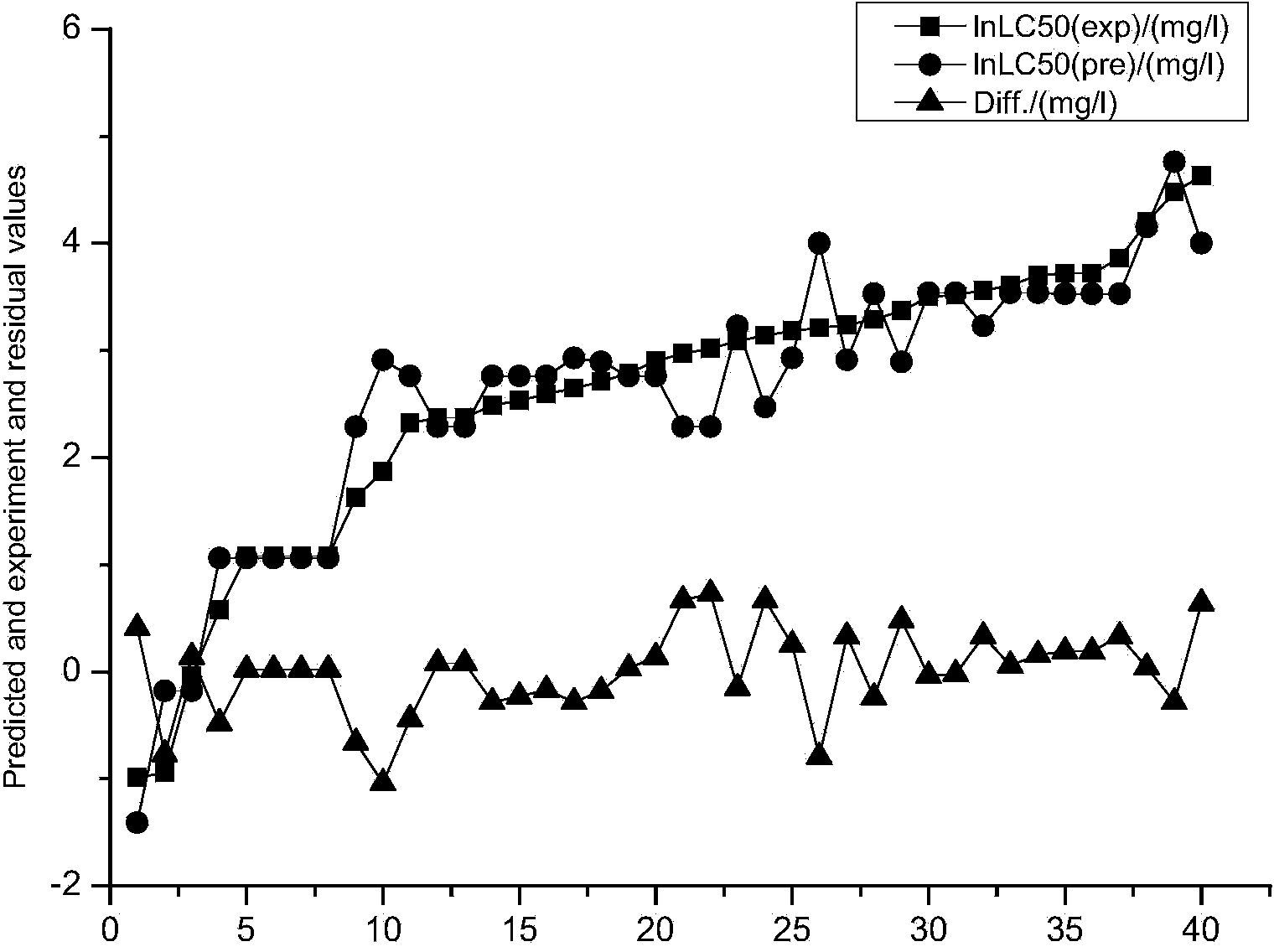
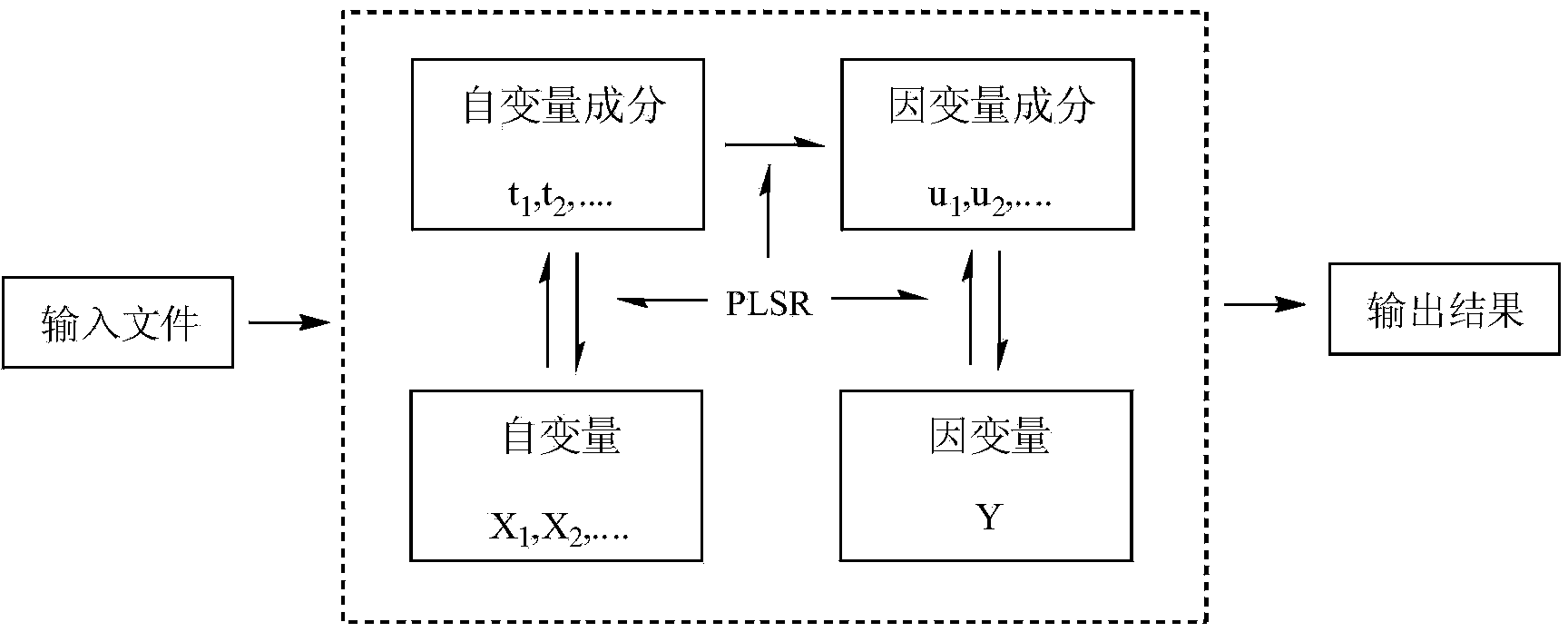
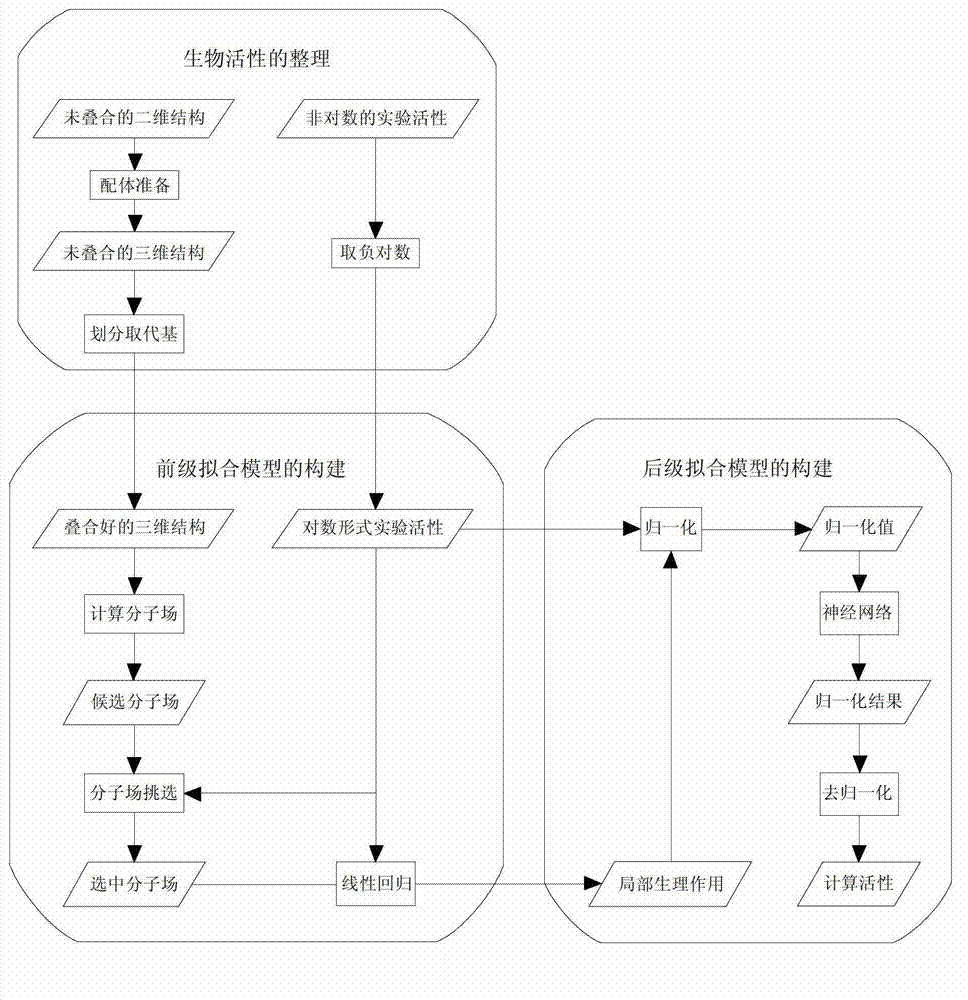
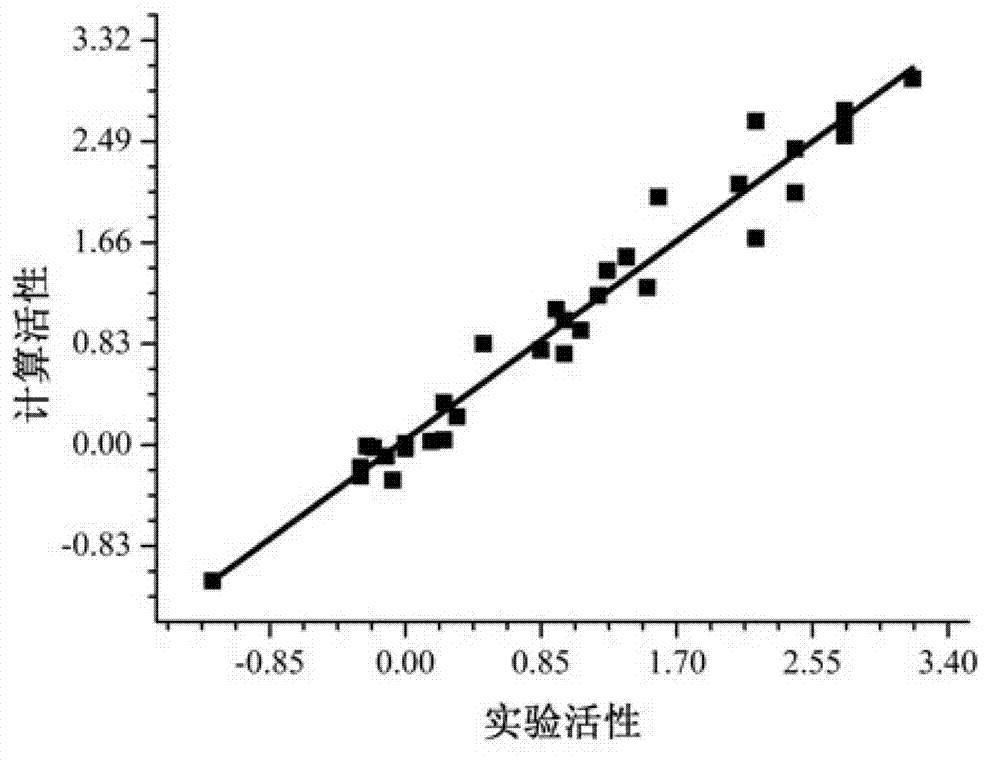
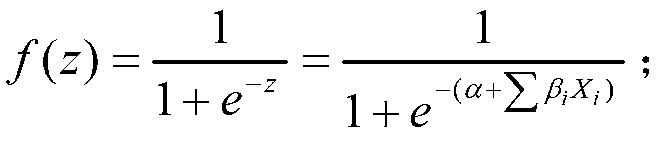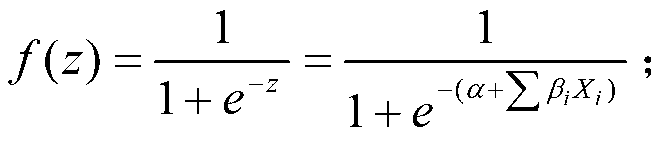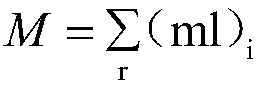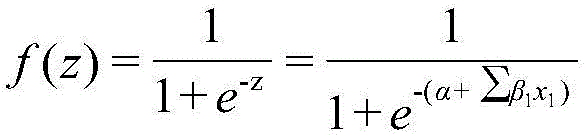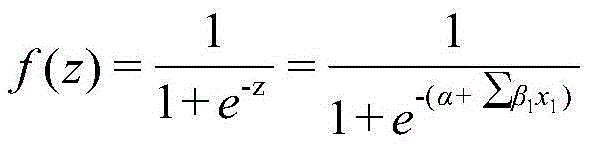Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Quantitative structure–activity relationship" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quantitative structure–activity relationship models (QSAR models) are regression or classification models used in the chemical and biological sciences and engineering. Like other regression models, QSAR regression models relate a set of "predictor" variables (X) to the potency of the response variable (Y), while classification QSAR models relate the predictor variables to a categorical value of the response variable.
Method for forecasting acute toxicity of organic compounds by building quantitative structure-activity relationship model with quantum chemistry method
InactiveCN103646180APredict toxicityChemical property predictionSpecial data processing applicationsMolecular orbital energyAb initio quantum chemistry methods
The invention discloses a method for forecasting the acute toxicity of organic compounds by building a quantitative structure-activity relationship model with a quantum chemistry method. The method fully geometrically optimizes compound structures by using a Gaussian procedure so as to obtain quantum chemistry parameters including molecular volume, relative molecular mass, highest occupied molecular orbital energy, lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energy, energy gaps of frontier molecular orbital, dipole moment, solvation energy, electron energy and the like; using the quantum chemistry parameters and a hydrophobicity parameter as structural descriptors; in combination with toxicity data, quantitative relationship equations between various structural descriptors and toxicity are established according to a written procedure based on partial least square stepwise linear regression to obtain the multiple correlation coefficient, F-test value and sum of squared residuals, and then the model is verified so as to guarantee the external predictive ability. Therefore, the method can quickly and effectively forecast the toxicity of organic compounds to be studied, and provide necessary basic data for risk assessment and supervision of chemicals.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
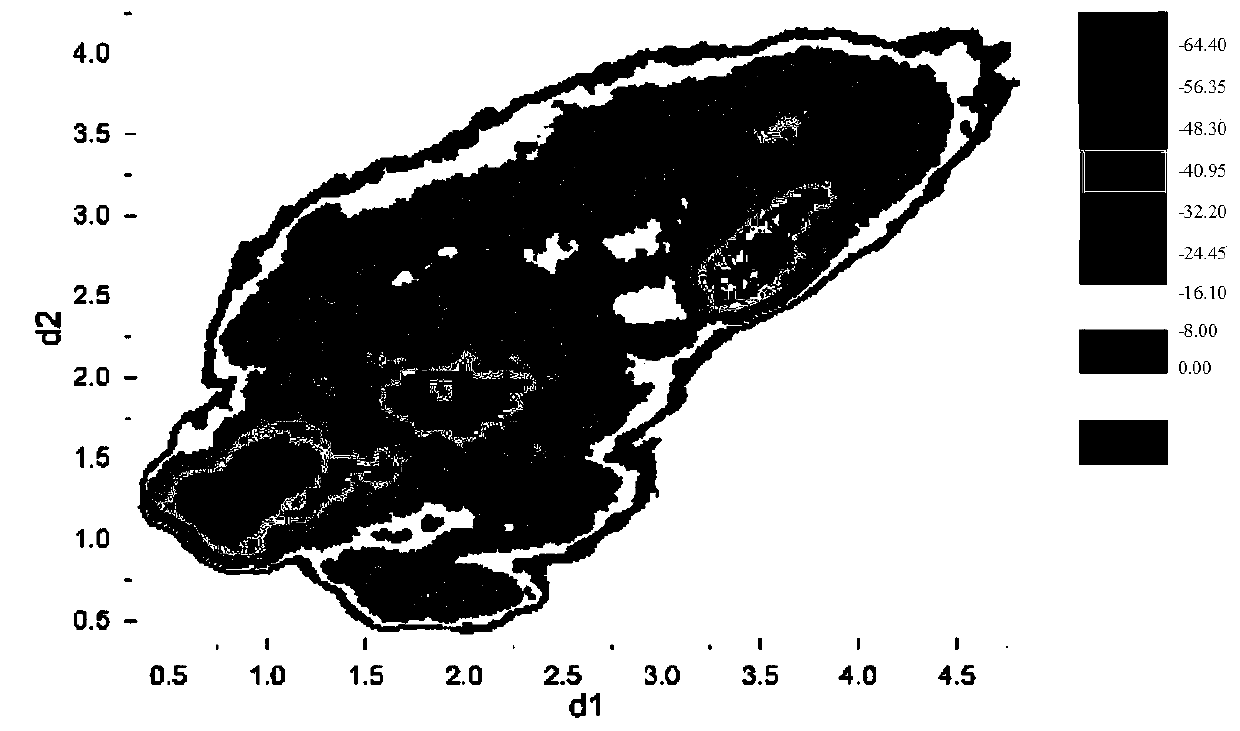
Building method of two-level fitting quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) model for forecasting compound activity
InactiveCN102930113APredict biological activityTight fitBiological neural network modelsSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringLinear model
The invention discloses a building method of a two-level fitting quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) model for forecasting compound activity. The building method includes following procedures: 1 a plurality of compounds with the same frames are utilized as a training set, and the train set compounds are divided into substituent groups and are coincided; 2 a linear regression method is utilized to calculate local physiological action produced by each substituent group, and a preceding-stage fitting model is built; 3 according to the local physiological action which is obtained in calculating mode in the procedure 2, a neural network method is utilized to calculate the whole biological activity, and a backward-stage fitting model is built; and 4 the preceding-stage fitting model and the backward-stage fitting model are combined to form the front-and-back two-stage QSAR model. According to the building method, the linear regression method and the neural network method are combined to build the model, the neural network method has good fitting performance, and compared with a traditional linear model, the built model can accurately forecast the biological activity of the compounds.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
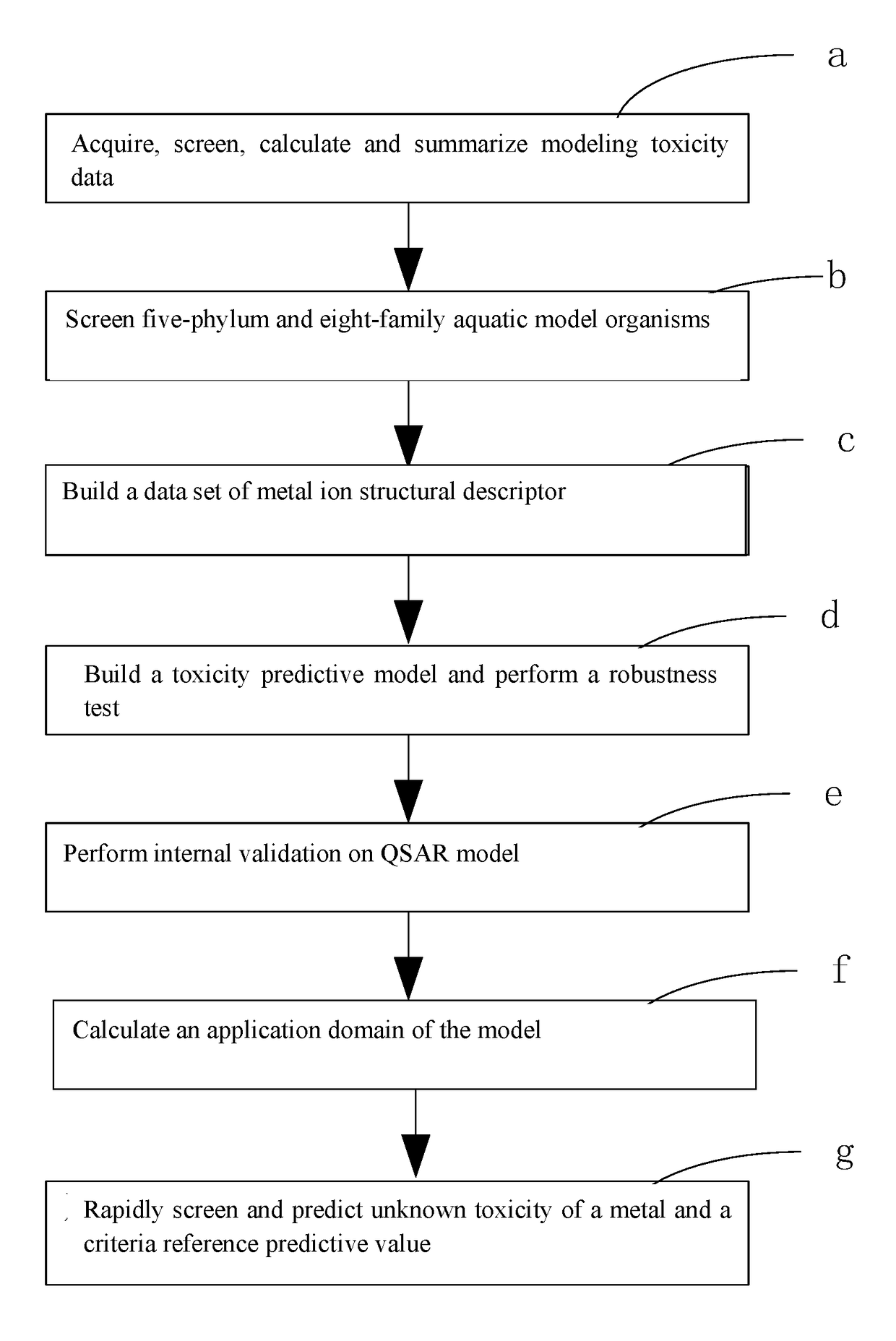
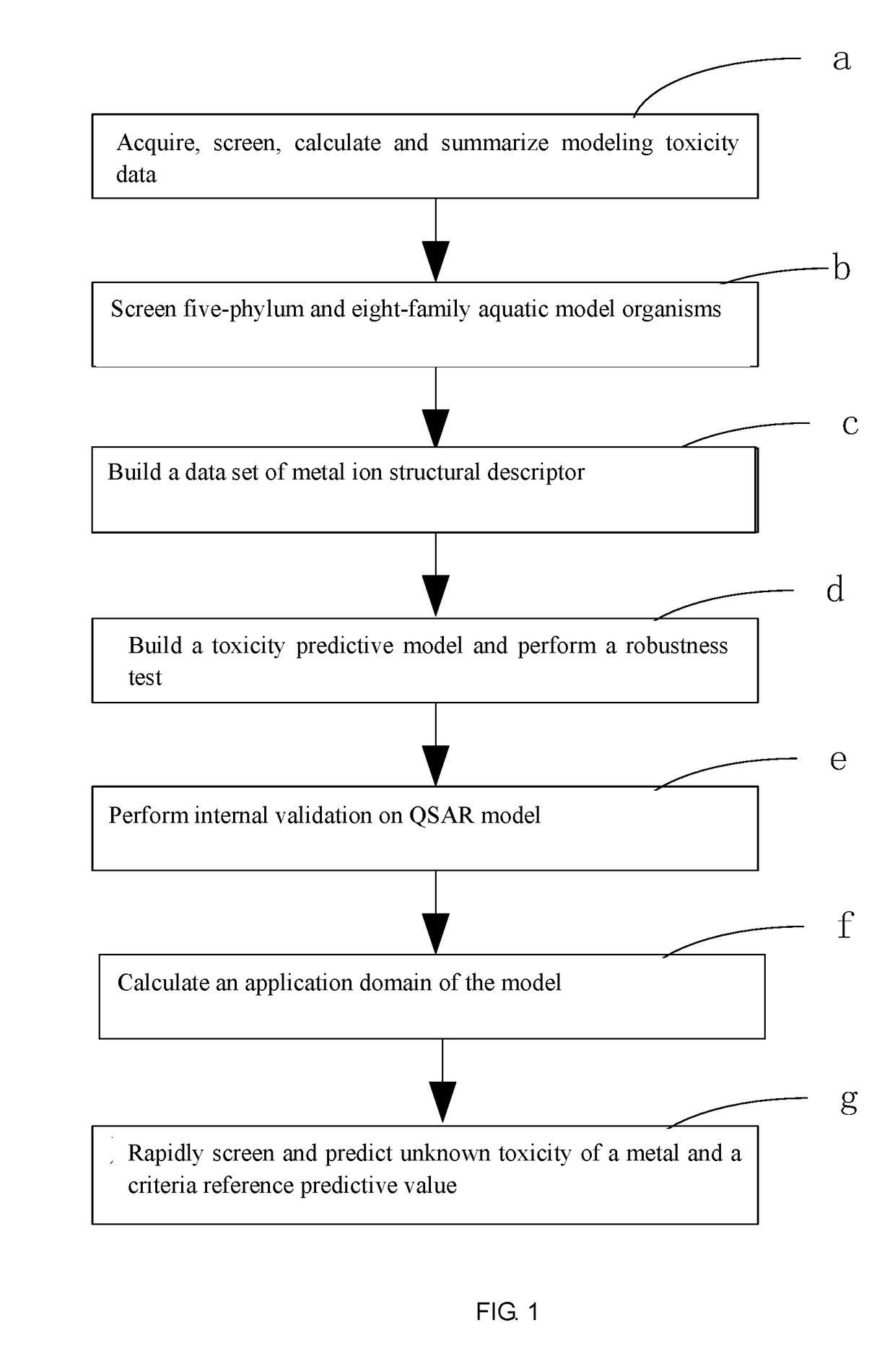
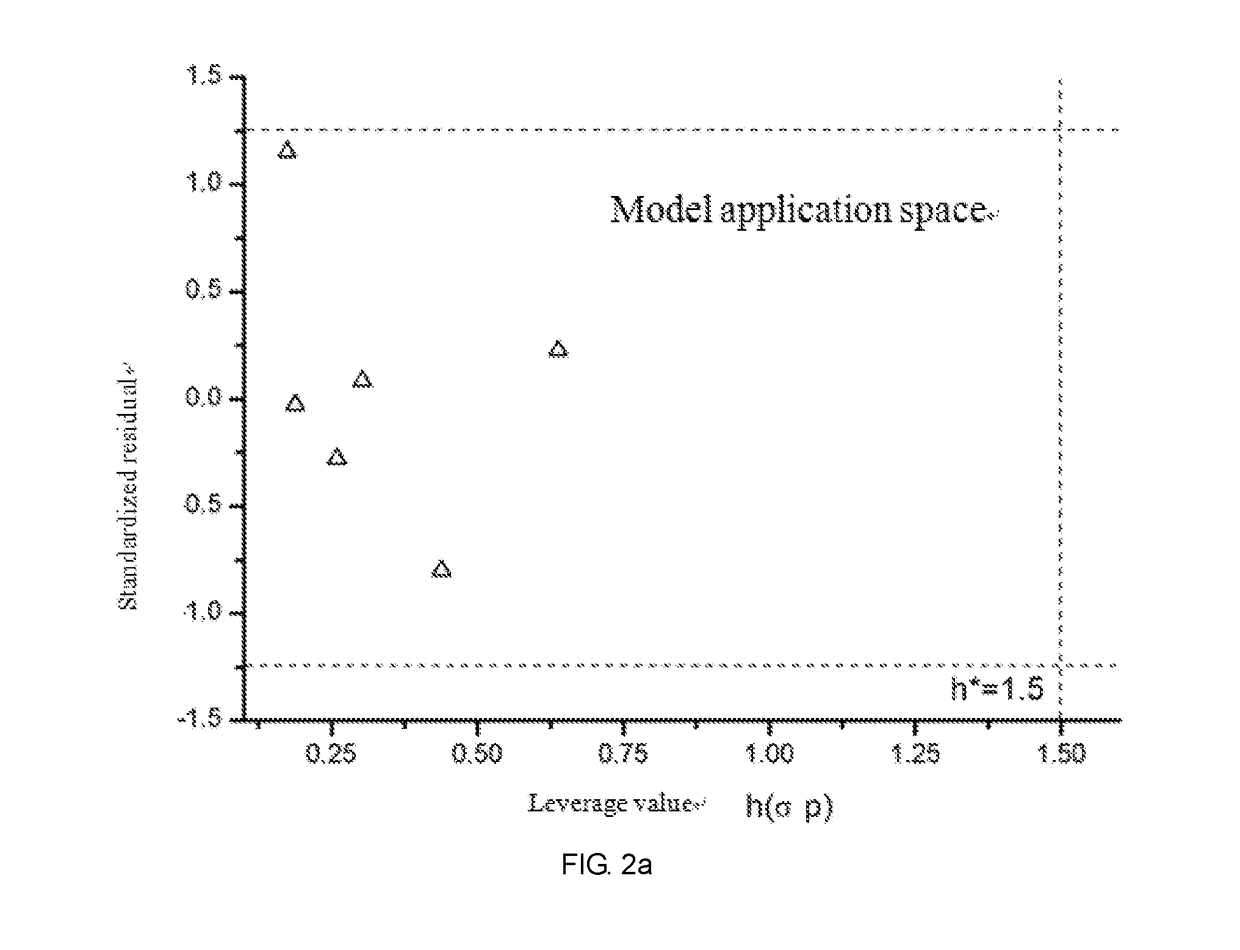
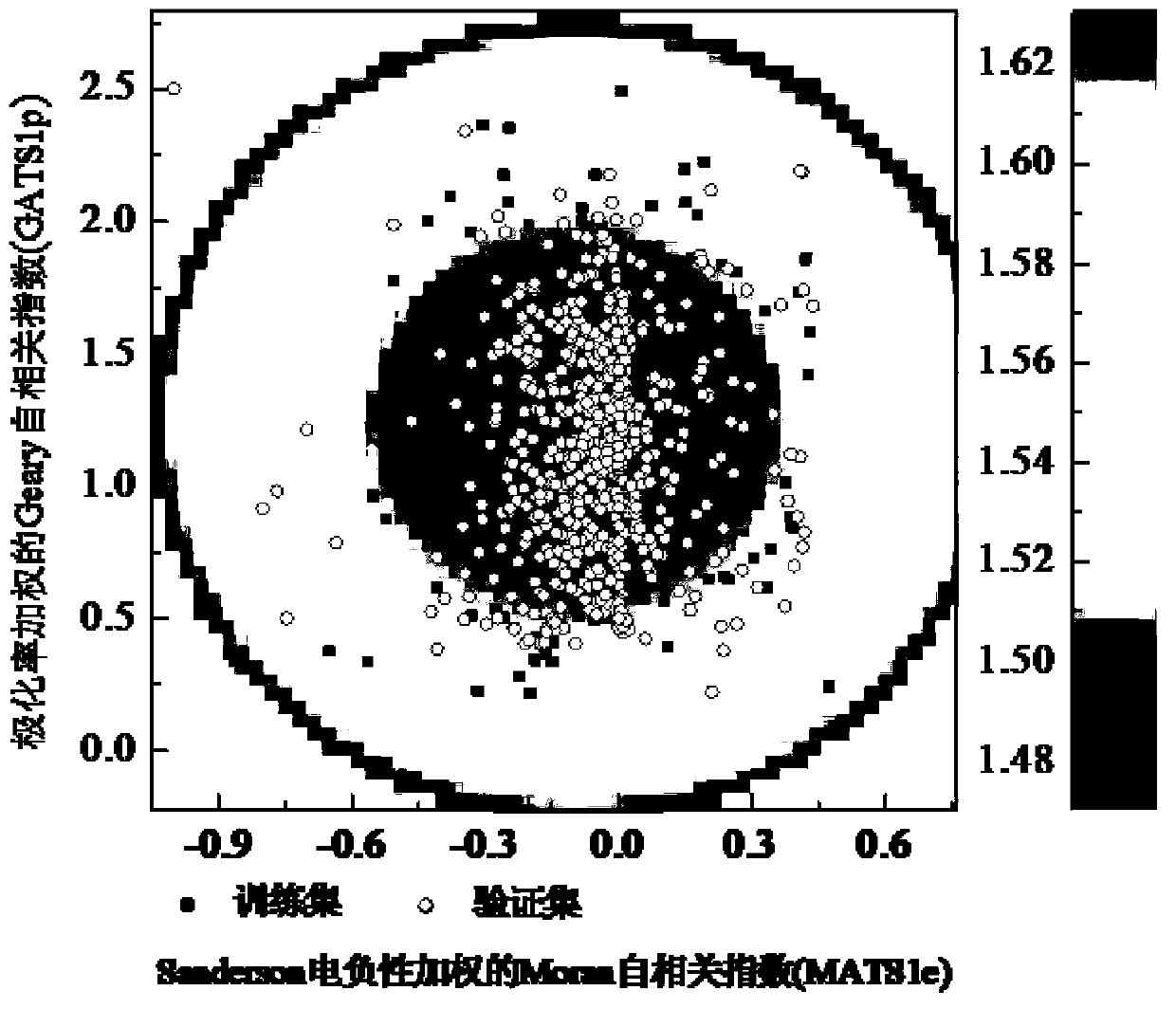
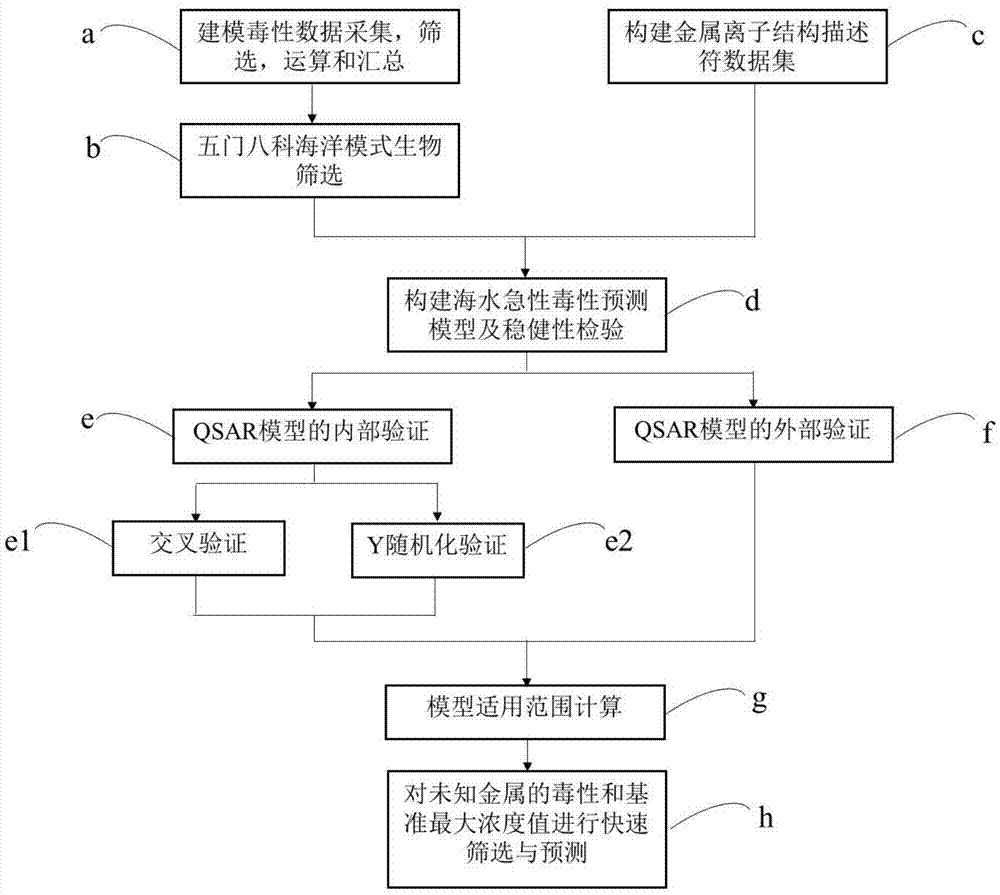
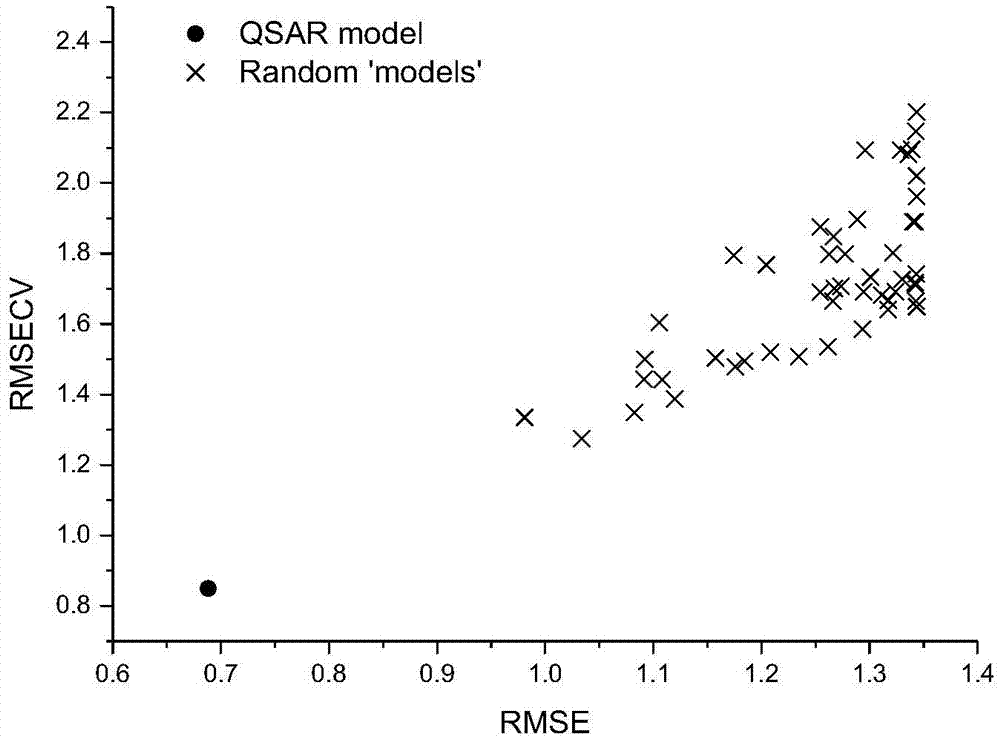
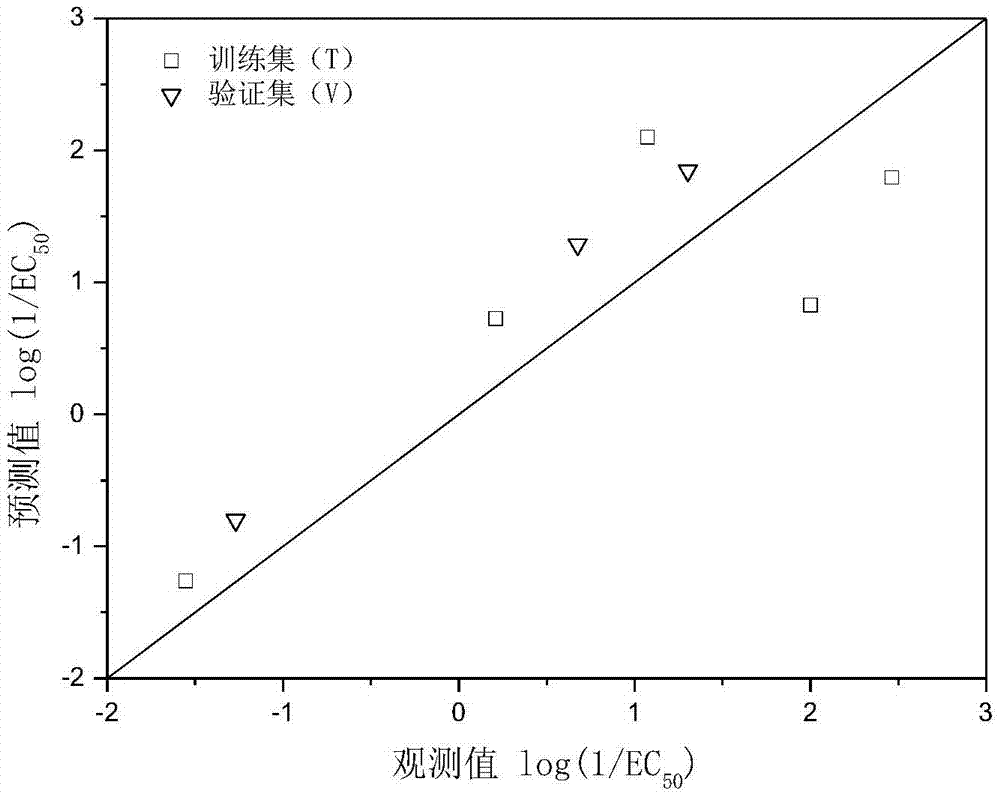
Fresh water acute criteria prediction method based on quantitative structure-activity relationship for metals
ActiveUS20170323085A1Improve precisionPredict in advanceChemical property predictionForecastingChemical structureAcute toxicity testing
The present invention relates to a fresh water acute criteria prediction method based on a quantitative structure-activity relationship for metals. An unknown toxic endpoint of a metal is predicted according to a quantitative relationship between structural characteristics of heavy metal ions and acute toxicity effects of aquatic organisms, and hazard concentrations for protecting the aquatic organisms of different proportions are derived from sensitivity distribution analysis on different species. The fresh water acute criteria prediction method is a method for establishing a metal toxicity predictive model by integrating physicochemical structural parameters of heavy metals and toxic mechanisms of different aquatic organisms and applying the metal toxicity predictive model to prediction of an unknown criteria reference value.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Predicting organic chemical biodegradability according to logistic regression method
ActiveCN103345544AQuick forecastEffective predictionSpecial data processing applicationsGuidelineCvd risk
The invention discloses a method for predicting organic chemical biodegradability according to a logistic regression algorithm. According to the method for predicting organic chemical biodegradability, on the basis that the molecular structure of a compound is obtained, a person just needs to calculate descriptors of representational structure characteristics and use a built quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) model, and accordingly the biodegradability of the organic compound can be fast and efficiently predicted. The method for predicting organic chemical biodegradability is low in cost, and easy and convenient and fast to adopt, and saves large required labor sources, cost and time. According to the method for predicting organic chemical biodegradability, modeling completely accords with the QSAR model building and guidelines for use of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), only 14 molecular structure descriptors are adopted, the logistic regression method which is clear and transparent in algorithm is applied, and therefore the method for predicting organic chemical biodegradability is easy to understand and apply. Model application fields are explicit, and 1629 kinds of compounds are covered. The method for predicting organic chemical biodegradability according to the logistic regression method has good fitting effect, robustness and prediction ability, can effectively predict biodegradability of a plurality of organic compounds and provide important data support to organic chemical risk assessment and management, and has important significance in ecological risk assessment.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
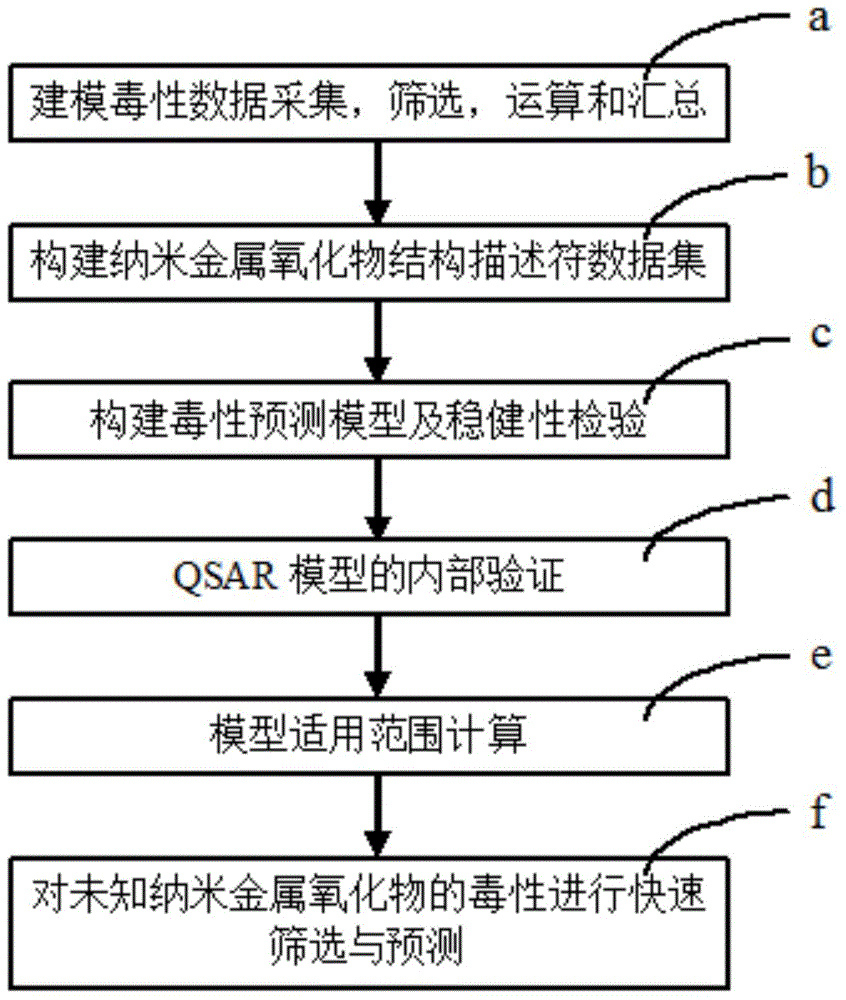
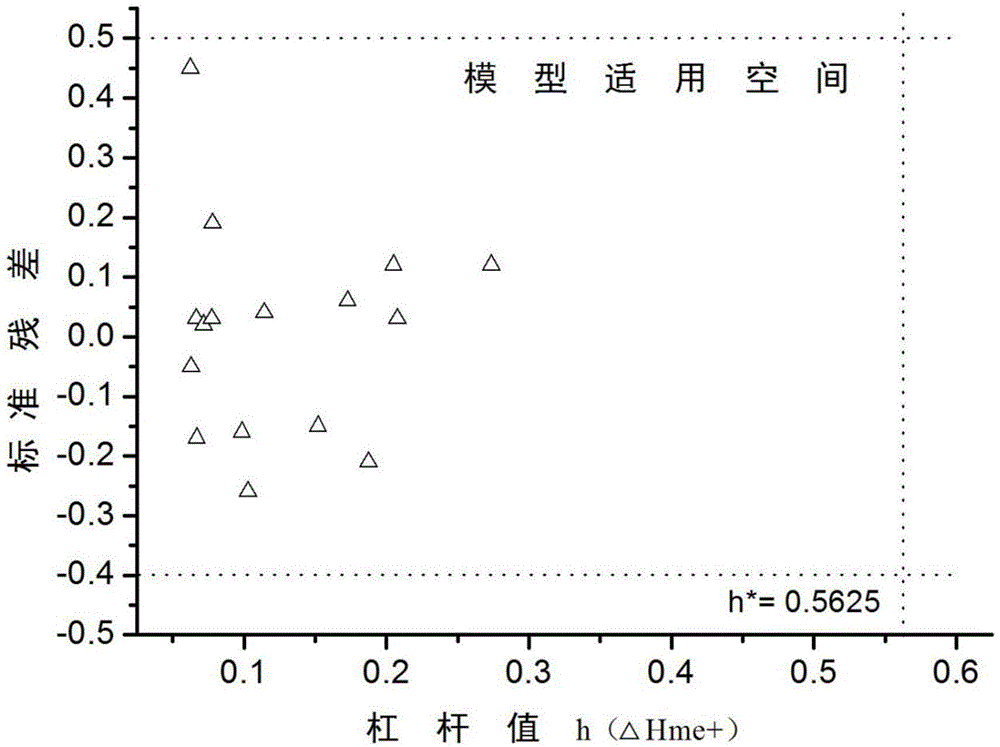
QSAR (Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship) toxicity prediction method for evaluating health effect of nano-crystalline metal oxide
The invention relates to the field of toxic substance prediction in an environment, in particular to a QSAR (Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship) toxicity prediction method for evaluating the health effect of nano-crystalline metal oxide. The method comprises the steps of predicting the toxicity endpoint of unknown metallic oxide according to a quantitative relation between structural features and cytotoxicity effect of the nano-crystalline metal oxide; building a nano-crystalline metal oxide prediction model by combining the physicochemical structure parameter and a special mechanism of toxication of the nano-crystalline metal oxide, and applying the nano-crystalline metal oxide prediction model to predict the toxicity endpoint of the unknown metallic oxide. According to the QSAR toxicity prediction method provided by the invention, based on a function model and the toxicity prediction method of the nano-crystalline metal oxide, and the nano-crystalline metal oxide prediction model can be built to predict an unknown toxicity value through the QSAR model method, therefore the toxicity endpoint prediction of various compounds lack of toxicity data can be completed quickly and simply with less dependency.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
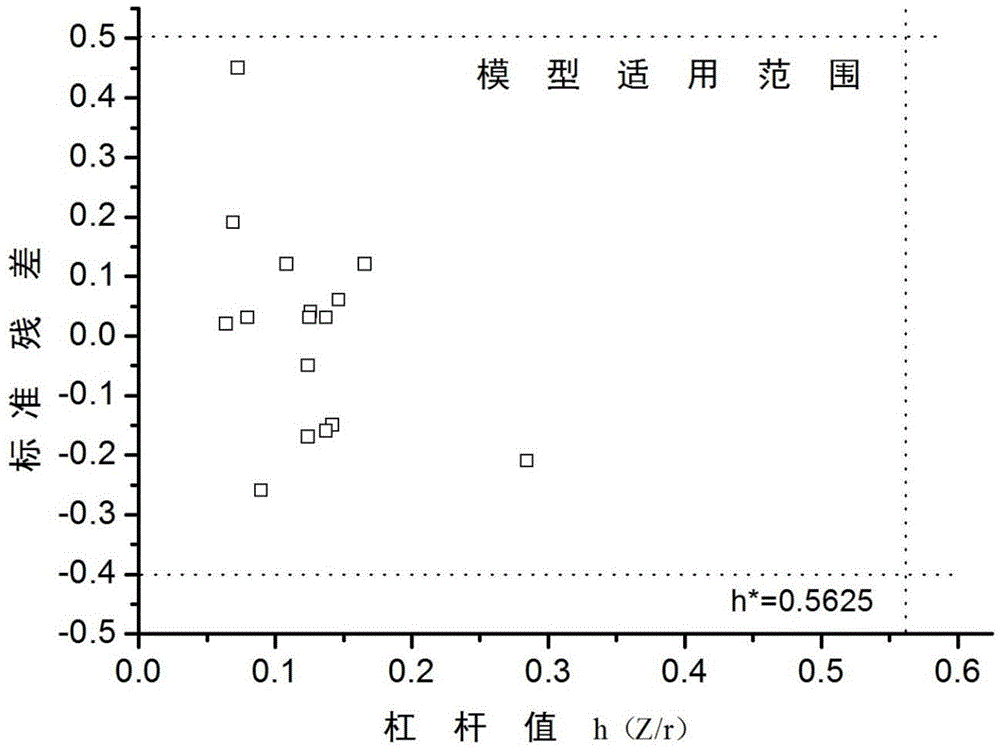
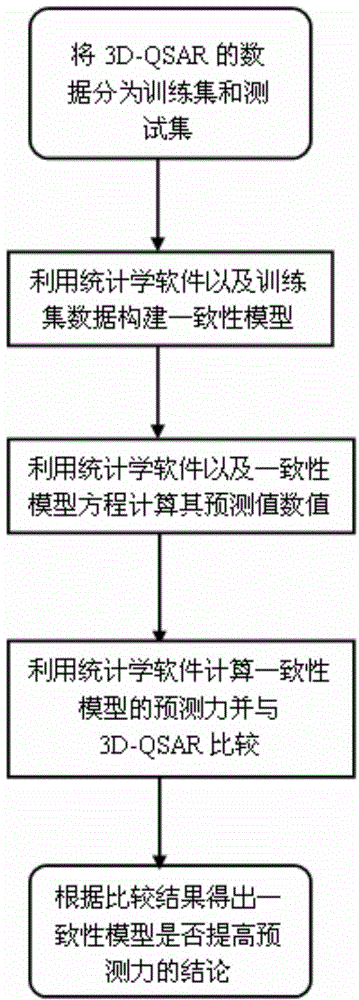
Consistency model building method based on 3-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model
InactiveCN104834831AQuality improvementQuick discoverySpecial data processing applicationsEntity–relationship modelRelational model
The invention relates to a building method of a 3-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (3D-QSAR) model, in particular to building of the 3D-QSAR model based on HIV-1 inhibitor molecules and consistency model building, and belongs to the technical field of biological information. The HIV-1 inhibitor molecules are selected to perform 3D-QSAR and consistency model research so as to mine the relationship between the structure of an inhibitor and the anti-HIV activity of the inhibitor. According to the method, the bioactivities of compounds with similar structures are predicted through building of a mathematical model based on the chemical characteristics (such as hydrophilcity, hydrophobicity, electrostatic property, polarity and three-dimensional structure) of the inhibitor. A consistency model is built with a statistics method on the basis of three 3D-QSAR models, and the aim is to further enhance the prediction capability of the model. The obtained model can better predict the anti-HIV activities of compounds, and the prediction accuracy of the anti-HIV activity of a brand new compound is increased. Compared with other methods, the method has the advantages that the medicament discovery efficiency is increased, and the medicament discovery cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
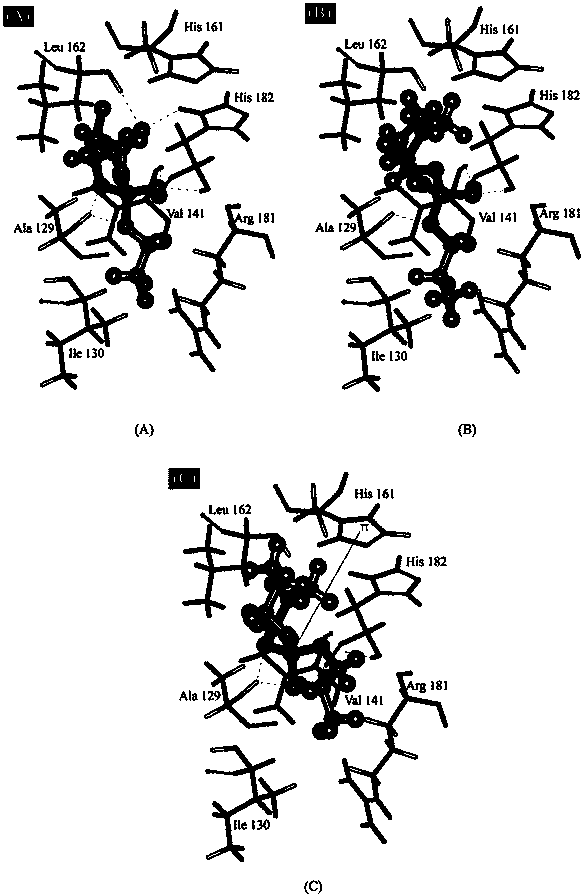
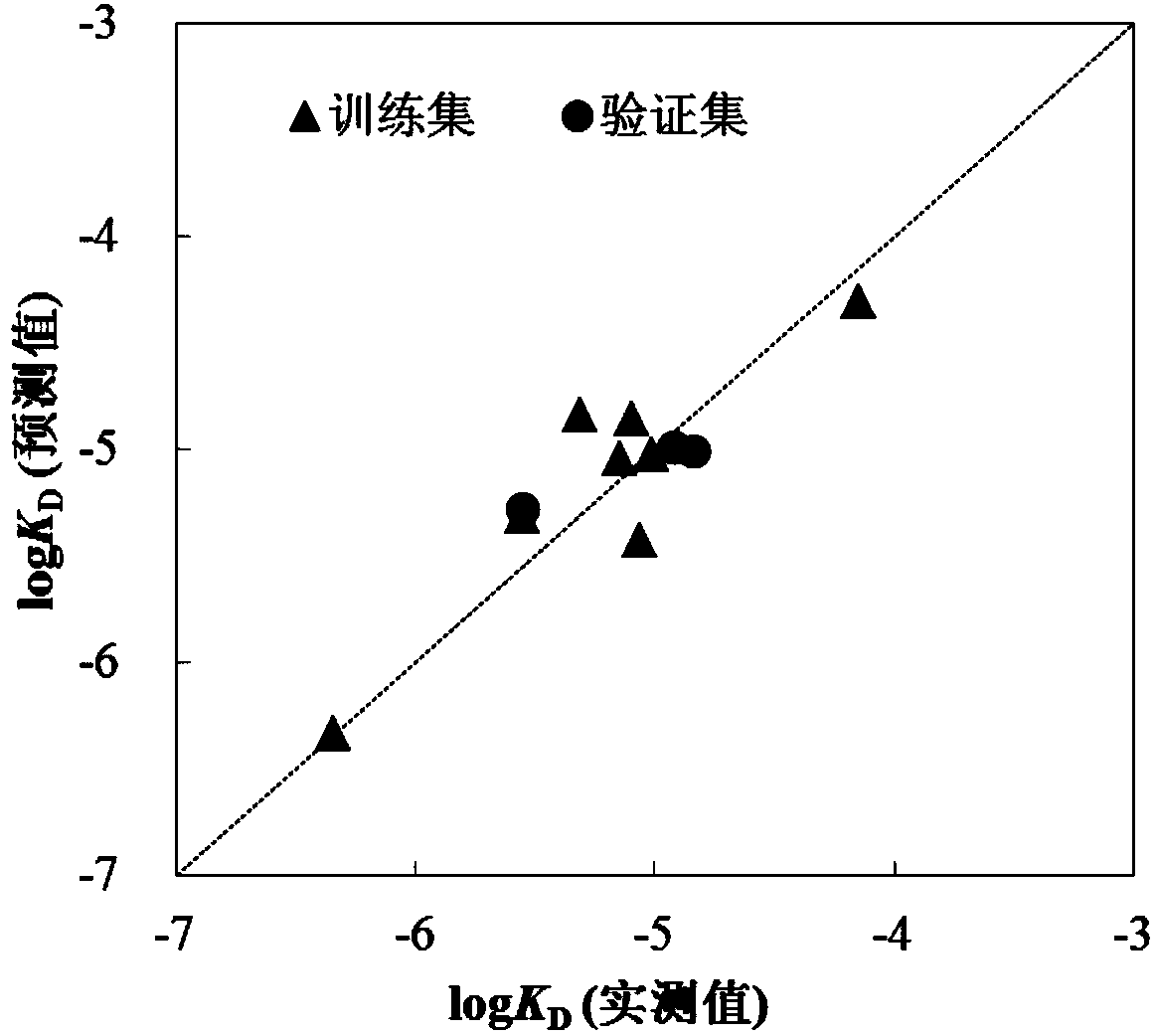
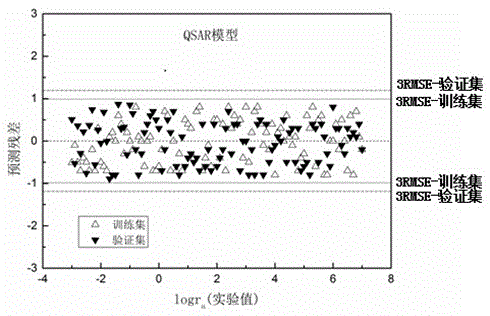
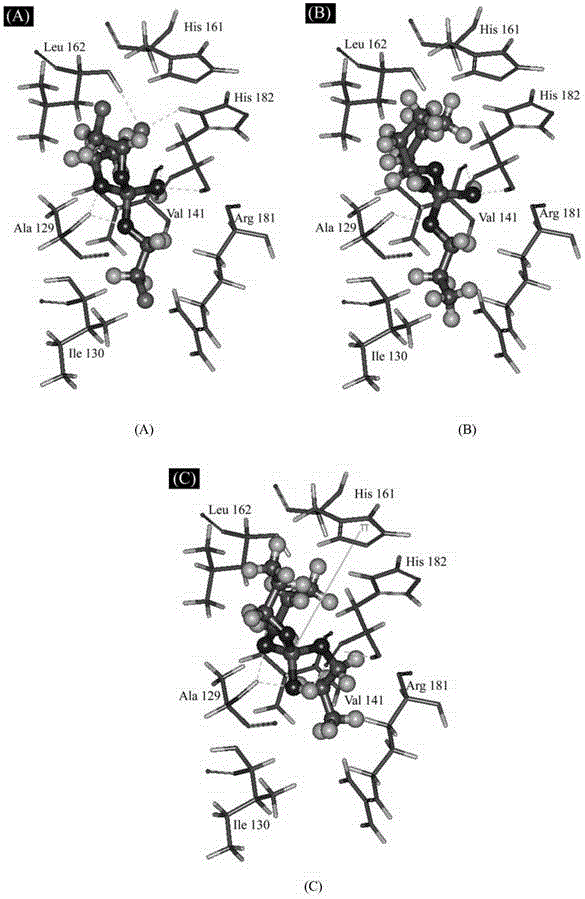
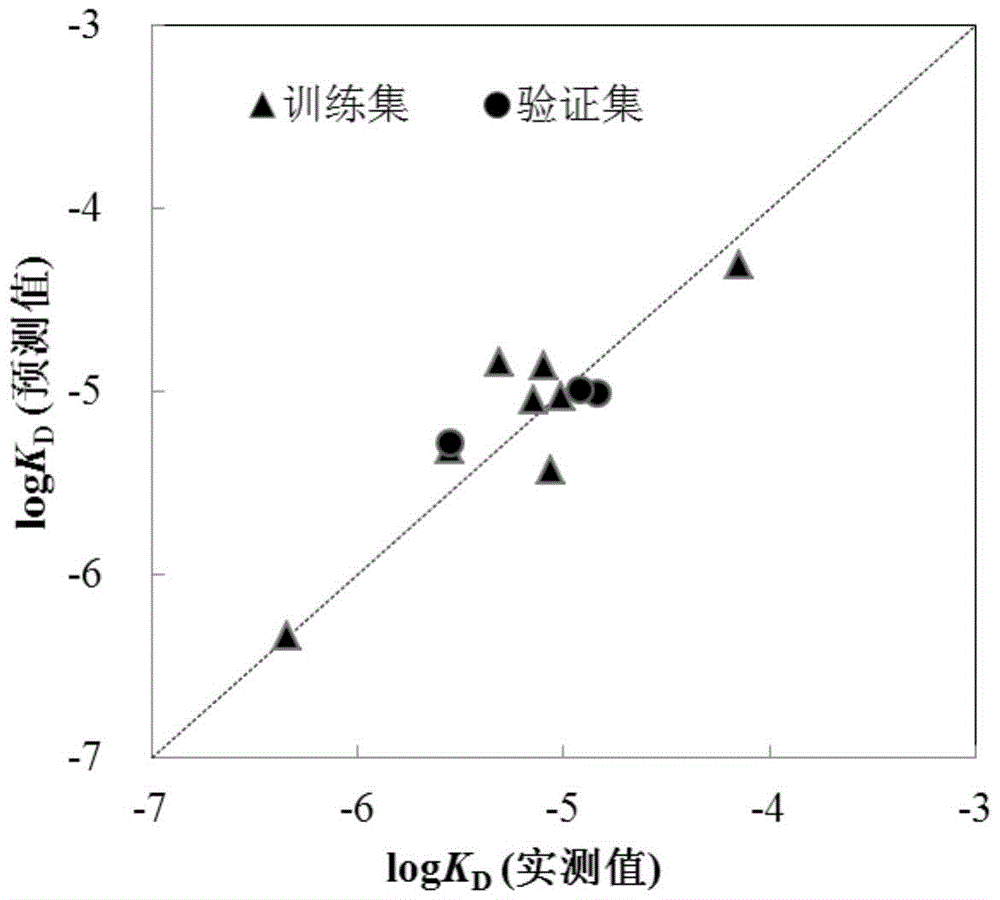
Method for predicting affinity of interaction between biomarker p53 and organic phosphate fire retardant
ActiveCN103971030ALow costSave human effortSpecial data processing applicationsExperimental testingPhosphate
The invention relates to a method for predicting affinity of the interaction between a biomarker p53 and an organic phosphate fire retardant. The method includes the following steps of establishing a quantitative structure-activity relationship QSAR model of the affinity KD and training set compound molecule descriptors through a partial least square method so as to obtain an affinity KD value, and predicting the affinity according to the affinity KD value. By the adoption of the method, interaction between the organic phosphate fire retardant and the biomarker p53 which are of different structures can be predicted, the method is low in cost and easy, convenient and rapid to achieve, and a large amount of labor, a large number of expenses and a large amount of time which are needed by experimental tests can be saved; the prediction result obtained through the method can provide the important data support for organic chemical ecological risk assessment and management, and the method has important theoretical and practical significance.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
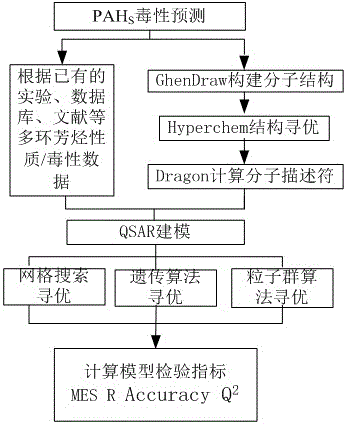
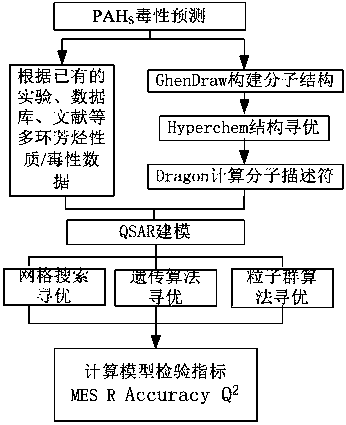
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon property/toxicity prediction method using an intelligent support vector machine
ActiveCN105868540AAchieving Toxicity TestingGuaranteed accuracyChemical property predictionCharacter and pattern recognitionSmall sampleEnvironmental index
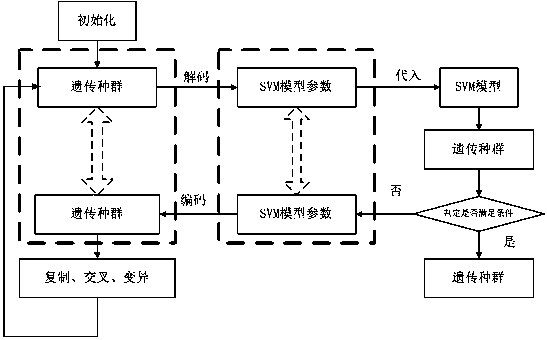
The invention relates to a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon property / toxicity prediction method using an intelligent support vector machine. The method, based on measured polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon molecule structures and the quantitative structure-activity relationship technology, establishes a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon environmental index prediction module and a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon carcinogenicity prediction module and employs the support vector machine algorithm, thereby realizing handing of problems of small samples, nonlinearity and high dimension. The method also optimizes the models by using the grid search method, the genetic algorithm, and the particle swarm algorithm, thereby preventing parameter influence and further improving the accuracy of the models. The method can predict the property and toxicity of unknown polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons rapidly by using intelligent optimized support vector machine; compared with conventional toxic test experiments, the method increases the test efficiency; compared with the conventional statistical prediction method, the method improves the generalization; compared with normal algorithms, the method prevents parameter influence, realizes programming and can provide referable decisional proof for environmental evaluation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for predicating vapor pressure of liquid phase of organic substance by quantitative structure-activity relationship model
InactiveCN102521507AQuick forecastEasy to predictSpecial data processing applicationsEntity–relationship modelCompound structure
The invention relates to a method for predicating vapor pressure of liquid phase of organic substance by quantitative structure-activity relationship model. On the basis of known compound structure, the method computes molecular structural descriptor of the structure and uses the quantitative relationship between the built molecular structure and vapor pressure to predicate liquid phase vapor pressure of the organic compound quickly and effectively. The method can be applied in a plurality of kinds of organic compounds, can predicate vapor pressure at different temperature values is suitable for obtaining vapor pressure data in different countries and areas in different latitudes and altitudes and provides necessary base data for risk assessment and supervision of chemicals.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
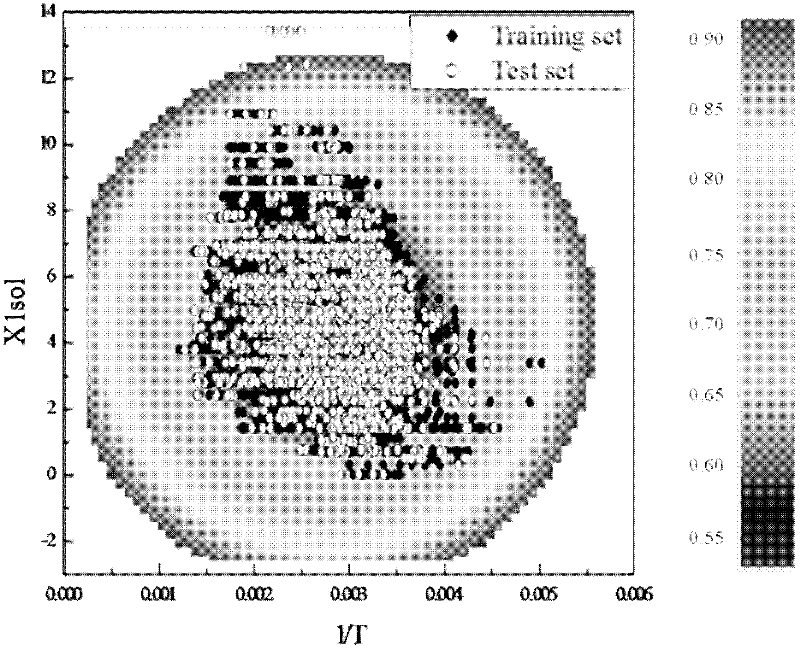
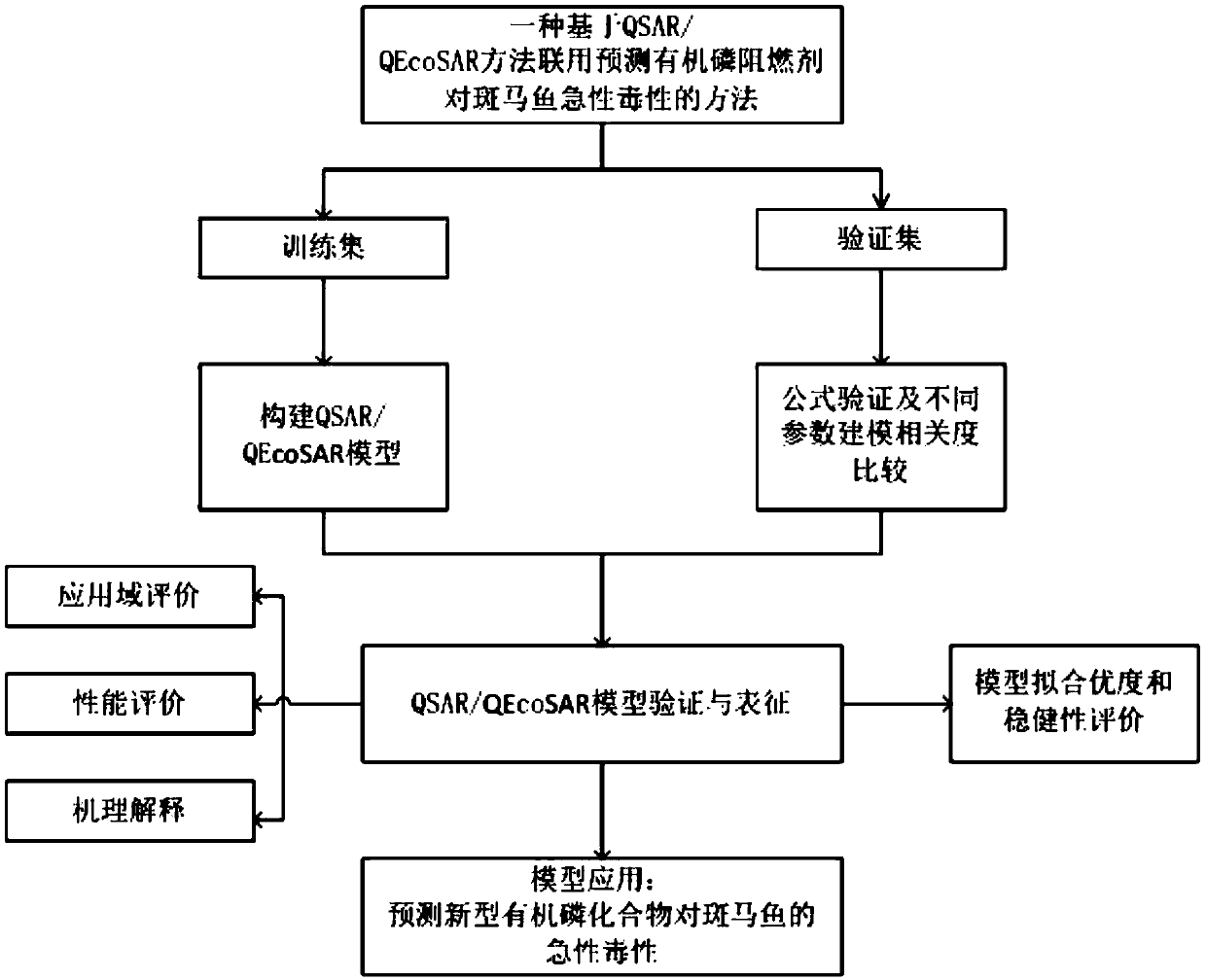
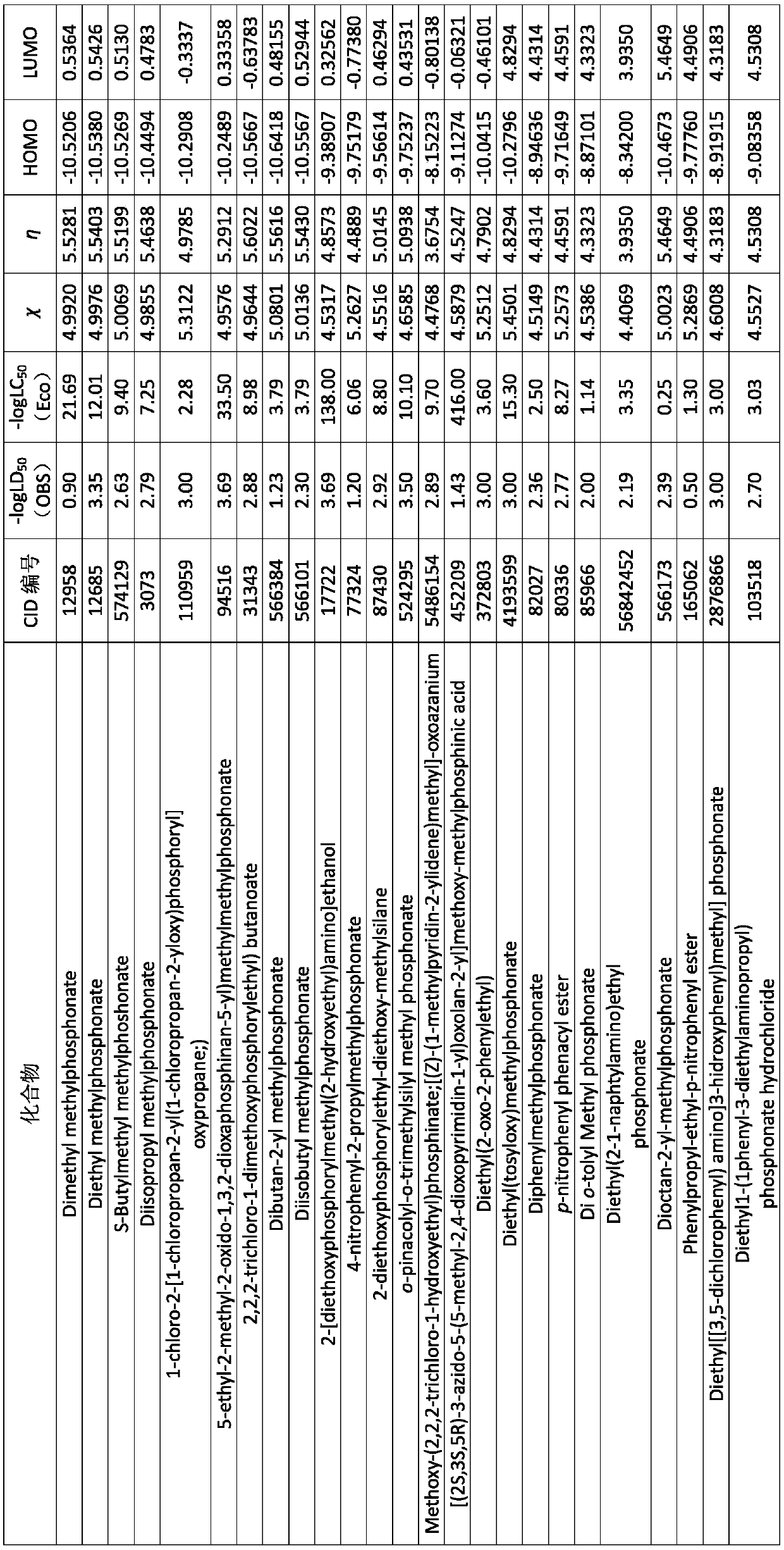
Method for predicting acute toxicity of organophosphorous flame retardant on zebra fish based on QSAR/QEcoSAR method combination
InactiveCN108733970APredict acute toxicityShortcut structureSpecial data processing applicationsAcute toxicity testingChemical reaction
The invention discloses a method for predicting acute toxicity of an organophosphorous flame retardant on a zebra fish based on QSAR / QEcoSAR method combination and belongs to the technical field of quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) for chemical environment supervision. The method comprises the steps that based on the chemical reaction principle and the minimum energy principle, QSAR and QEcoSAR are combined, and a multivariate linear regression method is adopted to construct a QSAR model of LC50 and training set compound molecule descriptors (electronegativity, chemical hardness, chemical force, eletrophilicity and other characteristics). The method is low in cost and convenient and fast to use, and a large amount of manpower, cost and time needed in experimental testingcan be saved; and by use of the prediction result, important data support can be provided for ecological risk evaluation and management of organophosphorous chemicals, and therefore the method has important realistic significance and theoretical value.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Method for predicating acute toxicity of organophosphorus pesticide on aquatic organisms through quantitative structure activity relationship
InactiveCN103778483AForecast QuickPrediction is simpleChemical property predictionForecastingAcute toxicity testingChemical compound
The invention discloses a method for predicating the acute toxicity of organophosphorus pesticide on aquatic organisms through the quantitative structure activity relationship. On the basis that the structure of chemical compound is known, geometrical full optimization is performed on a Gaussian program to obtain the MV, the MW, the EHOMO, the ELUMO, the difference value delta E (hartree), the DM and the like to serve as structural descriptors, regression parameters of all parameters, the multiple correlation coefficient and an F-test value are obtained in combination with data of toxicity of the organophosphorus pesticide on aquatic organisms through the programmed partial least squares stepwise linear regression program, and quantitative relationships between the various structural descriptors and the toxicity. Thus, the toxicity of the organophosphorus pesticide on the aquatic organisms can be fast, conveniently and effectively predicted, and essential basic data are provided for risk assessment and supervision on the organophosphorus pesticide.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Construction method and application of three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model of bcl-2 protein inhibitor
InactiveCN102262715APredicted binding constantFast Prediction of Binding ConstantsSpecial data processing applicationsEntity–relationship modelHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to a method for constructing a three-dimensional quantitative structure activity relationship model of a B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) protein inhibitor and application of the method and belongs to the technical field of biological information. The method comprises the following steps of: according to the known small molecule inhibitor, establishing the three-dimensional quantitative structure activity relationship model of the Bcl-2 protein inhibitor by using a three-dimensional quantitative structure activity relationship technology; and further improving the accuracy of the model by using technologies for analyzing molecular similarity, optimizing molecular conformation, optimizing parameters and the like. By the invention, the Bcl-2 protein binding constants of an active unknown compound can be quickly predicted, and clues of the active compound are acquired within short time. Compared with the conventional high-throughput screening technology, the invention has the advantages of greatly improving screening efficiency and reducing cost.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Seawater acute reference prediction method based on metal quantitative structure-activity relationship
InactiveCN105447248AHigh precisionImprove predictive performanceGeneral water supply conservationSpecial data processing applicationsChemical structurePredictive methods
The present invention relates to a seawater quality reference prediction method based on a quantitative structure-activity relationship of metal and metalloid. According to the method, the toxic endpoint of unknown metal is predicted according to a quantitative relationship between the structural feature of metallic ions and the marine life acute toxic effect, and a risk concentration for protecting different proportions of marine life is analyzed and deduced in conjunction with sensitivity distribution of different species; and a QSAR metal toxicity prediction model is established by integrating metal physical and chemical structure parameters and toxic mechanisms of different marine life and is applied to prediction of an unknown seawater quality reference maximum concentration. The seawater acute reference prediction method based on the metal quantitative structure-activity relationship is based on the ecology principle; the system screens various marine species and takes the screened marine species as smallest biological prediction sets; and single-parameter toxicity prediction models are established separately, thereby improving the model precision and prediction ability.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method for predicting and modeling Anti-psychotic activity using virtual screening model
InactiveUS20130184462A1Effective controlChemical property predictionOrganic chemistryStrong bindingDrug discovery
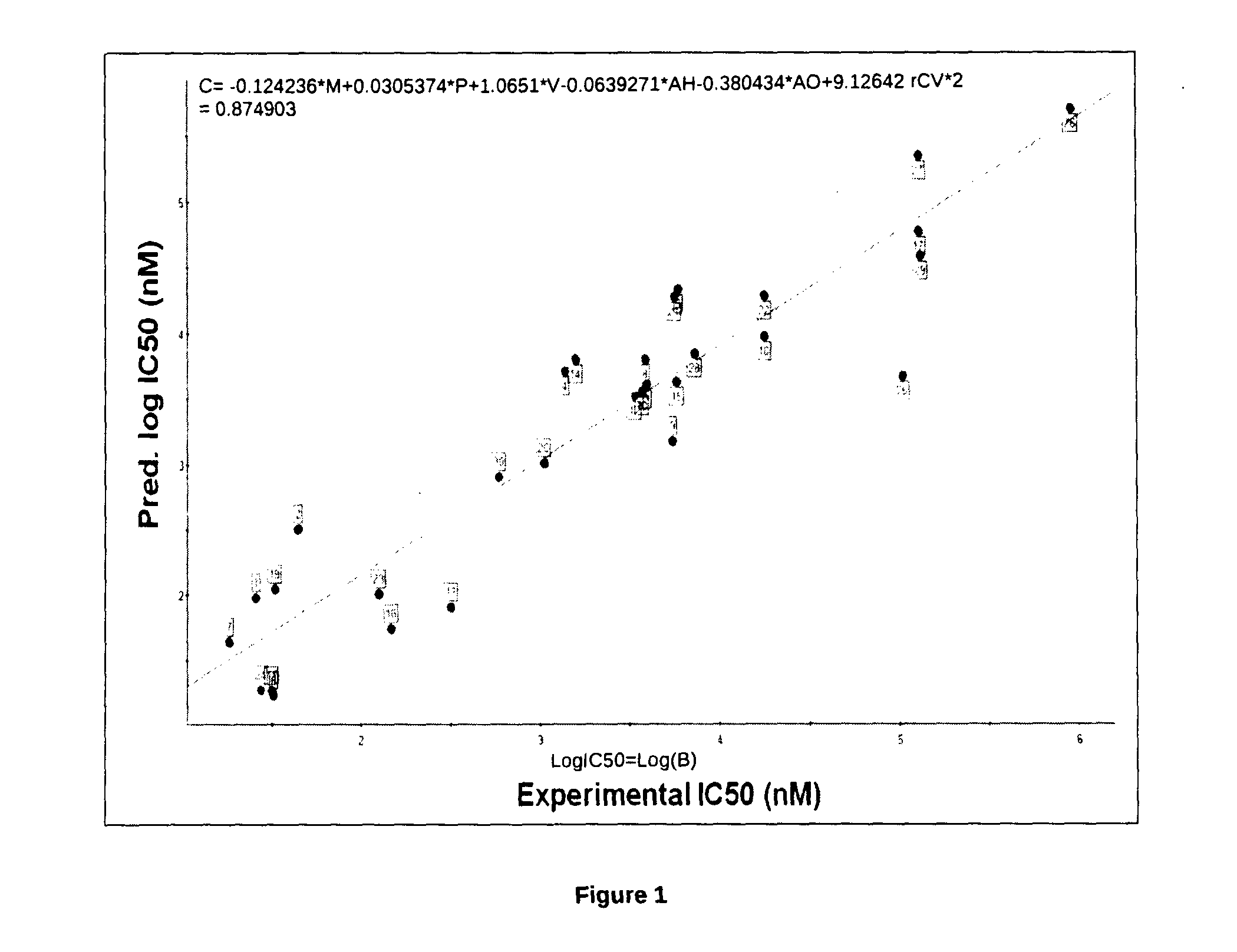
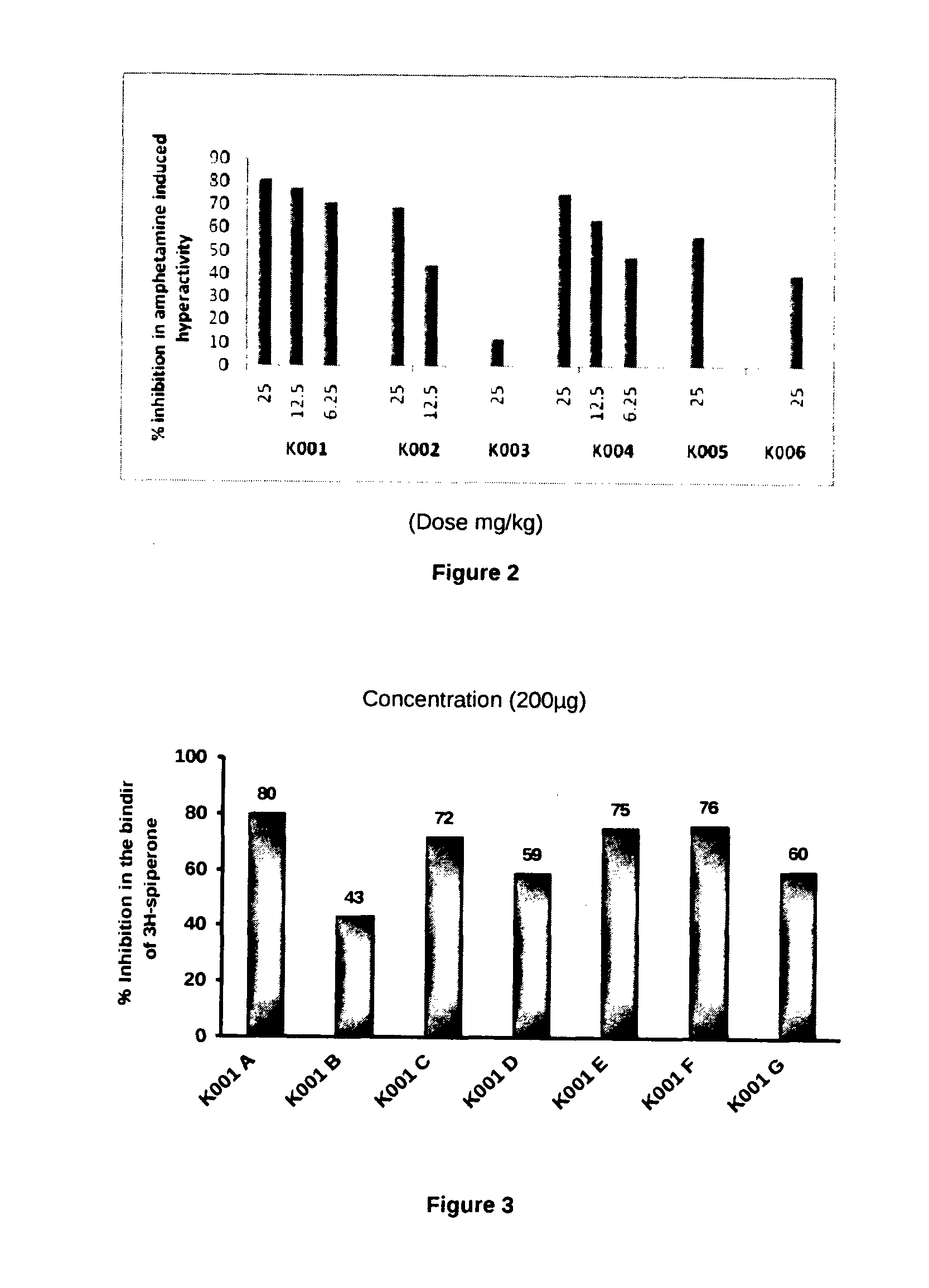
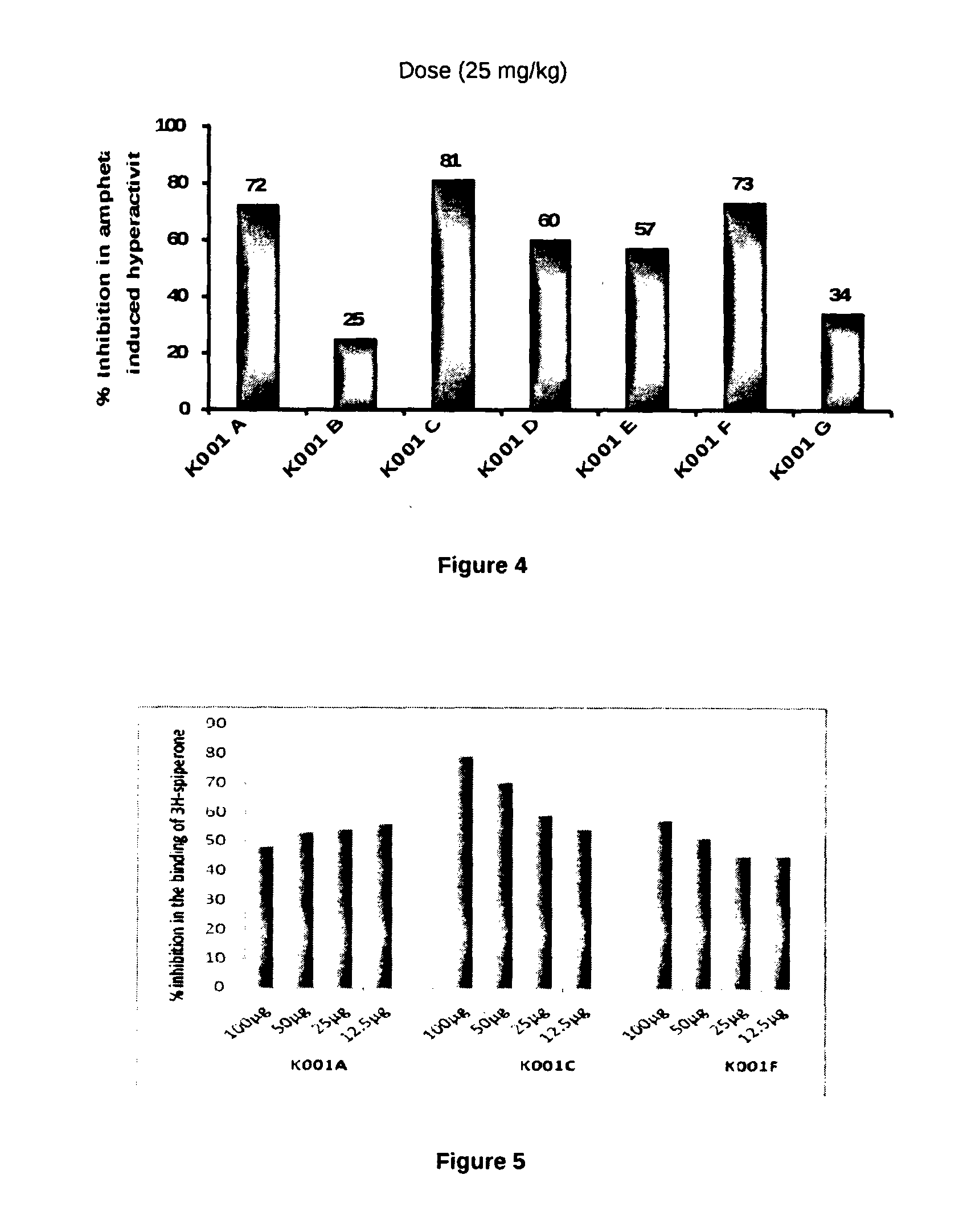
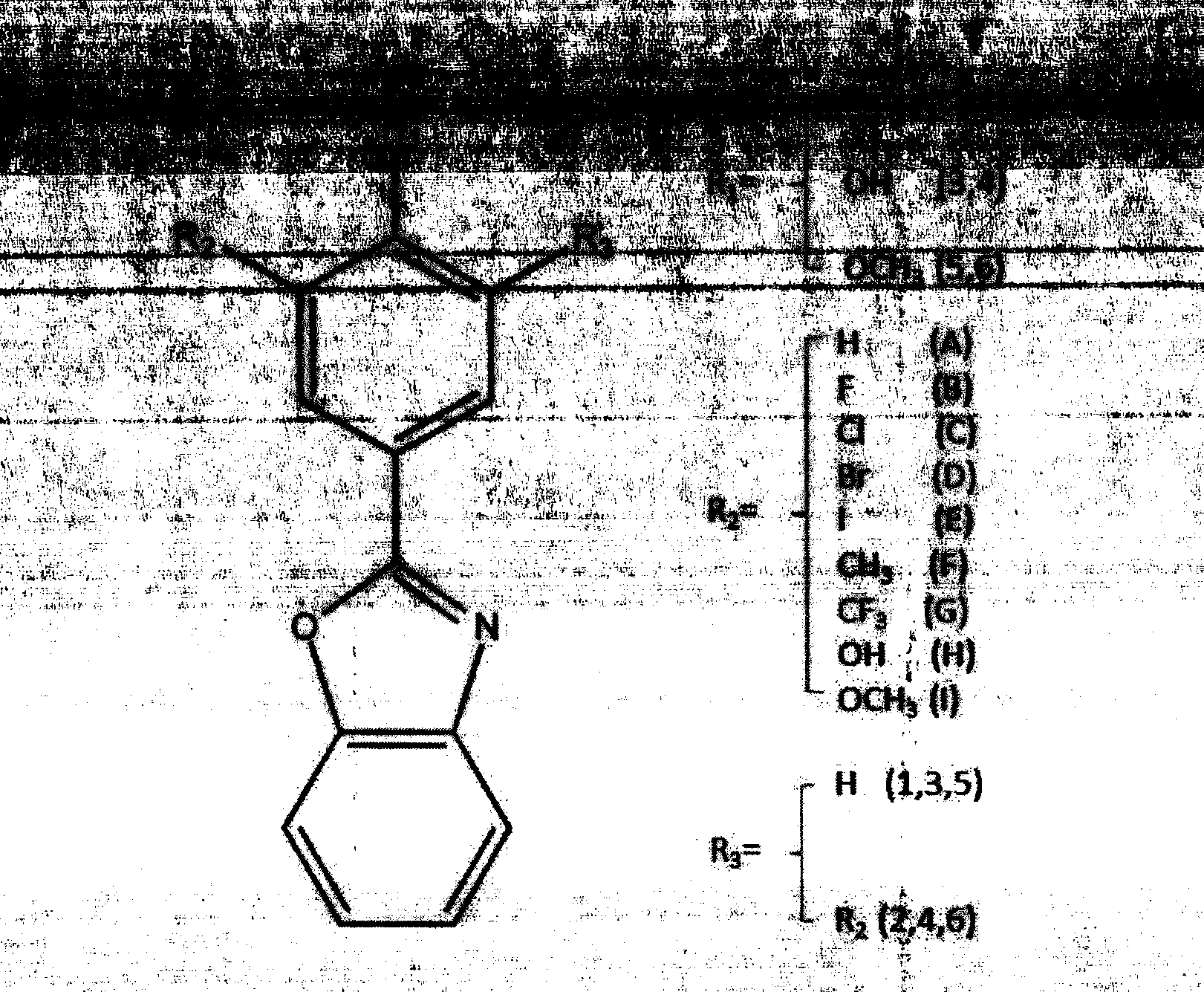
The present invention relates to the development of a virtual screening model for predicting antipsychotic activity using quantitative structure activity relationship (QSAR), molecular docking, oral bioavailability, ADME and Toxicity studies. The present invention also relates to the development of QSAR model using forward stepwise method of multiple linear regression with leave-one-out validation approach. QSAR model showed activity-descriptors relationship correlating measure (r2) 0.87 (87%) and predictive accuracy of 81% (rCV2=0.81). The present invention specifically showed strong binding affinity of the untested (unknown) novel compounds against anti-psychotic targets viz., Dopamine D2 and Serotonin (5HT2A) receptors through molecular docking approach. Theoretical results were in accord with the in vitro and in vivo experimental data. The present invention further showed compliance of Lipinski's rule of five for oral bioavailability and toxicity risk assessment for all the active Yohimbine derivatives. Therefore, use of developed virtual screening model will definitely facilitate the screening of more effective antipsychotic leads / drugs with improved antipsychotic activity and also reduced the drug discovery cost and duration.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Screening method of TTR (transthyretin) small-molecule inhibitors
InactiveCN103425859AImprove reliabilityShorten the development and research cycleSpecial data processing applicationsDiseasePharmacophore
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for distinguishing activities of complete agonist, partial agonist and antagonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
ActiveCN110426512AReduce usageReduce workloadMolecular designPeptide preparation methodsPharmacophoreReceptor for activated C kinase 1
The invention discloses a method for distinguishing the activities of a complete agonist, a partial agonist and an antagonist of a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. The method comprises: modeling of the receptor and a ligand; molecular docking; simulation of conventional molecular dynamics; simulation of well-tempered meta-dynamic molecular dynamics; and construction of a pharmacophore. The method disclosed by the invention can quickly distinguish the activities of the PPARs gamma of different structural compounds, so that use of chemical drugs and cells in a conventional toxicity experiment process in a laboratory is greatly reduced, the workload in the laboratory is relieved, and expenses on the laboratory are saved; therefore, the activities of the PPARs gamma of the compounds are distinguished before QSAR (quantitative structure-activity relationship) modeling, and a QSAR model result is closer to an actual model; and a traditional QSAR is used more widely.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Rabies virus inhibition polypeptide as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106866795AHigh activityStrong targetingPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide-nucleic acidsViral replicationBiological organism
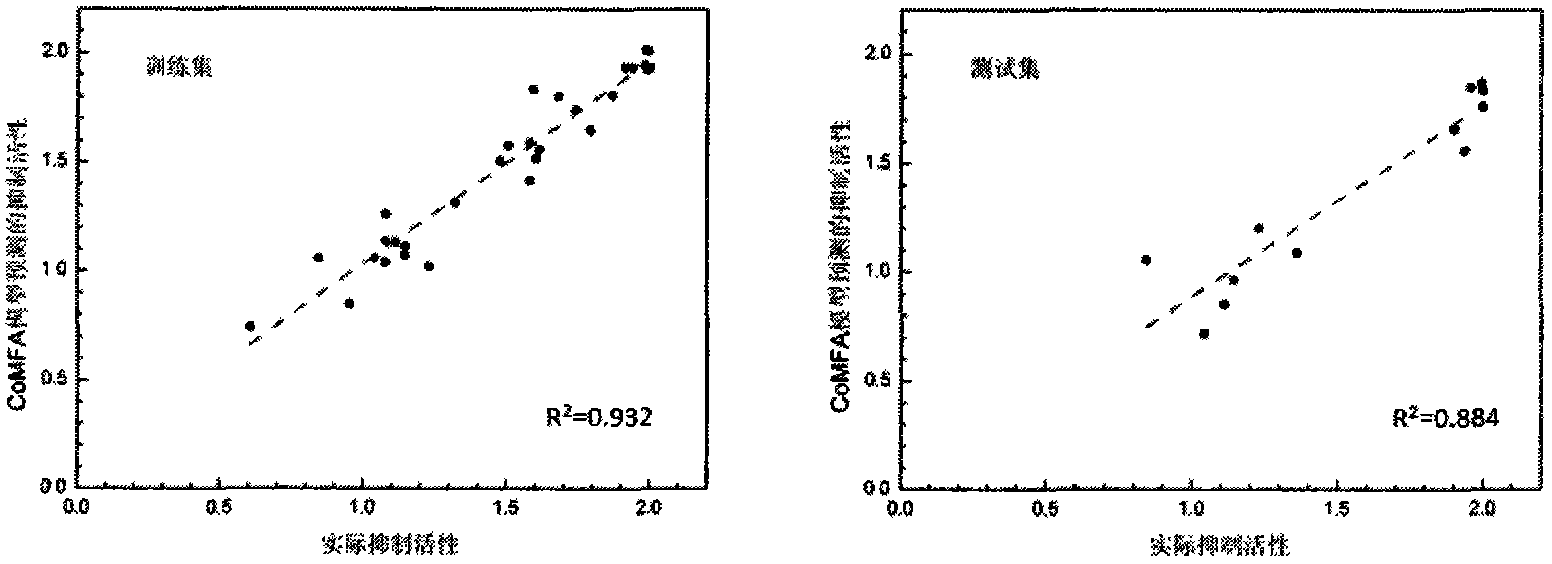
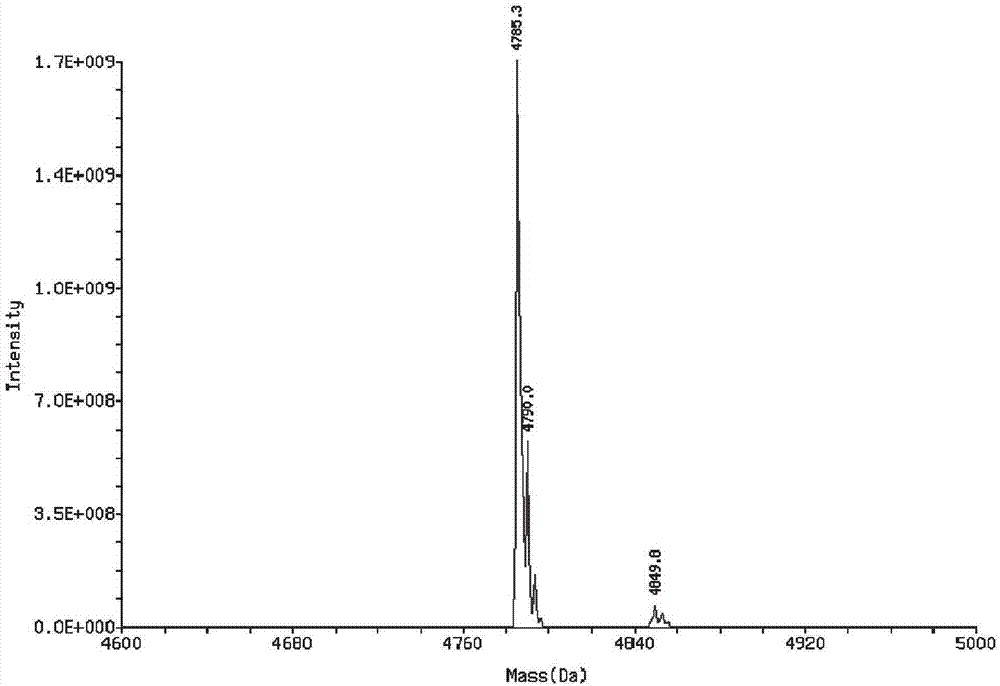
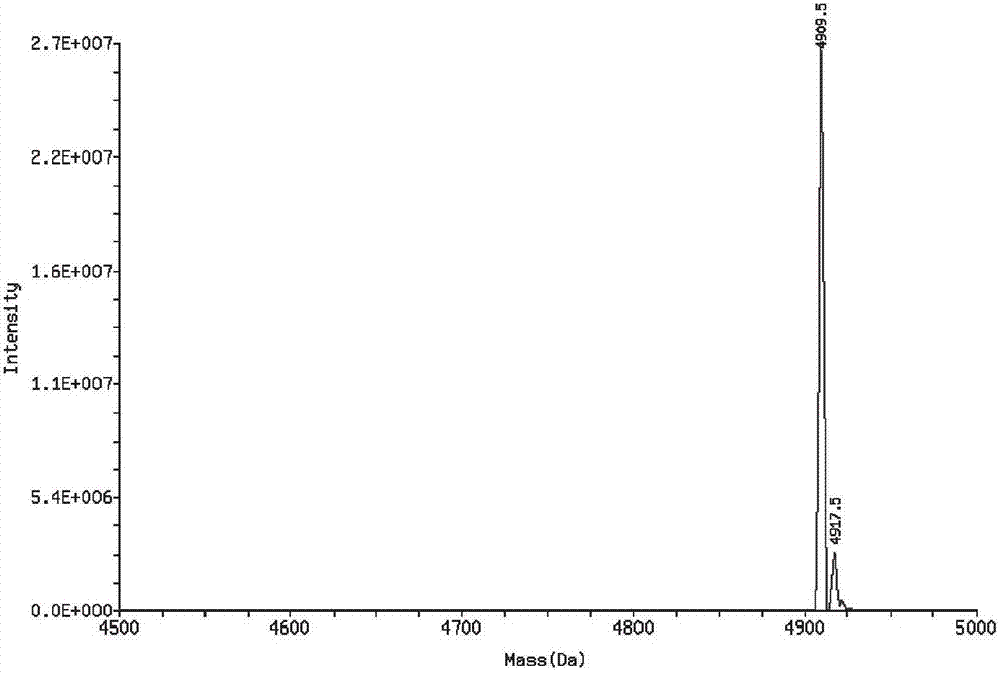
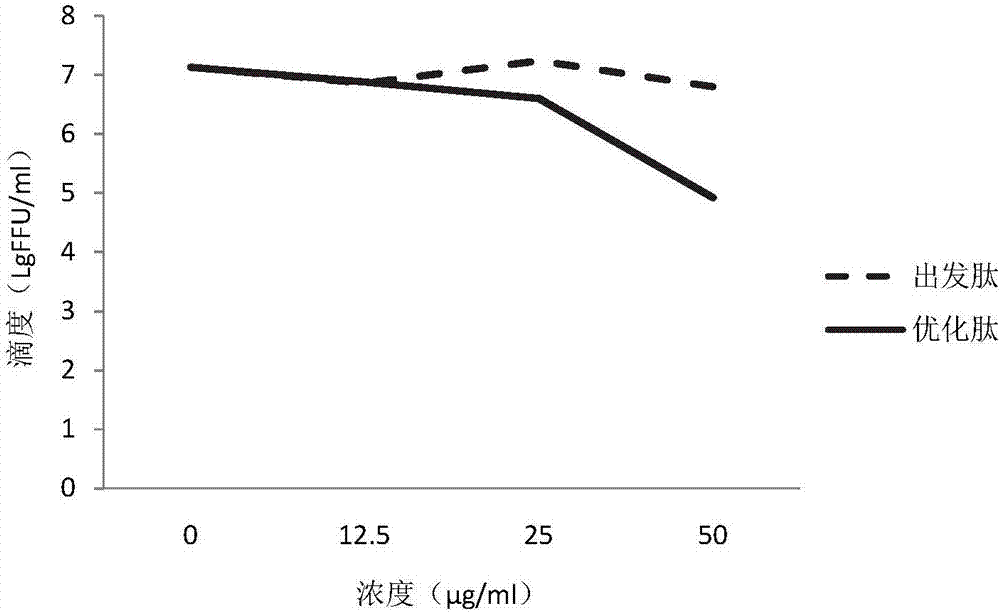
The invention provides rabies virus inhibition polypeptide. The sequence of the rabies virus inhibition polypeptide is PPDVHTPPHALWRLHLILRVELVRMWWH, and belongs to the field of biochemistry and molecular biology. After being optimized by using QSAR (Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship), the polypeptide and cell-penetrating peptide form fusion peptide, and thus a function of inhibiting virus replication in cells can be achieved. The method is high in specificity, easy to operate and applicable to control on post-cell rabies viruses.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel nonlinear high-efficient model building method and application of phenols for toxicity prediction and evaluation of photogenic bacteria
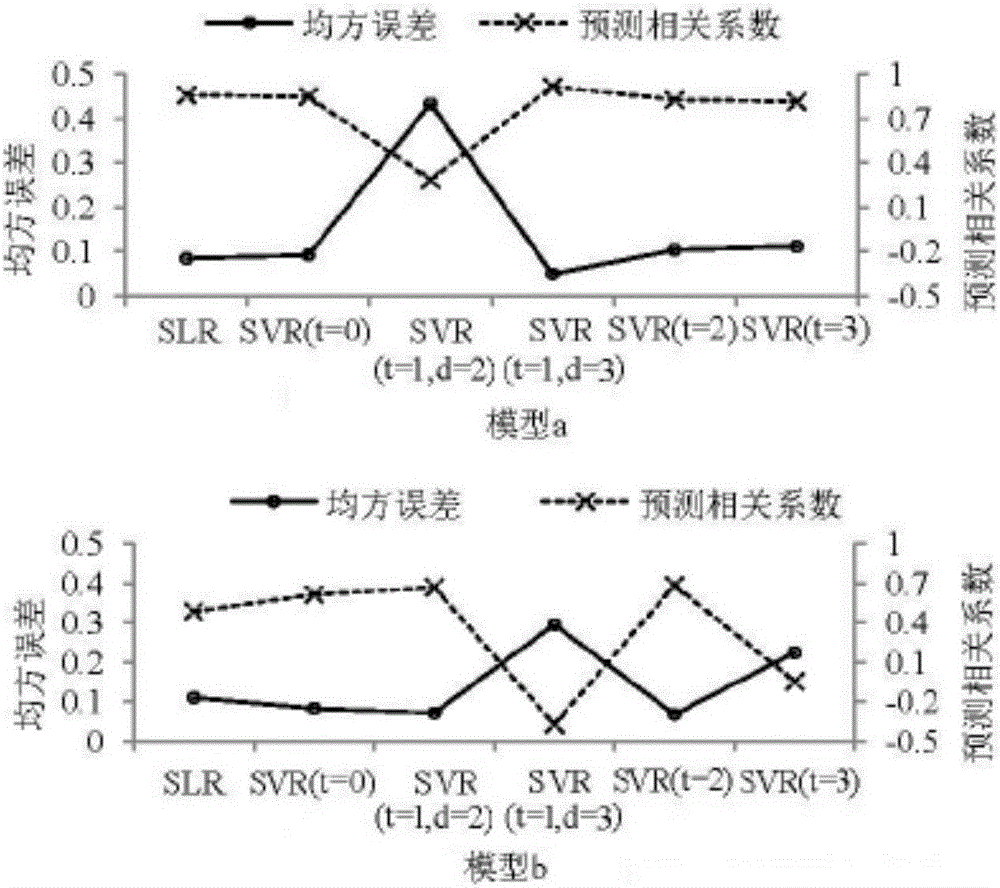
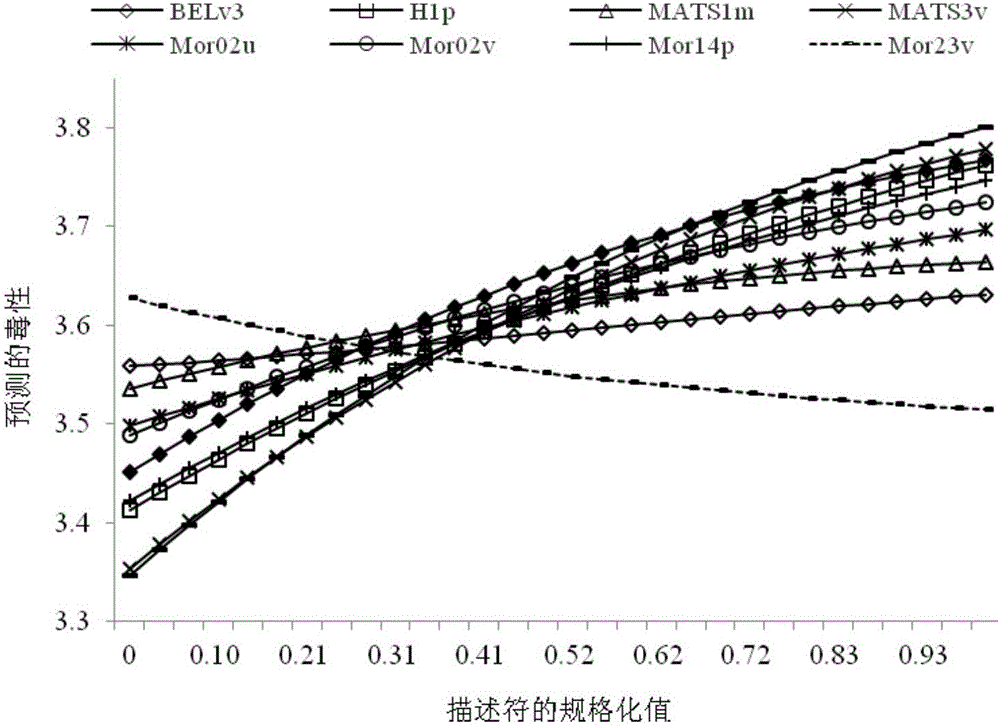
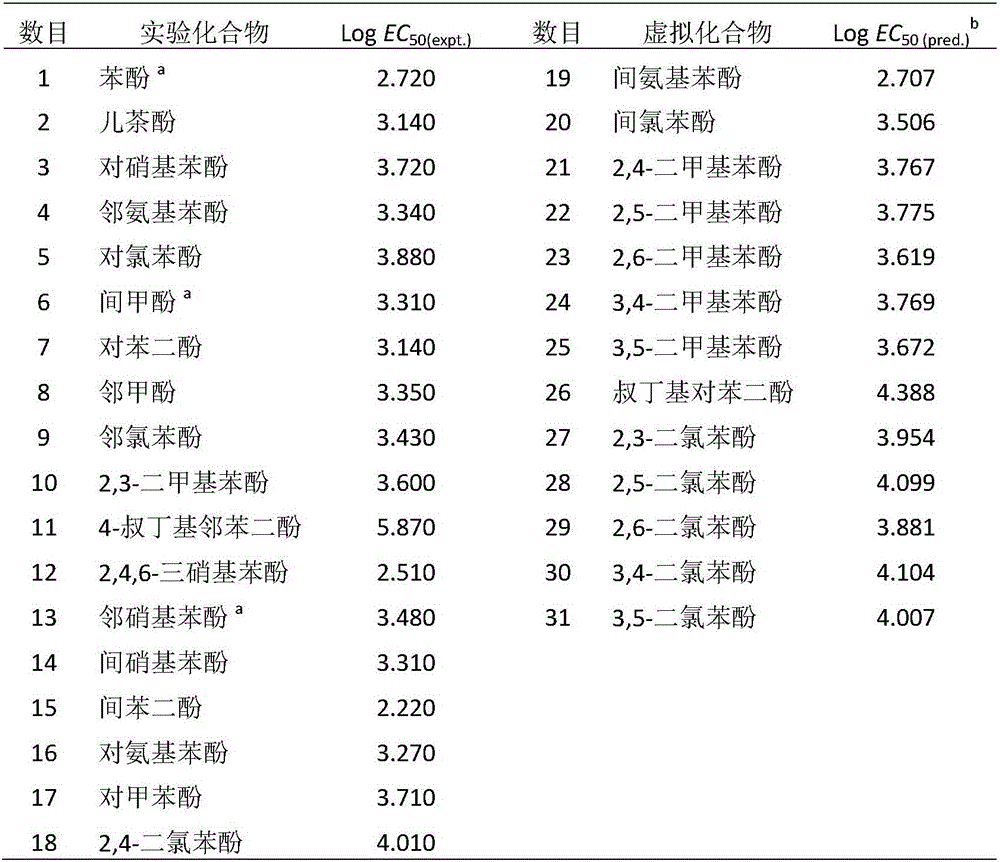
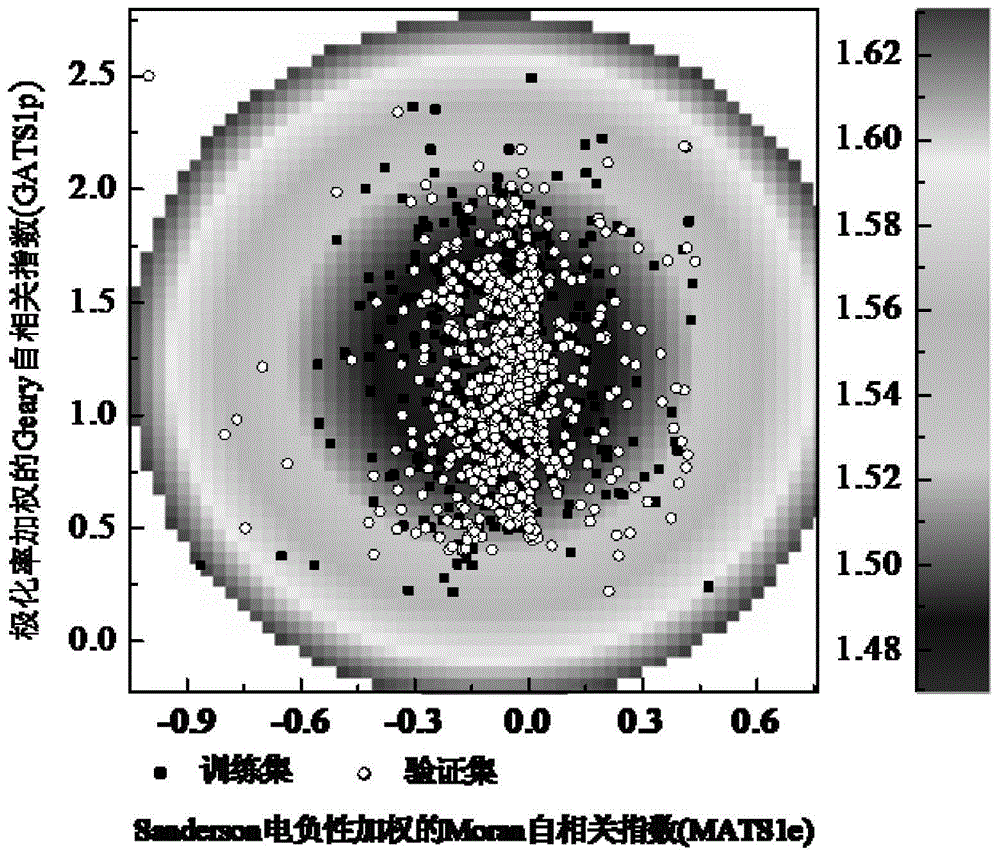
The invention discloses a novel nonlinear high-efficient model building method and application of phenols for toxicity prediction and evaluation of photogenic bacteria. A non-linear SVR (Sustained Virological Response) technology is utilized to carry out QSAR (Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship) research on the toxicity of the photogenic bacteria represented as logEC50 through eighteen phenol compounds in the prior art. The work aims to look for a more reliable QSAR model with more reasonable characteristics through a nonlinear chemometric tool based on low-dimension characteristic data and high-dimension characteristic data, and analyze in detail the most valuable model relative to the toxicity and the most important molecular characteristic thereof. The novel nonlinear high-efficient model building method and the application of the phenols for the toxicity prediction and evaluation of the photogenic bacteria provide effective theoretical references for the design of phenol analogues for strengthening or weakening the toxicity of the photogenic bacteria.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for determining magnetic type of hexagonal crystal system metal oxide by utilizing computer
ActiveCN107942270AQuick forecastEfficient forecastingMagnetic property measurementsHexagonal crystal systemQuantitative structure–activity relationship
The invention relates to a method for determining a magnetic type of a hexagonal crystal system metal oxide by utilizing a computer. The method belongs to the technical field of quantitative structure-activity relationship for ecological risk assessment. The method utilizes a Visualizer module of MS software to construct a crystal model based on lattice parameters of hexagonal crystal system metaloxidation; converting an original unit cell into a rhombohedral lattice primitive cell by utilizing Symmetry in a Build function of the Visualizer module of the software; setting magnetic propertiesand magnetic moment for metal atoms in the lattice along a diagonal of a formal spin in electronic configuration by utilizing a Modify function of the Visualizer module of the software; performing quantum mechanics structure optimization processing by utilizing a Geometry Optimization function in a Dmol3 module of the MS software, and calculating energy of the metal oxide with different magnetic properties by using an Energy function in the Dmol3 module; and finally comparing the energy under different magnetic conditions by utilizing the Visualizer module of the MS software, and determining the magnetic type of the hexagonal crystal system metal oxide. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of rapid computing, simple operation, low equipment requirement, wide measurementrange and high precision.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
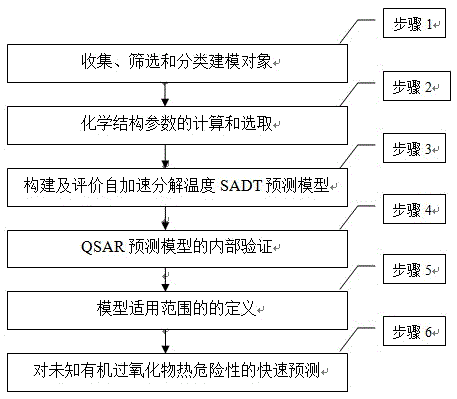
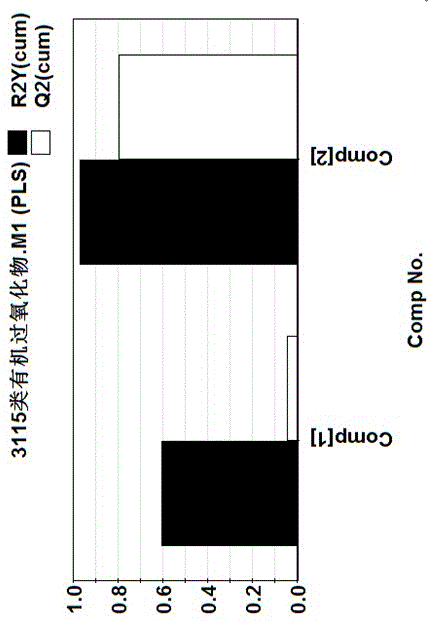
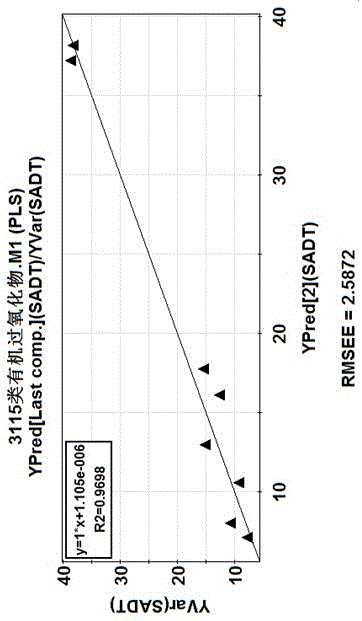
Detection method of self-accelerating decomposition temperature of organic peroxide
InactiveCN105653795AAddress the situation of scarcityOvercome the deficiency of high risk factorSpecial data processing applicationsChemical structureModel method
The invention discloses a detection method of the self-accelerating decomposition temperature of organic peroxide. The detection method comprises the following steps: (1) collecting and classifying common organic peroxide; (2) optimizing the structure of the same type of organic peroxide, and calculating the chemical structure parameter of the organic peroxide; (3) constructing a SADT (Self Accelerating Decomposition Temperature) prediction model and the evaluation of the model; (4) carrying out internal authentication on the constructed model; (5) defining the optimal applicable range of the model; and (6) carrying out quick analysis and prediction on the organic peroxide at an unknown self-accelerating decomposition temperature. Through a QSAR (Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship) model method, the self-accelerating decomposition temperature of the unknown organic peroxide is detected, the situation of parameter shortage is solved, the deficiency of the high danger coefficient of the traditional method is overcome, and the accuracy of the obtained self-accelerating decomposition temperature parameter is improved. The method is safe, simple in operation, short in period, uniform in period and low in dependency and greatly reduces the loss of financial resources and material resources.
Owner:HUIZHOU RES INST OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Application of Intelligent Support Vector Machines to Predict the Properties/Toxicity of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
ActiveCN105868540BAchieving Toxicity TestingGuaranteed accuracyChemical property predictionCharacter and pattern recognitionSmall sampleEnvironmental index
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Three-dimensional structural activity correlation method
InactiveUS20060080073A1Reduce in quantityReduce the amount of calculationChemical property predictionMolecular designVirtual spaceThree-dimensional space
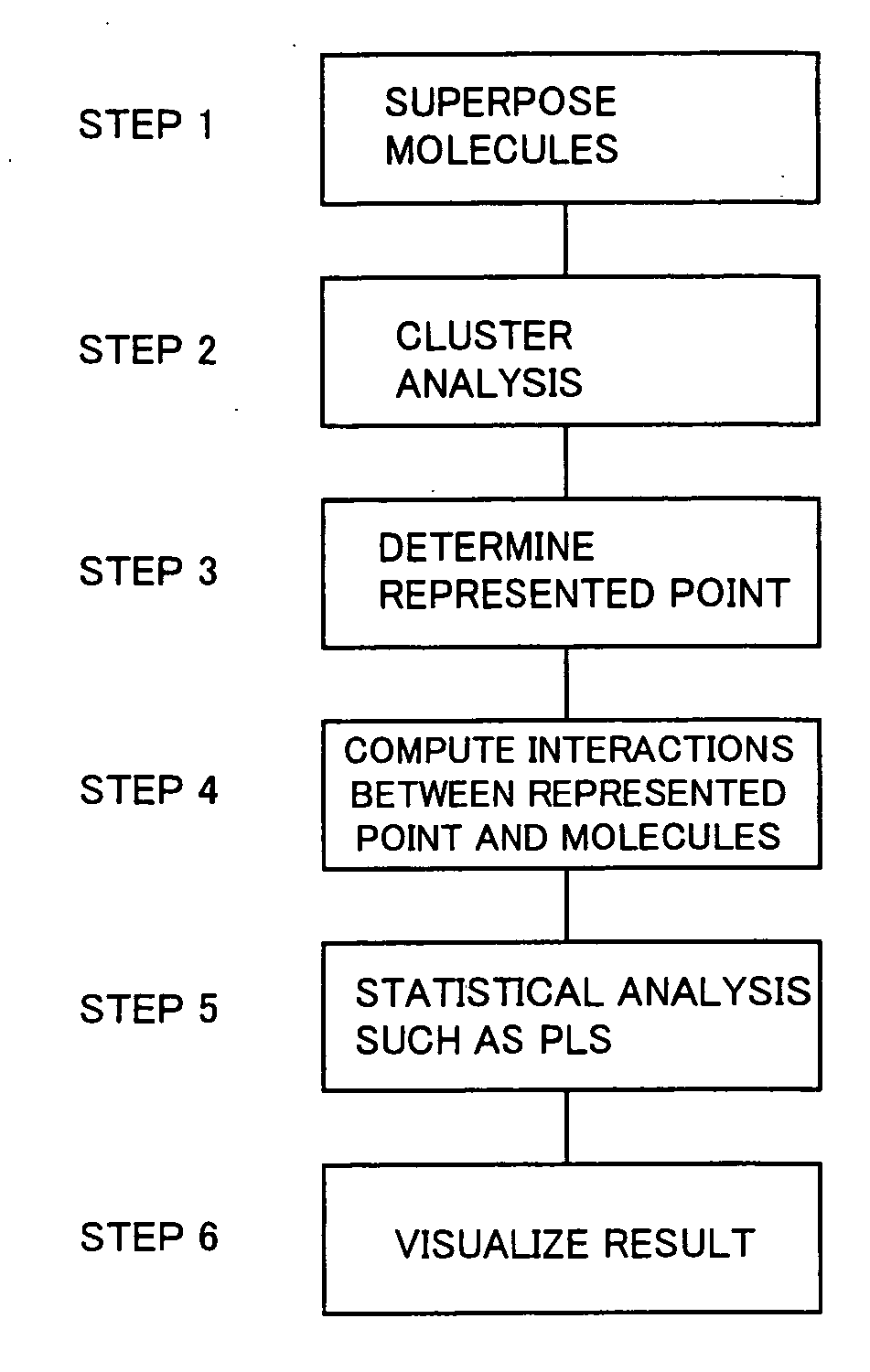
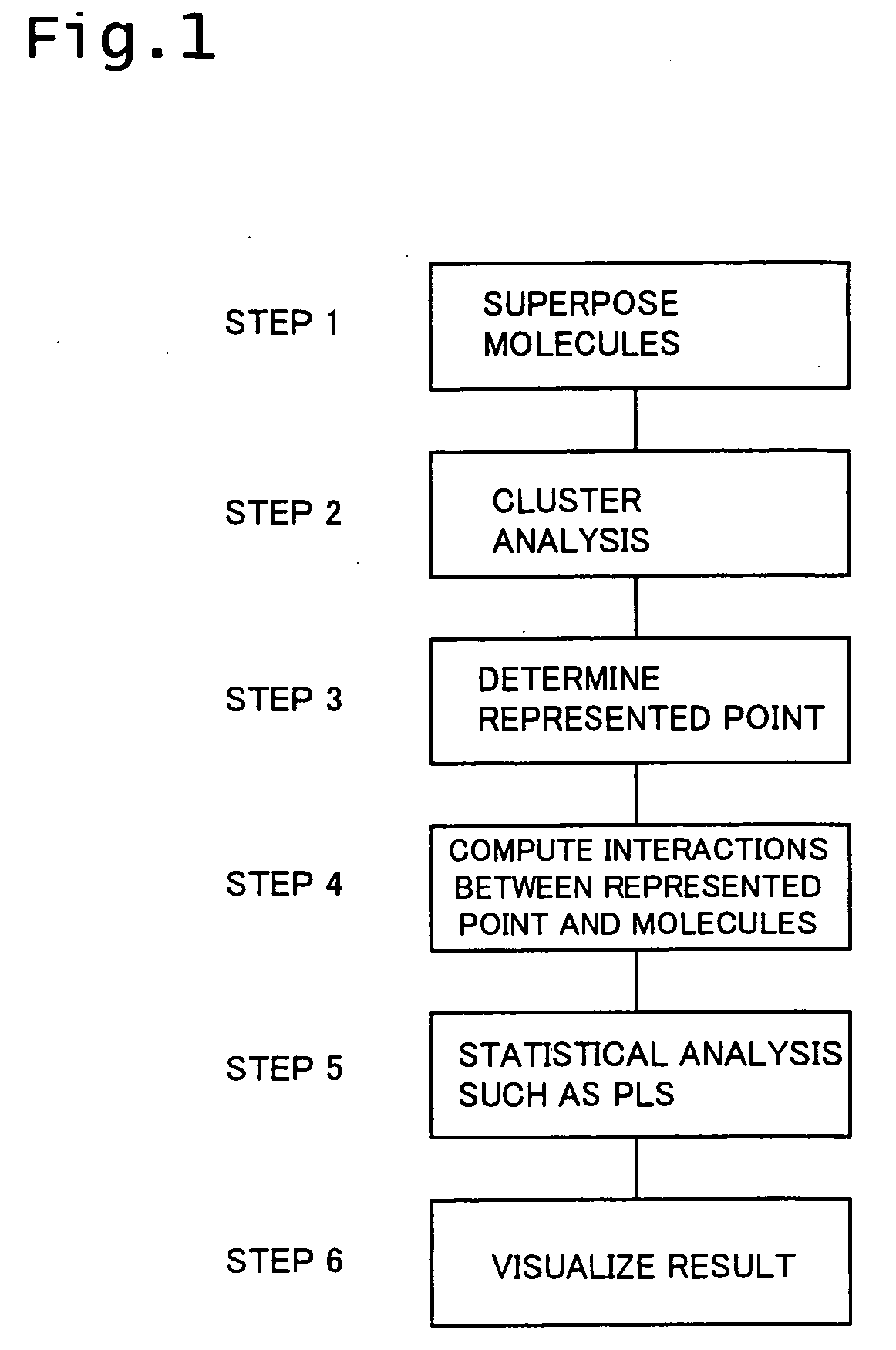
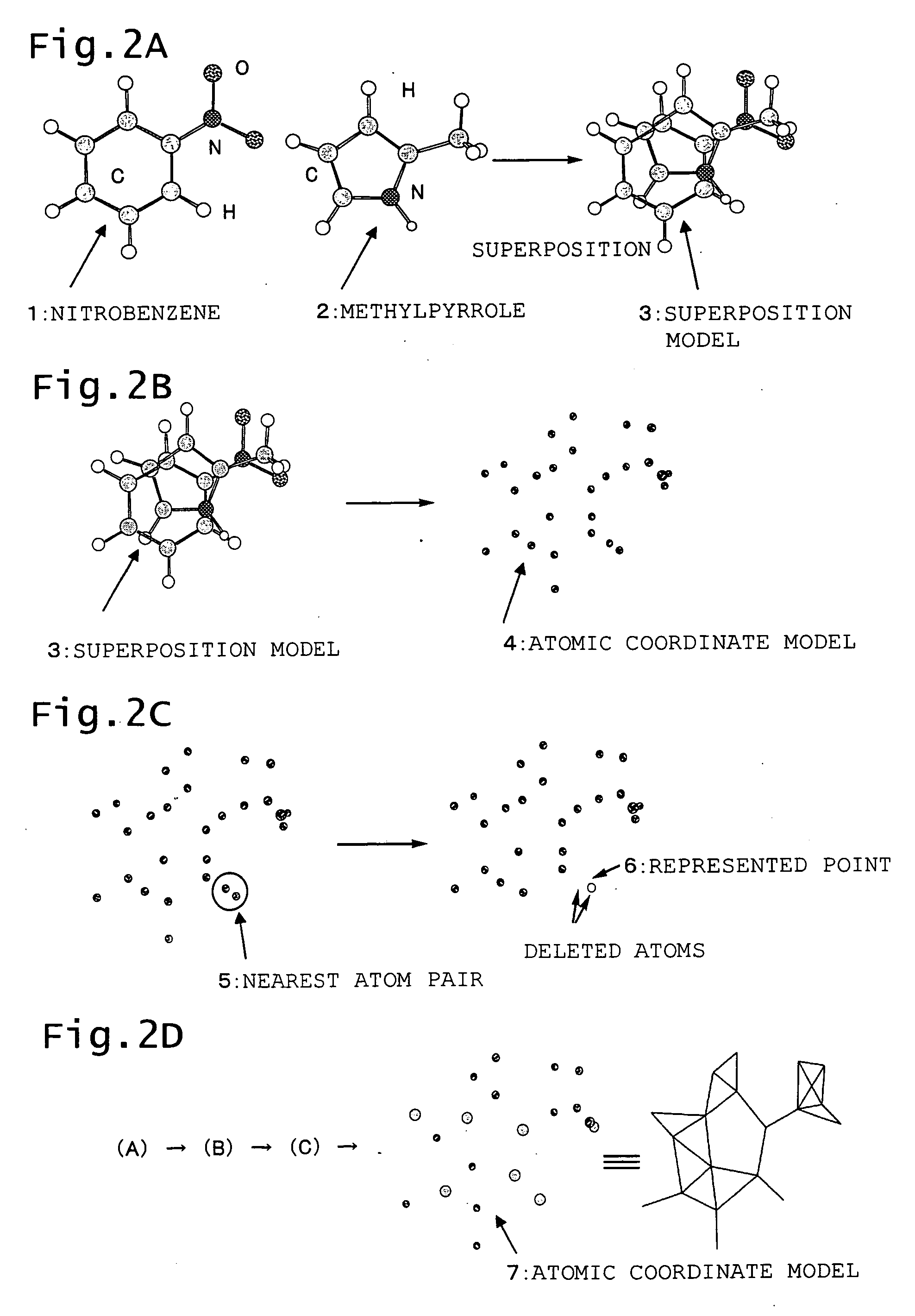
A three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship method has process B1 of calculating the coordinates of the respective atoms contained in the plural molecules thus superposed in the virtual space, process B2 of calculating interatomic distances between each atom and other atoms and identifying the shortest interatomic distance among thus calculated interatomic distances and two atoms constituting the shortest interatomic distance; process B3 of deleting the two atoms having the shortest interatomic distance from the three-dimensional space and generating an atom which represents the two atoms in the weighted average coordinates of the two atoms to delete, when the shortest interatomic distance thus calculated is equal to or smaller than a predetermined threshold value; process B4 of returning to the second process B2 after the third process B3 and executing the second process B2 including the atoms formed during the third process B3; and process B5 of terminating the process B when the shortest interatomic distance thus calculated is exceeds the predetermined threshold. This method enables strikingly reducing the memory zone and amount of computation required for 3D QSAR analysis.
Owner:NIPPON ZOKI PHARM CO LTD
Method for predicating toxicity MOA (mode of action) of pharmaceutical product
InactiveCN108268749AImprove accuracyReduce development costsChemical property predictionSpecial data processing applicationsMode of actionMedicine
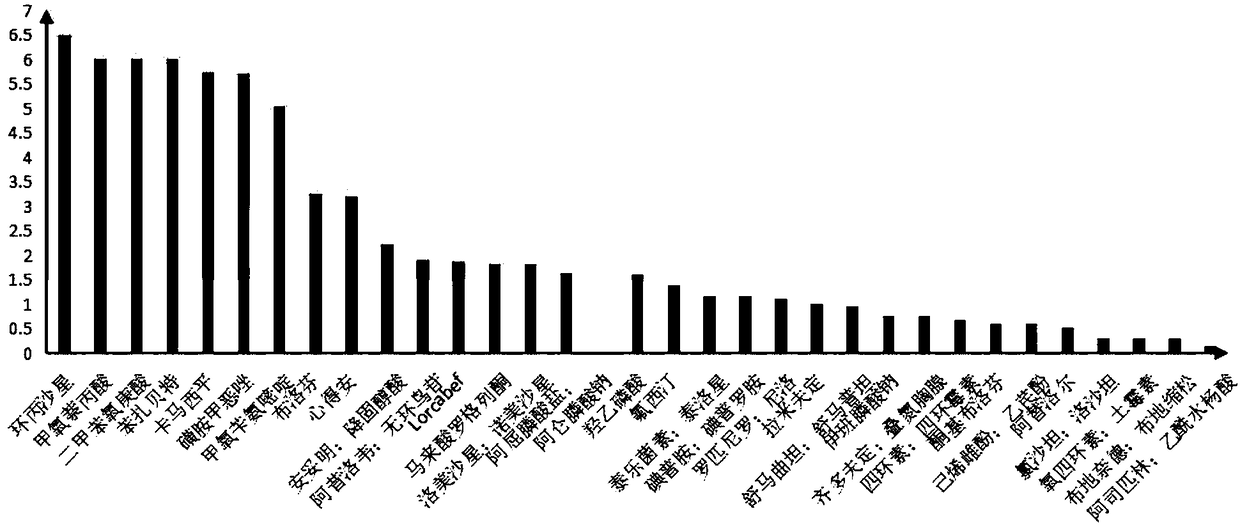
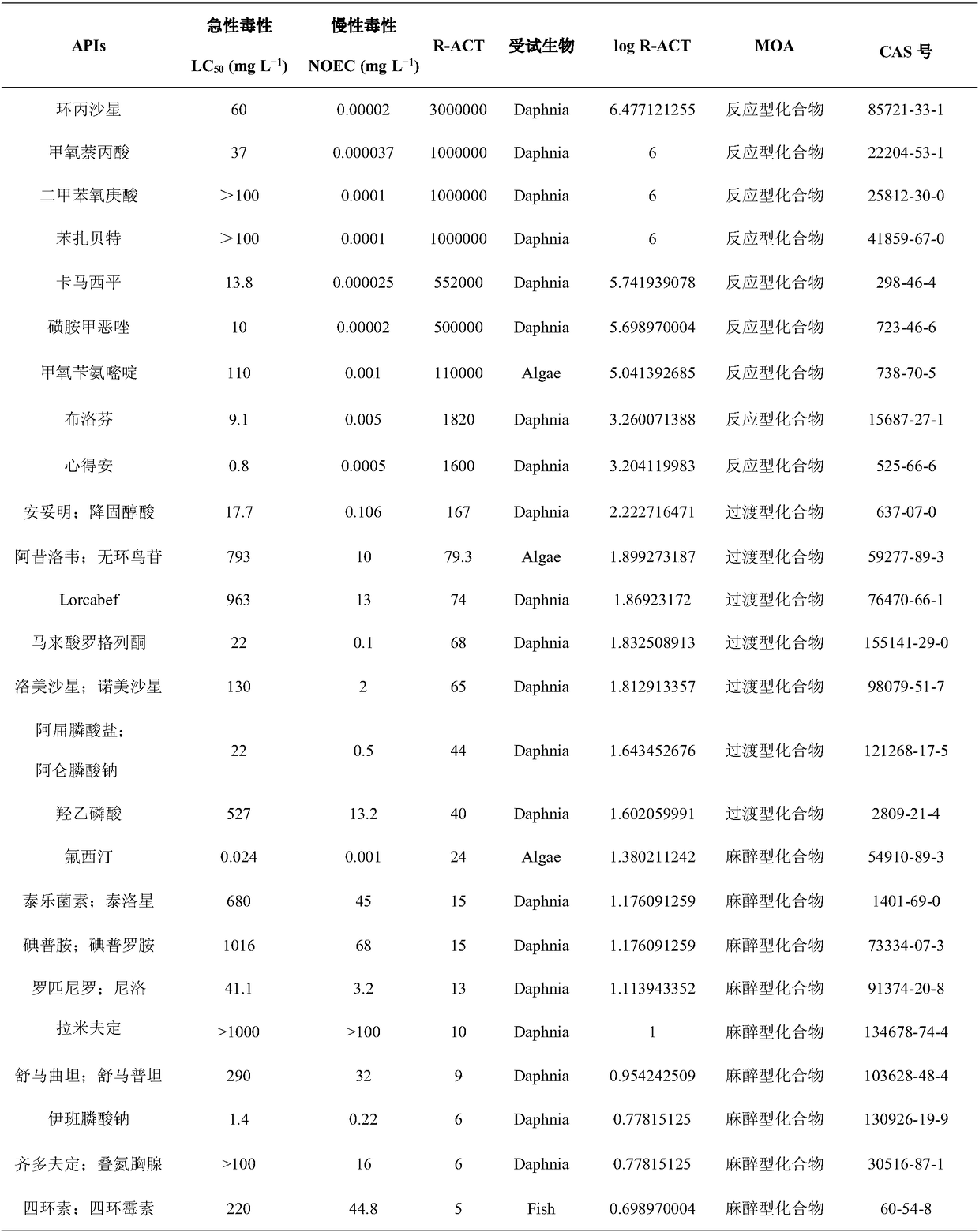
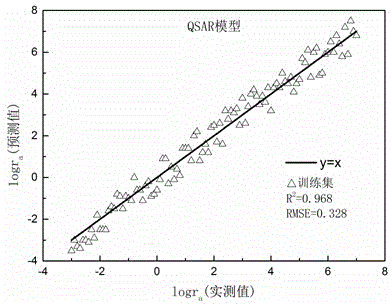
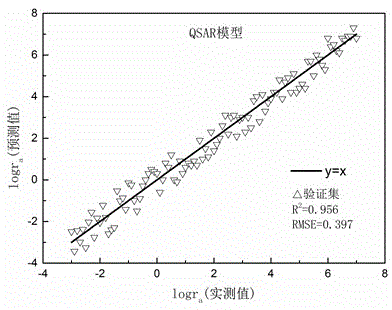
The invention belongs to the field of medicine toxicity analysis and provides a method for predicating a toxicity MOA (mode of action) of a pharmaceutical product. LC50 concentration data and NOCE concentration data are substituted into a formula shown in the description, an R-ACT value is obtained, a logR-ACT is substituted into an evaluation scope, and the toxicity MOA of the pharmaceutical product is judged. By means of the method, the MOA of the pharmaceutical product can be rapidly predicted and distinguished, the evaluation result accuracy is higher, the test cycle can be shortened to acertain extent, the development of drugs is reduced, limitation of the influence of toxicity MOA of a toxicity predication model is relieved, the stability of the joint toxicity predication model is improved, and the method has great significance in establishment of a toxicological effect QSAR (quantitative structure-activity relationship) model.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
Method for predicting hydrolysis rate of sulfur-containing organic compounds in atmosphere
InactiveCN105468914AEasy to calculateImprove stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsPredictive methodsLinear regression
The invention discloses a method for predicting a hydrolysis rate of sulfur-containing organic compounds in the atmosphere, and belongs to the field of ecological risk assessment test strategies. A QSAR (Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship) model is constructed by adopting a partial least squares and a multiple linear regression, and the hydrolysis rate of the sulfur-containing organic compounds is obtained according to the QSAR model. The model of the invention is wide in application and has good practicability, stability and prediction effect. The hydrolysis rate of the sulfur-containing organic compounds in the atmosphere can be effectively and quickly predicted on the basis of obtaining a sulfur-containing organic molecular structure only by calculating a descriptor which represents a structural feature and applying the QSAR model. The prediction method has the characteristics of being convenient and fast, low in cost, and can provide important data support for the ecological risk assessment and management of the sulfur-containing organic compounds and is of great significance.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method for predicting the interaction affinity of biomarker p53 with organophosphate flame retardants
ActiveCN103971030BLow costSave human effortSpecial data processing applicationsExperimental testingPhosphate
The invention relates to a method for predicting affinity of the interaction between a biomarker p53 and an organic phosphate fire retardant. The method includes the following steps of establishing a quantitative structure-activity relationship QSAR model of the affinity KD and training set compound molecule descriptors through a partial least square method so as to obtain an affinity KD value, and predicting the affinity according to the affinity KD value. By the adoption of the method, interaction between the organic phosphate fire retardant and the biomarker p53 which are of different structures can be predicted, the method is low in cost and easy, convenient and rapid to achieve, and a large amount of labor, a large number of expenses and a large amount of time which are needed by experimental tests can be saved; the prediction result obtained through the method can provide the important data support for organic chemical ecological risk assessment and management, and the method has important theoretical and practical significance.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
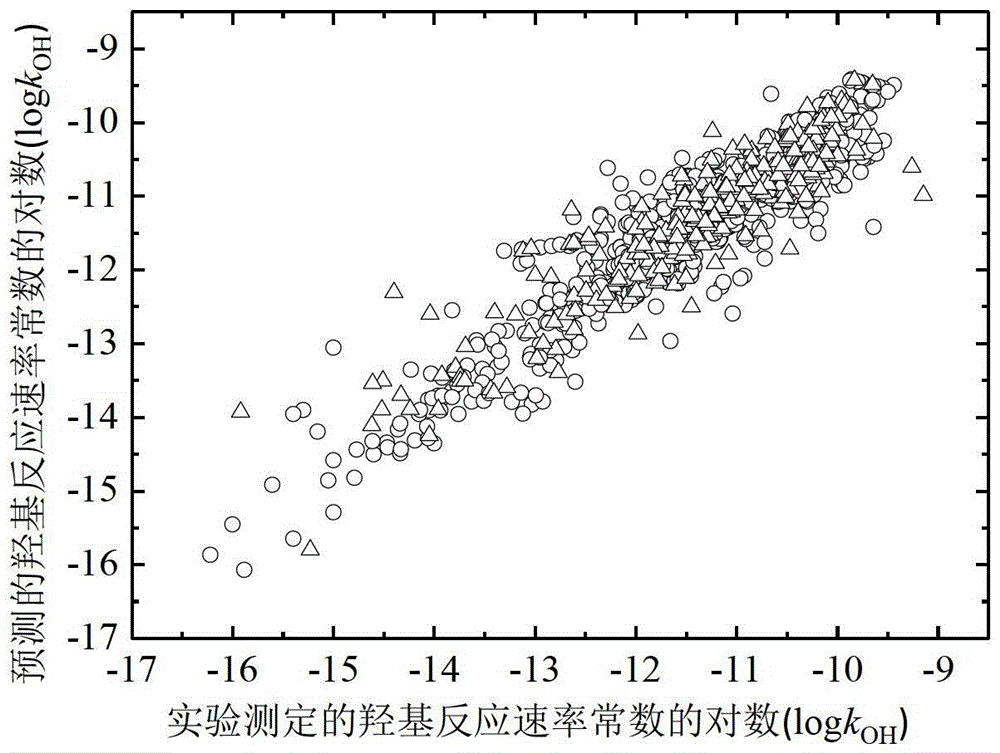
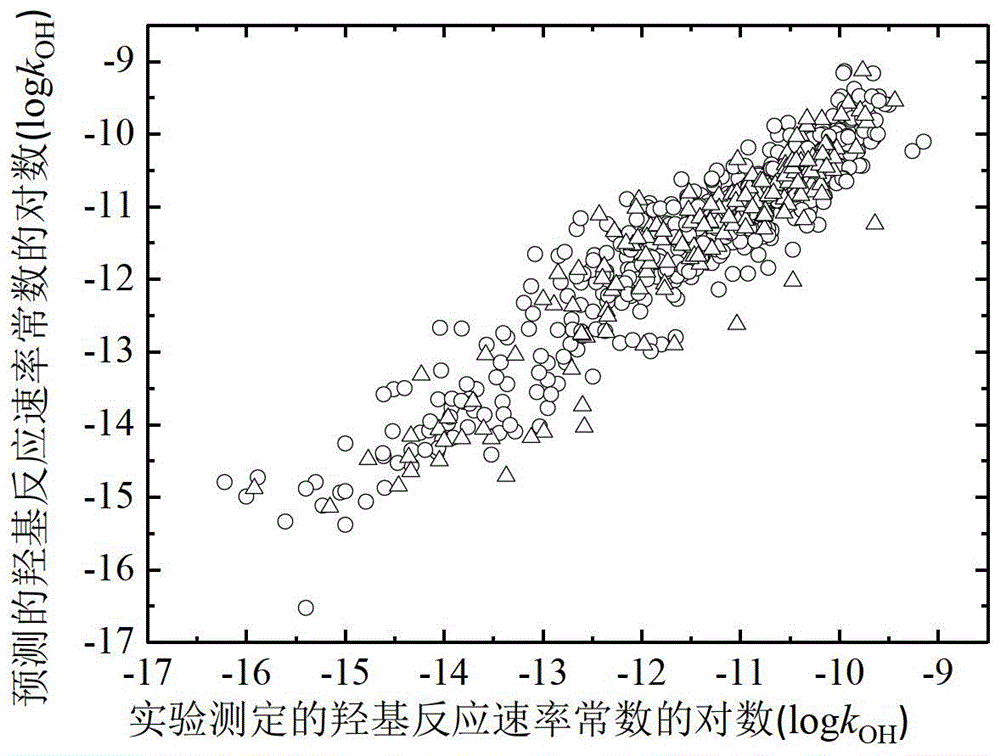
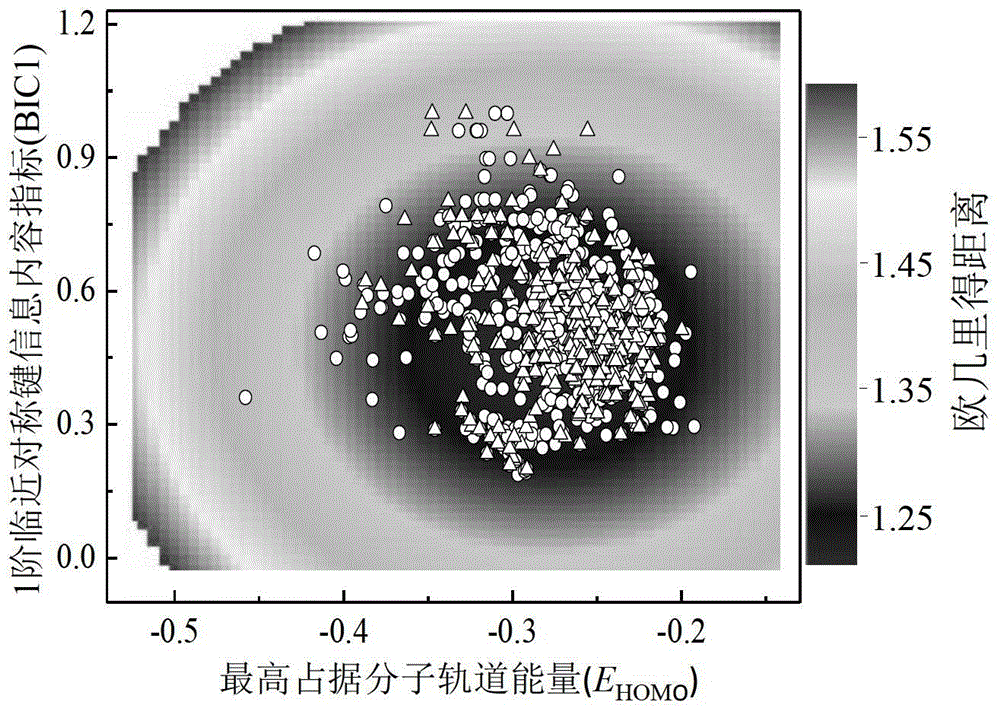
A Method for Predicting the Rate Constant of the Reaction of Organic Compounds with Hydroxyl in the Atmosphere Using Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Model
ActiveCN103425872BLow costSave human effortSpecial data processing applicationsRelational modelOrganic reaction
The invention discloses a model method for predicting reaction rate constant (kOH) of organic matter in atmosphere and hydroxyl. On the basic of obtaining a compound molecular structure, through a multiple linear regression method, a kOH model with 298K and temperature adherence is built, and a kOH value of organic compounds under 298K or other temperature can be predicted rapidly and efficiently; the goodness of fit, robustness and prediction capacity of the model are represented according to the guide rule, about the building and verification of the QSAR model, of the OECD. The application area of the model is definite, and compounds of nearly 900 different kinds are included; the prediction model is simple and is programmed easily, and significance data support can be provided for evaluation of environment durability of organic chemicals.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
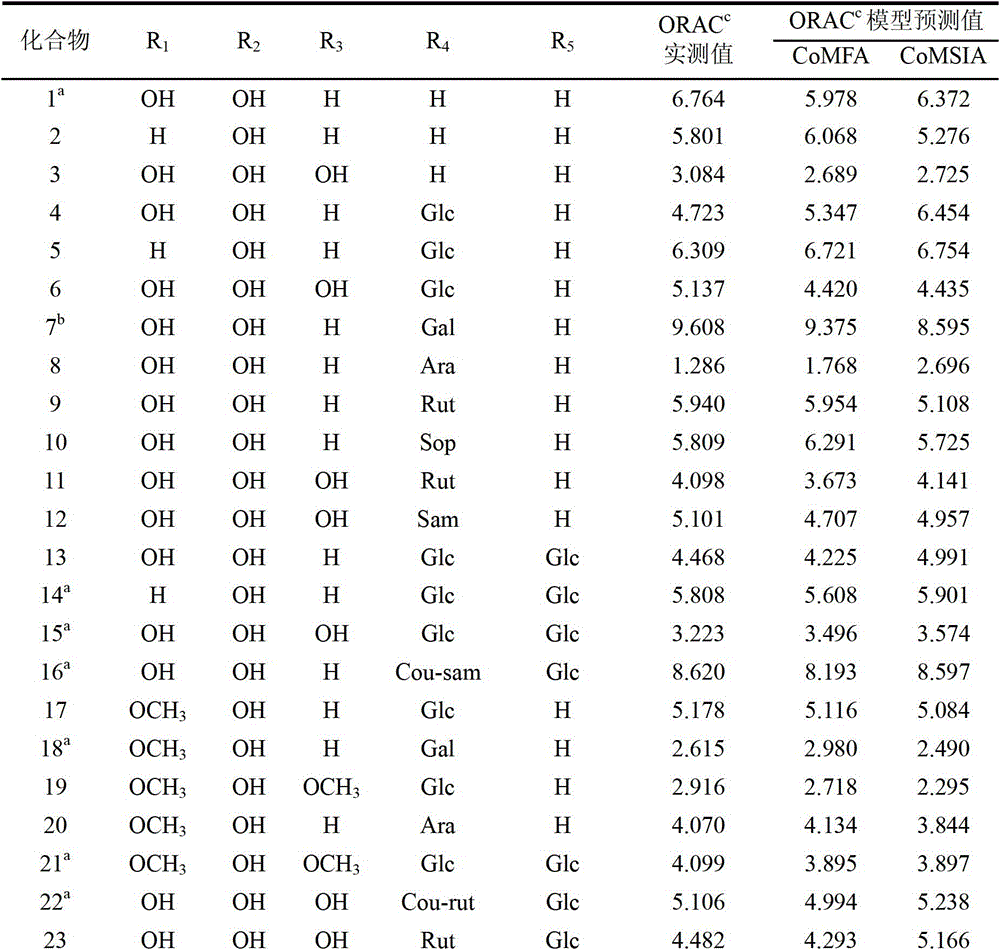
Construction method of three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model for antioxidant activity of anthocyanins
InactiveCN103093100BGood forecastPredictive activitySpecial data processing applicationsEntity–relationship modelResearch Object
The invention relates to a building method of an anthocyanin antioxidant activity three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model. An anthocyanin antioxidant with a known activity is taken as a study object, a technology of three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship is used, an anthocyanin antioxidant three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model is built, an accurate structure-activity relationship model is built through a molecular force field method and a molecular similarity coefficient analytical method for analyzing technologies of molecular conformation optimization, parameter optimization and the like. The building method of the anthocyanin antioxidant activity three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model can quickly predict activity value of an unknown activity compound, and can reasonably interpret the relation between the size of the nthocyanin antioxidant activity and the structure characteristics of the nthocyanin antioxidant activity.
Owner:广州市威伦食品有限公司
Compound medicine screening method, obtained medicines and application thereof
InactiveCN102636626ALow costReduce the burden onPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical active ingredientsSide effectTreatment effect
The invention belongs to the field of medicines and provides a medicine screening method and relative medicines, a medicine package, a sustained release preparation, a targeting preparation, a controlled release preparation, a quick release preparation and a treatment method. The medicine screening method provided by the invention is used for screening compounds with the same parent nucleus (or the same framework) in a combined manner, wherein the compounds include synthetic compounds and bio-transformed compounds but not include compounds contained in organisms. The compounds only refer to the compounds with the same structural formula, and chemical isomers with the same molecular formula are regarded as one compound. The screening method does not comprise a step of screening the compounds with the same parent nucleus which are obtained through combinatorial chemistry. The medicine screening method, the obtained medicines and the application thereof provided by the invention have the advantages as follows: 1, combinations of chemicals in hundreds of years are retrospectively studied, thereby improving the medicine screening purposiveness and reducinig the development cost and the societal public burden; 2, the treatment effect is improved, and the toxic and side effects are reduced; and 3, the research dimensionality of the quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) is widened.
Owner:程宇镳
Non-linear high-efficiency model construction method and application for prediction and evaluation of phenol toxicity to photobacteria
The invention discloses a novel nonlinear high-efficient model building method and application of phenols for toxicity prediction and evaluation of photogenic bacteria. A non-linear SVR (Sustained Virological Response) technology is utilized to carry out QSAR (Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship) research on the toxicity of the photogenic bacteria represented as logEC50 through eighteen phenol compounds in the prior art. The work aims to look for a more reliable QSAR model with more reasonable characteristics through a nonlinear chemometric tool based on low-dimension characteristic data and high-dimension characteristic data, and analyze in detail the most valuable model relative to the toxicity and the most important molecular characteristic thereof. The novel nonlinear high-efficient model building method and the application of the phenols for the toxicity prediction and evaluation of the photogenic bacteria provide effective theoretical references for the design of phenol analogues for strengthening or weakening the toxicity of the photogenic bacteria.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Prediction of Biodegradability of Organic Chemicals Using Logistic Regression Method
ActiveCN103345544BQuick forecastEffective predictionSpecial data processing applicationsGuidelineBest fitting
The invention discloses a method for predicting organic chemical biodegradability according to a logistic regression algorithm. According to the method for predicting organic chemical biodegradability, on the basis that the molecular structure of a compound is obtained, a person just needs to calculate descriptors of representational structure characteristics and use a built quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) model, and accordingly the biodegradability of the organic compound can be fast and efficiently predicted. The method for predicting organic chemical biodegradability is low in cost, and easy and convenient and fast to adopt, and saves large required labor sources, cost and time. According to the method for predicting organic chemical biodegradability, modeling completely accords with the QSAR model building and guidelines for use of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), only 14 molecular structure descriptors are adopted, the logistic regression method which is clear and transparent in algorithm is applied, and therefore the method for predicting organic chemical biodegradability is easy to understand and apply. Model application fields are explicit, and 1629 kinds of compounds are covered. The method for predicting organic chemical biodegradability according to the logistic regression method has good fitting effect, robustness and prediction ability, can effectively predict biodegradability of a plurality of organic compounds and provide important data support to organic chemical risk assessment and management, and has important significance in ecological risk assessment.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com