Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Trusted computing base" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
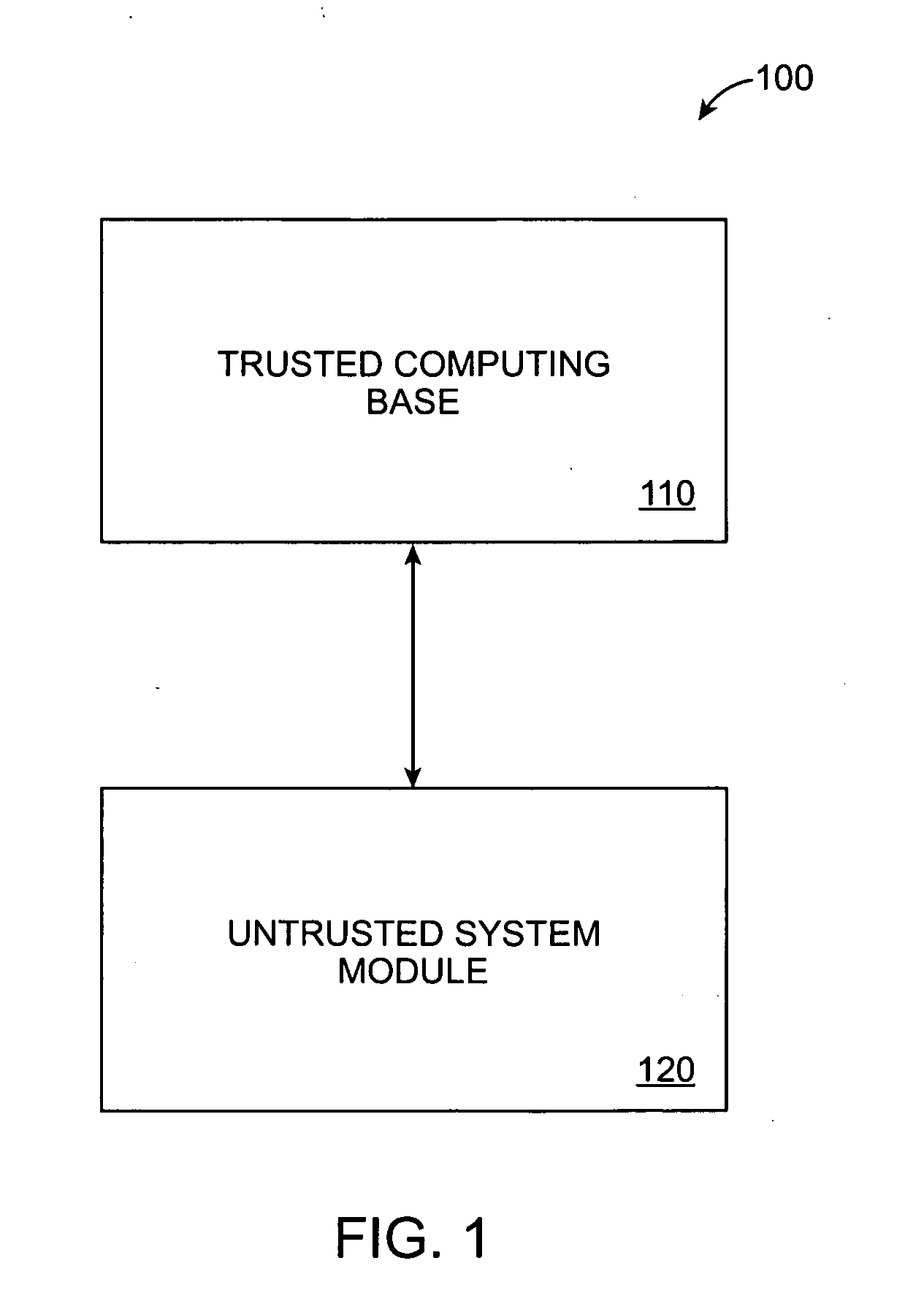
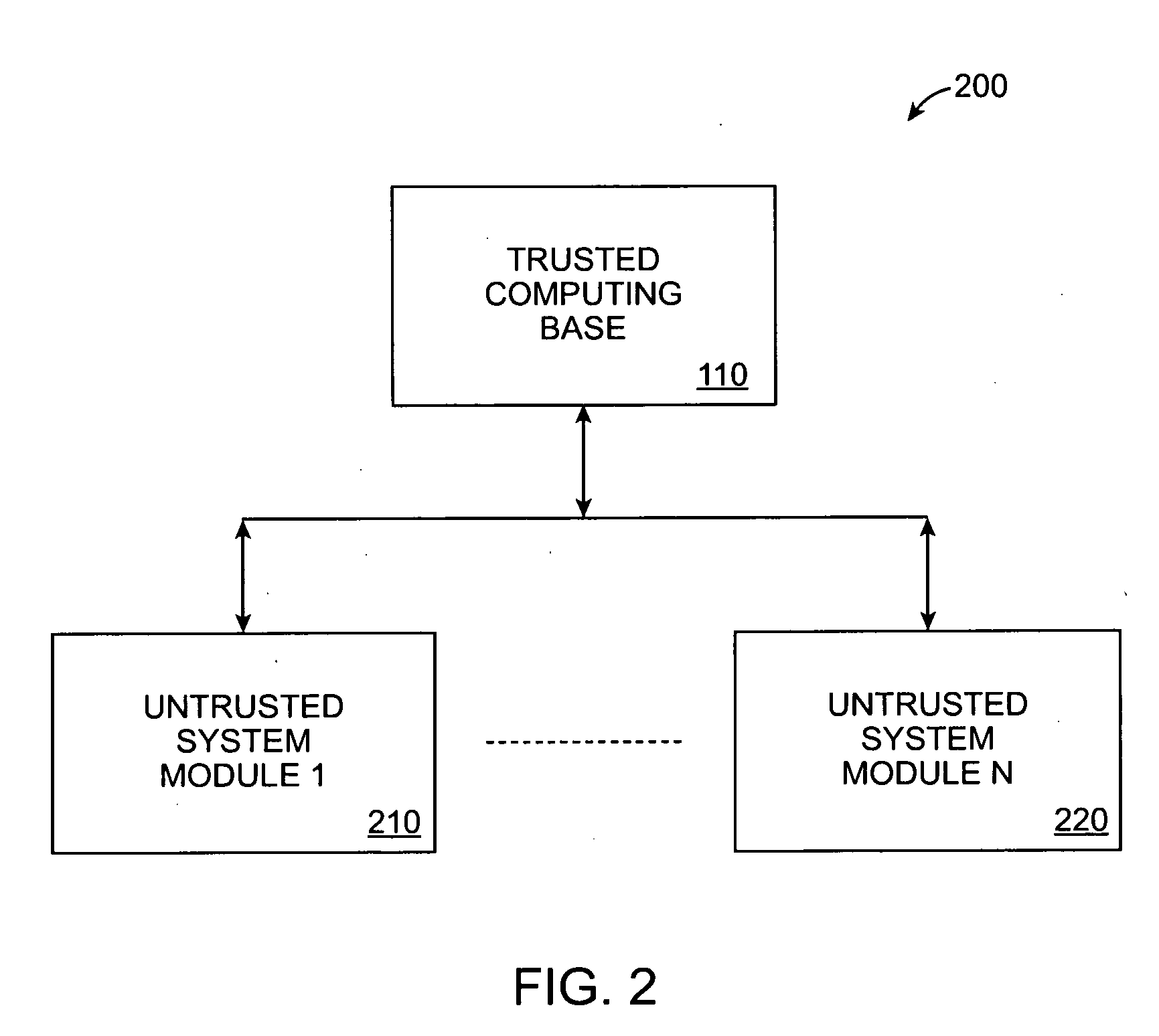
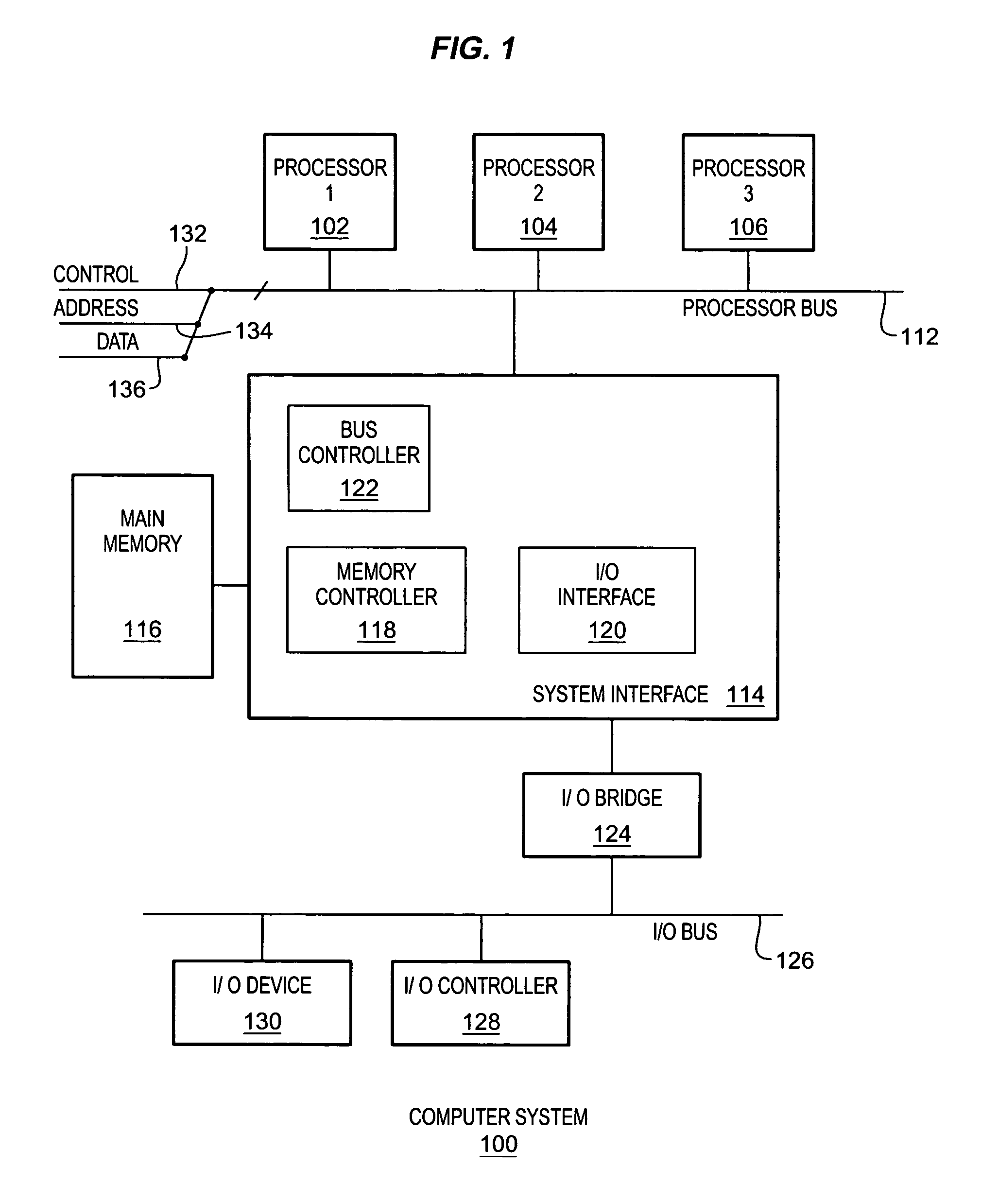
The trusted computing base (TCB) of a computer system is the set of all hardware, firmware, and/or software components that are critical to its security, in the sense that bugs or vulnerabilities occurring inside the TCB might jeopardize the security properties of the entire system. By contrast, parts of a computer system outside the TCB must not be able to misbehave in a way that would leak any more privileges than are granted to them in accordance to the security policy.
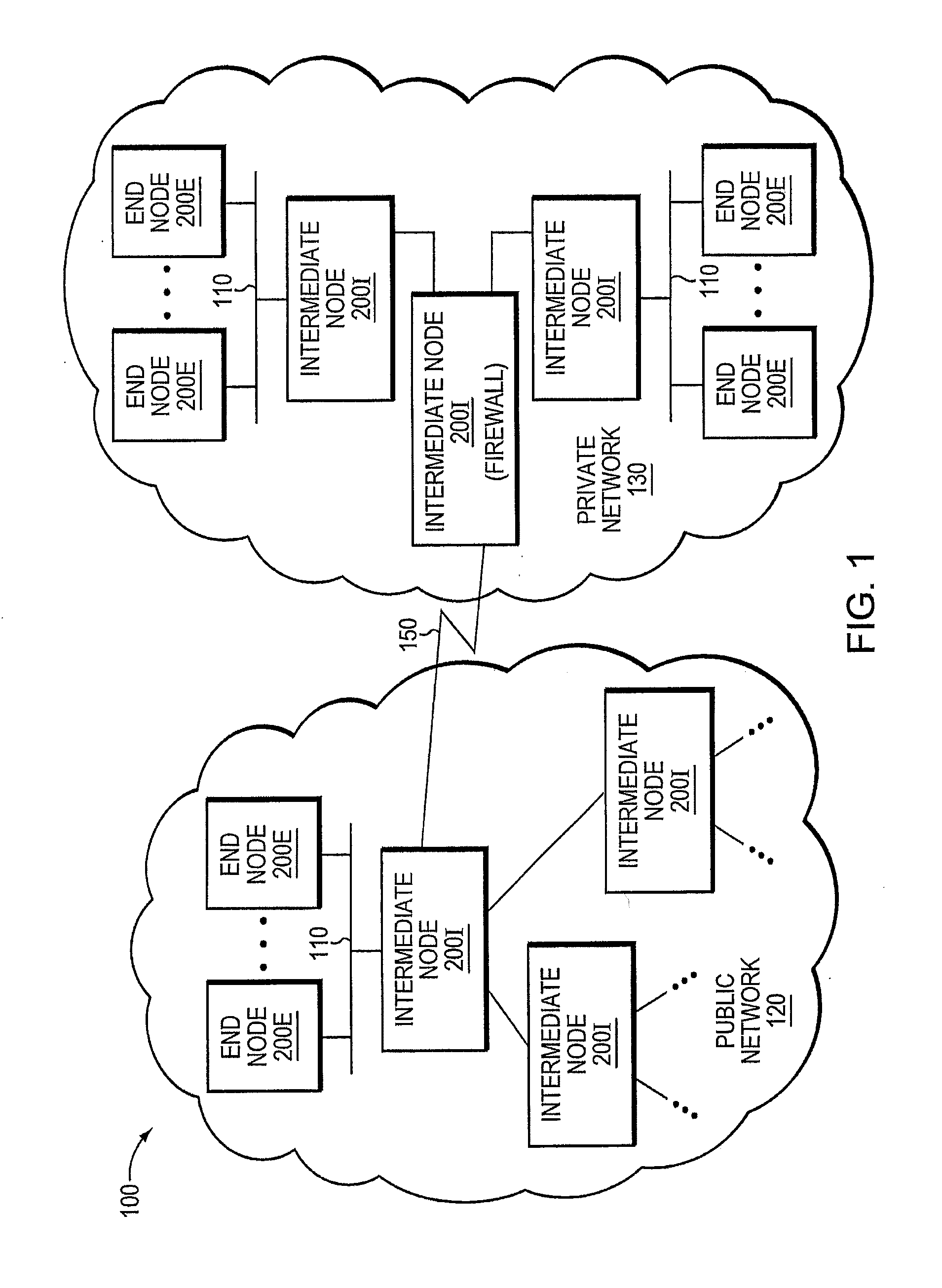
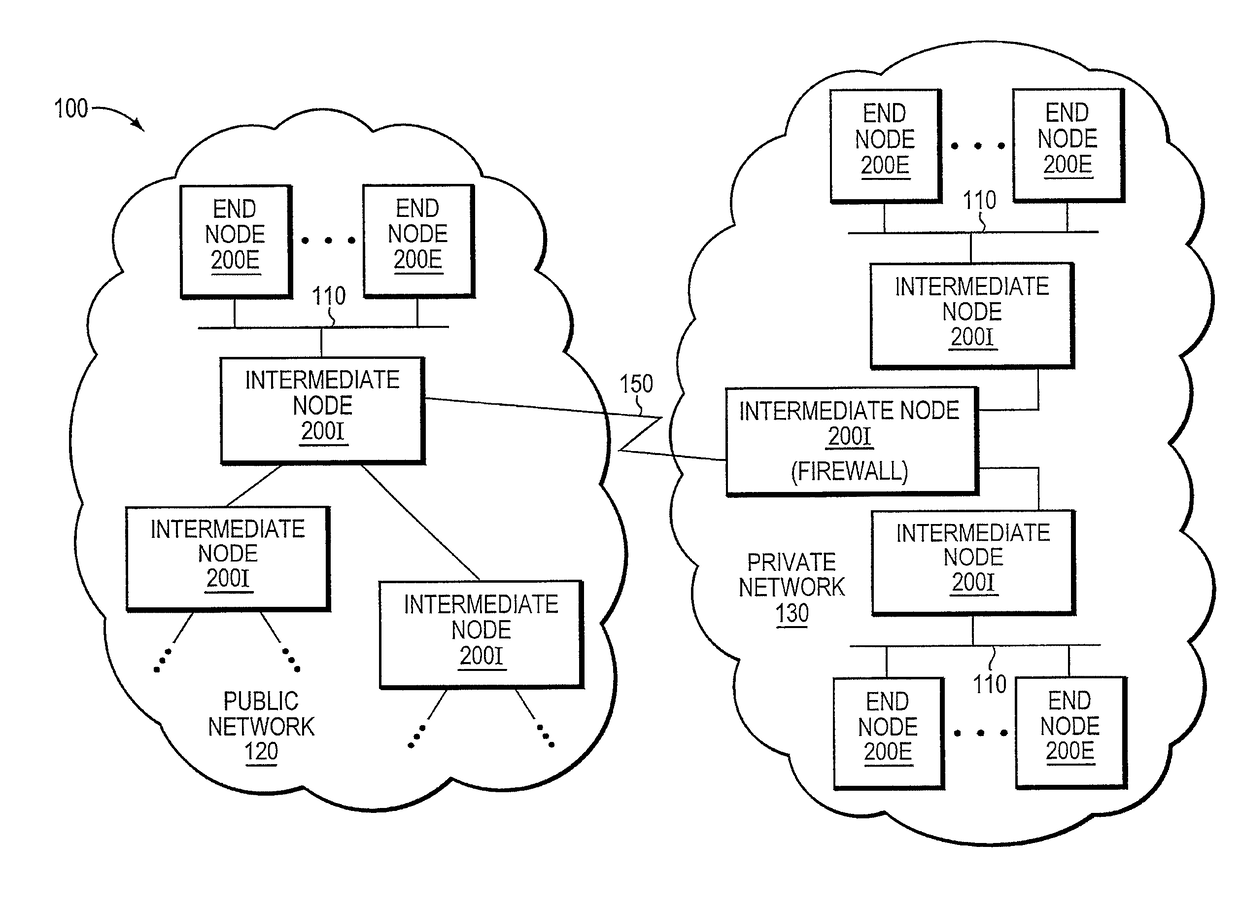
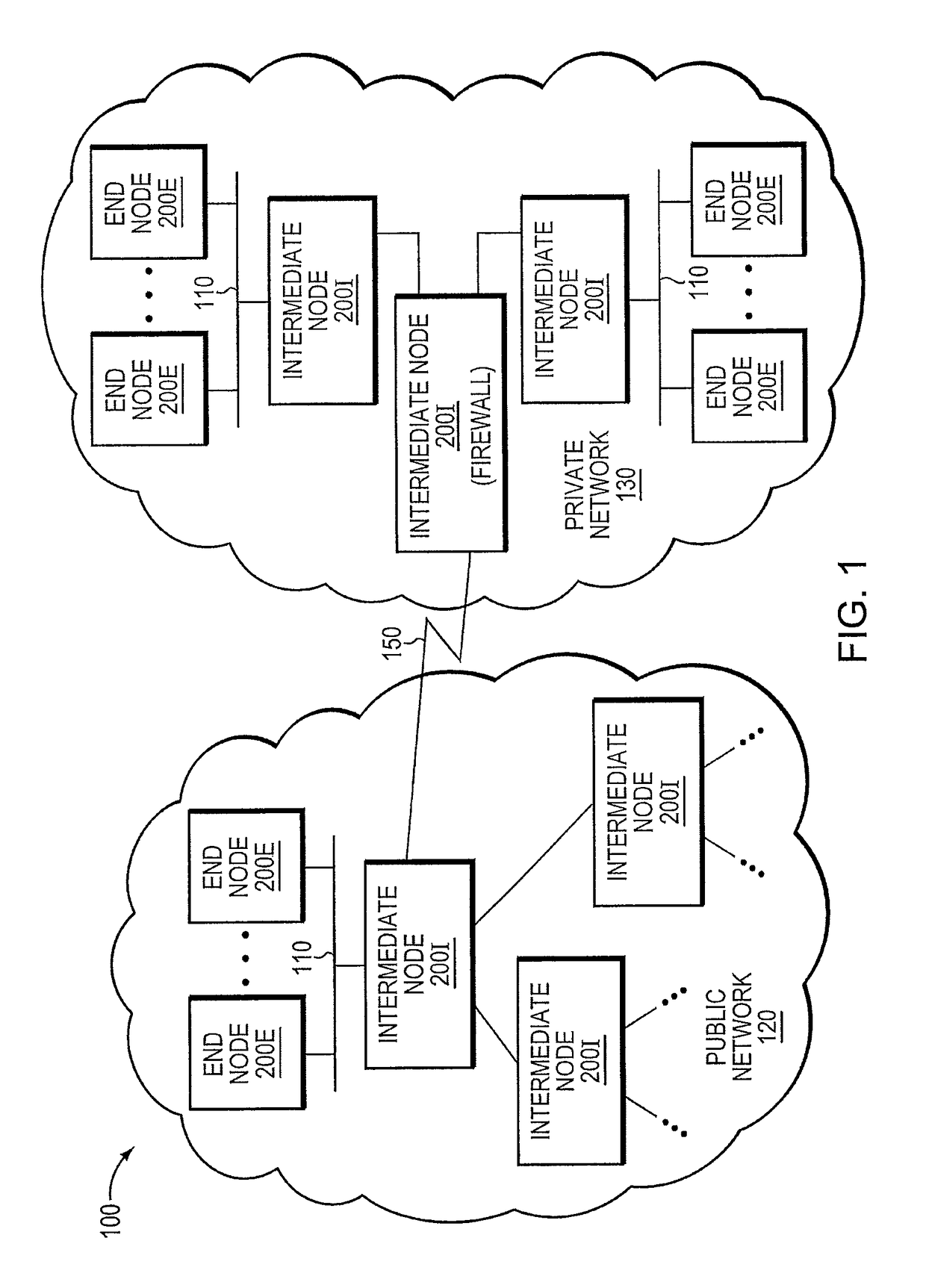
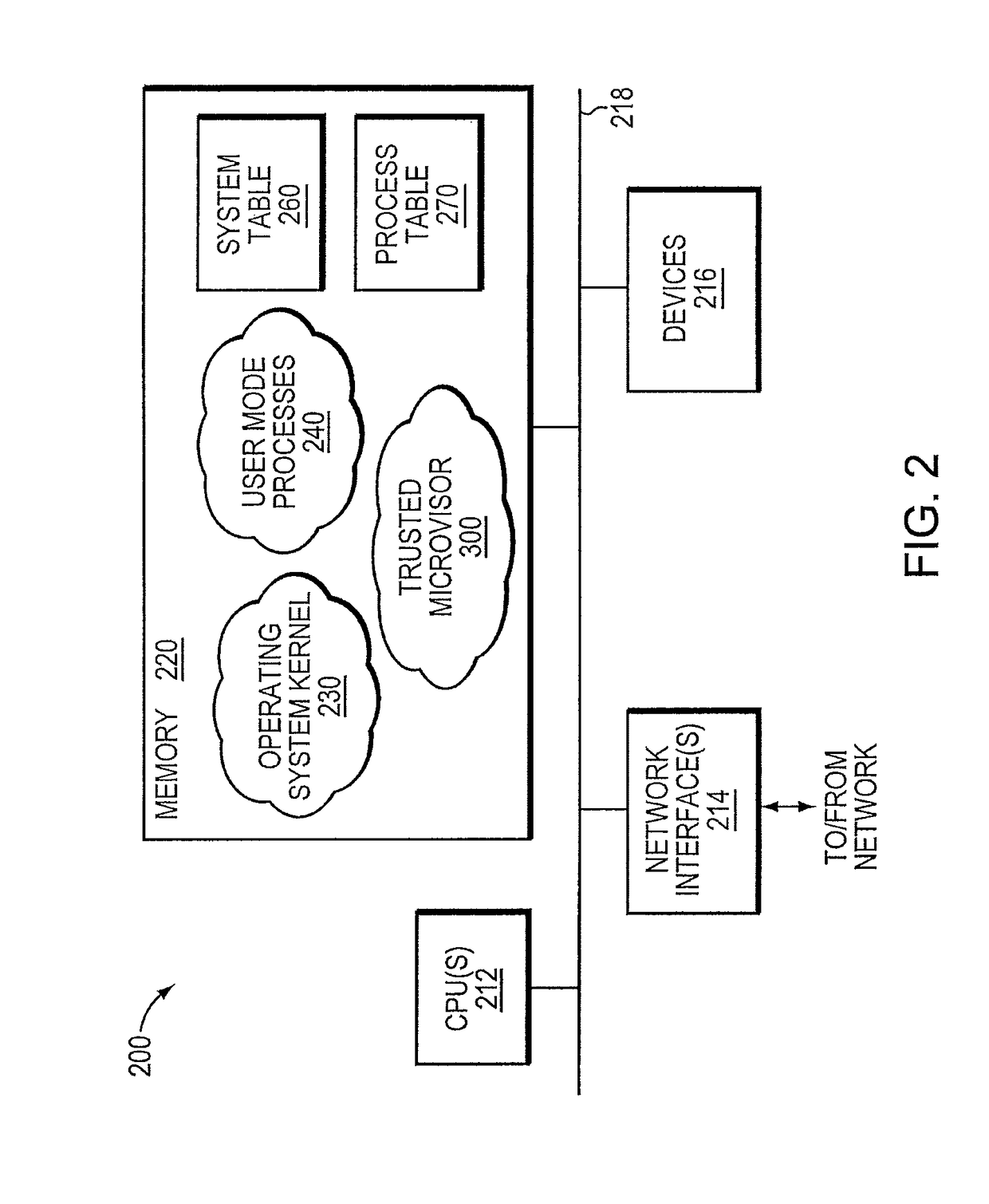
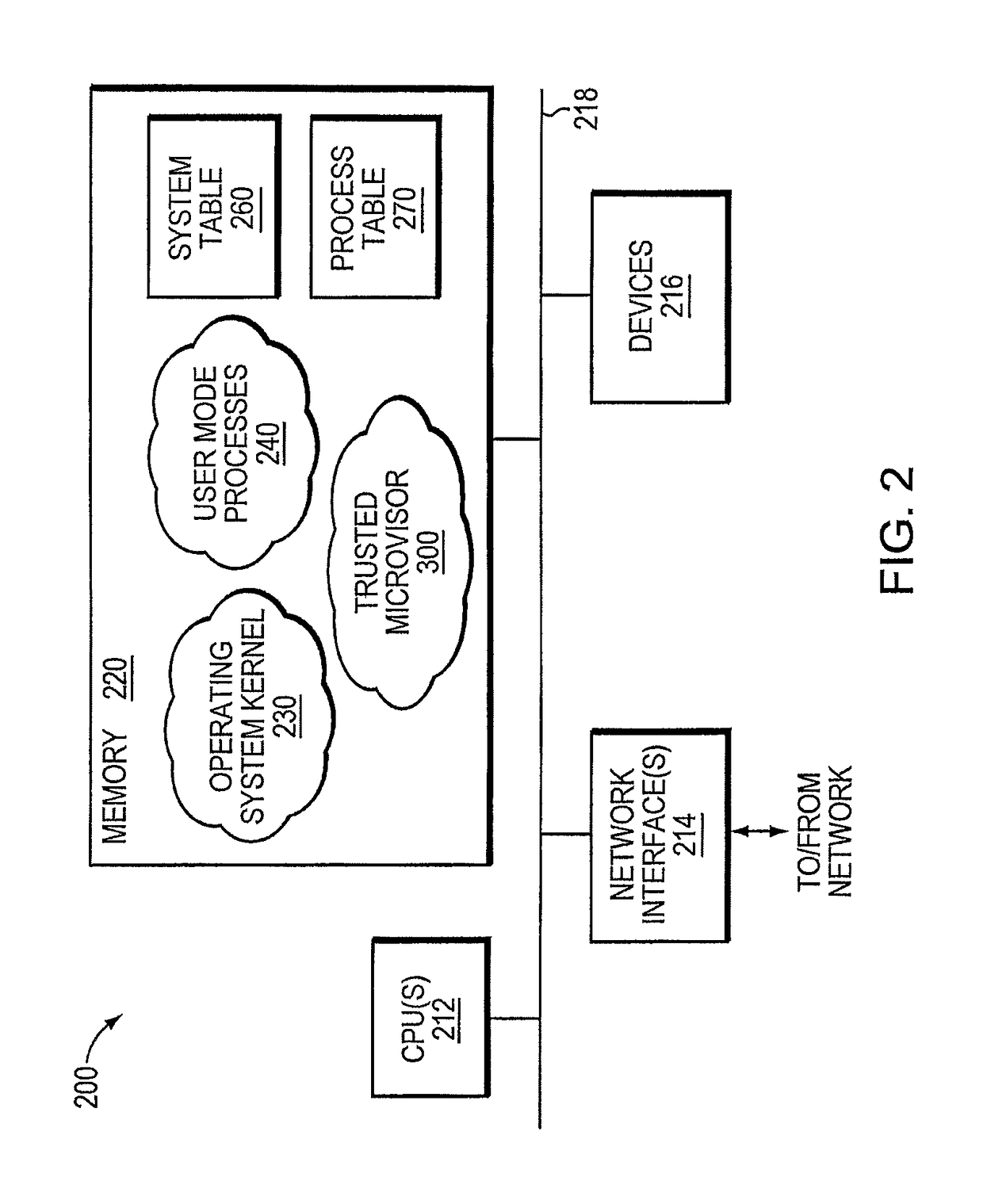
Trusted threat-aware microvisor
ActiveUS20160006756A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionTrusted ComputingSecurity properties
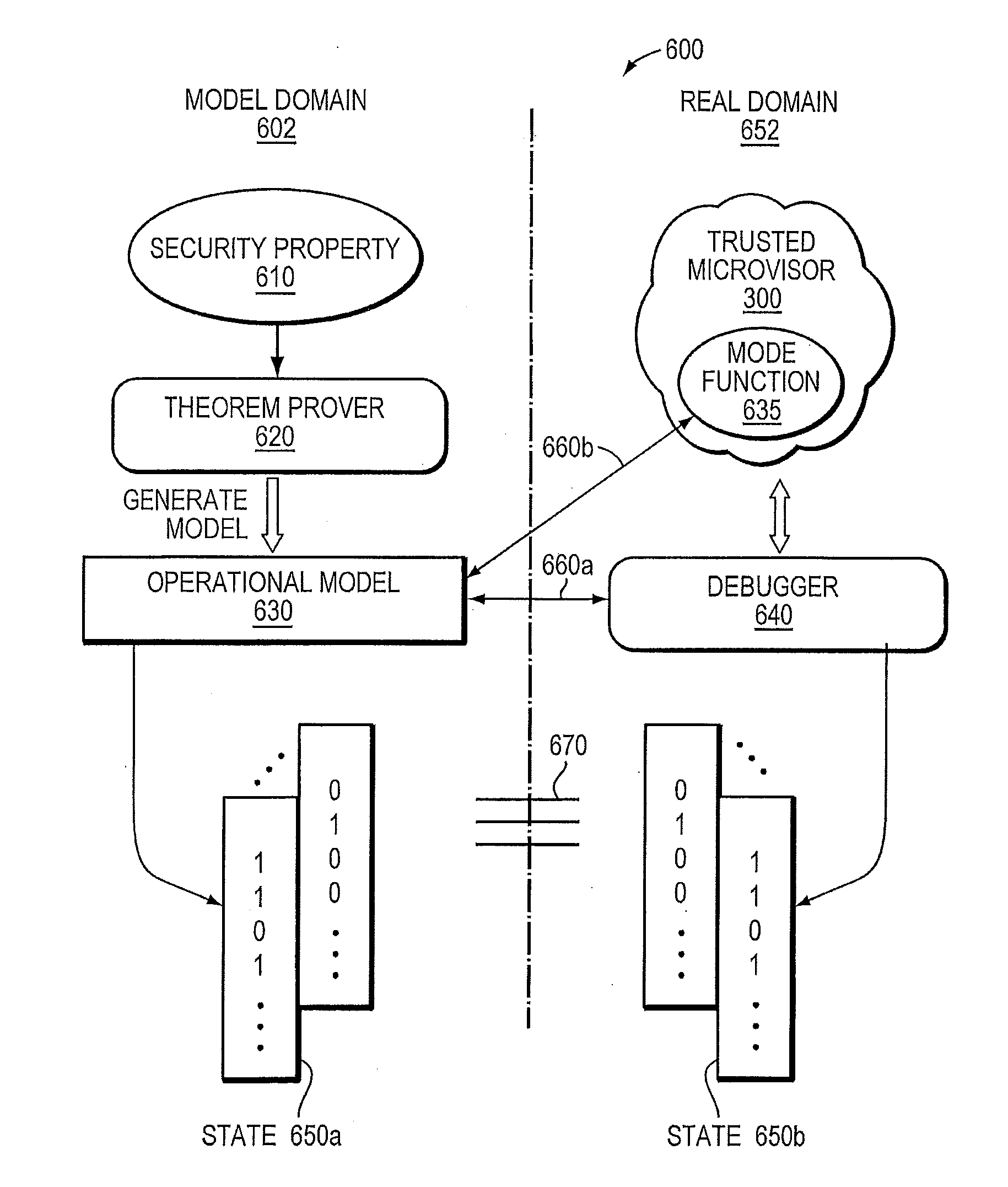
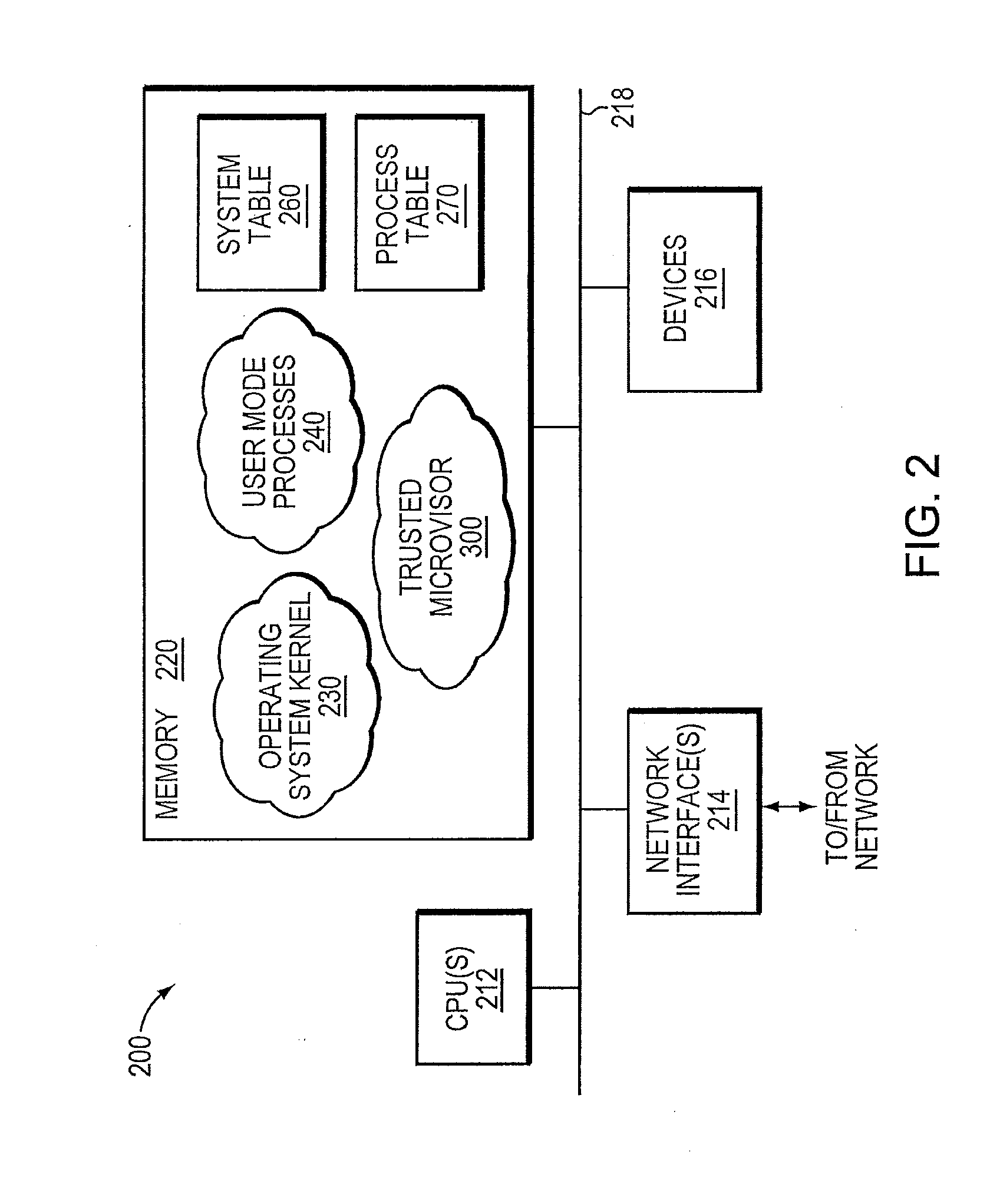
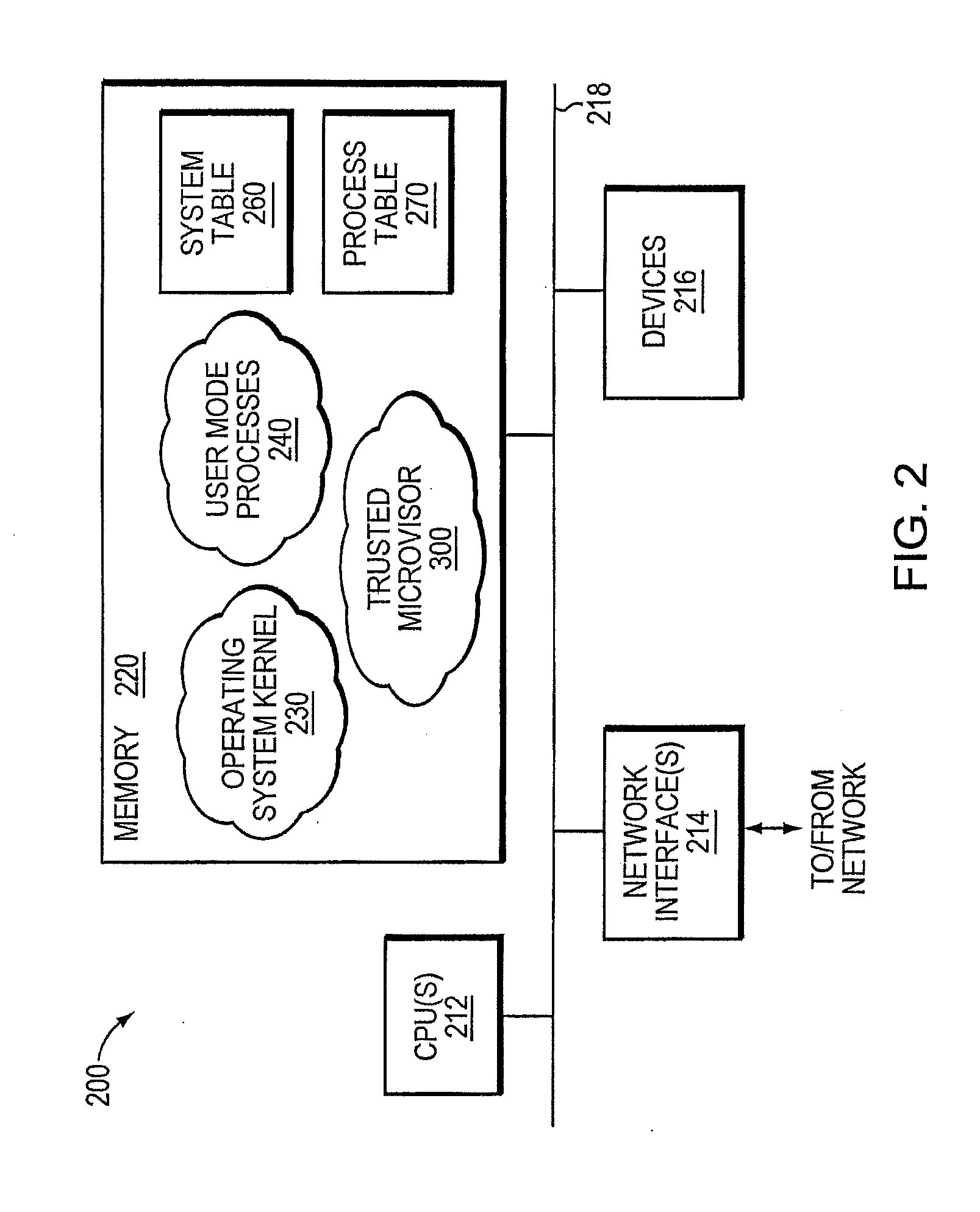
A trusted threat-aware microvisor may be deployed as a module of a trusted computing base (TCB) that also includes a root task module configured to cooperate with the microvisor to load and initialize one or more other modules executing on a node of a network environment. The root task may cooperate with the microvisor to allocate one or more kernel resources of the node to those other modules. As a trusted module of the TCB, the microvisor may be configured to enforce a security policy of the TCB that, e.g., prevents alteration of a state related to security of the microvisor by a module of or external to the TCB. The security policy of the TCB may be implemented by a plurality of security properties of the microvisor. Trusted (or trustedness) may therefore denote a predetermined level of confidence that the security property is demonstrated by the microvisor.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
Verification of trusted threat-aware microvisor
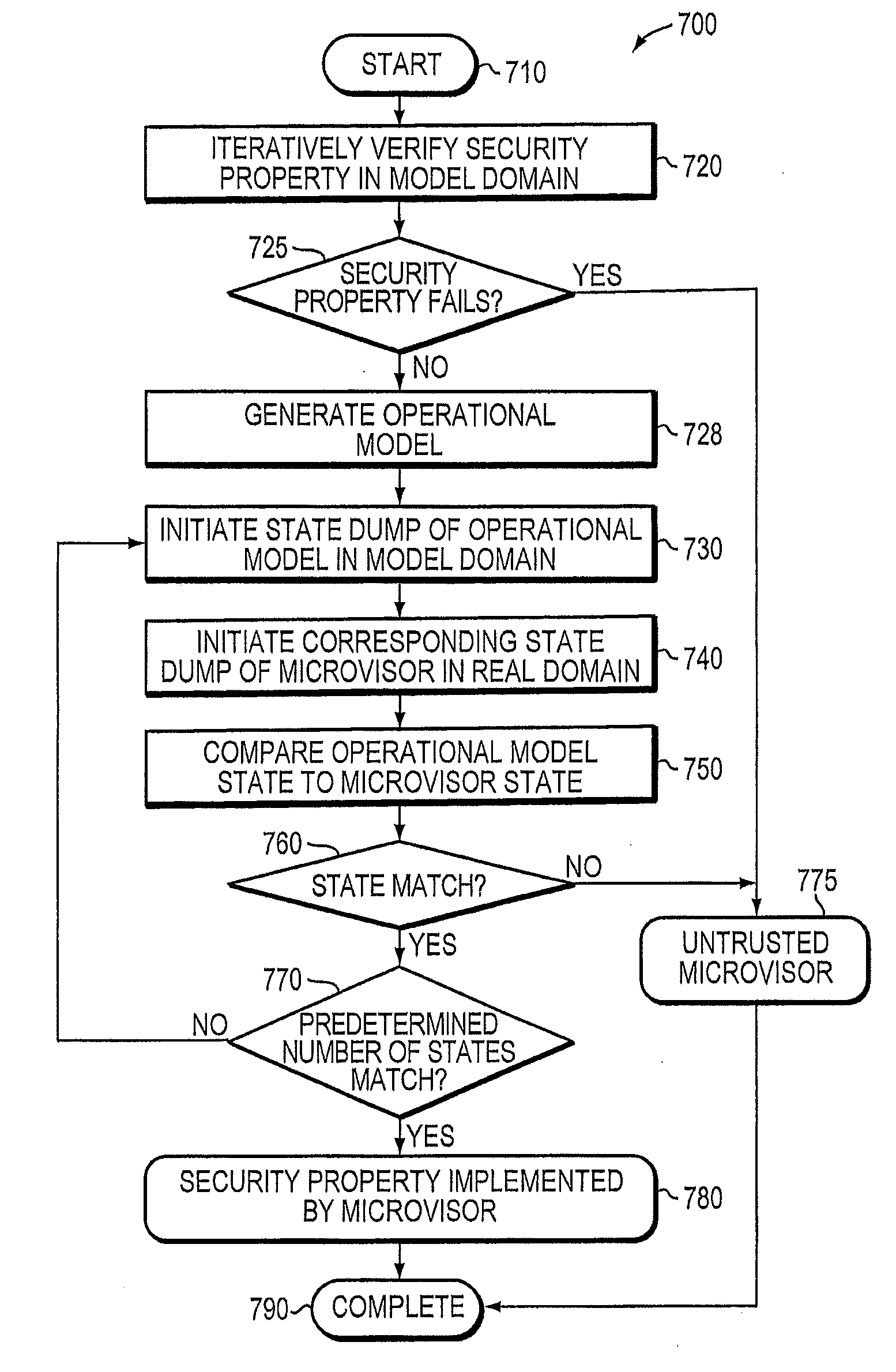
A trusted threat-aware microvisor may be deployed as a module of a trusted computing base (TCB). The microvisor is illustratively configured to enforce a security policy of the TCB, which may be implemented as a security property of the microvisor. The microvisor may manifest (i.e., demonstrate) the security property in a manner that enforces the security policy. Trustedness denotes a predetermined level of confidence that the security property is demonstrated by the microvisor. The predetermined level of confidence is based on an assurance (i.e., grounds) that the microvisor demonstrates the security property. Trustedness of the microvisor may be verified by subjecting the TCB to enhanced verification analysis configured to ensure that the TCB conforms to an operational model with an appropriate level of confidence over an appropriate range of activity. The operational model may then be configured to analyze conformance of the microvisor to the security property. A combination of conformance by the microvisor to the operational model and to the security property provides assurance (i.e., grounds) for the level of confidence and, thus, verifies trustedness.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
Trusted threat-aware microvisor
ActiveUS9680862B2Digital data protectionPlatform integrity maintainanceTrusted ComputingSecurity properties
A trusted threat-aware microvisor may be deployed as a module of a trusted computing base (TCB) that also includes a root task module configured to cooperate with the microvisor to load and initialize one or more other modules executing on a node of a network environment. The root task may cooperate with the microvisor to allocate one or more kernel resources of the node to those other modules. As a trusted module of the TCB, the microvisor may be configured to enforce a security policy of the TCB that, e.g., prevents alteration of a state related to security of the microvisor by a module of or external to the TCB. The security policy of the TCB may be implemented by a plurality of security properties of the microvisor. Trusted (or trustedness) may therefore denote a predetermined level of confidence that the security property is demonstrated by the microvisor.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
Verification of trusted threat-aware microvisor
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
Method and apparatus for securing the full lifecycle of a virtual machine
InactiveUS20130061293A1Small sizeLittle processingSpecific access rightsDigital data processing detailsVirtualizationResting time
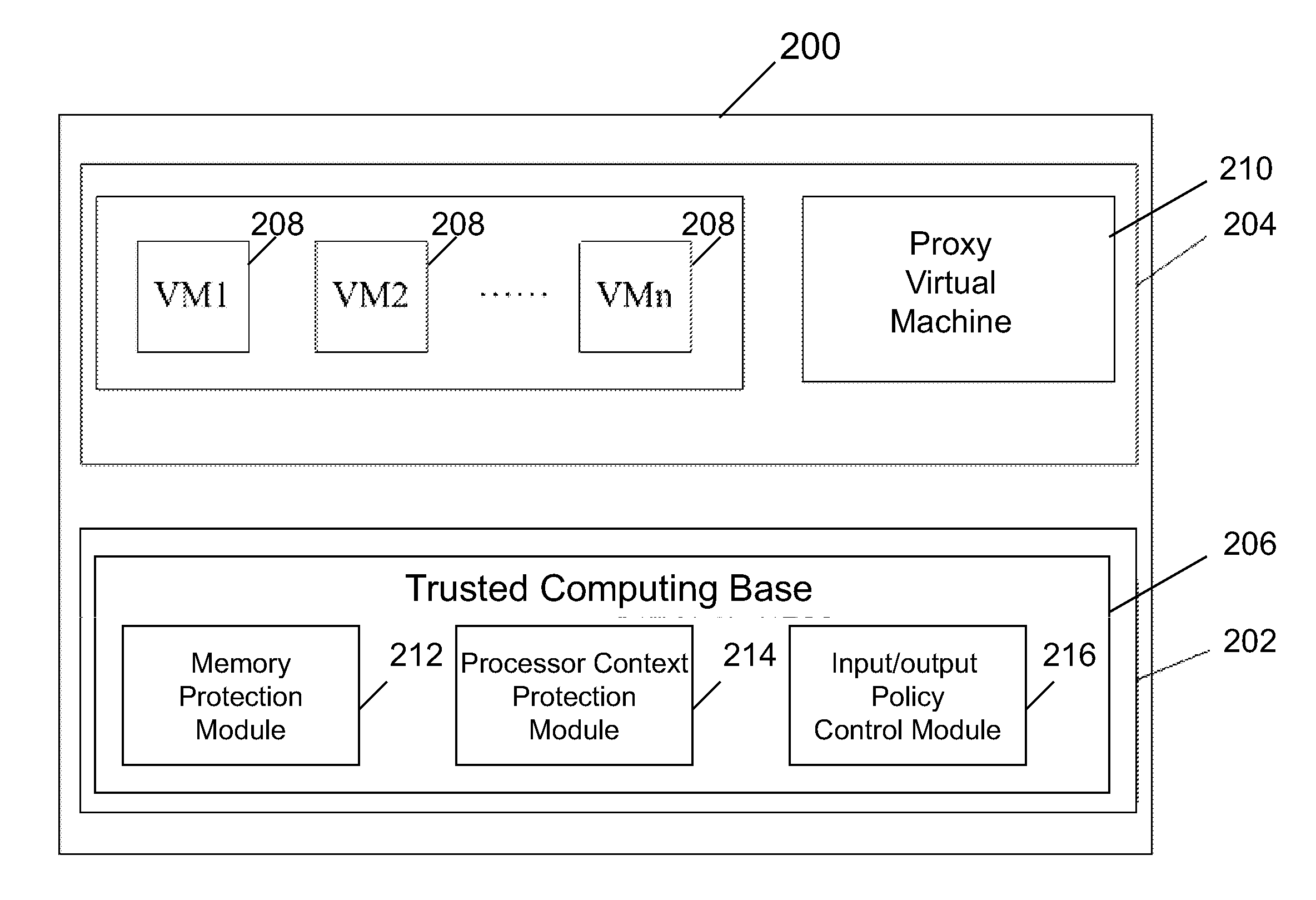
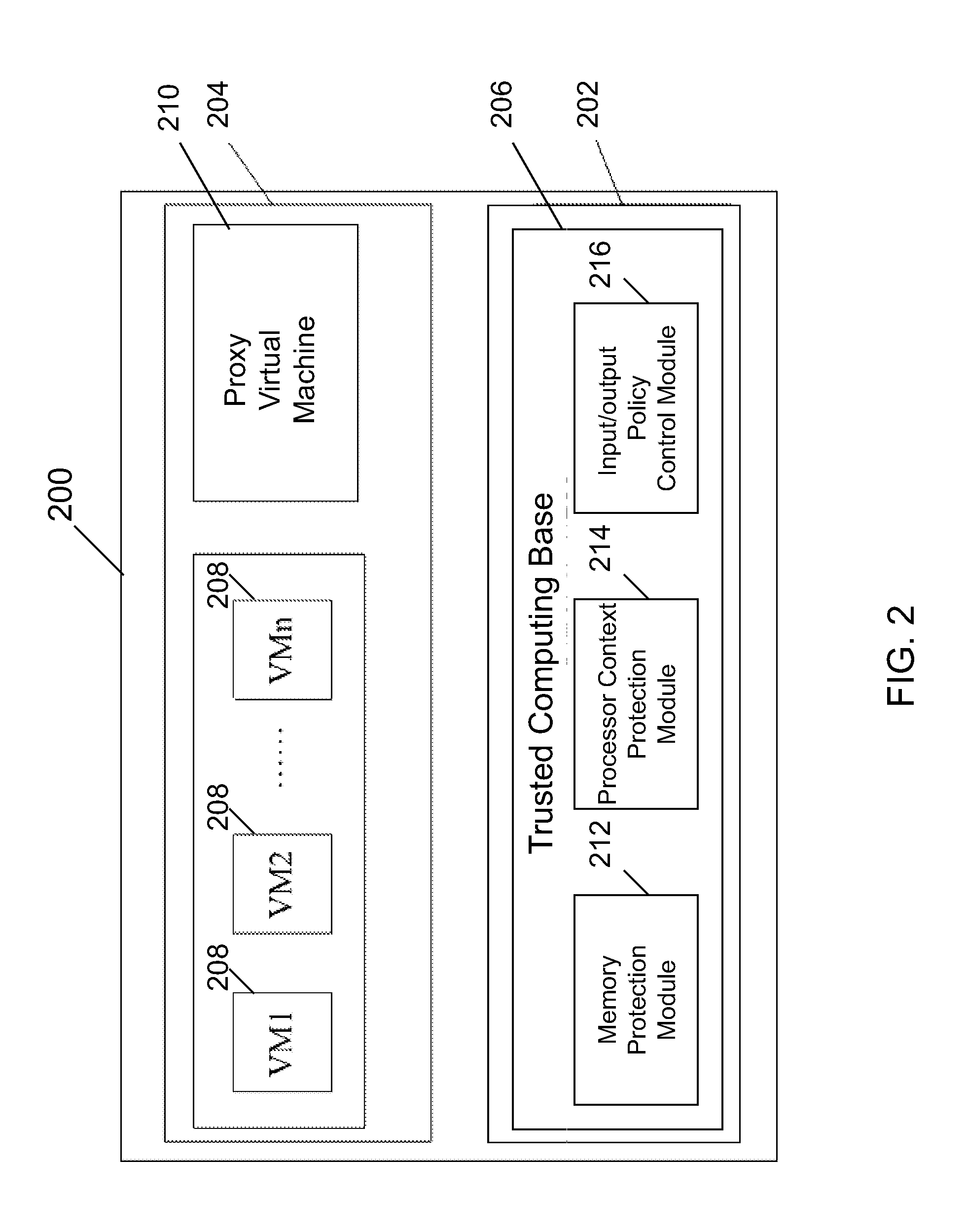
Systems and methods for securing a virtual machine are disclosed. Various embodiments of the systems and methods disclosed herein allow provisioning a trusted and secure computing environment to a user. Various embodiments enable securing a virtual machine during multiple states, such as during run time, construction time and rest time. In one embodiment, a virtualization infrastructure for securing a virtual machine includes a trusted computing base and a proxy virtual machine running on the virtualization infrastructure as a proxy of the trusted computing base, the trusted computing base being configured to cryptographically verify the proxy virtual machine to be authentic and to prevent unauthorized access to the proxy virtual machine. The proxy virtual machine may be configured to compute an exit state measurement of the virtual machine and to use the exit state measurement to prevent an unauthorized entry of the virtual machine into the virtualization infrastructure.
Owner:DAOLICLOUD INFORMATION TECH COMPANY BEIJING
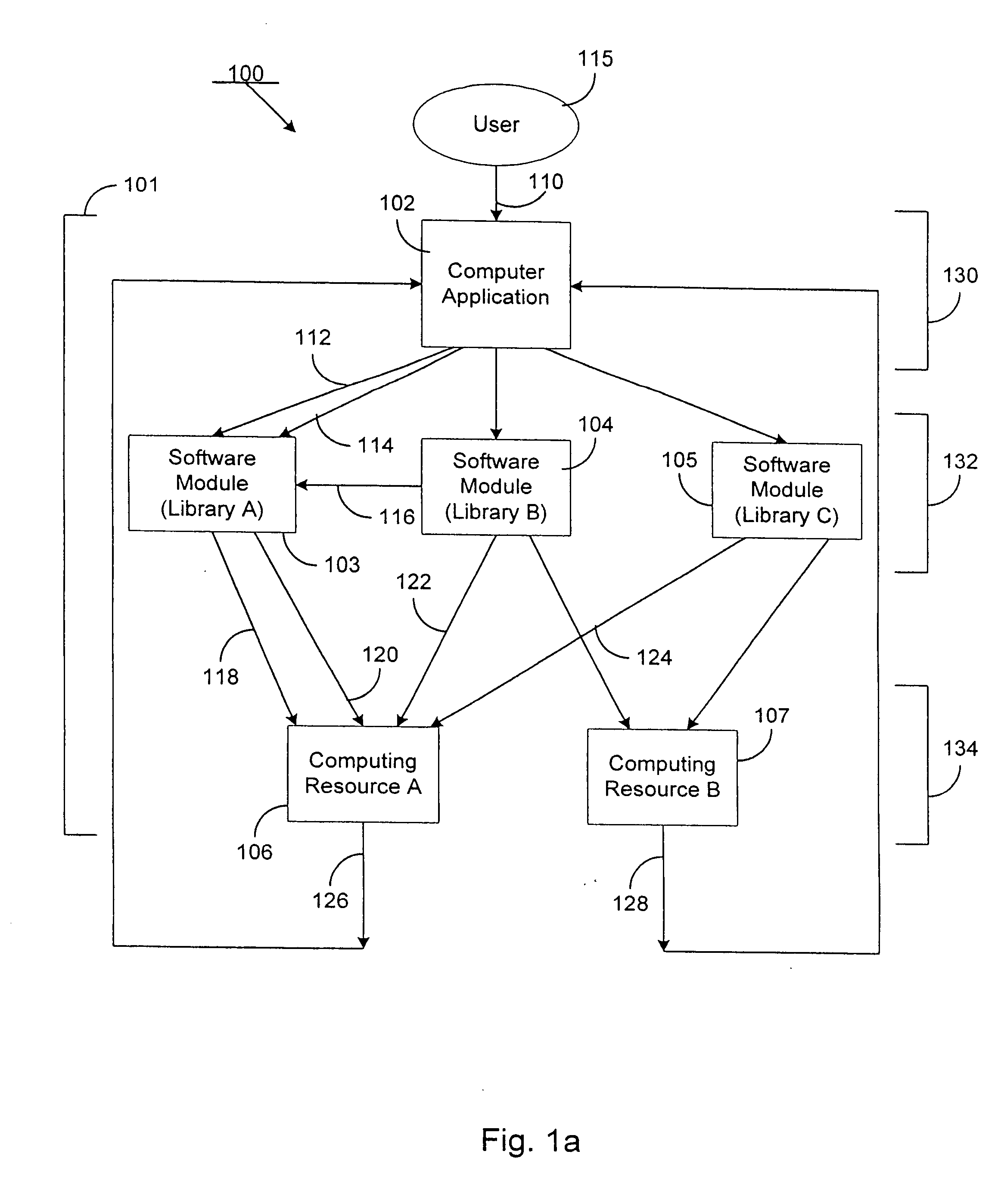
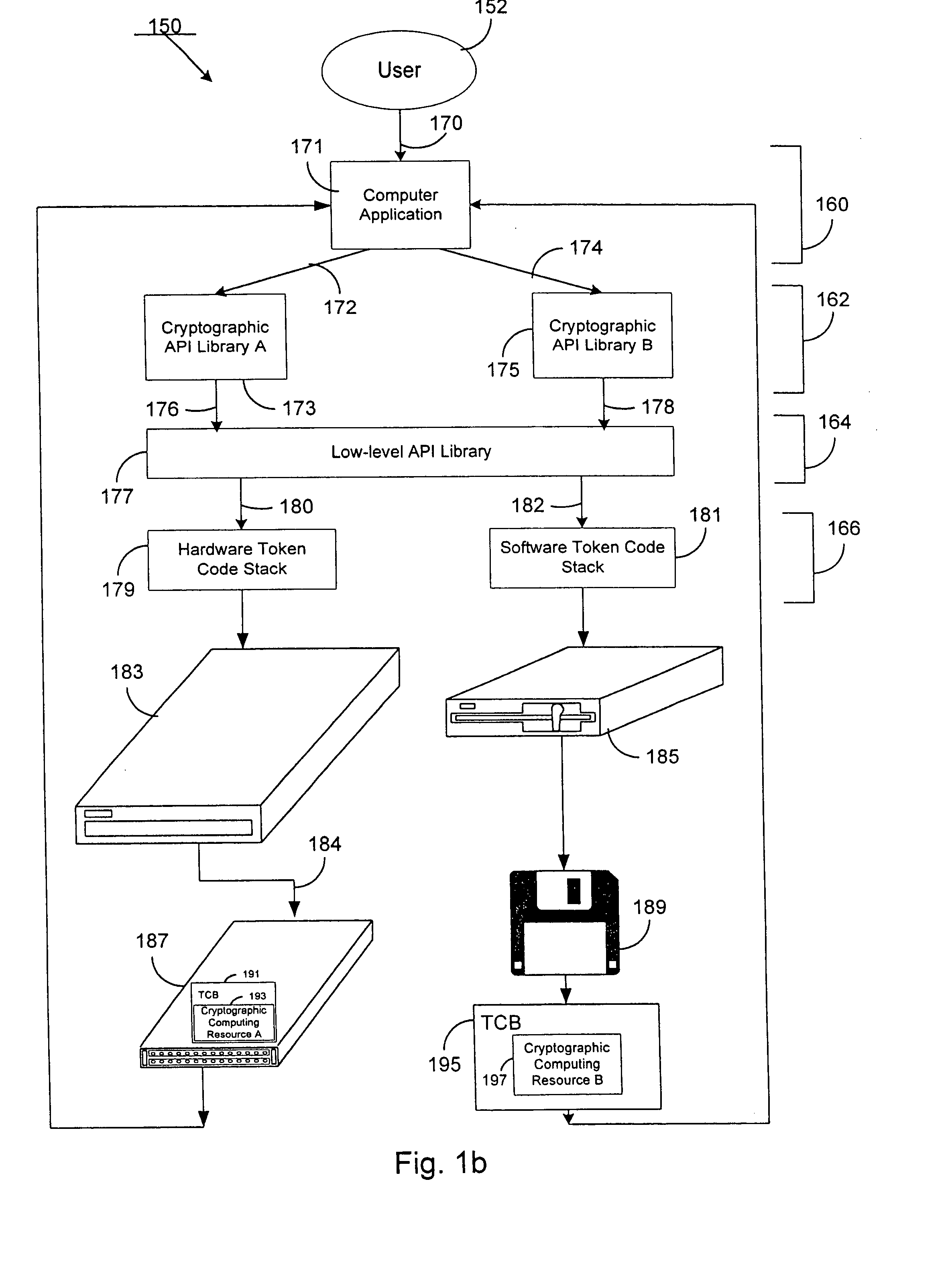
Method and system for enforcing access to a computing resource using a licensing attribute certificate
InactiveUS20050262553A1Reduce usageLower capability requirementsDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrusted ComputingTrusted computing base
A licensing attribute certificate enables a trusted computing base to enforce access to a computing resource by a computer application. The licensing attribute certificate can contain enforcement data which limits the use of the computing resource. The licensing attribute certificate can also contain information allowing for the tracking of licensing data about the use of the computing resource. The use of a licensing attribute certificate to enforce access to a computing resource can allow products to be fielded which have their capability limited to a specific subset of functions. The enforcement data, the licensing data, and the data limiting the application to a specific subset of functions are cryptographically bound to the computing resource using a licensing attribute certificate according to the invention. Prior to allowing access to the computing resource by the computer application, a trusted computing base strongly authenticates that usage via the licensing attribute certificate.
Owner:SPEX TECH
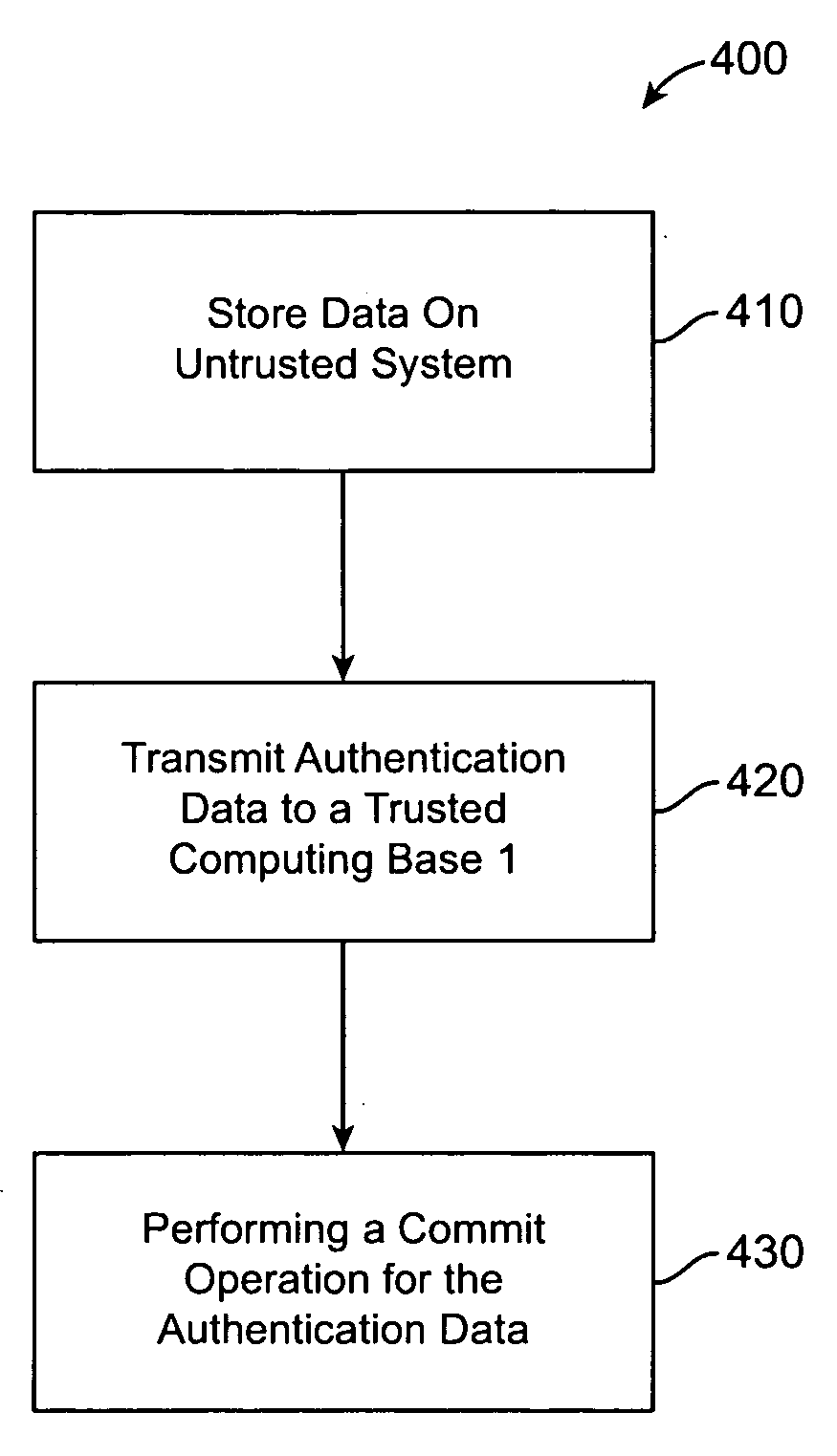
System and method for efficient trust preservation in data stores
InactiveUS20100212017A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTrusted computing baseTrustworthiness
The invention provides a method and system for preserving trustworthiness of data, the method includes storing data on an untrusted system, and committing the data to a trusted computing base (TCB). The committing includes upon an end of a predetermined time interval, transmitting a constant size authentication data from the untrusted system to the TCB, and the TCB preserving trustworthiness of the authentication data based on performing a single hash operation of a first root and a second root of a general hash tree representing authenticated data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Notification of modifications to a trusted computing base
InactiveUS6961855B1Fully understandDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrusted ComputingDecision taking
A mechanism that allows enterprise authorities to be informed when security-sensitive decisions or actions have been or are attempting to be made by users of untrusted code executing in the trusted computing base. The mechanism may be implemented as an abstract class that is part of the trusted computing base. The class provides a framework abstract enough to permit multiple possible notifications (e.g., providing an e-mail to a system operator, sending an Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) alert, making an entry in an online database, or the like) in the event that a given action is taken by a user of untrusted code. The abstract class may provide a default notification, or the class may be extended to enable an authority to provide its own set of customized notifications.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Processing trusted commands in trusted and untrusted environments
InactiveUS6871283B1Less codeQuantity minimizationDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrusted ComputingTrusted computing base
A method for executing trusted commands, in which a trusted command is first received from a user at a user terminal and parsed by untrusted code; then passed to a trusted computing base for execution. The trusted computing base displays some indication of what is to be done back to the user for confirmation. Confirmation of the commands prevents unauthorized modification of the commands and increases system confidence. A randomly (or pseudo-randomly) generated process identifier is employed to verify the existence of a trusted path.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Extended trusted computing base
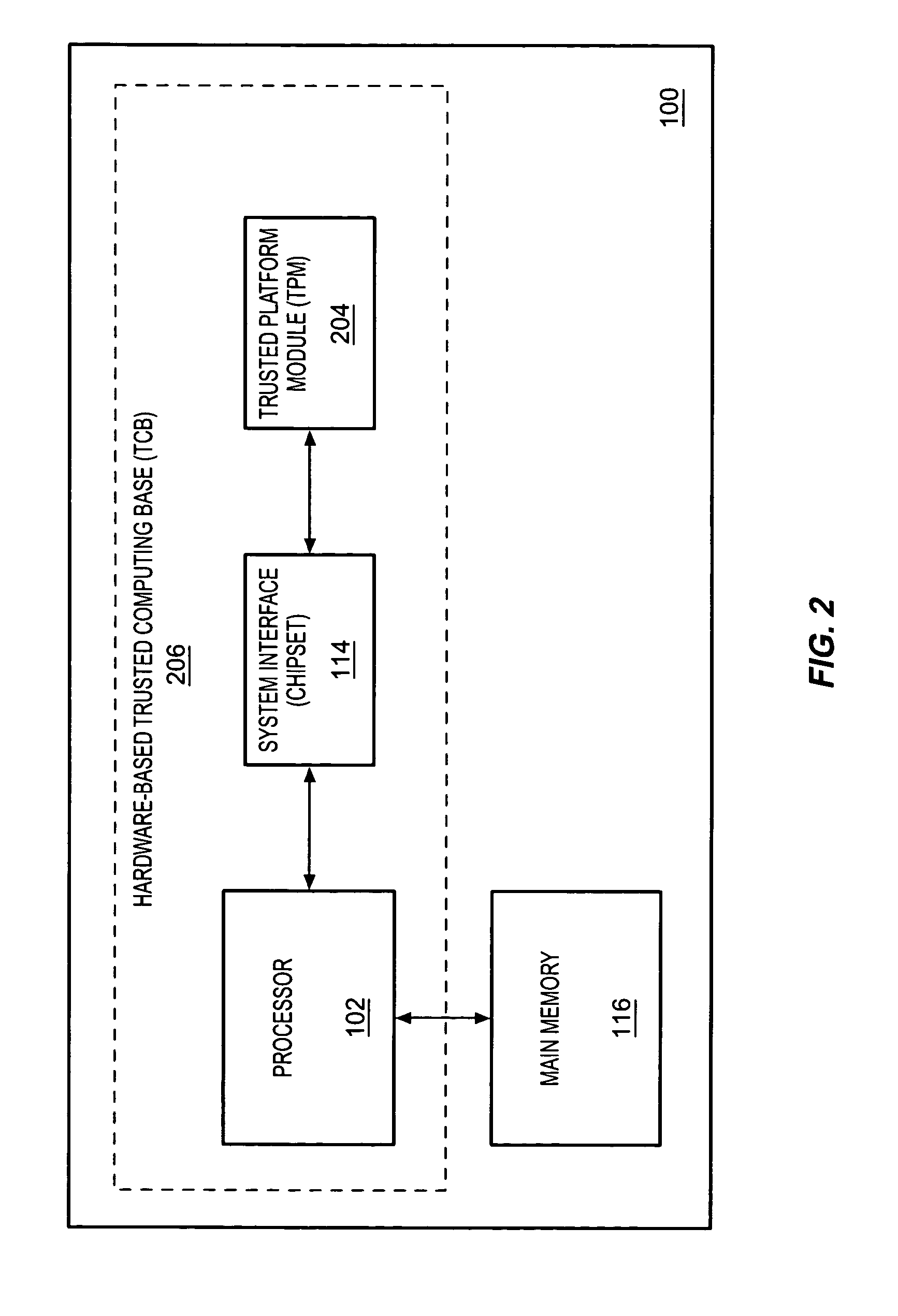
InactiveUS7313679B2Flexible, secure, trustworthy, and feature-richEnsure trustworthinessVolume/mass flow measurementDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareTrusted Platform Module
A method, apparatus, and system are provided for extending a trusted computing base (TCB). According to one embodiment, a first level trusted computing base (TCB) is generated having hardware components including a trusted platform module (TPM), and an extended TCB is formed by adding a second level software-based TCB to the first level TCB, and properties associated with the first level TCB are transferred to the second level TCB.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Executing Trusted Applications with Reduced Trusted Computing Base
ActiveUS20110154500A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTrusted ComputingApplication software
A system for executing trusted applications with a reduced trusted computing base. In one embodiment, the system includes a processor to dynamically instantiate an application protection module in response to a request by a program to be executed under a trusted mode. The system further includes memory to store the program which is capable of interacting with a remote service for security verification. In one embodiment, the application protection module includes a processor-measured application protection service (P-MAPS) operable to measure and to provide protection to the application.
Owner:INTEL CORP
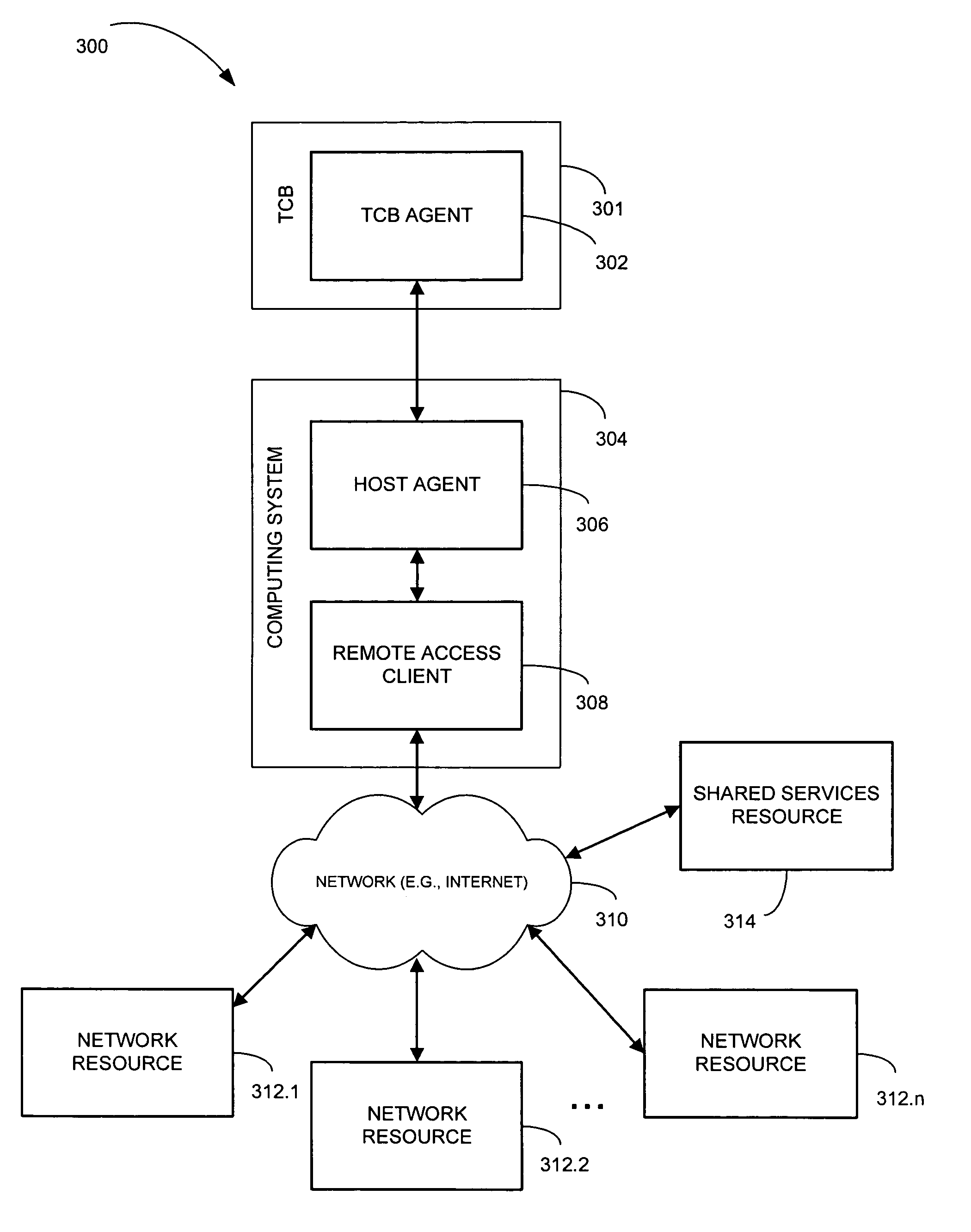
Method and system for access authentication
ActiveUS20080028228A1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsTrusted ComputingTrusted computing base
A method and a system for access authentication. A shared services resource includes a second factor authentication module. At least one network resource each include a first factor authentication module. A trusted computing base communicates with the shared services and the at least one network resource through a pipe. An assertion may be obtained on a trusted computing base for accessing at least one network resource. At least one of the at least one network resource may be accessed with the trusted computing base when the assertion has been obtained by the trusted computing base and is valid.
Owner:PAYPAL INC
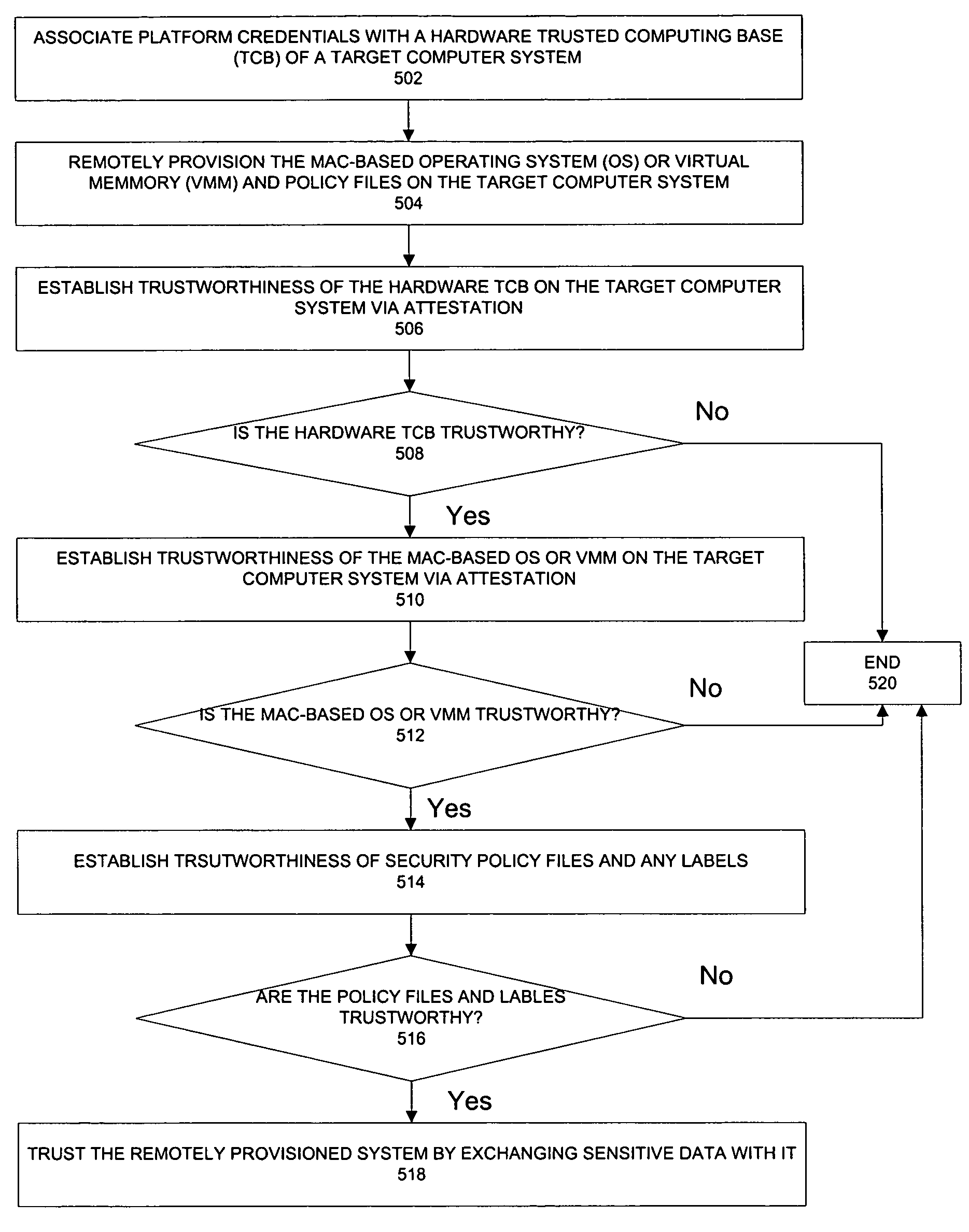
Remote provisioning of secure systems for mandatory control
InactiveUS7424610B2Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionOperational systemTrusted Computing
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and system for isolating computing environment
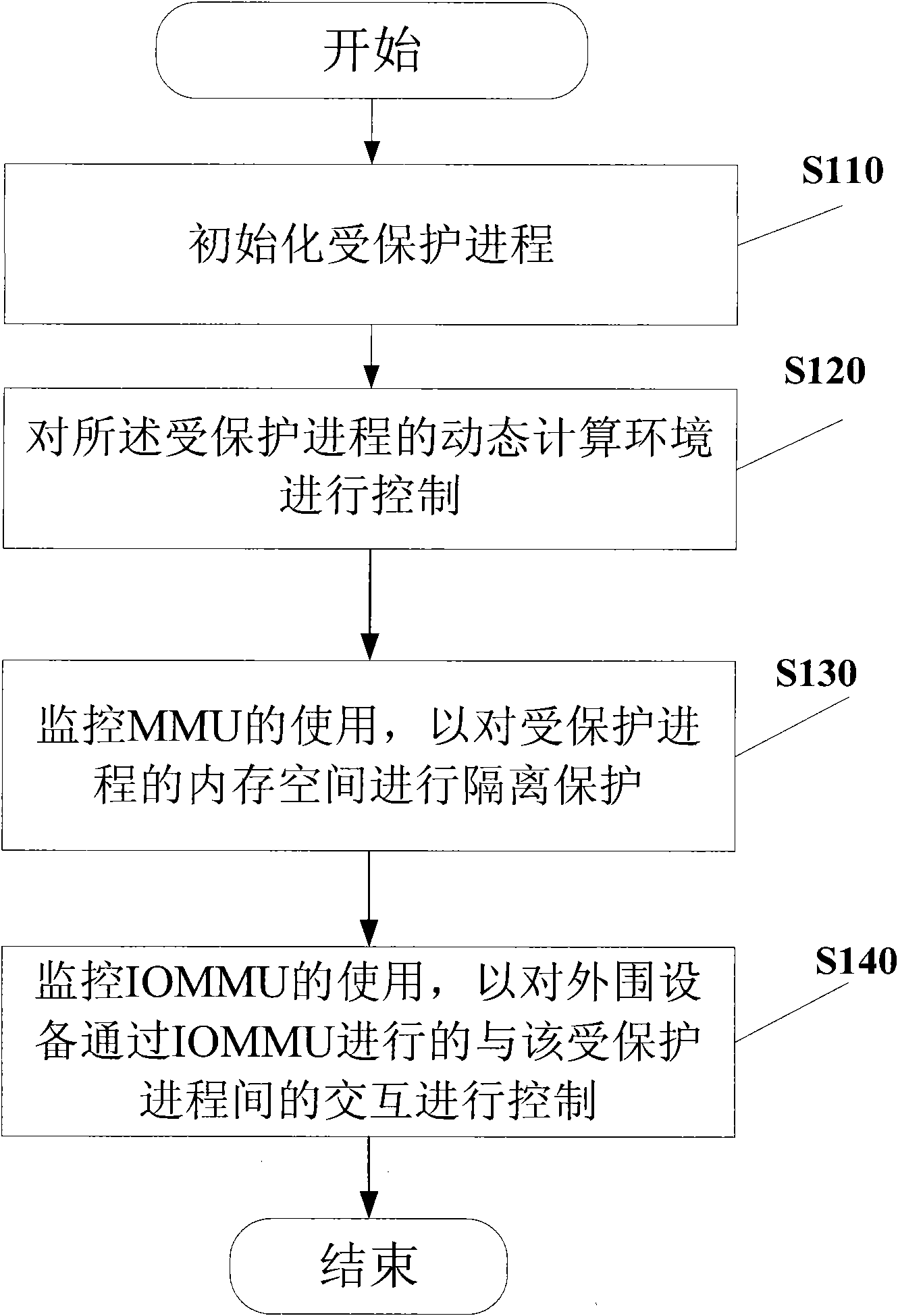
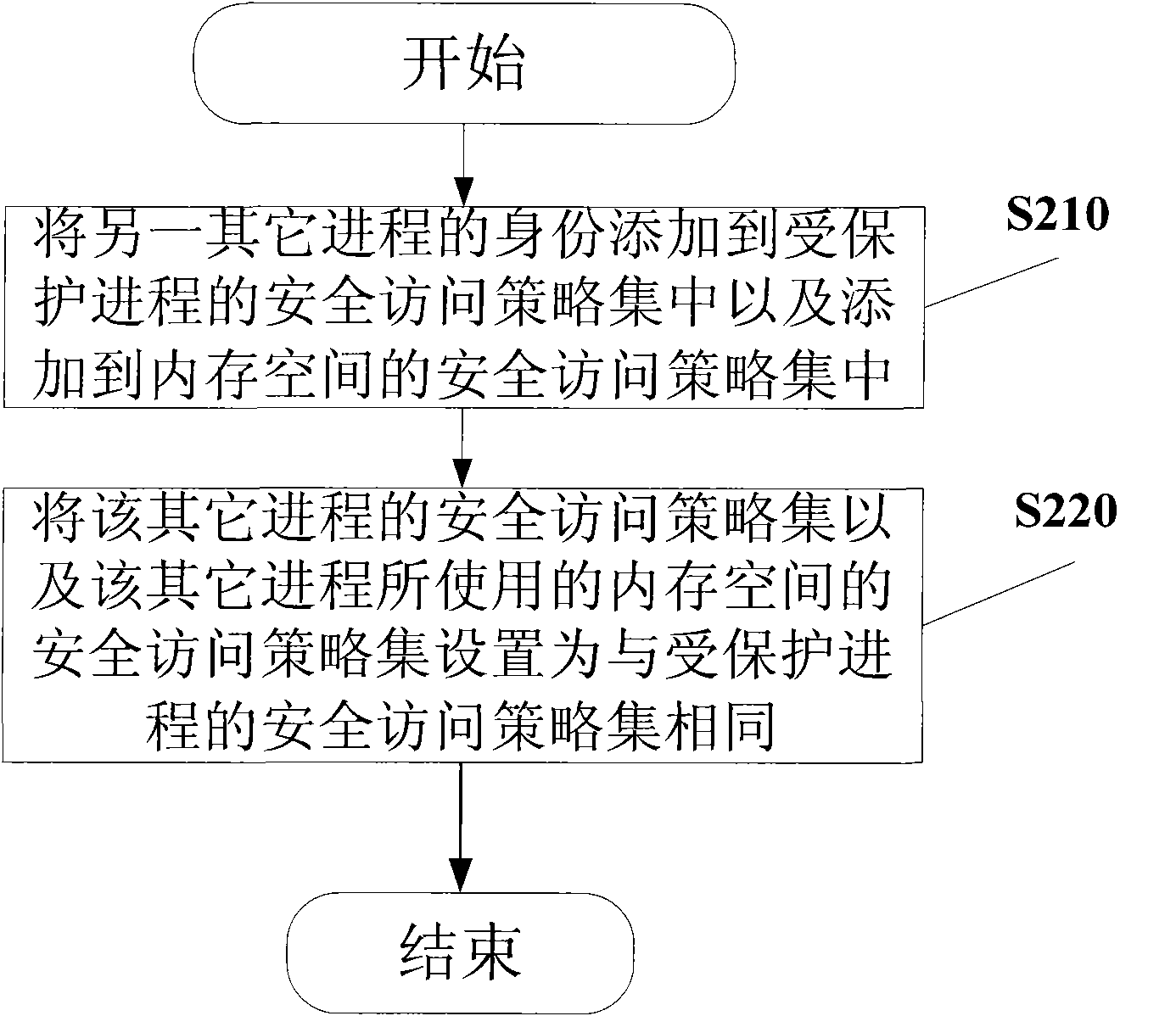
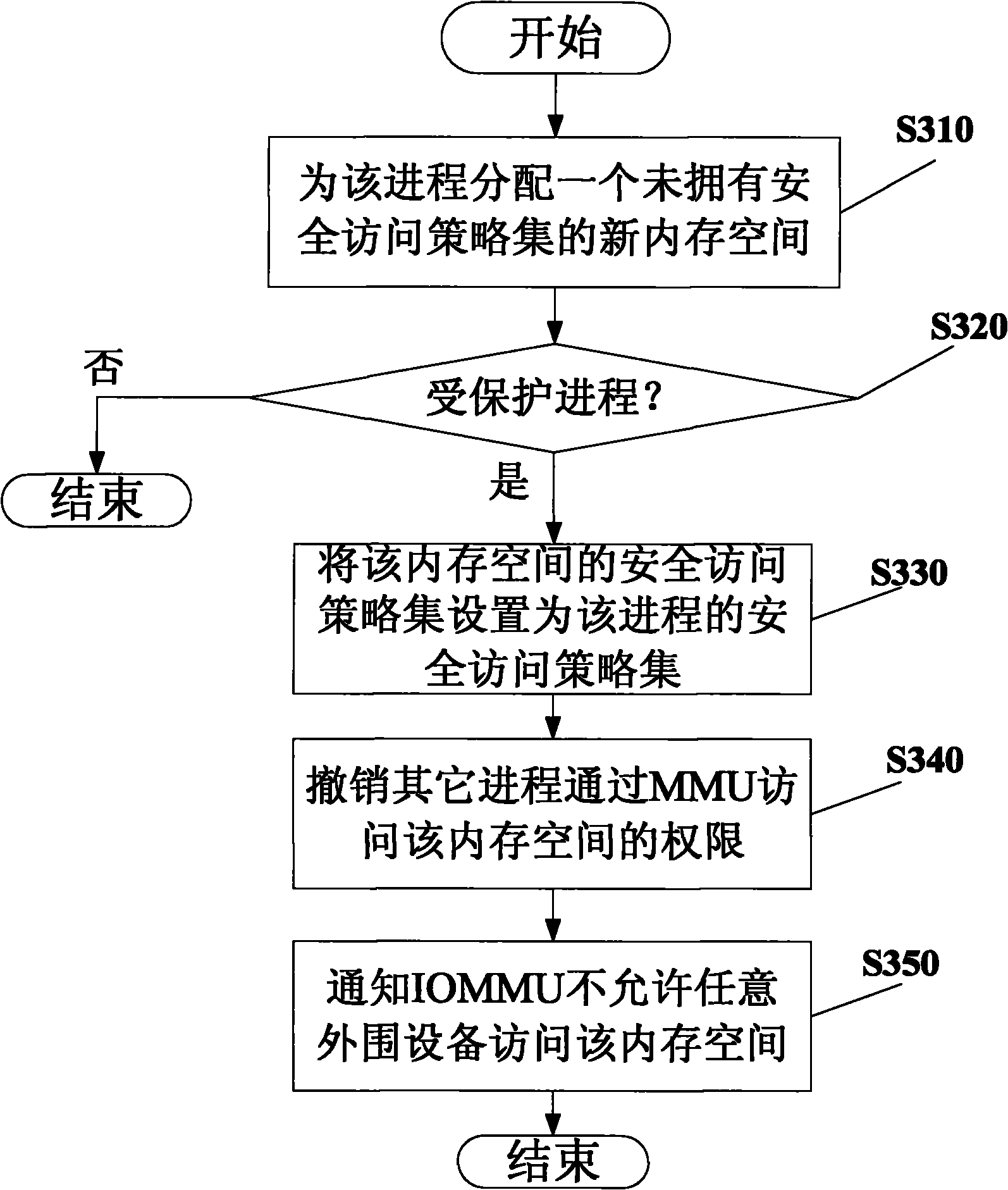
The invention provides a method for isolating and protecting a computing environment in a protected process by using root trusted computing base (RTCB), which comprises an initialized protected process; controlling the dynamic computing environment in a protected process to prevent the dynamic computing environment from being used illegally; monitoring the use of a memory management unit (MMU) and isolating and protecting the memory space in a protected process; and monitoring the use of an input / output memory management unit (IOMMU), and controlling the interaction operation conducted by peripheral equipment with the protected process through the IOMMU. When the method is used, other processes beyond a safe access policy collection of the protected process are prevented from accessing the memory space through the MMU or any input / output (IO) equipment from accessing the memory space according to the memory space distributed to the protected process when the protected process is run, and thus, real safe isolation can be formed.
Owner:EMC CORP
Trustworthy computing base cutting method used for virtual machine system
InactiveCN101599022AImprove securityImprove startup speedPlatform integrity maintainanceProgram loading/initiatingTrustworthy computingTrusted Platform Module
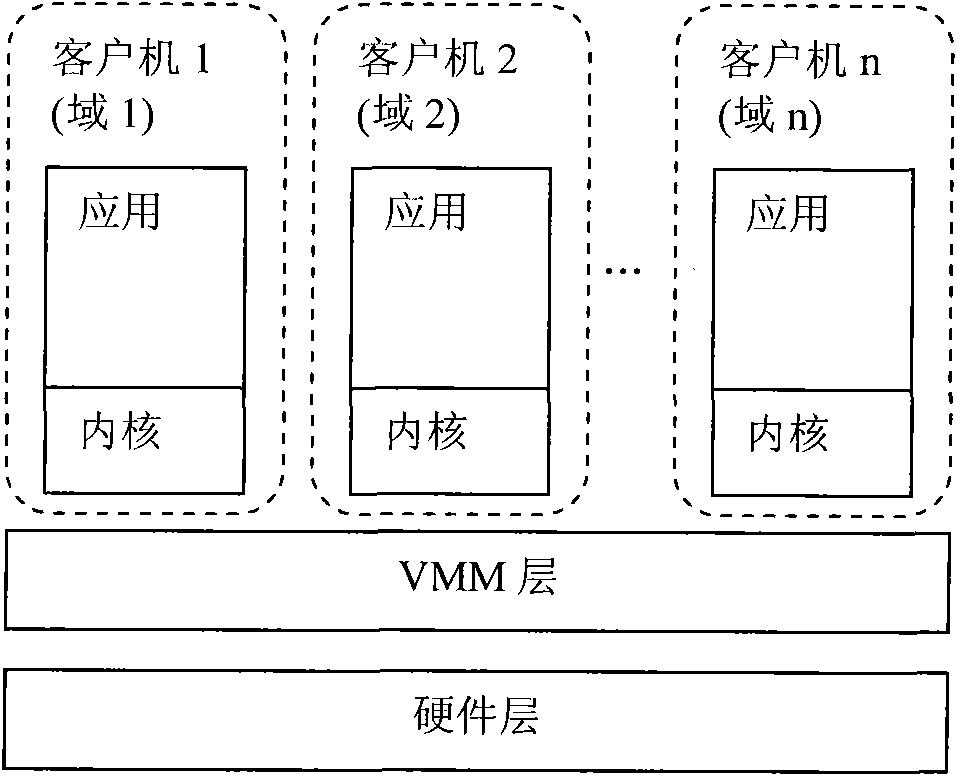
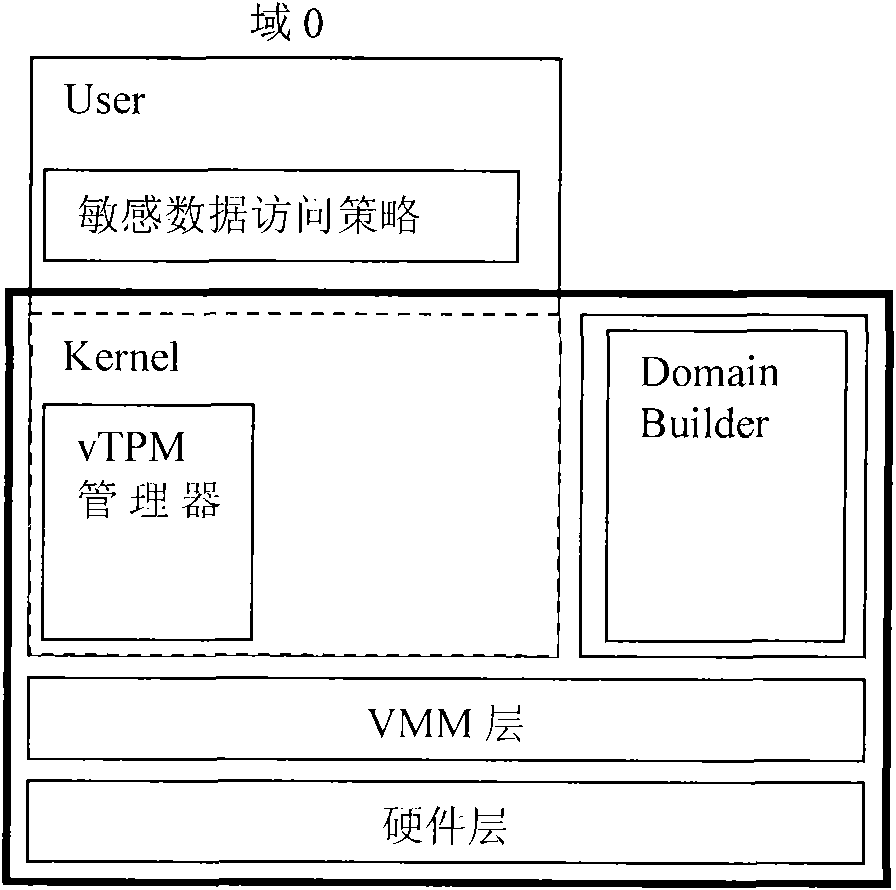
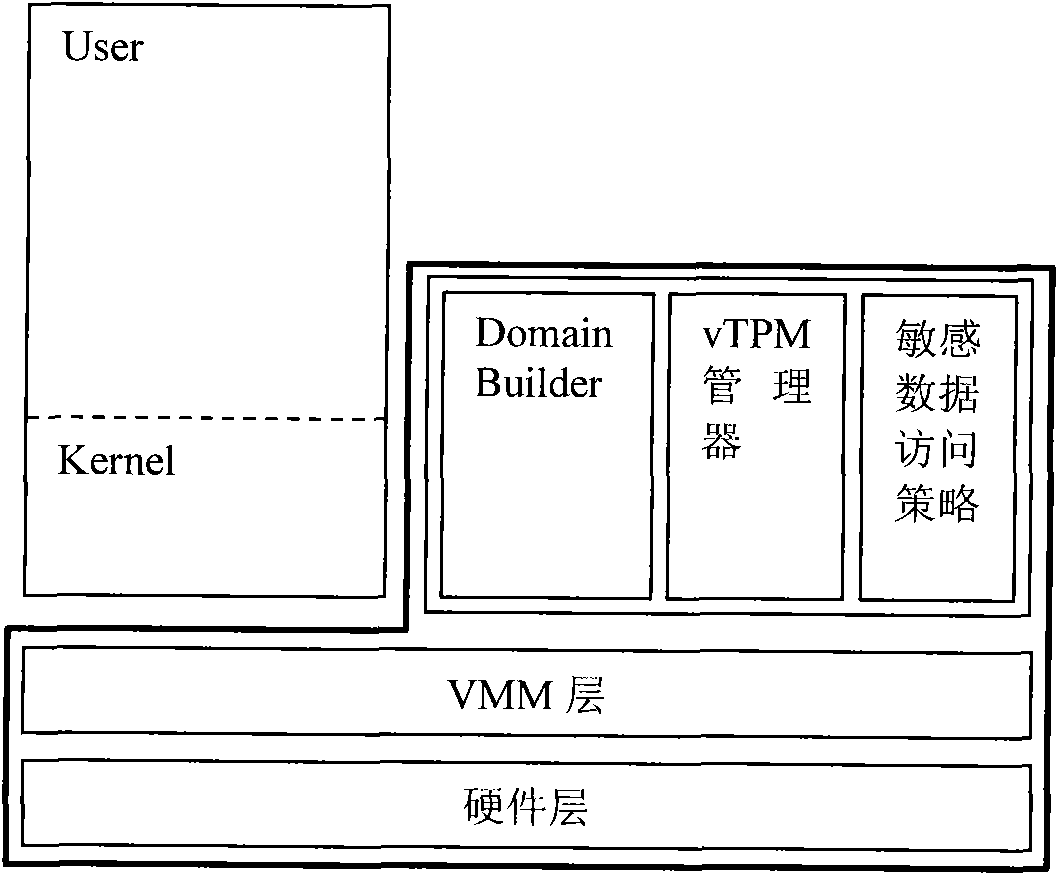
The invention discloses a trustworthy computing base anti-leakage cutting method used for a virtual machine system; the virtual machine system comprises a hardware layer, a virtual machine monitor layer, a virtual trusted platform module manager, a domain creating module, a kernel and a sensitive data access policy; the virtual trusted platform module manager, the domain creating module, the kernel and the sensitive data access policy are positioned at a privilege domain; the method is characterized in that: a special user domain which is isolated with the privilege domain is built, the virtual trusted platform module manager, the domain creating module and the sensitive data access policy are moved to the special user domain, and the kernel is kept in the privilege domain; communication is built between the privilege domain and the special user domain, and the trustworthy computing base is formed by the hardware layer, the virtual machine monitor layer, the virtual trusted platform module manager, the domain creating module and the sensitive data access policy; the invention provides a trustworthy computing base cutting proposal, the advantages of the traditional trustworthy computing base proposal is not only kept, but also the safety and starting speed of the virtual machine system are enhanced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
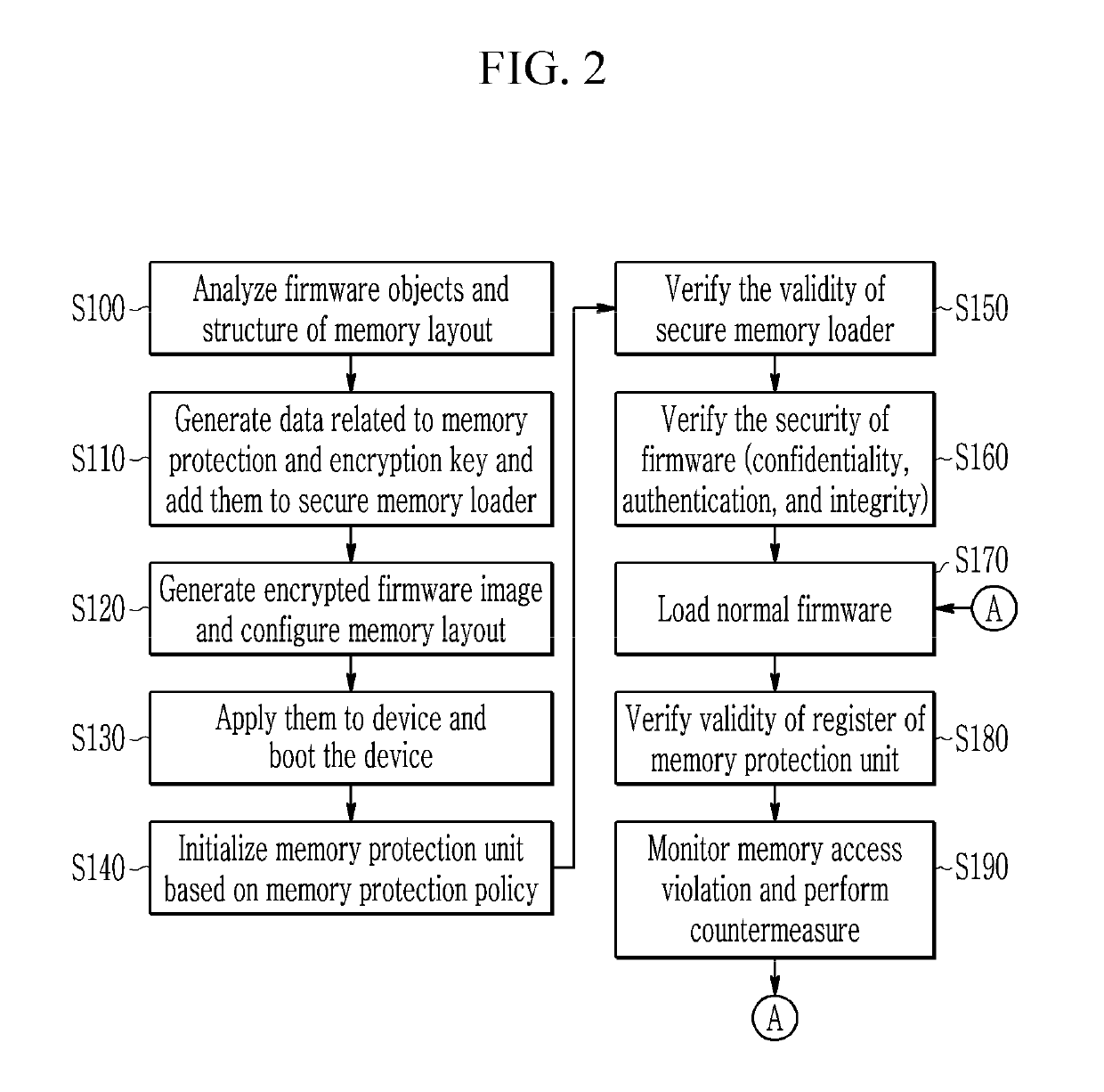
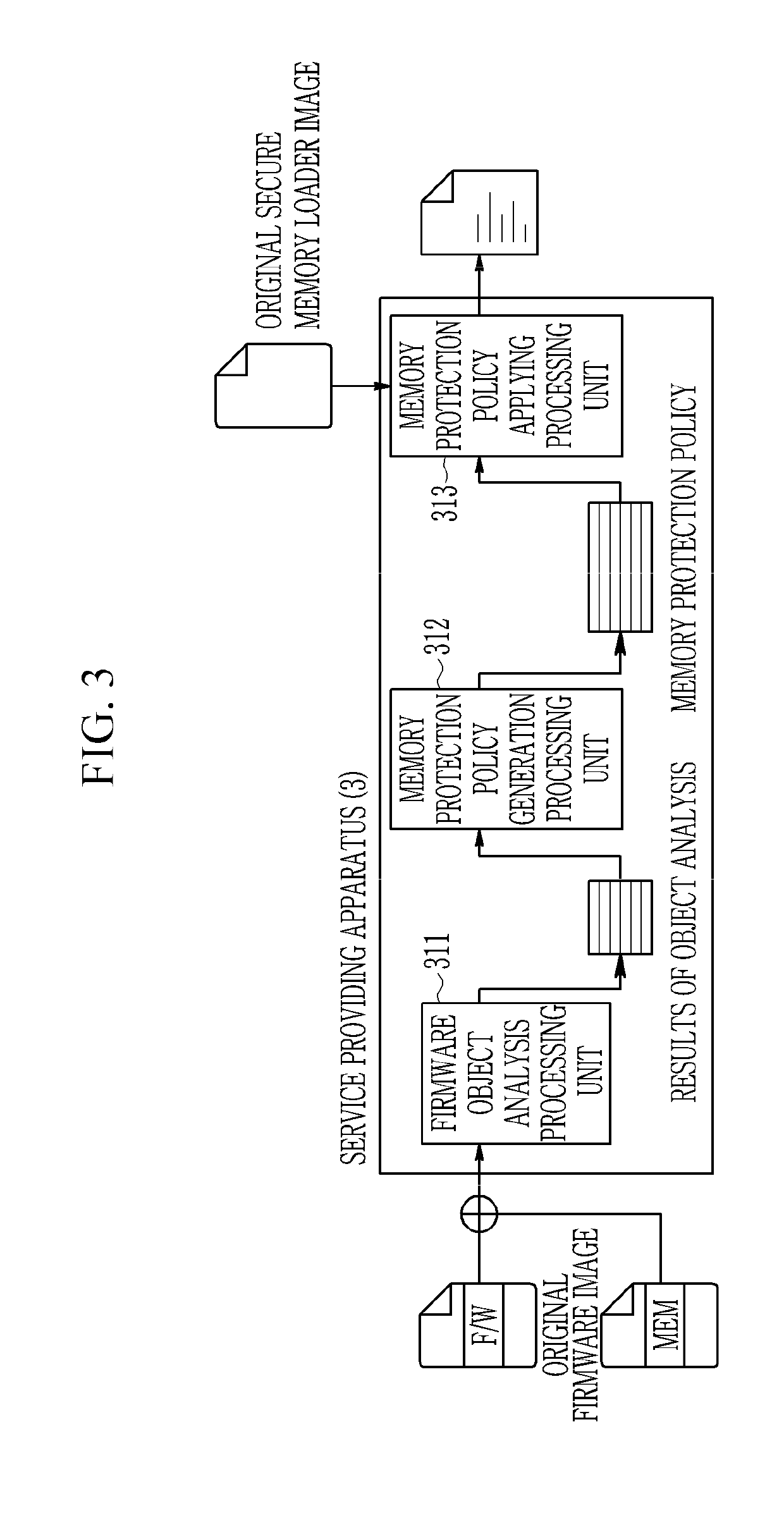
Method and apparatus for device security verification utilizing a virtual trusted computing base
ActiveUS20190163910A1Efficient executionMemory architecture accessing/allocationKey distribution for secure communicationConfidentialityTrusted Computing
A method and an apparatus for device security verification utilizing a virtual trusted computing base are provided. The validity of a key for decryption is verified by a secure memory loader running on a processor of a device after booting of the device which is a computing device, and if the key is valid, encrypted firmware stored in a memory of the device is decrypted using the key to verify the confidentiality of the firmware. Then, the security memory loader verifies the authentication and integrity of the firmware by comparing a signature value generated for the decrypted firmware with an existing signature value.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method for implementing credible recovery system in operating system
InactiveCN101251814AImprove throughputMeet needsProgram initiation/switchingPlatform integrity maintainanceLogfileTrusted computing base
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
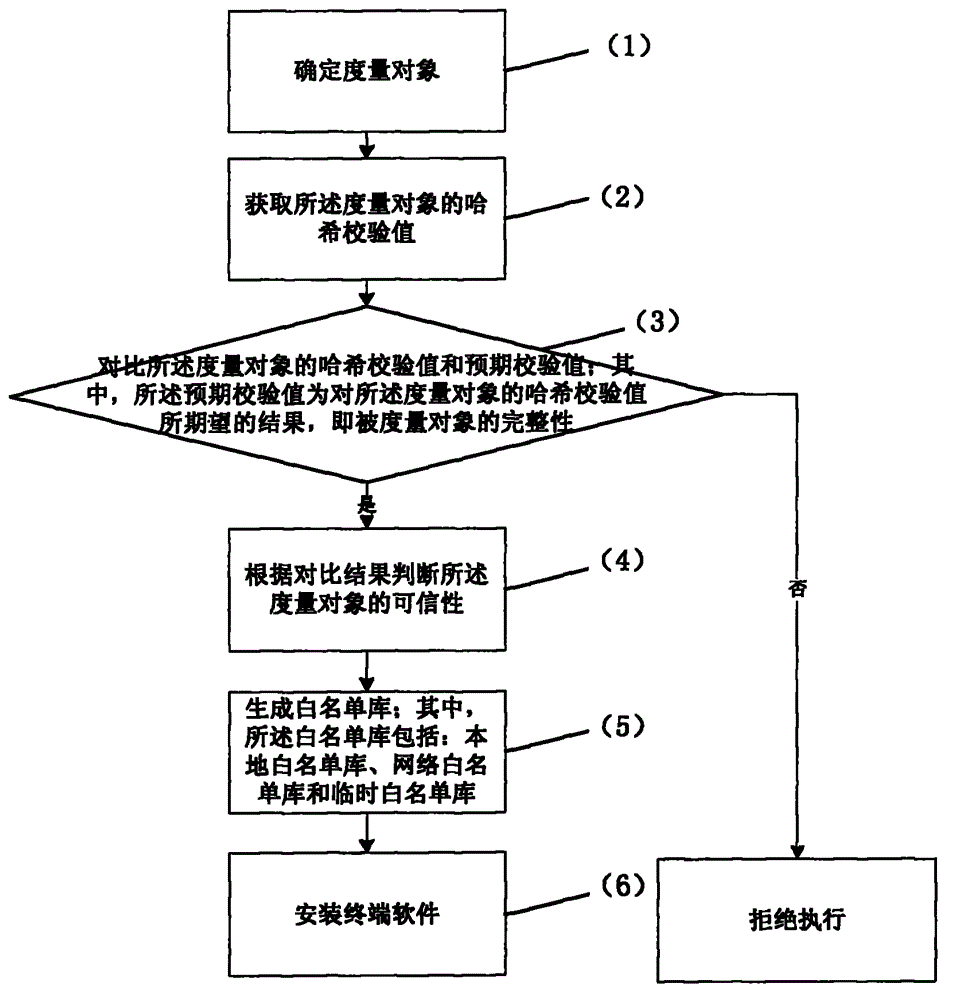
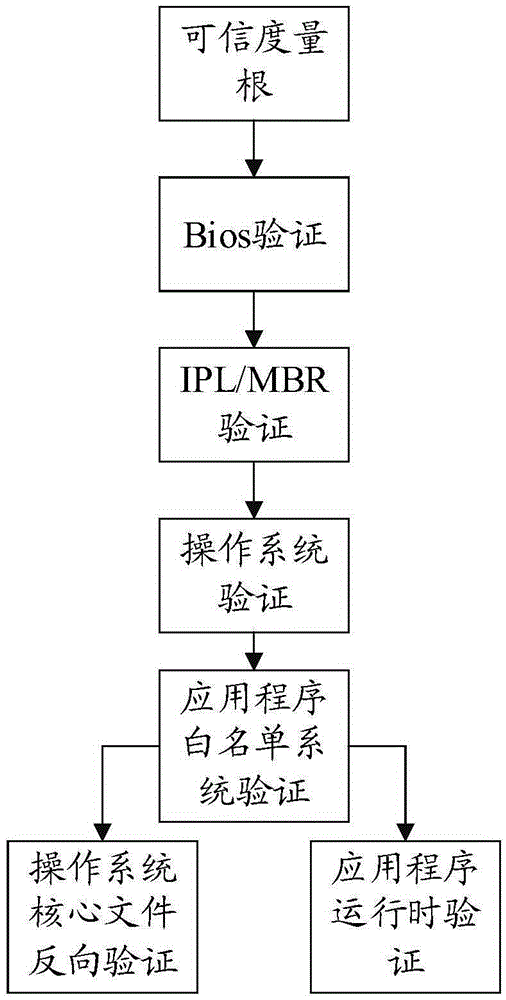
Trusted computing based white list static measurement method
InactiveCN104933354AGuaranteed Execution AuthoritySource of protectionPlatform integrity maintainanceChecksumTrusted Computing
The present invention relates to a trusted computing based white list static measurement method. The method comprises: determining a measurement object; acquiring a Hash checksum of the measurement object; comparing the Hash checksum of the measurement object with a predetermined checksum; judging trustability of the measurement object according to the comparison result; generating a while list library, wherein the while list library comprises a local white list library, a network white list library and a temporary white list library; and installing a terminal software. In this way, integrity of execution rights, source and trustability of the software is ensured.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Mobile wireless device with protected file system
InactiveUS20050204127A1Ensure integrityDigital data processing detailsDigital data protectionConfidentialityTrusted computing base
A mobile wireless device programmed with a file system which is partitioned into multiple root directories. The partitioning of the file system ‘cages’ processes as it prevents them from seeing any files they should not have access to. A Trusted Computing Base verifies whether or not a process has the required privileges or capabilities to access root sub-trees. The particular directory a file is placed into automatically determines its accessibility to different processes—i.e. a process can only access files in certain root directories. This is a light weight approach since there is no need for a process to interrogate an access control list associated with a file to determine its access rights over the file—the location of the file taken in conjunction with the access capabilities of a process intrinsically define the accessibility of the file to the process. Another aspect of this invention is that each process can have its own private area of the file system guaranteeing confidentiality and integrity to its data.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and system for access authentication
ActiveUS7673332B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrusted ComputingTrusted computing base
A method and a system for access authentication. A shared services resource includes a second factor authentication module. At least one network resource each include a first factor authentication module. A trusted computing base communicates with the shared services and the at least one network resource through a pipe. An assertion may be obtained on a trusted computing base for accessing at least one network resource. At least one of the at least one network resource may be accessed with the trusted computing base when the assertion has been obtained by the trusted computing base and is valid.
Owner:PAYPAL INC
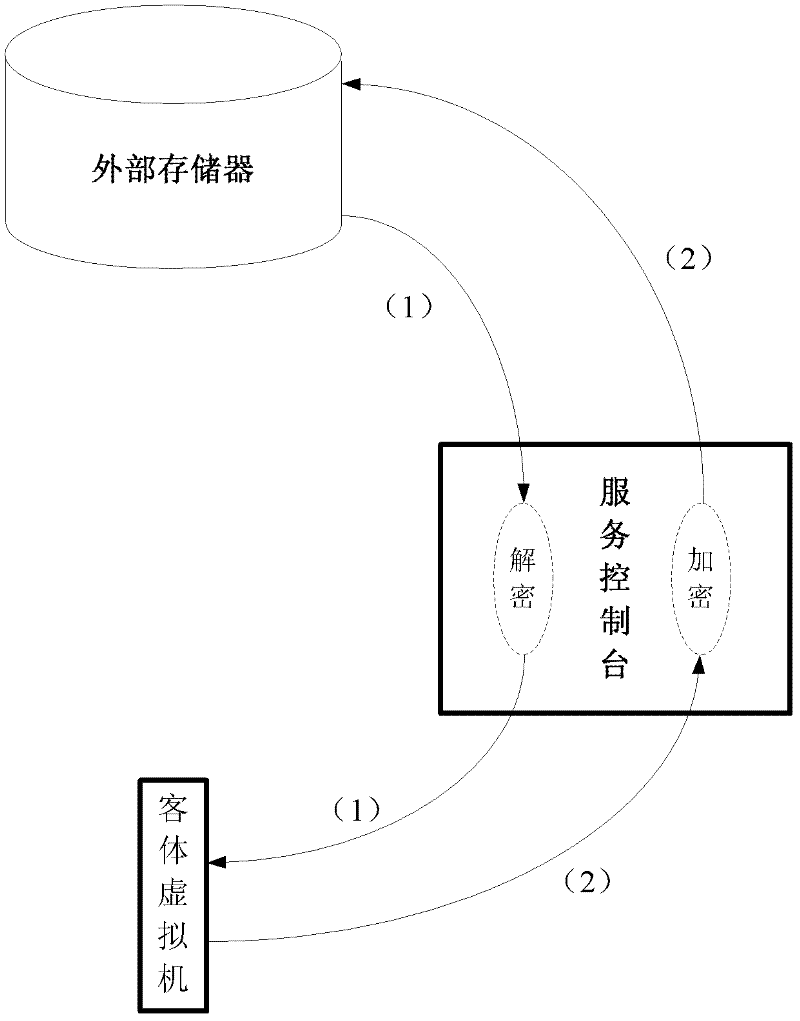
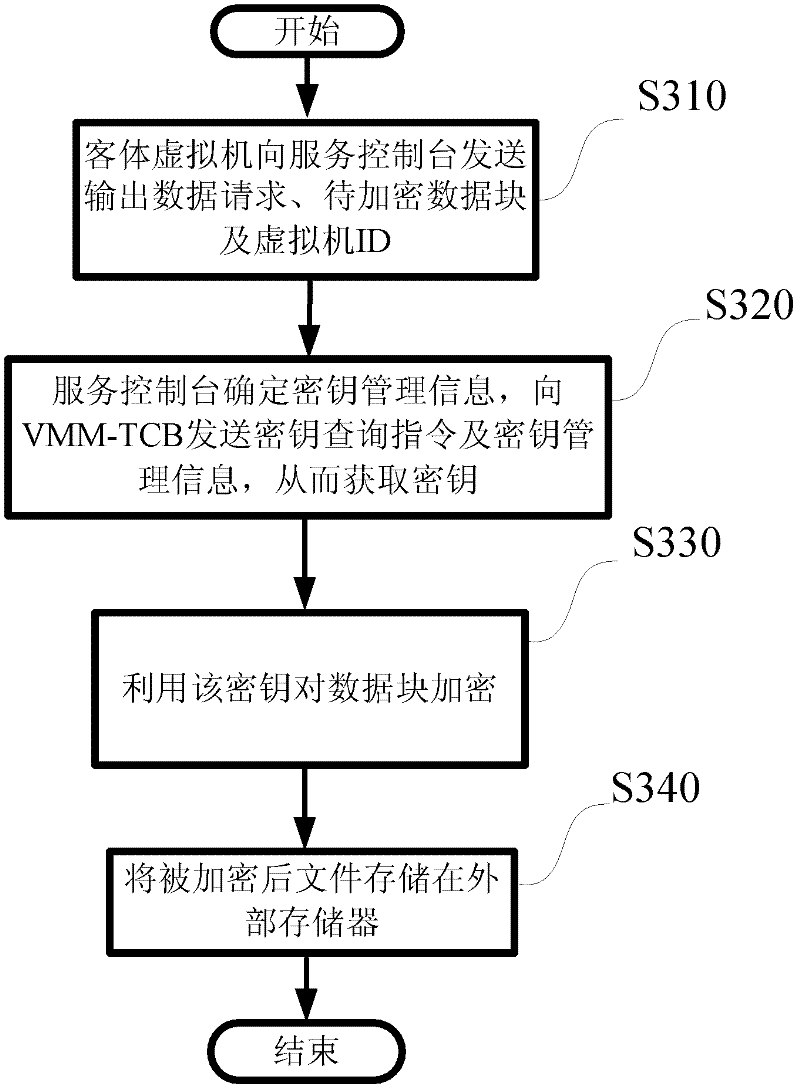
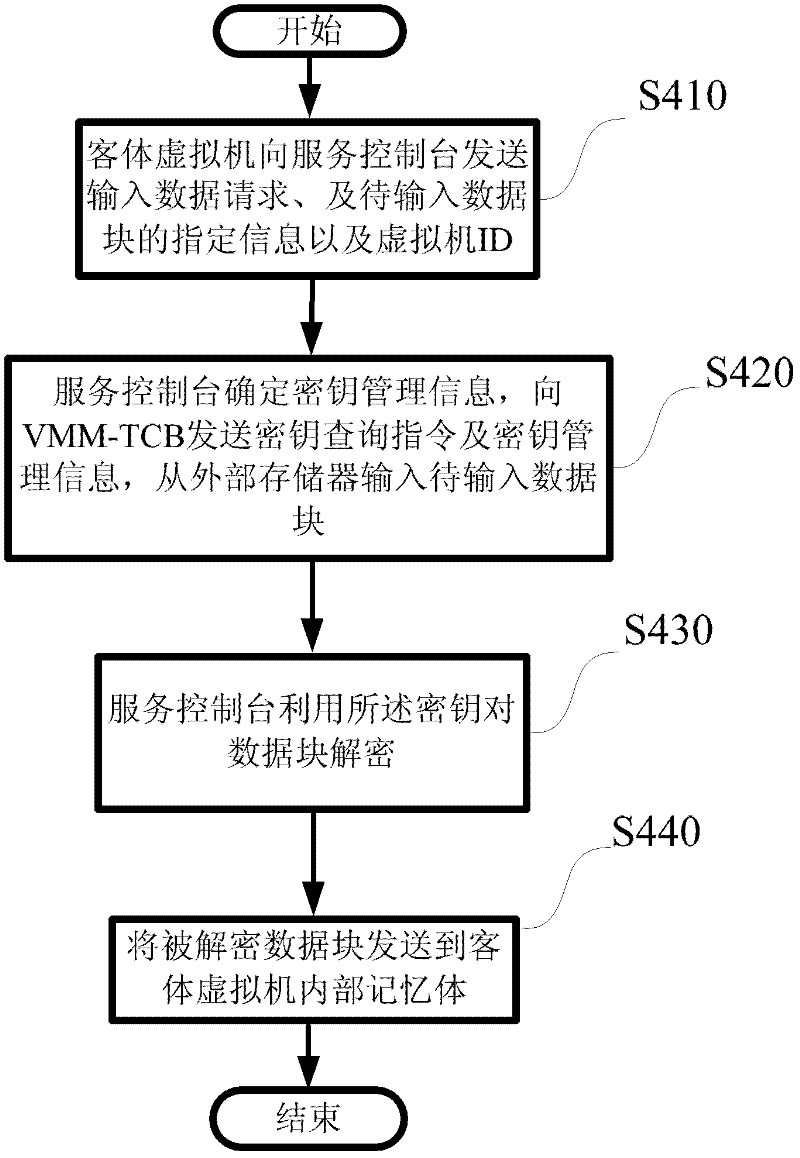
Dynamic cryptography protection for virtual machines and key management method thereof
InactiveCN102609643AImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data authenticationInternal memoryService control
Provided are dynamic cryptography protection for virtual machines and a management method for keys required by dynamic cryptography protection. The management method for the keys required by dynamic cryptography protection includes that each of the virtual machines is divided into multiple data blocks, dynamic encryption and decryption process are performed when the data blocks are in input and output states, keys required for the encryption and decryption are protected by the virtual machine monitor secondary trusted computing base or the hardware-based trusted computing base and are protected in a higher safety level, a service console inquires and acquires the keys from the virtual machine monitor secondary trusted computing base and encrypts the data blocks of guest virtual machines by the aid of the keys, and the encrypted data blocks are stored in image data packages of the guest virtual machines, thus the stolen encrypted data packages are hard to decrypt even when the image data packages of the guest virtual machines are stolen. Besides, when data blocks are input to the guest virtual machines from external storages, the service console utilizes the keys to decrypt the data blocks and then sends the decrypted data blocks to internal memories of the guest virtual machines to be further processed.
Owner:道里云信息技术(北京)有限公司
Method and apparatus for secure online credit card transactions and banking
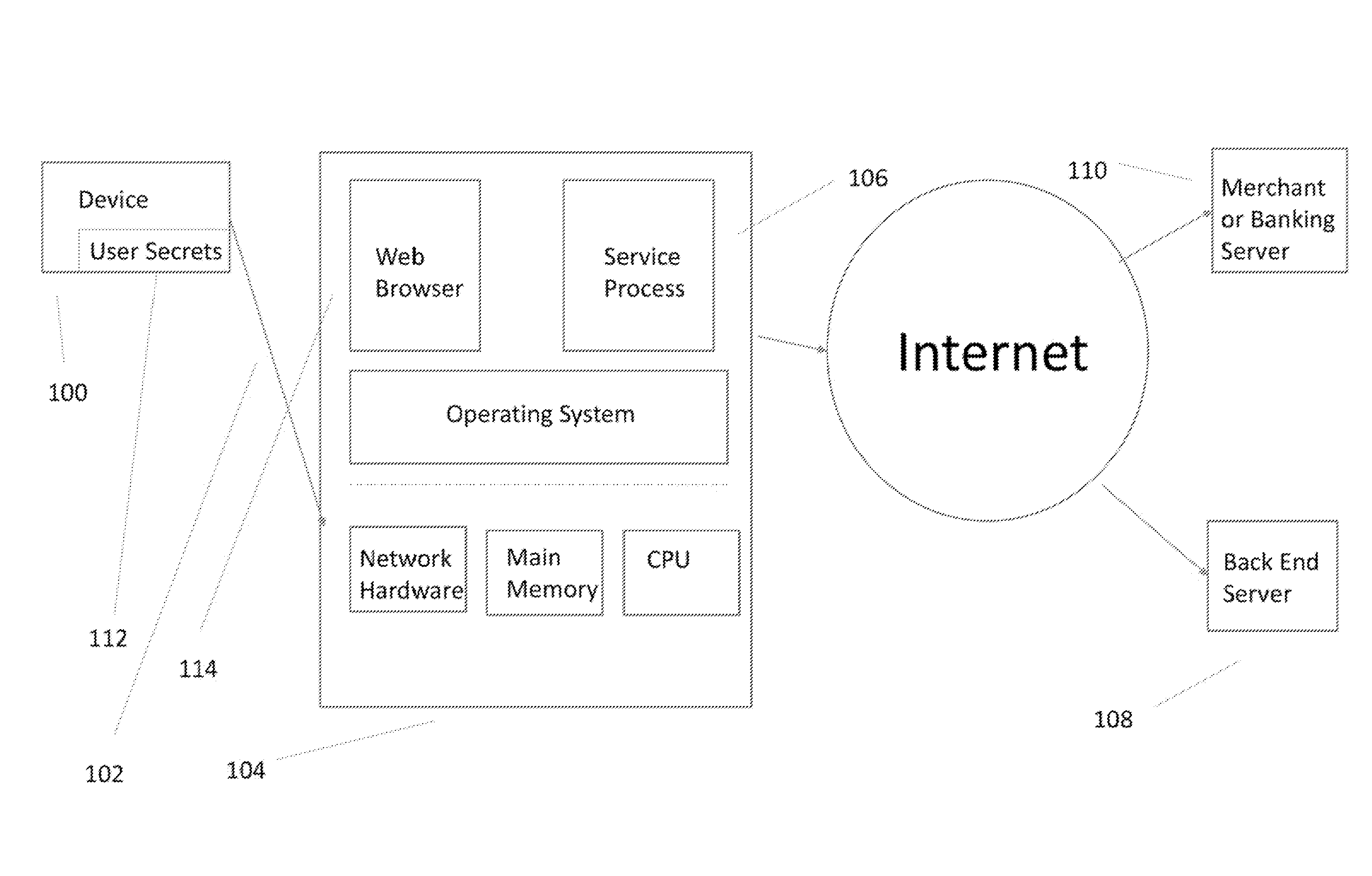
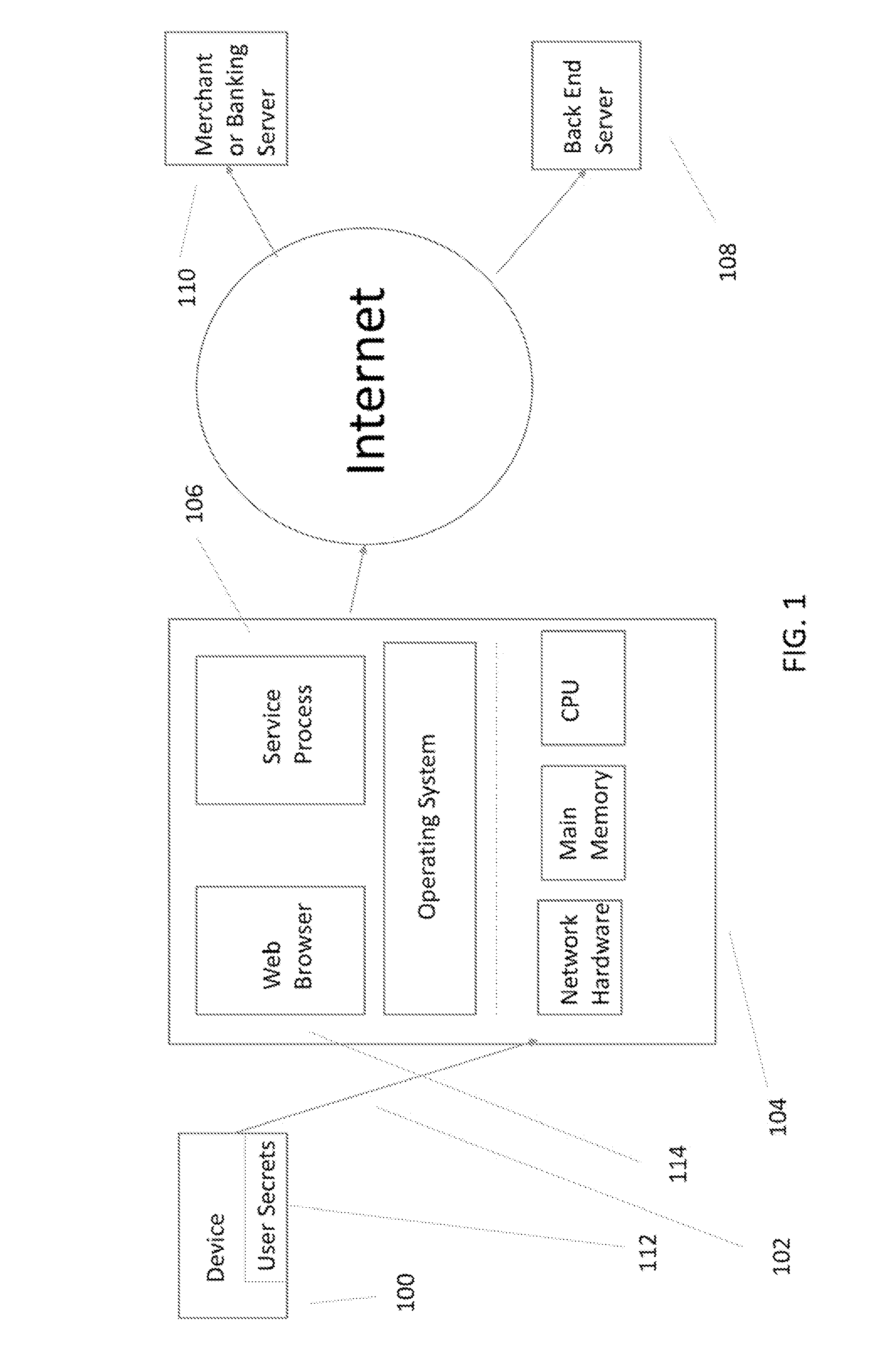
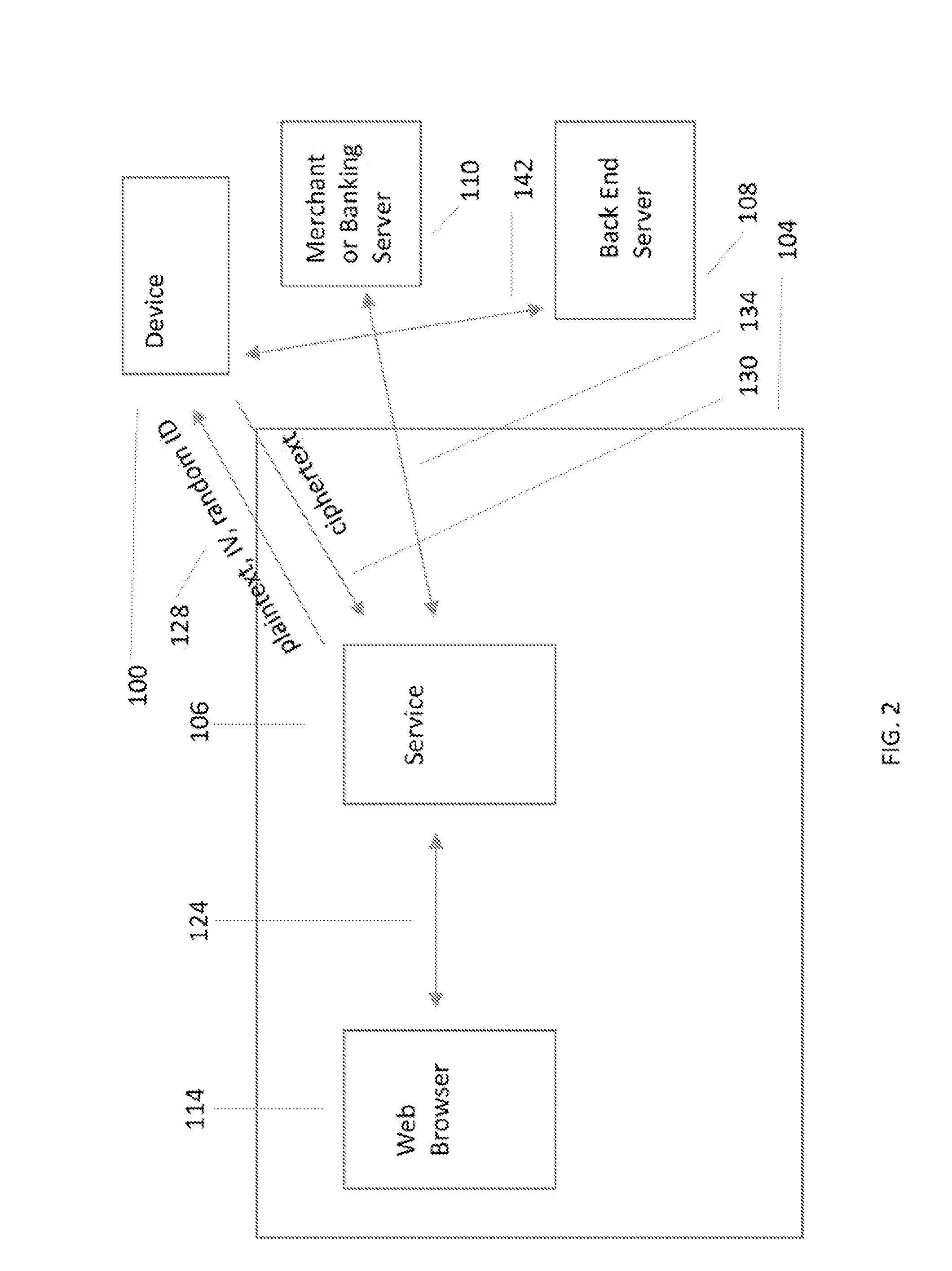
A hardware based system and method that detects fraudulent financial activity originating from malicious programs on a user's computer and ensures that user sensitive information is not accessible to programs on the user's computer. The system includes an untrusted service process on the user's computer, a back end server / cloud based infrastructure, and a user device that records the user's computer at the time the transactions are executed. The device has a minimal TCB (Trusted Computing Base) and is trusted to carry out its functions. The device stores sensitive user information and enters this information into secure channels ensuring that the user's computer does not have access to this information. Periodic statement review is accomplished by comparing the device's record of transactions against the record in the payment system and discrepancies result in notifications to the user. The payment system entities may be unaware of the system, or they may exchange information with the system in order to obtain security benefits including fraud detection and tokenization services.
Owner:TROSTLE JONATHAN
Security risk assessment method for block chain
InactiveCN110309657APlatform integrity maintainanceProtocol authorisationTrusted ComputingSensitivity analyses
The invention provides a security risk assessment method for a block chain. The security risk of the block chain is quantified at the two aspects of technical architecture and activeness. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, establishing a block chain trusted computing base (BTCB) model according to a block chain technical system architecture; designing a security sensitivity analysis method combining AHP (Analytic Hierarchy Process) and pairing comparison, distributing a security sensitivity weight for each security risk influence factor, and finally constructing a security risk scoring function of the block chain. At an experiment part, the method is adopted to score 30 important public chain block chain projects at present, the comparison and analysis are carried out onthe scores, the scores are compared and analyzed with a Cydive public chain technology evaluation index and a Weis encrypted currency rating, and an experiment result shows that the method has certainfeasibility.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
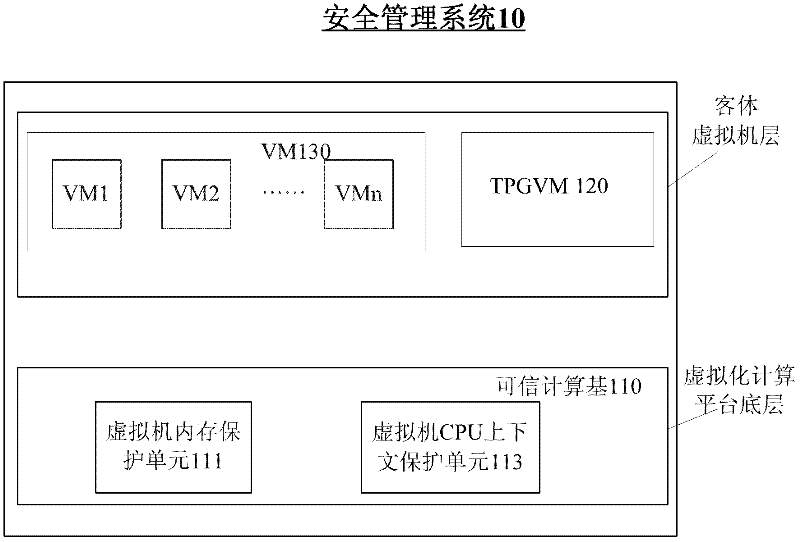
Method and system for full life cycle security management of virtual machine
InactiveCN102332069APlatform integrity maintainanceSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationFull life cycleData center
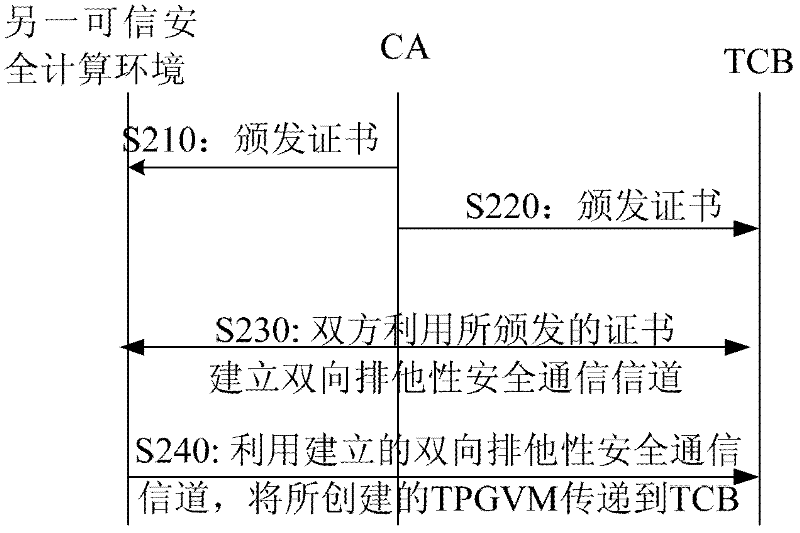
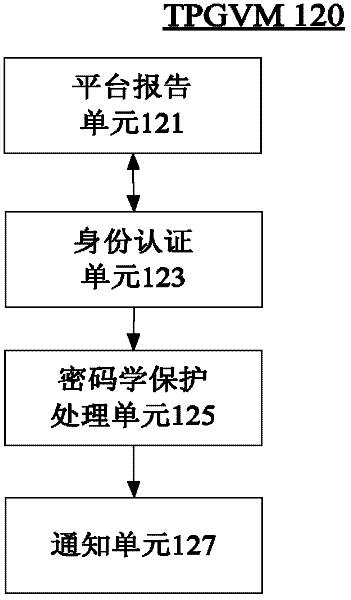
The invention provides a system and a method for providing full life cycle security management of a virtual machine on a virtualized computing platform. The system comprises a trusted computing base, a trusted computing base proxy object virtual machine and one or more object virtual machines, wherein the trusted computing base is operated on the bottom layer of the virtualized computing platform, and the trusted computing base proxy object virtual machine and one or more object virtual machines are operated on an object virtual machine layer of the virtualized computing platform. The trusted computing base proxy object virtual machine is established in another independent trusted secure computing environment of the virtualized computing platform, and is transmitted to the trusted computing base through an exclusive private secure communication channel established on the basis of a public key cryptography mechanism and a trusted authentication mechanism which is provided by a third party; moreover, the trusted computing base proxy object virtual machine is operated as a special object virtual machine which is deployed after the virtualized computing platform is started so as to act as an agent of the trusted computing base to provide service for client users. By using the system, the attacks initiated even by an internal system administrator from a data center can be resisted.
Owner:道里云信息技术(北京)有限公司
Password protection system based on hardware virtualization
InactiveCN102521531AImprove securityIncrease flexibilityDigital data authenticationOperational systemTrusted Computing
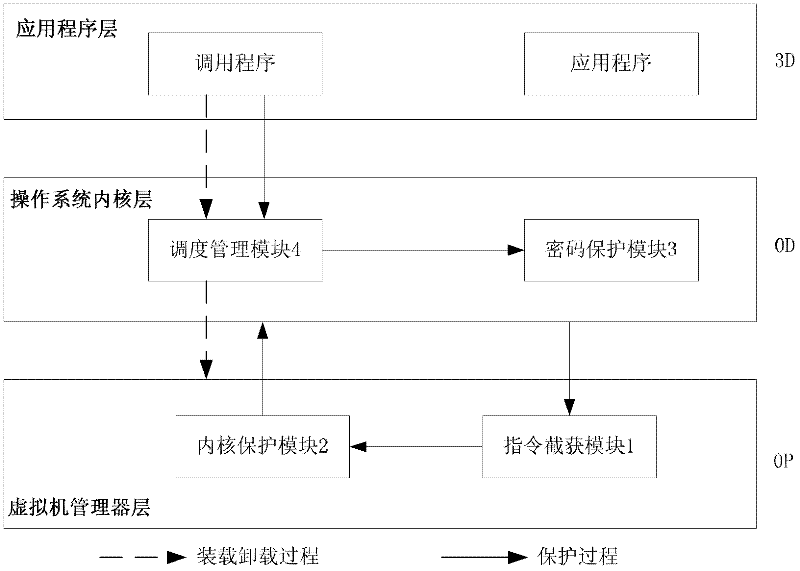
The invention provides a password protection system based on hardware virtualization, which aims at the current situation that a traditional password protection system cannot defend an inner nuclear layer rootkit. The password protection system based on hardware virtualization deploys a password protection module and a scheduling management module in an inner nuclear layer of an operation system, provides a safe input environment and an interactive interface, and simultaneously deploys an instruction intercepting module and an inner core protection module in a manager layer of a virtual machine. The instruction intercepting module is used for intercepting privileged instructions, and transmitting the current privileged instruction information to the inner core protection module so as to lead an execution flow path to enter a manger of the virtual machine from the inner nuclear layer of the operation system. The inner core protection module prevents the rootkit from randomly modifying nuclear data and service in the operation system, and guarantees password protection in the inner nuclear layer of the operation system. The password protection system based on hardware virtualization moves a trusted computing base (TCB) from the inner nuclear layer of the operation system to the manager layer of the virtual machine, thereby achieving lower level and higher safety.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
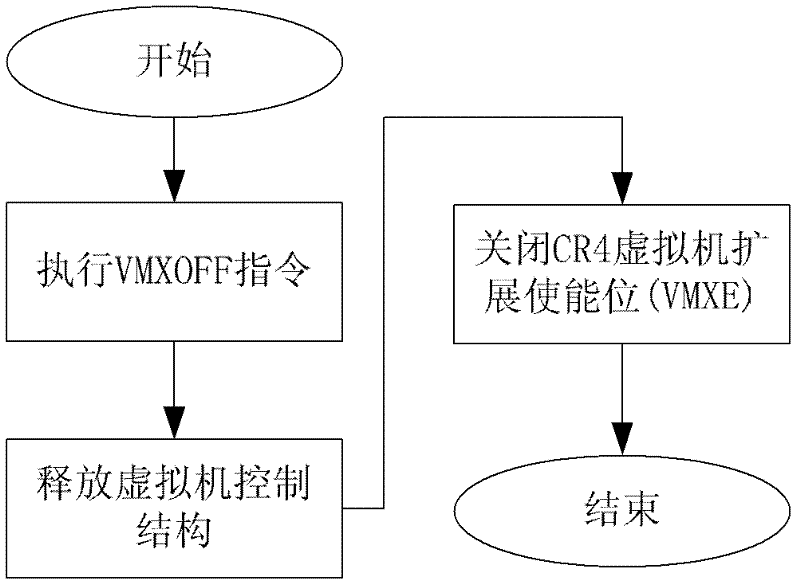
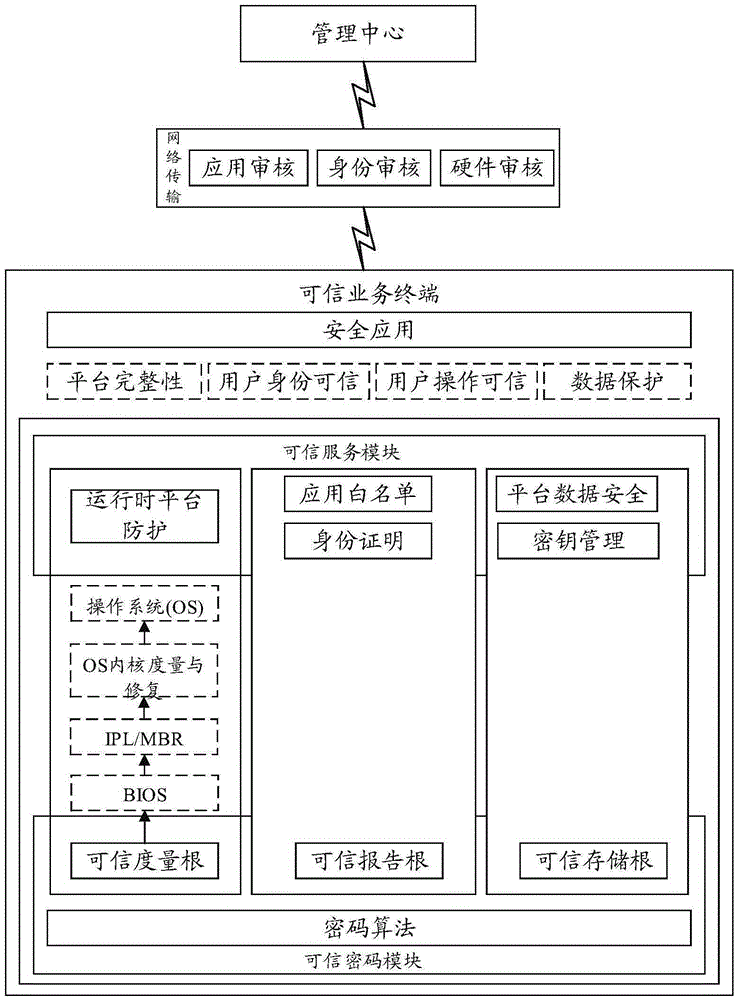
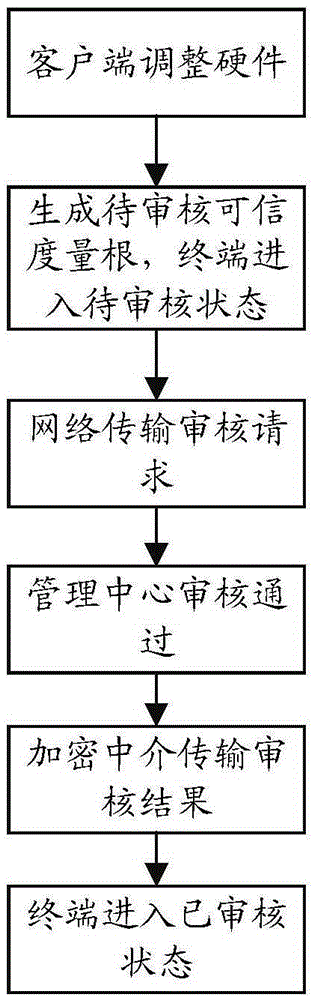
Trusted computing-based dynamic management service system and method
InactiveCN105429808AIntegrity guaranteedAvoid data breachesInternal/peripheral component protectionProgram loading/initiatingOperational systemIdentity recognition
The invention relates to a trusted computing-based dynamic management service system and method. The system comprises a trusted service terminal and a management center; the trusted service terminal comprises a trusted cryptography module for providing a trust measurement root, a trust storage root and a trust report root and realizing a trusted mechanism, and a trusted service module used for providing trusted services; and the management center is used for communicating with the trusted service terminal and verifying the hardware credibility, application credibility and user credibility of the trusted service terminal. With the trusted computing-based dynamic management service system and method adopted, the integrity of hardware and an operating system can be ensured, data leakage and system tampering can be prevented; a trusted identity recognition system is established to identify fake platforms; and a centralized management system is established, so that the configuration performance of clients can be improved.
Owner:THE THIRD RES INST OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Credible computer platform based on domestic autonomous dual-system framework
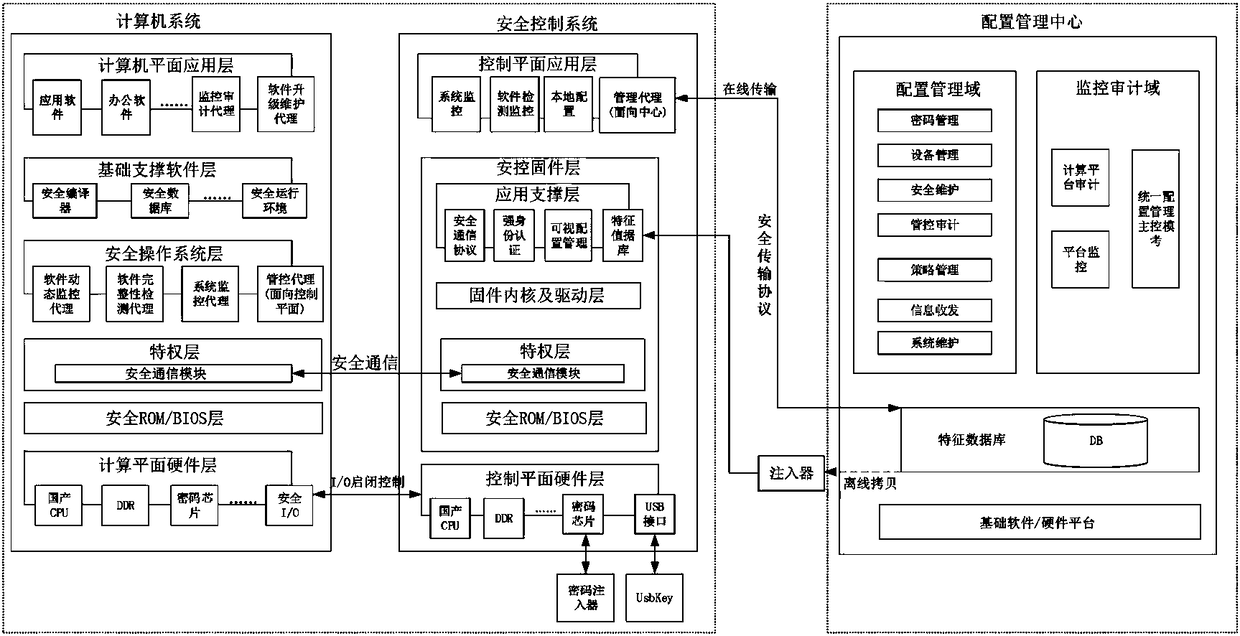
ActiveCN108804927AStrict monitoringImprove securityPlatform integrity maintainanceGeneral purpose computerStructure of Management Information
The invention discloses a credible computer platform based on a domestic autonomous dual-system framework. The platform comprises a configuration management center and a terminal, wherein the terminalcomprises a universal computer system, a miniature operating system responsible for monitoring is built in the terminal to serve as a security control system, the security control system is responsible for monitoring the running condition of the universal computer system, and reporting the running condition to the configuration management center; the configuration management center and the terminal communicate with each other via a bottom-layer customized communication protocol, and two operating systems in the terminal communicate with each other in a hardware sharing manner. The invention is an implementation scheme of a completely domestic autonomous credible computer platform based on a credible computing base theory; main structural designs such as a bottom layer, a BIOS, a core anda driver, operating systems and upper-layer application software are completely controllable; and the credible computer platform is built via layers of constraint and monitoring of the dual-system built in the interior.
Owner:郑州信大壹密科技有限公司
Key storage method, device and server
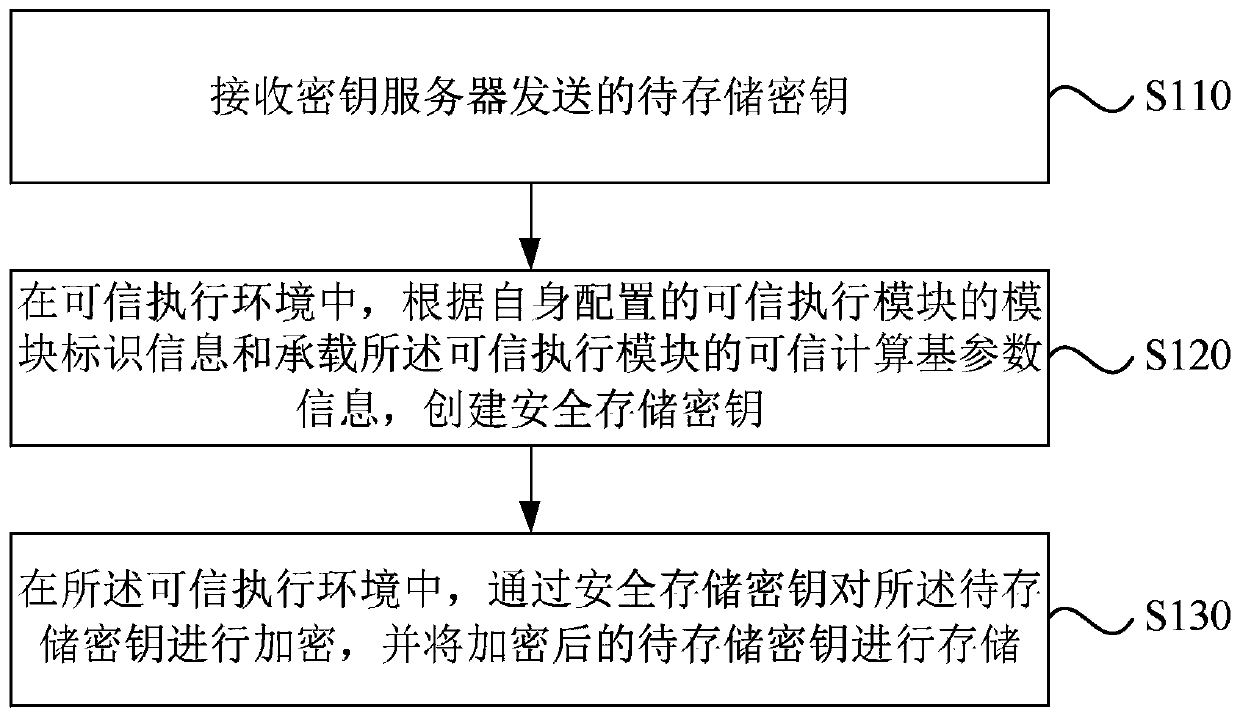
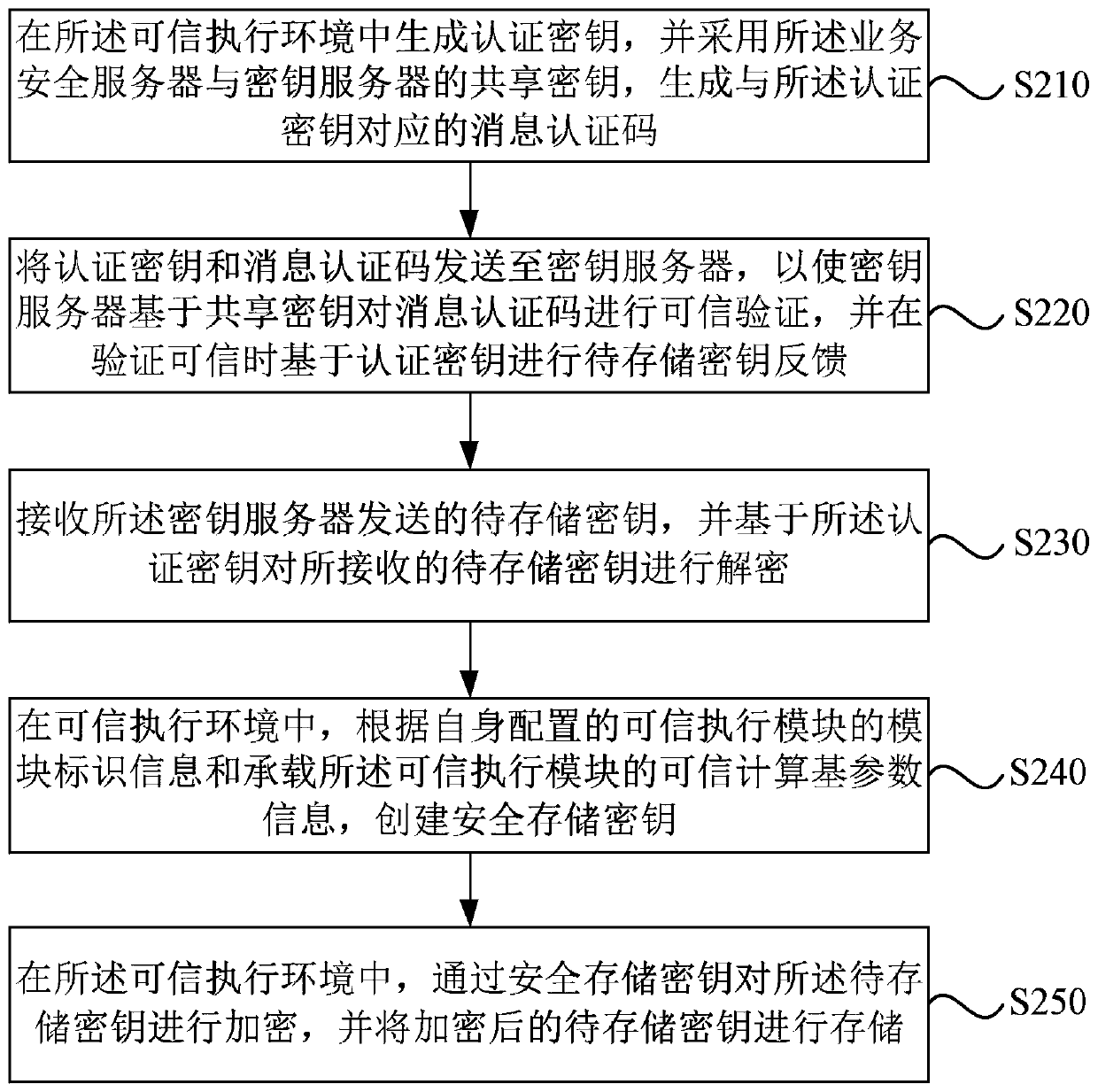
ActiveCN110430051AImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationTrusted ComputingKey storage
The embodiment of the invention discloses a secret key storage method, a secret key storage device and a server. The method comprises the following steps: receiving a to-be-stored key sent by a key server; in the trusted execution environment, creating a secure storage key according to module recognition information of a trusted execution module configured by the trusted execution module and trusted computing base parameter information for bearing the trusted execution module; and in the trusted execution environment, encrypting the to-be-stored key through the secure storage key, and storingthe encrypted to-be-stored key. According to the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, in a trusted execution environment; based on the module recognition information and the trusted computing base parameter information, a secure storage key which is only visible to the system during trusted operation is generated. The security of the security storage secret key is enhanced. The security storage secret key is adopted to store the secret key to be stored in the trusted execution environment. The isolation of codes and data is achieved. The security of secret key storageis enhanced, and then the security of the stored secret key to be stored is improved.
Owner:BEIJING NOVEL SUPER DIGITAL TV TECH
Mobile Wireless Device with Protected File System
InactiveUS20080066187A1Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionTrusted computing baseMobile wireless
A mobile wireless device programmed with a file system which is partitioned into multiple root directories. The partitioning of the file system ‘cages’ processes as it prevents them from seeing any files they should not have access to. A Trusted Computing Base verifies whether or not a process has the required privileges or capabilities to access root sub-trees. The particular directory a file is placed into automatically determines its accessibility to different processes—i.e. a process can only access files in certain root directories.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method for carrying out centralized control on internal memory of safety control module
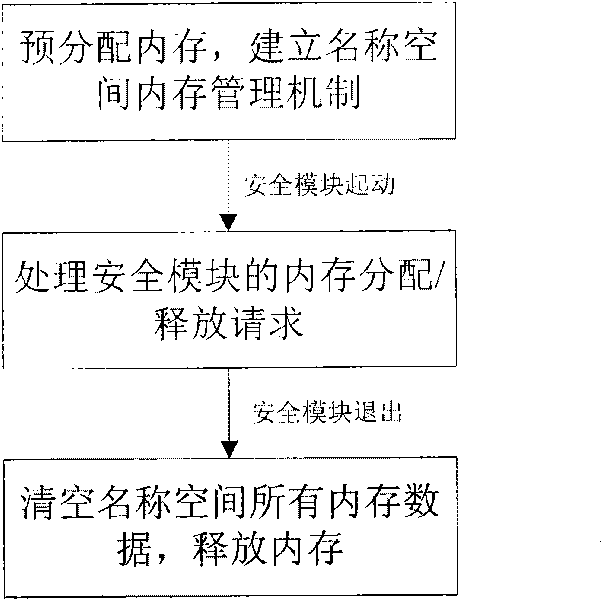
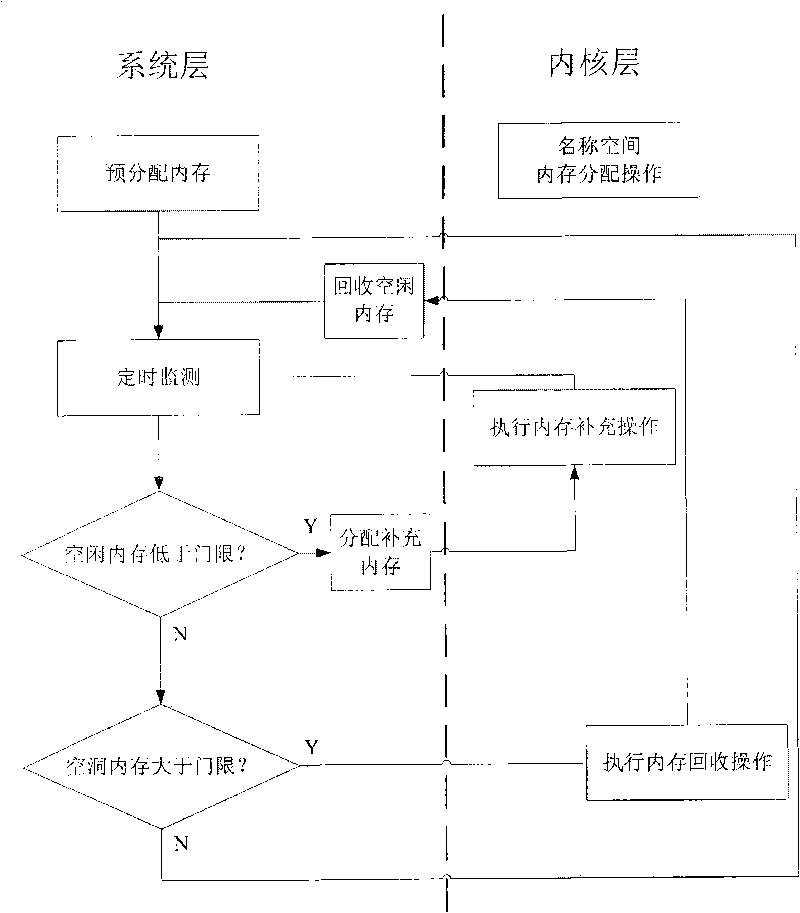
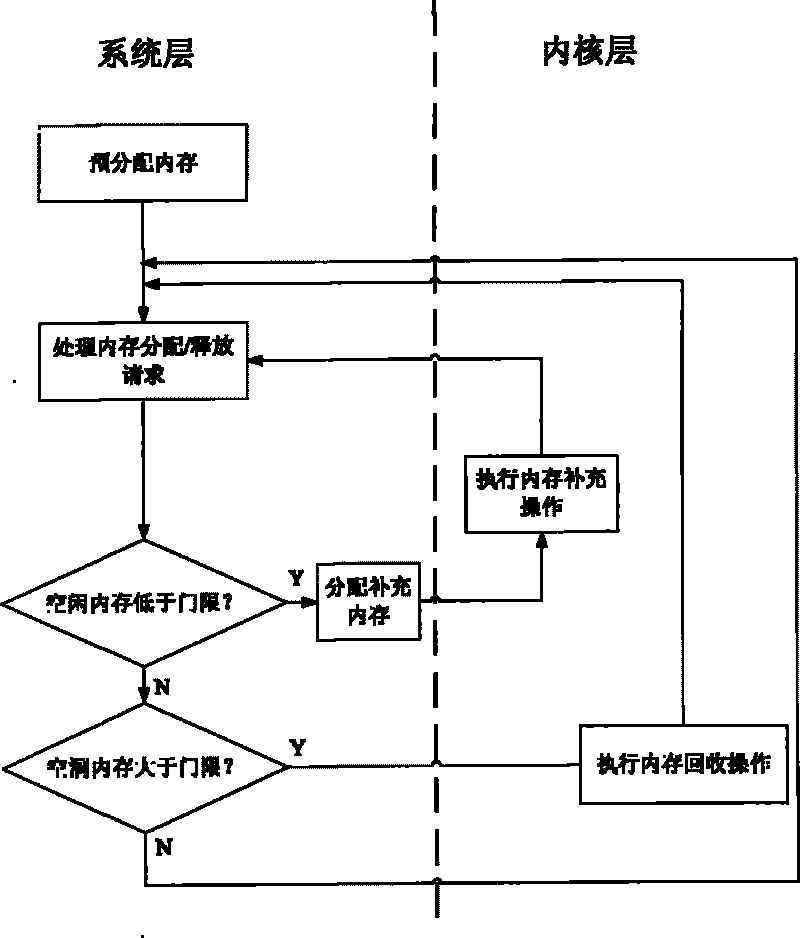
InactiveCN101739346APrevent reuseGuaranteed atomicityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInternal/peripheral component protectionInternal memorySafety control
The invention discloses a method for carrying out centralized control on internal memory of safety control module, which maintains name space memory blocks by using double linked list, distributes the name space by a stack mechanism and sequences the dynamically added hole memory blocks with dynamically added hole values by partitioned sequencing method. The method comprises the following steps: pre-defining parameters; distributing N memory blocks with the size being Bz and establishing a name space management mechanism by using the alloc pages () function; processing the memory distribution request from the security module by the name space; processing the memory release request from the security module by the name space; self-checking by the name space. The method can ensure that the processing of the trusted computing base security name space conforms to the principle of one-way call, the system monitors the situation of the security name space by a monitoring program, when the holes of the memory blocks are comparatively large, the hole memories are recycled; when the number of the idle memory blocks is insufficient, the idle memory blocks are supplemented. And meanwhile the trusted computing base is provided with a stable and efficient security name space memory distribution mechanism.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com