Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
61 results about "Storage class memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
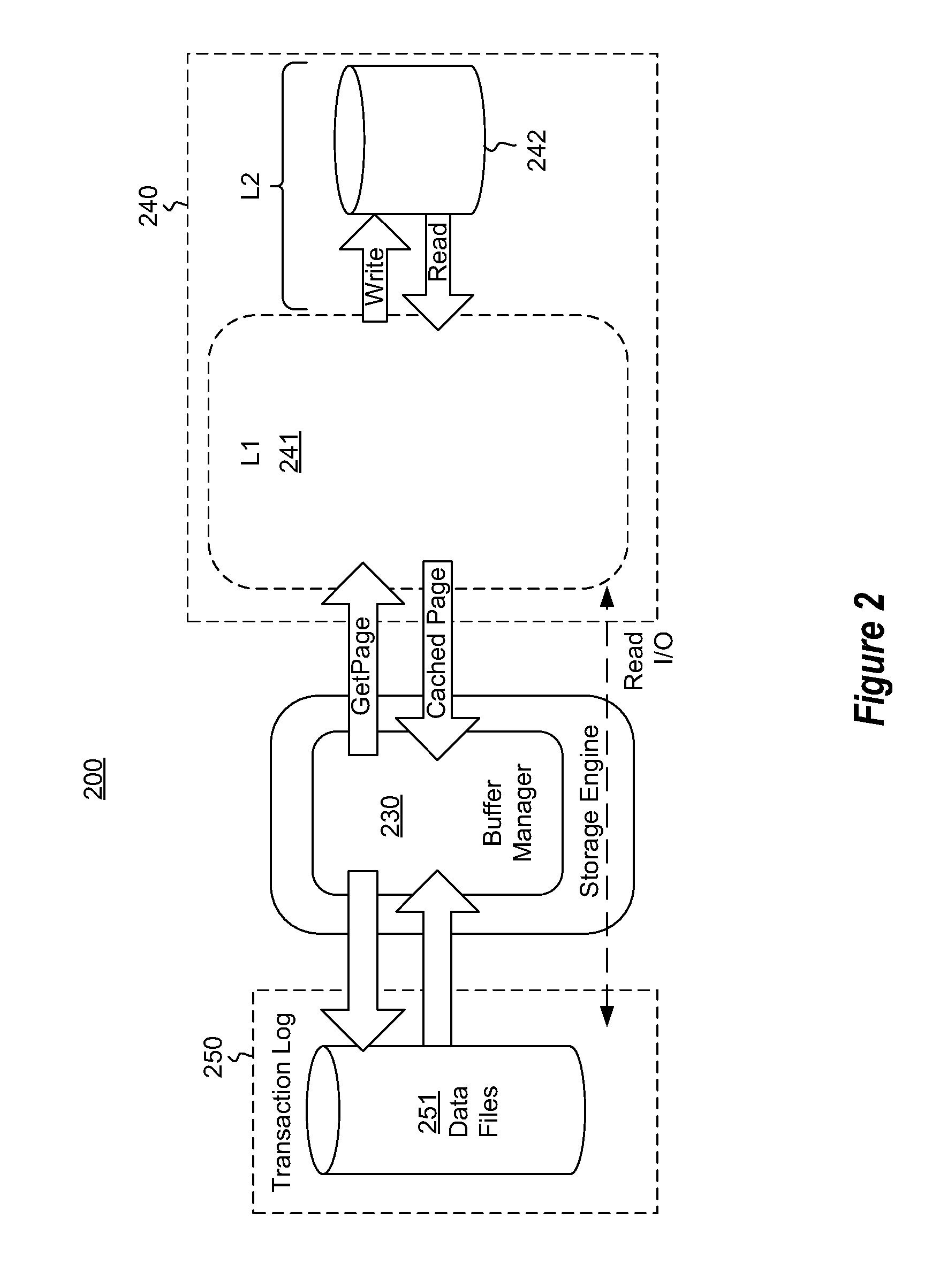
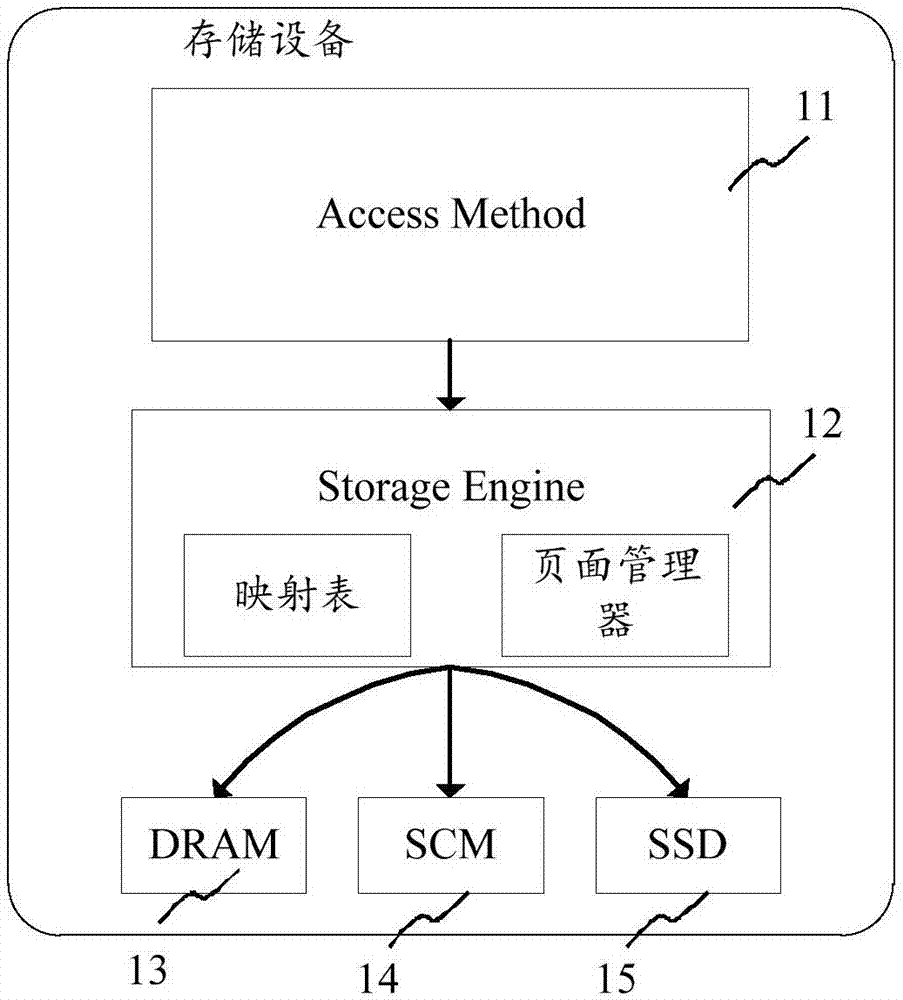
Multi-level buffer pool extensions
ActiveUS20120072652A1Convenience to workAvoid settingSoftware engineeringMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputational scienceParallel computing
A buffer manager that manages blocks of memory amongst multiple levels of buffer pools. For instance, there may be a first level buffer pool for blocks in first level memory, and a second level buffer pool for blocks in second level memory. The first level buffer pool evicts blocks to the second level buffer pool if the blocks are not used above a first threshold level. The second level buffer pool evicts blocks to a yet lower level if they have not used above a second threshold level. The first level memory may be dynamic random access memory, whereas the second level memory may be storage class memory, such as a solid state disk. By using such a storage class memory, the working block set of the buffer manager may be increased without resorting to lower efficiency random block access from yet lower level memory such as disk.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
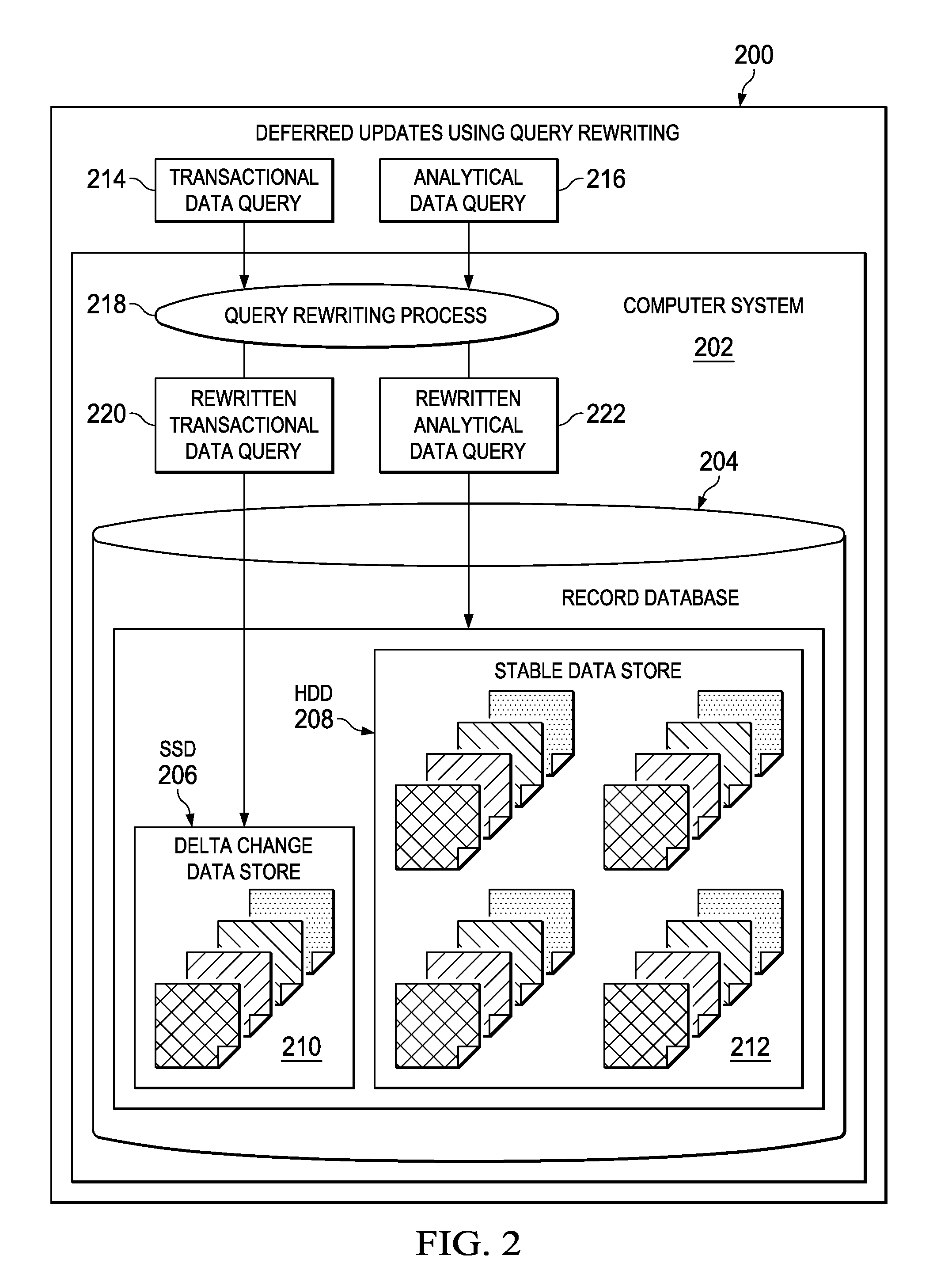
Deferring data record changes using query rewriting
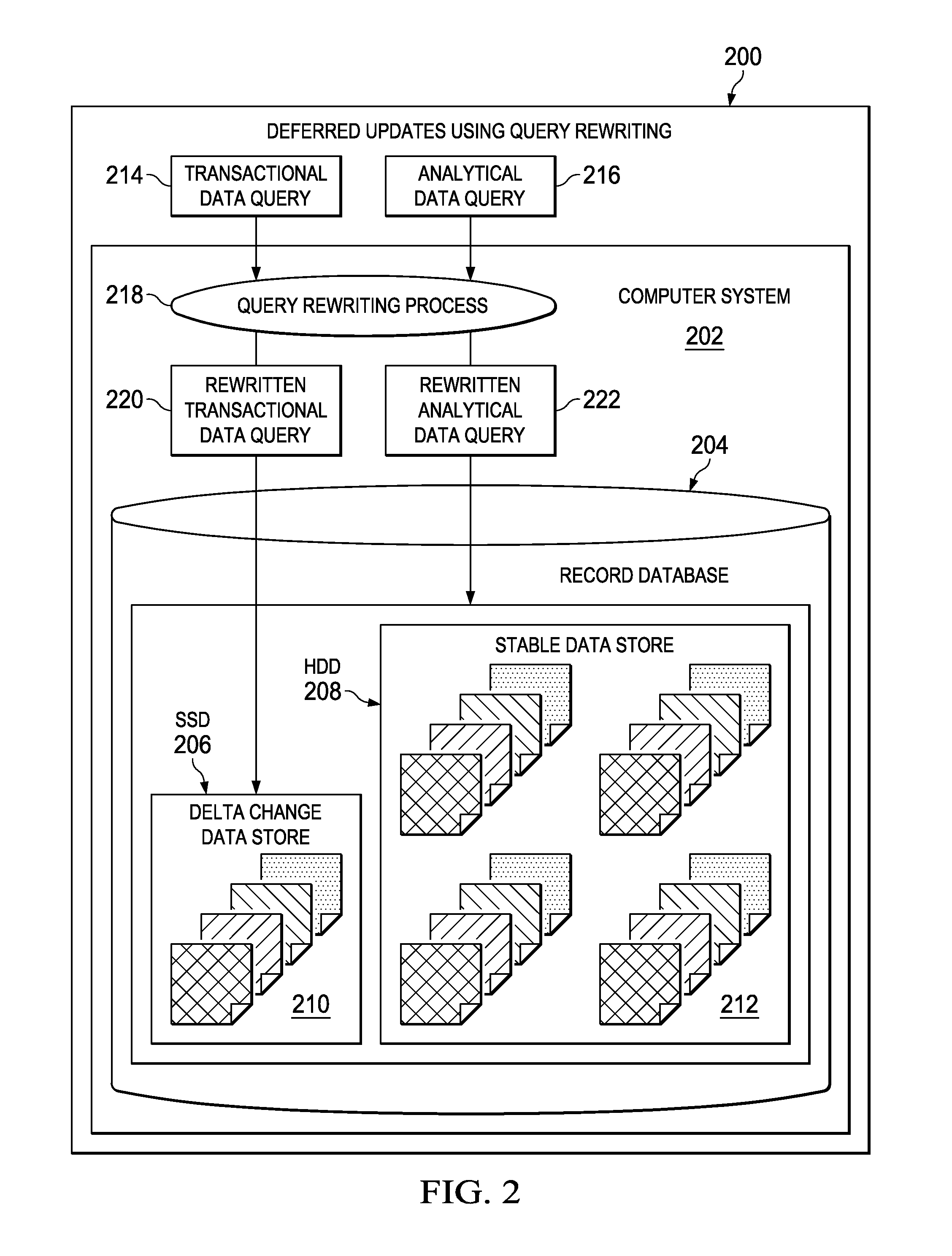
InactiveUS20150074041A1Digital data processing detailsMulti-dimensional databasesAnalysis dataData query
Staging data record changes from a faster storage medium to a slower storage medium using data query rewriting is provided. In response to receiving a data query corresponding to a particular data record, it is determined whether the data query is one of a transactional data query or an analytical data query. In response to determining that the data query is a transactional data query, the transactional data query is rewritten to apply transactional delta changes to the particular data record on a storage-class memory of a computer. In response to determining that the data query is an analytical data query, the analytical data query is rewritten to select and reconcile each data record corresponding to the particular data record stored on the storage-class memory with the particular data record stored on a persistent data storage device of the computer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for low power low latency high capacity storage class memory
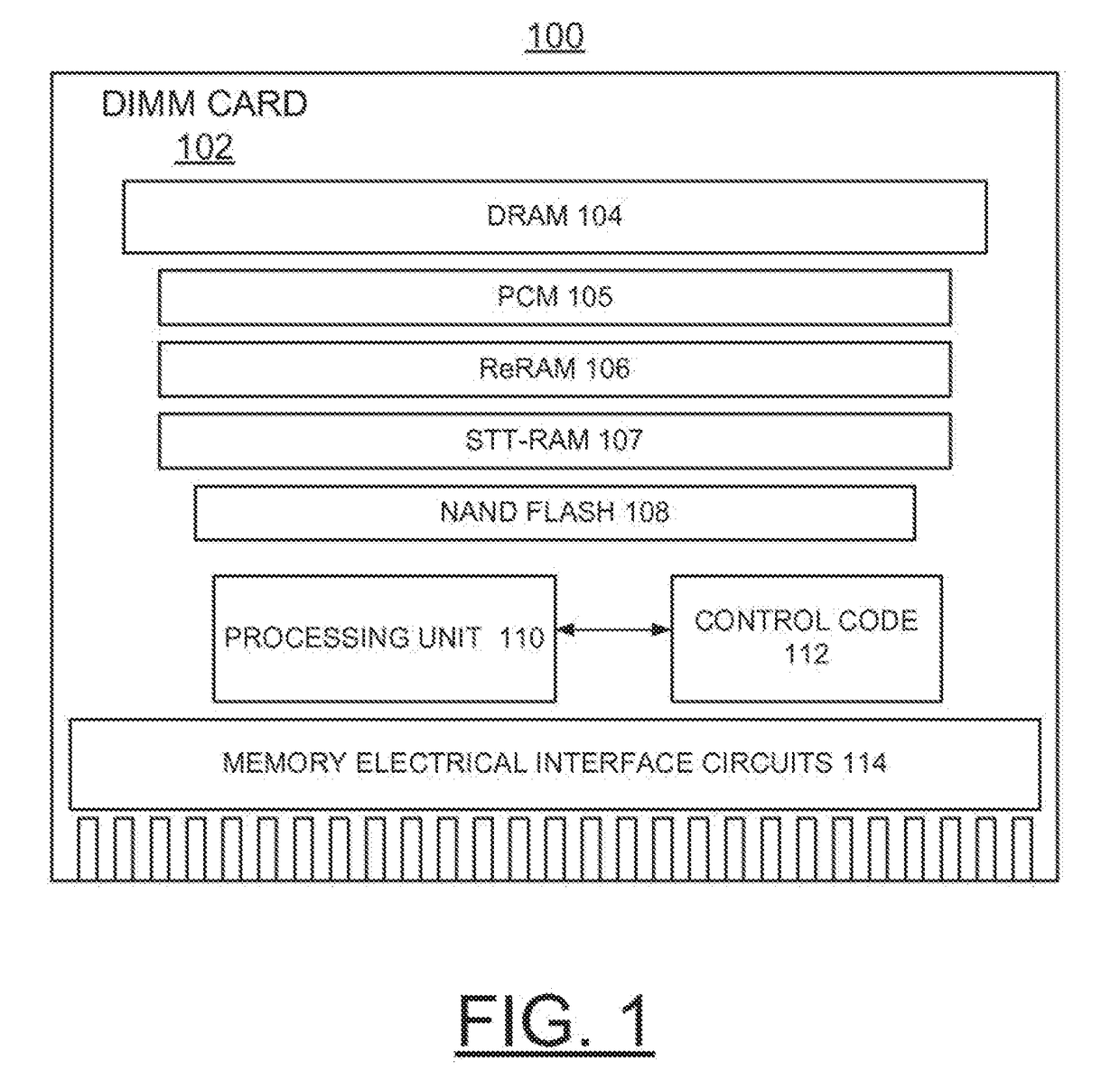
InactiveUS20140101370A1Enhanced solid-state storage usageOvercome disadvantagesMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSolid-state storageDIMM
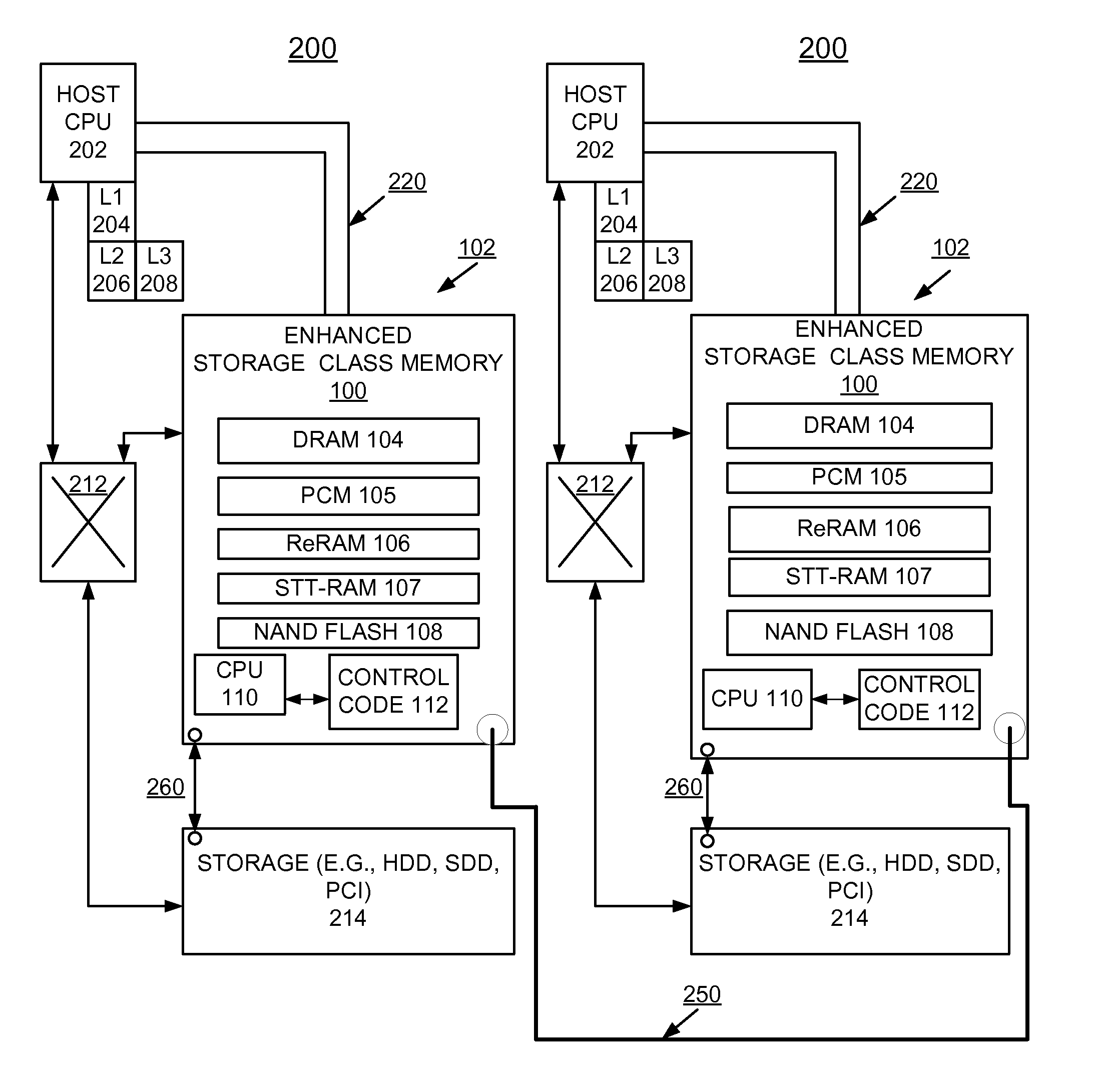
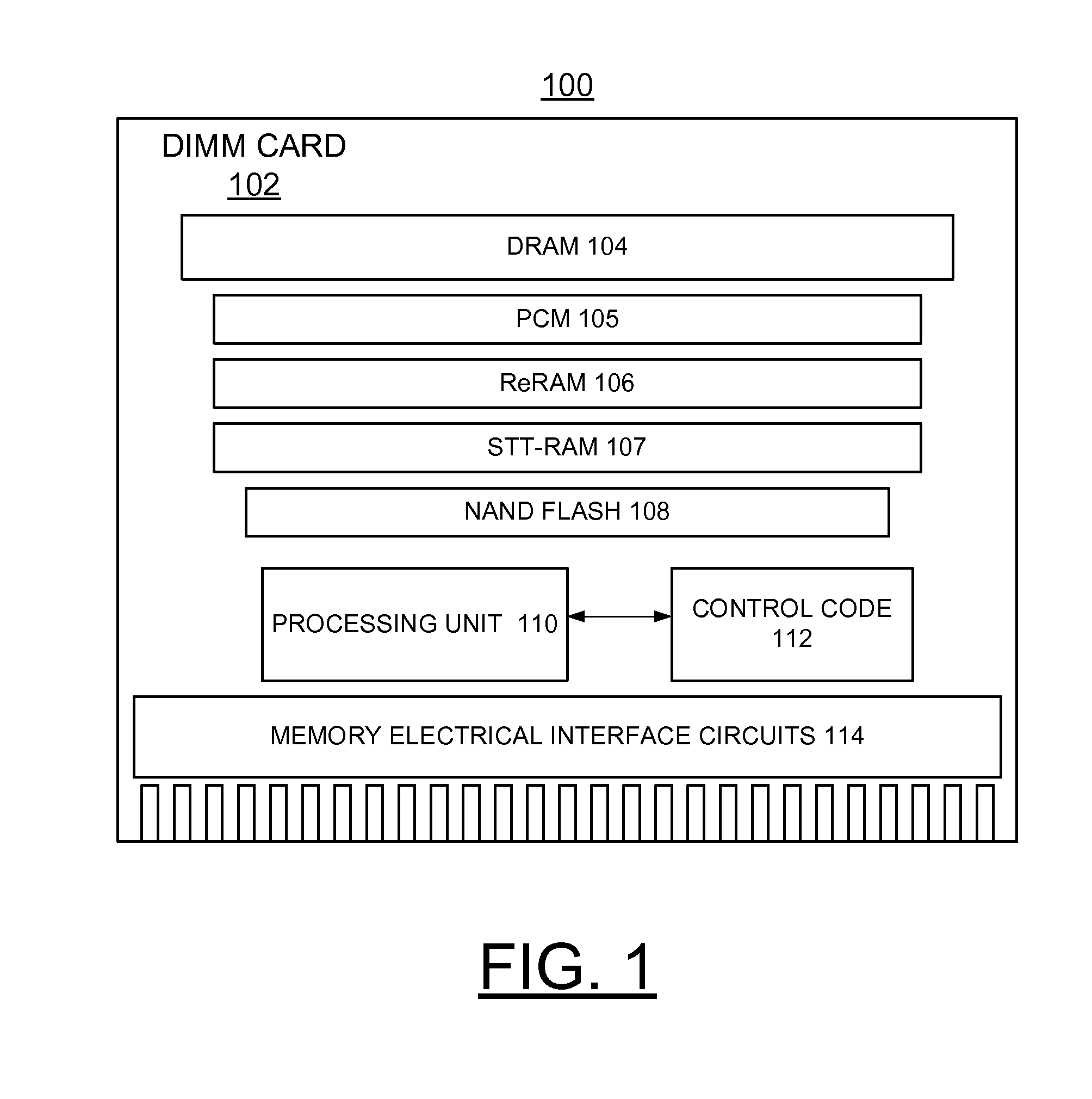
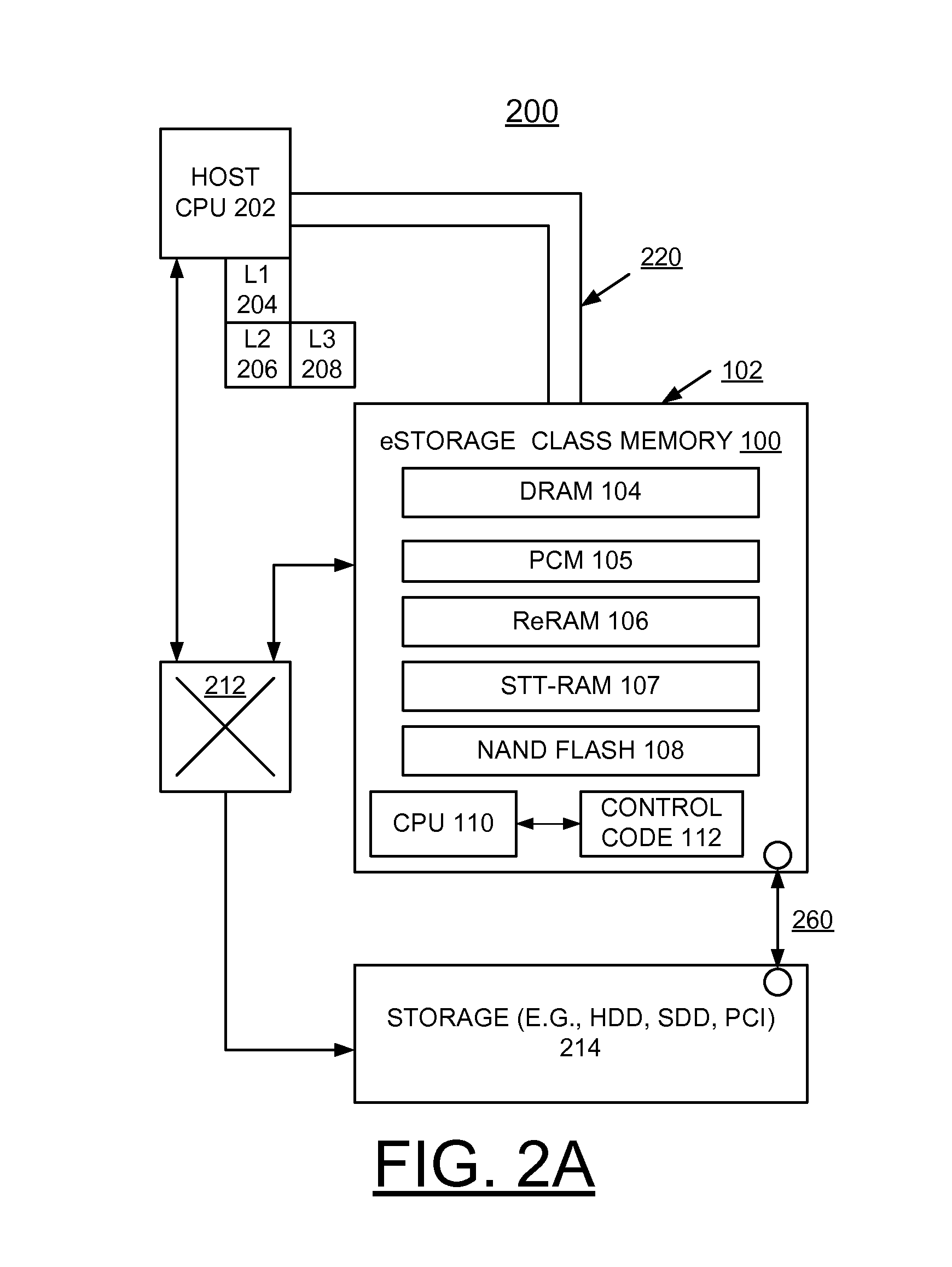
A method and a storage system are provided for implementing enhanced solid-state storage class memory (eSCM) including a direct attached dual in line memory (DIMM) card containing dynamic random access memory (DRAM), and at least one non-volatile memory, for example, Phase Change memory (PCM), Resistive RAM (ReRAM), Spin-Transfer-Torque RAM (STT-RAM), and NAND flash chips. An eSCM processor controls selectively allocating data among the DRAM, and the at least one non-volatile memory primarily based upon a data set size.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
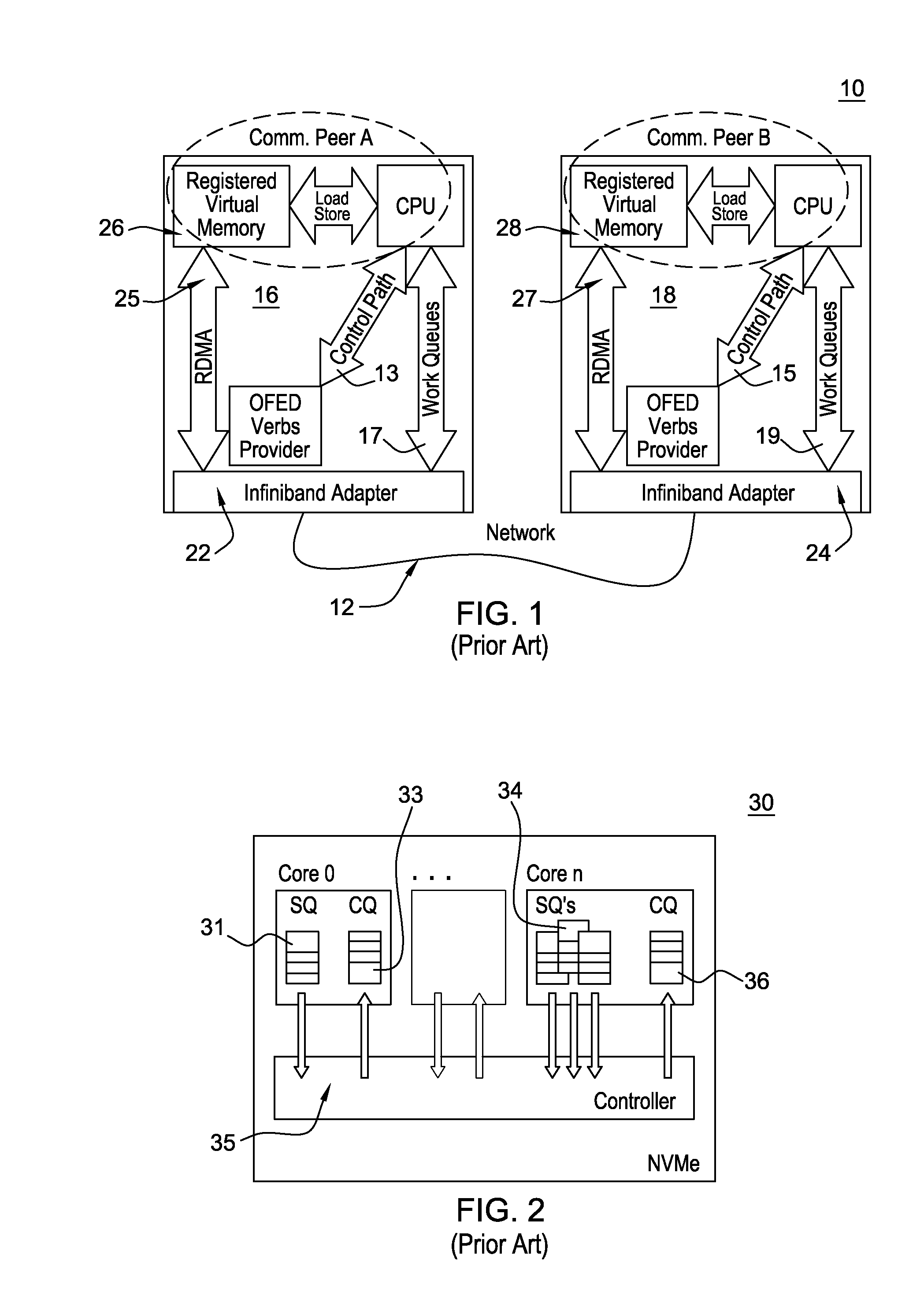
Local direct storage class memory access
ActiveUS20140317336A1Reduce the burden onEasy accessMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTransmissionZero-copyGranularity
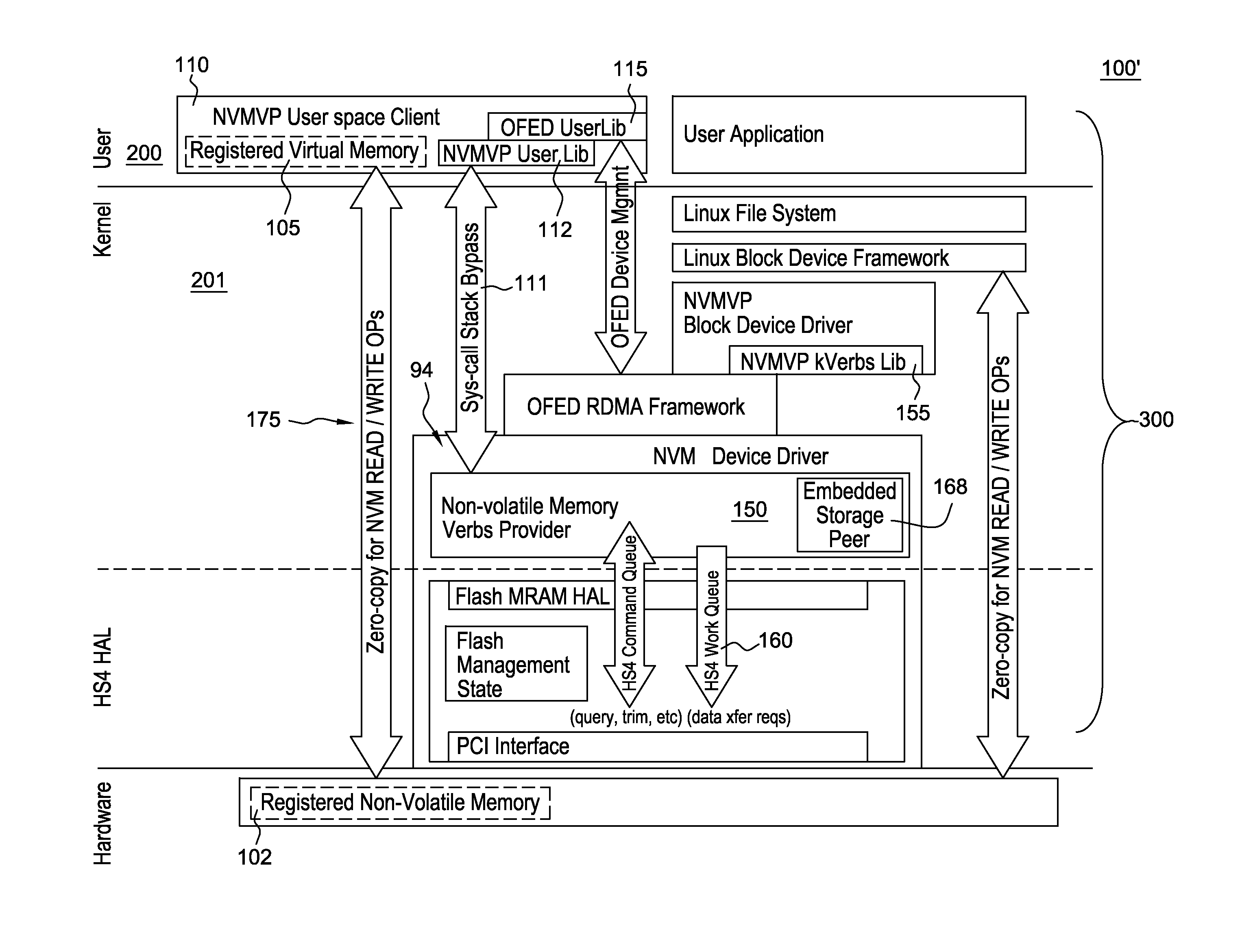
A queued, byte addressed system and method for accessing flash memory and other non-volatile storage class memory, and potentially other types of non-volatile memory (NVM) storage systems. In a host device, e.g., a standalone or networked computer, having attached NVM device storage integrated into a switching fabric wherein the NVM device appears as an industry standard OFED™ RDMA verbs provider. The verbs provider enables communicating with a ‘local storage peer’ using the existing OpenFabrics RDMA host functionality. User applications issue RDMA Read / Write directives to the ‘local peer (seen as a persistent storage) in NVM enabling NVM memory access at byte granularity. The queued, byte addressed system and method provides for Zero copy NVM access. The methods enables operations that establish application private Queue Pairs to provide asynchronous NVM memory access operations at byte level granularity.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Snapshots and versioning of transactional storage class memory
ActiveUS20140351535A1Input/output to record carriersError detection/correctionArray data structureGranularity
A system and method enables efficient implementation of snapshots of data organized as arbitrary data structures on a byte-addressable persistent memory of a host computer. A user-level library of the host computer may configure the persistent memory as a software transactional memory (STM) system defined by operations, such as a STM commit operation, that ensure safe and consistent storage of the data (i.e., the data structures) within a region of the persistent memory. The library may then cooperate with an application executing on the host computer to control access to a data structure, e.g., to change a datum, stored in the region of the persistent memory as a transaction using the STM commit operation. Within a context of the transaction, the library may precisely determine which byte or bytes of the datum have changed within the region, as well as how and when the bytes have changed. Armed with precise knowledge of the context of the transaction, the library may efficiently implement a snapshot (i.e., point-in-time copy) of the changed datum and its associated data structure at the granularity at which it was modified, e.g., at the byte-addressable granularity.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
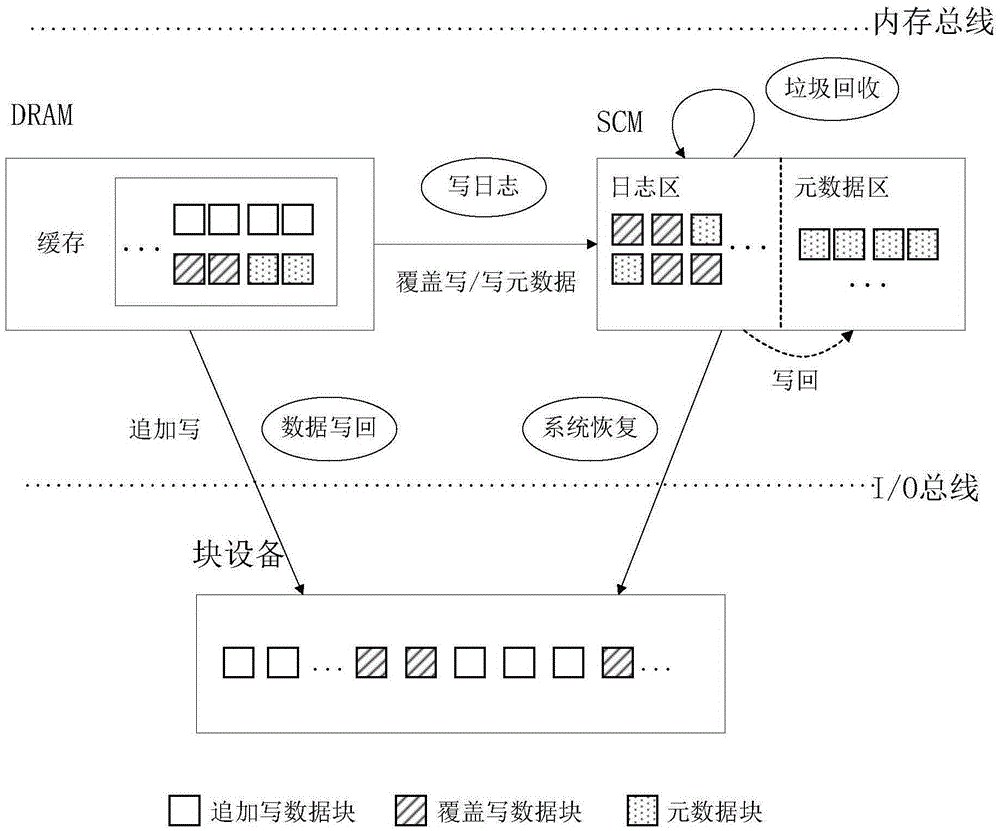
Storage-class memory based method for improving performance of log file system
ActiveCN105335098ATroubleshoot disk I/O issuesEnsure consistencyInput/output to record carriersSpecial data processing applicationsData streamSystem recovery
The invention discloses an SCM (storage-class memory) based method for improving the performance of a log file system. An SCM serves as a memory device for storing metadata and logs of the file system, so that the reading and writing of the metadata are optimized; coverage writing and additional writing are distinguished, only coverage writing data are written in the logs, additional writing data are directly written in the file system, and an update sequence is controlled to ensure the consistency of the file system, reduce the log overhead, and improve the performance of the file system; and the characteristic of modification by byte for the SCM is utilized, and the difference between new and old log blocks is computed, so that the update of log byte granularity is realized, and log data streams are reduced. The method mainly comprises five operations of storage system construction, log writing, garbage collection, data back-writing and system recovery, can be used for various log file systems, is suitable for constructing high-performance, high-capacity and high-reliability large-sized storage systems, and solves the problems of high extra overhead, high metadata back-writing frequency, low recovery speed after downtime and the like of a log technology in an existing log file system.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Memory data quick persistence method based on storage-class memory
ActiveCN105446899ALower latencyLow densityMemory systemsMetadata managementApplication programming interface
The present invention provides a memory data quick persistence method based on a storage-class memory. The method is based on a flat mixed memory architecture, and is implemented by collaborative design of a user layer and a kernel layer. The method comprises: abstracting an SCM with a certain capacity and data stored in the SCM into a persistent area; designing an application programming interface (API) at the user layer, and making a response to memory access of an application to the persistent area; extending a Buddy system of a kernel to implement heterogeneous mixed memory management; and designing a persistent area manager to implement the functions of persistent mapping in the persistent area, metadata management in the persistent area and the like. According to the memory data quick persistence method based on the storage-class memory, a data linearization process required for data persistence in a traditional storage architecture can be avoided, direct access and in-place update of persistent data can be implemented, hierarchy invoking of a software stack in the traditional architecture is simplified, the I / O bottleneck can be effectively alleviated, and the memory access performance of the persistent data can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Methods and system for incorporating a direct attached storage to a network attached storage
InactiveUS20150201016A1Accelerating client readLevelDigital computer detailsTransmissionSystems managementData access
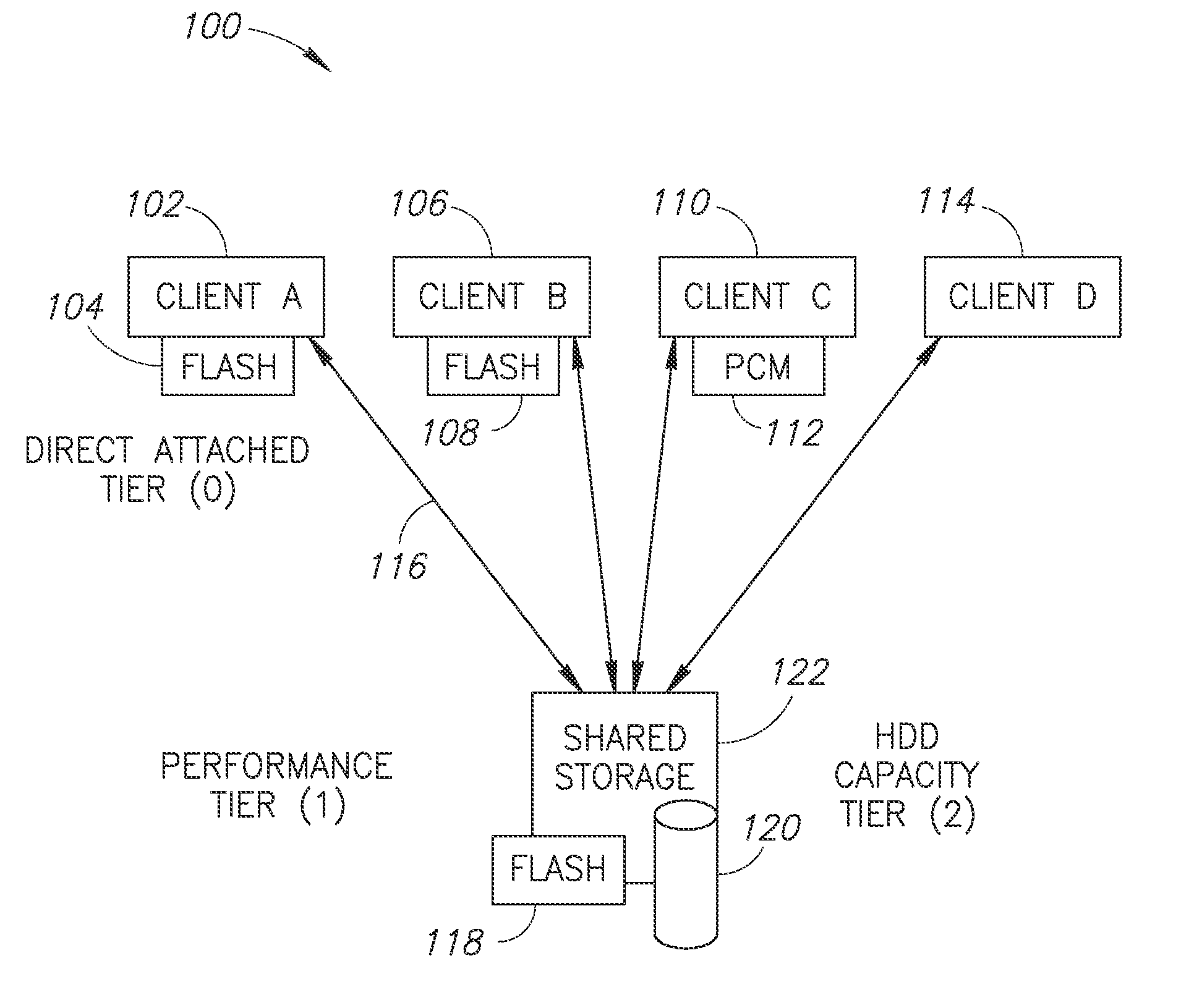
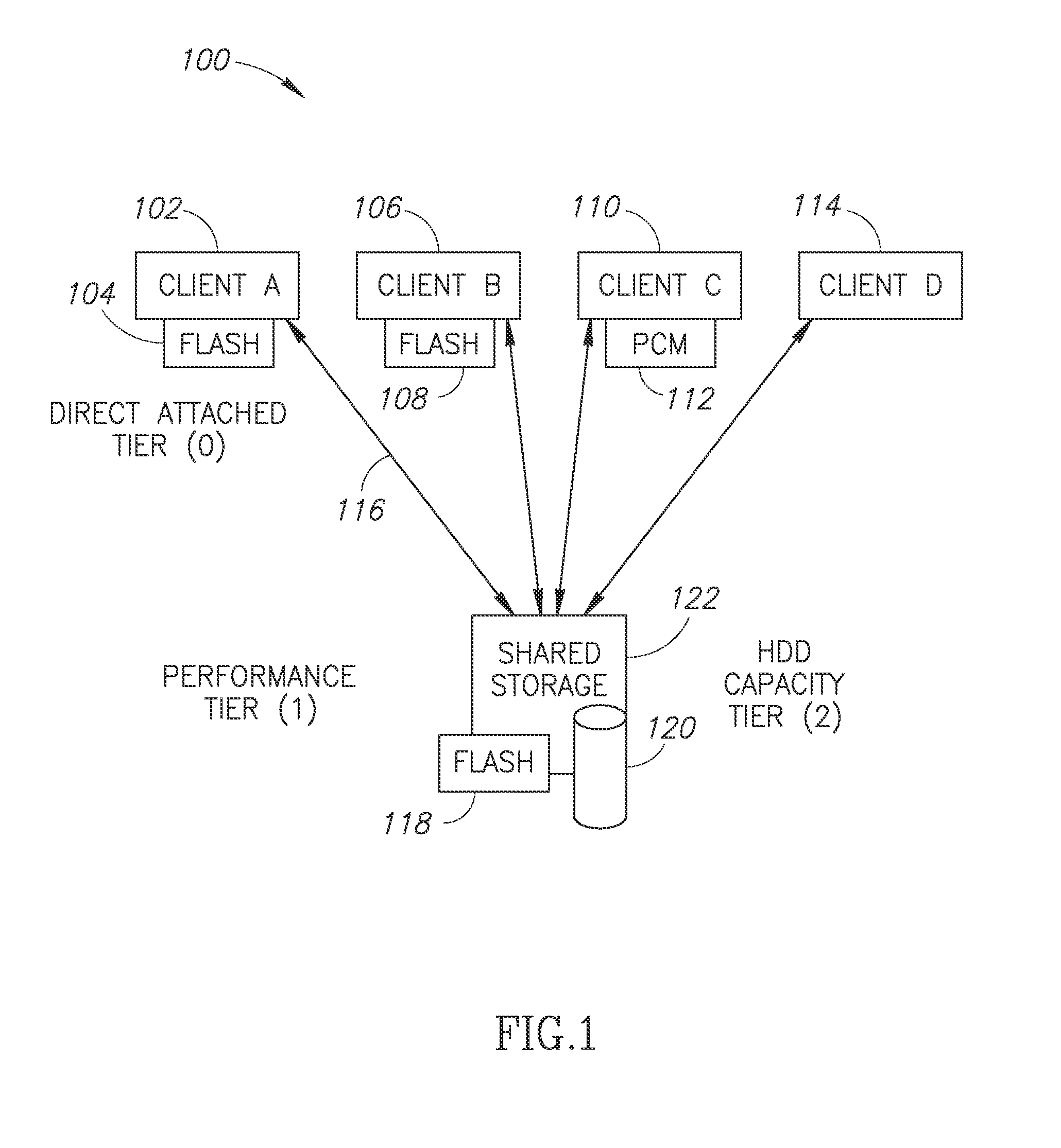
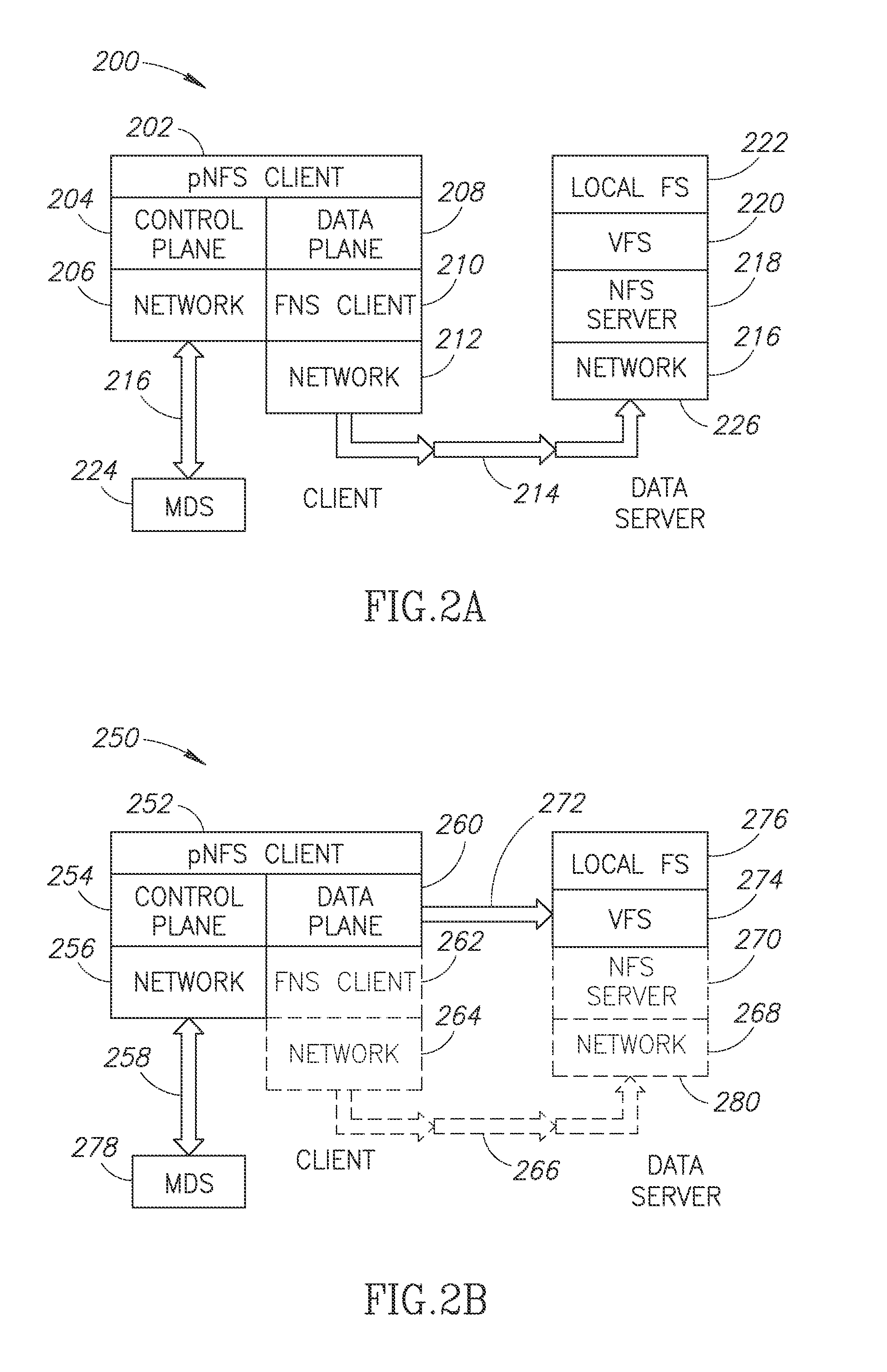
A Computerized storage system management methods and system configurations. In some embodiments the invention comprises a computer storage data access structure, a DS management and a storage system solution related to methods and a system geared for implementing a scale-out NAS that can effectively utilize client side Flashes while the Flash utilization solution is based on pNFS, the pNFS is comprised of a meta-data server (MDS) and data servers (DSs). There are at least one client and two Data servers, wherein at least one of them is a Direct Attached (Tier0), client level DS. Tier0 DS is a client-side resident low latency memory selected from a group of solid state memories, defined as Storage Class Memories, such as a Flash memory, serving as an integral lowest level of a storage system with a shared storage hierarchy of levels (Tier 0, 1, 2 and so on) and the unified name space.
Owner:PD MANAGEMENT HLDG INC
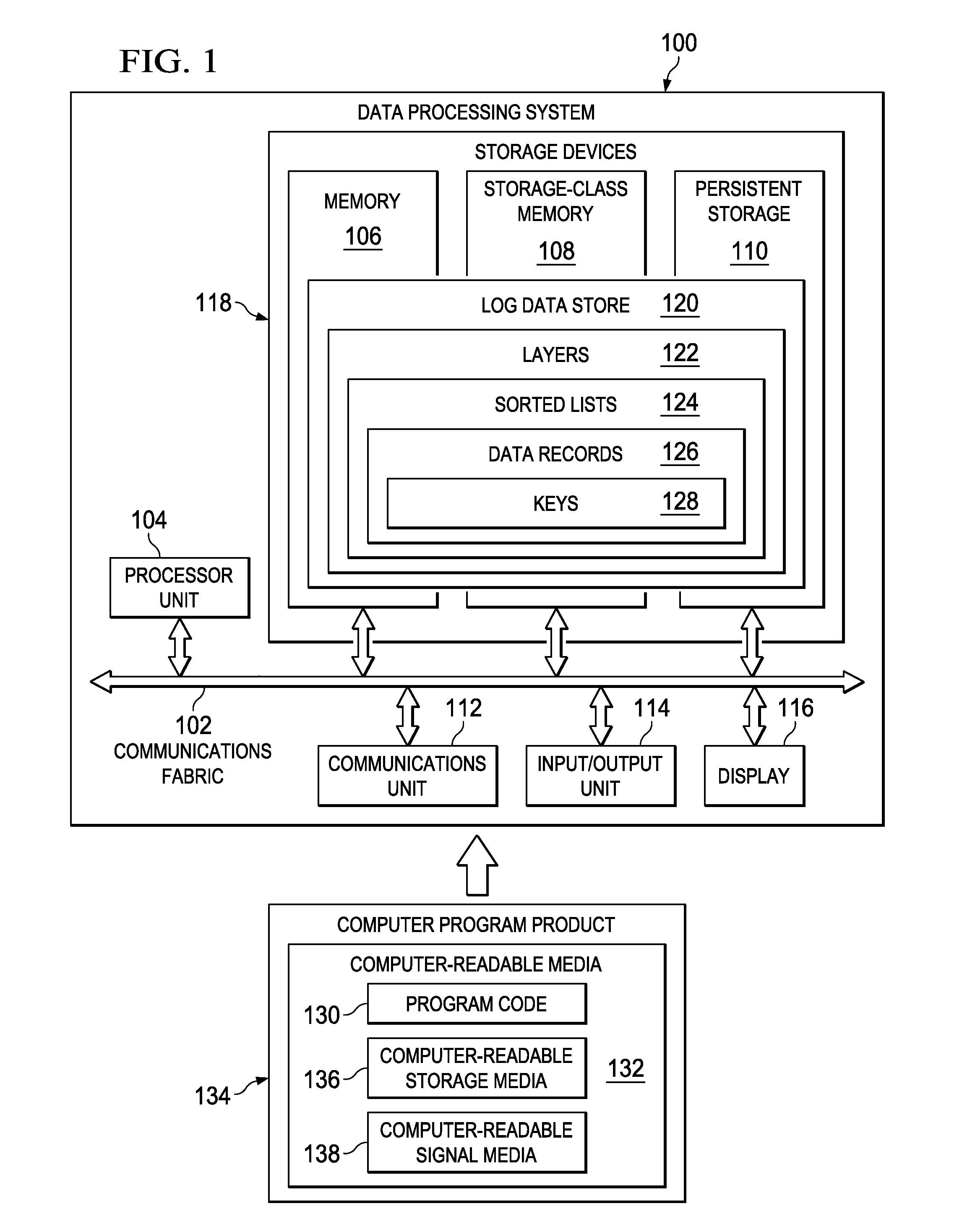
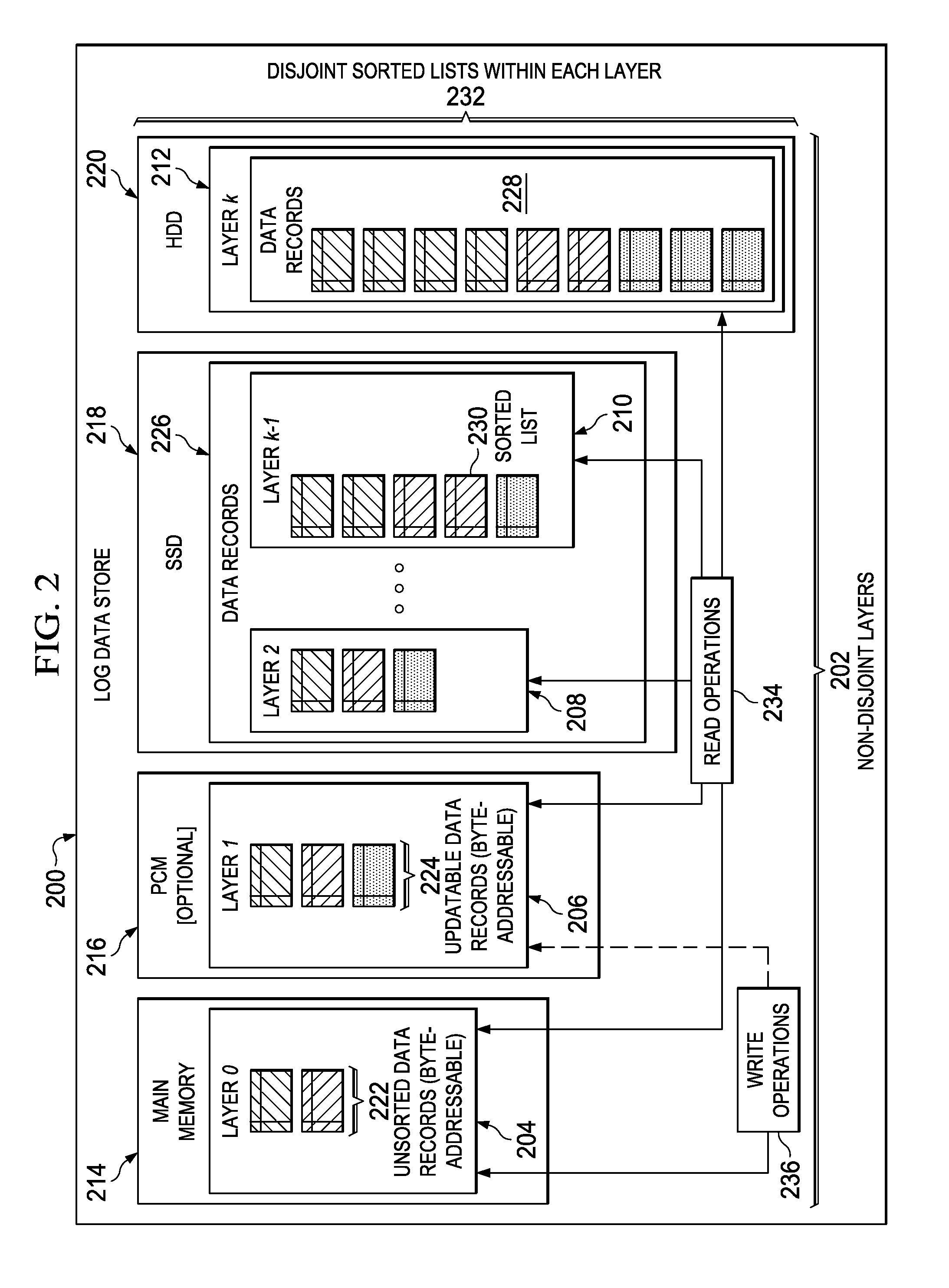
Log data store that stores data across a plurality of storage devices using non-disjoint layers
ActiveUS20150058556A1Input/output to record carriersMemory systemsData processing systemData recording
Storing data records within a log data store is provided. The log data store that stores data records within a plurality of successive non-disjoint layers inserted across a plurality of different types of data storage devices associated with a data processing system is generated. A first non-disjoint layer of the plurality of successive non-disjoint layers is inserted within a main memory device. A set of intermediate non-disjoint layers of the plurality of successive non-disjoint layers is inserted within a set of storage-class memory devices. A last non-disjoint layer of the plurality of successive non-disjoint layers is inserted within a hard disk drive. A size of each successive non-disjoint layer in the plurality of successive non-disjoint layers is increased exponentially. The data records are organized into the plurality of successive non-disjoint layers of the log data store inserted across the plurality of different types of data storage devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems, methods and computer program products memory space management for storage class memory
InactiveUS20140059284A1Input/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationStorage managementSpace management
Embodiments of the present invention provide a system, method and computer program products for memory space management for storage class memory. One embodiment comprises a method for information storage in an information technology environment. The method comprises storing data in a storage class memory (SCM) space, and storing storage management metadata corresponding to said data, in the SCM in a first data structure. The method further includes buffering storage management metadata corresponding to said data, in a main memory in a second data structure.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and Method of Wear Leveling for Storage Class Memory
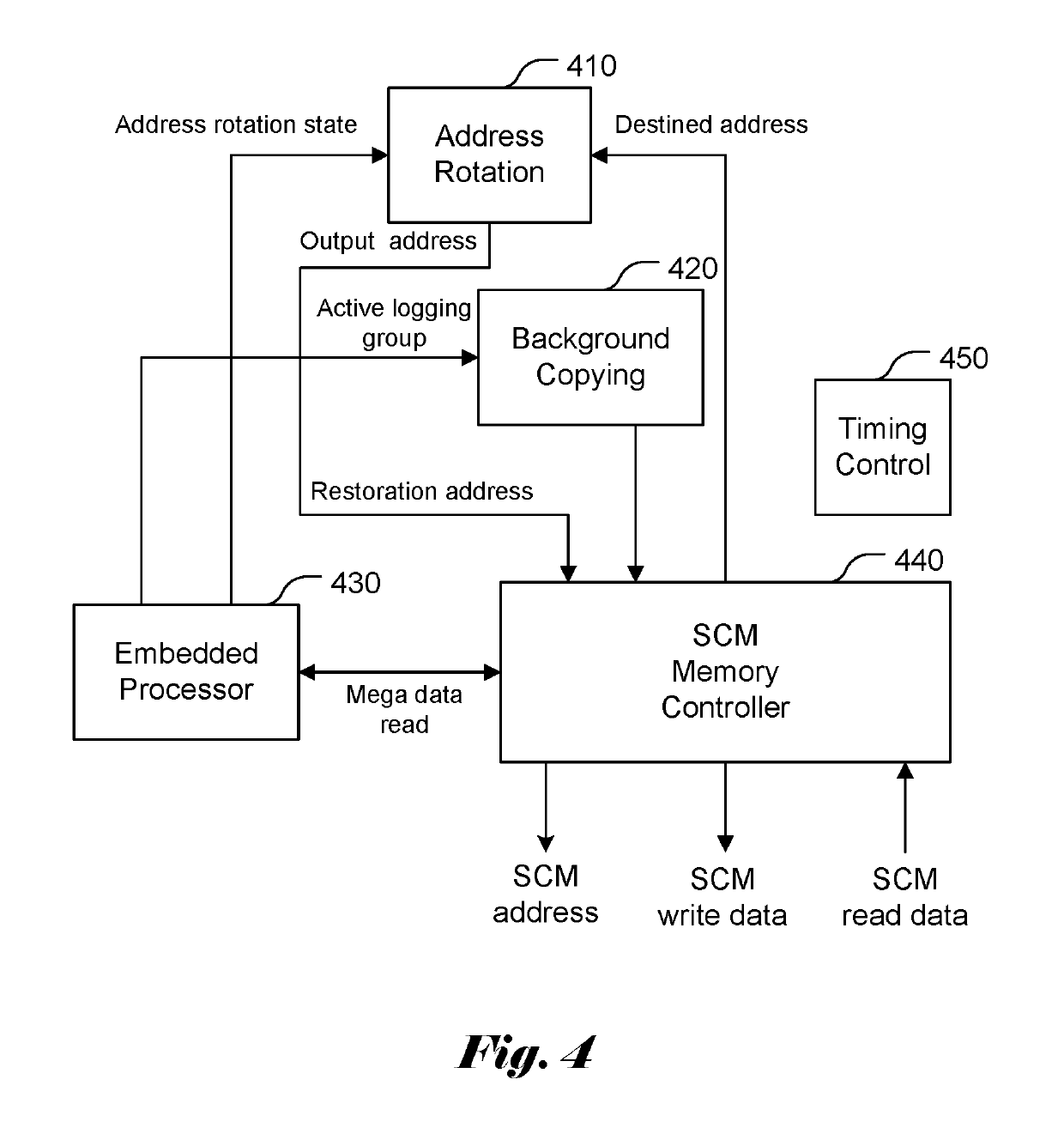
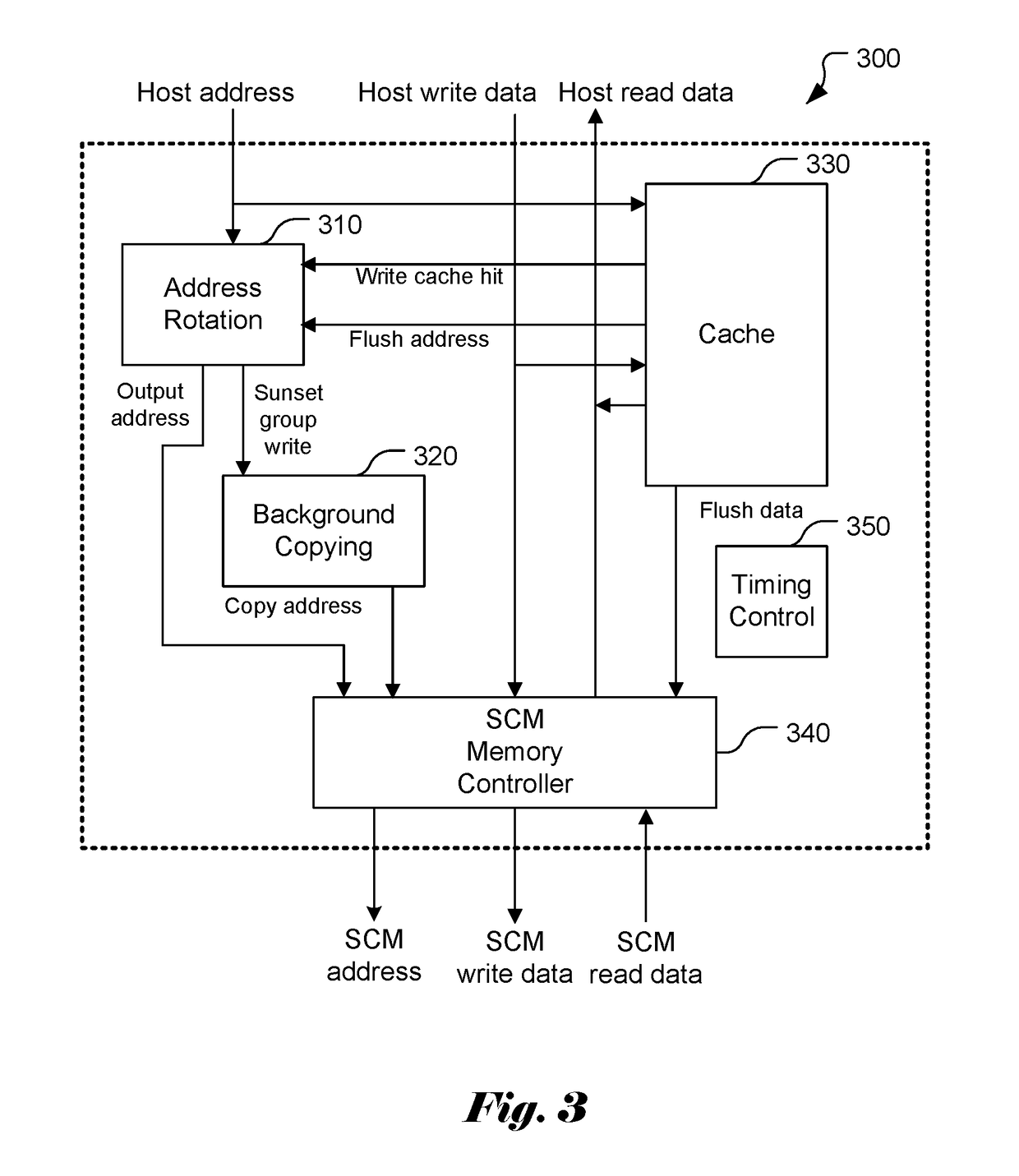
ActiveUS20180039573A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersParallel computingStorage class memory
A method and apparatus of wear leveling control for storage class memory are disclosed. According to the present invention, whether current data to be written to a nonvolatile memory corresponds to a write cache hit is determined. If the current data to be written corresponds to the write cache hit, the current data are written to a write cache as well as to a designated location in the nonvolatile memory different from a destined location in the nonvolatile memory. If the current data to be written corresponds to a write cache miss, the current data are written to the destined location in the nonvolatile memory. If the current data to be written corresponds to the write cache miss and the write cache is not full, the current data is also written to the write cache. In another embodiment, the wear leveling control technique also includes address rotation process to achieve long-term wear leveling as well.
Owner:WOLLEY INC
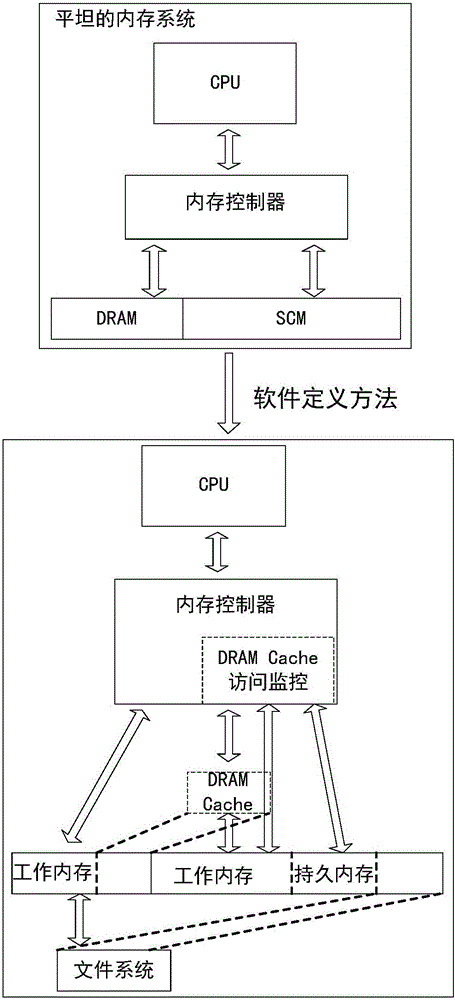
Software-defined heterogeneous hybrid memory management method
ActiveCN105938458AEliminate dependenciesMeet a variety of application needsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHardware architectureComputer architecture
The present invention provides a software-defined heterogeneous hybrid memory management method. Based on a flat hybrid memory architecture, flat and hierarchical memory management modes are achieved in a software-defined manner. The software-defined heterogeneous hybrid memory management method comprises respectively dividing logic function roles of a dynamic random access memory and a storage class memory, designing a function adapter and a dynamic random access memory to serve as function modules such as cache, achieving adaption of the roles and the function modules according to configuration parameters of users, and constructing the flat or hierarchical memory management mode according to the need. Different memory access modes can be provided for applications without changing the hardware architecture, and diversified memory access requirements can be satisfied.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Extending remote direct memory access operations for storage class memory access
ActiveUS20170039164A1Digital computer detailsElectric digital data processingDirect memory accessSemantics
Embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for extending the remote direct memory access (RDMA) operations for accessing data from storage class memory (SCM). The method includes receiving an RDMA request in a first semantic, to a memory in a second semantic. The RDMA request in the first semantic is encoded, by encoding a type of the RDMA request into a memory area identifier, which includes an 8-bit key used to define additional storage semantics for the RDMA operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
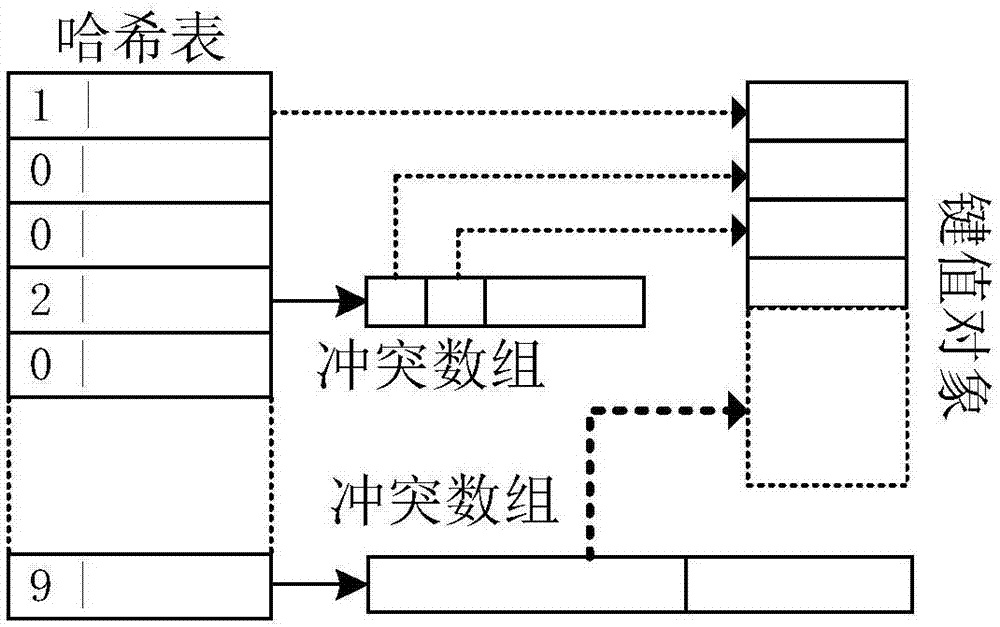
SCM (Storage Class Memory)-based Key-Value log-type local-storage method
ActiveCN107544756AIncrease profitExtended service lifeInput/output to record carriersResource allocationArray data structureHash table
The invention provides an SCM (Storage Class Memory)-based Key-Value log-type local-storage method. The storage method comprises the following steps: an SCM dividing step, wherein partition dividing is carried out on an SCM according to functions, that is, the SCM is divided into five different logic partitions of a superblock area, a checkpoint area, a page management area, a static-hash-table area and a data storage area; a multilayer memory management step, wherein three layers of memory management modules are built, the memory is managed at different layers, and dynamic allocation and reclaimation of pages are realized; and a high-concurrency hash-table building step, wherein a static hash table is used to index key-value objects, and a dynamically allocated array is used to store hash-conflicting elements. According to the method realized in the invention, storage space is reasonably scheduled and allocated according to hardware characteristics of a heterogeneous memory medium, autilization rate of the storage medium is increased, service life of hardware is prolonged, and concurrency and data throughput of a hybrid key-value storage system are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Write-through-and-back cache
InactiveUS20120284459A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer scienceStorage class memory
Embodiments are provided for cache memory systems. In one general embodiment, a system that includes a storage device, and at least one storage class memory device operating as a write cache for the storage device. The storage device further includes a first storage location for data received from a host computer during a host write request and a second storage. Data received from a host write request is written to the storage class memory device, to the first location in the storage device, and to the second location in the storage device that logically reflects the location of the data in the storage class device location configured as a log structured file.
Owner:IBM CORP
KV (Key Value) storage method and device
ActiveCN107066498ALow resolutionImprove performanceSpecial data processing applicationsSolid-state driveVariable length
The embodiment of the invention provides a KV (Key Value) storage method and device, and relates to the field of data storage. The method comprises the following steps that: when a target KV is stored, storing a Value in the target KV into a variable-length page in an SCM (Storage Class Memory); updating a primary index and a mapping table, wherein the primary index comprises a mapping relationship between a Key and a logic address in the stored KV, and the mapping table comprises a mapping relationship between the logic address and the physical address of the stored KV; when a first combination condition is met, combining the Value in the variable-length page to a fixed-length page in the SCM; updating the mapping table; when a second combination condition is met, combining the Value in the fixed-length page to a block page in an SSD (Solid State Drive); and updating the mapping table again. By use of the method, the problem of low performance of KV storage in the prior art is solved, and an effect on improving KV storage performance can be achieved.
Owner:CHENGDU HUAWEI TECH
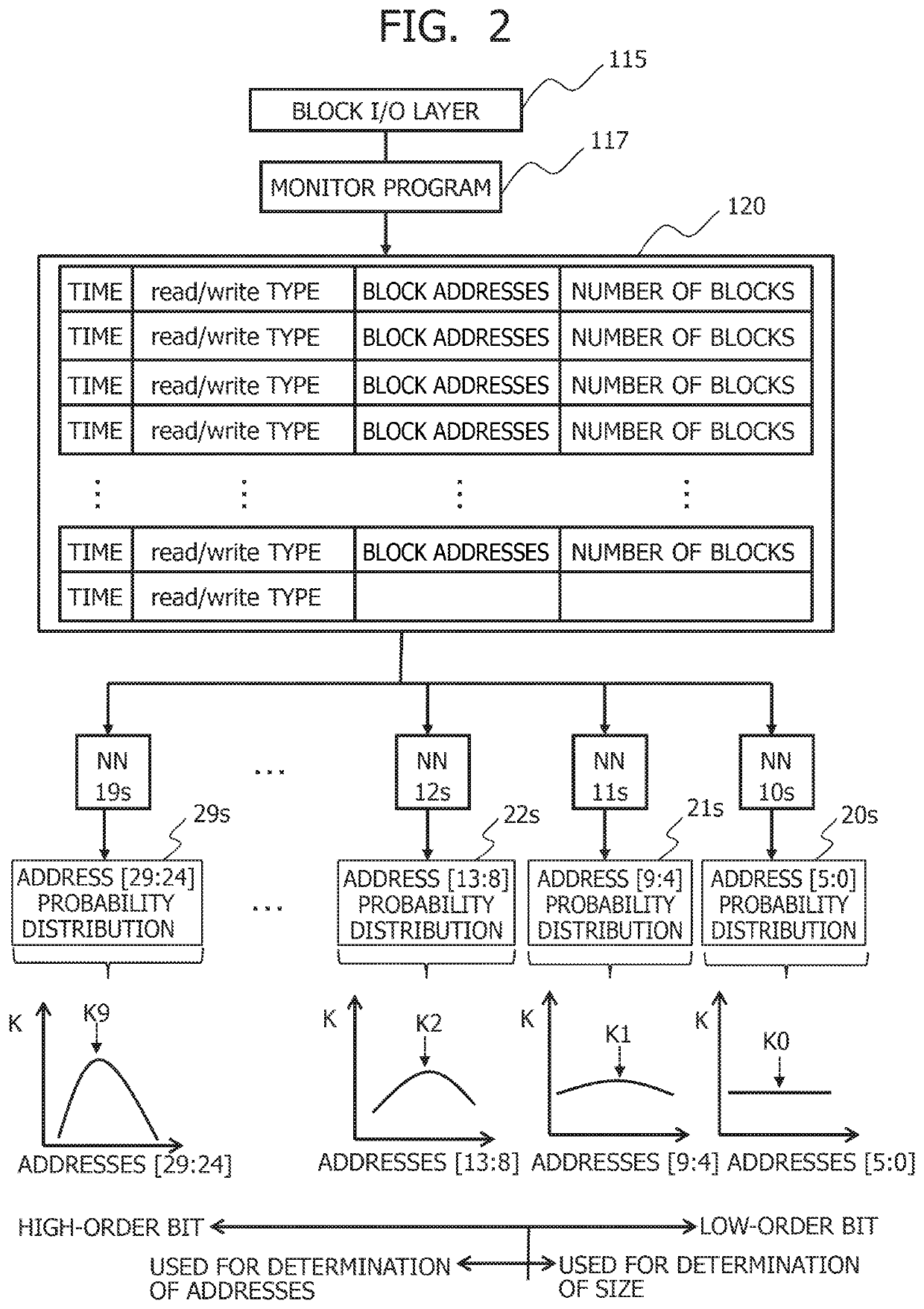
Data processing apparatus and prefetch method
ActiveUS20190361811A1Increase in block address spaceIncrease spacingMemory architecture accessing/allocationMathematical modelsParallel computingStorage class memory
An area for prefetching is determined while accommodating an increase in a block address space. A prediction model predicts prefetch addresses for each of bit ranges into which block addresses are split by using a plurality of neural networks assuming charge of the different bit ranges having performed machine learning on I / O trace data, a prediction accuracy determination section determines a size of an area for prefetching on the basis of addresses in the bit range for which prediction accuracy in prefetch is lower than a predetermined value, a predicted value determination section determines addresses of the area for prefetching on the basis of addresses in the bit range for which the prediction accuracy in the prefetch is equal to or higher than the predetermined value, and a prefetch issuance section caches data in the area for prefetching in a storage class memory from a NAND flash memory.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
System and method for atomic persistence in storage class memory
ActiveUS10163510B1Atomicity of operationDurability of operationMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersFast pathMemory hierarchy
Emerging byte-addressable persistent memory technologies, generically referred to as Storage Class Memory, offer performance advantages and access similar to Dynamic Random Access Memory while having the persistence of disk. Unifying storage and memory into a memory tier that can be accessed directly requires additional burden to ensure that groups of memory operations to persistent or nonvolatile memory locations are performed sequentially, atomically, and not caught in the cache hierarchy.The present invention provides a lightweight solution for the atomicity and durability of write operations to nonvolatile memory, while simultaneously supporting fast paths through the cache hierarchy to memory. The invention includes a hardware-supported solution with modifications to the memory hierarchy comprising a victim cache and additional memory controller logic. The invention also includes a software only method and system that provides atomic persistence to nonvolatile memory using a software alias in DRAM and log in nonvolatile memory.
Owner:GILES ELLIS ROBINSON +1
Systems and methods for suppressing latency in non-volatile solid state devices
InactiveUS20170228191A1Lower latencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersStorage class memoryWaiting time
Methods and systems for suppressing the latency in a non-volatile memory are provided. The non-volatile memory can include a flash memory and a storage class memory. The storage class memory can be divided in a first region and a second region. A method for suppressing the latency in the non-volatile memory can determine whether a received host command requires access to the flash memory. When the host command does not require access to the flash memory, the method can further determine whether the host command requires access to the first region or the second region of the storage class memory. The method can suppress the latency in the non-volatile memory by copying valid pages of flash memory blocks into the storage class memory.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Data transmission method, device and system
The embodiment of the invention provides a data transmission method, device and system, relates to the field of computers, can lower memory bus bandwidth occupied by data transmission and improves the use efficiency of the memory bus bandwidth. The method comprises the following steps: the data transmission device receives data sent from other hosts; the data transmission device writes the data into a SCM (Storage Class Memory) through a memory controller according to the address of the SCM; and after the data transmission device receives data writing finishing response fed back from the SCM, the data transmission device sends a data processing instruction to a CPU (Central Processing Unit), and the CPU is used for indicating the memory controller to write data in a cache into the SCM according to the data processing instruction. The method is used for data transmission.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Multi-level buffer pool extensions
ActiveUS9235531B2Convenience to workReduced operating requirementsSoftware engineeringMemory adressing/allocation/relocationStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
A buffer manager that manages blocks of memory amongst multiple levels of buffer pools. For instance, there may be a first level buffer pool for blocks in first level memory, and a second level buffer pool for blocks in second level memory. The first level buffer pool evicts blocks to the second level buffer pool if the blocks are not used above a first threshold level. The second level buffer pool evicts blocks to a yet lower level if they have not used above a second threshold level. The first level memory may be dynamic random access memory, whereas the second level memory may be storage class memory, such as a solid state disk. By using such a storage class memory, the working block set of the buffer manager may be increased without resorting to lower efficiency random block access from yet lower level memory such as disk.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Log data store that stores data across a plurality of storage devices using non-disjoint layers
ActiveUS20150058552A1Input/output to record carriersMemory systemsData processing systemData storing
Storing data records within a log data store is provided. The log data store that stores data records within a plurality of successive non-disjoint layers inserted across a plurality of different types of data storage devices associated with a data processing system is generated. A first non-disjoint layer of the plurality of successive non-disjoint layers is inserted within a main memory device. A set of intermediate non-disjoint layers of the plurality of successive non-disjoint layers is inserted within a set of storage-class memory devices. A last non-disjoint layer of the plurality of successive non-disjoint layers is inserted within a hard disk drive. A size of each successive non-disjoint layer in the plurality of successive non-disjoint layers is increased exponentially. The data records are organized into the plurality of successive non-disjoint layers of the log data store inserted across the plurality of different types of data storage devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
Local direct storage class memory access
ActiveUS9311230B2Reduce the burden onEasy accessMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsZero-copyGranularity
A queued, byte addressed system and method for accessing flash memory and other non-volatile storage class memory, and potentially other types of non-volatile memory (NVM) storage systems. In a host device, e.g., a standalone or networked computer, having attached NVM device storage integrated into a switching fabric wherein the NVM device appears as an industry standard OFED™ RDMA verbs provider. The verbs provider enables communicating with a ‘local storage peer’ using the existing OpenFabrics RDMA host functionality. User applications issue RDMA Read / Write directives to the ‘local peer (seen as a persistent storage) in NVM enabling NVM memory access at byte granularity. The queued, byte addressed system and method provides for Zero copy NVM access. The methods enables operations that establish application private Queue Pairs to provide asynchronous NVM memory access operations at byte level granularity.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Apparatus and method for low power low latency high capacity storage class memory
ActiveUS20180018259A1Easy to useOvercome disadvantagesMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTSolid-state storageDIMM
A method and a storage system are provided for implementing enhanced solid state storage class memory (eSCM) including a direct attached dual in line memory (DIMM) card containing Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM), and at least one 5 non-volatile memory, for example, Phase Change Memory (PCM), Resistive RAM (ReRAM), Spin-Transfer-Torque RAM (STT-RAM), and NAND Flash chips. An eSCM processor controls selectively allocating data among the DRAM, and the at least one non-volatile memory primarily based upon a data set size.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Memory access method, storage-class memory and computer system
ActiveCN105808455AGuaranteed correctnessReduce power consumptionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageStatic random-access memoryRefresh cycle
The embodiment of the invention provides a memory access method, a storage-class memory and a computer system. The computer system comprises a memory controller and a hybrid memory, wherein the hybrid memory comprises a DRAM (dynamic random access memory) and the SCM (Storage-Class Memory); the memory controller is used for sending a first access instruction to the DRAM and the SCM; and when the SCM determines that a first memory cell set of the DRAM to which a first address points in the received first access instruction comprises a memory cell of which the retention time is shorter than the refresh cycle of the DRAM, a second address which has a mapping relationship with the first address can be obtained. Furthermore, the SCM transforms the first access instruction to a second access instruction for accessing the SCM according to the second address to realize the access of the SCM. The computer system provided by the embodiment of the invention can guarantee data correctness on the basis of the reduction of DRAM refresh power consumption.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Apparatus and Method of Wear Leveling for Storage Class Memory Using Address Cache
ActiveUS20190102111A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersParallel computingStorage class memory
A method and apparatus of wear leveling control for storage class memory are disclosed. According to the present invention, where current data to be written to a nonvolatile memory corresponds to an address cache hit is determined. If the current data to be written corresponds to an address cache hit, the current data are written to a designated location in the nonvolatile memory different from a destined location in the nonvolatile memory. If the current data to be written corresponds to an address cache miss, the current data are written to the destined location in the nonvolatile memory. In another embodiment, the wear leveling control technique also includes address rotation process to achieve long-term wear leveling as well.
Owner:WOLLEY INC
Deferring data record changes using query rewriting
InactiveUS20150074040A1Digital data processing detailsMulti-dimensional databasesAnalysis dataData query
Staging data record changes from a faster storage medium to a slower storage medium using data query rewriting is provided. In response to receiving a data query corresponding to a particular data record, it is determined whether the data query is one of a transactional data query or an analytical data query. In response to determining that the data query is a transactional data query, the transactional data query is rewritten to apply transactional delta changes to the particular data record on a storage-class memory of a computer. In response to determining that the data query is an analytical data query, the analytical data query is rewritten to select and reconcile each data record corresponding to the particular data record stored on the storage-class memory with the particular data record stored on a persistent data storage device of the computer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Storage translation layer
InactiveCN104854554AMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data processing detailsStorage managementBlock level
Method and systems for distributing the translation layer of storage media (such as NAND Flash or Storage Class Memory Storage) system across various storage system components are described herein. Non-limiting examples of storage system components include a Persistent Storage Device (PSD), a Storage Aggregation Controller (SAC), and a Storage Management Writer (SMW). The SMW may be configured to maintain a table of the logical address of each page it writes to a PSD via a SAC. The SAC may maintain the status of the validity of previously written pages with the SMW informing the SAC when any page is no longer valid. The PSD may handle device specific issues including error correction and block-level mapping for management of block-level failures and internal wear-leveling. The SAC may handle garbage collection of the physical pages within the PSDs it is managing, while the SMW may maintain the actual page-level tables.
Owner:百科容(科技)公司
Apparatus and method of wear leveling for storage class memory using cache filtering
ActiveUS10229047B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersParallel computingStorage class memory
A method and apparatus of wear leveling control for storage class memory are disclosed. According to the present invention, whether current data to be written to a nonvolatile memory corresponds to a write cache hit is determined. If the current data to be written corresponds to the write cache hit, the current data are written to a write cache as well as to a designated location in the nonvolatile memory different from a destined location in the nonvolatile memory. If the current data to be written corresponds to a write cache miss, the current data are written to the destined location in the nonvolatile memory. If the current data to be written corresponds to the write cache miss and the write cache is not full, the current data is also written to the write cache. In another embodiment, the wear leveling control technique also includes address rotation process to achieve long-term wear leveling as well.
Owner:WOLLEY INC
Quality of service aware storage class memory/NAND flash hybrid solid state drive
ActiveUS10430329B2Input/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationQuality of serviceSolid-state drive
A device having a controller configured to interface with a host, a storage class memory configured to interface with the controller and a flash memory configured to interface with the controller, wherein both the storage class memory and the flash memory are configured to store data, and wherein the controller is configured to separate the data according to latency critical data and non-latency critical data.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com