Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
933results about "Additive manufacturing processes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
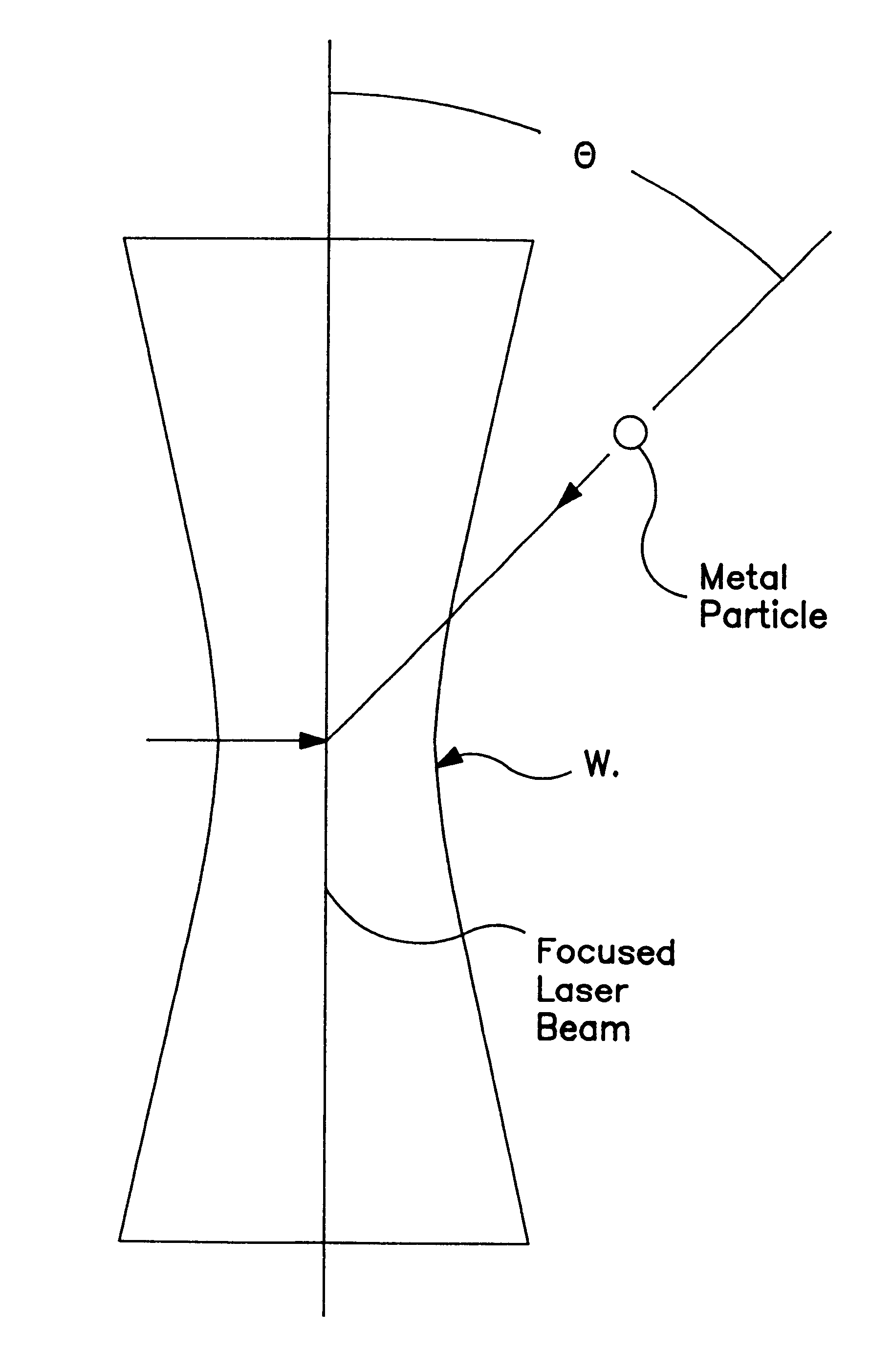
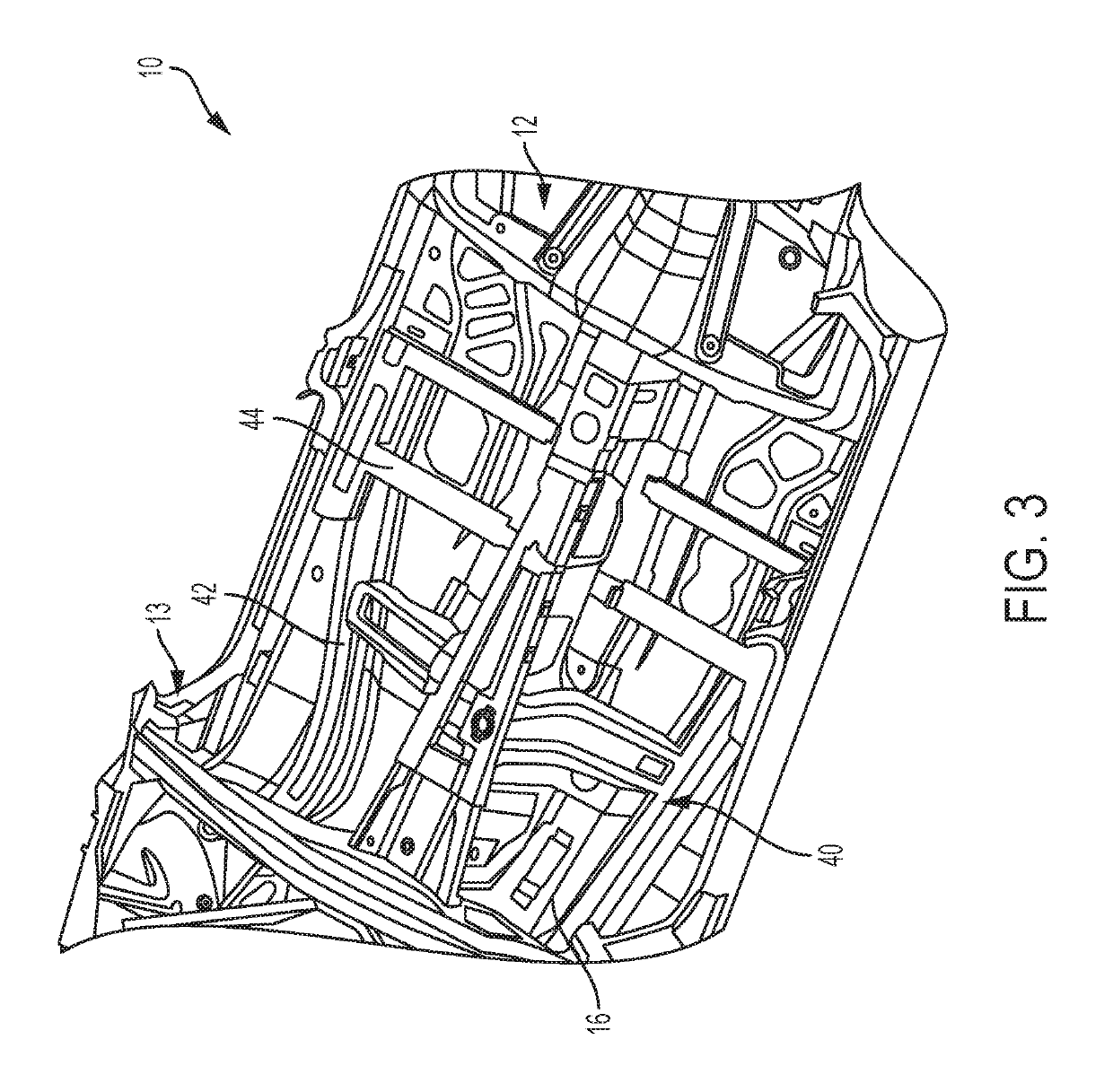
Precision spray processes for direct write electronic components
InactiveUS6251488B1Keep for a long timeIncrease probabilityMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingElectrical resistance and conductanceElectronic component
This invention combines the precision spray process with in-flight laser treatment in order to produce direct write electronic components. In addition to these components, the process can lay down lines of conductive, inductive, and resistive materials. This development has the potential to change the approach to electronics packaging. This process is revolutionary in that components can be directly produced on small structures, thus removing the need for printed circuit boards.
Owner:OPTOMEC DESIGN CO
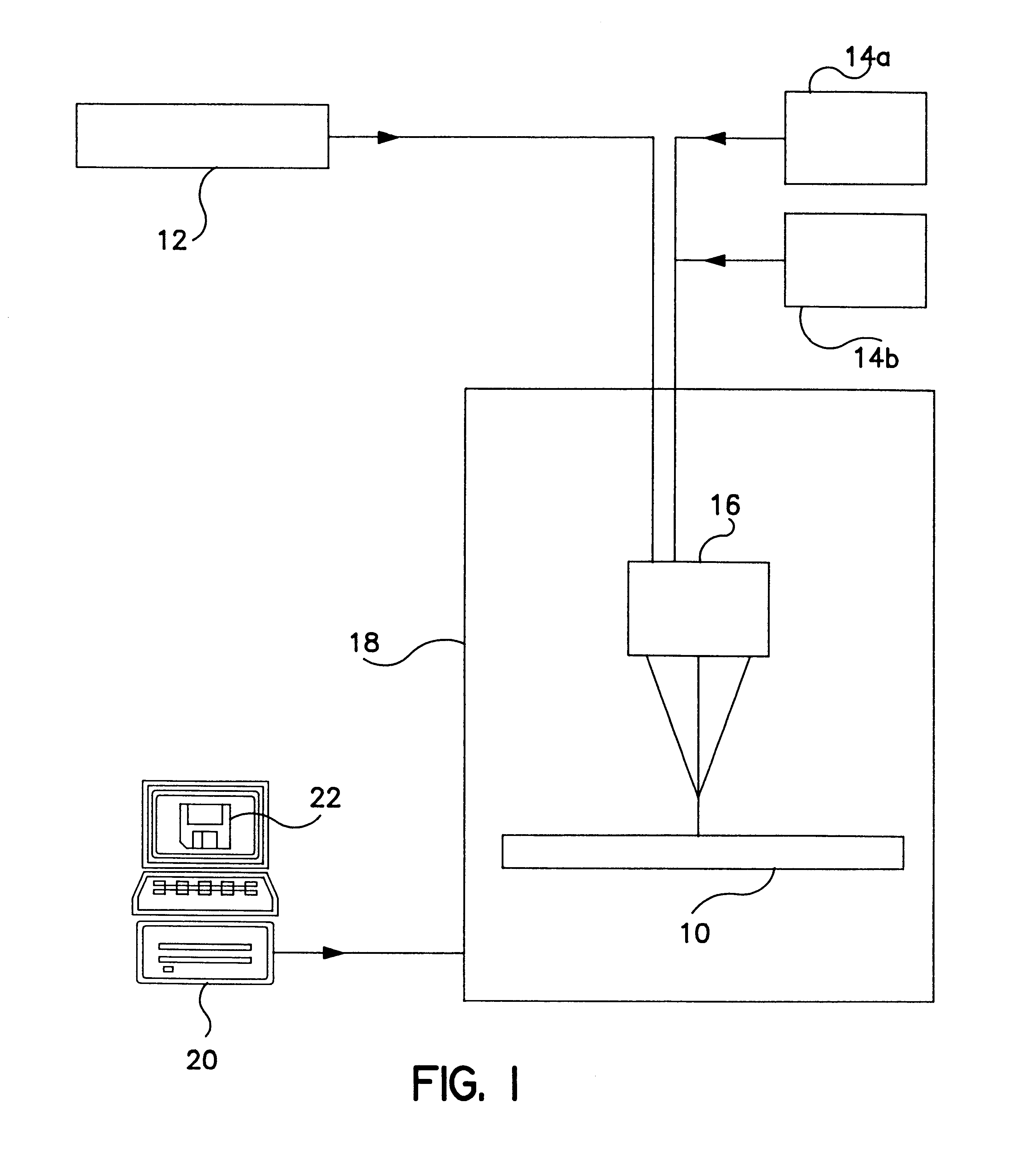
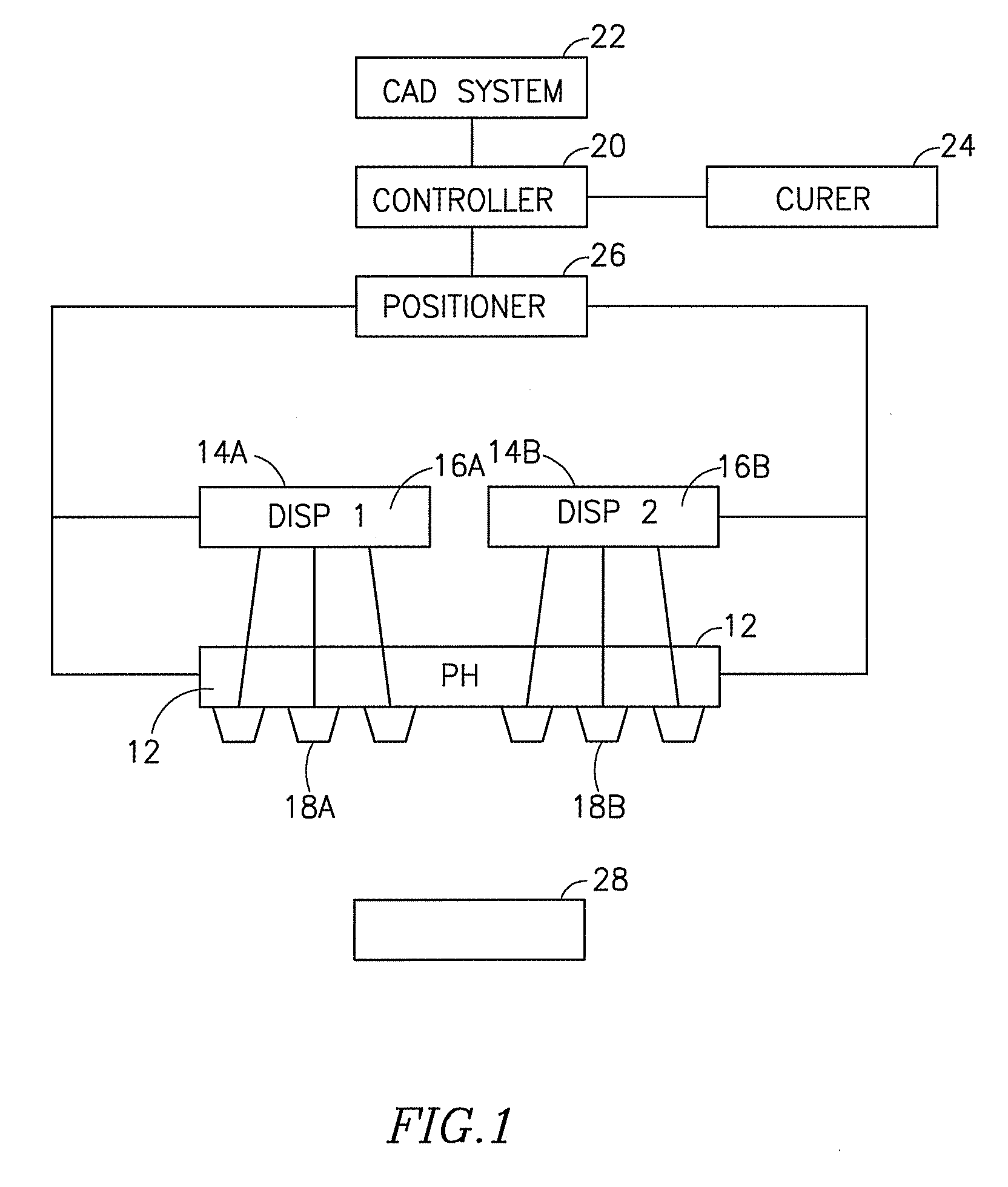
Method and apparatus for computer-aided tissue engineering for modeling, design and freeform fabrication of tissue scaffolds, constructs, and devices
ActiveUS20060105011A1Clear processProgramme controlAnimal cellsData processing systemProcess systems
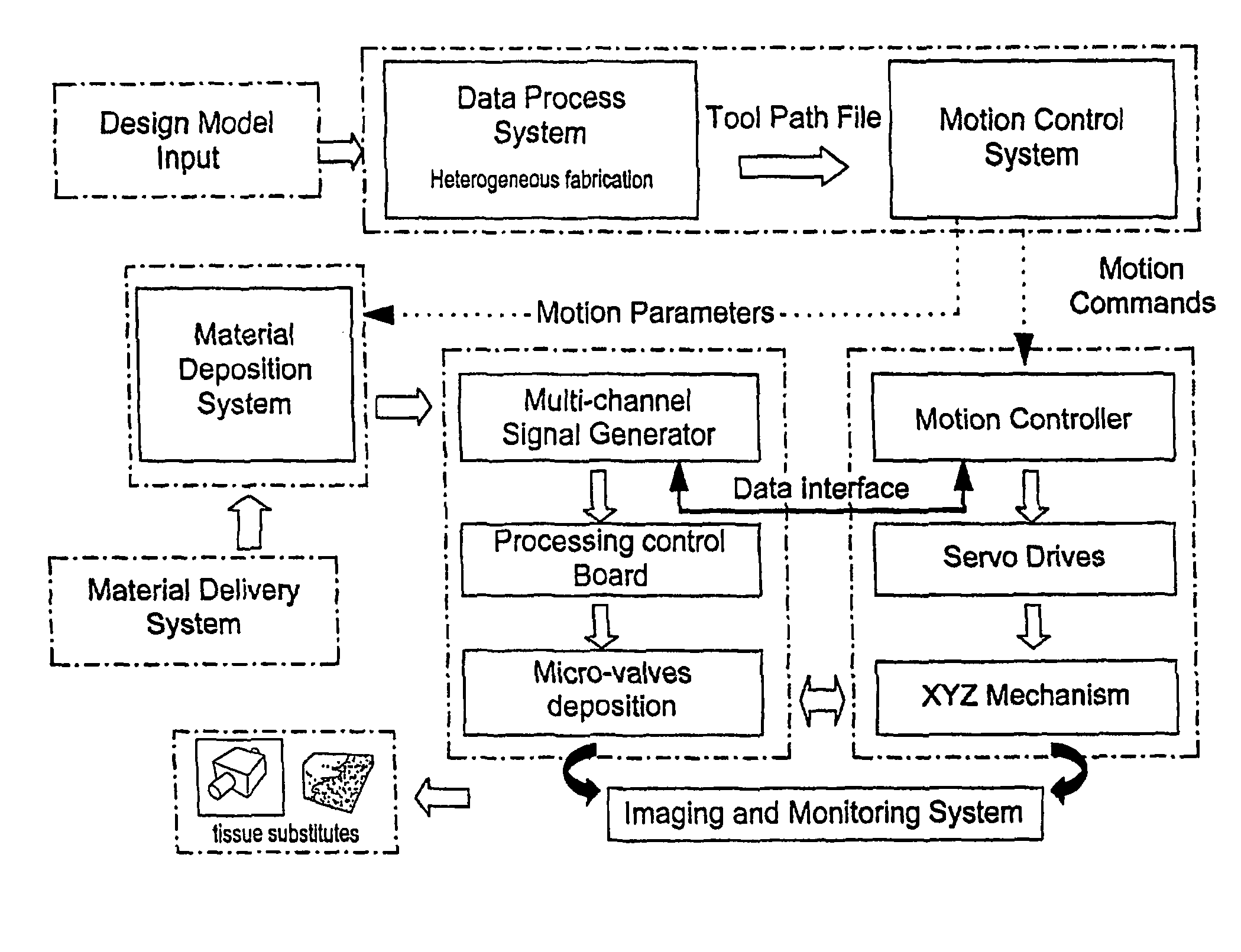
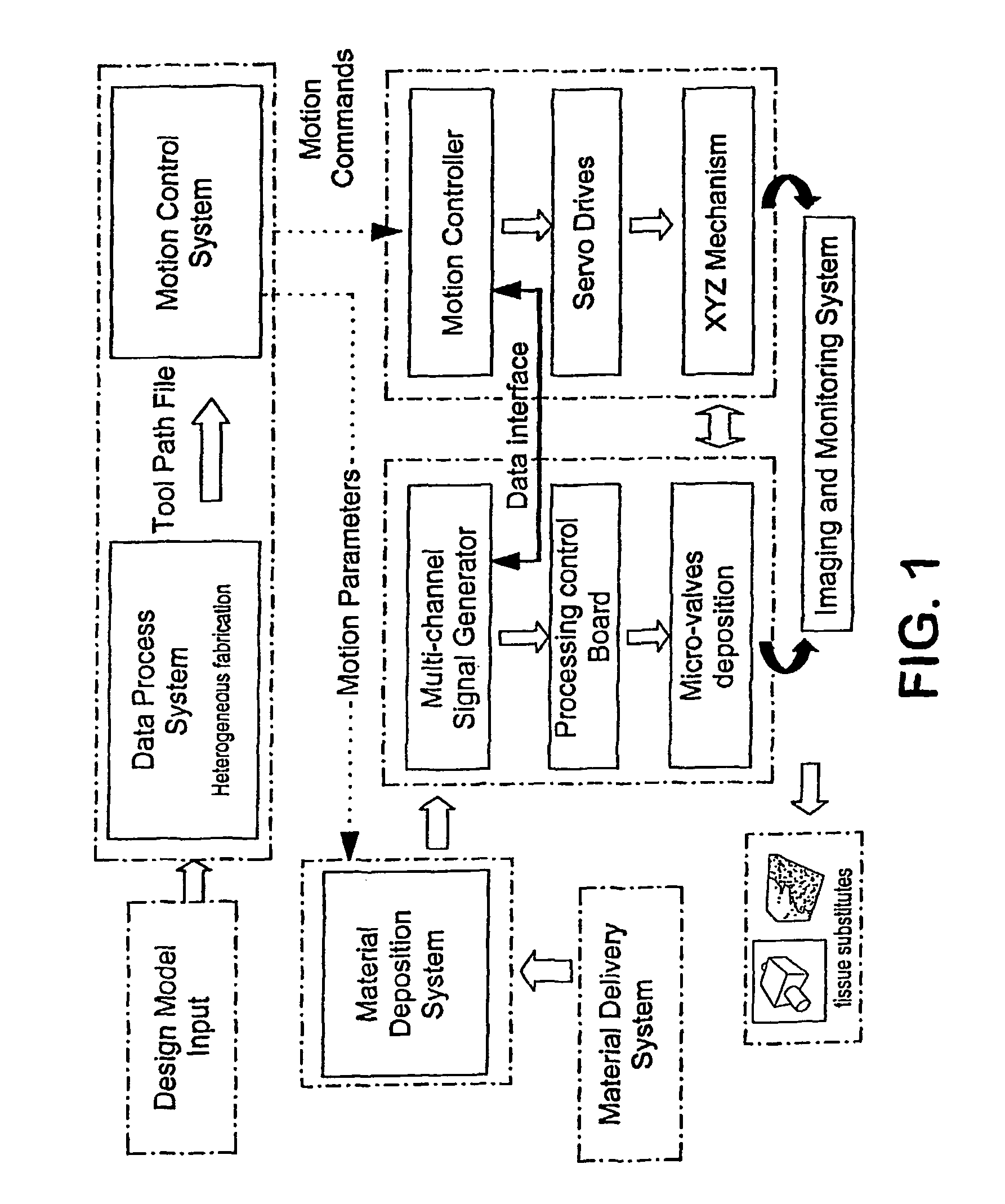
A process and apparatus are provided for manufacturing complex parts and devices which utilize a CAD environment to design a part or device to be created (FIG. 1); Boolean, scaling, smoothing, mirroring, or other operations to modify the CAD design; a software interface to convert the CAD designed part (Data Process System) or device into a heterogeneous material and multi-part assembly model (Design Input Model) which can be used for multi-nozzle printing; and a multi-nozzle system to print the designed part or device using different, specialized nozzles (Tissue substitutes).
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
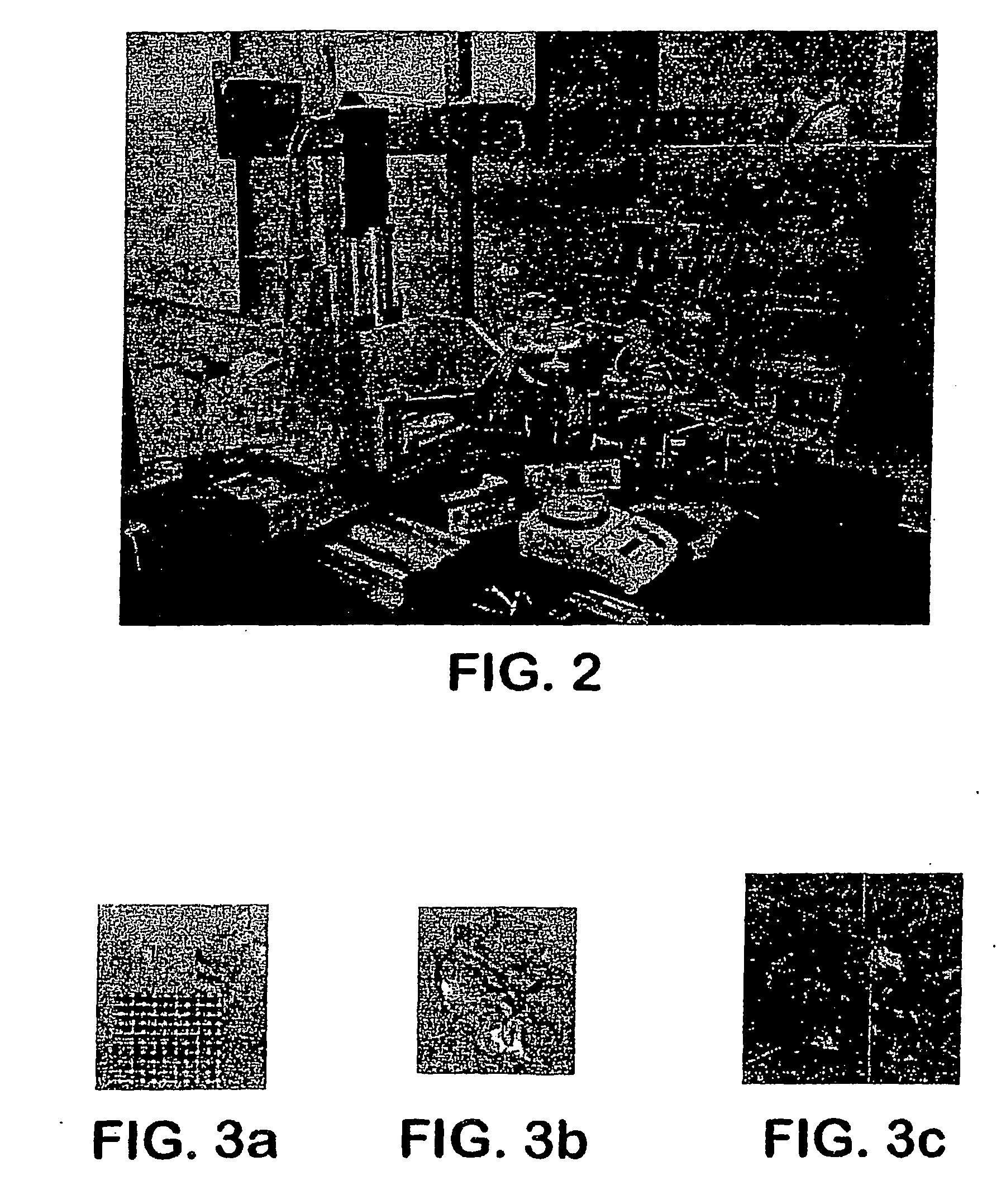
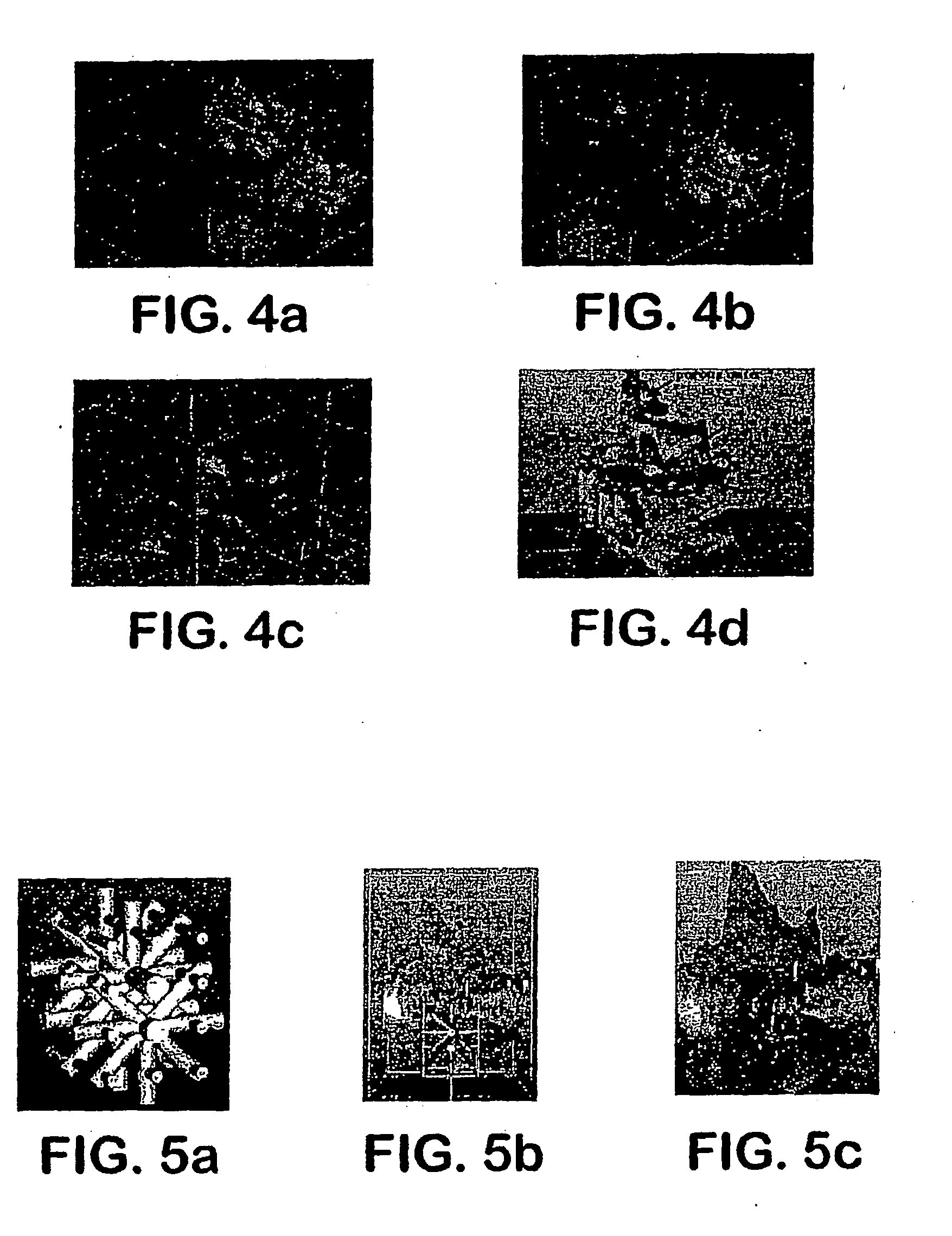
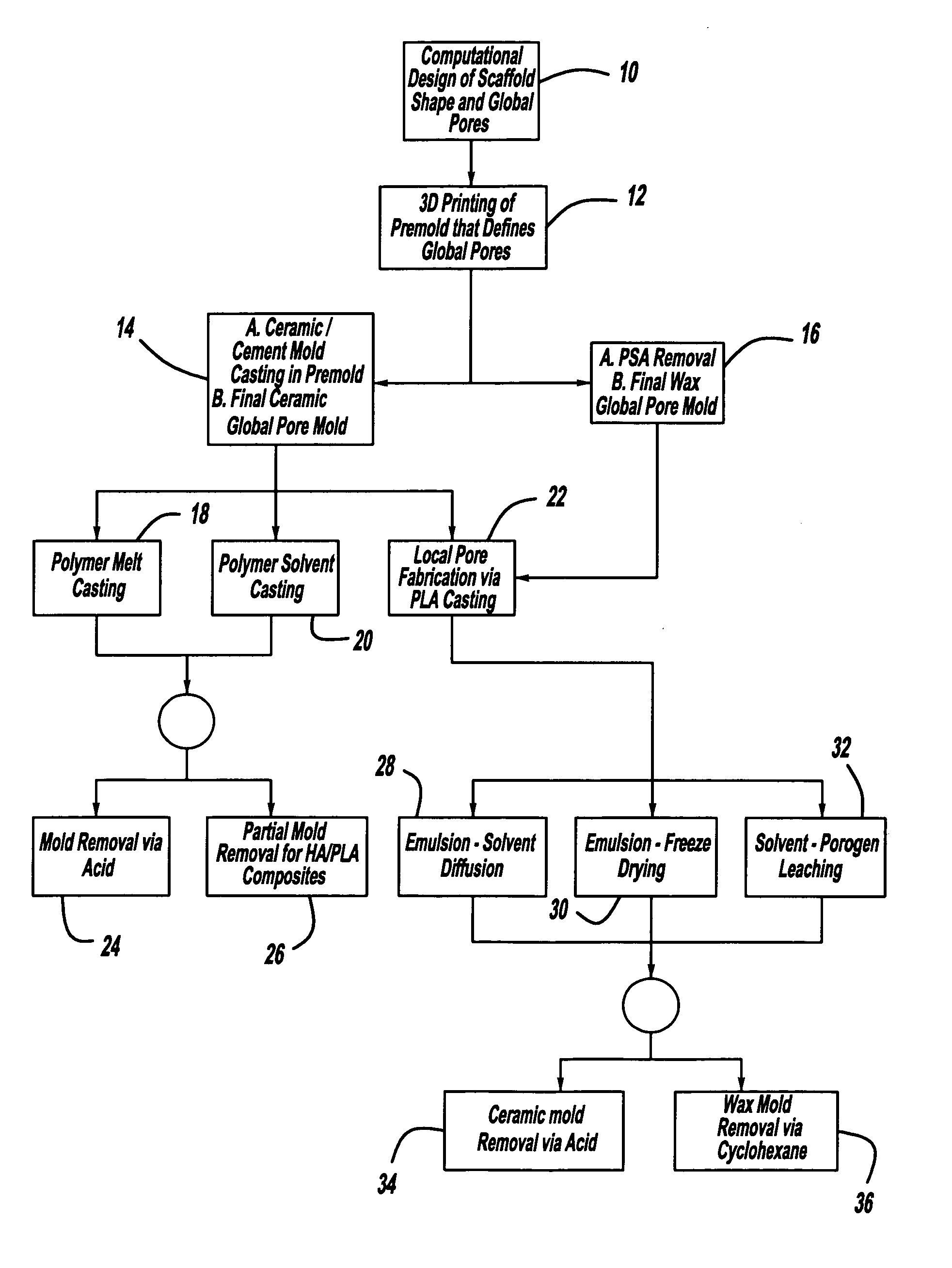
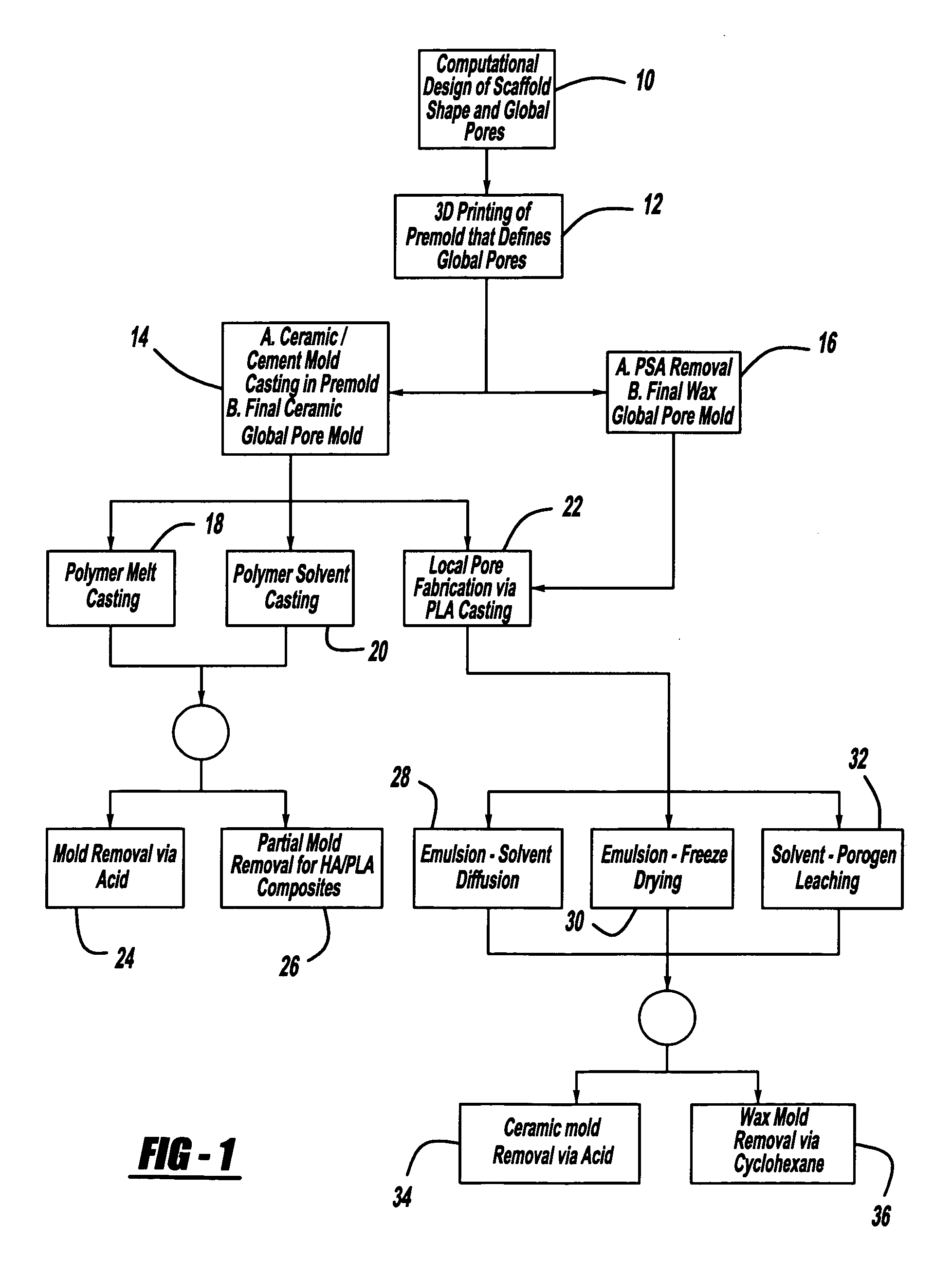
Controlled local/global and micro/macro-porous 3D plastic, polymer and ceramic/cement composite scaffold fabrication and applications thereof
InactiveUS7087200B2Easy to controlImprove interconnectivityMouldsJoint implantsManufacturing technologyFree form
An indirect solid free form scaffold manufacturing technique is provided. More particularly, the present invention provides a set of molds, casting methods, mold removals, and surface modification techniques that are compatible with image-based design methods and with solvent, melt, and slurry casting of polymers and ceramics.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
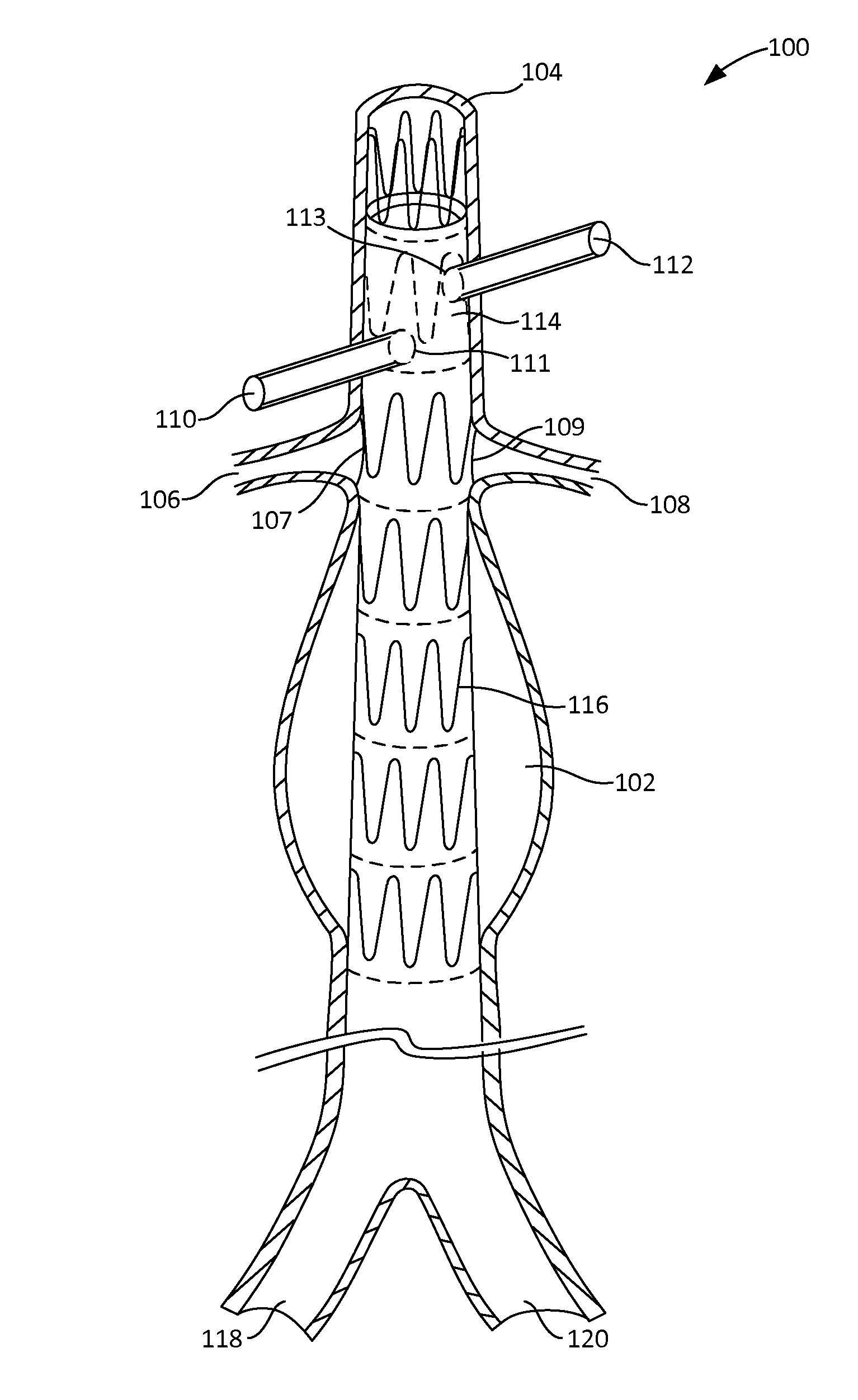
Fenestration template for endovascular repair of aortic aneurysms
ActiveUS20130296998A1Improving fenestration processStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusMedical imaging dataComputed tomography
To provide simple yet accurate stent graft fenestration, a patient-specific fenestration template is used as a guide for graft fenestration. To generate the fenestration template, a patient's medical imaging data such as CT scan data may be used to generate a 3-D digital model of an aorta lumen of the patient. The aorta lumen may encompass one or more branch vessels, which may be indicated on the 3-D digital model. Based on the 3-D digital model or a segment thereof, the fenestration template may be generated, for example, using 3-D printing technology. The fenestration template may include one or more holes or openings that correspond to the one or more branch vessels. To fenestrate a stent graft, the fenestration template is coupled to the stent graft so that the holes or openings on the fenestration template indicate the fenestration locations.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
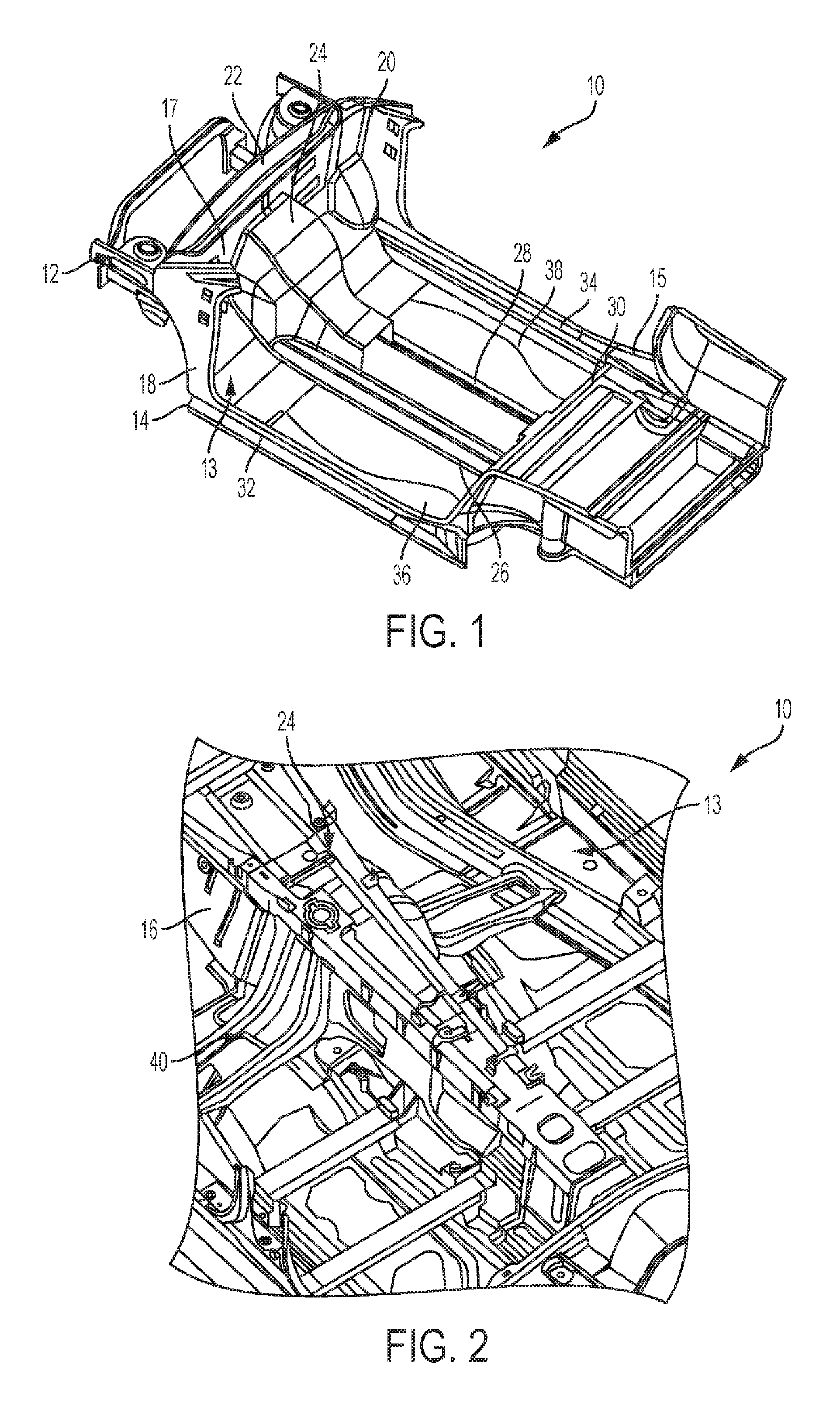
System and method for fabricating structures
ActiveUS10343724B2Additive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyEngineeringMechanical engineering
A system and method for fabricating a vehicle structure includes a first portion and a second portion having a body cooperating with the first portion using an additive manufacturing process. The body of the second portion includes one or more projections extending from the body. A third portion includes at least one opening and operatively engages the one or more projections of the second portion.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Pressure Vessels, Design and Method of Manufacturing Using Additive Printing
InactiveUS20160061381A1Less materialNo wasteLarge containersArc welding apparatusManufacturing technologyEngineering
Method and design of a pressure vessel having an internal supportive structure that reduces pressure forces applied to the external shell of the vessel by distributing such forces via internal bonds mostly connected to a central supporting element. The method and design allow making much lighter and stronger pressure vessels and containers using additive manufacturing technology, known as 3D printing.
Owner:KOTLIAR IGOR K
Method and apparatus for computer-aided tissue engineering for modeling, design and freeform fabrication of tissue scaffolds, constructs, and devices
A process and apparatus are provided for manufacturing complex parts and devices which utilize a CAD environment to design a part or device to be created (FIG. 1); Boolean, scaling, smoothing, mirroring, or other operations to modify the CAD design; a software interface to convert the CAD designed part (Data Process System) or device into a heterogeneous material and multi-part assembly model (Design Input Model) which can be used for multi-nozzle printing; and a multi-nozzle system to print the designed part or device using different, specialized nozzles (Tissue substitutes).
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
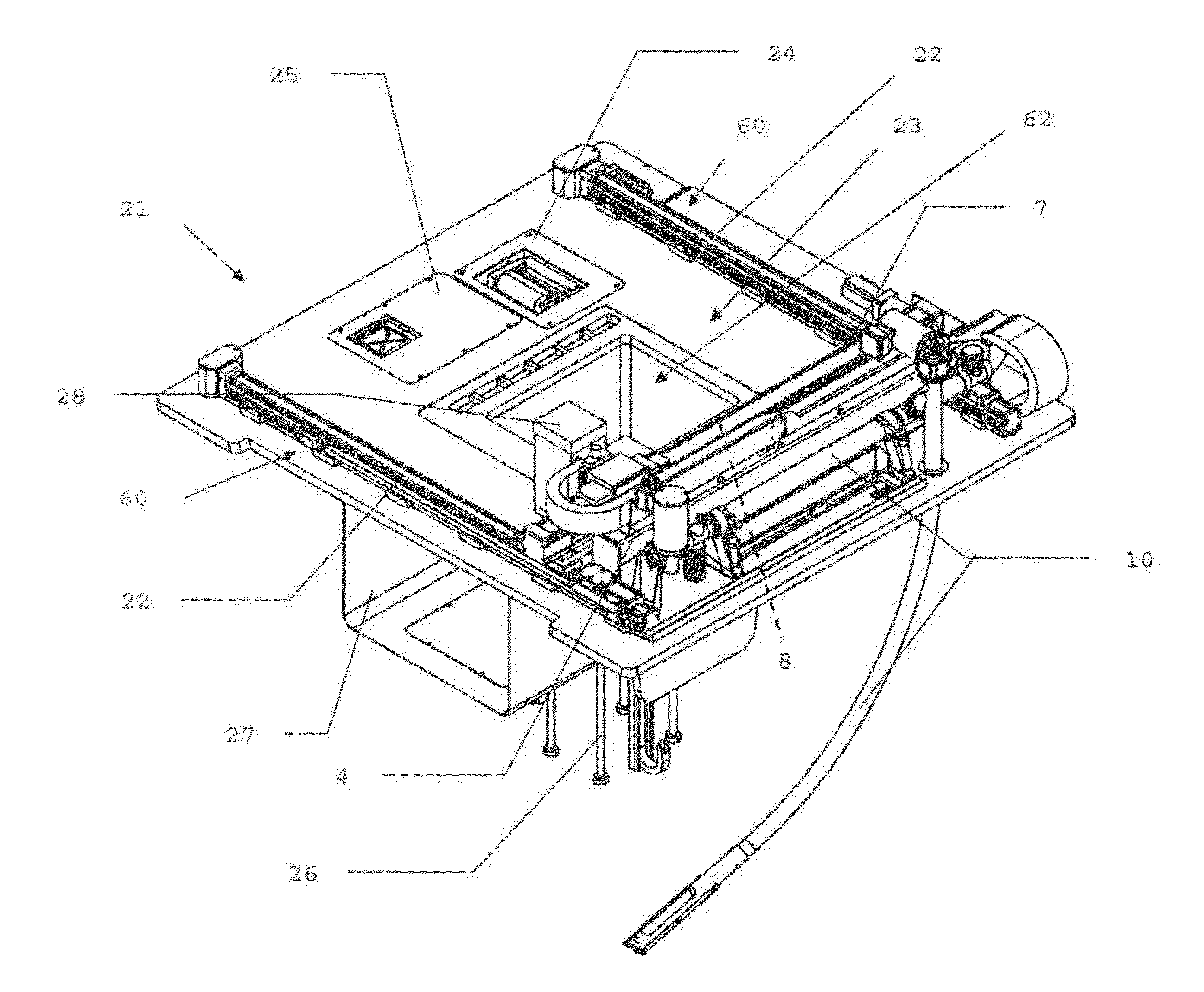
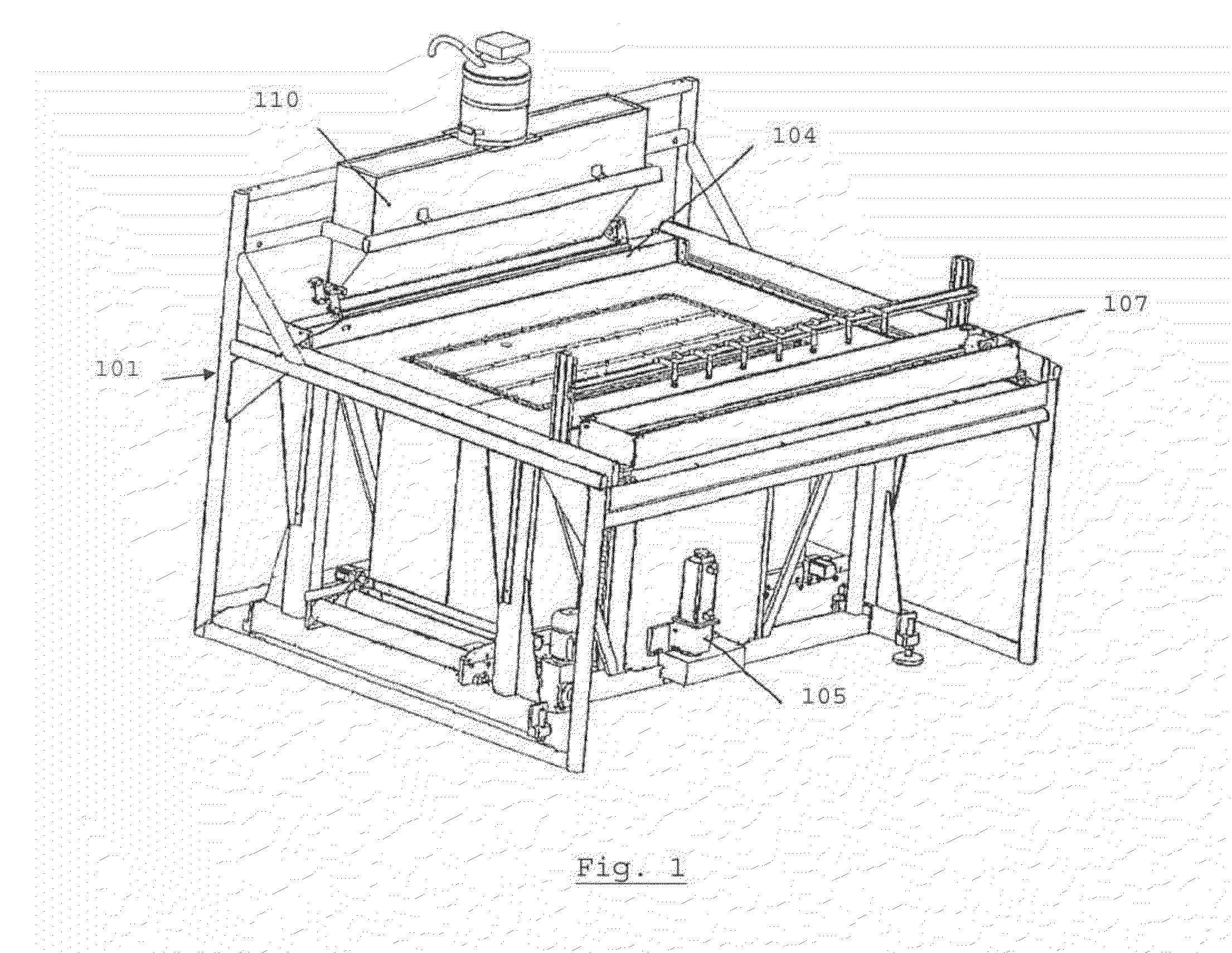
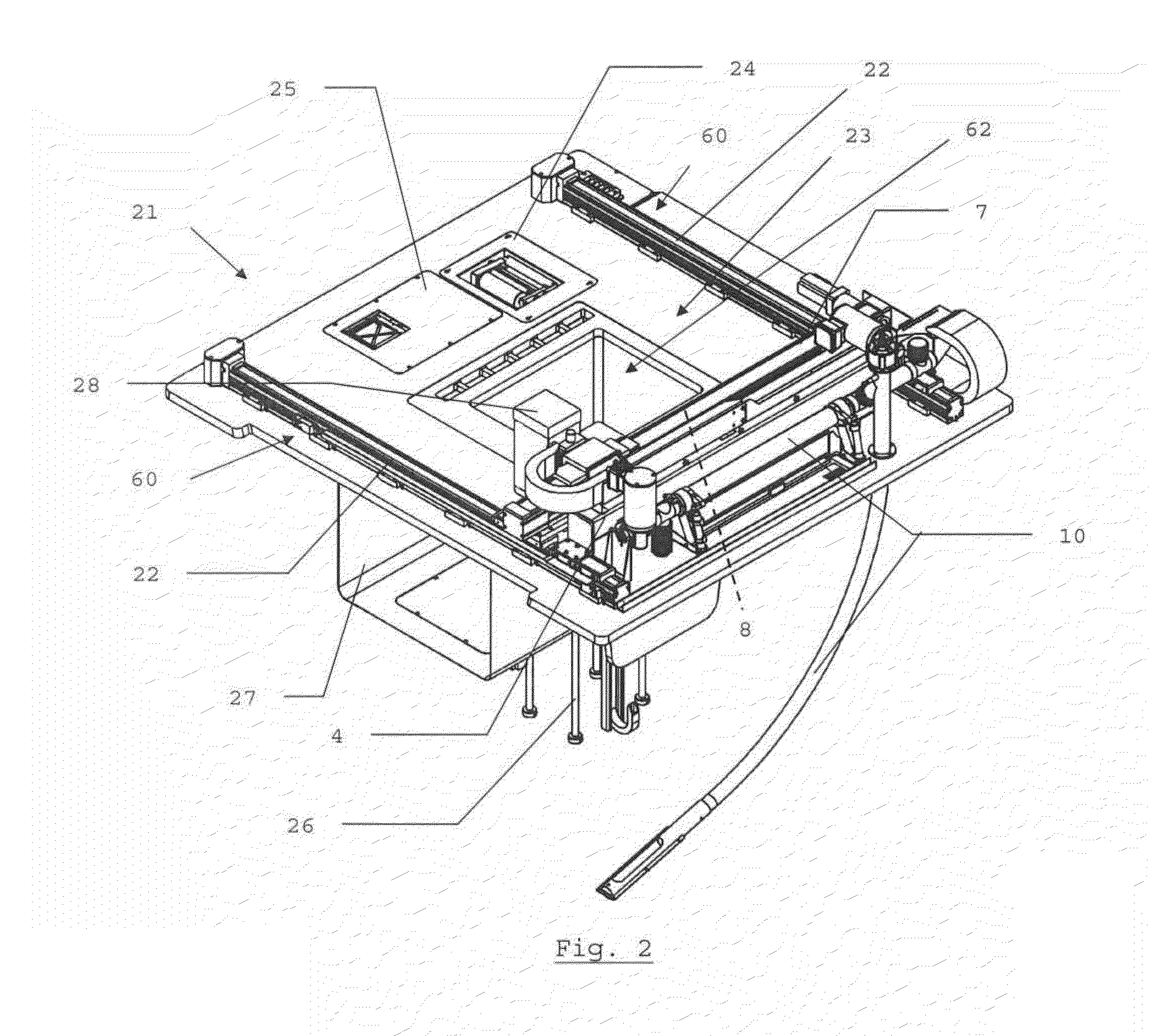
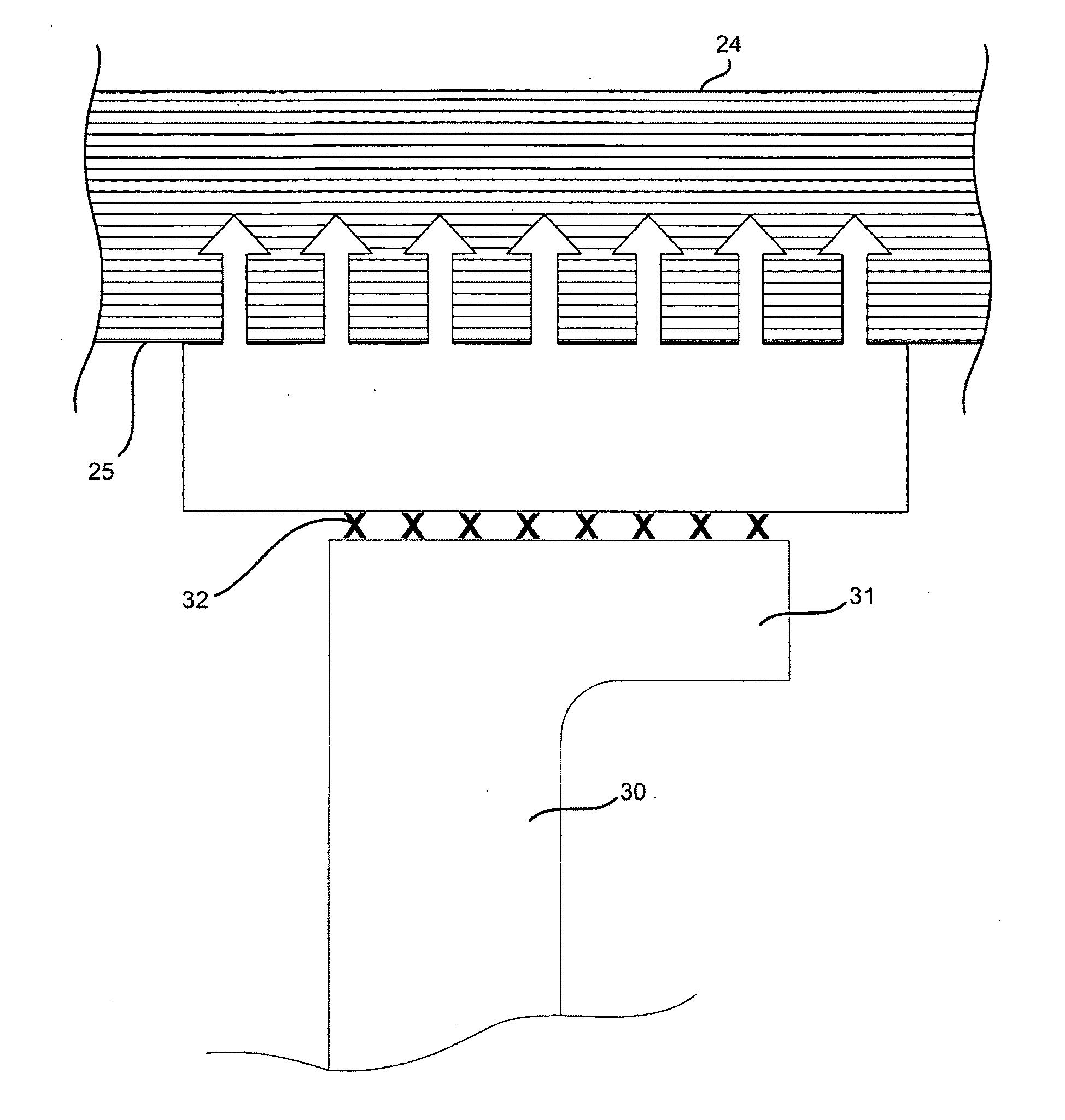
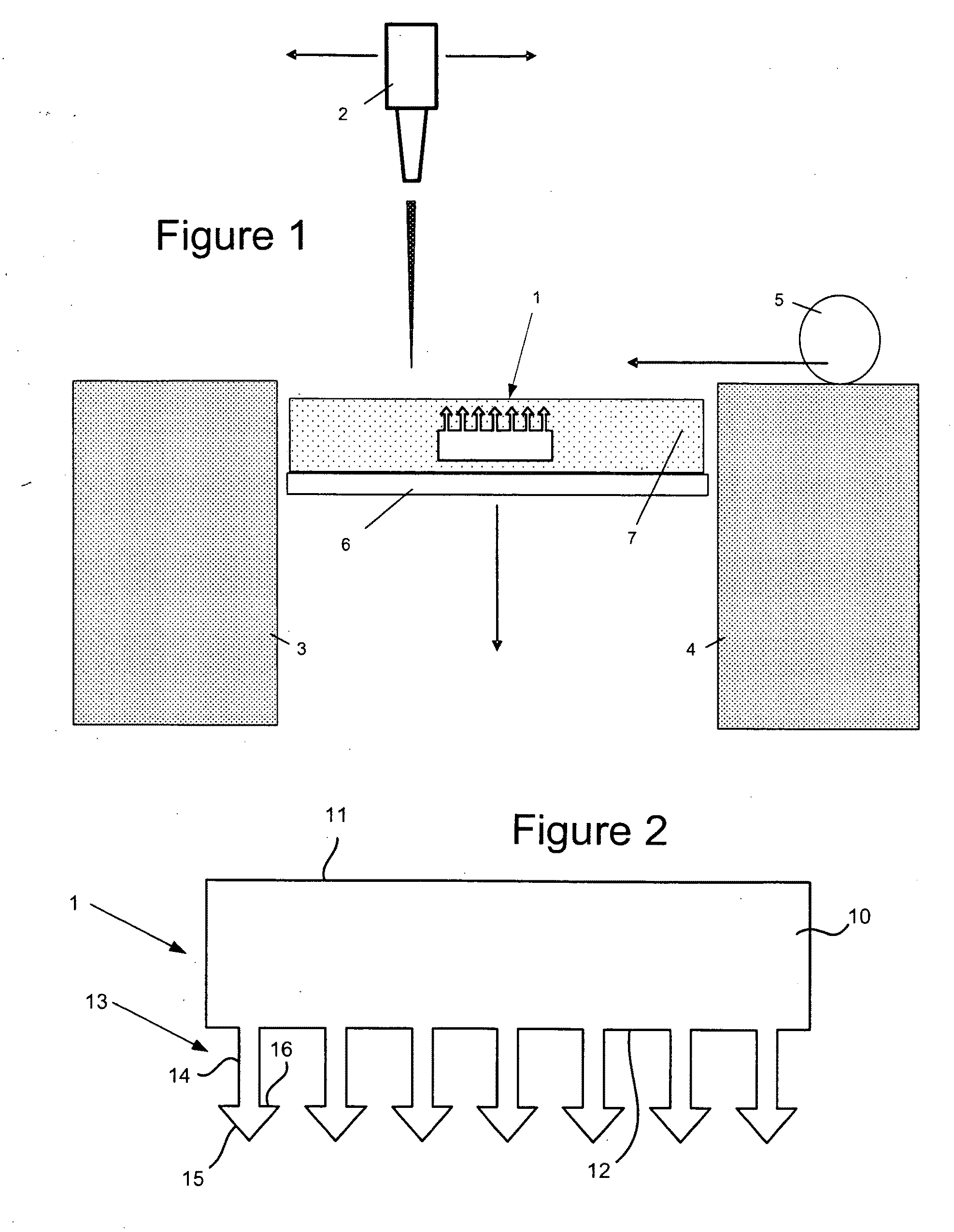
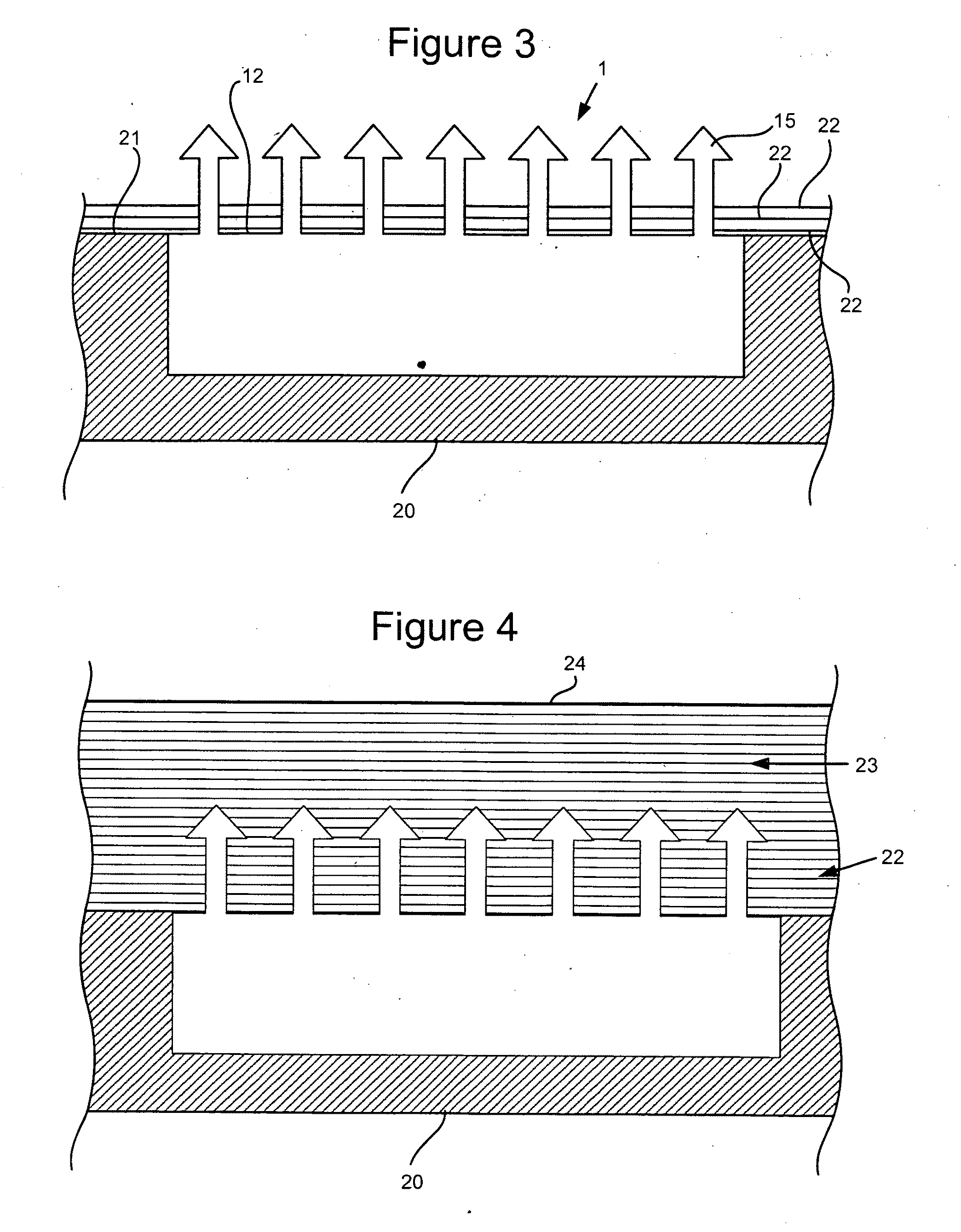
Device for the layer-wise production of patterns
The instant invention relates to a device and method for manufacturing patterns in layers. The device includes an auxiliary frame, a vertically displaceable build platform, a dispensing device for applying a binder material onto the build platform, a mounting platform, a mounting platform, and a spreader device for applying particulate material. The mounting platform preferably is connected to the auxiliary frame and includes a cut-out for the build platform. The dispensing device, the spreader device, and the build platform are connected to the mounting platform, so that the dispensing device, the spreader device and the build platform are cable of being mounted, adjusted, and wired to the mounting platform while located outside the auxiliary frame.
Owner:VOXELJET AG
3D printing method for continuous fibre-reinforced thermoplastic resin matrix composite material, and printing head
ActiveCN106313496AImprove adaptabilityImprove mechanical propertiesAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing processesFiber bundleResin matrix
The invention discloses a 3D printing method for a continuous fibre-reinforced thermoplastic resin matrix composite material, and a printing head. According to the method, fibre bundles and molten thermoplastic resins can be subjected to rotary blending and then subjected to rotary extrusion, and extruded wires are spiral; and the printing head is capable of charging the fibre bundles and the thermoplastic resins in a melting cavity, and spiral tooth rings are arranged at the inner sides of the melting cavity and an extrusion head, and rotate in opposite directions. The heated-molten resins and fibres are stirred by the spiral tooth rings which bidirectionally rotate after being blended, so that the fibres are compactly wound into a spiral column shape from a flat shape, the resins are uniformly distributed in each fibre orientation, and then a blend is extruded to a forming area from an extrusion port and cooled and cured to form a spatial entity. According to the method and the printing head, which are disclosed by the invention, the flat large-tow fibres can be used as reinforcements in a 3D printing process, the compactly-wound fibres have a high compaction degree, the fibres and the matrixes are adequately soaked, and the formed fibres and resins are uniformly distributed; and therefore, the method and the printing head are capable of greatly improving the mechanical property of a member, and improving the forming quality.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
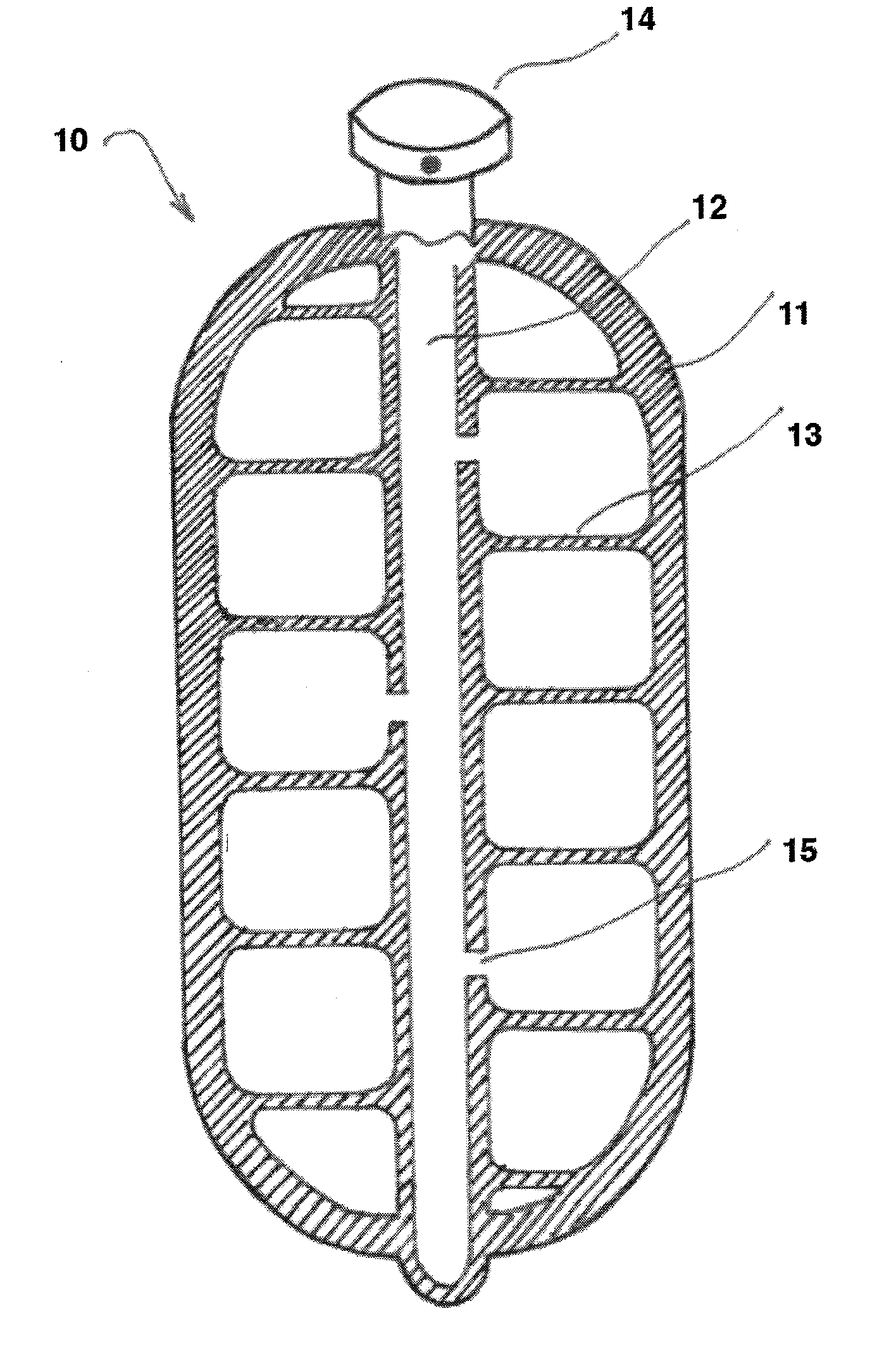
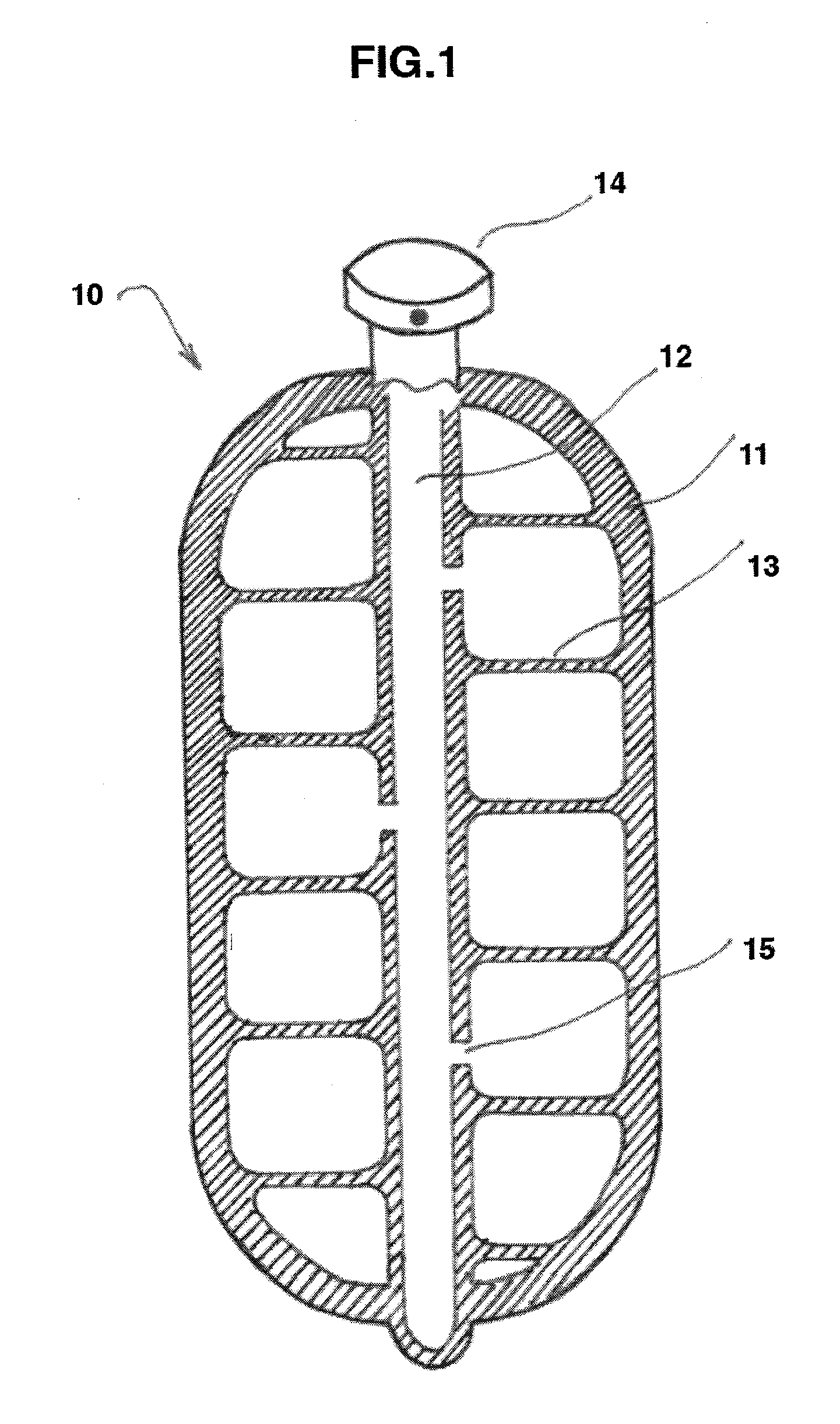
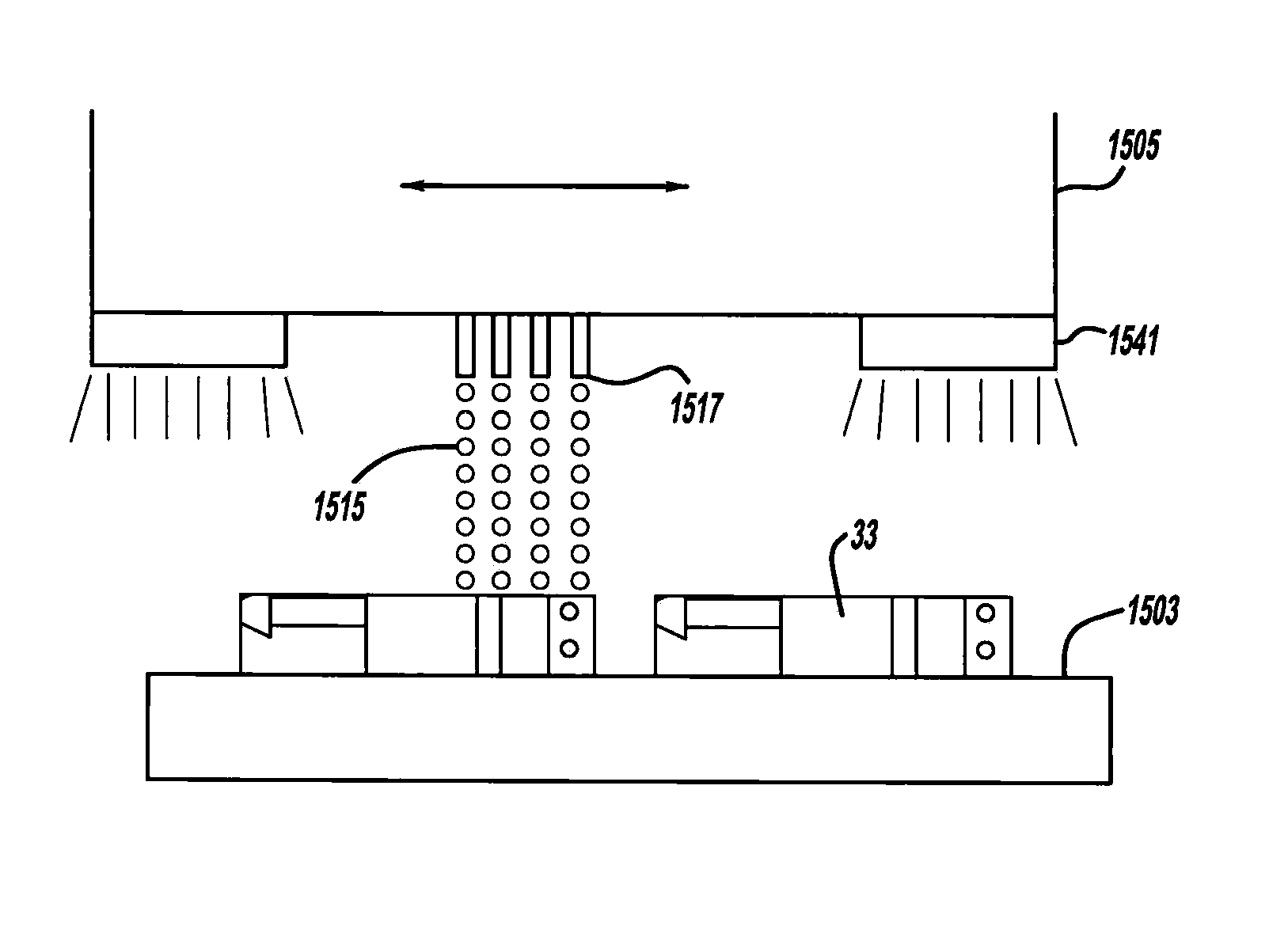
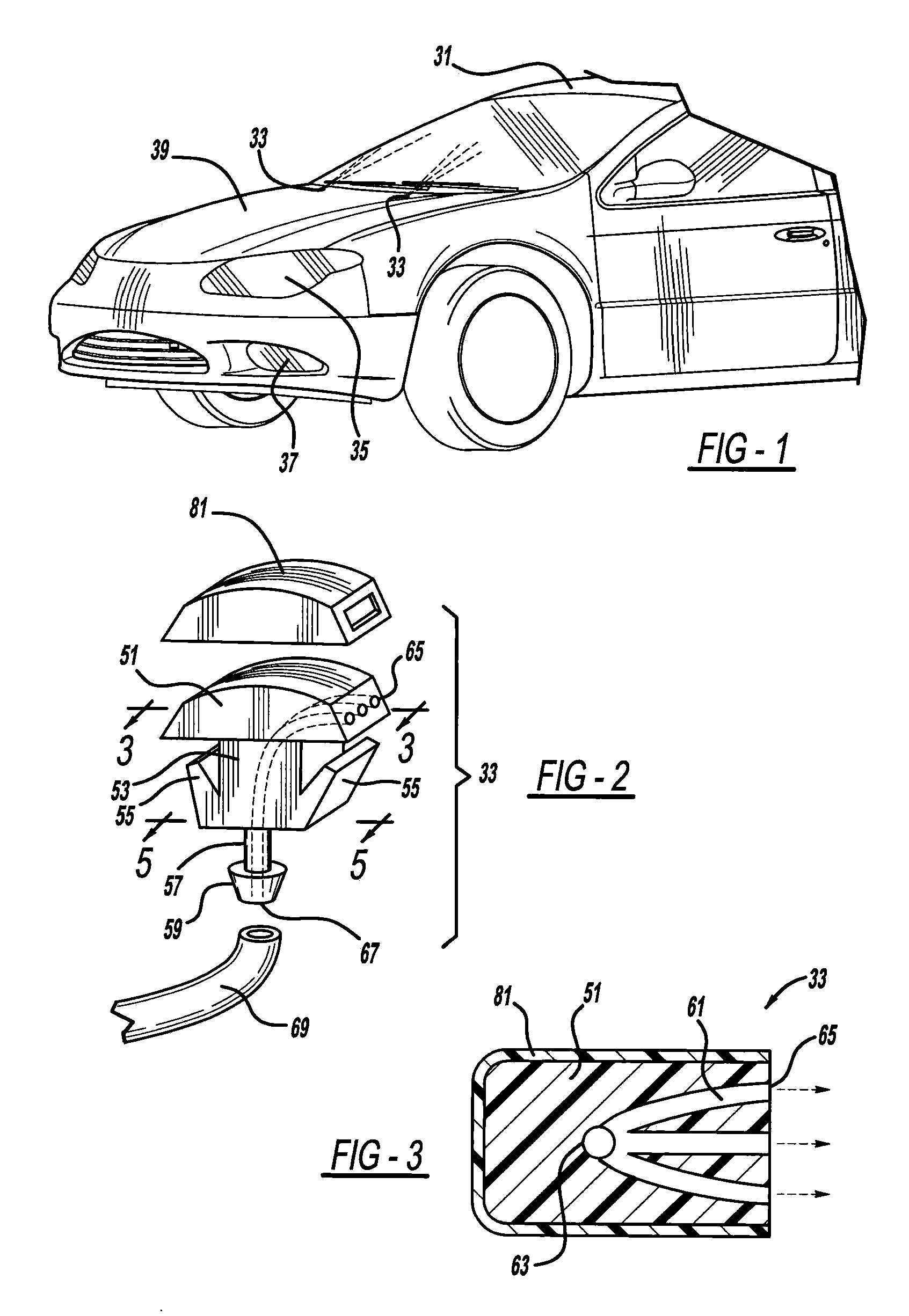
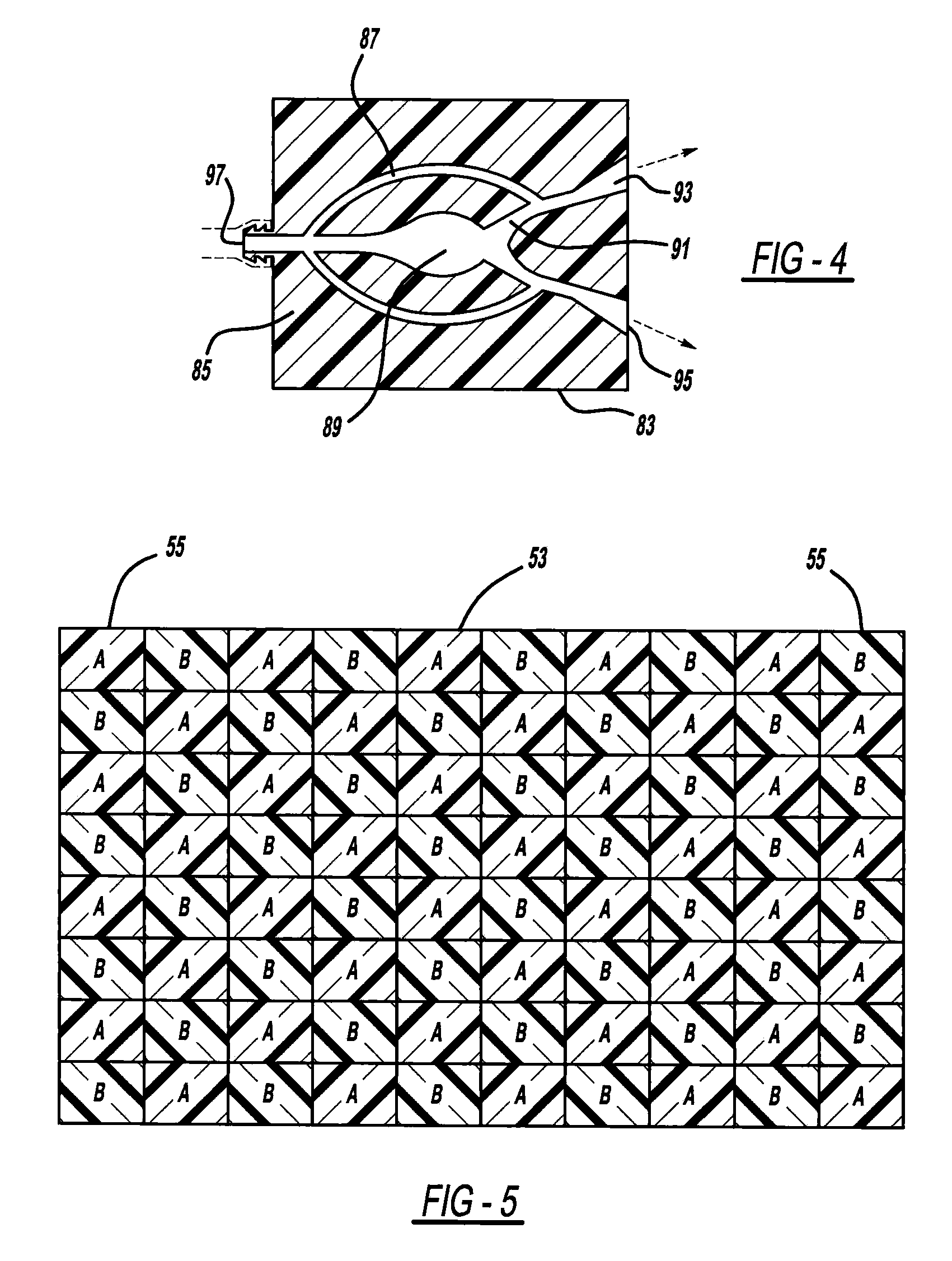
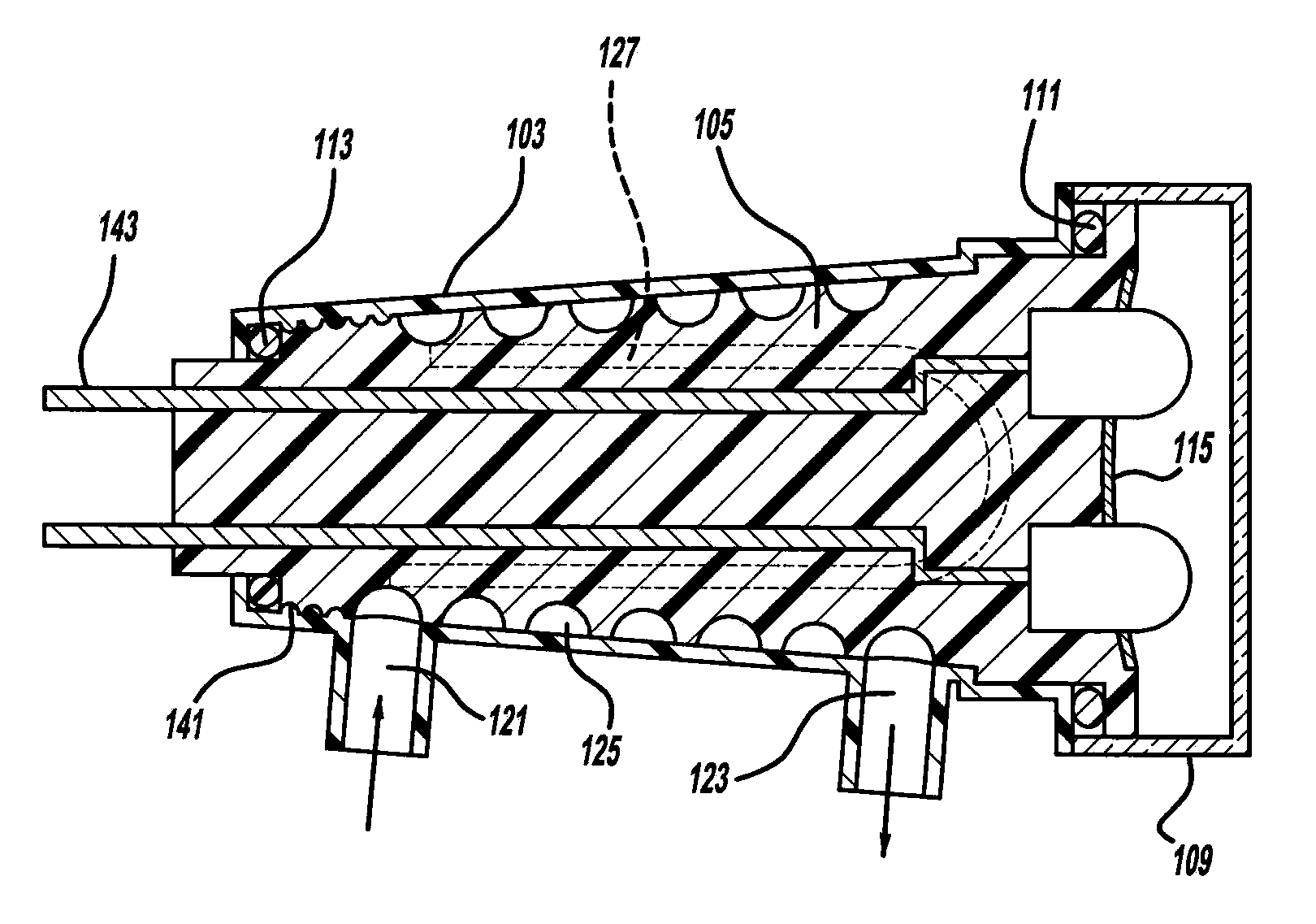
Process of making a component with a passageway
A component is provided that includes at least one passageway. In another aspect, a component, such as a lamp or a vehicular washer jet, is made of layers of material, a light curable material and / or multiple built-up materials. Another aspect uses a three-dimensional printing machine to emit material from an ink jet printing head to build up a component.
Owner:A RAYMOND & CO
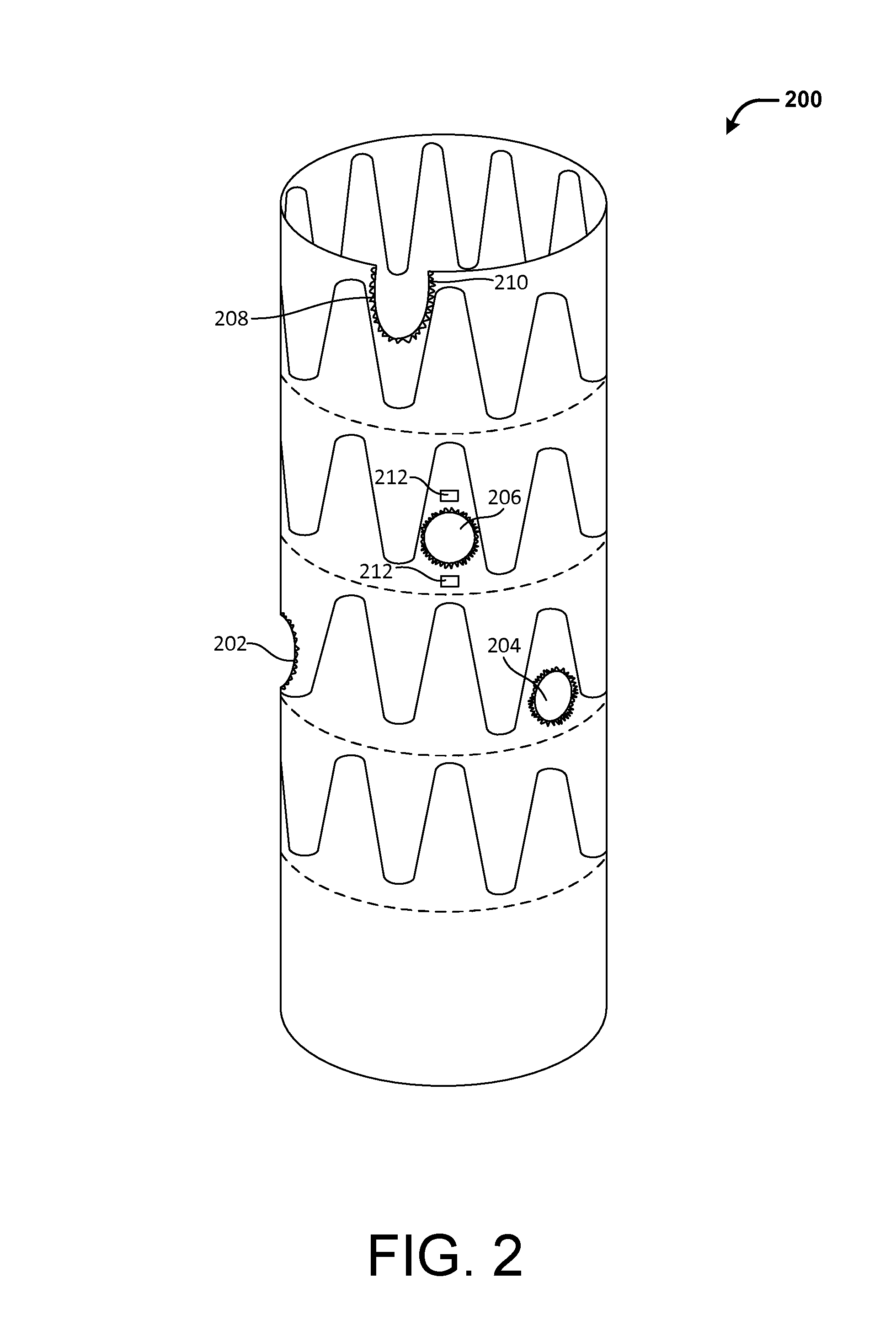
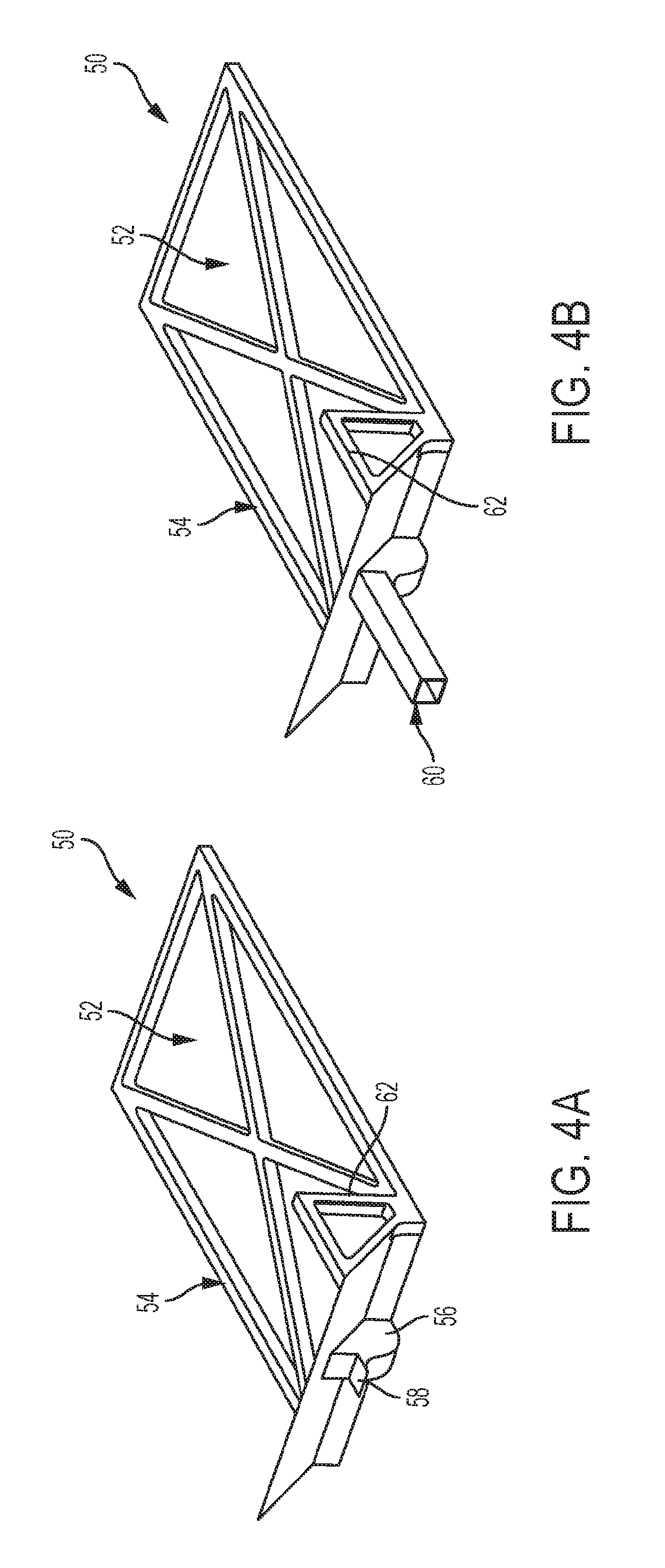
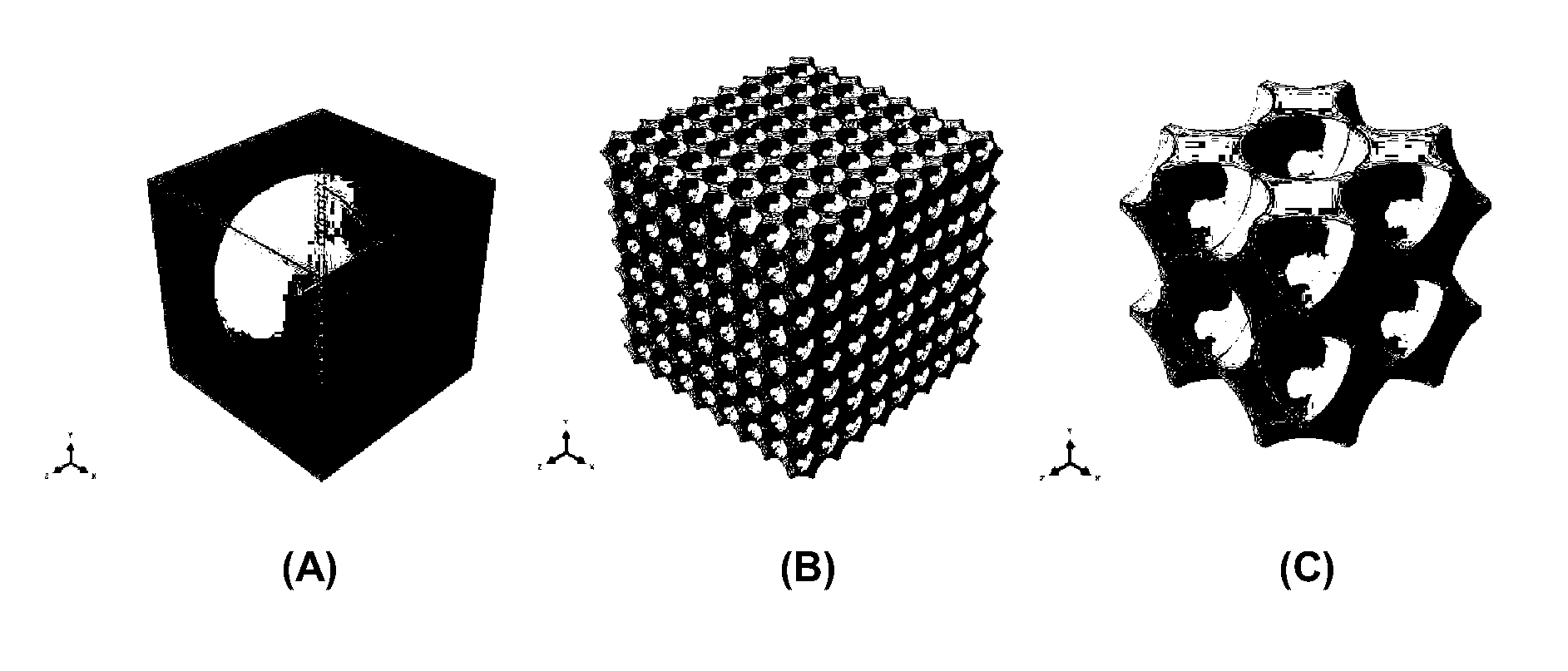
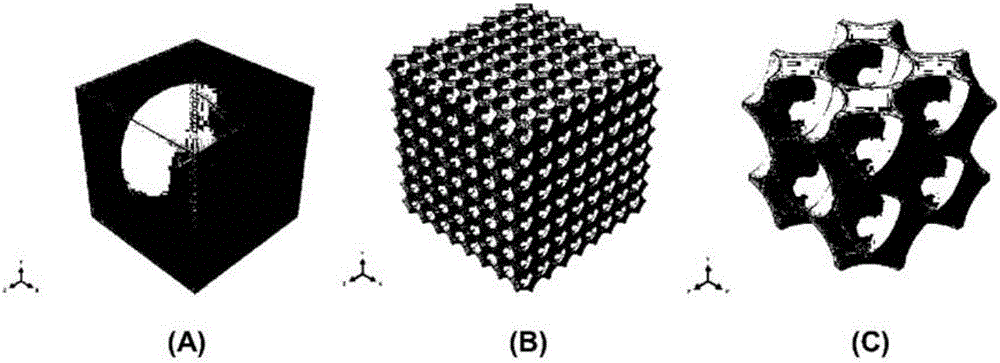
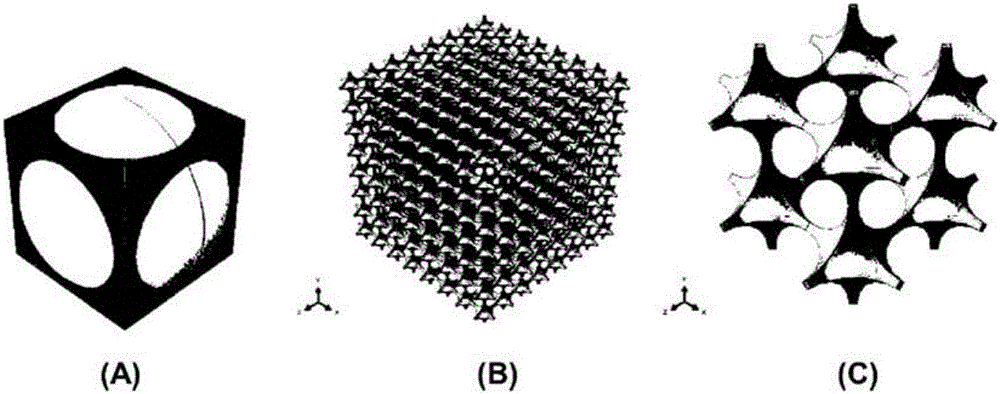
Structured Porous Metamaterial
InactiveUS20170009036A1Convenient lengthEffective supportAdditive manufacturing apparatusMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesPorosityThree dimensional matrix
A structured porous metamaterial includes a three-dimensional matrix of at least one repeating base unit. The matrix is formed from an array of at least eight base units, each base unit including a platonic solid including at least one shaped void, wherein each base unit has void geometry tailored to provide a porosity of between 0.3 and 0.97, and to provide the metamaterial with a response that includes a Poisson's ratio of 0 to −0.5 when under tension and compression, or negative linear compression (NLC), negative area compression (NAC), zero linear compression (ZLC), or zero area compression (ZAC) behaviour when under pressure.
Owner:RMIT UNIVERSITY
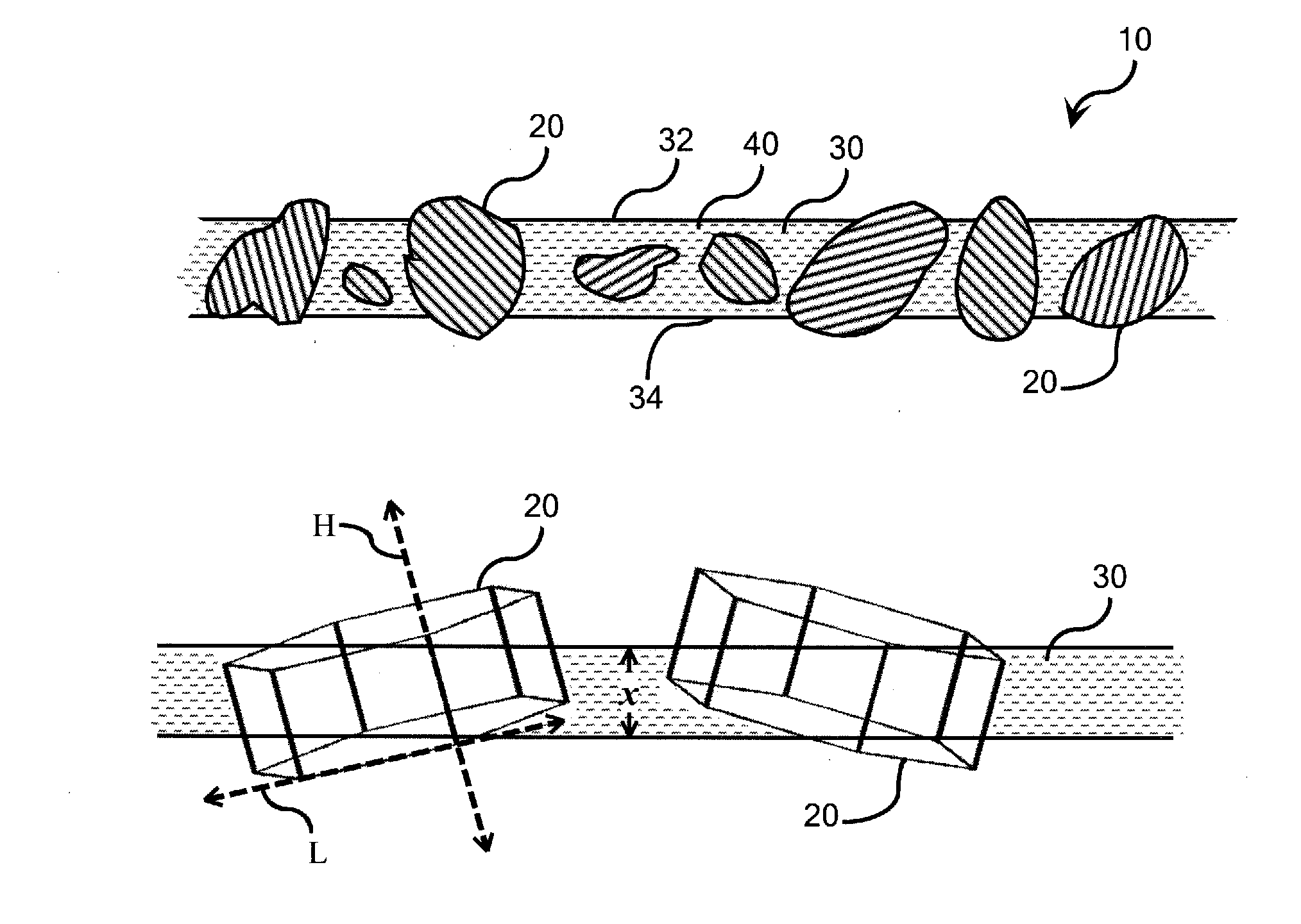
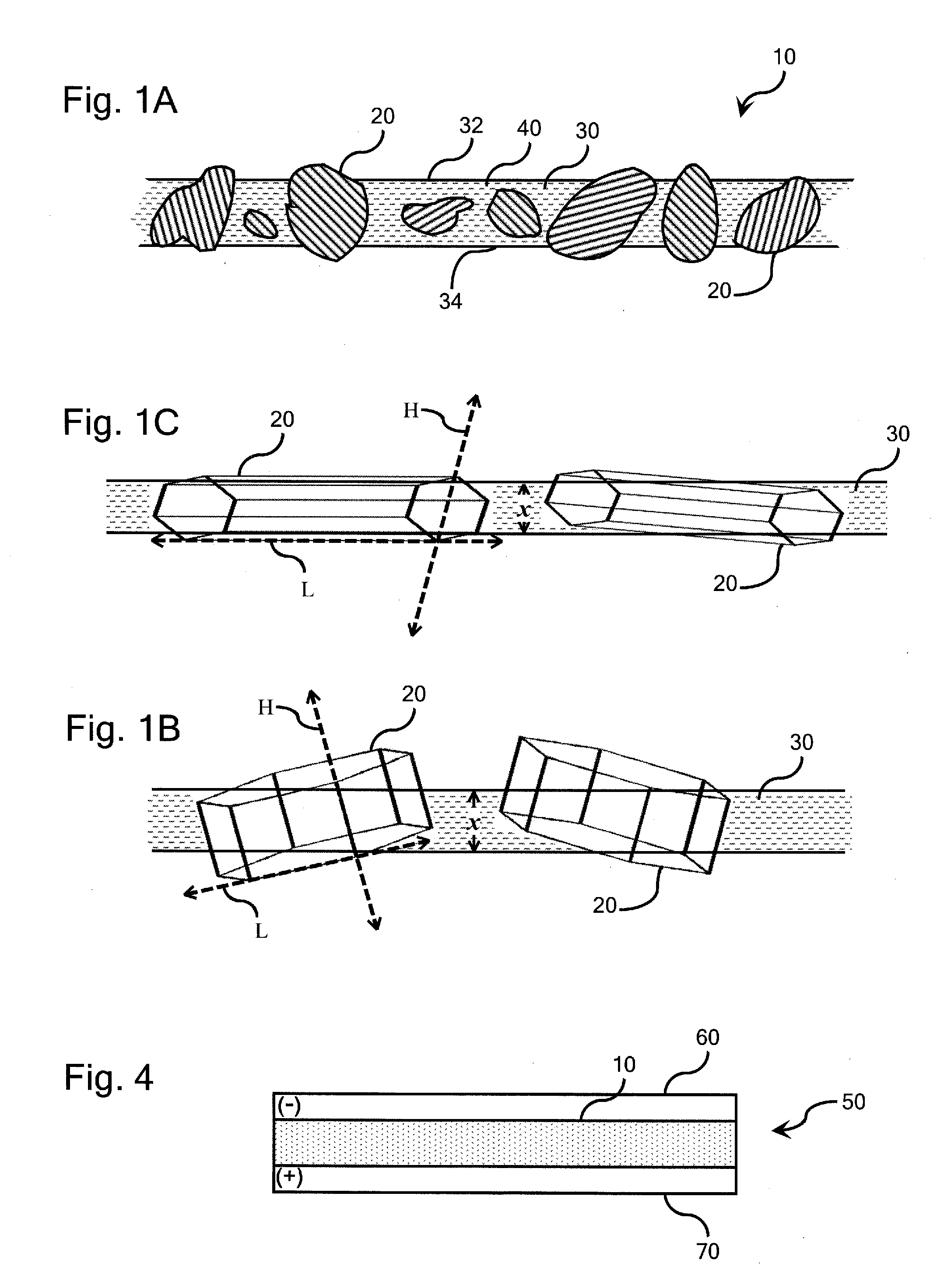
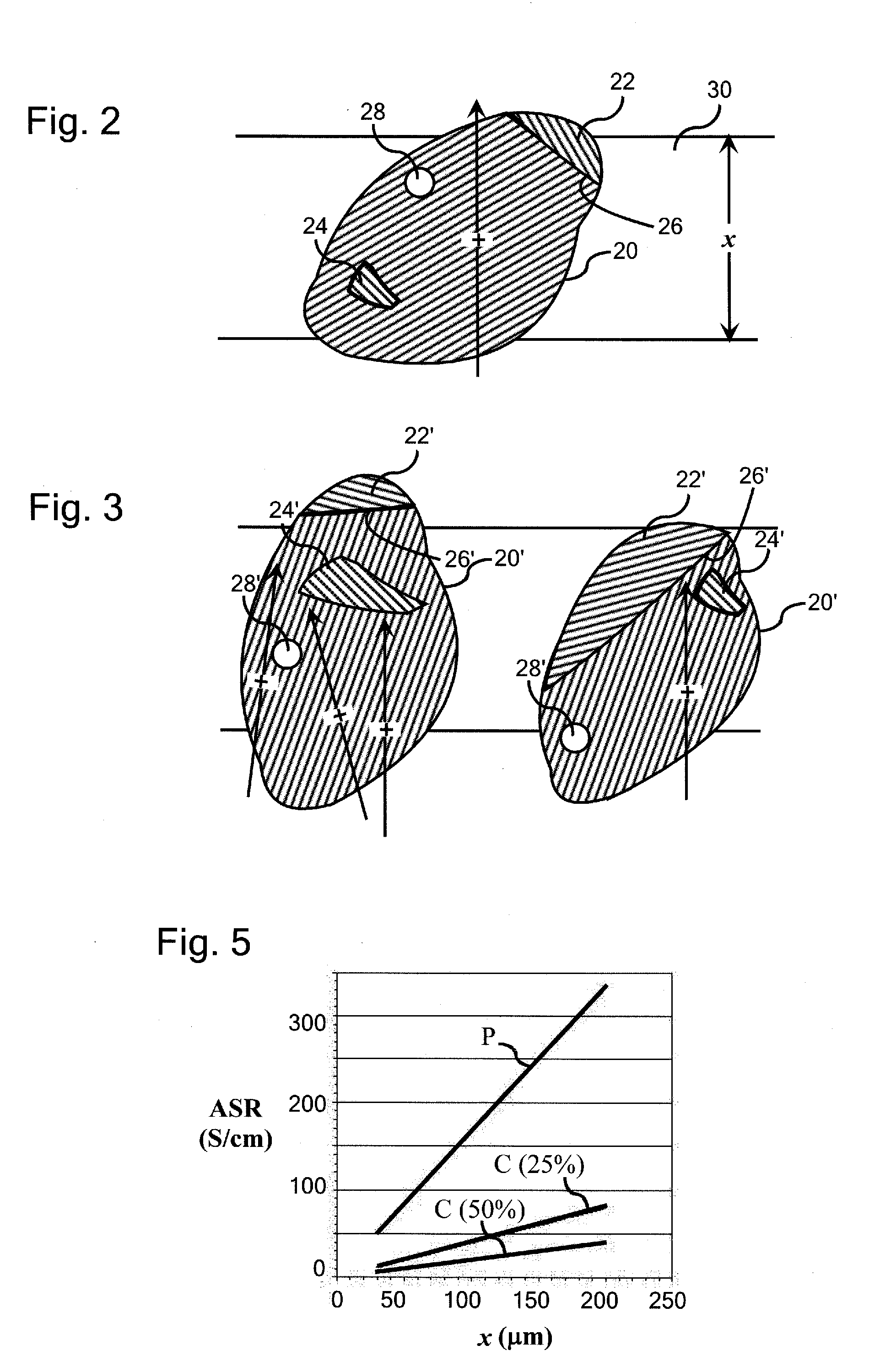
Ion-conducting composite electrolyte comprising path-engineered particles
ActiveUS20140065513A1Made practicalLimit ionic conductivityFrom normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricityPath lengthComposite electrolyte
An ion-conducting composite electrolyte is provided comprising path-engineered ion-conducting ceramic electrolyte particles and a solid polymeric matrix. The path-engineered particles are characterized by an anisotropic crystalline structure and the ionic conductivity of the crystalline structure in a preferred conductivity direction H associated with one of the crystal planes of the path-engineered particle is larger than the ionic conductivity of the crystalline structure in a reduced conductivity direction L associated with another of the crystal planes of the path-engineered particle. The path-engineered particles are sized and positioned in the polymeric matrix such that a majority of the path-engineered particles breach both of the opposite major faces of the matrix body and are oriented in the polymeric matrix such that the preferred conductivity direction H is more closely aligned with a minimum path length spanning a thickness of the matrix body than is the reduced conductivity direction L.
Owner:CORNING INC
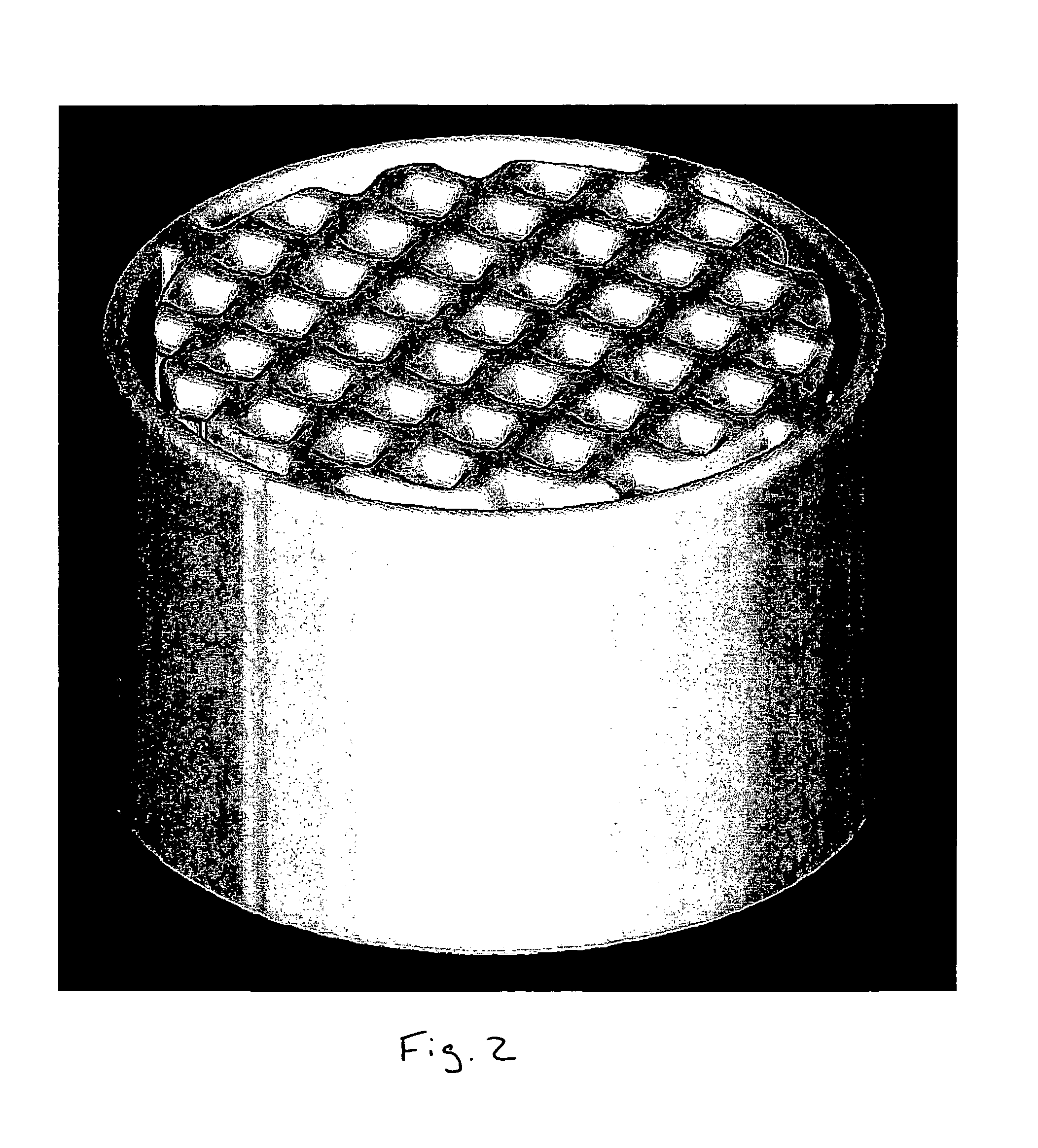
Porous structures produced by additive layer manufacturing
ActiveUS20180361510A1Bone ingrowth may be facilitatedPromote bone ingrowthStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
A three-dimensional structure is formed when layers of a material are deposited onto a substrate and scanned with a high energy beam to at least partially melt each layer of the material. Upon scanning the layers at predetermined locations a tube device having a first tube and a second tube intersected with the first tube is formed.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
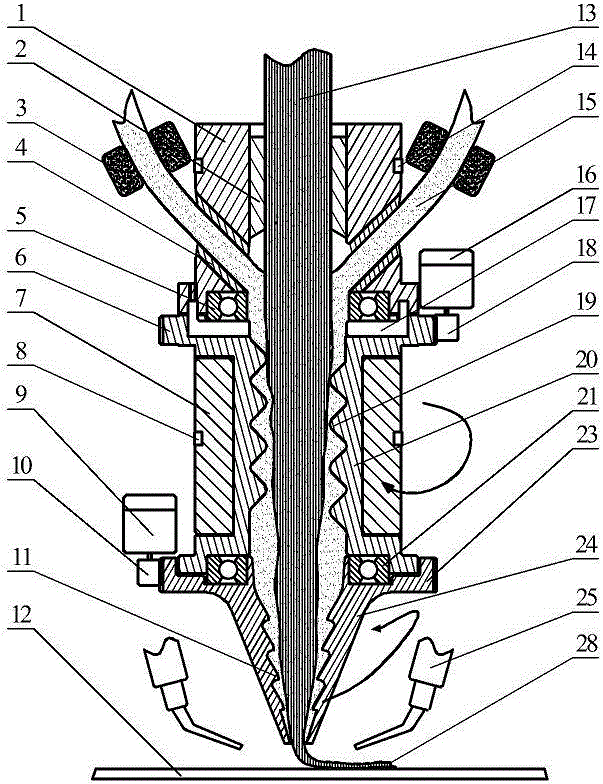
Method for rapid generation of multiple investment cast parts such as turbine or compressor wheels
ActiveUS20100006252A1Remove capital expenditureReduce processing timeAdditive manufacturing apparatusFoundry mouldsInvestment castingRefractory
The process for investment casting of complex shapes has historically had 6 basic steps in it. Depending upon the path taken, these discrete steps have been reduced to either 5 steps, or to 2 steps, discarding the unwanted steps. Instead of having to generate the shape of each sacrificial pattern, the process generates either(A) a male tree containing a plurality of sacrificial patterns, already on their runners, onto which a mold shell can be formed, or,(B) a female shell, made of a refractory material, and forming internally the outside surfaces of the plurality of patterns and runners.This process removes both capital expenditure for tooling and process time by up to 90%. By removing several lengthy, time-dependant steps from the process the part cost and lead time are reduced.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Compositions and methods for use in three dimensional model printing
InactiveUS20080105818A1Similar elasticitySimilar strengthButtonsRecord carriersInvestment castingMaterials science
Embodiments of the invention are directed to a method of producing three-dimensional prototype molds for use in investment casting. The method includes dispensing modeling material and support material in a predetermined arrangement, in layers, to produce a three-dimensional mold having an outer shell. Generally, the out shell includes modeling material and the interior of the mold includes support material. Then the mold is cured.
Owner:OBJET GEOMETRIES
Silicone compositions for producing elastomeric molded parts by means of ballistic methods
InactiveUS20180066115A1High-quality industrial productionAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
3D printing of curable silicone cam positions is made possible by employing a mixture of Si—H-functional silicon compounds and silicon compounds bearing aliphatically unsaturated groups, a hydrosilylation catalyst, and a combination of a reinforcing filler and a rheological agent containing polar groups, exhibiting shear thinning behavior.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
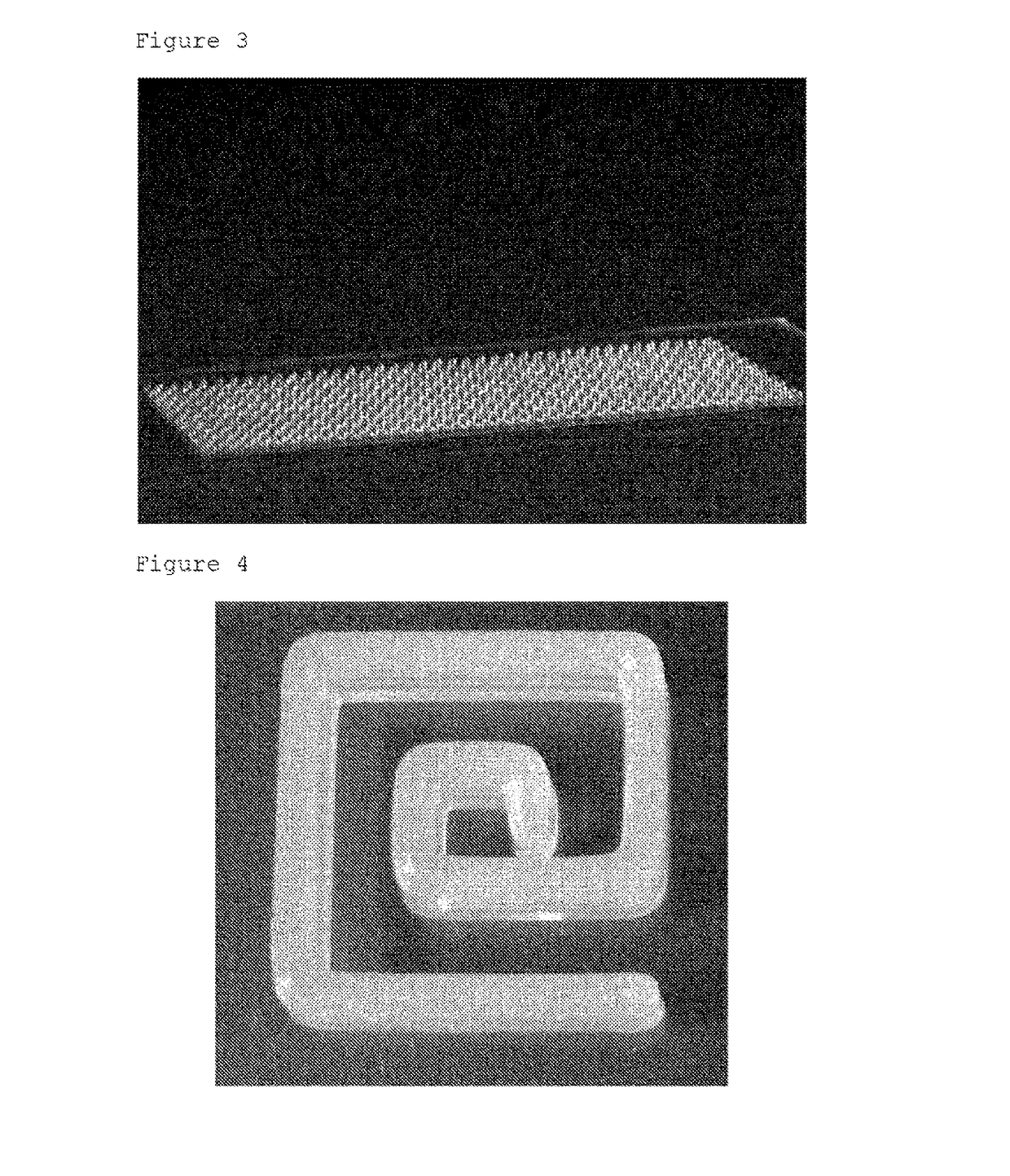
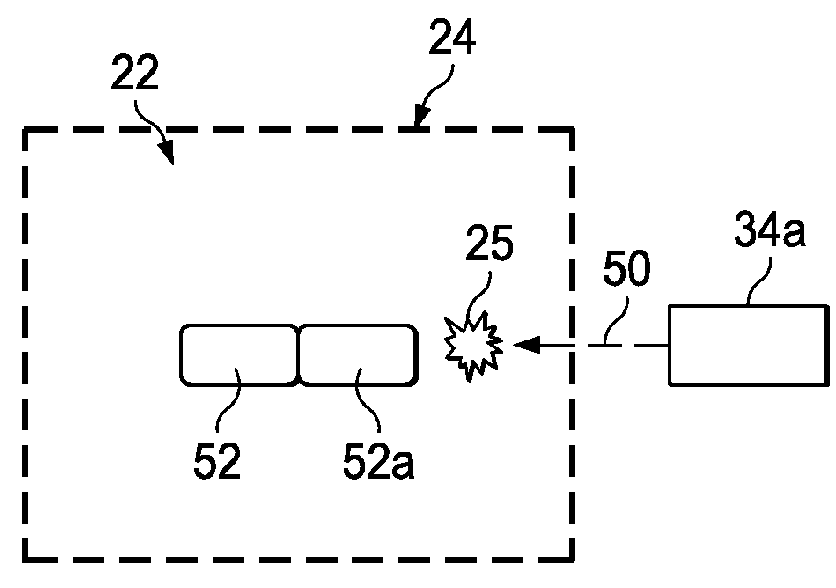
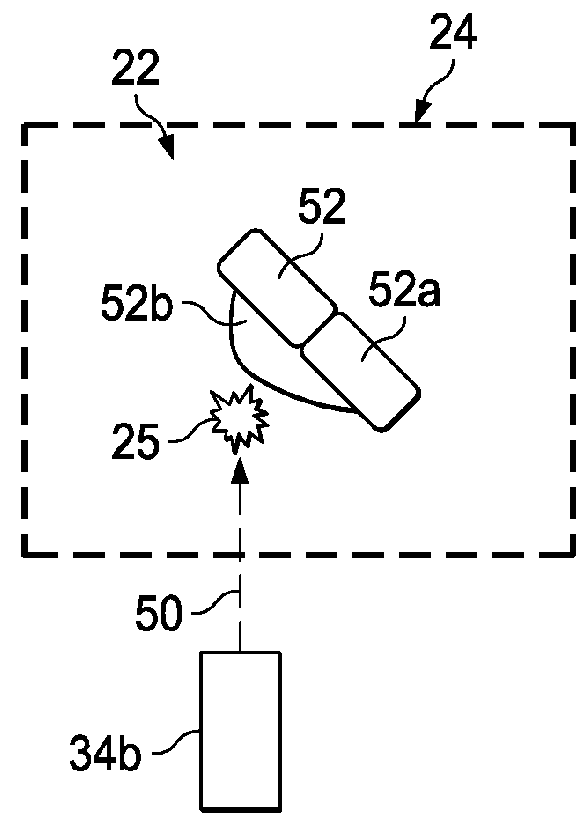
Free-Form Spatial 3-D Printing Using Part Levitation
ActiveUS20160031156A1Improve manufacturing speedAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectric discharge heatingSpatial OrientationsLevitation
A part is fabricated by an additive manufacturing process while levitating in space. Constituent features of the part are formed by 3-D printing. A part levitation system allows the spatial orientation of the part to be manipulated relative to one or more print heads.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method of forming a joint
ActiveUS20110240200A1High peel strengthHigh strengthVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesFiberEngineering
A method of forming a joint between a first component and a second component, the first component comprising a plurality of layers of fibres impregnated with a thermosetting matrix. A welding interface element is provided with an array of pointed prongs. One or more of the layers of fibres are penetrated with the prongs, either before or after the fibres have been impregnated with the thermosetting matrix. The first component is cured by heating the thermosetting matrix after the prongs have been embedded. A thermoplastic weld is formed between the second component and the welding interface element.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Structured porous metamaterial
InactiveCN106457748AAdditive manufacturing apparatusLayered productsPorosityThree dimensional matrix
The invention relates to a structured porous metamaterial. The structured porous metamaterial comprises a three-dimensional matrix of at least one repeating base unit, wherein the matrix is formed from an array of at least eight base units, each base unit comprises a platonic solid including at least one shaped void, each base unit has void geometry tailored to provide a porosity of between 0.3 and 0.97; or provide the metamaterial with a response comprising at least one of a Poisson's ratio of 0 to -0.5 when under tension and compression; or negative linear compression (NLC), negative area compression (NAC), zero linear compression (ZLC), or zero area compression (ZAC) behaviour when under pressure.
Owner:RMIT UNIVERSITY
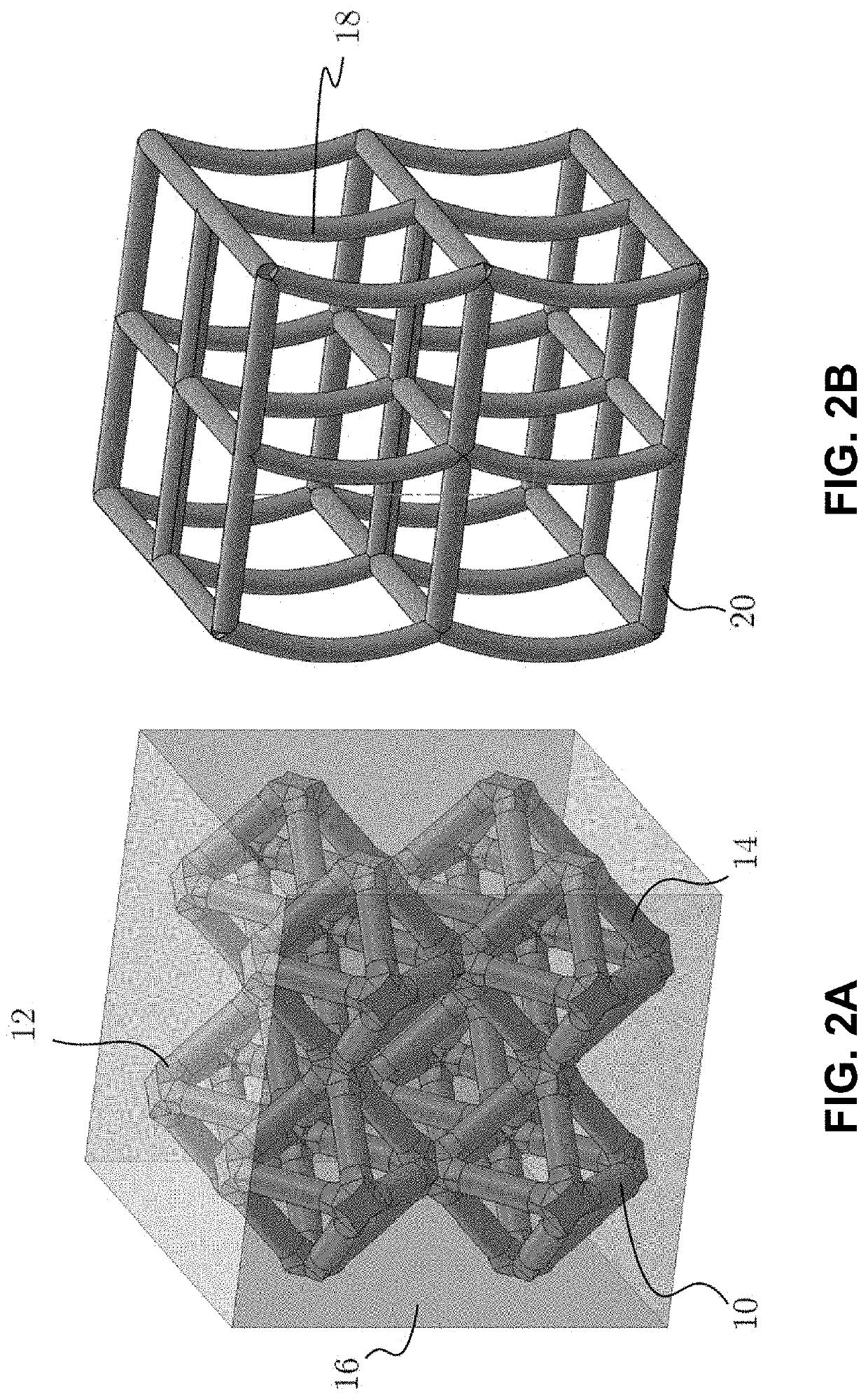
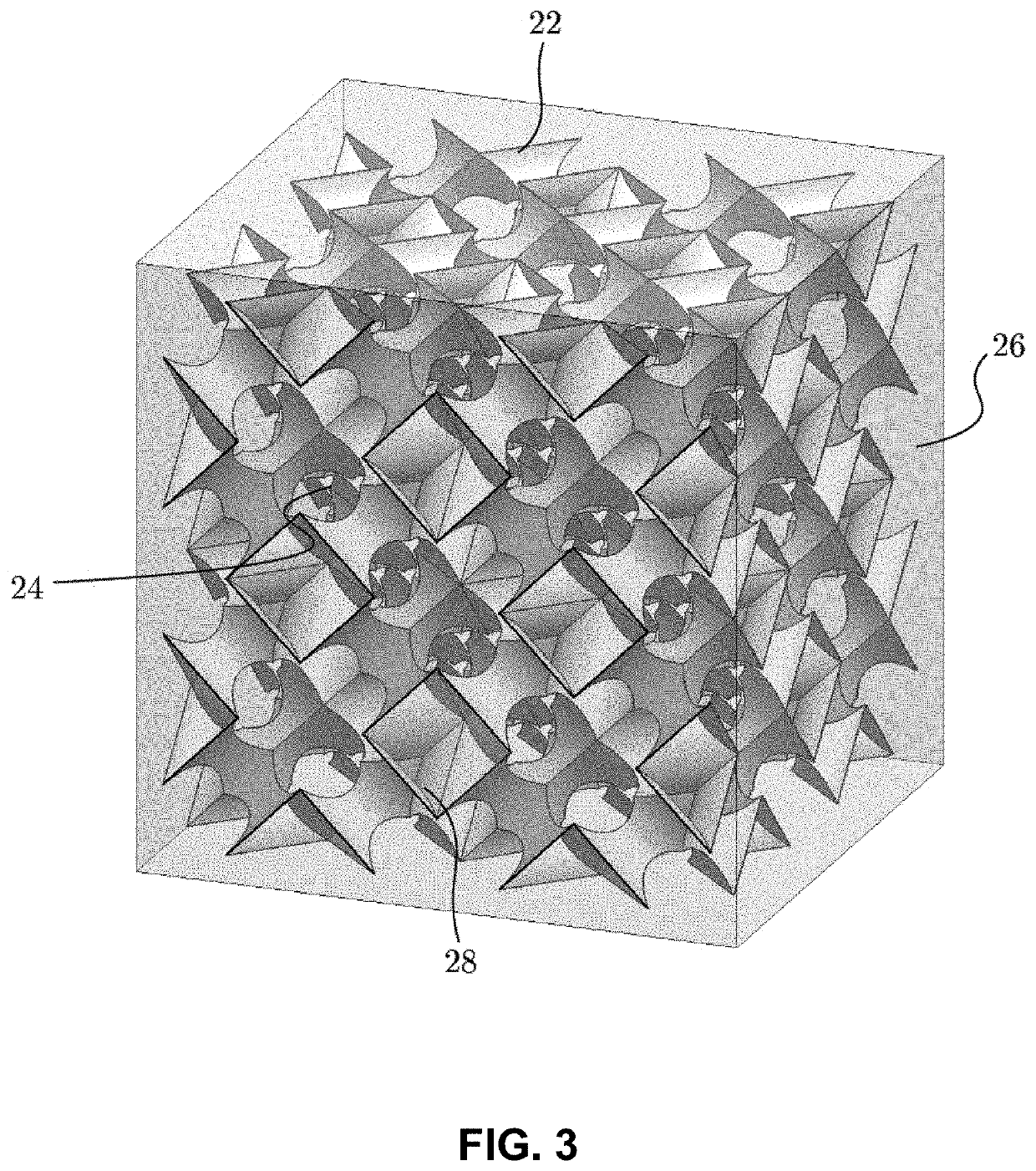
Fabrication and design of composites with architected layers
PendingUS20200023584A1Improve adhesionAdditive manufacturing apparatusSpringsEngineeringMechanical engineering
In an aspect, a composite material system comprises: a structure having an architected three-dimensional geometry; wherein said three-dimensional geometry is monolithic and deterministic; and a matrix phase; wherein said matrix phase at least partially infiltrates said structure. In some embodiments, the three-dimensional geometry is a nano- or micro-architected three-dimensional geometry.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
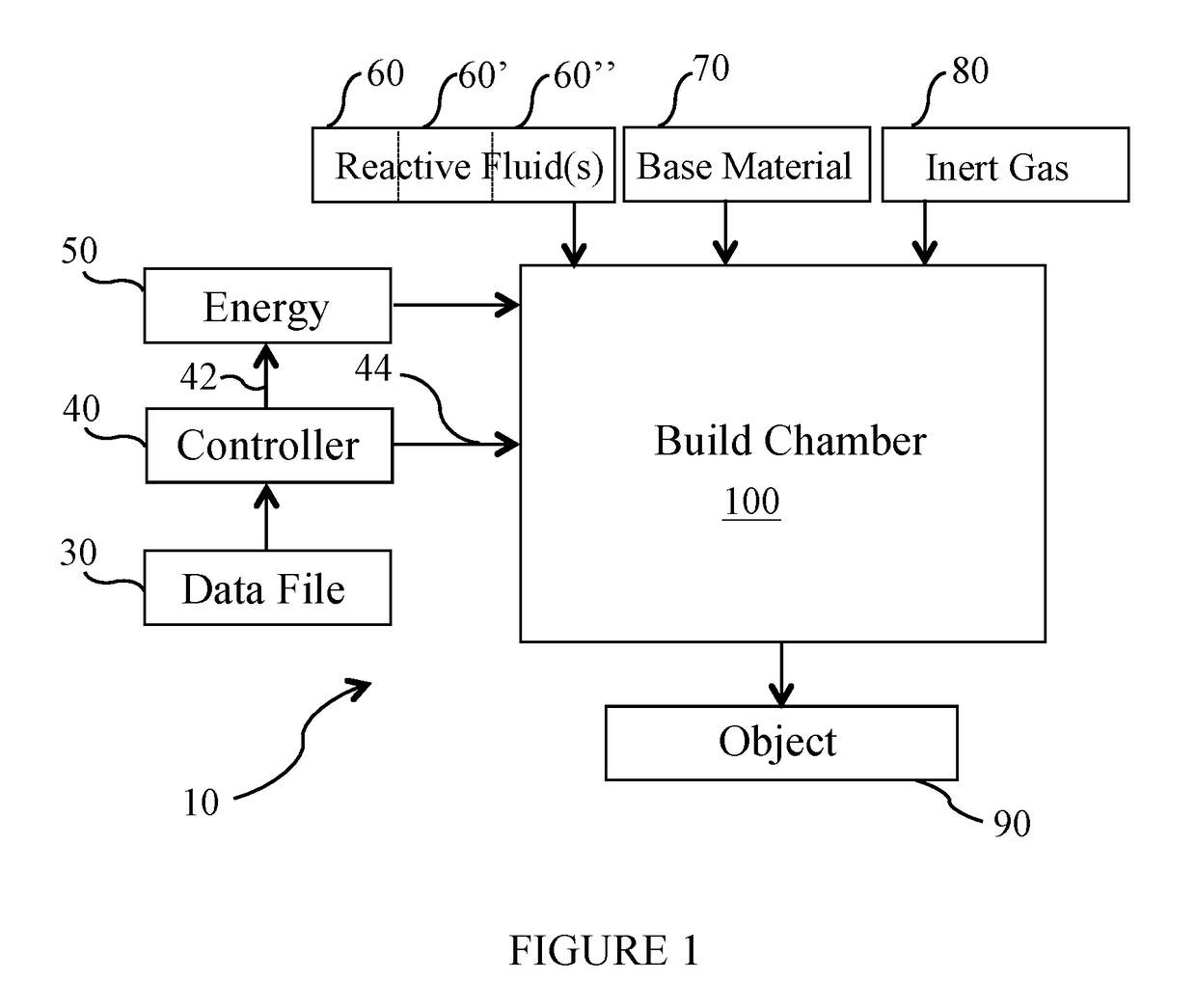
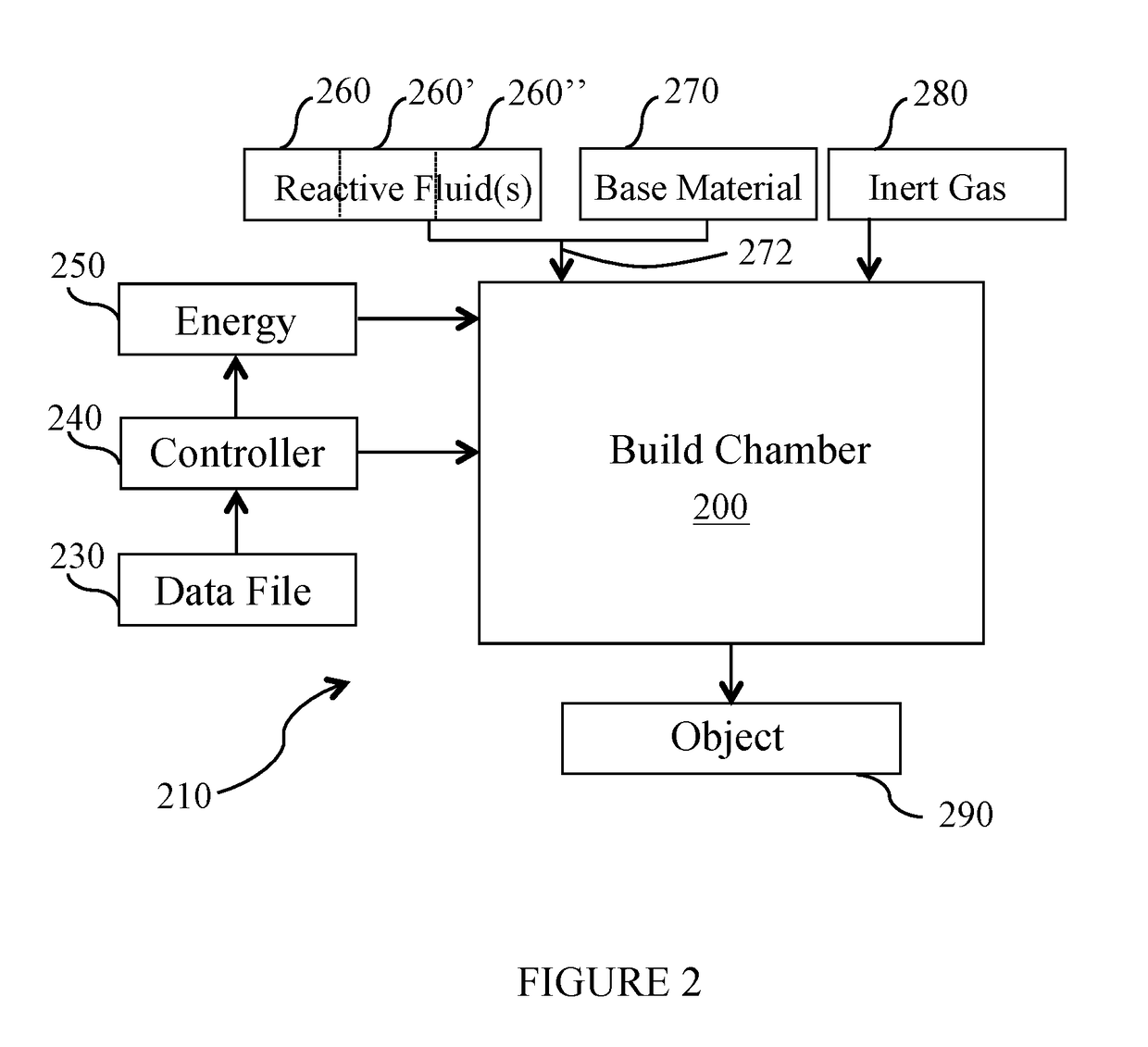
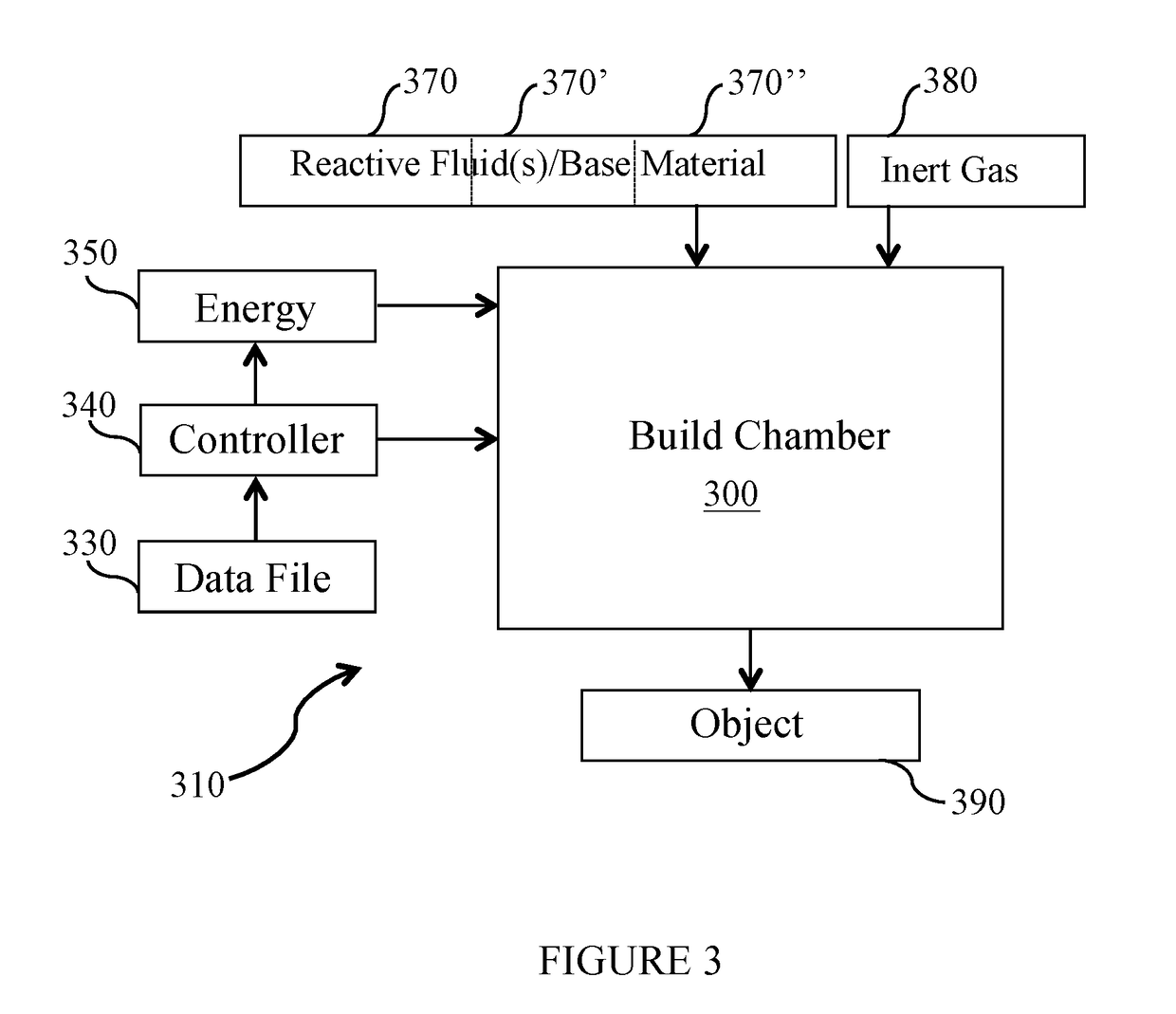
Use of reactive fluids in additive manufacturing and the products made therefrom
PendingUS20170182558A1Improve mechanical propertiesAvoid stickingAdditive manufacturing apparatusSolid state diffusion coatingAdditive layer manufacturingManufacturing engineering
The present invention generally relates to methods and apparatuses adapted to perform additive manufacturing (AM) processes and the resulting products made therefrom, and specifically, to AM processes that employ an energy beam to selectively fuse a base material to produce an object. More particularly, the invention relates to methods and systems that use reactive fluids to actively manipulate the surface chemistry of the base material prior to, during and / or after the AM process.
Owner:MATHESON TRI GAS
Monomer formulations and methods for 3D printing of preceramic polymers
ActiveUS20180148380A1Prevent degradationGood compatibilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusInks3d shapesFree form
This invention provides resin formulations which may be used for 3D printing and pyrolyzing to produce a ceramic matrix composite. The resin formulations contain a solid-phase filler, to provide high thermal stability and mechanical strength (e.g., fracture toughness) in the final ceramic material. The invention provides direct, free-form 3D printing of a preceramic polymer loaded with a solid-phase filler, followed by converting the preceramic polymer to a 3D-printed ceramic matrix composite with potentially complex 3D shapes or in the form of large parts. Other variations provide active solid-phase functional additives as solid-phase fillers, to perform or enhance at least one chemical, physical, mechanical, or electrical function within the ceramic structure as it is being formed as well as in the final structure. Solid-phase functional additives actively improve the final ceramic structure through one or more changes actively induced by the additives during pyrolysis or other thermal treatment.
Owner:HRL LAB
Component with a passageway made by three-dimensional printing
InactiveUS20120304449A1Many timesQuick and inexpensive designTube/lamp screens manufacturePoint-like light sourcePrinting press3 dimensional printing
A component is provided that includes at least one passageway. In another aspect, a component, such as a lamp or a vehicular washer jet, is made of layers of material, a light curable material and / or multiple built-up materials. Another aspect uses a three-dimensional printing machine to emit material from an ink jet printing head to build up a component.
Owner:A RAYMOND & CO
Formulations and methods for 3D printing of ceramic matrix composites
ActiveUS20180148379A1Prevent degradationGood compatibilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusInks3d shapesFree form
This invention provides resin formulations which may be used for 3D printing and pyrolyzing to produce a ceramic matrix composite. The resin formulations contain a solid-phase filler, to provide high thermal stability and mechanical strength (e.g., fracture toughness) in the final ceramic material. The invention provides direct, free-form 3D printing of a preceramic polymer loaded with a solid-phase filler, followed by converting the preceramic polymer to a 3D-printed ceramic matrix composite with potentially complex 3D shapes or in the form of large parts. Other variations provide active solid-phase functional additives as solid-phase fillers, to perform or enhance at least one chemical, physical, mechanical, or electrical function within the ceramic structure as it is being formed as well as in the final structure. Solid-phase functional additives actively improve the final ceramic structure through one or more changes actively induced by the additives during pyrolysis or other thermal treatment.
Owner:HRL LAB
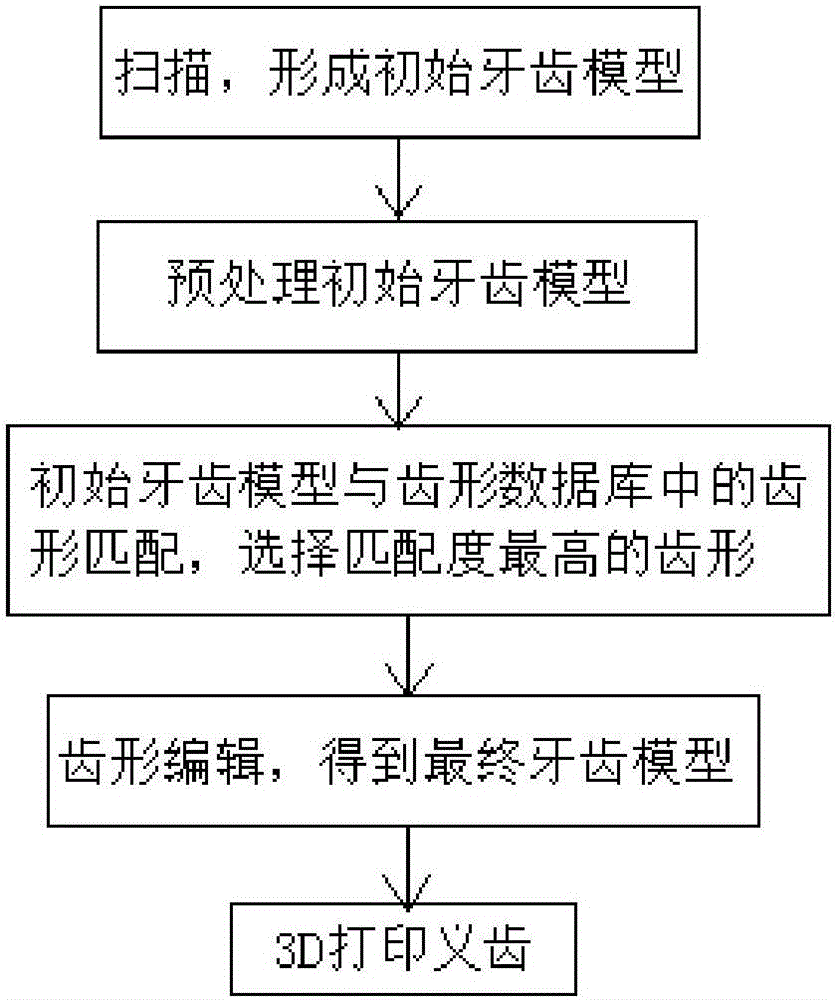
Rapid denture forming method and rapid denture forming device
InactiveCN106626351ASimplified molding stepsHigh forming precisionAdditive manufacturing apparatusArtificial teethDentures3d printed
The invention relates to a rapid denture forming method. The rapid denture forming method comprises the following steps: scanning teeth by using an oral scanner, and forming an initial tooth model; pretreating the initial tooth model; matching the pretreated tooth model with tooth shapes in a tooth shape database, and selecting the tooth shapes with highest matching degree; compiling selected tooth shapes according to an international denture repairing standard, thus obtaining a tooth model which is finally required; carrying out 3D (Three-Dimensional) printing to obtain the denture according to the tooth model which is finally obtained. By adopting the rapid denture forming method disclosed by the invention, the denture forming steps are simple, the forming time is greatly shortened, and the denture forming accuracy is high; the manufacturing cost of the denture is greatly reduced, and promotion and use of the technology are convenient.
Owner:深圳晗竣雅科技有限公司
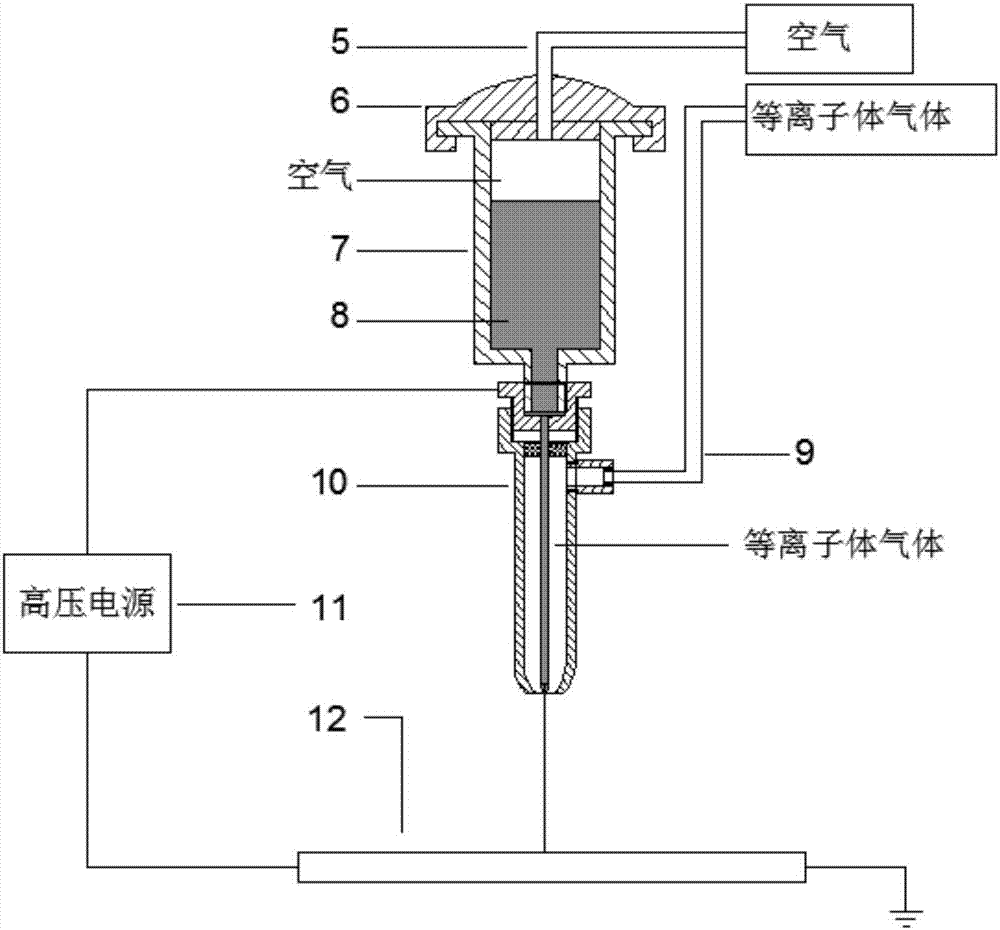
Integrated spray printing device used for additive and subtractive manufacturing
ActiveCN107199693ARealize electrojet printing processAchieve surface modificationManufacturing material handlingAdditive manufacturing processesPlasma jetProduct gas
The invention discloses a spray printing device integrating a plasma jet technology. The device comprises a spraying head, a high pressure power source, a collecting base plate and a liquid inlet barrel. According to the spray printing device, the high pressure power source is used for generating spray printing process electric field requirements and serving as a plasma jet excitation source, gas discharge is used for generating plasma jets, unified application of electric fluid spray printing machining (additive machining) and plasma etching machining (subtractive machining) is achieved on one device, and real-time surface modification of plasmas on electric spray printing materials in the machining process, sintering curing of electric spray printing deposition materials and additive and subtractive synchronization machining are included for achieving quick molding of complex patterns and multi-layer structures. By means of the spray printing device, application in a combination manner or an array manner can be achieved, and the spray printing device can be used for preparing large-area multi-layer complex structures. Through application of the spray printing device, the machining efficiency and the material performance are improved, and wide application prospects in the fields of MEMS machining and manufacturing and electric fluid jet printing are achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Encapsulated materials in porous particles
InactiveUS20170306221A1High white lightNarrow emission bandAdditive manufacturing apparatusGranule coatingParticulatesRadioactive agent
The invention provides a process for the production of a (particulate) luminescent material comprising particles, especially substantially spherical particles, having a porous inorganic material core with pores, especially macro pores, which are at least partly filled with a polymeric material with a first material embedded therein, wherein the process comprises (i) impregnating the particles of a particulate porous inorganic material with pores with a first liquid (“ink”) comprising the first material and a curable or polymerizable precursor of the polymeric material, to provide pores that are at least partly filled with said first material and curable or polymerizable precursor; and (ii) curing or polymerizing the curable or polymerizable precursor within pores of the porous material, as well as a product obtainable thereby. The first material comprises one or more materials selected from a group of materials comprising organic luminescent materials, rare-earth luminescent materials, organic dye materials, inorganic dye materials, thermochromic materials, photochromic materials, liquid crystal materials, magnetic materials, scattering materials, high-refractive index materials, radio-active materials, contrast agents and therapeutic agents.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
System having layered structure and method of making the same
A system includes a layered structure. The layered structure includes first and second coalesced layers and an intermediate layer disposed between the first and second coalesced layers. The first and second coalesced layers have a higher degree of coalescence than the intermediate layer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Three-dimensional negative Poisson ratio periodic porous material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106541568AImprove energy consumptionImprove sound absorptionAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing processesPull forceThree-dimensional space
Owner:XIEYIMIN ENG SCI & TECH CHANGZHOU CO LTD
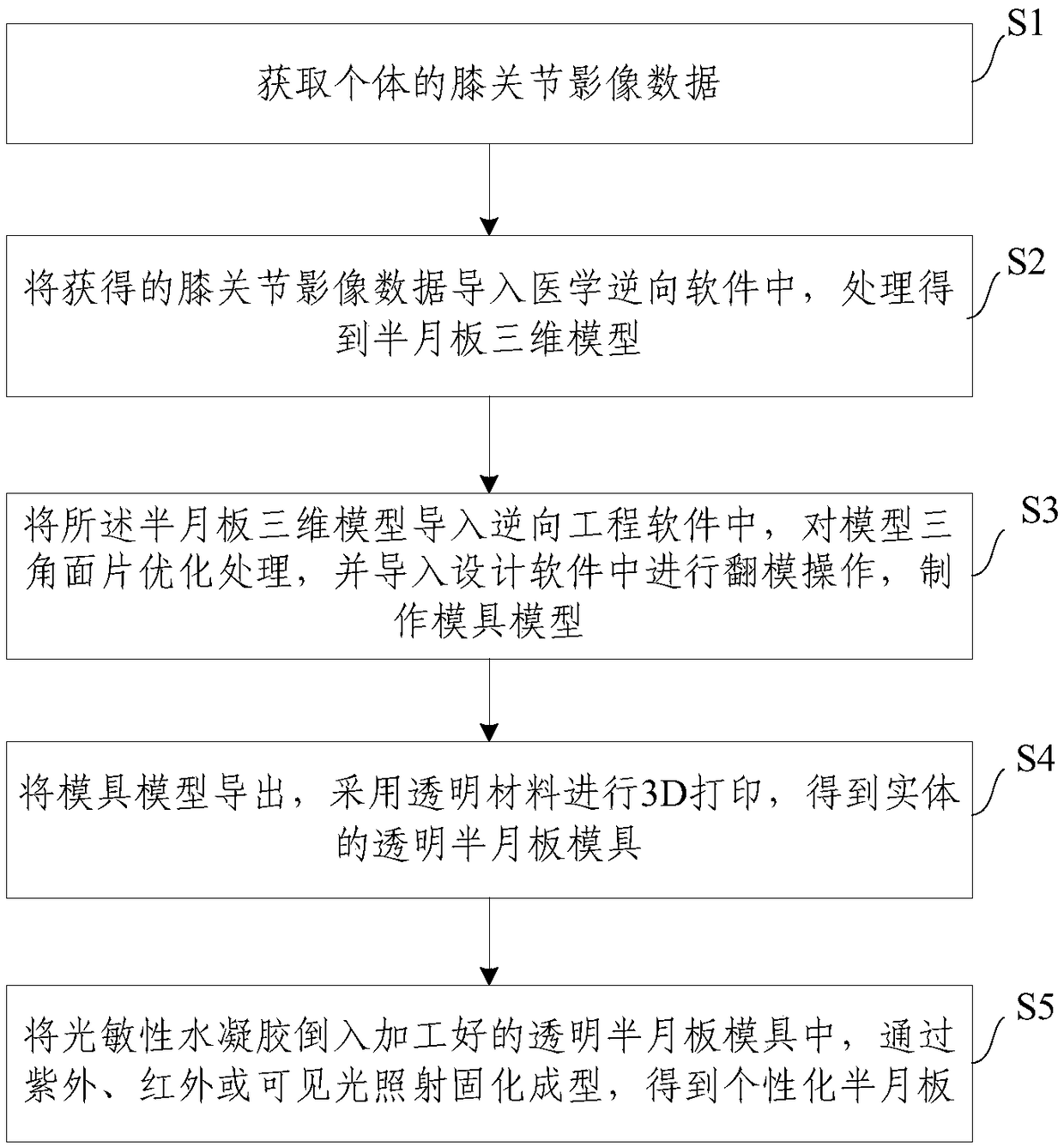
Individualized meniscus forming method based on 3D printing, meniscus and die
PendingCN109501091AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed repeatabilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusJoint implantsInfraredDesign software
The invention relates to an individualized meniscus forming method based on 3D printing, a meniscus, a meniscus die and a manufacturing method. The forming method includes the steps that knee joint image data of an individual are acquired; the acquired knee joint image data are guided in medical reverse software, and a meniscus three-dimensional model is obtained after processing is completed; themeniscus three-dimensional model is guided in reverse engineering software, a model triangular patch is optimized and guided in design software for turnover operation, and a die model is manufactured; a transparent material is adopted for 3D printing, and a physical transparent meniscus die is obtained; and light-sensitive hydrogel is poured into the machined meniscus die, curing and forming arecarried out through ultraviolet or infrared or visible light irradiation, and the individualized meniscus is obtained. The meniscus three-dimensional model is established based on the knee joint imagedata of the individual, the transparent die is designed and printed through 3D printing, the light-sensitive hydrogel is injected, curing and forming are completed after light irradiation, the stentprecision is improved, and the mechanical strength is guaranteed.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL +2
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com