Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
281 results about "Radiant heater" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
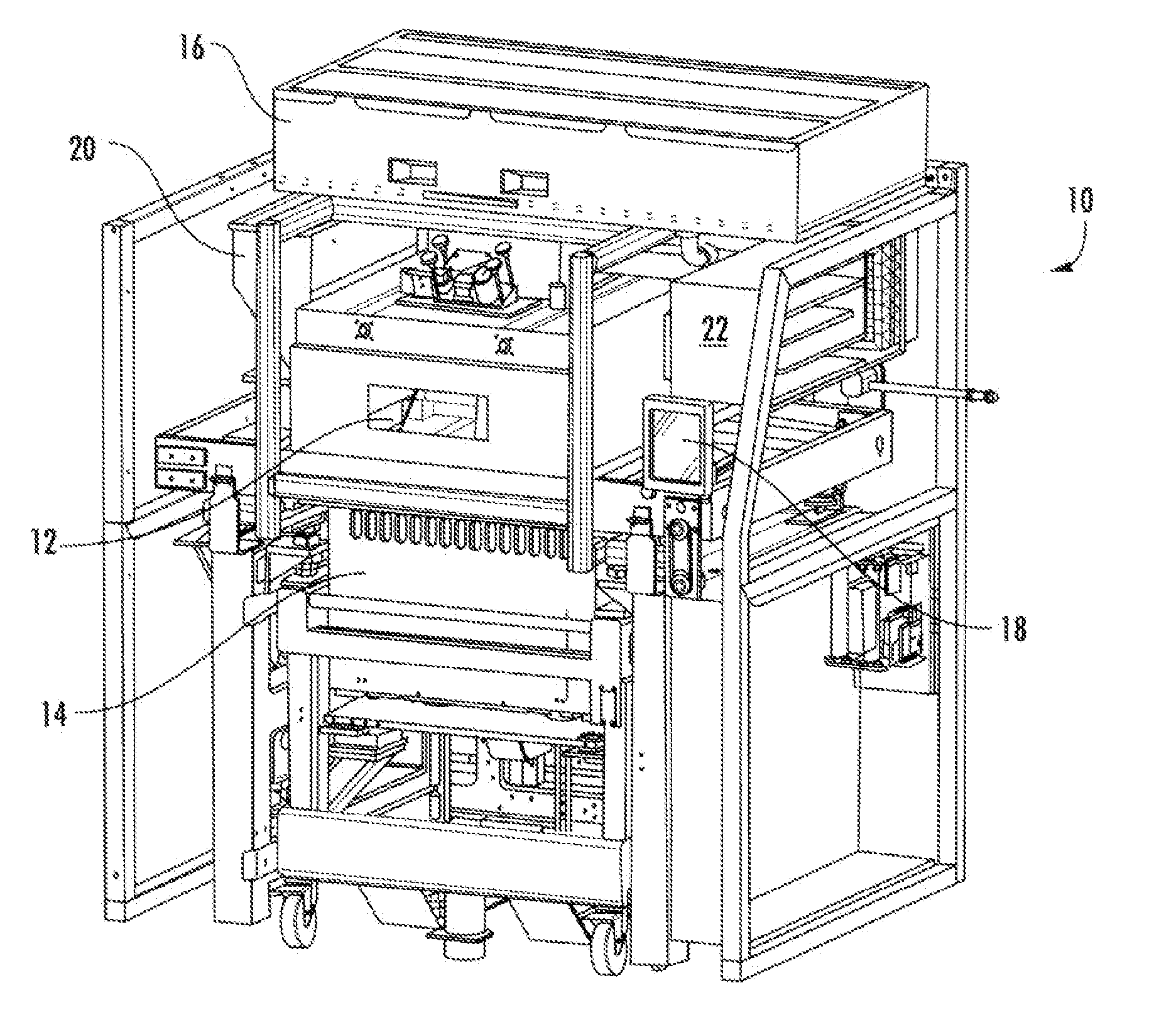
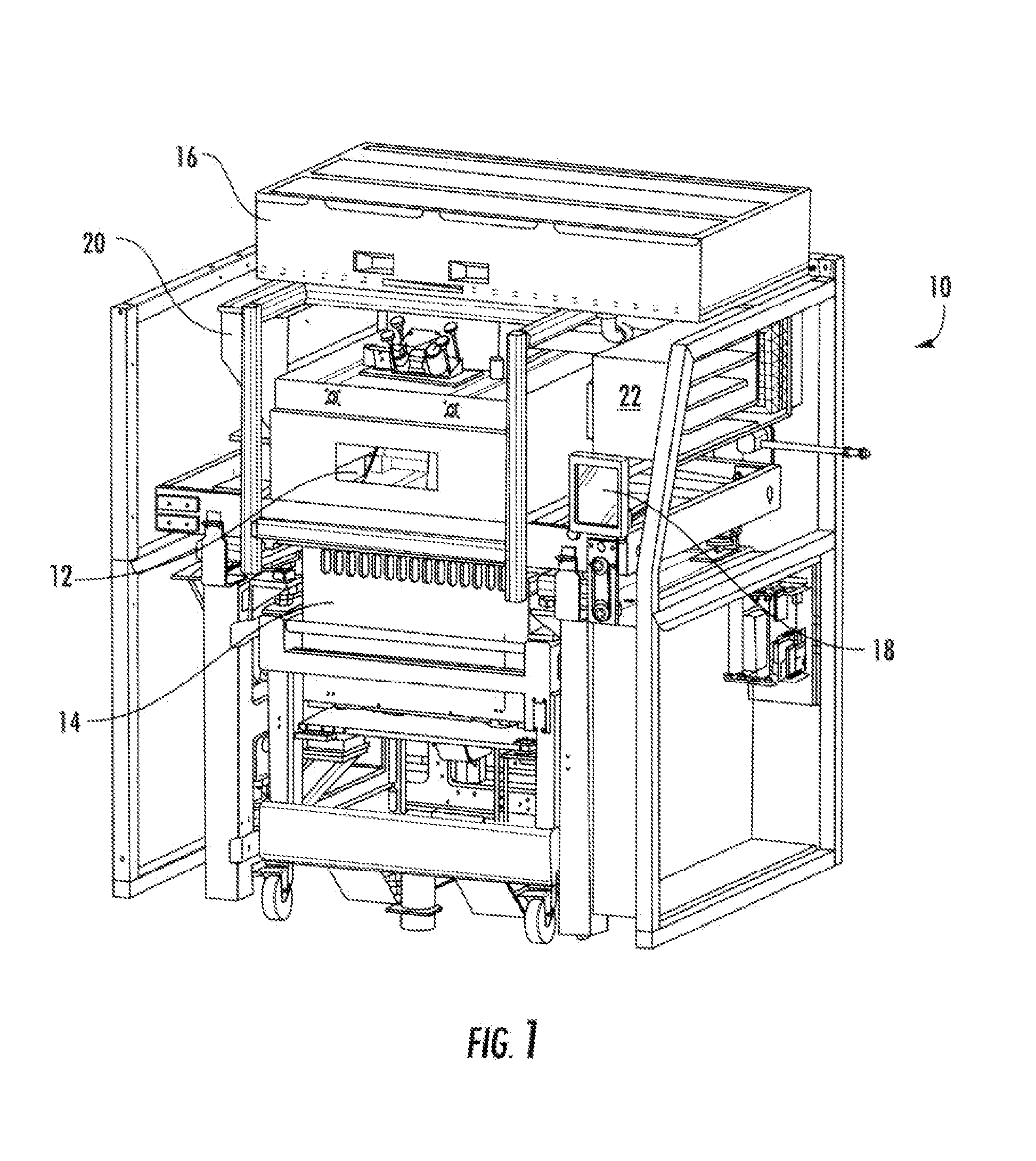
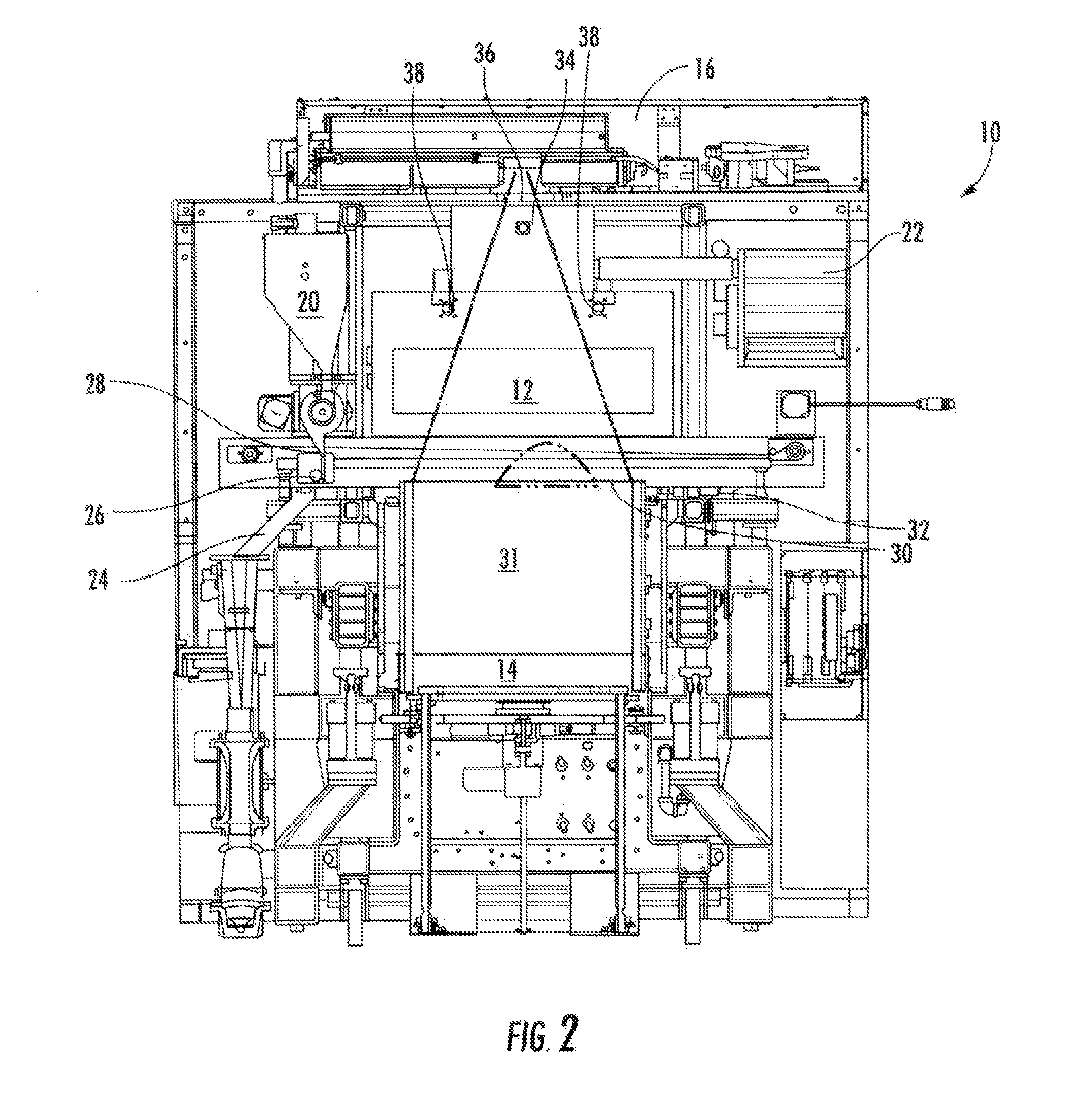
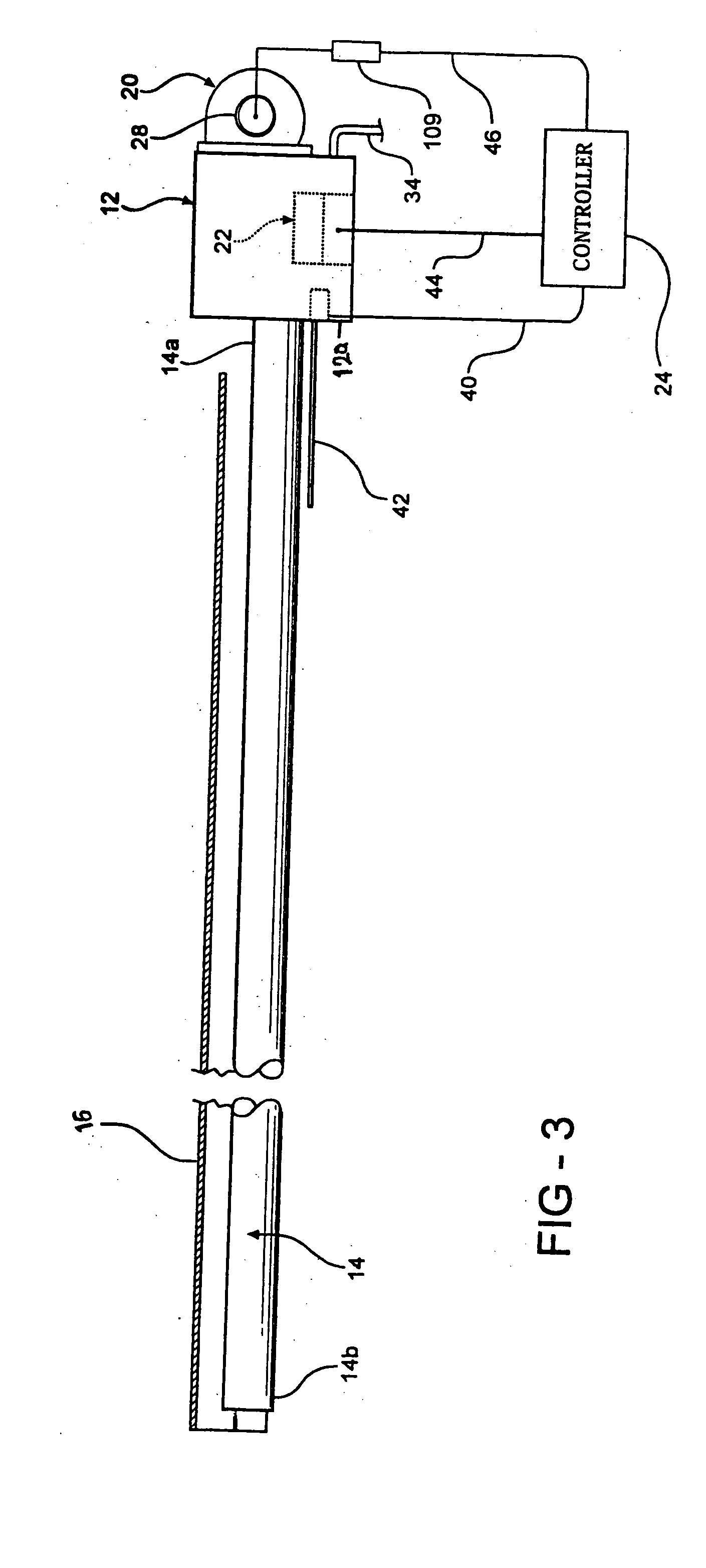
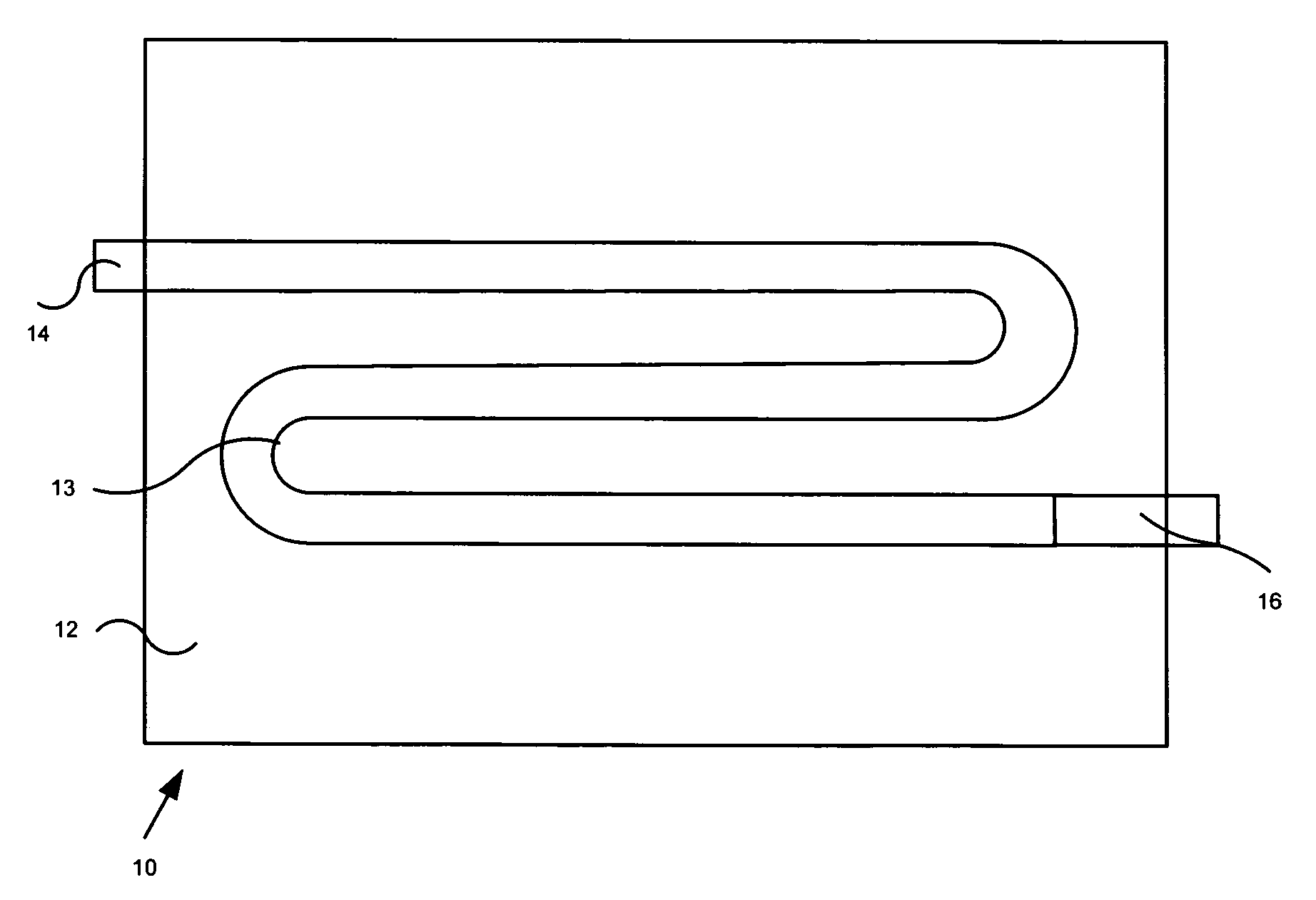
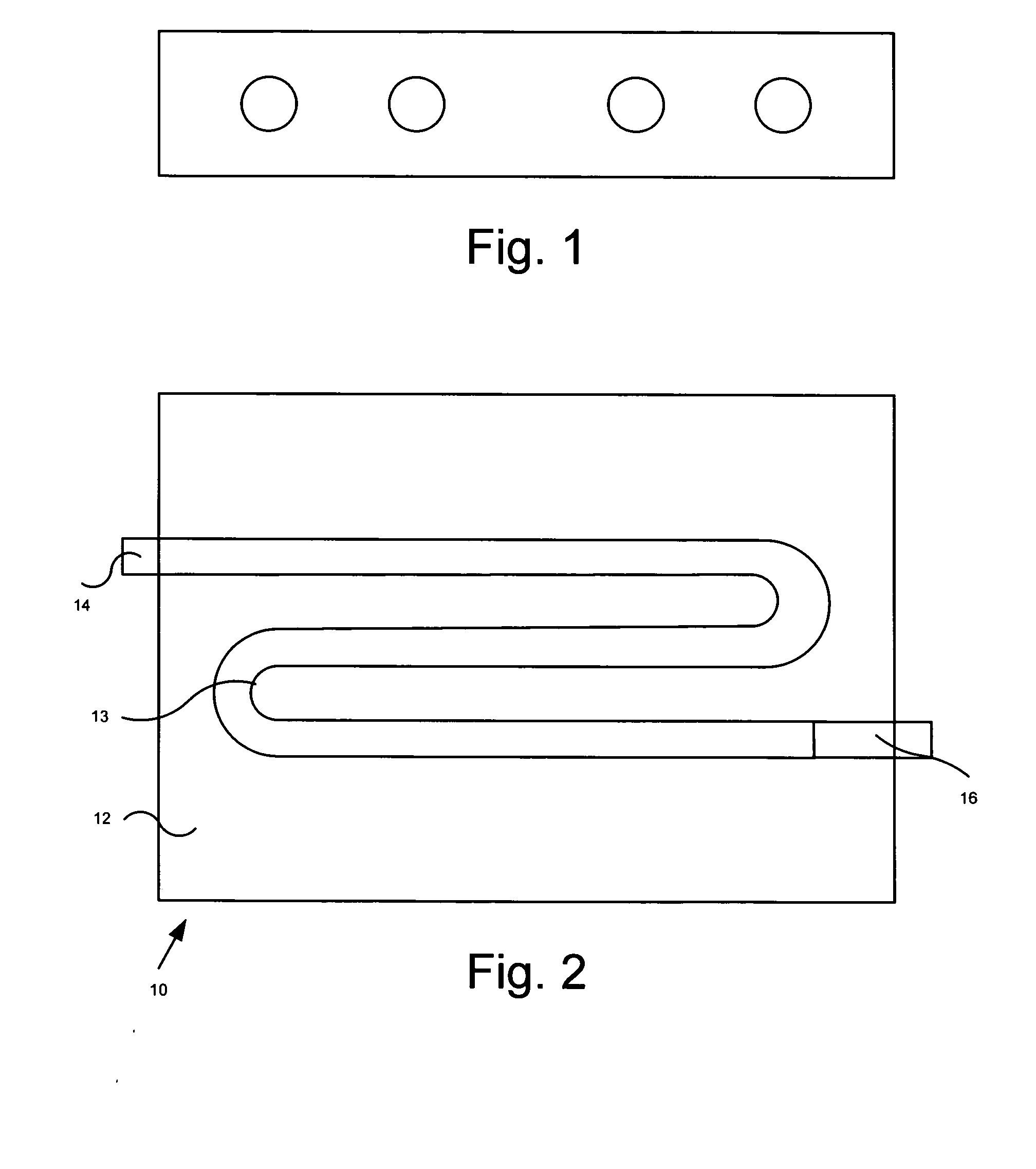
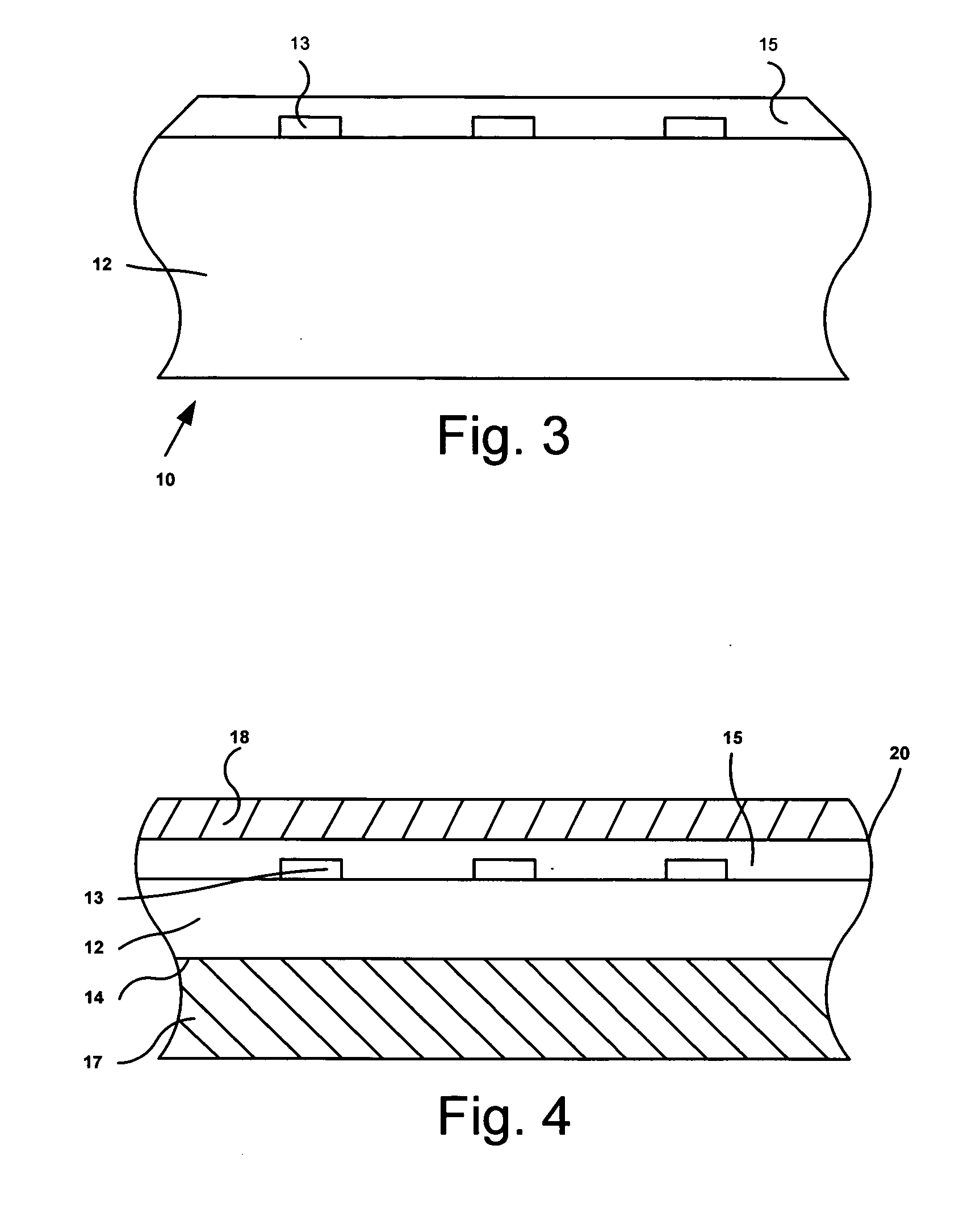
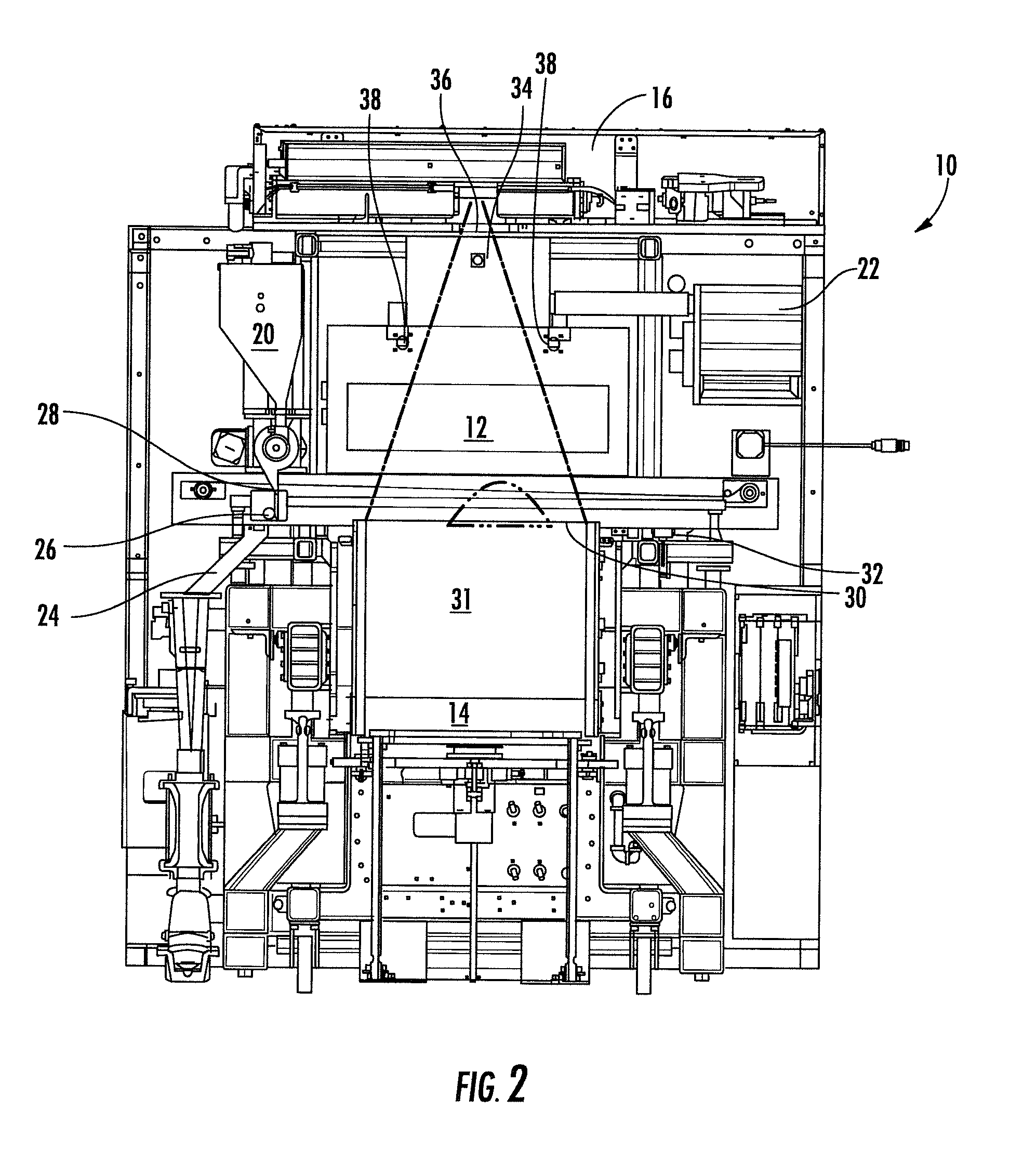
Chute for Laser Sintering Systems
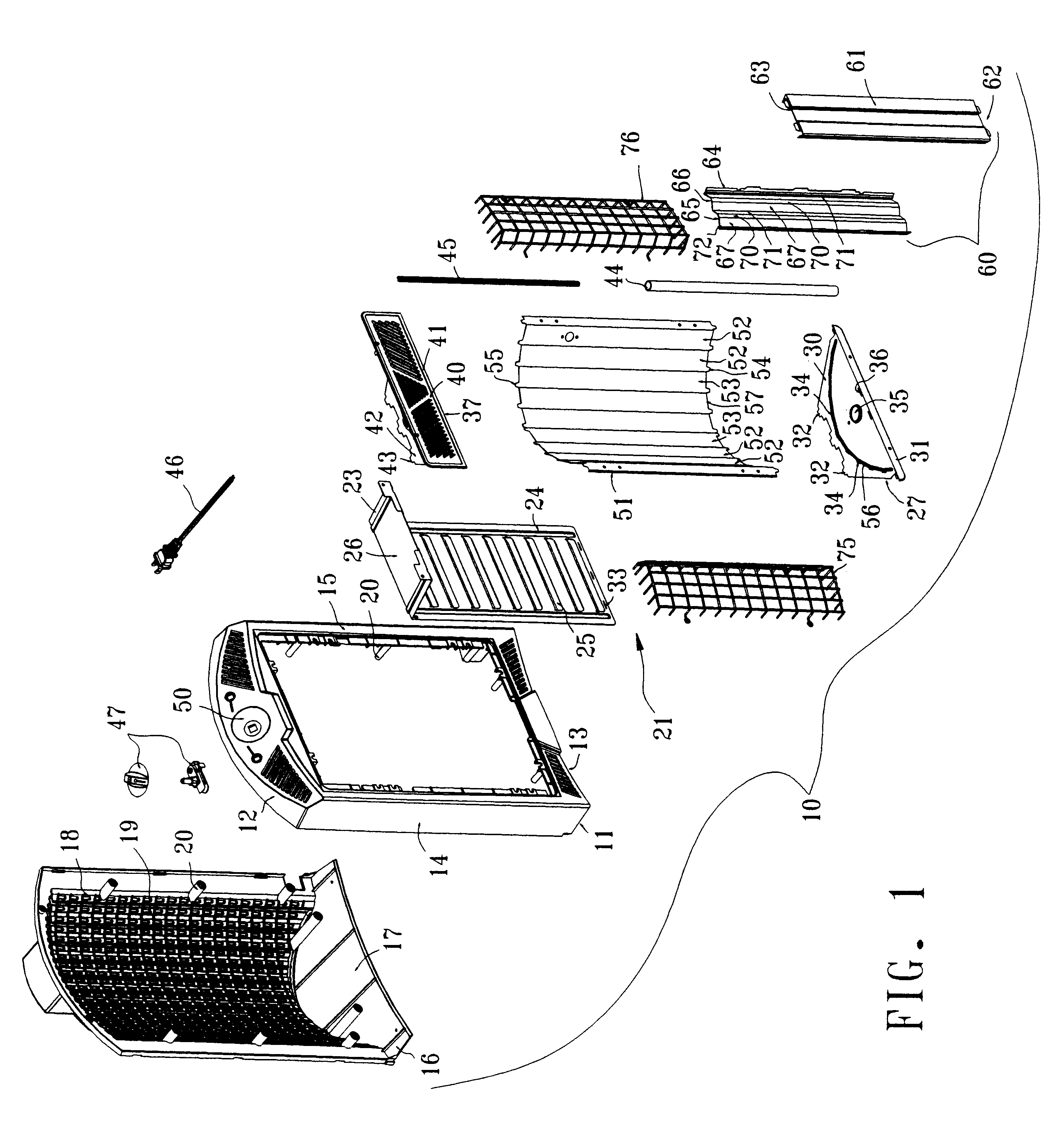
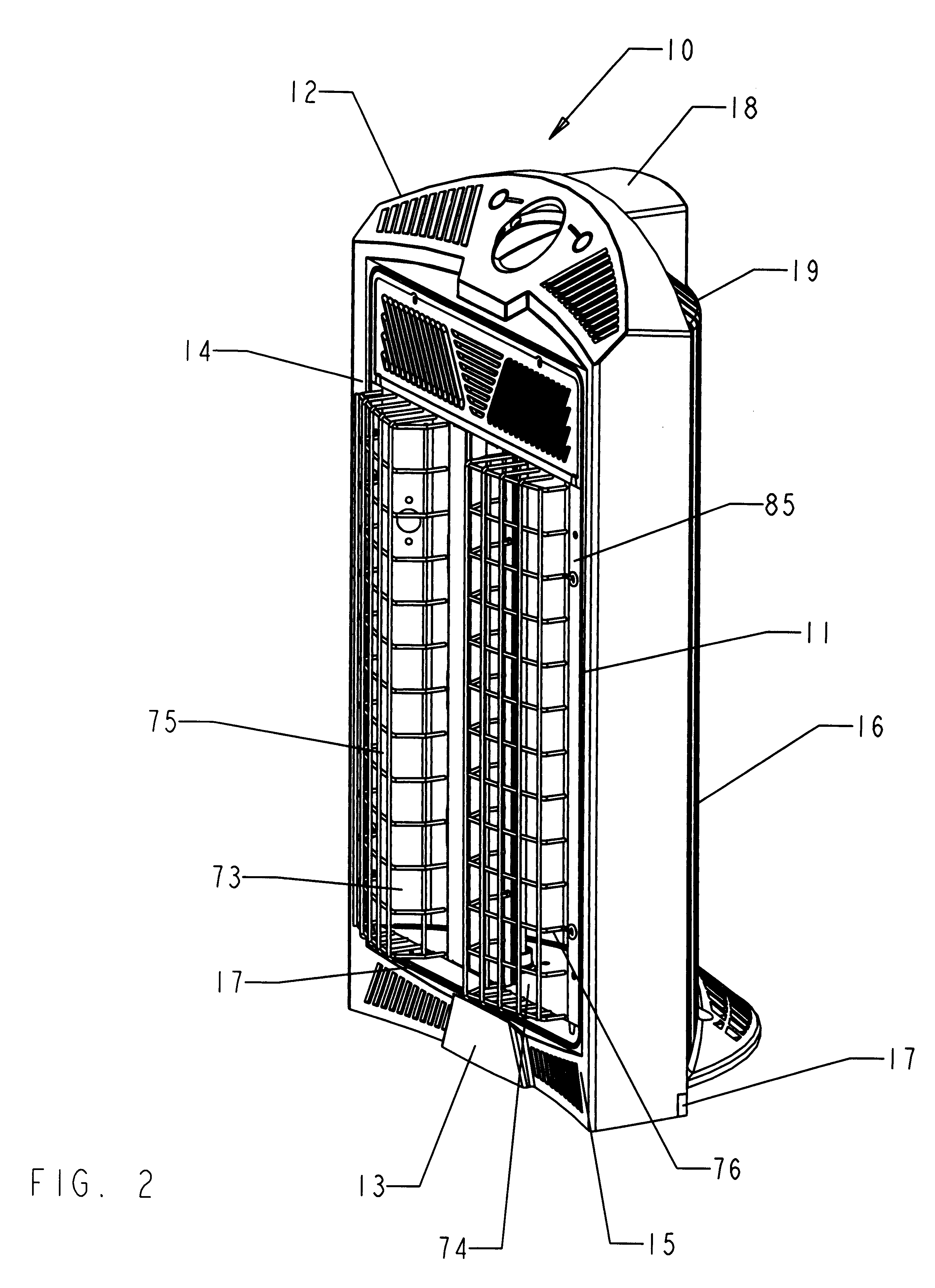
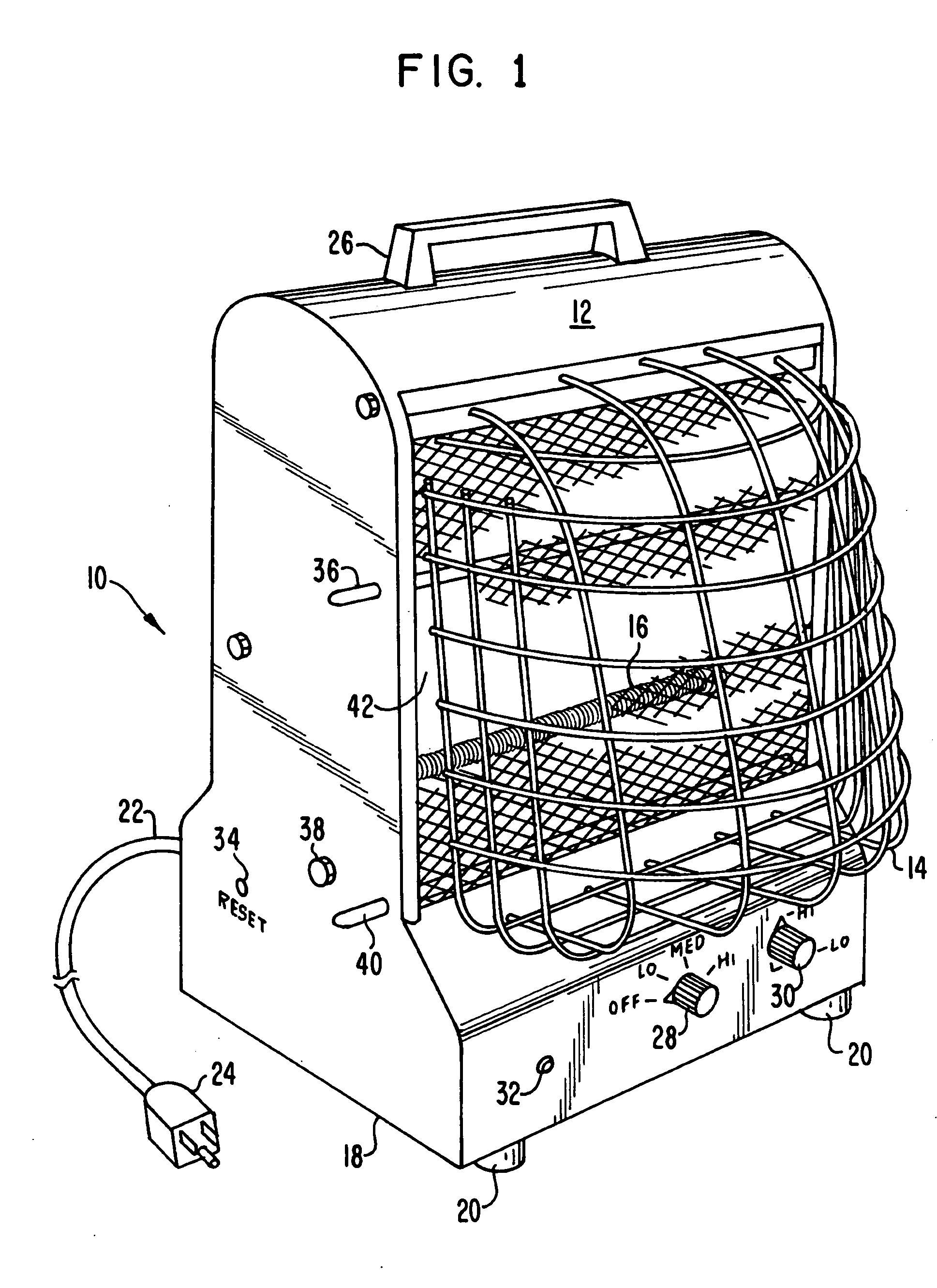
ActiveUS20140265045A1Reduce the possibilityHigh densityManufacturing heating elementsAuxillary shaping apparatusRadiant heaterUltimate tensile strength
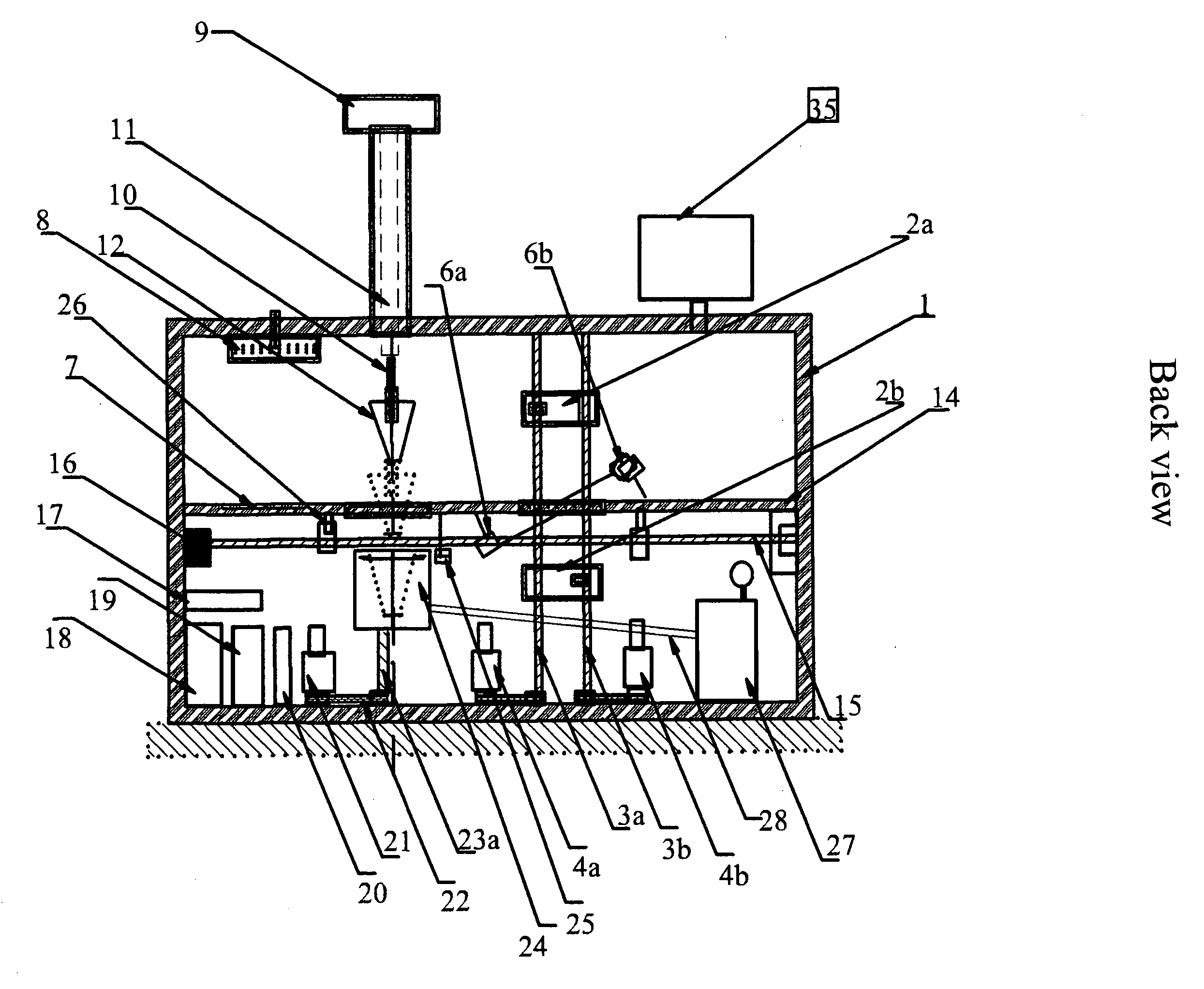
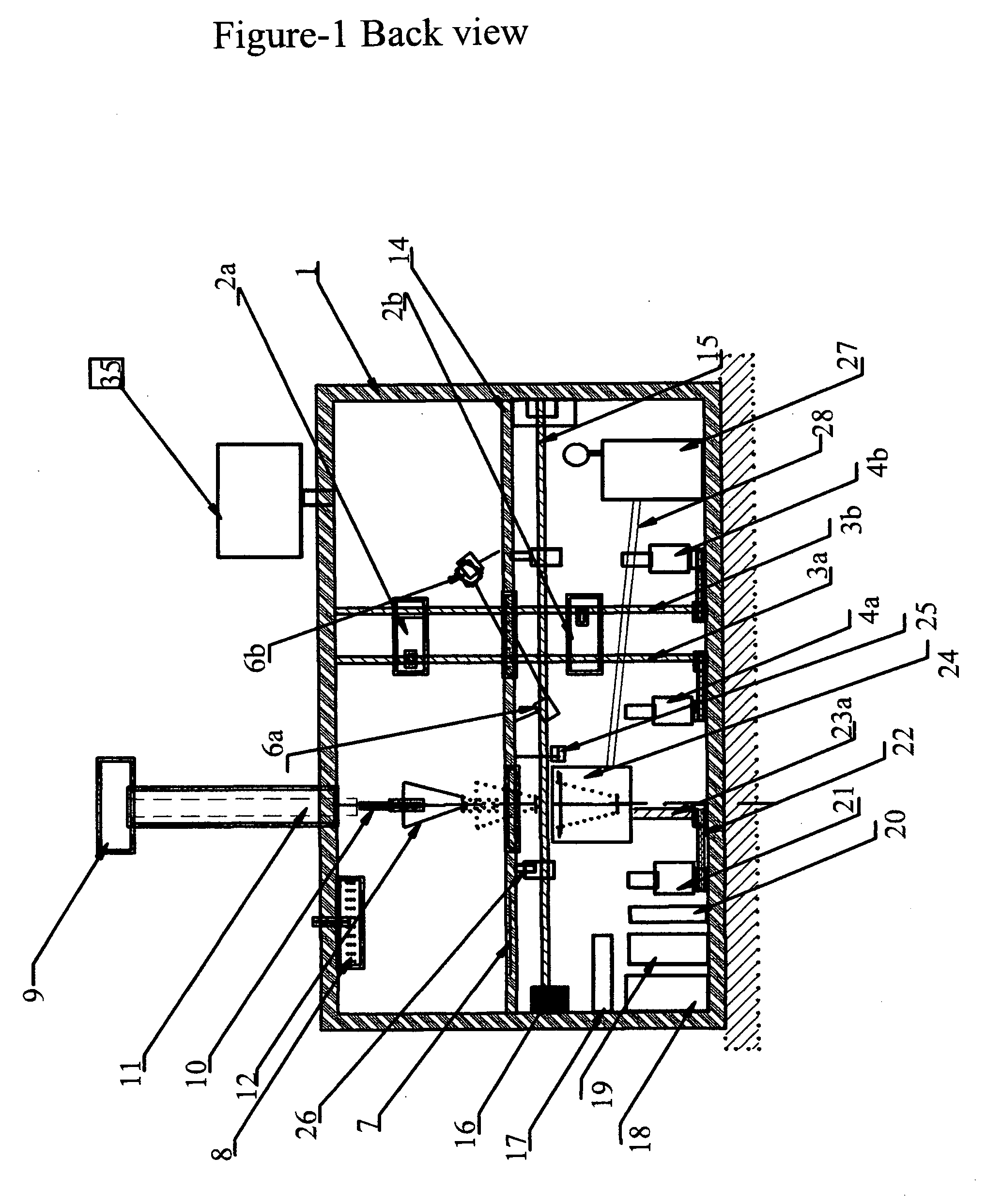
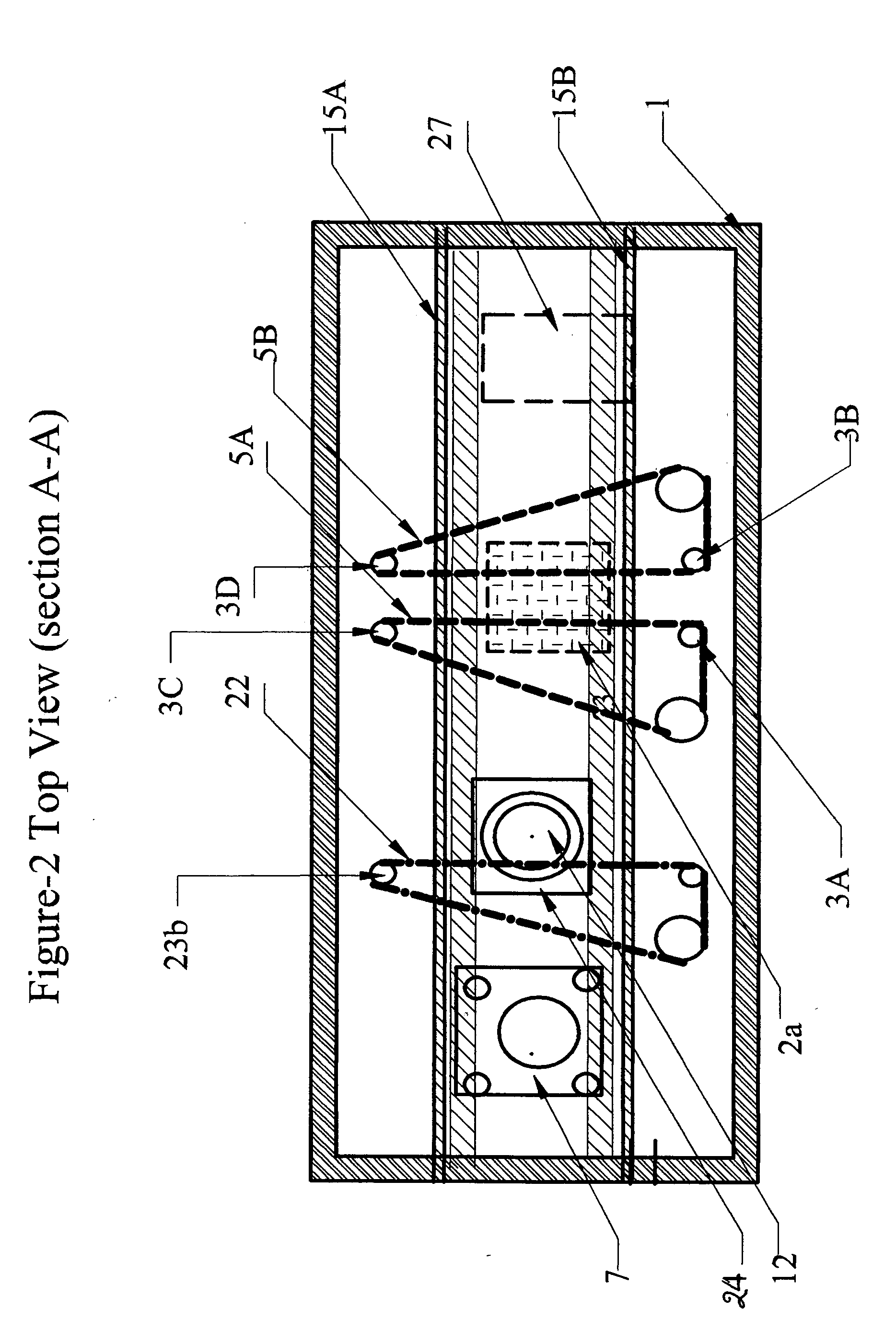
There is provided improved laser sintering systems that increase the powder density and reduce anomalies of the powder layers that are sintered, that measure the laser power within the build chamber for automatic calibration during a build process, that deposit powder into the build chamber through a chute to minimize dusting, and that scrubs the air and cools the radiant heaters with recirculated scrubbed air. The improvements enable the laser sintering systems to make parts that are of higher and more consistent quality, precision, and strength, while enabling the user of the laser sintering systems to reuse greater proportions of previously used but unsintered powder.
Owner:3D SYST INC
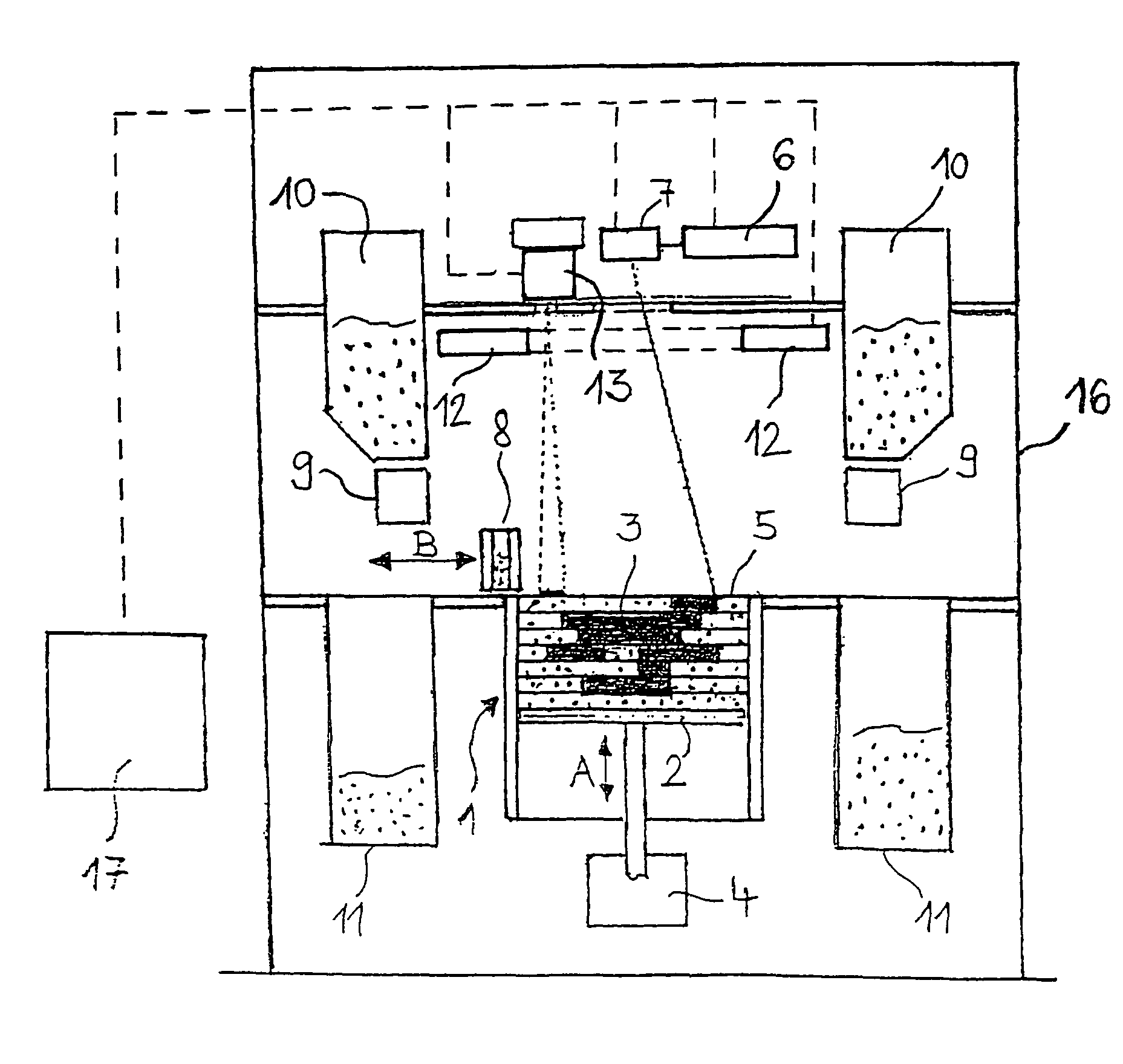
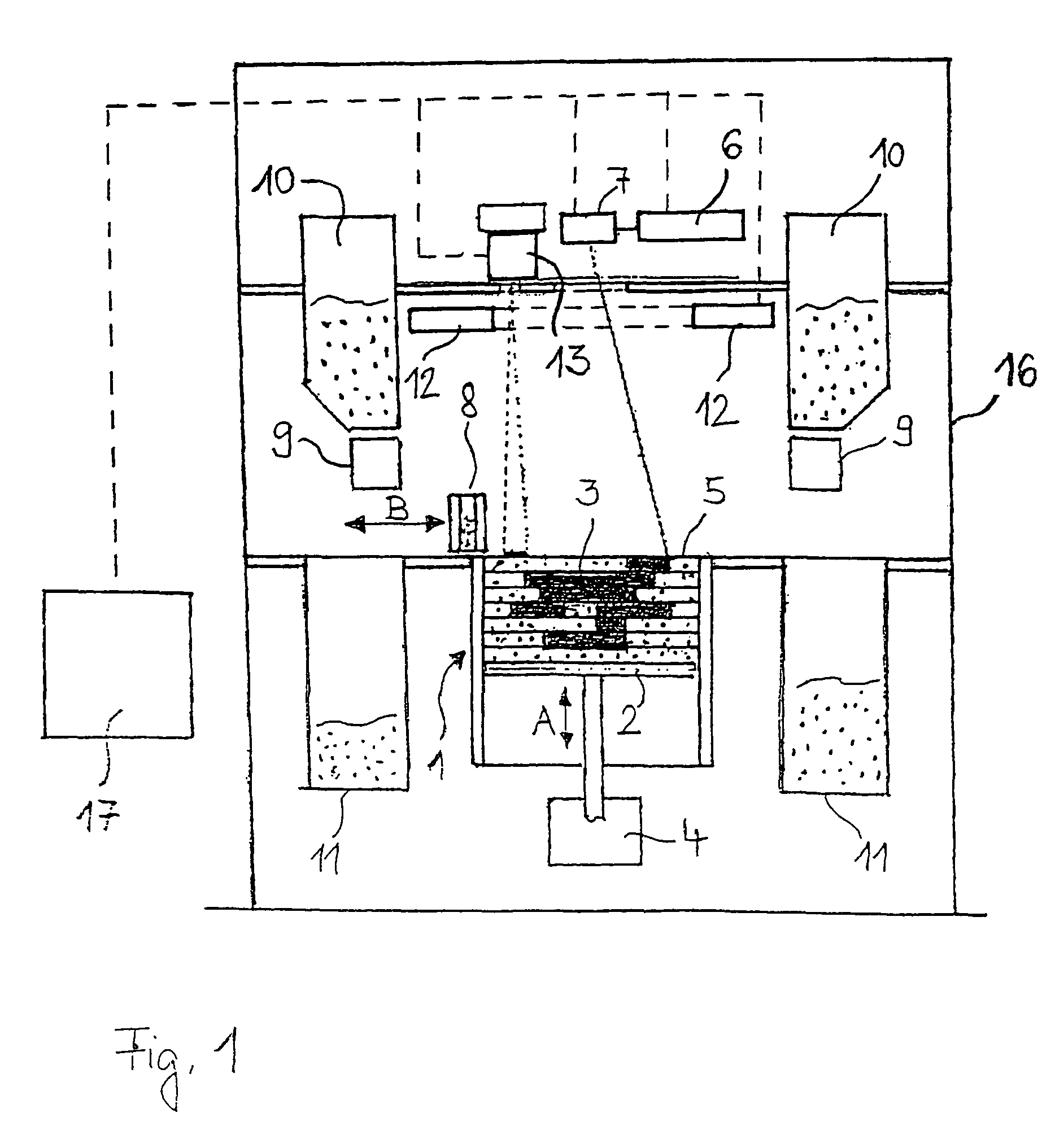
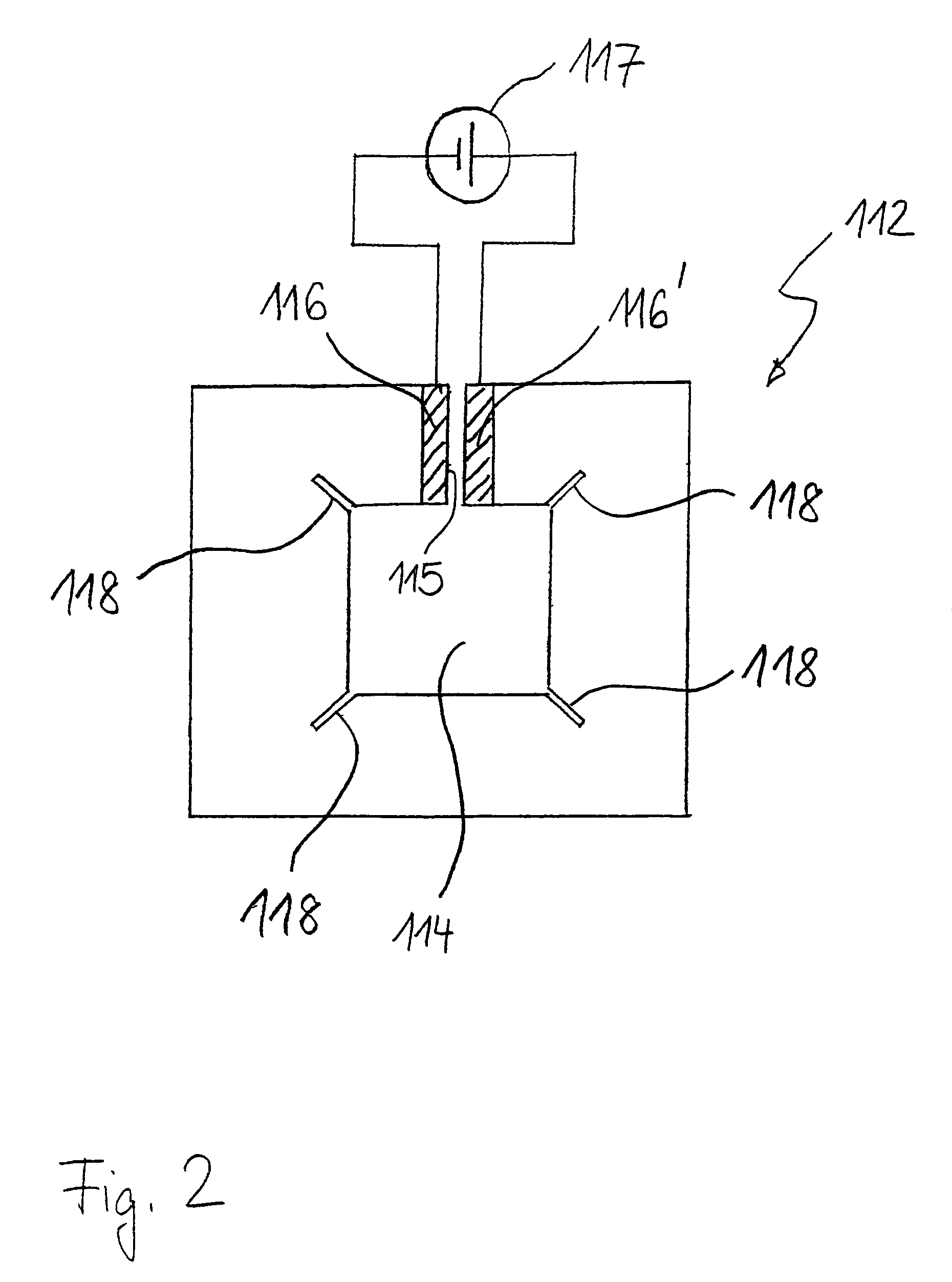
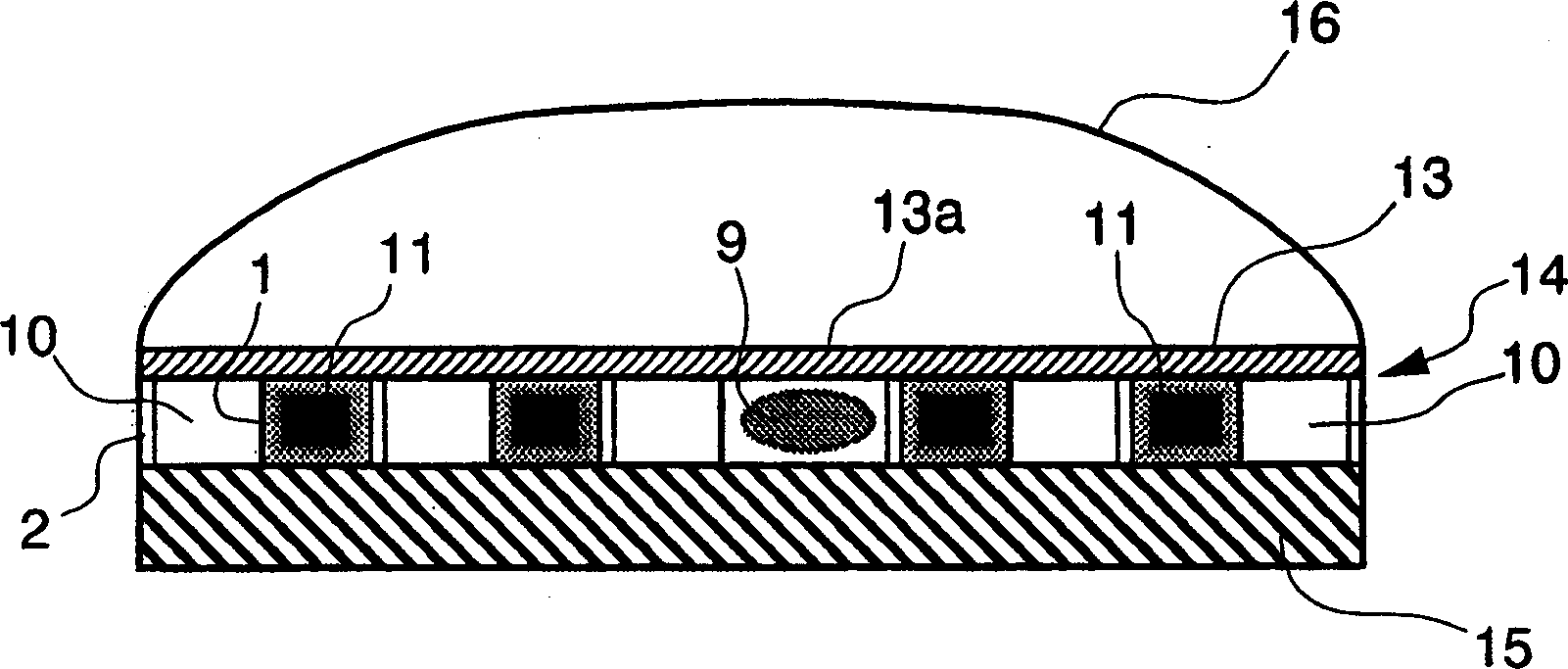
Radiant heater for heating the building material in a laser sintering device
InactiveUS8073315B2Reduce the temperatureThermal inertiaDomestic stoves or rangesDrying solid materials with heatRadiant heaterMetallurgy
A radiant heating for heating the building material in a laser sintering device and a laser sintering device having such a radiant heating are described. The radiant heating has a sheet-like heat radiating element (113, 213, 313), which is characterized in that it is made of a material, that has a low thermal inertia with a thermal diffusivity of preferably more than 1.5·10−4 m2 / s and preferably has a thickness of 2 mm or less.
Owner:EOS ELECTRO OPTICAL SYST
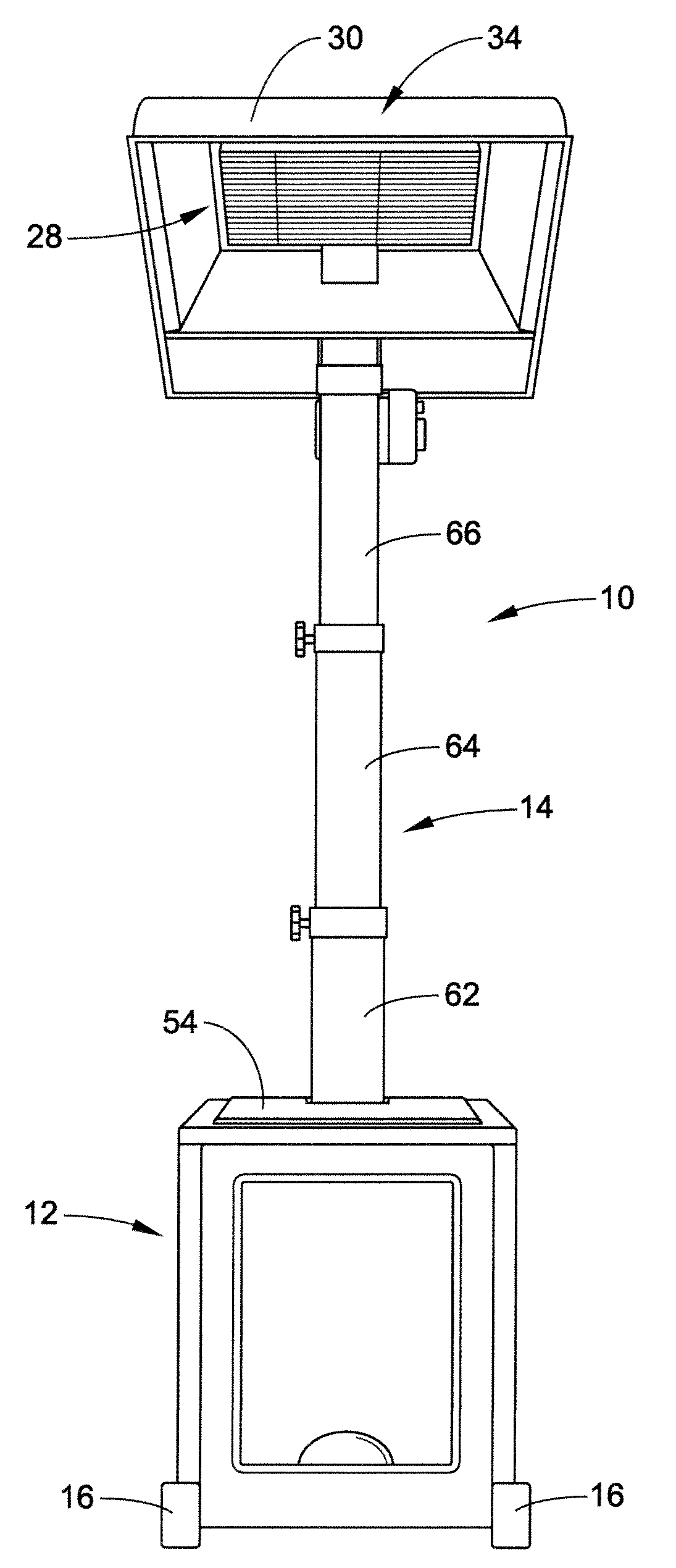
Portable collapsible radiant heater
InactiveUS20080152329A1Easy to storeVehicle headlampsDomestic stoves or rangesRadiant heaterEngineering
A portable, collapsible radiant heater includes a base and a support mounted to the base. The support has a collapsed position wherein the base is configured to at least partially receive the support, and an extended position wherein the support extends upwardly from the base. A heater-head for generating radiant heat is connected to the support. A reflector is mounted to one of the heater-head and the support. The reflector at least partially surrounds the heater-head for downwardly reflecting radiant heat generated by the heater-head. The reflector and heater-head are reciprocally movable between the collapsed position wherein the reflector and heater-head are in close proximity to the base and the extended position wherein the reflector and heater-head are distant from the base.
Owner:J F MESKILL ENTERPRISES
Glass molding system and related apparatus and method
A glass molding system and a method of making glass articles using the glass molding system are disclosed. The glass molding system includes an indexing table, a plurality of enclosures arranged along the indexing table, and a plurality of stations defined on the indexing table such that each of the stations is selectively indexable with any one of the enclosures. At least one radiant heater is arranged in the at least one of the enclosures. A radiation reflector surface and a radiation emitter body are arranged in at least one of the enclosures. The radiation emitter body is between the at least one radiant heater and the radiation reflector surface and has a first surface in opposing relation to the at least one radiant heater and a second surface in opposing relation to the radiation reflector surface.
Owner:CORNING INC
Heat reflector and substrate processing apparatus comprising the same
ActiveUS20060249695A1Heating fastIncrease ratingsMuffle furnacesLayered productsRadiant heaterEngineering
A substrate processing apparatus includes a process chamber including upper and lower quartz walls, a substrate support disposed in the process chamber, radiant heaters respectively provided above and below the quartz walls of the chamber, and heat reflectors disposed outside the process chamber for reflecting heat towards the substrate support. Each of the heat reflectors has heating has a first thermally reflective section oriented to reflect the heat towards an outer peripheral region of the substrate support and a second thermally reflective section oriented to reflect the heat towards a central region of the substrate support. Each heat reflector also has a reflection angle adjusting mechanism by which an angle at which the second thermally reflective section reflects heat can be adjusted. The angle is adjusted depending on the temperature distribution across the substrate so that the substrate can be processed uniformly.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
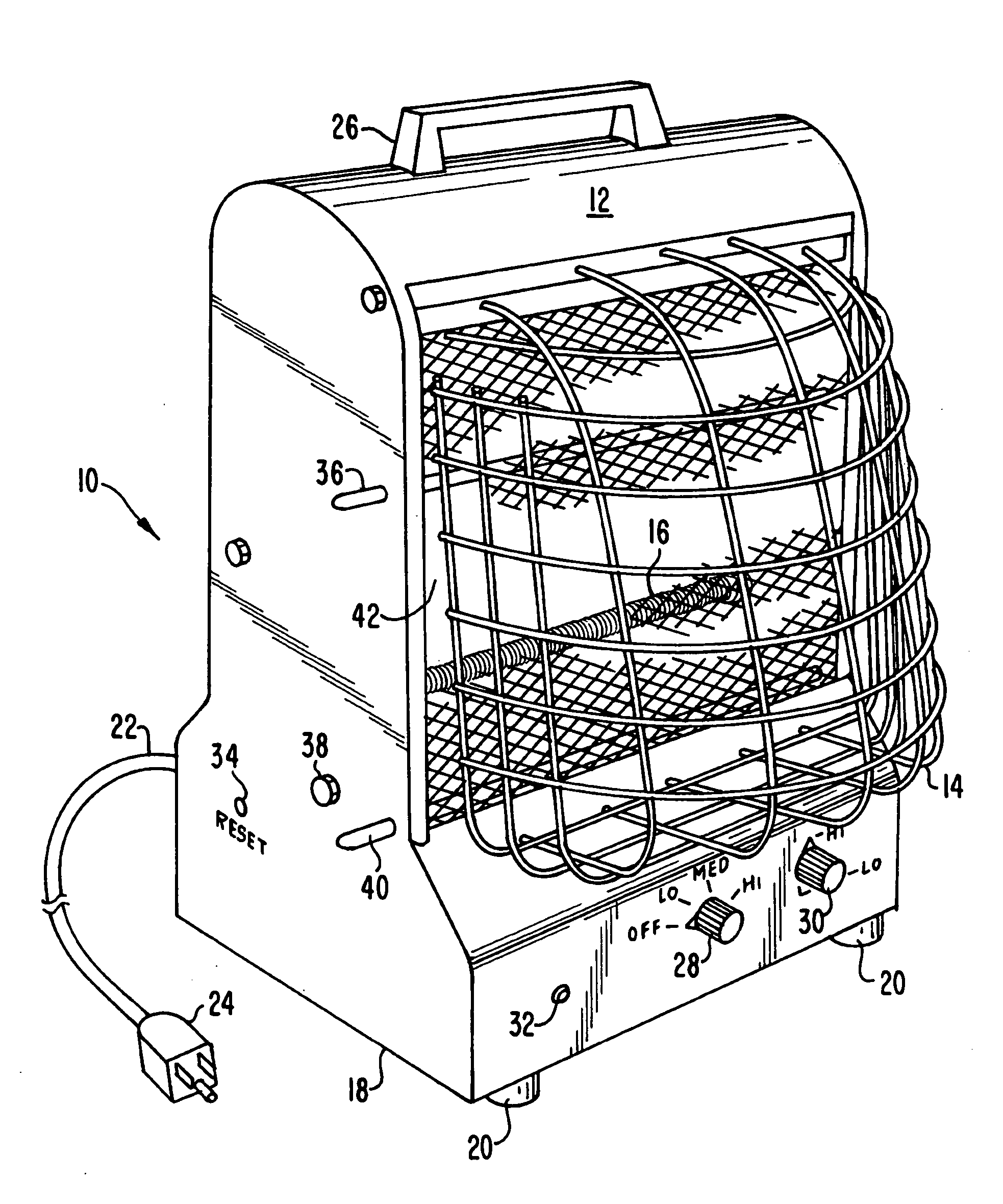
Portable radiant heater with two reflectors
InactiveUS6188836B1Beautiful appearanceStoves/ranges with convection heatingElectrical heating fuelElectricityRadiant heater
A portable radiant heater comprises an electrically energized heating element extending along a vertical axis. A first, multi-faceted, concave reflective surface is positioned to the rear of the heating element. A second reflector is positioned forward of and in close proximity to the heating element. The first reflector directs radiant energy received directly from the heating element and indirectly from the second reflector forward with minimal radial dispersion.
Owner:APPLIANCE DEVMENT
Variable low intensity infrared heater
ActiveUS20050175944A1Improve liquidityEasy to controlDomestic stoves or rangesPilot flame ignitersRadiant heaterCombustor
A radiant heater including a burner having an inlet for receiving an air and gas mixture and an exhaust for emitting exhaust gases generated by combustion of the air and gas mixture within the burner, an elongated radiant heating tube having an inlet for receiving the exhaust gases emitted by the burner, a gas flow control assembly for controlling the flow of gas to the burner, and a blower for controlling the flow of air to the burner. The blower comprises a two-stage blower including a motor having a low winding corresponding to a low blower speed and a high winding corresponding to a high blower speed. The gas flow control assembly comprises a two-stage regulator or two stage two-stage valve having a low setting for delivering a low gas flow to the burner and a high setting for delivering a high gas flow to the burner.
Owner:SOLARONICS
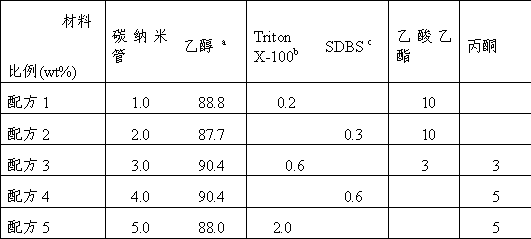
Low-temperature radiation electrothermal film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103305051AHigh peel strengthImprove adhesion strengthInksOhmic-resistance heatingPolyesterRadiant heater
The invention discloses a low-temperature radiation electrothermal film and a preparation method thereof. The carbon nanometer conductive ink comprises the following components in mass percent: 1 to 5% of carbon nano tube, 94 to 98% of solvent, and 0.2 to 2% of surface active agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: manufacturing a hot melt adhesive layer on a polyester film; printing a carbon nanometer conductive ink layer onto the hot melt adhesive layer; printing a generating and heating ink layer on the ink layer; manufacturing an electrode; and then hot-processing and compounding the polyester film through a hot melt adhesive film. The low-temperature electric radiant heater film has the characteristics that the peeling strength is high and the electro thermal power can be flexibly adjusted.
Owner:KMT纳米科技(香港)有限公司
Electric heating element and method for its production
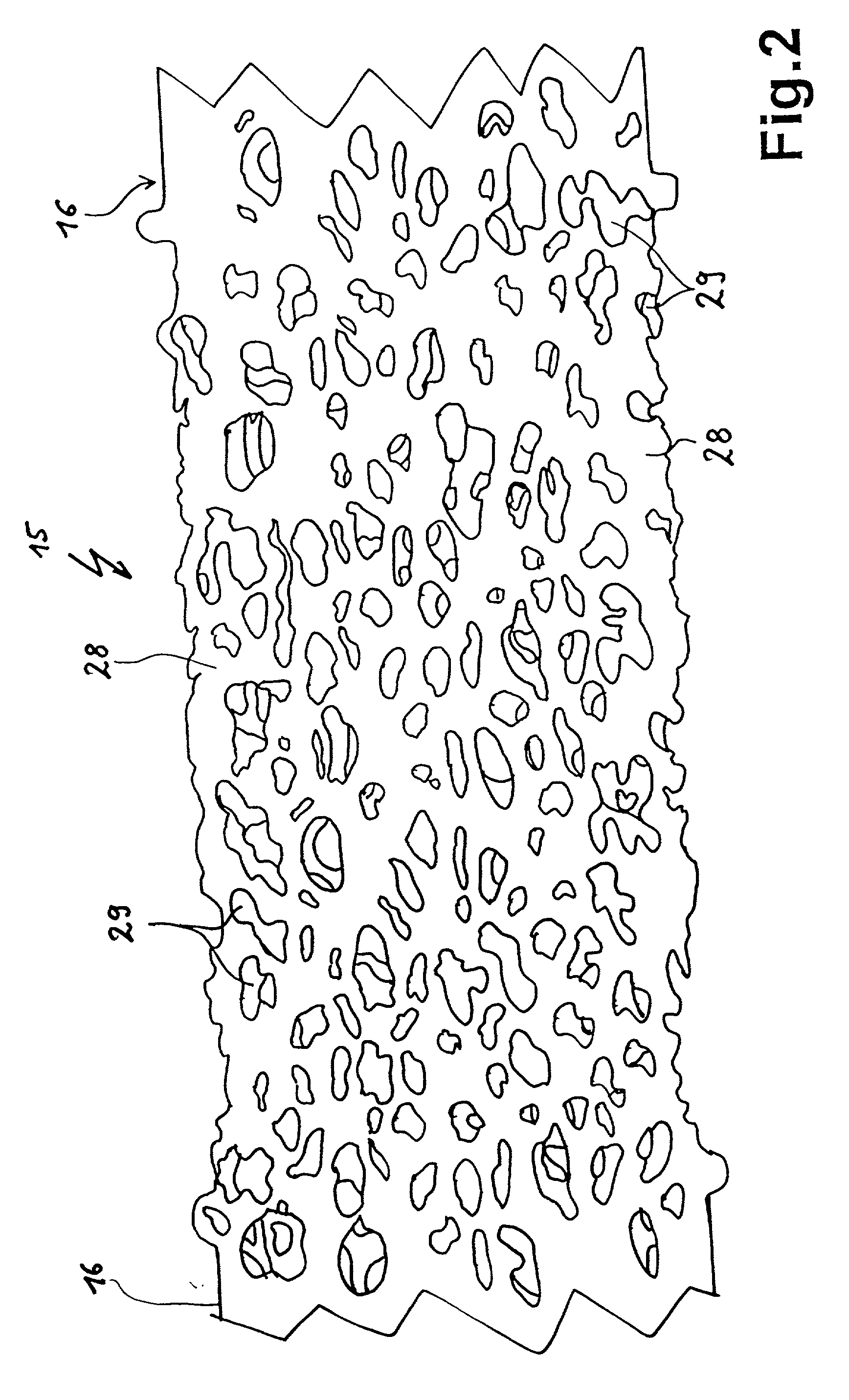
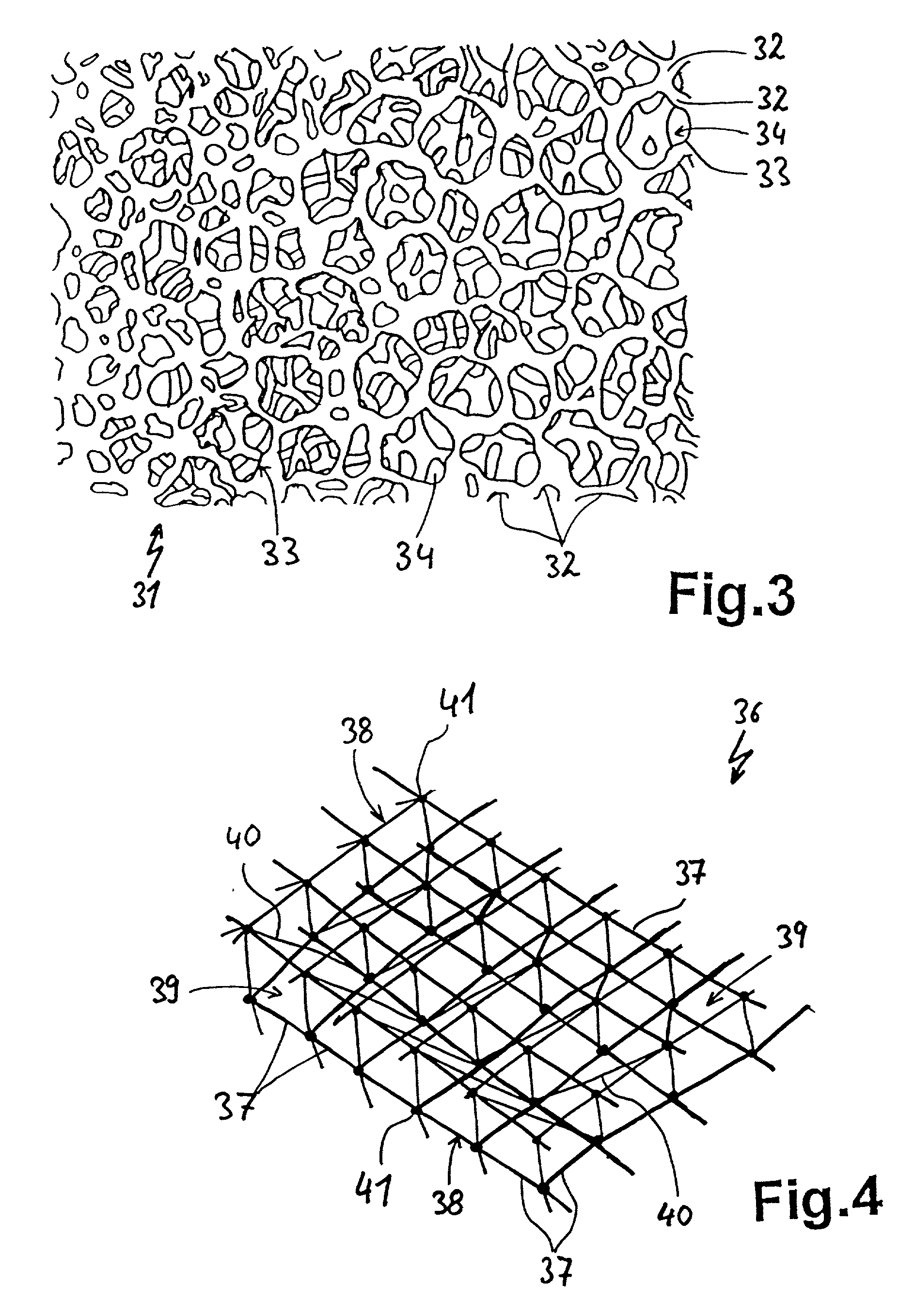
On the one hand is provided an electric heating element (15, 31) consisting of a semiconducting ceramic (28, 32) as well as a method for its production. The semiconducting ceramic material may be porous or foamed to thus contain pores (29, 34) open outwardly. The pores are attainable by admixing filler bodies, which dissolve during sintering, to the starting material or by impreganting a textile substrate material (36) with a ceramic material. Due to the porosity of the heating element (15, 31) an increased radiant surface area is attained. On the other hand is provided an electric heating element (115, 132, 145, 150, 158, 160, 162) as well as a method for its production which consists of semiconducting ceramic and comprises a negative temperature coefficient of the electrical resistance. The temperature coefficient is negative throughout over the full operating temperature range. The material suitable for the heating element (115, 132, 145, 150, 158, 160, 162) is doped silicon carbide or TiN. One such heating element (115, 132, 145, 150, 158, 160, 162) may be put to use, for example, rod-shaped in a radiant heater body (111) or foil-shaped at the underside of a surface element (30) of a cooktop (31). The electric conductivity of the material of the heating element (115, 132, 145, 150, 158, 160, 162) can be adjusted by nitrogen absorption during annealing in a nitrogen atmosphere subsequent to the sintering process.
Owner:E G O ELEKTRO GERAETEBAU GMBH
Heating system
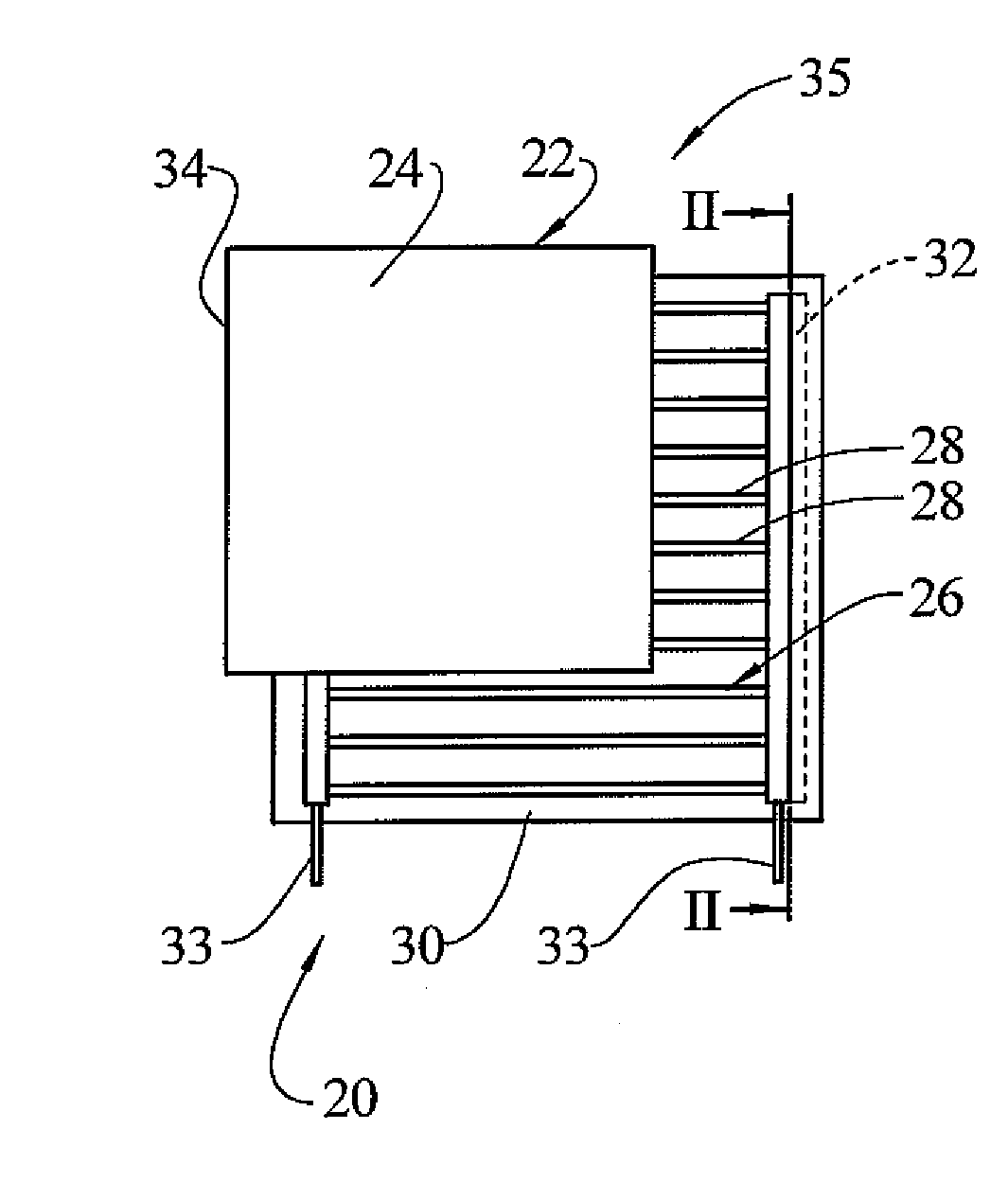
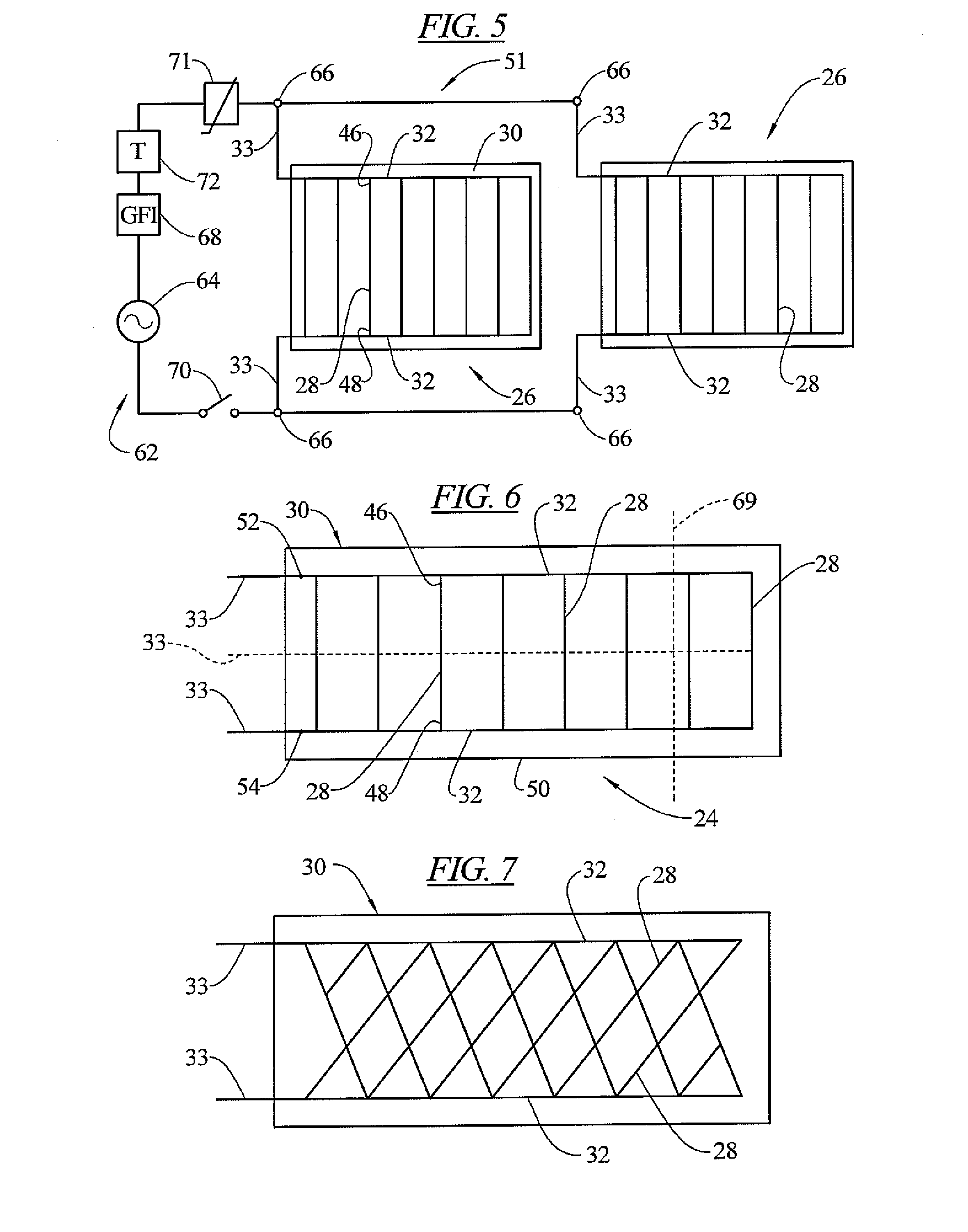
A heating system which may include a bonding membrane having a water permeable lamina, an electrically conductive ink-based radiant heater, and a first adhesive adapted to adhere to both the conductive ink-based radiant heater and the bonding membrane. The heating system may be incorporated in a floor including a substrate, the heating system and a decorative floor surface. The heating system may also be in the form of a multilayer panel having a bonding membrane, an electrically conductive ink-based heater including a plurality of electrically resistive strips printed on a first polymer sheet connected by electrically conductive buses, and electrical conductors extending from the buses to at least an edge of the panel.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
Device for heating preforms provided with supporting ring
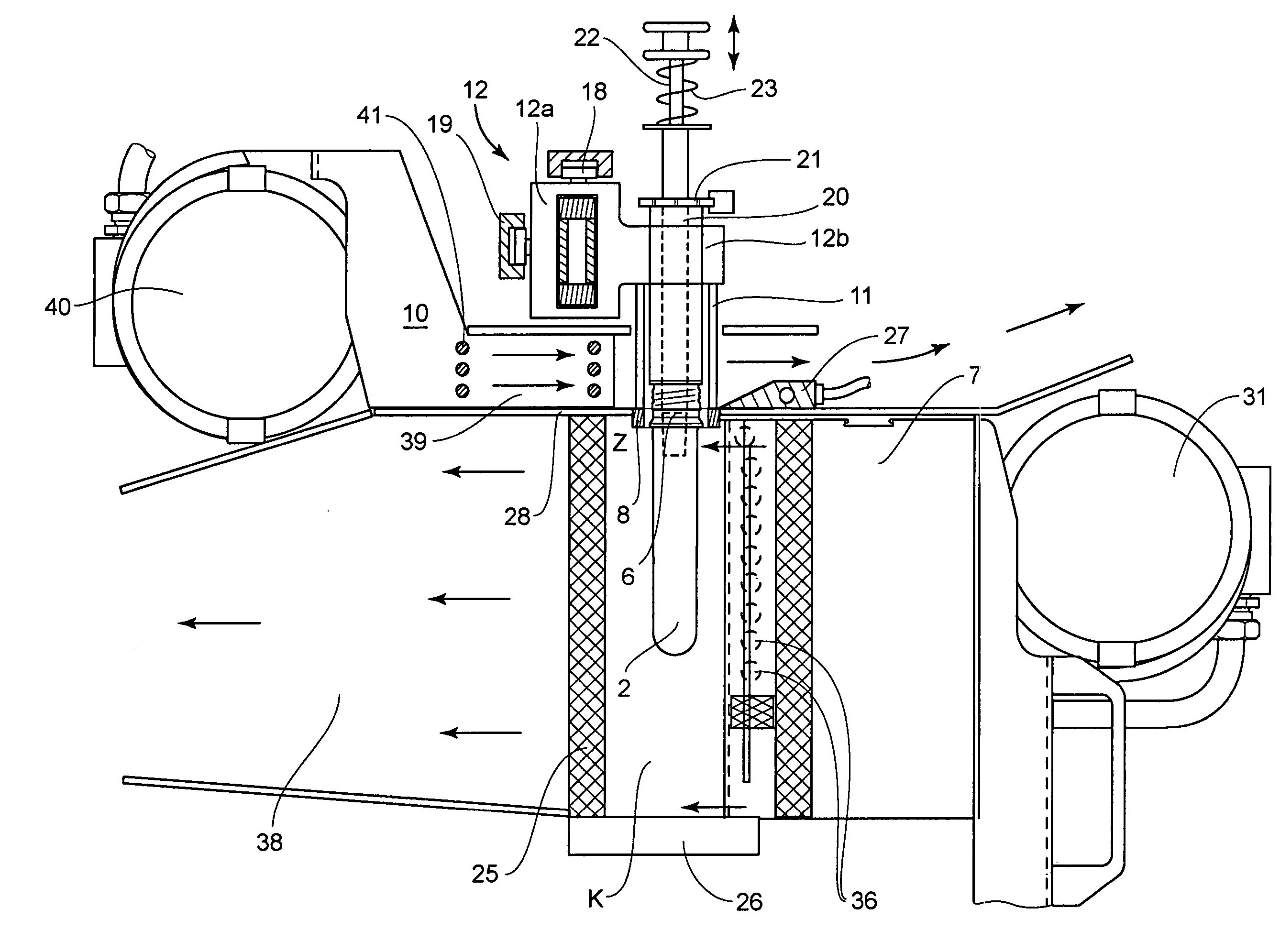
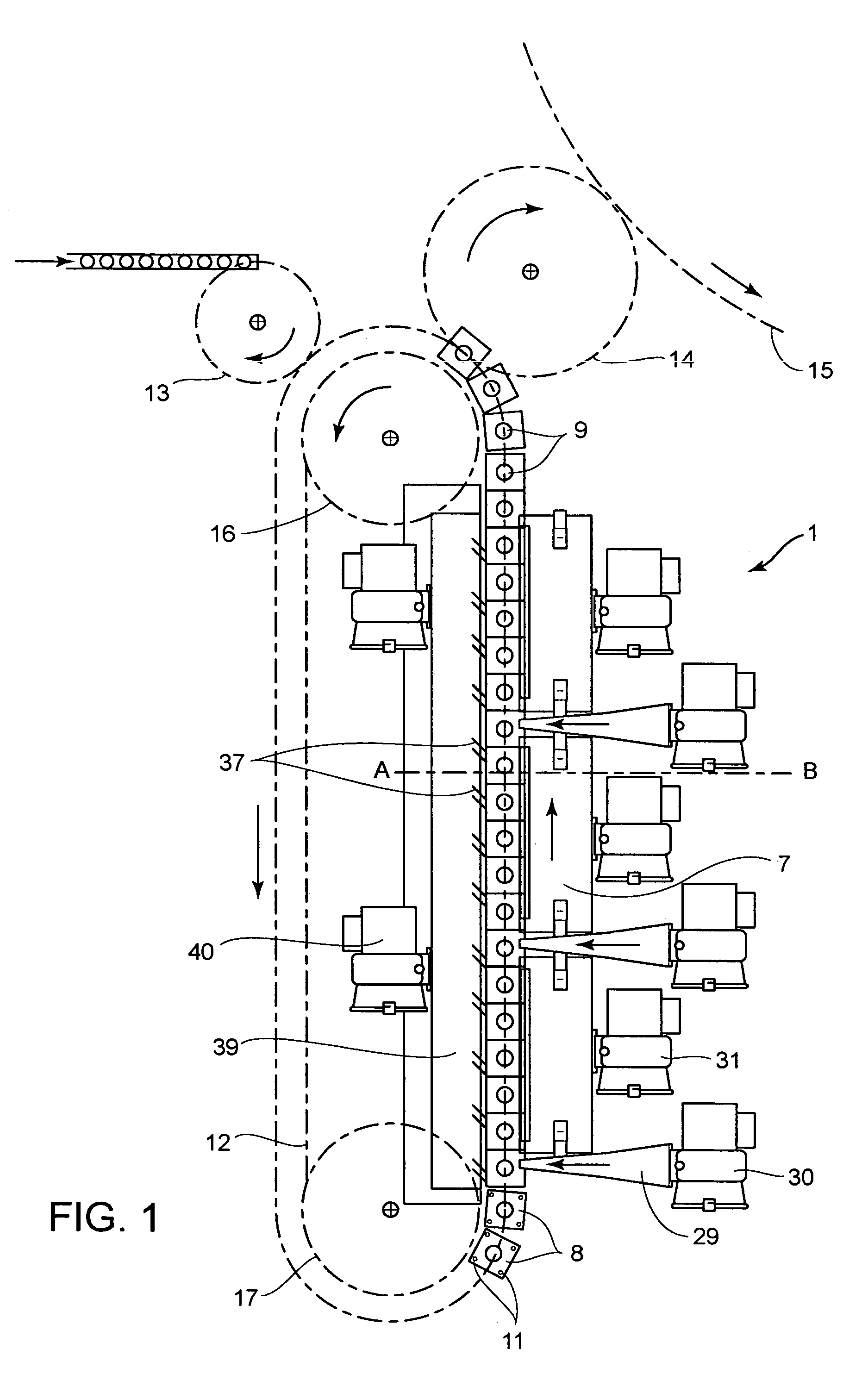
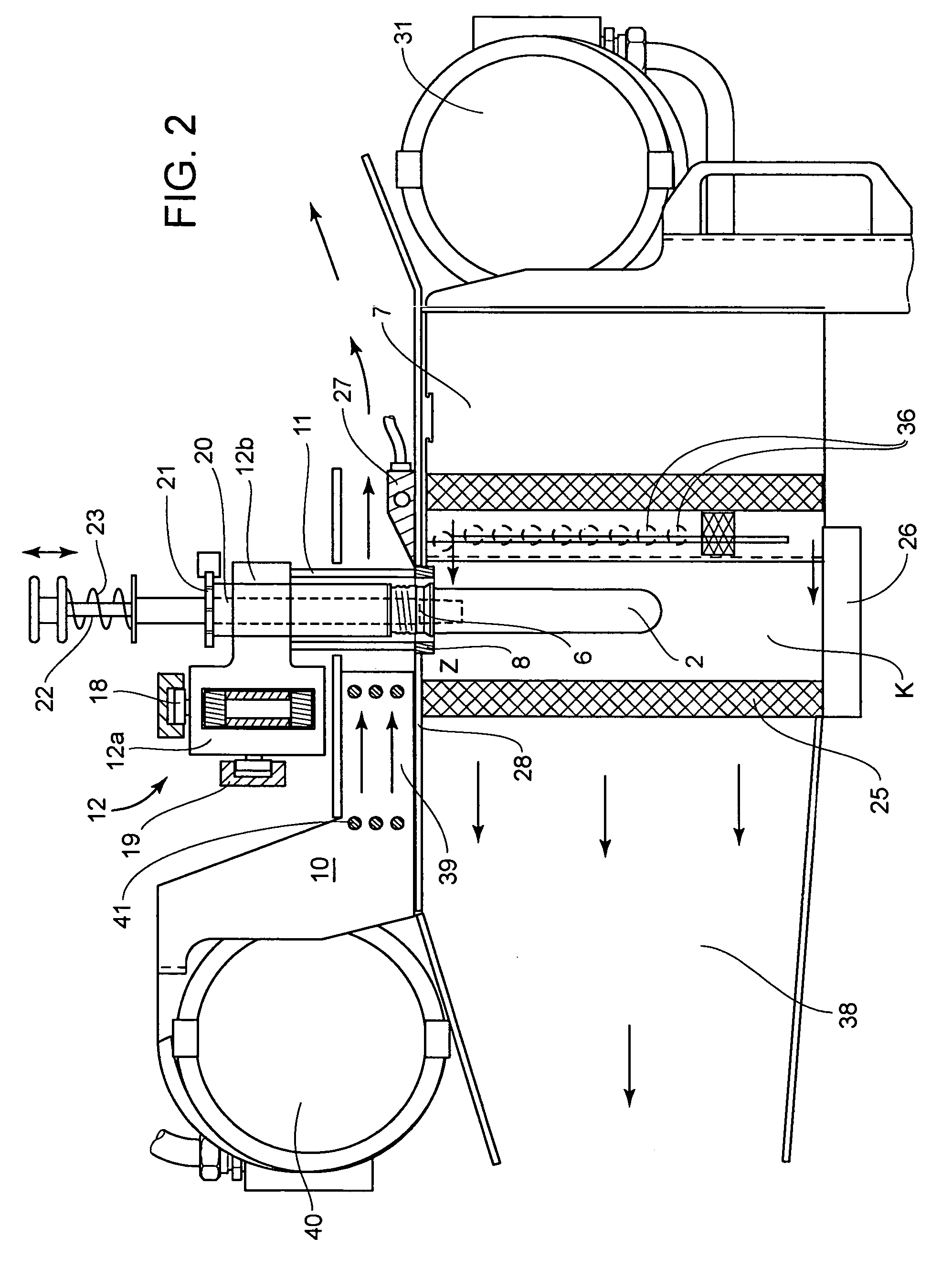
InactiveUS7121821B2Improve protectionHeating fastAuxillary shaping apparatusElectric/magnetic/electromagnetic heatingBlow moldingRadiant heater
A device for heating parisons made of a thermoplastic material and having a supporting ring for blow molding hollow bodies, having a conveyor means, a plurality of holding means which are arranged on the conveyor means and grip the head area of the parisons between the supporting ring and the mouth and radiant heaters arranged on the path of movement of the parisons carried by the holding means, a shield supported by the conveying means being assigned to each holding mandrel in the form of a cover plate which is located at the height of the supporting ring and has a borehole to receive the supporting ring. Furthermore, there is also a cooling device, which acts directly on the exposed head area. This permits optimum protection of the head area of the parisons, which is not to be shaped or deformed, to prevent unacceptable heating.
Owner:KRONES AG
Heater with reflector and method for reflecting heat
A radiant heater includes a radiant heat source and a reflector to direct the bulk of the heat generated by the radiant source in one direction. The shape of the reflector determines the radiant pattern of the heater, and generally defocuses the output to provide a diffuse heat pattern that is substantially free of hot spots.
Owner:MARLEY ENGINEERED PRODS
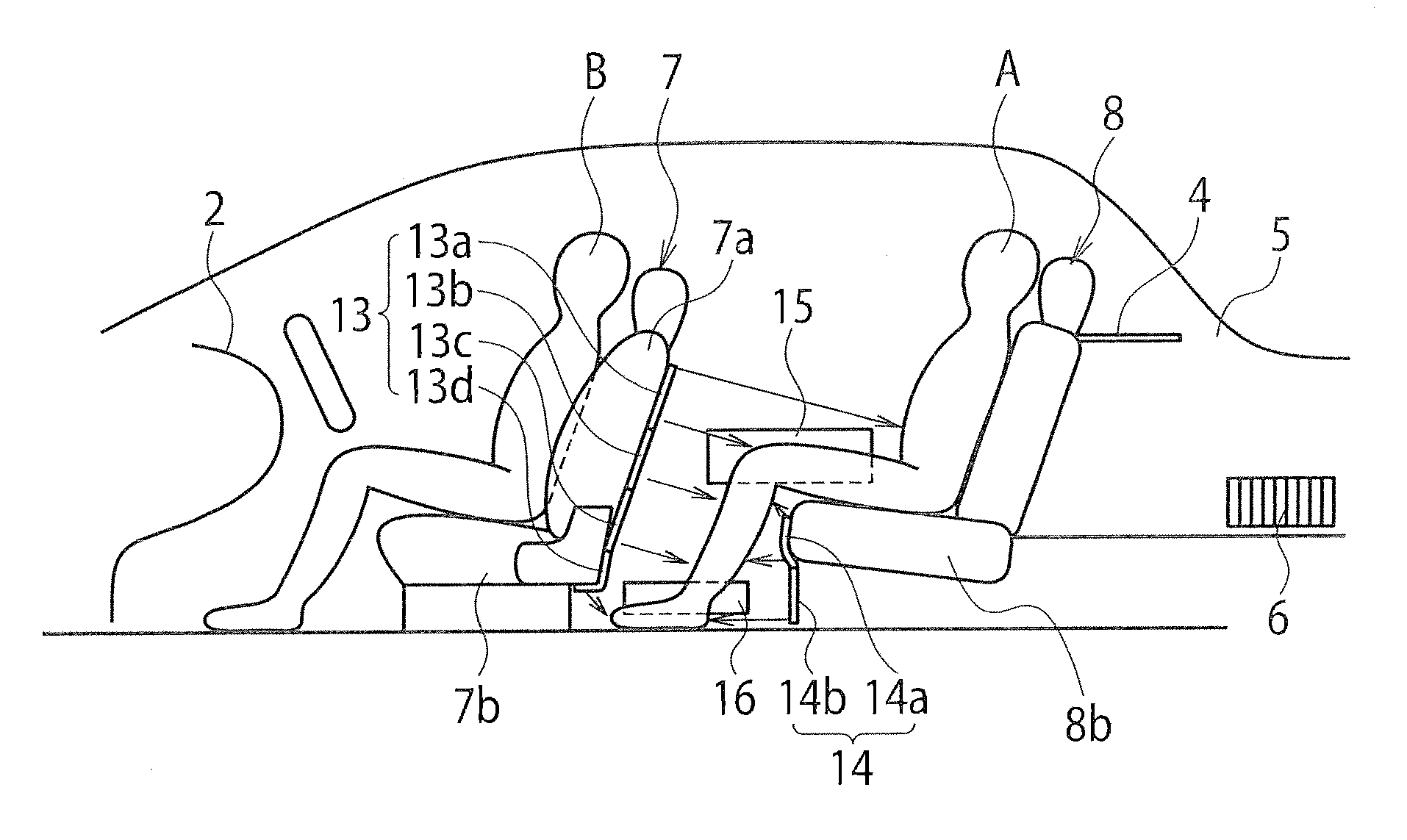
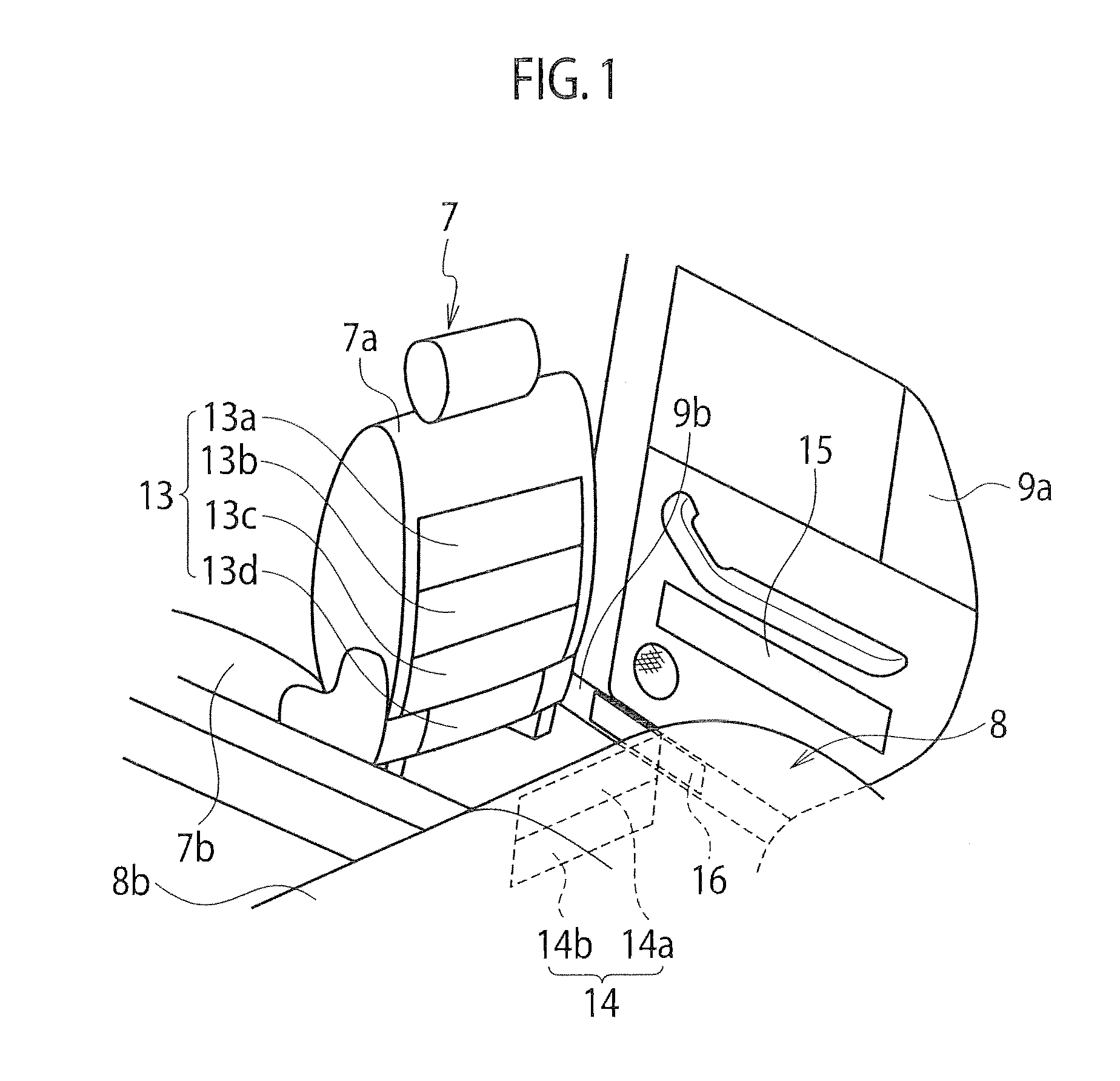
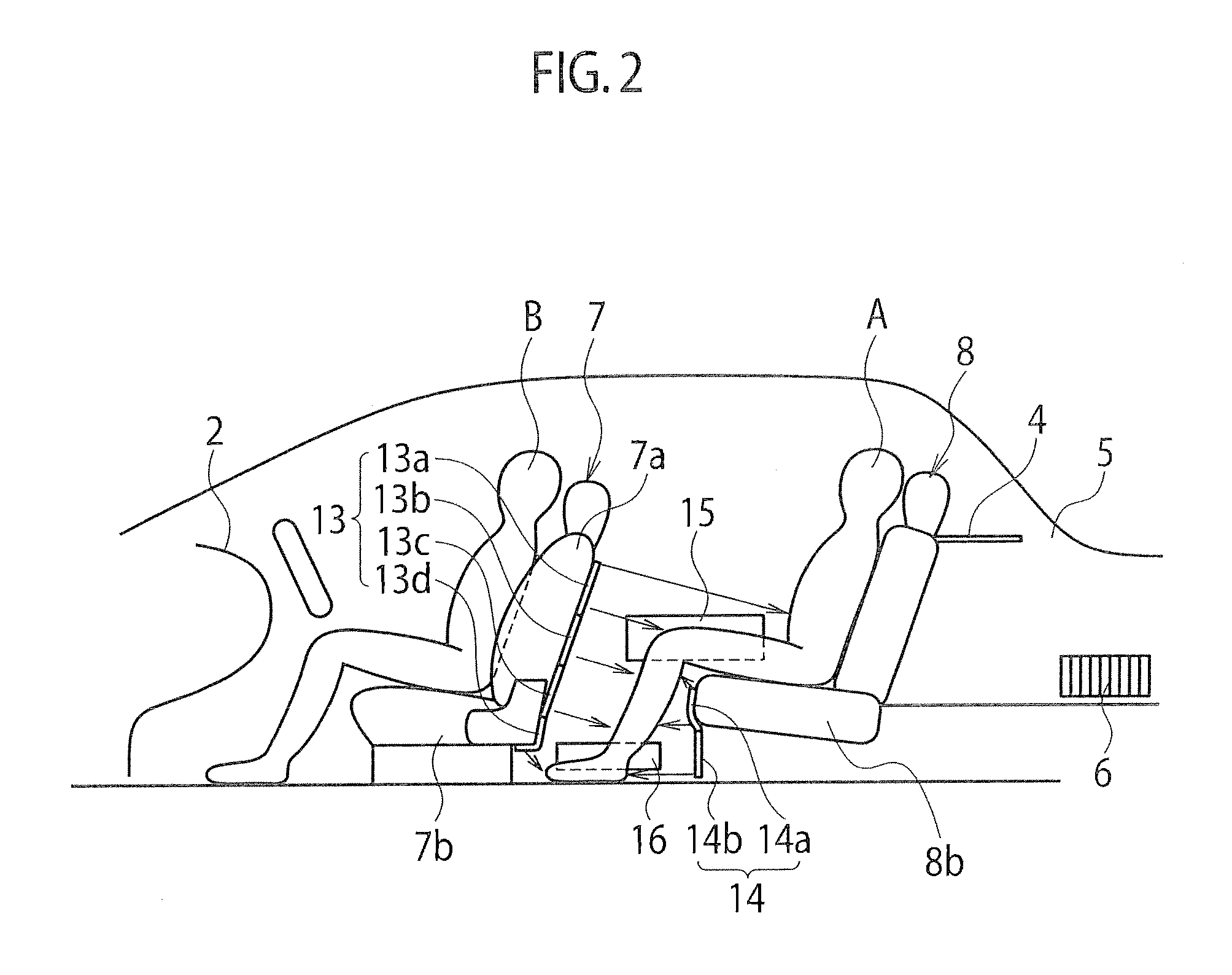
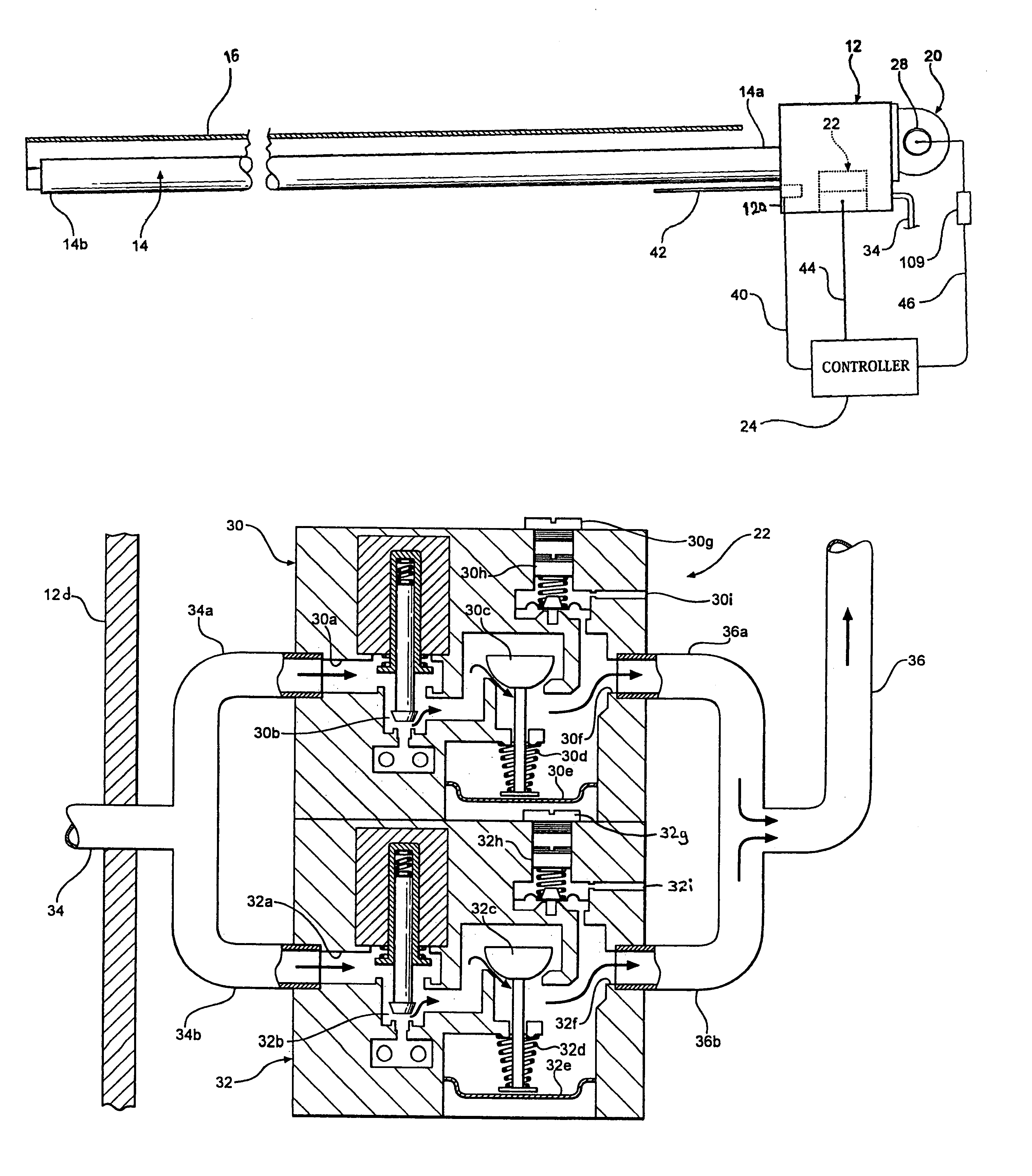
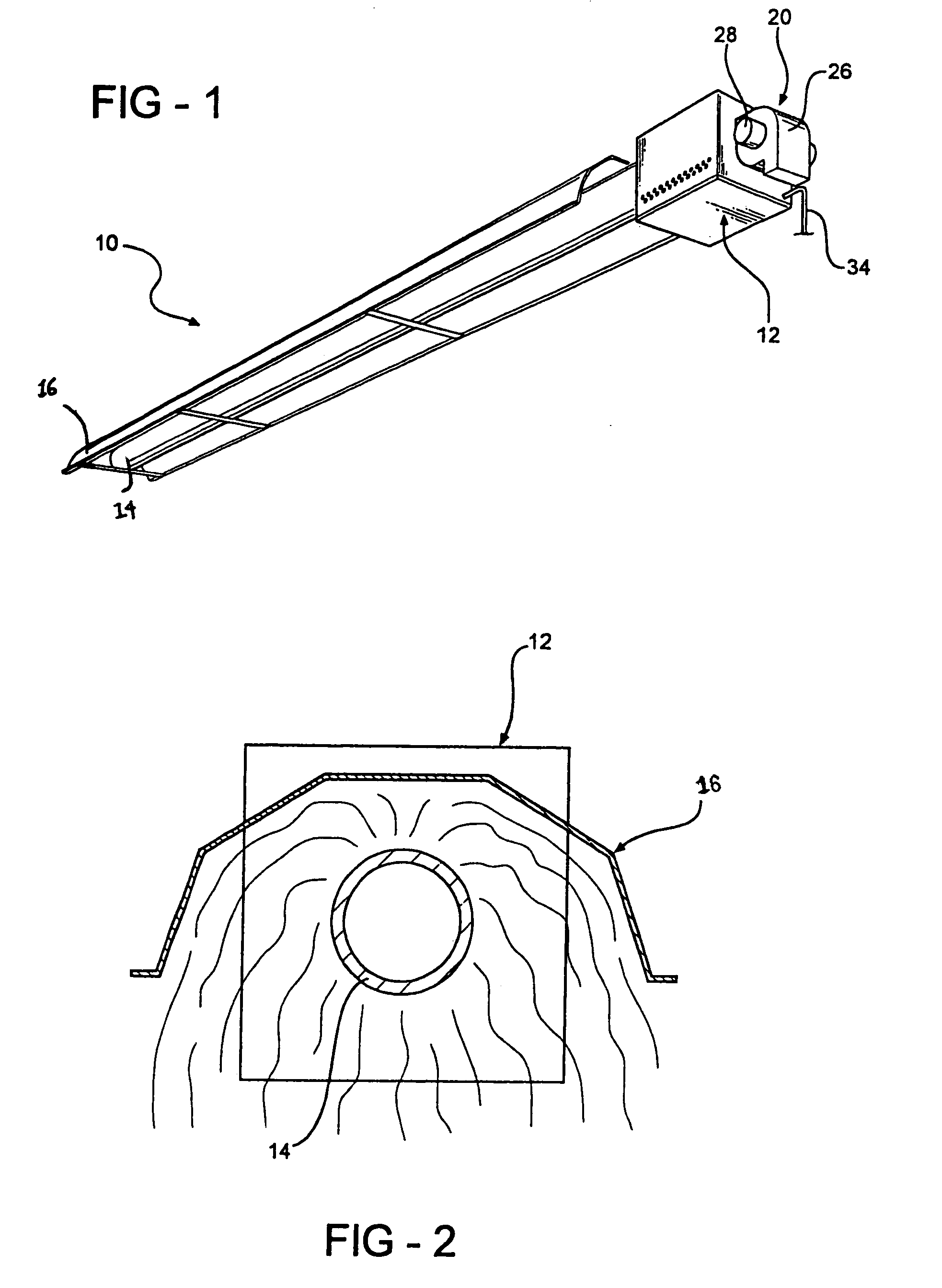
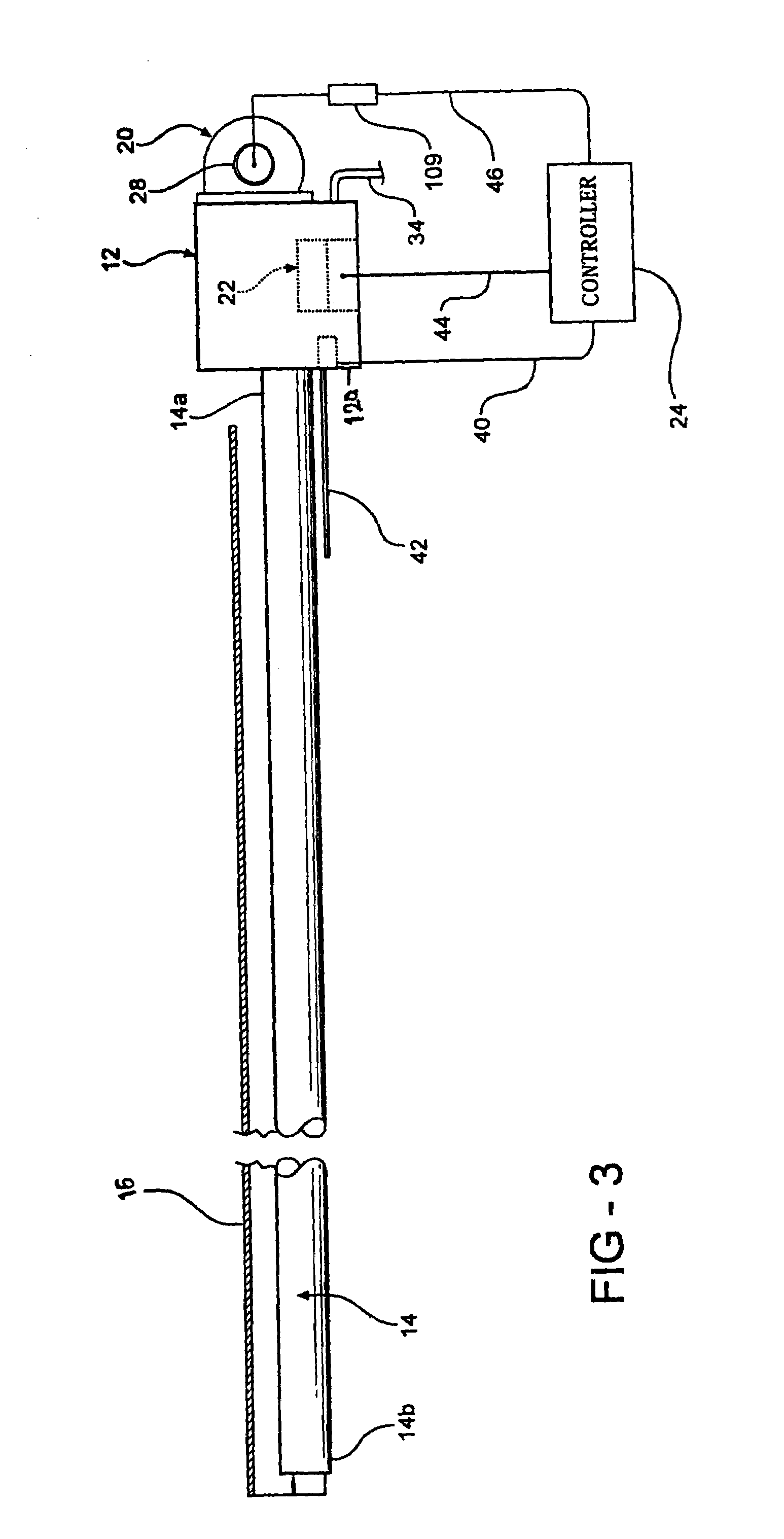
Radiant heating device for vehicle
A radiant heating device for a vehicle includes a radiant heater that radiates radiant heat toward a passenger and is provided together with an air-conditioner that selectively introduces air outside a passenger compartment or air inside the passenger compartment and then supplies conditioned air generated from the introduced air into the passenger compartment. The radiant heating device includes a controller that differentiates a radiant energy amount of the radiant heater when the introduced air into the air-conditioner is the air outside the passenger compartment from when the introduced air is the air inside the passenger compartment. According to the radiant heating device, the passenger can be provided with warm comfort feeling both in an outside air intake mode and in an inside air intake mode of the air-conditioner.
Owner:HIGHLY MARELLI JAPAN CORPORATION
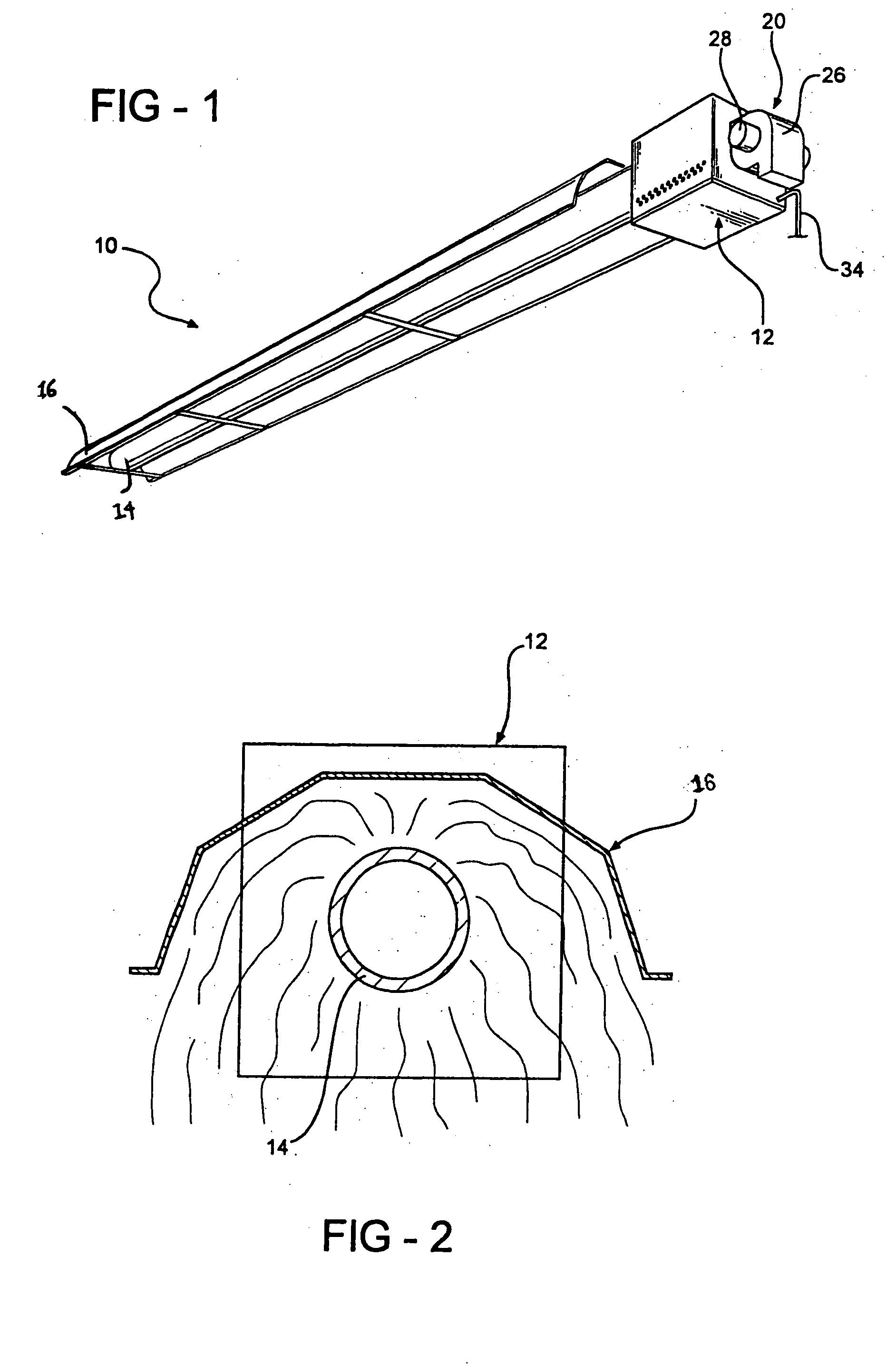
Variable input radiant heater
A variable demand radiant heating system applies variable burner control technology to singular or mulit-burner radiant heating systems. A radiant heater consists of a burner connected to an elongated heat exchanger tube. The combustion air is supplied to the burner via blower or draft inducer. Fuel is supplied to the burner via fuel regulator. Fuel and air are mixed in burner and communicated to the inlet end of the heat exchanger tube. Spent products of combustion are expelled from the heat exchanger at the outlet end. The burner controls continuously vary gas supply pressure (volume), via a modulating gas regulator, and combustion air pressure (volume), via a variable speed blower, communicated to the burner mixing chamber, which in turn, varies the burner input on a continuous curve (not stepped or staged) within a pre-determined input range as heat demand varies.
Owner:ROBERTS GORDON INC
Heat reflector and substrate processing apparatus comprising the same
ActiveUS7772527B2Heating fastIncrease ratingsMuffle furnacesLayered productsRadiant heaterEngineering
A substrate processing apparatus includes a process chamber including upper and lower quartz walls, a substrate support disposed in the process chamber, radiant heaters respectively provided above and below the quartz walls of the chamber, and heat reflectors disposed outside the process chamber for reflecting heat towards the substrate support. Each of the heat reflectors has heating has a first thermally reflective section oriented to reflect the heat towards an outer peripheral region of the substrate support and a second thermally reflective section oriented to reflect the heat towards a central region of the substrate support. Each heat reflector also has a reflection angle adjusting mechanism by which an angle at which the second thermally reflective section reflects heat can be adjusted. The angle is adjusted depending on the temperature distribution across the substrate so that the substrate can be processed uniformly.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
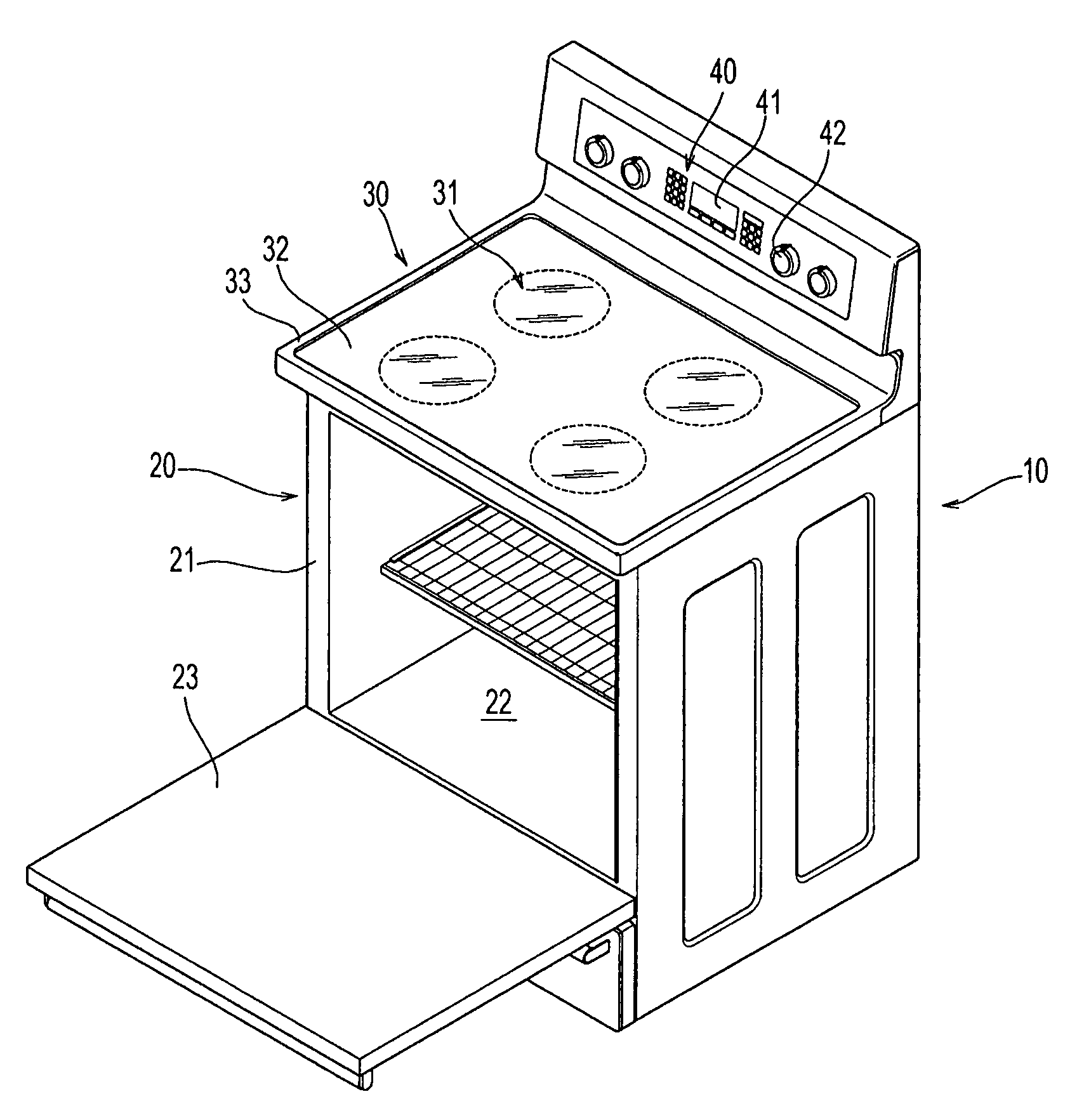
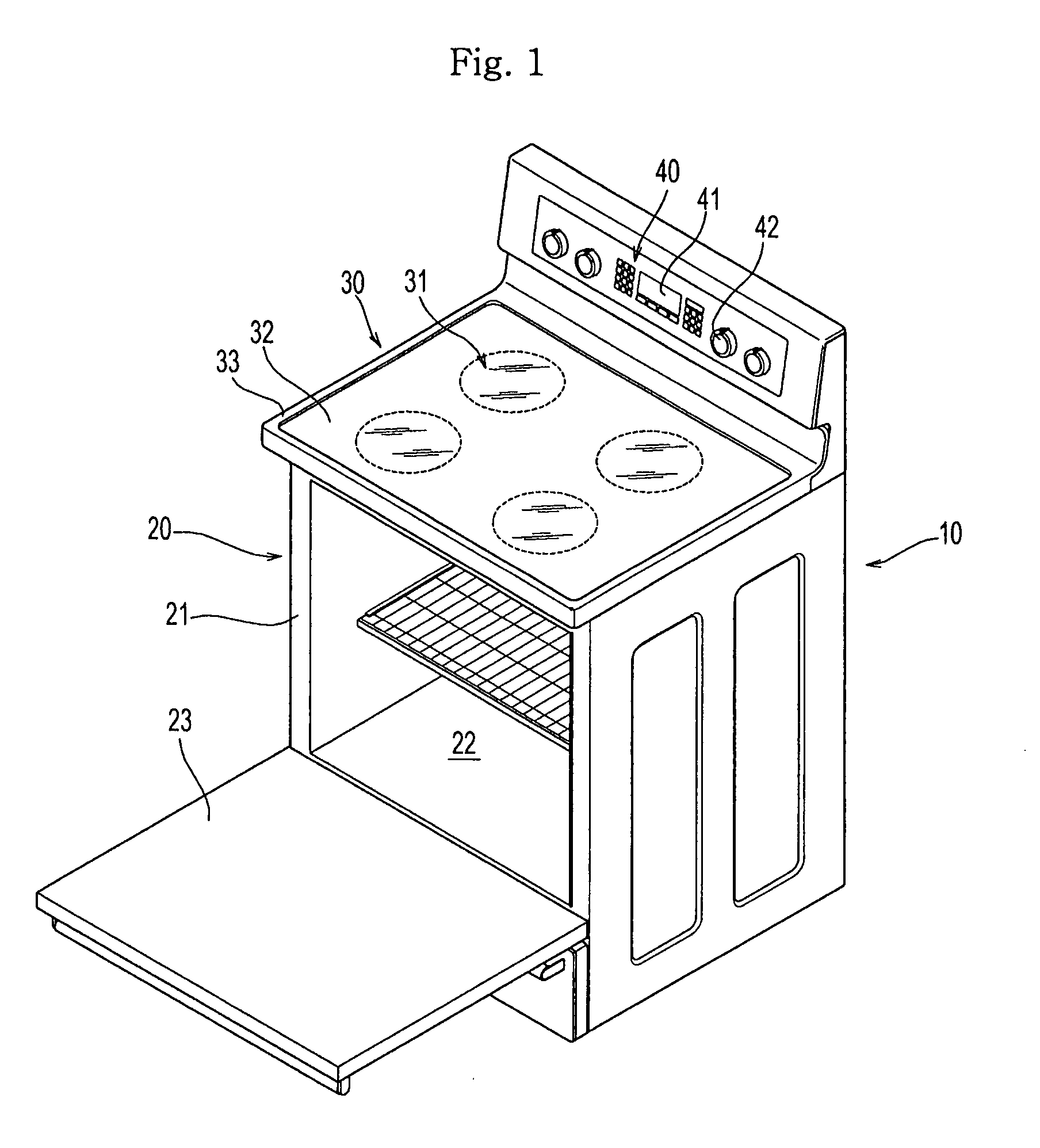
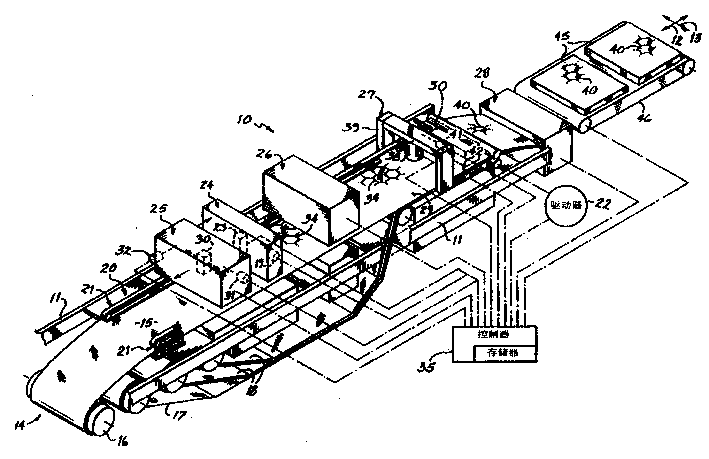
Pan sensor and heat generation unit having the pan sensor and cooking range having the heat generation unit and control method thereof
InactiveUS20080173632A1Stable detectionDomestic stoves or rangesCooking fumes removalCapacitanceRadiant heater
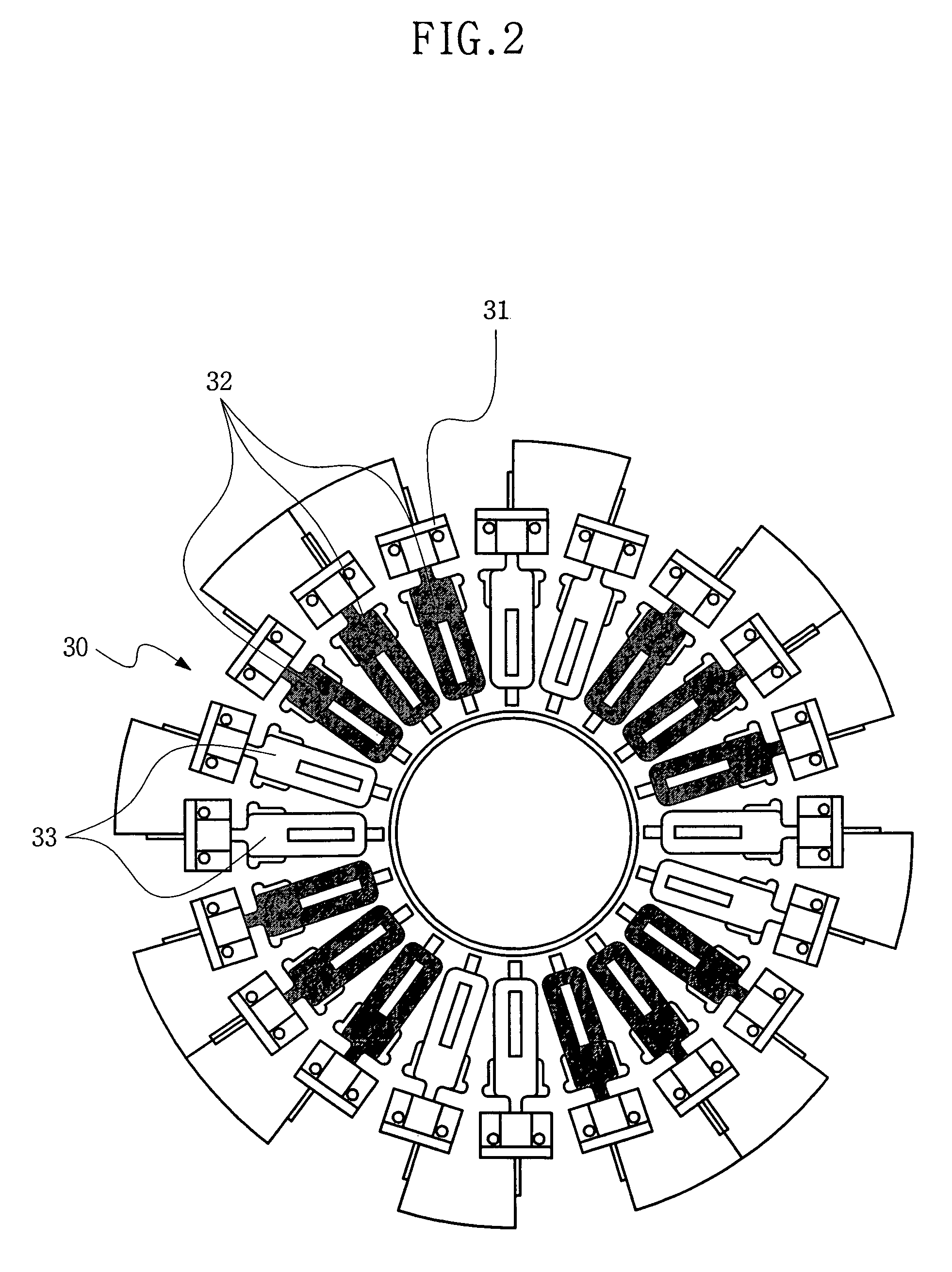
A pan sensor capable of stably detecting the mounting of a cooking pan without error, a heat generation unit having the pan sensor, a cooking range having the heat generation unit and a control method thereof are disclosed. The cooking range includes a top plate for mounting a cooking pan thereon, one or more radiant heaters installed in the top plate for supplying heat to the cooking pan, one or more pan sensors, respectively installed in the radiant heaters, for sensing the presence of the cooking pan, each pan sensor having a sensor ring for detecting variation in electrostatic capacitance depending on whether the cooking pan is present, and a controller for controlling each radiant heater based on a sensor output value of each pan sensor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Construction flat plate shaped split wall hanging vacuum solar superconducting heat collection apparatus
InactiveCN101319821ALow flow resistanceReduce flow rateSolar heating energySolar heat devicesBuilding integrationRadiant heater
The invention discloses a building flat plate shaped split typed wall-mounted vacuum solar energy superconductive heat collector, comprising a separating heat pipe formed by a flat plate collector with an automatic liquid separator, a circulating steam pipe, a circulating liquid pipe, a condenser and a heat accumulator. A plurality group of precise metering holes and capillaries are horizontally distributed between a liquid storage accumulator and a finned tube which are communicated with the circulating liquid pipe. The work condition of balanced film high temperature evaporation can be realized. The heat collector is characterized in that the heat collector has high temperature heat collection output, high efficiency and high energy heat transmission, long distance circulation without pump, low temperature and freeze proof, can be harmonized with buildings, is economical, has long service life and so on. The heat collector exploits the novel applied field of the solar energy with high temperature and separation structure, which can form devices of solar energy boiled water generator, radiant heater, air conditioner, additional water heater, etc. The heat collector is presented in a square and flat shape, which can be mounted and hung on the roof, the wall, the position above the window, the position below the window and the balcony of the buildings, is beautiful and harmonious. The heat collector is suitable for being used in high rise buildings with multiple floors, which is an ideal technology of solar energy for building integration.
Owner:喜春野
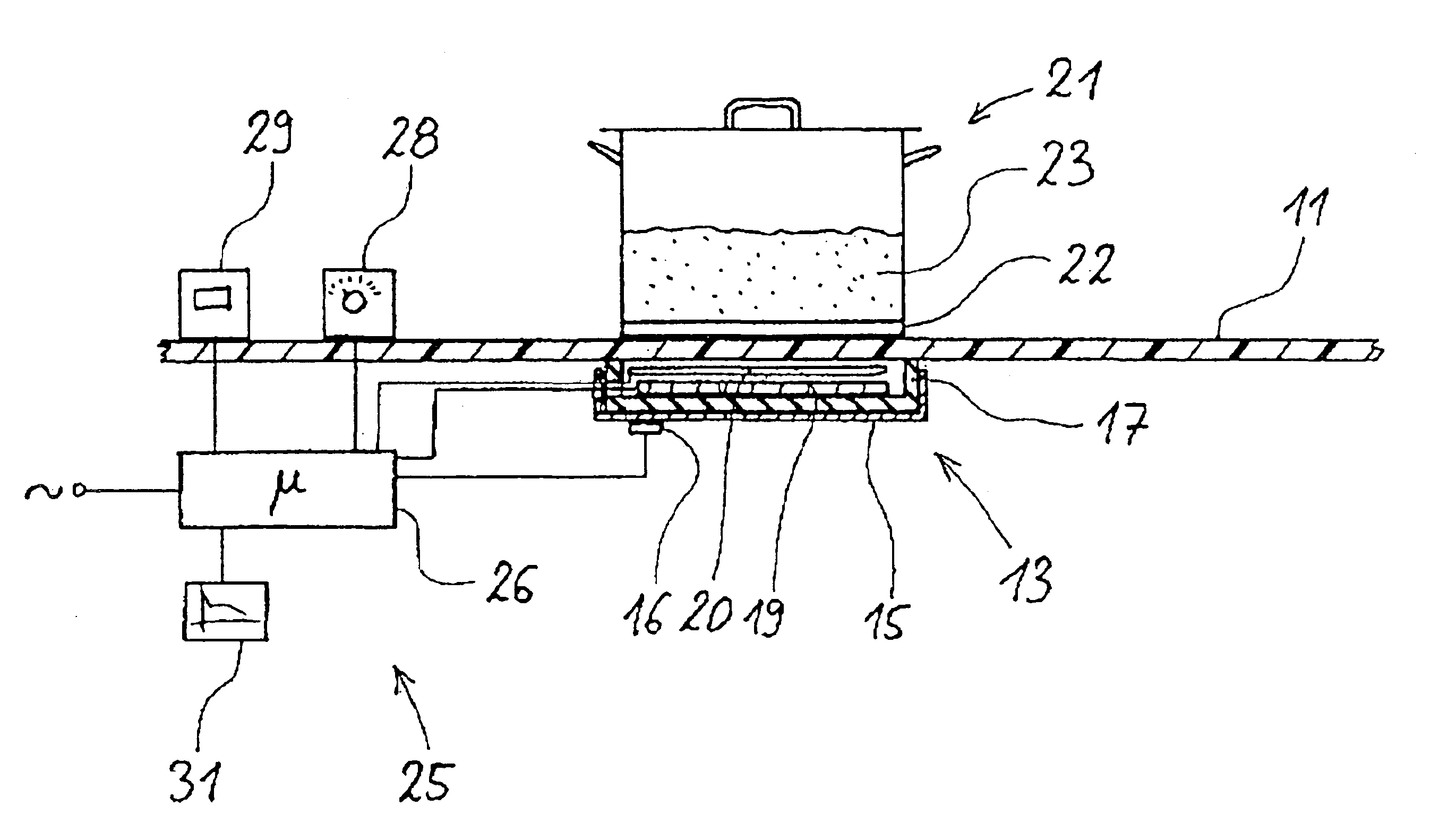
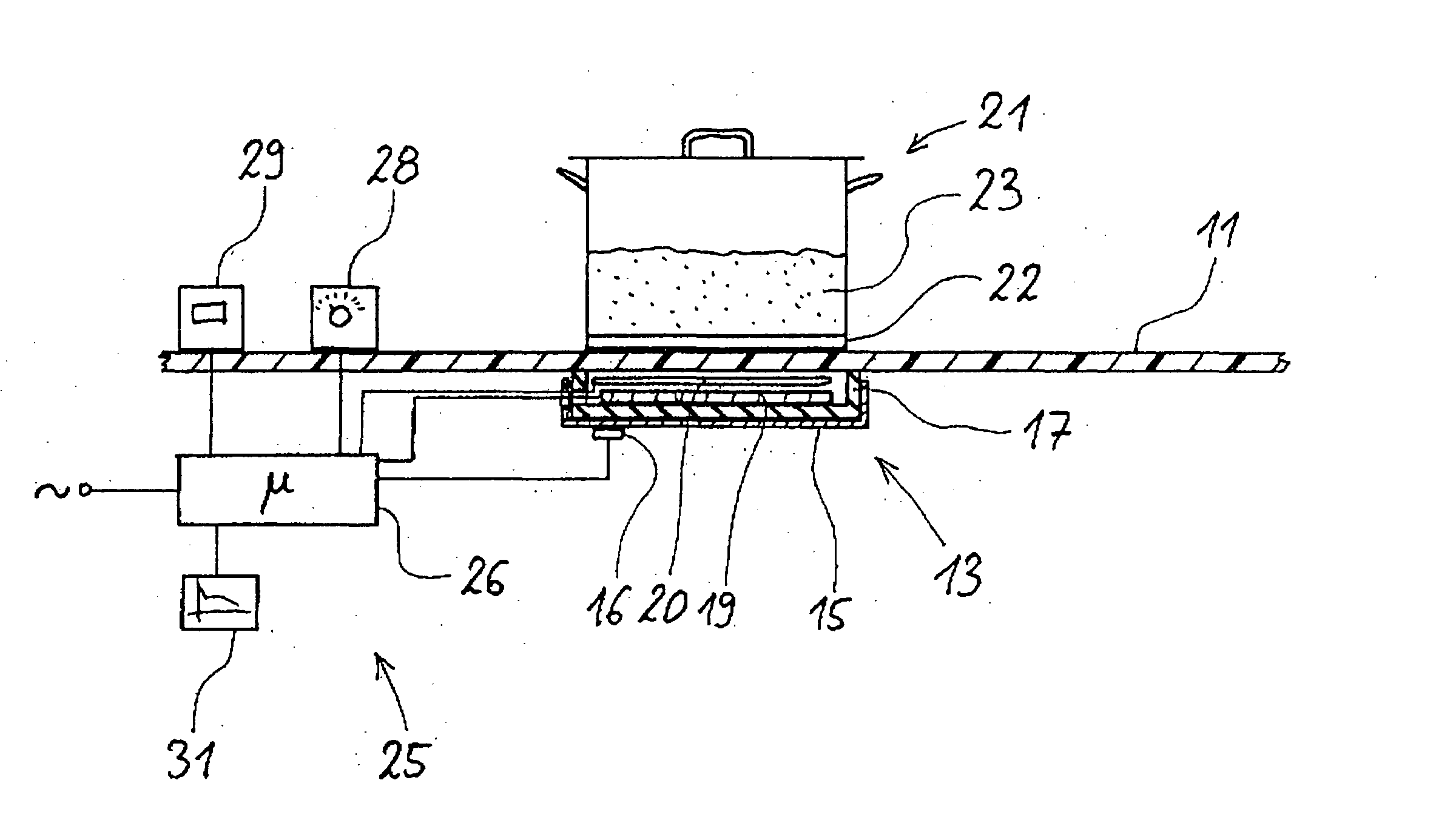
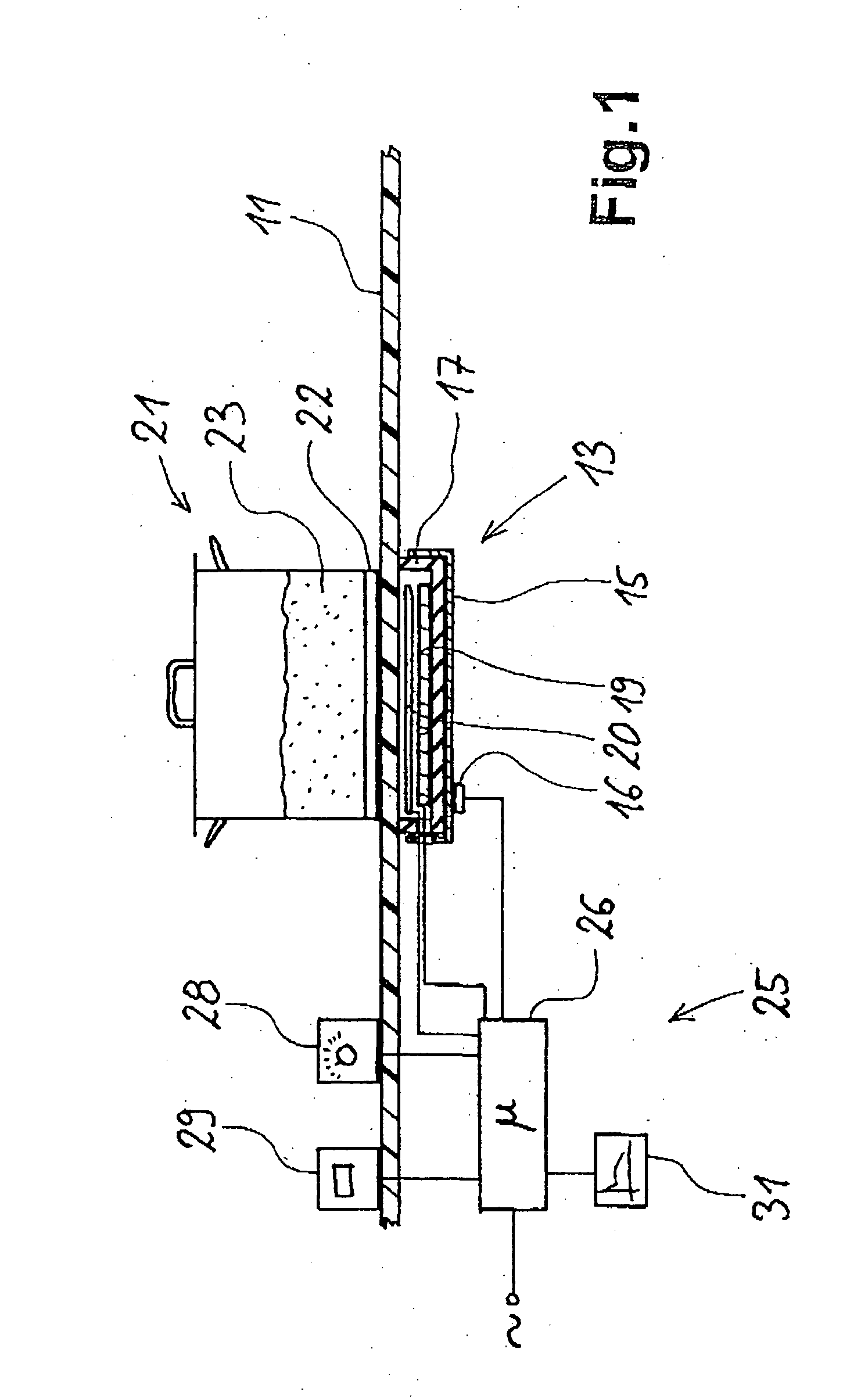
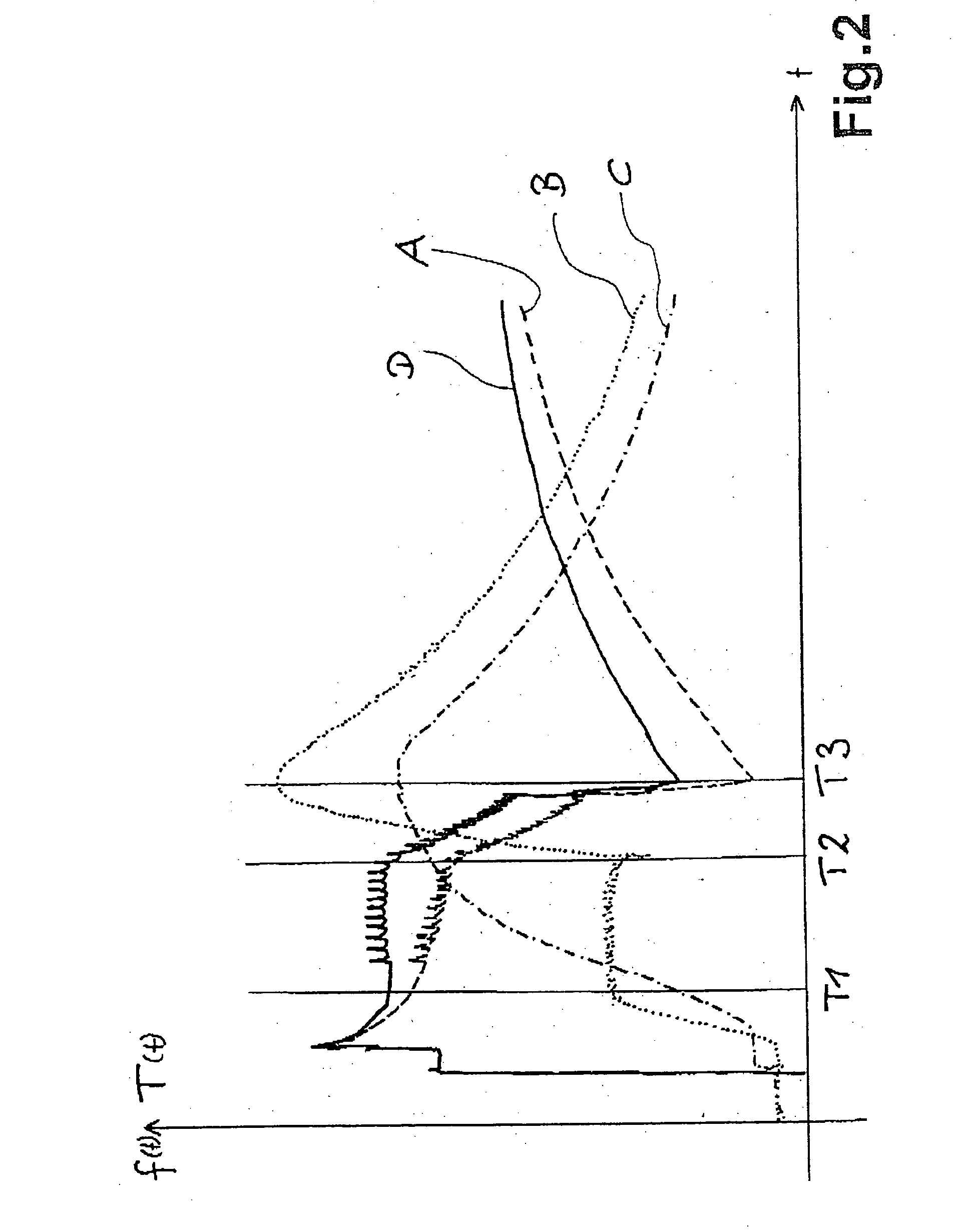
Method for measuring the temperature of a metal saucepan
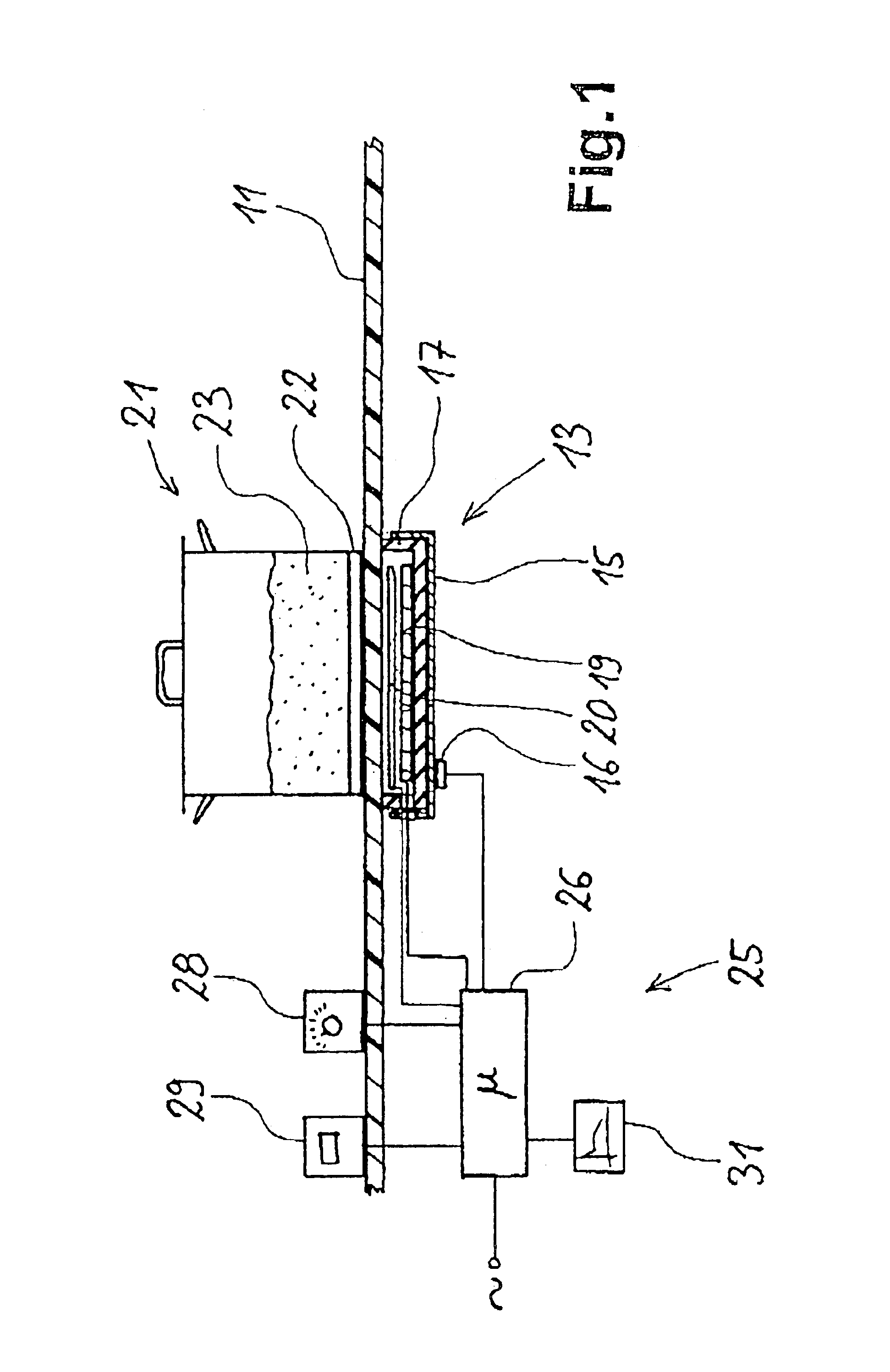
InactiveUS6904378B2Value can be obtainedReduce further influenceThermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionRadiant heaterThermodynamics
A method for measuring the temperature of a cooking vessel or saucepan using a radiant heater. The radiant heater has a heating coil with a corresponding control and an induction coil as an inductive sensor and which is located in a metal tray. With the inductive sensor, measurement takes place of the frequency of the inductive resonant circuit comprising saucepan, heating coil, induction coil and metal tray, which is dependent on the temperature of the components. In the control is stored known slopes or paths of the temperature and therefore the frequency of the metal tray over the time. From this the control gathers correction values in order to produce from the measured curve a compensated curve. At characteristic points, such as the start of a cooking or boiling process or an empty cooking or boiling of the saucepan, it is possible to detect the temperatures.
Owner:E G O ELEKTRO GERAETEBAU GMBH
Visual display
InactiveUS6517403B1Cathode-ray/electron-beam tube electrical connectionGas filling substance selectionRadiant heaterIrradiation
The apparatus for sealing face plates (753) and cathodes (754) has three stations (701, 702, 703). The first (701) is a preheater, the second (702) is an alignment and irradiation station and the third (703) is a controlled cooling station. Beneath each station, a vacuum pump (710) capable of drawing ultralow pressures is provided. The preheater is equipped with upper and lower banks of radiant heaters and reflectors (712). The upper heaters are Provided above a quartz: window (713) of a chamber (714) constituting the station. The pressure in the preheater is pumped down to that in the alignment and irradiation station prior to opening of the gate valve between them and transfer of the face plate and cathode. At the alignment and irradiation station, further heaters (716) are provided. Those above the face plate and cathode, the face plate being uppermost, are mounted on frames (717) about hinges (718), whereby they can be swung up to clear this station's top quartz window, exposing the face plate to the view of an optical system (719) and a laser (720). Manipulation controls (722) are provided for manipulating the position of the face plate to be pixel alignment, as measured by the optical system (719), with the cathode. The laser is traversed around further. The cooling station (703) has meanwhile been pumped down and the sealed device is transferred to it. The temperature of the device is allowed to rise very slowly, in order to reduce the risk of thermal cracking to as great an extent as possible. As the temperature slowly falls, air is slowly introduced, so that the finished device can be removed to the ambient surroundings.
Owner:COMPLETE MULTILAYER SOLUTIONS +1
Radiant heater for heating the building material in a laser sintering device
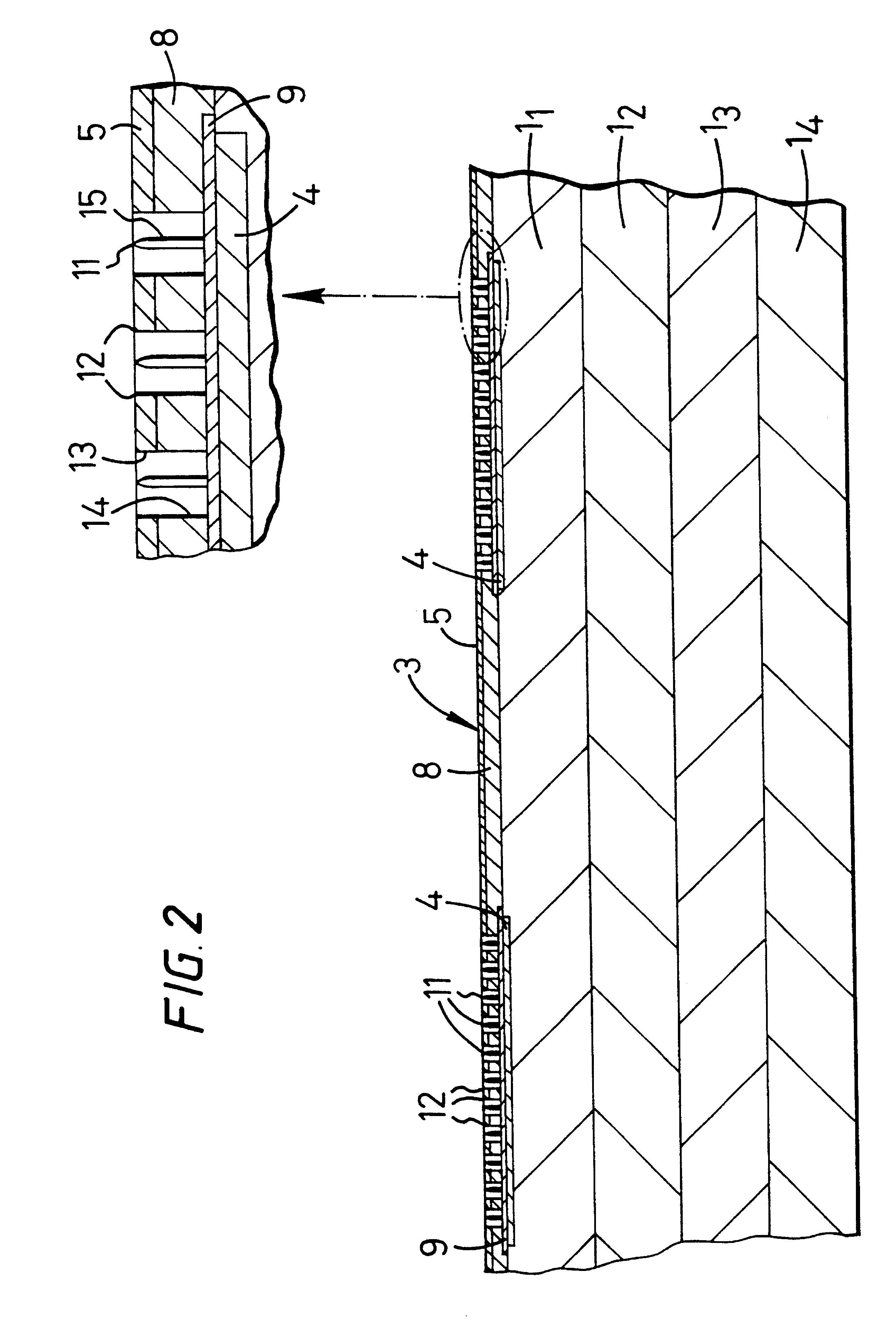
InactiveCN101107882ALess lateral radiationLow thermal inertiaAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyRadiant heaterThermal diffusion coefficient
The invention relates to a radiant heater for heating the building material in a laser sintering device and to a laser sintering device comprising a radiant heater of this type. The radiant heater comprises a flat heat-emission element (113, 213, 313), which is characterised in that it consists of a material with low thermal inertia and a thermal diffusivity preferably in excess of 1.5 10-4 m2 / s and preferably a thickness less than or equal to 2 mm.
Owner:EOS ELECTRO OPTICAL SYST
Radiant heater
InactiveUS20080056694A1Prevent moistureFluid heatersElectric heating systemRadiant heaterPortland cement
A thick film, large area resistance heater including a substrate having an electrically non-conductive surface on which is deposited a film electrical resistor such as a thermally sprayed, photo resist etched foil or sol-gel graphite based material. A combination of an electrically conductive film coated backer board substrate composed of portland cement, sand, cellulose fibers and other selected additives. A mica substrate heater can be cemented to a cement backer board or a vinyl with adhesive backing.
Owner:COOPER RICHARD
Method nad apparatus for UV ink jet printing on fabric and combination printing and quilting thereby
InactiveCN1377313AChanging the time of exposure to energyIncrease or decrease the time of energy exposureSewing-machine elementsLayered productsUV curingRadiant heater
Ink jet printing is provided on large area substrates such as wide width textile webs. The printheads are driven by linear servo motors across a bridge that extends across the substrate. The timing of the jetting of the ink is coordinated with the motion of the printheads, so that the heads can be rapidly moved and the ink can be jetted while the printheads are accelerating or decelerating as they move on the bridge. Preferably, ultraviolet (UV) light curable ink is jetted and first partially cured with UV light and then subjected to heating to more completely reduce uncured monomers of the ink on the substrate.
Owner:L & P PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO
Method for measuring the temperature of a metal saucepan
InactiveUS20040054486A1Value can be obtainedReduce further influenceThermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionRadiant heaterBoiling process
A method for measuring the temperature of a cooking vessel or saucepan by means of a radiant heater is described. The radiant heater has a heating coil with a corresponding control and an induction coil as an inductive sensor and which is located in a metal tray. With the inductive sensor, measurement takes place of the frequency of the inductive resonant circuit comprising saucepan, heating coil, induction coil and metal tray, which is dependent on the temperature of the components. In the control is stored known slopes or paths of the temperature and therefore the frequency of the metal tray over the time. From this the control means gathers correction values in order to produce from the measured curve a compensated curve. At characteristic points, such as the start of a cooking or boiling process or an empty cooking or boiling of the saucepan, it is possible to detect said temperatures.
Owner:E G O ELEKTRO GERAETEBAU GMBH
Variable low intensity infrared heater
ActiveUS6971871B2Reduce speedReduce airflowDomestic stoves or rangesPilot flame ignitersEngineeringConductor Coil
A radiant heater including a burner having an inlet for receiving an air and gas mixture and an exhaust for emitting exhaust gases generated by combustion of the air and gas mixture within the burner, an elongated radiant heating tube having an inlet for receiving the exhaust gases emitted by the burner, a gas flow control assembly for controlling the flow of gas to the burner, and a blower for controlling the flow of air to the burner. The blower comprises a two-stage blower including a motor having a low winding corresponding to a low blower speed and a high winding corresponding to a high blower speed. The gas flow control assembly comprises a two-stage regulator or two-stage valve having a low setting for delivering a low gas flow to the burner and a high setting for delivering a high gas flow to the burner.
Owner:SOLARONICS
Radiant heater in a cooking hob with a thermal switch
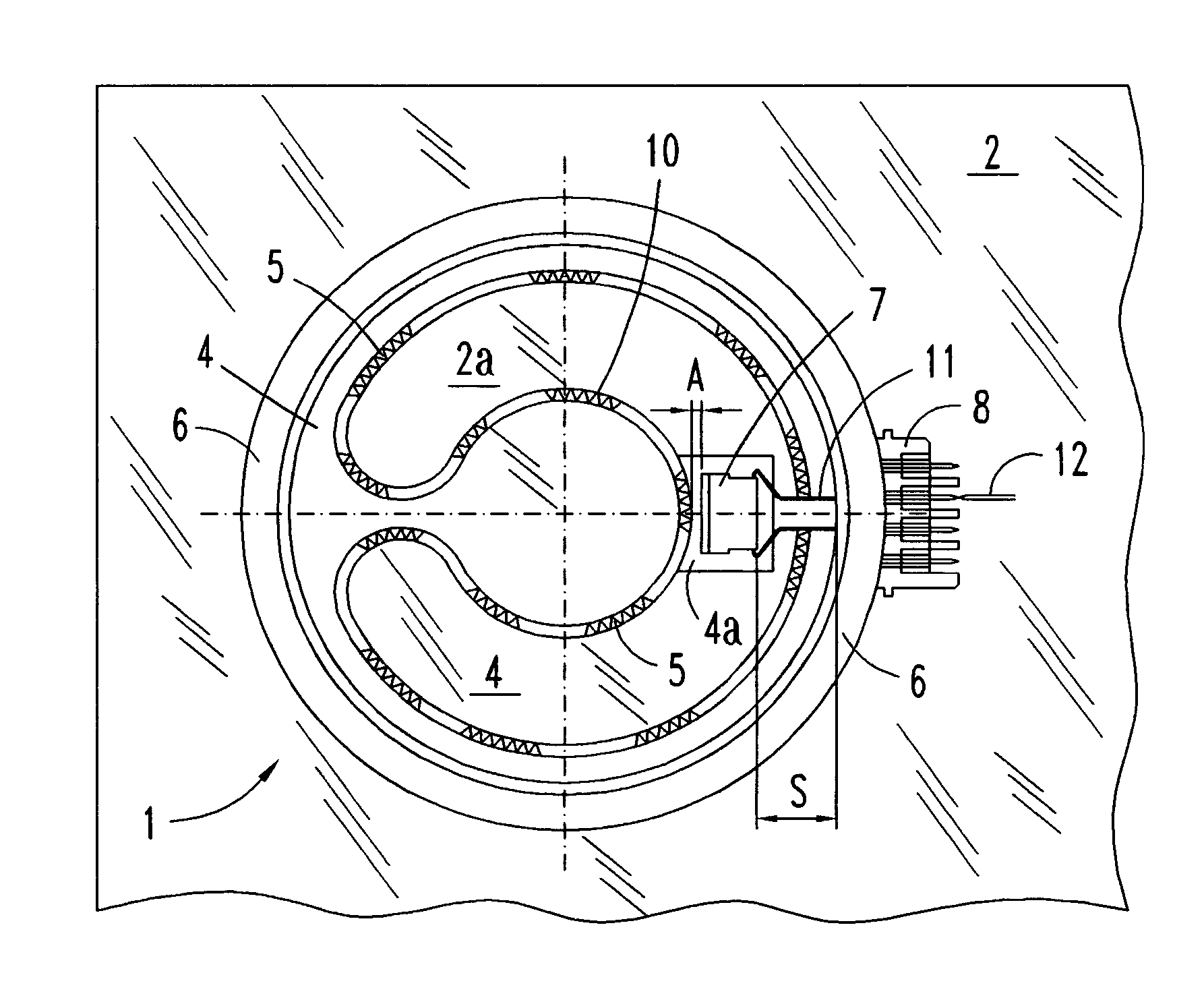
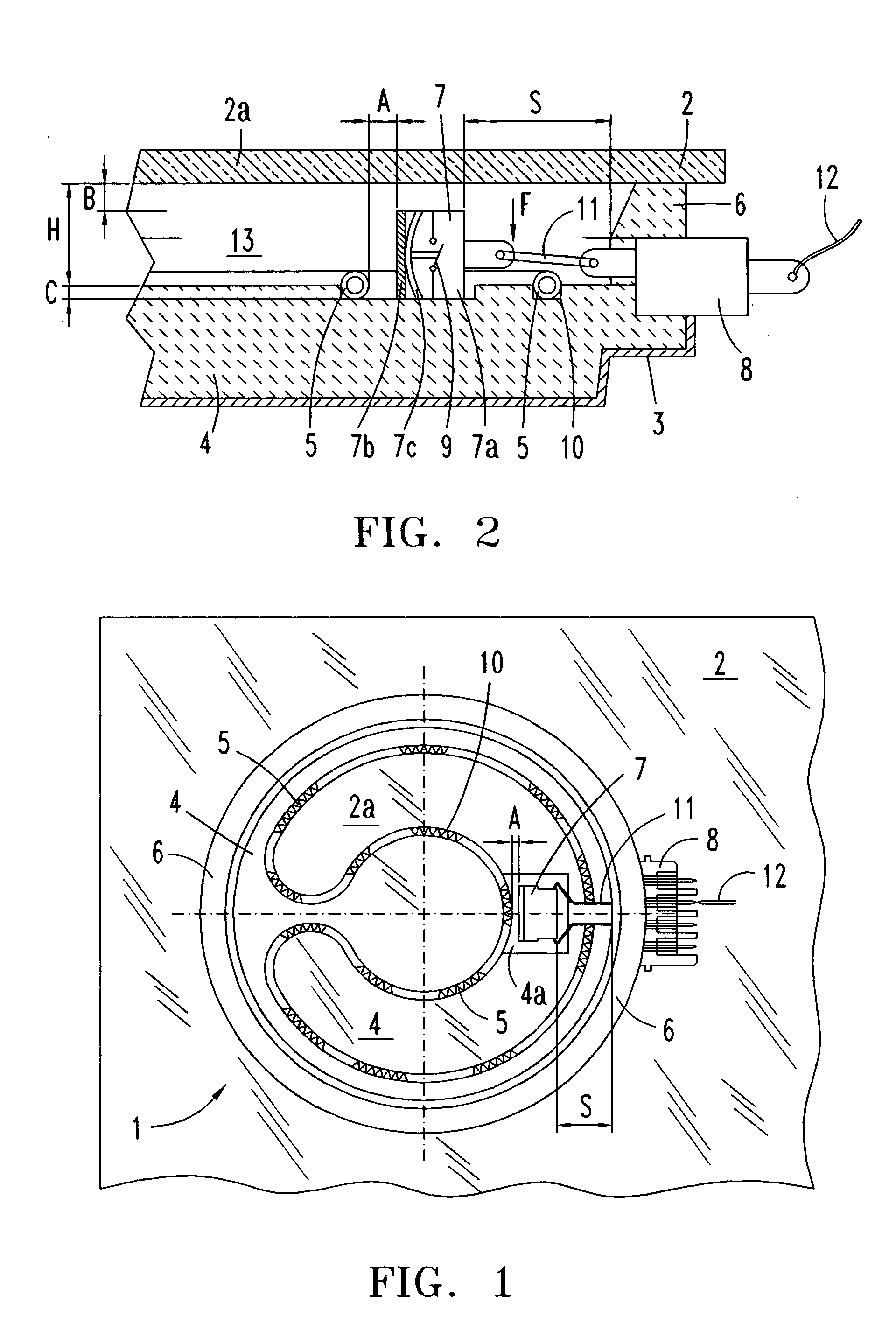
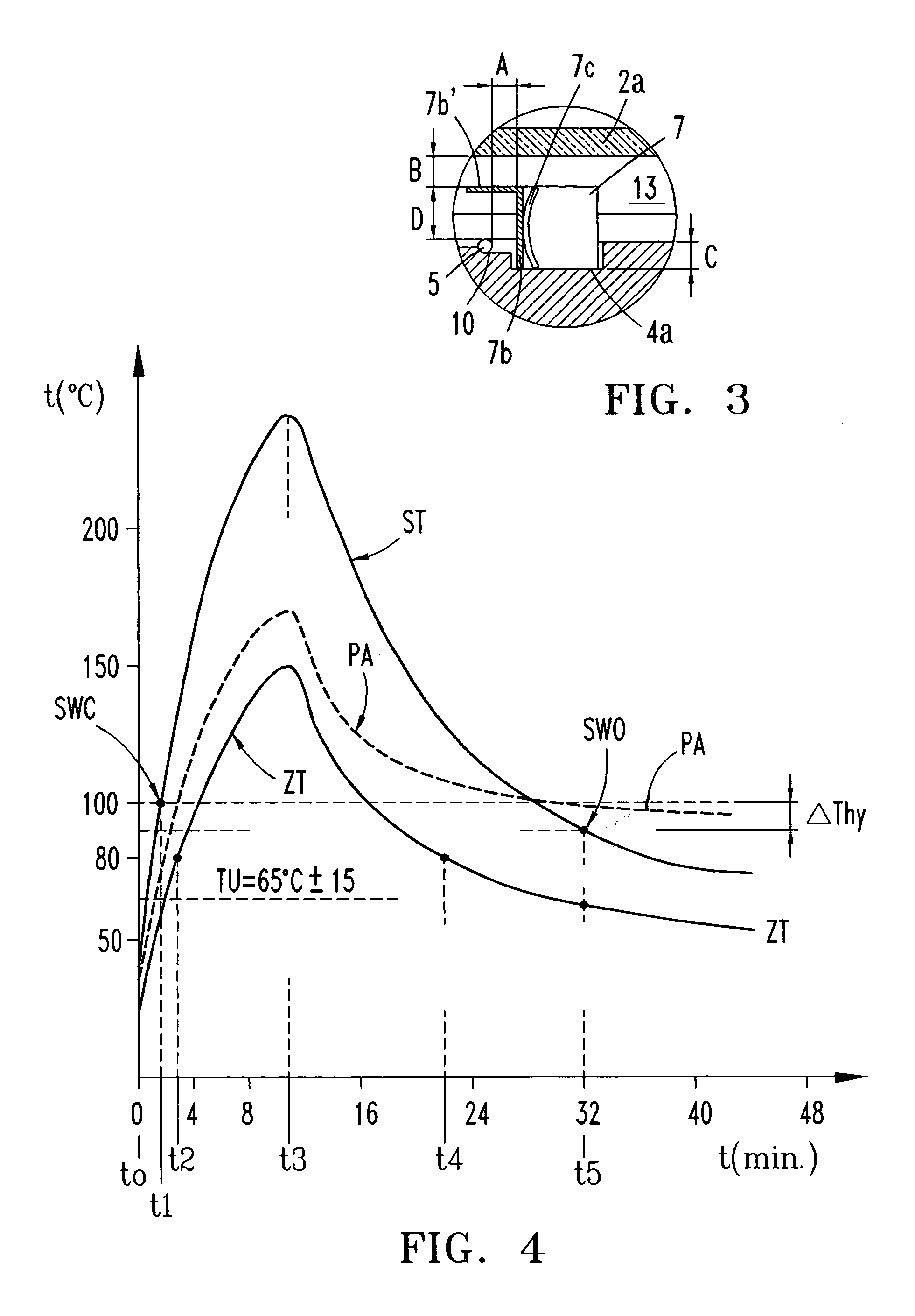
ActiveUS20050274710A1Quick sensor responseAccurate temperature detectionDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusRadiant heaterMetal
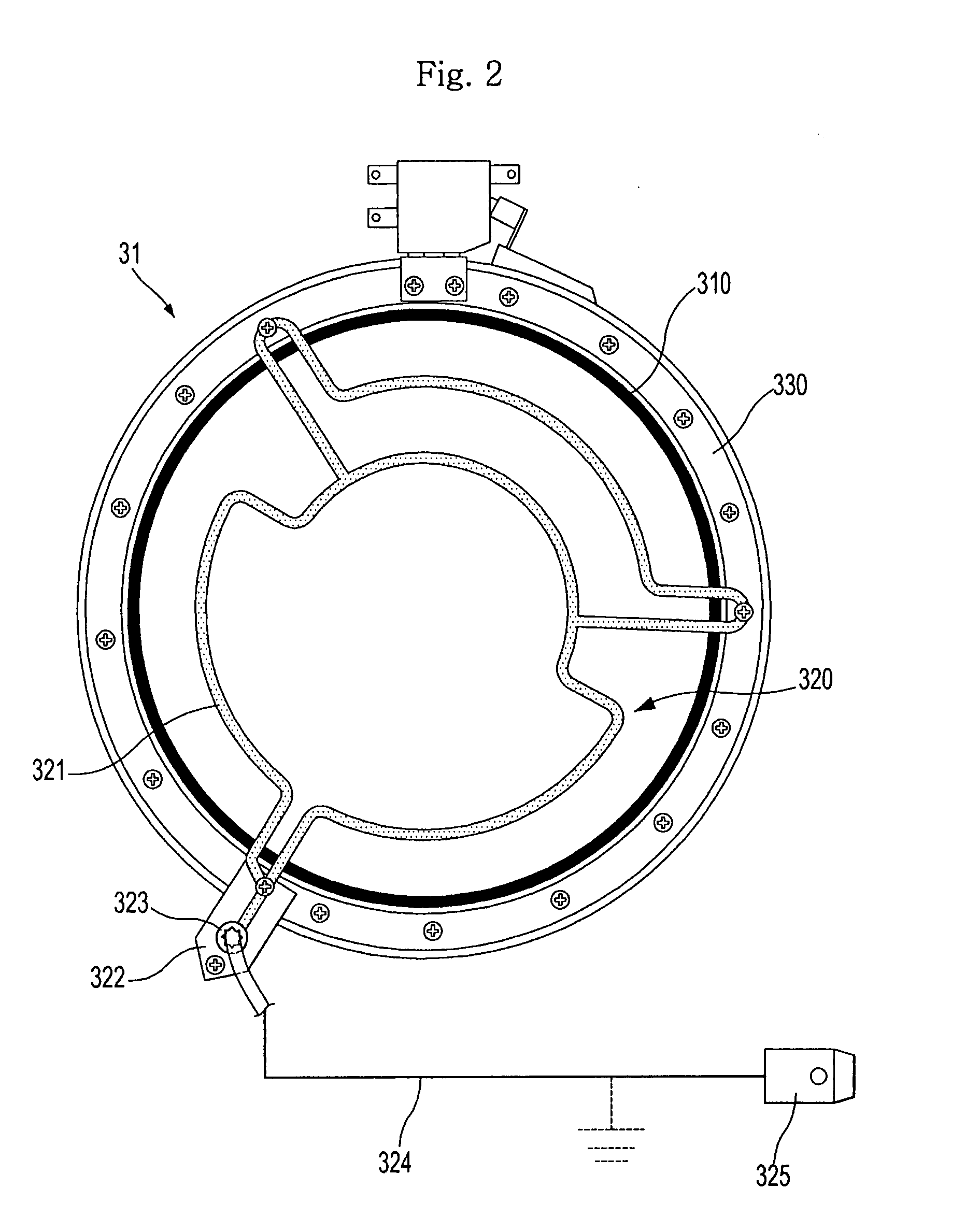
The electric radiant heater (1) adapted to a cooking hob is attached to the cooking plate (2a) forming with it an air cavity (13) inside which the extended heating resistor (5) is housed on an insulating base (4). A peripheral insulating ring (6) and an outer metal tray form a peripheral external wall (3,6) defining said cavity (13) in which there is positioned a bimetal thermal switch (7), which has a compact body (7a) resting on the surface (4a) of the insulating base, and a heat receiver base (7b) in a position facing a part of the heating resistor (5). The position of the compact body (7a) relative to the heating resistor (5) is determined so as to obtain an actuating temperature point (SWC, SWO) adjusted for switching a hotplate warning light on and off.
Owner:EIKA S COOP LTDA
Powder Distribution for Laser Sintering Systems
ActiveUS20170008234A1Reduce the possibilityHigh densityManufacturing heating elementsCeramic shaping apparatusRadiant heaterMetallurgy
There is provided improved laser sintering systems that increase the powder density and reduce anomalies of the powder layers that are sintered, that measure the laser power within the build chamber for automatic calibration during a build process, that deposit powder into the build chamber through a chute to minimize dusting, and that scrubs the air and cools the radiant heaters with recirculated scrubbed air. The improvements enable the laser sintering systems to make parts that are of higher and more consistent quality, precision, and strength, while enabling the user of the laser sintering systems to reuse greater proportions of previously used but unsintered powder.
Owner:3D SYST INC
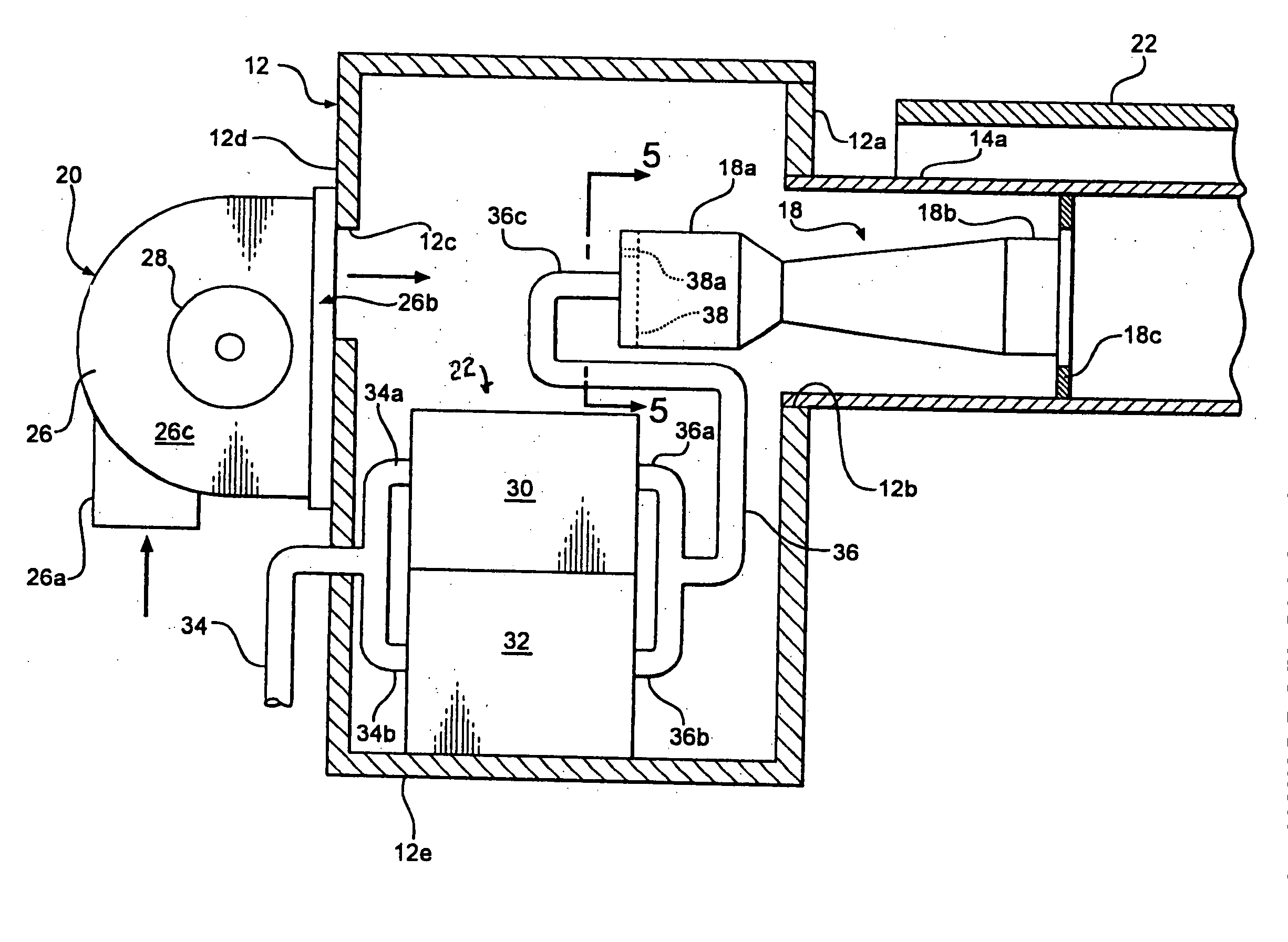
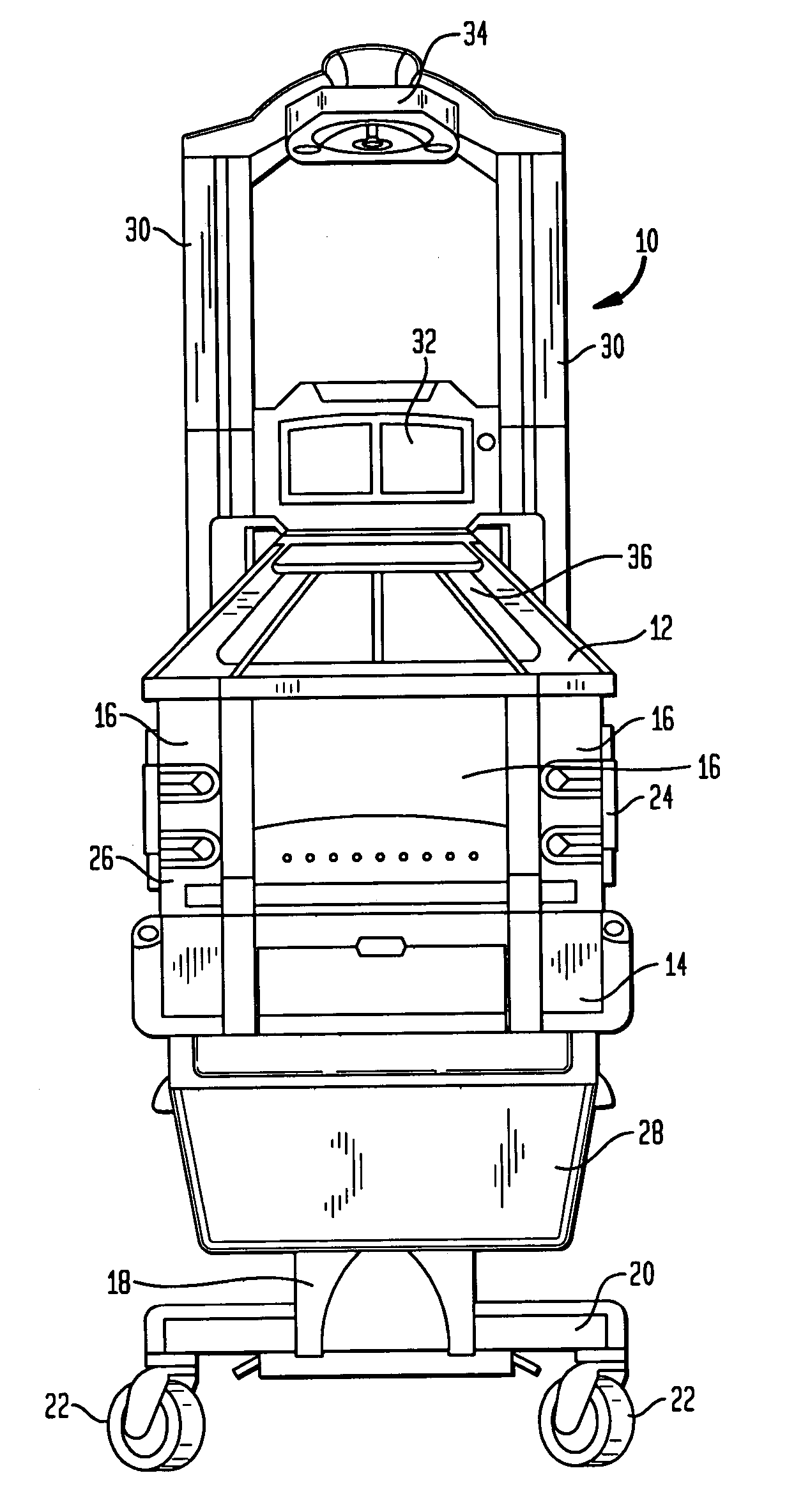
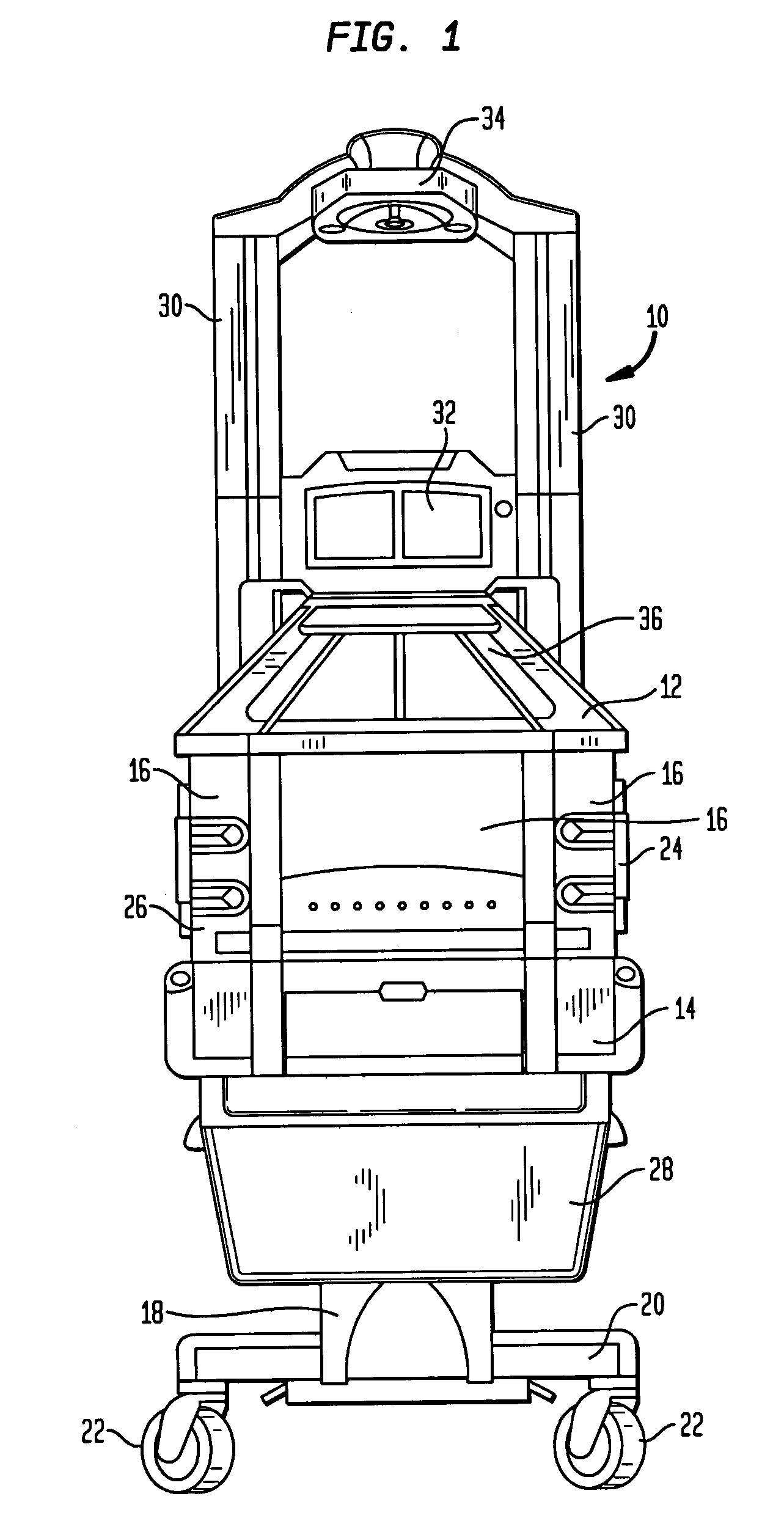
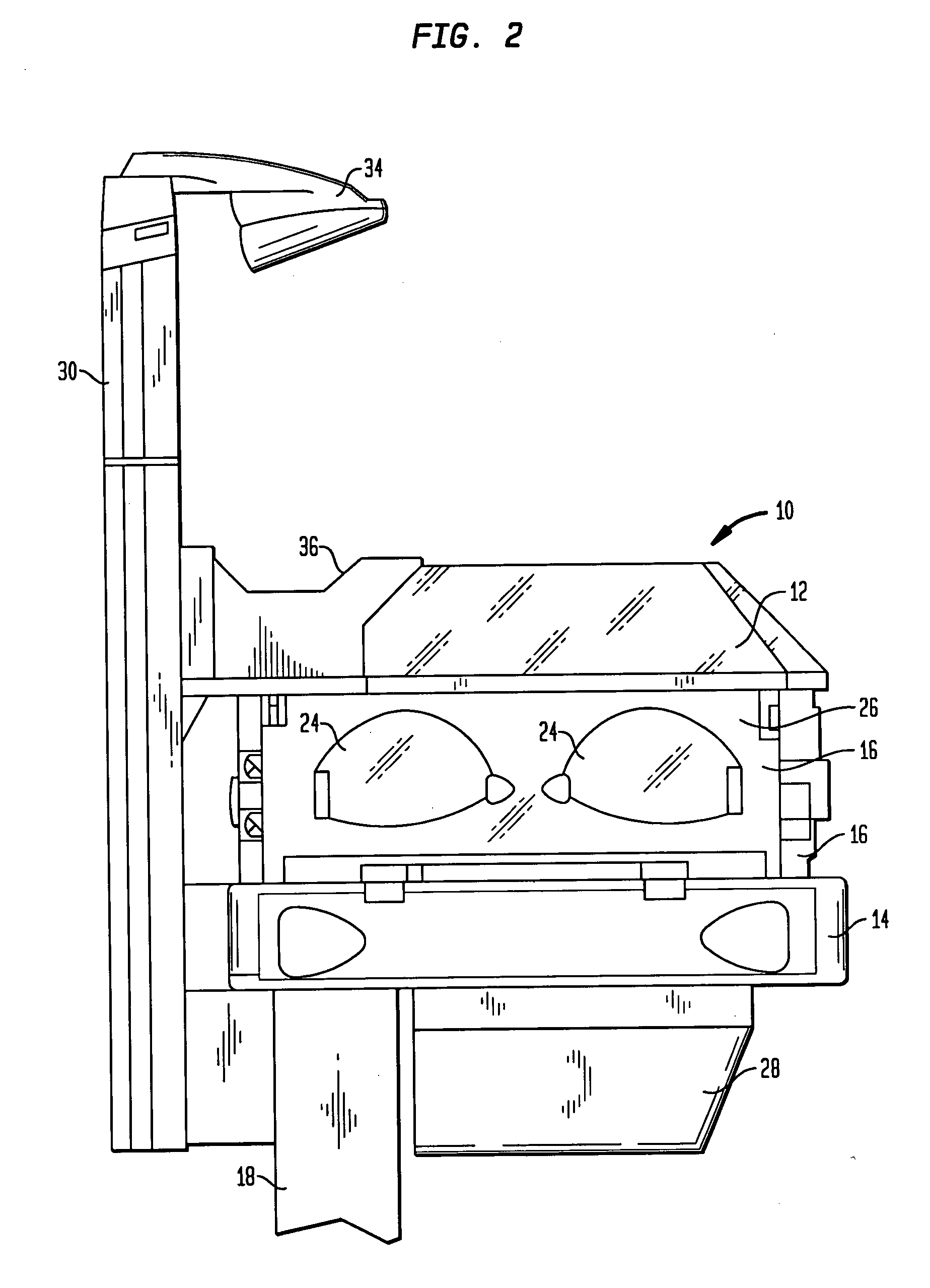
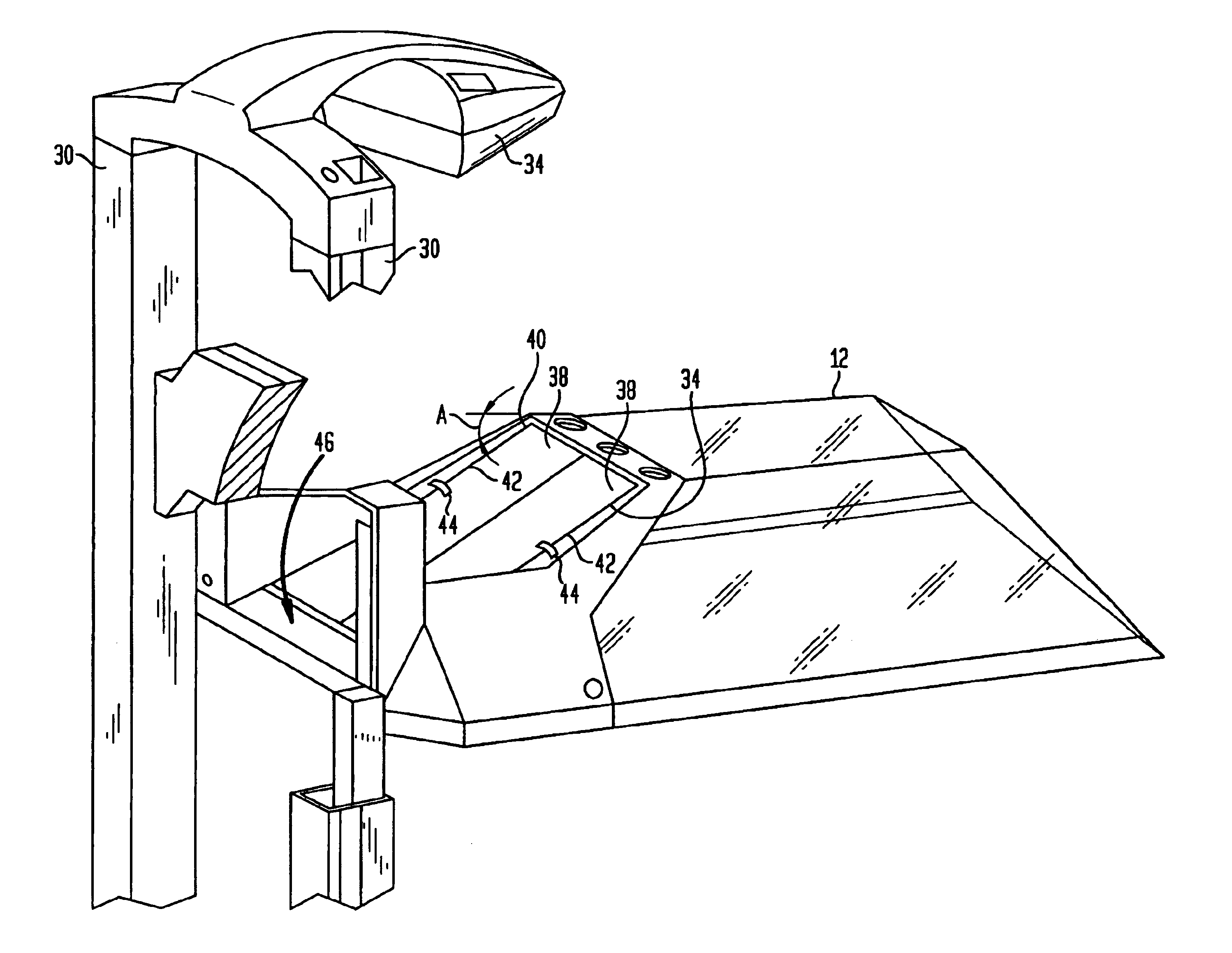
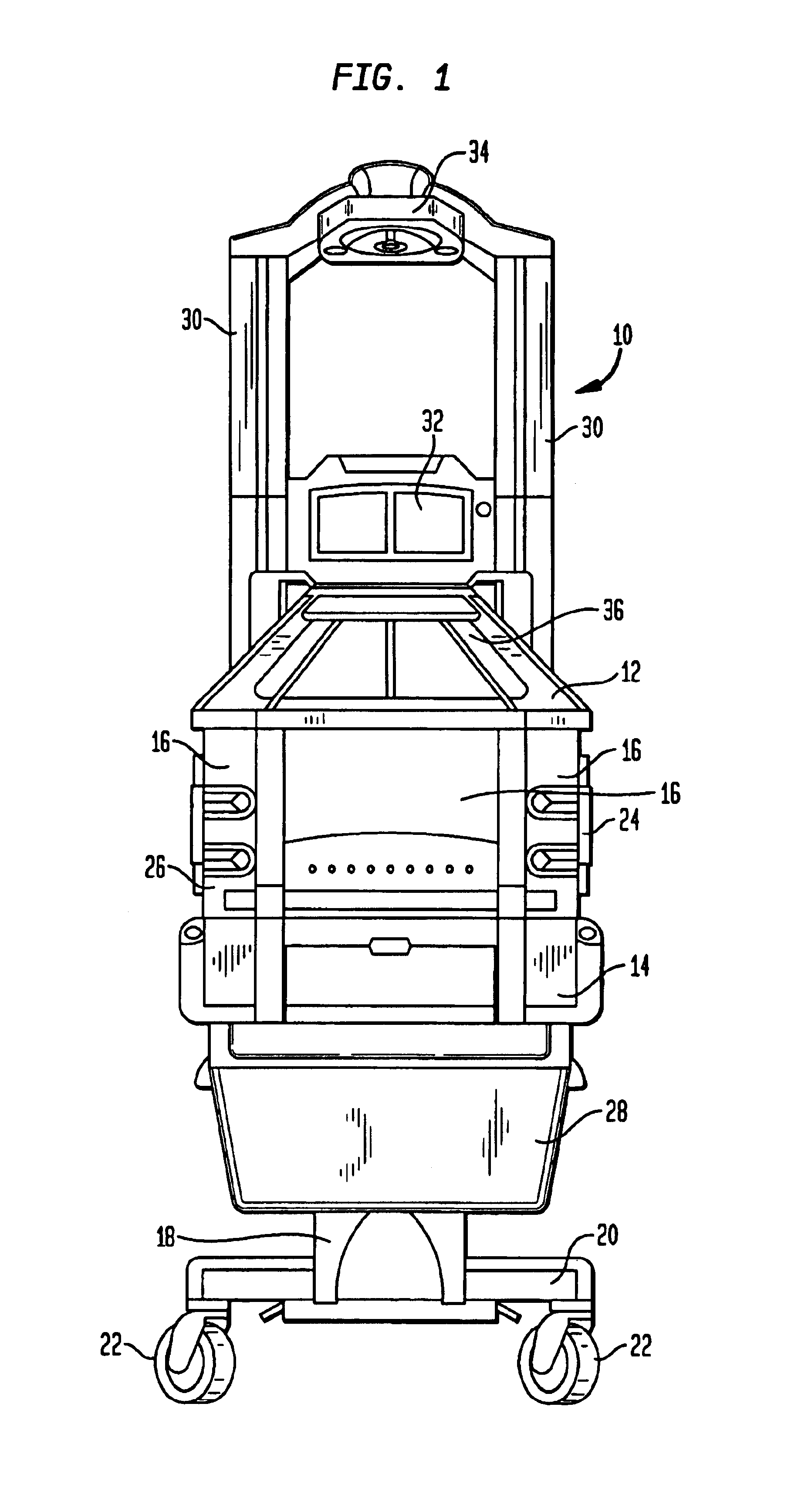
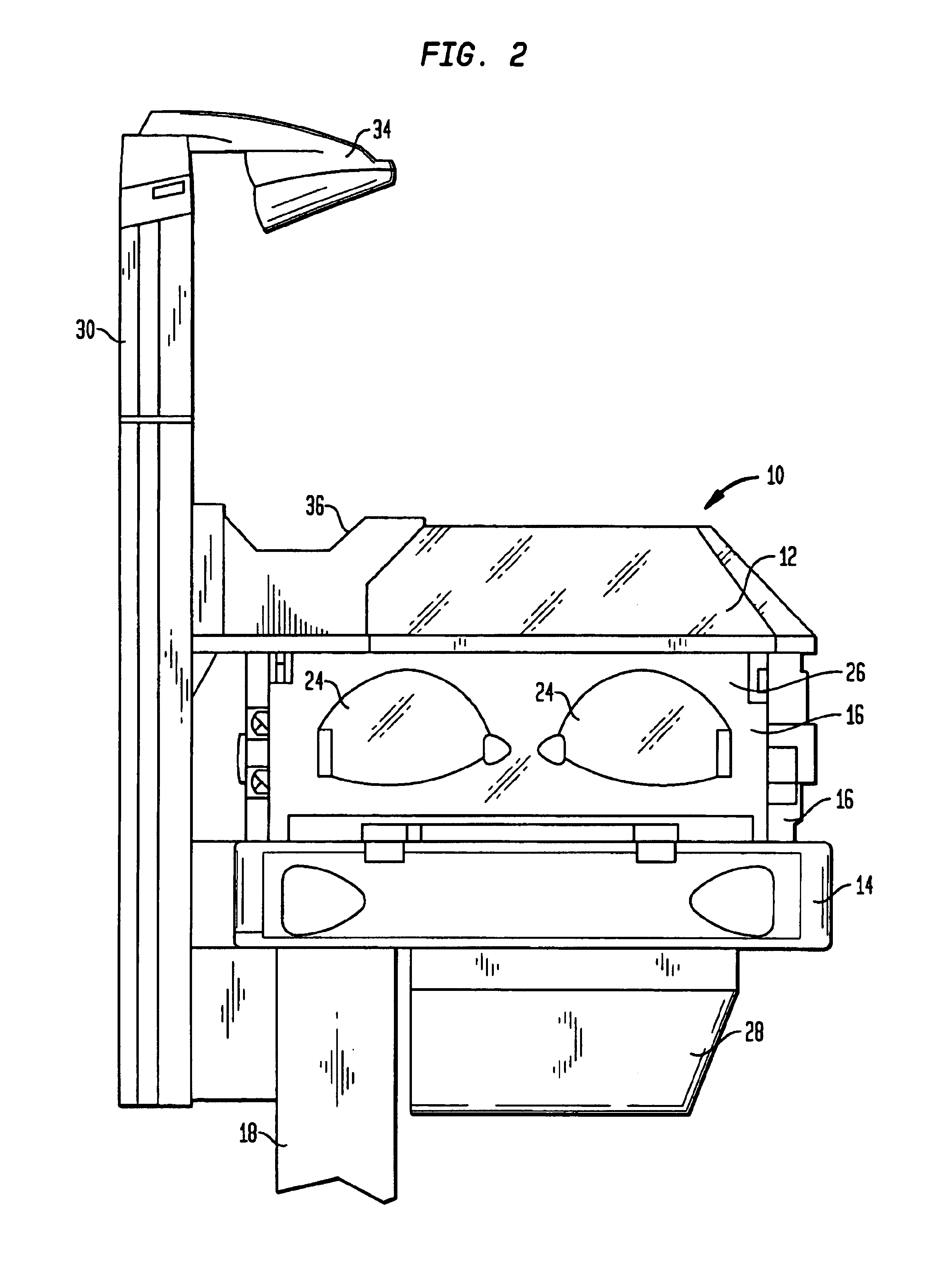
Infant care apparatus with fixed overhead heater
An infant care apparatus having a canopy movable with respect to an infant support for supporting an infant between a lower position enclosing the infant in an infant compartment and an upper position opening the infant compartment. The canopy has an opening and a door that can be closed to block the opening and opened to unblock the opening. A radiant heater is located in a fixed position above the infant support to direct infrared energy toward the infant support. When the canopy is in its lower position, a convective heating system warms the infant compartment. The door either closes as the canopy moves to its lower position or opens as the canopy moves to its upper position.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
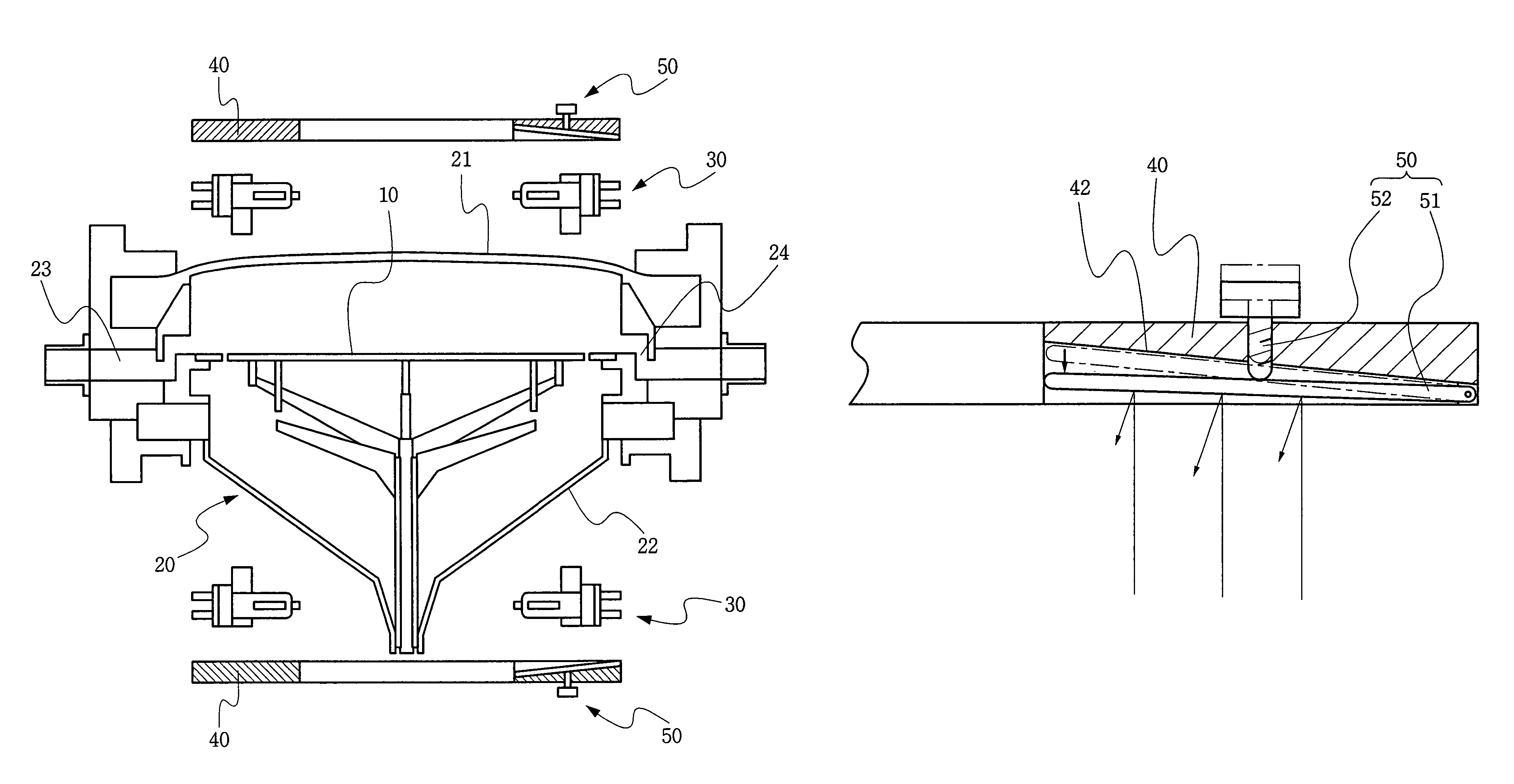
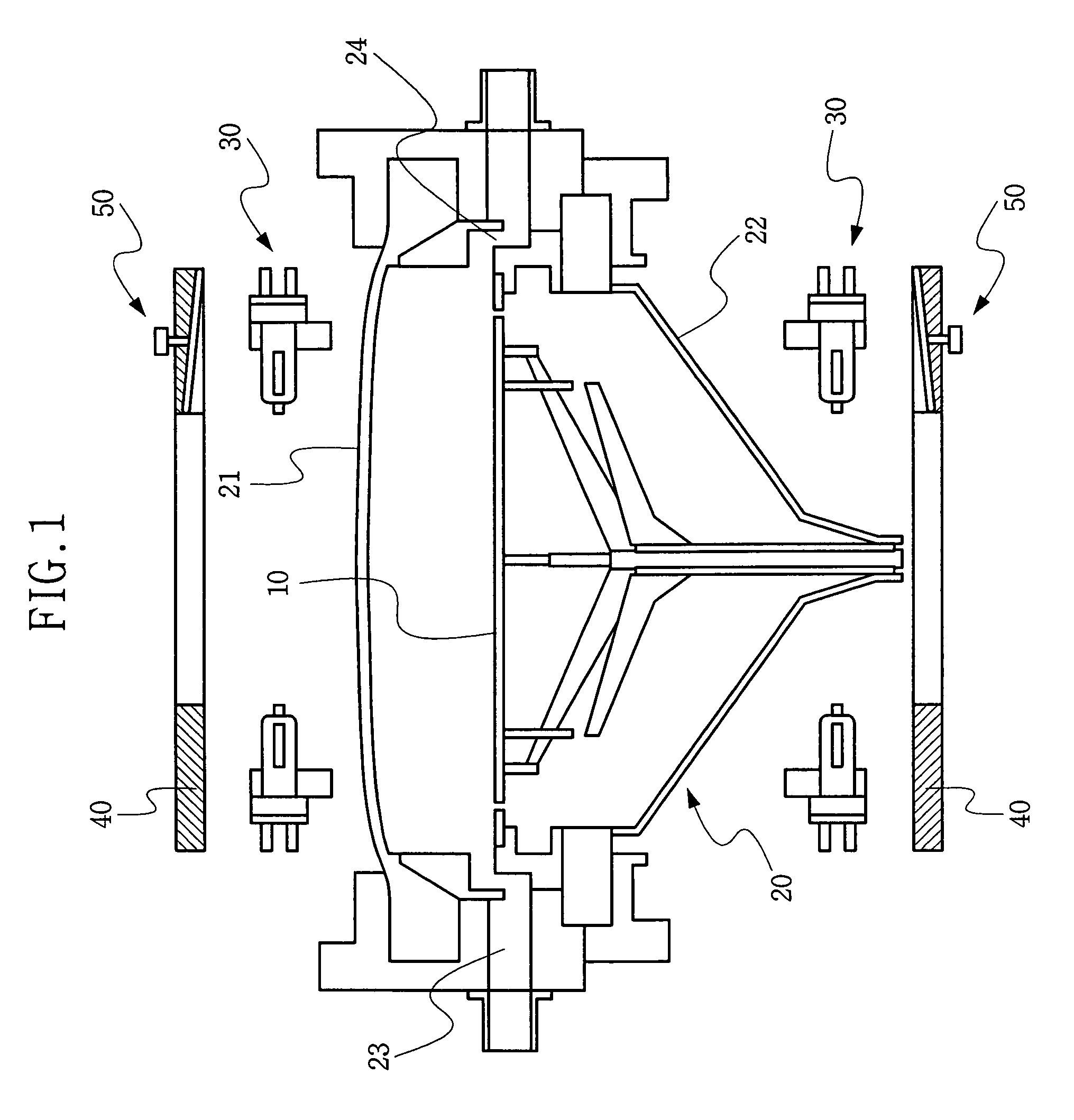
Apparatus to determine ability of plastic material to be shaped by thermoforming process
ActiveUS20060037406A1Easy loading and unloadingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesAuxillary shaping apparatusRadiant heaterPlastic materials
A device to evaluate the thermoformability of plastics using pressure, vacuum or both is provided. The device includes at least one set of adjustable radiant heater panels laid parallel to the plastic material, a non-contact temperature measuring device, a carriage to move the plastic heated to preset temperature to forming, where a forming die attached to an end of mechanical device moves downwards or upwards at an adjustable speed forcing the heated plastic material to conform to the outer shape of the die while providing the actual force required to push the hot plastic as function of time or forming distance. A processor under the control of software measures the thermoforming characteristics of the sample.
Owner:DHARIA AMITKUMAR N
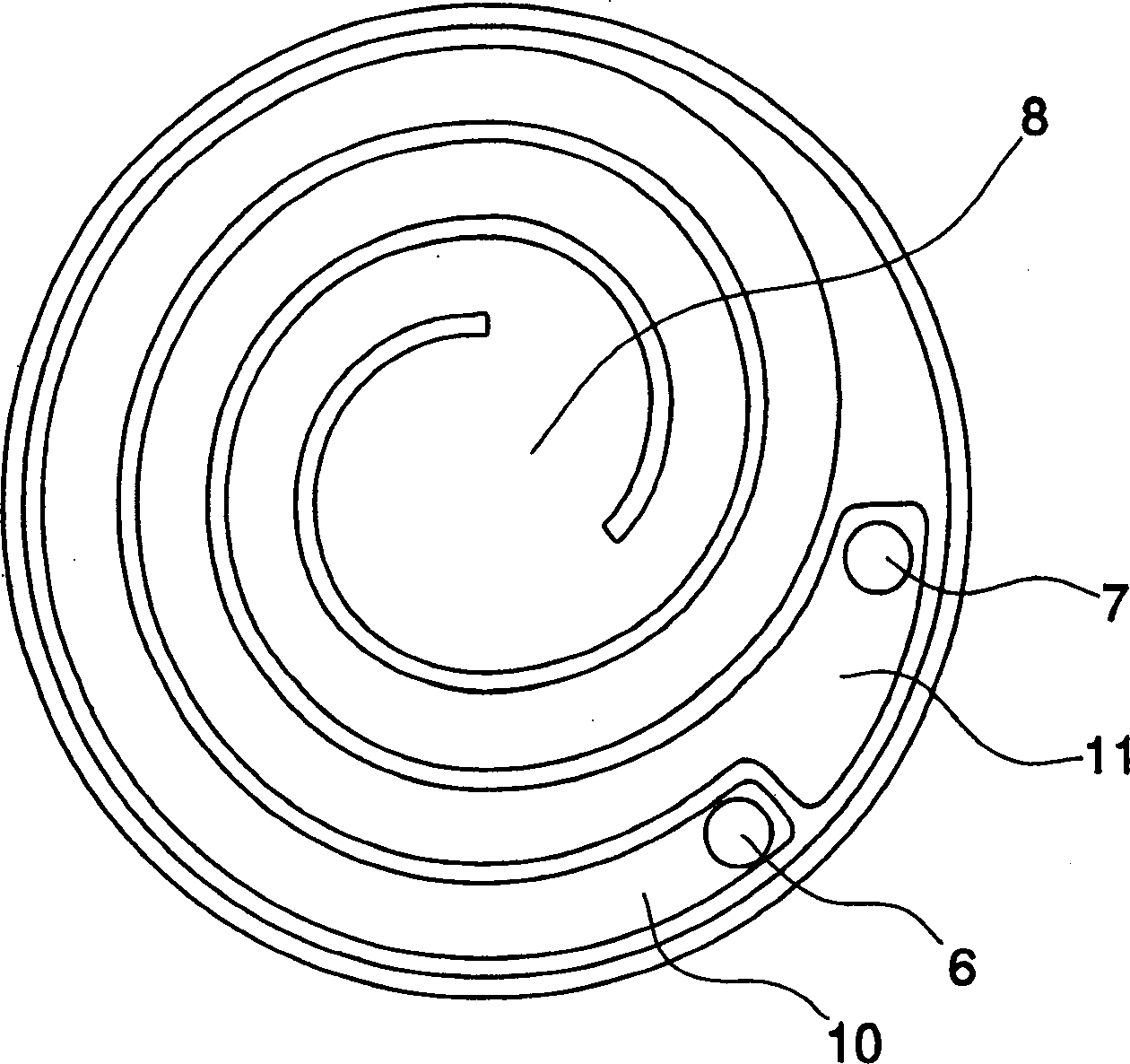
Microcombustion heater having heating surface which emits radiant heat
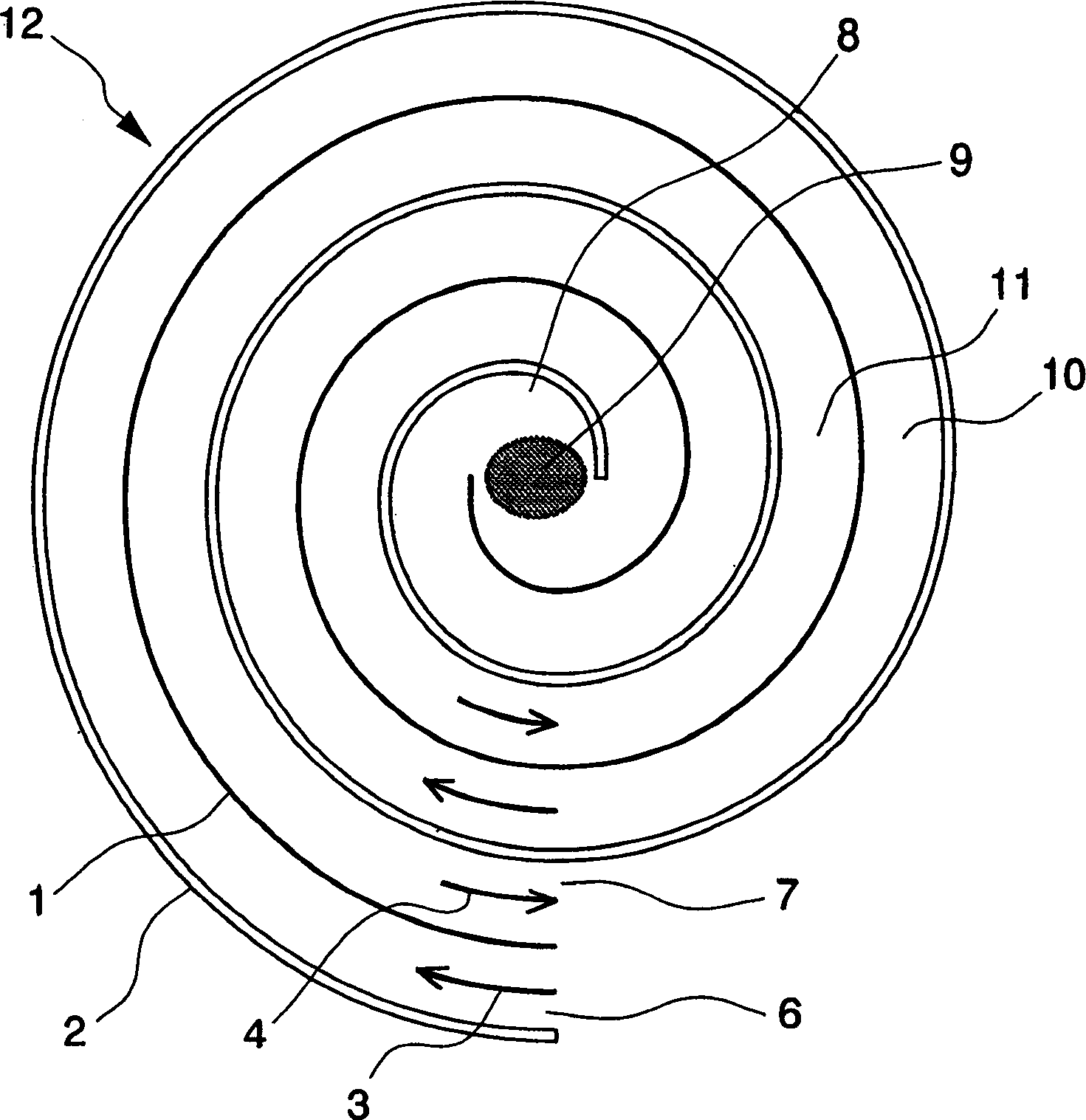
InactiveCN1467404AImprove thermal efficiencyImprove performanceIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationGaseous fuel burnerCombustion chamberRadiant heater
A small microcombustion heater which can realize reliable combustion. The heater has a premixed gas passage which reaches a combustion chamber, and a passage for a combustion gas drawn from the combustion chamber. The passages are arranged in a spiral form in a manner such that a heating wall is provided between the passages. The width of the premixed gas passage is a quenching distance or less, where the quenching distance is determined depending on the premixed gas. The heater has two outer faces for holding the spiral passages from both sides of the upper and lower edges of the heating wall, and at least one of the outer faces is a heating surface for emitting radiant heat. Typically, the spiral passages are placed between a heat-resisting heating plate and a heat insulating plate, and an outer face of the heat-resisting heating plate functions as the heating surface.
Owner:丸田薰 +1
Infant care apparatus with object detection sensing
An infant care apparatus having a canopy movable with respect to an infant support for supporting an infant between a lower position enclosing the infant in an infant compartment and an upper position opening the infant compartment. The canopy has an opening and a door that can be closed to block the opening and opened to unblock the opening. A radiant heater is located in a fixed position above the infant support to direct infrared energy toward the infant support. The door closes as the canopy moves to its lower position and opens as the canopy moves to its upper position. An object sensing means is provided to detect the presence of an object resting on the upper surface of the door.
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com