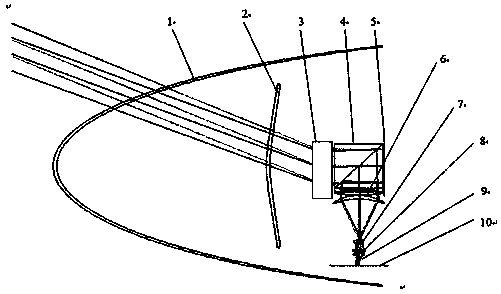
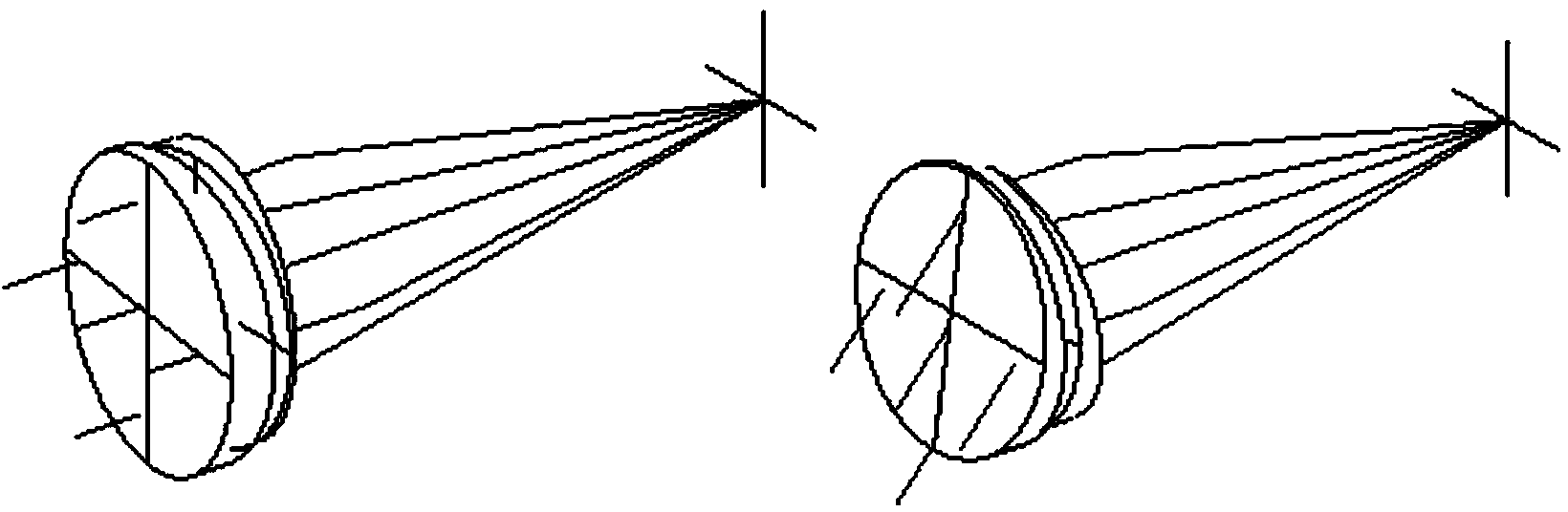
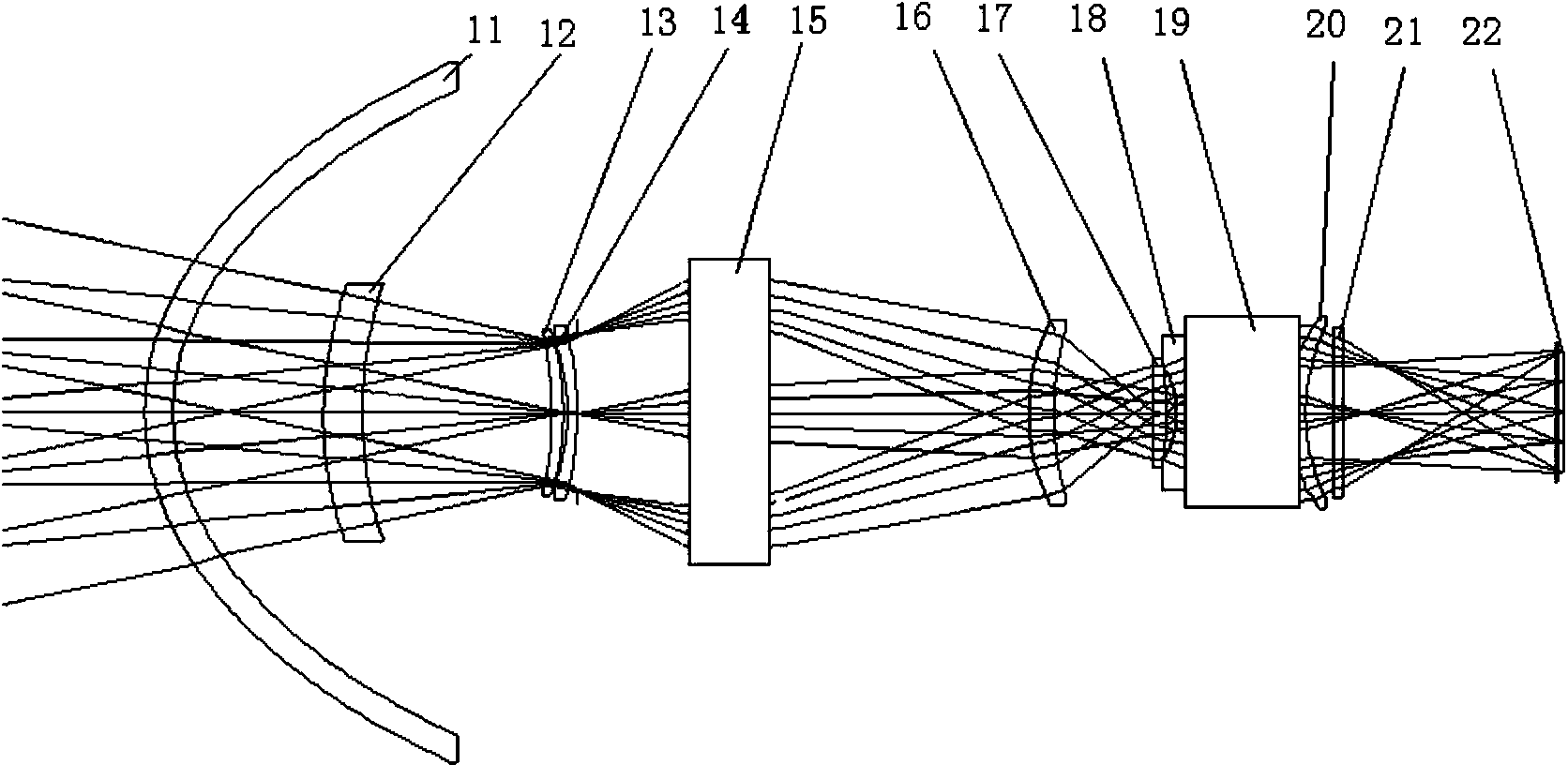
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
136 results about "Prism pair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gun sight compensator
A range compensator for a gun sight for an associated gun is provided. The compensator includes at least one Risley prism pair that is rotatable in opposite relative directions about a common axis; mounting means for mounting the Risley prism pair to the sight between the sight and a target at a distance; and, a respective rotator associated with the Risley prism pair for rotating each prism in the Risley prism pair about the axis that is generally aligned with the path. The prisms are rotatable between an unrefracted range finding position in which a “line of departure” required to ensure the projectile strikes the target is determined and a refracted firing position in which the path of light extending between the sight and the target is refractively deviated to maintain the target centered with the sight when the gun is positioned along the required “line of departure”.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
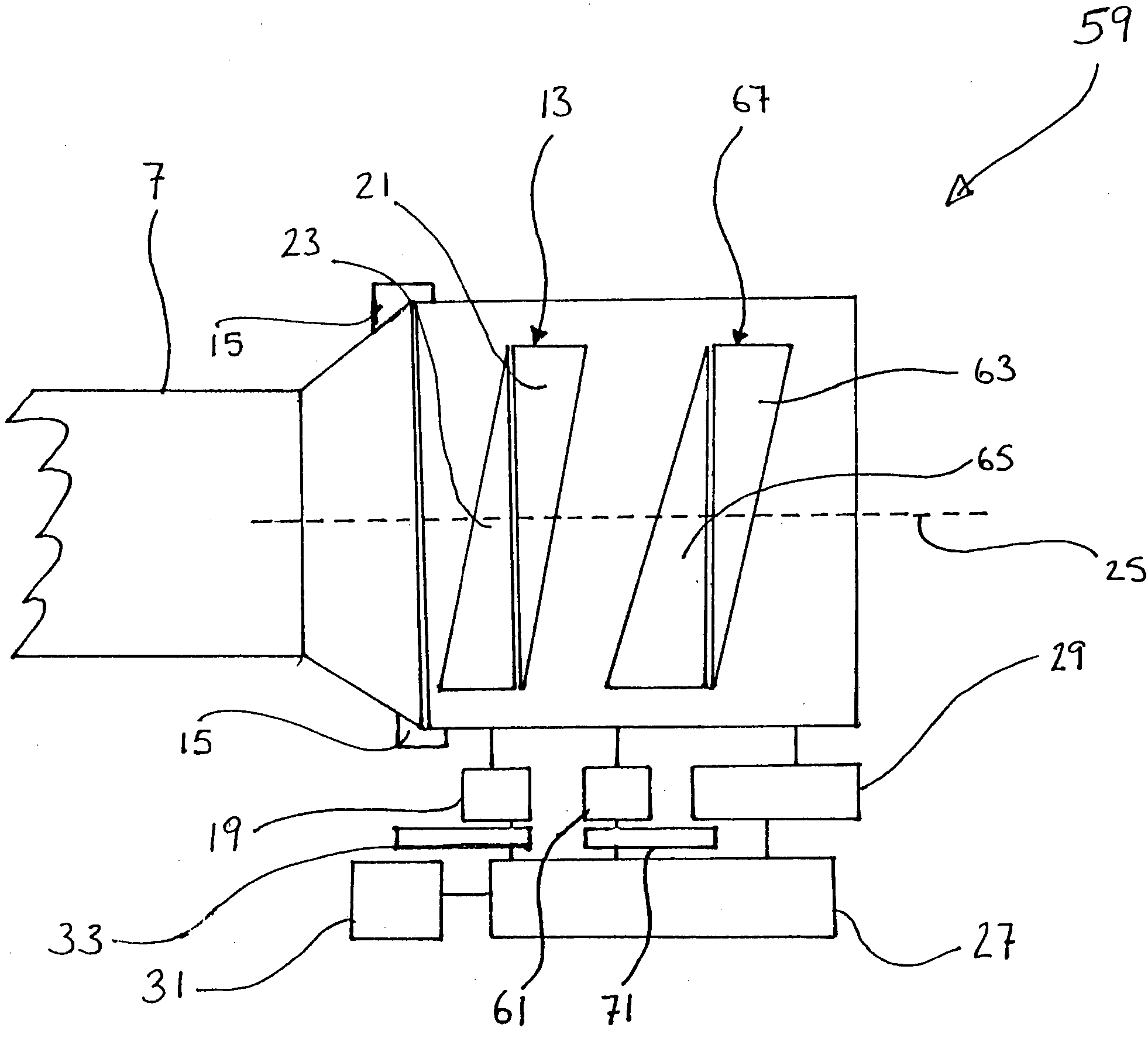
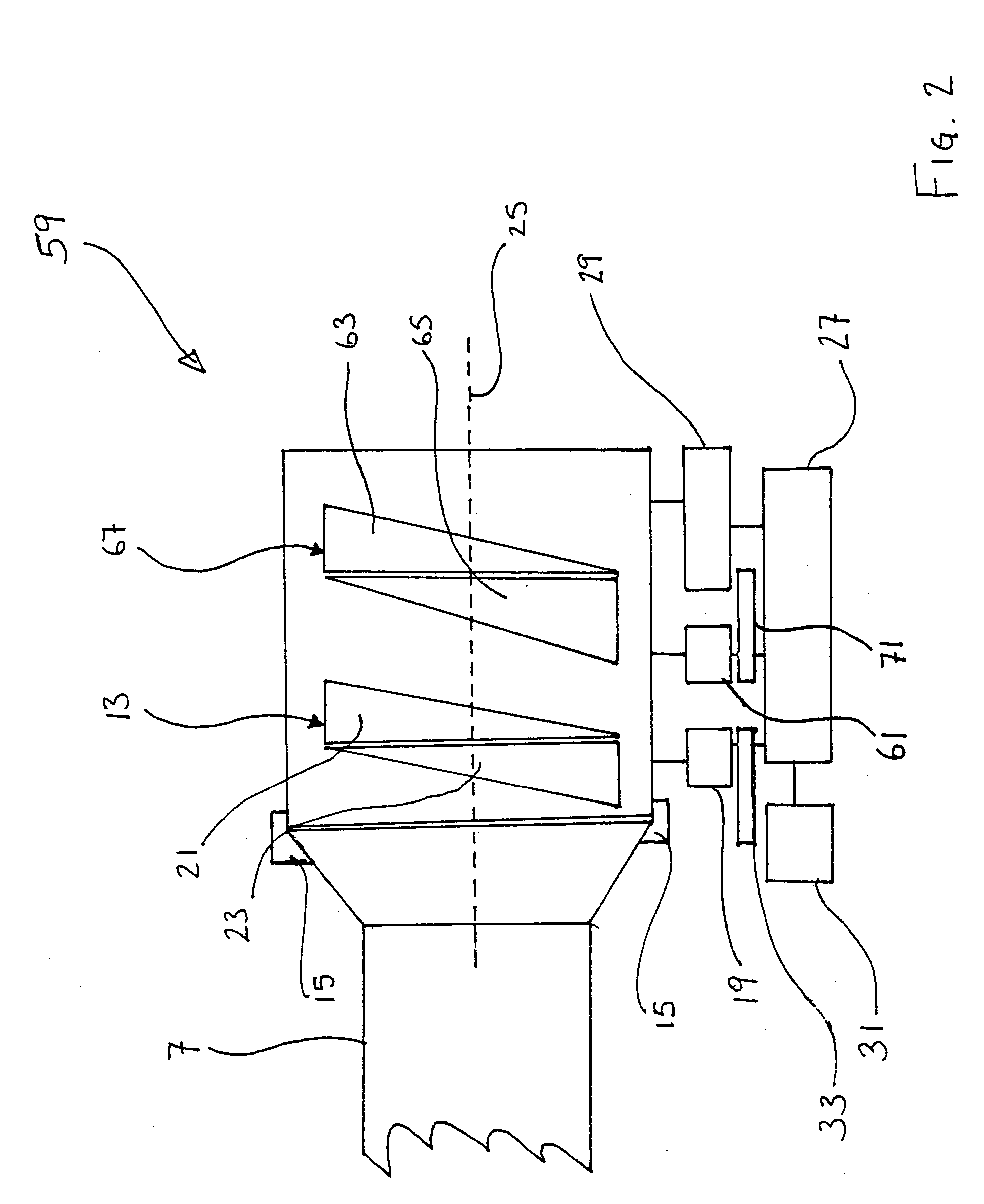
Rotary scanning laser head with coaxial refractive optics
ActiveUS7009141B1Expand accessMinimized cross sectionLaser beam welding apparatusCamera lensMotor speed
A rotary refractive laser scanner head uses two sets of lenses and prisms aligned along a common optical axis. Each prism is paired with one of the lenses. The lens-prism pairs are separately mounted rotatable on a common axis coaxial with the optical axis. A motor drives two gear sets. Each gear set is separately coupled to one of the two lens-prism pairs and rotates them at selected, typically different speeds. An input laser beam is directed along the optical axis at one of the lens-prism pairs. The first pair collimates and refracts the input beam into an intermediate deflected beam according to Snell's law and the characteristics of the laser beam and optics. The second pair receives the intermediate beam and further deflects it to form an output beam. By selecting the motor speed, gear ratios, optics spacing, characteristics and prism wedge (deflection) angle, the scanner head effectively can scan an output laser beam over a desired pattern area.
Owner:GEN LASERTRONICS
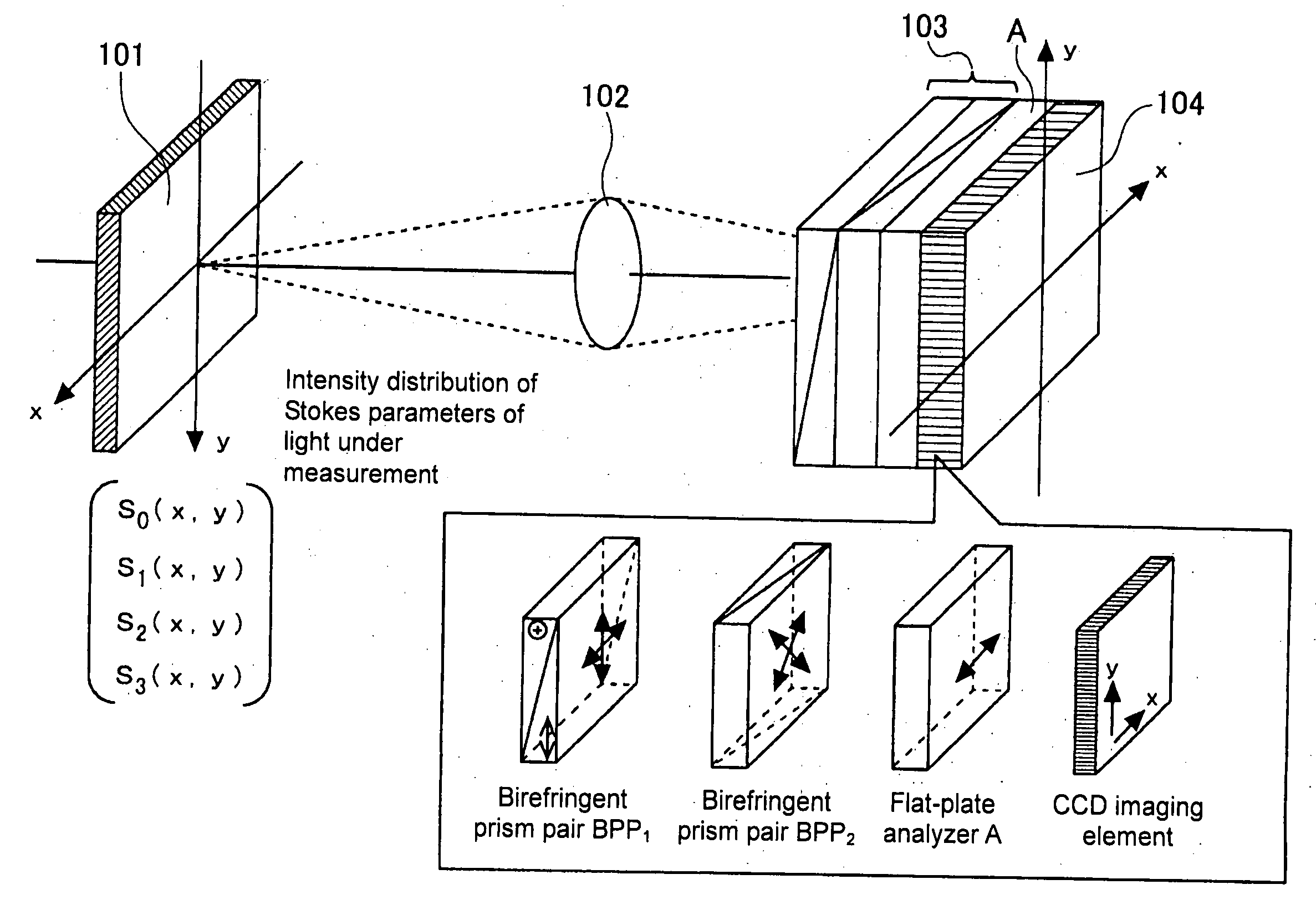
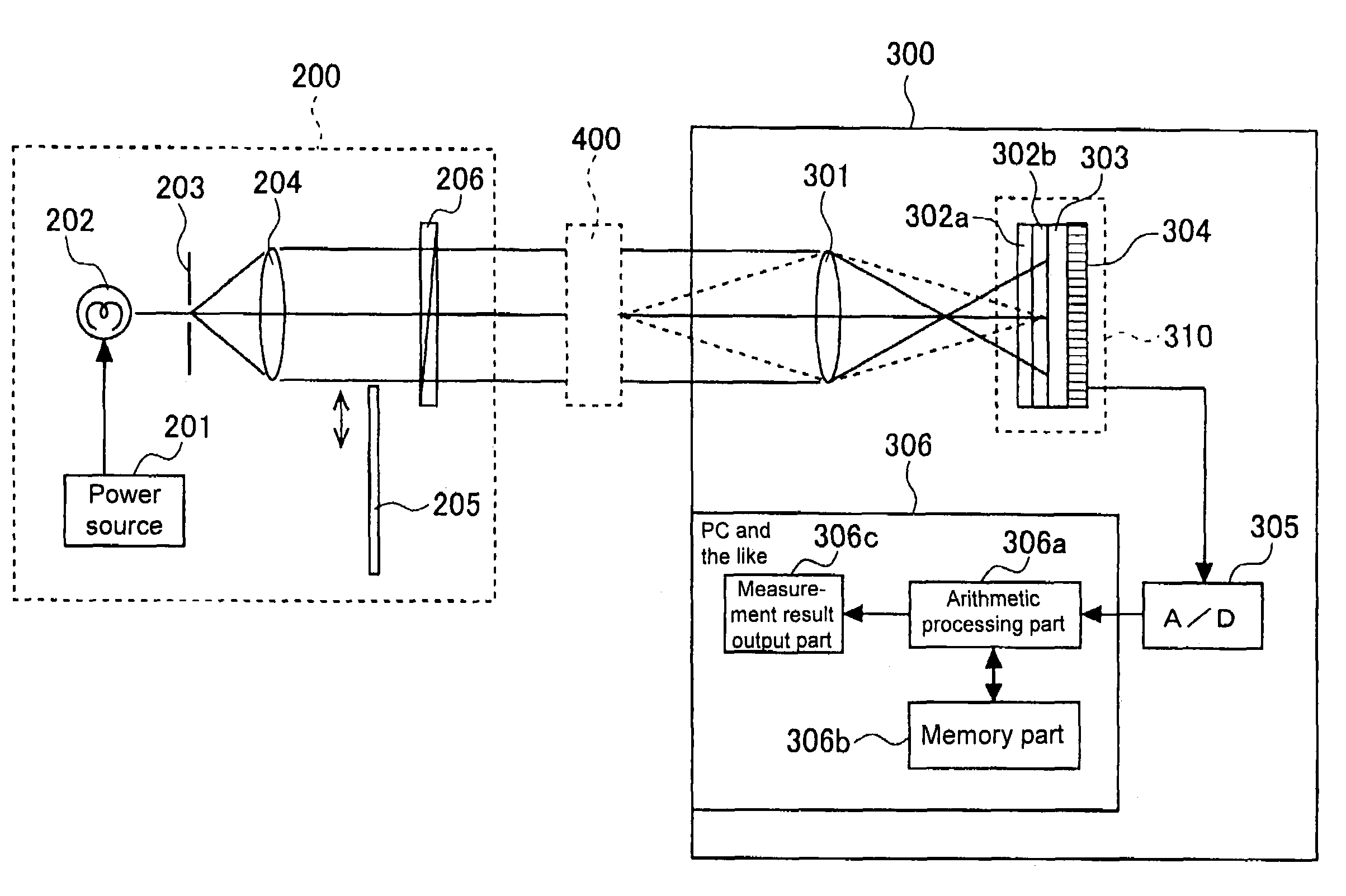
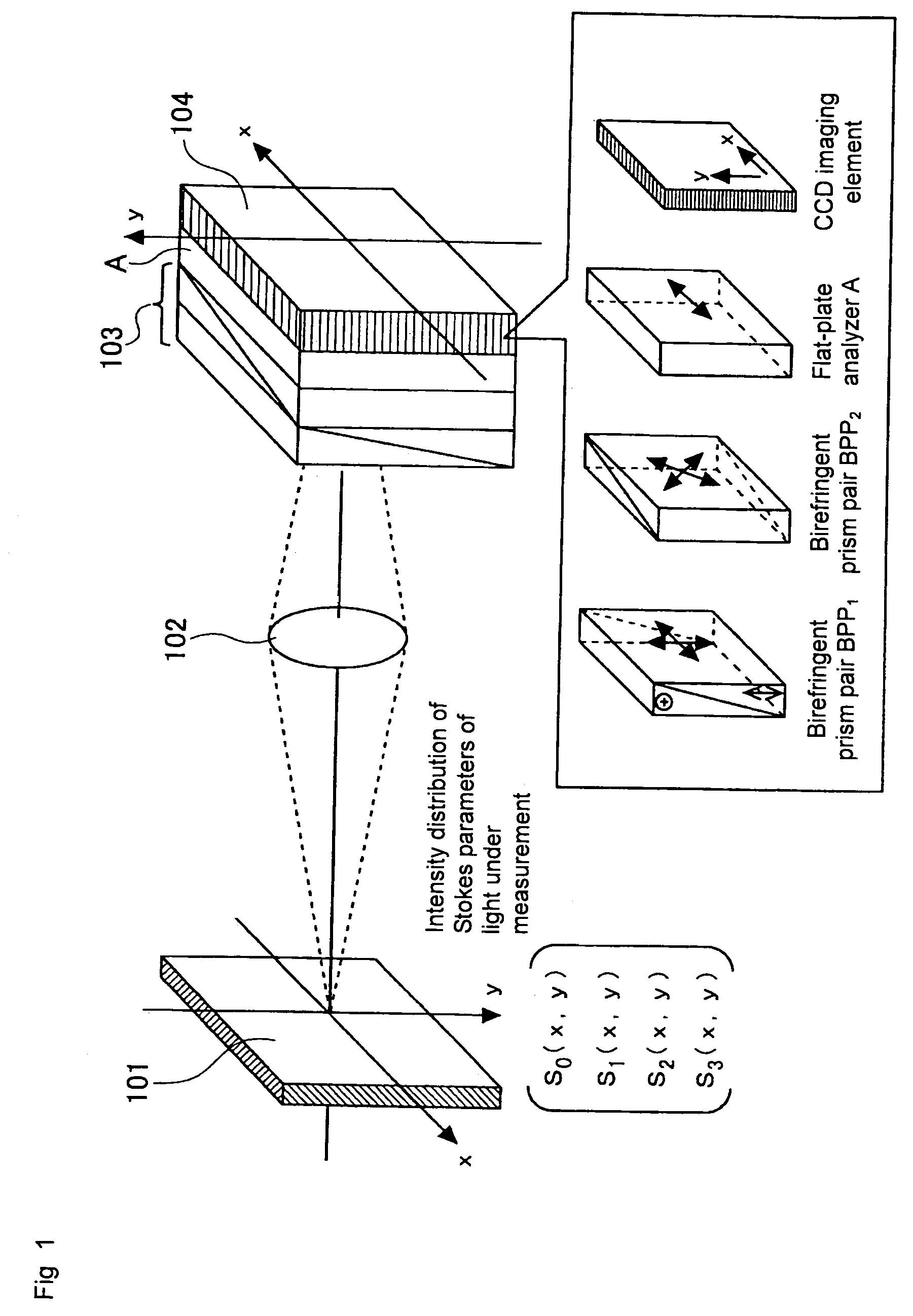
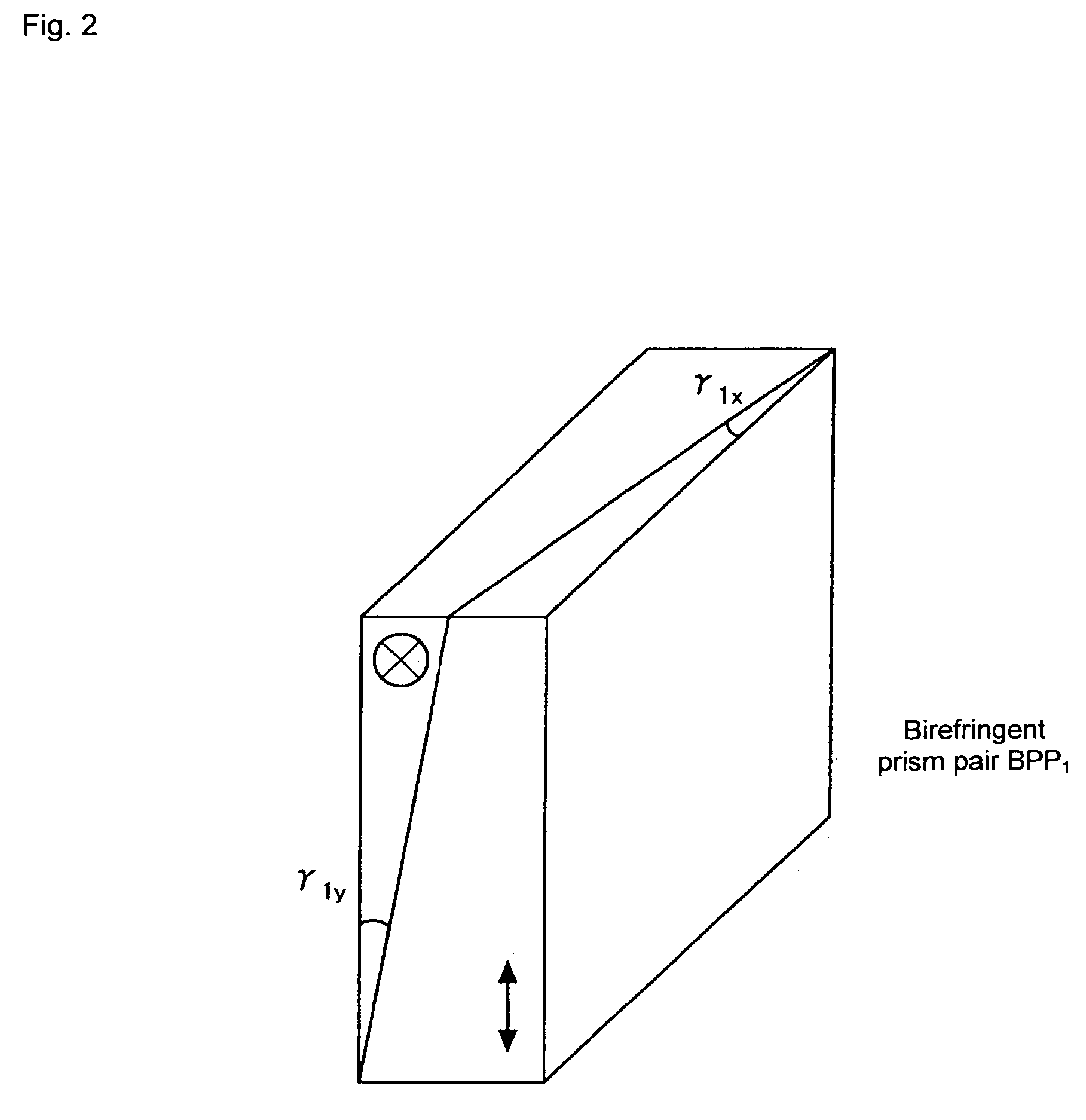
Imaging polarimetry
ActiveUS20070030551A1Reduce measurement errorLight polarisation measurementNon-linear opticsPhase functionPolarimetry
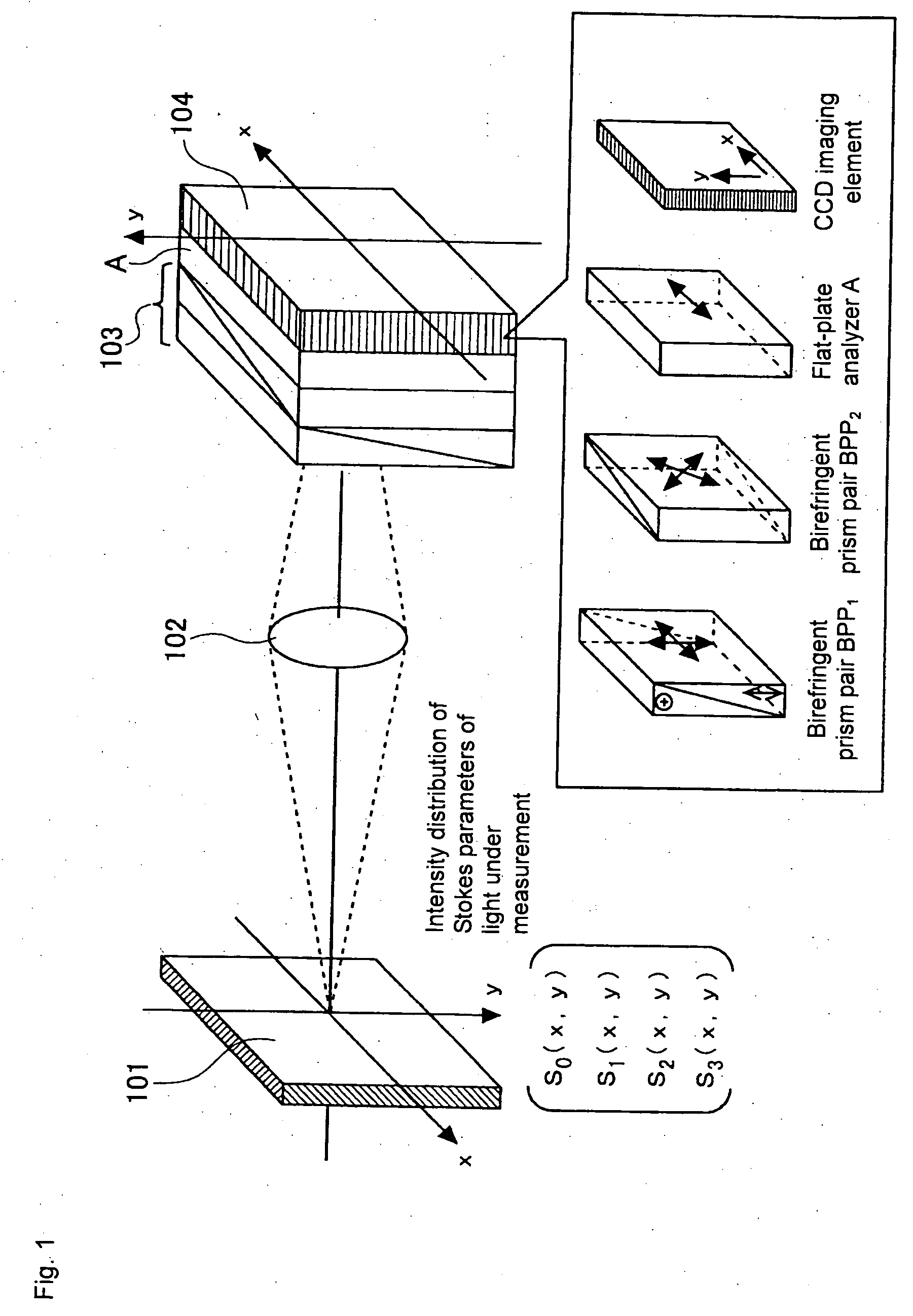
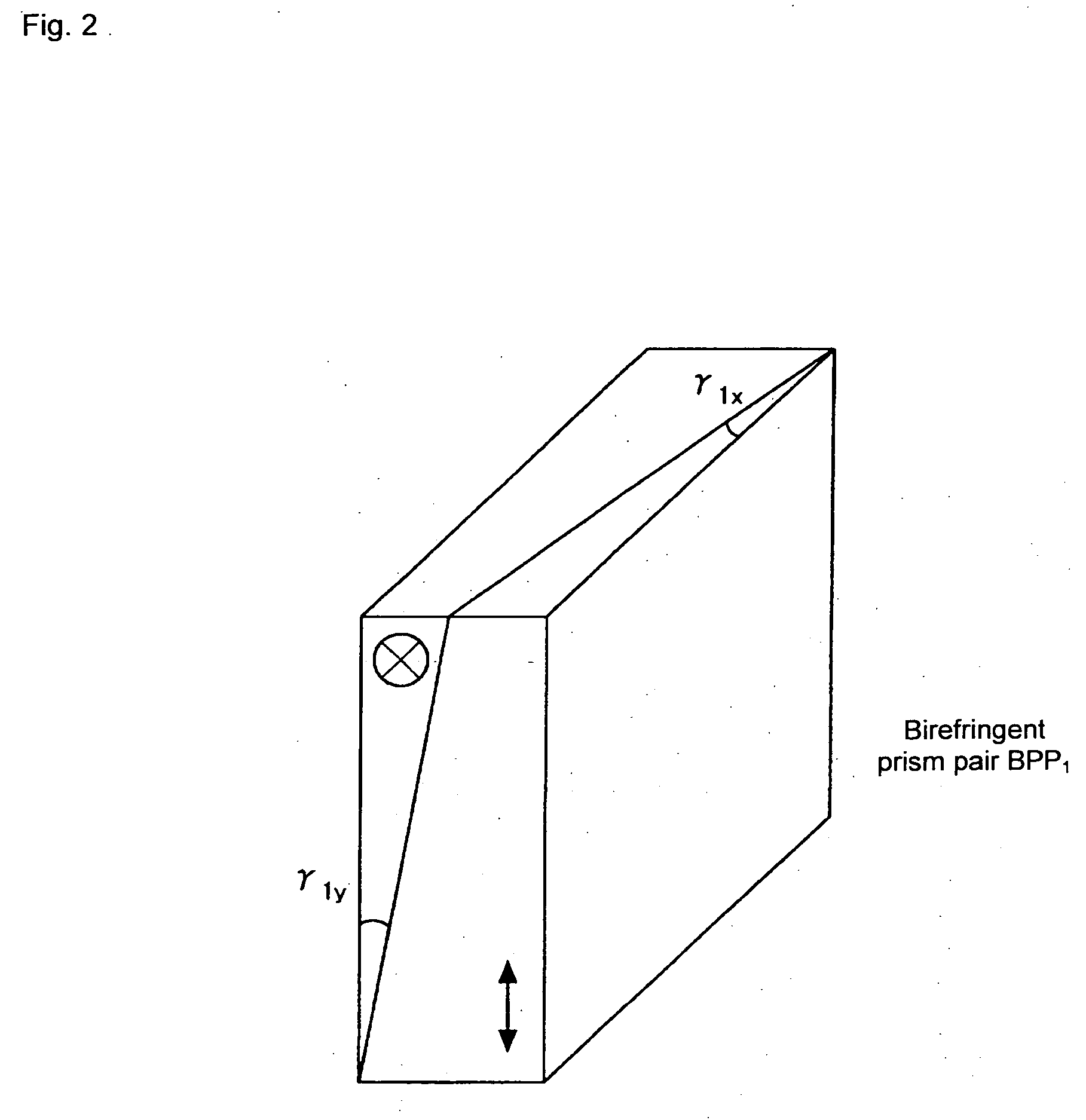
To effectively reduce a measurement error in a parameter indicating two-dimensional spatial distribution of a state of polarization generated by variations in retardation of a birefringent prism pair due to a temperature change or other factors, while holding a variety of properties of an imaging polarimetry using the birefringent prism pair. By noting that reference phase functions φ1(x, y) and φ2(x, y) are obtained by solving an equation from each vibration component contained in an intensity distribution I(x, y), the reference phase functions φ1(x, y) and φ2(x, y) are calibrated concurrently with measurement of two-dimensional spatial distribution S0(x, y), S1(x, y), S2(x, y), and S3(x, y) of Stokes parameters.
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY +1
Method for measuring optical phase by using synchronous phase-shifting interference method and implementing light path
InactiveCN101776488AEasy to getSimple methodOptical measurementsNon-linear opticsTarget surfaceBeam splitter
The invention discloses a method for acquiring an optical phase by using a synchronous phase-shifting interference method and an implementing light path, and relates to a method and a device for dynamically detecting wave surface information. According to the method, a light source is split into six beams by adopting a semi-transparent semi-reflective prism and a polarizing beam splitter prism, and meanwhile a polarizing interference method is combined to acquire six synchronous phase-shifting interference fringe patterns at one time in an air space, wherein the six interference fringe patterns are imaged on six CCD target surfaces respectively. The shape of a tested wave surface can be acquired by analyzing the six interference fringe patterns. Because the influence of vibration is consistent with the influence on the synchronous phase-shifting interference fringe patterns, the influence of the vibration can be eliminated by subtracting and deducting methods in a phase-shifting algorithm; therefore, the method is adaptive to high-precision wave surface measurement for more working environments, and does not need to perform PZT linear correction before each measurement. Moreover, the method is simple, the principle is clear, each component in the light path is easy to obtain, and the whole device is compact and easy to use.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Imaging polarimetry
To effectively reduce a measurement error in a parameter indicating two-dimensional spatial distribution of a state of polarization generated by variations in retardation of a birefringent prism pair due to a temperature change or other factors, while holding a variety of properties of an imaging polarimetry using the birefringent prism pair. By noting that reference phase functions φ1(x, y) and φ2(x, y) are obtained by solving an equation from each vibration component contained in an intensity distribution I(x, y), the reference phase functions φ1(x, y) and φ2(x, y) are calibrated concurrently with measurement of two-dimensional spatial distribution S0(x, y), S1(x, y), S2(x, y), and S3(x, y) of Stokes parameters.
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY +1
Optical switch using risley prisms
InactiveUS6859120B2Precise and independent rotationPrecise rotationElectrostatic generators/motorsCoupling light guidesLight beamEngineering
An optical switch using Risley prisms and rotary microactuators to independently rotate the wedge prisms of each Risley prism pair is disclosed. The optical switch comprises an array of input Risley prism pairs that selectively redirect light beams from a plurality of input ports to an array of output Risley prism pairs that similarly direct the light beams to a plurality of output ports. Each wedge prism of each Risley prism pair can be independently rotated by a variable-reluctance stepping rotary microactuator that is fabricated by a multi-layer LIGA process. Each wedge prism can be formed integral to the annular rotor of the rotary microactuator by a DXRL process.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Auto-stereoscopic display device
InactiveUS20100259819A1Increase the number ofResolution is sacrificedSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
An auto-stereoscopic display device which addresses the problem of how to provide an improved three dimensional effect without degrading the resolution of the views. The auto-stereoscopic display device comprises: image forming means having an array of display pixels for producing a display; view forming means positioned in registration with the image forming means and having an array of view forming elements, the view forming elements each being configurable to focus the outputs of groups of the display pixels into a plurality of views projected towards a user in different directions; and view deflecting means positioned in registration with the view forming means, the view deflecting means being arranged to selectably change the directions in which the plurality of views are projected towards the user. The view deflecting means comprise at least one birefringent prism having a first refractive index for light having a first polarization direction and a second refractive index for light having a second polarization direction. The view deflecting means further comprise a polarization switch in registration with the birefringent prism for providing the birefringent prism with display light having the first or second polarization direction. Specific arrangements of the image forming means, the view forming means and the view deflection means provide an even distribution of pixels and virtual pixels associated with the deflected views
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Road surface detection system
InactiveUS20180321142A1Reduce road surface frictionPresent hazardScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsLight beamEngineering
A road surface detection system for a vehicle includes an optical emitter disposed at the vehicle and configured to emit a beam of light downward and forward of the vehicle. A receiver is disposed at the vehicle so as to receive light emitted by the optical emitter that is scattered or reflected from the road surface. The receiver includes a prism and an imager, and the prism refracts the light so that the imager captures received light that is refracted by the prism. A control includes a processor operable to process image data captured by the imager. The control, responsive to processing of image data captured by the imager, determines spectral characteristics of materials present on the road surface. The control may determine the type of material present on the road surface by determining the parts of the spectrum absorbed by the material.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS
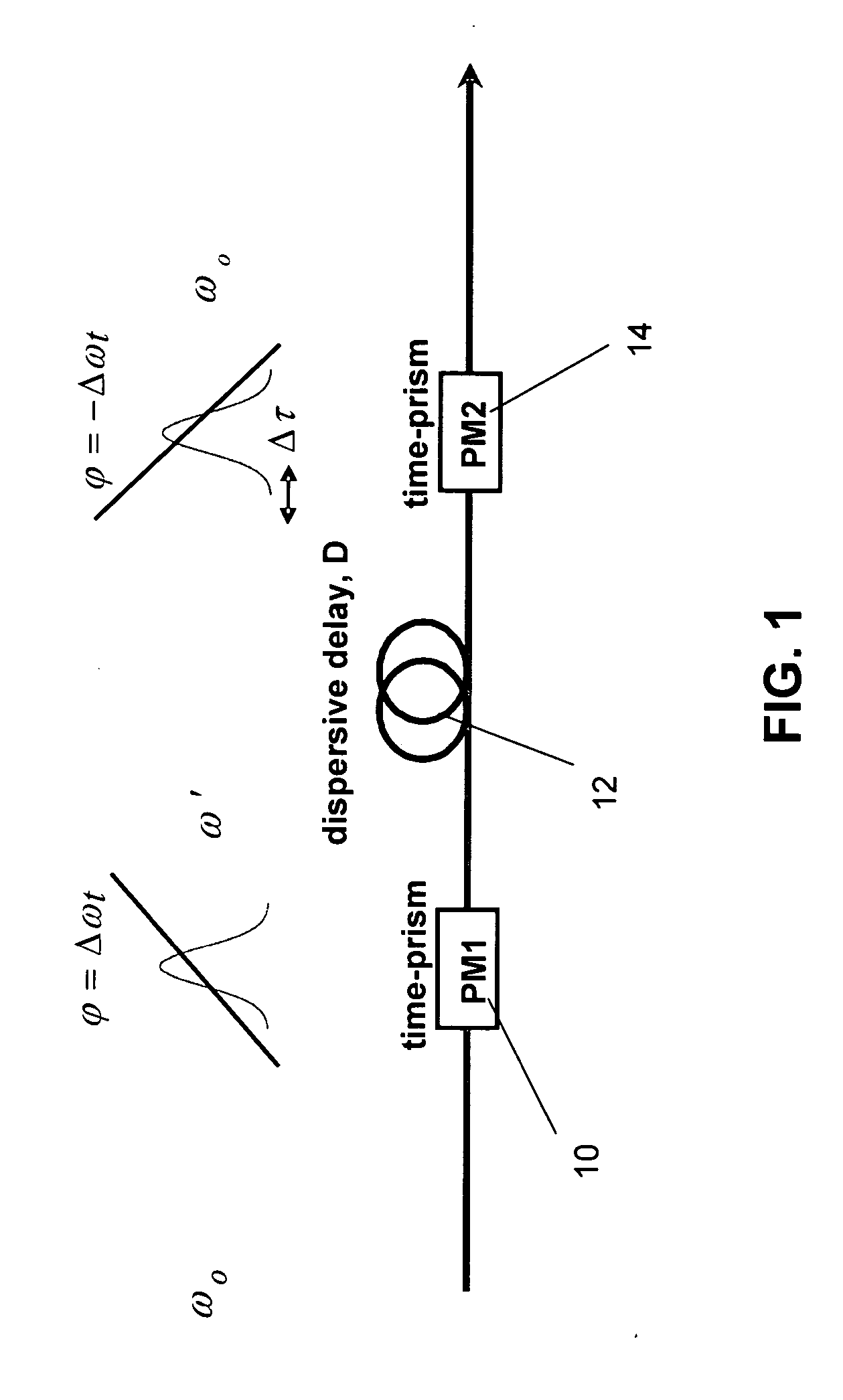
Ultrafast optical delay lines using a time-prism pair
InactiveUS20050286108A1Avoid input pulse broadening effectIncreases delay-to-pulse width ratioNon-linear opticsFiberPulse sequence
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Multi-channel dynamic optical dispersion compensator
InactiveCN102590952AReduce lossLow insertion lossCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionPhase gratingRoof prism
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
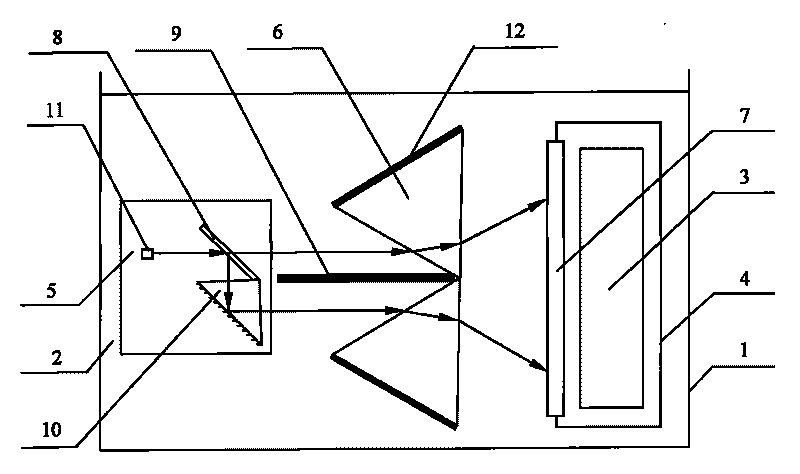
Intermediate infrared femtosecond mode-locked laser
InactiveCN102570270AStable continuous femtosecond laser pulse outputAvoid expensive pricesLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersMode-lockingChemical vapor deposition
The invention relates to an intermediate infrared femtosecond mode-locked laser which comprises a collimating mirror, a focusing mirror, an input spherical surface mirror, a laser medium and a spherical surface high-reflection mirror which are sequentially arranged along a direction of a pumping light beam outputted by a laser diode, wherein lasers in a five-mirror laser resonance cavity formed by the input spherical surface mirror, the spherical surface high-reflection mirror, the spherical surface high-reflection focusing mirror, an output coupling mirror and a graphene mode-locking element is reflected onto the high-reflection focusing mirror through the input spherical surface mirror, is focused on the graphene mode-locking element, returns back along the original path by sequentially passing through the spherical surface high-reflection focusing mirror, the input spherical surface mirror, a laser crystal and the spherical surface high-reflection mirror, is deflected and reflected to a dispersion compensation prism pair by the spherical surface high-reflection mirror, and is output from the output coupling mirror through a slit. According to the intermediate infrared femtosecond mode-locked laser, graphene growing by adopting a CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) method is transferred to a laser wavelength high-reflection mirror, and is protected by using inert gas, and thus stable mode-locked laser pulse output is realized in an intermediate infrared band. The intermediate infrared femtosecond mode-locked laser has the advantages of being simple in regulation, low in manufacture cost, and easy to realize single layer (little non-saturated loss).
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
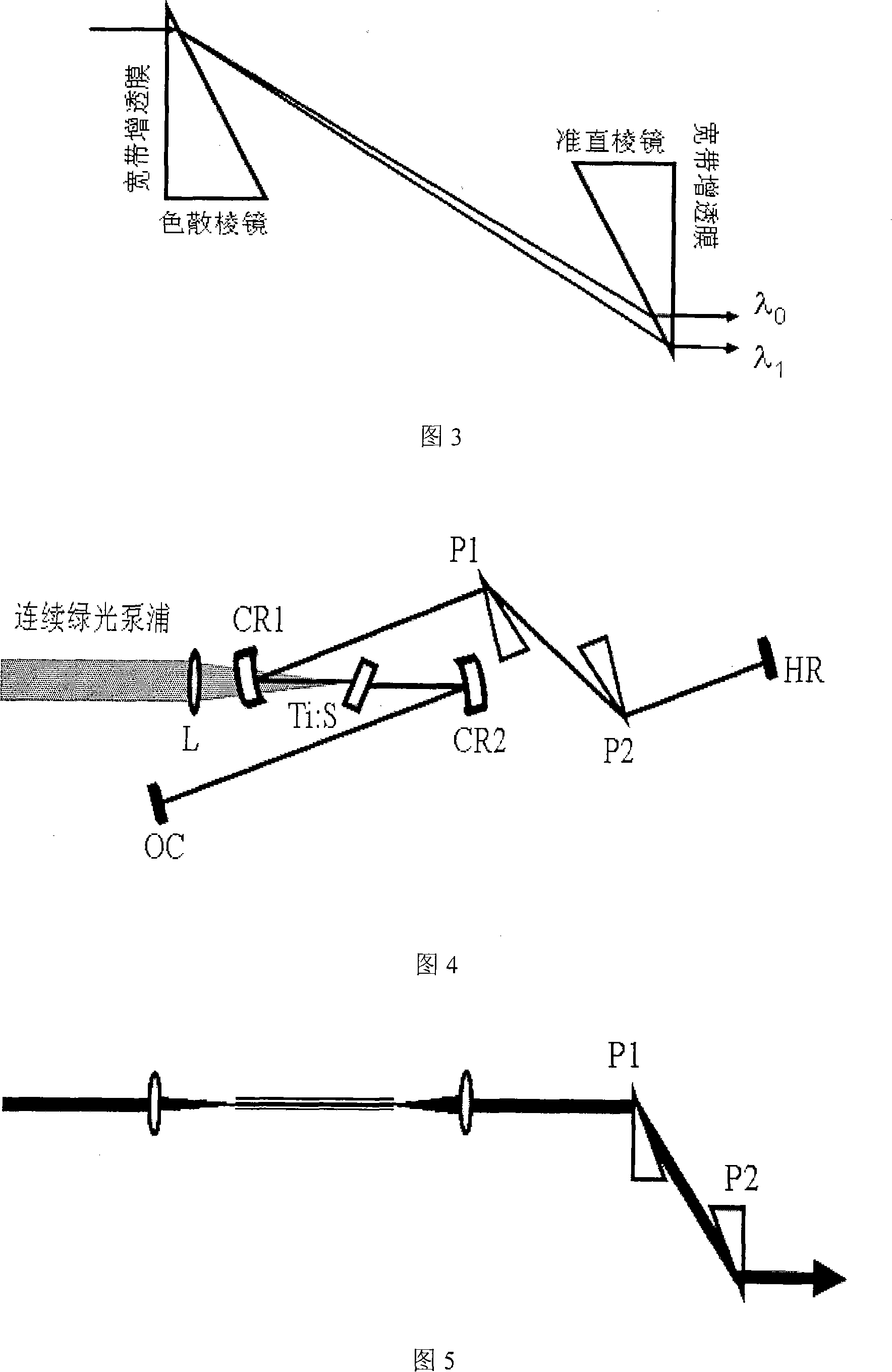
Novel prism pair pulse chromatic dispersion compensator
InactiveCN101131478ASmall amount of insertionLow dispersionLaser detailsNon-linear opticsLength wavePrism pair
The invention relates to a new impulse dispersion compensator by the prism. It is made up of two right-angle prisms which are parallel. The top angle is the complement angle of Brewster's angle corresponding to the light impulse center wavelength. The invention can decrease the material dispersion caused by the Brewster's angle prism and the compensating effect is ideal, the structure is compact.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Differential solution concentration measuring device and method
InactiveCN101762567AEasy to measureEasy to usePhase-affecting property measurementsDifferential measurementLight beam
The invention provides differential solution concentration measuring device and method. Laser is used as a light source, and a semi-reflective and semi-transparent lens and a reflector are utilized to divide an incidence beam into two parallel beams which respectively enter the same sides of a prism pair in opposite positions in a prism set by liquid, are emitted from the other side of the prism set and finally received by a linear array CCD through the liquid. When the concentration changes, the refraction angle of the incidence light changes in the prism and causes the deflection angle of the emergent beam changes accordingly so that the image spot of a beam emitted from the other end of the prism changes the position on the CCD. After the corresponding relation between the positions relation of the two image spots on the CCD and the solution concentration is established, the concentration of the liquid is measured. The invention has the shared advantage of differential measurement technology as well as stable and reliable measuring result and easy distribution, can measure the change of the solution concentration in real time and can work in adheres industrial environment, such as causticity, and the like.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Arrangement for retroreflection of a ray using triple prisms
InactiveUS6123427AHigh measurement accuracyImprove accuracySurveyor's staffsPrismsShortest distanceConstruction surveying
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 03577 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 19, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 19, 1998 PCT Filed Aug. 13, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 08572 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 6, 1997The invention relates to an arrangement for retroreflection of an optical ray using triple prisms. Six to ten triple prisms (1, 2, 3, 131, 132, 133) arm provided with triangular light entry surfaces, wherein the side faces of adjacent triple prisms are in contact. This results in continuous retroreflection at a high level of intensity for one angle area, of 360 DEG . When used in particular in geodesy or in construction surveying, this all-round reflector provides a high degree of measurement accuracy for angles and distances from any direction on which a bearing is taken. Alignment towards a surveying instrument is therefore not necessary. Measurement of short distances is also definite and reliable. The all-round reflector is particularly advantageous for automatic surveying, since, irrespective of its orientation, it can be automatically tracked by a motorised surveying instrument.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
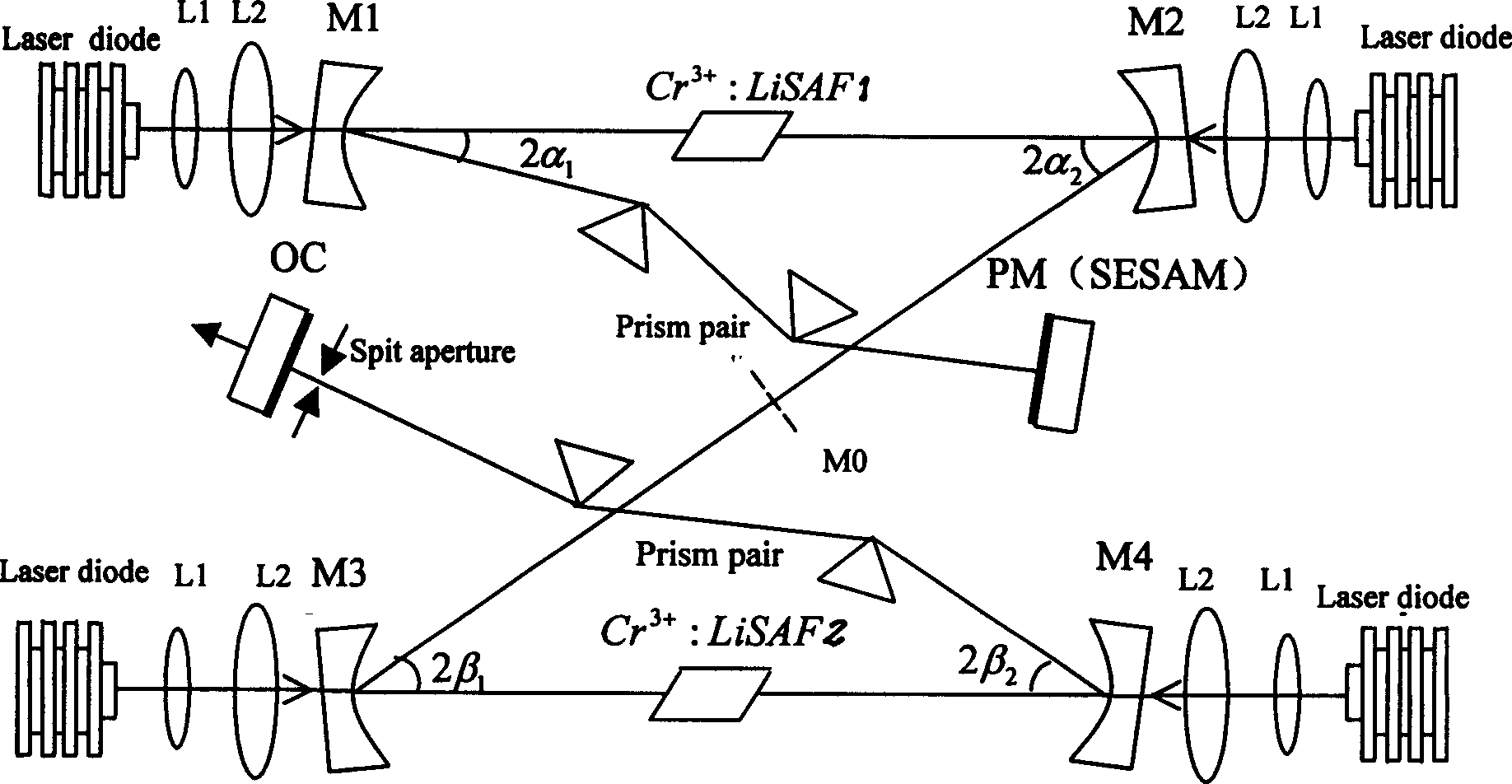
Bicavity series full solidifying fly second laser
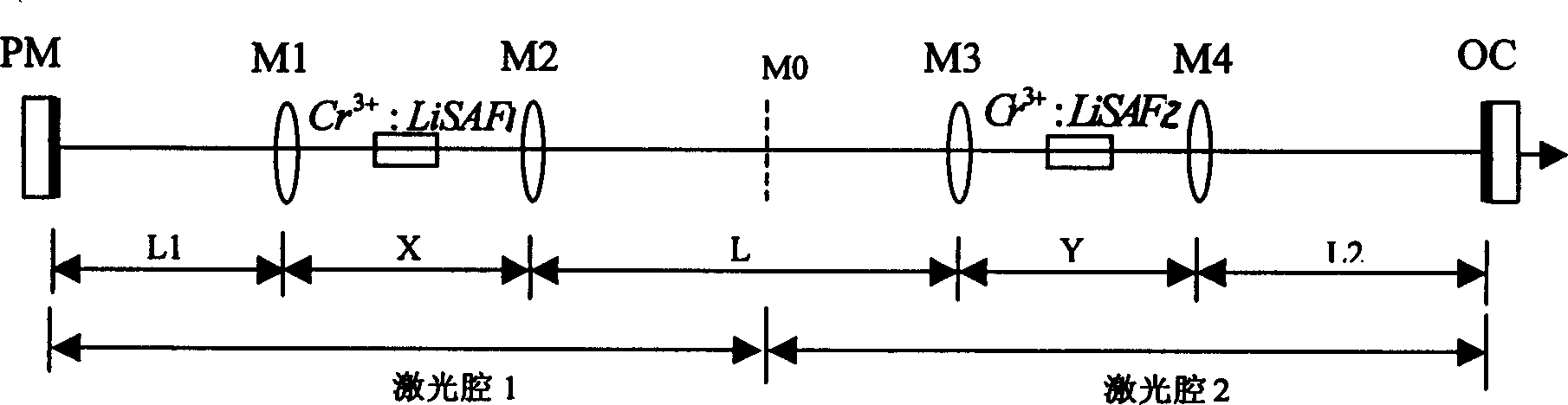
The invention relates to a totally solidified femtosecond laser with a double cavities series structure, which is made up of four semiconductor laser pumping sources, four plating sphere mirrors, two blocks of laser crystals used as gain media, two prism pairs, a fully reflector (or semiconductor saturated absorbing mirror) and a output coupling mirror. The centre wavelength outputted by the laser is 830nm, the tuning range is 100nm, and the outputted pulse width is about 100fs. The centre wavelength outputted by semiconductor pumping light source is 673nm. The laser is compact, the cost is low and the performance is stable.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Large visual field scanning infrared optical system containing aspherical fairing
InactiveCN102322959AShorten the overall lengthOverall small sizeRadiation pyrometryOptical elementsVisual field lossOptical instrument
The invention relates to a large visual scanning infrared optical system containing an aspherical fairing, belonging to the technical field of optical instruments. The system comprises a rotary symmetrical aspherical fairing, an achromatic rotary Risley prism pair, an optical imaging system and a detector image surface. The special aspherical fairing according with hydrokinetics is applied to the system and has favorable hydrodynamic performance; the detected target is subjected to dynamic scanning and imaging by using an optical wedge; an imaging optical system in a subsequent light path is fixed; and a low-temperature coil and electronic equipment do not pass through a rotating mechanical device. The large visual scanning infrared optical system meets the characteristics of medium dynamics, has the advantages of favorable quality of system imaging, light weight, shortness in length and simple structure, can reach a scanning visual field with more than 60 degrees and can be widely applied to the fields of investigation, rescue and the like.
Owner:YANCHENG GOLDEN IDEA OPTICAL TECH CO LTD
Device for alternately outputting dual-wavelength Q-switched pulse lasers
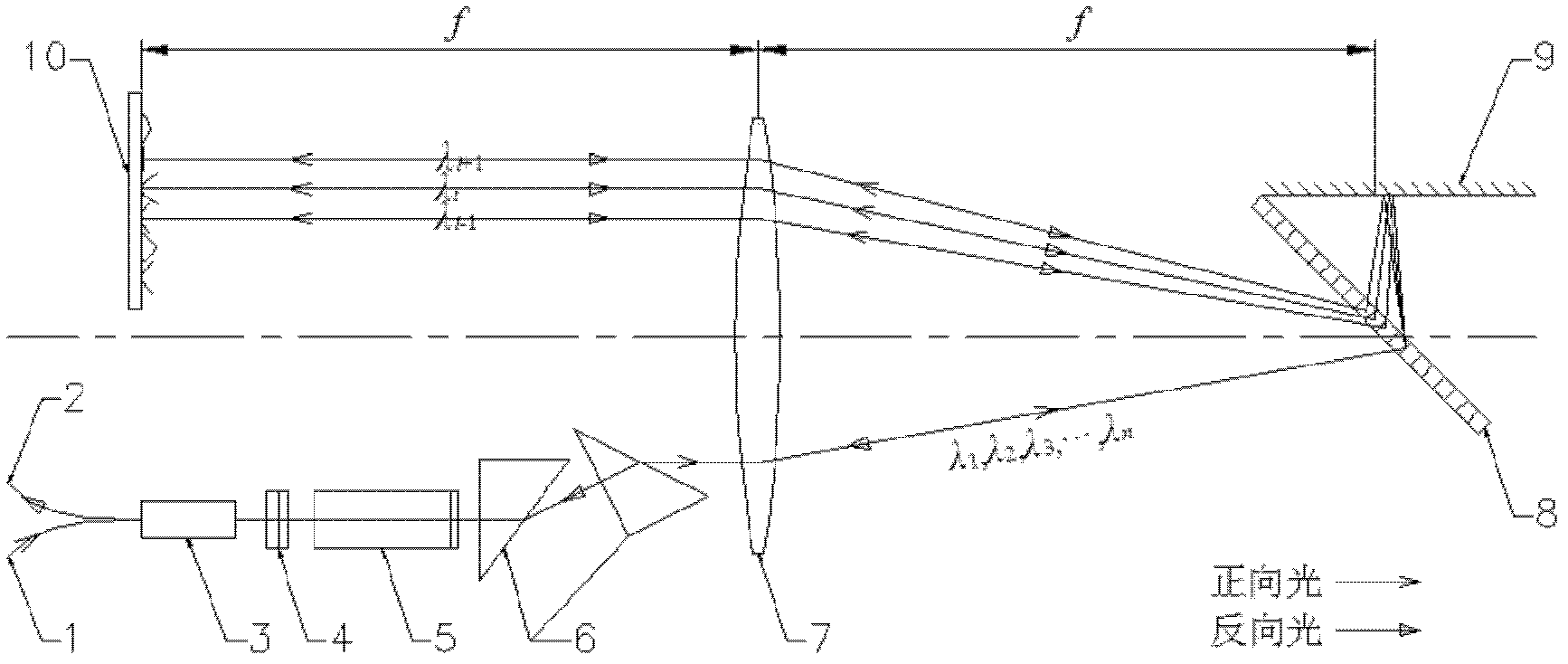
The invention discloses a device for alternately outputting dual-wavelength Q-switched pulse lasers and belongs to the technical field of lasers. The device is characterized in that a lambda1 laser and a lambda2 laser are formed by respective pumps, total reflection mirrors and laser crystals as well as a common output coupling mirror; a Q-switched prism pair comprises an inhibition prism and a total reflection prism, inclined planes of the inhibition prism and the total reflection prism form an inclined plane group of the Q-switched prism pair, and a piezoelectric ceramic transducer is mounted on the inhibition prism and used for adjusting the interval d between two inclined planes of the inclined plane group; the Q-switched prism pair is located between the laser crystal of the lambda1 laser and the output coupling mirror, and a resonance optical path of the lambda1 laser is perpendicular to a group of right-angled surfaces of the Q-switched prism pair; an optical axis of the lambda2 laser is perpendicular to the other group of right-angled surfaces of the Q-switched prism pair and passes the inclined plane group, and the laser crystal of the lambda2 laser is adjacent to the total reflection prism; a timing power supply containing a timing control circuit is electrically connected with the pumps of the lambda1 laser and the lambda2 laser as well as the piezoelectric ceramic transducer respectively; a beam splitting prism is located on the optical path on the outer side of the output coupling mirror.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Super-strong chirped laser pulse step-by-step compression device
ActiveCN111600190ARaise the incident laser energyIncreased incident laser energyLaser detailsOptical elementsGratingLight beam
A super-strong chirped laser pulse step-by-step compression device comprises a light beam smoothing and initial pre-compression module composed of prism peer-to-peer negative dispersion elements, a pulse main compression module composed of a grating compressor and the like, and a final compression module composed of a space-time focusing process and (or) a self-compression process in a transparentmedium sheet. By utilizing the smoothing effect of the pre-compression module on the spatial intensity modulation of the incident laser, the modulation of the spatial intensity of the laser is reduced, and the damage of the spatial modulation of the laser intensity to the incident grating and the emergent grating is reduced, so that the energy of the incident laser can be improved, and stronger laser output can be obtained at a single stage. And in the pulse self-compression process of the final compression module, the spectrum can be further broadened, and the laser pulse can be compressed to obtain shorter laser pulse output.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-resolution high-speed polarization difference imaging method
InactiveCN102230883AHigh-resolutionImprove resolution accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh resolution imagingAcousto optic deflector
The invention relates to a high-resolution high-speed polarization difference imaging method. In the method, linearly polarized light which can be controlled and of which the polarization directions are orthogonally changed at a high speed is generated by using characteristics of a high-speed time division deviated light path of an acousto-optic deflector and a characteristic that a lateral displacement polarization prism spectrometer integrates orthogonal line polarized light, system resolutions in the two directions are improved, and the high-speed polarization difference imaging method is formed. By the method, the defect that only the system resolution in one direction can be improved in the prior art is overcome; the scanning efficiency of a system is improved; system errors are reduced; resolving accuracy is improved; and the system has higher stability and high high-resolution imaging speed.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Device and method for measuring refractive index of intermediate infrared multi-wavelength material
InactiveCN102323238AEnables direct measurementReliable data supportPhase-affecting property measurementsChannel powerMeasurement cost
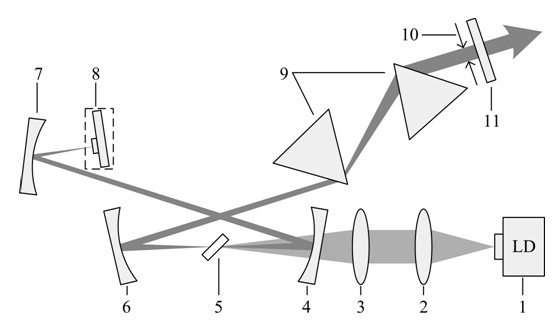
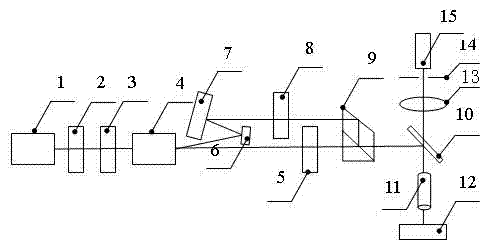
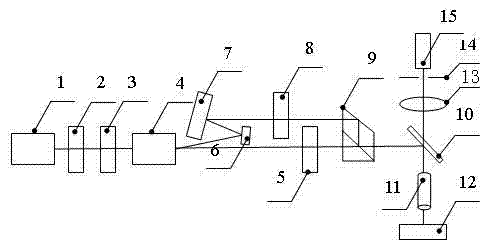
The invention discloses a device and method for measuring a refractive index of an intermediate infrared multi-wavelength material. The device comprises a laser diode, a beam shaping device, an input mirror, a laser crystal, a spherical surface high reflection mirror, a prism pair, a slit, an output coupling mirror, a Faraday isolator, a half-transparent and half-reflecting mirror, an adjustable diaphragm, a precise rotating platform, a spectrograph and a dual-channel power meter. The invention realizes direct measurement of refractive indexes of a material to be measured in a wide-spectrum range under different intermediate infrared wavelengths, solves the problem of difficulty in measurement of the refractive index of the material with intermediate infrared wavelength, and is simple andeasy in a measurement process, thus the measurement process of the refractive index is greatly simplified and the measurement cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Liquid crystal optical phase shift detection system and method based on interference method
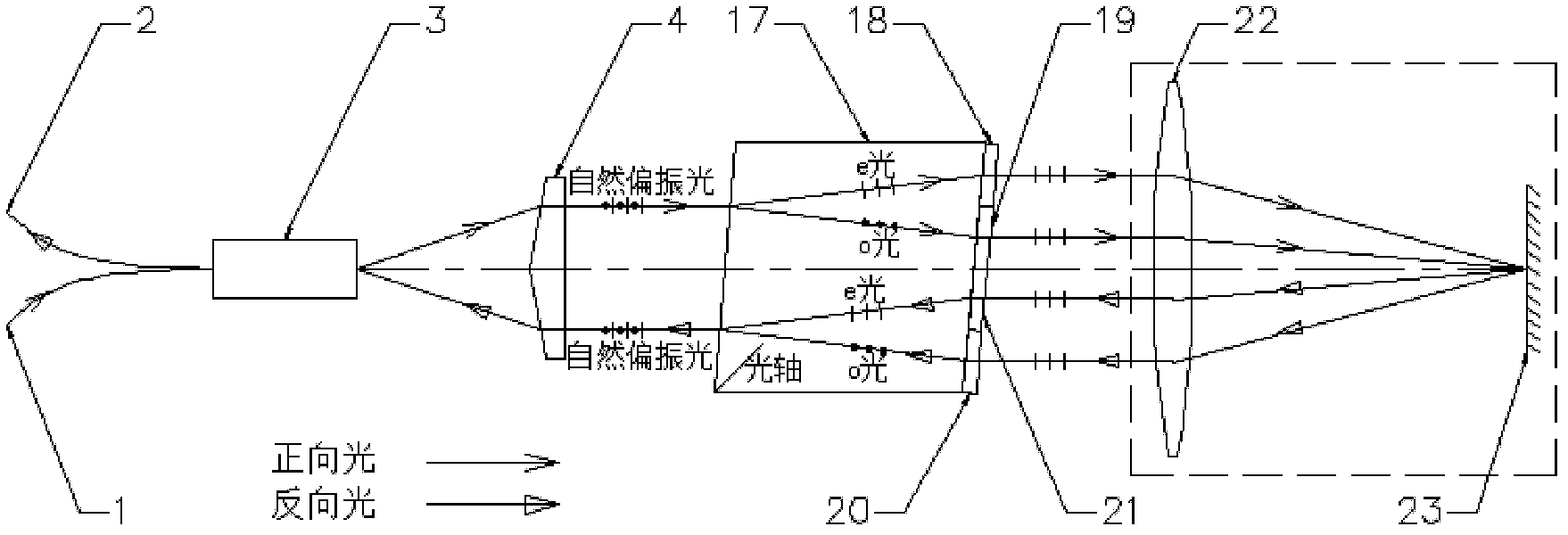
The invention discloses a liquid crystal optical phase shift detection system and method based on an interference method. The system is structurally characterized in that light emitted by a laser light source passes through a half-wave plate and then is divided into two beams of linearly polarized light by a first polarization splitting prism, wherein the polarization directions of the two beams of linearly polarized light are perpendicular to each other; one beam of linearly polarized light irradiates a liquid crystal optical phased array sample, is reflected by a first reflector and then enters a second polarization splitting prism; the other beam of linearly polarized light is reflected by the second reflector and then enters the second polarization splitting prism; and the second polarization splitting prism combines the two incident light beams, the combined light beam sequentially passes through a quarter-wave plate and a polarization analyzer and then irradiates the target surface of a charge coupling element, and the charge coupling element is connected with a computer control center. According to the invention, the absolute phase retardation of the sample is determined, high-precision, high-resolution, rapid and automatic detection of the two-dimensional liquid crystal phase shifter is realized, and the resolution and precision of phased array phase distribution detection are improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A femtosecond ultraviolet laser
The invention discloses a femtosecond ultraviolet laser. The femtosecond ultraviolet laser is composed of an optically connected seed source, a pulse broadener, an optical amplifier, a pulse compression module and a third frequency multiplication module. The seed source is an all-fiber passive mode-locked seed source or a solid mode-locked seed source; The pulse broadener is an all-optical fiber broadener or a spatial light broadener; The optical amplifier is an optically connected multi-stage optical amplifier; The pulse compression module is a prism pair or a grating pair or a chirped volumeBragg grating (CVBG); The frequency tripling module sequentially comprises a 1 / 2 wave plate, a polarization beam splitting prism, a convex lens, a concave lens, a frequency doubling crystal, a frequency tripling crystal, an absorbing block and an ultraviolet window plate. The second harmonic generation crystal is a kind of phase-matched lithium triborate (LBO) crystal, and the third harmonic generation crystal is a kind of phase-matched lithium triborate (LBO) crystal. The back surface of the third harmonic generation crystal is not coated and cuts the Brewster angle Theta B 1 of ultravioletlight, and the front surface of the second harmonic generation crystal is not coated and cuts the Brewster angle Theta B 2 of infrared light. The femtosecond ultraviolet laser realized according to the invention has simple and stable structure, long service life and is suitable for generating high-power femtosecond ultraviolet light.
Owner:WUHAN YANGTZE SOTON LASER CO LTD
Miniature solid mode locked laser
The invention relates to the short pulse laser field; a rectangular prism combination is employed in a chamber; a multi-reflection method between rectangular prism pairs can enlarge a physics chamber length of a laser chamber; a full reflection surface of the rectangular prism is plated with a chirp mirror reflection film so as to generate chamber inner element dispersion compensation effect; in addition, a semiconductor saturable absorber serves as a front chamber mirror or a rear chamber mirror of a standing-wave chamber, thus realizing the full solid miniature mode locked laser, and realizing burst pulse or ultrashort pulse output with a high peak power a narrow pulse width; in addition, each optical element in the laser chamber can form an integrated body through optical cement or deepening optical cement.
Owner:FUJIAN CASTECH CRYSTALS
Astigmatism eliminating light beam shaping system based on prism pair and cylindrical mirror
ActiveCN103885186AAchieve shapingImprove signal-to-noise ratioOptical elementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Light spot
The invention discloses an astigmatism eliminating light beam shaping system based on a prism pair and a cylindrical mirror. The system comprises a collimating lens, the prism pair, a light beam displacement block and the cylindrical mirror, wherein the collimating lens, the prism pair, the light beam displacement block and the cylindrical mirror are sequentially arranged on the same light path. According to the astigmatism eliminating light beam shaping system based on the prism pair and the cylindrical mirror, light beams are shaped, the dimensional proportion of light spots obtained in the fast axis direction and the slow axis direction and converged through a converging lens is larger than 1:5, and meanwhile the astigmatism of the light beams and the astigmatism generated by the prism pair are eliminated. The system has the advantages of being high in light beam quality after the light beams are shaped, capable of improving the signal to noise ratio of an instrument, easy to adjust in the installation and manufacture processes and the like.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION CORP SUZHOU
Wavelength selecting switch
InactiveCN106291822ACompact structureReduce in quantityCoupling light guidesUltrasound attenuationGrism
The invention discloses a wavelength selecting switch. The wavelength selecting switch comprises a collimating input / output device (101), a polarizing and beam-splitting device (102), a beam-expanding and light-splitting prism group (103), a reflective grating (104), a focusing device (105) and an attenuating and switching device (106) which are sequentially arranged, wherein the beam-expanding and light-splitting prism group (103) comprises multiple pairs of prism pairs arranged in pairs, and performs beam expansion on linear polarized light; the reflective grating (104) splits the beam-expanded linear polarized light, and the beam-expanded linear polarized light runs through a part of the prism pairs in the beam-expanding and light-splitting prism group (103) for further expanding the light-splitting capability so as to uniformly disperse optical signals, corresponding to respective wavelengths, in input optical signals; the focusing device (105) focuses the uniformly-dispersed optical signals corresponding to the respective wavelengths into the attenuating and switching device (106); the attenuating and switching device (106) adjusts the attenuation amount and selects an output port. The wavelength selecting switch is compact in optical path structure and the number of packaging components is reduced.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
Broadband Ti:sapphire tunable Raman laser
ActiveCN103427327APlay a role in frequency shiftContinuously tunable wavelengthActive medium materialAcousto-opticsWavelength
The invention provides a broadbandTi:sapphire tunable Raman laser. According to the broadband Ti:sapphire tunable Raman laser, a green laser is composed of a laser total-reflection mirror, an acousto-optic Q switch, a semiconductor laser module, a harmonic wave sheet, a frequency doubling crystal and a green laser output mirror. An LDA pump laser gain material is used for generating 1064mm laser. A 532mm laser is generated through the frequency doubling crystal. Pumping is conducted by the 532mm laser on a Ti:sapphire crystal, so that 1000nm-1100nm wave length is generated. A Raman reflecting mirror and a Raman output mirror constitute a resonance cavity. The laser generates simulated Raman scattering under the feedback action of the resonance cavity after passing through a Raman crystal. Through selection of a prism pair and a reflecting mirror, the wave length continuous tunable function is achieved. After the laser passes through the Raman crystal, due to the Raman effect, the frequency shift function is achieved. Finally, long wave length beyond the spectral line of emission of the Ti:sapphire laser is output. The broadband Ti:sapphire tunable Raman laser expands the output wave length range of the Ti:sapphire laser.
Owner:LASER TECH TIANJIN MAIMAN
Multi-way pulse compressor and using method thereof
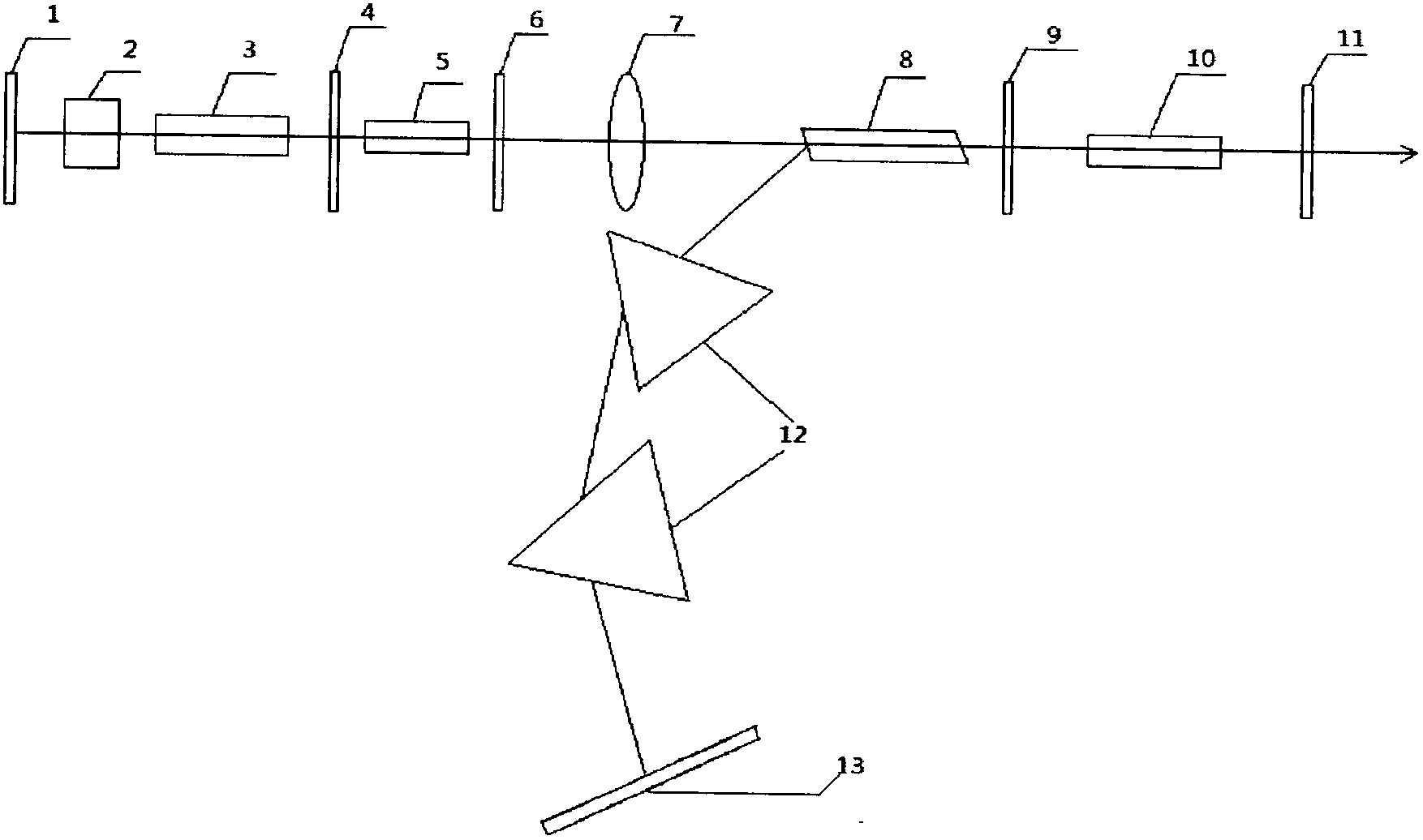
The invention discloses a multi-way pulse compressor and a using method thereof. The main body of the compressor comprises two end mirrors, the concave spherical surfaces of which are relatively coaxially placed; rotating rings are arranged on the end mirrors; and concave spherical reflectors are arranged in the rotating rings. Dispersion compensation film series are plated on the concave spherical surfaces of the concave spherical reflectors, and through grooves are processed on the reflectors. When the compressor is used, closed annular light spot tracks can be obtained on the concave spherical surfaces by setting and repeatedly adjusting the two end mirrors, and then discrete adjustment is implemented by rotating the compression of the rotating rings on the pulse. The compressor and the using method have the advantages that: the compressor has low loss, a compact structure and no spatial dispersion light path; the concave spherical surfaces can effectively counteract the beam broadening caused by the diffraction effect of beams so as to effectively overcome the defects of the conventional grating pair technology, prism pair technology and plane mirror-based dispersion mirror compensation technology; and the using and adjusting method is simple and convenient.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Liquid consumption device and method
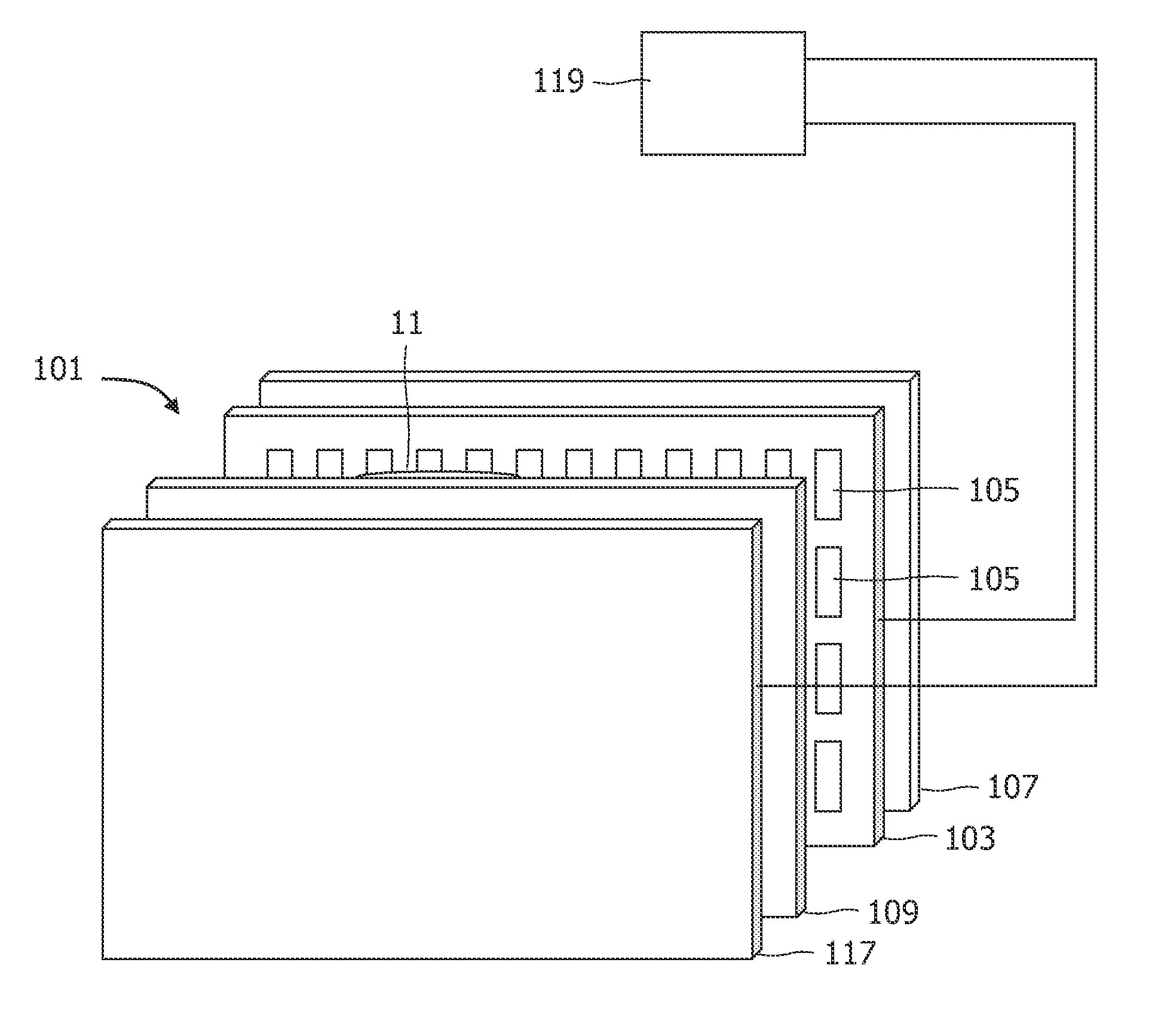
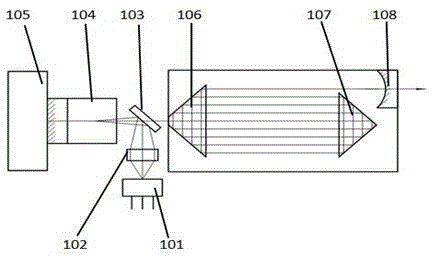
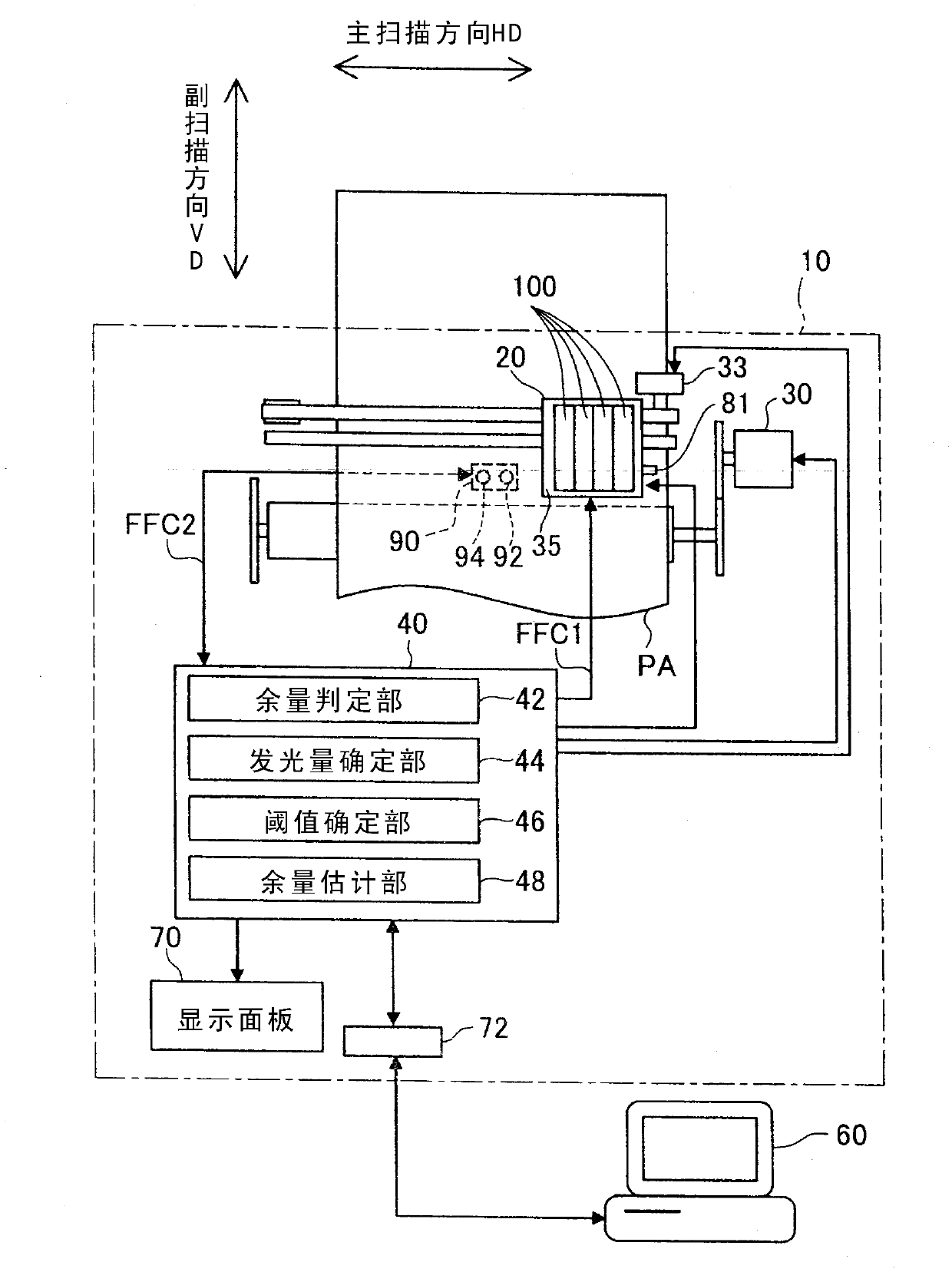
The invention relates to a liquid consumption device and a method. The present invention intends to provide a liquid consumption device technology capable of determining with good precision the residual state of liquid inside a liquid container mounted in the liquid consumption device. The liquid consumption device includes a liquid container, a prism, a light emitting unit, a light receiving unit and a control unit. The liquid container is configured to supply liquid to the liquid consumption device. The prism is provided to the liquid container, and configured to receive light that is made incident from outside and to emit the incident light again toward the outside according to a liquid residual state inside the liquid container. The light emitting unit is configured to radiate the light to the prism. The light receiving unit is configured to receive the light emitted from the prism. The control unit is configured to control the light emitting unit to radiate the light, and to determine the liquid residual state based on a light volume of the light received by the light receiving unit. Before the liquid residual state is determined, the control unit is configured to determine a threshold value of the liquid container for determining at least one of a light radiation volume by the light emitting part and the liquid residual state, based on a light volume of reflected light that was reflected by an outer surface of the prism and received by the light receiving unit upon radiation of the light by the light emitting unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Dispersion control using chirped mirrors in femtosecond laser system for ophthalmic application
ActiveUS20180221200A1Complex alignment processLaser surgeryOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingFemto second laser
A femtosecond laser system for ophthalmic applications, which employs a number of chirped mirrors in the laser beam delivery system between the laser head and the objective lens. The chirped mirrors perform the dual function of both turning the laser beam in desired directions and compensating for beam broadening due to group delay dispersion (GDD) of the optical elements of the system. Each chirped mirror reflects the laser beam only once. Four chirped mirrors are used, each providing up to −5000 fs2 of negative GDD per bounce, to provide a total of −18,000 fs2 negative GDD to compensate for the positive GDD of +18,000 fs2 introduced by other optical elements in the laser beam delivery system. This eliminates the need for a pulse compressor that would employ a grating pair, prism pair or grism pair, and therefore significantly reduces the size of the system and the alignment requirements.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Large view field scanning infrared optical system comprising reflective spatial light modulator
InactiveCN103760670ALarge scanning angleReduce complexityOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorImaging quality
The invention relates to a large view field scanning infrared optical system comprising a reflective spatial light modulator, and belongs to the technical field of optical instruments. The system comprises a rotational symmetry aspheric surface fairing, an achromatic rotating Ray weasley prism pair, the reflective spatial light modulator, an optical imaging system and a detector image plane. The special aspheric surface fairing meeting the fluid dynamics is adopted for the system, and thus the fluid dynamic performance is good; the reflective spatial light modulator is adopted for performing phase compensation on residual aberration of the systems when different scanning view fields exist; a detected target is dynamically scanned and imaged through an optical wedge, an imaging optical system in a subsequent optical path is fixed, and a low-temperature coil and electronic equipment do not pass through a mechanical rotating device. The system meets the dynamic characteristics of mediums and is good in imaging quality, light in weight, short in length, simple in structure and capable of achieving + / -60-degree view field scanning and being widely applied to the fields of investigation, rescue and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com