Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
96 results about "Vaccine efficacy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vaccine efficacy is the percentage reduction of disease in a vaccinated group of people compared to an unvaccinated group, using the most favorable conditions. Vaccine efficacy was designed and calculated by Greenwood and Yule in 1915 for the cholera and typhoid vaccines. It is best measured using double-blind, randomized, clinical controlled trials, such that it is studied under “best case scenarios.” Vaccine effectiveness differs from vaccine efficacy in that vaccine effectiveness shows how well a vaccine works when they are always used and in a bigger population whereas vaccine efficacy shows how well a vaccine works in certain, often controlled, conditions. Vaccine efficacy studies are used to measure several possible outcomes such as disease attack rates, hospitalizations, medical visits, and costs.
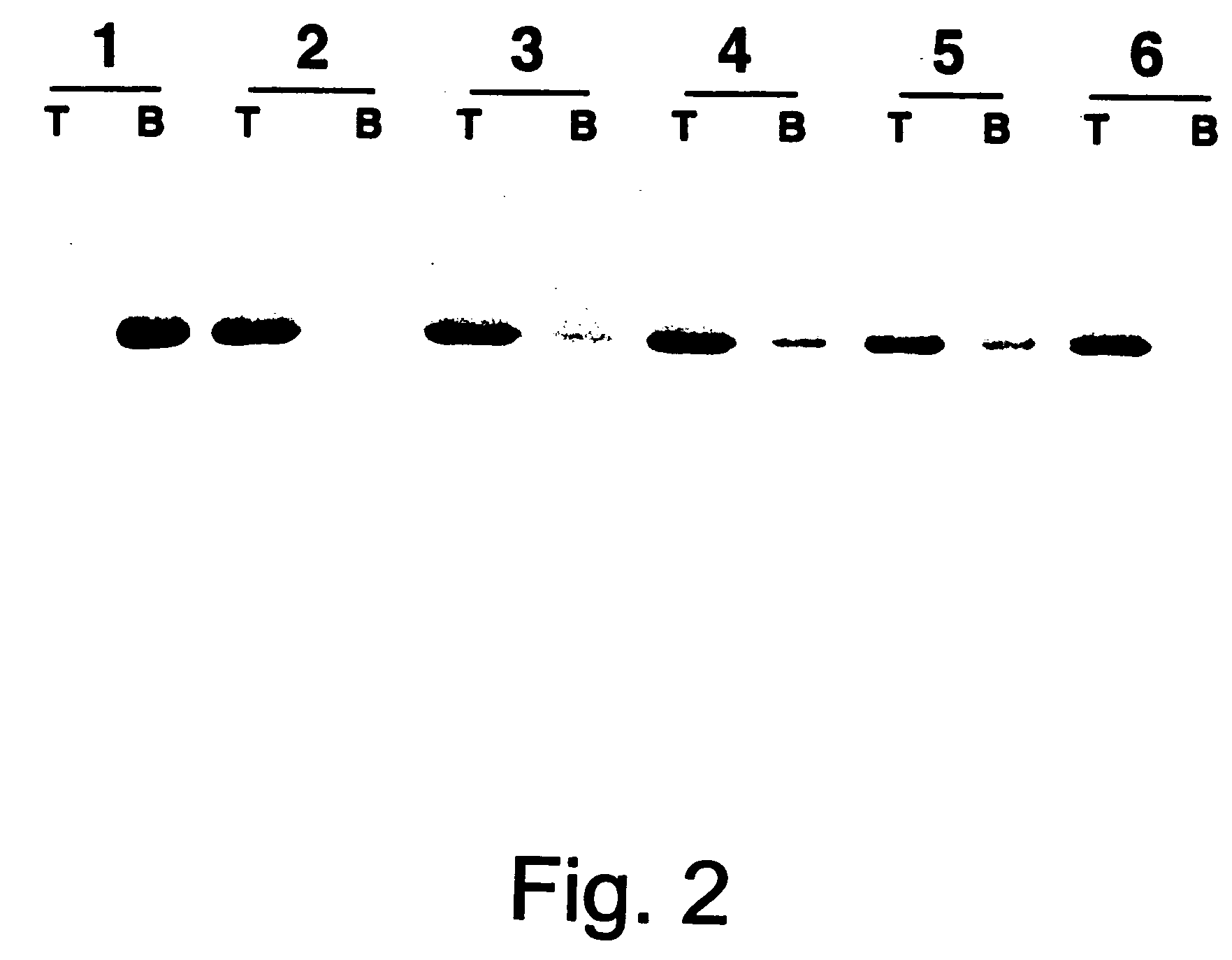
Vitro method for disassembly/reassembly of papillomavirus virus-like particles (VLPS)
A method of disassembly / reassembly of papillomavirus VLPs is provided. The resultant VLPs have enhanced homogeneity, present conformational, neutralizing PV epitopes, and therefore are useful prophylactic and diagnostic agents. Further, these VLPs can be used to encapsulate desired moieties, e.g., therapeutic or diagnostic agents, or "marker" DNAs, and the resultant VLPs used as in vivo delivery vehicles or as pseudovirions for evaluating vaccine efficacy.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
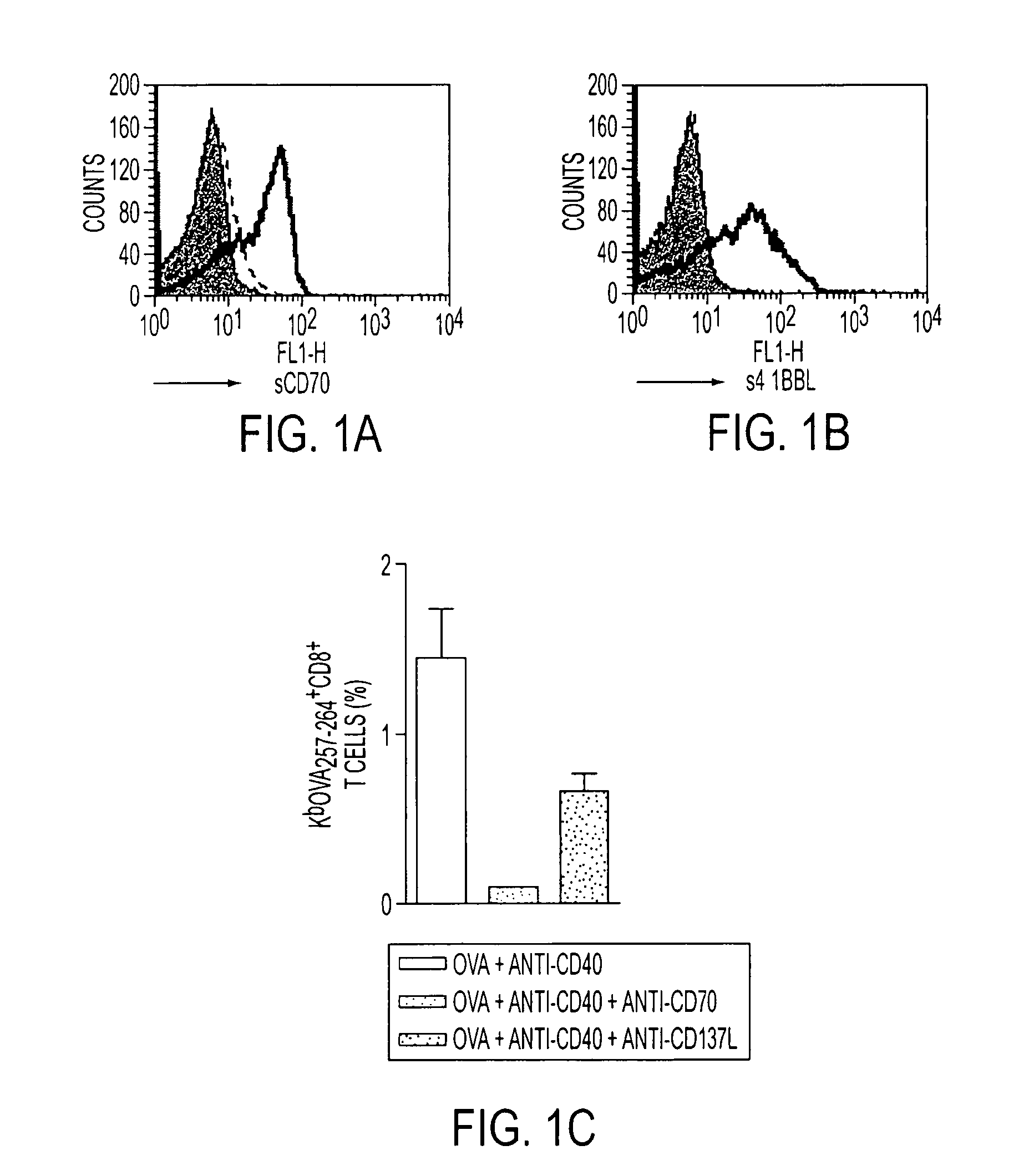
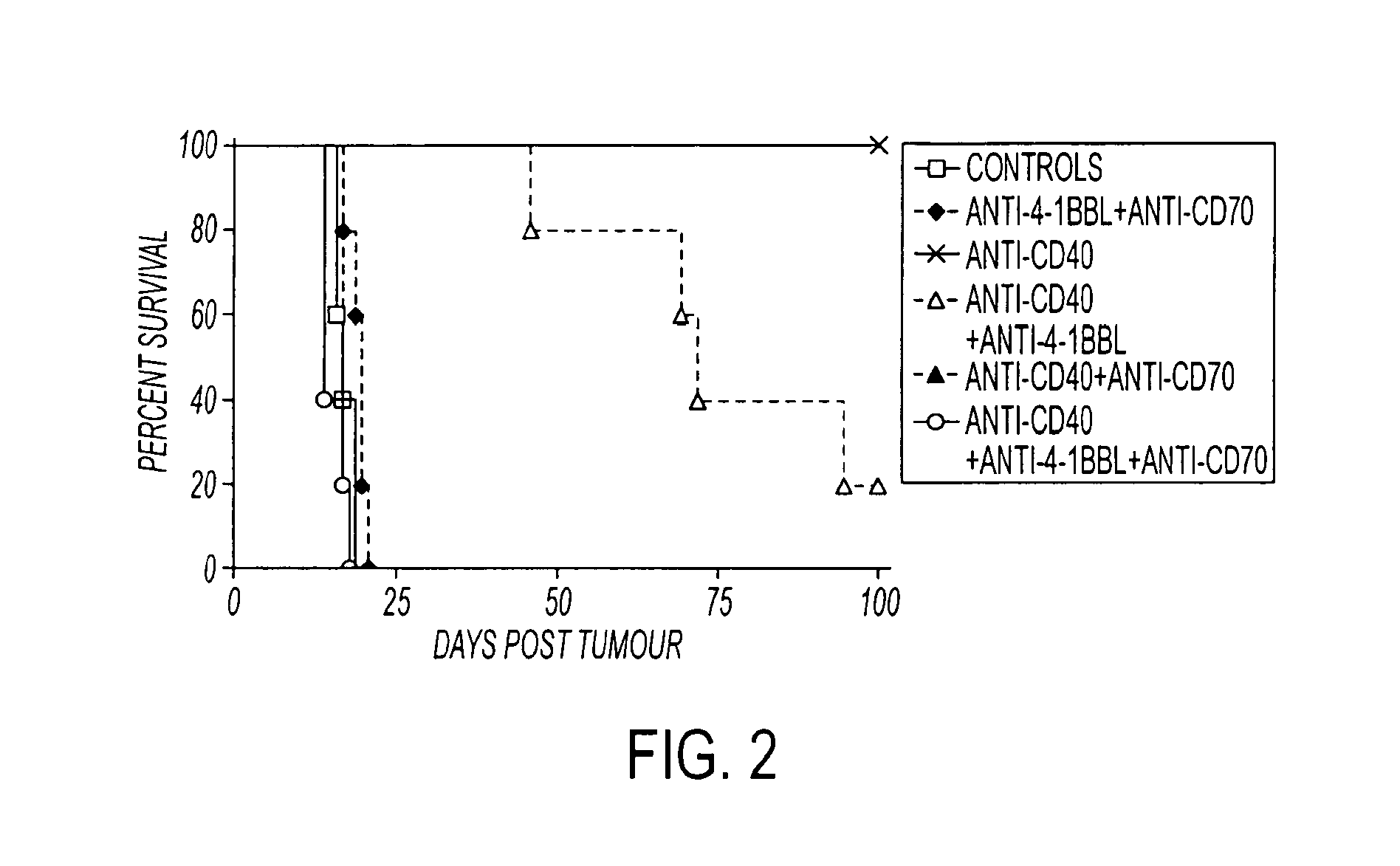
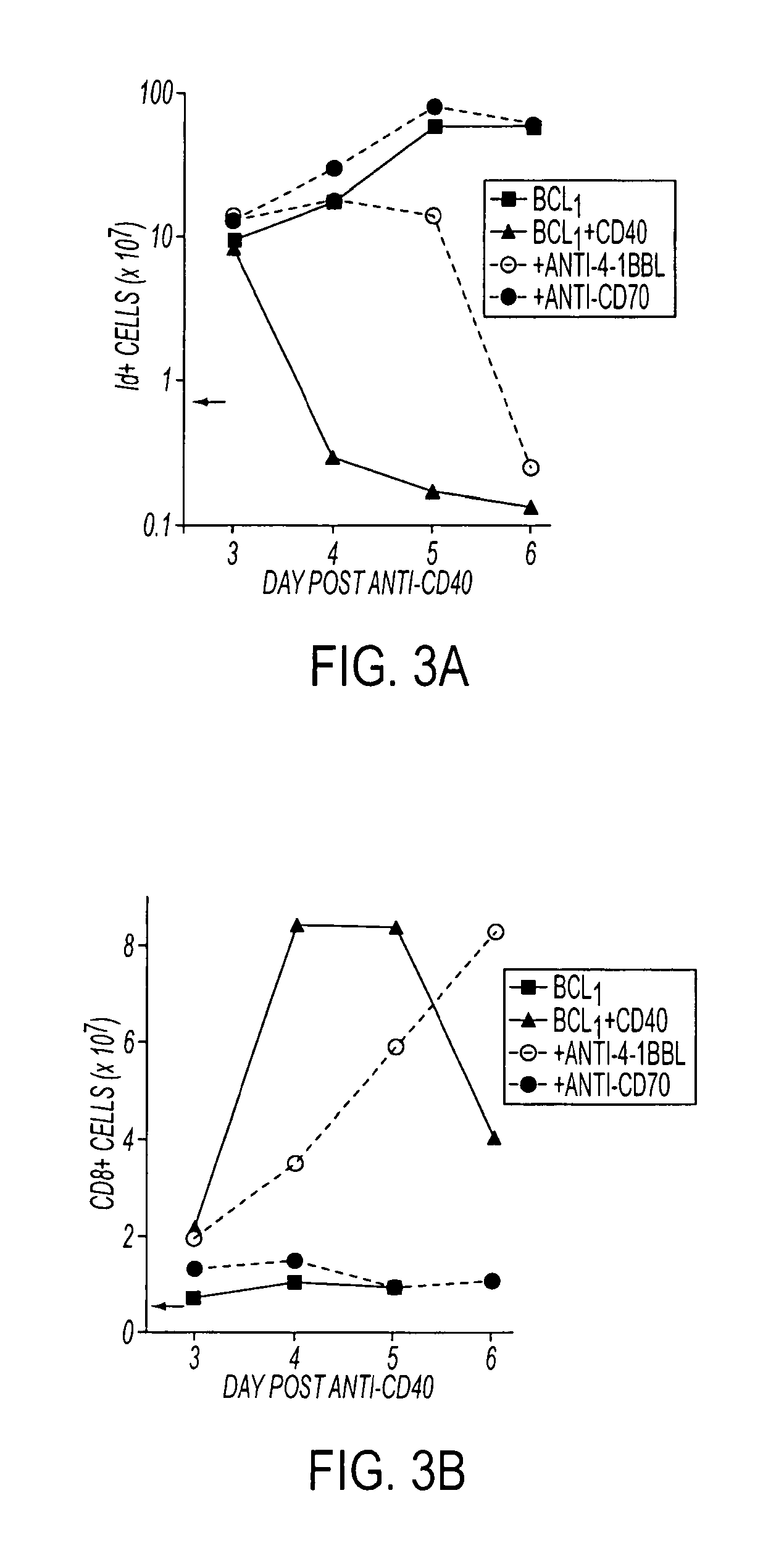
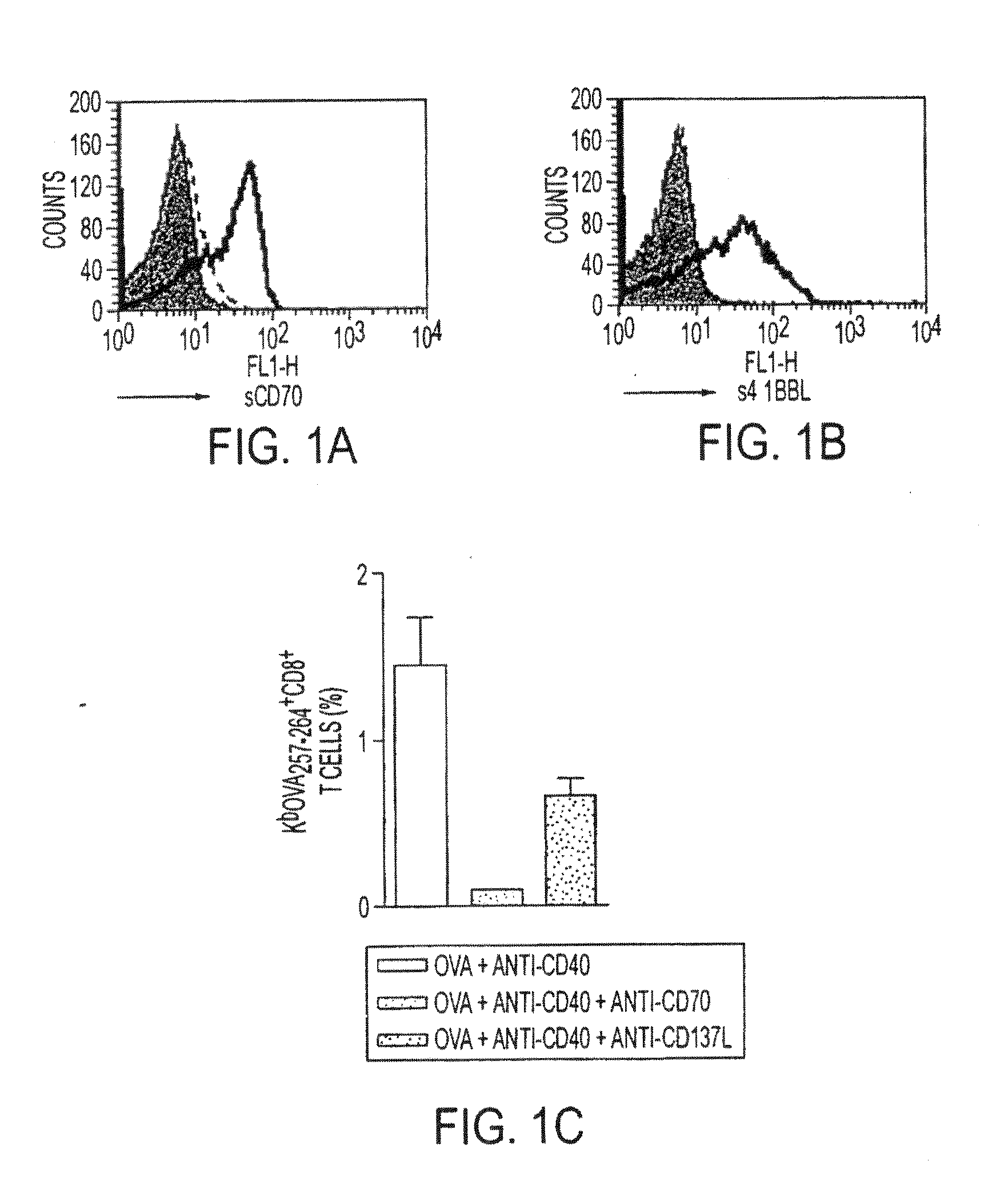
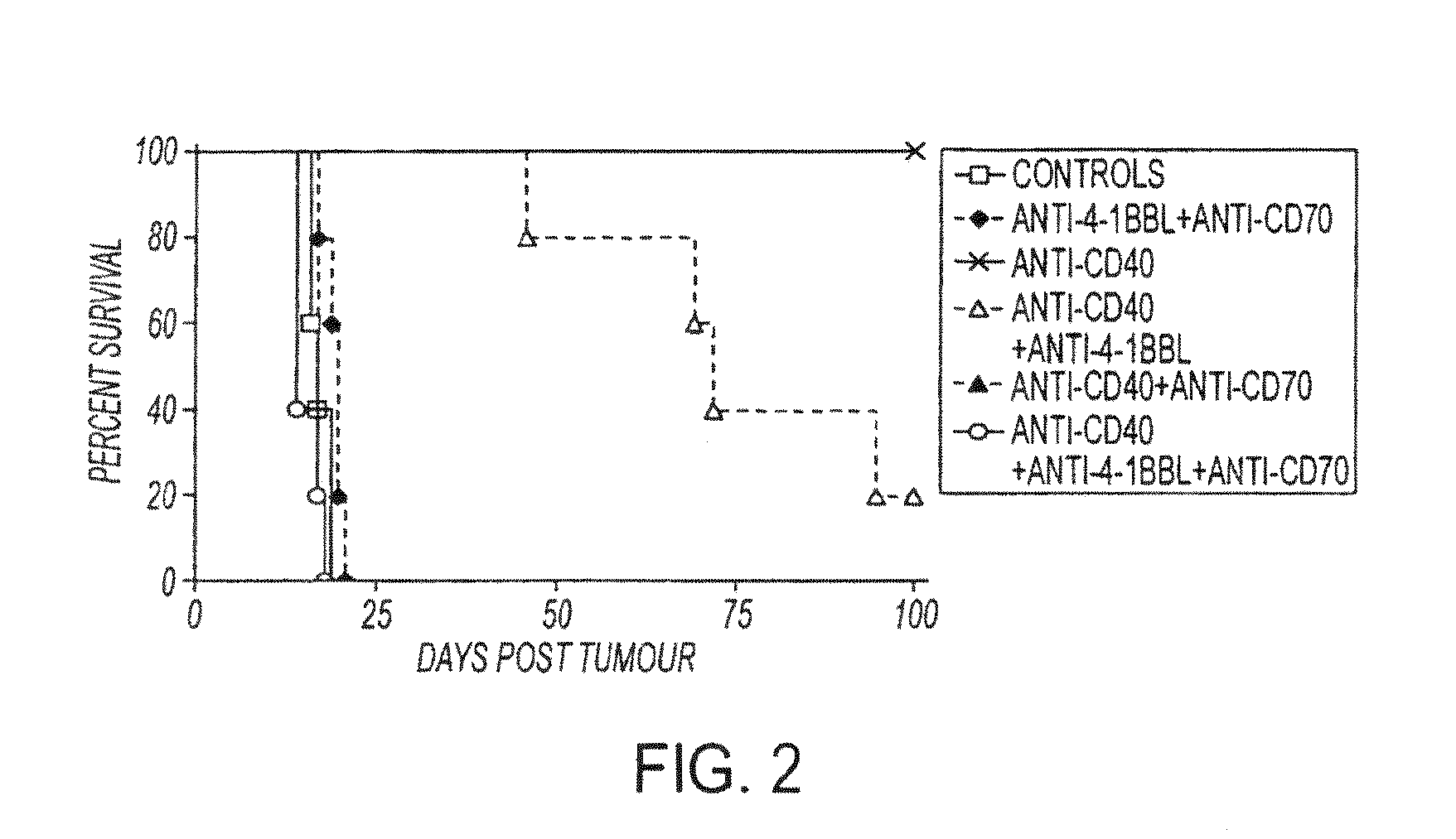
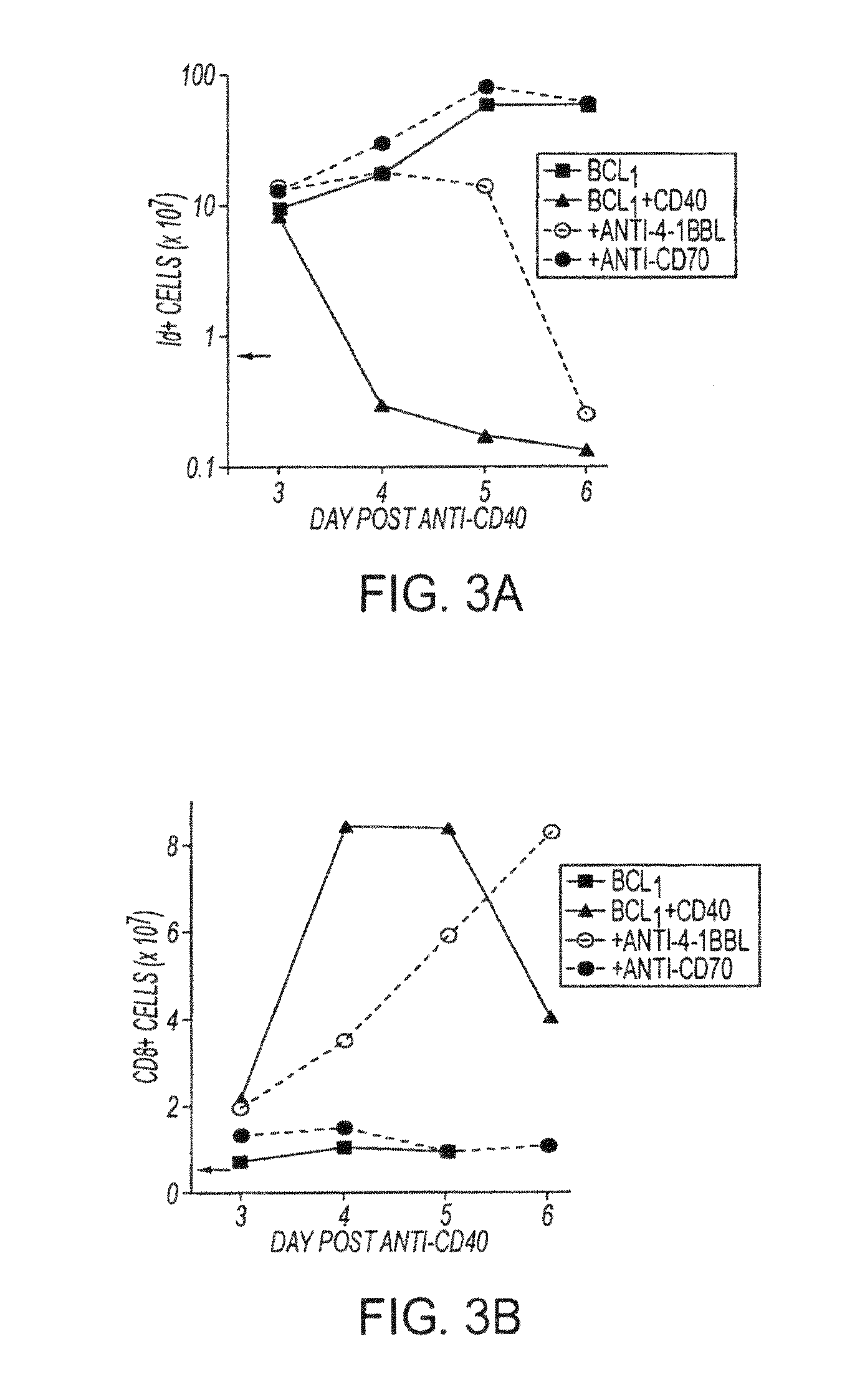
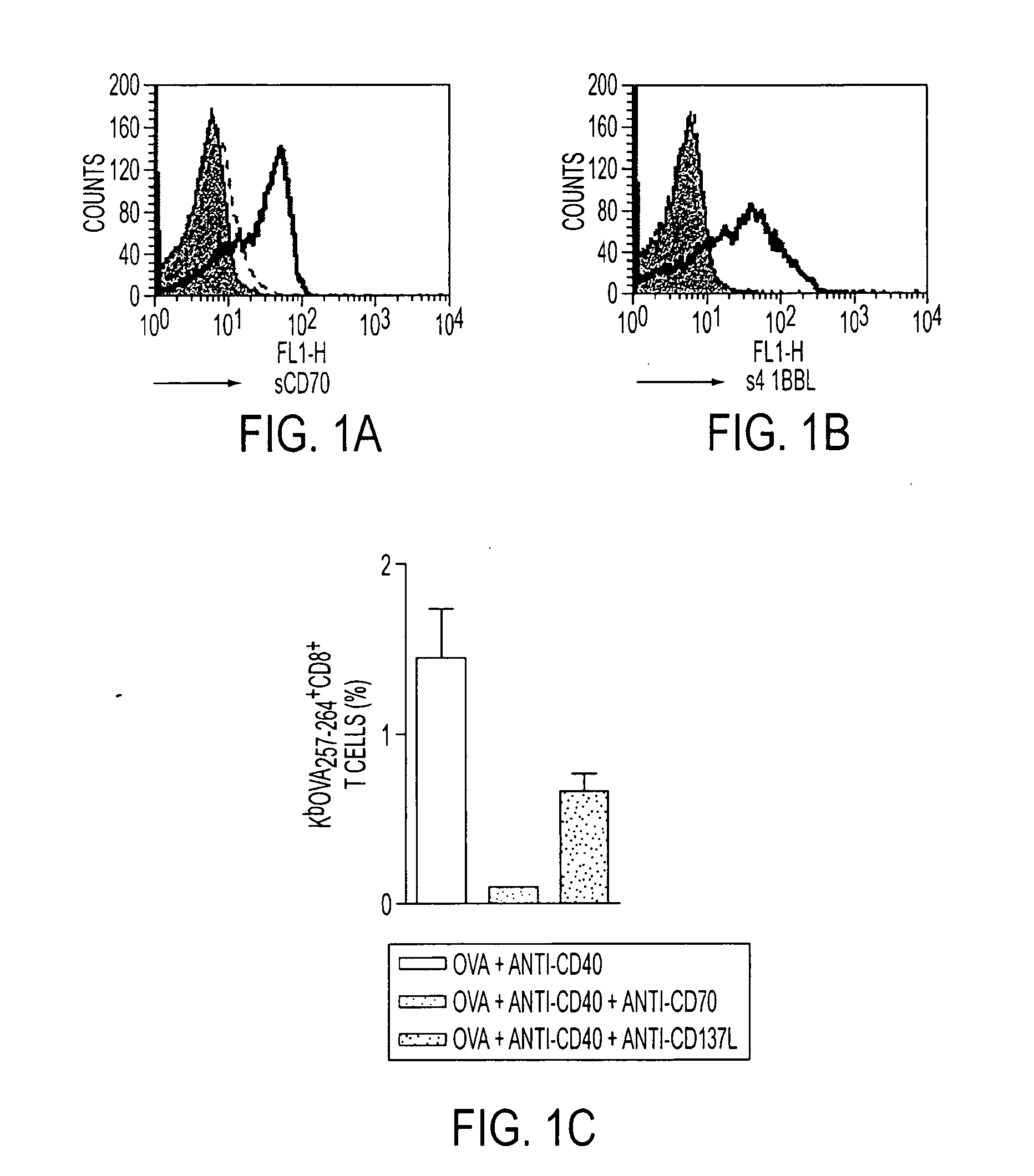
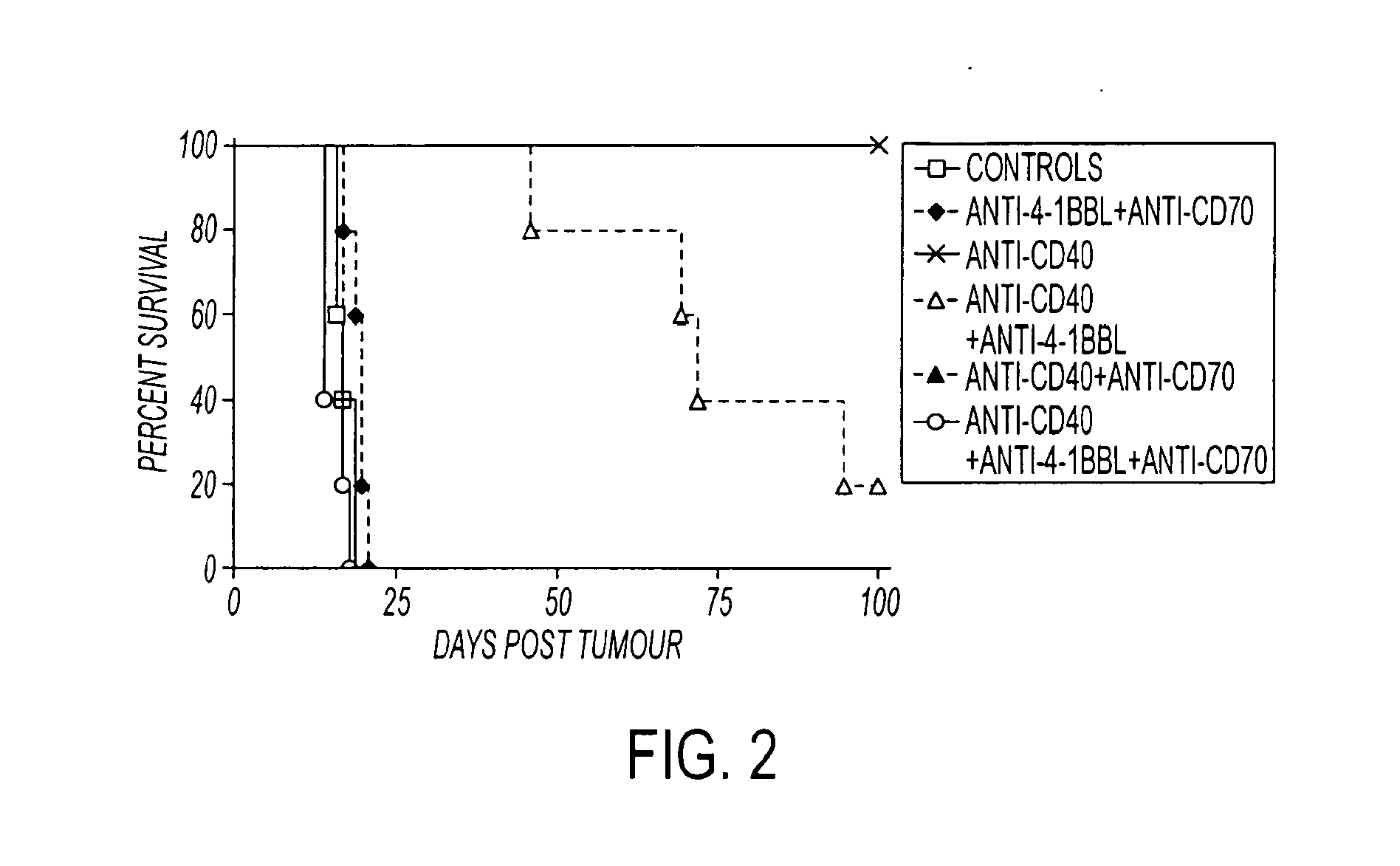
Human immune therapies using a CD27 agonist alone or in combination with other immune modulators
ActiveUS8481029B2Promotes strong expression of 4-1BBImprove responseAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderAutoimmune responsesImmune modulator
Methods of inducing T cell proliferation and expansion in vivo for treating conditions wherein antigen-specific T cell immune response are therapeutically desirable such as cancer, infection, inflammation, allergy and autoimmunity and for enhancing the efficacy of vaccines are provided. These methods comprise the administration of at least one CD27 agonist, preferably an agonistic CD27 antibody, alone or in association with another moiety such as immune stimulant or immune modulator such as an anti-CD40, OX-40, 4-IBB, or CTLA-4 antibody or an agent that depletes regulatory cells, or a cytokine. These mono and combination therapies may also optionally include the administration of a desired antigen such as a tumor antigen, an allergen, an autoantigen, or an antigen specific to an infectious agent or pathogen against which a T cell response (often CD8+) is desirably elicited.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
Prediction and assessment of immunogenicity
InactiveUS20060148009A1Low immunogenicityBiological material analysisVaccine efficacyImmunocompatibility
A system and method to predict and assess immunogenicity, especially prior to on-set of immunogenic conditions. Also disclosed are methods to identify relevant peptides associated with the formation of antibodies in patients treated with a given protein therapeutic. In various aspects, the present application is directed to methods of determining the immunological compatibility of a subject with a therapeutic agent such as a proteinaceous therapeutic agent, methods of determining vaccine efficacy by determining the immunological compatibility of a subject with a therapeutic agent, and selecting a therapeutic agent for a subject in need of treatment. Methods of designing a therapeutic agent with reduced immunogenicity for a subject and methods for designing vaccines with enhanced immunogenicity for a subject are also contemplated.
Owner:XENCOR
Probiotic enterococci for improved immunity
InactiveUS20070098744A1Reduce morbidityReduce mortalityOrganic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiologyVaccine efficacy
Compositions and methods for modulating immunity and vaccine efficacy in animals are disclosed. The compositions and methods utilize probiotic organisms, specifically probiotic Enterococcus strains, and are particularly applicable to felines.
Owner:NESTEC SA
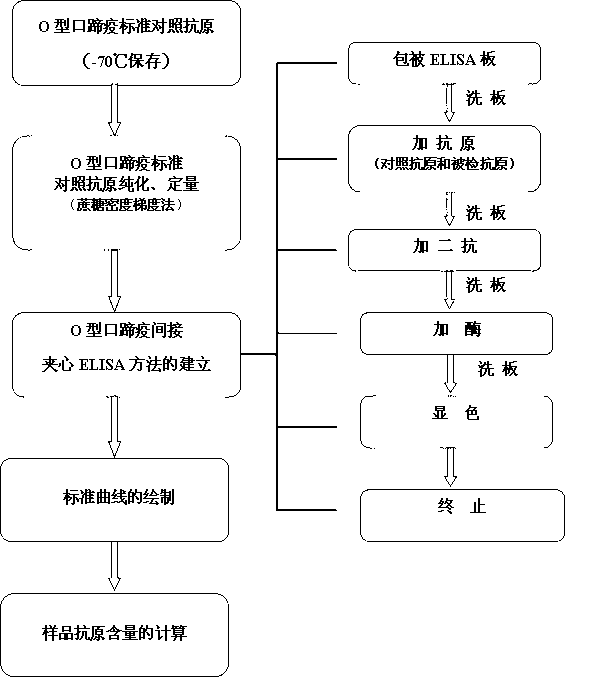
O type foot-and-mouth disease 146S antigen quantitative ELISA detection kit and method for using same
ActiveCN103076451ASolve efficiency problemsSolving the power test substitution problemMaterial analysisDiseaseVaccine Potency
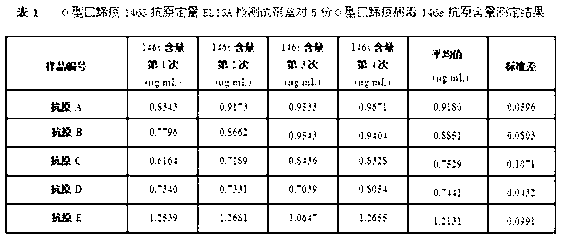
The invention discloses an O type foot-and-mouth disease 146S antigen quantitative ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay) detection kit and a method for using the same. The kit comprises an ELISA plate, an O type foot-and-mouth disease standard reference antigen, a demulsifier, an O type foot-and-mouth disease rabbit antiserum, an O type foot-and-mouth disease guinea pig antiserum, a rabbit anti-guinea pig-horse radish peroxidase conjugate, a guinea pig antiserum dilute solution, a 25-fold PBST (phosphate buffer solution tween) concentrated solution, a carbonate buffer solution capsule, a citric acid-phosphate buffer solution tablet, an OPD (o-phenylenediamine) tablet, a stop solution, a plate sealing membrane, a moving liquid tank and a 96-mesh U-shaped dilution plate. The kit is an organic combination of a sucrose density gradient centrifugation method and an indirect sandwich ELISA method, integrates the advantages of the sucrose density gradient centrifugation method and the indirect sandwich ELISA method, is simple to operate and good in stability, is suitable for batch detection, can be used for distinguishing serum types, and is an ideal substitution method for antigen quantitative and vaccine efficacy detection.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Immuno-modulating effects of chemokines in DNA vaccination
InactiveUS6569418B1Reduce in quantityEnhance immune responseGenetic material ingredientsImmunoglobulinsAntigenDNA vaccination
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAD BIOTECH INST
Human immune therapies using a cd27 agonist alone or in combination with other immune modulators
InactiveUS20130336976A1Promotes strong expression of 4-1BBImprove responseAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsIMMUNE STIMULANTSCD8
Methods of inducing T cell proliferation and expansion in vivo for treating conditions wherein antigen-specific T cell immune response are therapeutically desirable such as cancer, infection, inflammation, allergy and autoimmunity and for enhancing the efficacy of vaccines are provided. These methods comprise the administration of at least one CD27 agonist, preferably an agonistic CD27 antibody, alone or in association with another moiety such as immune stimulant or immune modulator such as an anti-CD40, OX-40, 4-1BB, or CTLA-4 antibody or an agent that depletes regulatory cells, or a cytokine. These mono and combination therapies may also optionally include the administration of a desired antigen such as a tumor antigen, an allergen, an autoantigen, or an antigen specific to an infectious agent or pathogen against which a T cell response (often CD8+) is desirably elicited.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
In vitro method for disassmbly/reassembly of papillomavirus virus-like particles (VLPs). Homogeneous VLP and cavsomere compositions produced by said methods: use thereof as vehicle for improved purification, and delivery of active agents
InactiveUS7351533B2Increase ionic strengthStabilize VLPsMicroencapsulation basedMicrobiological testing/measurementEpitopeDiagnostic agent
A method of disassembly / reassembly of papillomavinis VLPs is provided. The resultant VLPs have enhanced homogeneity, present conformational, neutralizing PV epitopes, and therefore are useful prophylactic and diagnostic agents. Further, these VLPs can be used to encapsulate desired moieties, e.g., therapeutic or diagnostic agents, or marker” DNAs, and the resultant VLPs used as in vivo delivery vehicles or as pseudovirions for evaluating vaccine efficacy.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
In vitro method for disassembly/reassembly of papillomavirus virus-like particles (VLPs)
InactiveUS6261765B1Stabilize VLPsHigh strength conditionNanotechMicroencapsulation basedEpitopeDiagnostic agent
A method of disassembly / reassembly of papillomavirus VLPs is provided. The resultant VLPs have enhanced homogeneity, present conformational, neutralizing PV epitopes, and therefore are useful prophylactic and diagnostic agents. Further, these VLPs can be used to encapsulate desired moieties, e.g., therapeutic or diagnostic agents, or "marker" DNAs, and the resultant VLPs used as in vivo delivery vehicles or as pseudovirions for evaluating vaccine efficacy.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Stabilization of alum-adjuvanted immunologically active agents
InactiveUS20060067943A1Improve the level ofEnhancement is mitigated or avoidedBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAdjuvantAlum adjuvant
A composition and method for formulating and delivering an adjuvanted immunological active agent, especially a vaccine, wherein adjuvant coagulation and concomitant loss of vaccine efficacy enhancement is mitigated or avoided. The adjuvanted, immunologically-active agent can be subjected to freezing, drying, freeze-drying, or lyophilization, and when reconstituted, retains a high level of potency. The present invention further provides for a composition and method for formulating and delivering a stable, adjuvanted, immunologically-active agent capable of being deposited on a transdermal delivery device or microprojection or array thereof.
Owner:ALZA CORP
Compositions and methods useful for modulating immunity, enhancing vaccine efficacy, decreasing morbidity associated with chronic FHV-1 infections, and preventing or treating conjunctivitis
InactiveUS20070280964A1Enhance vaccine efficacyReduce morbidityBiocideSenses disorderTreated animalMicrobiology
Compositions and methods useful for modulating immunity, enhancing vaccine efficacy, decreasing morbidity associated with chronic FHV-1 infections, and / or preventing or treating conjunctivitis in animals. The compositions contain effective amounts of probiotic Enterococcus bacteria and the methods involve administering such compositions to animals alone, in supplements, or in food compositions in amounts suitable for the intended purpose. In certain embodiments, the probiotic is Enterococcus faecium strain NCIMB 10415 (SF68) and the animal is a feline.
Owner:NESTEC SA
In vitro method for disassmbly/reassembly of papillomavirus virus-like particles (VLPs). Homogeneous VLP and cavsomere compositions produced by said methods: use thereof as vehicle for improved purification, and delivery of active agents
InactiveUS20040152181A1Stabilize VLPsIncrease ionic strengthMicroencapsulation basedMicrobiological testing/measurementEpitopeDiagnostic agent
A method of disassembly / reassembly of papillomavinis VLPs is provided. The resultant VLPs have enhanced homogeneity, present conformational, neutralizing PV epitopes, and therefore are useful prophylactic and diagnostic agents. Further, these VLPs can be used to encapsulate desired moieties, e.g., therapeutic or diagnostic agents, or marker" DNAs, and the resultant VLPs used as in vivo delivery vehicles or as pseudovirions for evaluating vaccine efficacy.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Methods and compositions to enhance vaccine efficacy by reprogramming regulatory t cells
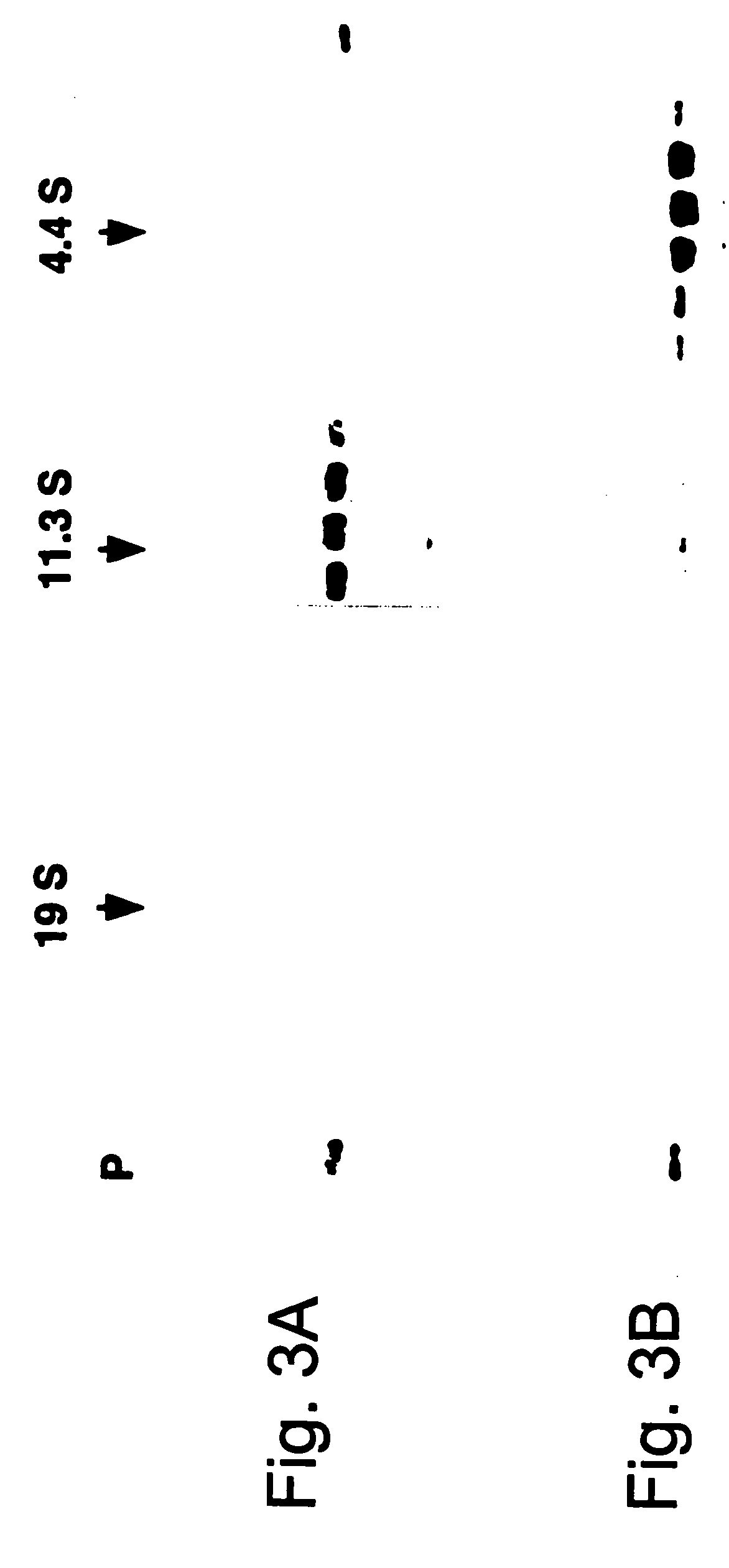
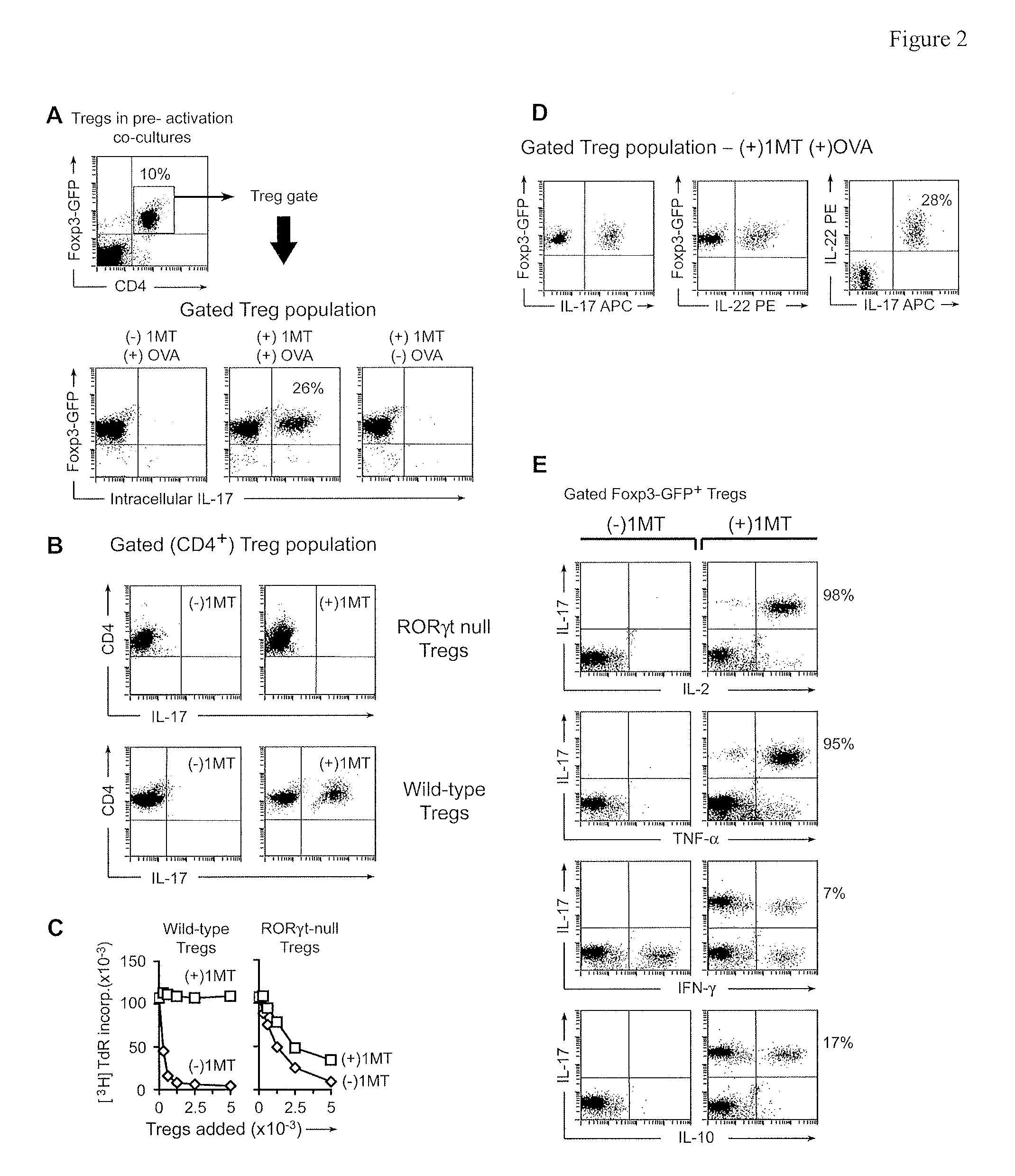
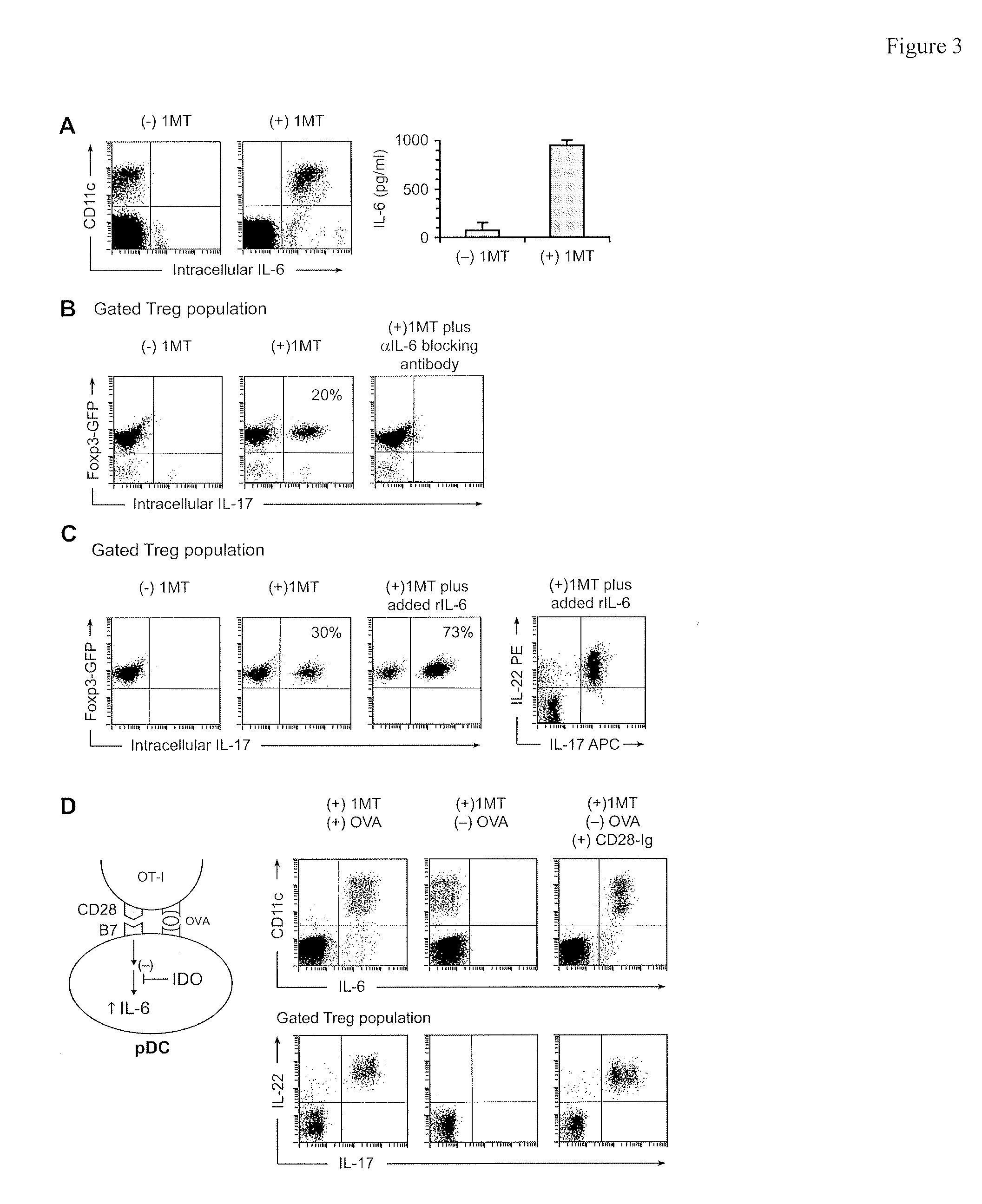
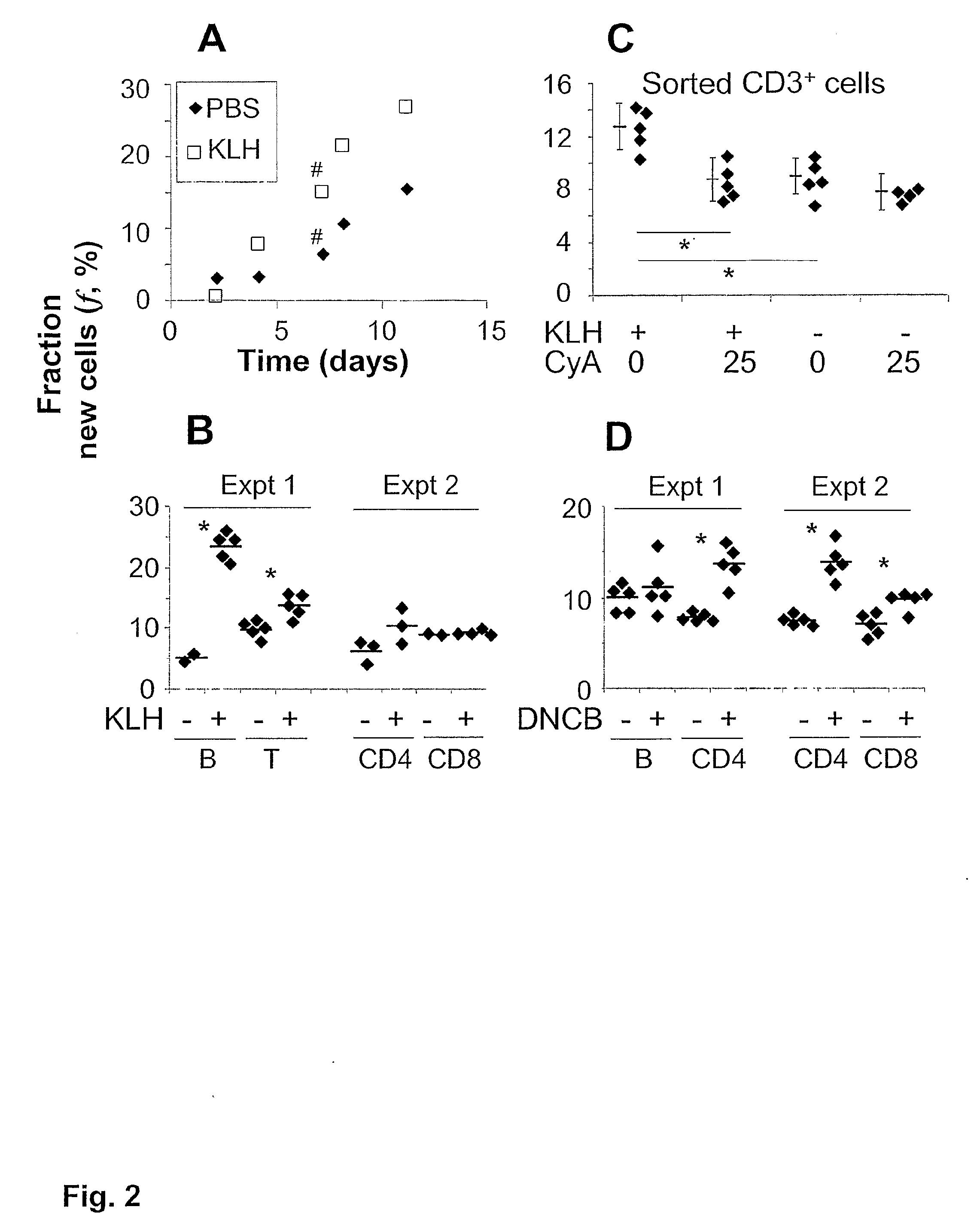
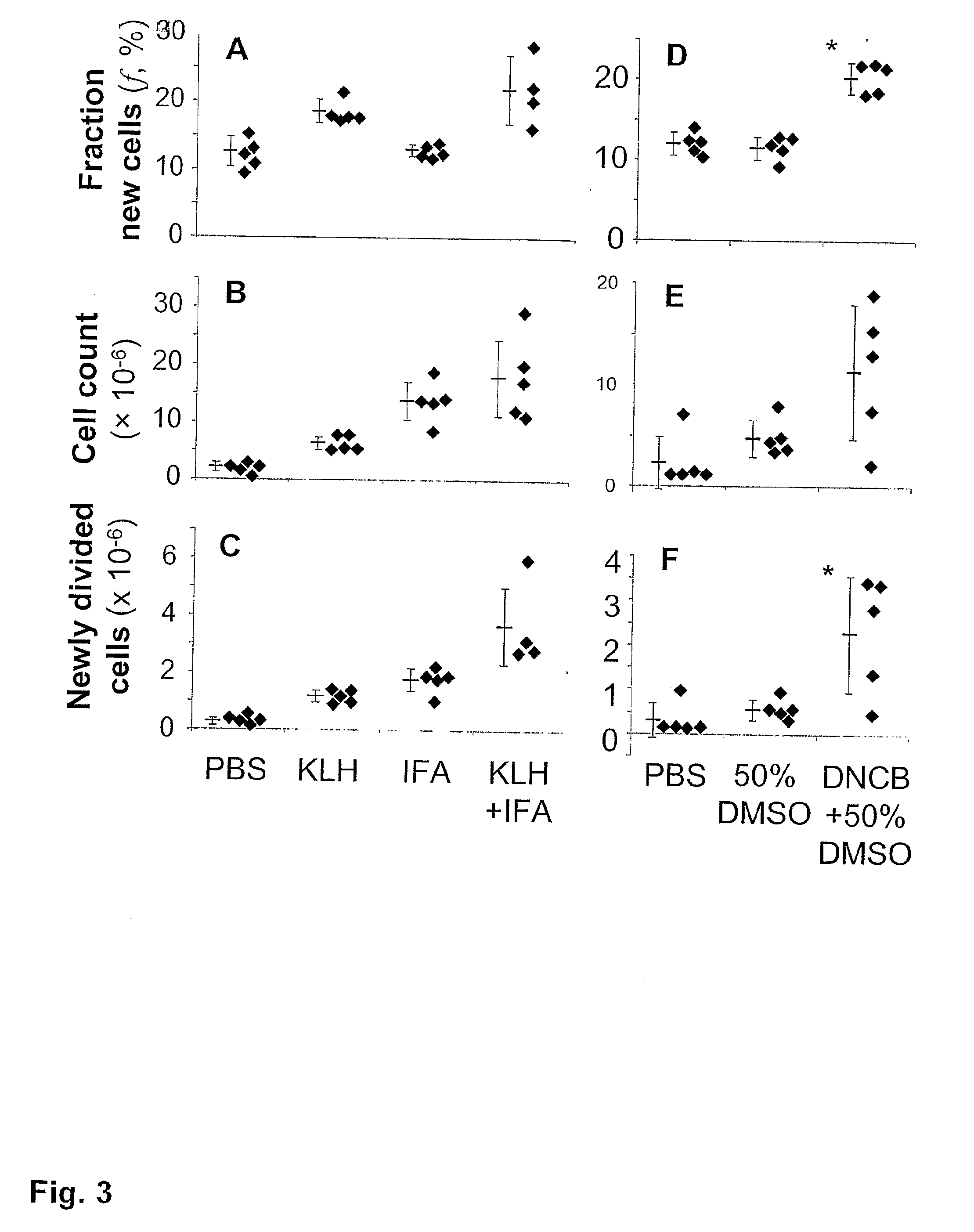
The immunoregulatory enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is expressed by a subset of murine plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs) in tumor-draining LNs, where it can potently activate Foxp3 regulatory T cells (Tregs). We now show that IDO functions as a molecular switch in tumor-draining LNs, maintaining Tregs in their normal suppressive phenotype when IDO was active, but allowing inflammation-induced conversion of Tregs to a polyfunctional T-helper phenotype similar to proinflammatory TH17 cells when IDO was blocked. In vitro, conversion of Tregs to the TH17-like phenotype was driven by antigen-activated effector T cells, and required IL-6 produced by activated pDCs. IDO regulated this conversion by dominantly suppressing production of IL-6 in pDCs, in a GCN2-kinase dependent fashion. In vivo, using a model of established B16 melanoma, the combination of an IDO-inhibitor drug plus anti-tumor vaccine caused upregulation of IL-6 in pDCs and in situ conversion of a majority of Tregs to the TH17 phenotype, with marked enhancement of CD8+ T cell activation and anti-tumor efficacy. Thus, Tregs in tumor-draining LNs can be actively re-programmed in vitro and in vivo into T-helper cells, without the need for physical depletion, and IDO serves as a key regulator of this critical conversion.
Owner:GEORGIA HEALTH SCI UNIV RES INST
Method of preventing and treating inflammatory diseases and disorders with abscisic acid
ActiveUS20130142825A1Improve treatment outcomesRelieve symptomsBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsAbscisic acidVaccine efficacy
The present invention relates to the use of a therapeutically effective amount of abscisic acid (ABA) or its analogs to treat or prevent inflammation induced by exposure to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or respiratory inflammation. The invention also relates to methods and composition for enhancing vaccine efficacy using ABA.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Methods of enhancing the immunogenicity of mycobacteria and compositions for the treatment of cancer, tuberculosis, and fibrosing lung diseases
InactiveUS20110243992A1Enhance recruitmentIncreased activationAntibacterial agentsBacteriaMycobacterium immunogenumCancer cell
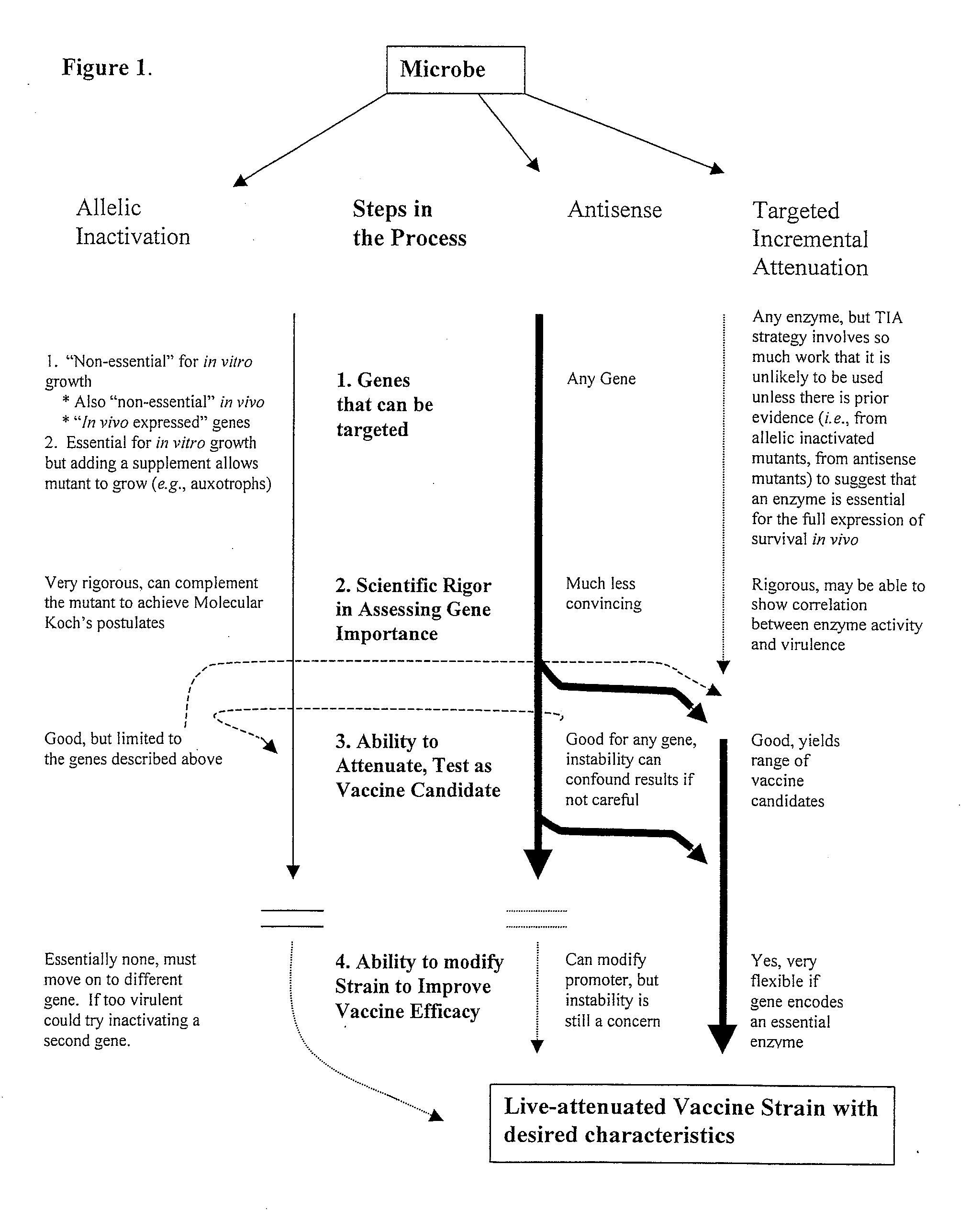
Whole-cell vaccines and methods for enhancing the immunogenicity of cellular microorganisms for use in producing protective immune responses in vertebrate hosts subsequently exposed to pathogenic bacteria or for use as vectors to express exogenous antigens and induce responses against other infectious agents or cancer cells. The present invention involves an additional method of enhancing antigen presentation by intracellular bacteria in a manner that improves vaccine efficacy. After identifying an enzyme that has an anti-apoptotic effect upon host cells infected by an intracellular microbe, the activity of the enzyme produced by the intracellular microbe is reduced by expressing a mutant copy of the enzyme, thereby modifying the microbe so that it increases immunogenicity.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Circulating water aquaculture device for aquatic animal aquaculture and drug application evaluation
The invention relates to a circulating water aquaculture device for aquatic animal aquaculture and drug application evaluation. The circulating water aquaculture device integrates aquatic animal aquaculture, water treatment and water quality monitoring, can achieve circulating water or still water aquaculture of fresh water or seawater aquatic animals, treatment and drainage of aquaculture water and aquaculture water physical and chemical parameter detection and can guarantee that the aquaculture environment is excellent, and the experiment condition is controllable in the drug application evaluation (for example, vaccine efficacy evaluation) process.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for quantification of 146S content in foot-and-mouth disease antigen by using liquid chromatography detection system
The present invention discloses a method for quantification of 146s content in foot-and-mouth disease antigen by using a liquid chromatography detection system. The method comprises: adopting protamine sulfate to purify virus, adopting PEG6000 to concentrate the virus, carrying out sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation on the concentrated virus, adopting a liquid chromatography detection system to detect an absorption peak of the centrifugated sample at a wavelength of 259 nm, and calculating 146S content according to the following formula: C=FRS / 76Wb. The method can be used for determination of the 146S content in various types of foot-and-mouth disease antigens. With quantification of the 146S content in the foot-and-mouth disease antigen, foot-and-mouth disease vaccine preparation can be guided, vaccine efficacy can be indirectly evaluated, and major guiding significances are provided for enhancing quality of the foot-and-mouth disease vaccine in our country.
Owner:内蒙古必威安泰生物科技有限公司
Human immune therapies using a CD27 agonist alone or in combination with other immune modulators
ActiveUS20110033449A1Profound effect on anti-tumor immunityImprove scalabilityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsAutoimmune responsesImmune modulator
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
In vitro method for disassembly/reassembly of papillomavirus virus-like particles (VLPS), homogeneous vlp and capsomere compositions produced by said methods; use thereof as vehicle for improved purification, and delivery of active agents
InactiveUS6962777B1Stabilize VLPsIncrease ionic strengthMicrobiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesEpitopeDiagnostic agent
A method of disassembly / reassembly of papillomavirus VLPs is provided. The resultant VLPs have enhanced homogeneity, present conformational, neutralizing PV epitopes, and therefore are useful prophylactic and diagnostic agents. Further, these VLPs can be used to encapsulate desired moieties, e.g., therapeutic or diagnostic agents, or “marker” DNAs, and the resultant VLPs used as in vivo delivery vehicles or as pseudovirions for evaluating vaccine efficacy.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Method and apparatus for discovery, development and clinical application of multiplex assays based on patterns of cellular response
InactiveUS20150025812A1Improve diagnostic capabilitiesHealth-index calculationBiostatisticsVaccine efficacyCell type
A method for the discovery, development and clinical application of multidimensional multiplex synthetic biomarker assays based on patterns of cellular response.After stimulation or inhibition, a selected multiplicity of cell types are assayed for a multiplicity of cellular or molecular responses, and known machine learning techniques are used to synthesize the cellular responses into an optimized clinical biomarker. The computationally derived algorithm includes the relationships within and between the component steps so as to produce an optimized synthetic clinical biomarker. During discover of the assay one or more of the component steps are repeated iteratively until a final clinically optimized algorithm is produced.Such a multidimensional multiplex cell response assay may provide improved diagnostic performance with respect to entities such as immune status, infection, and antibiotic and vaccine efficacy, among others.
Owner:PARADIS NORMAN A
Spinner bottle production method of inactivated singapore grouper iridovirus (SGIV) vaccine
ActiveCN102727879AProtectReduce manufacturing costViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsVaccine efficacyBottle
The invention discloses a spinner bottle production method of inactivated singapore grouper iridovirus (SGIV) vaccine. The production method comprises spinner bottle culture of cells, amplification and harvest of viruses and inactivation of the viruses. By using the spinner bottle production method of the inactivated SGIV vaccine disclosed by the invention, the inactivated SGIV vaccine can be produced on a large scale, and the production cost is low and the labor intensity is small since the production is industrial streamline production; after vaccine inspection on the produced inactivated SGIV vaccine, the inactivated SGIV vaccine is safe from the aspect of cell level and fish level; vaccine efficacy detection proves that the relative protection rate of the inactivated SGIV vaccine provided by the invention is 87.0-95.7%, so that inactivated SGIV vaccine provides obvious protection for immune grouper, the immune protection efficacy is good and quality between batches is stable.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vaccine for periodontal disease
The present invention relates to novel bacterial isolates identified by their 16S rRNA DNA, that cause periodontal disease in companion animals, polynucleotide sequences contained therein, polypeptides encoded by such polynucleotide sequences and vaccines comprising such bacteria, polynucleotides, or polypeptides. Also provided are methods for treating and preventing periodontal disease and kits for detecting and treating periodontal disease kits for detecting and preventing periodontal disease. In addition, methods for assessing the efficacy of a vaccine against periodontal diseases in an animal are provided.
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
Rabies virus glycoprotein and nucleoprotein antigen epitope polypeptides, and screening and identification method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to screening and identification of antigen epitope polypeptides. The invention discloses screening, identification and application of a series of rabies virus glycoprotein and nucleoprotein antigen epitope polypeptides. The rabies virus glycoprotein and nucleoprotein are predicted by biological information means to obtain the candidate epitope polypeptides; and a lymphopoiesis experiment, ELISPOT experiment and a stream-type cell method are utilized to carry out in-vitro experimental verification on the subsequent epitope polypeptides to obtain the four rabies virus protein antigen epitope polypeptides. The invention is characterized in that the antigen epitope polypeptides respectively comprise a Th epitope and a CTL epitope, can stimulate the lymphopoiesis of the vaccine-immunized mouse in vitro and induce the cells to secrete related cell factors, and have the functions of killing virus-infected cells and stimulating the generation of the antibody. The invention can be used for developing rabies virus epitope vaccines and detecting the vaccine effect, and has important value for developing and producing immunologic function detection kits for rabies virus vaccines.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
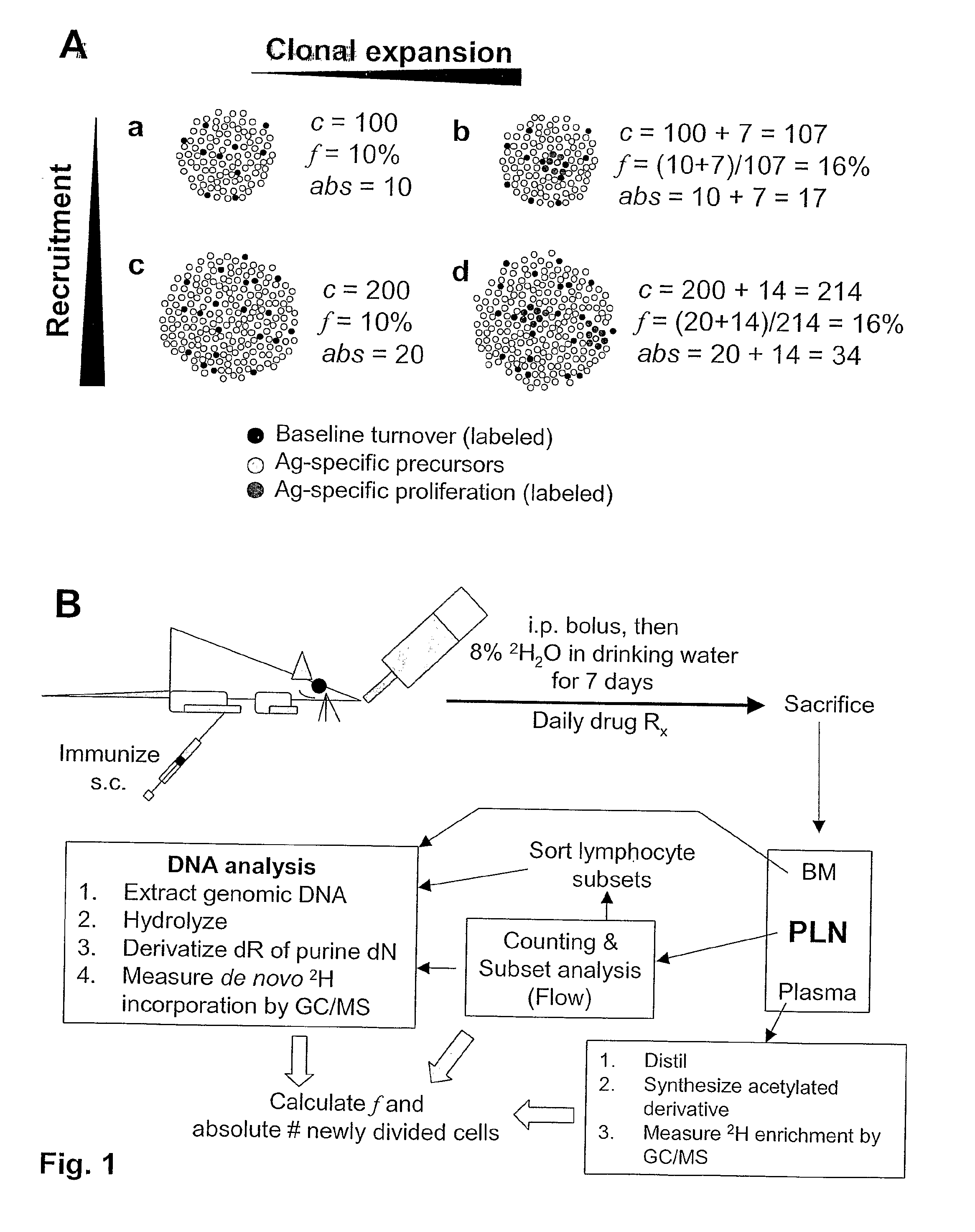
Kinetic biomarker for quantification of lymphoproliferation, clonal expansion, recruitment and trafficking in lymphoid tissues and of the in vivo actions of antigens and modulating thereon
InactiveUS20090155179A1Reduction of immune activationShorten the progressIn-vivo testing preparationsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseStable Isotope Labeling
Owner:KINEMED
Pro-Apoptotic Bacteria and Compositions for Delivery and Expression of Antigens
InactiveUS20090325298A1Enhance antigen presentationImproves vaccine efficacyBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaCancer cellApoptosis
Whole-cell vaccines and methods for enhancing the immunogenicity of cellular microorganisms for use in producing protective immune responses in vertebrate hosts subsequently exposed to pathogenic bacteria or for use as vectors to express exogenous antigens and induce responses against other infectious agents or cancer cells. The present invention involves an additional method of enhancing antigen presentation by intracellular bacteria in a manner that improves vaccine efficacy. After identifying an enzyme that has an anti-apoptotic effect upon host cells infected by an intracellular microbe, the activity of the enzyme produced by the intracellular microbe is reduced by expressing a mutant copy of the enzyme, thereby modifying the microbe so that it increases immunogenicity.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV +1
Multibacterial vaccines and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060292173A1Inhibiting and preventing diseaseBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseGram
The present invention provides methods for establishing standards for Gram-negative, Gram-positive, and mixed bacterial cultures. The present invention also provides methods for reproducing Gram-negative, Gram-positive, and mixed bacterial cultures. The present invention further provides methods for preparing multibacterial vaccines. Also provided are multibacterial vaccines prepared in accordance with these methods, and methods for treating and / or preventing disorders using these multibacterial vaccines. In addition, the present invention provides methods for predicting the efficacy of multibacterial vaccines, and methods for enhancing the efficacy of multibacterial vaccines.
Owner:MBVAX BIOSCI
Method for preparing vaccine vectors for swine from swine IgG1 Fc recombinant baculoviruses
ActiveCN105039406AHigh transduction efficiencyImprove antagonistic abilityAntibody medical ingredientsFermentationAntigenSurface display
The invention discloses a method for preparing vaccine vectors for swine from swine IgG1 Fc recombinant baculoviruses, and belongs to the field of biological medicine. The method includes connecting cloned swine IgG Fc genes and swine fever virus E2 genes to baculovirus surface display vectors to obtain recombinant transfer vectors; enabling the recombinant transfer vectors to acquire recombinant baculovirus Bacmid vectors by means of Tn7 transposition; enabling the recombinant baculovirus Bacmid vectors to carry out transfection on insect cells by the aid of a liposome process, collecting culture supernatants to acquire recombinant baculoviruses, infecting the insect cells by the recombinant baculoviruses, and collecting cells to carry out Western blot analysis and confocal microscopic analysis on the cells; enabling recombinant baculovirus swine fever vectors to carry out vaccine efficacy tests on the swine. The method has the advantages that surface display swine IgG Fc recombinant baculoviruses prepared by the aid of the method is high in survival ability in swine serum and can be prevented from being removed by serum complements, and accordingly the contents of effective antigens of vaccine immunity can be increased.
Owner:武汉中拓康明生物科技有限公司 +3
In vitro method for disassembly/reassembly of papillomavirus virus-like particles (VLPs), homogeneous VLP and capsomere compositions produced by said methods; use thereof as vehicle for improved purification, and delivery of active agents
InactiveUS20030096259A1Stabilize VLPsHigh strength conditionMicrobiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesEpitopeDiagnostic agent
A method of disassembly / reassembly of papillomavirus VLPs is provided. The resultant VLPs have enhanced homogeneity, present conformational, neutralizing PV epitopes, and therefore are useful prophylactic and diagnostic agents. Further, these VLPs can be used to encapsulate desired moieties, e.g., therapeutic or diagnostic agents, or "marker" DNAs, and the resultant VLPs used as in vivo delivery vehicles or as pseudovirions for evaluating vaccine efficacy.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Pro-Apoptotic Bacterial Vaccines To Enhance Cellular Immune Responses
InactiveUS20120276144A1Diminishing intracellular survivalReduced activityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsVaccine PotencyVaccine efficacy
Whole-cell vaccines and methods for their use in producing protective immune responses in vertebrate hosts subsequently exposed to pathogenic bacteria. The present invention involves a method of enhancing antigen presentation by intracellular bacteria in a manner that improves vaccine efficacy. After identifying an enzyme that has an anti-apoptotic effect upon host cells infected by an intracellular microbe, the activity of the enzyme is reduced, thereby modifying the microbe so that it increases immunogenicity. Also, the present invention provides a method of incrementally modifying enzyme activity to produce incrementally attenuated mutants of the microbe from which an effective vaccine candidate can be selected.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Clostridium perfringens Beta toxin recombination subunit vaccine and production method thereof
ActiveCN109078178AEfficient expressionEfficient soluble expressionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridium perfringens beta toxinVaccine Production
The invention relates to a clostridium perfringens Beta toxin recombination subunit vaccine and a production method thereof. The prepared clostridium perfringens Beta toxin recombination subunit vaccine is produced by using a recombination clostridium perfringens Beta toxin protein which is processed by codon optimization and contains 4 amino acid mutations, namely integrity and spatial conformation of a natural toxin protein are reserved in the greatest degree, so immunogenicity of the natural toxin protein is kept, and a biological potential safety hazard caused by the single amino acid mutation is avoided. The vaccine further has the advantages of simple preparation process, low immunizing dose, good vaccine efficacy and the like. Compared with a current commercial clostridium perfringens natural toxin inactivated vaccine in China, a bio-safety risk in a vaccine production process is greatly reduced. The vaccine is a perfect candidate vaccine for updating a current C-type clostridium perfringens toxin vaccine in China. In addition, while a mixed vaccine is prepared by the vaccine with other antigens, the mixed vaccine can be prepared without increasing a using dose of the mixedvaccine.
Owner:CHINA INST OF VETERINARY DRUG CONTROL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com