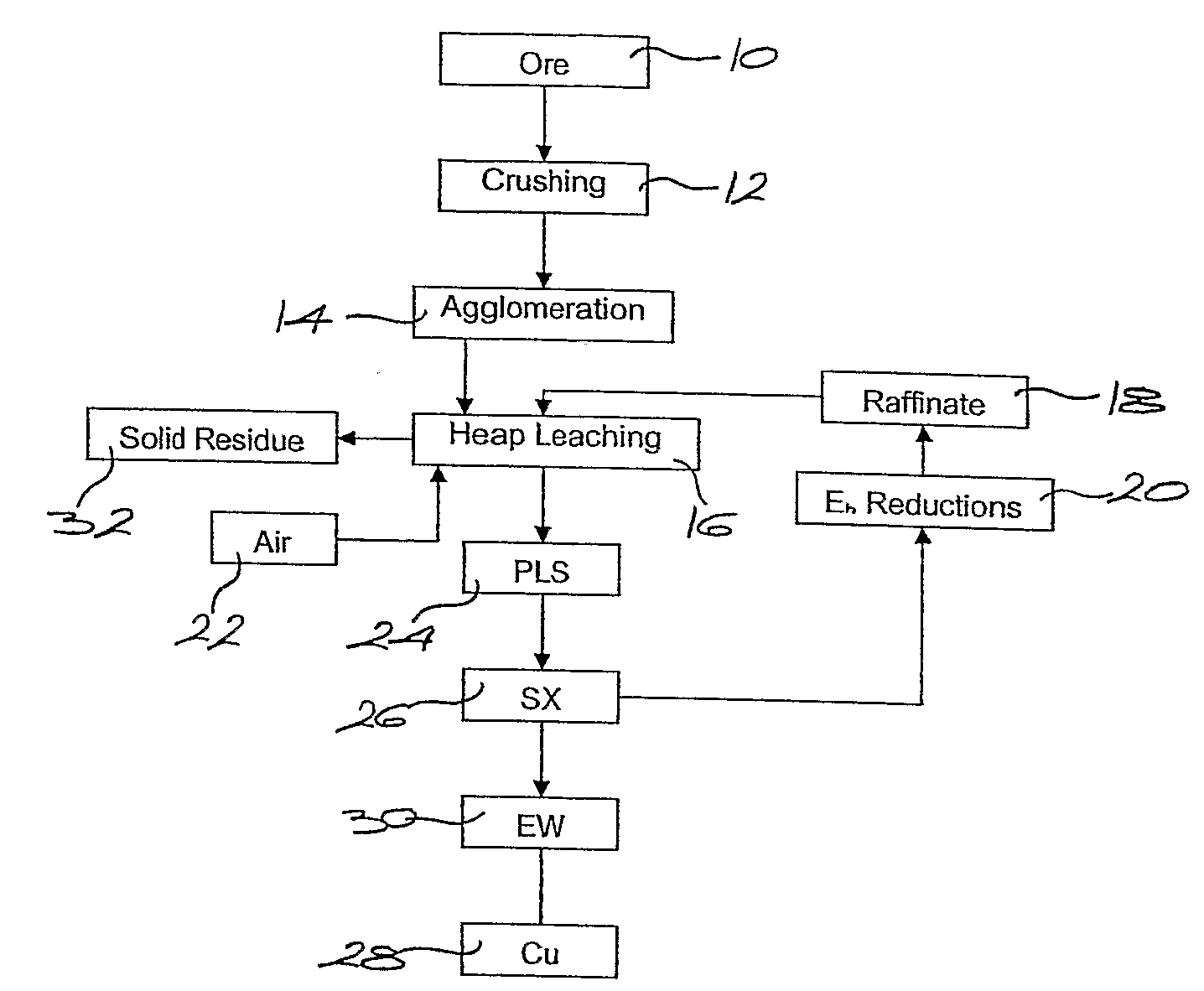
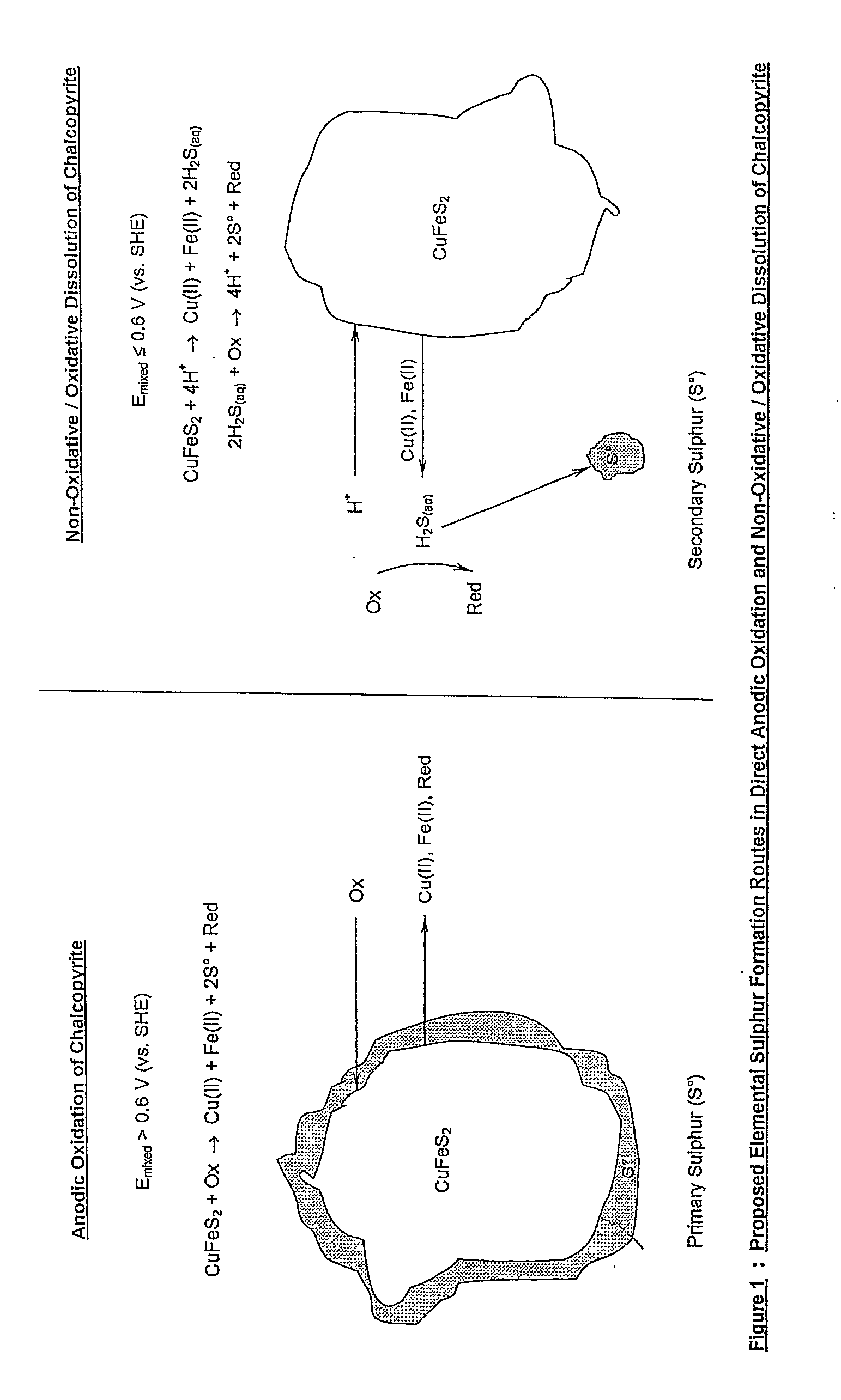
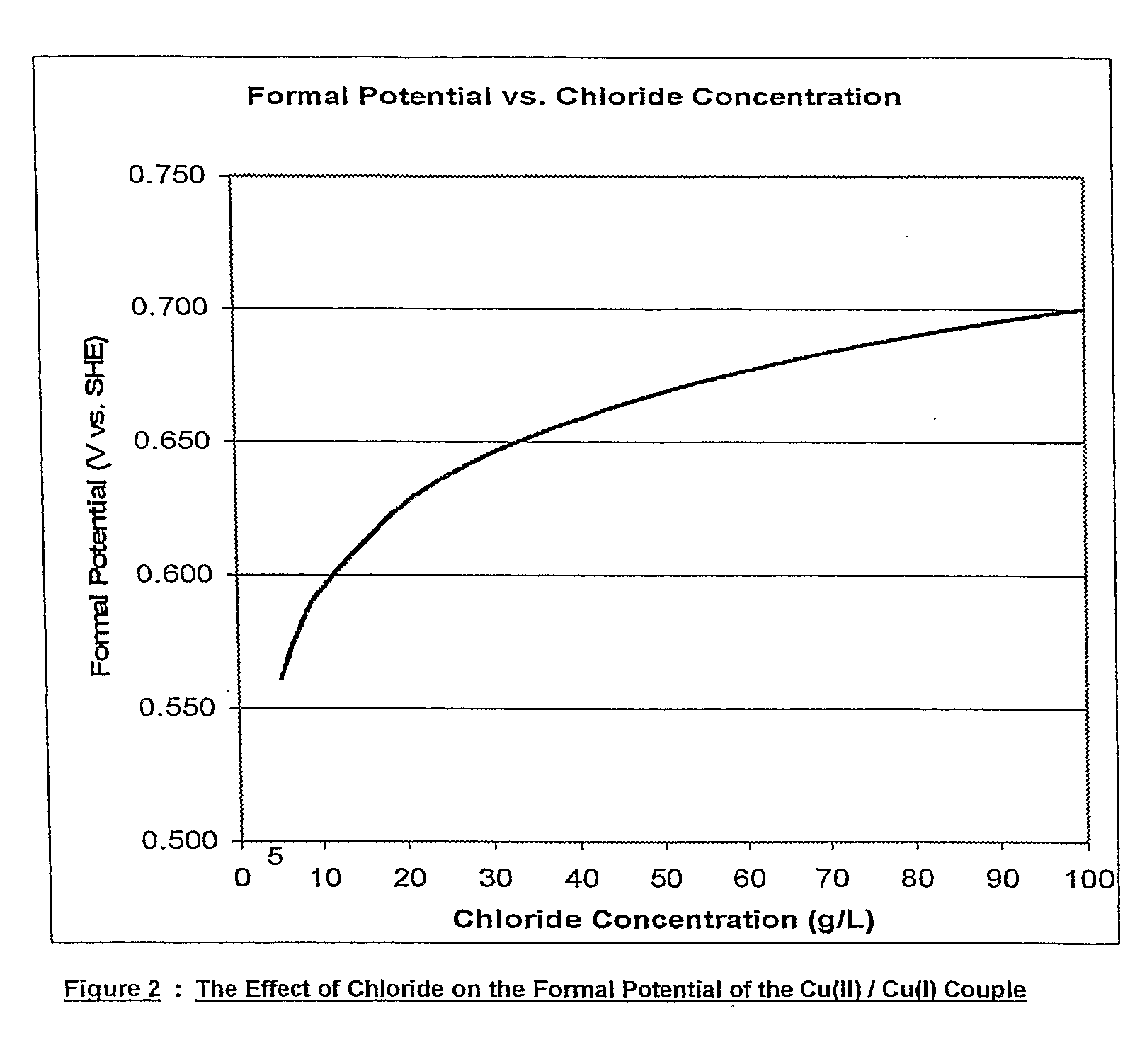
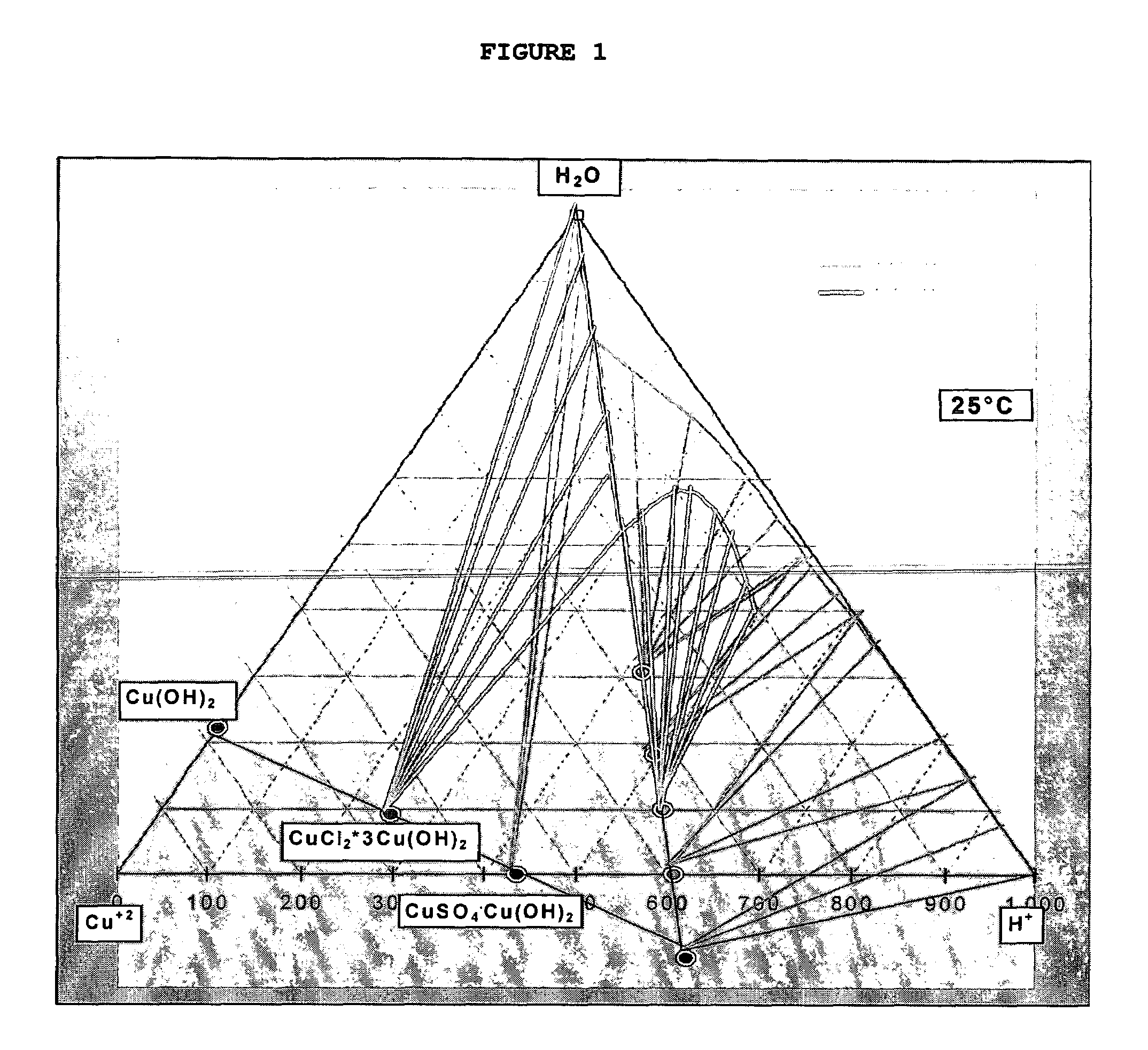
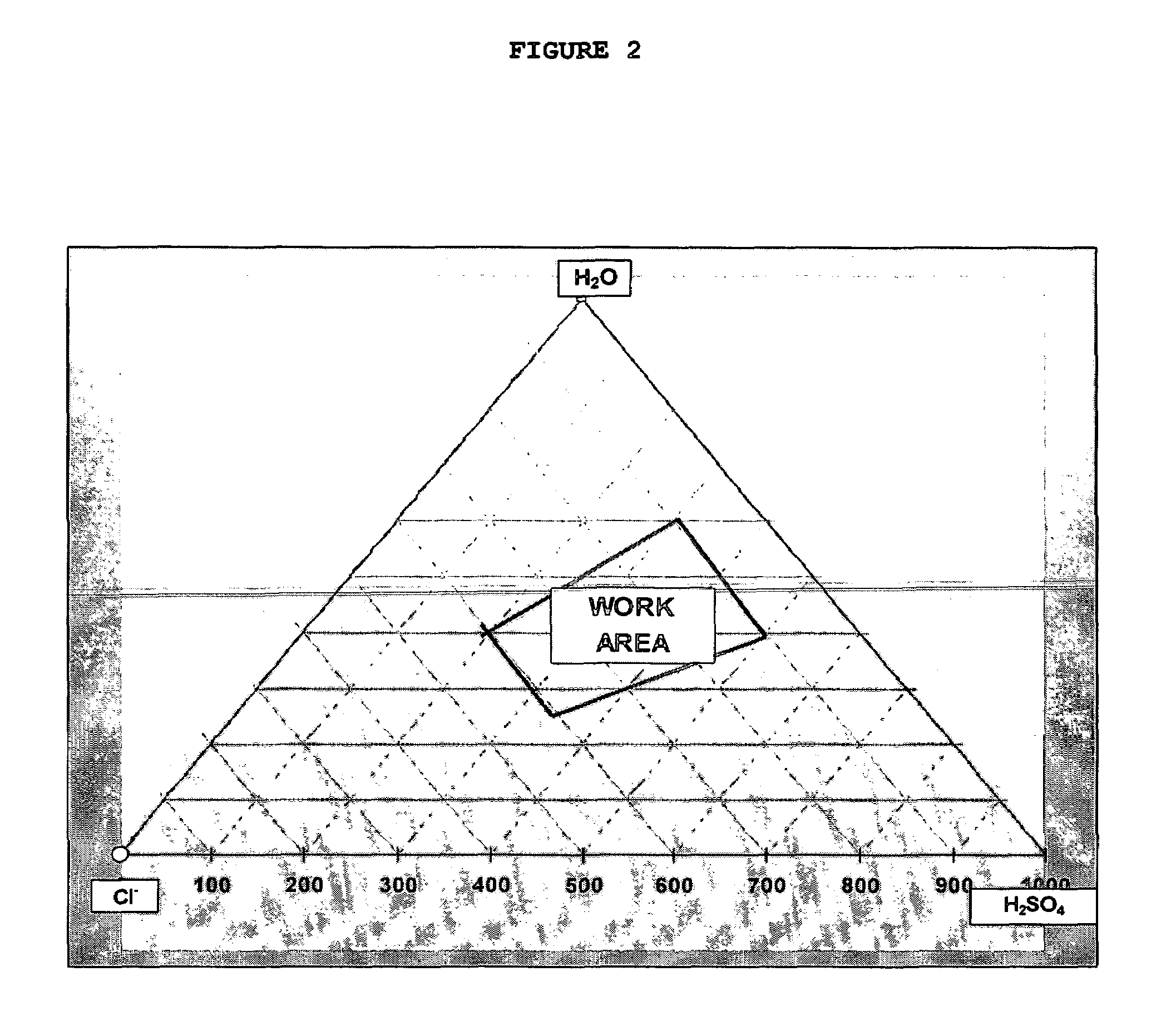
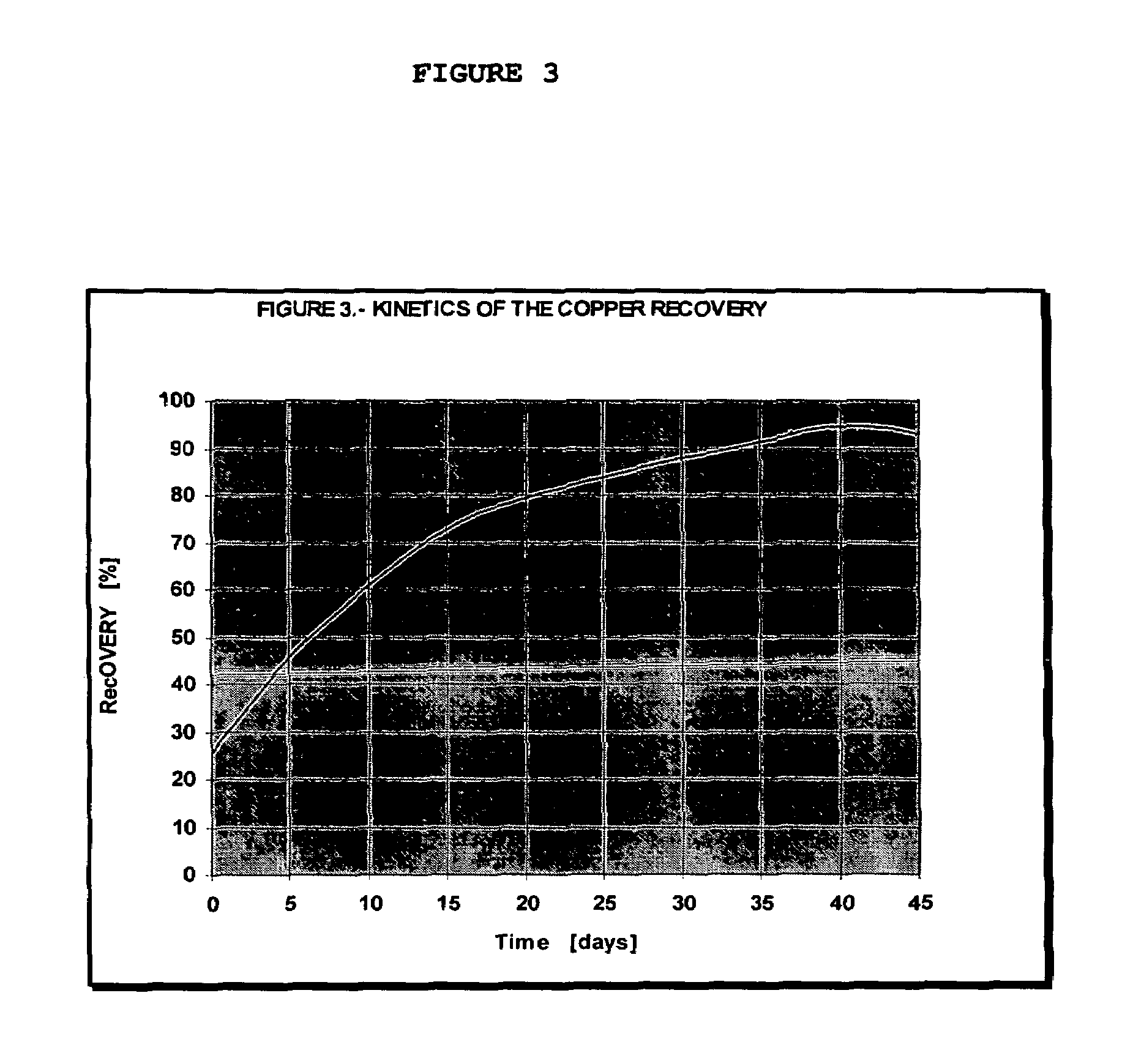
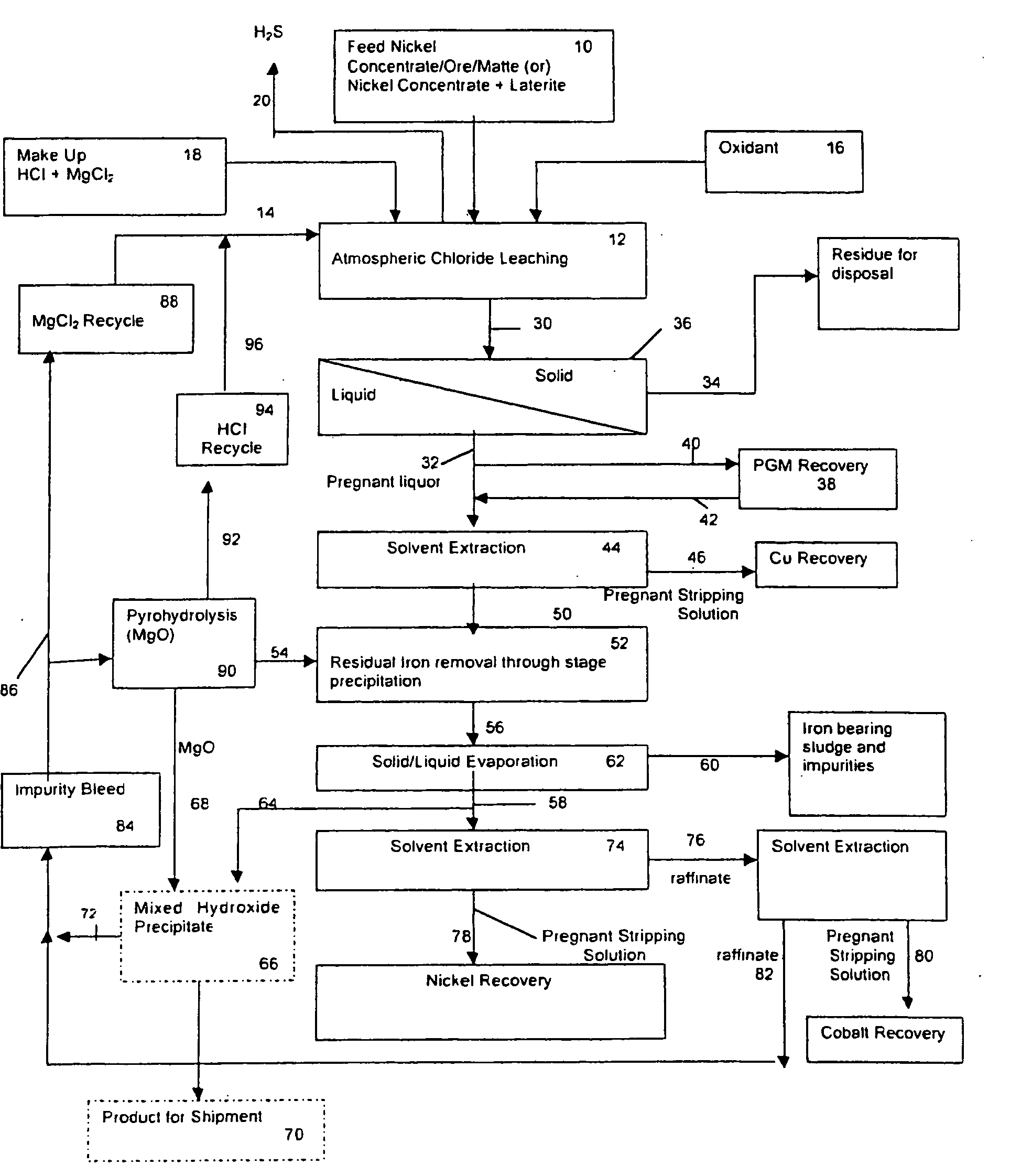
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
110results about "Copper halides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spin-coatable liquid for formation of high purity nanotube films
ActiveUS20050058590A1Lower Level RequirementsPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid mediumSpins
Certain spin-coatable liquids and application techniques are described, which can be used to form nanotube films or fabrics of controlled properties. A spin-coatable liquid for formation of a nanotube film includes a liquid medium containing a controlled concentration of purified nanotubes, wherein the controlled concentration is sufficient to form a nanotube fabric or film of preselected density and uniformity, and wherein the spin-coatable liquid comprises less than 1×1018 atoms / cm3 of metal impurities. The spin-coatable liquid is substantially free of particle impurities having a diameter of greater than about 500 nm.
Owner:ZEON CORP
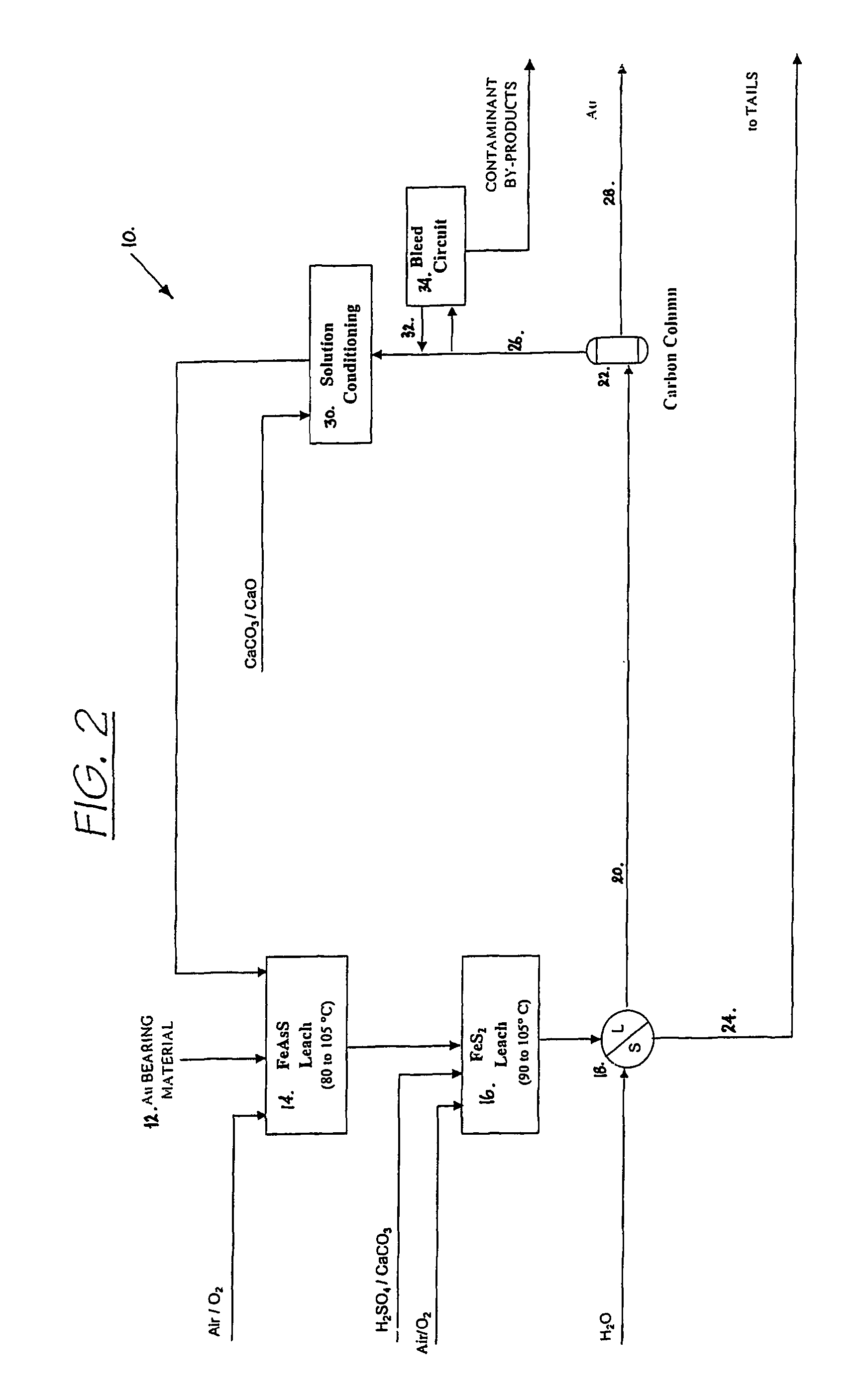
Process for the recovery of value metals from base metal sulfide ores
InactiveUS20050118081A1Simple gas/liquidReduce the amount requiredSulfur compoundsSolid sorbent liquid separationSulfideDissolution
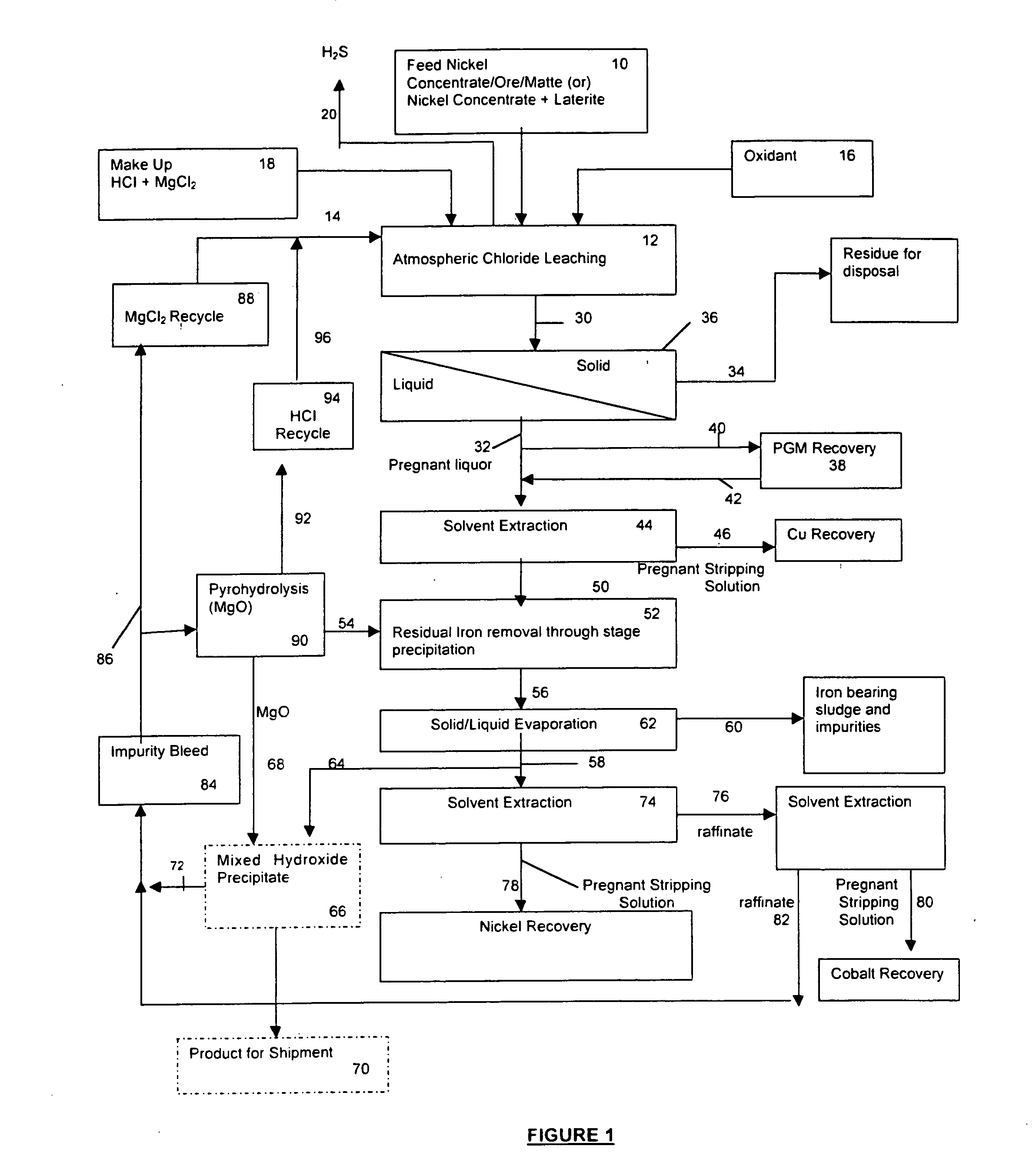
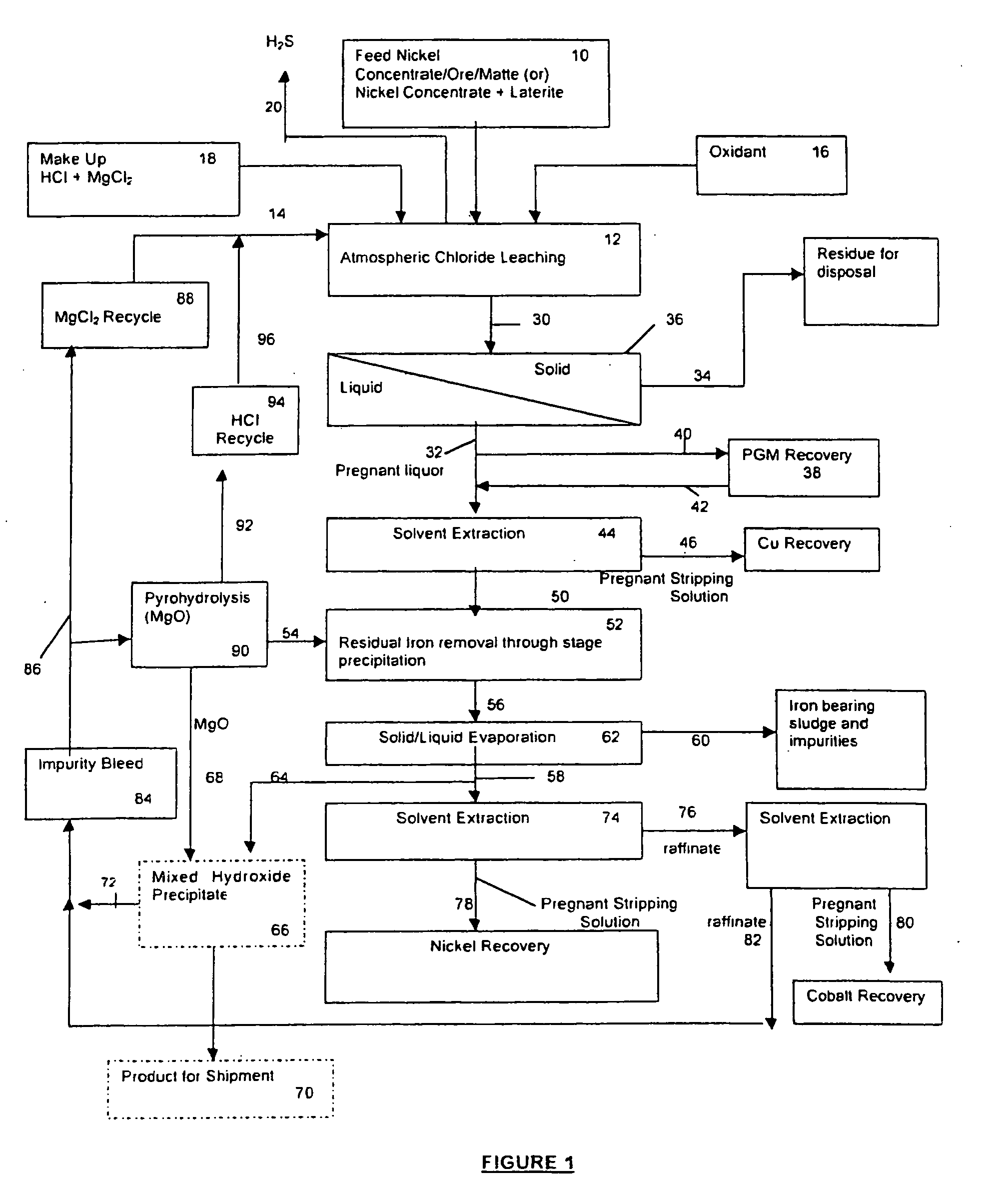
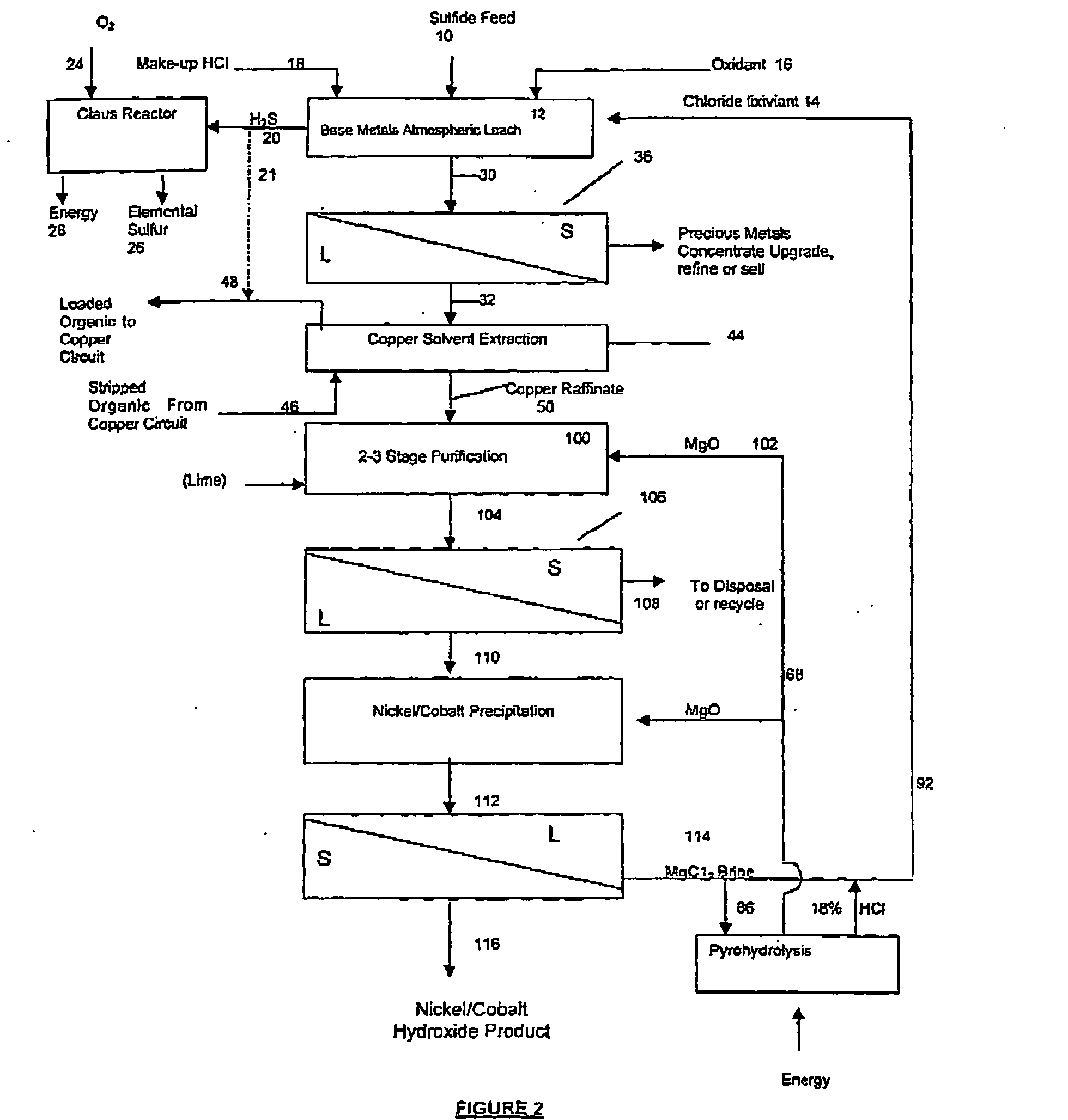
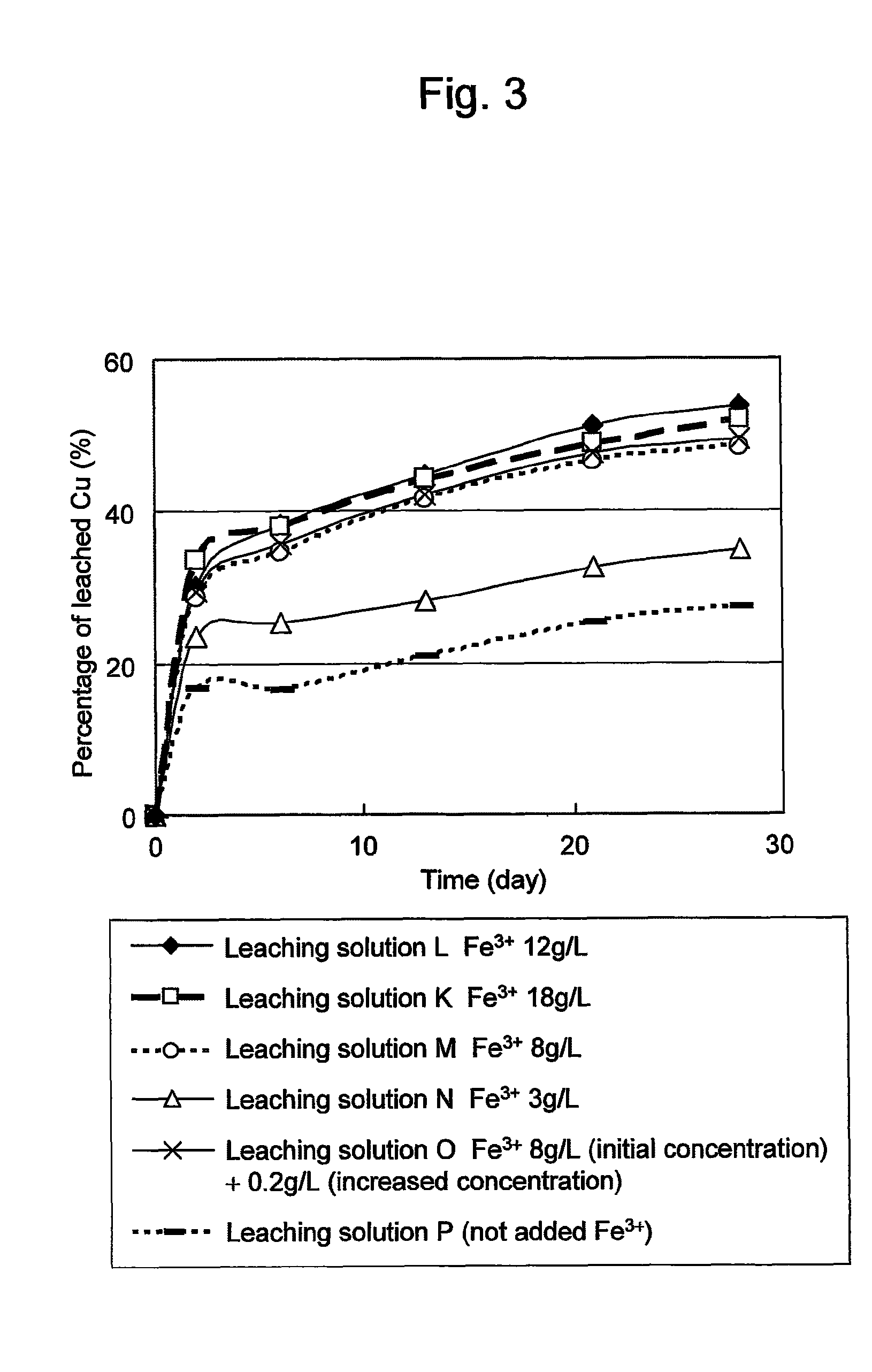
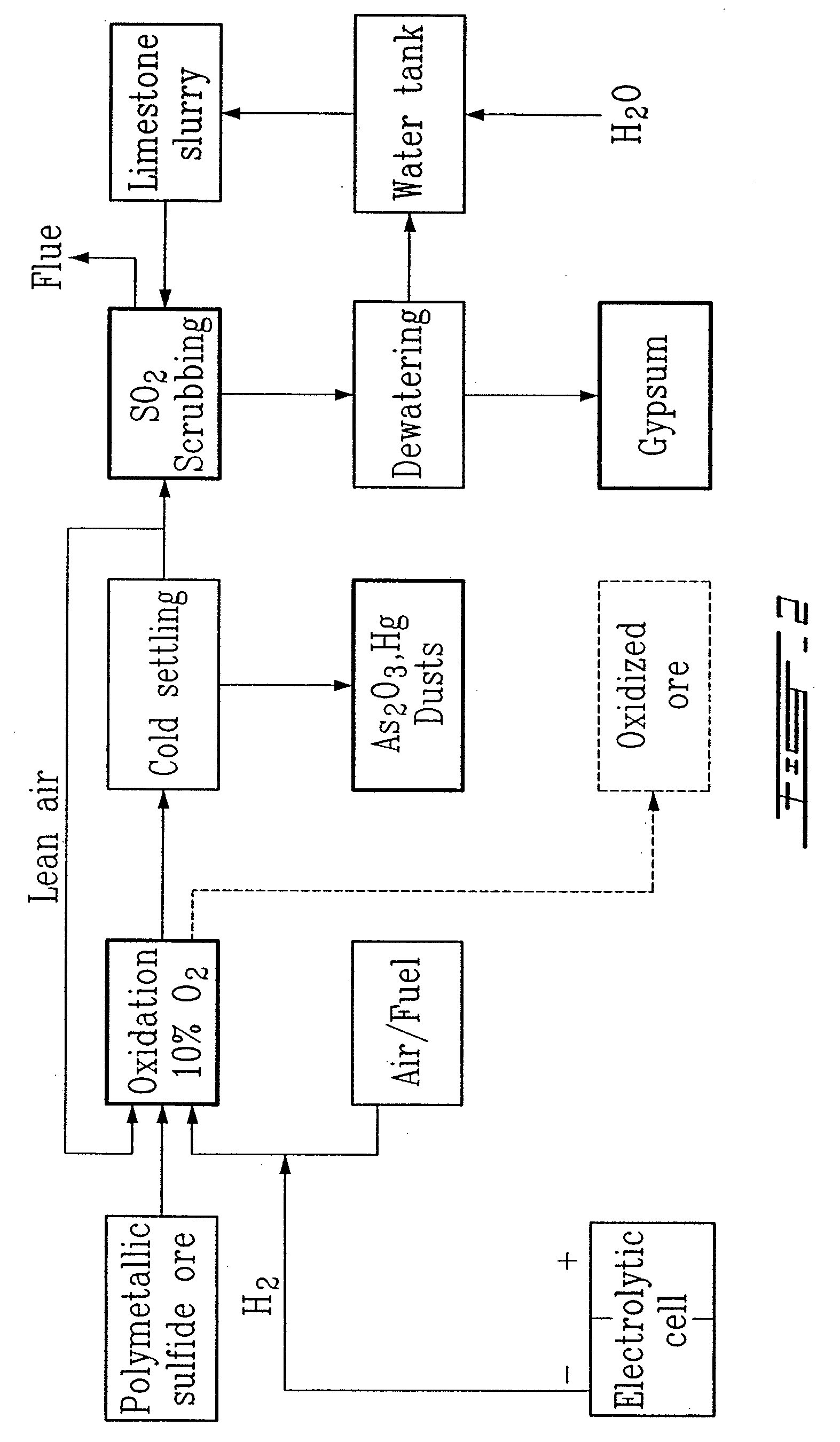
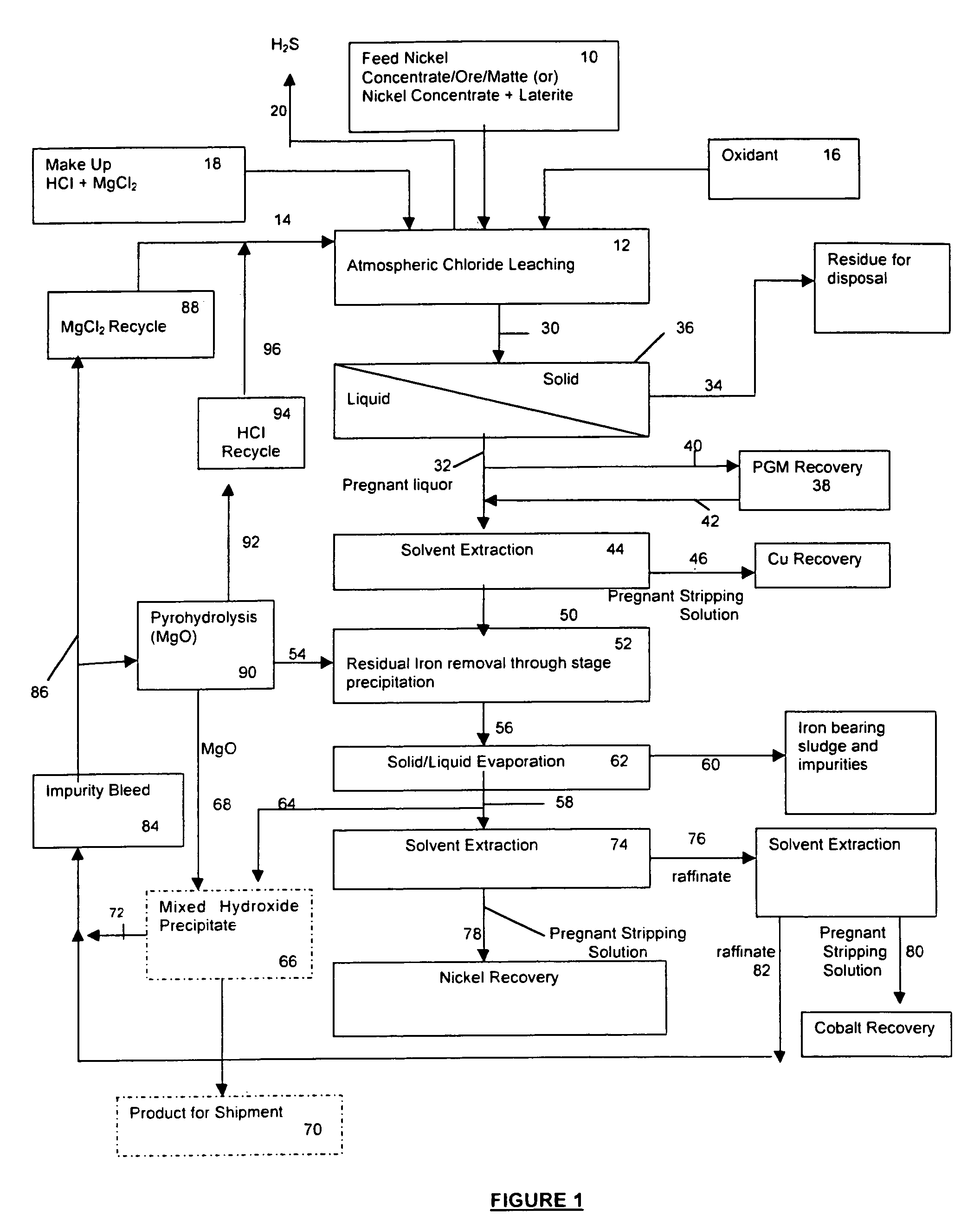
A process for leaching a value metal from a base metal sulfide ore, comprising the step of leaching the ore with a lixiviant comprising a chloride, an oxidant and hydrochloric acid is disclosed. The leaching is controlled, by use of low concentrations of hydrochloric acid and a redox potential, to effect formation of hydrogen sulfide from the base metal sulfide ore. The hydrogen sulfide is stripped from the leach solution, thereby reducing the amount of sulfate generated in the leach to very low levels. The leaching may also be conducted to limit the co-dissolution of platinum group metals and gold with the base value metals. The leach forms a value metal-rich leachate and a solids residue. The solids residue may be subsequently leached to recover the platinum group metals and gold. The value metal-rich leachate can be is oxidized and neutralized to recover the value base metals. In an embodiment, the chloride is magnesium chloride and lixiviant solution is regenerated.
Owner:JAGUAR NICKEL INC
Continuous fiber of single-wall carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20020127162A1High yieldCarbon compoundsElectrolytic capacitorsFiberElectric power transmission
A method for purifying a mixture comprising single-wall carbon nanotubes and amorphous carbon contaminate is disclosed. The method includes the steps of heating the mixture under oxidizing conditions sufficient to remove the amorphous carbon, followed by recovering a product comprising at least about 80% by weight of single-wall carbon nanotubes. A method for producing tubular carbon molecules of about 5 to 500 nm in length is also disclosed. The method includes the steps of cutting single-wall nanotube containing-material to form a mixture of tubular carbon molecules having lengths in the range of 5-500 nm and isolating a fraction of the molecules having substantially equal lengths The nanotubes may be used, singularly or in multiples, in power transmission cables, in solar cells, in batteries, as antennas, as molecular electronics, as probes and manipulators, and in composites.
Owner:RICE UNIV
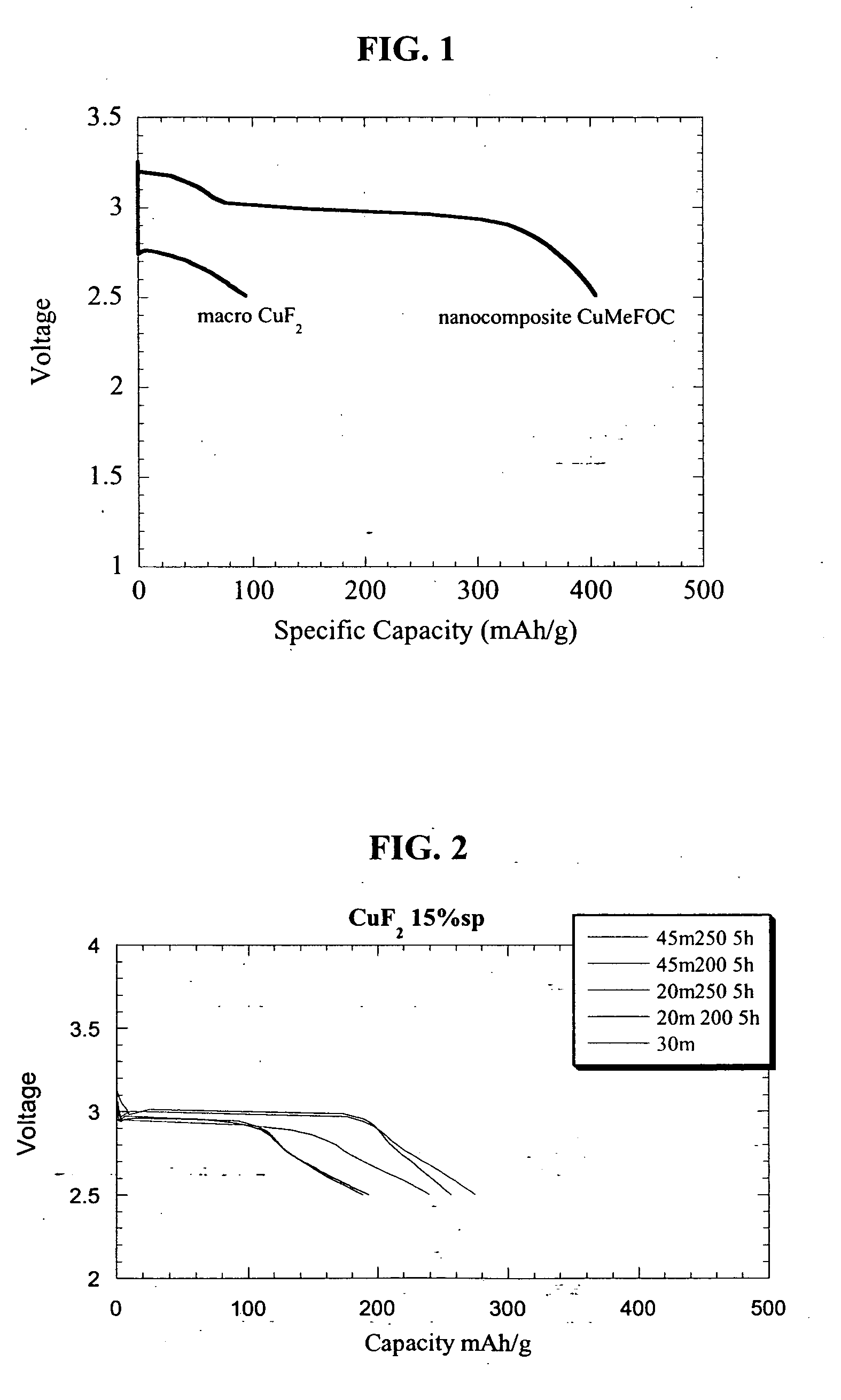
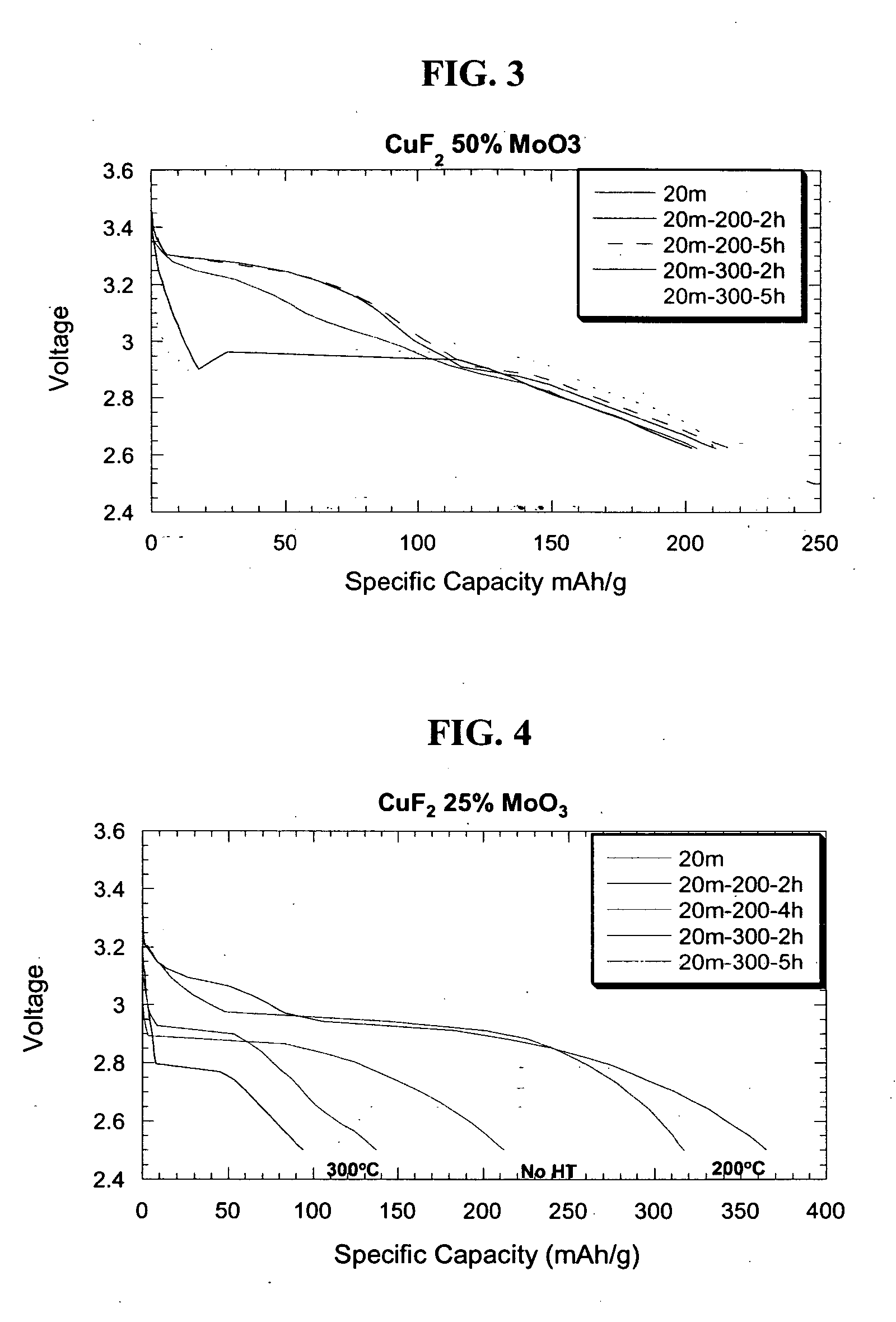
Copper fluoride based nanocomposites as electrode materials
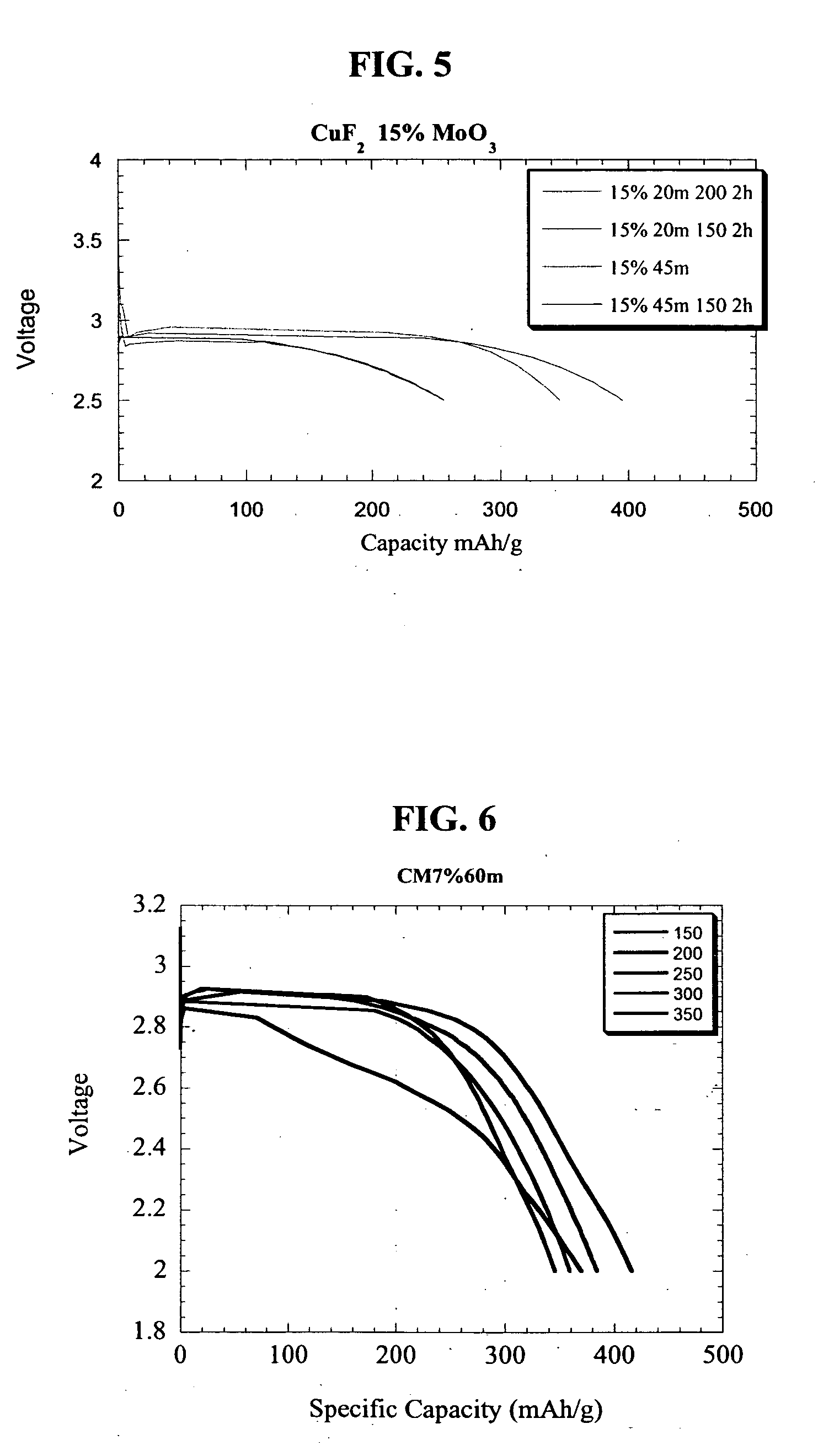
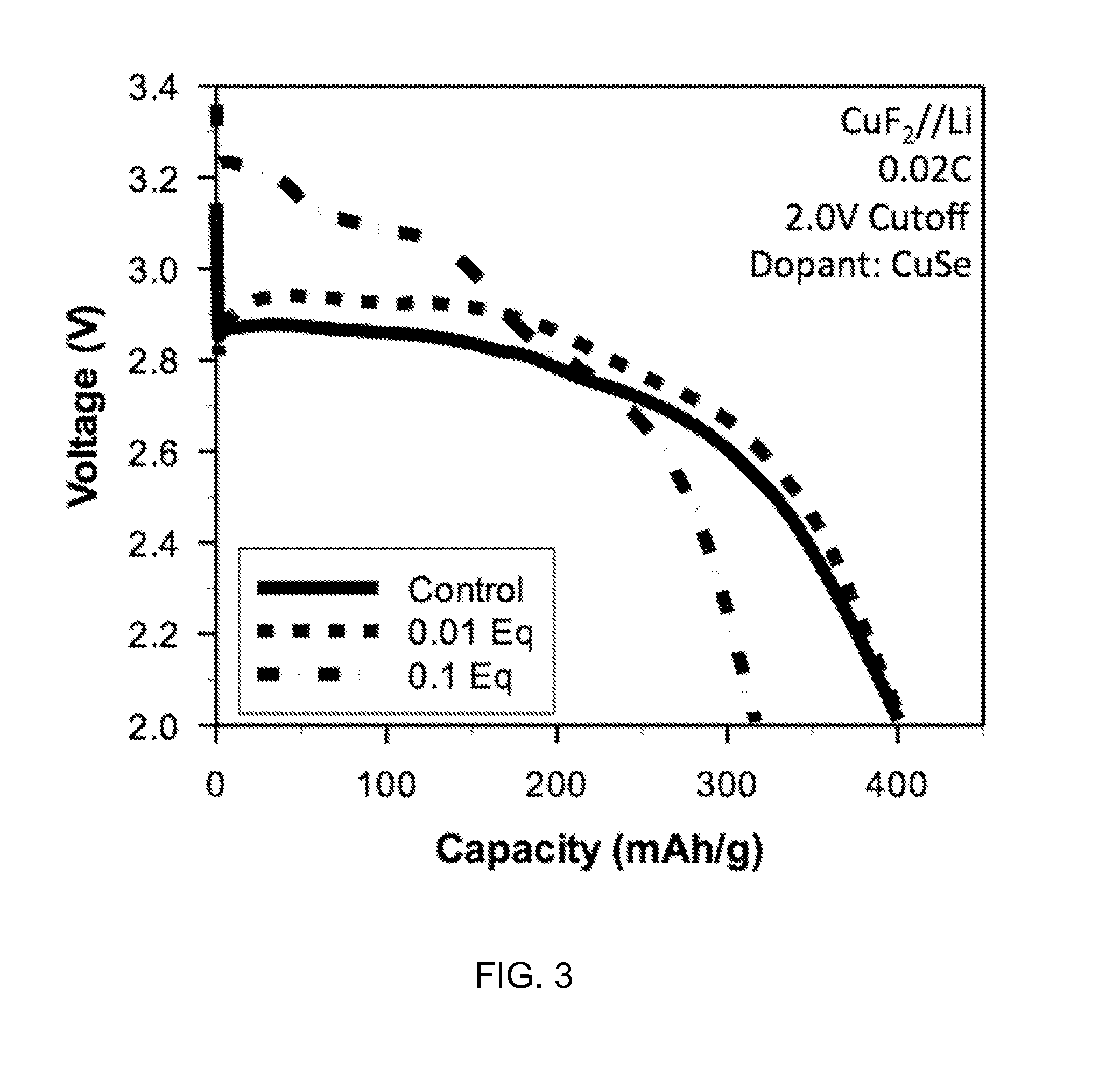
ActiveUS20060019163A1High specific capacityHigh discharge rateSecondary cellsPositive electrodesCopper fluorideEngineering
The present invention relates to primary and secondary electrochemical energy storage systems, particularly to such systems as battery cells, which use materials that take up and release ions as a means of storing and supplying electrical energy.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
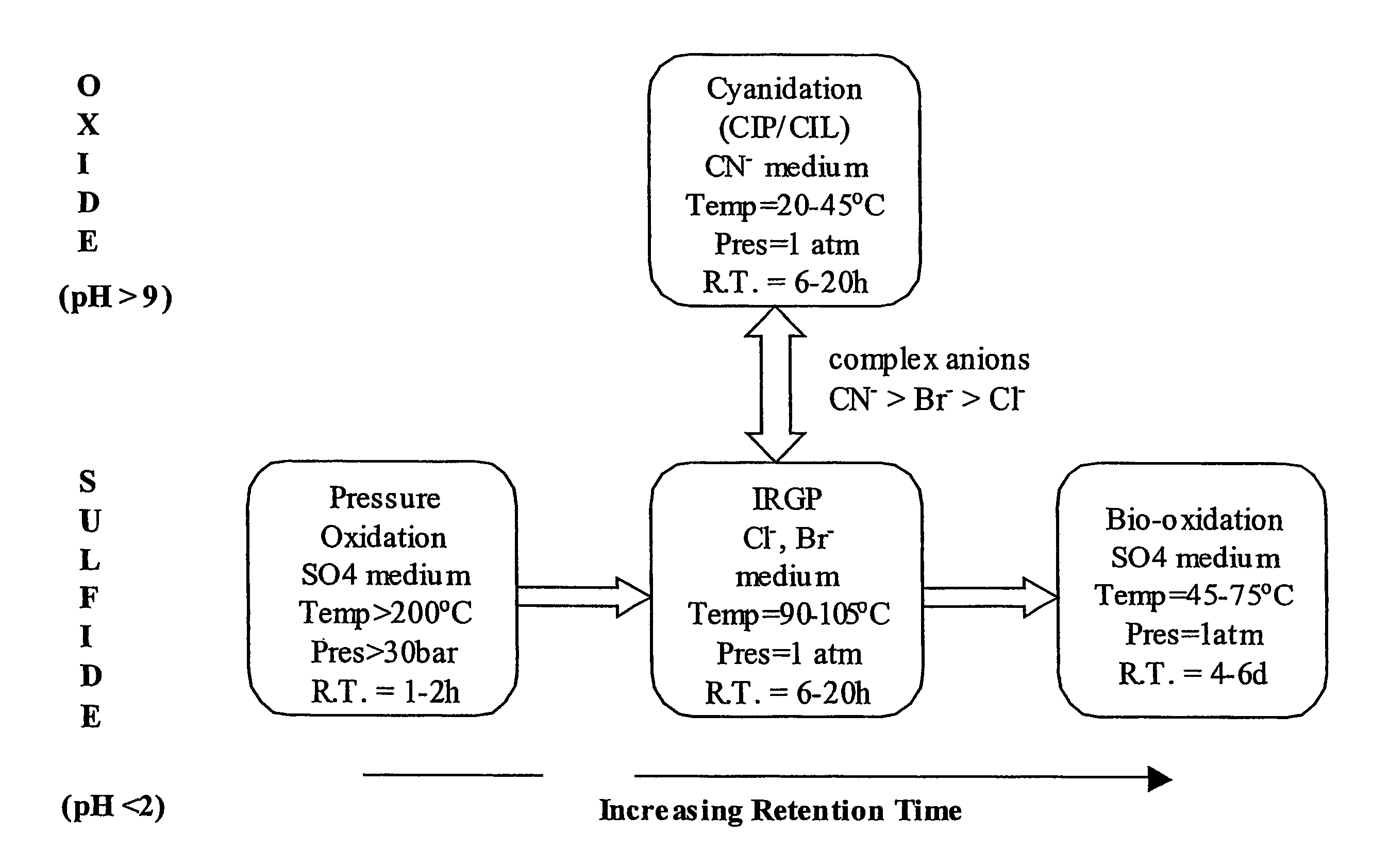
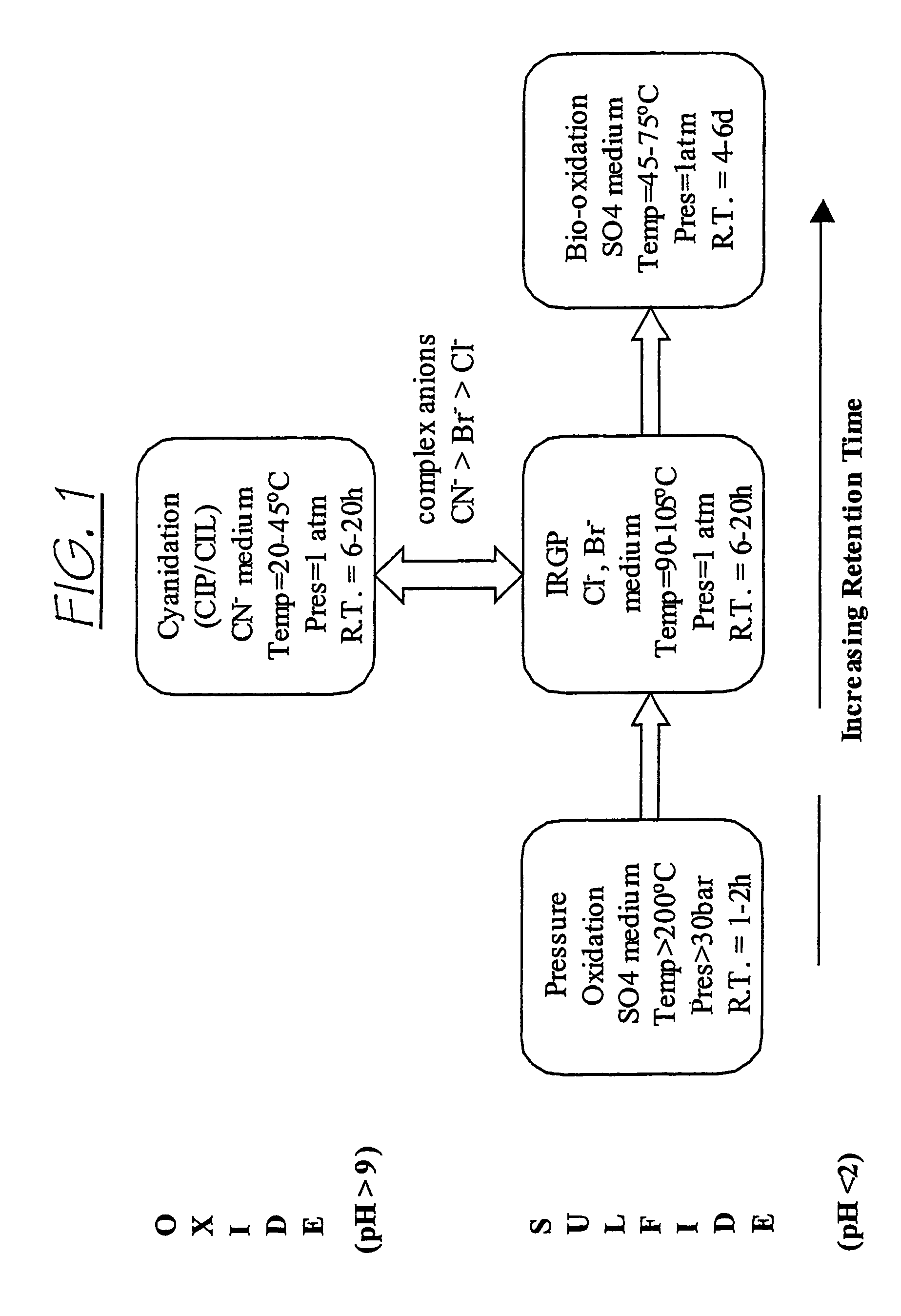
Recovering metals from sulfidic materials
InactiveUS20070014709A1Facilitate precious metal dissolution precious metalFacilitate precious metal subsequent precious metal recoveryPhotography auxillary processesSolvent extractionOxidation stateSulfide
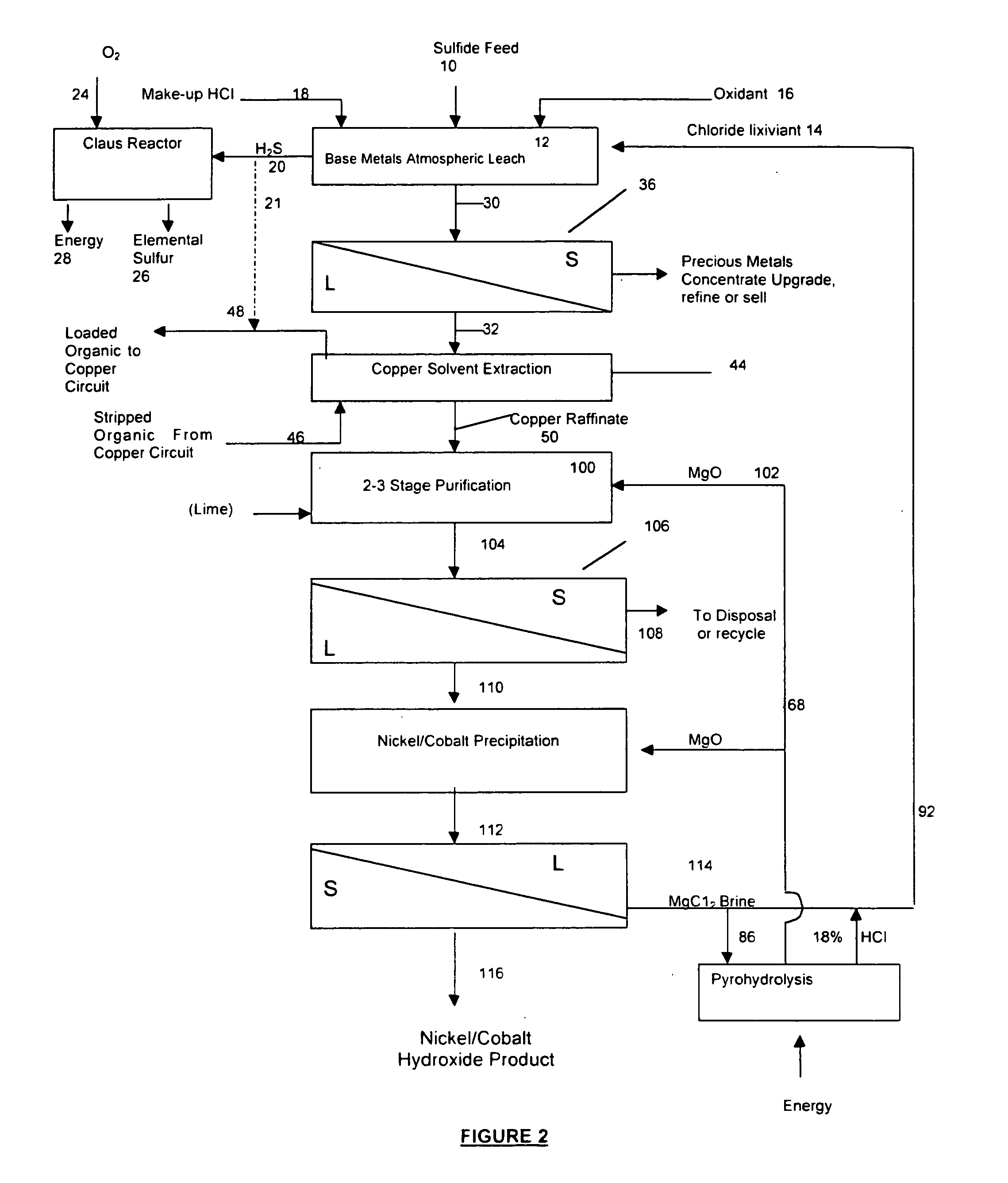
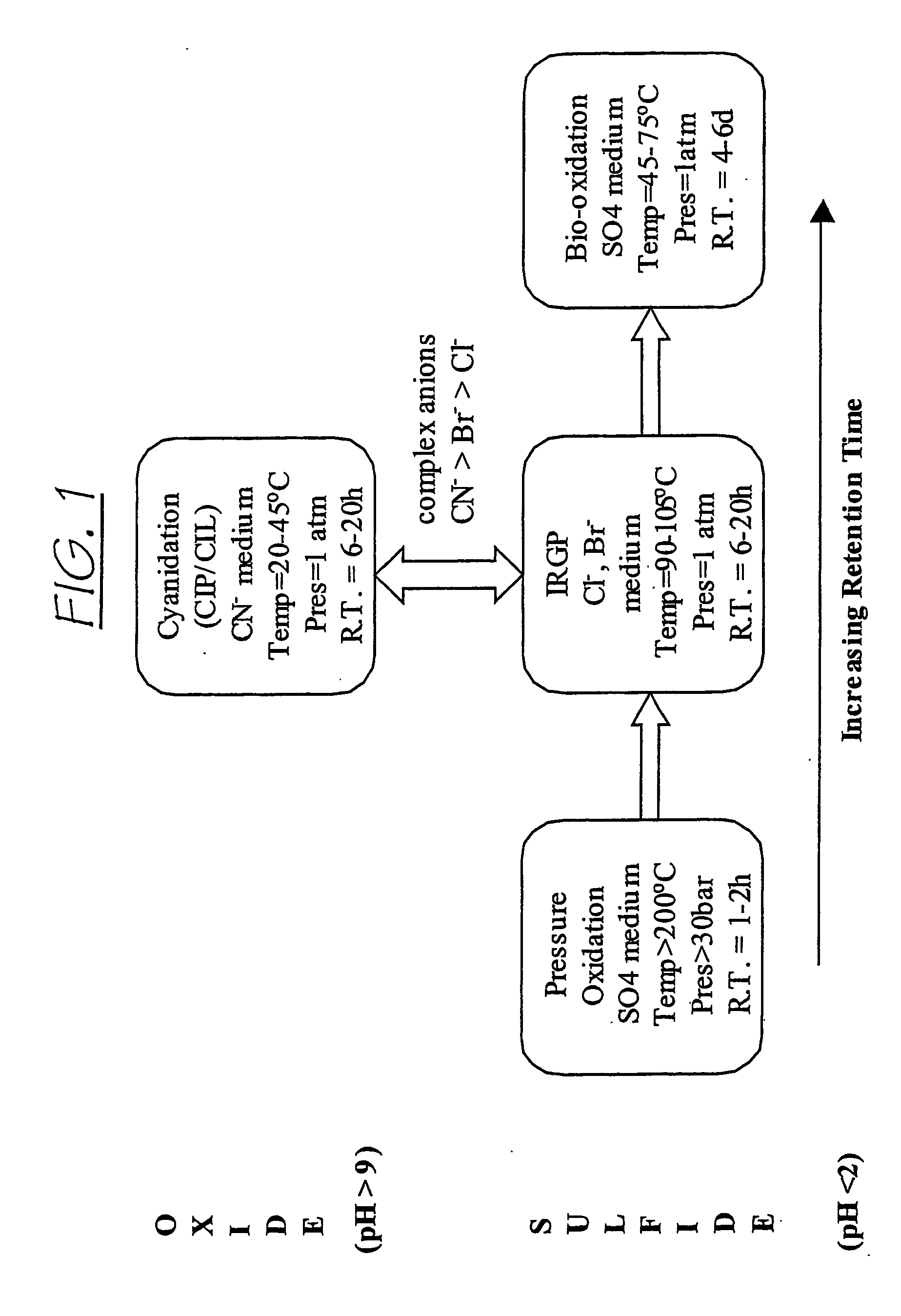
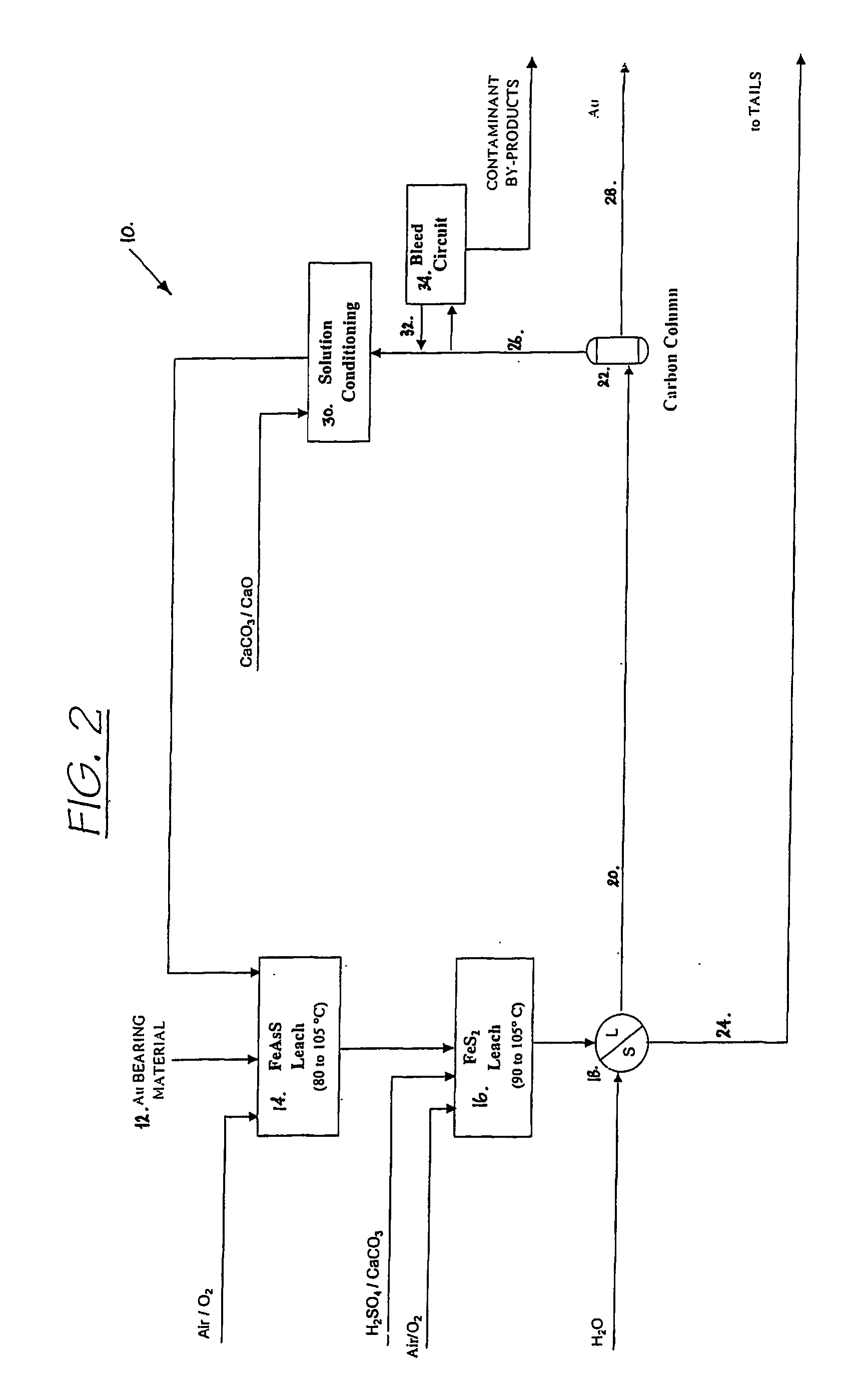
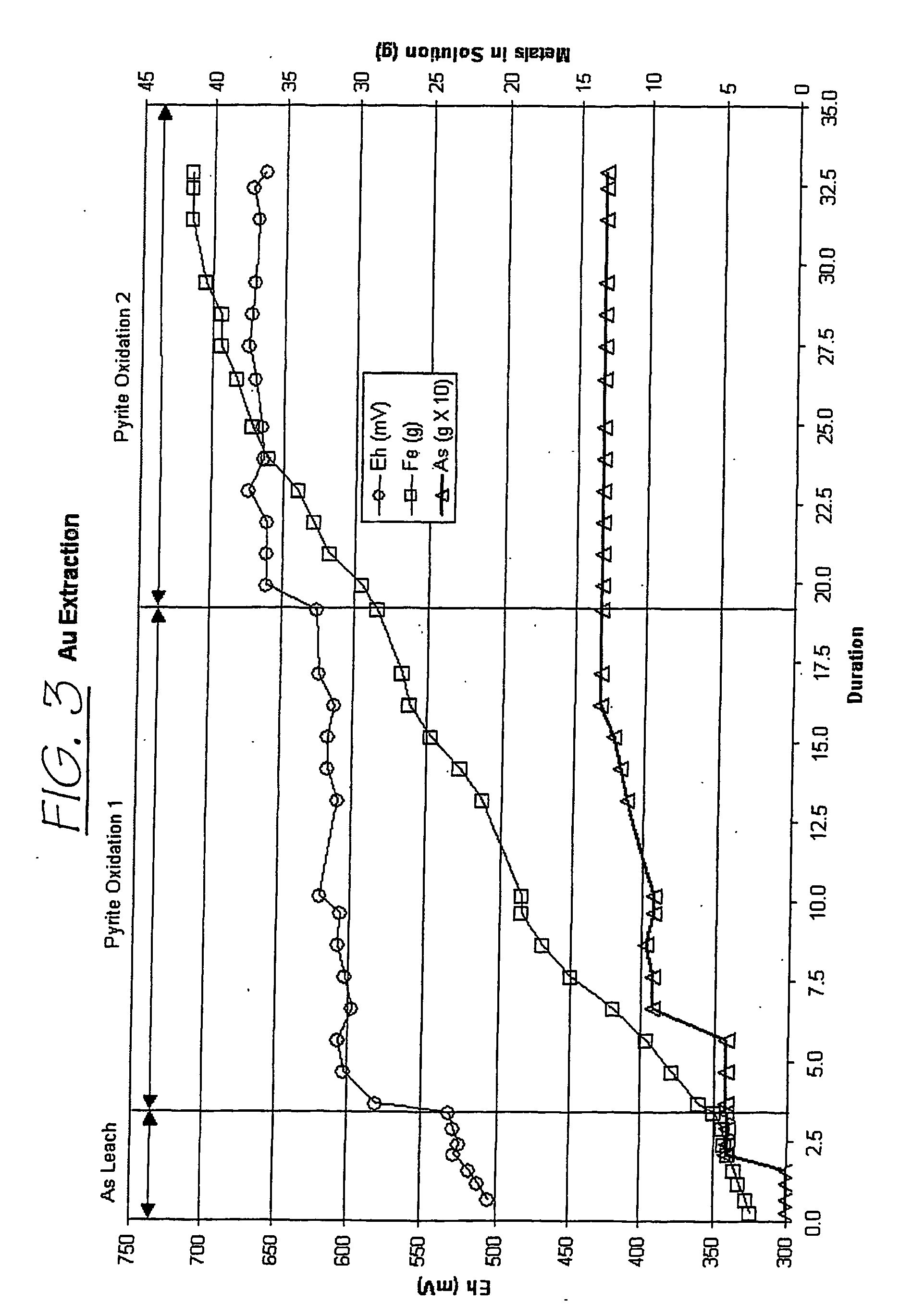
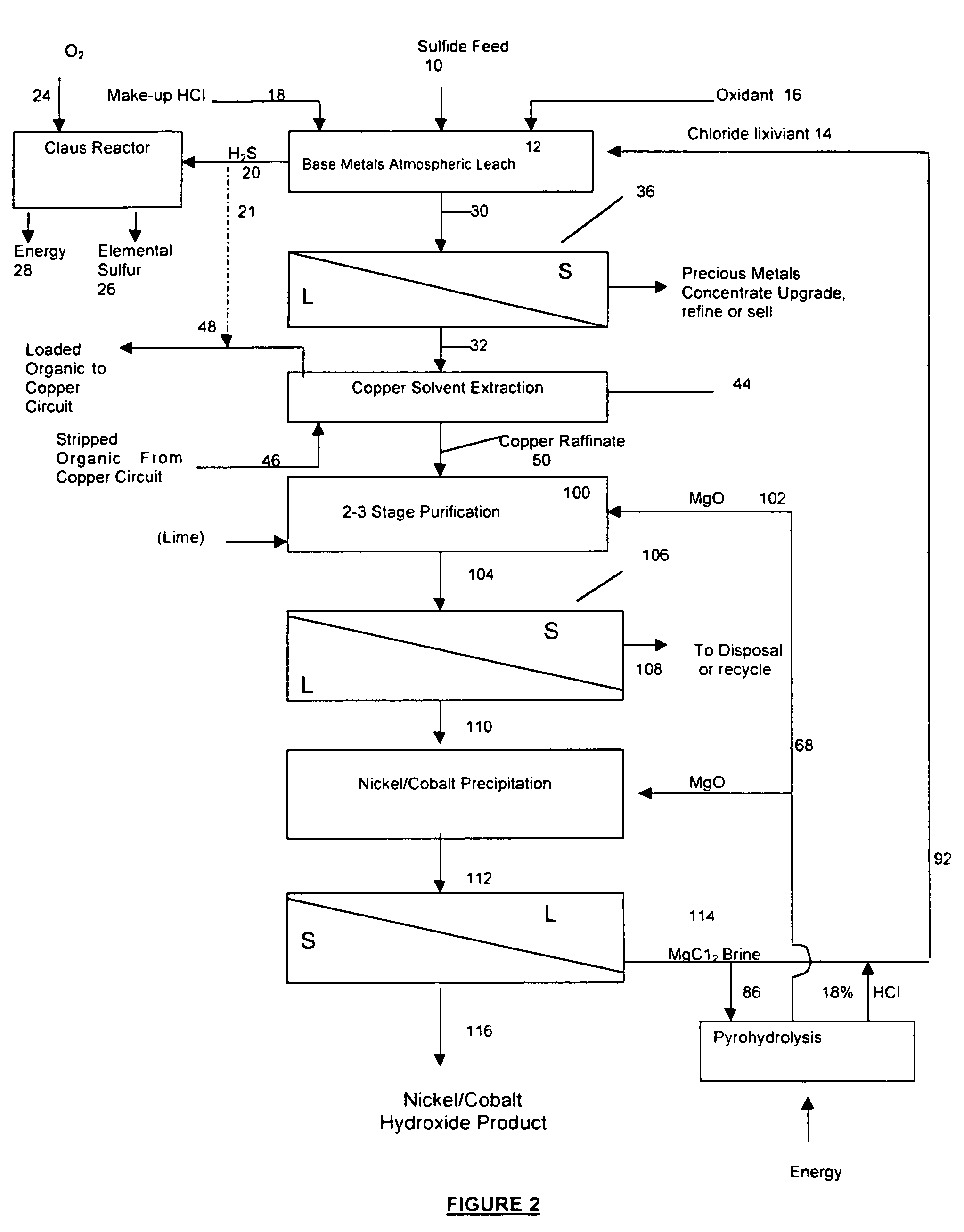
A process for recovering a precious metal from a sulfidic material comprises the steps of preparing an acidic aqueous halide solution having an oxidation potential sufficient to oxidise the sulfidic material and render the precious metal soluble in the solution, adding the material to the acidic aqueous halide solution so that the sulfidic material is oxidised and the precious metal is solubilised and separating the precious metal from the oxidised sulfidic material. In addition, a process for removing a contaminant from a contaminated sulfidic material comprises the steps of mixing the material in an aqueous solution wherein a multi-valent species of a relatively high oxidation state oxidises the contaminant to render it soluble in the solution, produces a contaminant refined material, and is reduced to a relatively lower oxidation state; and removing the contaminant from the solution whilst regenerating the multi-valent species to its relatively high oxidation state.
Owner:INTEC INT PROJECTS
Hydrometallurgical process for the treatment of metal-bearing sulfide mineral concentrates
InactiveUS20070098609A1Improve efficiencyReduce the amount requiredSolvent extractionGold compoundsAmmonium compoundsMetallic sulfide
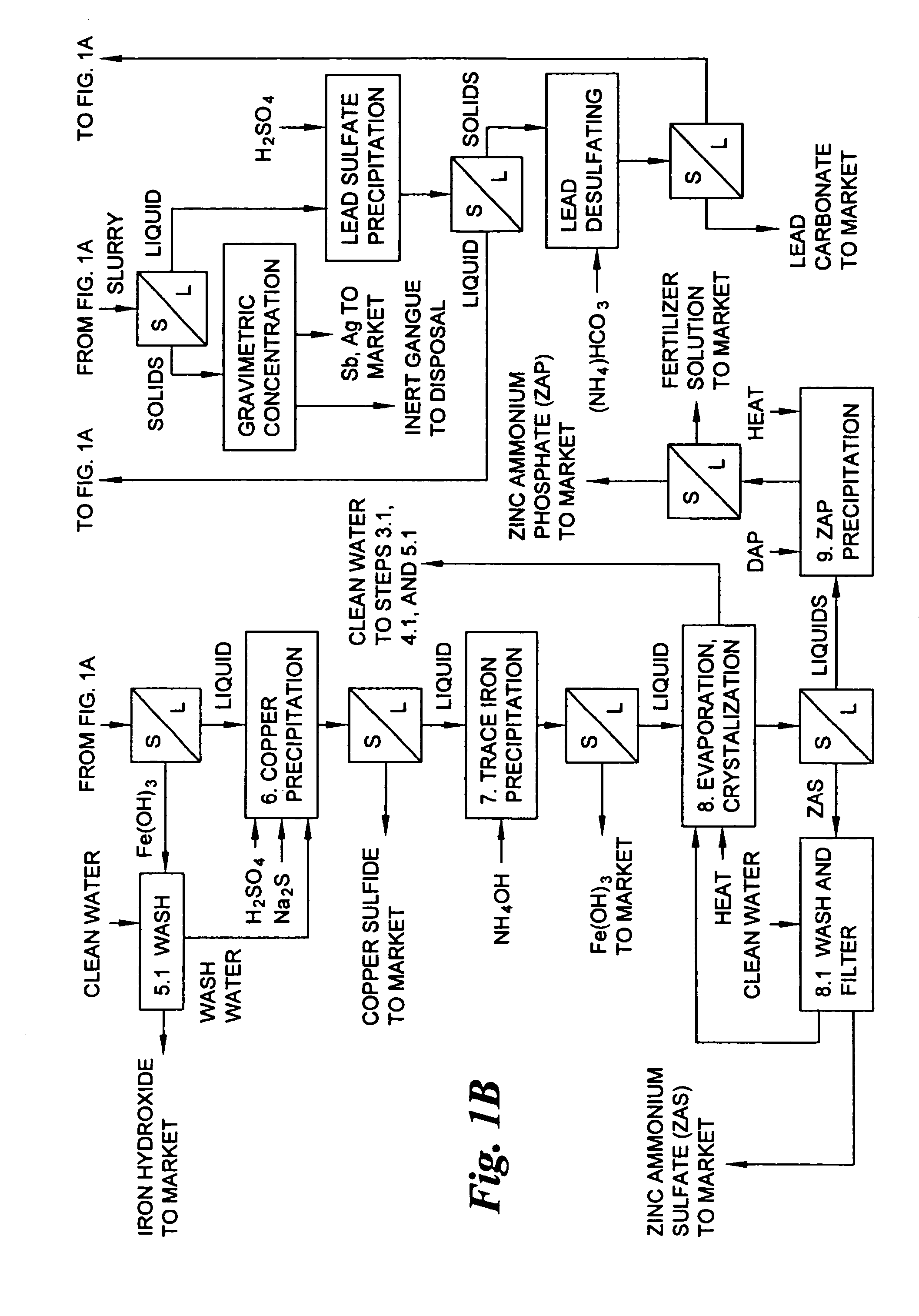
A hydrometallurgical process for the treatment of complex silver-bearing sulfide ores and concentrates that recovers substantially all silver, lead, antimony, zinc, copper and sulfur, along with the chemical reagents utilized during the process. Finely ground ores and concentrates are leached under heat and pressure with water, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, oxygen, and a catalyst, and are further treated to recover silver in the form of silver chloride; iron in the form of iron hydroxide; copper and all traces of soluble toxic metals as sulfides; zinc as zinc ammonium sulfate and specifically nitric acid, sulfuric acid, oxygen, ammonia, and ammonium compounds as valuable fertilizer products.
Owner:ROYAL SILVER PANAMA
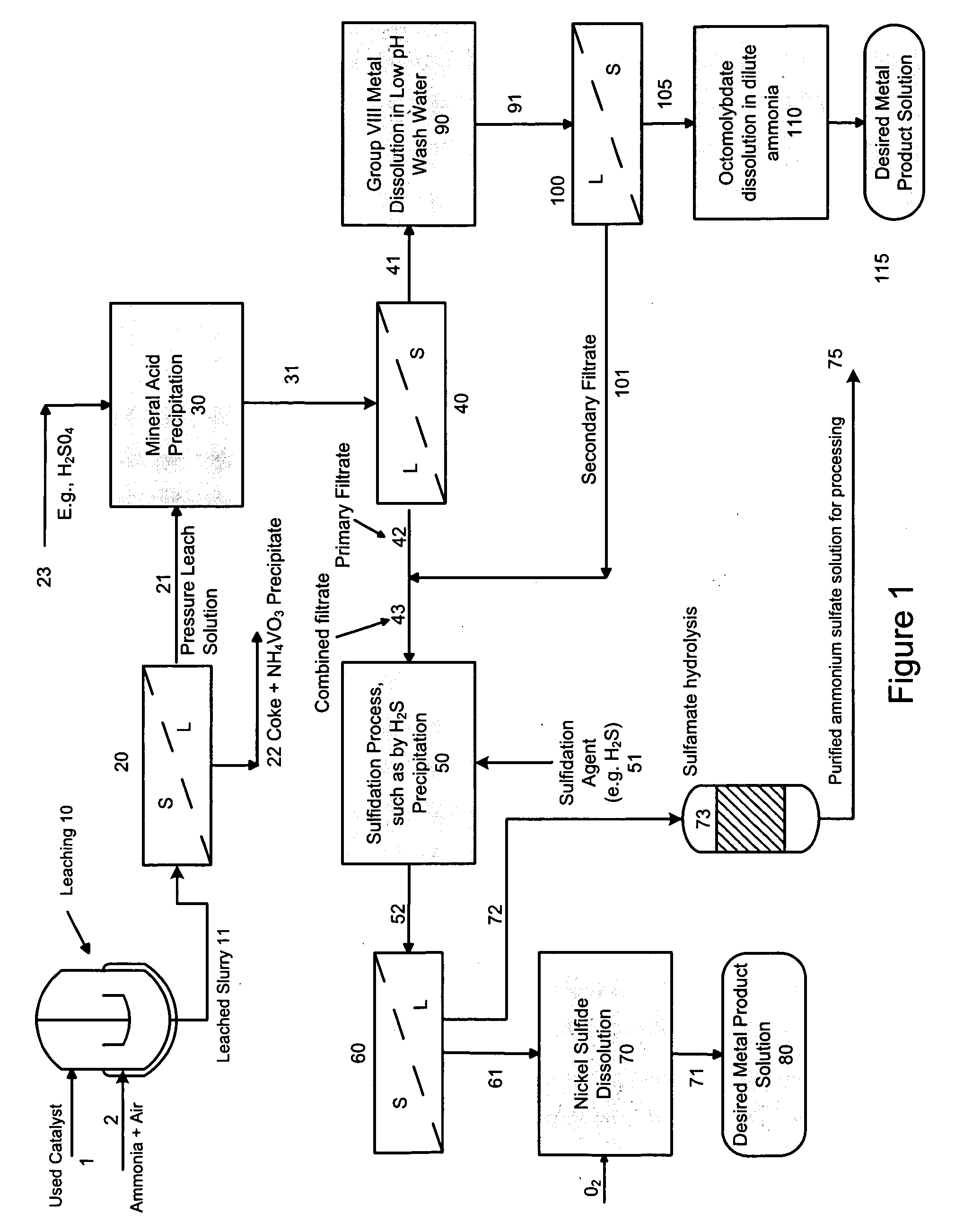
Process for separating and recovering base metals from used hydroprocessing catalyst
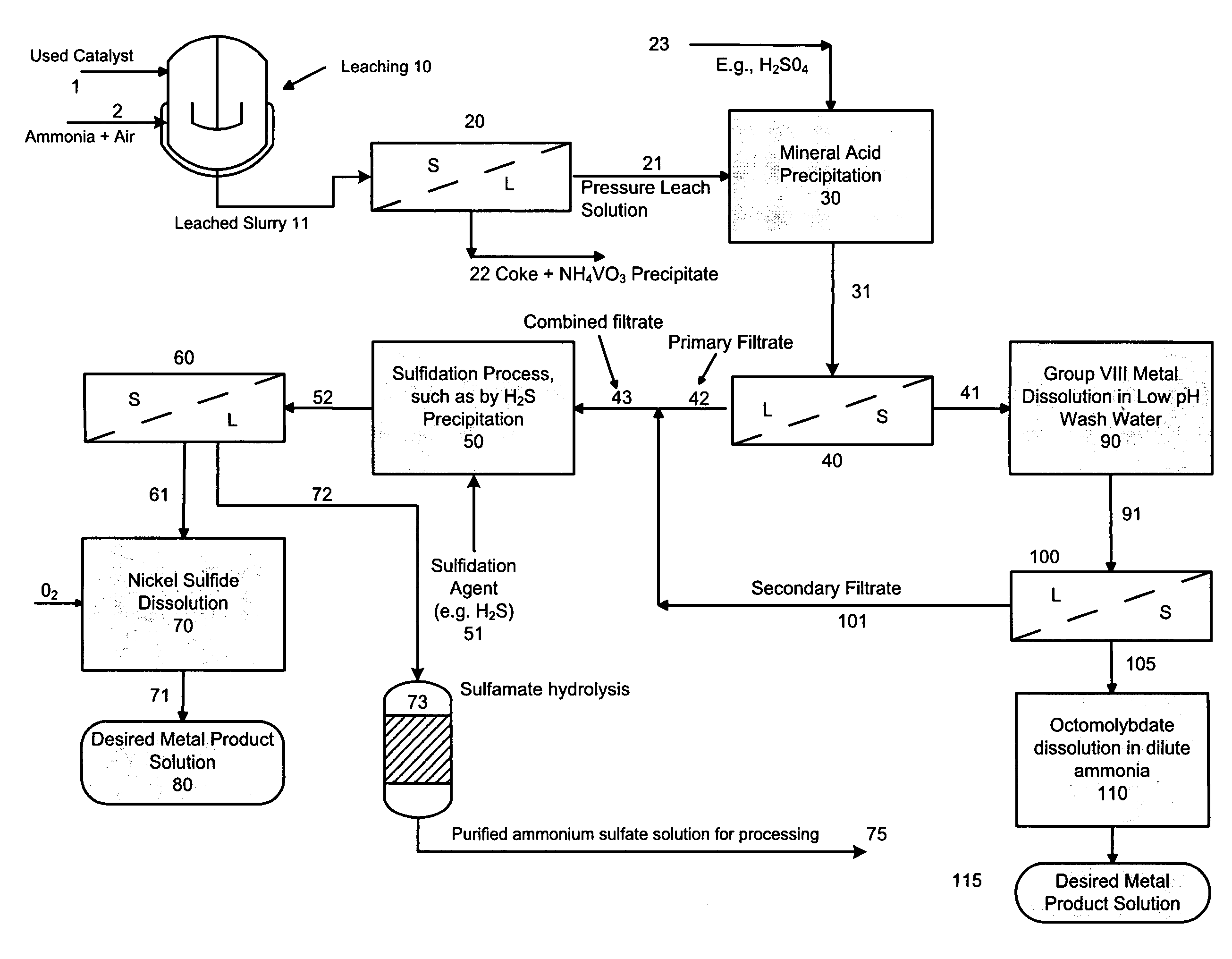
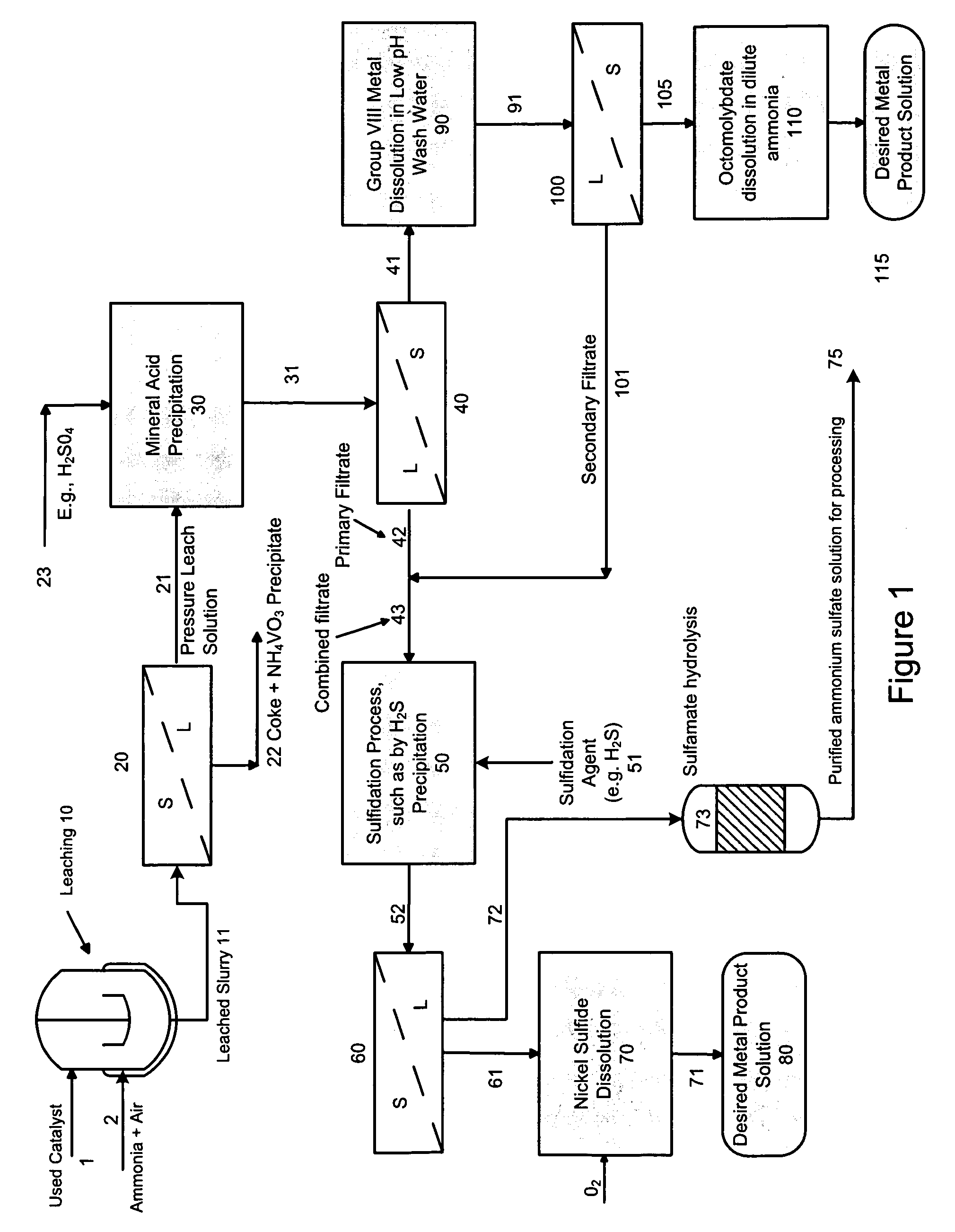
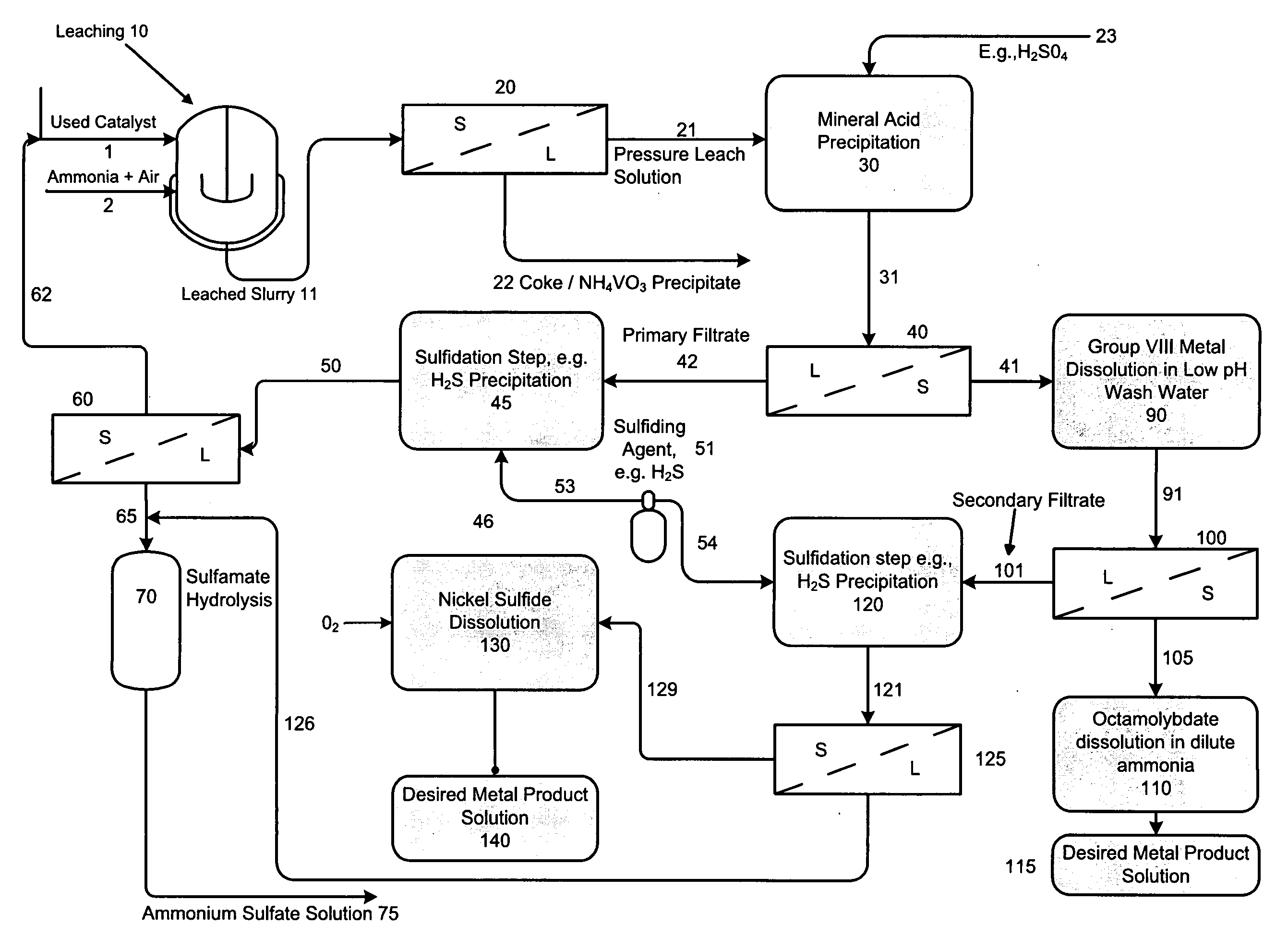
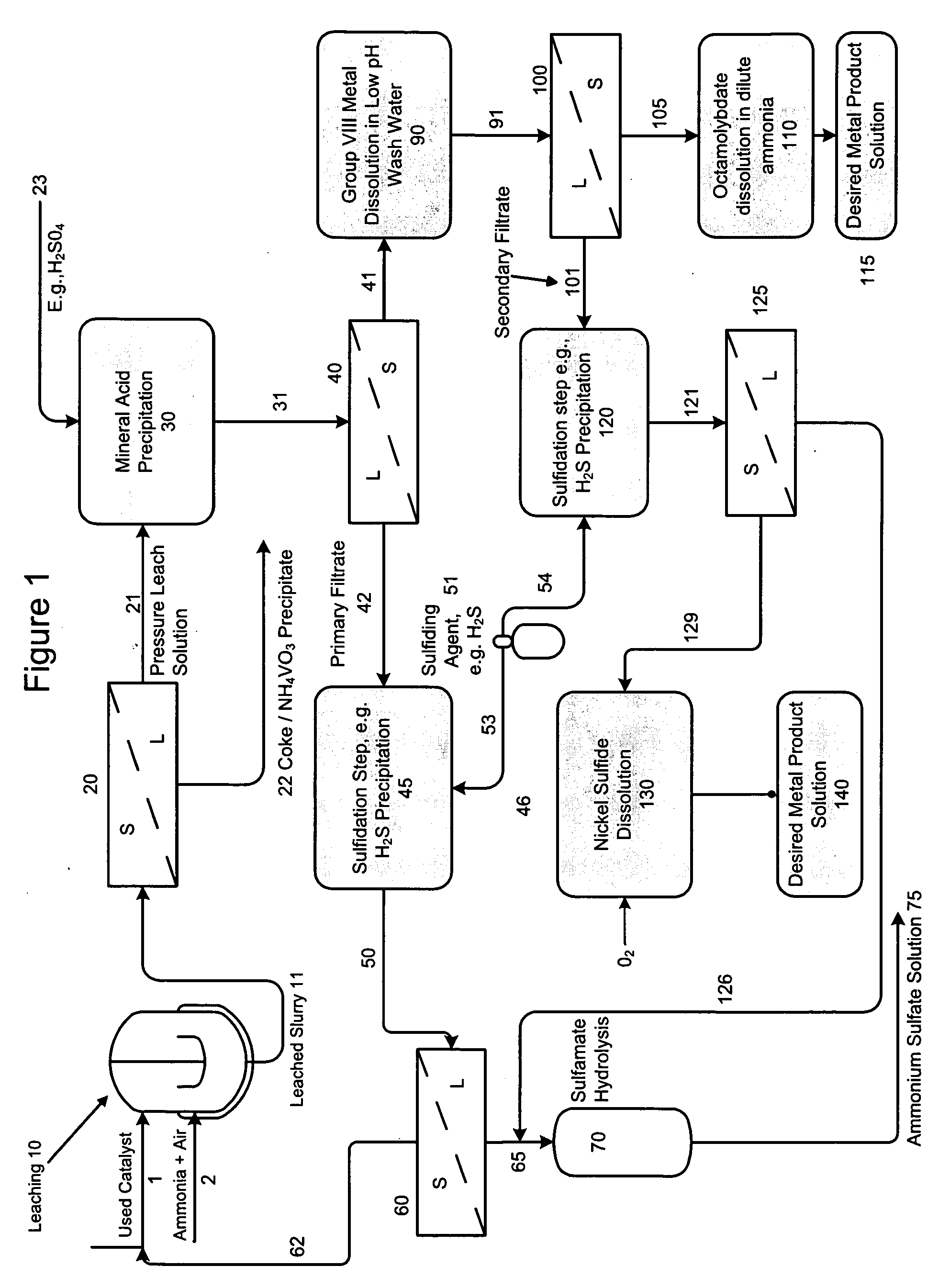
A method is disclosed for separating and recovering base metals from a used hydroprocessing catalyst originating from Group VIB and Group VIII metals and containing at least a Group VB metal. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of: contacting the used catalyst with an ammonia leaching solution under conditions sufficient to dissolve the group VIB metal and the Group VIII metal into the leaching solution; forming a leached slurry containing at least a group VIB metal complex and at least a group VIII metal complex, ammonium sulfate and a solid residue containing at least a Group VB metal complex and coke; separating and removing from the leached slurry the solid residue and coke; precipitating from the remaining solution at least a portion of the Group VIB metal complex and at least a portion of the Group VIII metal complex by controlling the pH to form a liquid material substantially free of Group VB, Group VIB and Group VIII metals and another solid material comprising substantially Group VIB and Group VIII metal complexes. Said solid material is further processed by dissolution, means of separation, further means of precipitation and oxidative dissolution to produce, separately, a Group VIB metal product solution, a Group VIII metal product solution and a purified ammonium sulfate product solution.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Process for separating and recovering base metals from used hydroprocessing catalyst
A method is disclosed for separating and recovering base metals from a used hydroprocessing catalyst originating from Group VIB and Group VIII metals and containing at least a Group VB metal. In one embodiment, the used catalyst is contacted with an ammonia leaching solution to dissolve and separate the Group VIB and VIII metals from the Group VB metal complex and coke associated with the used catalyst. The resulting Group VIB and VIII metal containing solution is processed through at least two additional precipitation and liquid / solid separation steps to produce, in separate processing streams, a Group VIB metal product solution (such as ammonium molybdate) and a Group VIII metal product solution (such as nickel sulfate). Additionally, two separate filtrate streams are generated from liquid-solid separation steps, which filtrate streams are combined and subjected to hydrolysis and oxidation (oxydrolysis) to generate a purified ammonium sulfate solution for further processing, such as for fertilizer.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
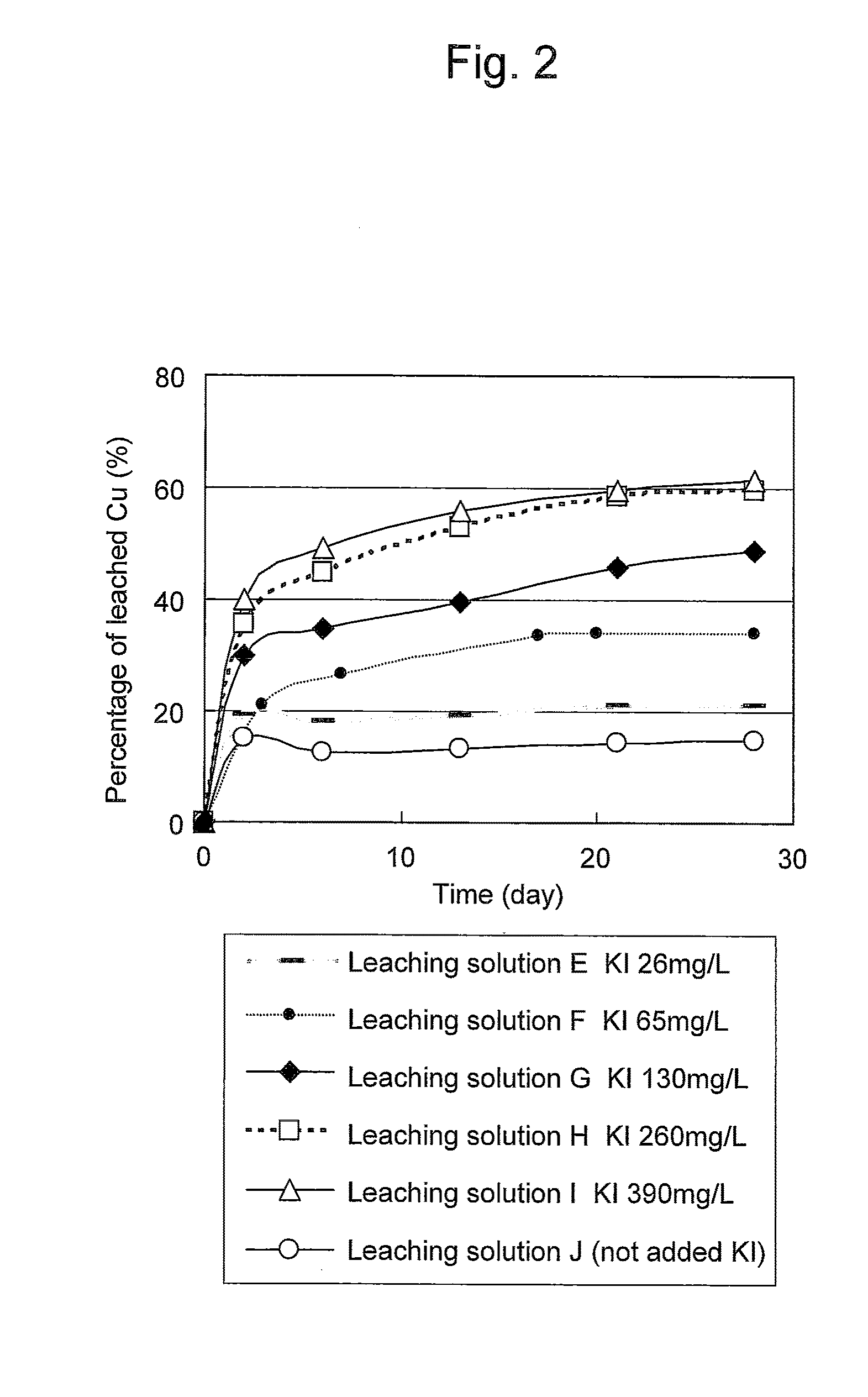
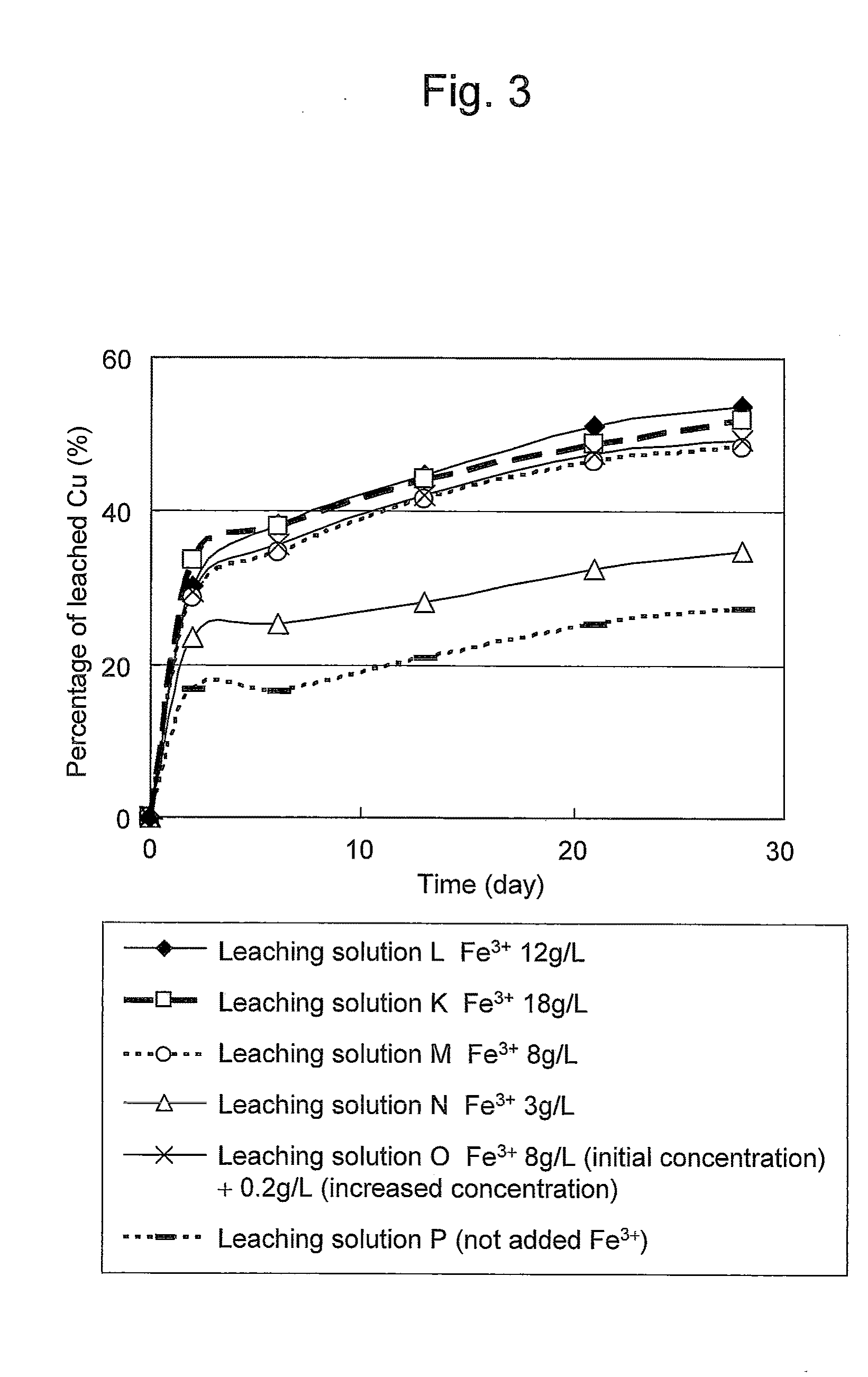
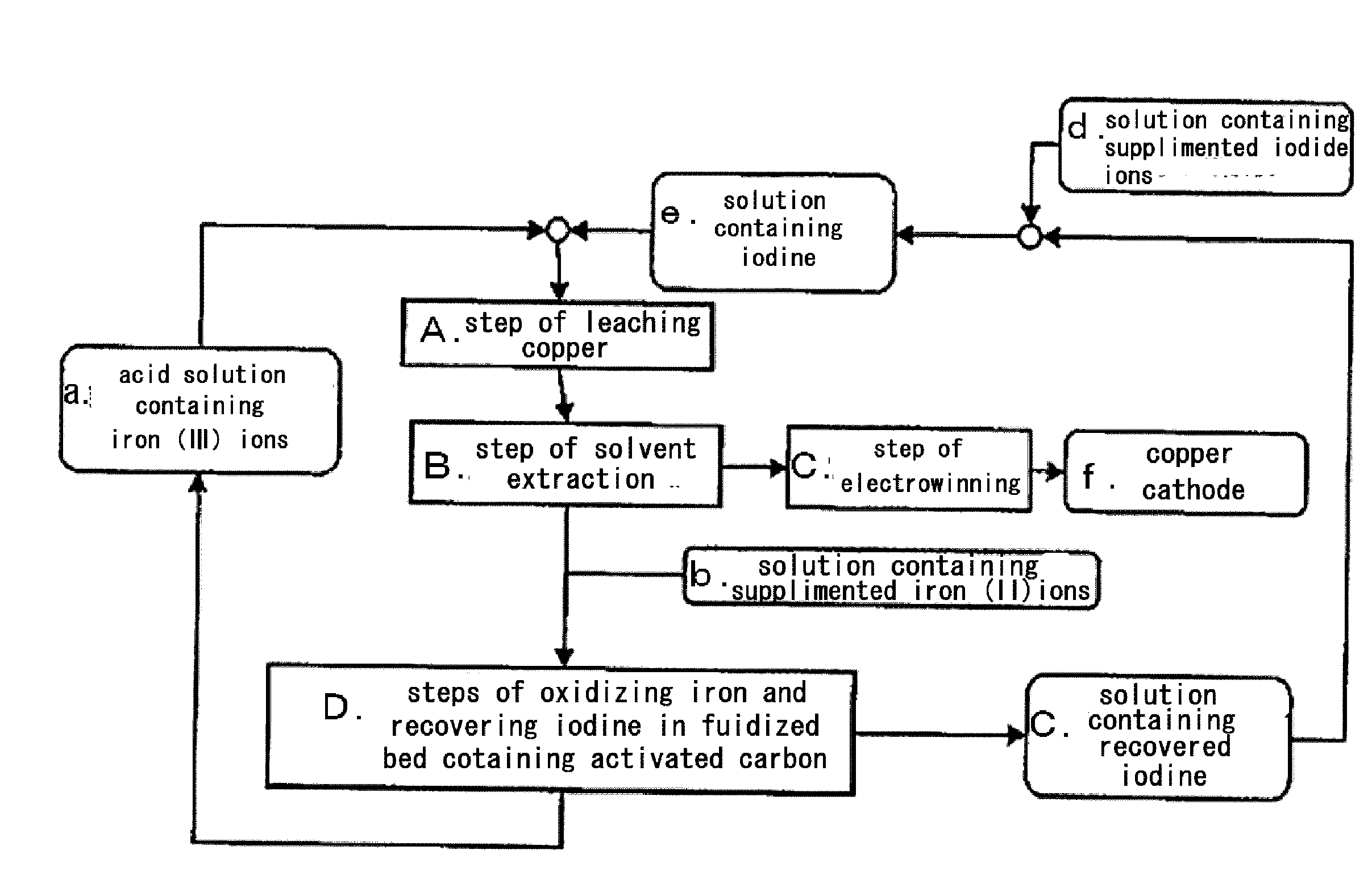
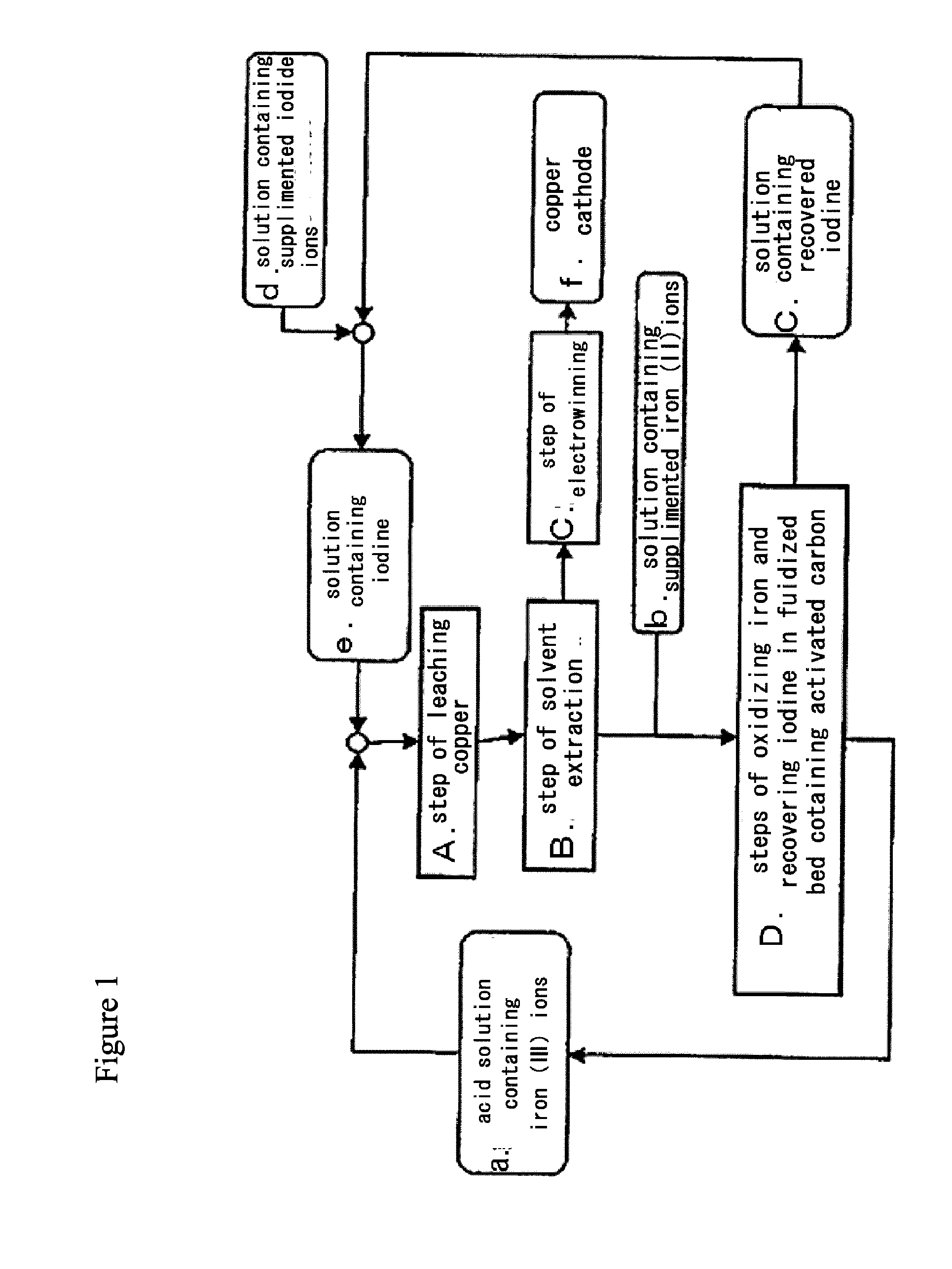
Method of leaching copper sulfide ore with the use of iodine
ActiveUS20100018349A1Efficient leachingEfficient executionSolvent extractionGold compoundsPregnant leach solutionChalcopyrite
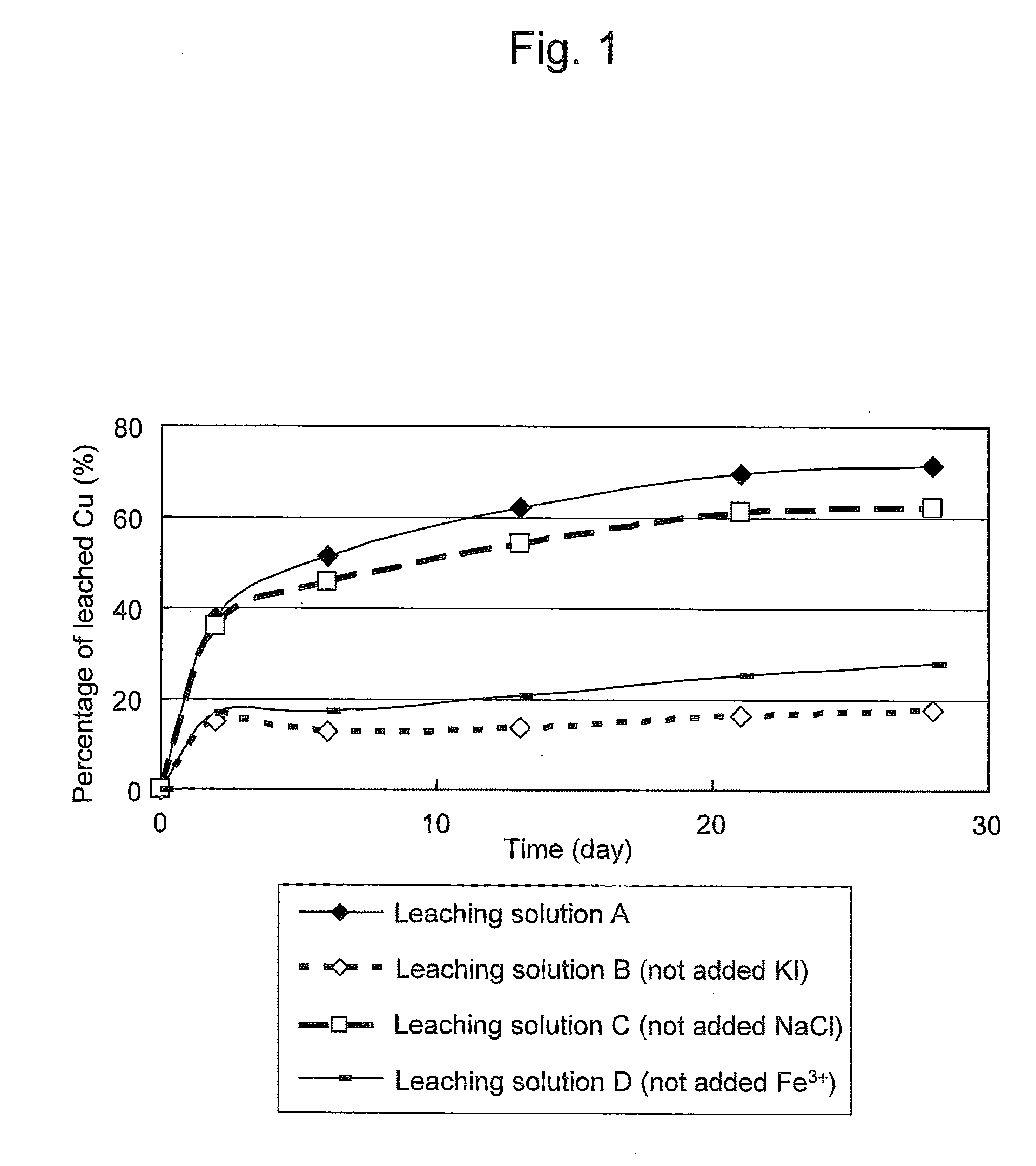
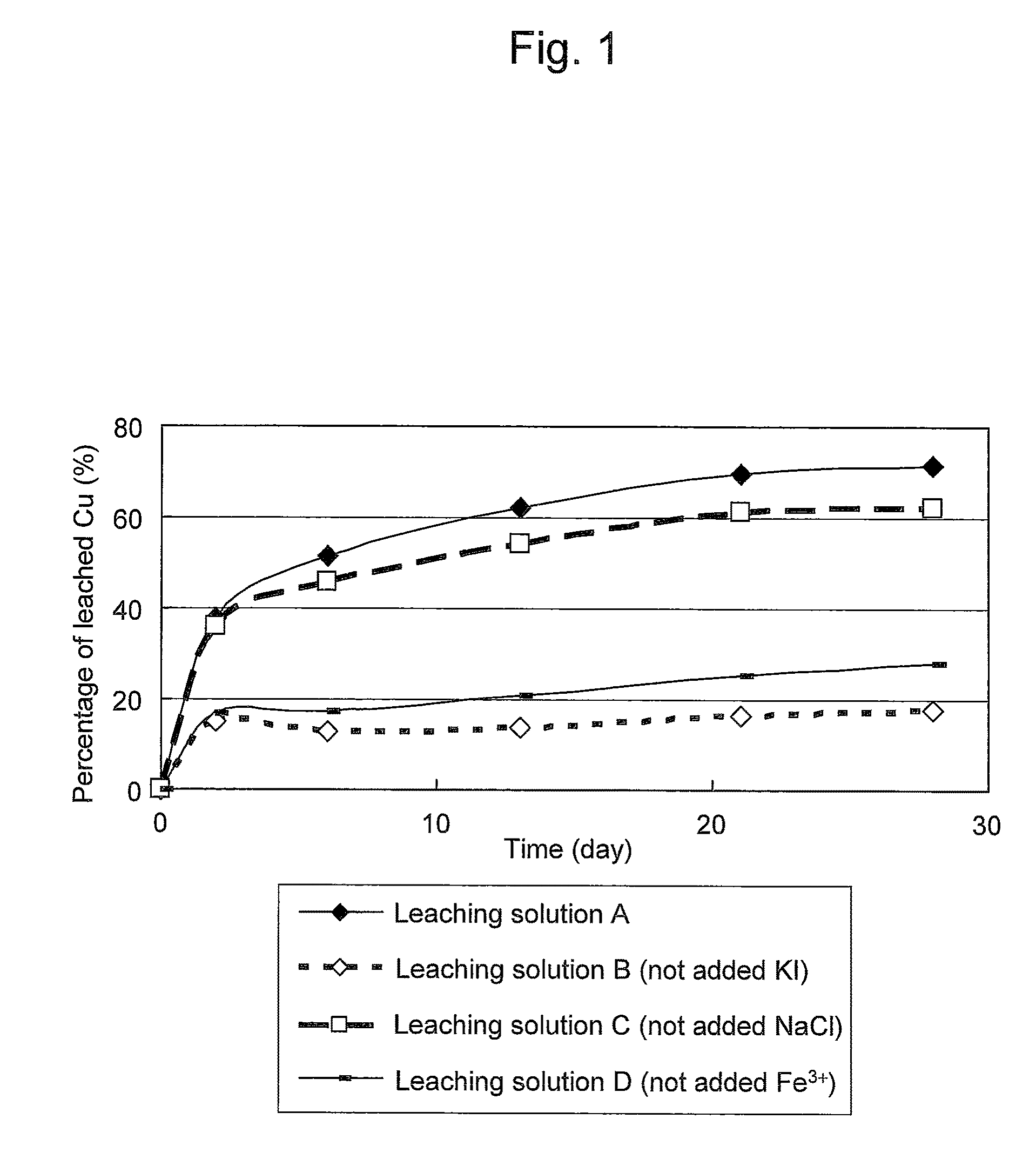
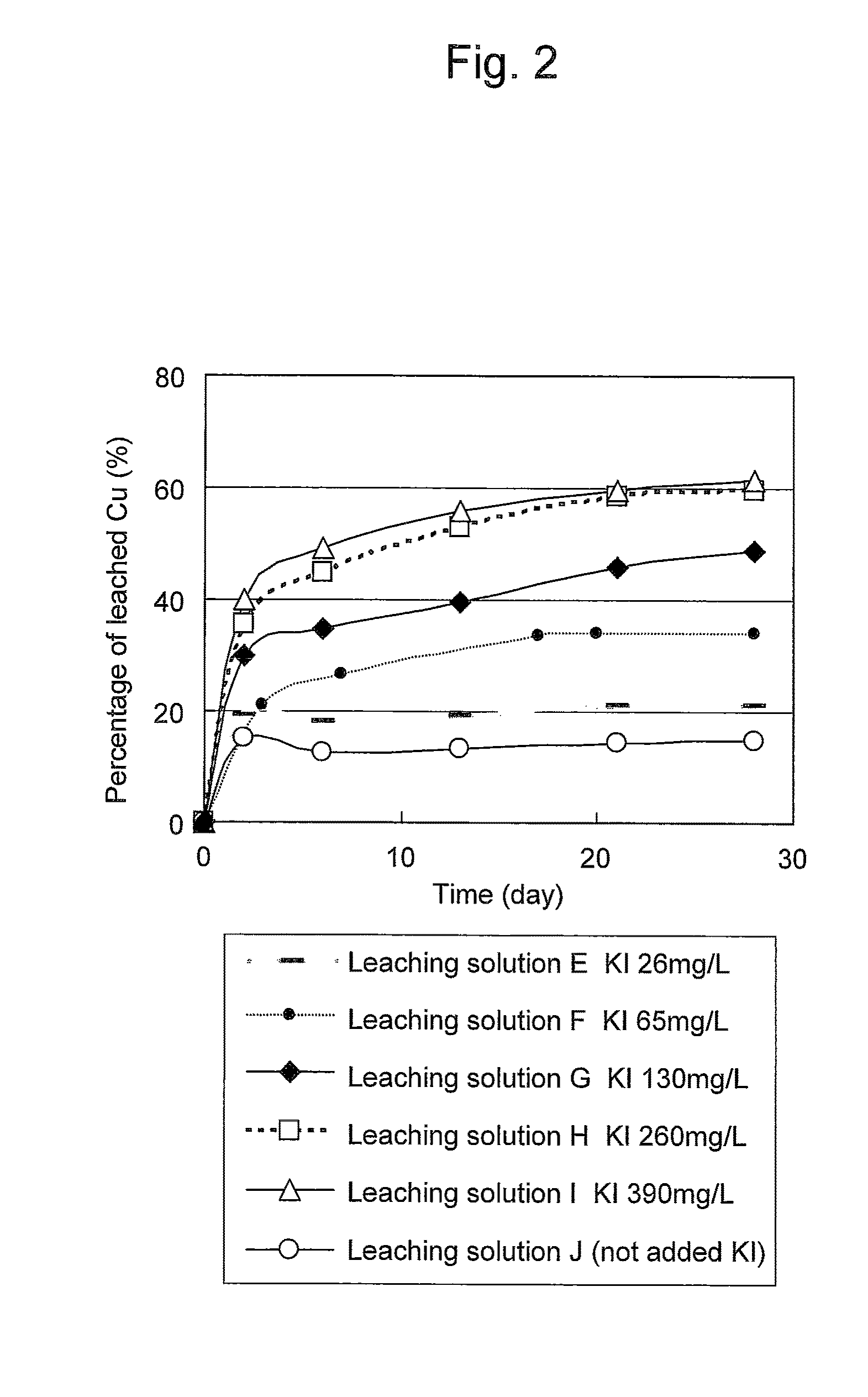
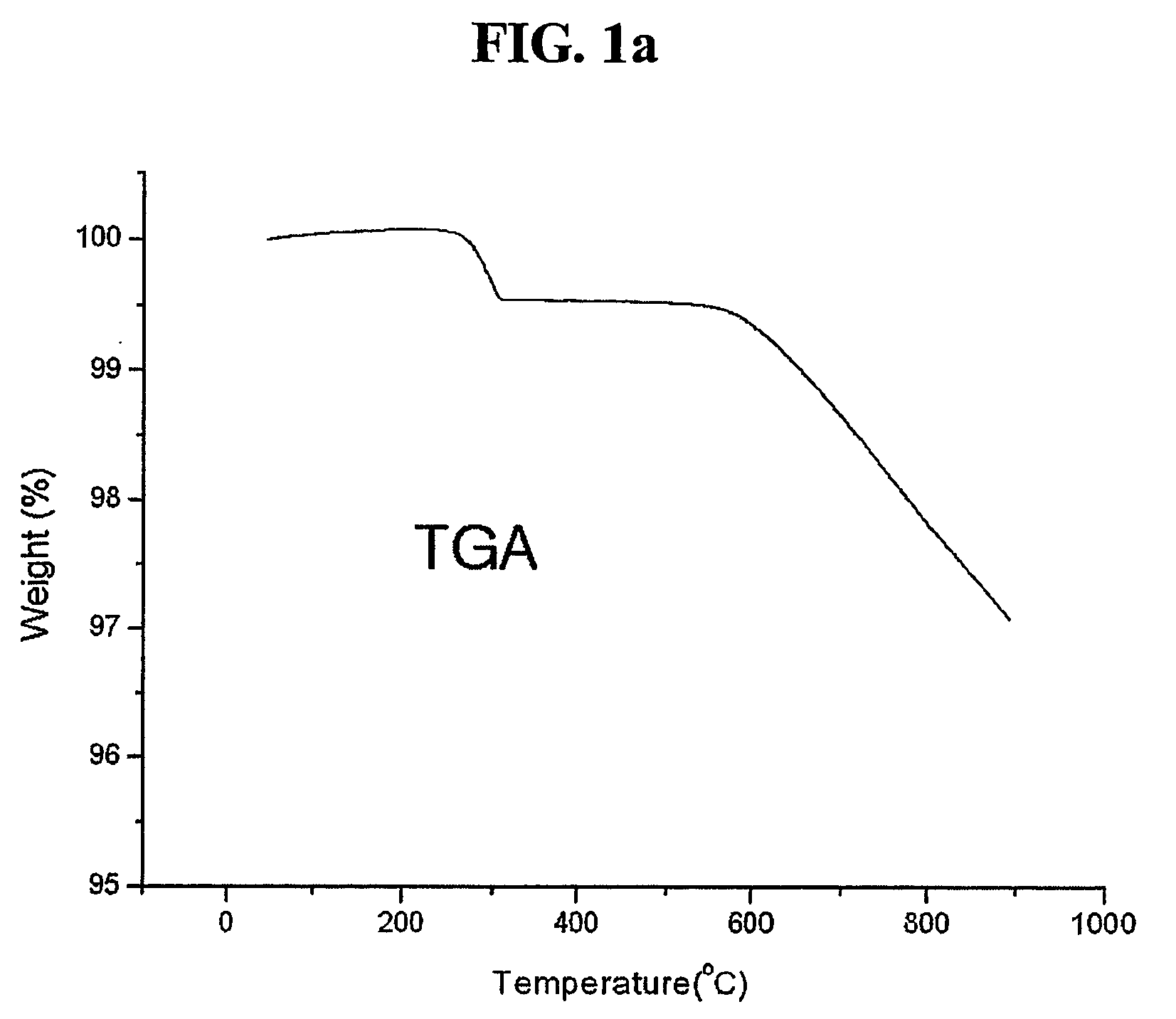
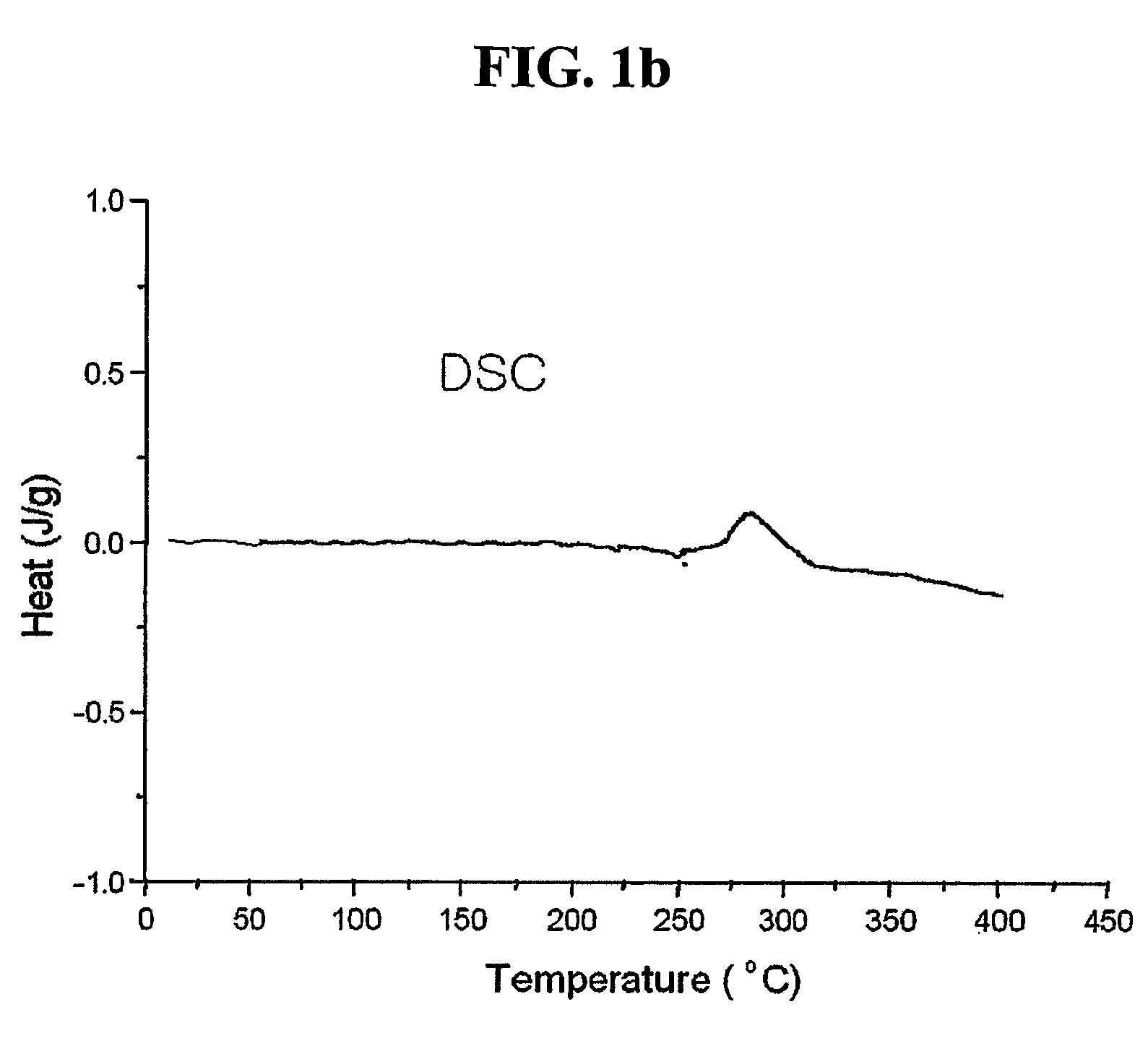
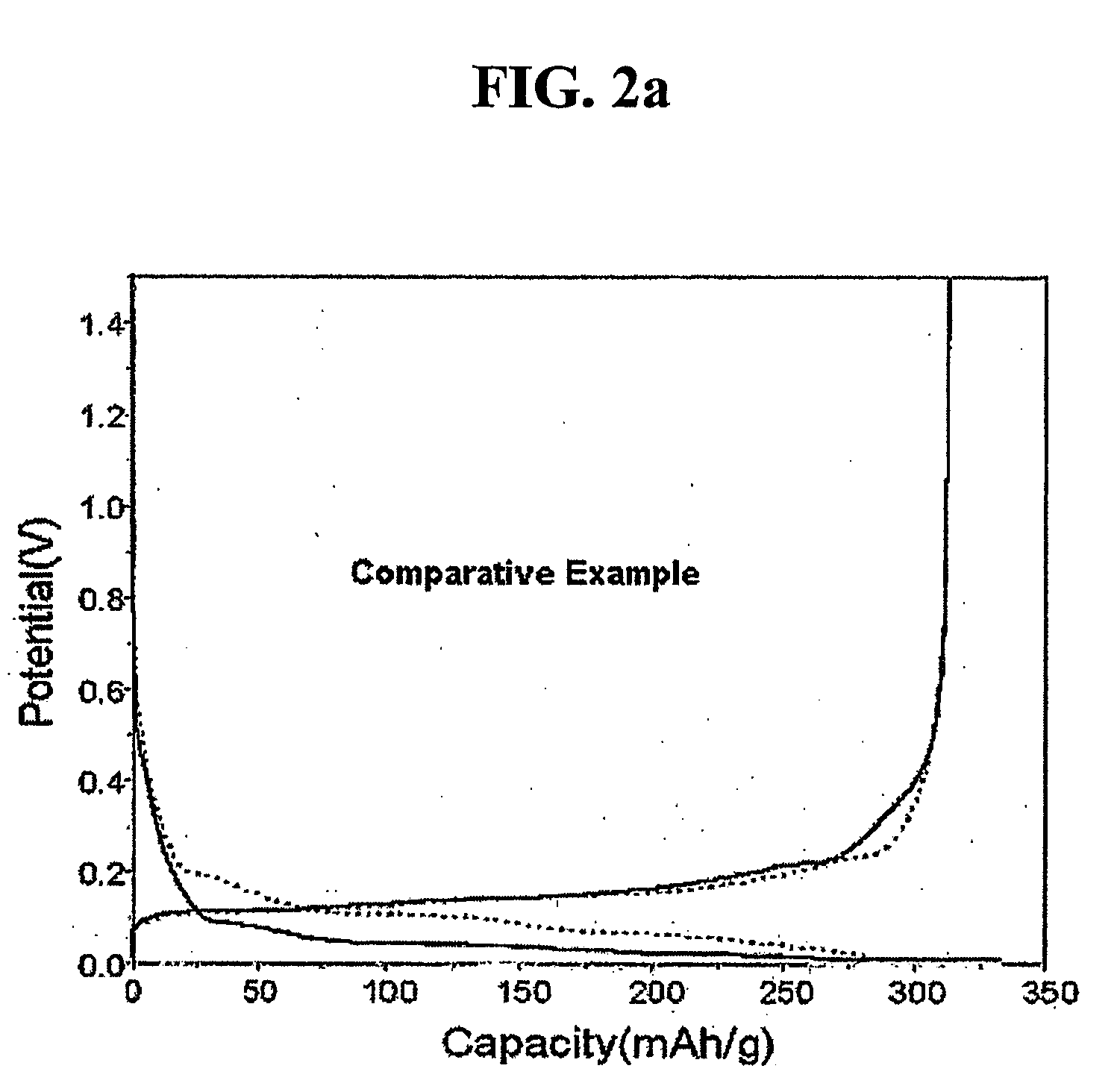
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of efficiently leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore containing chalcopyrite or enargite as a main constituent under versatile conditions for actual operation.A method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising using, as a leaching solution, a sulfuric acid solution containing iodide ions and ferric (III) ions in an excessive amount relative to the iodide ions and leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore; or a method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore with the use of a leaching solution further containing water-soluble ligands such as chloride ions that can stabilize ferric (III) ions in addition to the above components, is provided.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Petroleum pitch-based carbon foam
InactiveUS20030071384A1Useful and reliableEasy to implementPigmenting treatmentHarvestersLow densityNet shape
Petroleum or coal tar pitch-based cellular or porous products having a density of preferably between about 0.1 g / cm3 and about 0.8 g / cm3 are produced by the controlled heating of mesophase carbon materials derived from coal tar or petroleum pitch having a softening point in excess of about 300° C. and preferably between about 300 and about 400° C. in a "mold" and under a non-oxidizing atmosphere. The porous product thereby produced, preferably as a net shape or near net shape, can be machined, adhered and otherwise fabricated to produce a wide variety of low cost, low density products.
Owner:TOUCHSTONE RES LAB
Process for separating and recovering base metals from used hydroprocessing catalyst
A method is disclosed for separating and recovering base metals from a used hydroprocessing catalyst originating from Group VIB and Group VIII metals and containing at least a Group VB metal. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of: contacting the used catalyst with an ammonia leaching solution under conditions sufficient to dissolve the group VIB metal and the Group VIII metal into the leaching solution; forming a leached slurry containing at least a group VIB metal complex and at least a group VIII metal complex, ammonium sulfate and a solid residue containing at least a Group VB metal complex and coke; separating and removing from the leached slurry the solid residue and coke; precipitating from the remaining solution at least a portion of the Group VIB metal complex and at least a portion of the Group VIII metal complex by controlling the pH to form a liquid material substantially free of Group VB, Group VIB and Group VIII metals and another solid material comprising substantially Group VIB and Group VIII metal complexes. Said solid material is further processed by dissolution, means of separation, further means of precipitation and oxidative dissolution to produce, separately, a Group VIB metal product solution, a Group VIII metal product solution and a purified ammonium sulfate product solution.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Composite nanofiber, composite nanofiber association, complex structure, and production method thereof
InactiveUS20070197708A1Easy to produceEasy to disassembleMaterial nanotechnologySolvent extractionFiberWater insoluble
Owner:KAWAMURA INST OF CHEM RES
Photochromic glass nanoparticles and methods of preparation
InactiveUS6516633B1Material nanotechnologyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsNanoparticleWater soluble
The present invention is directed to microemulsion techniques for rapidly preparing photochromic glass nanoparticles and to the photochromic glass nanoparticles so prepared. More particularly, the method of the invention comprises the combination of two microemulsions, one containing a water-soluble silver salt and a glass precursor and the other containing a halide salt and an initiator for glass formation, which process rapidly yields silver halide particles. This invention gives nanometer-sized silver halide particles embedded in glass, thus providing photochromic glass nanoparticles without further annealing, or at most mild annealing. These nanoparticles are valuable as added components to any macro-material that one might wish to have photochromic properties. The particles would impart photochromism while not affecting the physical properties of the material.
Owner:NANO TEX +1
Chloride Heap Leaching
ActiveUS20090173188A1Lower potentialRaise the potentialSolvent extractionGold compoundsSulfateChloride
A heap leaching method to recover copper from a primary copper sulphide mineral wherein the mineral is leached in an acidic chloride / sulphate solution in the presence of oxygen with the surface potential of the mineral below 600 mV (vs. SHE) to cause dissolution of the copper sulphide.
Owner:CONSOL NOMINEES
Procedure to leach copper concentrates, under pressure and at ambient temperature, by forming a reactive gel in a sulfate-chloride medium
ActiveUS7491372B2Reduce investmentKeep for a long timeSolvent extractionGold compoundsHigh concentrationChemical process
A chemical process to leach copper concentrates in the presence of a concentrated solution of sulfates and chlorides. The process includes forming a high reactivity chemical paste containing a high concentration of ions in the liquid phase of the paste which react with copper ores and forms a series of soluble salts. The salts are extracted by a simple wash. Mixing equipment for handling high viscosity liquids is used. The total mixing time is about 5 minutes, after which the paste is poured into a rectangular mold, of several hundred meters per side, and is left to settle and breathe. During settling, water and sulfuric acid are added at intervals to replace that consumed by the reactions taking place during the aeration, until the reactions have virtually end. This treatment results in a dry, very resistant mass, containing the copper extracted in form of chlorine salts, and sulfate.
Owner:MINERA MICHILLA
Process for the recovery of value metals from base metal sulfide ores
InactiveUS20090013829A1Simple gas/liquidReduce the amount requiredSolid sorbent liquid separationGold compoundsLixiviantSulfide
A process for leaching a value metal from a base metal sulfide ore, comprising the step of leaching the ore with a lixiviant comprising a chloride, an oxidant and hydrochloric acid is disclosed. The leaching is controlled, by use of low concentrations of hydrochloric acid and a redox potential, to effect formation of hydrogen sulfide from the base metal sulfide ore. The hydrogen sulfide is stripped from the leach solution, thereby reducing the amount of sulfate generated in the leach to very low levels. The leaching may also be conducted to limit the co-dissolution of platinum group metals and gold with the base value metals. The leach forms a value metal-rich leachate and a solids residue. The solids residue may be subsequently leached to recover the platinum group metals and gold. The value metal-rich leachate can be oxidized and neutralized to recover the value base metals. In an embodiment, the chloride is magnesium chloride and lixiviant solution is regenerated
Owner:JAGUAR NICKEL INC
Method of leaching copper sulfide ore with the use of iodine
ActiveUS8163063B2Efficient leachingEfficient executionSolvent extractionGold compoundsPregnant leach solutionChalcopyrite
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of efficiently leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore containing chalcopyrite or enargite as a main constituent under versatile conditions for actual operation.A method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising using, as a leaching solution, a sulfuric acid solution containing iodide ions and ferric (III) ions in an excessive amount relative to the iodide ions and leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore; or a method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore with the use of a leaching solution further containing water-soluble ligands such as chloride ions that can stabilize ferric (III) ions in addition to the above components, is provided.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
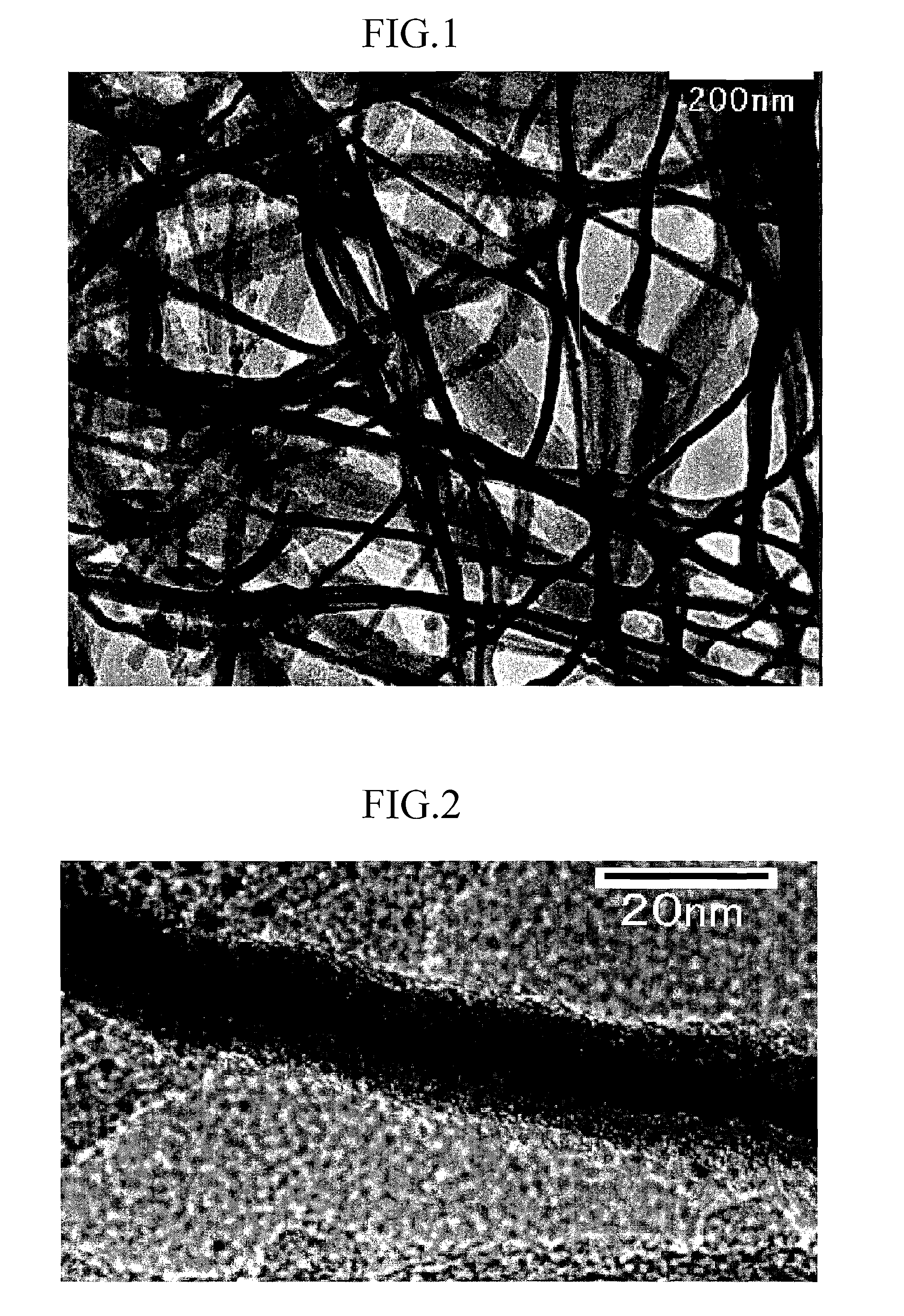
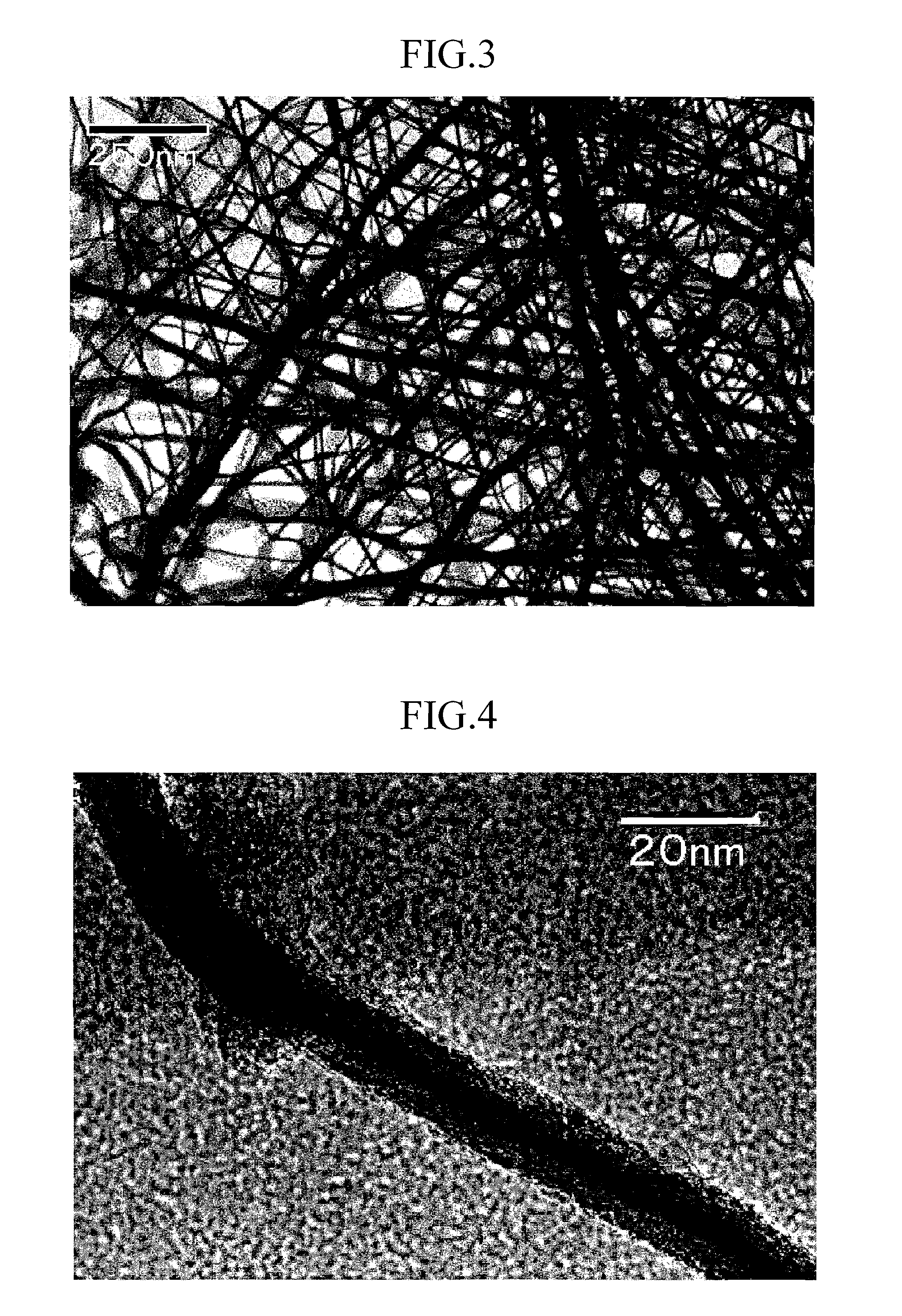
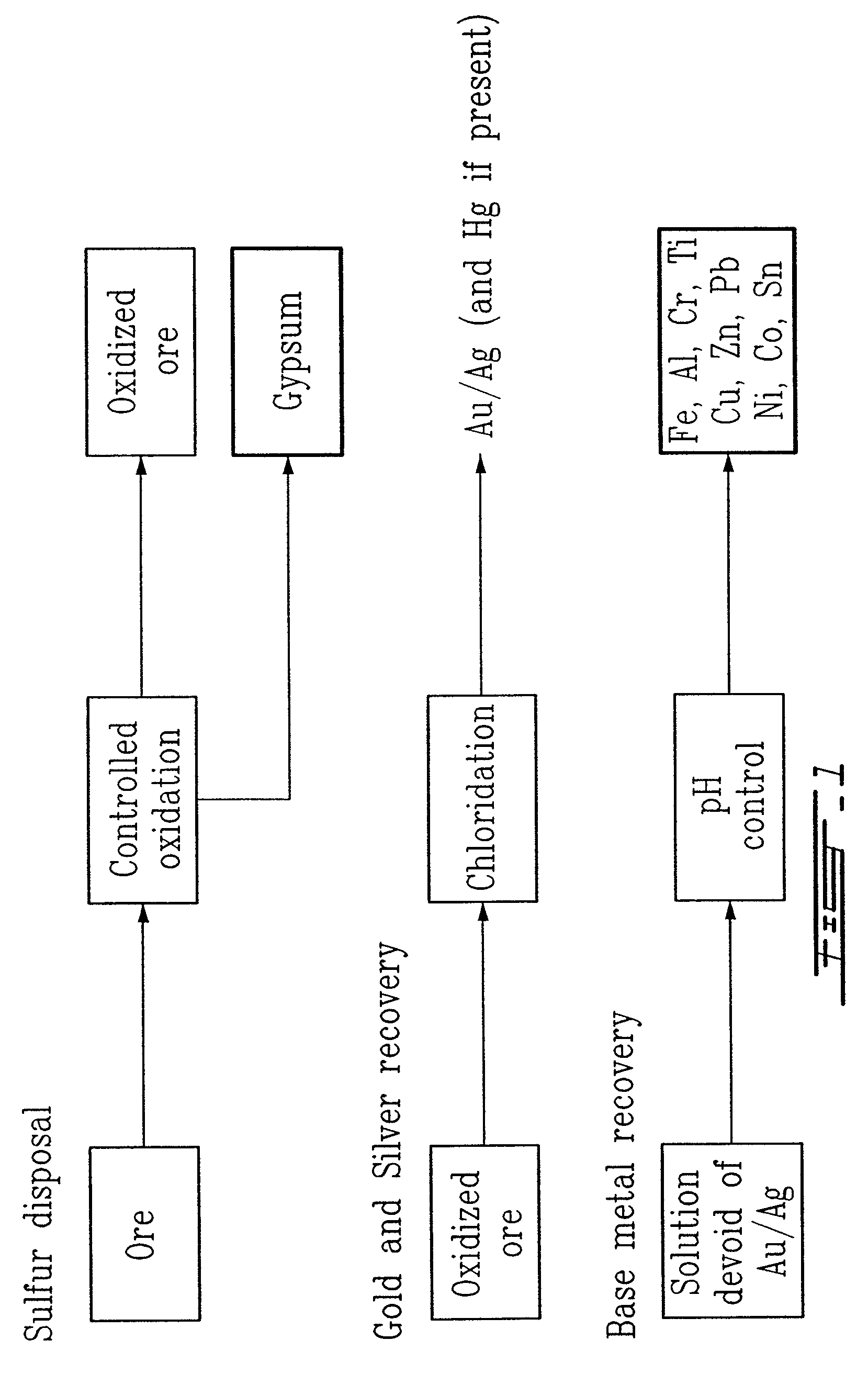
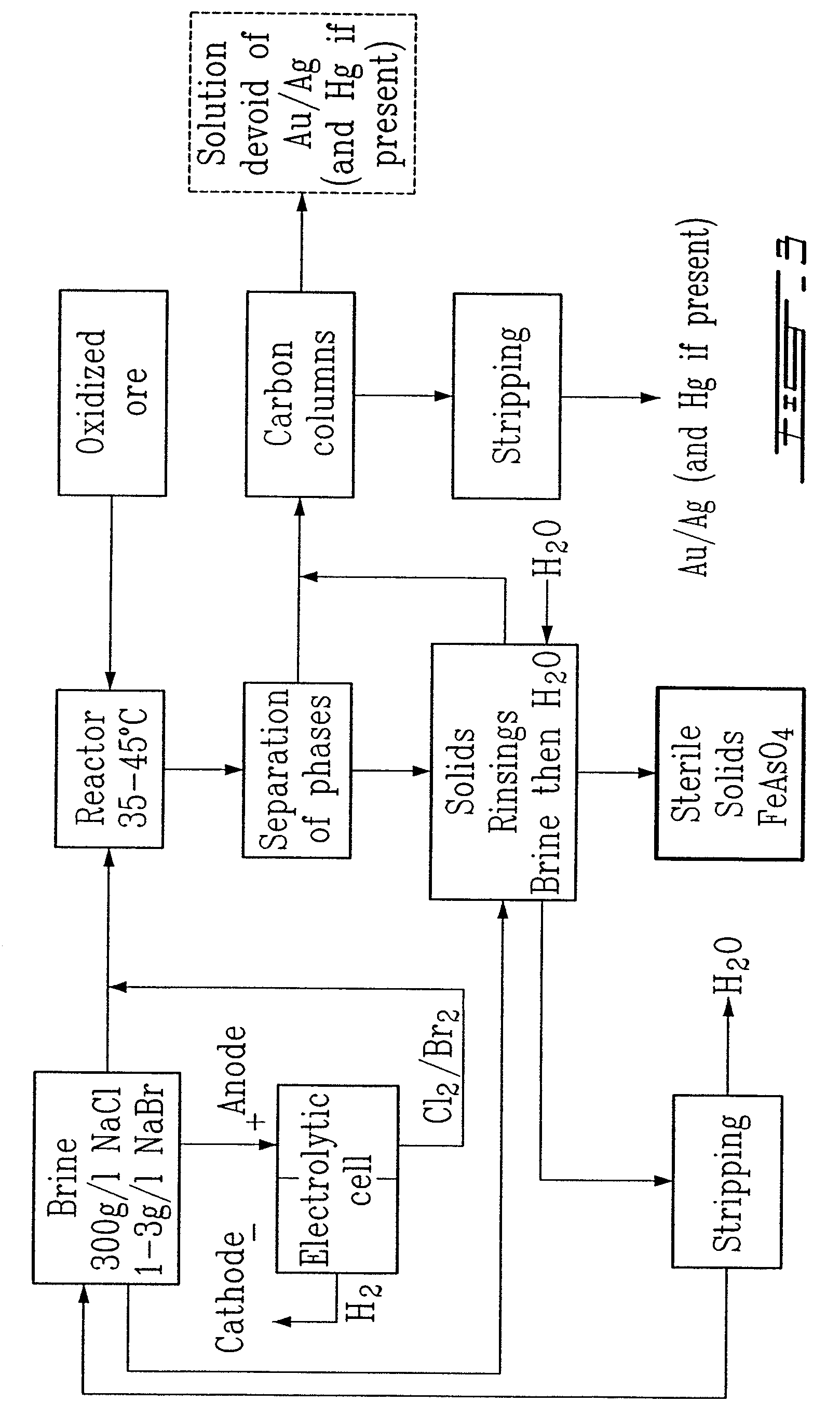
Gold and silver recovery from polymetallic sulfides by treatment with halogens
ActiveUS20080112864A1Quick responseHigh treatment rateAluminium compoundsSolvent extractionMetallic sulfideTitanium
A method for treating a polymetallic sulfide ore containing gold and / or silver, and further containing base metals selected from the group consisting of iron, aluminum, chromium, titanium, copper, zinc, lead, nickel, cobalt, mercury, tin, and mixtures thereof, is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of grinding the polymetallic sulfide ore to produce granules, oxidizing the granules to produce oxidized granules, and chloride leaching the granules using a brine solution including dissolved halogens, as well as chloride and bromide salts.
Owner:DUNDEE SUSTAINABLE TECH
Process for the recovery of value metals from base metal sulfide ores
InactiveUS7736606B2Simple gas/liquidReduce the amount requiredSulfur compoundsSolid sorbent liquid separationLixiviantSulfide
A process for leaching a value metal from a base metal sulfide ore, comprising the step of leaching the ore with a lixiviant comprising a chloride, an oxidant and hydrochloric acid is disclosed. The leaching is controlled, by use of low concentrations of hydrochloric acid and a redox potential, to effect formation of hydrogen sulfide from the base metal sulfide ore. The hydrogen sulfide is stripped from the leach solution, thereby reducing the amount of sulfate generated in the leach to very low levels. The leaching may also be conducted to limit the co-dissolution of platinum group metals and gold with the base value metals. The leach forms a value metal-rich leachate and a solids residue. The solids residue may be subsequently leached to recover the platinum group metals and gold. The value metal-rich leachate can be is oxidized and neutralized to recover the value base metals. In an embodiment, the chloride is magnesium chloride and lixiviant solution is regenerated.
Owner:JAGUAR NICKEL INC
Process for separating and recovering base metals from used hydroprocessing catalyst
A method is disclosed for separating and recovering base metals from a used hydroprocessing catalyst originating from Group VIB and Group VIII metals and containing at least a Group VB metal. In one embodiment, the used catalyst is contacted with an ammonia leaching solution to dissolve and separate the Group VIB and VIII metals from the Group VB metal complex and coke associated with the used catalyst. The resulting Group VIB and VIII metal containing solution is processed through at least two additional precipitation and liquid / solid separation steps to produce, in separate processing streams, a Group VIB metal product solution (such as ammonium molybdate) and a Group VIII metal product solution (such as nickel sulfate). Additionally, two separate filtrate streams are generated from liquid-solid separation steps, which filtrate streams are combined and subjected to hydrolysis and oxidation (oxydrolysis) to generate a purified ammonium sulfate solution for further processing, such as for fertilizer.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Preparation method of gamma-copper iodide
The invention discloses a preparation method of gamma-copper iodide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding iodine into water so as to obtain an iodic aqueous solution and adding hydrazine hydrate into the iodic aqueous solution for mixed reaction to obtain an iodide ion solution, wherein the molar ratio of the iodine to the water is controlled at 1:(50-90) and the molar ratio of the hydrazine hydrate to the iodine is controlled at (4.1-4.5):1.0; and adding the iodide ion solution into a copper sulfate solution under the stirring effect, controlling the molar ratio of copper sulfate to iodine at (2.0-2.2):1.0, fully reacting, filtering and drying to obtain gamma-copper iodide. According to the preparation method, the iodine utilization rate is high, a product is less in possibility of being oxidized and decomposed, the production cost is low, and the process is simple.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
High energy materials for a battery and methods for making and use
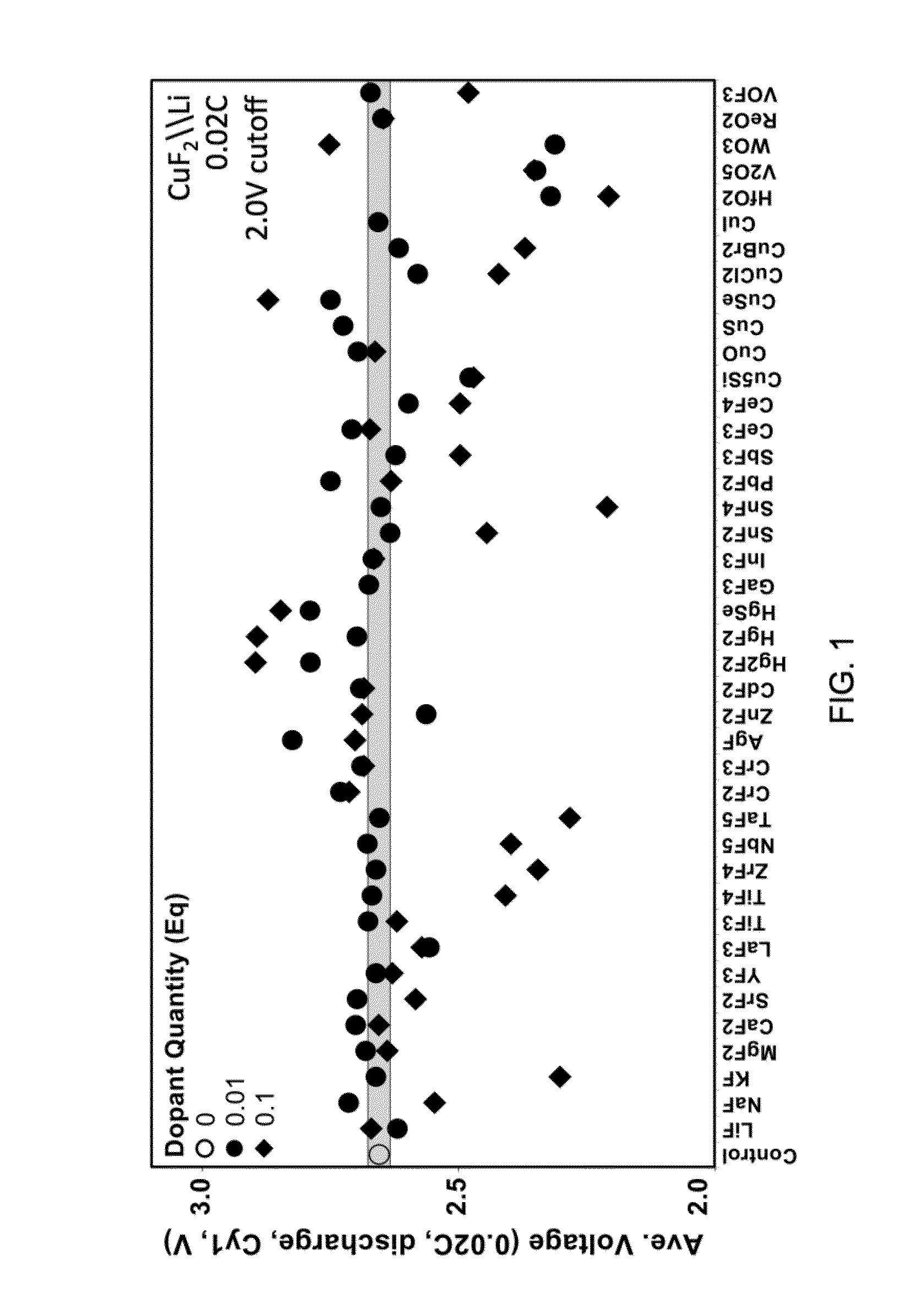
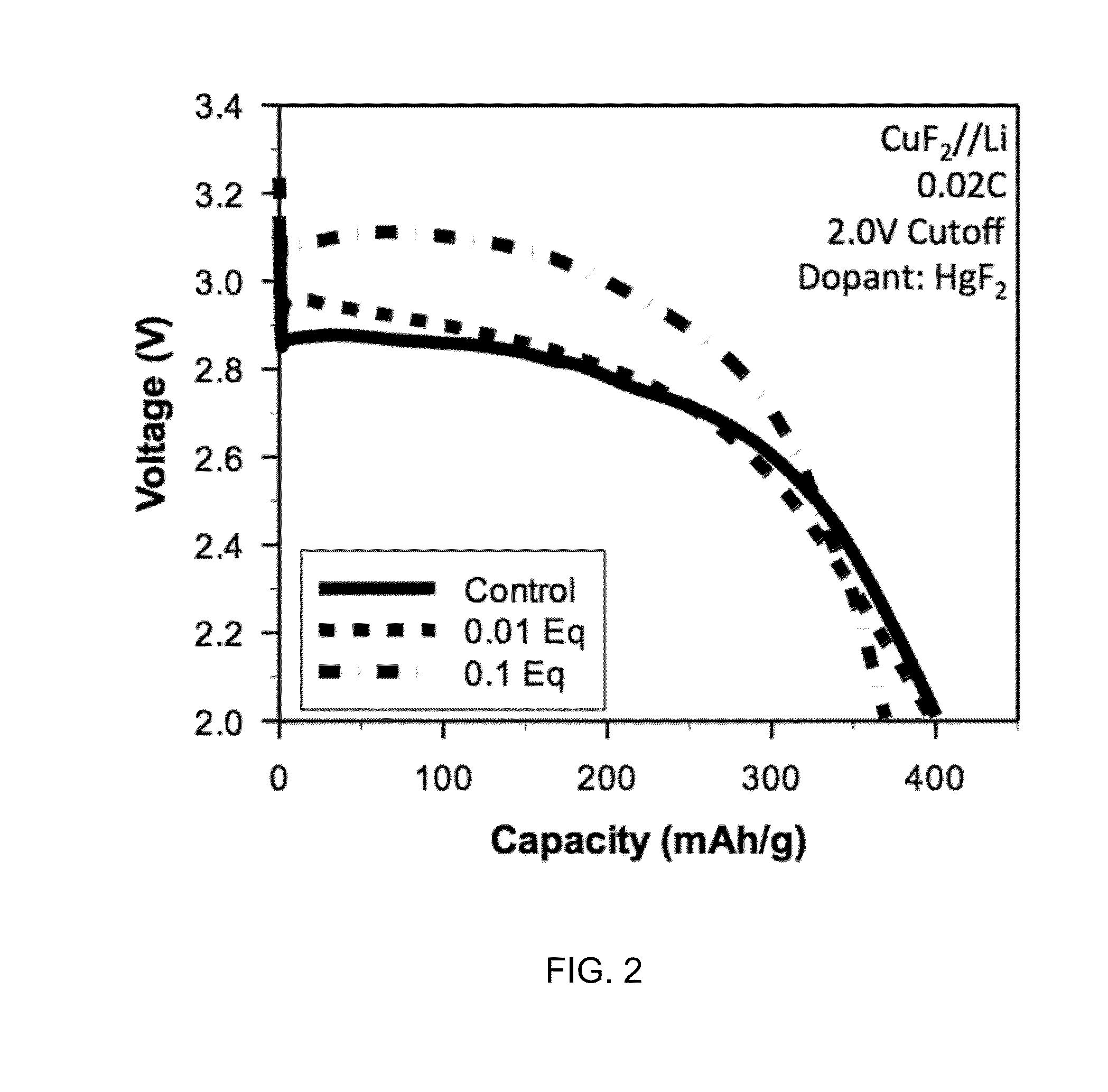
A composition for forming an electrode. The composition includes a metal fluoride compound doped with a dopant. The addition of the dopant: (i) improves the bulk conductivity of the composition as compared to the undoped metal fluoride compound; (ii) changes the bandgap of the composition as compared to the undoped metal fluoride compound; or (iii) induces the formation of a conductive metallic network. A method of making the composition is included.
Owner:WILDCAT DISCOVERY TECH
Recovering metals from sulfidic materials
InactiveUS7858056B2Improve solubilityPromote recoveryPhotography auxillary processesSolvent extractionOxidation stateSulfide
A process for recovering a precious metal from a sulfidic material comprises the steps of preparing an acidic aqueous halide solution having an oxidation potential sufficient to oxidize the sulfidic material and render the precious metal soluble in the solution, adding the material to the acidic aqueous halide solution so that the sulfidic material is oxidized and the precious metal is solubilized and separating the precious metal from the oxidized sulfidic material. In addition, a process for removing a contaminant from a contaminated sulfidic material comprises the steps of mixing the material in an aqueous solution wherein a multi-valent species of a relatively high oxidation state oxidizes the contaminant to render it soluble in the solution, produces a contaminant refined material, and is reduced to a relatively lower oxidation state; and removing the contaminant from the solution while regenerating the multi-valent species to its relatively high oxidation state.
Owner:INTEC INT PROJECTS
Composite nanofiber, composite nanofiber association, complex structure, and production method thereof
InactiveUS7670509B2Simple manufacturing methodEasy to assembleMaterial nanotechnologySolvent extractionFiberComposite construction
Owner:KAWAMURA INST OF CHEM RES
Gold and silver recovery from polymetallic sulfides by treatment with halogens
InactiveUS7537741B2Reduce cost investmentHigh treatment rateAluminium compoundsSolvent extractionMetallic sulfideTitanium
A method for treating a polymetallic sulfide ore containing gold and / or silver, and further containing base metals selected from the group consisting of iron, aluminum, chromium, titanium, copper, zinc, lead, nickel, cobalt, mercury, tin, and mixtures thereof, is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of grinding the polymetallic sulfide ore to produce granules, oxidizing the granules to produce oxidized granules, and chloride leaching the granules using a brine solution including dissolved halogens, as well as chloride and bromide salts.
Owner:DUNDEE SUSTAINABLE TECH
Electrode material and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS20040042954A1Increase capacityProlong lifePigmenting treatmentElectrode thermal treatmentLithiumRoom temperature
The present invention relates to an anode material for a battery and a preparation method thereof, and particularly to surface-treated carbon that has a large capacity and superior room temperature and high temperature cycle life properties, and that comprises a carbon core and a coating layer containing a fluorine-type organometal salt, and thus can be used as an anode material for a battery; and a preparation method thereof. A lithium or lithium ion secondary battery comprising the surface-treated carbon as an anode material has improved high temperature cycle life properties and stability.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
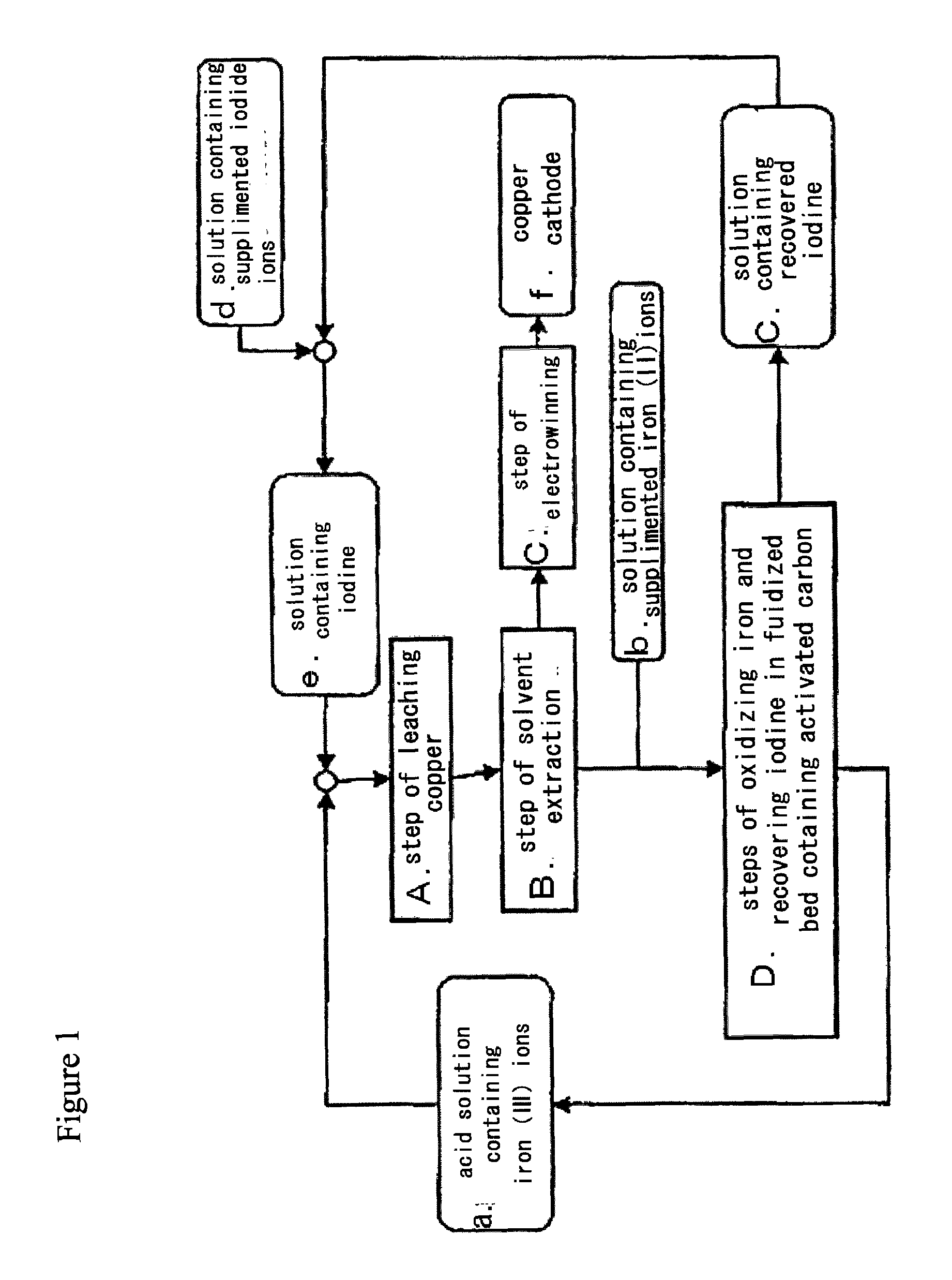
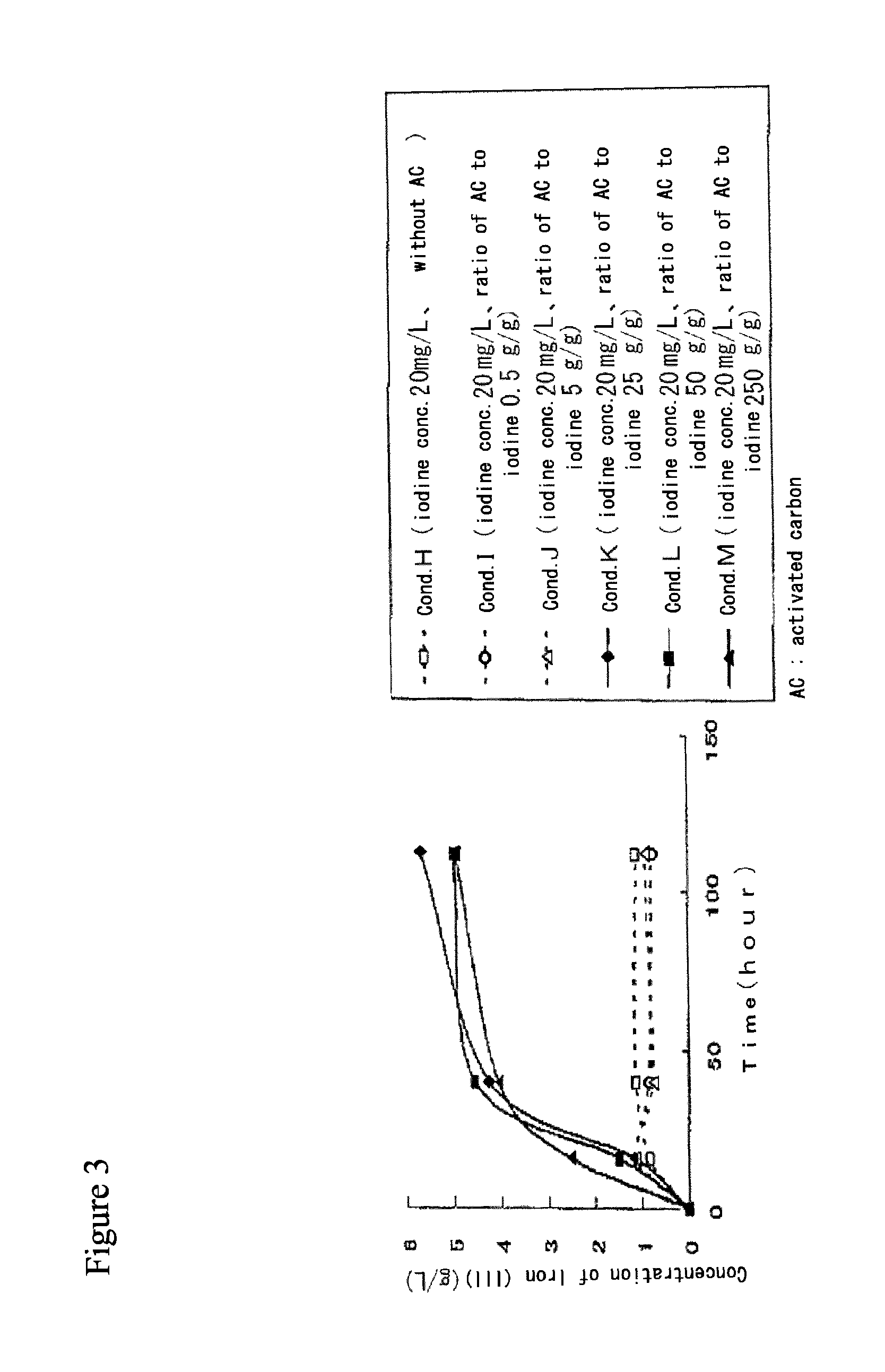
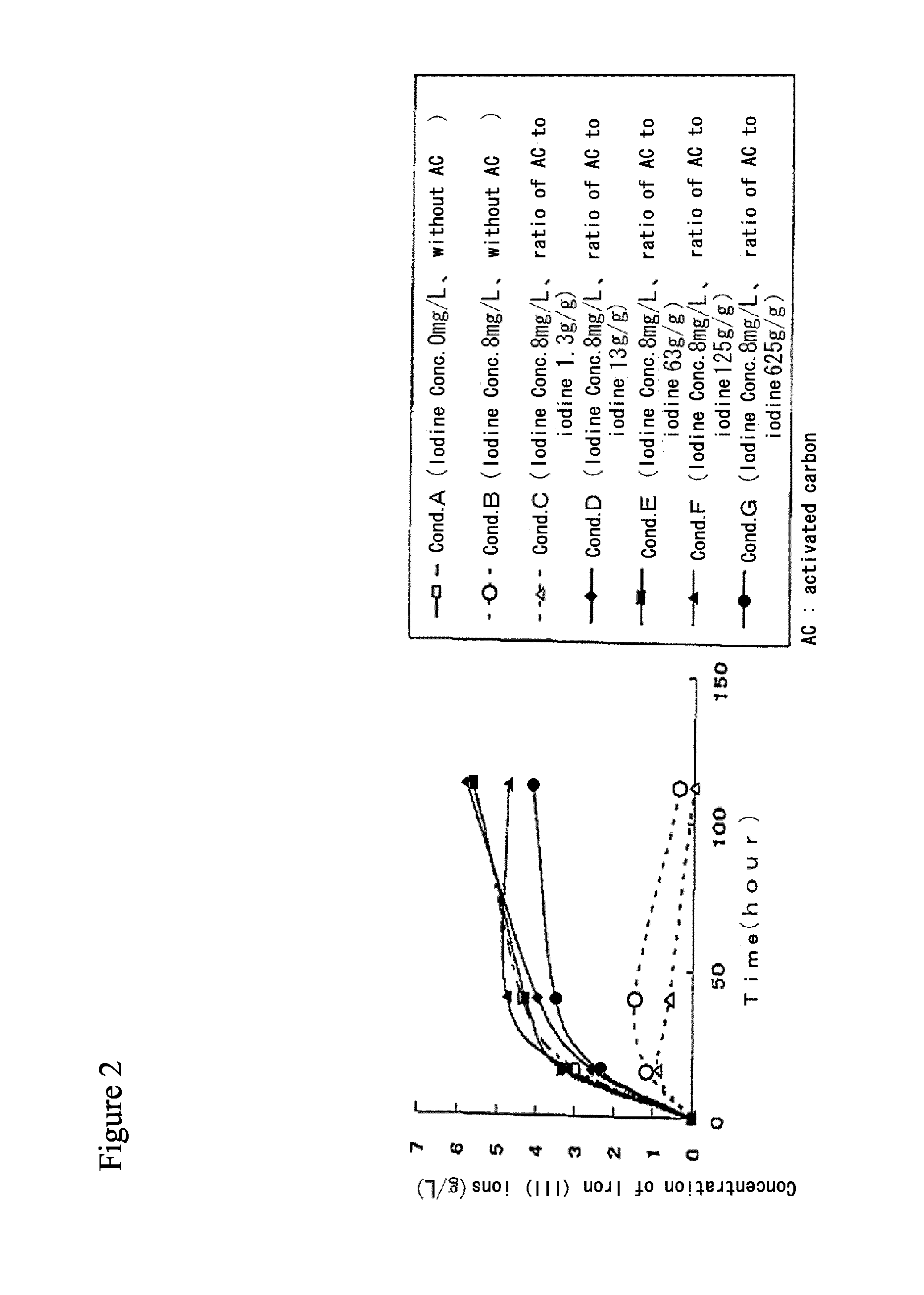
Method for processing acidic solution that contains iodide ions and iron ions
ActiveUS8865119B2Efficient regenerationModerate toxicitySolvent extractionIodineActivated carbonMicroorganism
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
Technology for preparing cuprous chloride crystal by hydrothermal reduction method
The invention is a technique for preparing cuprous chloride crystals with hydrothermal reduction, a truly original economic and environmental- protection method for producing cuprous chloride crystals, comprising the steps of: batching, dissolving, reacting, separating, post processing, etc, i.e. preparing water soluble divalent copper salt and water soluble fluoride into a mixed solution, placing still and filtering out nonsoluble impurities, using corresponding acid to regulate the [H+] concentration of the mixed solution, transferring the feed liquid into a pressure- resistant and corrosion-resistant reaction kettle, then calculating and adding in reducer, sealing and heating to not lower than 50 deg.C, making hydrothermal reaction for less than 48 h, and directly obtaining cuprous chloride crystals, cooling and filtering, then processing the obtained crystals by acid washing, water washing, alcohol washing, drying, etc, to obtain target product, where the mother filtrate can be recycled.
Owner:YANCHENG TEACHERS UNIV
Method for processing acidic solution that contains iodide ions and iron ions
ActiveUS20130058846A1Simple processModerate toxicitySolvent extractionWater contaminantsActivated carbonFerric
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
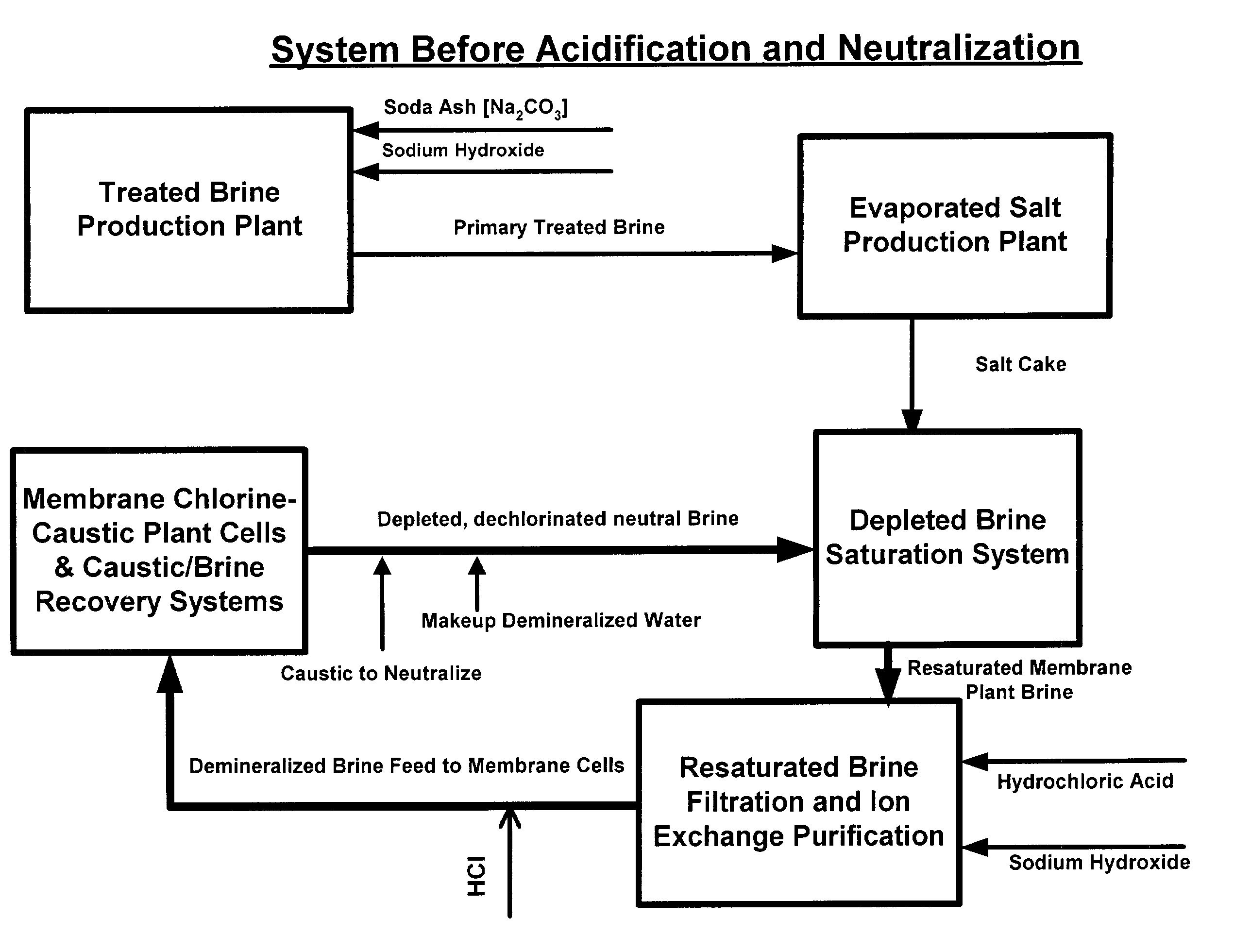
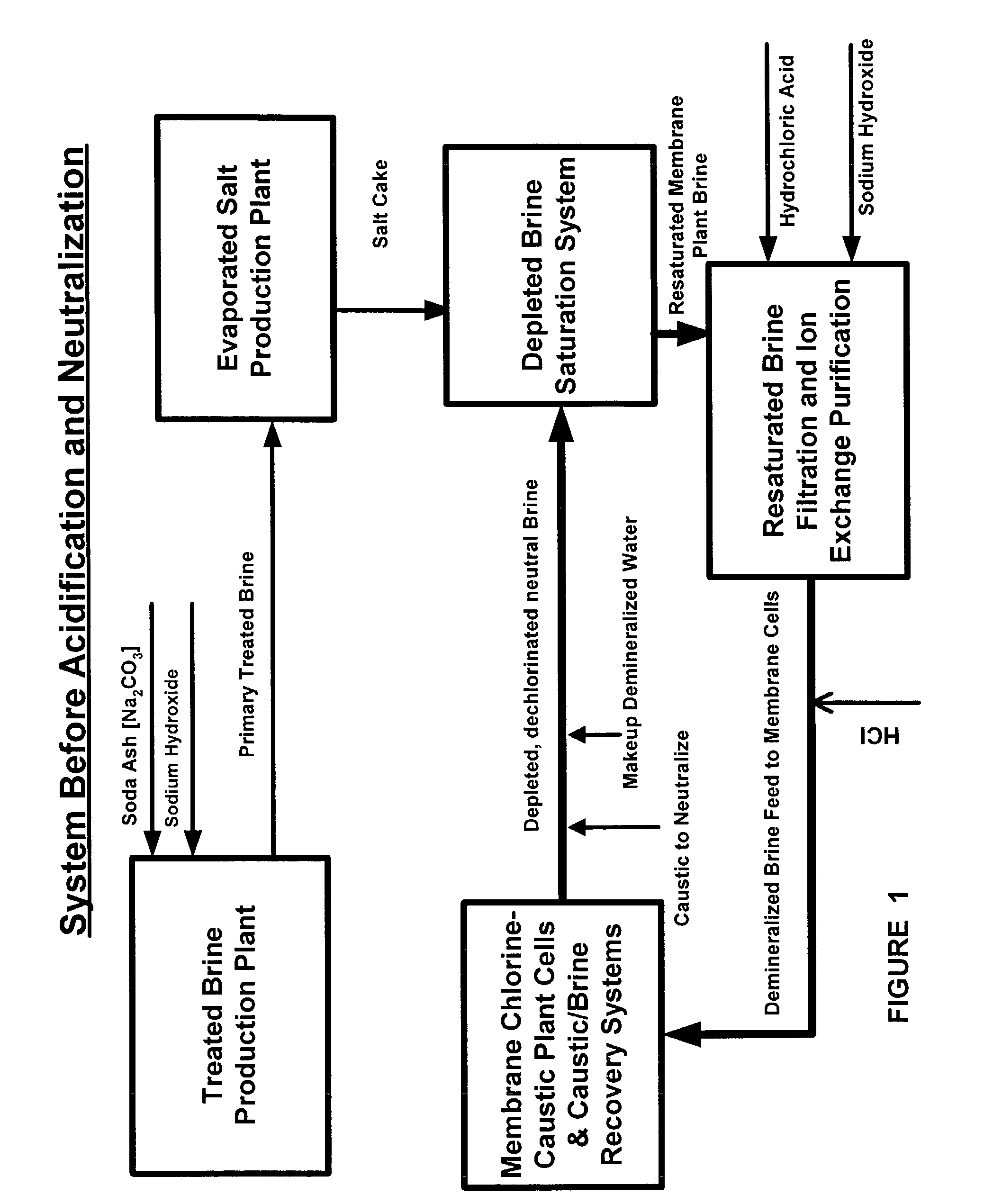
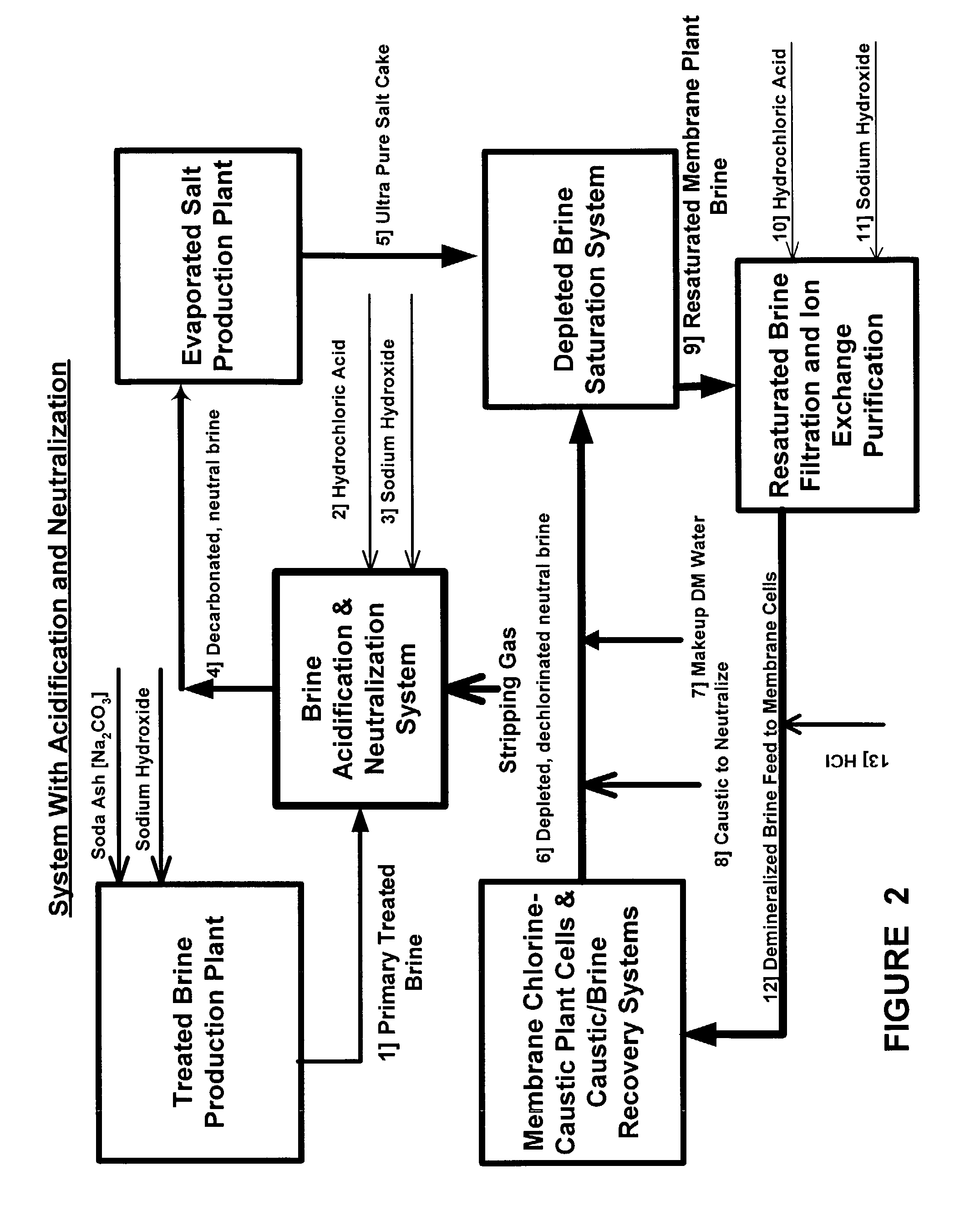
Production of ultra pure salt
ActiveUS7037481B2Reduce stepsReduce material costsElectrolysis componentsDispersed particle separationElectrolysisHydrogen
This invention relates to methods and installations for producing ultra pure sodium chloride salt crystals primarily for use in saturating depleted brine resulting from the electrolytic decomposition of saturated brine in chlor alkali membrane cells for the production of chlorine, caustic soda and hydrogen. More particularly, this invention relates to the production of ultra pure sodium chloride salt crystals by processing primary treated brine by first acidifying the primary treated brine, then stripping the carbonic acid produced by acidification as carbon dioxide, and then returning the brine to a pH of about 6 or higher which is sufficient for processing it in evaporation equipment where the ultra pure salt crystals are produced.
Owner:UNITED BRINE SERVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com