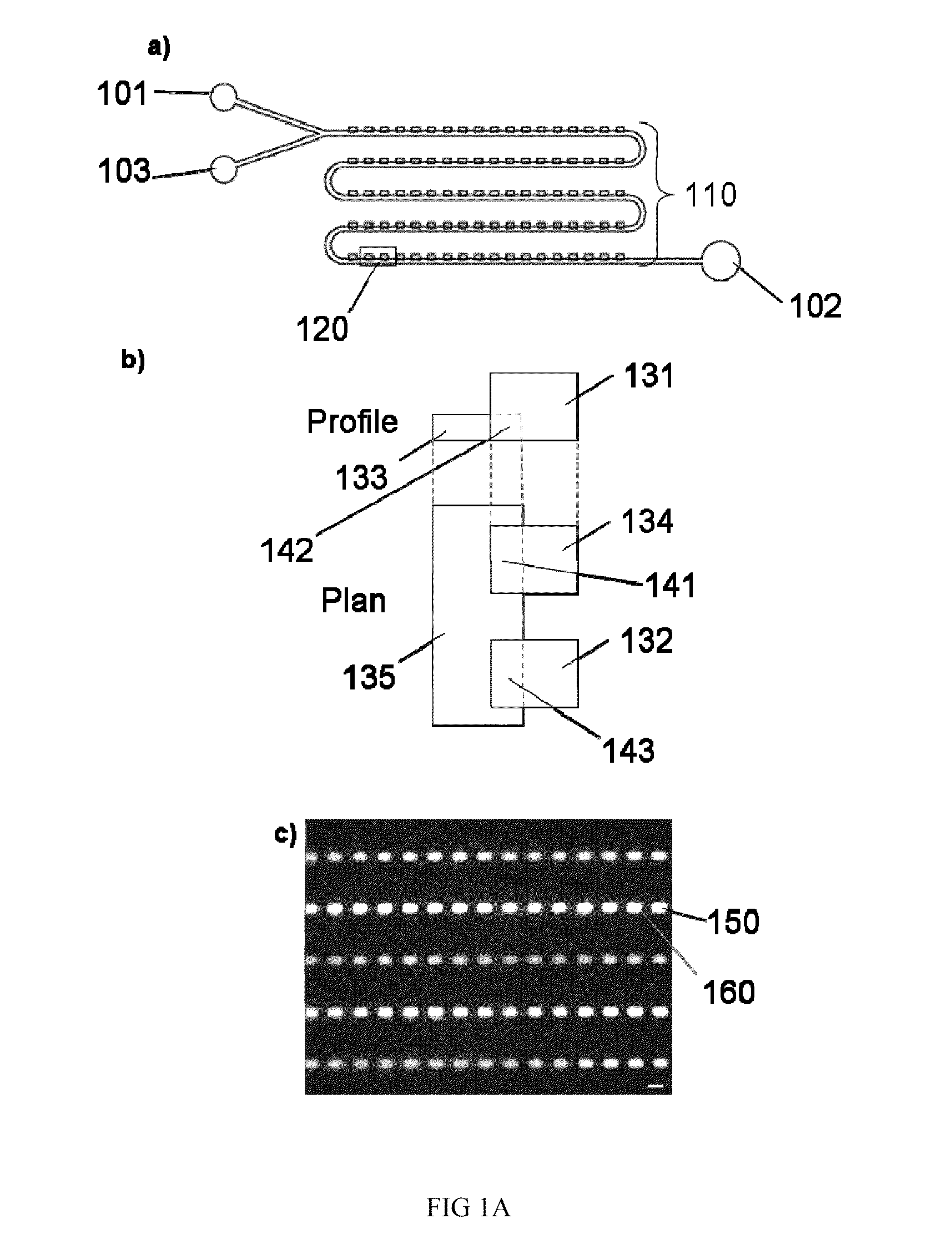
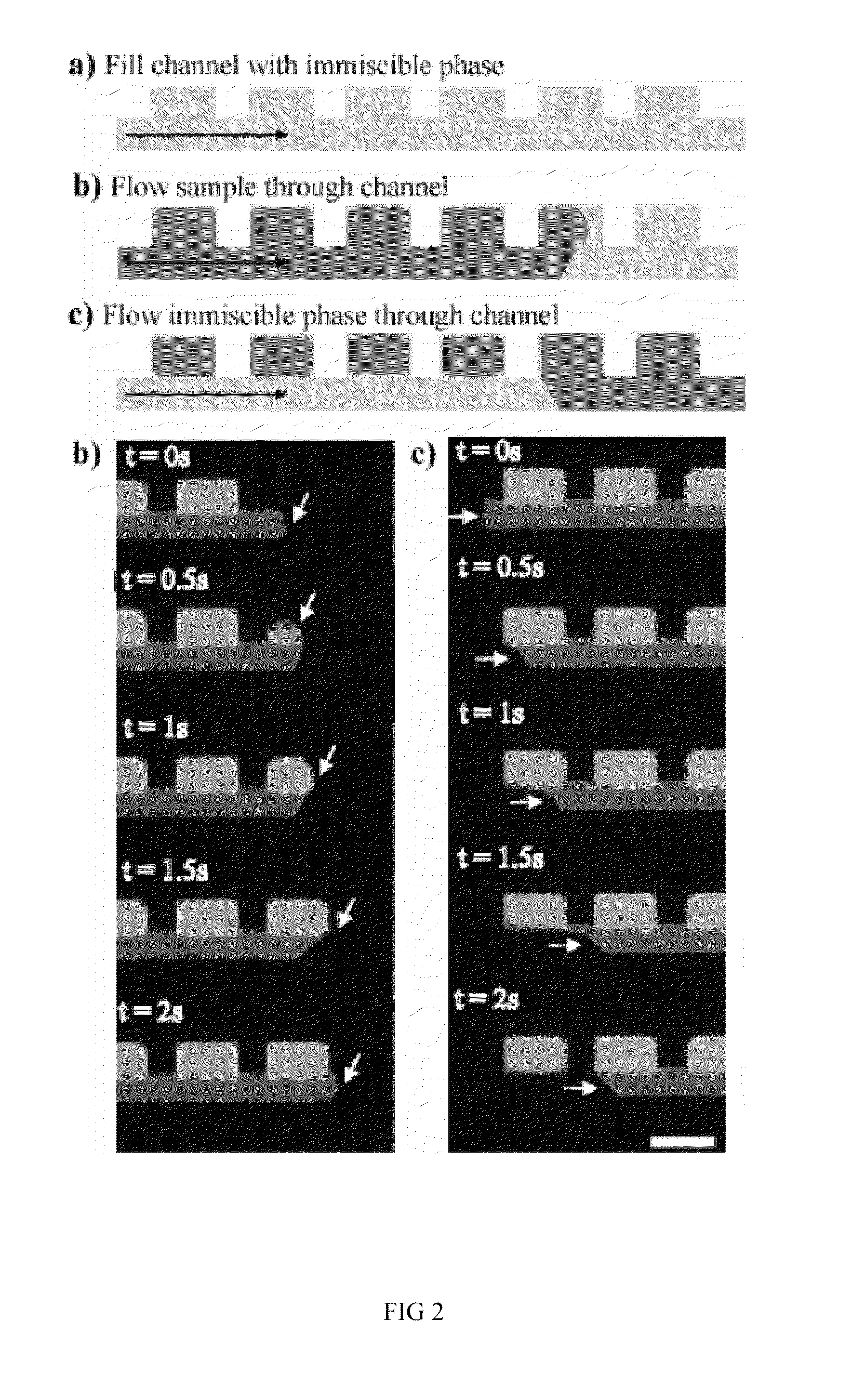
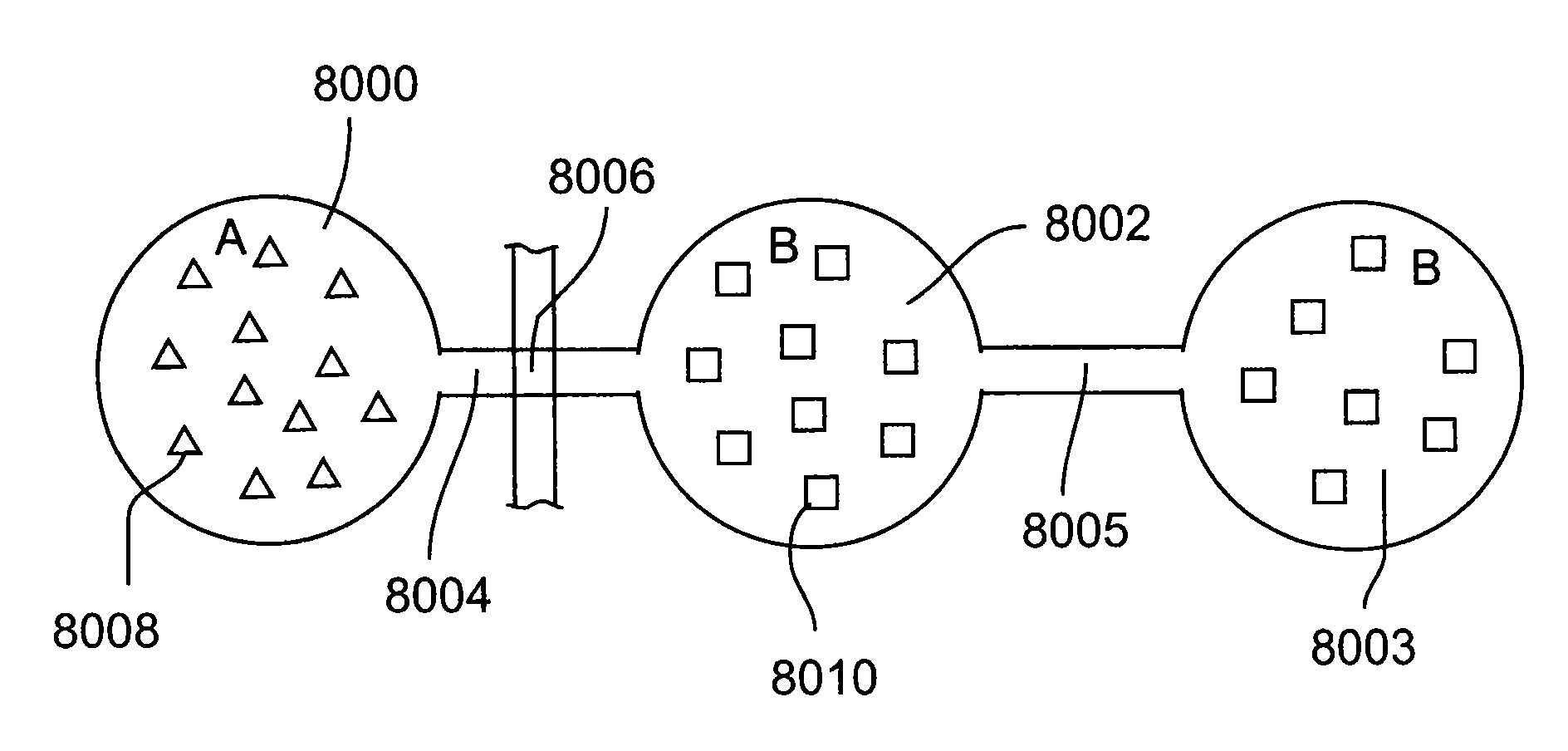
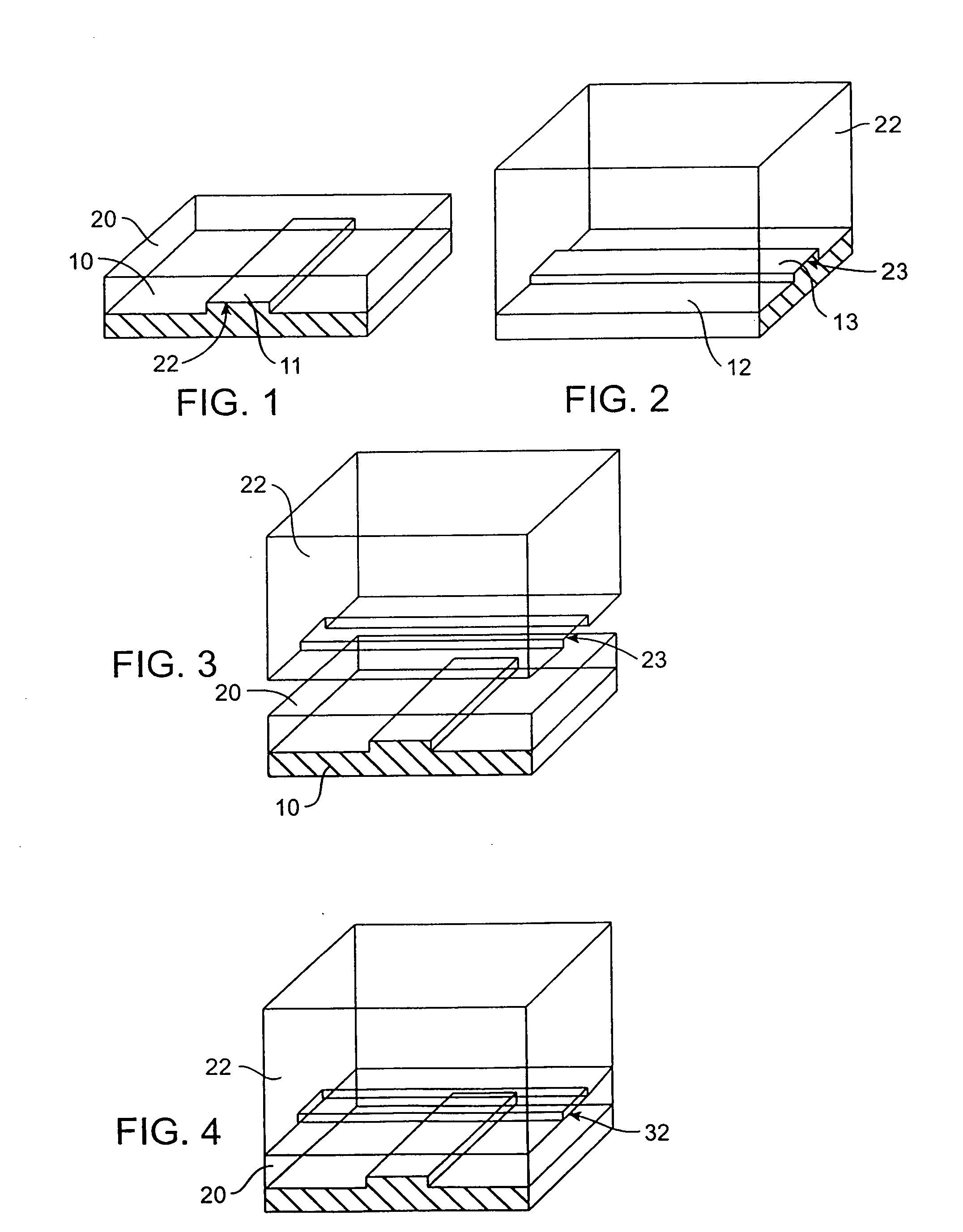
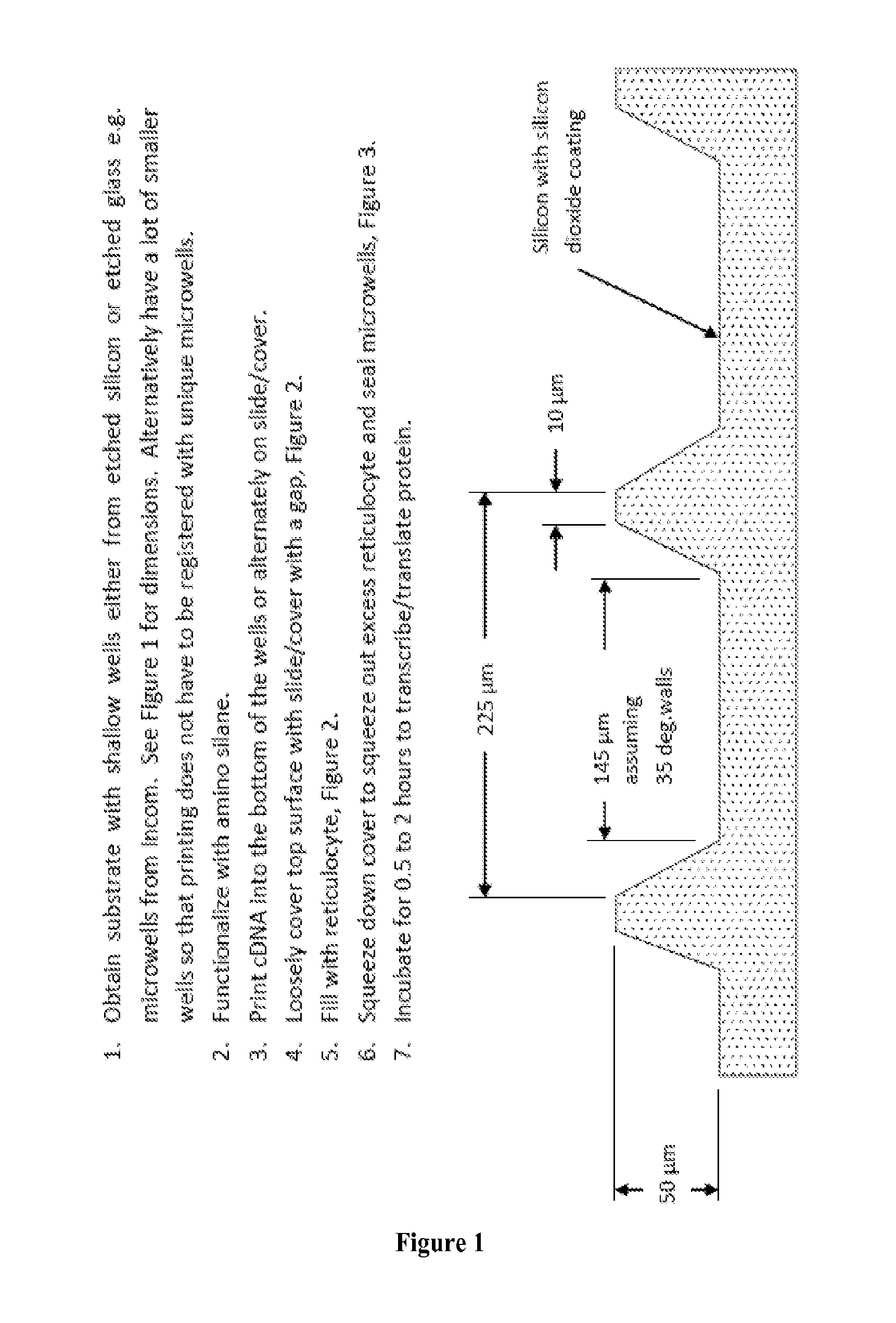
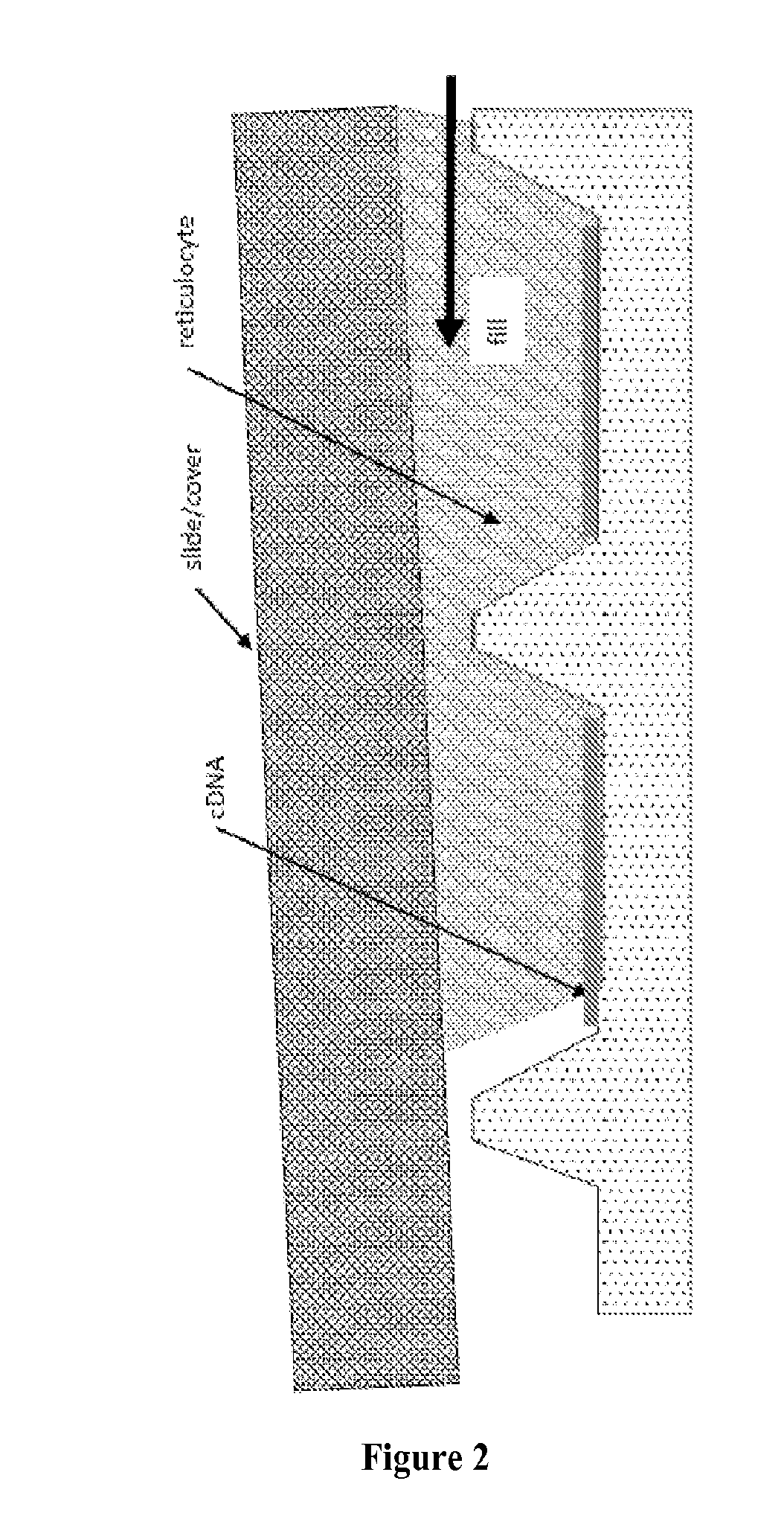
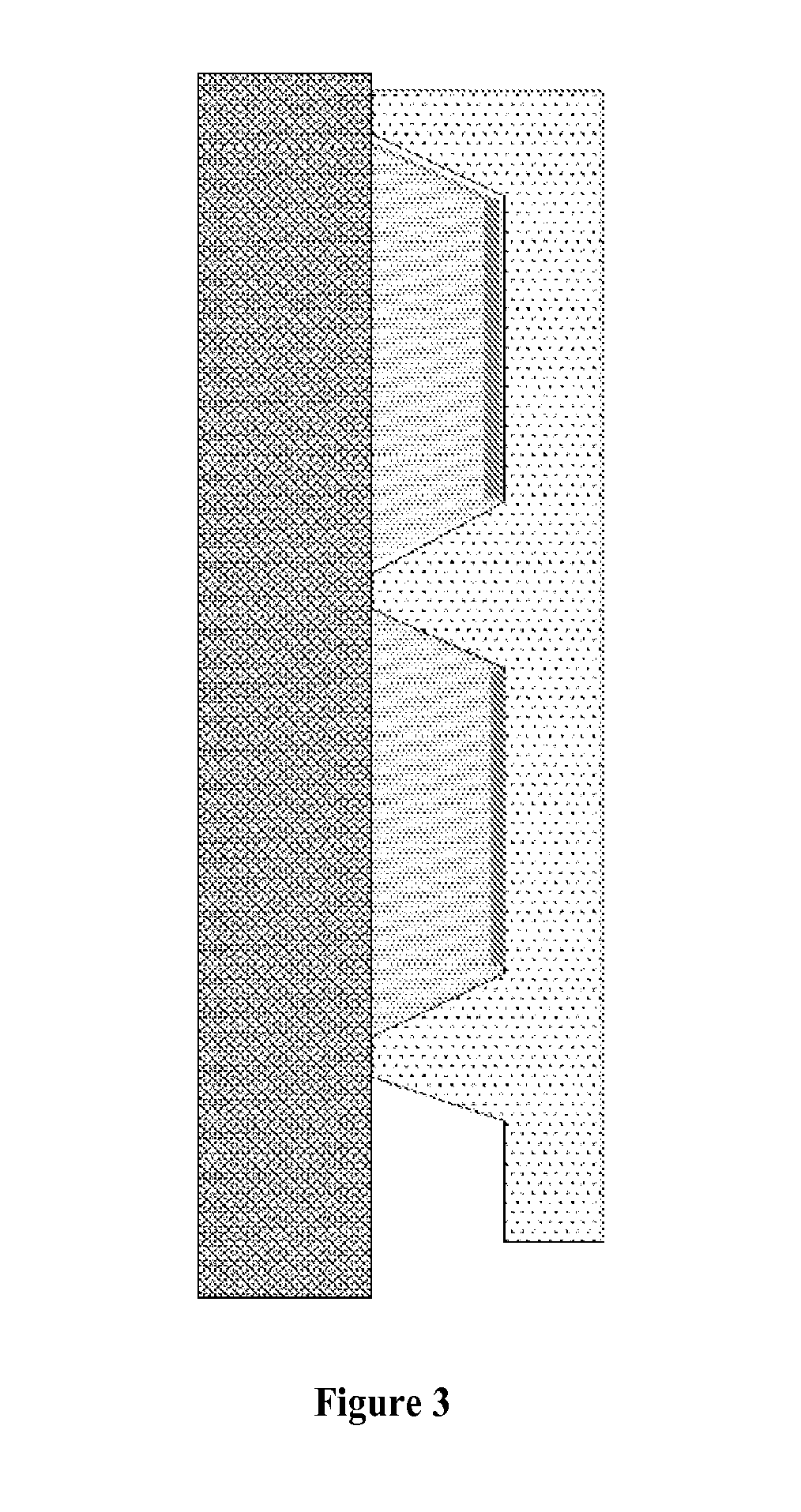
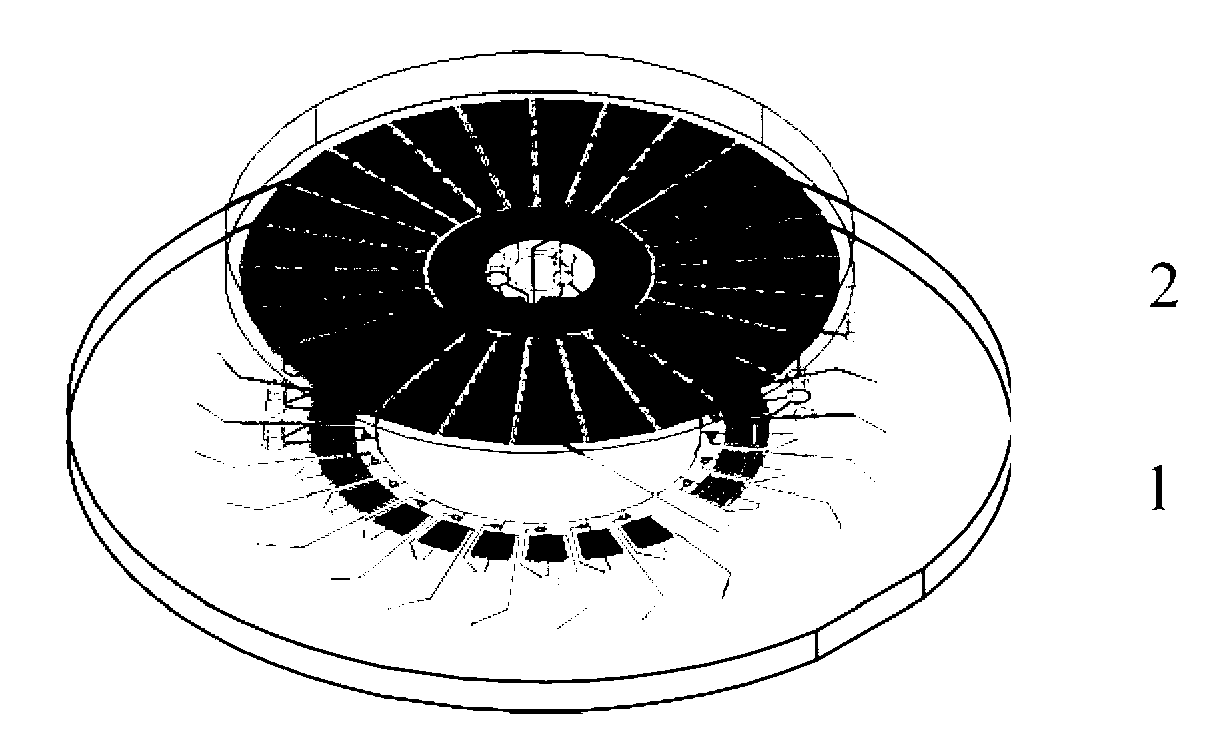
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
158 results about "Protein crystallization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
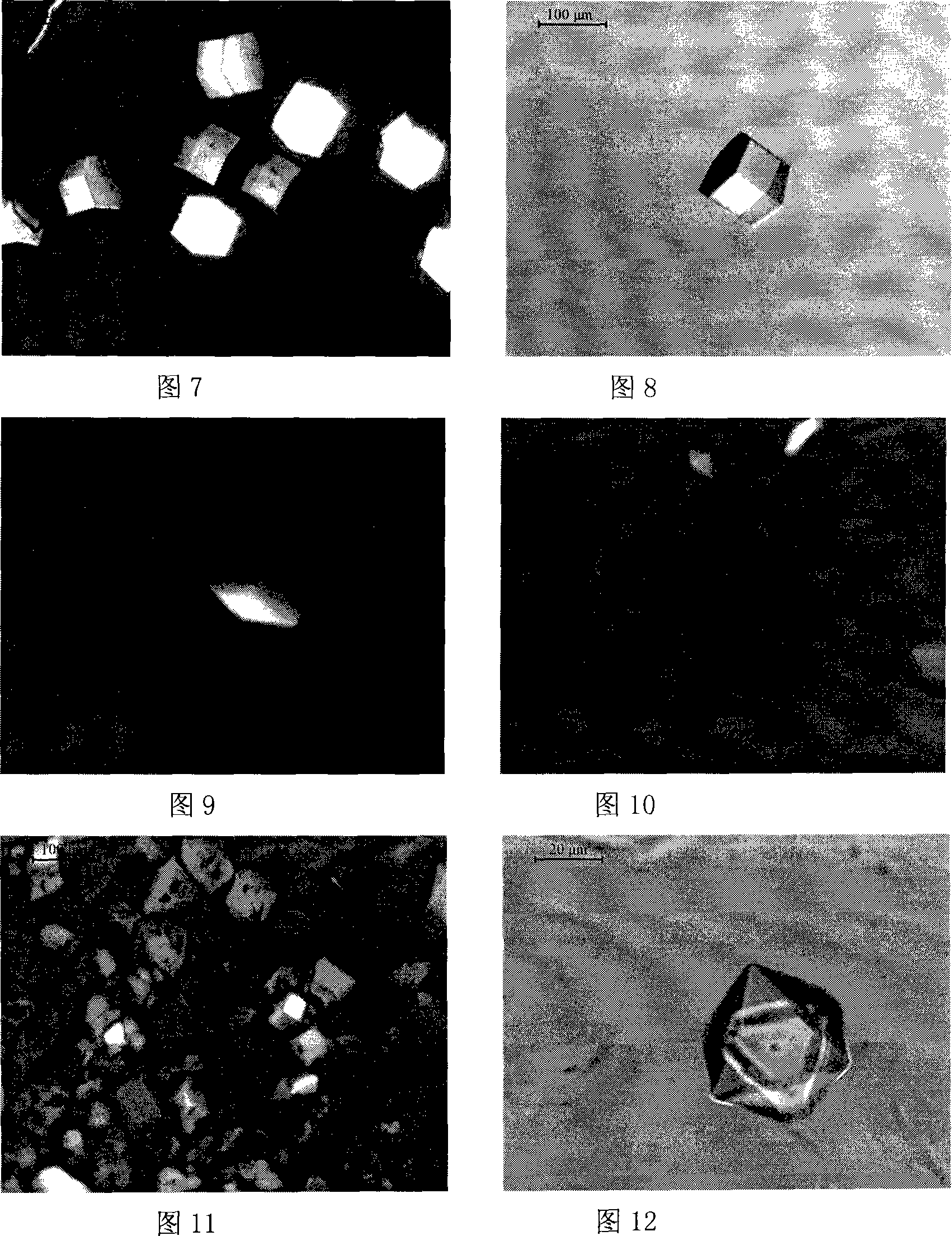
Protein crystallization is the process of formation of a protein crystal. Protein crystals are useful in the study of protein structures for use in medicine, amongst other applications. In the process of protein crystallization, proteins are dissolved in an aqueous environment and sample solution in order to reach the supersaturated state. This supersaturated state allows researchers to study the internal structure of proteins. Different methods are used to reach that state such as vapor diffusion, microbatch, microdialysis, and free-interface diffusion. Developing protein crystals is difficult, as the process is influenced by many factors, including pH, temperature, ionic strength in the crystallization solution, and even gravity. Once properly developed, these crystals can be used in structural biology to study the molecular structure of the protein, particularly for various industrial or biotechnological purposes, such as developing cancer treatment.
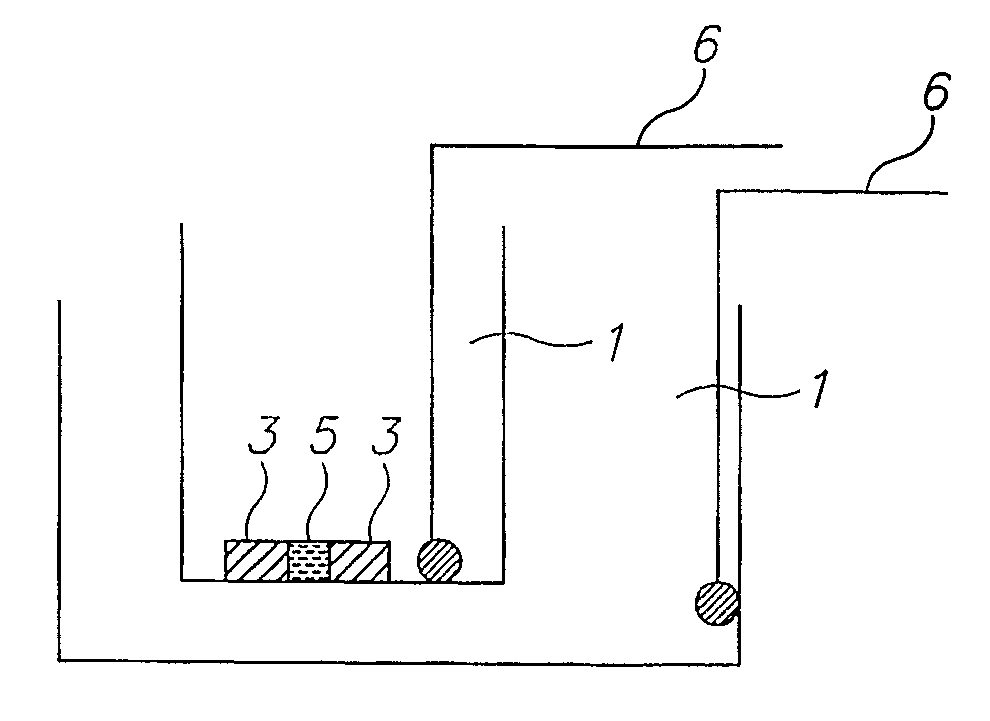
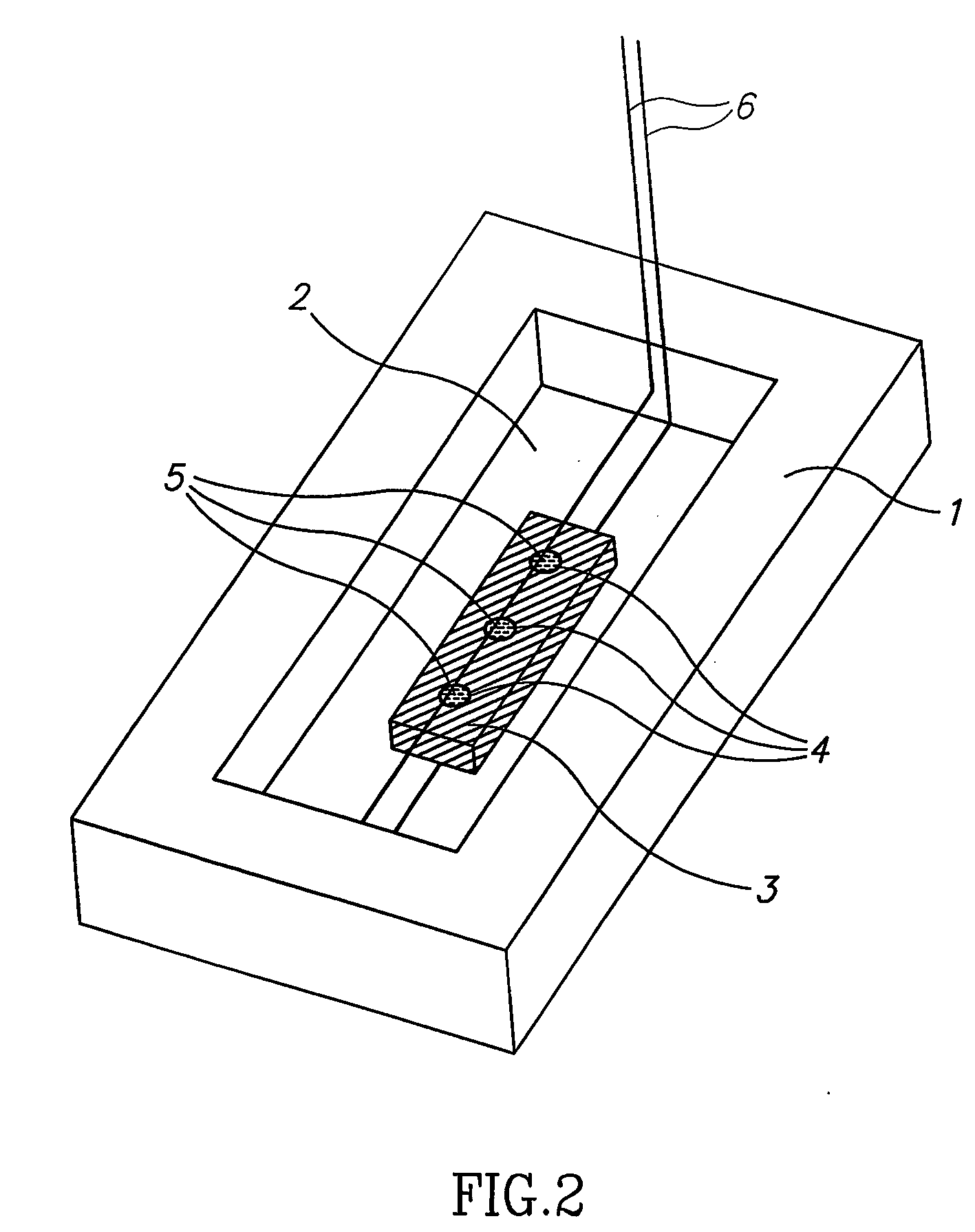
Crystallization control method for organic compound and crystallization control solid-state component employed therefor
InactiveUS6123769APolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsValence electronBiopolymer
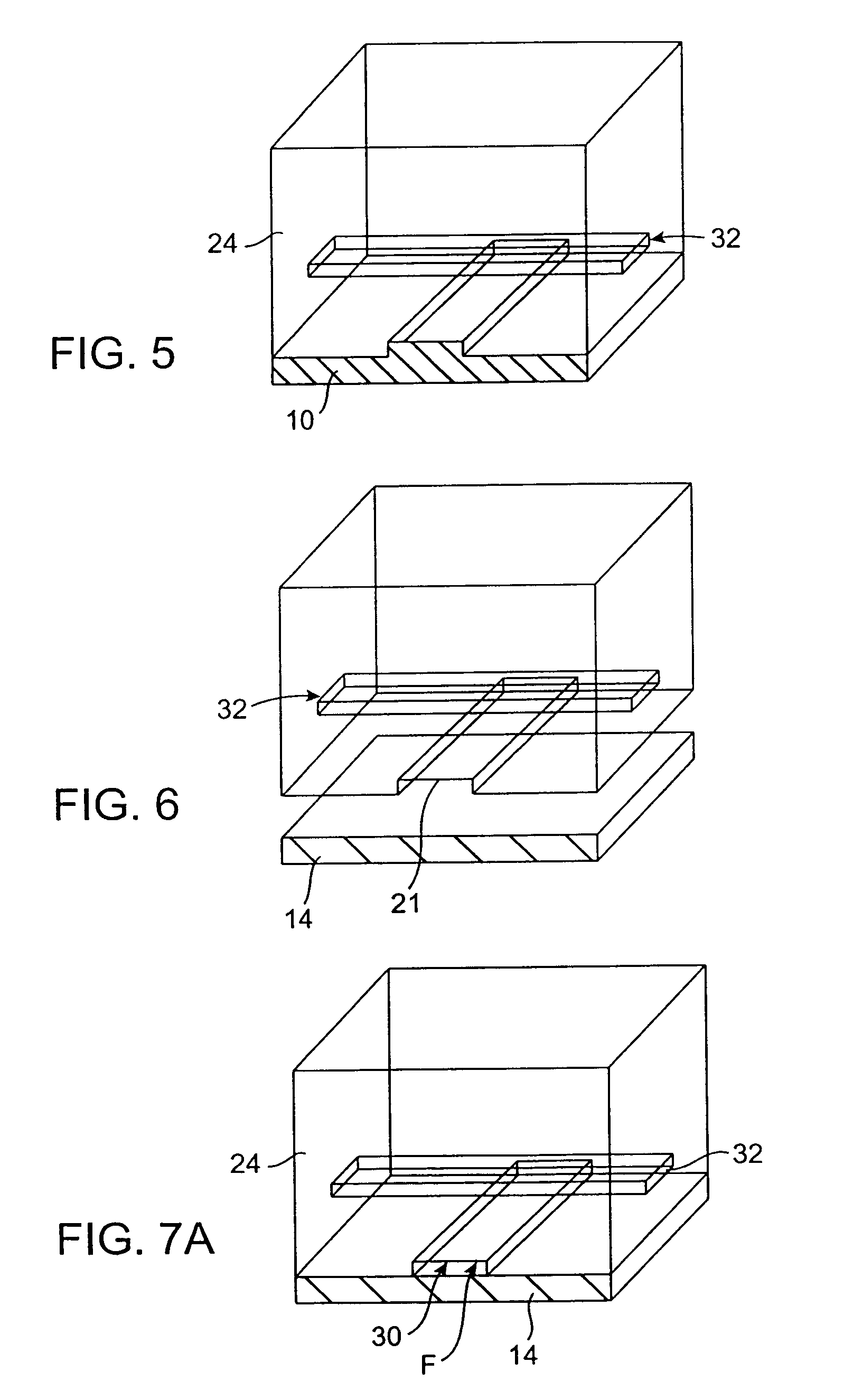
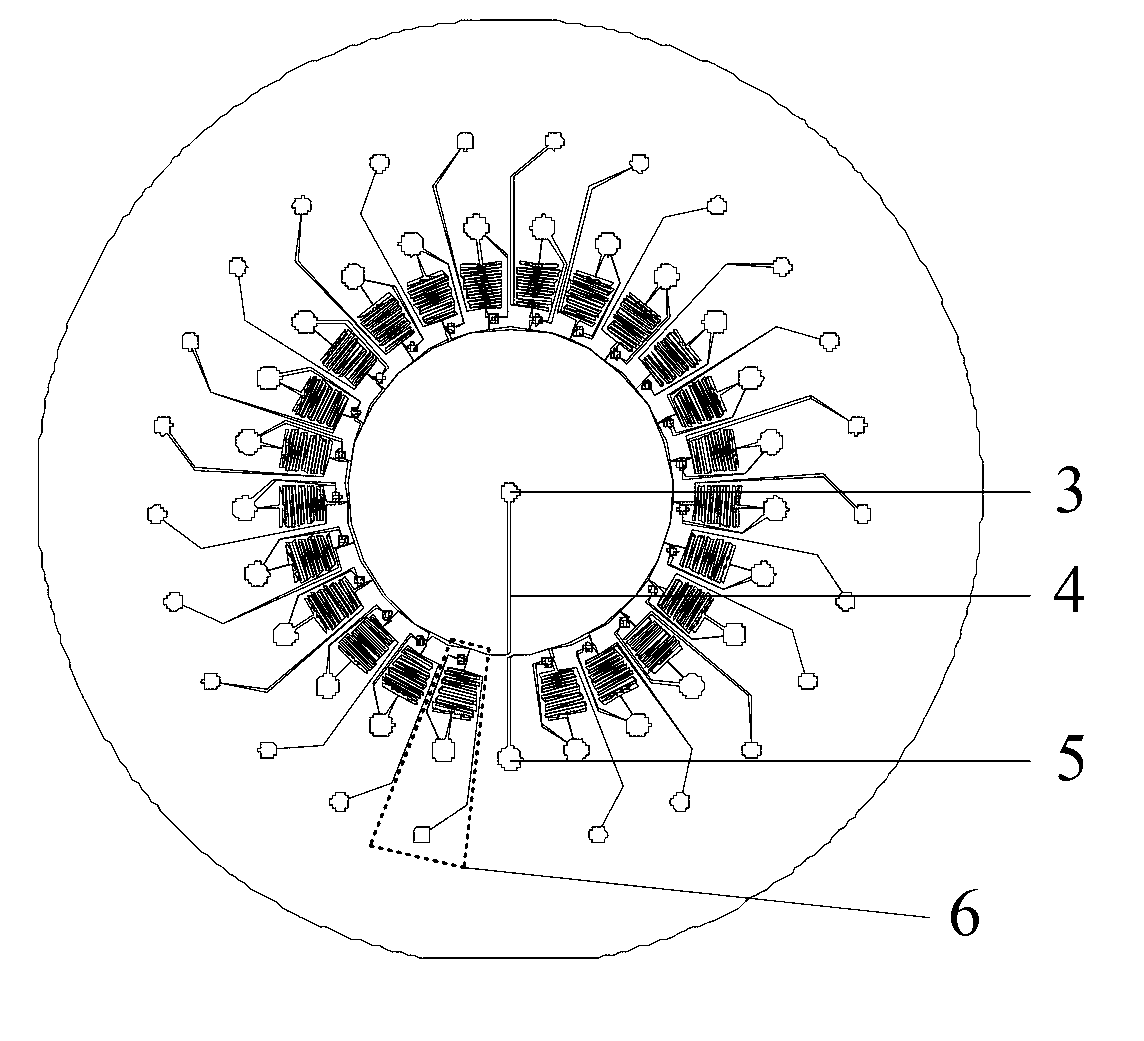
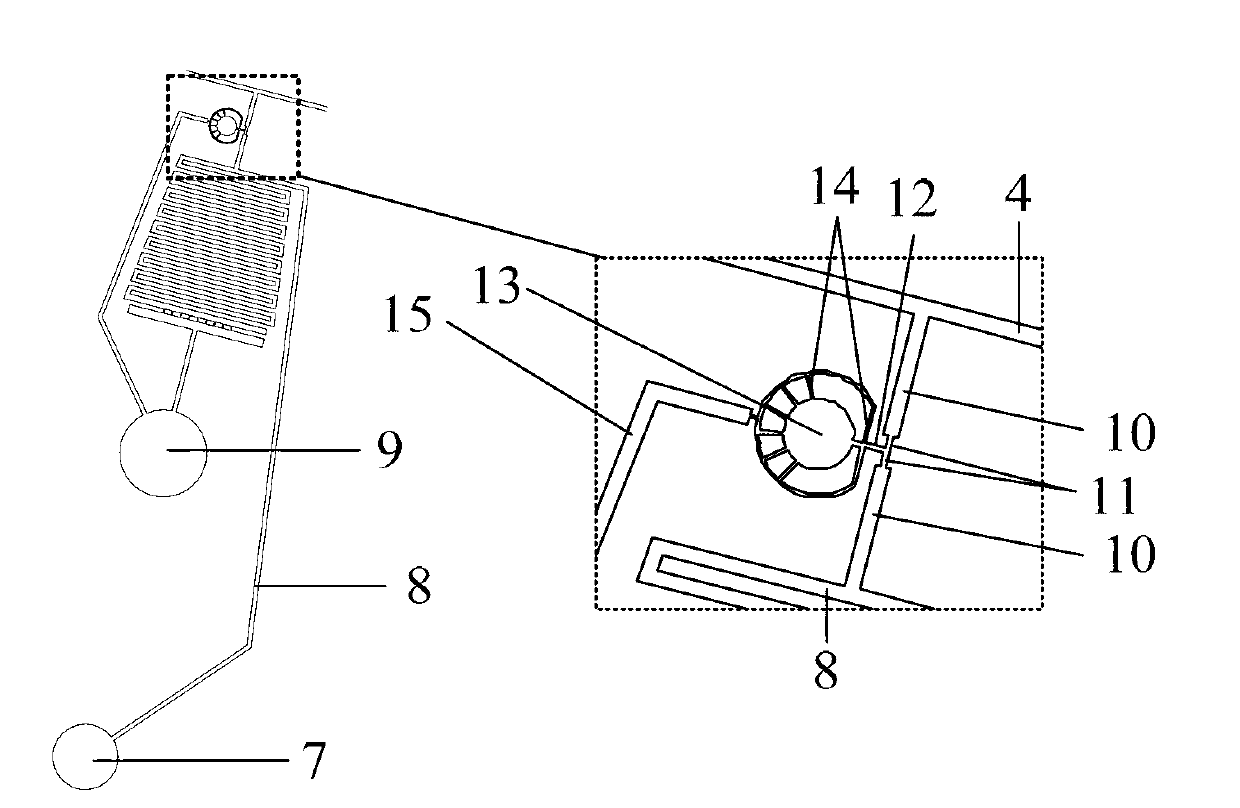
A method which can control crystallization of a biopolymer such as protein is provided. A silicon crystal (15) whose valence electrons are controlled to be capable of controlling the concentration of holes or electrons of the surface part in response to the environment of a buffer solution (14) containing the biopolymer such as protein is brought into contact with the solution (14), for getting a crystal of the biopolymer deposited on the surface of the silicon crystal (15). Crystallization is controlled by an electrical state which is generated by the controlled valence electrons on the surface of the silicon crystal (15).
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL IND LTD
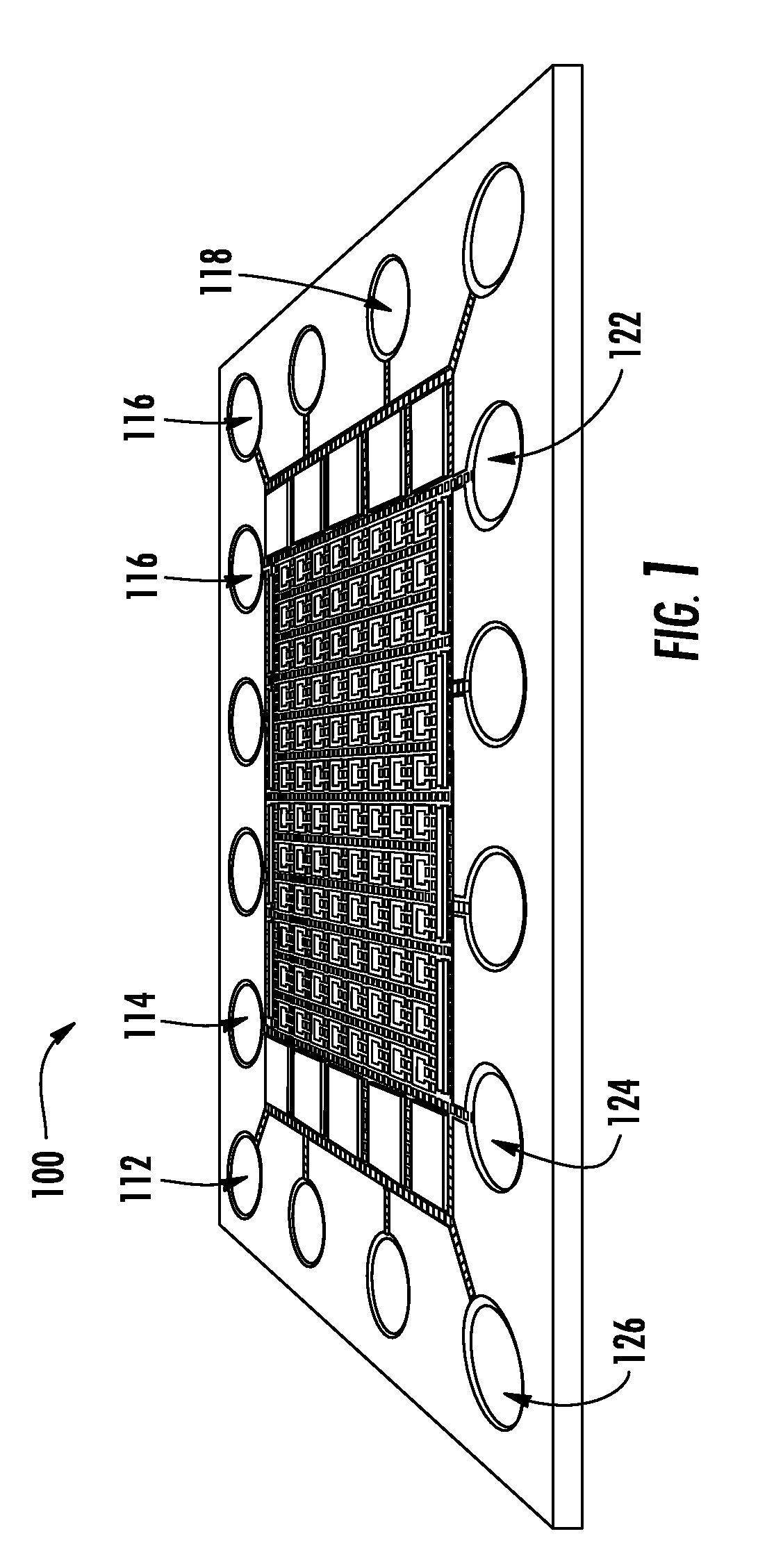
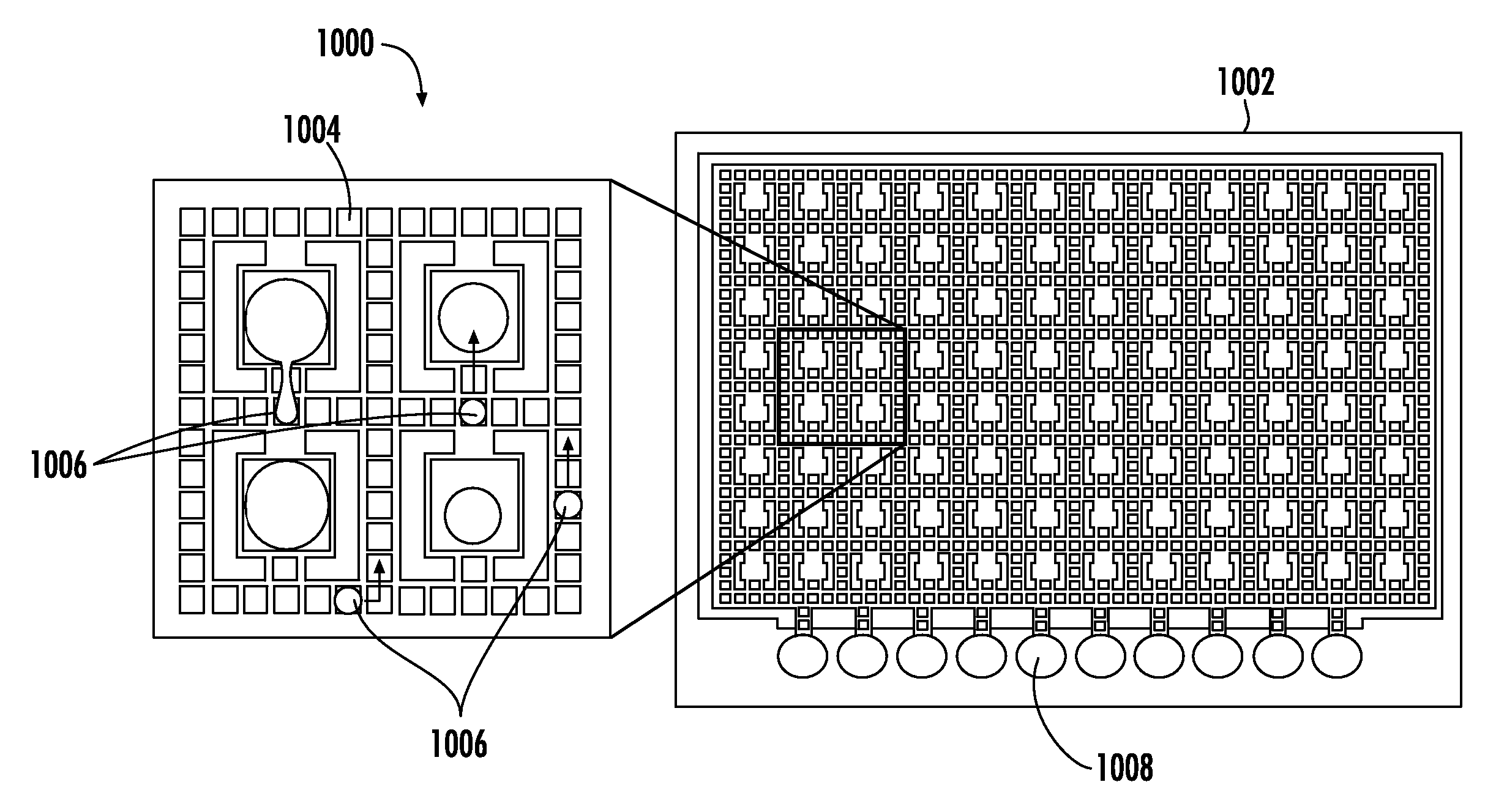
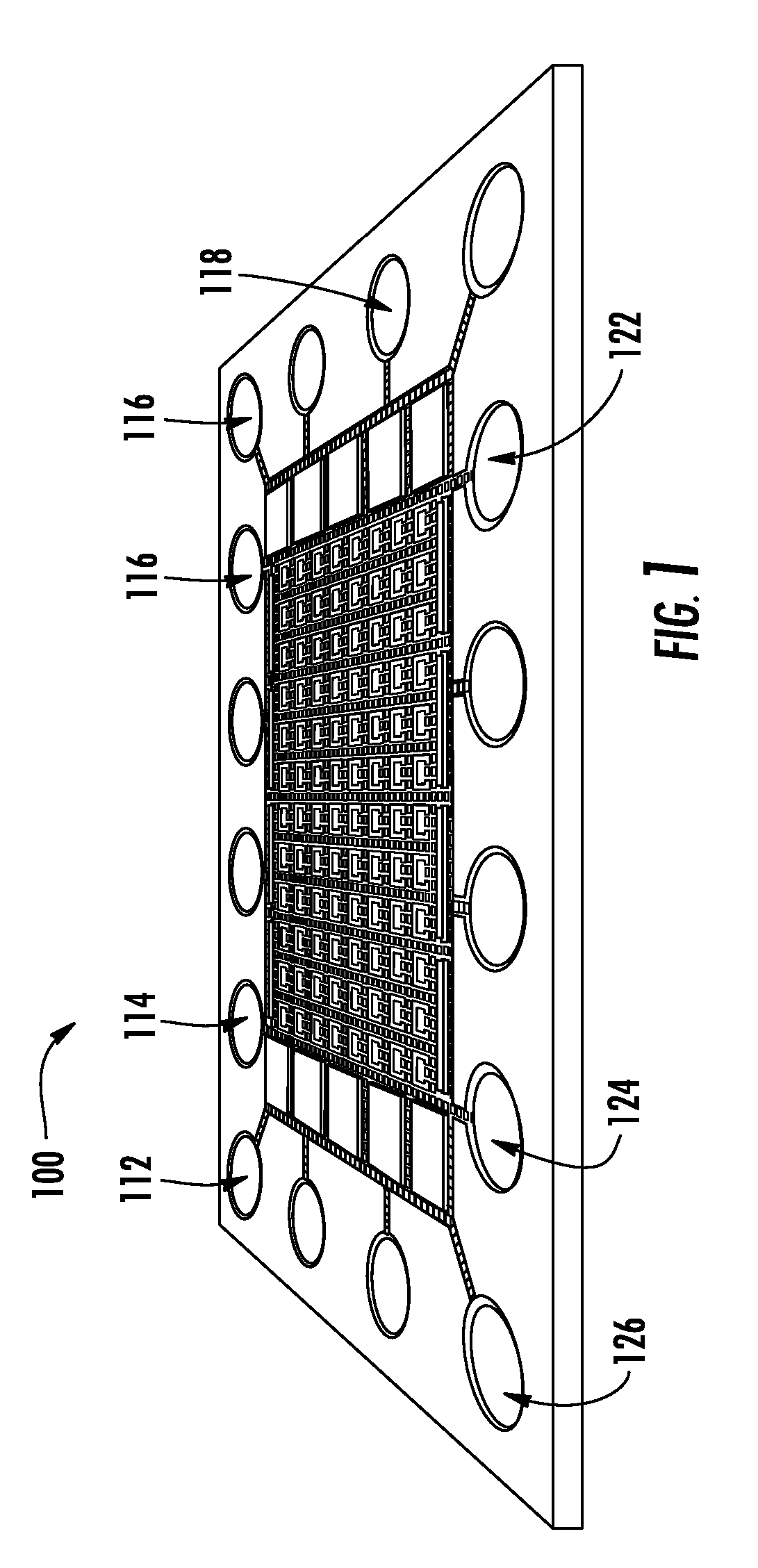
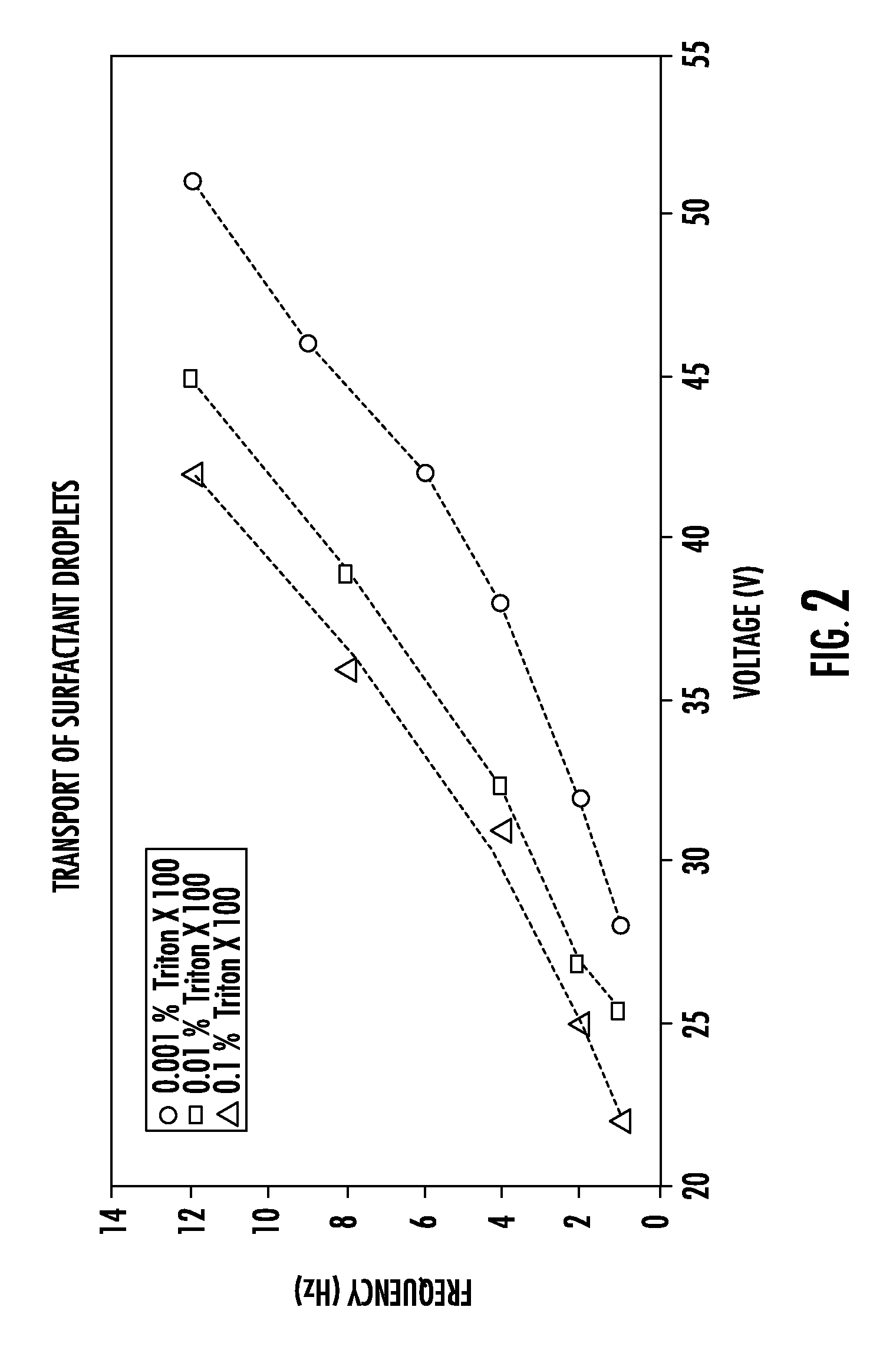
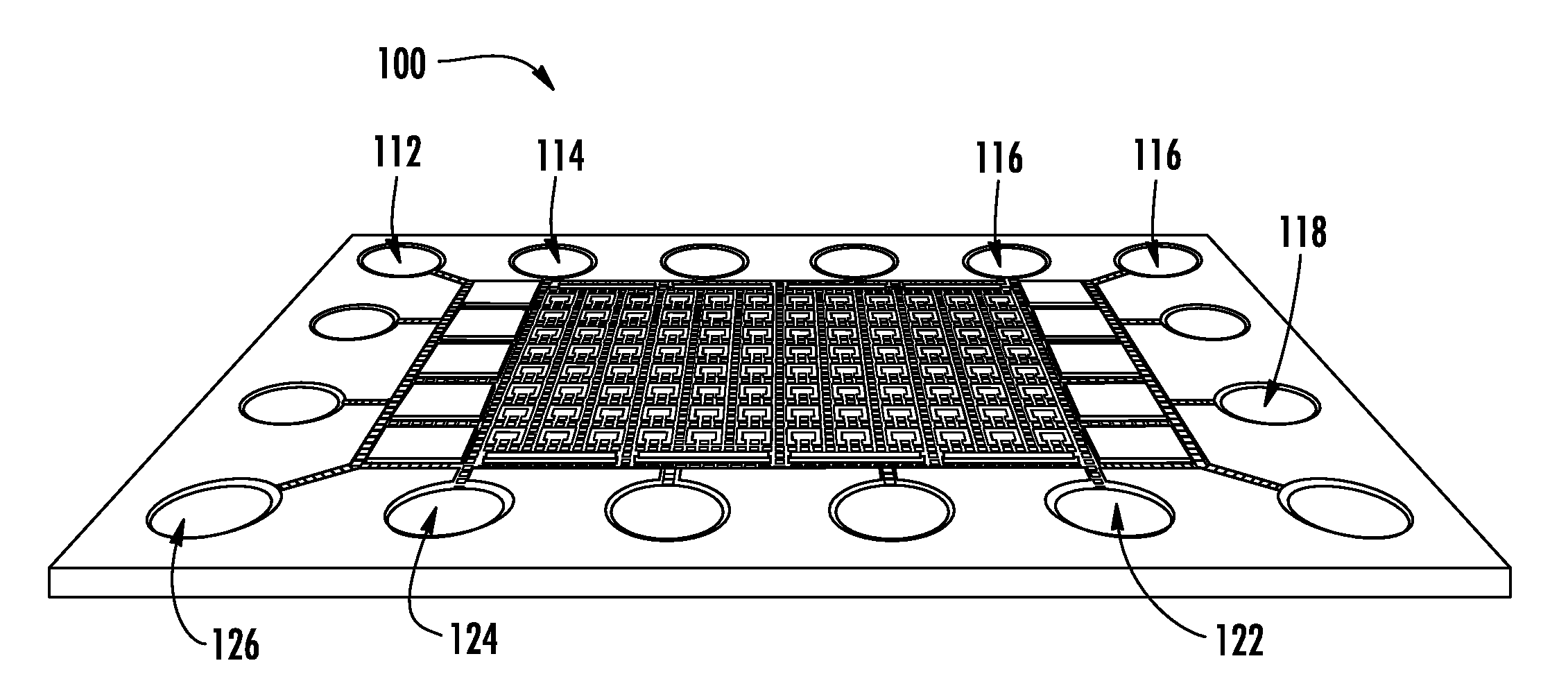
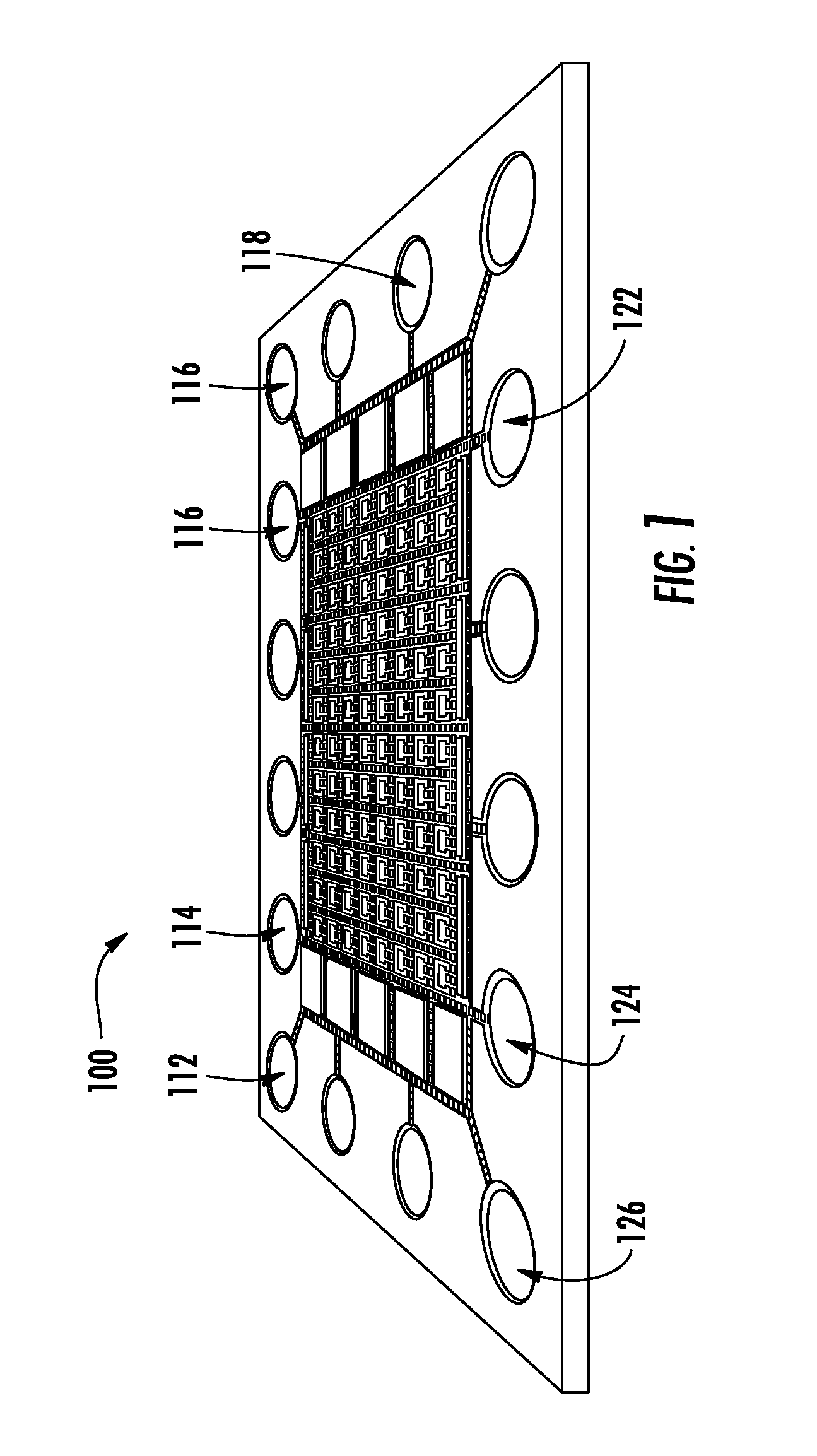
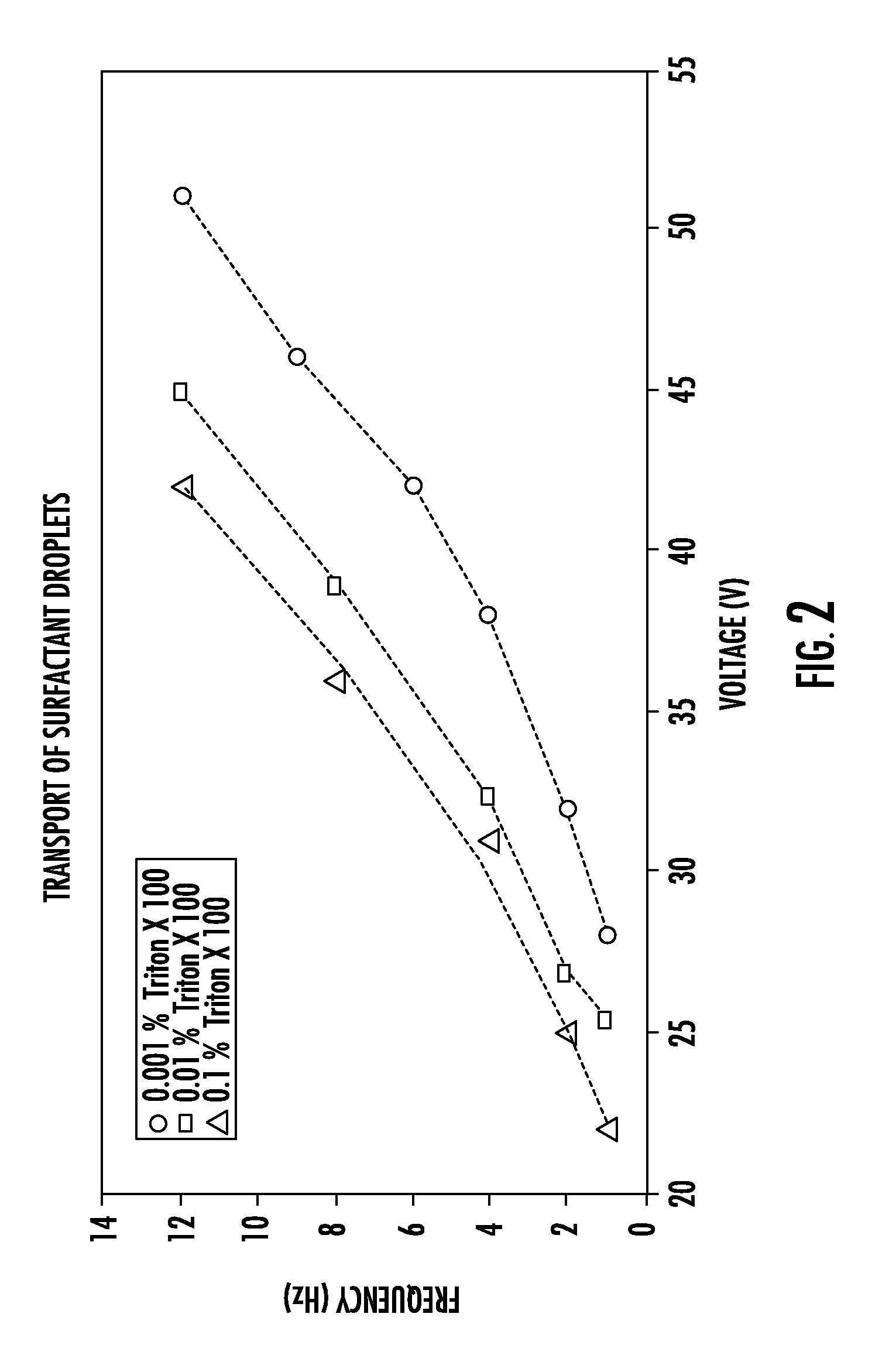
Method of electrowetting droplet operations for protein crystallization
InactiveUS7763471B2Easy to useFacilitates of propertySamplingBiological testingChemical physicsActuator
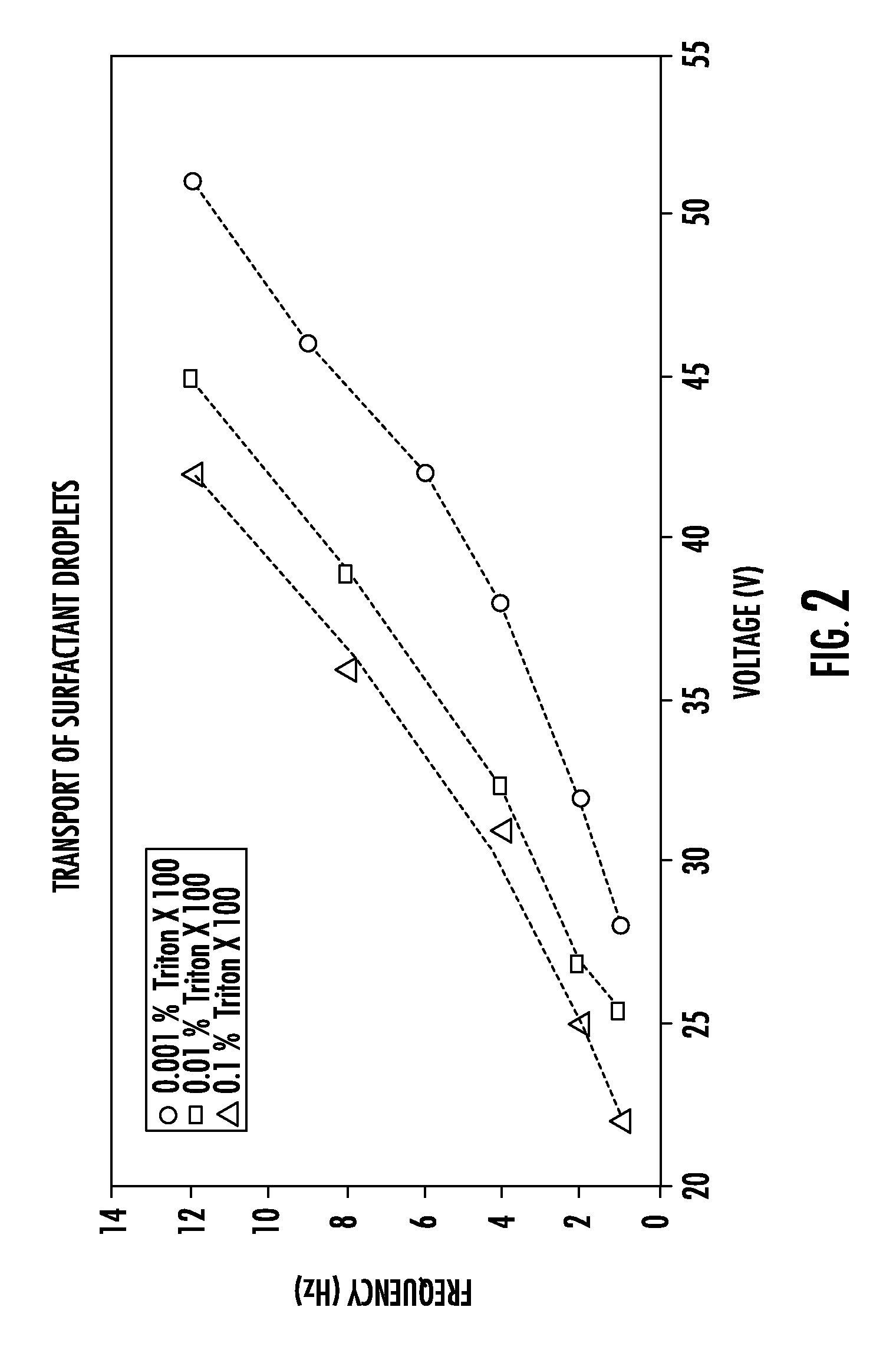
Methods of using protein crystallization droplet actuators are provided. Protein sample droplets and reagent droplets are dispensed, transported, and merged to yield an array of crystallization conditions by electrowetting droplet operations in a gap comprising oil filler fluid. The oil filler fluid is doped with a surfactant that enhances droplet operations using the protein sample.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
Protein Crystallization Droplet Actuator, System and Method
InactiveUS20080050834A1High resolutionHigh sensitivityPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingActuatorReagent
Protein crystallization droplet actuators, systems and methods are provided. According to one embodiment, a droplet actuator for providing an array of crystallization conditions is provided and includes: (a) two or more processing reservoirs; (b) two or more dispensing reservoirs collectively comprising two or more crystallization reagents; and (c) a port for introducing a sample for crystallization analysis. Systems including the droplet actuator, methods of providing an array of crystallization conditions, and methods of identifying crystallization conditions are also provided.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
Protein Crystallization Screening and Optimization Droplet Actuators, Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20080044914A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsFrom normal temperature solutionsProtein solutionMicrofluidics
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
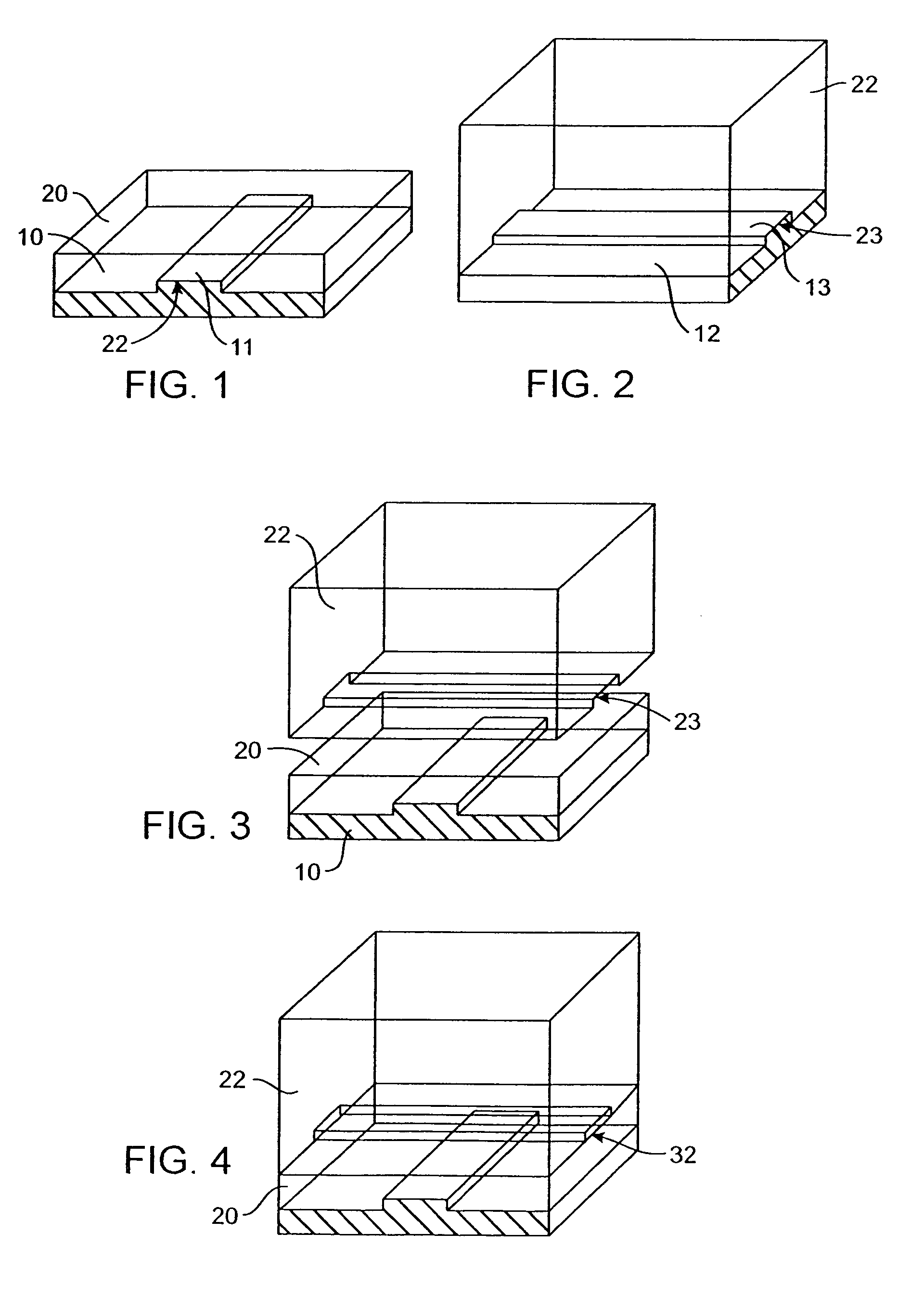
Microfluidic protein crystallography
InactiveUS20050205005A1High throughput screeningImprove throughputValve arrangementsPeptide librariesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsAgent Combination
The use of microfluidic structures enables high throughput screening of protein crystallization. In one embodiment, an integrated combinatoric mixing chip allows for precise metering of reagents to rapidly create a large number of potential crystallization conditions, with possible crystal formations observed on chip. In an alternative embodiment, the microfluidic structures may be utilized to explore phase space conditions of a particular protein crystallizing agent combination, thereby identifying promising conditions and allowing for subsequent focused attempts to obtain crystal growth.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
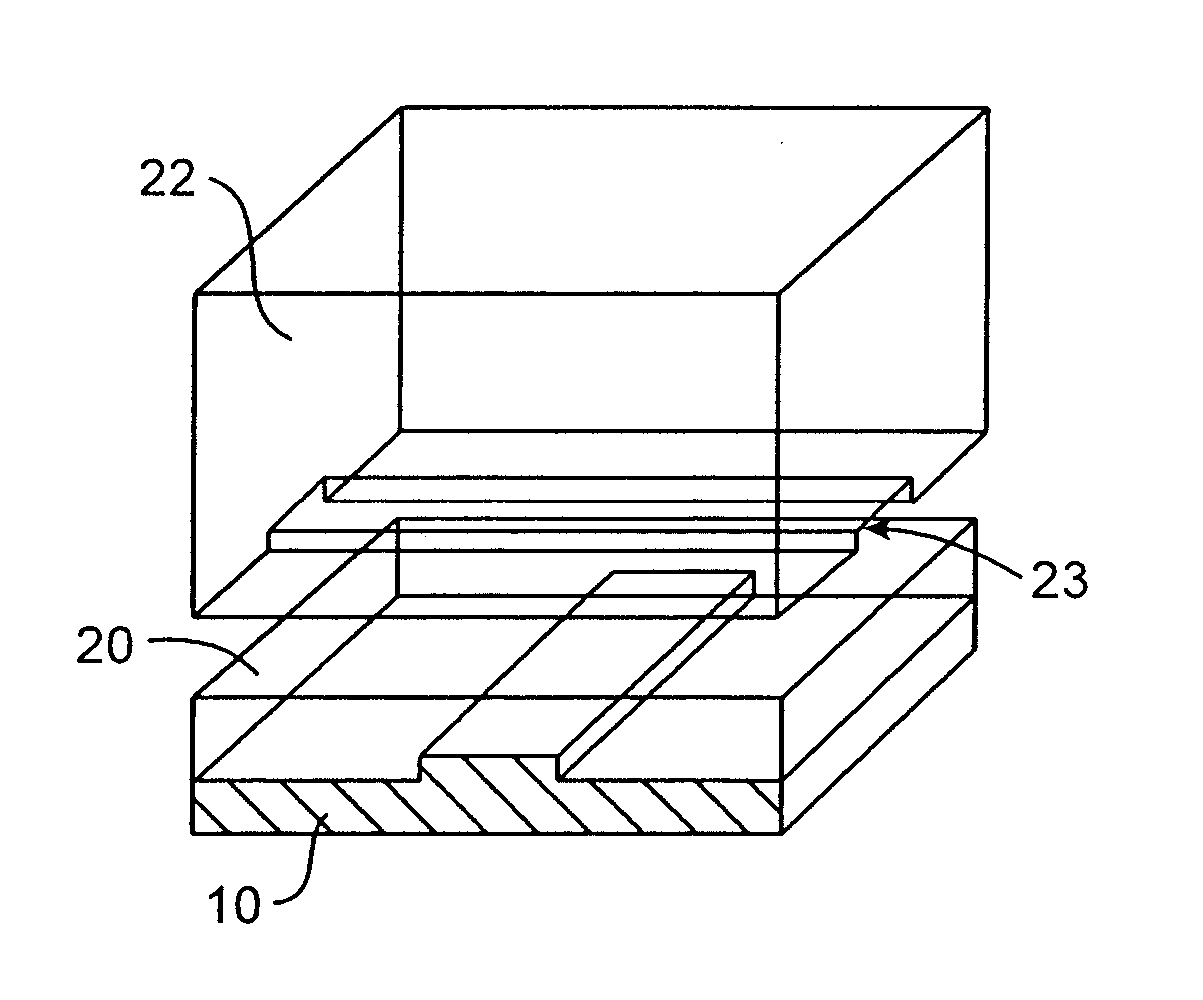
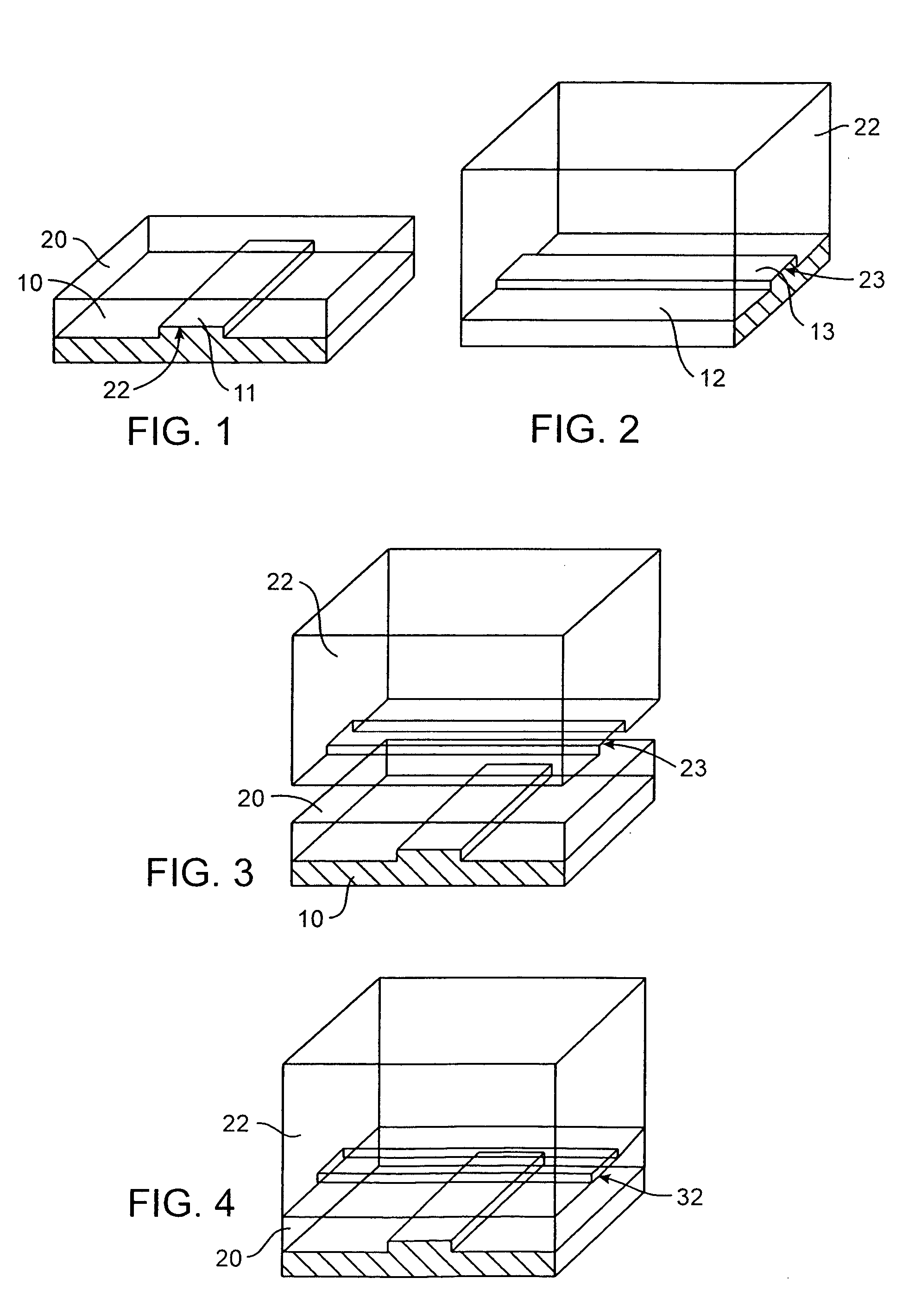
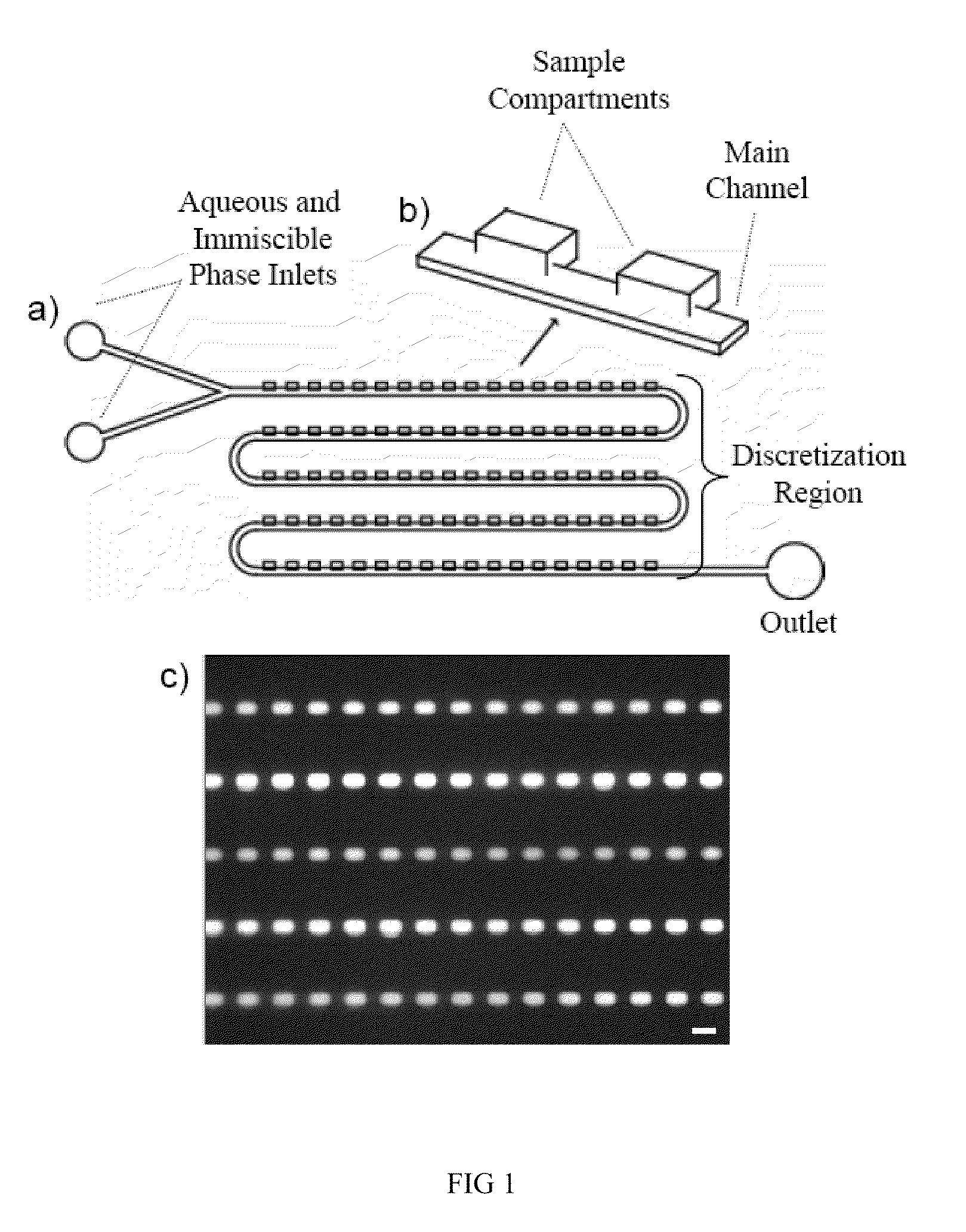
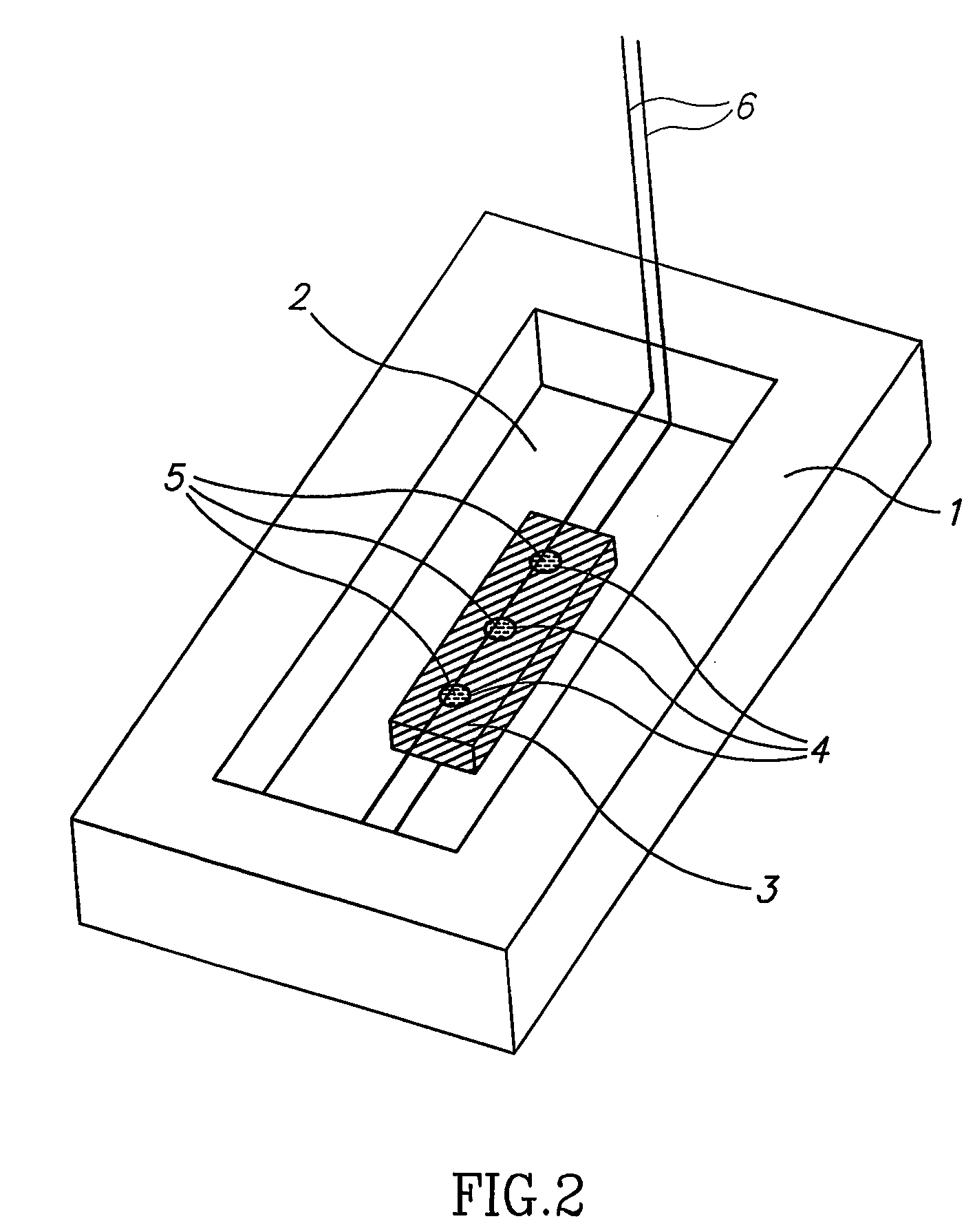
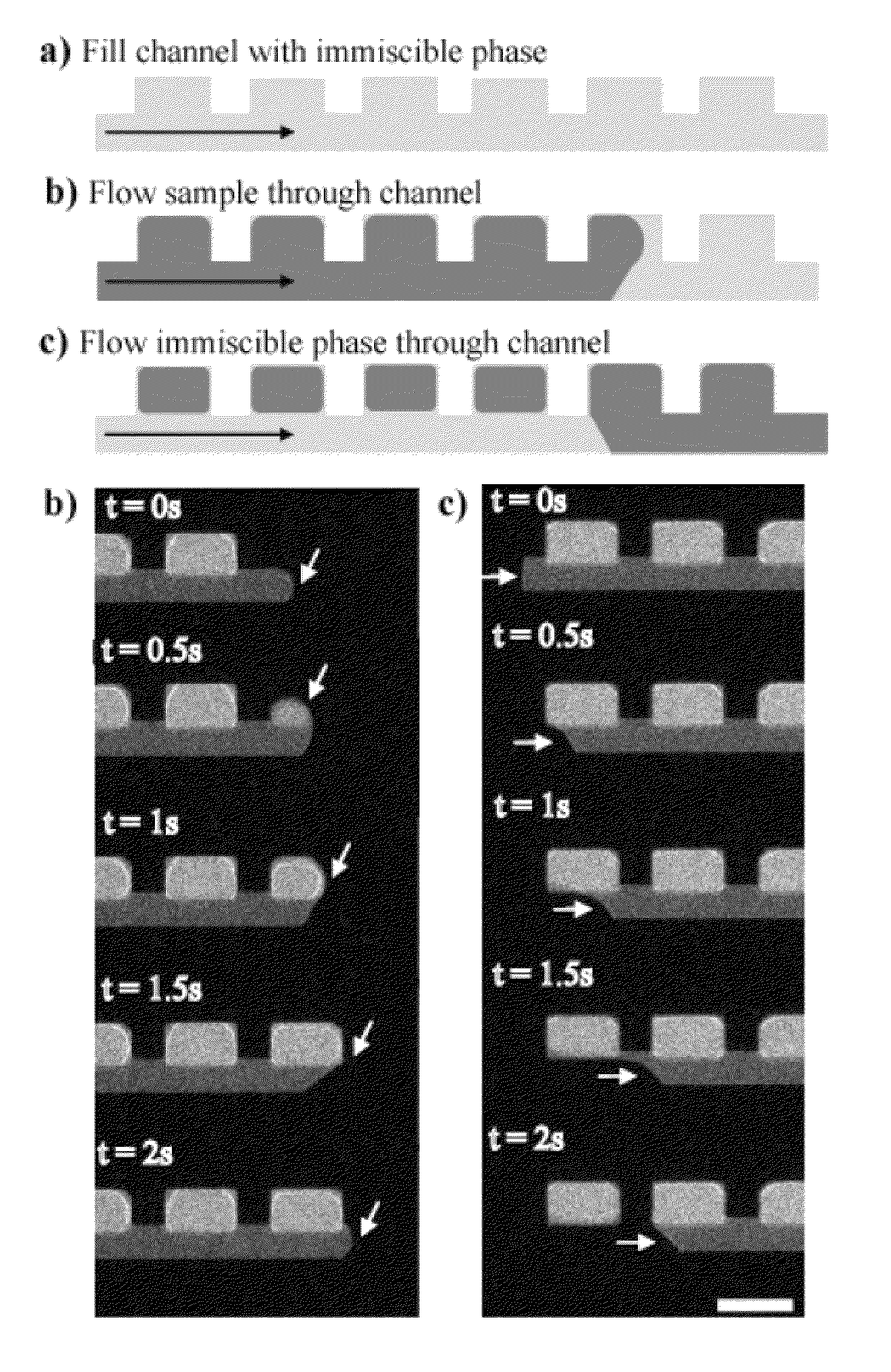
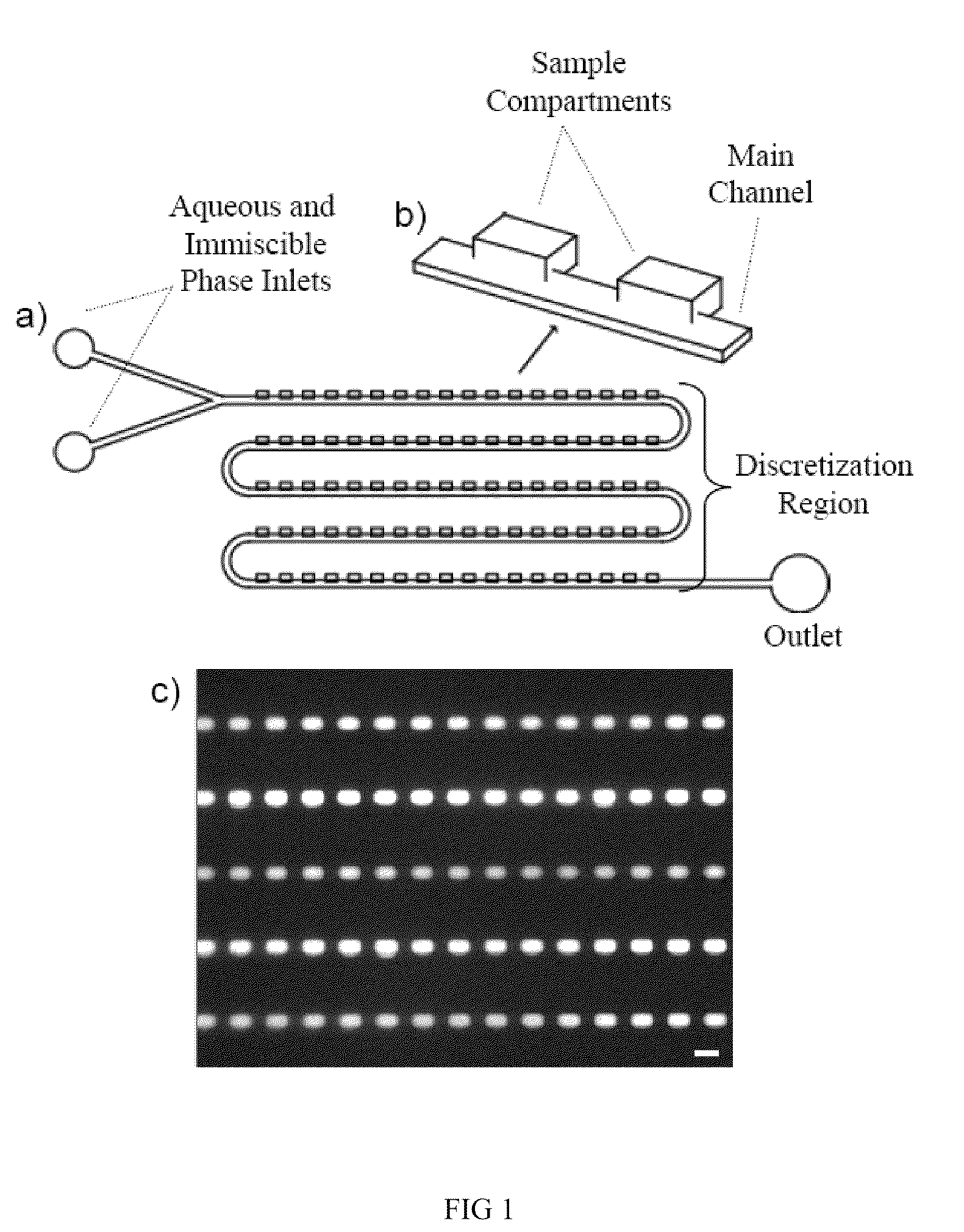
Method and apparatus for the discretization and manipulation of sample volumes
ActiveUS20100041046A1Easy to useEasy to implementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChannel geometryAssay
Embodiments of the present invention relate to methods and apparatuses for the discretization and manipulation of sample volumes that is simple, robust, and versatile. It is a fluidic device that partitions a sample by exploiting the interplay between fluidic forces, interfacial tension, channel geometry, and the final stability of the formed droplet and / or discretized volume. These compartmentalized volumes allow for isolation of samples and partitioning into a localized array that can subsequently be manipulated and analyzed. The isolation of the discretized volumes along with the device's inherent portability render our invention versatile for use in many areas, including but not limited to PCR, digital PCR, biological assays for diagnostics and prognostics, cancer diagnosis and prognosis, high throughput screening, single molecule and single cell reactions or assays, the study crystallization and other statistical processes, protein crystallization, drug screening, environmental testing, and the coupling to a wide range of analytical detection techniques for biomedical assays and measurements. The minimal fluid interconnects and simple flow geometry makes the device easy to use and implement, economical to fabricate and operate, and robust in its operations.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Microfluidic free interface diffusion techniques
InactiveUS20080182273A1Reduce concentrationFrom normal temperature solutionsFlow mixersFree interfaceCompetitive binding
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Automated protein crystallization imaging
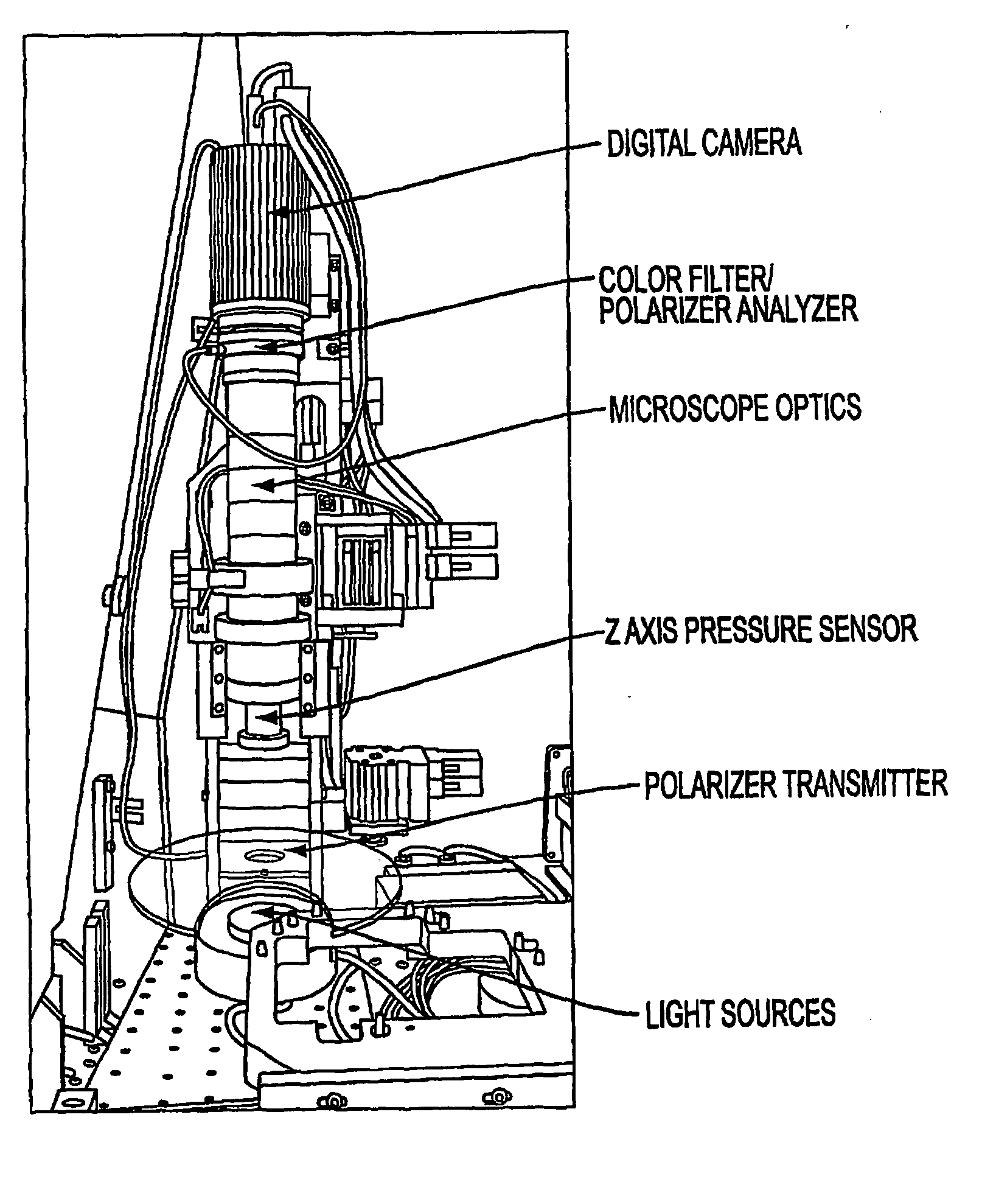
An apparatus that automatically captures, stores and analyzes images of crystallization experiments contained in a number of crystallization plates. The apparatus includes a plate nest capable of accommodating protein crystallization plates of a plurality of different types, image acquisition optics, including an objective lens and an image capturing device, for focusing an image of a crystallization well, a light source including a bright field illumination device and a dark field illumination device, a nest positioning controller for moving the position of the plate nest with respect to the image acquisition optics to align various selected wells with said objective lens for imaging of the content of the wells. A database stores experiment information associated with each of the crystallization plates, the experiment information including identification of specific crystal forming parameter values, each of the crystallization plates is identified in said database by a unique identification code. A crystallization imaging controller controls crystallization imaging by retrieving the experiment information for each crystallization plate inserted into the apparatus, and controlling the nest positioning controller and the image acquisition optics in accordance with the retrieved experiment information. The apparatus captures multiple images of each crystal site using different light source and polarization conditions, and processes the multiple images to form extended fused images of each crystal site.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI ASHEVILLE
Microfluidic free interface diffusion techniques
InactiveUS7306672B2Reduce concentrationFrom normal temperature solutionsFlow mixersDiffusionFree interface
A static fluid and a second fluid are placed into contact along a microfluidic free interface and allowed to mix by diffusion without convective flow across the interface. In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, the fluids are static and initially positioned on either side of a closed valve structure in a microfluidic channel having a width that is tightly constrained in at least one dimension. The valve is then opened, and no-slip layers at the sides of the microfluidic channel suppress convective mixing between the two fluids along the resulting interface. Applications for microfluidic free interfaces in accordance with embodiments of the present invention include, but are not limited to, protein crystallization studies, protein solubility studies, determination of properties of fluidics systems, and a variety of biological assays such as diffusive immunoassays, substrate turnover assays, and competitive binding assays.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
System and method for increased cooling rates in rapid cooling of small biological samples
ActiveUS20090133410A1Reduce condensationReduce freezingPreparing sample for investigationDead animal preservationProcess engineeringLiquid nitrogen
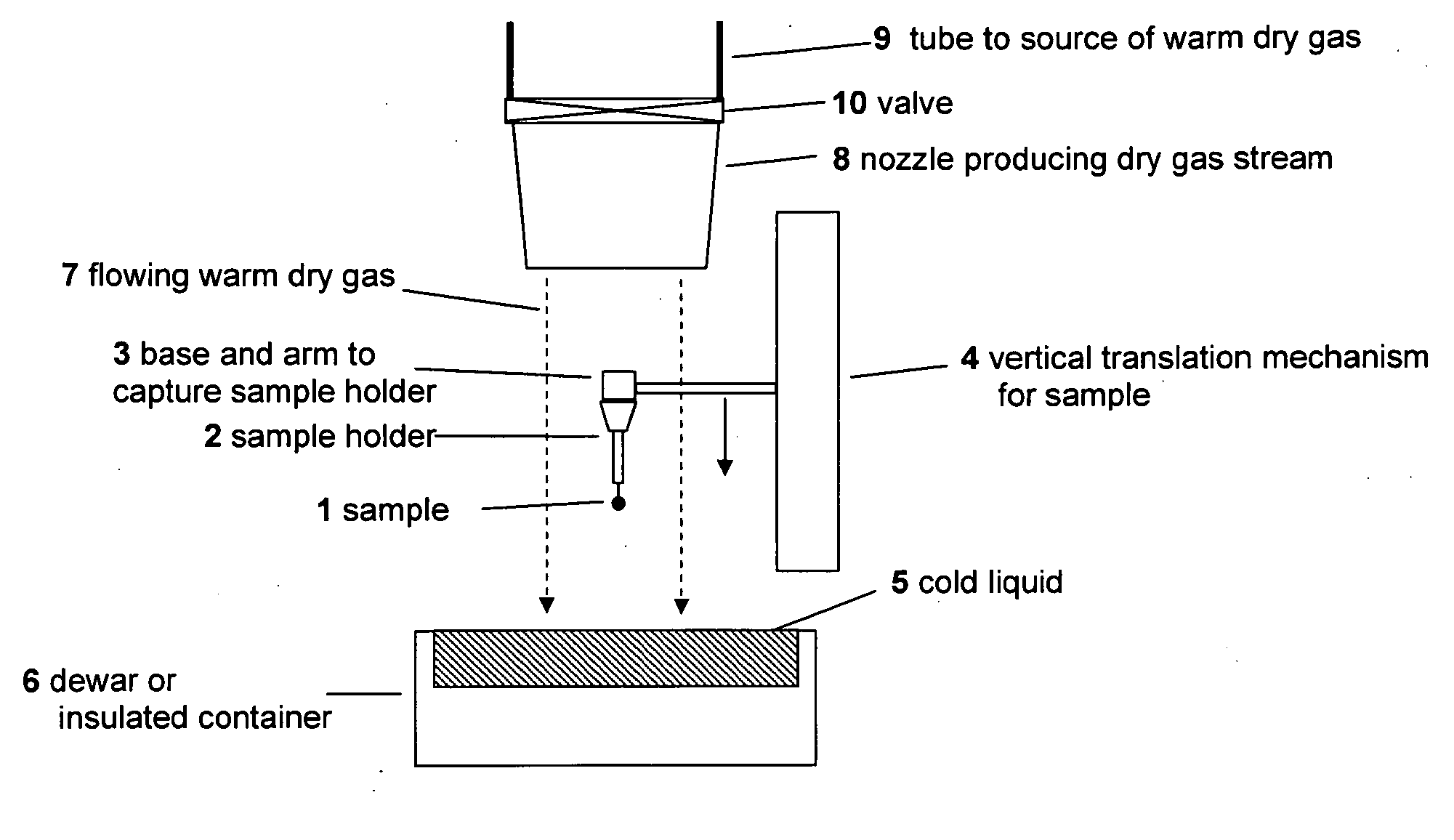
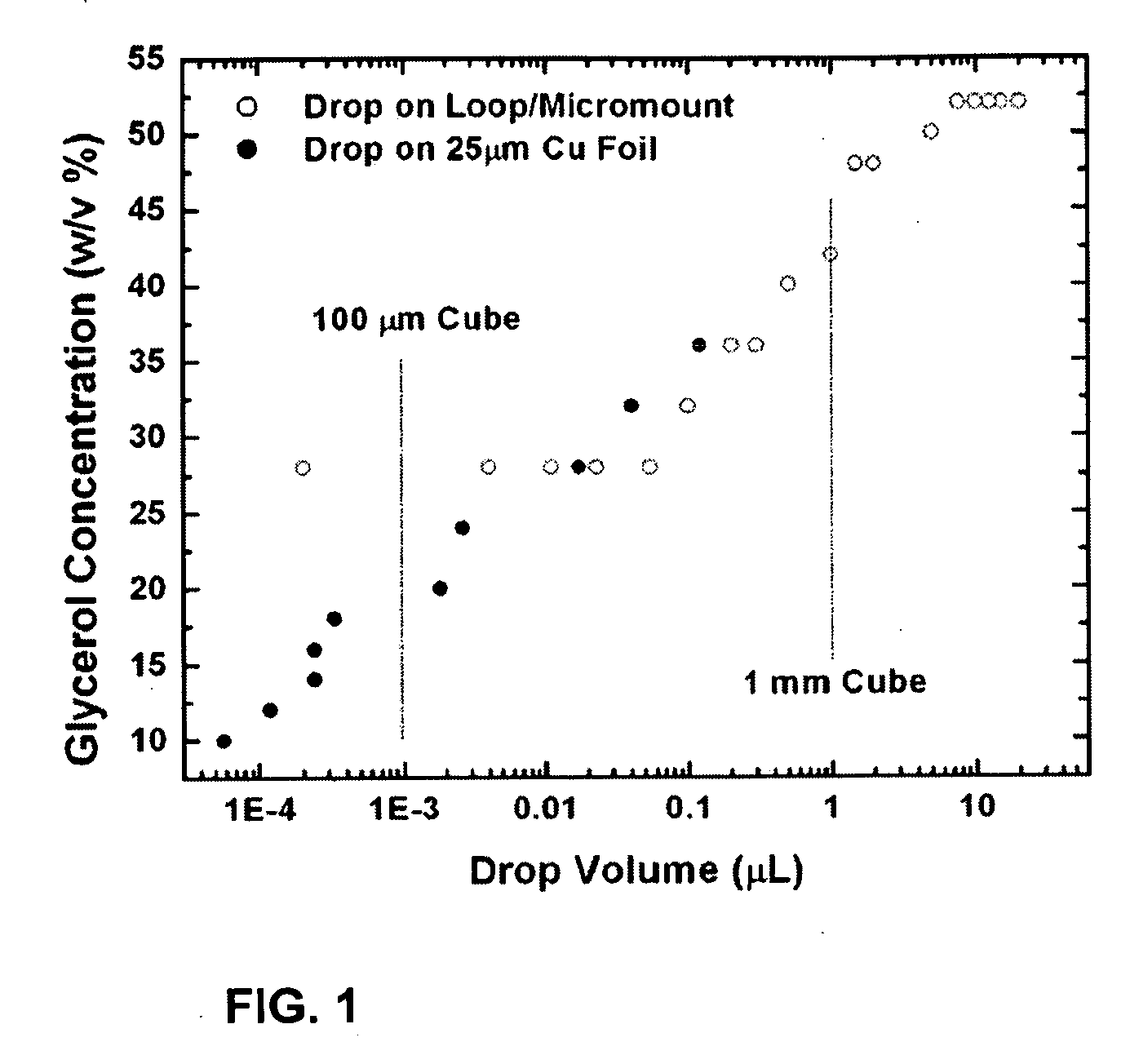
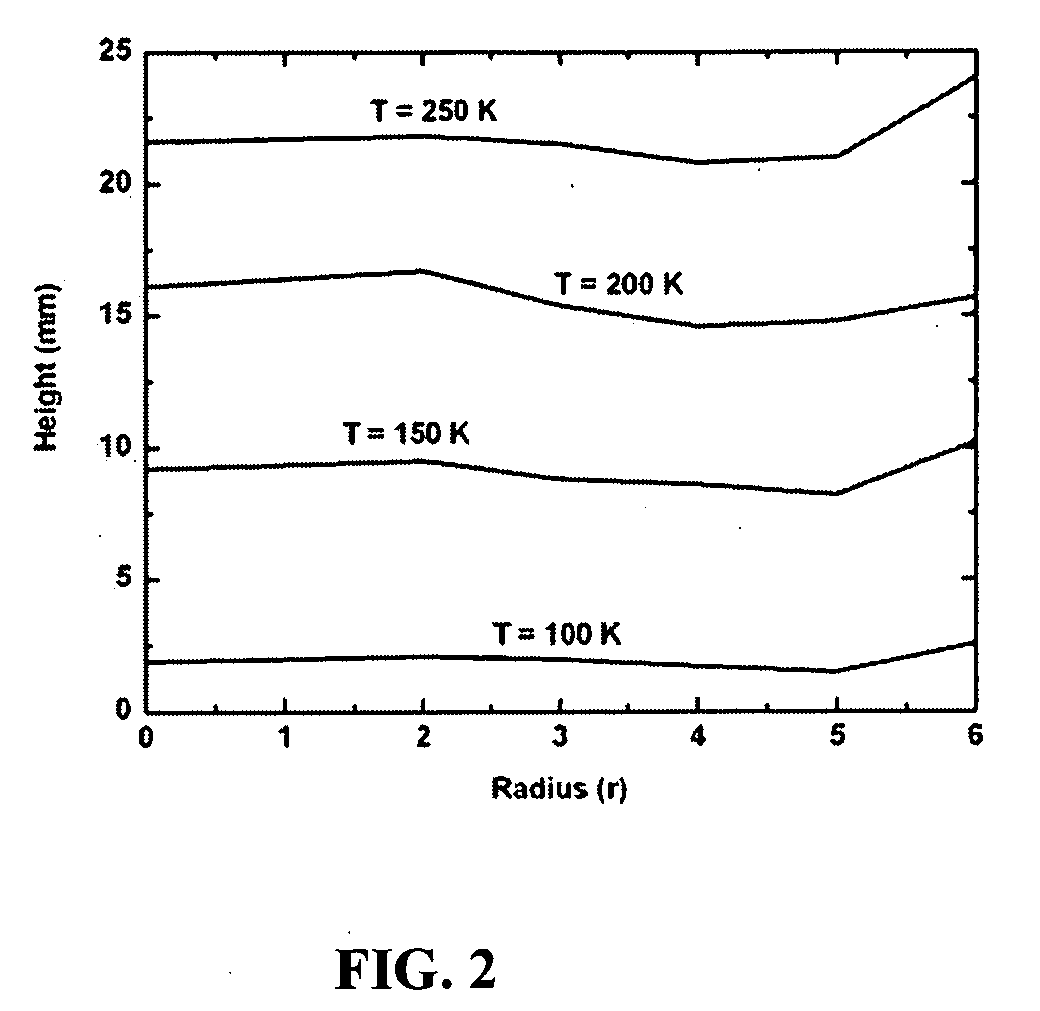
A method and devices for rapid cooling of small biological samples by plunging them in a cryogenic liquid, such as liquid nitrogen, or contacting them with a cryogenic metal surface, reduce or eliminate the cold gas layer that forms above the liquid cryogens or cryogenic surfaces, producing an abrupt transition from ambient (e.g., room) temperature to the cryogen temperature as the sample enters the liquid or contacts the surface. To reduce or eliminate the effects of the cold gas layer, a flow of warm dry gas can be directed along the plunge path, for example. By removing this cold gas layer, cooling times for a 10 micron sample (the size of single cells and the smallest protein crystals now used protein crystallography) will decrease to ˜0.001 s.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods and devices for high throughput crystallization
InactiveUS7229500B2Avoid large quantitiesHigh densityMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthNucleationPhotoresist
Crystallization Photoresist (PR) apparatus and methods which allow for fast screening and determination of protein crystallization conditions with small protein quantities and rapid crystallization. The apparatus comprise a first region comprising a first nucleation catalyst material and a second region comprising a second nucleation catalyst material, with the first and second regions positioned adjacent to each other and configured to support at least one crystal, and with the first region having a variation in a nucleation property of the first nucleation catalyst material in the first region. The crystal may be supported at an interface of the adjacent regions. The methods comprise providing a first region of a first nucleation catalyst material and a second region of a second nucleation catalyst material adjacent said first region, with the first region having a variation in a nucleation property of the first nucleation catalyst material, exposing the first and second regions to a solution of a selected molecule, and growing at least one crystal of the molecule in association with the first and second regions.
Owner:PARALLEL SYNTHESIS TECH
Semi-contact under-oil continuous droplet sample applying and liquid adding method
The invention provides a semi-contact under-oil continuous droplet sample applying and liquid adding method, which is suitable for sequentially operating a droplet array system. According to the method, the distance between the pointed end of a capillary tube sample applying needle and the lower surface of a micro-hole (or a generated droplet) is controlled accurately, and the affinity or interface tension interaction between the droplet and the surface (or the generated droplet) is utilized, so that rapid and reliable continuous droplet sample applying or continuous liquid adding is realized, and the problem of cross infection during sample applying is solved effectively. The method is suitable for biochemical analysis screening researches such as high-flux medicament screening, protein crystallization condition screening, enzyme kinetics research and drug toxicity determination.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods and apparatus for rapid crystallization of biomolecules
InactiveUS7459021B2Crystallize fastQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsProtein solutionIsoelectric point
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for promoting rapid formation of biomolecule crystals from a solution of biomolecules, preferably proteins, wherein the protein solution undergoes rapid concentration according to its isoelectric point in an electric field. Protein crystallization according to the methods of the present invention takes place within a period of hours or less.
Owner:BUKSHPAN SHMUEL
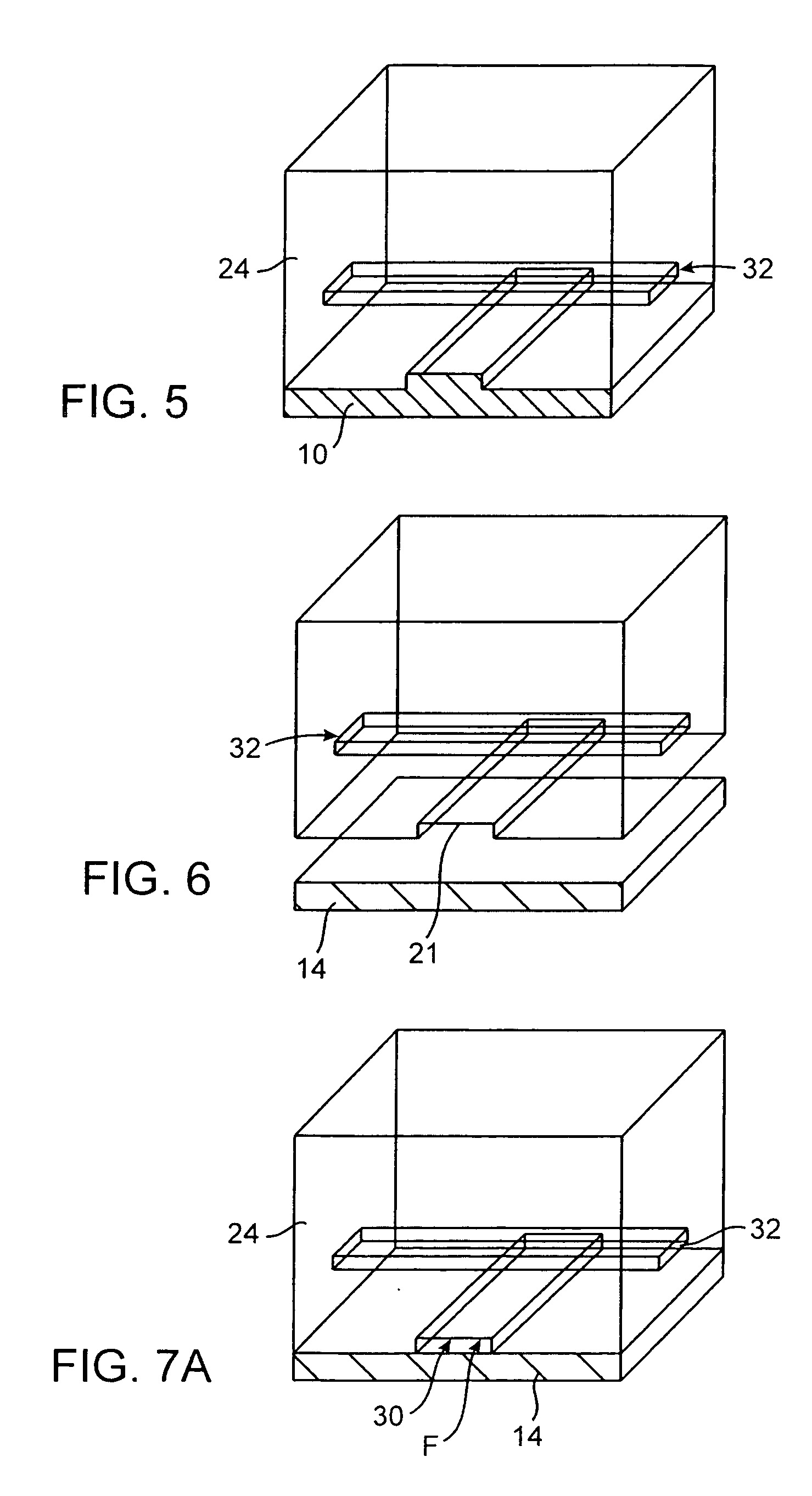
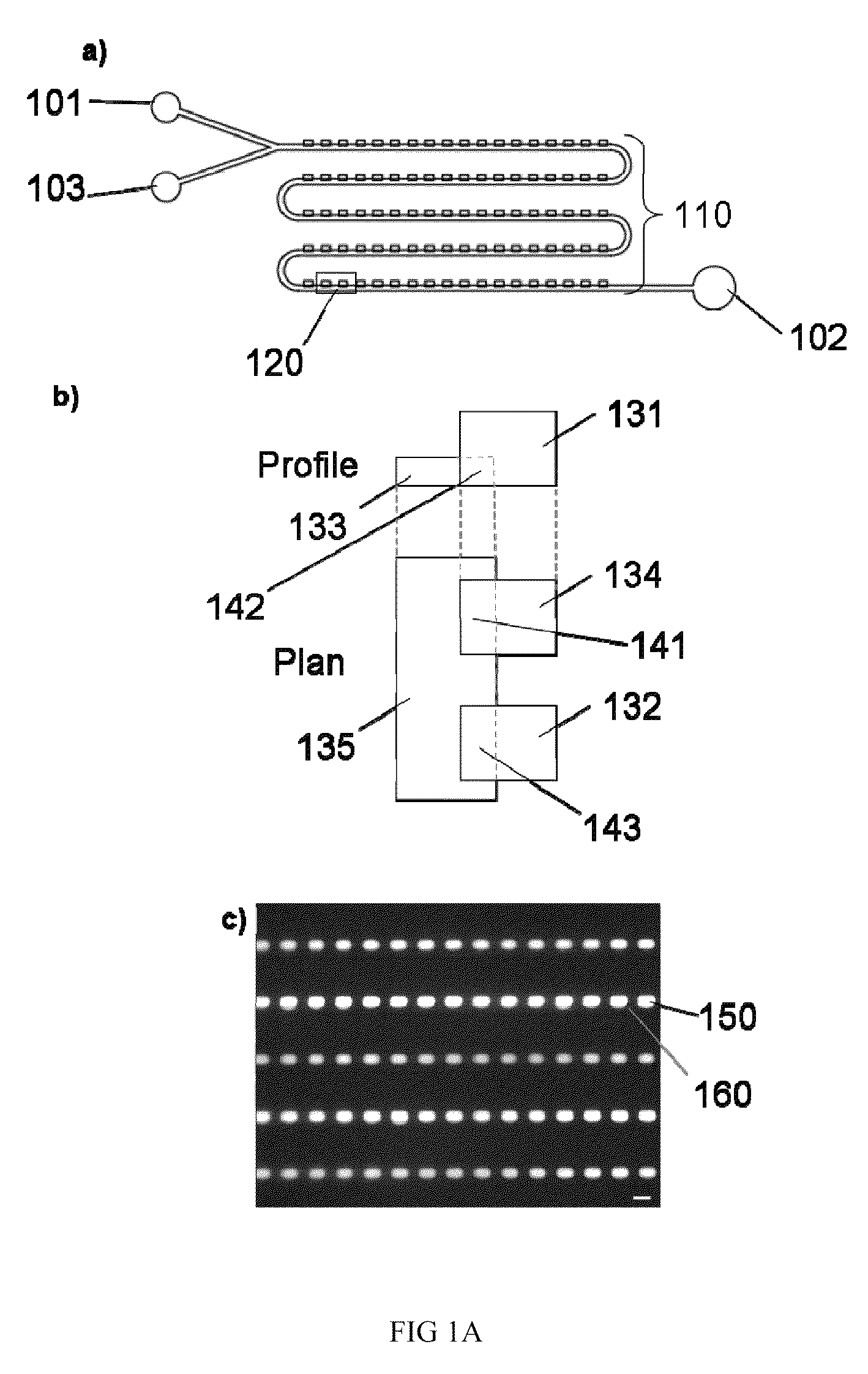
Method and apparatus for the discretization and manipulation of sample volumes
ActiveUS9180453B2Easy to useEasy to implementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusChannel geometryHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Embodiments of the present invention relate to methods and apparatuses for the discretization and manipulation of sample volumes that is simple, robust, and versatile. It is a fluidic device that partitions a sample by exploiting the interplay between fluidic forces, interfacial tension, channel geometry, and the final stability of the formed droplet and / or discretized volume. These compartmentalized volumes allow for isolation of samples and partitioning into a localized array that can subsequently be manipulated and analyzed. The isolation of the discretized volumes along with the device's inherent portability render our invention versatile for use in many areas, including but not limited to PCR, digital PCR, biological assays for diagnostics and prognostics, cancer diagnosis and prognosis, high throughput screening, single molecule and single cell reactions or assays, the study crystallization and other statistical processes, protein crystallization, drug screening, environmental testing, and the coupling to a wide range of analytical detection techniques for biomedical assays and measurements. The minimal fluid interconnects and simple flow geometry makes the device easy to use and implement, economical to fabricate and operate, and robust in its operations.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Programmable Arrays
Biomolecule arrays on a substrate are described which contain a plurality of biomolecules, such as coding nucleic acids and / or isolated polypeptides, at a plurality of discrete, isolated, locations. The arrays can be used, for example, in high throughput genomics and proteomics for specific uses including, but not limited molecular diagnostics for early detection, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis, monitoring clinical response, and protein crystallography.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Micro-fluidic chip for high-flux automatically rationing and mixing and use method and application of chip
ActiveCN102989533ASimple structureEasy to operateLaboratory glasswaresMaterial thermal analysisHigh fluxGeometric design
The invention discloses a micro-fluidic chip for high-flux automatically rationing and mixing and a use method and an application of the chip. The micro-fluidic chip is a combined micro-fluidic chip and consists of a micro-fluidic chip main body and a pre-degassing PDMS (polydimethyl siloxane) pump body which are combined; and based on the chip, negative pressure is produced in a closed micro-pipe system to form a fluid driving force by using the high dissolution property of the PDMS pump body to gases after de-gassing treatment, simultaneously a capillary valve is constructed by using the chip micro-pipe surface property and combining the geometric design, and automatic filling, rationing and mixing of fluid in the micro-fluidic chip main body are achieved through the coordinate action of the negative pressure driving and the capillary valve. Finally, the invention discloses the micro-fluidic chip used for high-flux screening of protein crystallization conditions.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and apparatus for rapid crystallization of biomolecules
InactiveUS20060137603A1Crystallize fastQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsProtein solutionIsoelectric point
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for promoting rapid formation of biomolecule crystals from a solution of biomolecules, preferably proteins, wherein the protein solution undergoes rapid concentration according to its isoelectric point in an electric field. Protein crystallization according to the methods of the present invention takes place within a period of hours or less.
Owner:BUKSHPAN SHMUEL
Gradient micro-droplet array forming method based on sequential injection and microfluidic technology
ActiveCN104849111AReduce consumptionHigh degree of automationPreparing sample for investigationLaboratory glasswaresHigh fluxDiluent
The invention discloses a gradient micro-droplet array forming method based on sequential injection and microfluidic technology. The gradient micro-droplet array forming method comprises following steps: step 1, one of a diluent and a sample I is taken using a capillary tube; step 2, the other one of the diluent and the sample I is taken using the capillary tube, and direct contact of the diluent with the sample I is ensured so as to form a sample zone belt with axial concentration gradient; and step 3, the sample zone belt is injected into certain areas of a microporous array chip via the capillary tube so as to obtain sample droplet array with different concentration on the microporous array chip. Advantages of the gradient micro-droplet array forming method are that: concentration gradient generation throughput is high, concentration information is abundant, automatic degree is high; sample consumption is low, and devices and principles are simple. The gradient micro-droplet array forming method can be used for biochemical analysis and screening such as high throughput drug screening, compound toxicity determination, protein crystallization condition screening, catalyst screening, and enzyme dynamic analysis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
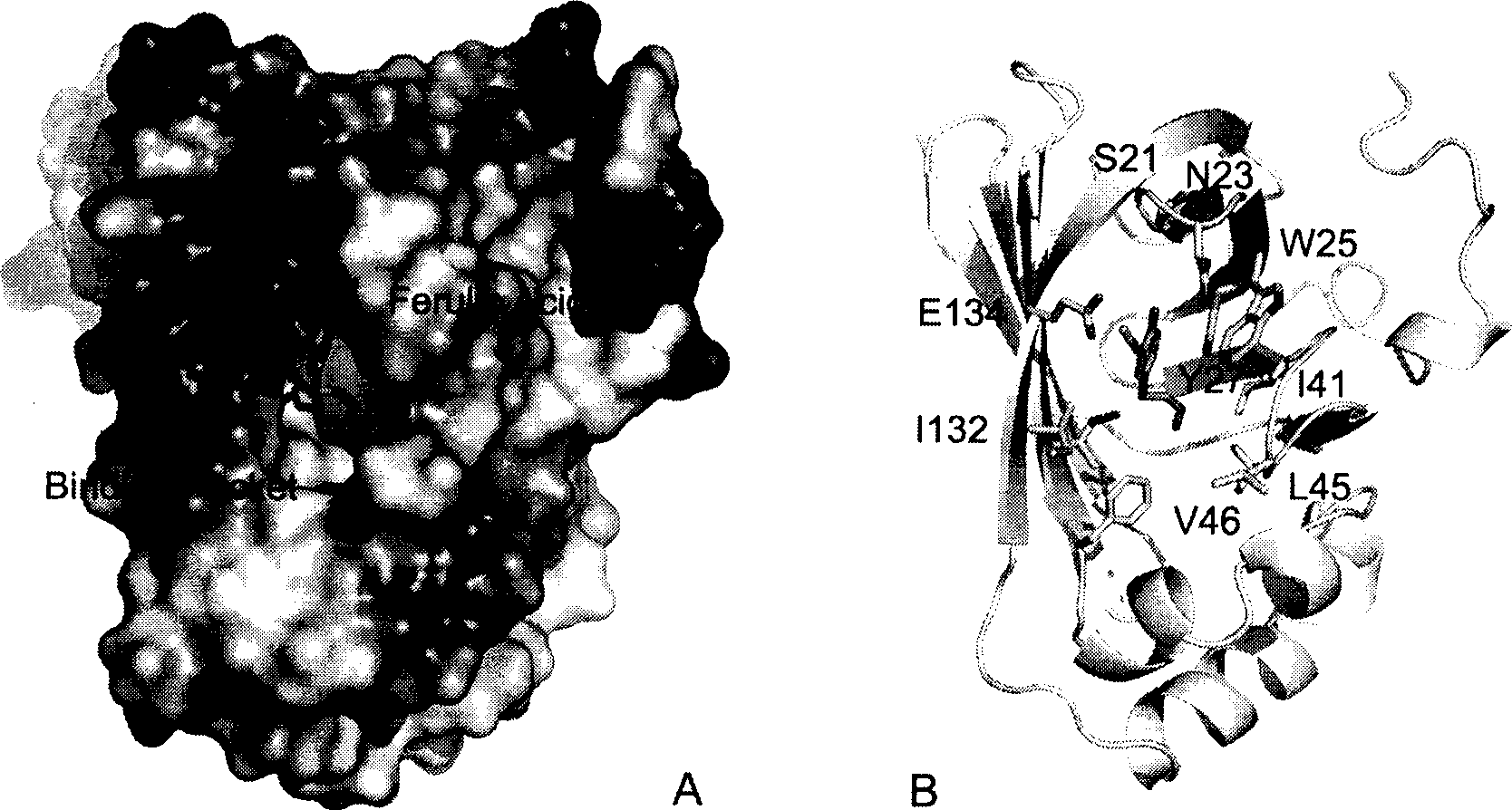
Bacteria ferulic acid decarboxylase gene and crystal structure thereof
InactiveCN101397568AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousEscherichia coli
The invention relates to an expression, purification, crystallization method, structure elucidation and the field of application technology of forulic acid decarboxylase, which belongs to the field of molecular biology and microbiology application. The invention obtains the coding area sequence of the key enzyme forulic acid decarboxylase which decomposes forulic acid to generate 4-vinyl guaiacol in Enterobacter sp.Px6-4 by the gene clone method, expresses the enzyme in a large amount in the colon bacillus ( E.coli BL21 ) by the heterogenous expressing technology, obtains the forulic acid decarboxylase pure products by the purification method and the forulic acid decarboxylase protein crystallization by the hanging-drop crystallization process, and grasps the structure and active centre of the enzyme. The invention can obtain a large amount of highly active forulic acid decarboxylase, and provide theoretical guidance for reconstructing engineering bacteria and improving the output of 4-vinyl guaiacol by analyzing the active centre of the enzyme, thus having good potential application.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
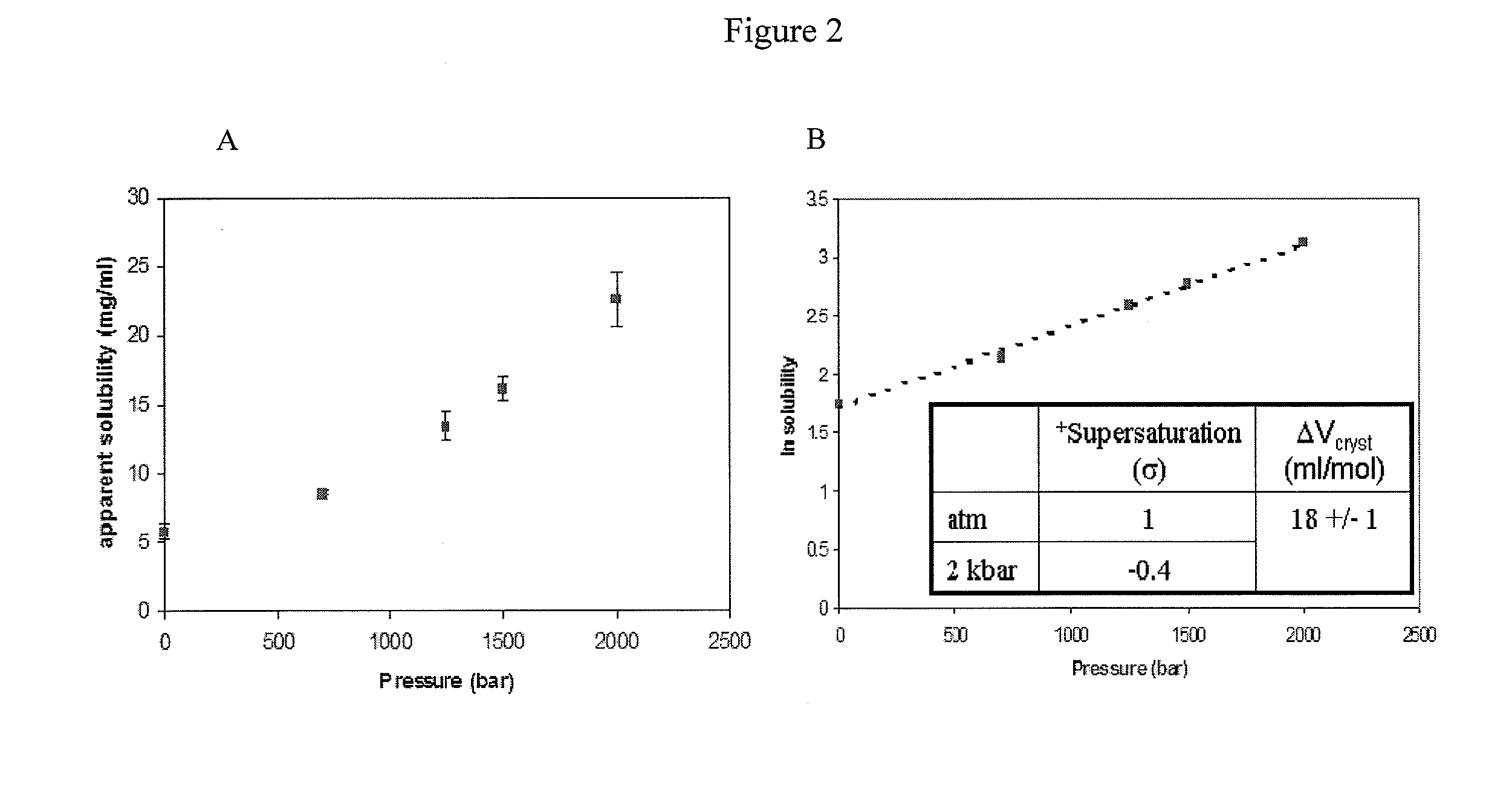
High pressure protein crystallization
InactiveUS20110070219A1Increase the rate of crystallizationFacilitated DiffusionPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsCrystallographyHigh pressure
The present disclosure provides an effective method for the crystallization of proteins at high pressure. A preferential excluding agent, and optionally other reagents may be incorporated into the method. The method is applicable to substantially all proteins.
Owner:SEEFELDT MATTHEW B +2
Zwitterion-containing water-soluble cross-linking agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103880714ASynthetic conditions are mildEasy to implementBacteriaOrganic compound preparationCell AggregationsProtein molecules
The invention discloses a zwitterion-containing water-soluble cross-linking agent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the compound is a formula I. The compound has good water solubility and anti-nonspecific adsorption feature, so that the compound can be used as a cross-linking agent to prepare the polymer with high cross-linking degree, the obtained polymer has excellent biological pollution resistant feature, and can be widely applied to the fields such as biomedicine and materials. The water-soluble cross-linking agent is capable of reducing the protein aggregation speed, so that the protein molecule can be more easily presented in crystal form, and therefore the water-soluble cross-linking agent can be used for synthesizing the biomaterial for promoting protein crystallization. Furthermore, the cross-linking agent molecule comprises two-NH-C=O groups capable of generating hydrogen bond interaction with the carbohydrate (-OH) abound on the surface of microorganism; therefore, the cross-linking agent molecule can be used as an additive to prepare a molecular imprinting film material so as to selectively separate the microorganism (structural formula).
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
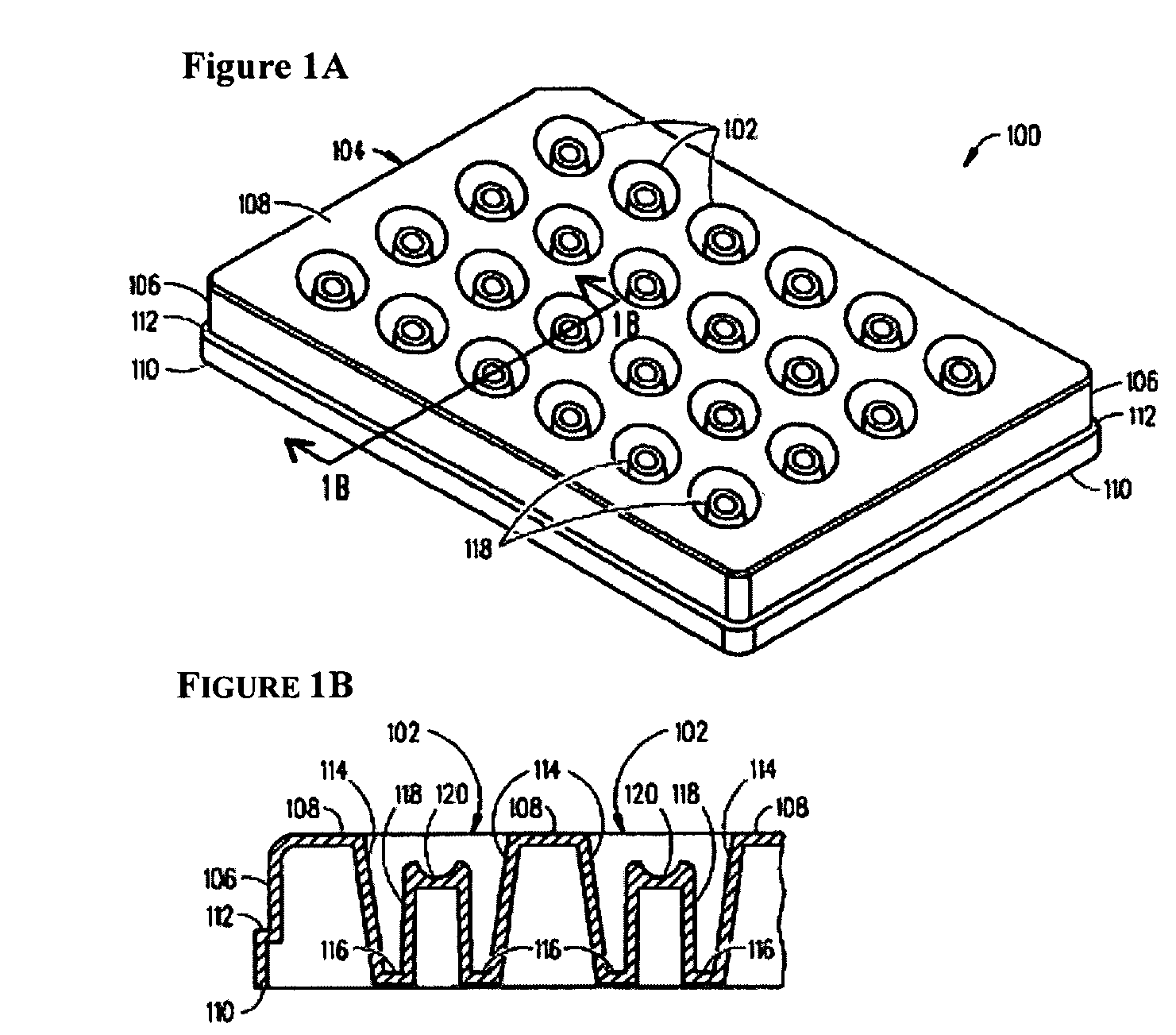
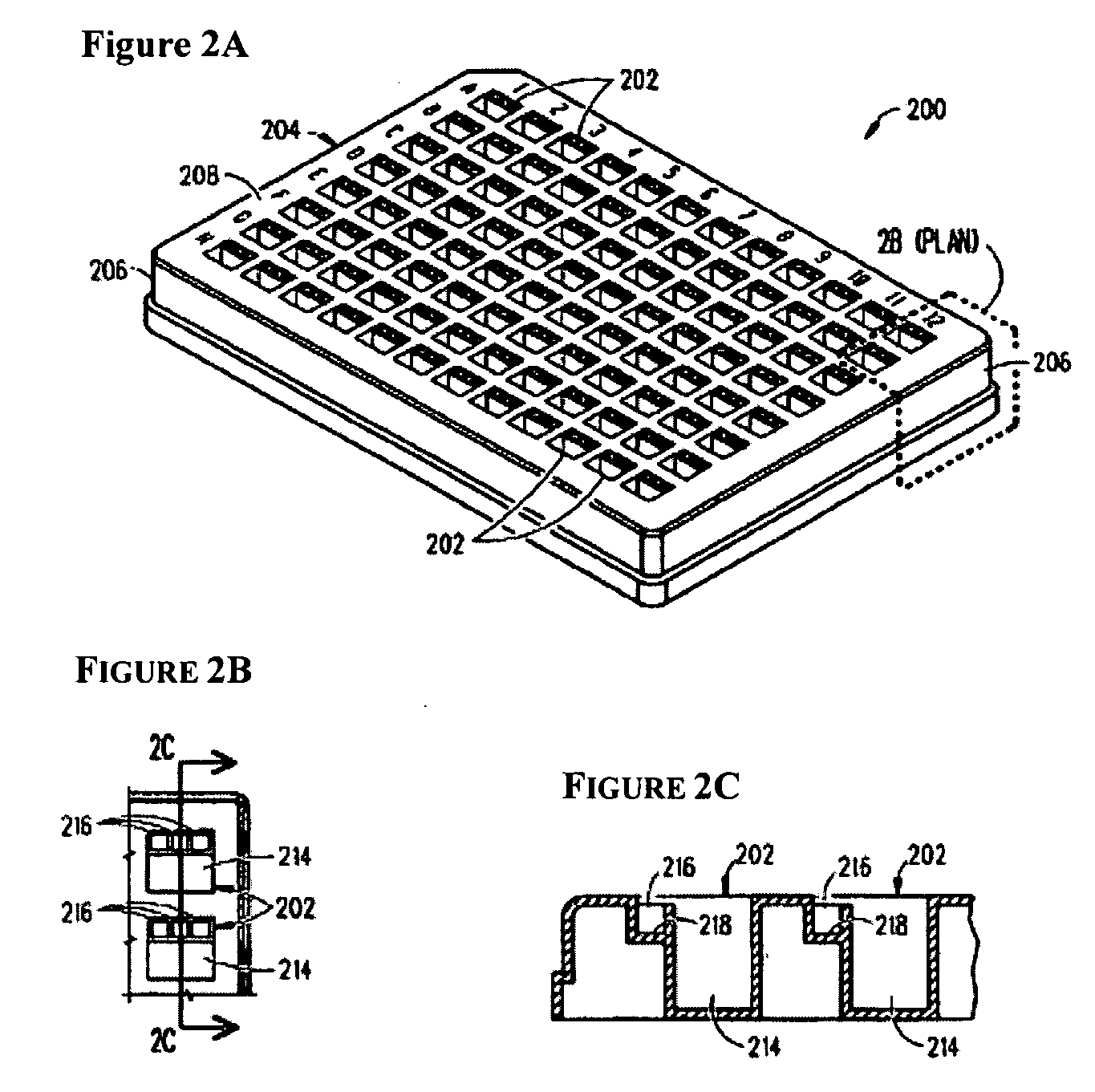
Array for crystallizing protein, device for crystallizing protein and method of screening protein crystallization using the same
InactiveUS20050075482A1Conveniently and highly efficiently crystallizingConveniently and highly efficiently crystallizing proteinBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsMicroarrayProtein crystallization
The present invention relates to a method of precipitating protein crystals from a protein-containing sample. The present invention also relates to a novel microarray and a novel device for screening for protein crystallization condition. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a method of conveniently and quickly screening for protein crystallization conditions using the microarray or the device having highly integrated and held crystallization conditions even with an extremely small quantity of a sample.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Automated sample analysis system and method
ActiveUS7596251B2Minimize movementFrom normal temperature solutionsDiagnosticsTemperature controlTransport system
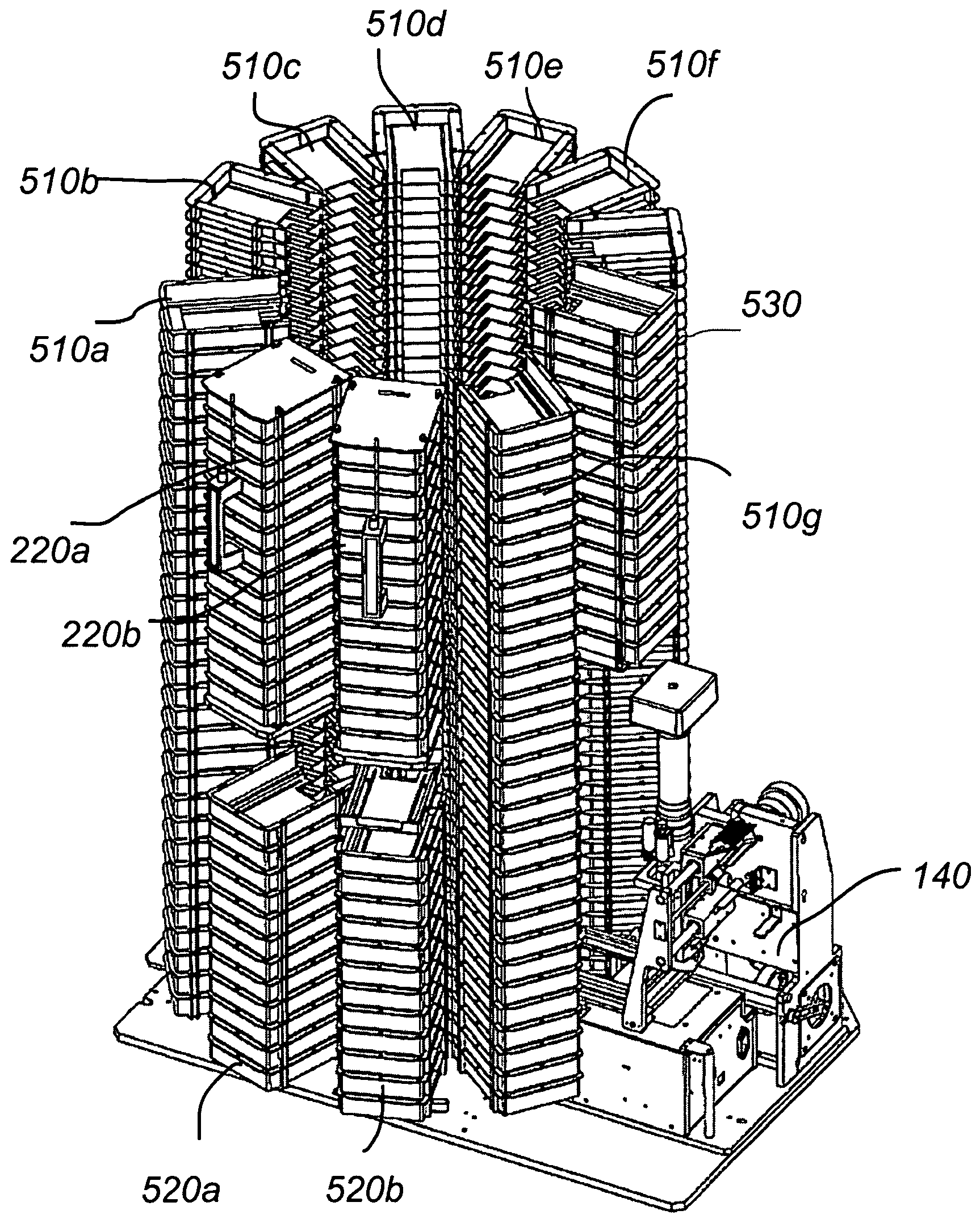
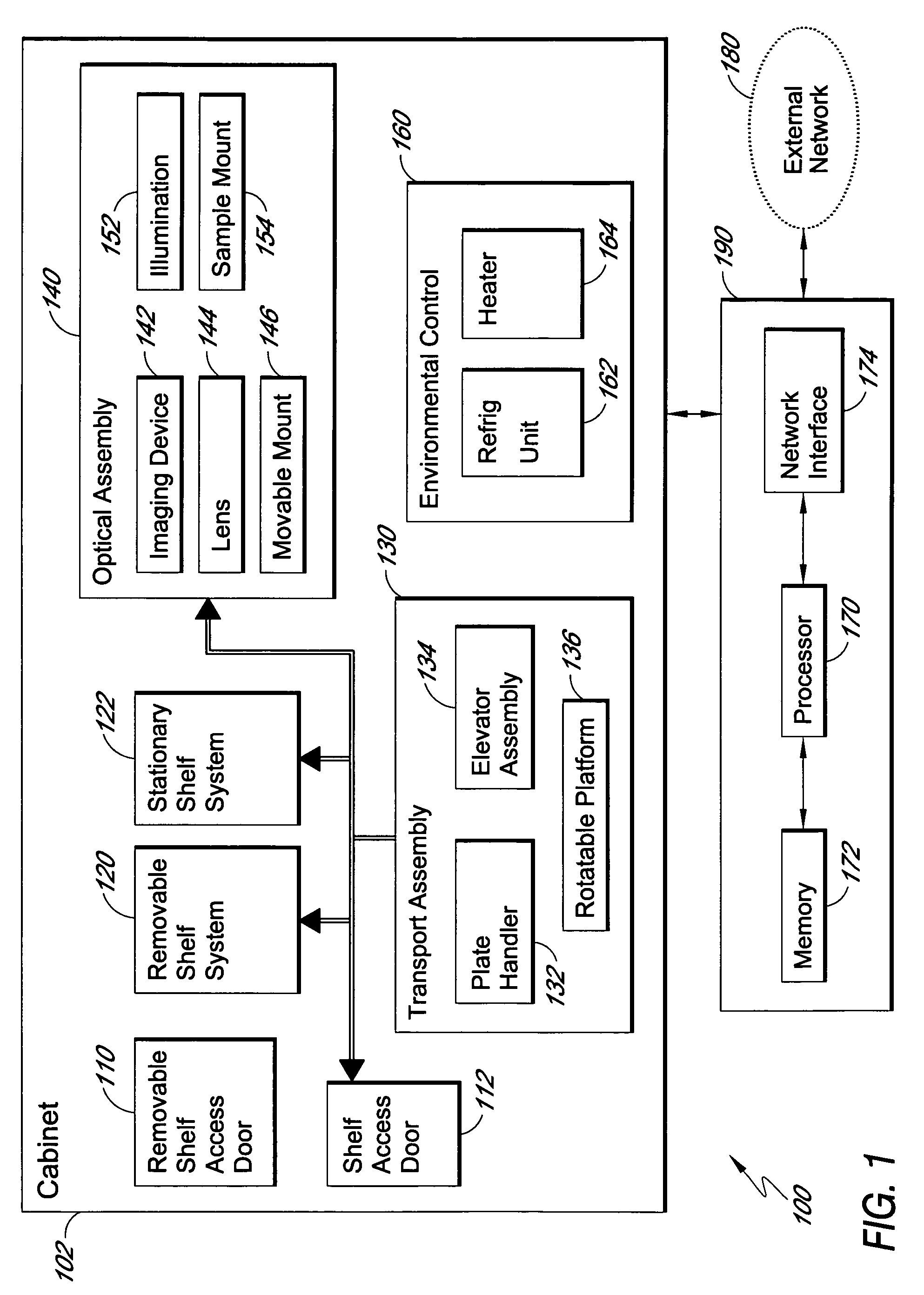
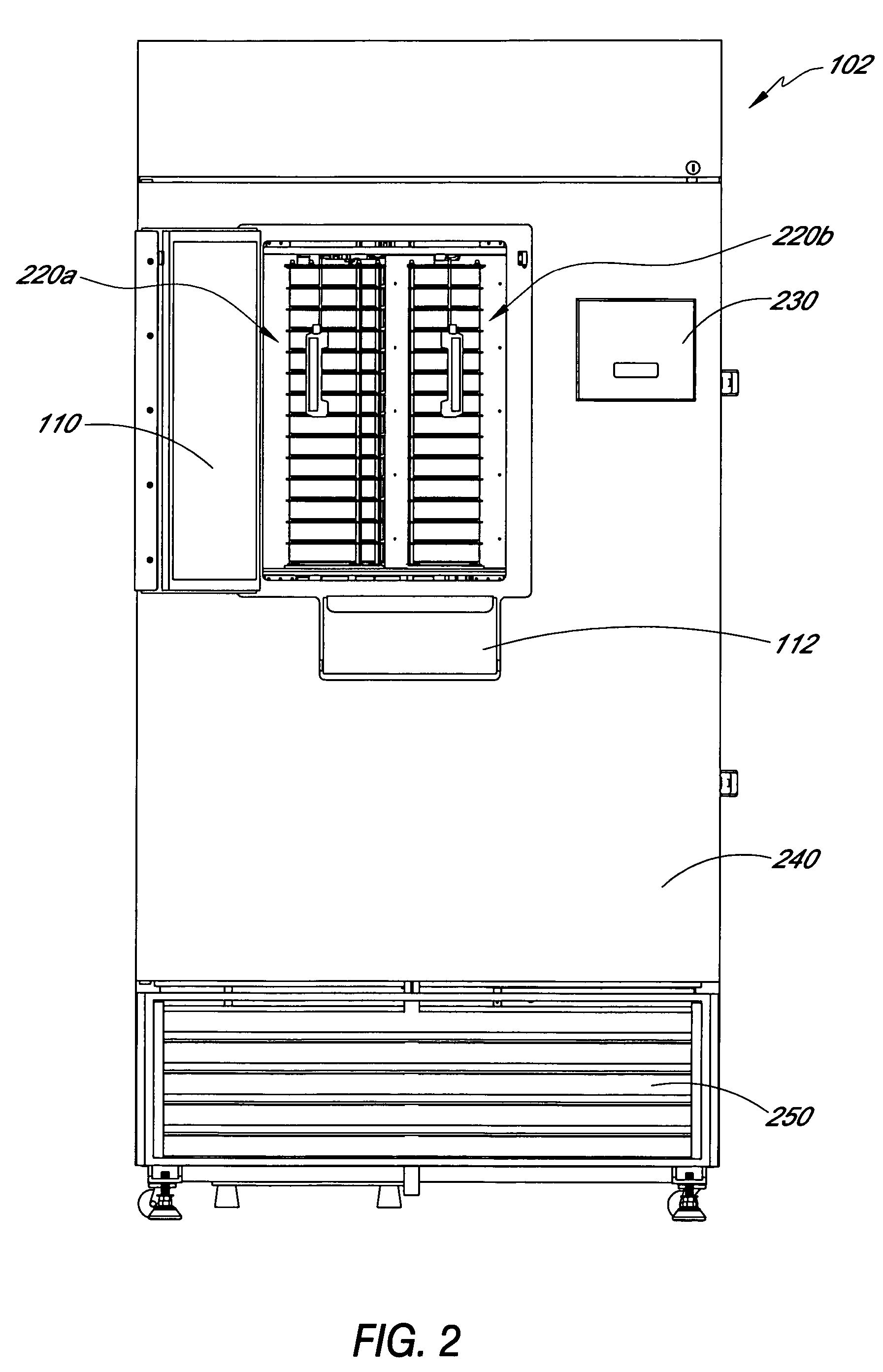
An automated biological sample analysis system and method for use in incubating and analyzing multiple samples for protein crystallization. A temperature controlled cabinet houses sample storage, sample transport, and sample imaging systems. The operation of the system is automated and can be controlled by software, which can be reconfigured remotely. An array of storage shelves includes multiple shelf columns arranged around a core. Multiple banks of removable shelves arranged as magazines are accessed through a door on the cabinet. Each shelf stores a multi-well plate and different sizes can be stored in different shelves. The core houses a sample transport system that includes a multi-axis robot that rotates about a vertical axis to access the shelves in the shelf array. The transport system retrieves and replaces the multi-well plates in the shelves and can move plates from the shelves to an imaging system where each sample can be automatically imaged.
Owner:NEXUS BIOSYSTEMS INC
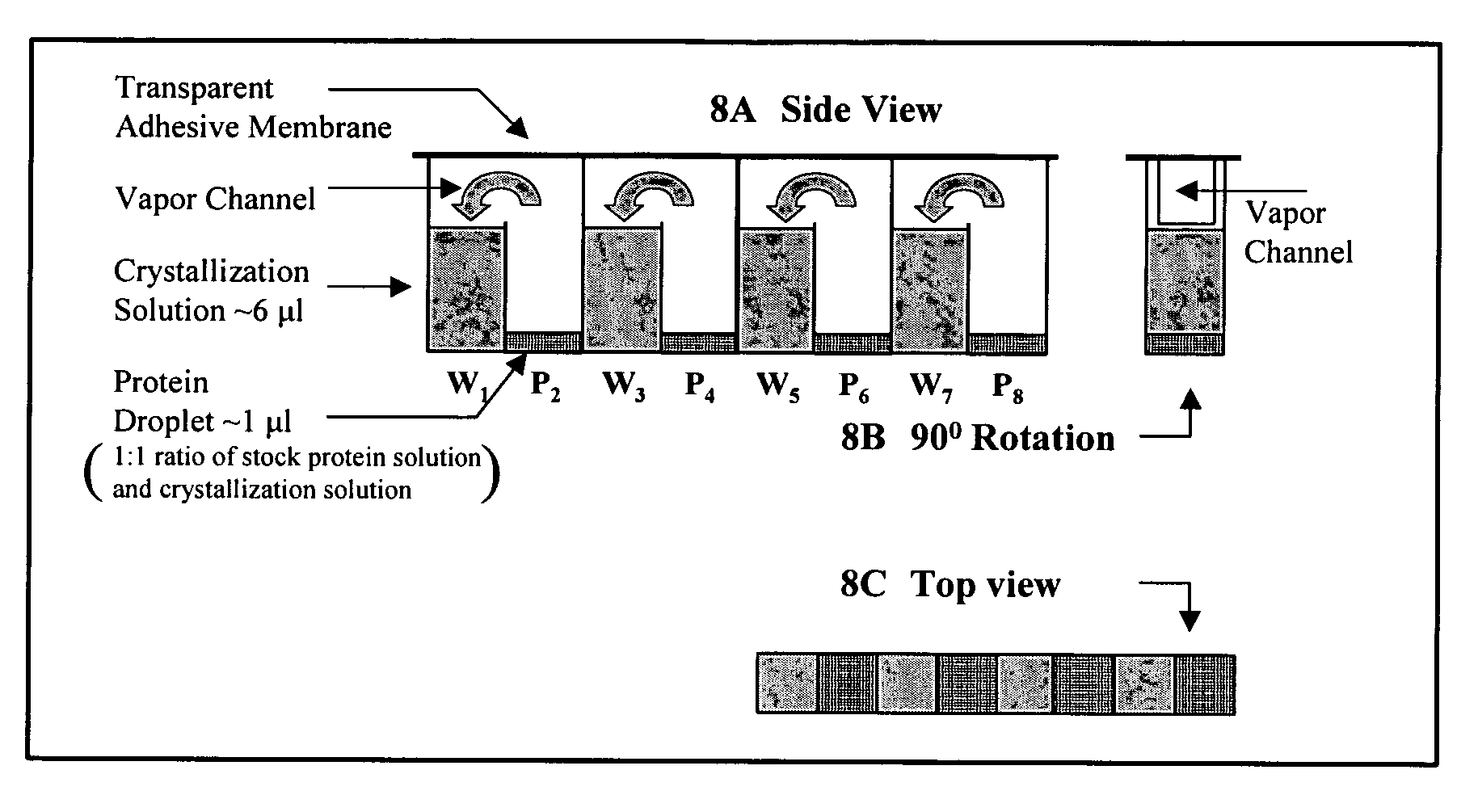
Device and method for high throughput screening of crystallization conditions in a vapor diffusion environment
InactiveUS20090111711A1Enable formationEasy to handlePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsProtein solutionMicro perforated plate
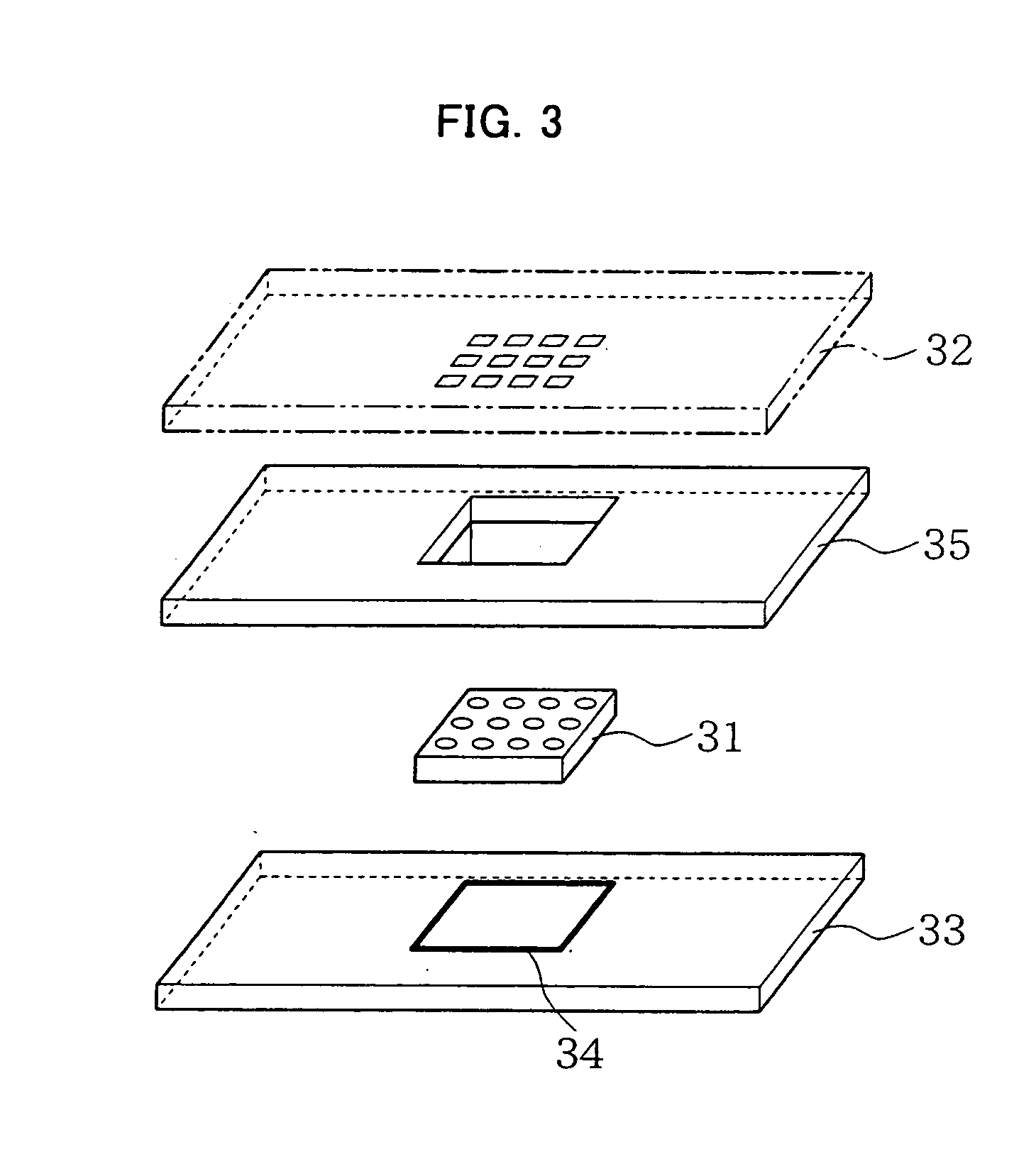
A high-density high-throughput microplate and methods for simultaneously screening a plurality of protein crystallization solutions and for producing diffraction quality protein crystals in a vapor-diffusion environment are disclosed. The microplate has defined side-by-side paired chambers of equal size, wherein the side-by-side paired chambers have a maximum volume of about 8 μl, and wherein the paired chambers have a vapor channel, therein providing vapor exchange between the side-by-side paired chambers. The microplate further includes a membrane to seal the surface of the microplate. The microplate is adapted to receive a crystallization solution in one of the side-by-side paired chambers and a protein solution in the other of the side-by-side paired chambers, wherein the protein solution and the crystallization solution interact via a vapor diffusion process, which enables the formation of protein crystals within the chamber that contains the protein solution.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Microfluidic protein crystallography
InactiveUS7244402B2High throughput screeningImprove throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsFrom normal temperature solutionsProtein crystallizationBiology
The use of microfluidic structures enables high throughput screening of protein crystallization. In one embodiment, an integrated combinatoric mixing chip allows for precise metering of reagents to rapidly create a large number of potential crystallization conditions, with possible crystal formations observed on chip. In an alternative embodiment, the microfluidic structures may be utilized to explore phase space conditions of a particular protein crystallizing agent combination, thereby identifying promising conditions and allowing for subsequent focused attempts to obtain crystal growth.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Process for producing crystalline nucleus and method of screening crystallization conditions
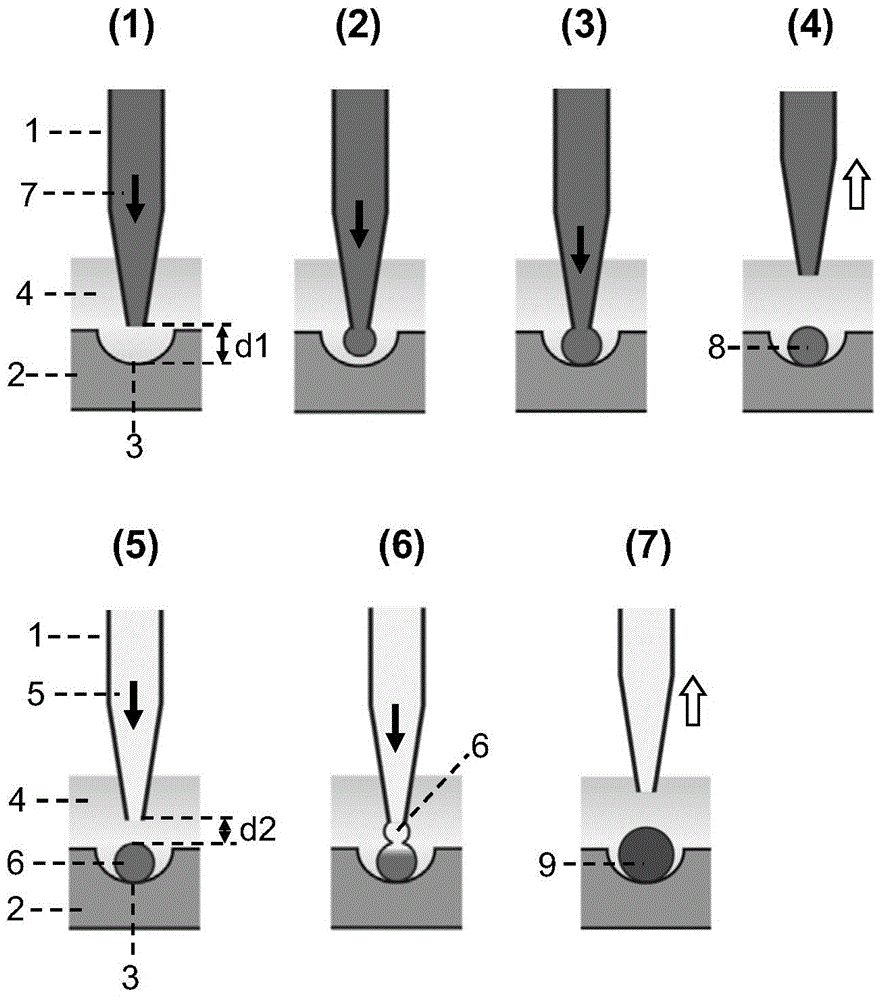
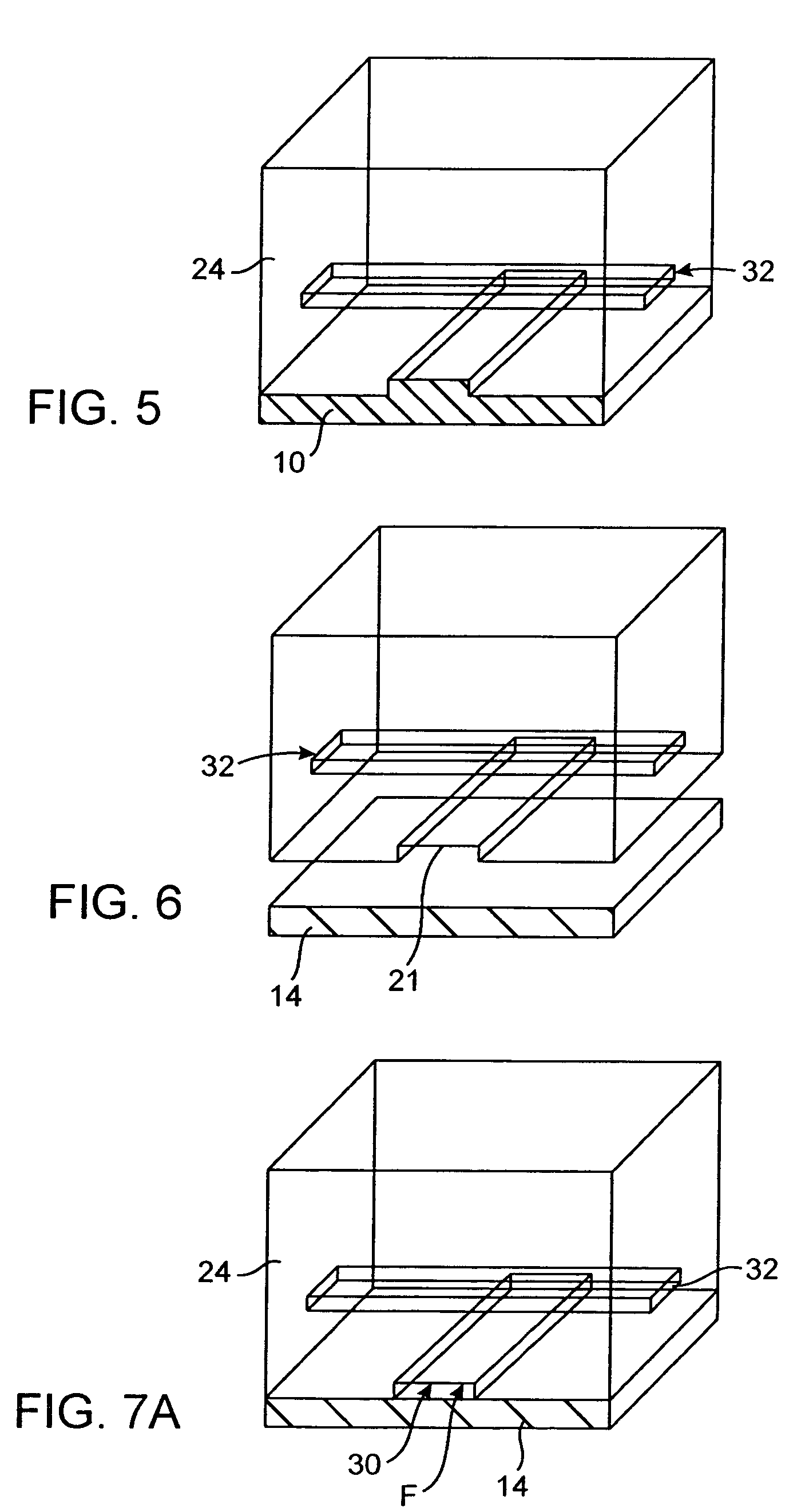
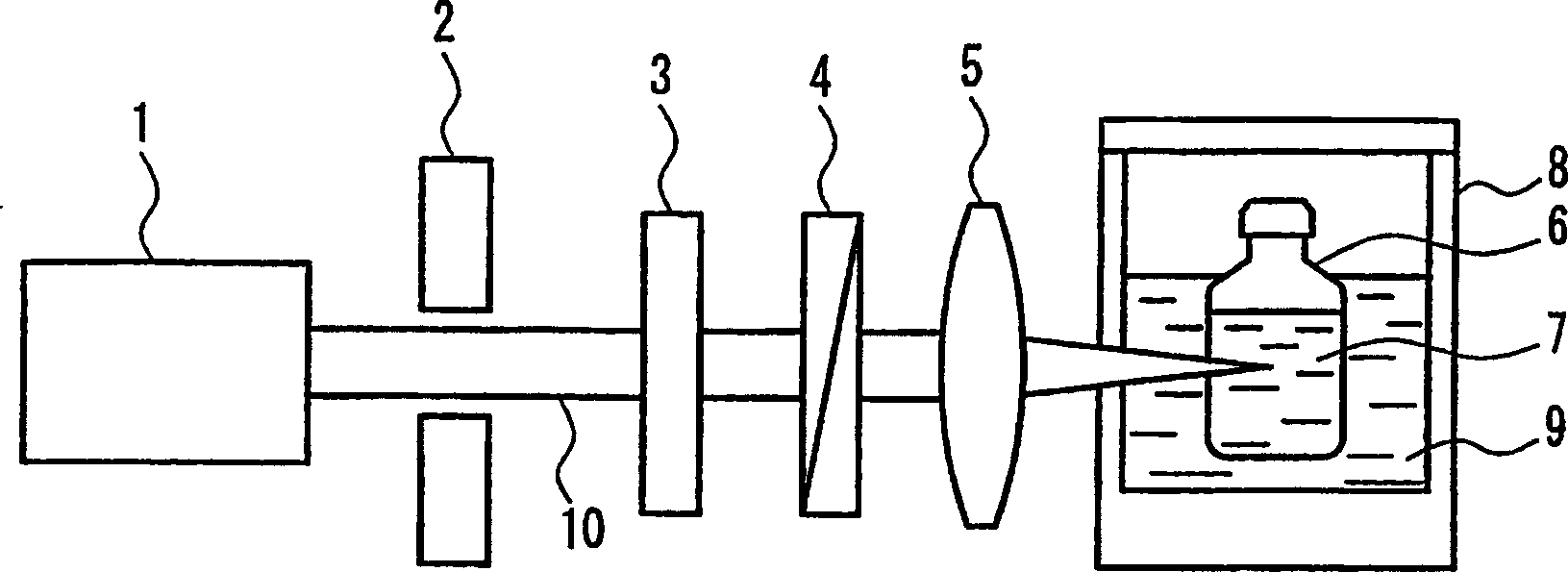
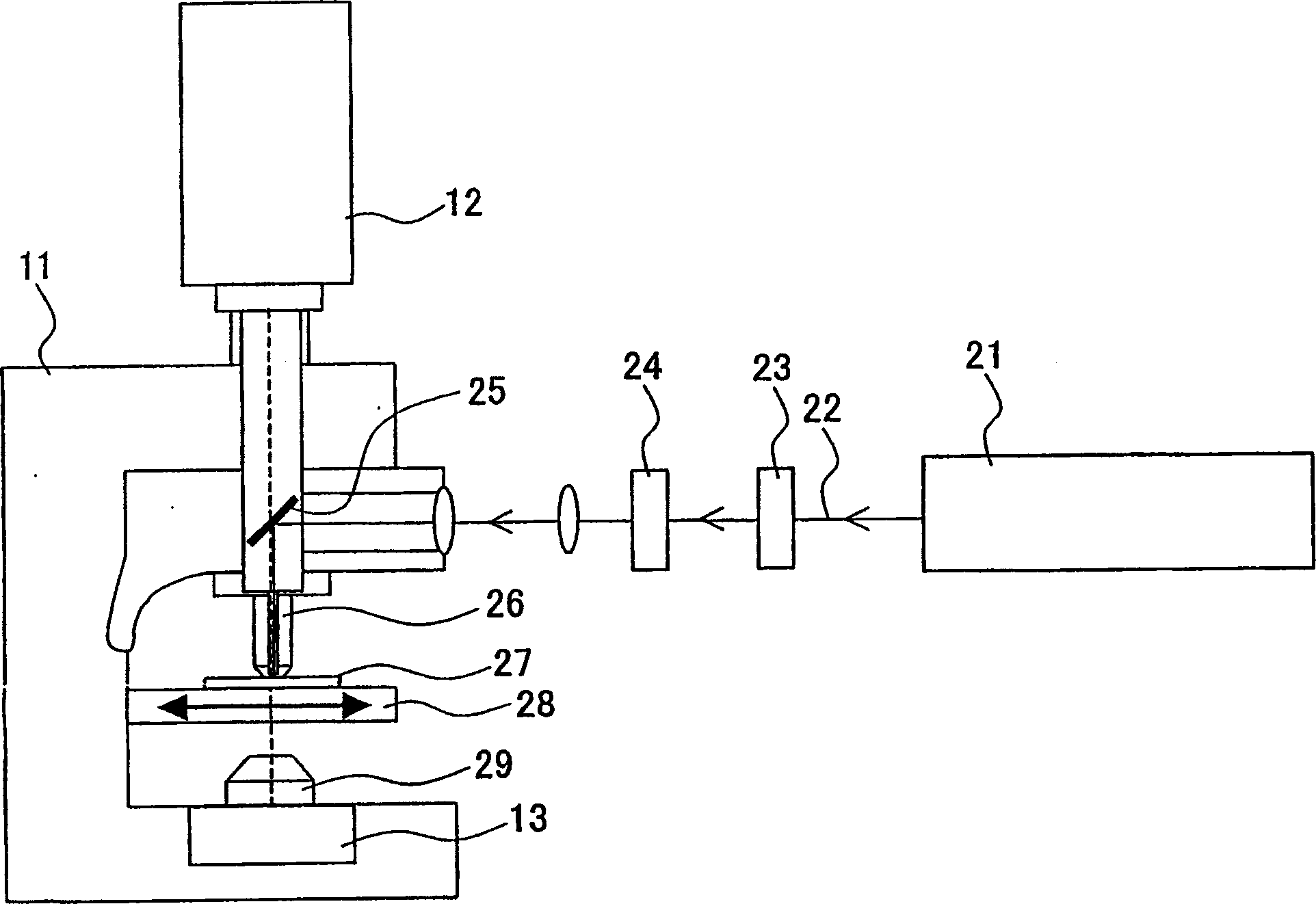
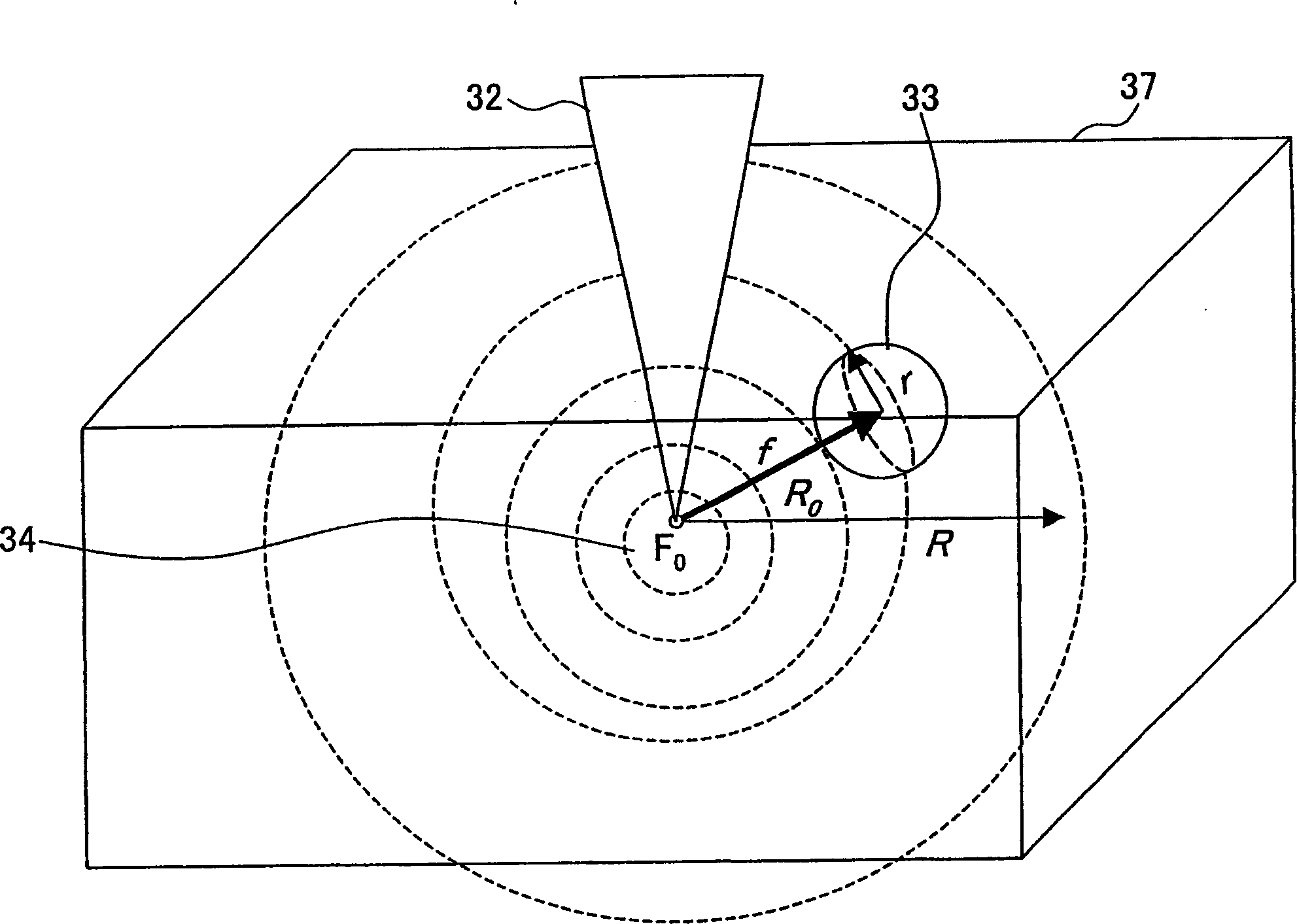
InactiveCN1678773AGenerate efficientlyQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsFemto second laserSapphire
The present invention relates to a process for producing high-quality crystals of protein or organic substances easily and efficiently. A solution of protein or an organic substance is prepared and then is cooled slowly to be supersaturated to a low degree. This supersaturated solution is irradiated with a femtosecond laser 10. A local explosion phenomenon occurs at the focal point of the laser and thereby a crystalline nucleus is generated. A high-quality crystal is obtained when a crystal is grown on the crystalline nucleus over a long period of time. The femtosecond laser to be used herein can be a titanium:sapphire laser having a wavelength of 800 nm, a duration of 120 fs, a frequency of 1 kHz, and an output of 400 mW.
Owner:CHUANGJING CO LTD
Method for crystallizing protein by using ion liquid
InactiveCN101092445AHigh diffraction intensityGood repeatabilityPeptide preparation methodsProtein solutionSingle crystal
This invention provides a method for crystallizing proteins from protein solution with ionic liquid-water mixed solution. The ionic liquid-water mixed solution is composed of ionic liquid 1-85wt.%, and buffer solution 1-25 wt.%, and the pH value is 4.0-11.0. The method has a wide process conditions, and can obtain protein single crystals with different morphologies under different conditions. The obtained protein single crystals have such advantages as high diffractive intensity, high repeatability and high operability.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Protein crystallization screening 96 condition kit using polyethylene glycol as precipitator
InactiveCN101817869AReduce typesLow costPeptide preparation methodsEnzymesPolyethylene glycolBiological macromolecule
The invention discloses a protein crystallization screening 96 condition kit using polyethylene glycol as a precipitator and aims to solve the technical problem existing in the conventional 96 condition screening kit that the success rate of protein crystallization condition screening is low. The PEG adopted in the technical scheme is the top eight types PEG which are most frequently used according to the statistical data of a BMCD database rather than selected randomly, so that the crystallization success rate of biological macromolecules is obviously improved. For example, the success rate of canavaline is increased from 4.2 percent in background technology to 81.2 percent, the success rate of lysozyme is increased from 29.2 percent in background technology to 46.9 percent, the success rate of protease K is increased from 58.3 percent in background technology to 66.7 percent, and the success rate of catalase is increased from 15.6 percent in background technology to 30.2 percent. In addition, the kit uses the PEG as the precipitator, a few types of reagents are used, and compared with the background technology kit, the kit of the invention is lower in cost.
Owner:海安华达石油仪器有限公司 +1
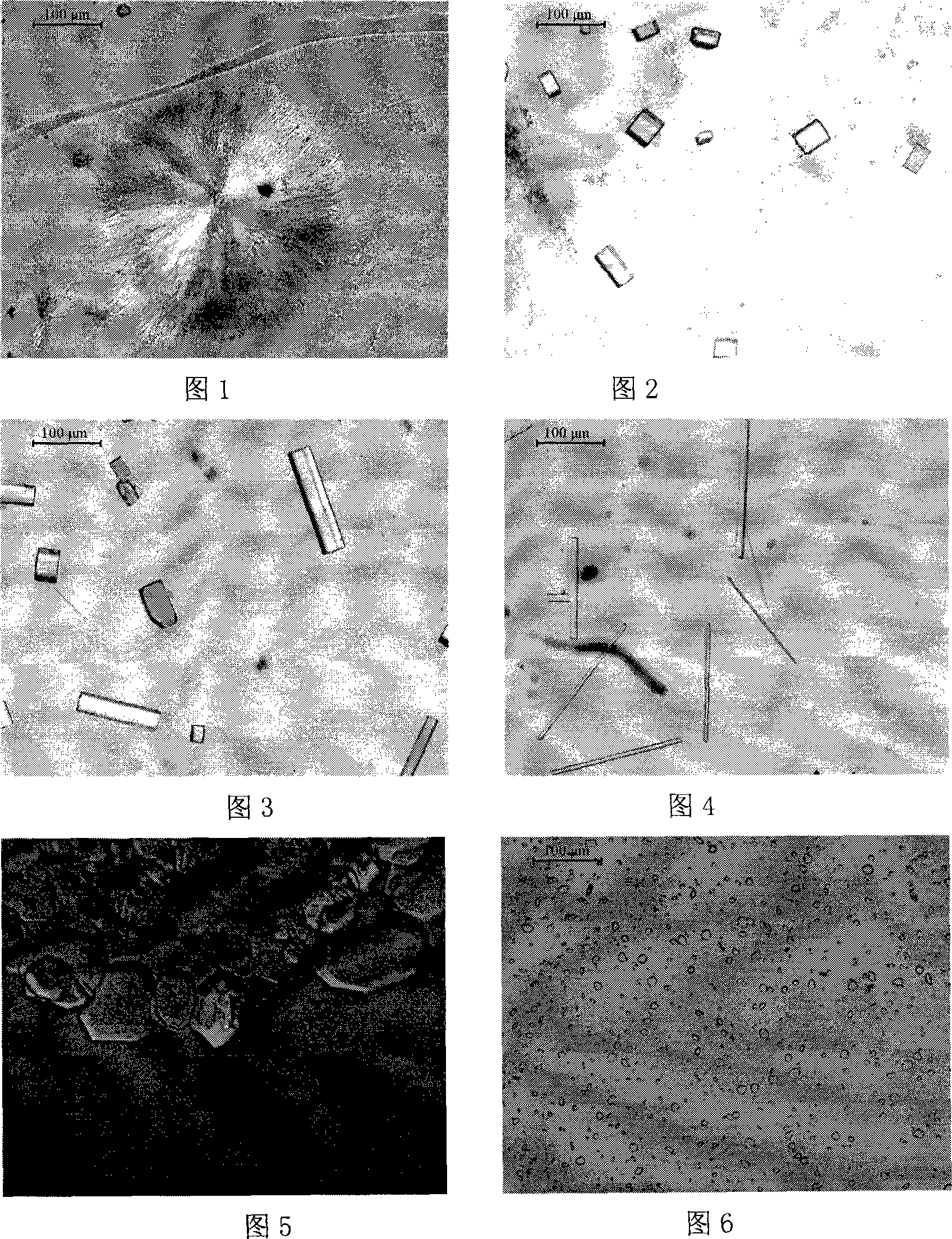
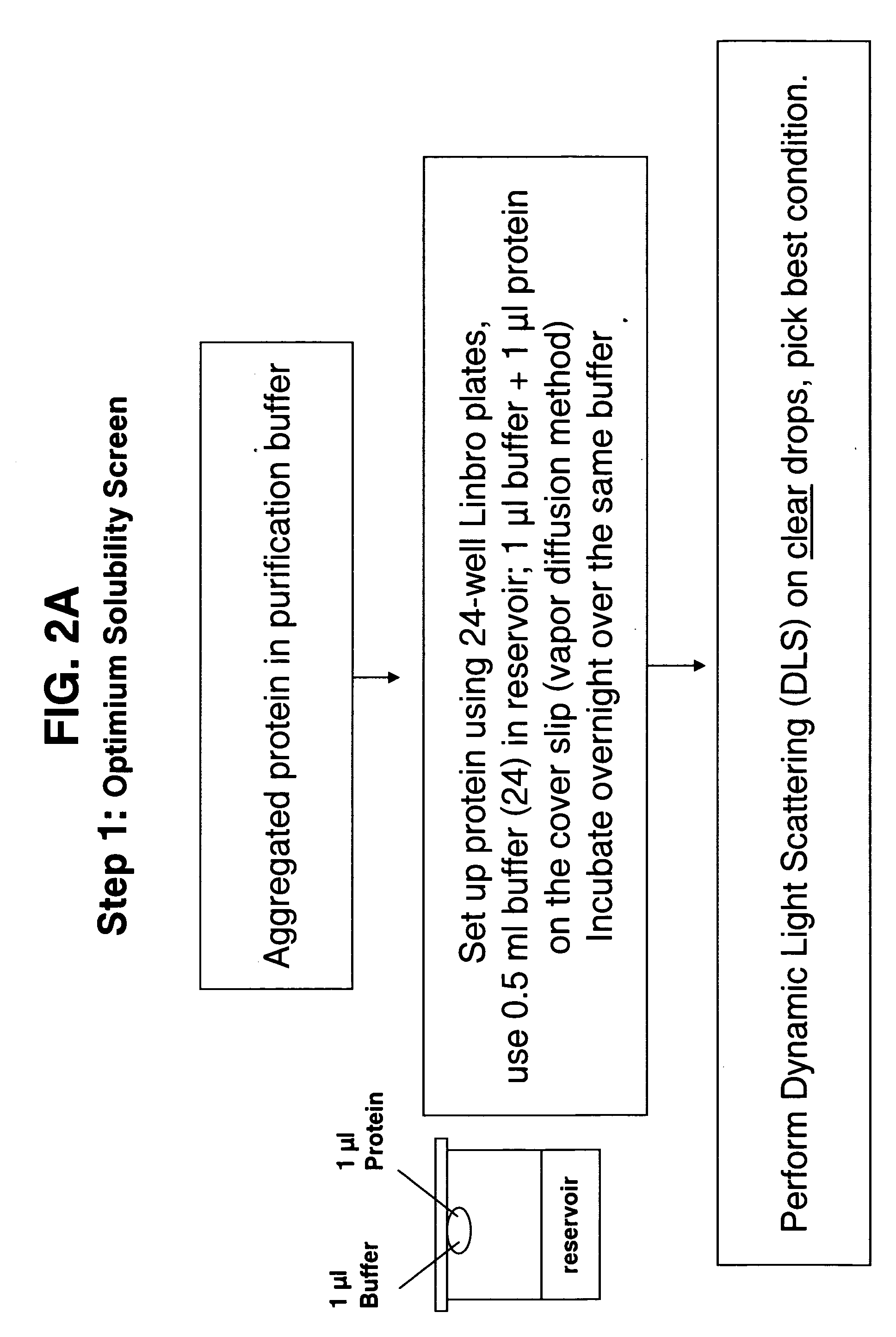
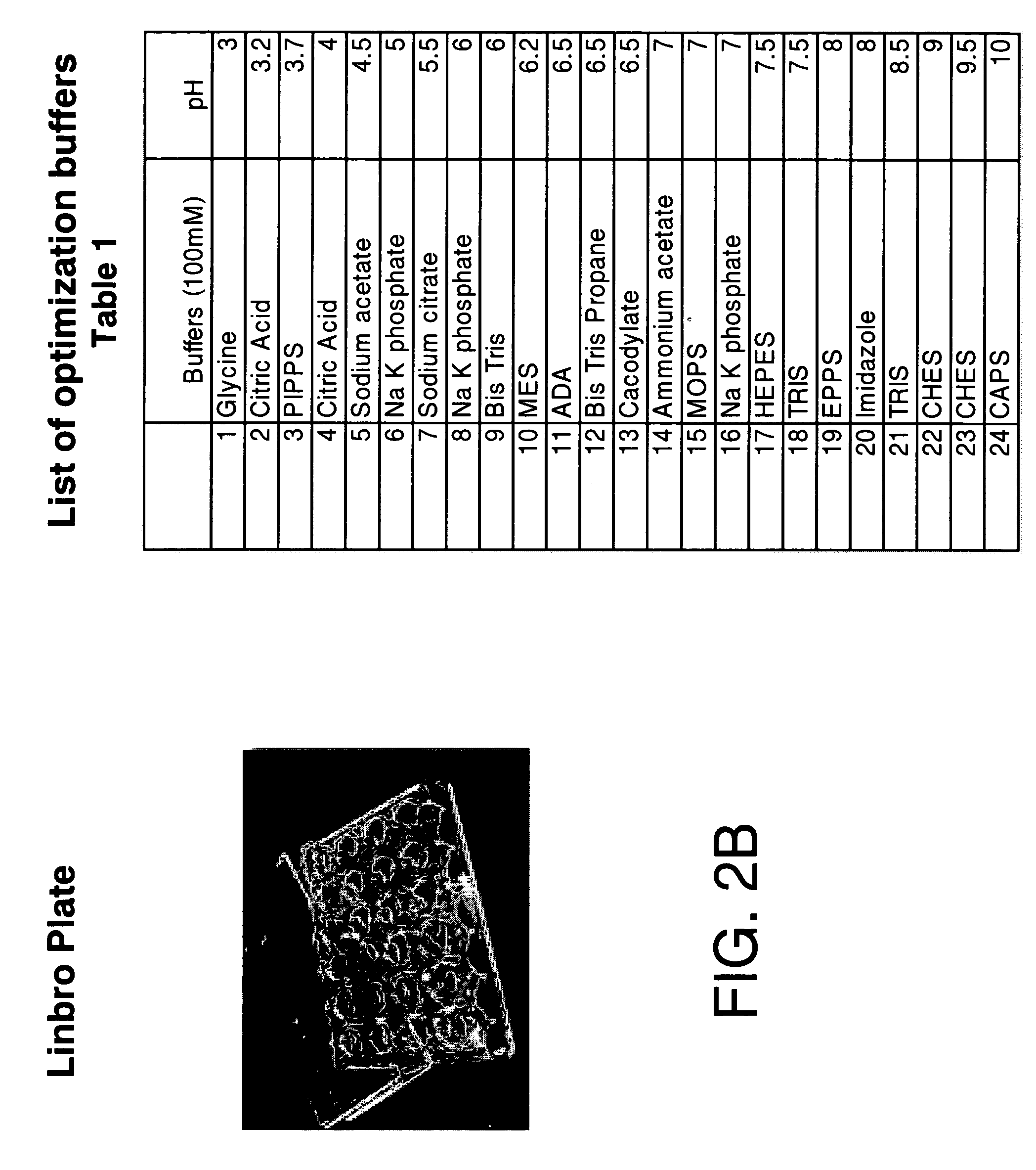
High-throughput method for optimum solubility screening for homogeneity and crystallization of proteins
Herein is described and optimum solubility screen in which a panel of buffers and many additives are provided in order to obtain the most homogeneous and monodisperse protein condition for protein crystallization. The present methods are useful for proteins that aggregate and cannot be concentrated prior to setting up crystallization screens. A broad range of buffers is intended for use in this screen. A high-throughput method using the hanging-drop method and vapor diffusion equilibrium and a panel of twenty-four buffers is further provided. After monitoring precipitation, the conditions leading to clear drops are selected for evaluation, preferably dynamic light scattering (DLS) characterization. If the DLS results are not optimal, a series of additives are tested in the presence of the best buffer selected from the initial screen and again DLS is used to determine the best condition. Using the present methods, 14 poorly behaving proteins have been screened, resulting in 11 of the proteins having highly improved DLS results allowing concentration of the proteins, and 9 were crystallized.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for selecting buffer solution for protein crystallization
InactiveCN103333219AIncrease nucleation rateImprove crystallization efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesProtein solutionNucleation
The present invention provides a method for selecting a buffer solution for protein crystallization. The method comprises: preparing a uniformly distributed buffer solution to dissolve protein; mixing a crystallization reagent and the protein solution or mixing a crystallization reagent, the buffer solution and a protein sample to prepare a protein crystallization solution; and standing in a sealed crystallization plate until crystallization. According to the present invention, the appropriate protein crystallization buffer solution pH value condition is selected, such that protein solubility is changed in a wide range, and protein crystal nucleation probability is increased so as to increase crystallization efficiency.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com