Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
247 results about "Stress gradient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Stress Gradient Hypothesis (SGH) proposes that competition prevails in undisturbed and productive environments, and shifts to facilitation in disturbed or stressful environments. Yet the environmental condition where facilitation or competition prevails is highly debated.
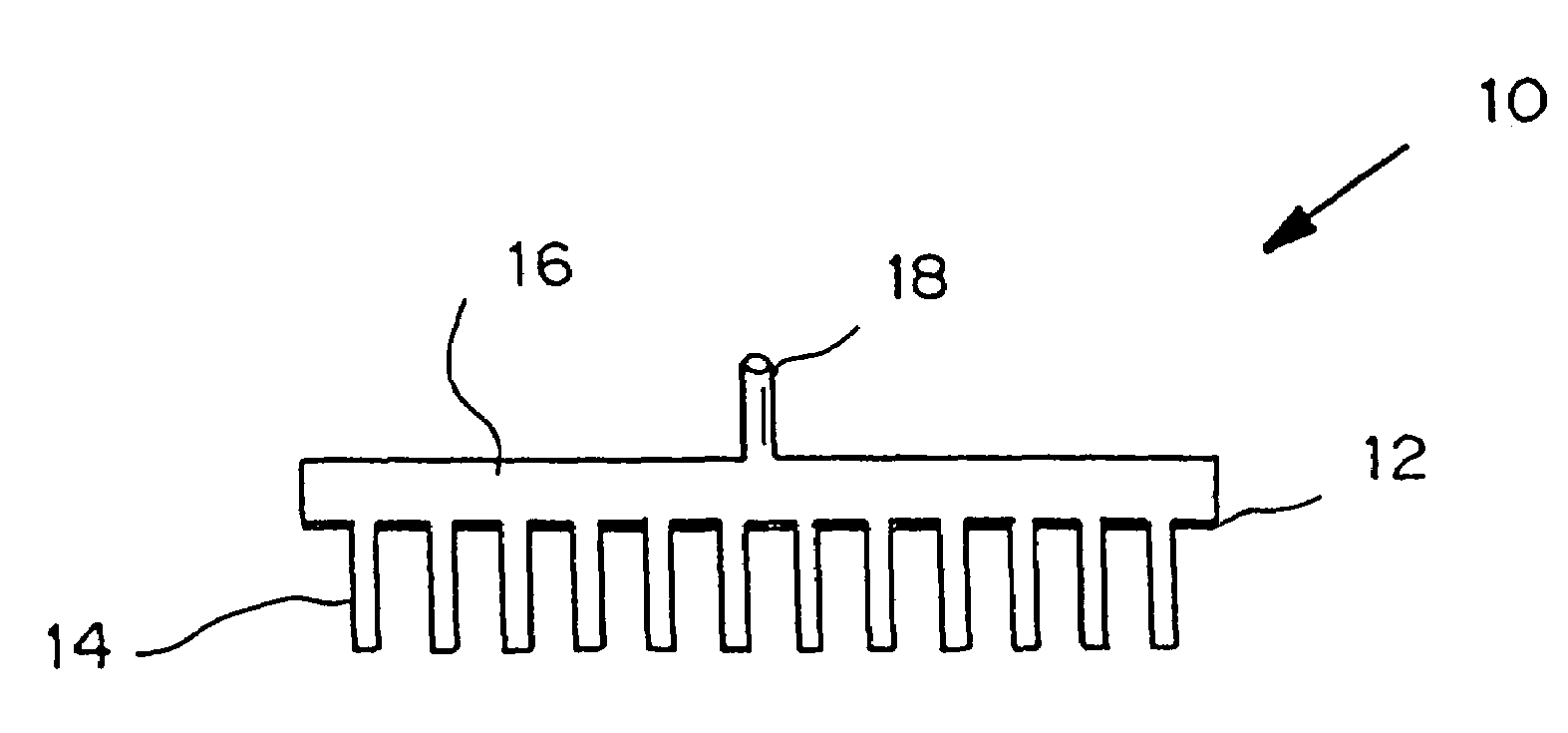
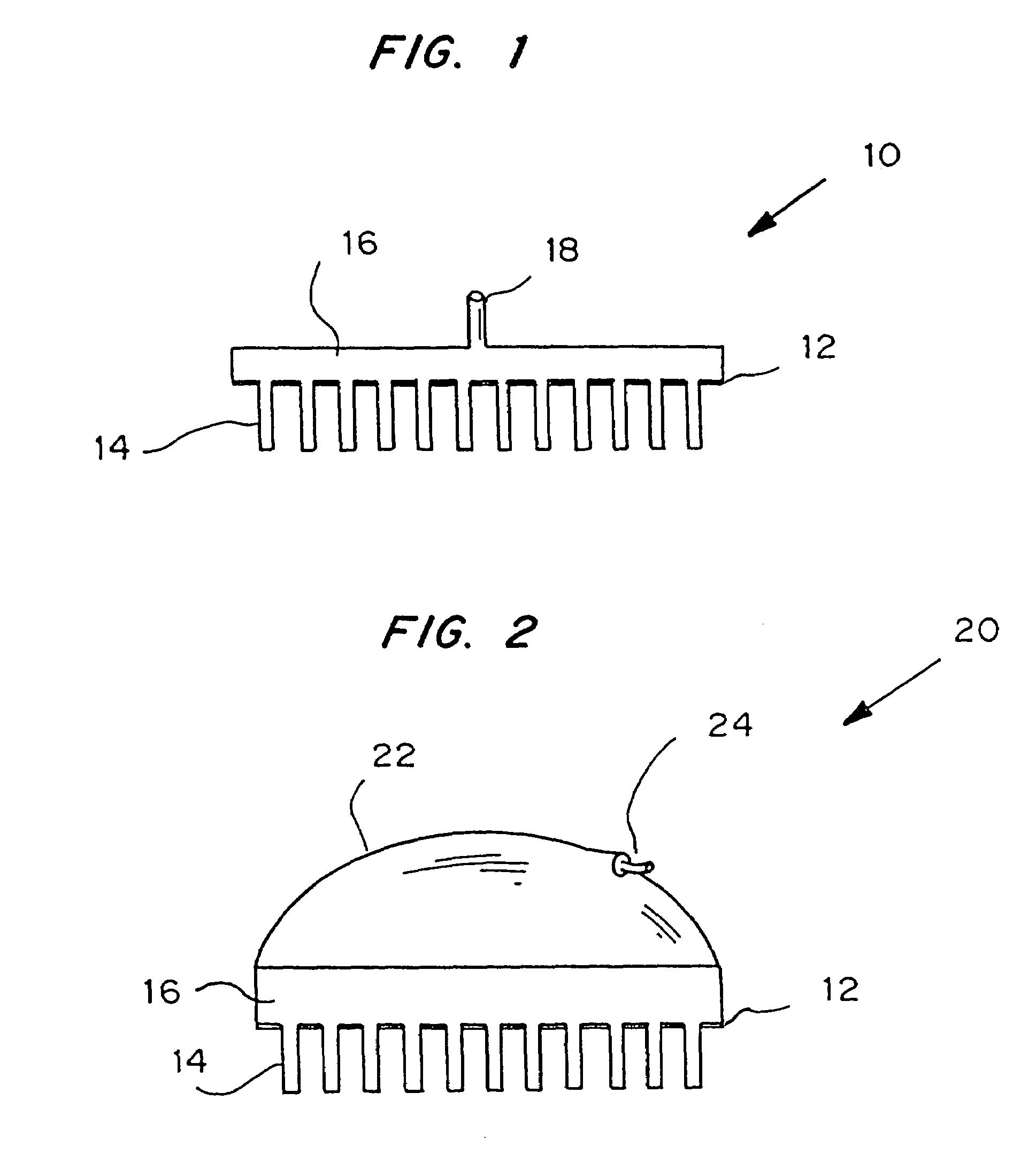
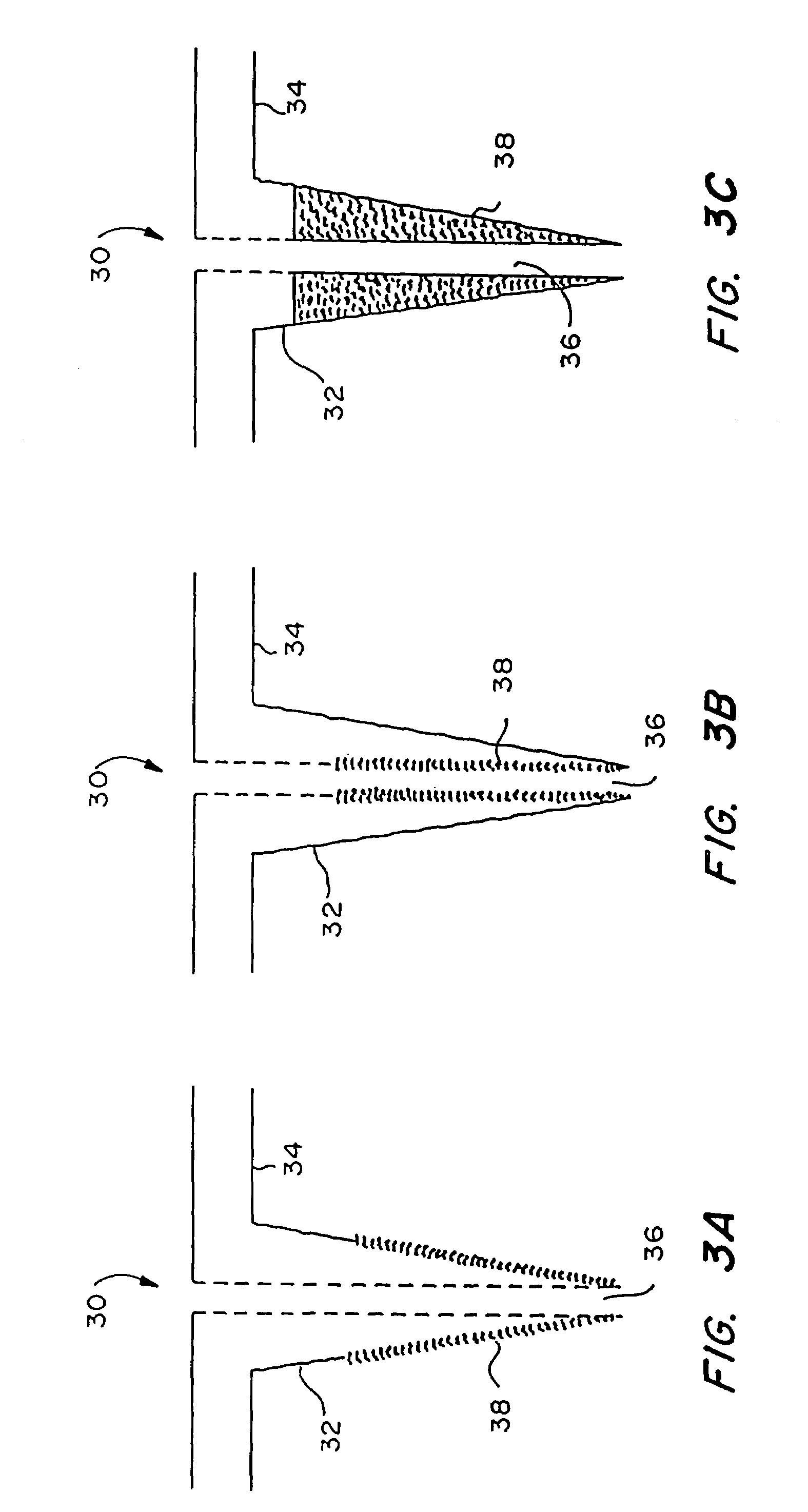
Microneedle device for extraction and sensing of bodily fluids
InactiveUS7344499B1Simple wayMinimal and no damageAdditive manufacturing apparatusMicroneedlesMetaboliteIrritation
Microneedle devices are provided for controlled sampling of biological fluids in a minimally-invasive, painless, and convenient manner. The microneedle devices permit in vivo sensing or withdrawal of biological fluids from the body, particularly from or through the skin or other tissue barriers, with minimal or no damage, pain, or irritation to the tissue. The microneedle device includes one or more microneedles, preferably in a three-dimensional array, a substrate to which the microneedles are connected, and at least one collection chamber and / or sensor in communication with the microneedles. Preferred embodiments further include a means for inducing biological fluid to be drawn through the microneedles and into the collection chamber for analysis. In a preferred embodiment, this induction is accomplished by use of a pressure gradient, which can be created for example by selectively increasing the interior volume of the collection chamber, which includes an elastic or movable portion engaged to a rigid base. Preferred biological fluids for withdrawal and / or sensing include blood, lymph, interstitial fluid, and intracellular fluid. Examples of analytes in the biological fluid to be measured include glucose, cholesterol, bilirubin, creatine, metabolic enzymes, hemoglobin, heparin, clotting factors, uric acid, carcinoembryonic antigen or other tumor antigens, reproductive hormones, oxygen, pH, alcohol, tobacco metabolites, and illegal drugs.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
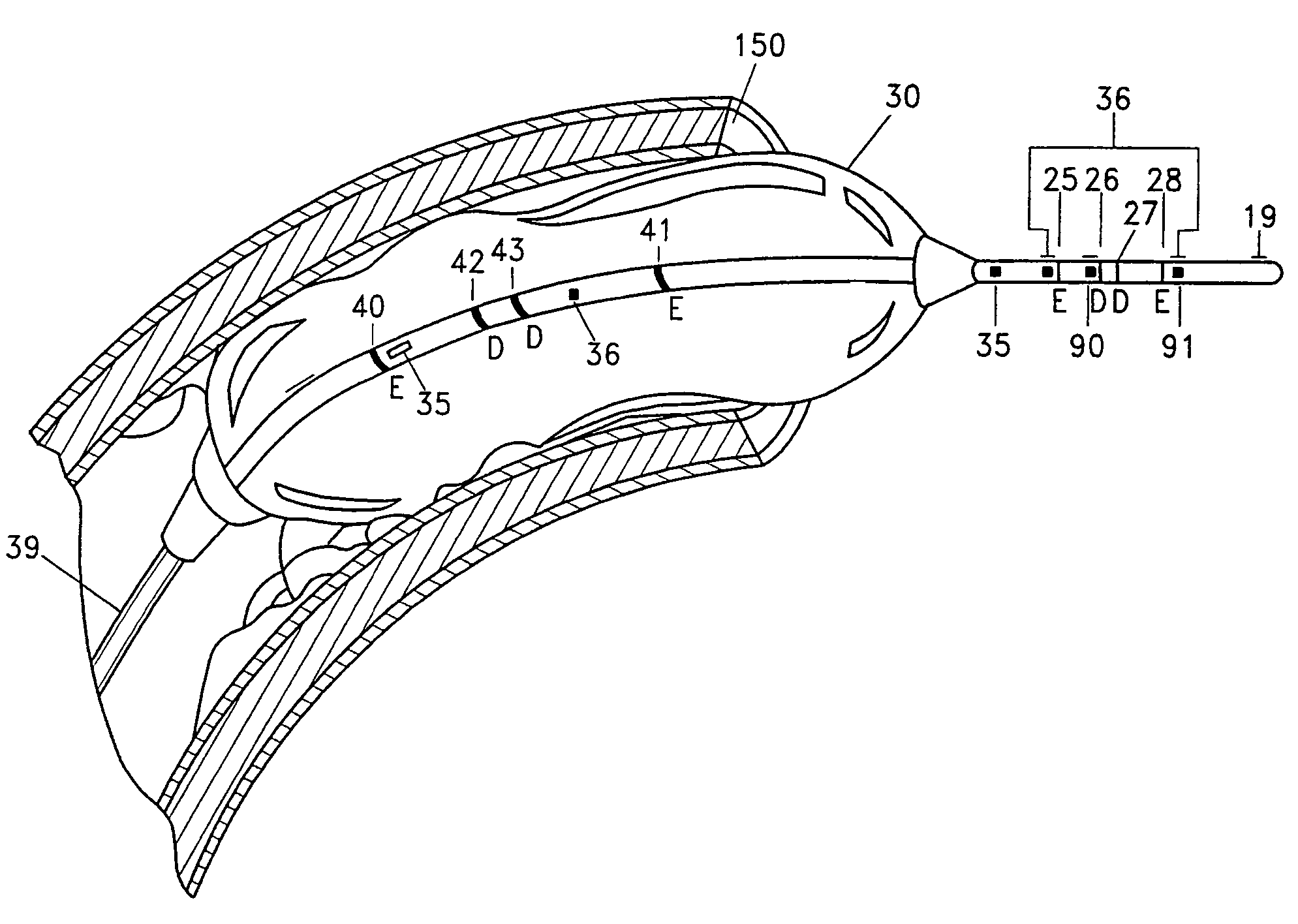
System and method for measuring cross-sectional areas and pressure gradients in luminal organs
The invention comprises a system, catheter and method for measuring the cross-sectional areas and pressure gradients in any hollow organ, such as, for example, blood vessels. One embodiment of such a system includes: an impedance catheter capable of being introduced into a targeted site; a solution delivery source; a constant current source; a balloon inflation control device; and a data acquisition and processing system that receives conductance and / or pressure gradient data from the catheter and calculates the cross-sectional area of the targeted site. In one embodiment, the catheter has an inflatable balloon along its longitudinal axis, thereby enabling the breakup of any materials causing stenosis at the targeted site and / or distention and delivery of an optional stent into the targeted site.
Owner:ELECTRO CAT
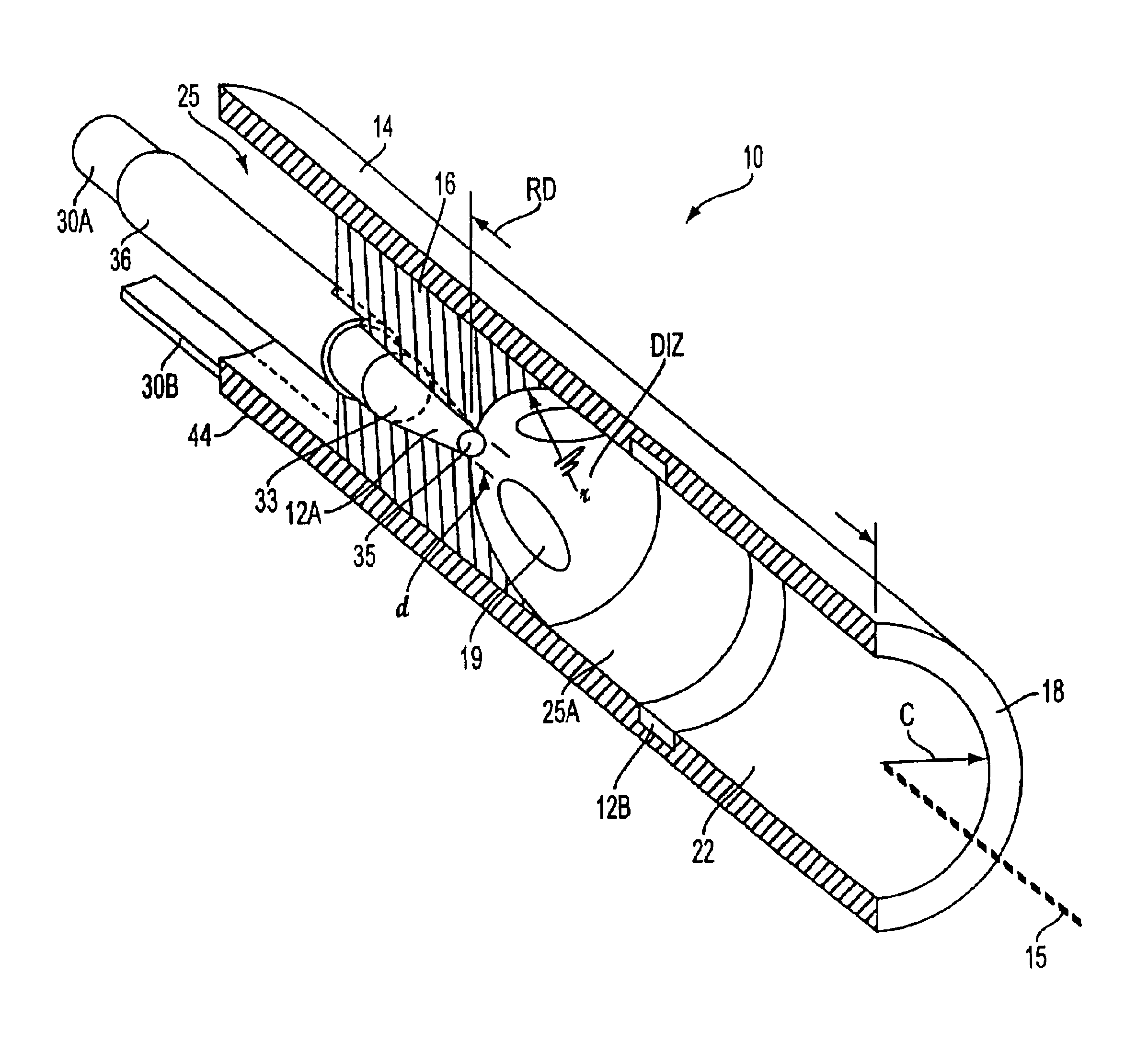
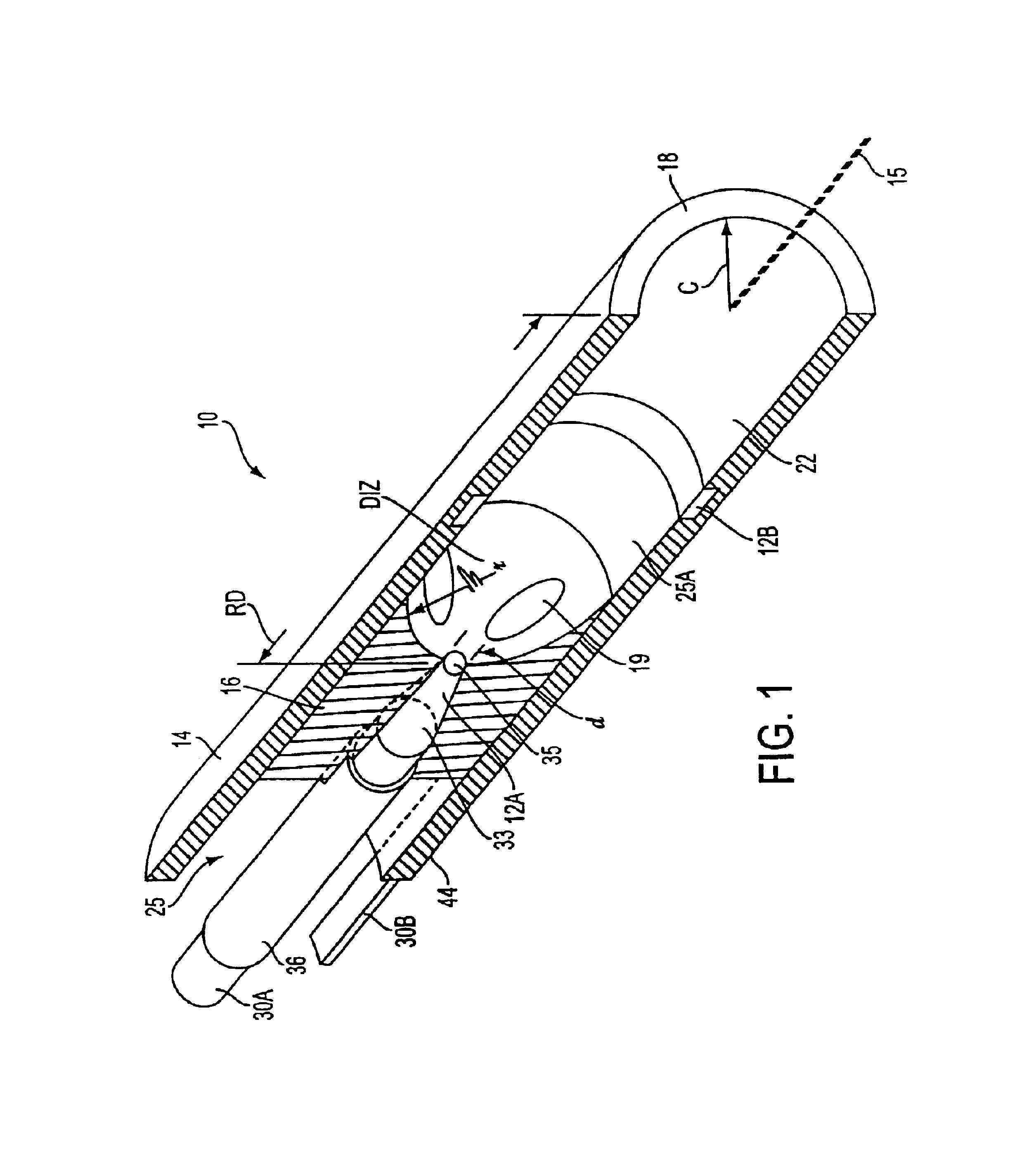
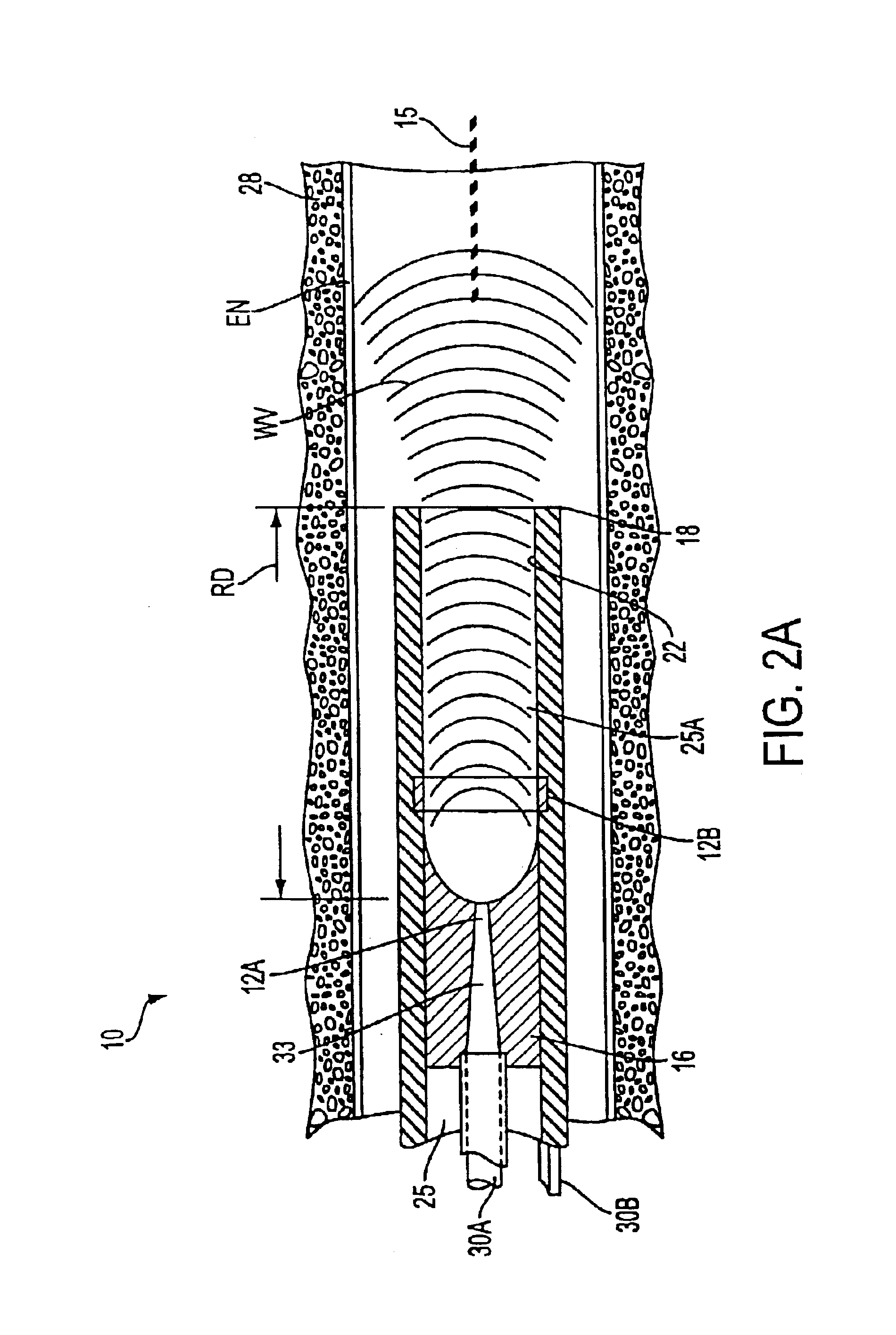
Medical instrument working end and method for endoluminal treatments
InactiveUS6911028B2Avoid damageEasily damagedSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingVaporizationThermal effect
A medical instrument that utilizes electrical energy delivery between first and second opposing polarity electrodes in an interior bore of a working end to cause vaporization of an inflowing fluid media. The vaporization and expansion of the fluid media creates pressure gradients in the working end that causes heated vapor to propagate distally from the working end. The propagation or jetting of the vapor media is used to controllably cause thermal effects in endoluminal environments. The instrument and method can be used to shrink and occlude blood vessels in a treatment for varicose veins.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
Method and Apparatus for Treatment of Adipose Tissue
InactiveUS20090221938A1Easy to produceImprove power densityUltrasound therapyElectrotherapySubcutaneous adipose tissueSkin surface
The invention provides methods and apparatuses (4) for the treatment of adipose tissue. The methods comprise application of ultrasound energy to a region of adipose tissue, and the apparatuses comprise at least one source of ultrasound energy (42a, 42b) configured to direct ultrasound energy through a skin surface into the subcutaneous adipose tissue. In one embodiment, a pressure gradient is created in the region generating relative movement between fat cell constituents having different densities. In another embodiment, a protrusion of skin and underlying adipose tissue containing is formed and ultrasound energy is radiated into the adipose tissue in the protrusion. In another embodiment, an RF electric field is generated inside a region of adipose tissue together with the ultrasound energy.
Owner:SYNERON MEDICAL LTD
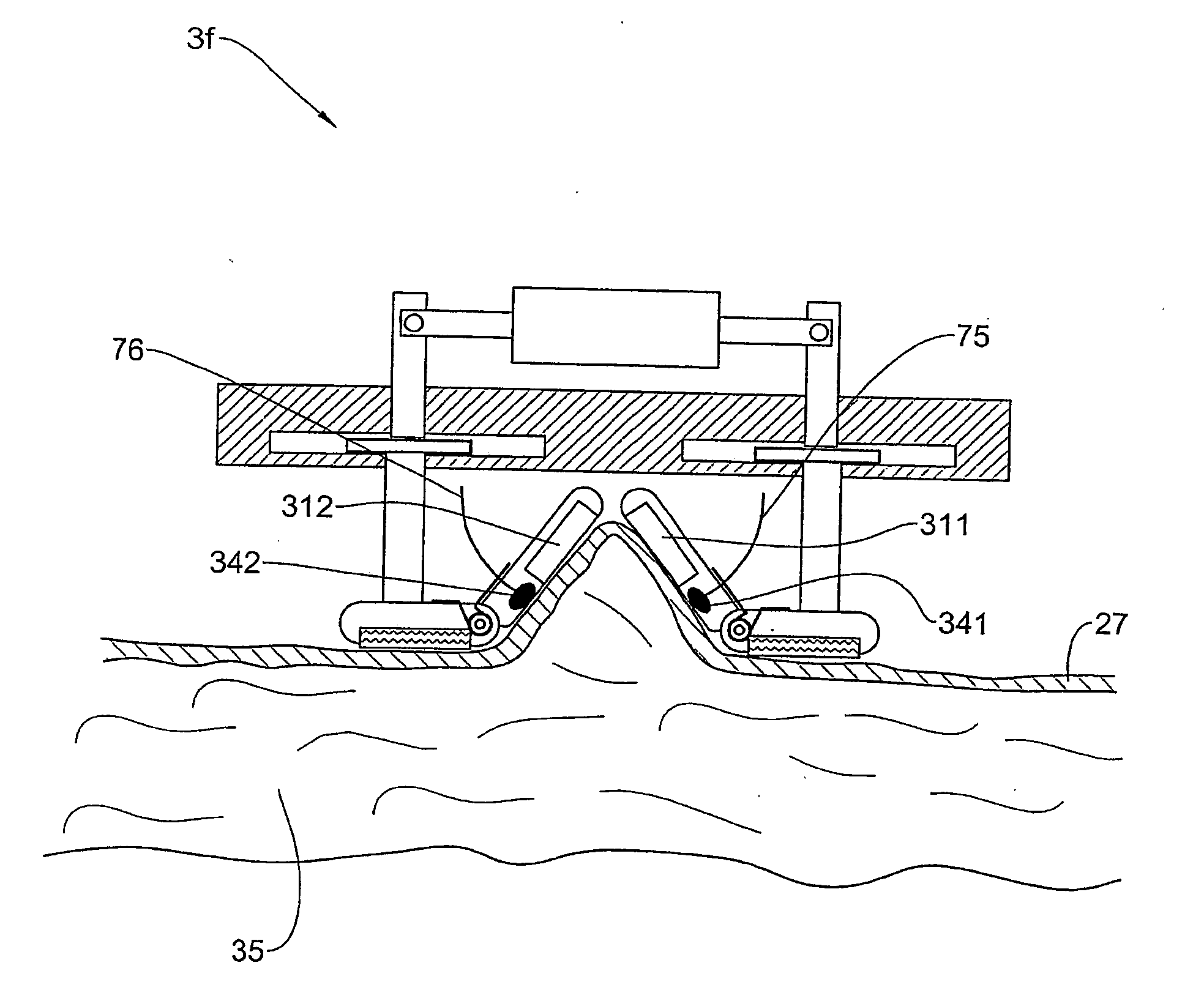
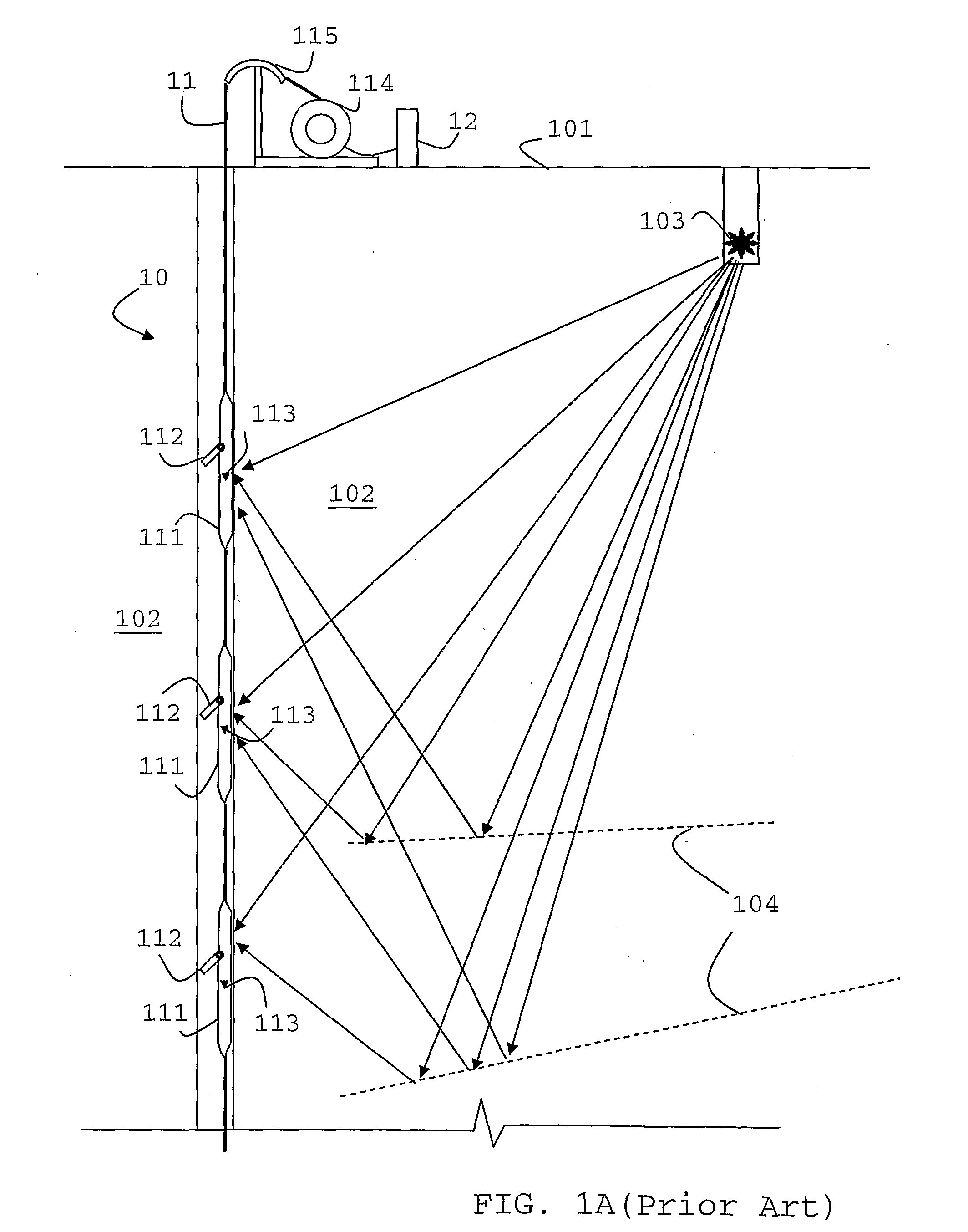
Borehole Seismic Acquisition System
ActiveUS20080316860A1Difference in pressureSeismology for water-loggingSeismic signal receiversS-waveStress gradient
A borehole seismic acquisition system is described with a plurality of sensors arranged so as to identify within the data measured by the pressure sensors P- and S-wave related signals converted at the boundary of the borehole into pressure waves, the sensors being best arranged in groups or clusters sensitive to pressure gradients in one or more directions.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Device, system and method for measuring cross-sectional areas in luminal organs
The disclosure of the present application provides for a system for measuring cross-sectional areas and pressure gradients in luminal organs. The disclosure of the present application also provides a method and apparatus for measuring cross-sectional areas and pressure gradients in luminal organs, such as, for example, blood vessels, heart valves, and other visceral hollow organs. In at least one embodiment, a method for measuring a cross-sectional area of a targeted treatment site comprises the steps of introducing a device, injecting two solutions, measuring a first conductance, moving the device, injecting two solutions, measuring a second conductance, and calculating cross-sectional areas based upon the two conductance measurements.
Owner:3DT HLDG
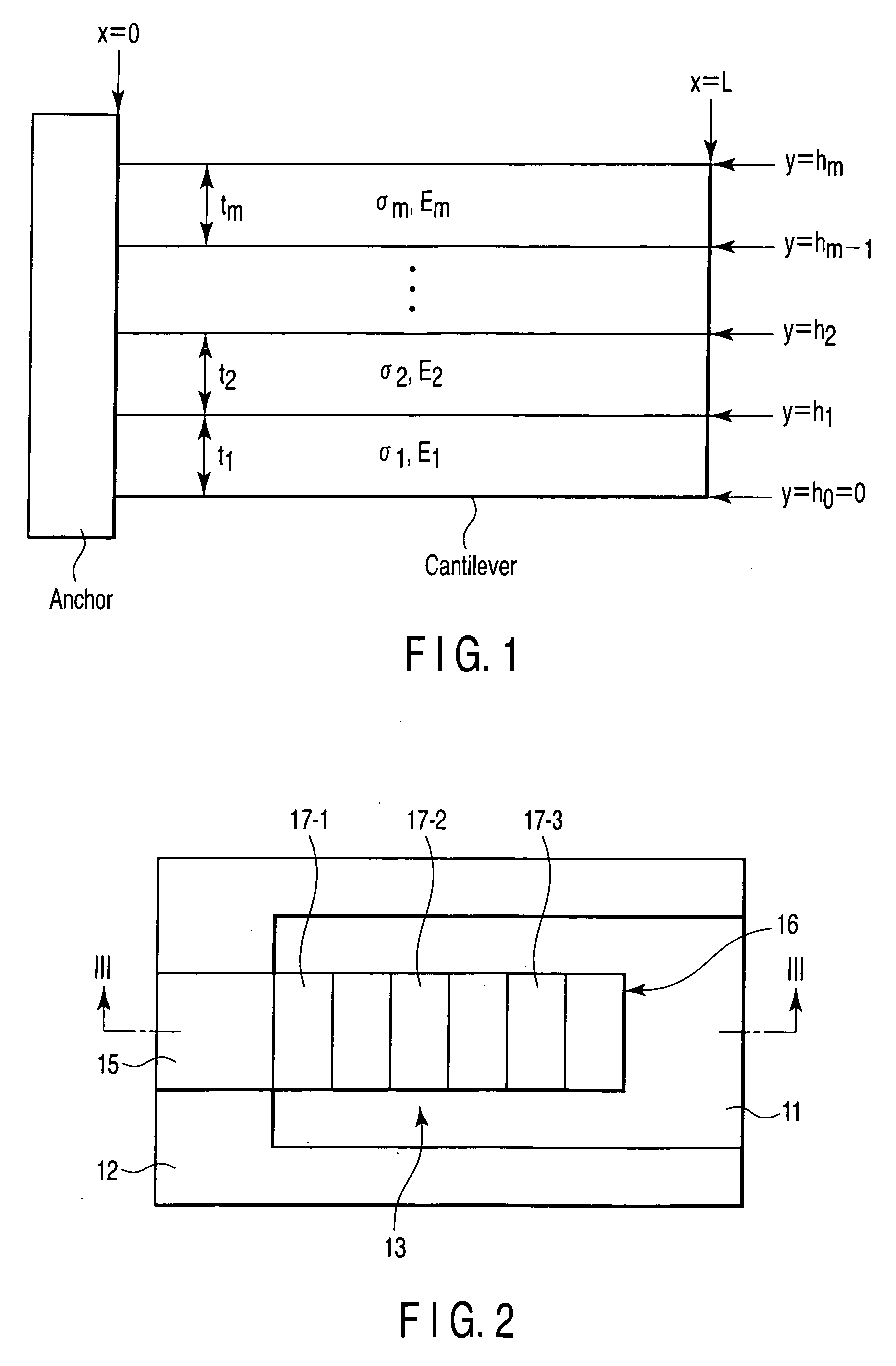
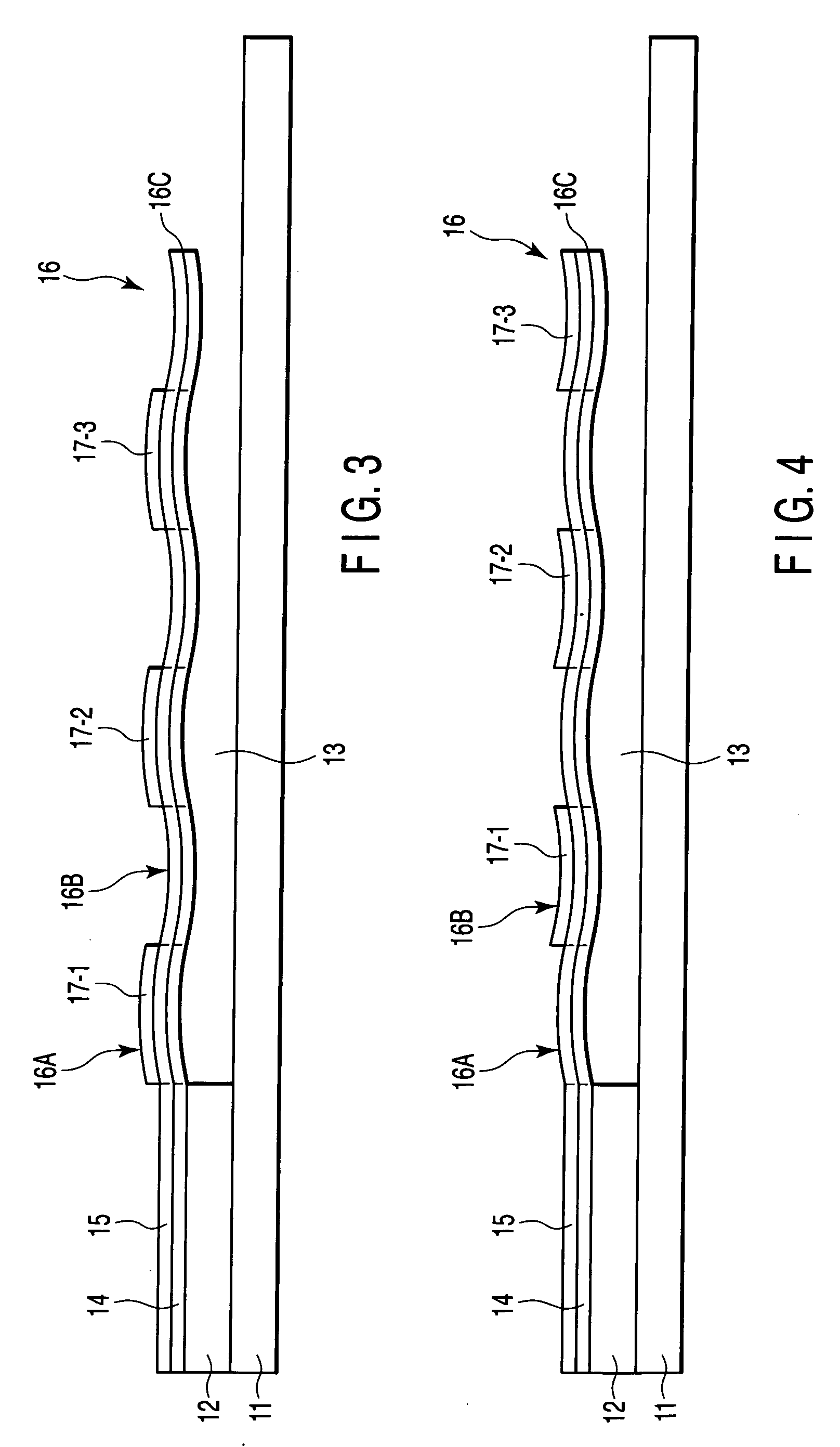
Device with beam structure, and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070138608A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitor with electrode distance variationDevice materialEngineering
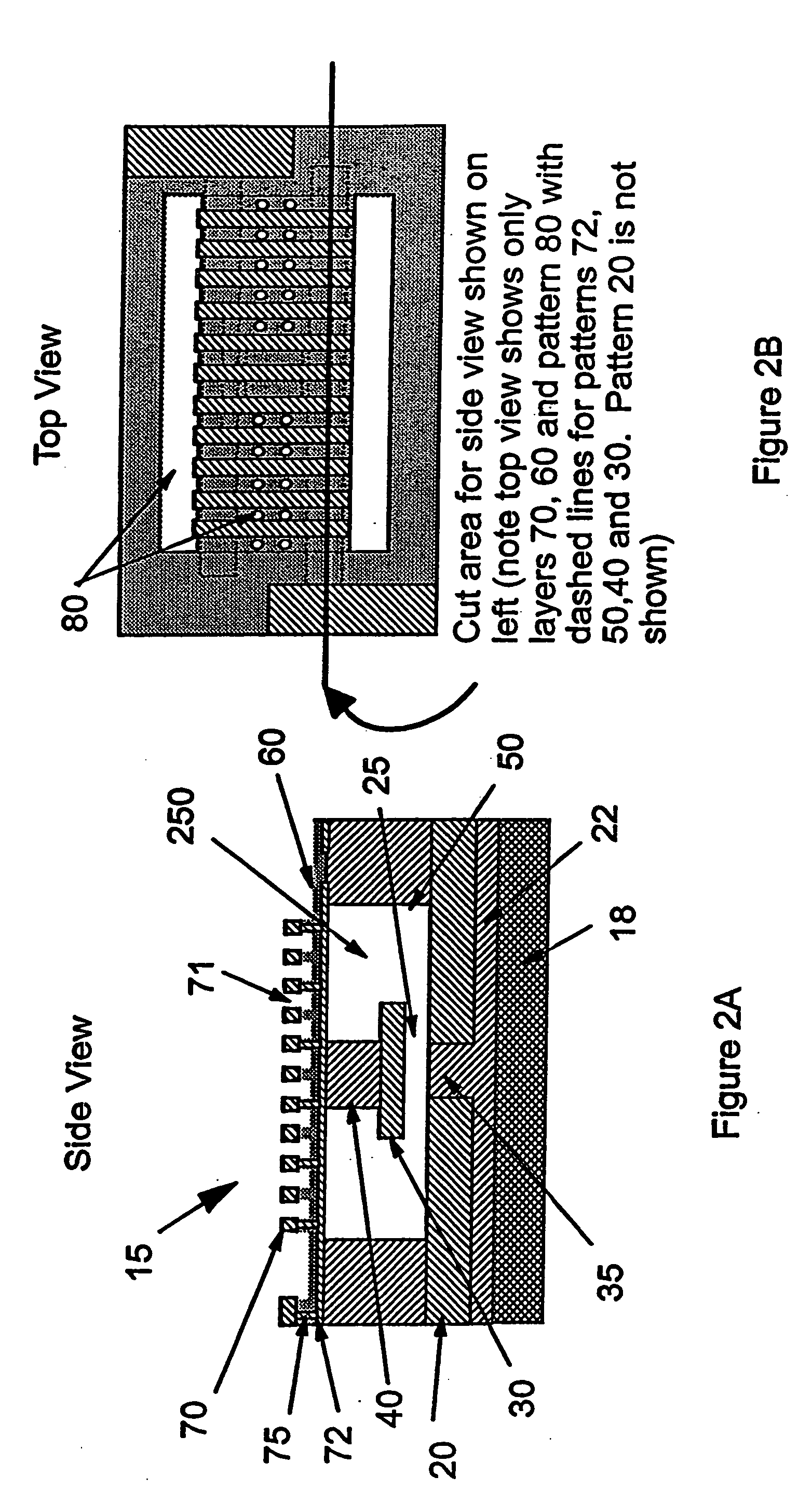
A device with a beam structure includes a substrate, an anchor and a cavity which are provided on and over the substrate, respectively, and a beam structure which is provided on the anchor and over the cavity, extends in a first direction and includes a plurality of convex portions and a plurality of concave portions, each of the convex portions having such a stress gradient as to provide a convex warp, and each of the concave portions having such a stress gradient as to provide a concave warp. The convex portions and the concave portions are alternately repeatedly arranged.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
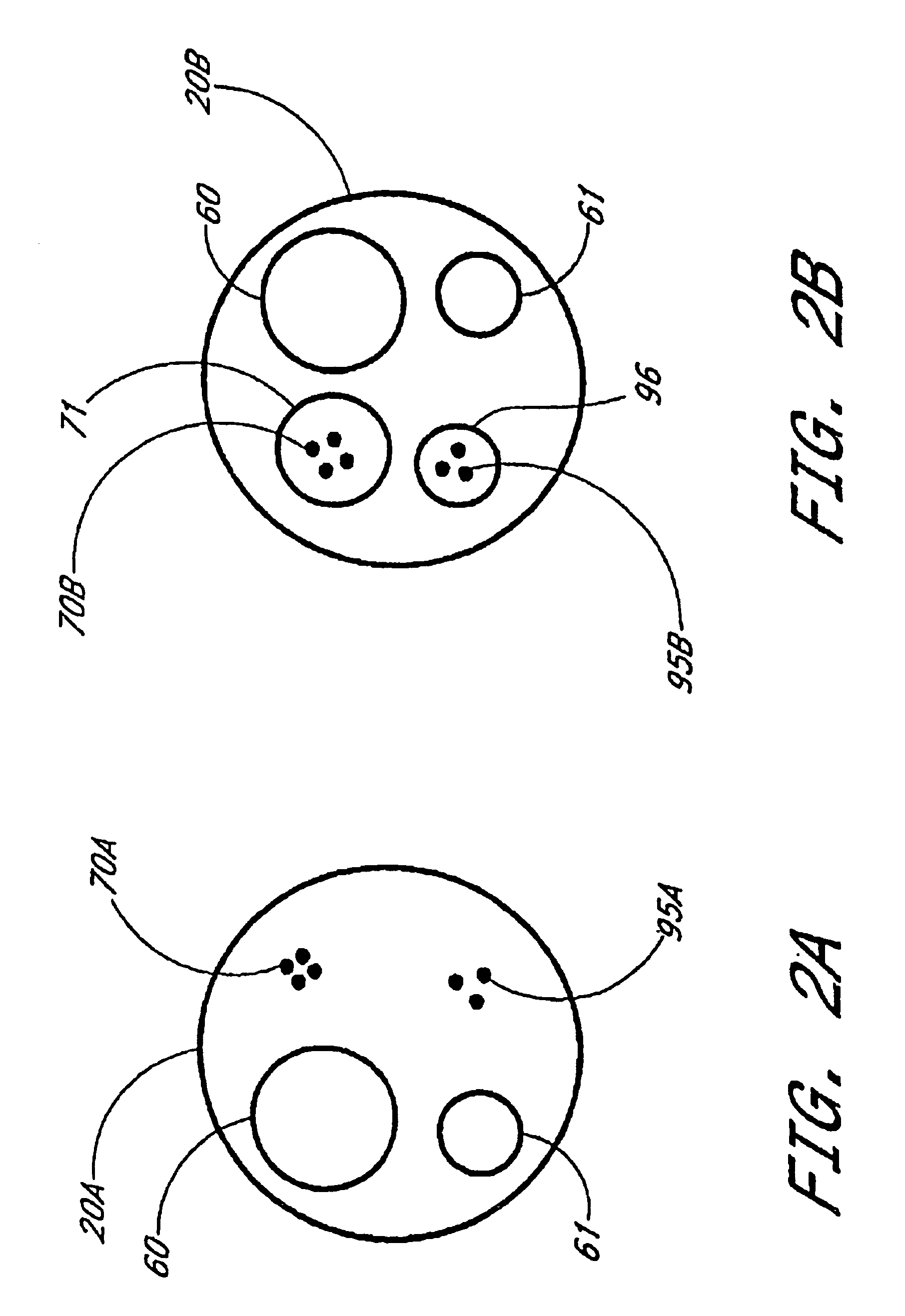
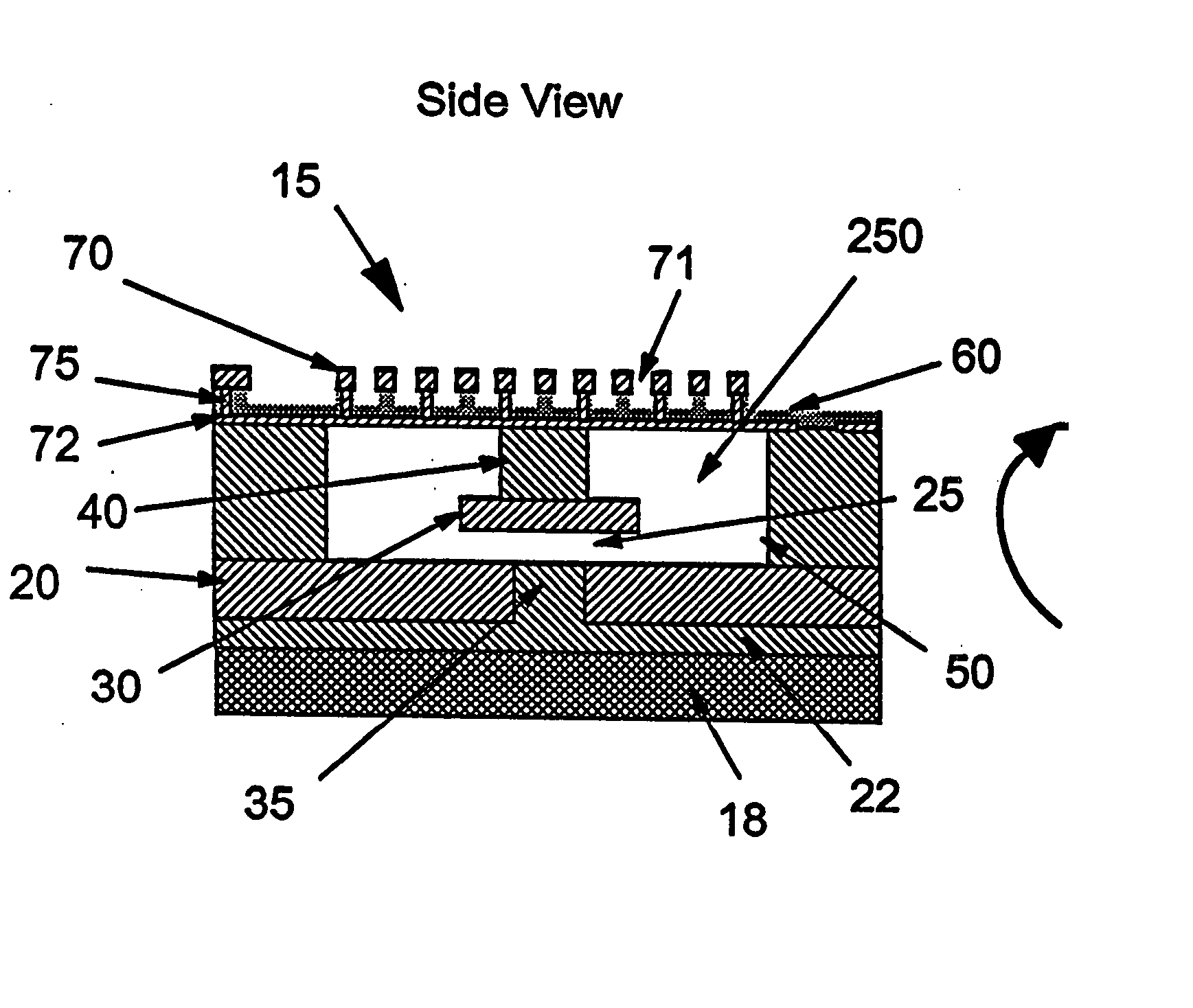
Diaphragm activated micro-electromechanical switch
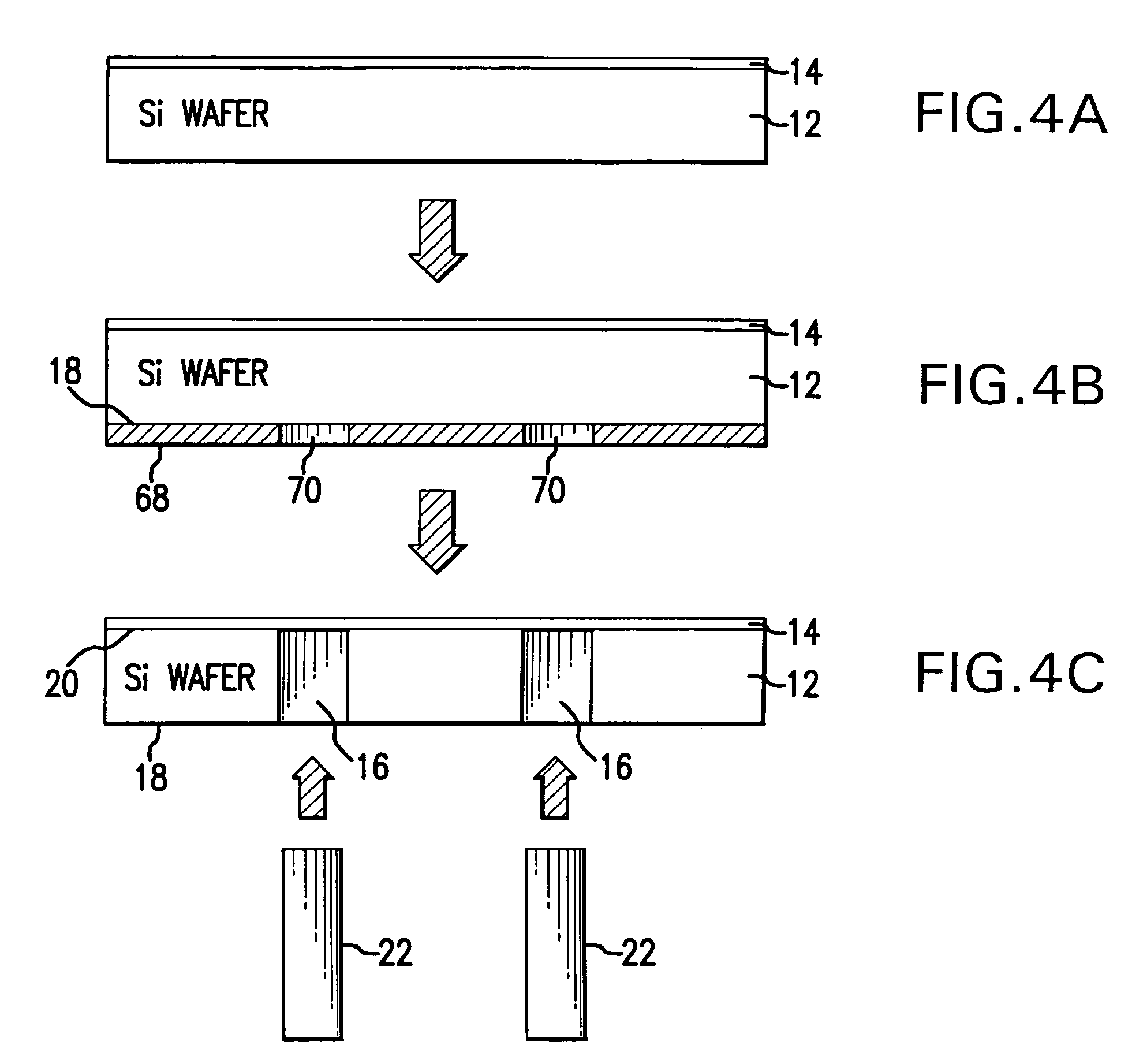
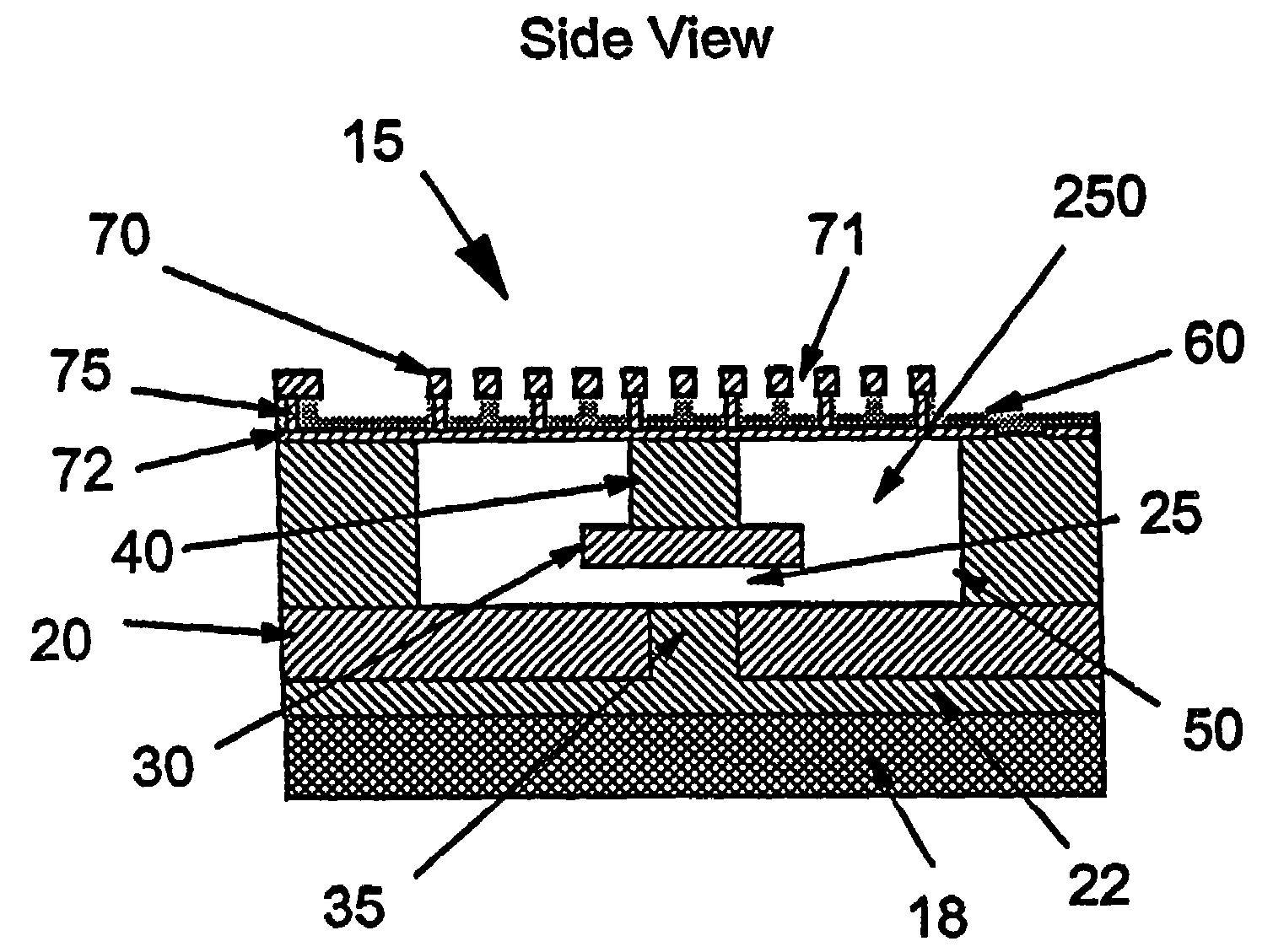
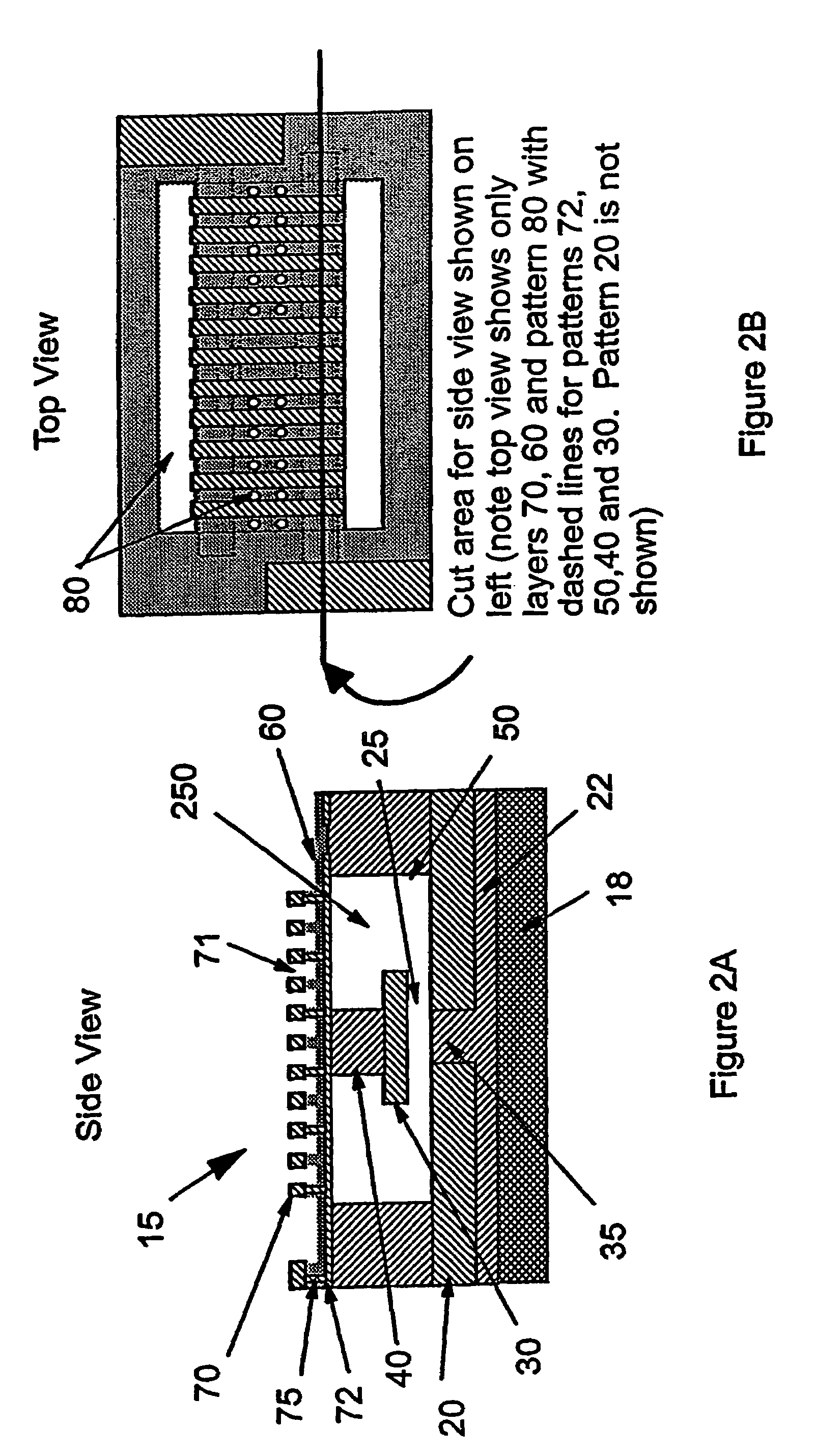
InactiveUS20060017533A1Low insertion lossImprove isolationElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysDecorative surface effectsElectricityEngineering
A micro-electromechanical (MEM) RF switch provided with a deflectable membrane (60) activates a switch contact or plunger (40). The membrane incorporates interdigitated metal electrodes (70) which cause a stress gradient in the membrane when activated by way of a DC electric field. The stress gradient results in a predictable bending or displacement of the membrane (60), and is used to mechanically displace the switch contact (30). An RF gap area (25) located within the cavity (250) is totally segregated from the gaps (71) between the interdigitated metal electrodes (70). The membrane is electrostatically displaced in two opposing directions, thereby aiding to activate and deactivate the switch. The micro-electromechanical switch includes: a cavity (250); at least one conductive path (20) integral to a first surface bordering the cavity; a flexible membrane (60) parallel to the first surface bordering the cavity (250), the flexible membrane (60) having a plurality of actuating electrodes (70); and a plunger (40) attached to the flexible membrane (60) in a direction away from the actuating electrodes (70), the plunger (40) having a conductive surface that makes electric contact with the conductive paths, opening and closing the switch.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method of making an electrostatic actuator
InactiveUS6933165B2Reduce stress concentrationHigh stressRailway roofsMaterial nanotechnologyElectrostatic actuatorOptoelectronics
A method of fabricating an electrostatic actuator with an intrinsic stress gradient is provided. An electrode is formed on a substrate and a support layer is formed over the electrode. A metal layer is deposited onto the support layer via a deposition process. Deposition process conditions are varied in order to induce a stress gradient into the metal layer. The intrinsic stress in the metal layer increases in the direction from the bottom to the top of the metal layer. The support layer under the electrode is removed to release the electrostatic actuator.
Owner:SUPERCONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGIES INC
Fiber tip based sensor system for measurements of pressure gradient, air particle velocity and acoustic intensity
InactiveUS20050146726A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansLight sourceFiber optic sensor
A fiber optic sensor system for pressure measurements where the design permits multiplexity on the input side of the system and the optical part of the system, which has a sensor Fabry-Perot interferometer and a read-out interferometer, is based on low coherence fiber-optic interferometry techniques. This permits a high dynamic range and low sensitivity to the wavelength fluctuation of the light source as well as to the optical intensity fluctuations. The system includes fiber tip based Fabry-Perot sensors, where each sensor includes a diaphragm as the transducer. A combined pressure gradient sensor, air particle velocity sensor, as well as acoustic intensity sensor is built based on the fiber tip based Fabry-Perot sensors.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Microelectromechanical system based sensors, sensor arrays, sensing systems, sensing methods and methods of fabrication
InactiveUS6844214B1Increase flexibilityReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsSensor arrayMicroelectromechanical systems
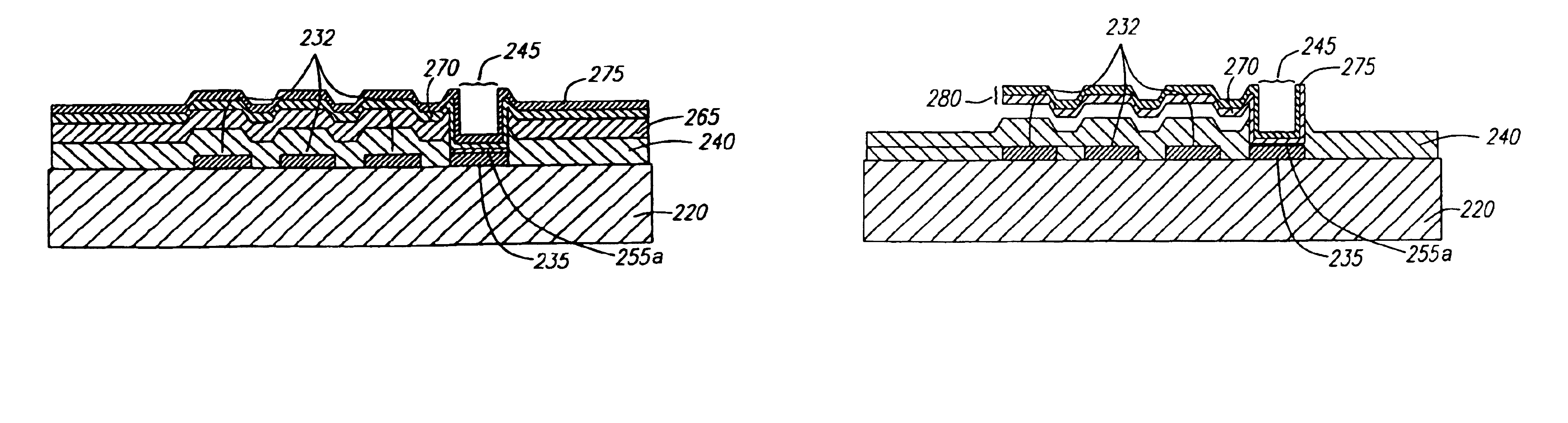
A microelectromechanical system (MEMS) based sensor comprises: a substrate defining a plane; a first conductive material layer having a first stress, a first portion of the first conductive material layer being connected to the substrate and extending in a substantially parallel direction to the plane defined by the substrate and a second portion being disconnected from the substrate and extending in a substantially non-parallel direction to the plane defined by the substrate; and a sensor material layer formed over at least the second portion of the first conductive material layer, the sensor material layer having a second stress that is less than the first stress of the first conductive material layer. The stresses form a stress gradient that bends the second portion of the first conductive material layer and the sensor material layer formed over the second portion of the first conductive material layer away from the substrate.
Owner:XEROX CORP
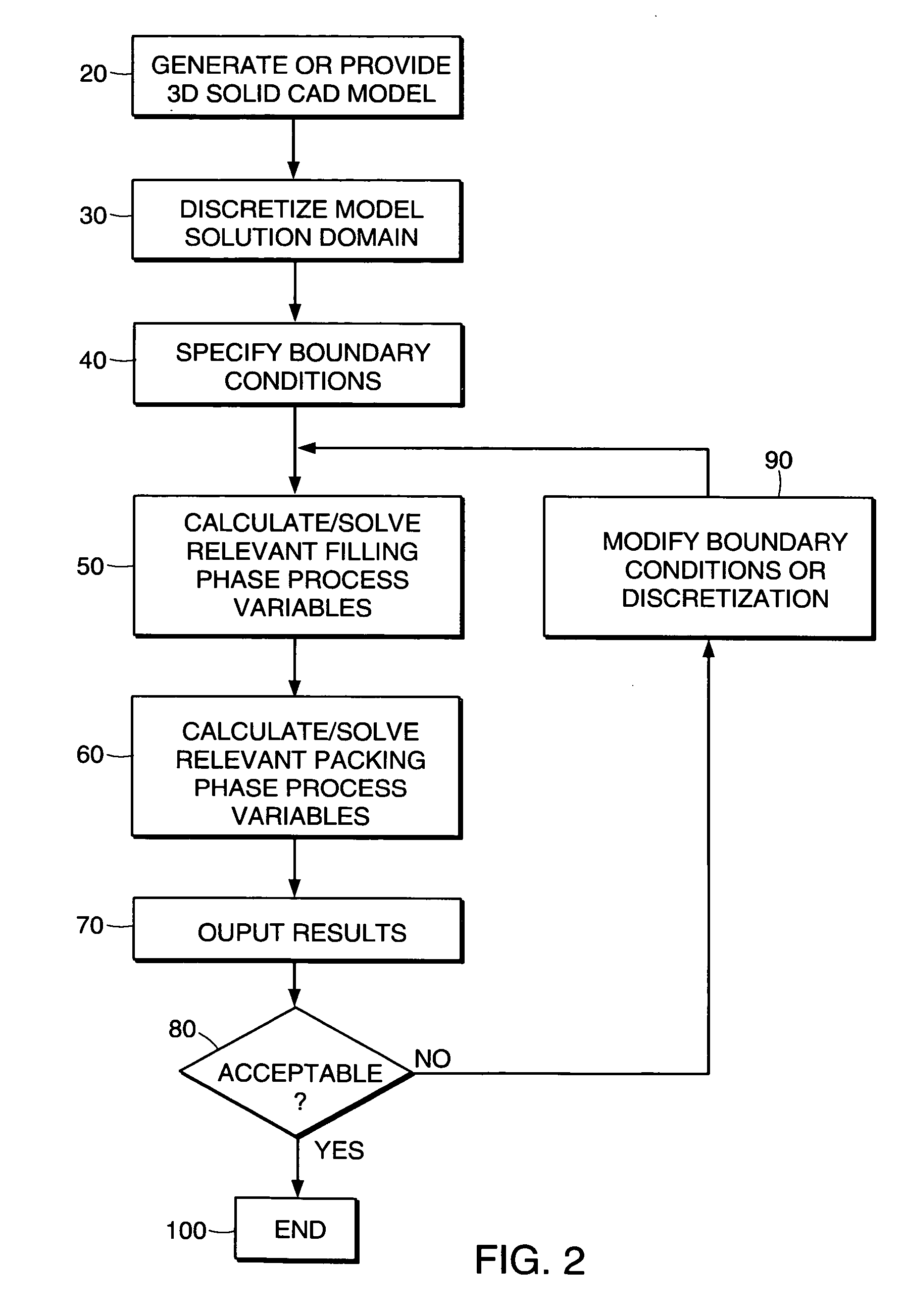
Method and apparatus for modeling injection of a fluid in a mold cavity
InactiveUS20050114104A1Accurate valueAccurately determineComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationThermoplasticMolten state
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for analyzing fluid flow while considering heat transfer effects and, in particular, a phase change from a molten state to a solid state. In particular, the method and apparatus may be applied to the analysis of an injection molding process for producing a molded polymer component from a thermoplastic or a thermosetting polymer. In one embodiment, the method may be used to determine pressure required to fill a mold cavity and pressure gradients introduced during filling and packing of the cavity of an injection mold. The results of these analyses may be used to determine the number and location of gates, to determine the best material for the component, and to optimize the process conditions used in the molding process.
Owner:MOLDFLOW IRELAND LTD
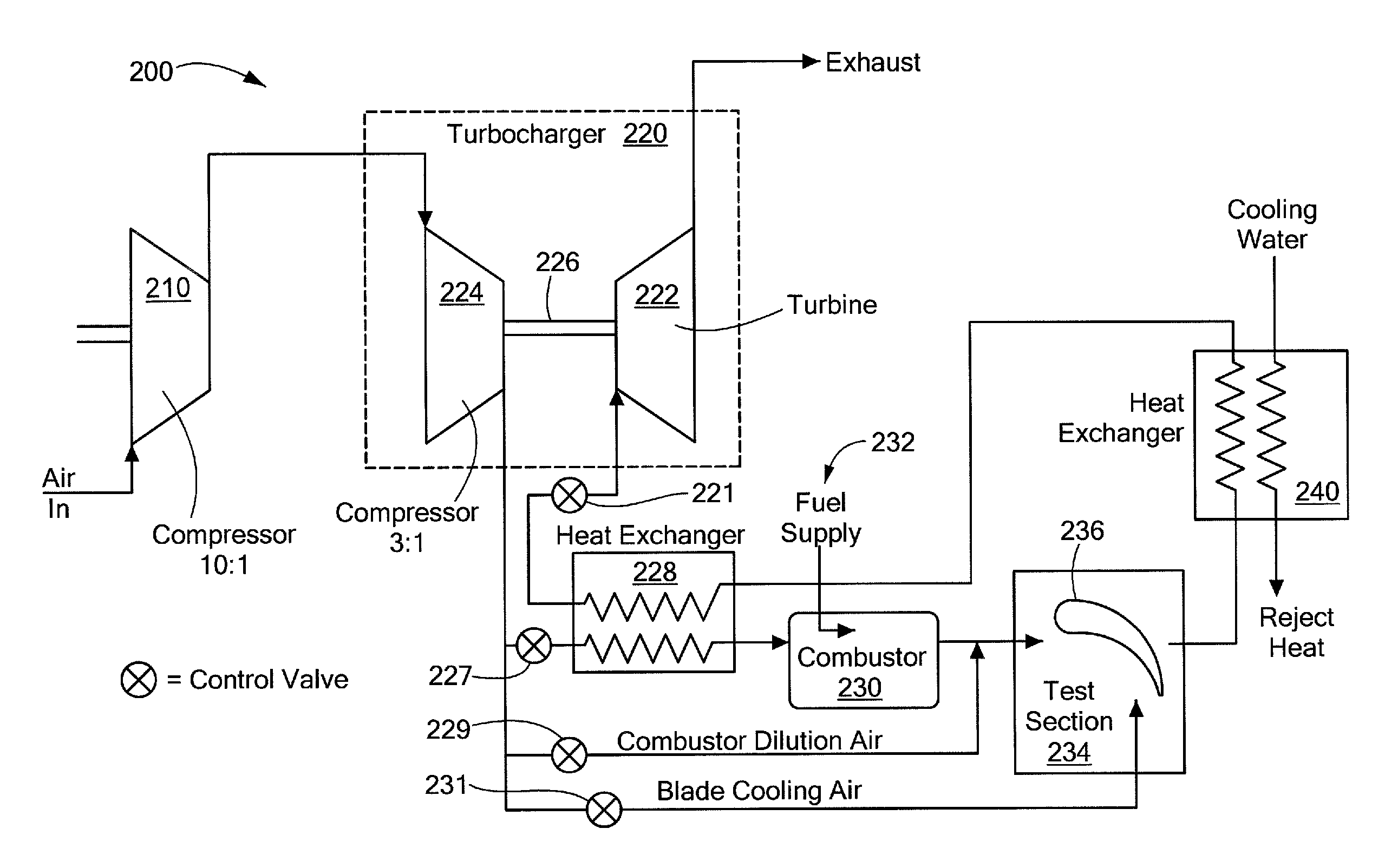
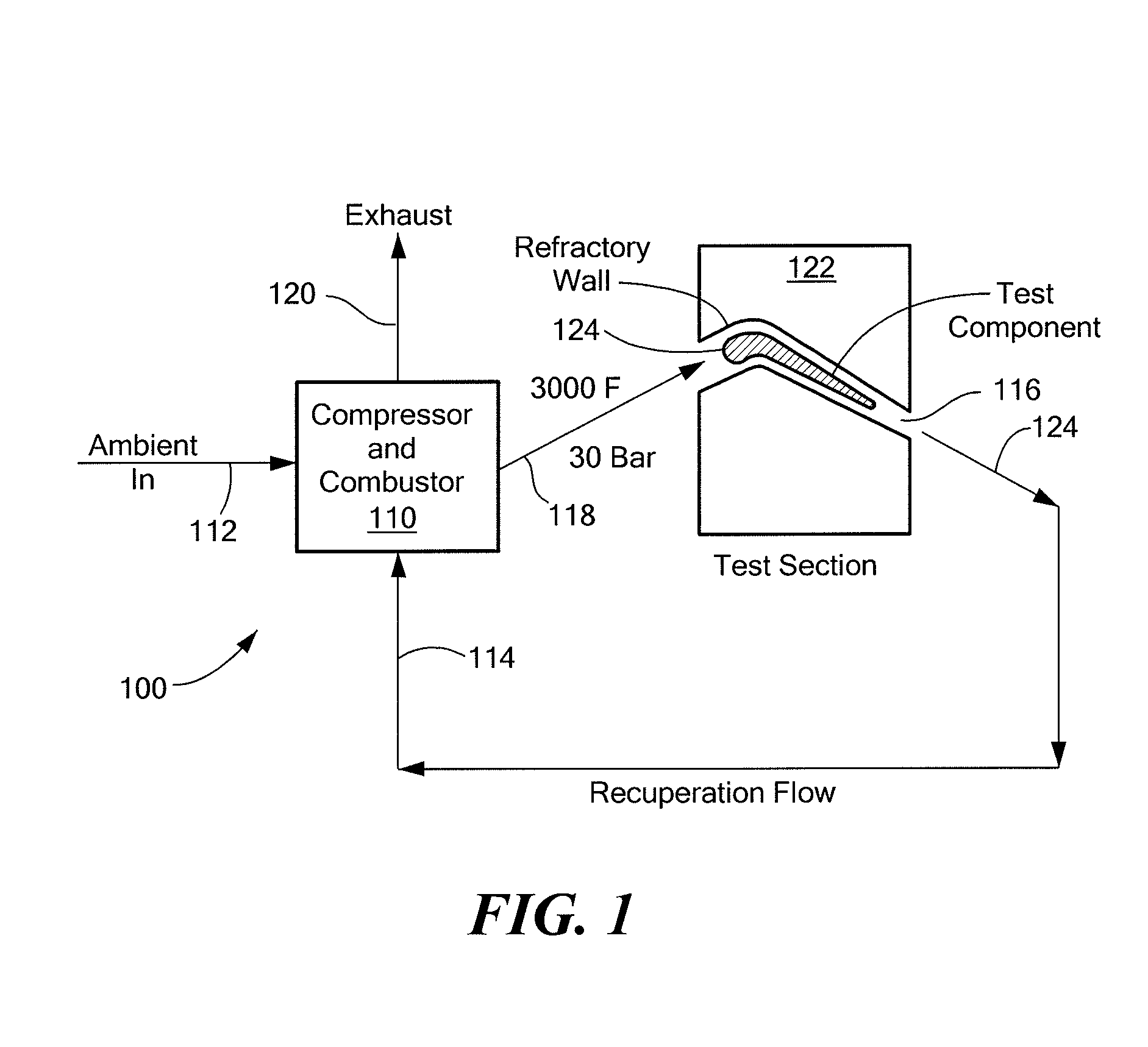
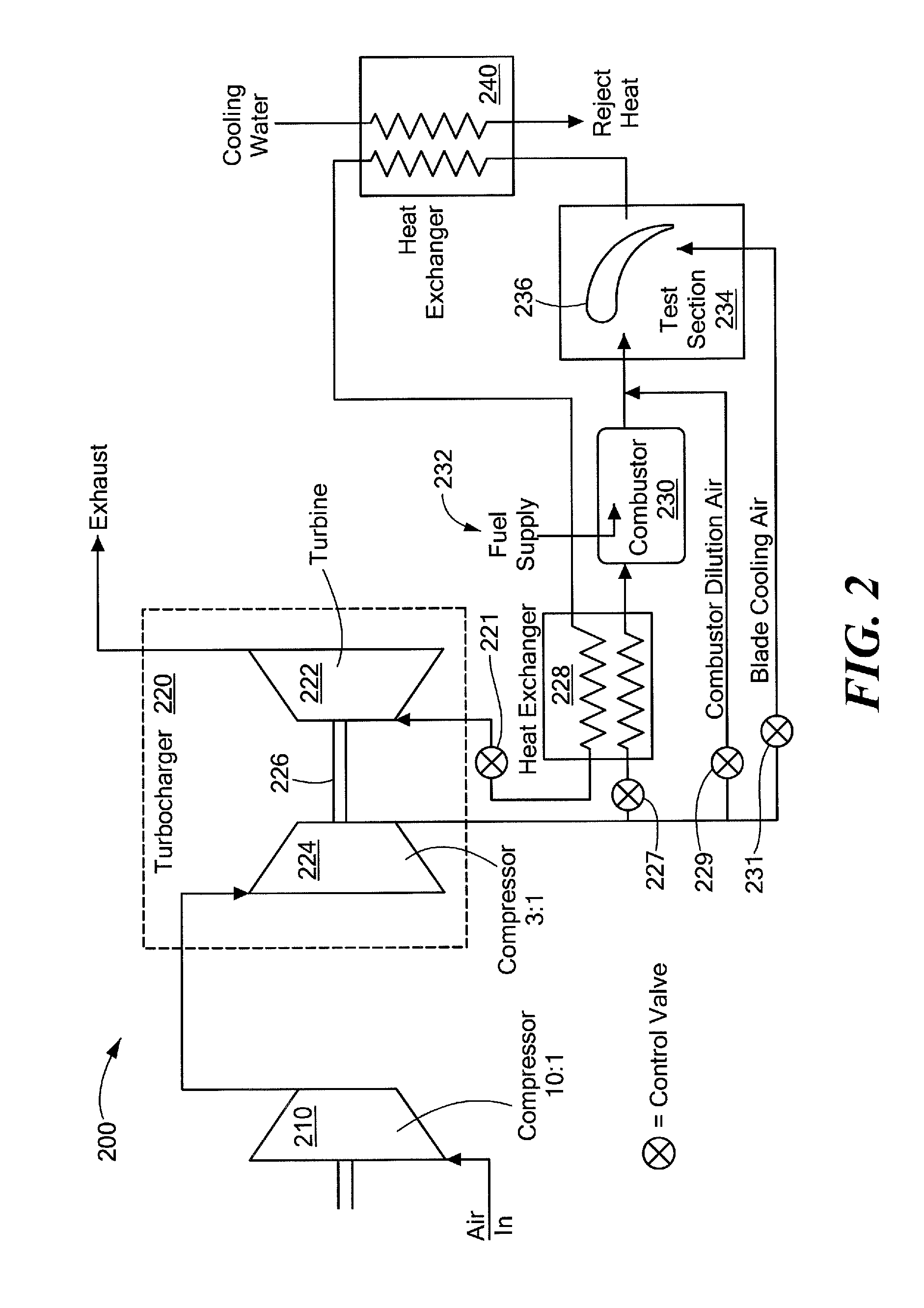
System and method for imposing thermal gradients on thin walled test objects and components
ActiveUS7966868B1Consume moreLow costGas-turbine engine testingEngine fuctionsEngineeringTest chamber
A test facility provides high temperature, high pressure and high mass flow fluid to a test object to form a relatively large thermal gradient on the object. Energy in the fluid is recuperated to drive system components, such as a heat exchanger and a turbocharger compressor. A test chamber housing the test object can be arranged to conform to a contour of the test object. A control system permits independent variation of pressure, temperature, cooling fluid and fluid velocity, as well as mechanical loading on the test object. Noncontact, optical inspection measurement techniques can be employed to measure test chamber and / or test object parameters. The test object can be configured to direct cooling airflow to permit various temperature or pressure gradients to be implemented. The test facility is relatively inexpensive to operate and provides a significant cost advantage over testing conducted in a full gas turbine engine.
Owner:SCHENCK USA CORP
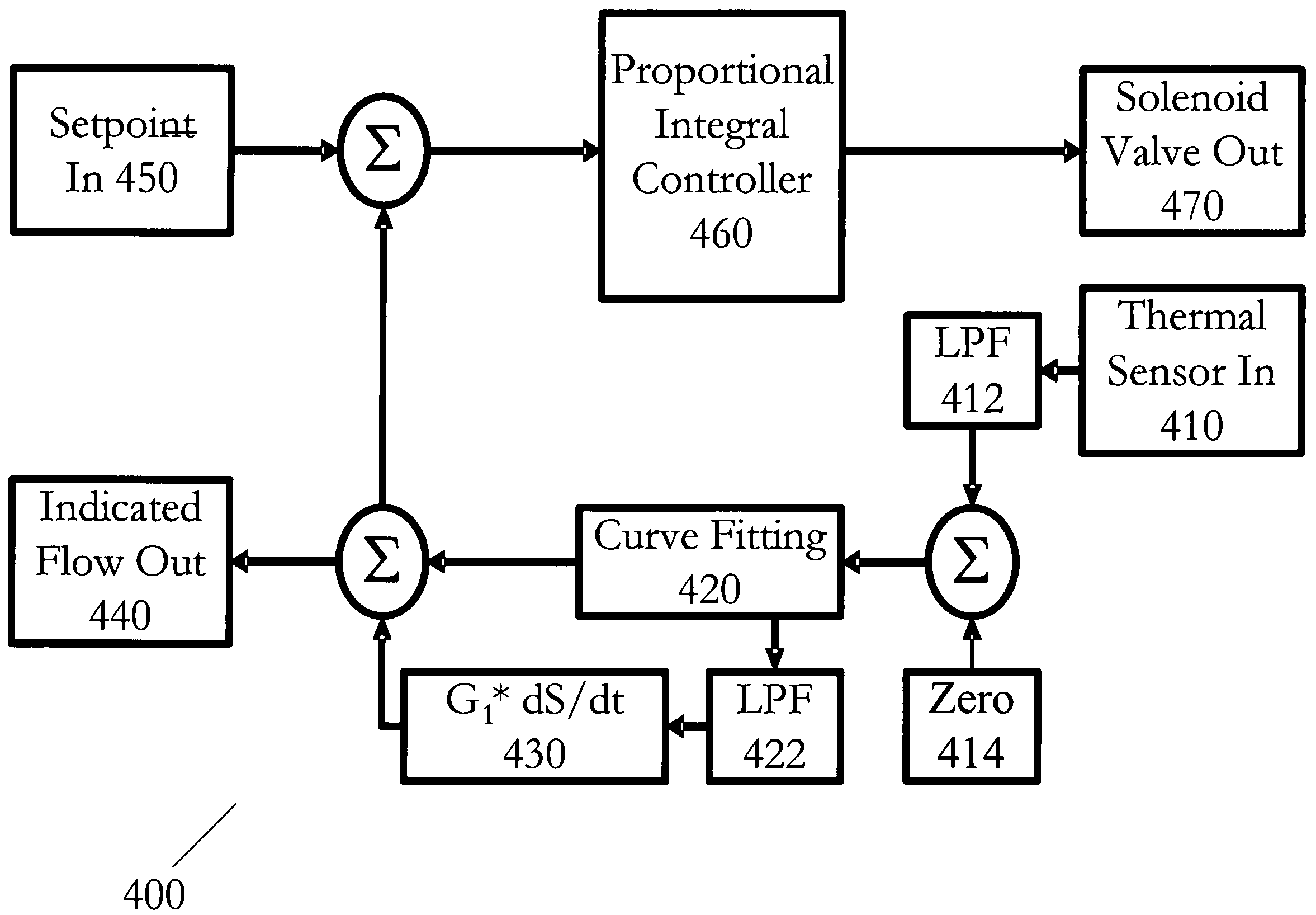
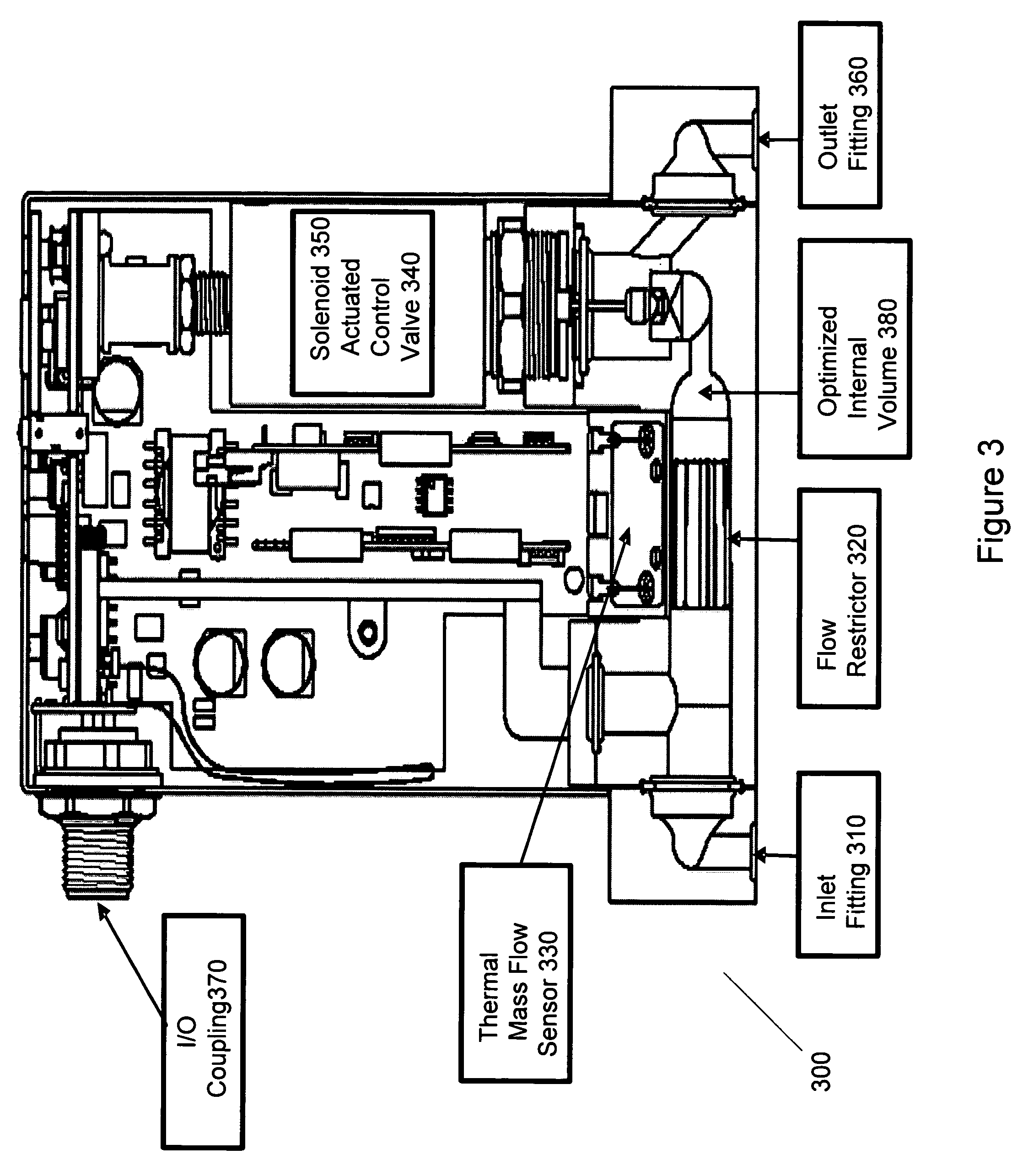
Method and system for a mass flow controller with reduced pressure sensitivity
InactiveUS7216019B2Reduce sensitivityReduce in quantityAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVolume/mass flow measurementIsolation valveTransducer
Systems and methods for mass flow controllers which minimize false flow conditions and display a reduced sensitivity to pressure transients are disclosed. Pressure gradients that exist within the volume of a mass flow controller fluid path are minimized in order to limit the potential energy contained in compressed or pressurized process gas. Additionally, process gas pressure may be monitored using a pressure sensor. This pressure signal is utilized in conjunction with a control algorithm to cancel the detrimental effect of certain flow components. These mass flow controllers may be used as drop in replacements for legacy mass flow controllers and reduce the cost of gas sticks due to elimination of discrete components such as pressure regulators, gas filters, pressure transducers, local pressure displays, isolation valves, seals, etc.
Owner:BROOKS INSTRUMENT +1
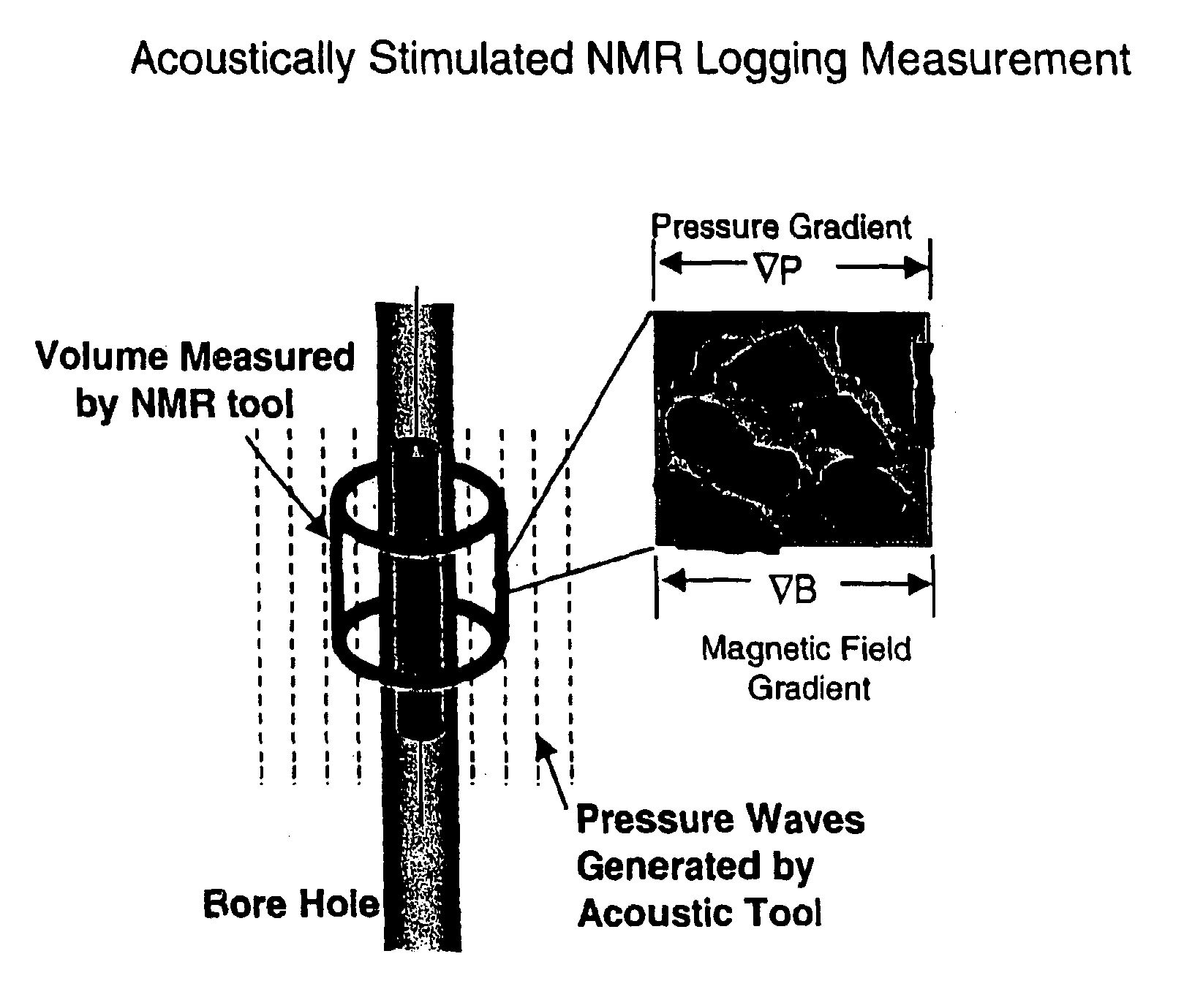
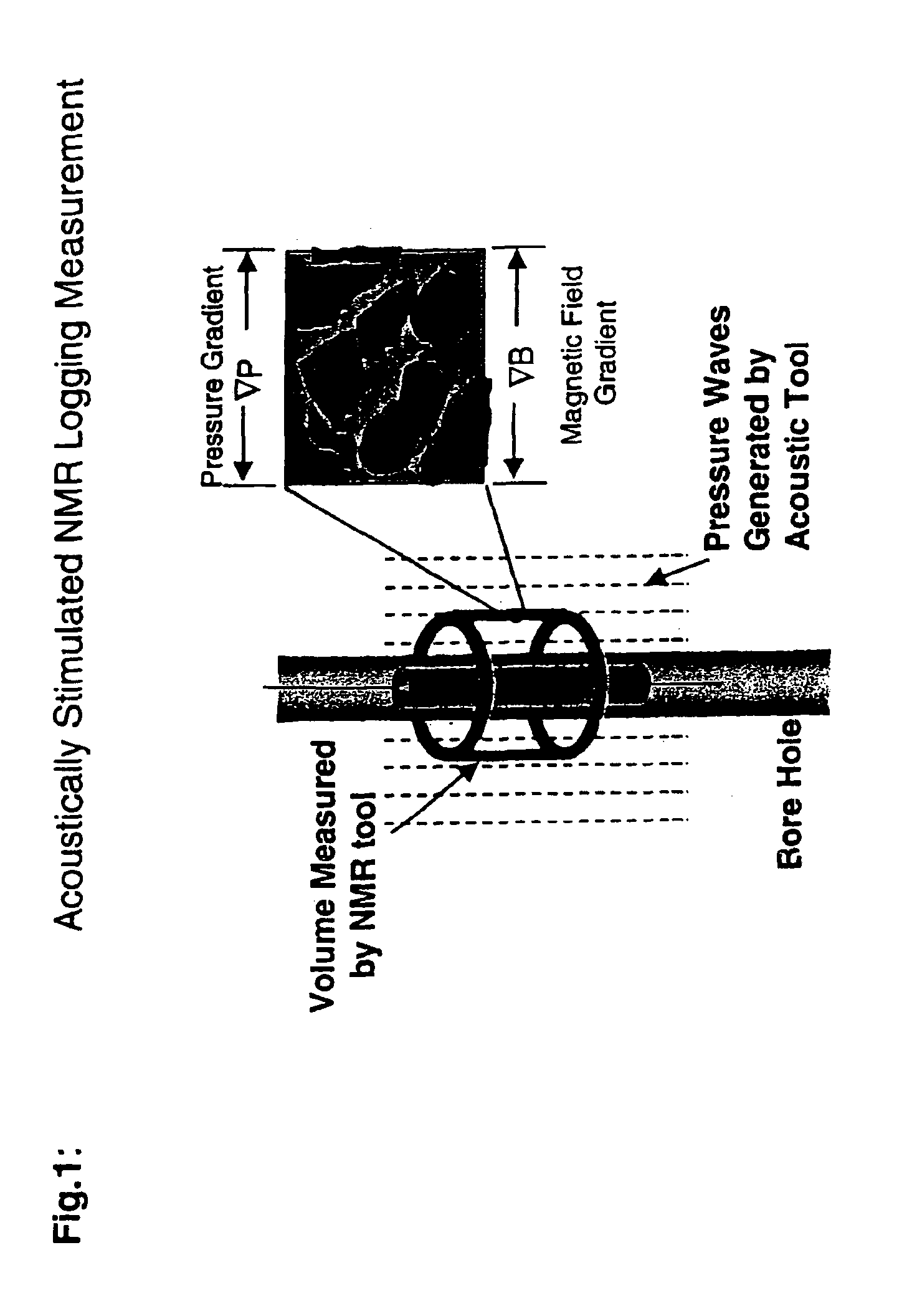
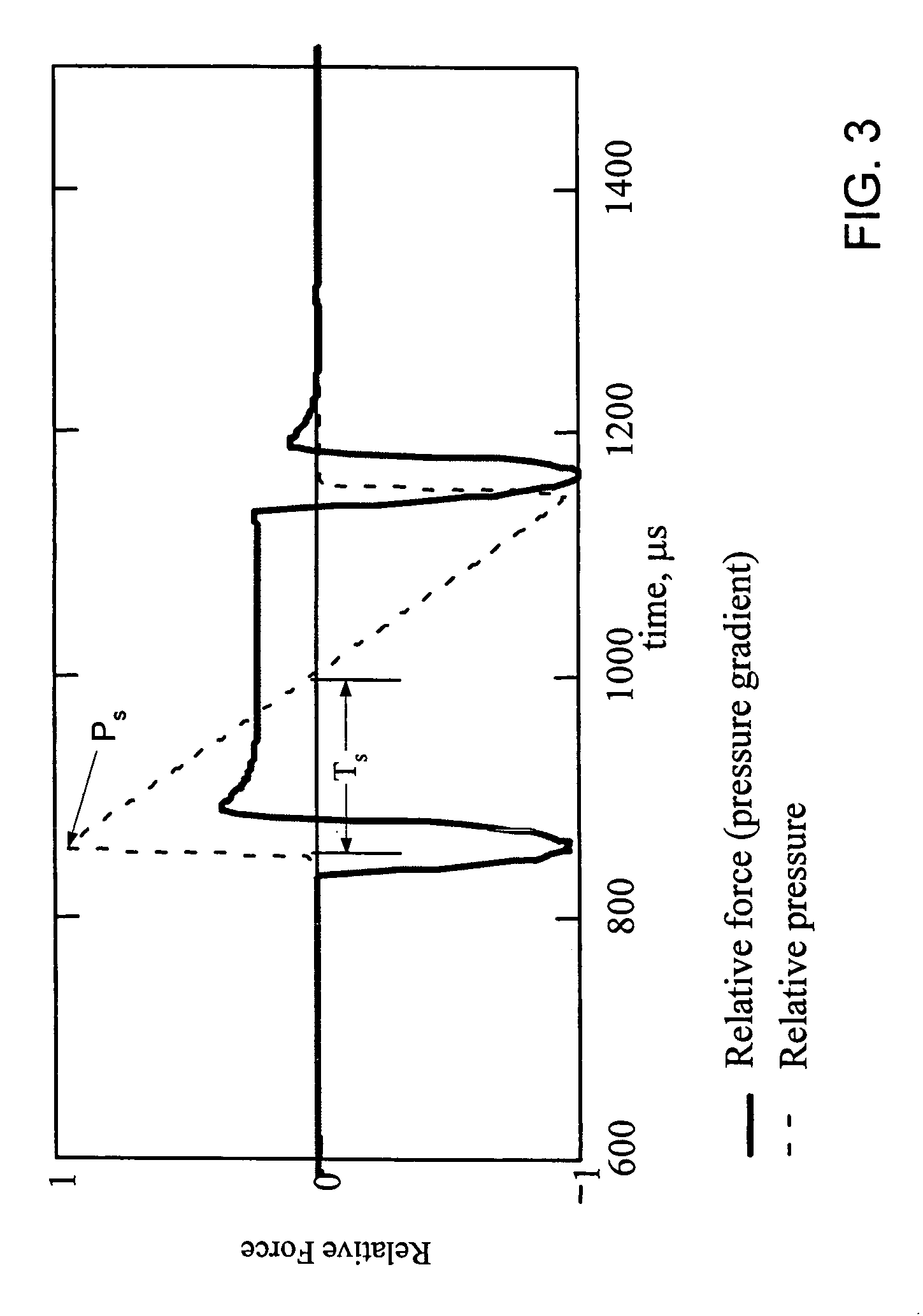
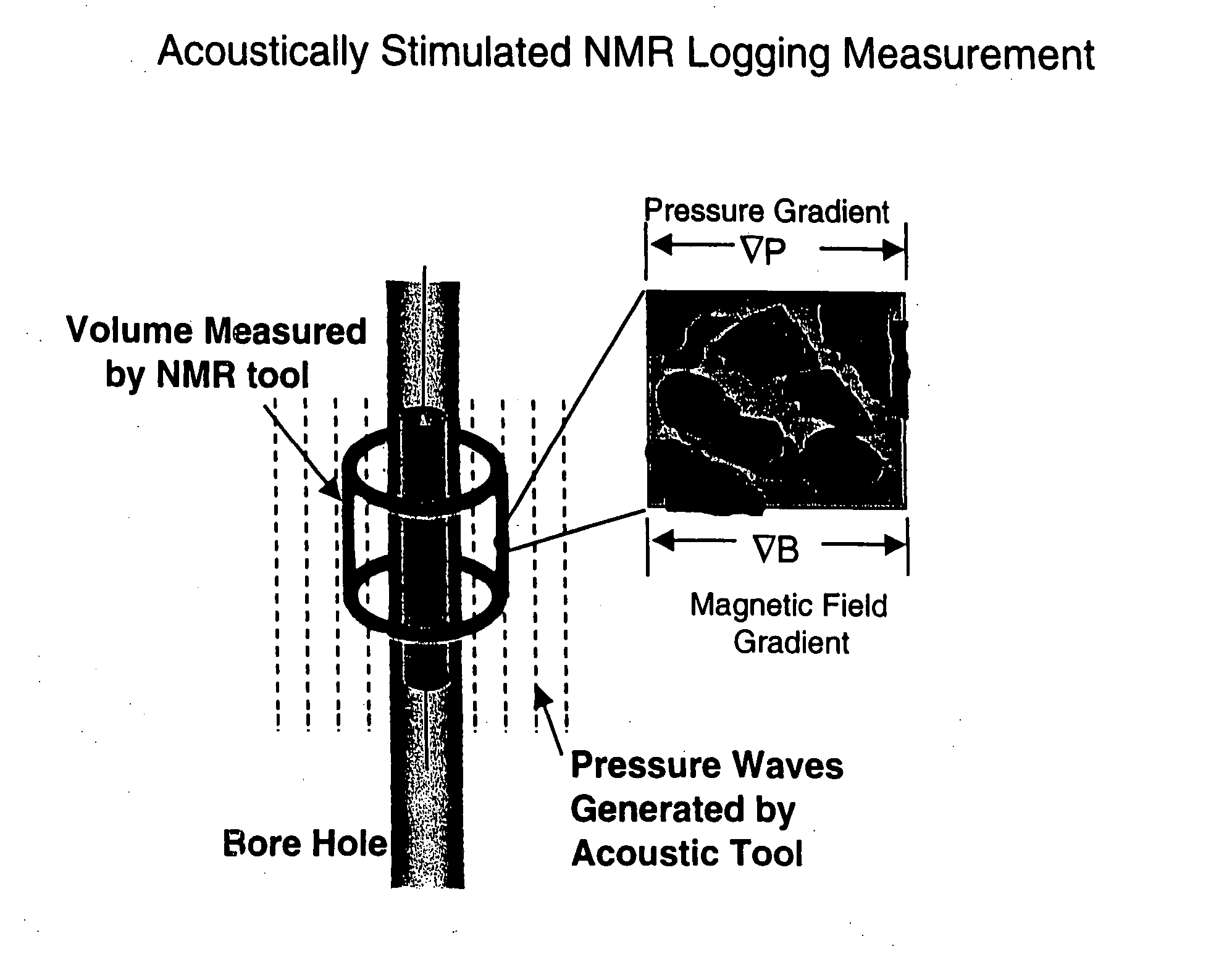
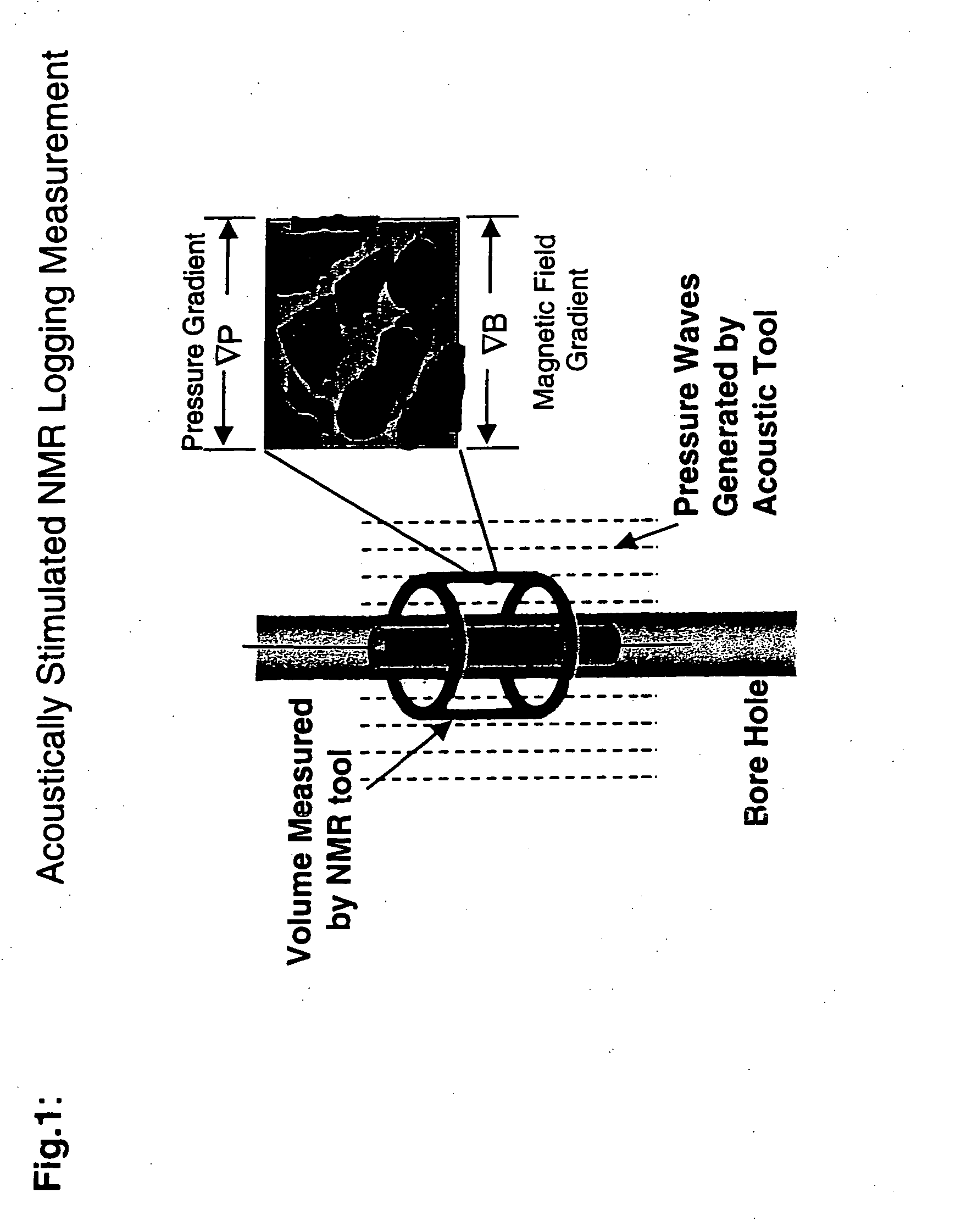
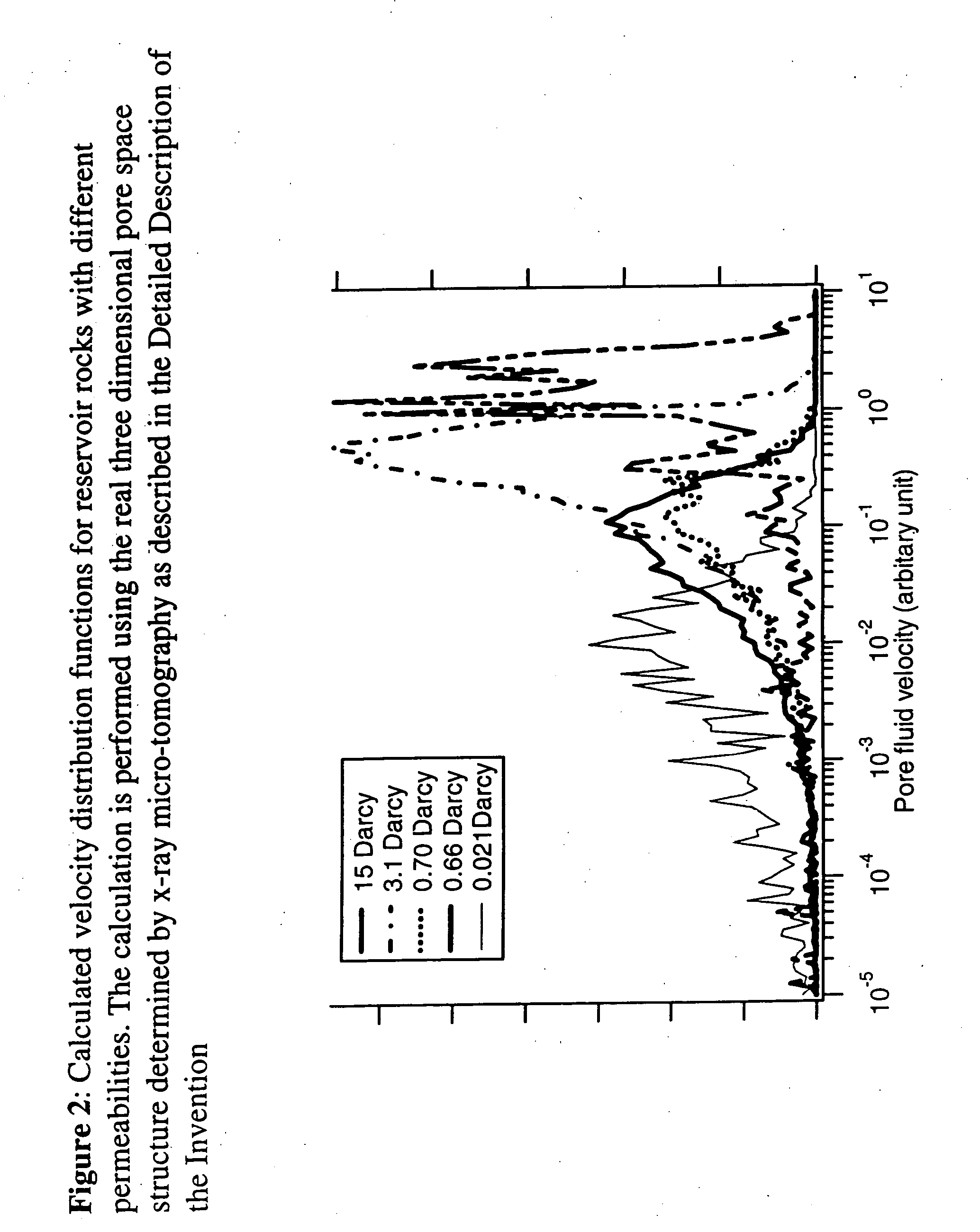
Fluid flow properties from acoustically stimulated NMR
ActiveUS6933719B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Engineered residual stress in golf clubs
InactiveUS8608590B2Surprising and improved result in performanceShorten the timeGolf clubsLaser beam welding apparatusHigh intensityGolf Ball
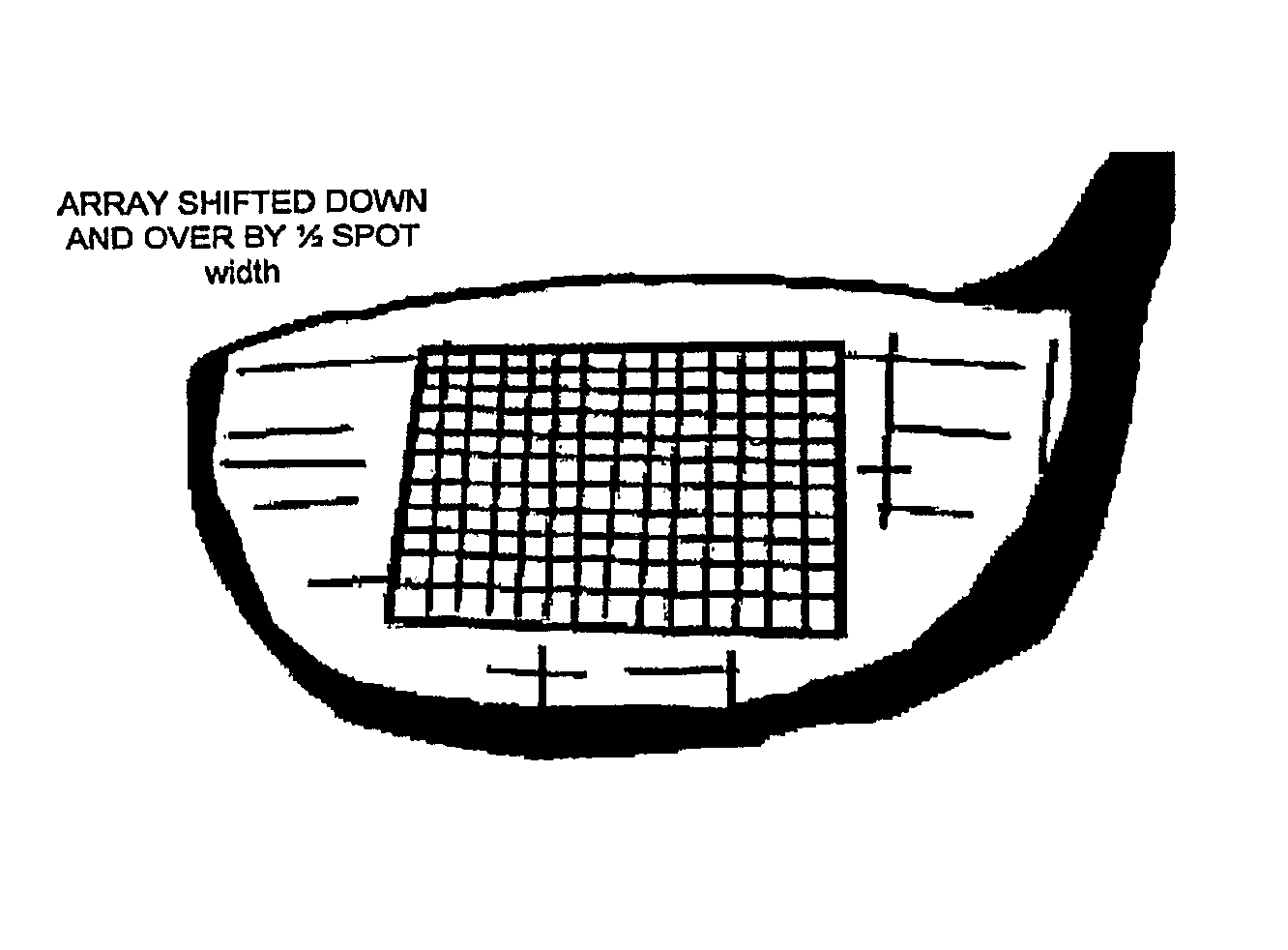
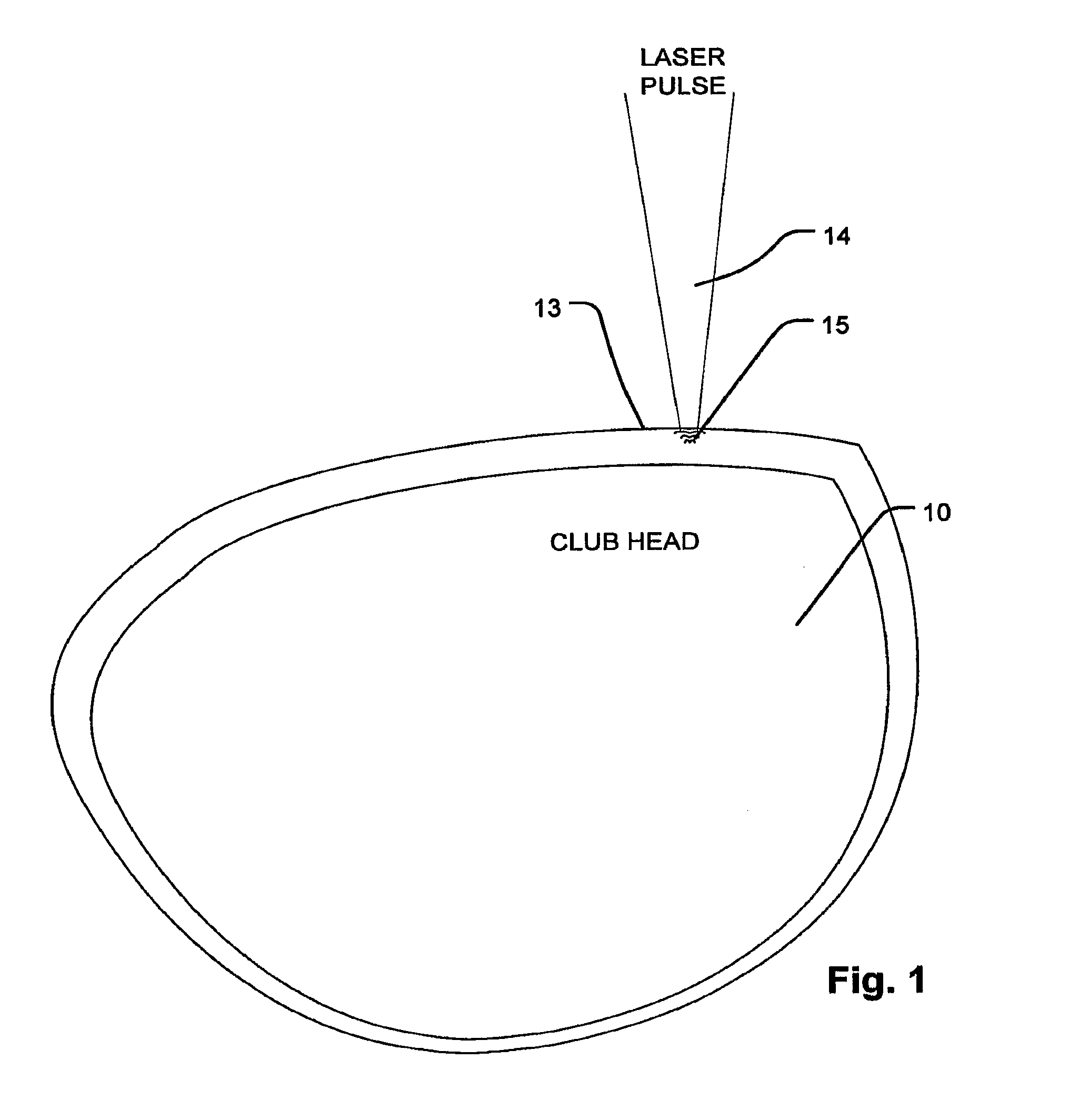
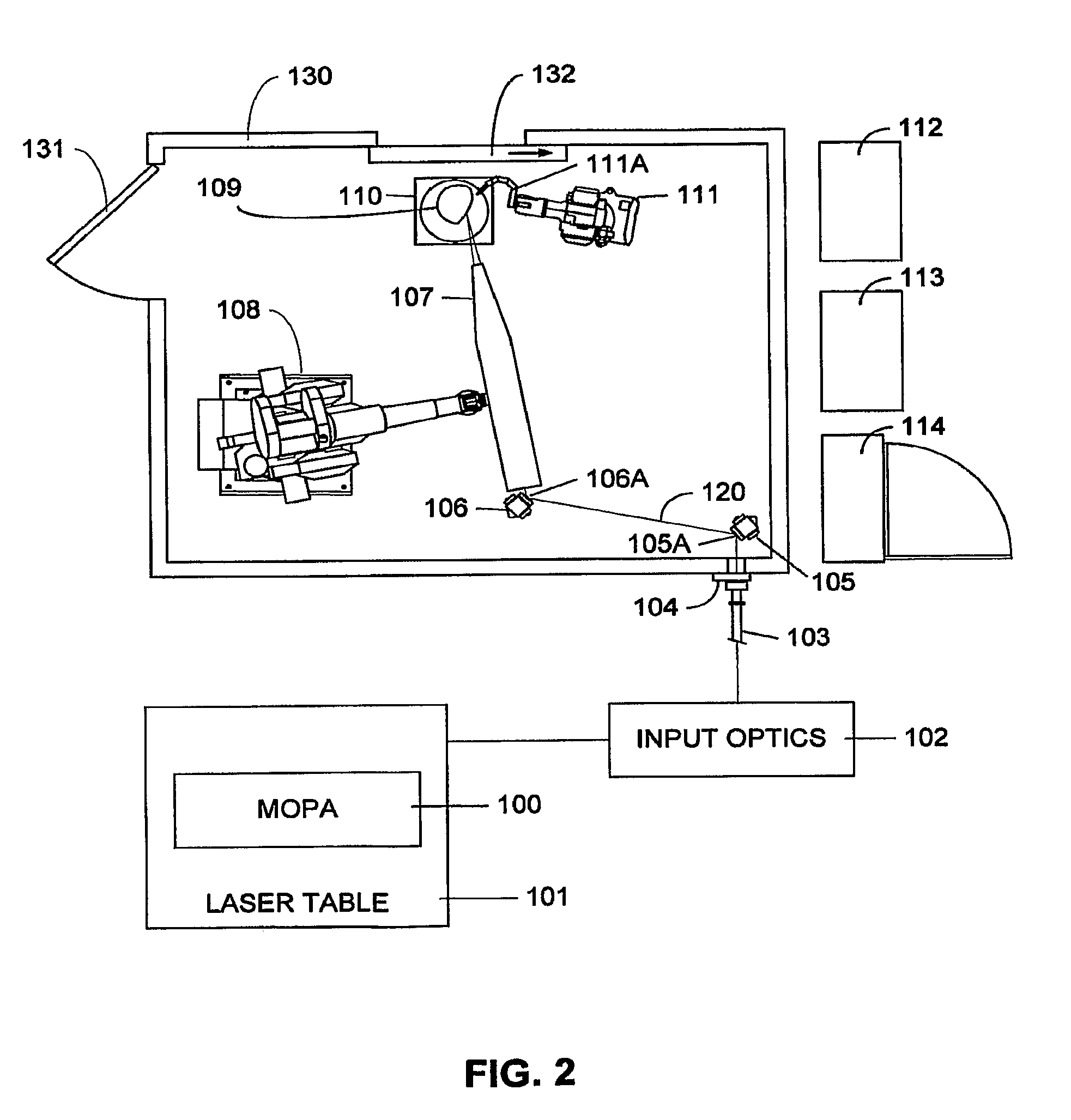
A method of manufacturing a driver, or other types of golf club, includes inducing residual compressive stress by high intensity laser shock peening to form an array of laser shock peened impact zones on the club face. Laser pulses having irradiance greater than 4 GW / cm2, with spot size greater than 4 mm2 are used, including a pulse with on the order of 16 ns, with spot size greater than 9 mm2. Residual compressive stress of more than 400 MPa penetrating with a depth of more than 0.2 mm are imparted, without increased hardening in or damage to the face of the club. Laser shock peening a pattern that covers an interior area leaves the perimeter unpeened, inducing a stress gradient between interior area and the perimeter of the club face. Multiple layers of arrays of laser shock impact zones are applied on the club. The technology is readily applied to assembled club heads.
Owner:METAL IMPROVEMENT CO INC
Production of X-ray stress measuring calibrated sample
InactiveCN1645091AEasy to carryBeautiful surfaceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationSurface stressStress measurement
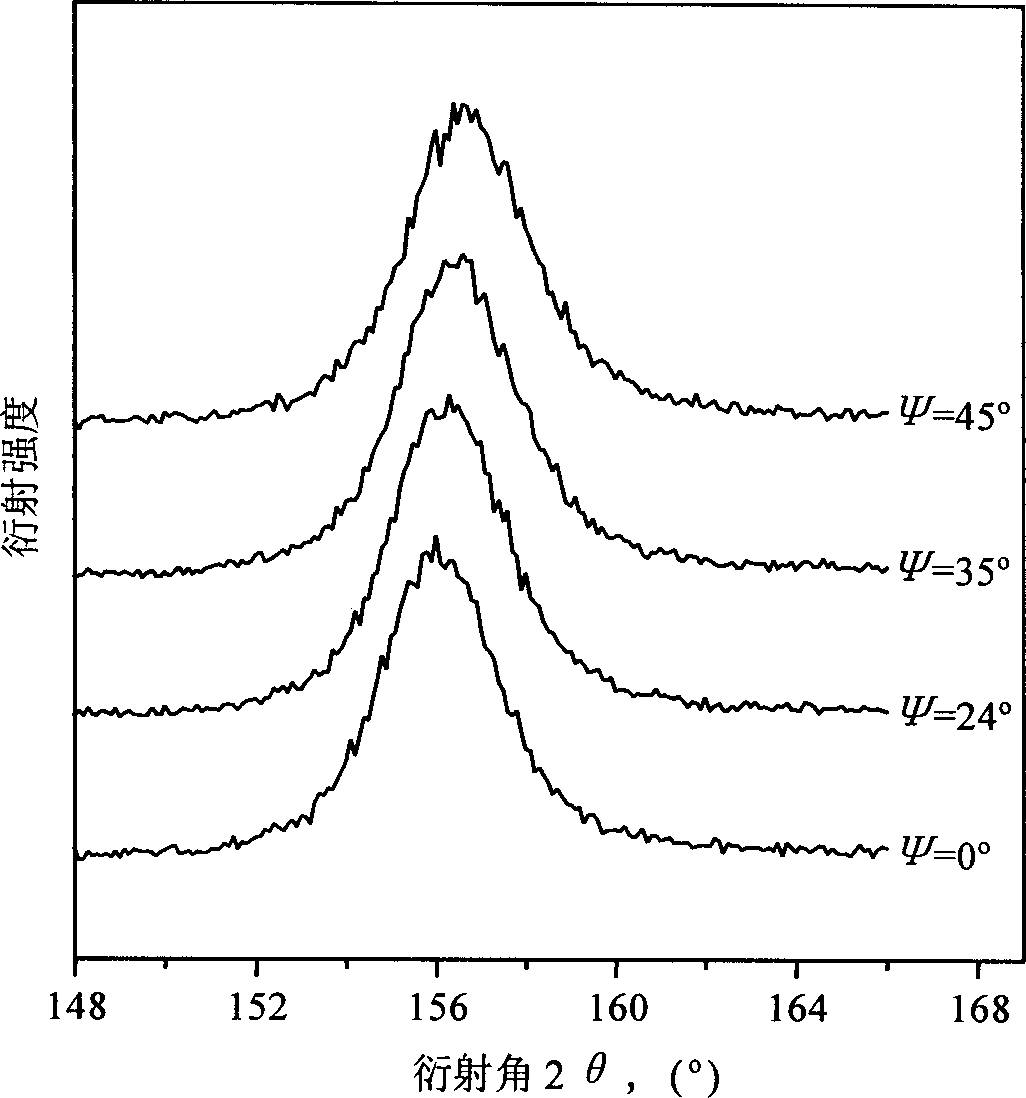
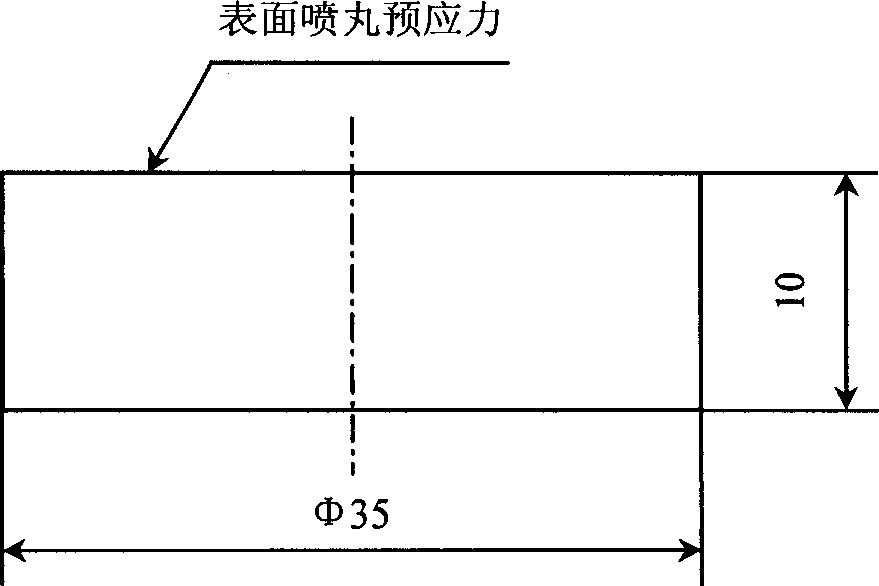
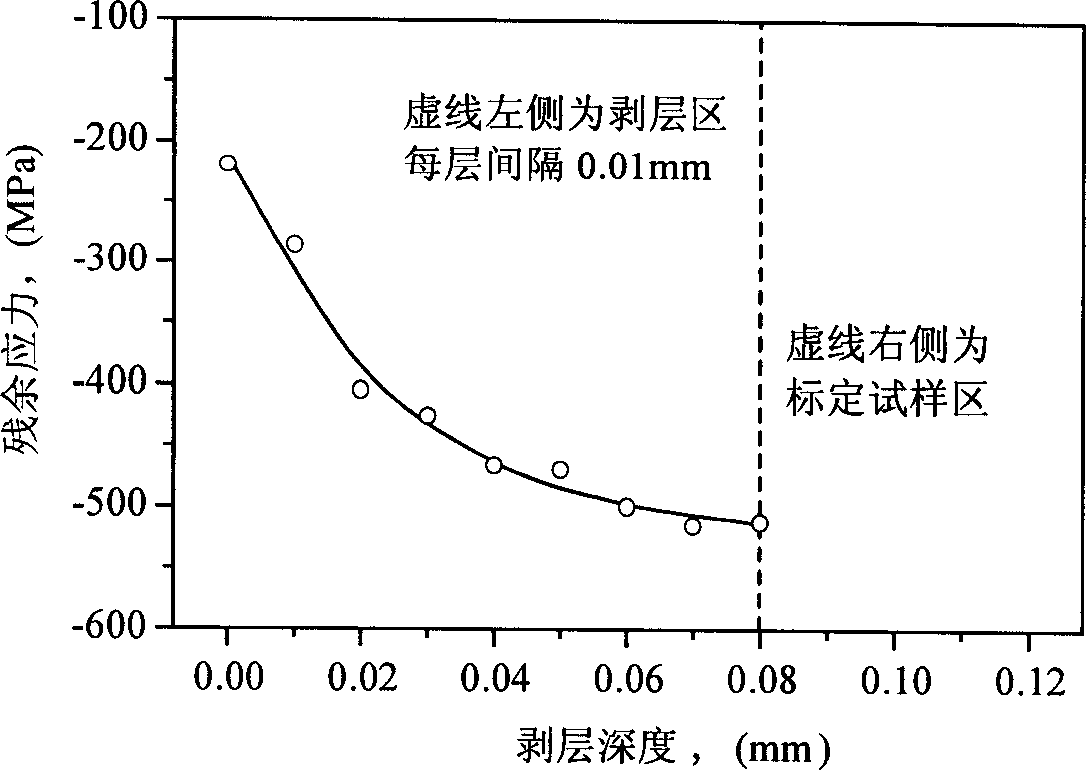
A method for preparing calibration test sample of X ray stress measurement includes removing phenomenon of crystal particle coarsening and crystal face preferred orientation, carrying out short blasting treatment for semiproduct of the sample, stripping layer by layer for portion with greater stress gradient by electrochemical corrosion, carrying out X ray stress measurement and calibrating out work surface of the sample by utilizing relation curve of stress to layer depth.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
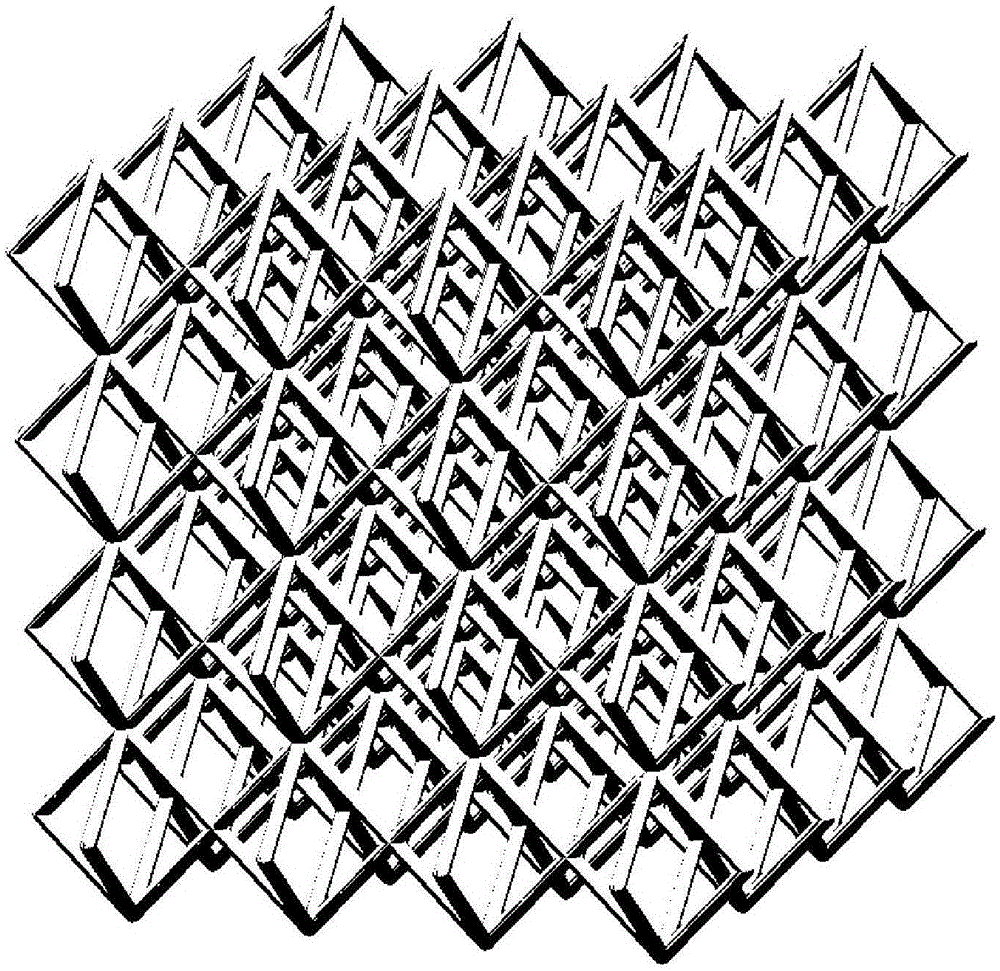
Section-variable metal lattice structure and machining method thereof
The invention discloses a section-variable metal lattice structure and a machining method thereof. The section-variable metal lattice structure comprises a plurality of section-variable lattice units arranged in the space. Each section-variable lattice unit is formed by connecting a plurality of section-variable rod pieces. The section-variable metal lattice structure is formed by conducting sintering layer by layer through a laser melting technology. A working bin of a metal powder sintering machine is kept sealed before machining with nitrogen being protection gas. For the internal force characteristics of all parts of the rod pieces, the rod pieces of the metal lattice units are optimized. Compared with an even lattice structure formed by weaving and welding metal wires, the section diameter of the section-variable rod pieces in the section-variable lattice structure is accurately determined by the internal force condition needing to be met under the load condition, materials forming the section-variable rod pieces are increased or decreased according to the stress gradient in the section-variable rod pieces, powder materials are saved, and the light characteristic is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
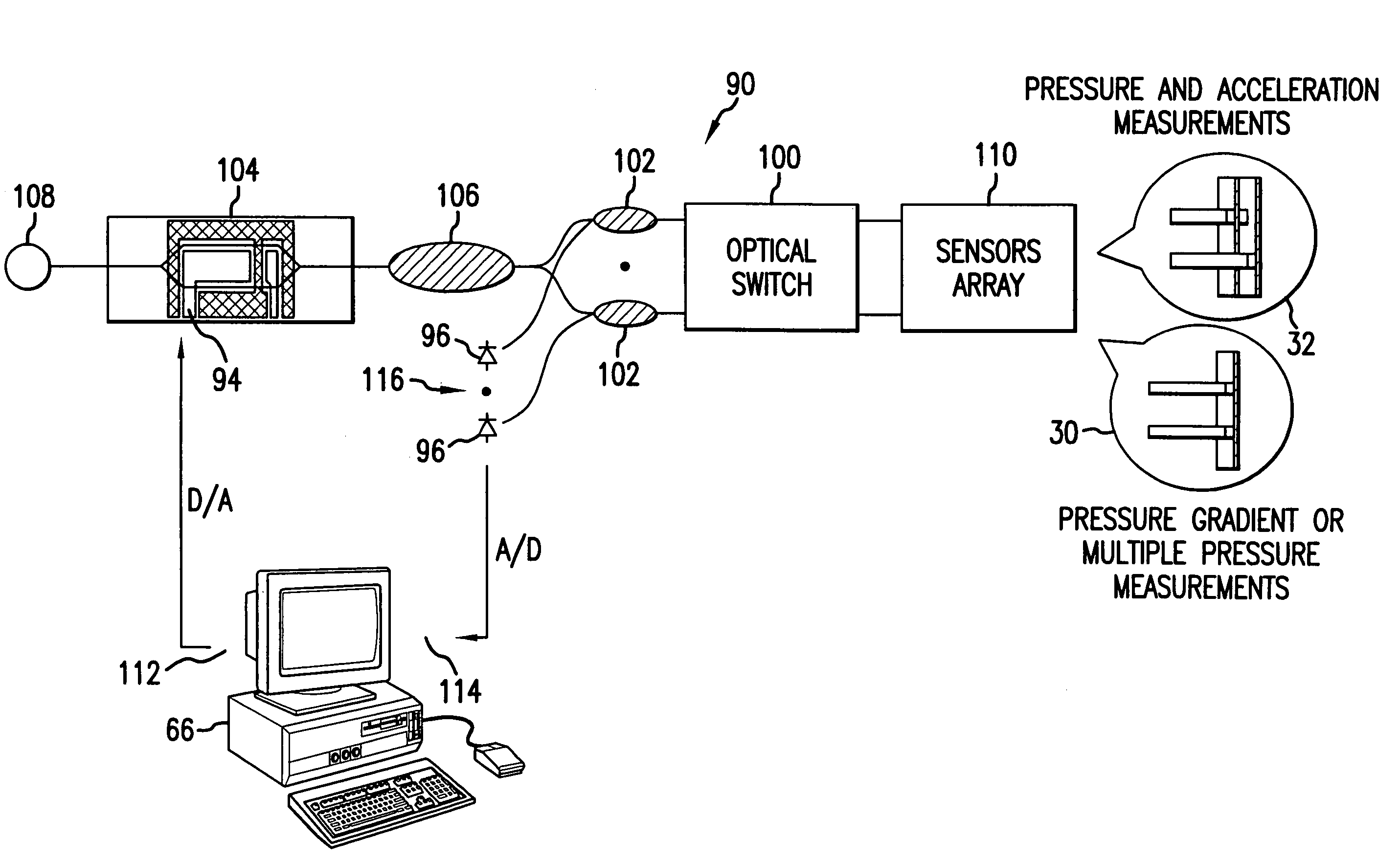
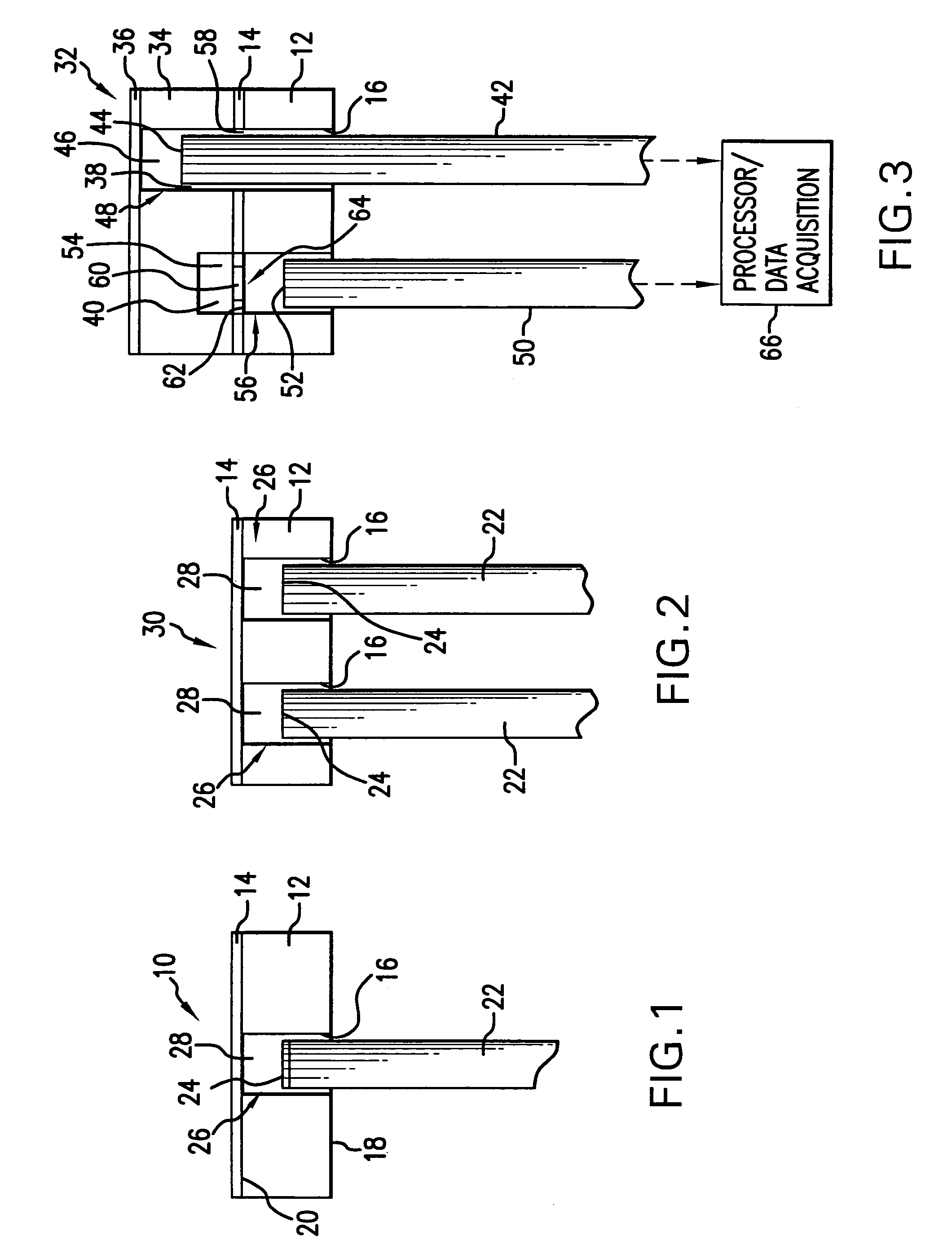
Micro-optical sensor system for pressure, acceleration, and pressure gradient measurements
InactiveUS7428054B2Good flexibilitySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansFiberPhase step
A micro-optical fiber tip based sensor system for pressure, acceleration, and pressure gradient measurements in a wide bandwidth, the design of which allows for multiplexity of the input side of the system is based on micro-electromechanical fabrication techniques. The optical portion of the system is based on low coherence fiber-optic interferometry techniques which has a sensor Fabry-Perot interferometer and a read-out interferometer combination that allows a high dynamic range and low sensitivity to the wavelength fluctuation of the light source. A phase modulation and demodulation scheme takes advantage of the Integrated Optical Circuit phase modulator and multi-step phase-stepping algorithm for providing high frequency and real time phase signal demodulation. The system includes fiber tip based Fabry-Perot sensors each of which has a diaphragm that is used as a transducer.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Diaphragm activated micro-electromechanical switch
InactiveUS7256670B2Electrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysDecorative surface effectsEngineeringMetal electrodes
A micro-electromechanical (MEM) RF switch provided with a deflectable membrane (60) activates a switch contact or plunger (40). The membrane incorporates interdigitated metal electrodes (70) which cause a stress gradient in the membrane when activated by way of a DC electric field. The stress gradient results in a predictable bending or displacement of the membrane (60), and is used to mechanically displace the switch contact (30). An RF gap area (25) located within the cavity (250) is totally segregated from the gaps (71) between the interdigitated metal electrodes (70). The membrane is electrostatically displaced in two opposing directions, thereby aiding to activate and deactivate the switch. The micro-electromechanical switch includes: a cavity (250); at least one conductive path (20) integral to a first surface bordering the cavity; a flexible membrane (60) parallel to the first surface bordering the cavity (250), the flexible membrane (60) having a plurality of actuating electrodes (70); and a plunger (40) attached to the flexible membrane (60) in a direction away from the actuating electrodes (70), the plunger (40) having a conductive surface that makes electric contact with the conductive paths, opening and closing the switch.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
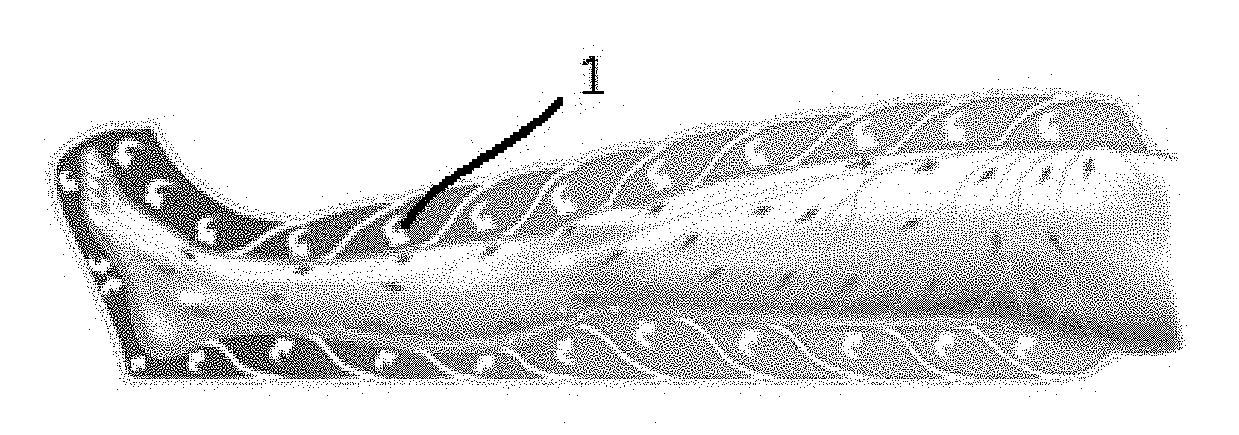
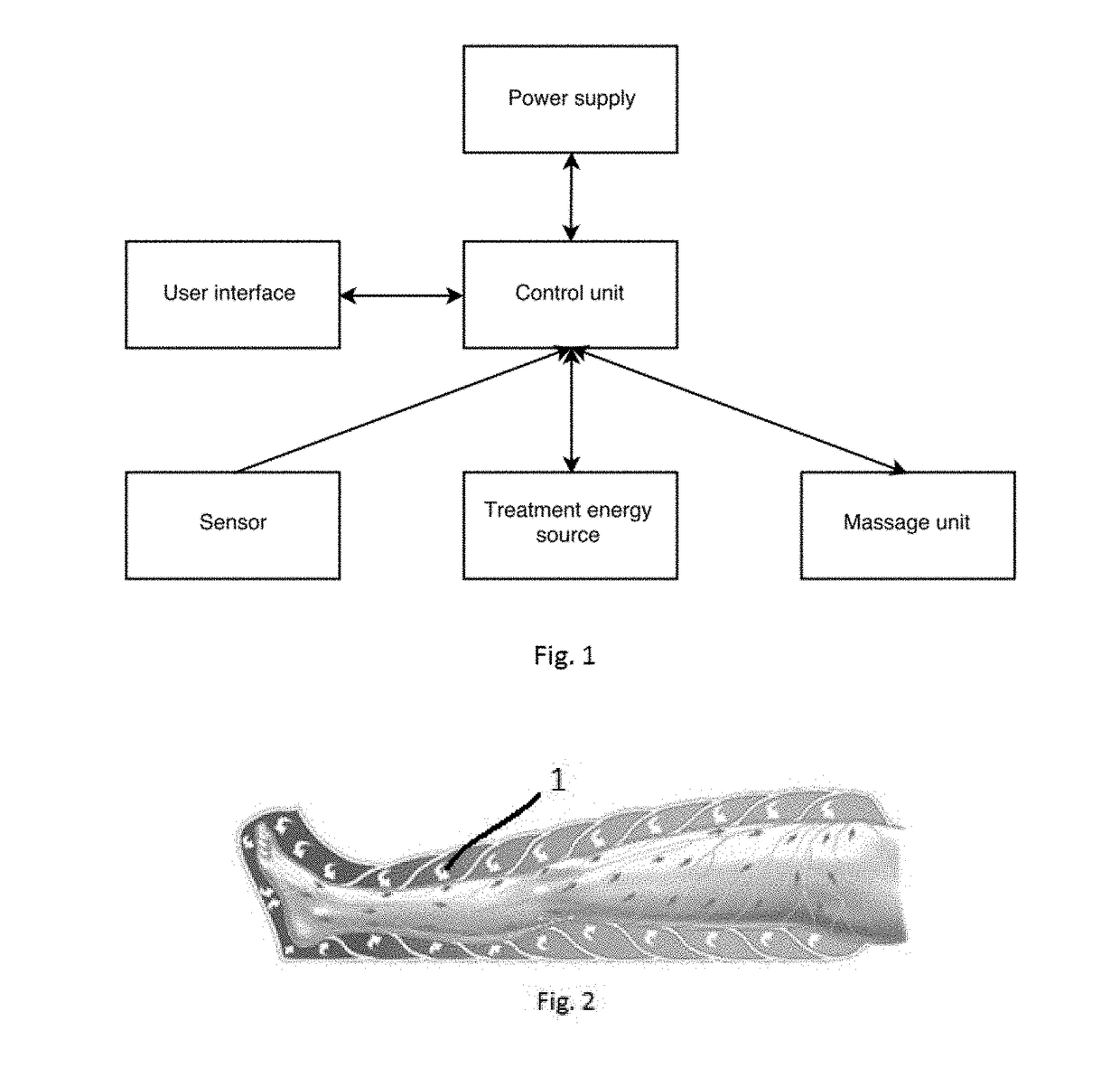
Method and device for body fluid stimulation
PendingUS20180229048A1Improve efficiencyImprove homogeneityUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyMassageBody area
A method of soft tissue treatment of a patient includes placing a treatment sleeve with at least one first treatment energy source onto the patient. Massage of the patient's soft tissue is provided by at least one massage unit, with the massage unit including at least two pressure changing elements applied on the patient's soft tissue. An additional or second treatment therapy, different from the massage, is provided by a second treatment energy source. The massage unit creates a pressure gradient between at least two successive elements changing a pressure value in range from 0% to 95% on the patient's soft tissue across a treated body area and stimulates body liquid flow.
Owner:BTL HEALTHCARE TECH AS
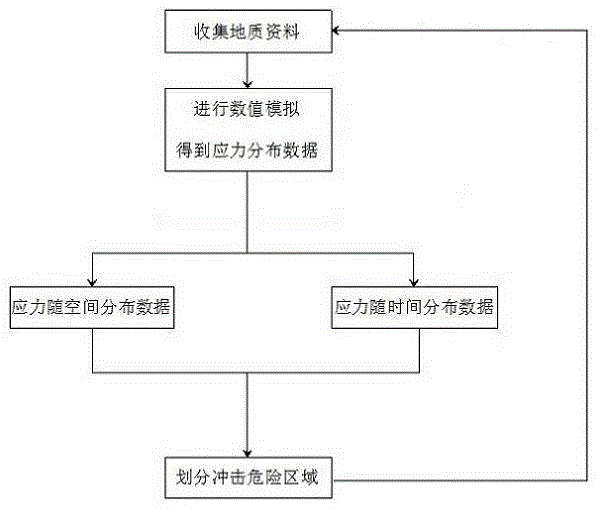
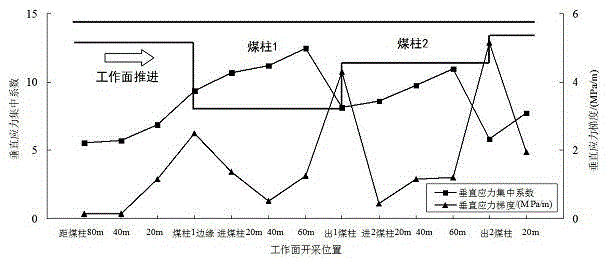
Stress-gradient-based method for dividing coal impact ground pressure danger area
InactiveCN104653226AGuarantee property securityGuarantee the safety of lifeMining devicesEnvironmental resource managementBusiness forecasting
The invention discloses a stress-gradient-based method for dividing a coal impact ground pressure danger area. The method comprises the following steps: collecting geological data; simulating a mining value; calculating stress space distribution data and stress time distribution data; dividing an impact danger area; simulating the divided impact danger area according to the above values after a working surface is mined, monitoring stress of the area on line in real time to obtain a stress filed of the monitoring area, repeating the above steps, collecting geological data, dividing, forecasting and early warning the impact ground pressure danger area according to stress data. According to the stress-gradient-based method for dividing the coal impact ground pressure danger area, an impact ground pressure is forecasted and early warned due to a coupling relation existing between the stress gradient of the area and the coal rock impact damage condition; the impact danger area is divided according to the abnormal stress gradient; the method is strong in applicability and high in accuracy, is capable of accurately forecasting and early warning the impact ground pressure danger area and ensuring the property safety of mine and the life safety of workers, and has great significance to the coal mine safety.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
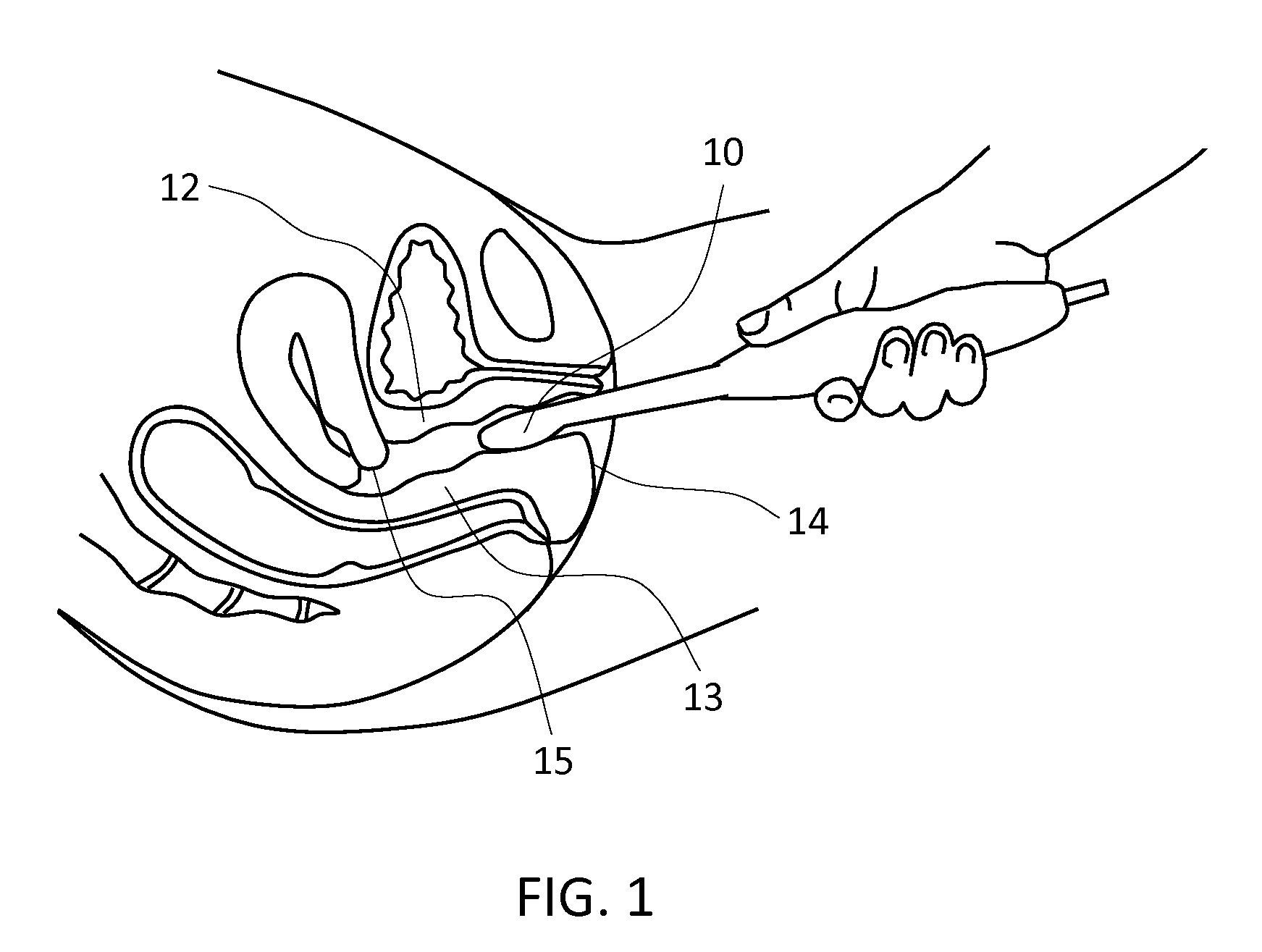
Methods for characterizing vaginal tissue elasticity
Methods for characterizing elasticity of vaginal tissue are provided. A transvaginal probe is used to deform vaginal tissue during examination. The probe is equipped with pressure sensors and a motion tracking sensor. Stress and strain data is recorded during examination. Elasticity of vaginal tissue is then characterized by calculating a stress gradient defined as a ratio of stress over strain for each point of measurement. Vaginal tactile image may also be compiled to include a family of surfaces representing locations of measurement points at predefined constant levels of stress. Pelvic organ abnormality condition may be detected if the stress gradient is below either a predetermined threshold or a normal stress gradient obtained from clinical data.
Owner:ARTANN LAB
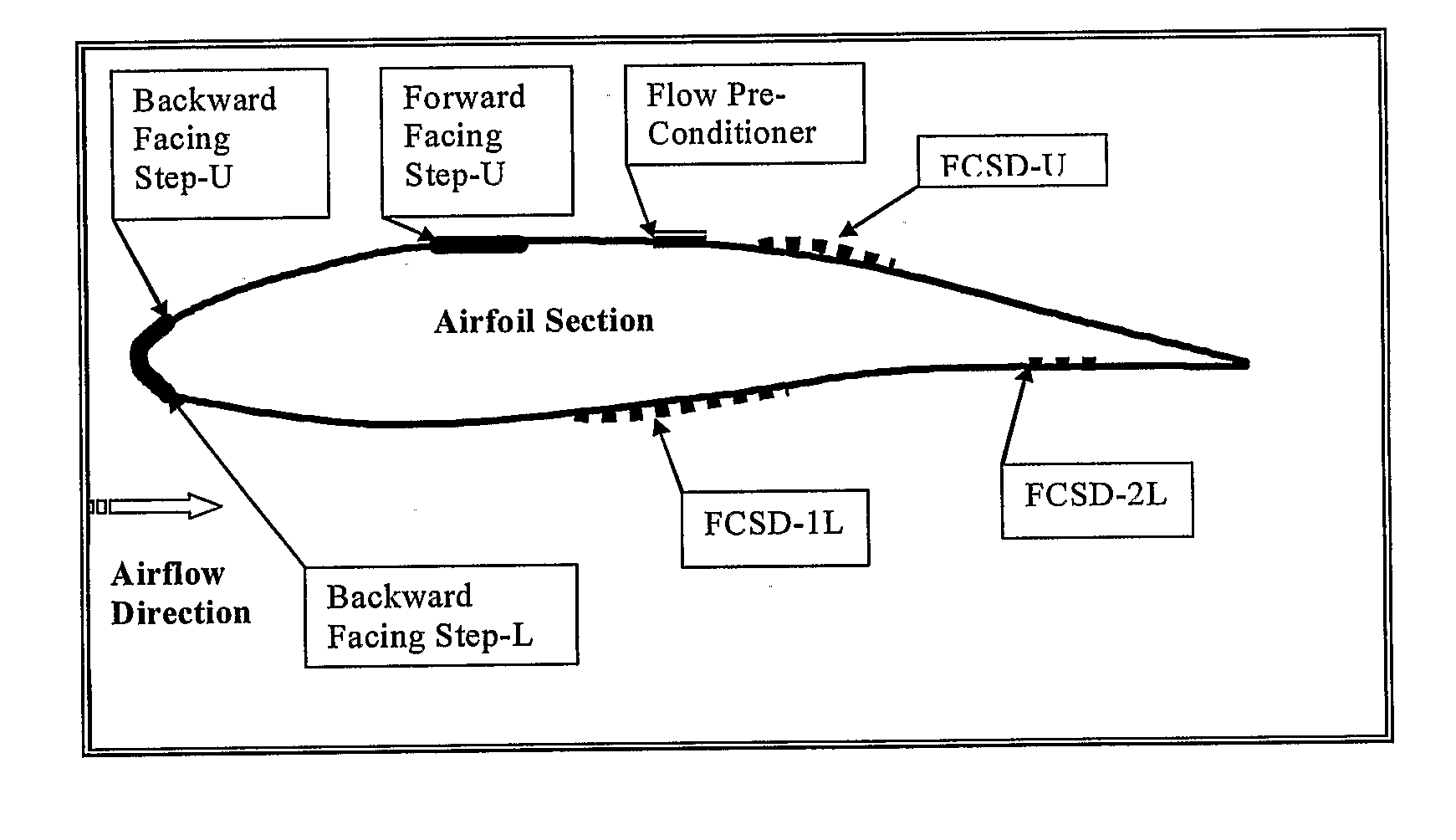
Method of Reducing Drag and Increasing Lift Due to Flow of a Fluid Over Solid Objects
InactiveUS20090294596A1Reduce skin friction dragReduce resistanceVehicle seatsFluid dynamicsLeading edgeGasoline
A method for reducing drag, increasing lift and heat transfer using a de-turbulating device is disclosed, with the preferred form of the deturbulator being a flexible composite sheet. The flexible composite sheet comprising a membrane, a substrate coupled to the membrane, and a plurality of ridges coupled between the membrane and the substrate, wherein a vibratory motion is induced from the flow to at least one segment of a membrane spanning a distances, wherein the vibratory motion is reflected from at least one segment of the membrane to the flow, and; wherein a reduction in fluctuations is caused in the flow pressure gradient and freestream velocity U at all frequencies except around f, where f>>U / s. hi one embodiment, the flexible composite sheet can be wrapped around a blunt leading edge of a plate facing an incoming flow of fluid, hi another embodiment, the flexible composite sheet can also be wrapped around one or more regions of an aerodynamic surface where a flow pressure gradient changes from favorable to adverse, hi another embodiment, the flexible composite sheet is replaced with a plurality of plates coupled to a substrate, wherein the plurality of plates has edges that interact with a fluid flow similar to a compliant surface. A method of adding a system of small viscous sublayer scale (around 30-80 micron height) backward and / or forward facing steps on the surface of an airfoil or other 2-D or 3-D streamlined aerodynamic body is disclosed, where the backward facing step is in a favorable pressure gradient and forward facing step is in an adverse pressure gradient, so as to speed up the freestream flow over the front portion of the airfoil or body and reduce skin friction drag by creating a marginally separated thin (0.1 to 10 microns) slip layer next to the wall behind the backward facing step and extending a significant distance behind said step. This method reduces the drag and increases lift if the body is a wing. Also the same method can be applied to a bluff body, such as an automobile to reduce flow separation induced drag by stabilizing the wake flow and making it appear to the flow as a solid streamiling extension of the original body. The gas mileage of a vehicle improves when treated in this manner.
Owner:SINHATECH (US)
Compact shooter localization system and method
ActiveUS7292501B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementAccelerometerLocalization system
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
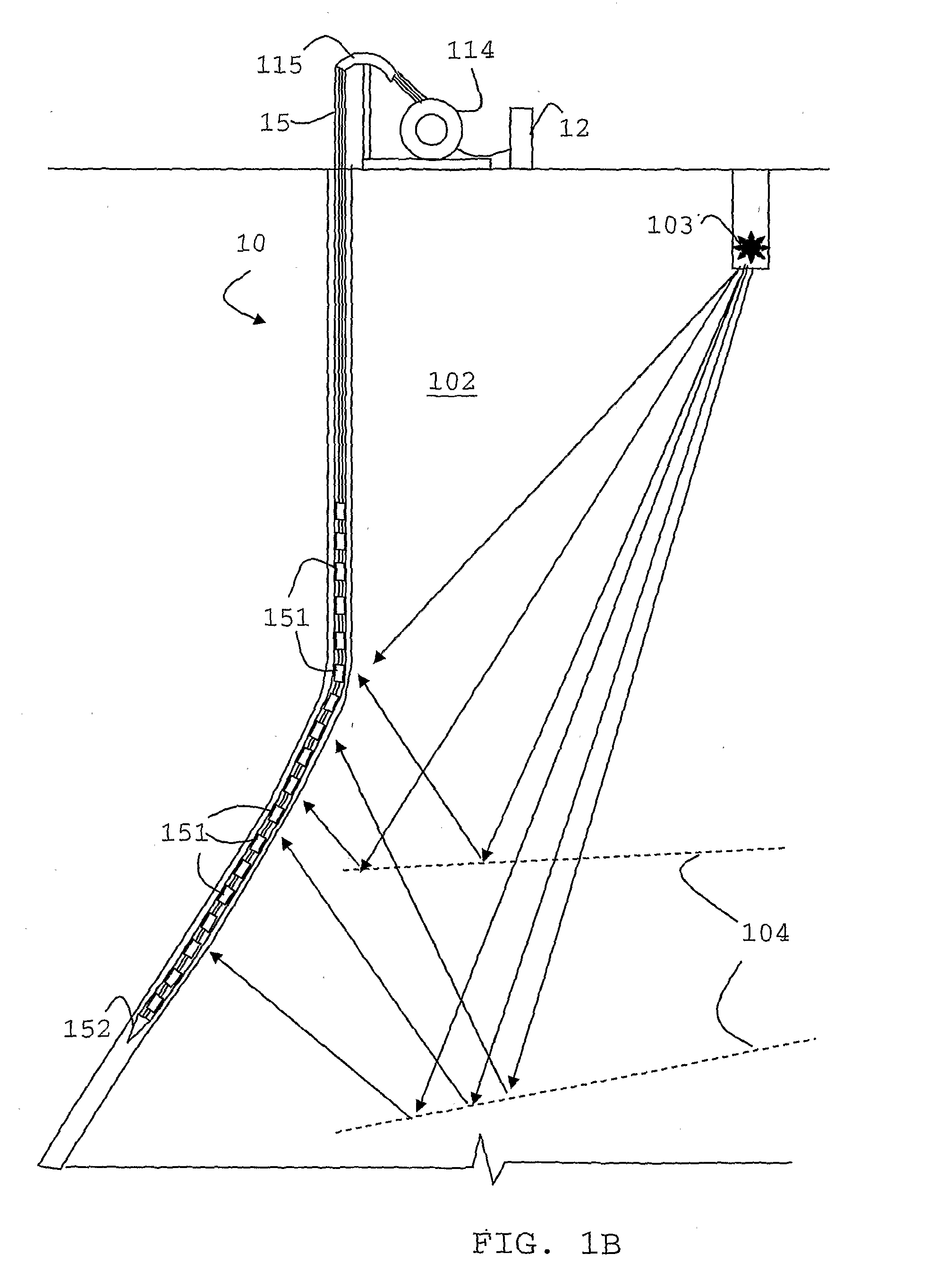
Marine Seismic Acquisition System
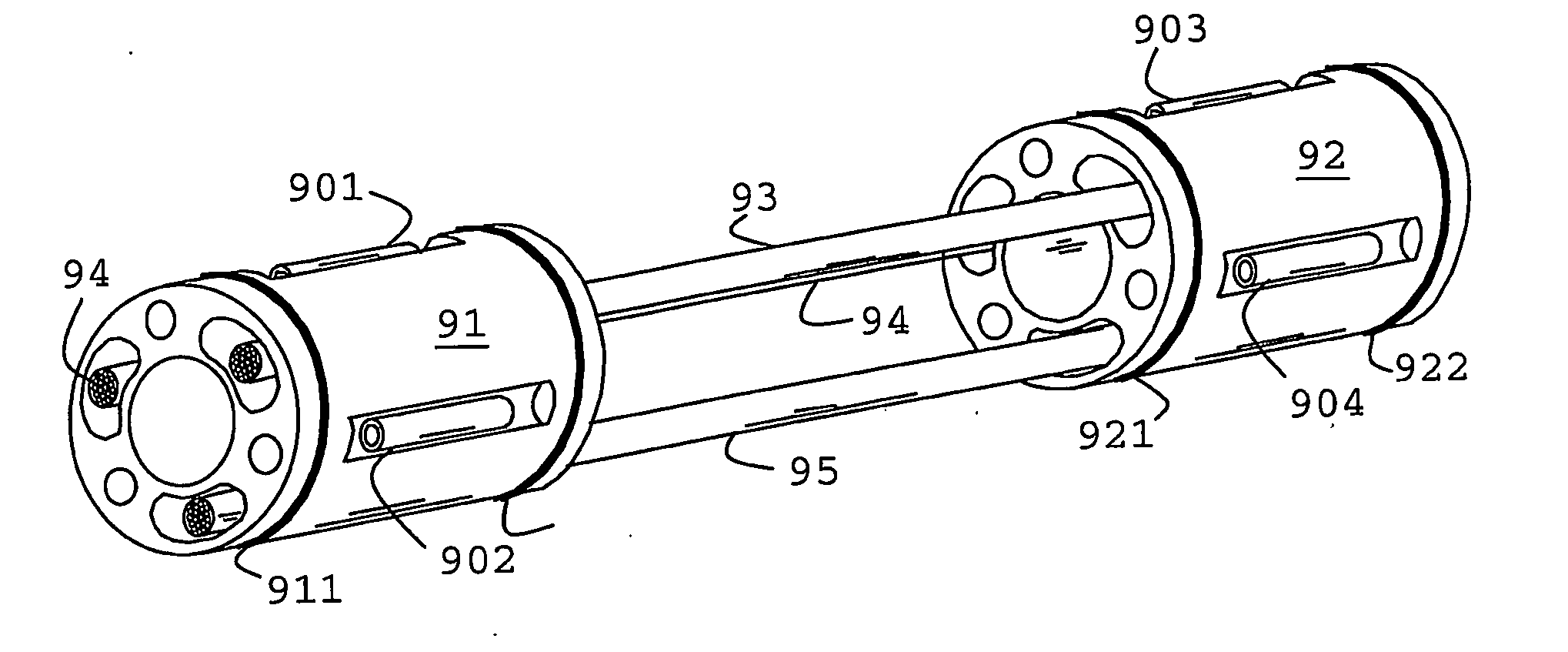
ActiveUS20080291779A1Difference in pressureSeismic signal receiversSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyTransducer
A marine cable for seismic surveys is described with a plurality of ceramic pressure sensors (901-904) arranged in groups of at least two pressure sensors with a group output being representative of the vertical pressure gradient at the group location, and an inclinometric system including one or more transducers for determining the orientation of the sensors of the group in order to determine their true vertical separation.
Owner:REFLECTION MARINE NORGE AS
Fluid flow properties from acoustically stimulated NMR
ActiveUS20050007109A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
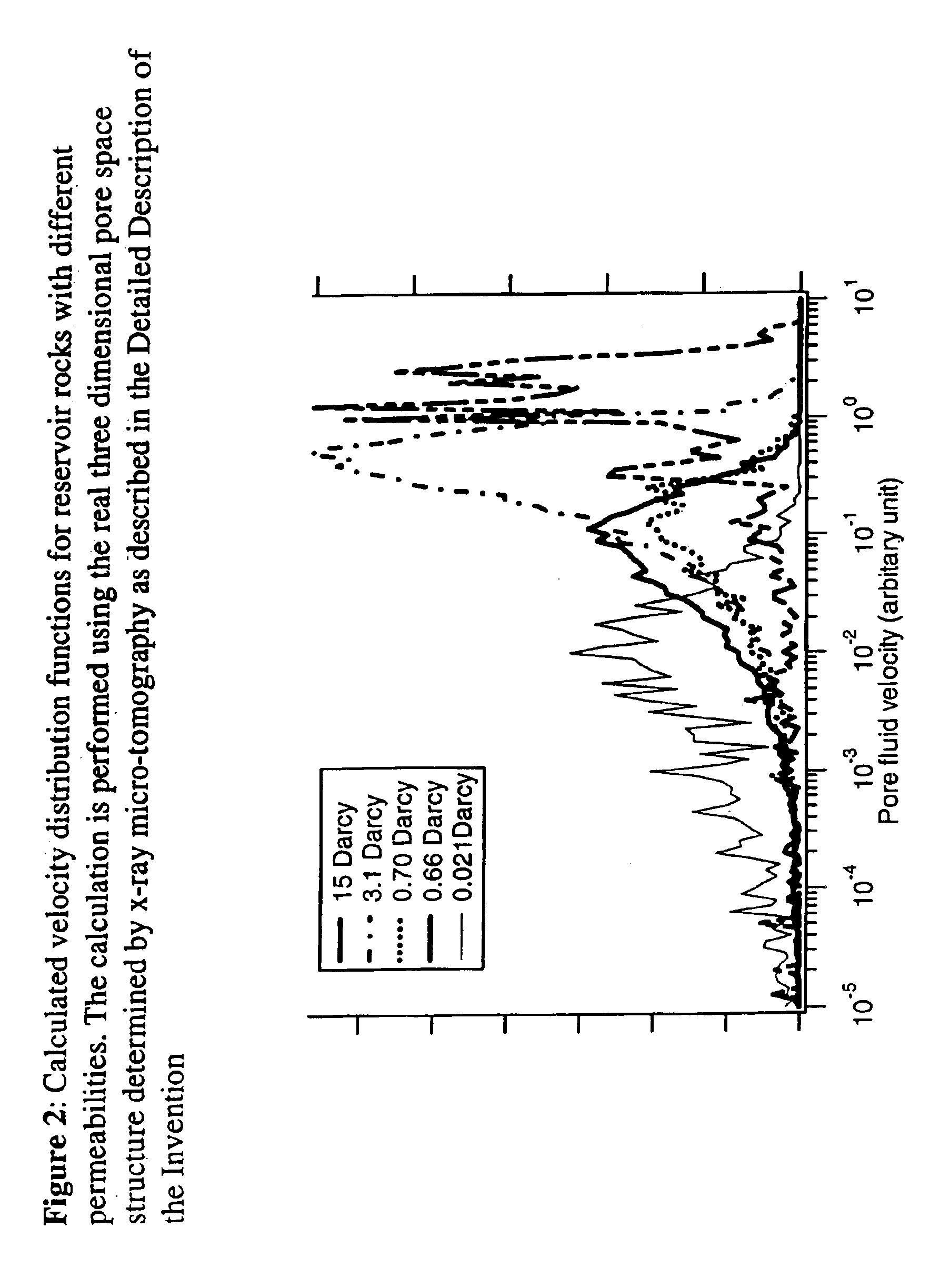
This invention is a method to measure fluid flow properties of a porous medium, including, but not limited to, the fluid flow permeability. In a preferred embodiment, the measurements are made down hole in drill wells exploring for hydrocarbons or acquifers. The measurement involves two types of instruments. One instrument creates a pressure wave in the porous medium, which generates motion of the fluid in the pore space. The second instrument measures the fluid motion in the pore space using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) methods. Any type of instrument that can generate a pressure gradient is suitable, including instruments that are remote from the NMR instrument. Magnetic field gradients can be used to localize the NMR signal to a specific region within the porous medium. The magnetic field gradient also provides the method by which the fluid motion is encoded on to the NMR signal. The permeability is calculated from the known pressure gradient present in the porous medium by virtue of the applied pressure gradient or pressure wave and the velocity of the fluid in the rock pore space as measured by NMR.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Flexoelectric - piezoelectric composite based on flexoelectric charge separation
InactiveUS20110006641A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesElectricityCharge separation
An example flexoelectric-piezoelectric apparatus provides an electrical response to an applied force, and / or an actuation in response to an applied electric field, that originates from the flexoelectric properties of a component. For example, shaped forms within the apparatus may be configured to yield a stress gradient on application of the force, and the stress gradient induces the flexoelectric signal. A flexoelectric-piezoelectric apparatus can be substituted for a conventional piezoelectric apparatus, but does not require the use of a piezoelectric material. Instead, the response of the apparatus is due to the generation of stress gradients and / or field gradients.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method of evaluating and selecting an enhanced oil recovery strategy for fractured reservoirs
The invention is a method of evaluating a recovery potential for hydrocarbons contained in a fractured reservoir, using an enhanced recovery technique. Characteristic reservoir data, data obtained from well test results and data relative to the development conditions are acquired. A pressure gradient related to the flow of a fluid injected to improve recovery is then estimated from the previously acquired data. A recovery coefficient is calculated for the hydrocarbons initially in place in matrix blocks by estimating water saturation for a state of equilibrium of the matrix blocks. Finally, the oil recovery time under the effect of the fluid circulation in fractures is estimated by determining the required for the matrix blocks to change from the initial state to a state of equilibrium.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
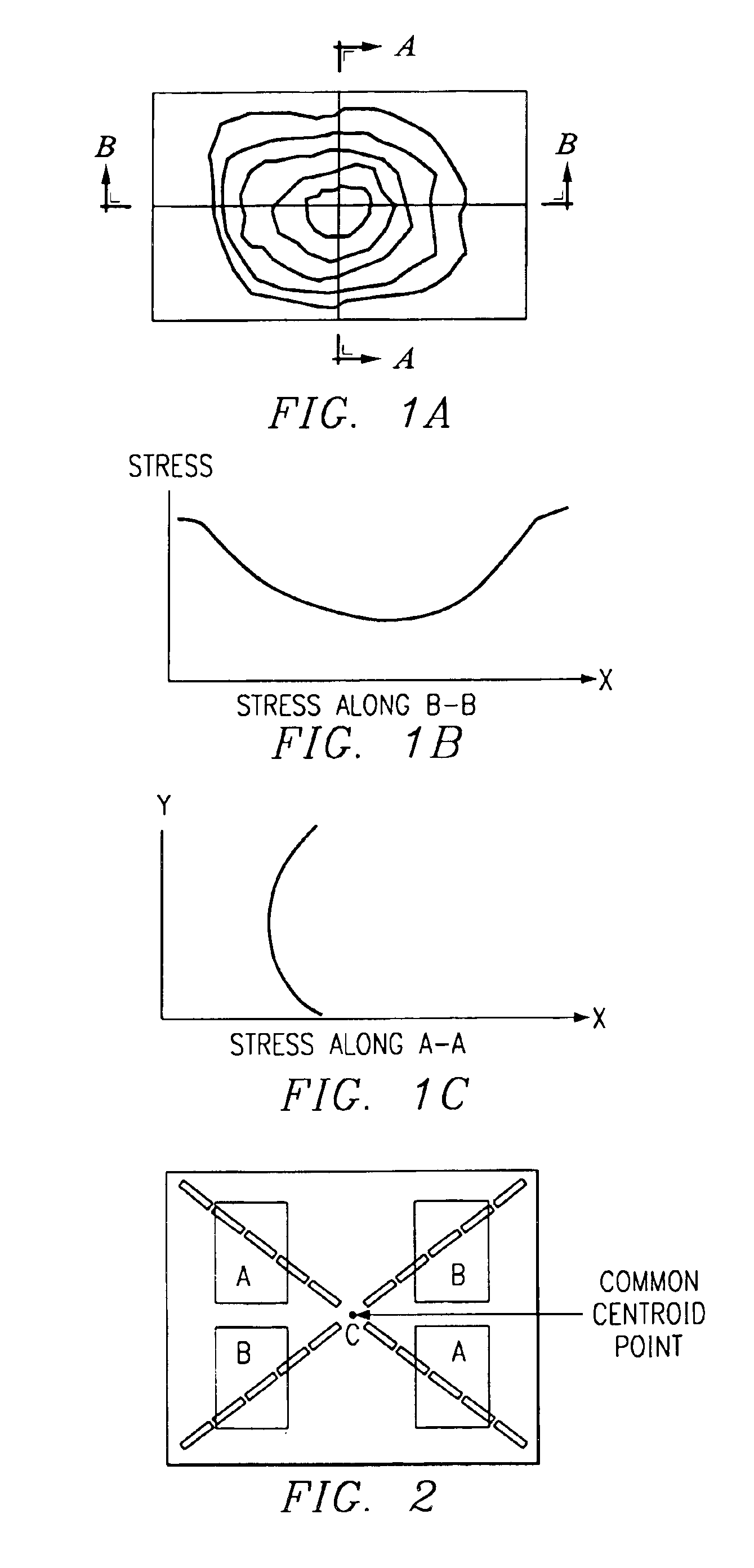
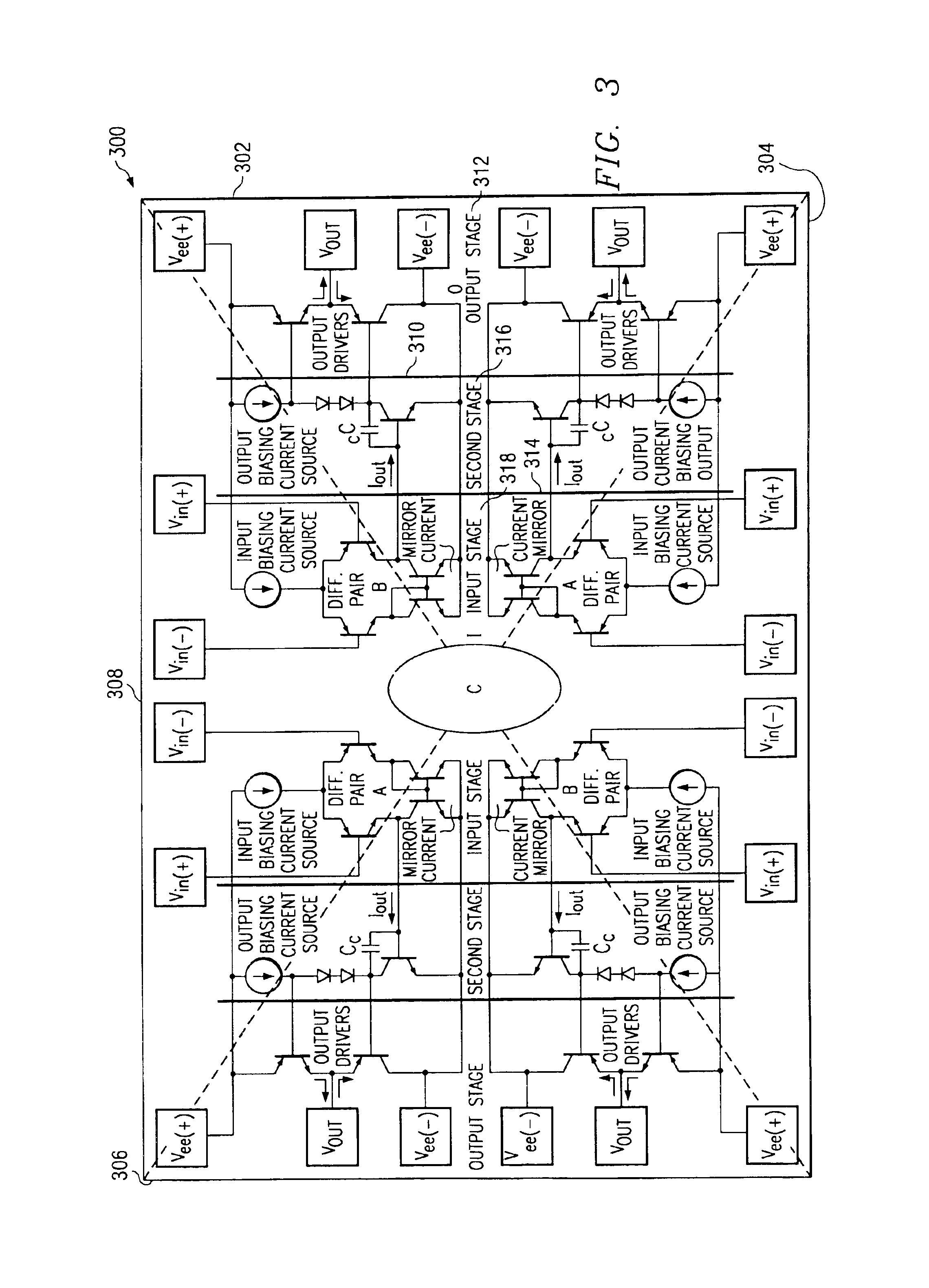
Ideal operational amplifier layout techniques for reducing package stress and configurations therefor
A method of reducing package stress includes placing matched components of an op-amp substantially in a region of a die having the least stress gradients. The region is located in the center of the die. Further, the center is the common centroid of the die. The matched components are the current mirror input stages of the op-amp. In one embodiment, a semiconductor configuration includes a die having a region with the least stress gradients, and an op-amp containing matched components that are located substantially in the region.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com