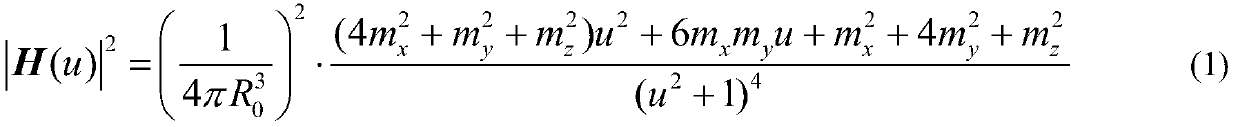Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "Orthonormal basis functions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Orthonormal functions are just functions which are real or complex whose inner product with itself results in 1 and with other functions results in 0.
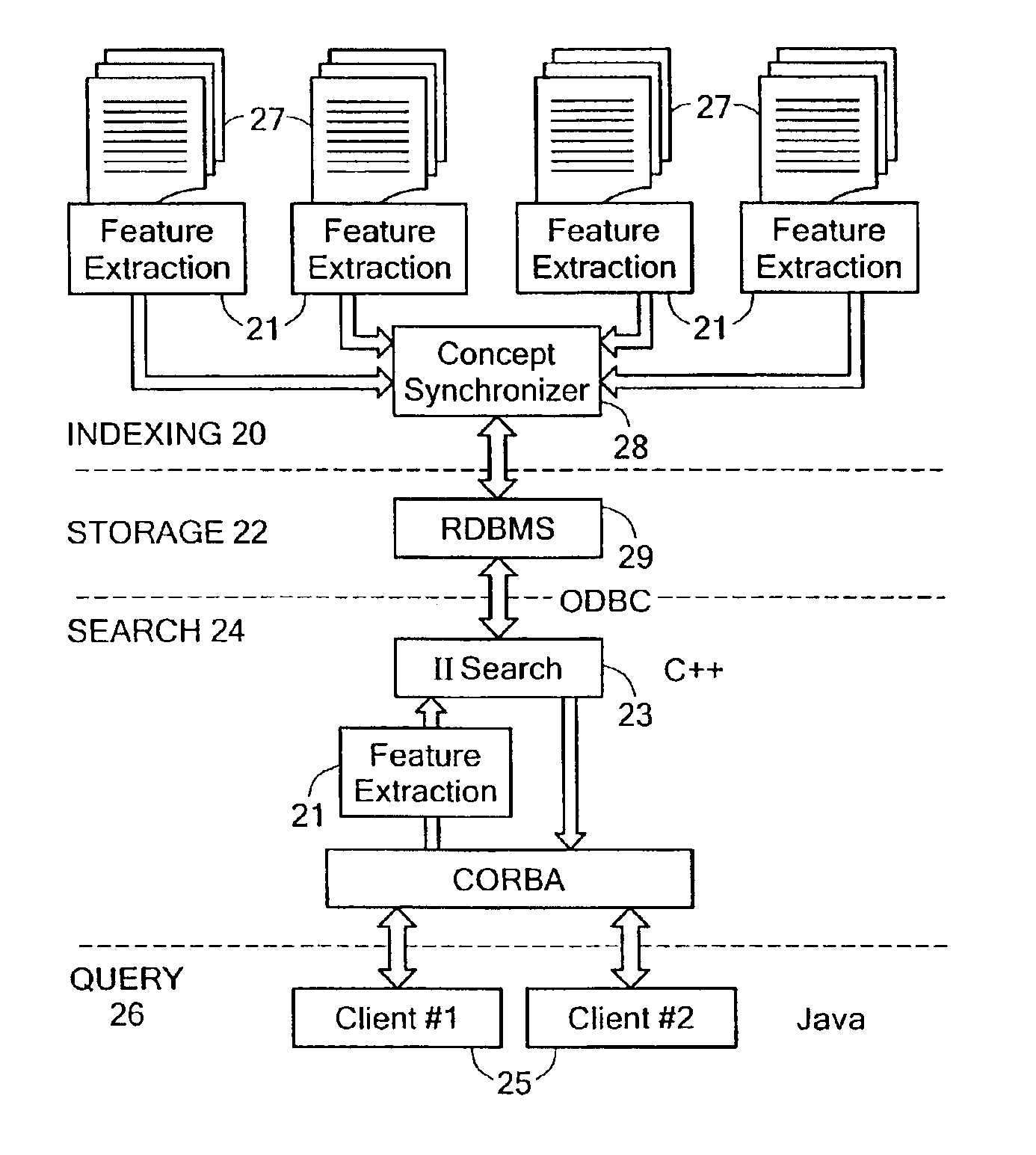
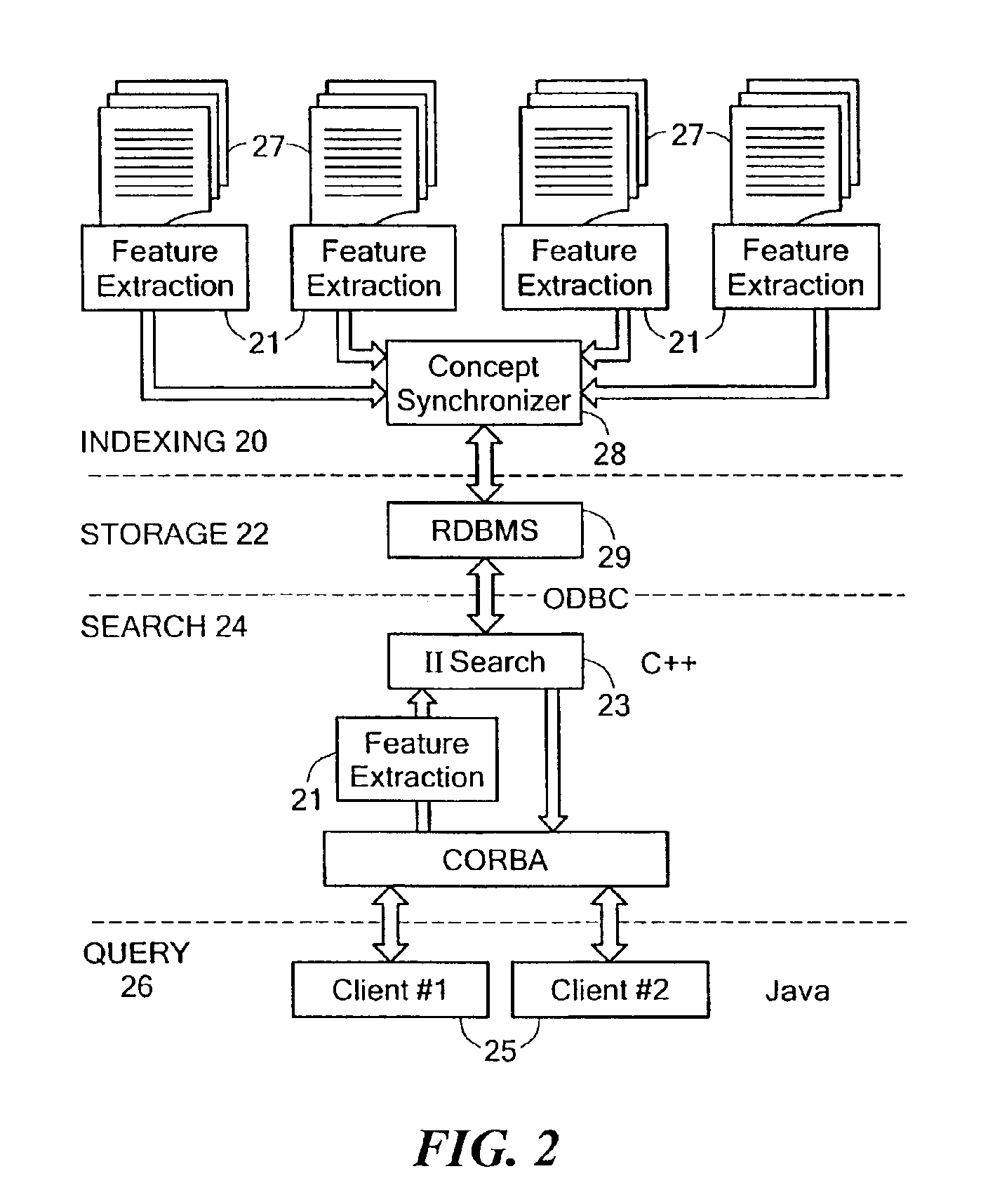
Inverse inference engine for high performance web search
InactiveUS7051017B2Eliminate needIncrease computing speedData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDecompositionOrthogonal basis
An information retrieval system that deals with the problems of synonymy, polysemy, and retrieval by concept by allowing for a wide margin of uncertainty in the initial choice of keywords in a query. For each input query vector and an information matrix, the disclosed system solves an optimization problem which maximizes the stability of a solution at a given level of misfit. The disclosed system may include a decomposition of the information matrix in terms of orthogonal basis functions. Each basis encodes groups of conceptually related keywords. The bases are arranged in order of decreasing statistical relevance to a query. The disclosed search engine approximates the input query with a weighted sum of the first few bases. Other commercial applications than the disclosed search engine can also be built on the disclosed techniques.
Owner:FIVER LLC
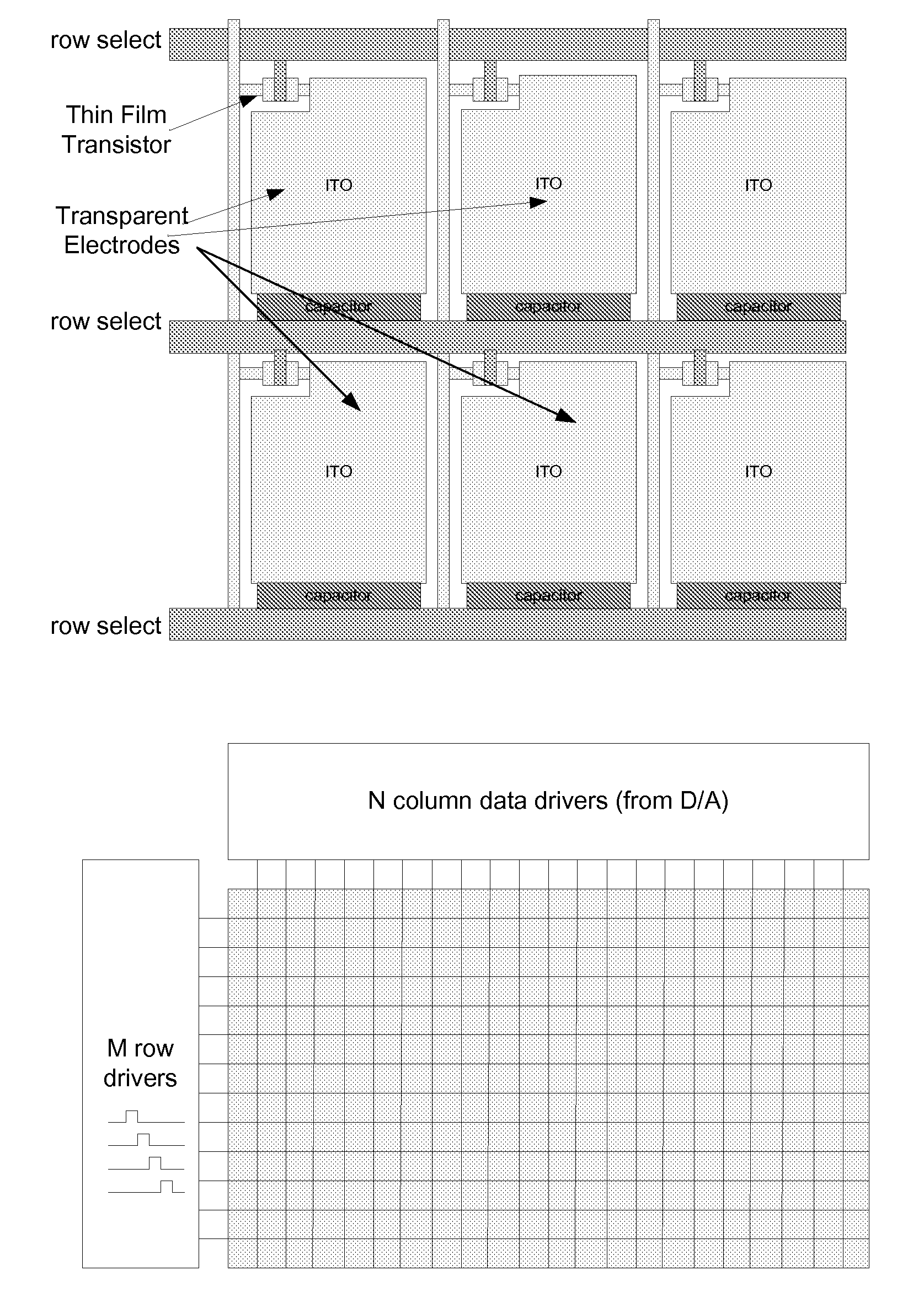
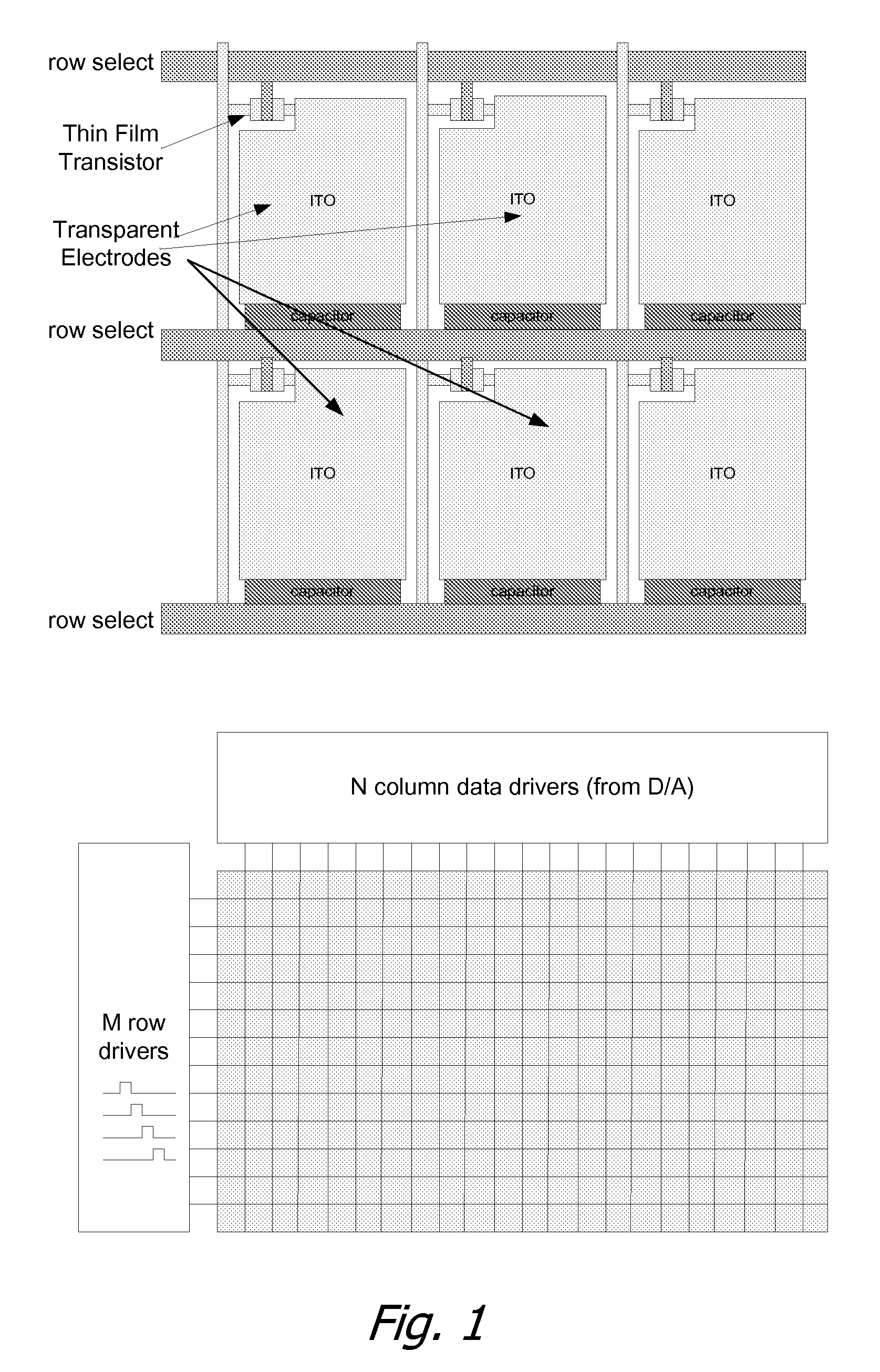
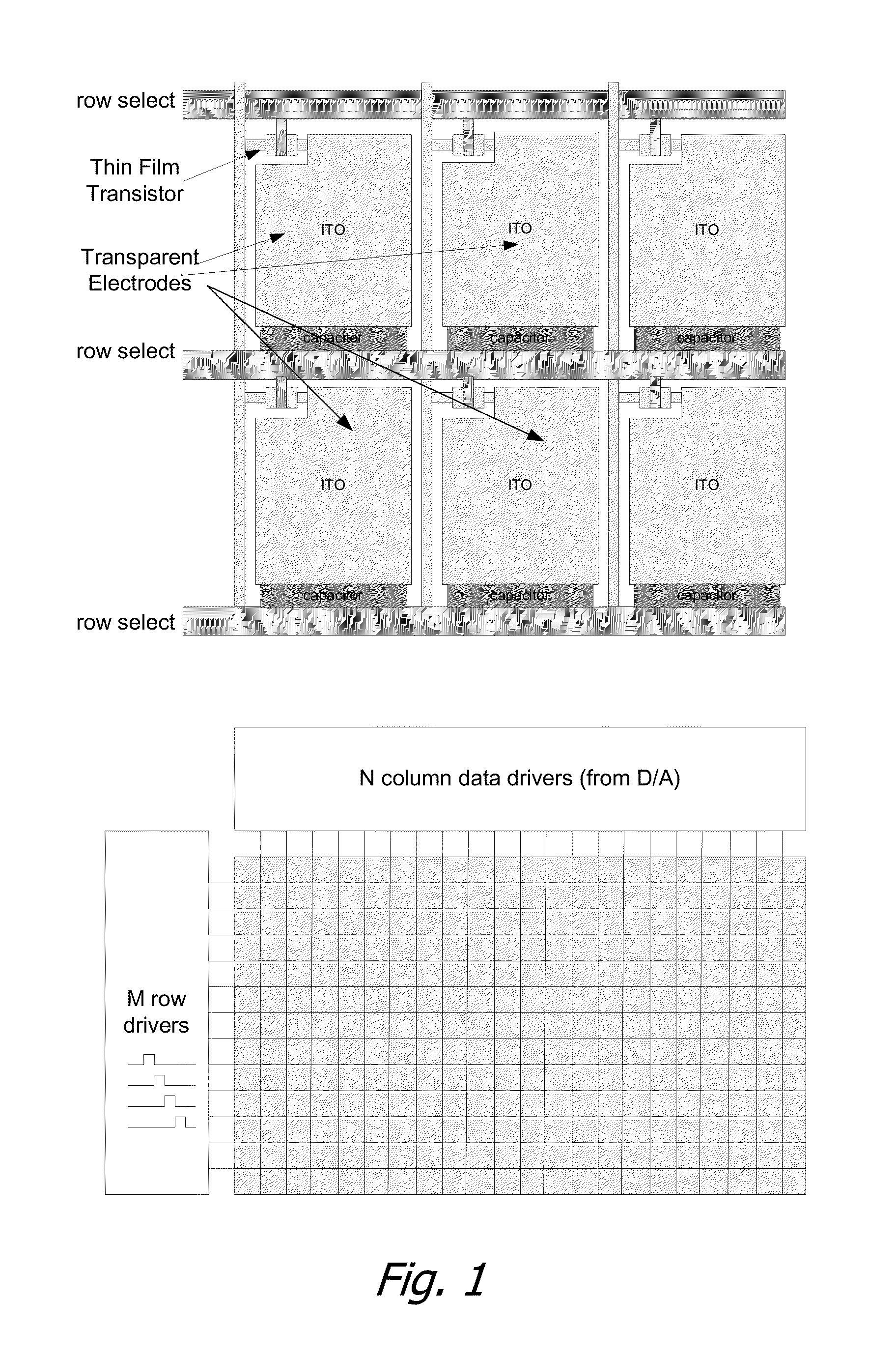
Image Construction Based Video Display System
InactiveUS20100007804A1Television system scanning detailsStatic indicating devicesSpatial light modulatorImaging quality
A video display system based on constructing images through displaying orthogonal basis function components of the image is disclosed. The system is comprised of two display components aligned and driven concurrently. The first display component is a coarse pixel array. The second display component is a spatial light modulator whose geometric details are finer than the first pixel array. The overall system reconstructs the intended video to be displayed at the finer geometric details of the second display component at a minimal image quality loss through the use of time-domain display of orthogonal image basis function components. The resultant system has a considerably reduced interconnection complexity and number of active circuit elements, and also requires a considerably smaller video data rate if a lossy image reconstruction scheme is used. An embodiment with a LED based display and an LCD based spatial light modulator utilizing the concepts, and methods to drive the displays are described herein.
Owner:OSTENDO TECH INC
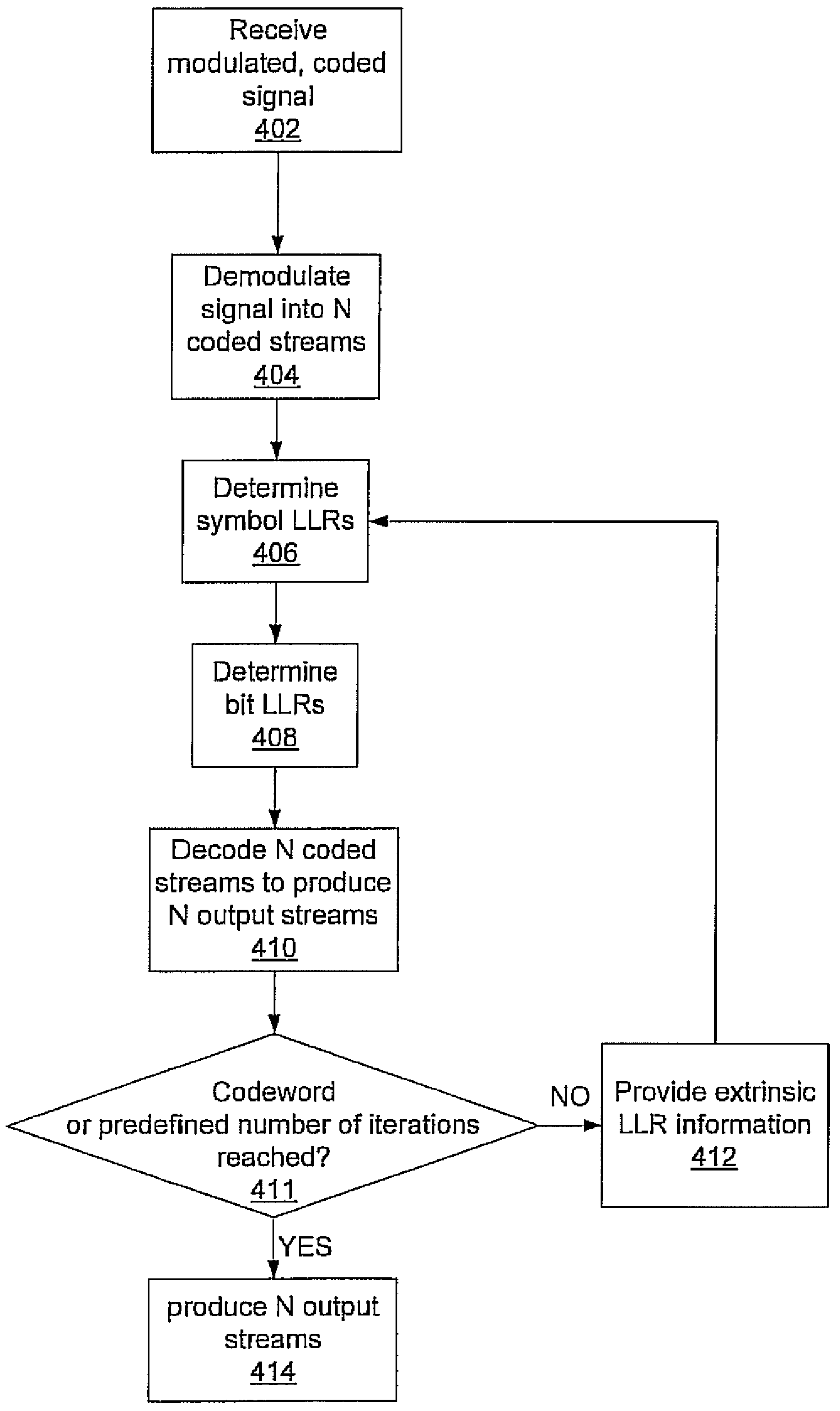
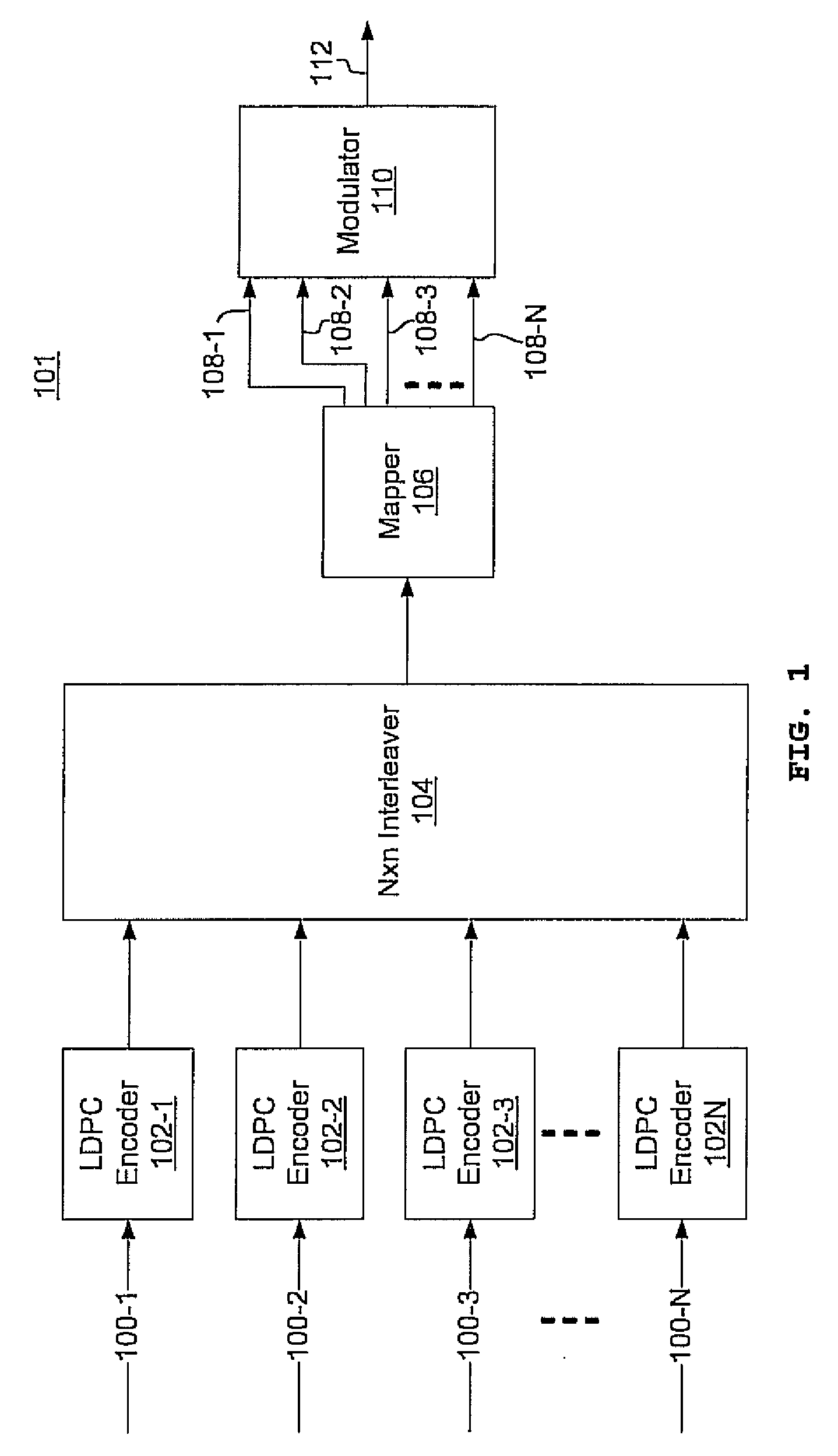
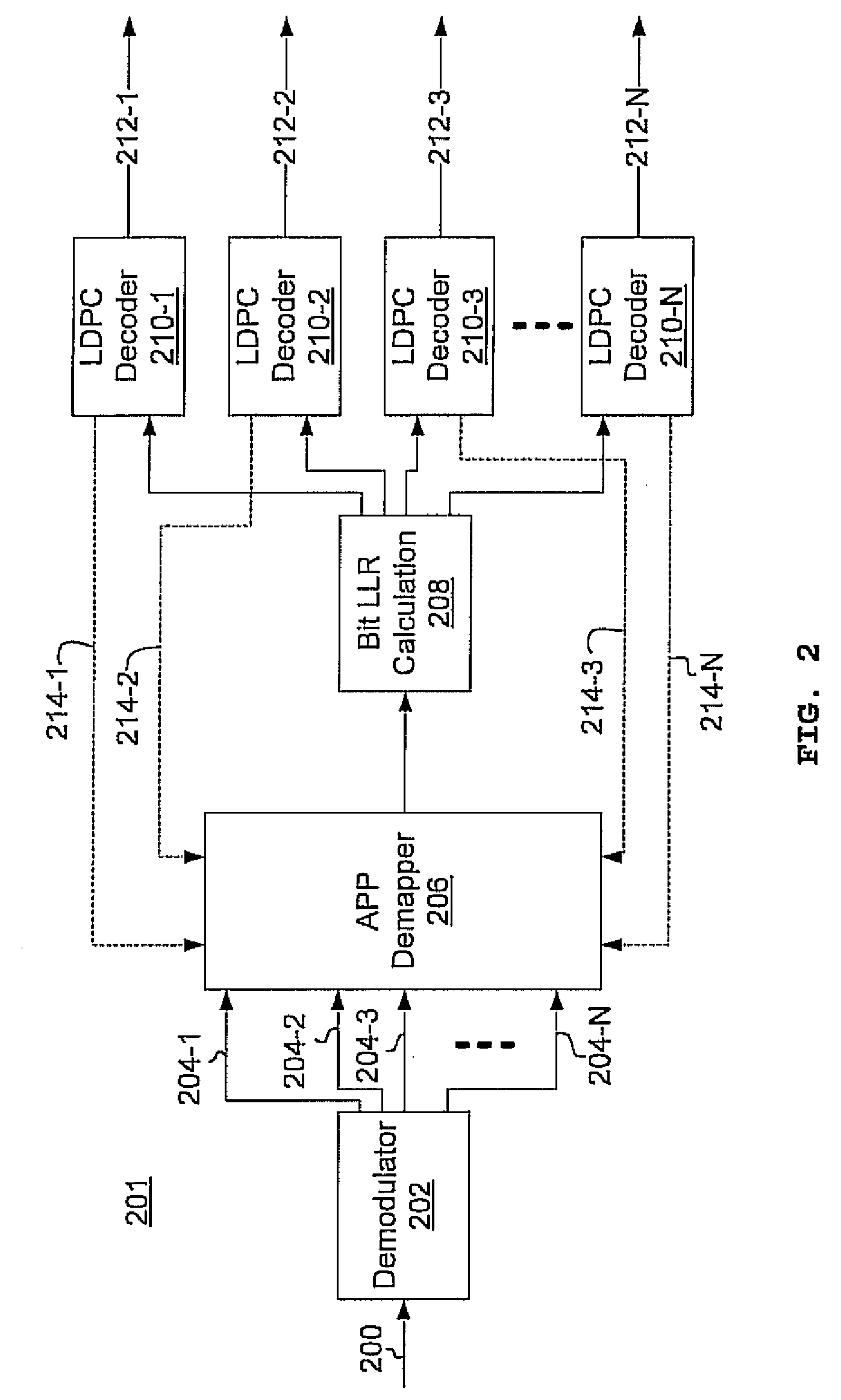
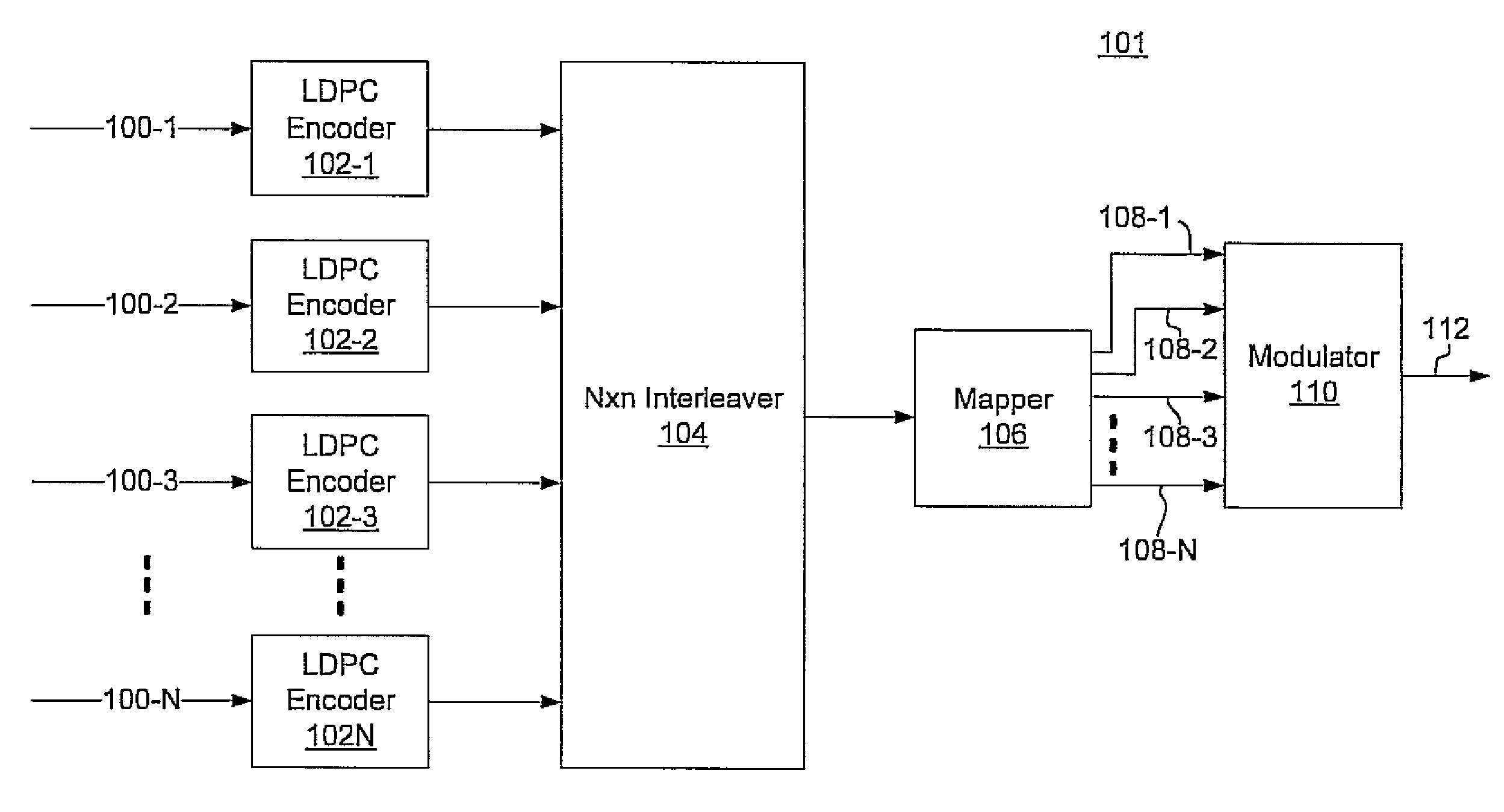
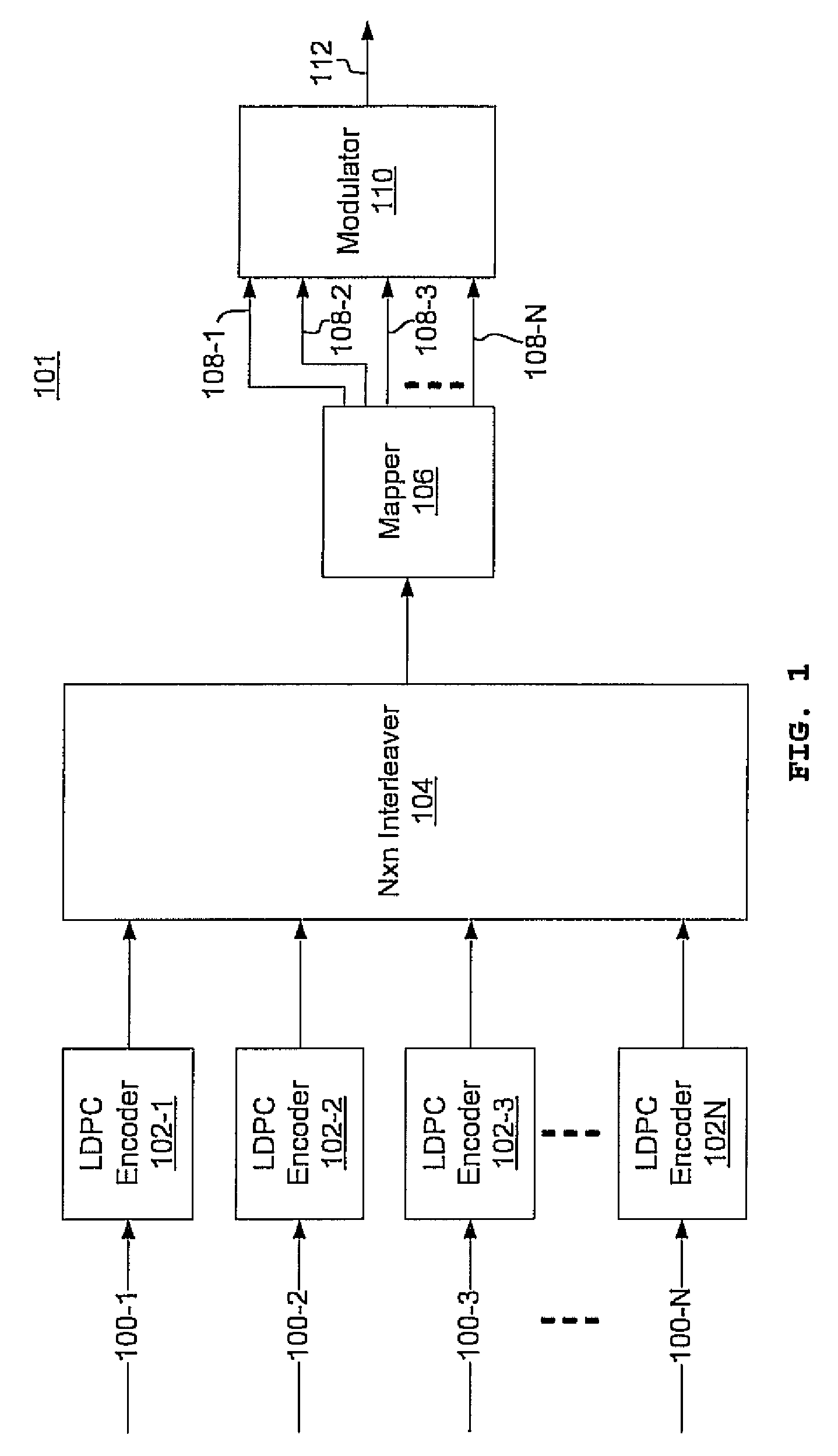
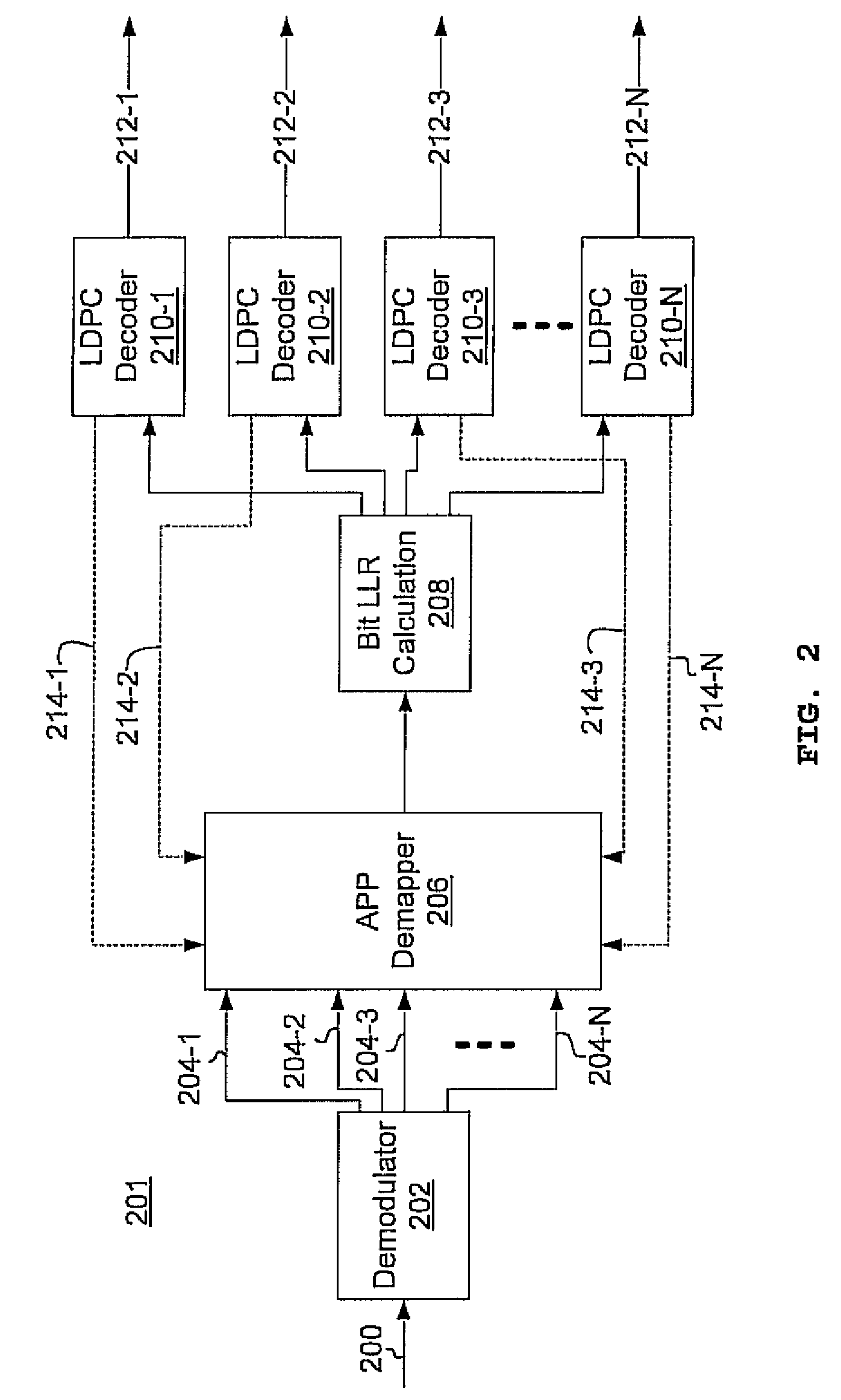
Multi-dimensional LDPC coded modulation for high-speed optical transmission systems
ActiveUS20100211849A1Error correction/detection using LDPC codesCode conversionEngineeringOrthonormal basis functions
Arbitrarily high data transmission rates may be achieved by the use of N-dimensional, LDPC-coded modulation. N orthonormal basis functions are employed using coherent reception, resulting in a proportional increase in transmission rate with only a modest increase in bit-error ratio.
Owner:NEC CORP
Image construction based video display system
InactiveUS8970646B2Television system scanning detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsTime domainSpatial light modulator
A video display system based on constructing images through displaying orthogonal basis function components of the image is disclosed. The system is comprised of two display components aligned and driven concurrently. The first display component is a coarse pixel array. The second display component is a spatial light modulator whose geometric details are finer than the first pixel array. The overall system reconstructs the intended video to be displayed at the finer geometric details of the second display component at a minimal image quality loss through the use of time-domain display of orthogonal image basis function components. The resultant system has a considerably reduced interconnection complexity and number of active circuit elements, and also requires a considerably smaller video data rate if a lossy image reconstruction scheme is used. An embodiment with a LED based display and an LCD based spatial light modulator utilizing the concepts, and methods to drive the displays are described herein.
Owner:OSTENDO TECH INC
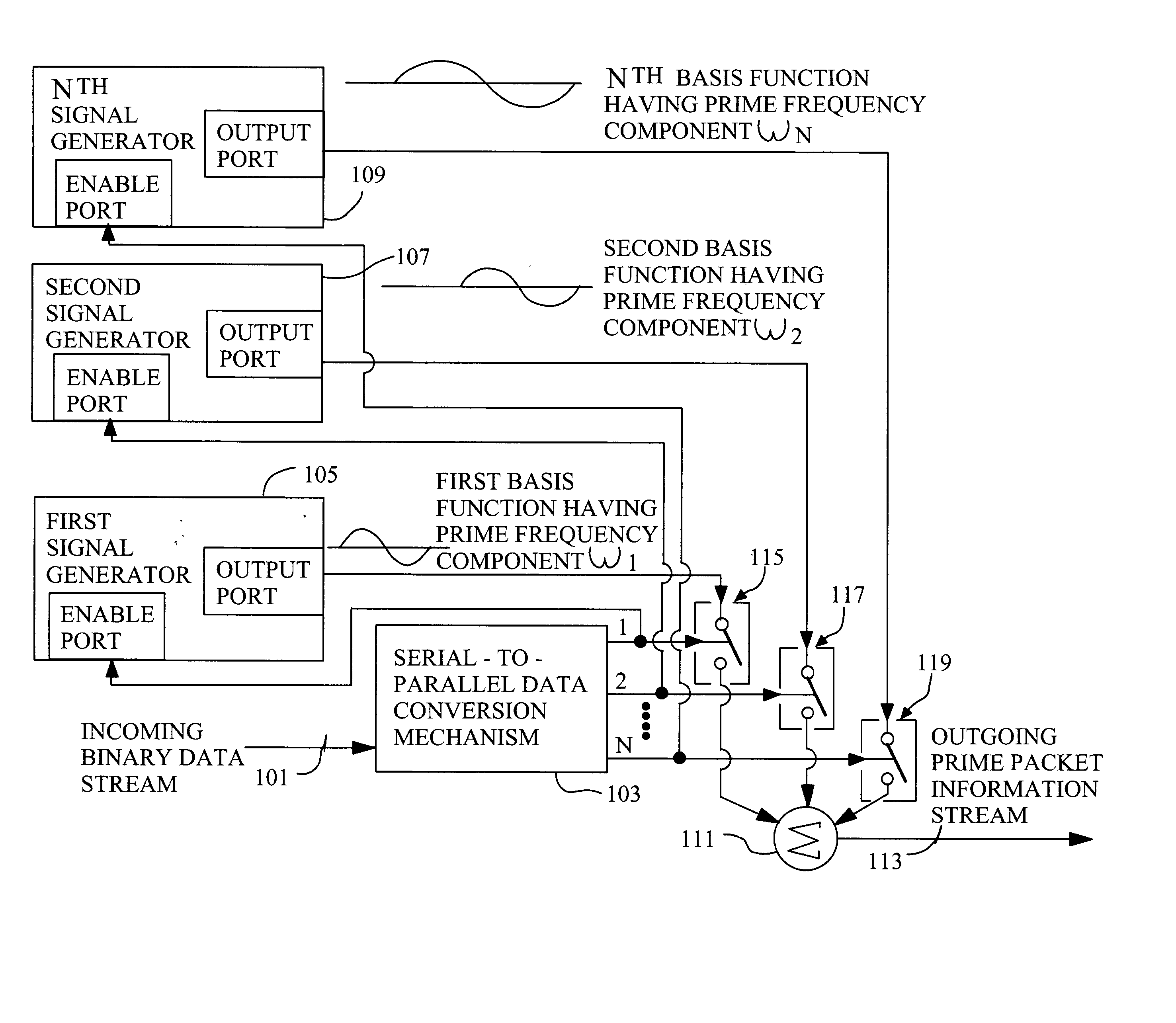
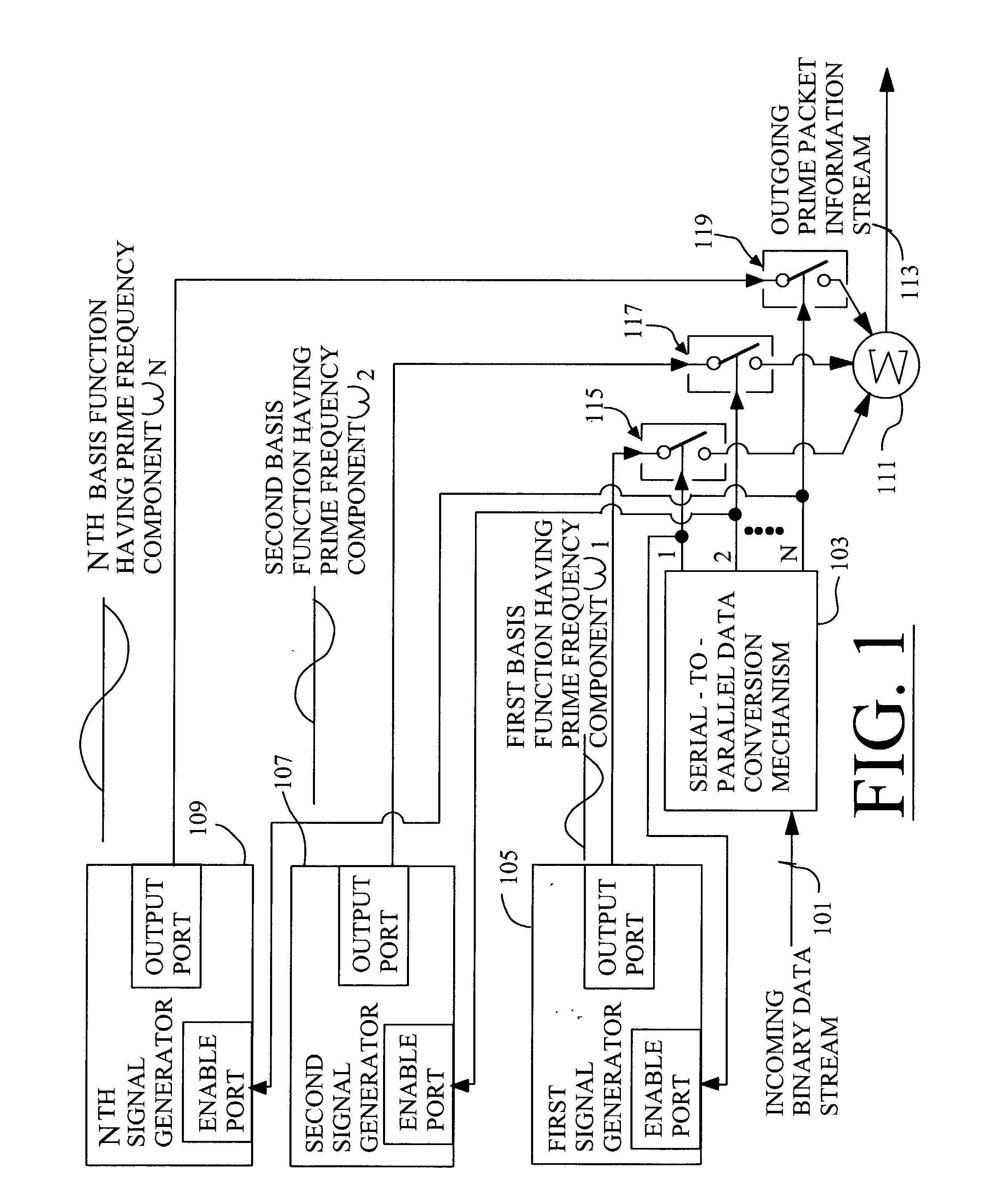
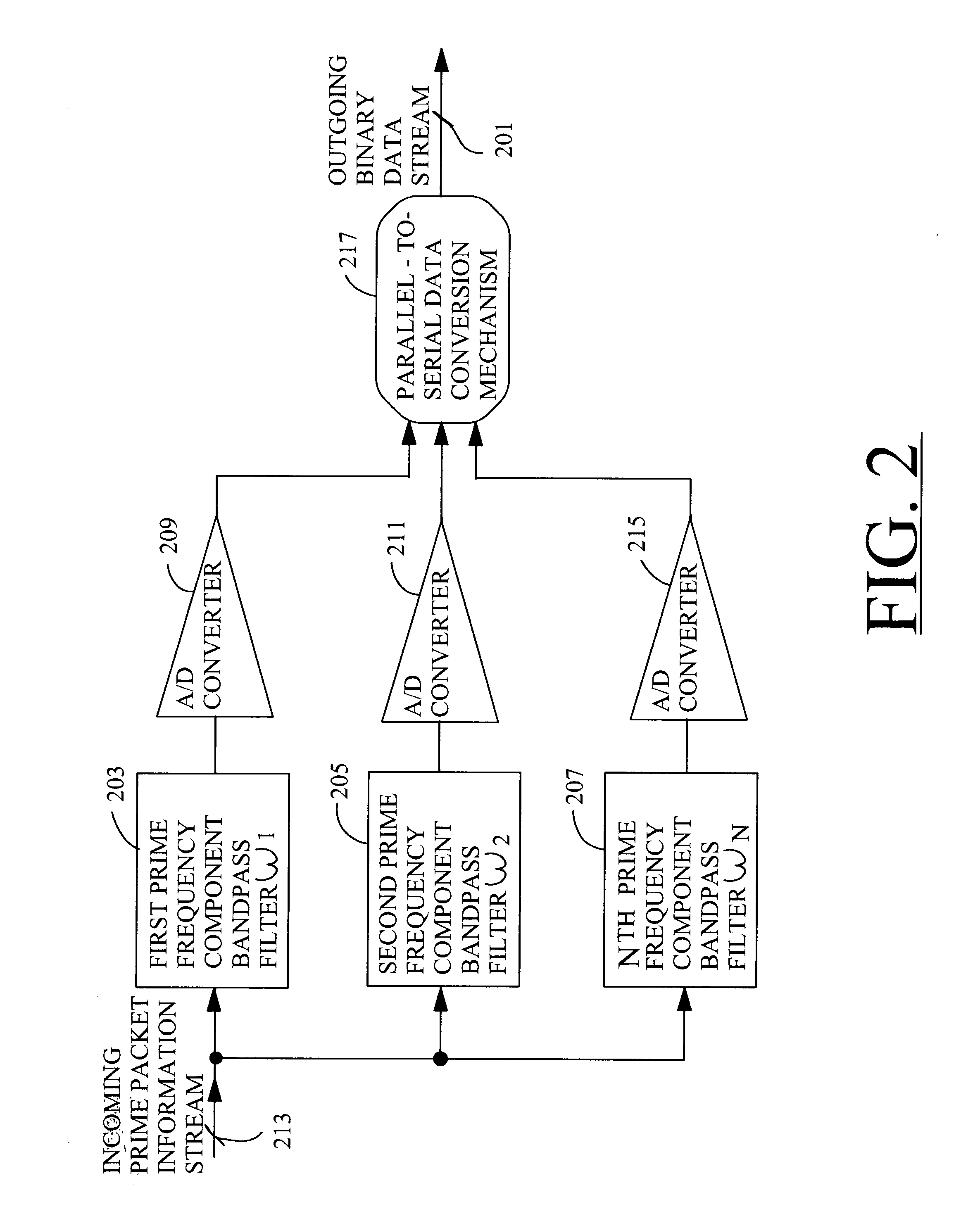
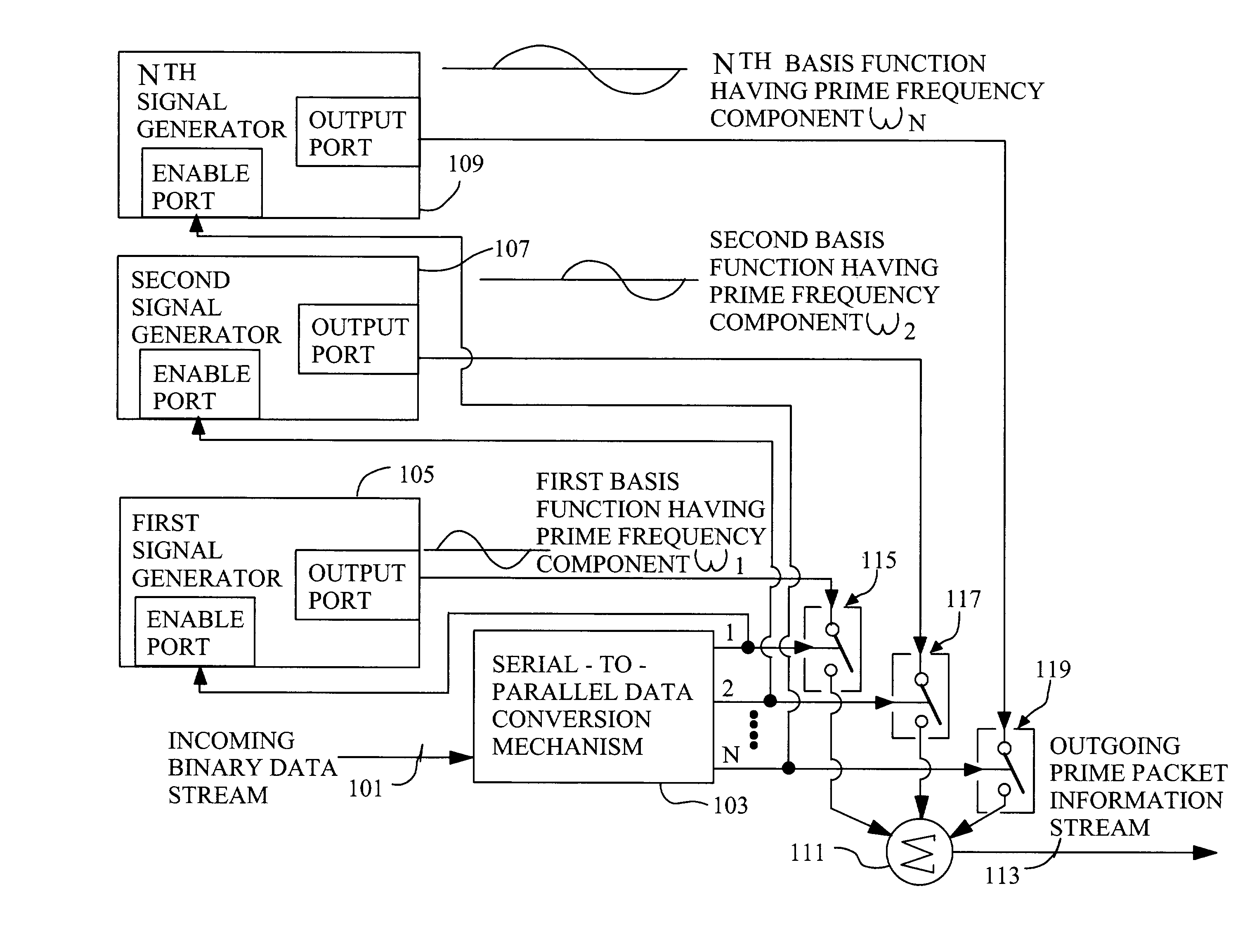
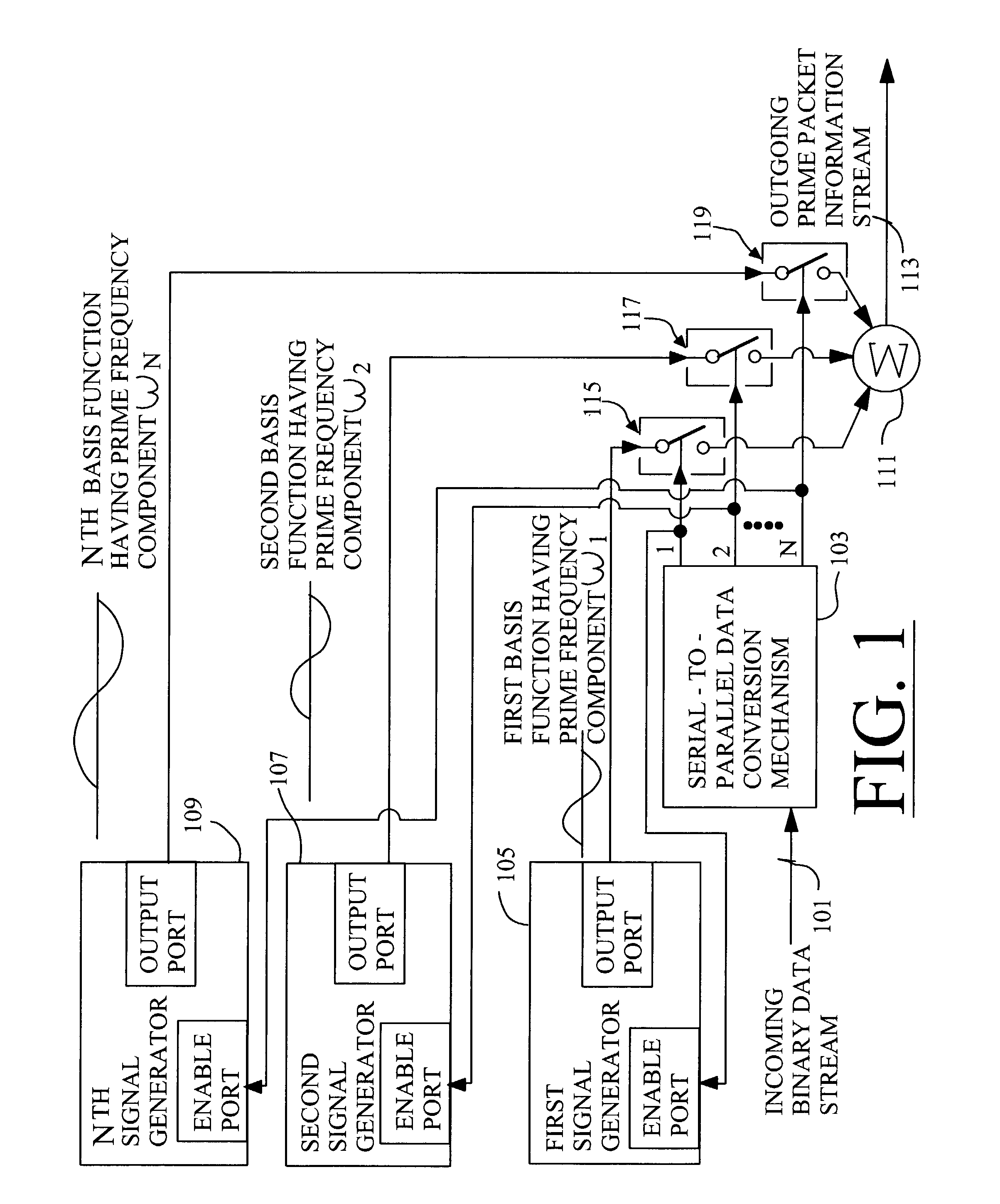
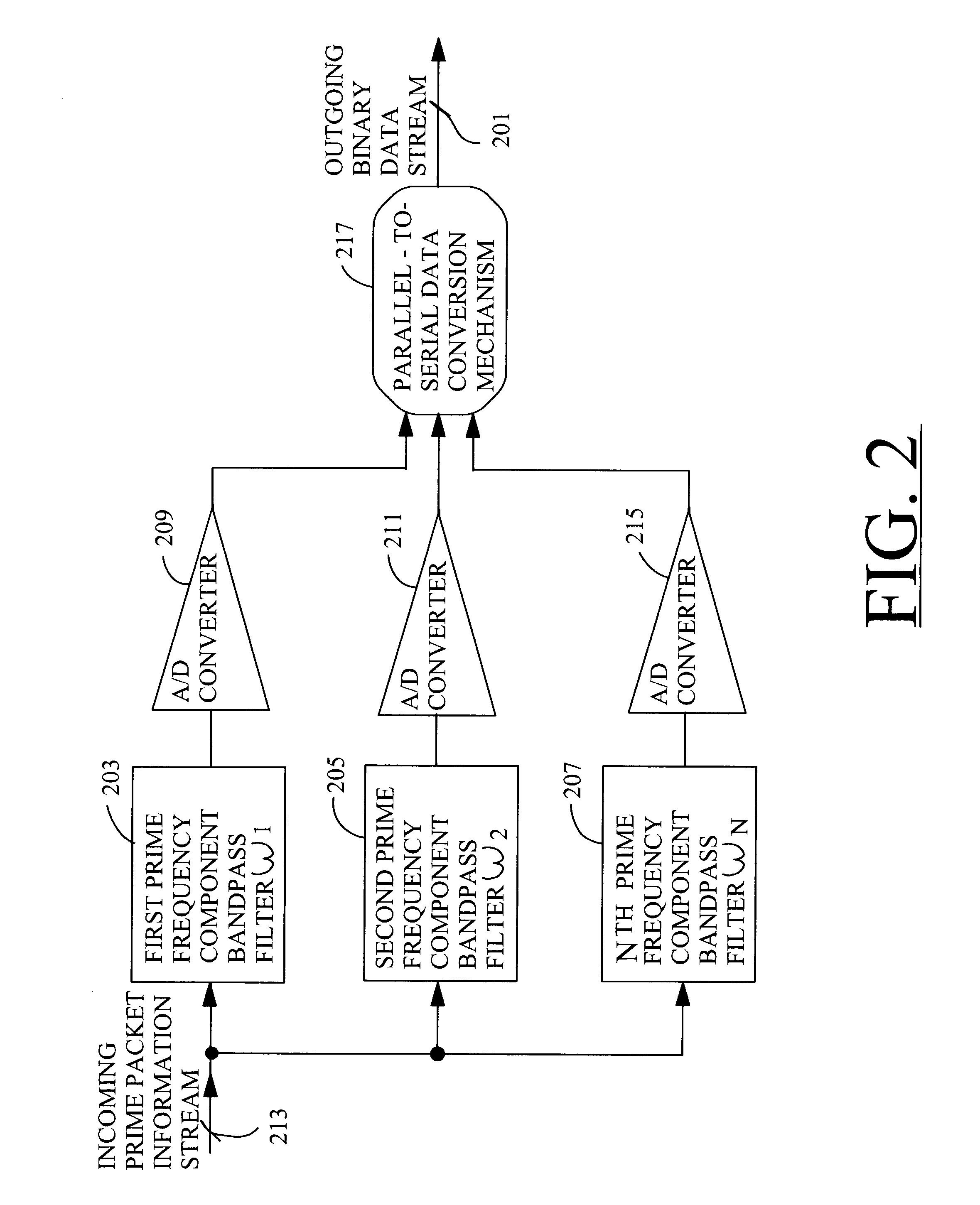
Techniques for communicating information using prime-frequency waveform mapping
InactiveUS20020191534A1Increase effective bandwidthReduce potential interferenceFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexOrthogonal basisOrthonormal basis functions
Systems and methods for efficiently conveying one or more broadband communication channels over a transmission medium. Communication is effected by transforming an incoming digital bit stream into a prime frequency information stream that includes a plurality of prime frequency components. This transformation can be accomplished through the use of a plurality of mathematical basis functions. The prime frequency information stream is then transmitted over the transmission medium. More particularly, digital bit streams carried on one or more incoming channels are in the form of binary "on" and "off" bits. These digital bits are converted into a plurality of prime frequency components which together comprise a prime frequency information stream. The conversion process maps each of respective incoming digital bits to a corresponding one of a group of orthogonal basis functions.
Owner:BANDWIDTH TECH
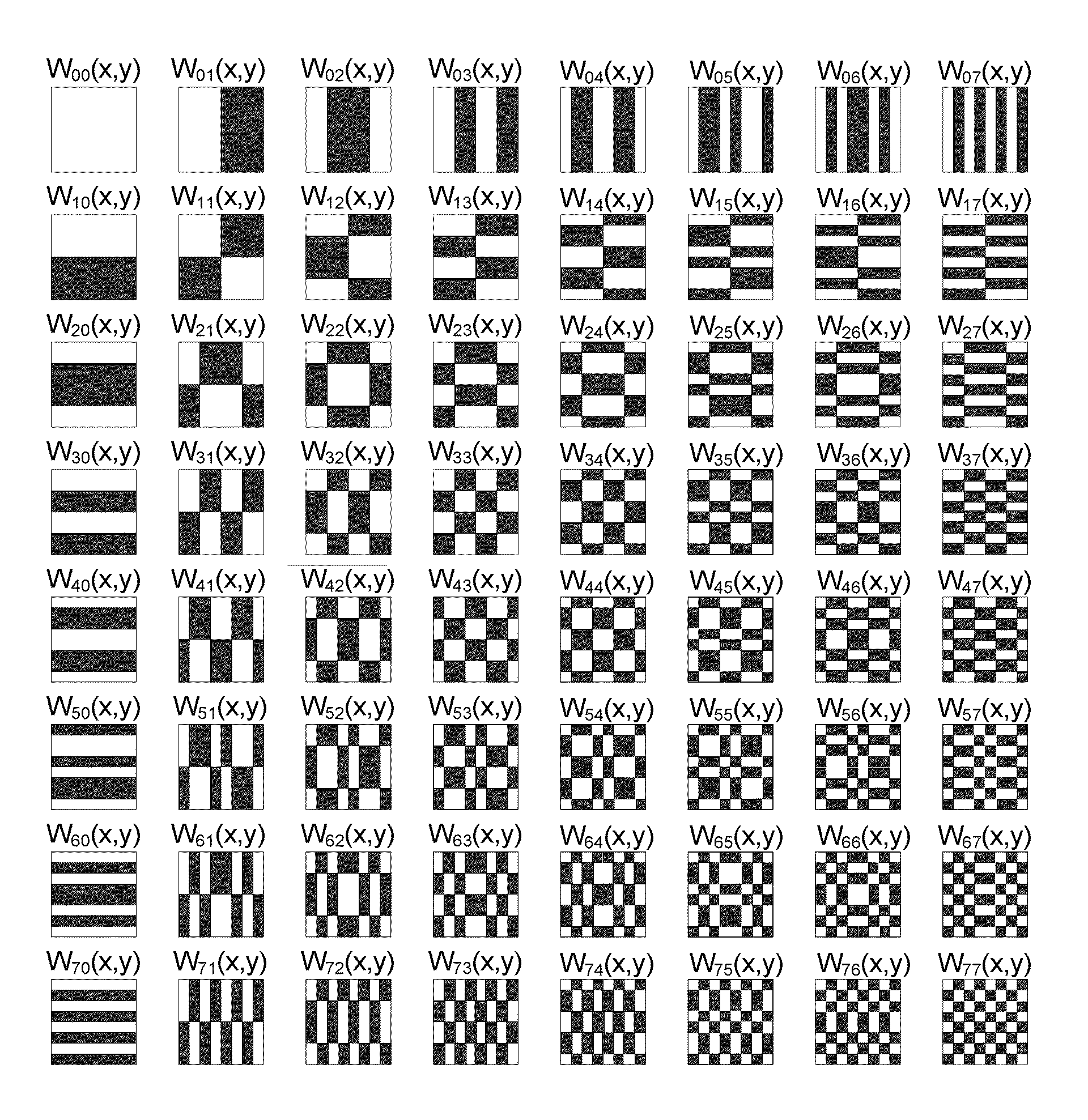
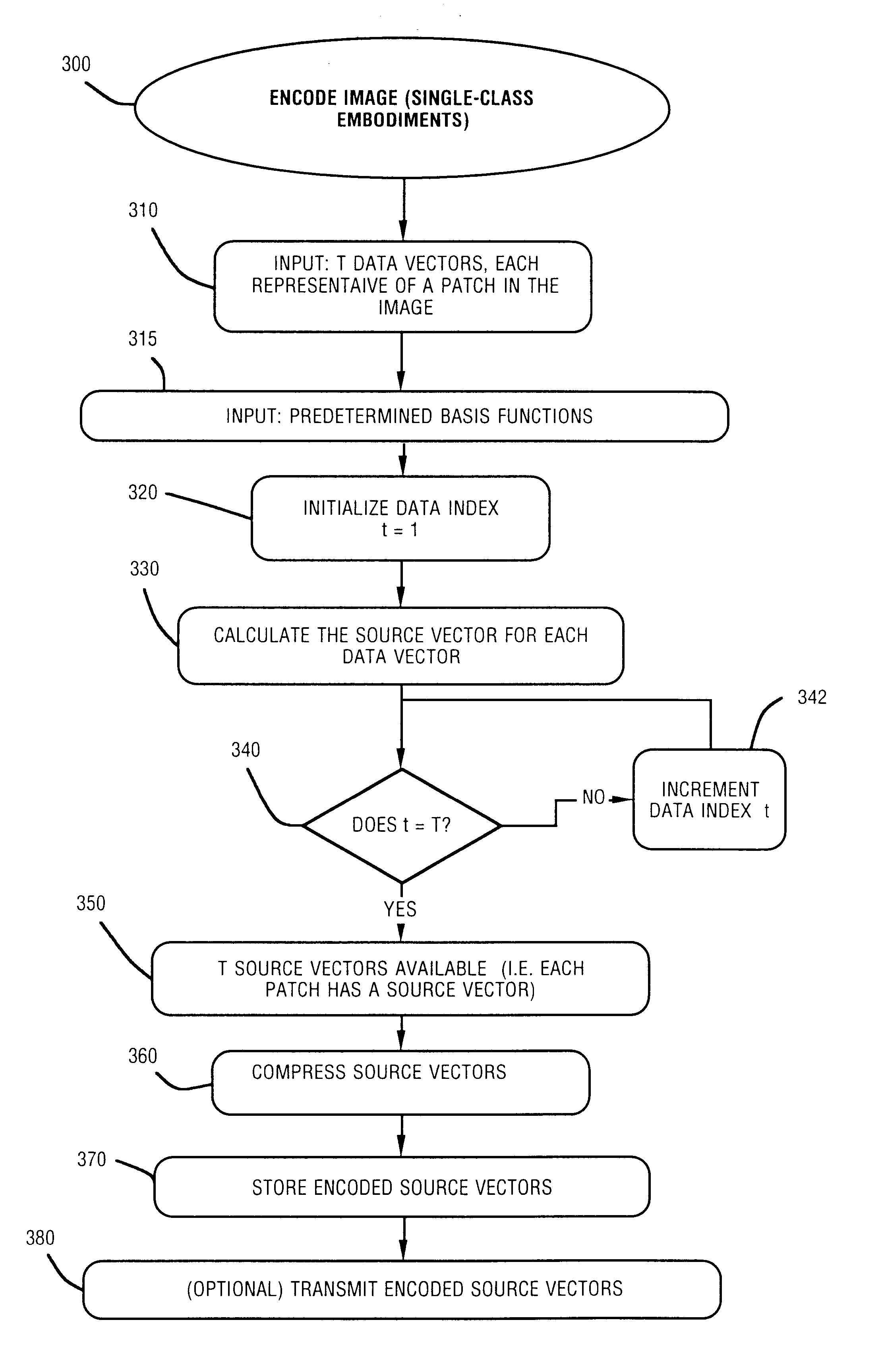
Method and apparatus for efficiently encoding chromatic images using non-orthogonal basis functions
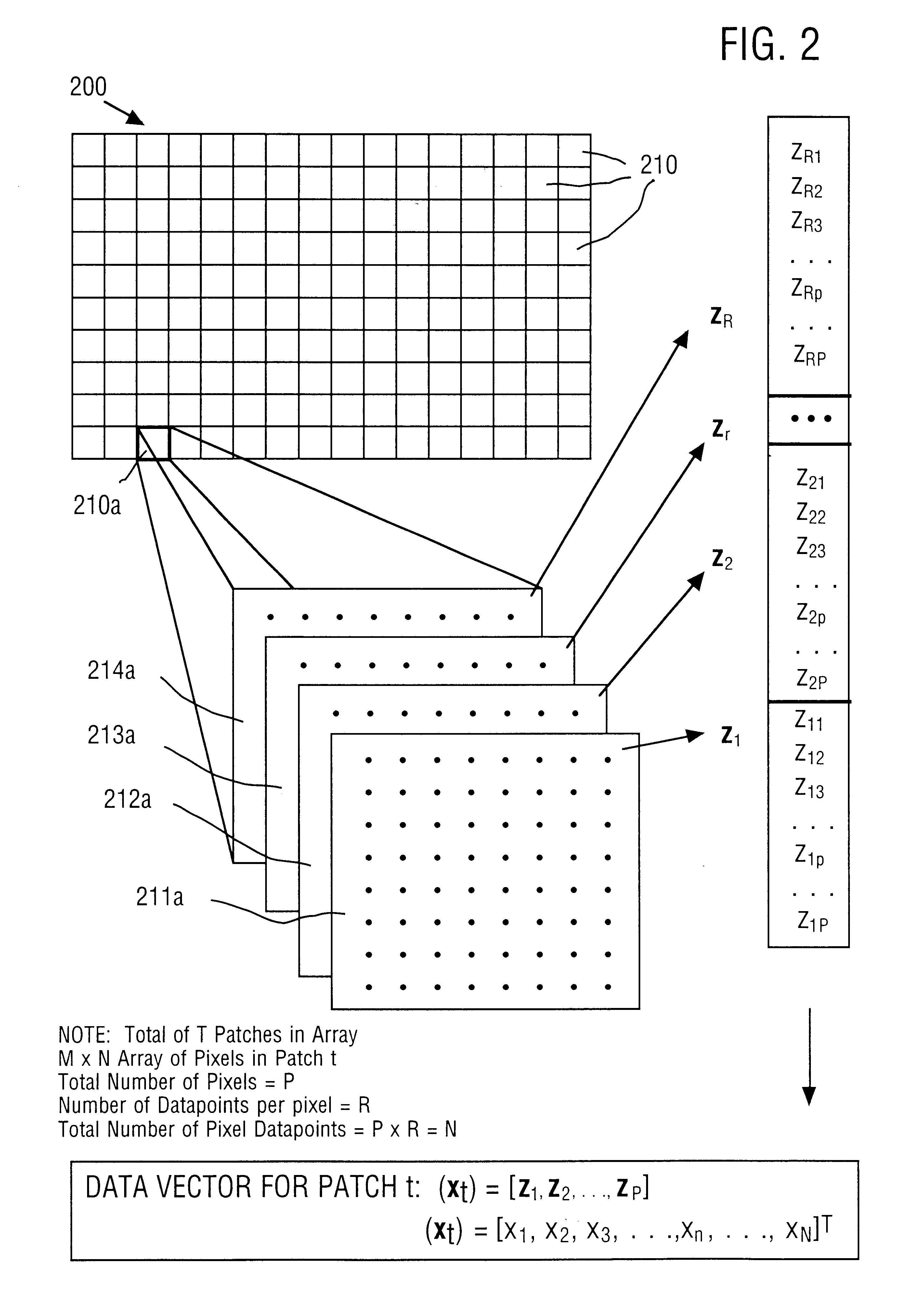
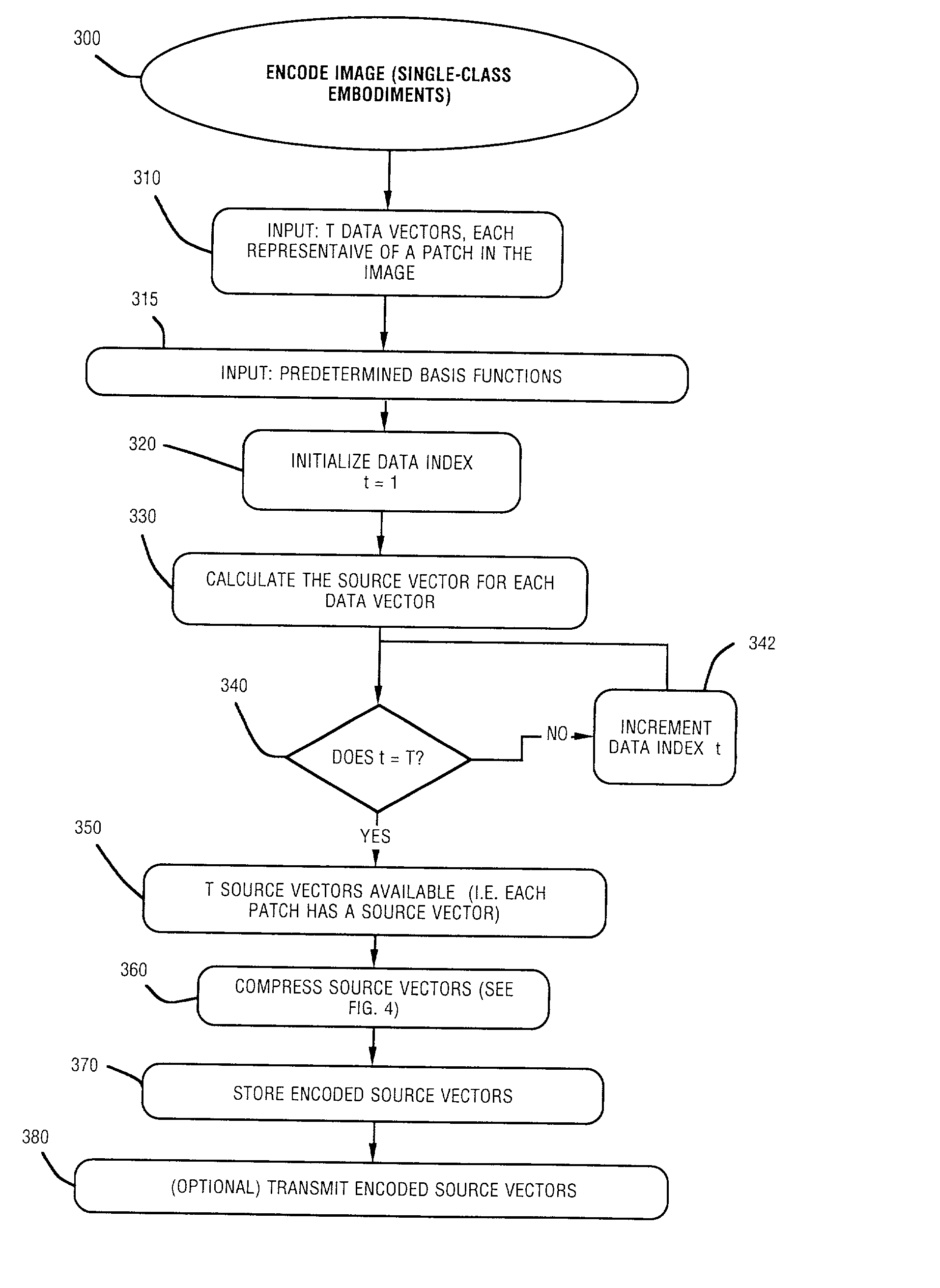
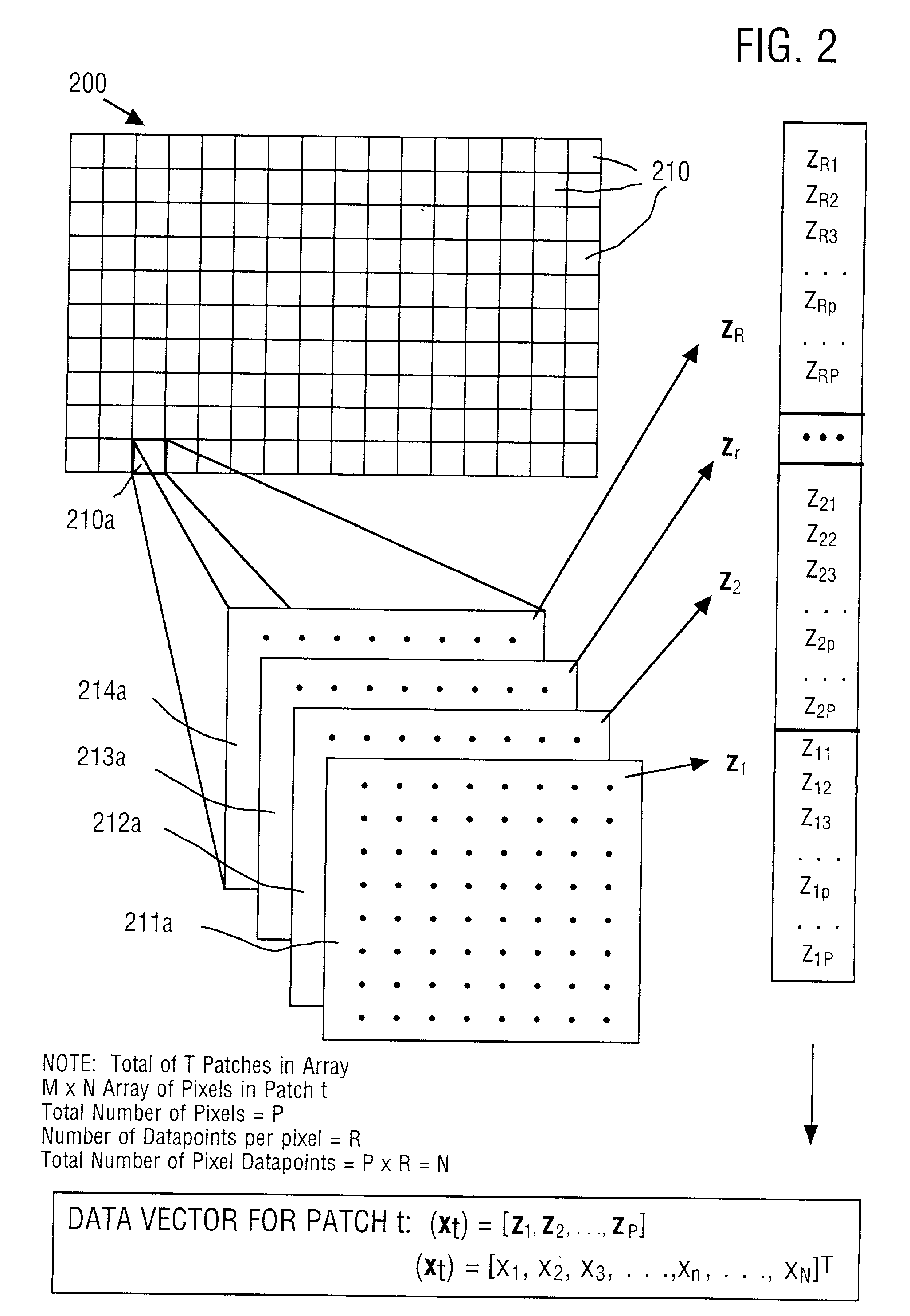
InactiveUS6870962B2Efficient representationReduce file sizeCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionTheoretical computer scienceChromatic scale
A method and apparatus for efficiently encoding images using a set of non-orthogonal basis functions, thereby allowing reduction of file size, shorter transmission time, and improved accuracy. The non-orthogonal basis functions include homogenous color basis functions, luminance-encoding basis functions that have luminance edges and chromatic basis functions that exhibit color opponency. Some of the basis functions are non-orthogonal with respect to each other. Using these basis functions, a source vector is calculated to provide a number of coefficients, each coefficient associated with one basis function. The source vector is compressed by selecting a subset of the calculated coefficients, thereby providing an encoded vector. Because the method is highly efficient, the image data is substantially represented by a small number of coefficients. In some embodiments, the non-orthogonal basis functions include two or more classes. A wavelet approach can also be utilized.
Owner:THE SALK INST +1
Method and apparatus for efficiently encoding chromatic images using non-orthogonal basis functions
A method and apparatus for efficiently encoding images using a set of non-orthogonal basis functions, thereby allowing reduction of file size, shorter transmission time, and improved accuracy. The non-orthogonal basis functions include homogenous color basis functions, luminance-encoding basis functions that have luminance edges and chromatic basis functions that exhibit color opponency. Some of the basis functions are non-orthogonal with respect to each other. Using these basis functions, a source vector is calculated to provide a number of coefficients, each coefficient associated with one basis function. The source vector is compressed by selecting a subset of the calculated coefficients, thereby providing an encoded vector. Because the method is highly efficient, the image data is substantially represented by a small number of coefficients. In some embodiments, the non-orthogonal basis functions include two or more classes. A wavelet approach can also be utilized.
Owner:THE SALK INST +1
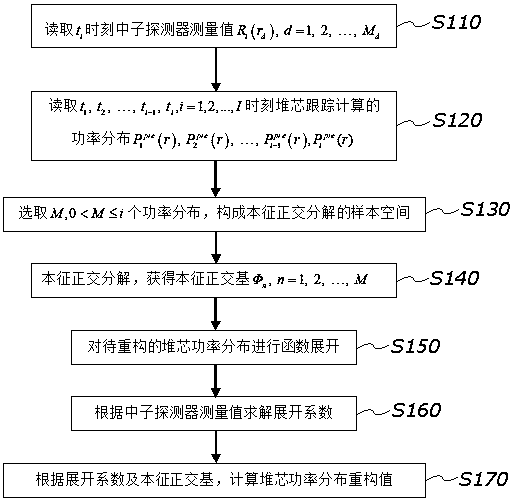
Reactor core power proper orthogonal decomposition online reconstruction method
ActiveCN109830317AImprove calculation accuracyDecrease the decisive influenceNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNeutron diffusionNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a reactor core power proper orthogonal decomposition online reconstruction method. The method includes: reading the neutron detector measured value of a reactor core at the current moment; reading the reactor core tracking calculation power distribution of the reactor core at the current moment and the previous moment; selecting the power distribution for proper orthogonaldecomposition to form a proper orthogonal decomposition sample; performing proper orthogonal decomposition on the proper orthogonal decomposition sample to obtain a proper orthogonal basis; using theorthogonal basis function to perform function expansion on to-be-reconstructed reactor core power distribution; solving an expansion coefficient according to the read neutron detector measured value;calculating a reactor core power distribution reconstruction value according to the expansion coefficient and the proper orthogonal basis. The method has the advantages that by applying the proper orthogonal decomposition technology and the reactor core power distribution of reactor core tracking calculation at different moments, the calculation precision of reactor core power distribution onlinereconstruction is increased, and the decisive influence of the neutron diffusion calculation result on the reactor core power distribution online reconstruction result is lowered evidently.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
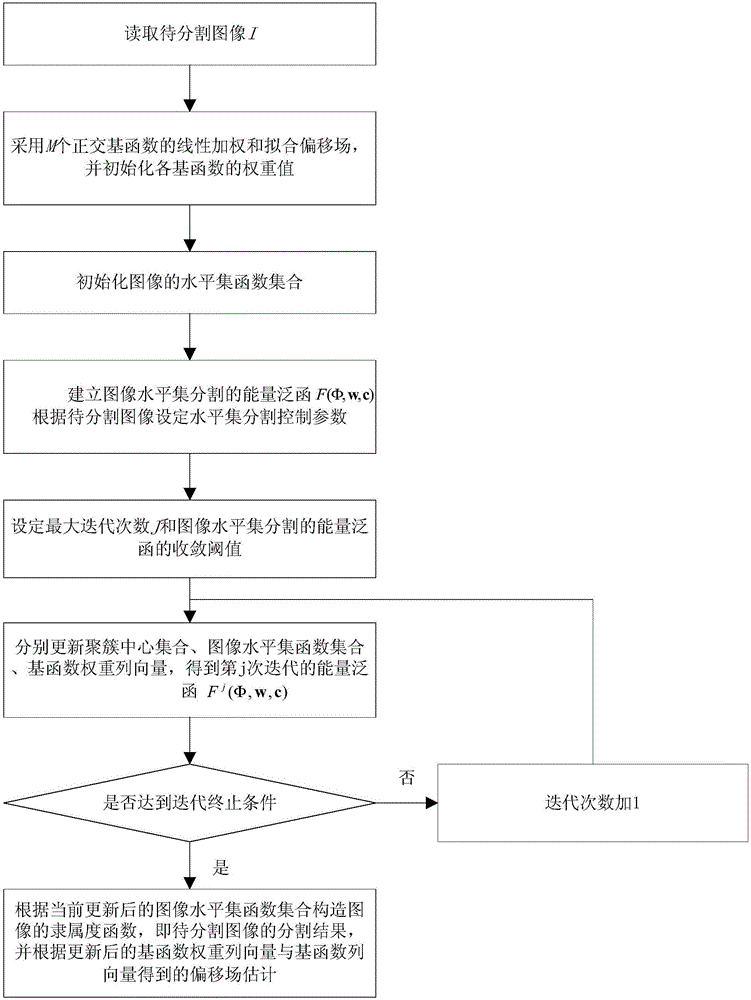
Image level set segmentation method based on local gray clustering characteristics
ActiveCN106204592AGray scale inconsistency estimationAvoid negative effectsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionOrthogonal basis
The invention provides an image level set segmentation method based on local gray clustering characteristics. The method comprises the steps that images to be segmented are read; linear weighting and fitting bias fields of orthogonal basis functions are used, and the weight value of each basis function is initialized; the level set function set of the images is initialized; the energy functional of image level set segmentation is established, and level set segmentation control parameters are set according to the images to be segmented; a clustering center set, the image level set function set and basis function weight column vectors are respectively updated until meeting the stop criterion for iteration so that the energy functional of iteration is obtained; the subordinating degree function of the images, i.e. the segmentation result of the images to be segmented, is constructed according to the currently updated image level set function set, and bias field estimation of the images to be segmented is obtained according to the updated basis function weight column vectors and basis function column vectors. According to the method, the adverse impacts of weak boundary, image noise and gray inconsistency on the accuracy of image segmentation can be overcome by the method so that the method has the effect of image gray correction.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Multi-dimensional LDPC coded modulation for high-speed optical transmission systems
ActiveUS8219874B2Error detection/correctionError correction/detection using LDPC codesEngineeringOrthonormal basis functions
Arbitrarily high data transmission rates may be achieved by the use of N-dimensional, LDPC-coded modulation. N orthonormal basis functions are employed using coherent reception, resulting in a proportional increase in transmission rate with only a modest increase in bit-error ratio.
Owner:NEC CORP
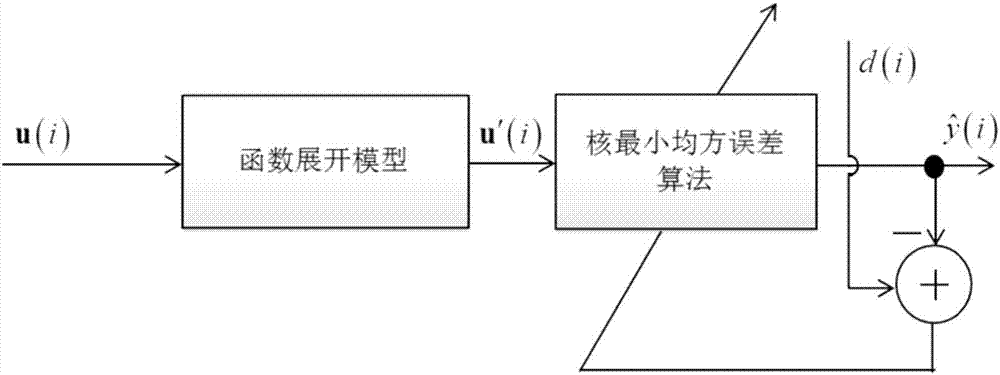
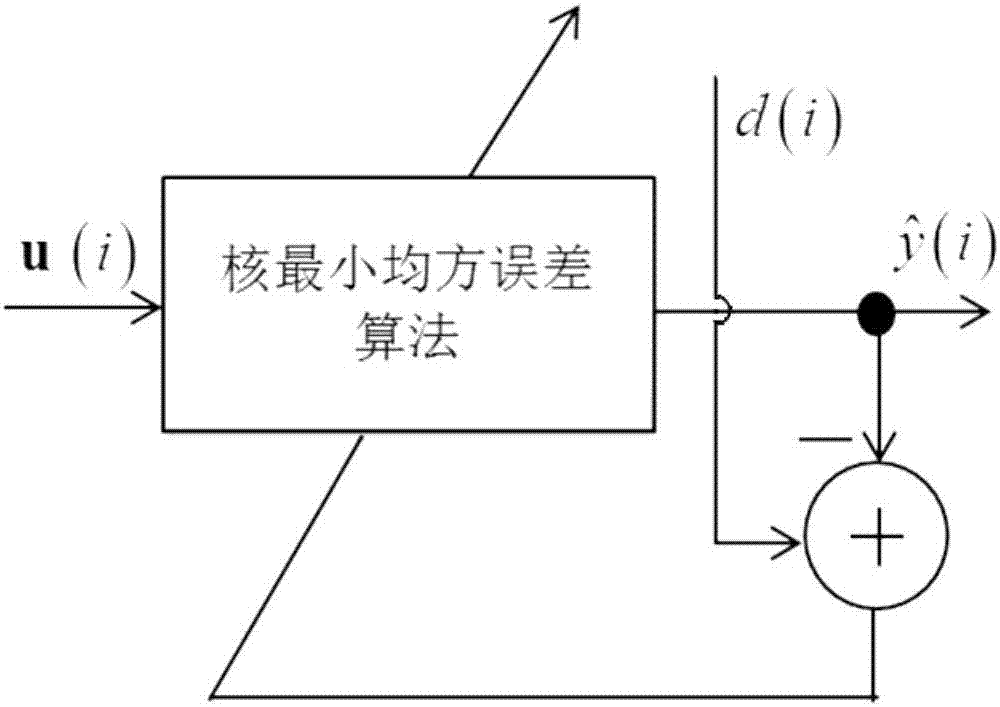
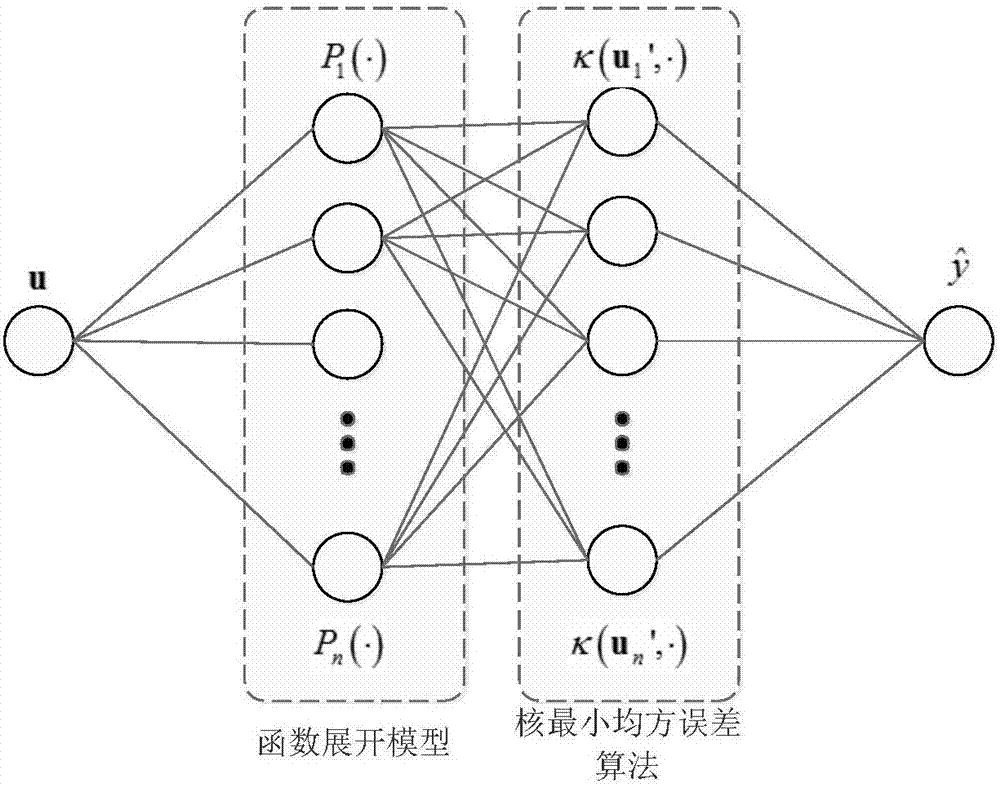
Kernel adaptive filter algorithm based on function expansion
InactiveCN107181474AFast convergenceImprove performanceAdaptive networkRound complexityOrthogonal basis
The invention provides a kernel adaptive filter algorithm based on function expansion. Through an orthogonal basis function expansion model, original input data is subjected to dimension expansion, then a kernel minimum squared error algorithm is used to carry out filtering, and the output of a filter is obtained, wherein the orthogonal basis function expansion model is formed by a Chebyshev orthogonal polynomial or a Legendre orthogonal polynomial. The invention provides the kernel adaptive filter algorithm based on function expansion, through a function expansion model, the input data is subjected to dimension expansion and then is taken as an input of a kernel least squares algorithm, the minimum squared error algorithm is used to carry out adaptive filtering, the algorithm performance can be improved further, a reasonable embedding dimension is given, since only the dimension of an input space is increased in the function expansion model, the computational complexity is not significantly increased, the convergence performance of the filter can be significantly improved under the premise of not significantly increasing the computational complexity, and the algorithm has an important research significance and a wide practical engineering value.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
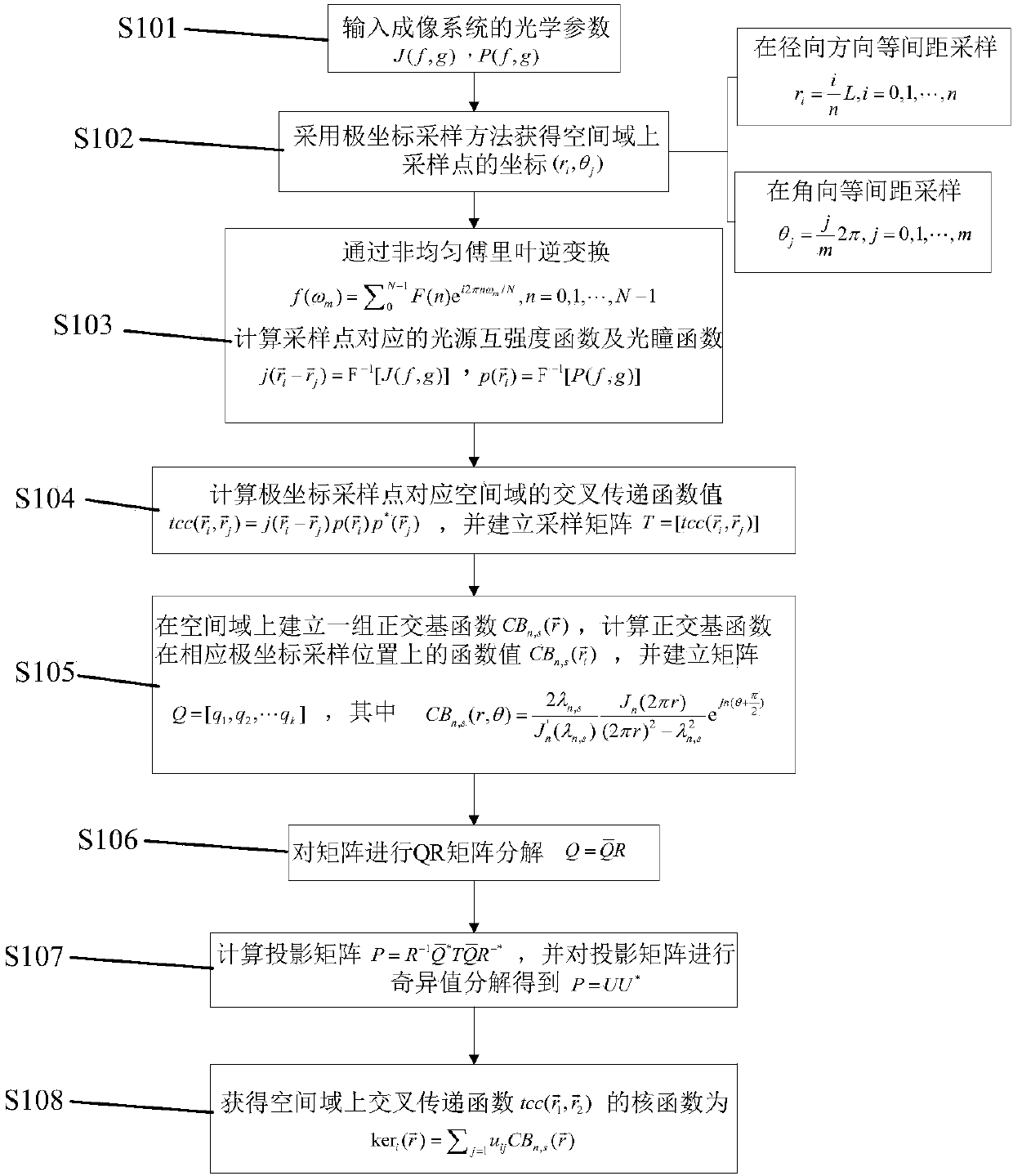
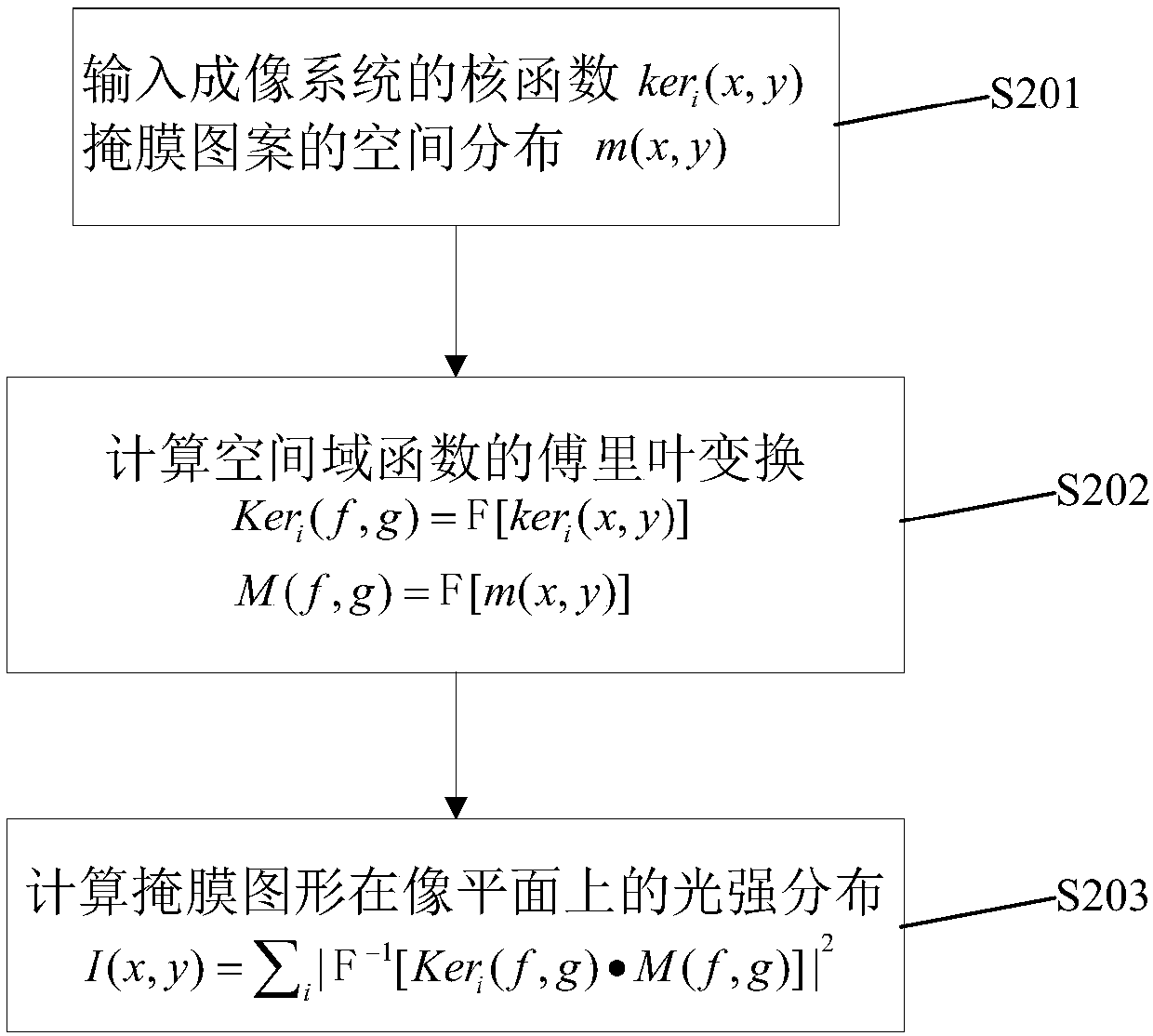
Polar coordinate sampling-based cross transfer function quick decomposition method
InactiveCN107644131APromote decompositionAchieve decompositionSpecial data processing applicationsSingular value decompositionMatrix decomposition
The invention discloses a polar coordinate sampling-based cross transfer function quick decomposition method. The method comprises the following steps of 1) obtaining optical parameters of an imagingsystem; 2) obtaining coordinates (ri, theta j) of sampling points on a spatial domain by adopting a polar coordinate sampling method; 3) calculating light source mutual intensity functions, defined inthe specification, and pupil functions, defined in the specification, corresponding to the sampling points through non-uniform inverse Fourier transform; 4) calculating a cross transfer function value, defined in the specification, of the spatial domain corresponding to the sampling points, and establishing a sampling matrix defined in the specification; 5) establishing a group of orthogonal basis functions defined in the specification, calculating function values, defined in the specification, of the orthogonal basis functions in corresponding polar coordinate sampling positions, and establishing a matrix Q=[q1, q2, ...qk]; 6) performing QR matrix decomposition, defined in the specification, on the matrix Q; 7) calculating a projection matrix and performing singular value decomposition on the projection matrix P to obtain P=UU*; 8) obtaining a kernel function, defined in the specification, of the cross transfer function, defined in the specification, on the spatial domain. Quick analysis can be performed to obtain the TCC kernel function, so that light intensity distribution calculation is quick and efficient, and actual photoetching process design demands are met.
Owner:SUZHOU COGENDA ELECTRONICS CO LTD
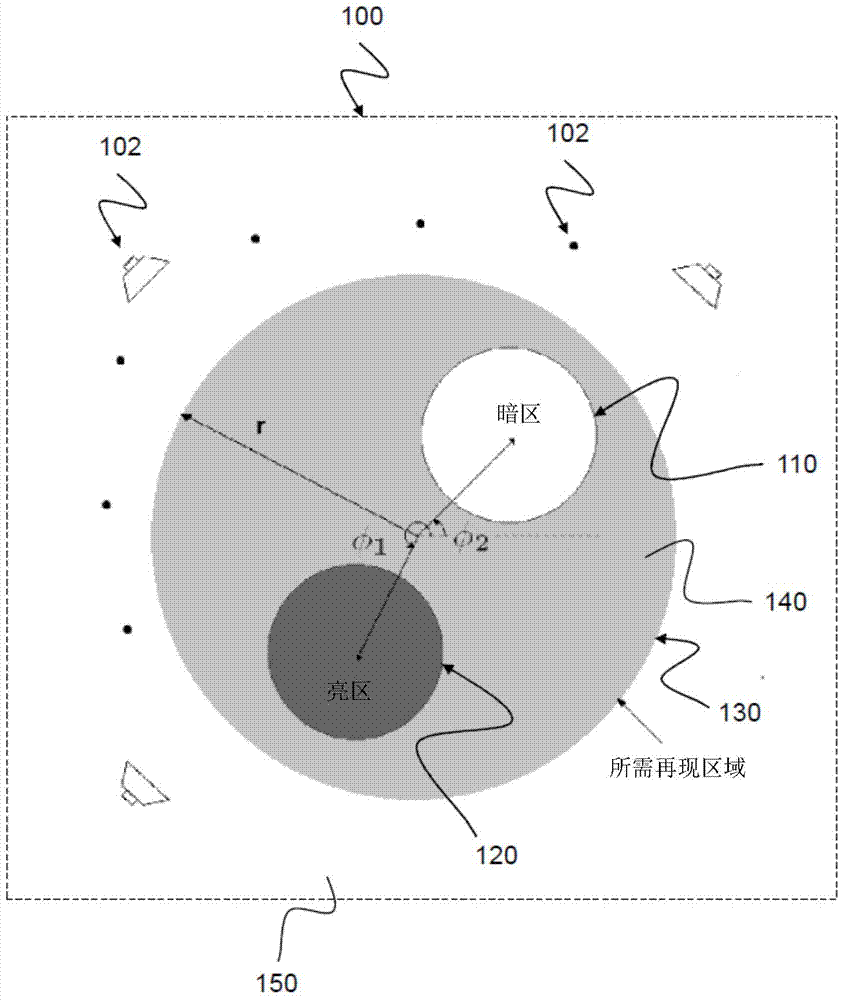
Audio rendering system
The invention relates to an audio rendering system (100), comprising: a plurality of loudspeakers (102) arranged to approximate a desired spatial sound field within a predetermined reproduction region (130), wherein the loudspeakers (102) are configured to approximate the sound field based on a weighted series of orthonormal basis functions for the reproduction region (130).
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Multi-rate prediction control method applied to train active suspension system
InactiveCN104950667AOptimizing Active Vibration Control PerformanceGuaranteed operational stabilityAdaptive controlTime lagPredictive controller
The invention relates to a multi-rate prediction control method applied to a train active suspension system. On the basis of the active suspension system model of the high-speed train, prediction control algorithm researches based on a standard orthogonal basis function orthogonal basis function-Laguerre function are carried out. under the circumstances that a state space model of the suspension system is used as a prediction control model and basic principles like rolling optimization in prediction control are combined, a corresponding prediction control is designed for the active suspension multi-rate and time-lag-contained multi-rate system of the high-speed train by considering influence factors like uncertain track interference excitation during the train running process. According to the system model, the controller parameters can be adjusted and optimized continuously to enable the system to realize an optimum control effect, thereby optimizing the vibration active control performance during the high-speed train running process and guaranteeing operation stability and comfort during the training running.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
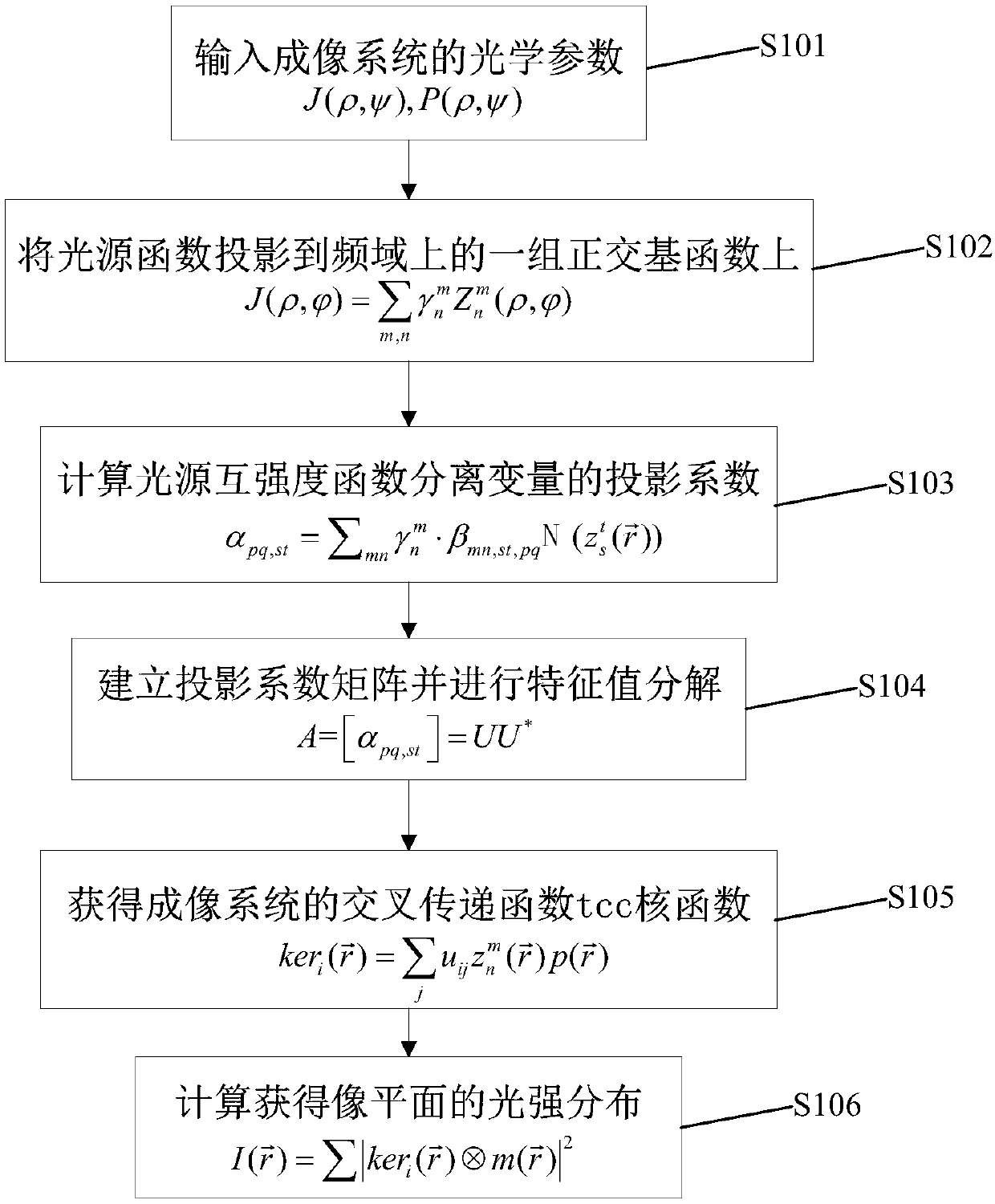
Rapid optical imaging calculation method based on light source mutual intensity function decomposition
InactiveCN107479335AQuick calculationEasy accessPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusHat matrixPupil function
The invention discloses a rapid optical imaging calculation method based on light source mutual intensity function decomposition. The rapid optical imaging calculation method comprises the following steps: 1) acquiring a light source function and a pupil function of an imaging system; 2) projecting the light source function to a group of orthogonal basis functions on a frequency domain; 3) solving a projection coefficient alpha pq,st of a base function corresponding to a light source mutual intensity function on a space domain; 4) establishing a positive definite projection matrix A=[alpha pq,st] by using the projection coefficient alpha pq,st, and performing feature vector decomposition A=UU*; 5) performing variables separation on the light source mutual intensity function, and establishing a kernel function of a cross transmission function on the space domain; and 6) calculating the convolution of the kernel function and a mask plate pattern, and acquiring an exposure pattern on an image plane. By adopting the method, Fourier function conversion pairs on a group of space domains and frequency domains are utilized, complex integral transformation is calculated according to convolution definition, then corresponding kernel functions are rapidly acquired, light intensity distribution can be rapidly and efficiently calculated, and thus actual photolithography process design requirements can be met.
Owner:SUZHOU COGENDA ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Techniques for communicating information using prime-frequency waveform mapping
InactiveUS7042902B2Increase effective bandwidthReduce distractionsFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexOrthogonal basisOrthonormal basis functions
Systems and methods for efficiently conveying one or more broadband communication channels over a transmission medium. Communication is effected by transforming an incoming digital bit stream into a prime frequency information stream that includes a plurality of prime frequency components. This transformation can be accomplished through the use of a plurality of mathematical basis functions. The prime frequency information stream is then transmitted over the transmission medium. More particularly, digital bit streams carried on one or more incoming channels are in the form of binary “on” and “off” bits. These digital bits are converted into a plurality of prime frequency components which together comprise a prime frequency information stream. The conversion process maps each of respective incoming digital bits to a corresponding one of a group of orthogonal basis functions.
Owner:BANDWIDTH TECH
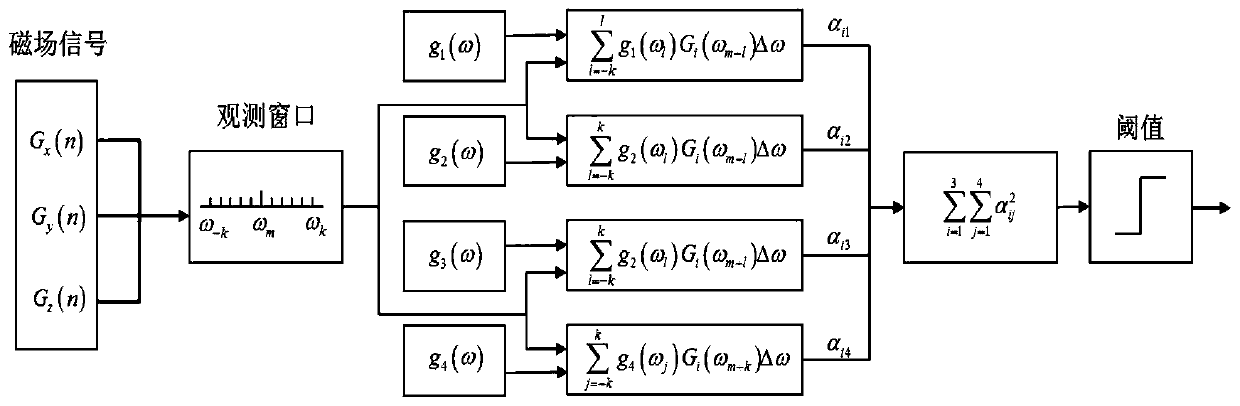
Method for processing scalar magnetic anomaly gradient signal based on orthogonal basis function
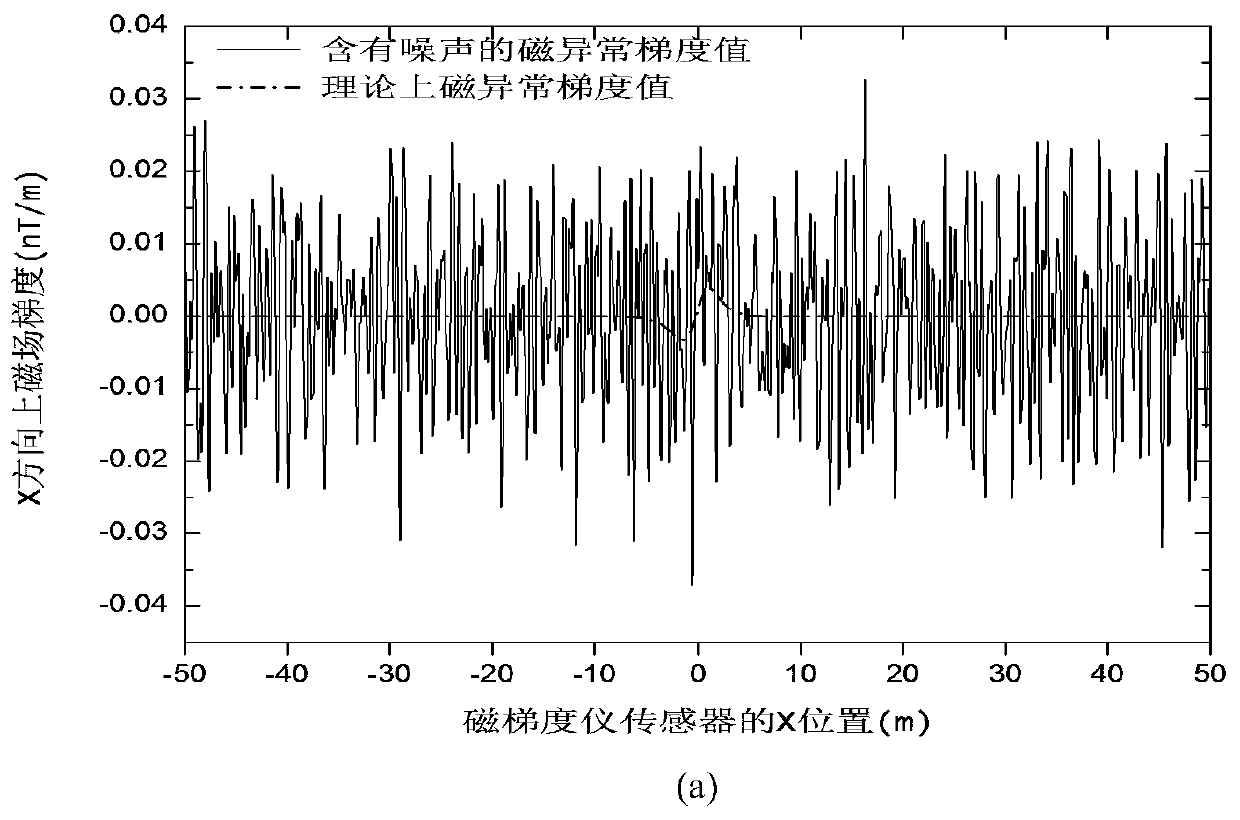
ActiveCN111399066AImprove detection abilityHigh detectionWater resource assessmentElectric/magnetic detectionComputational physicsOrthonormal basis functions
The invention relates to a method for processing scalar magnetic anomaly gradient signals based on orthogonal basis functions, which designs four basis functions of magnetic anomaly gradients by analyzing the magnetic anomaly gradients generated by a target. The method comprises: due to the fact that the four primary functions are linearly independent, obtaining the orthogonal primary functions ofthe scalar magnetic anomaly gradient signals through Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization and normalization; calculating a coefficient corresponding to the orthogonal basis function according to the property of the orthogonal basis function and the measured magnetic anomaly gradient signal; designing a detection index and a target azimuth parameter of the magnetic target by utilizing the coefficient; when the detection index is greater than a set threshold value, realizing magnetic anomaly detection; and then, obtaining azimuth information of the target according to the coefficient of the orthogonal basis function. According to the invention, the influence of magnetic noise on target detection can be effectively suppressed, the output signal-to-noise ratio is improved, and weak magnetic anomalydetection and positioning are realized.
Owner:西北工业大学青岛研究院 +2
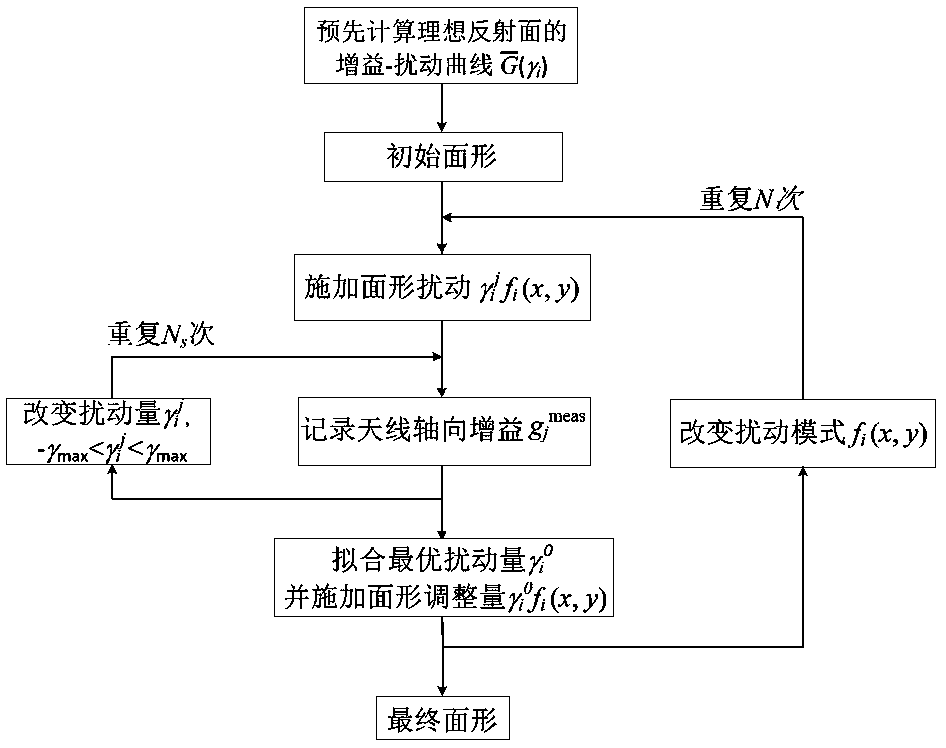
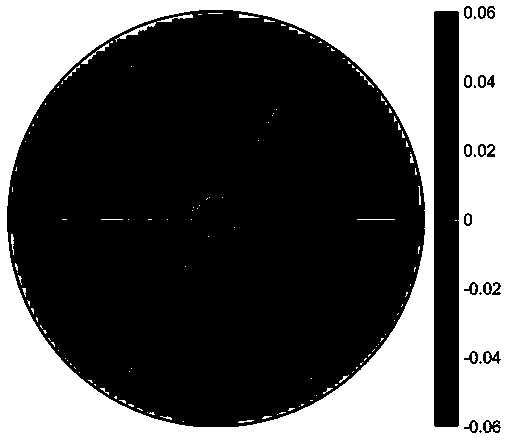
Active reflective surface shape adjustment method based on axial gain measurement
ActiveCN109873253AEnsure observation efficiencyProximity CorrectionComplex mathematical operationsAntennasPower detectorAntenna gain
The invention discloses an active reflective surface shape adjustment method based on axial gain measurement. According to the method, a series of micro-disturbance is applied to a reflective surfaceshape through an actuator network in an active surface system, and the change in antenna axial gain is measured in the disturbing process; a group of orthogonal basis functions defined on an antenna port surface are used as disturbance modes to disturb the surface shape one by one, and under each disturbance mode, a curve of the change in the antenna axial gain along with the disturbance quantityis recorded, and the optimal adjustment quantity under each disturbance mode is fitted out of the corresponding curve; and through a series of disturbance, measurement and adjustment processes, finally the antenna gain can reach a maximal value, and the surface shape error can reach a minimal value. The method has a low requirement on a detector, and a single-pixel power detector can be used; in the running process of a telescope, a scientific receiver and an astronomical point source target can be directly utilized to carry out surface shape measurement and adjustment frequently, and therefore the observation efficiency of the telescope in the running process is maintained.
Owner:ZIJINSHAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
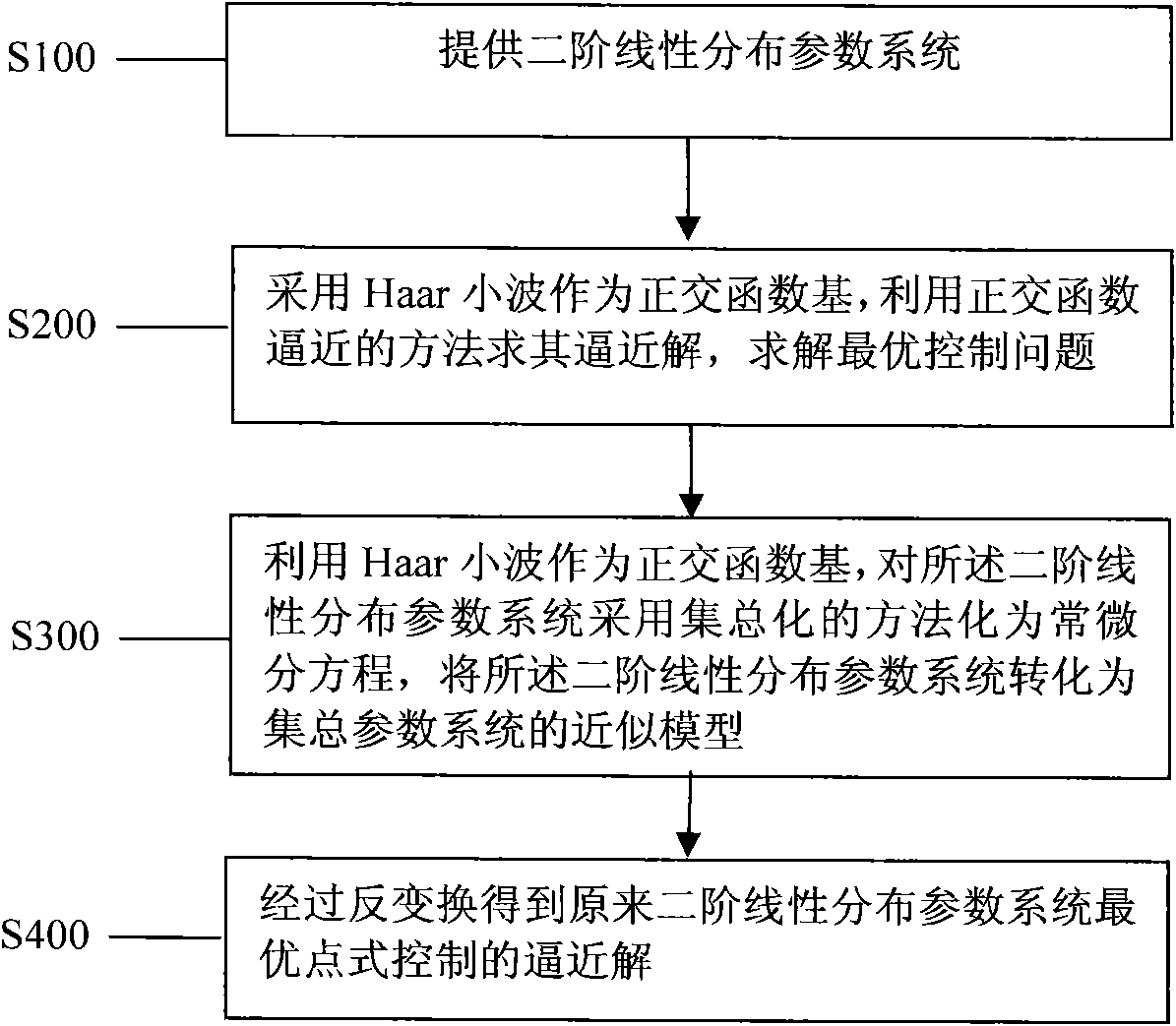
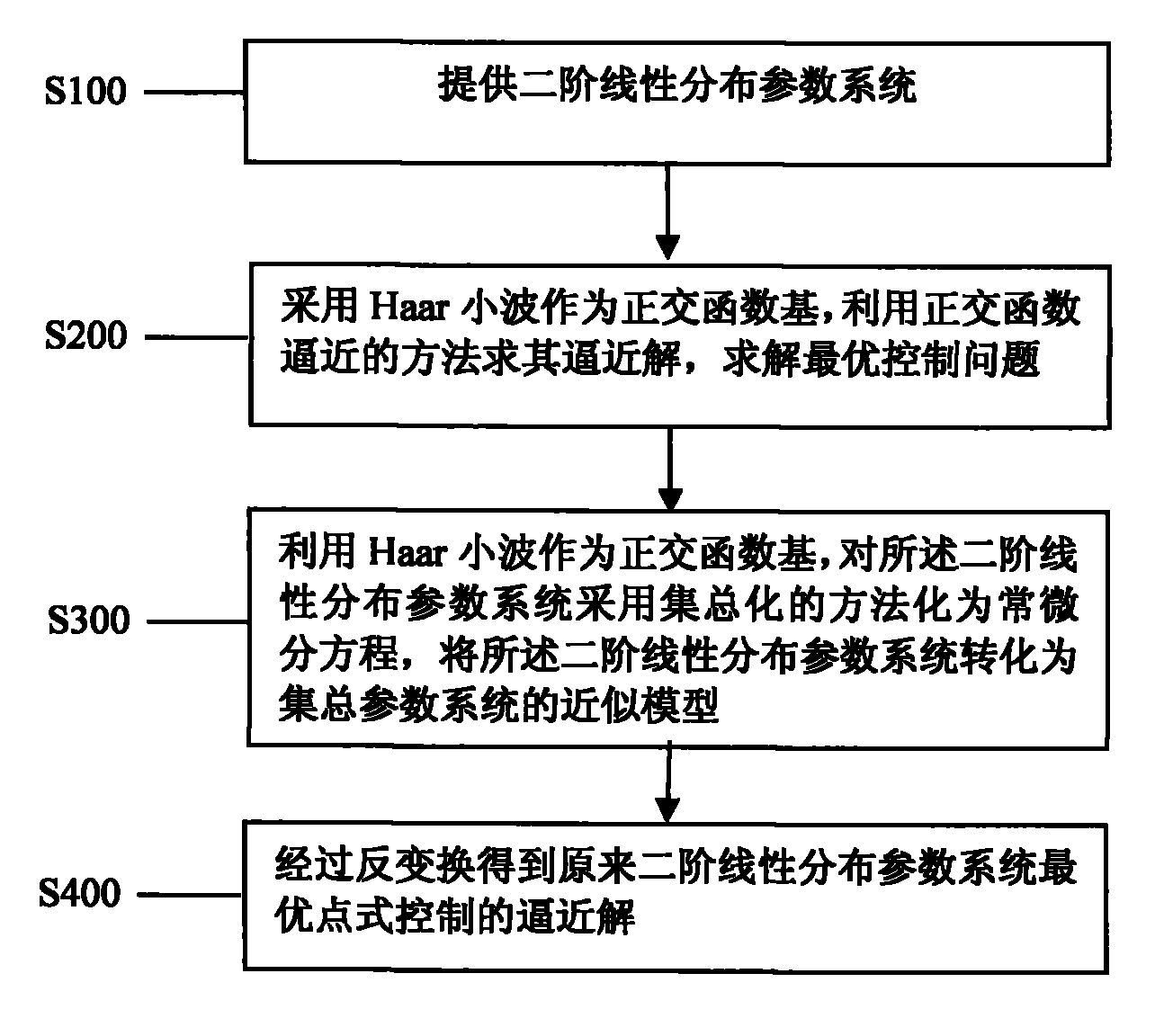
Wavelet analysis method of optimal point-wise control of distributed parameter system
InactiveCN101819412AGood effectSmall amount of calculationAdaptive controlDistributed parameter systemAlgorithm
The invention discloses a wavelet analysis method of the optimal point-wise control of a distributed parameter system, comprising the following steps of: detruding a differential operation matrix, a product integral operation and an element product operation matrix corresponding to Haar wavelet with the aid of an orthogonal function approximating method, and applying the differential operation matrix, the product integral operation and the element product operation matrix to the research of the problem of the optimal point-wise control of the distributed parameter system, converting the problem of the optimal pint-wise control of the distributed parameter system into a lumped parameter problem, and obtaining an approximating solution of the original optimal point-wise control of the distributed parameter system by an inverse transformation, such that the problem hardly to be solved is easy to solve and a wavelet approximating algorithm with better performance is obtained. In the invention, the provided Haar wavelet approximating algorithm is a method with better control effect, and the method provides a new way for solving the problem of the optimal point-wise control of the distribution parameter system.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
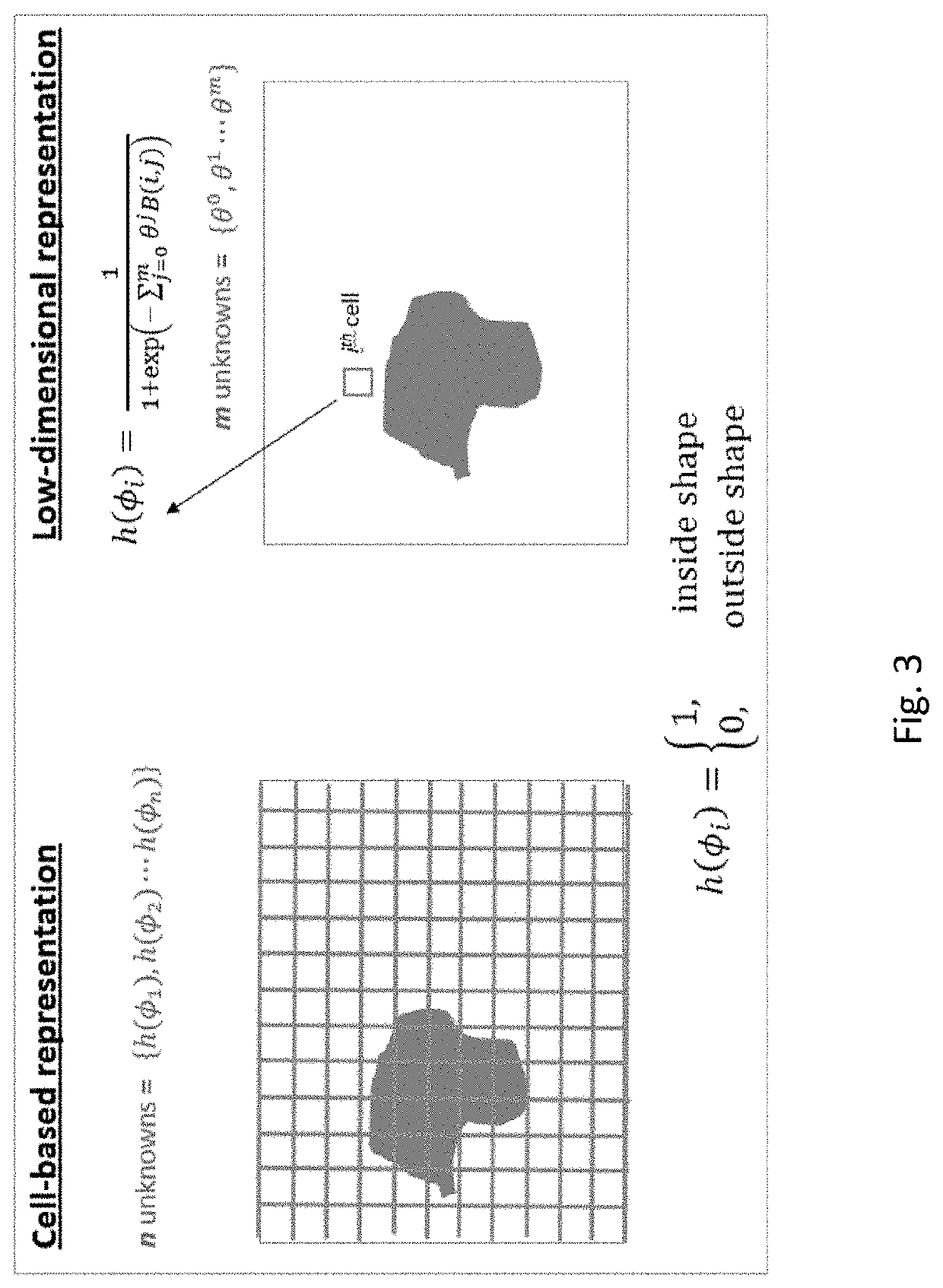
Inversion of large, nearly-homogeneous geobodies via ultra low-dimensional shape representation using orthogonal basis functions
ActiveUS20200066035A1Minimizing misfitSeismologyDesign optimisation/simulationData setSubsurface imaging
A two-stage method for iteratively inverting geophysical data for the purpose of subsurface imaging, including: obtaining at least one geophysical dataset and an initial subsurface model; representing subsurface such that a geometry of a geobody is defined using a set of basis functions, and a number of such basis functions is significantly smaller than the number of cells used in cell-based geobody representations, wherein an order of magnitude reduction is two or more for 2-D domains and 3 or more for 3-D domains; in a first stage, successively updating the initial subsurface model, only for the geobody, by performing iterative low-dimensional geophysical inversion based on minimizing a misfit between simulated geophysical data and the geophysical dataset, wherein the simulated geophysical data is generated from a current subsurface model at each iteration; generating a subsurface image from a final updated subsurface model obtained via the low-dimensional geophysical inversion, wherein the subsurface image includes an inverted geobody; in a second stage, successively updating the subsurface model with the inverted geobody by performing iterative cell-based geophysical inversion based on minimizing a misfit between simulated geophysical data and the geophysical dataset, wherein the simulated geophysical data is generated from a current subsurface model at each iteration.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
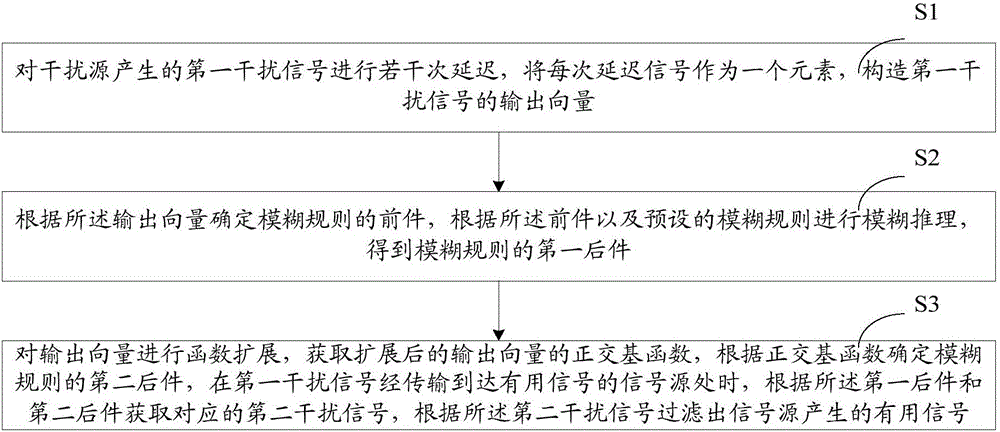
Signal filtering method and system
The present invention relates to a signal filtering method and system. The method comprises the following steps: delaying, for multiple times, a first interference signal generated by an interference source, and constructing an output vector of the first interference signal by using each delayed signal as an element; determining an antecedent of a fuzzy rule according to the output vector, and performing fuzzy reasoning according to the antecedent and a preset fuzzy rule, to obtain a first consequent of the fuzzy rule; and performing function expansion on the output vector, obtaining an orthogonal basis function of the expanded output vector, determining a second consequent of the fuzzy rule according to the orthogonal basis function, obtaining a corresponding second interference signal according to the first consequent and the second consequent when the first interference signal is transmitted and arrives at a signal source of a useful signal, and obtaining, through filtering according to the second interference signal, the useful signal generated by the signal source. The signal filtering method and system can effectively obtain the interference signal ,so as to extract the useful signal from the useful signal mixed with the interference signal.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SHIYUAN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
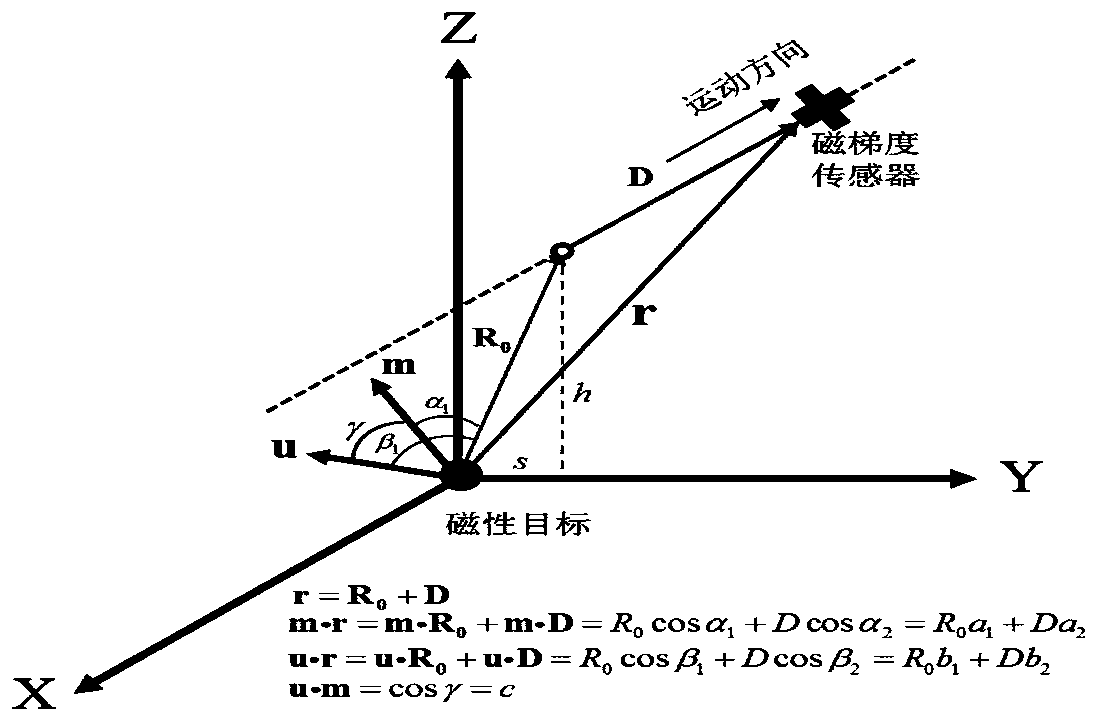
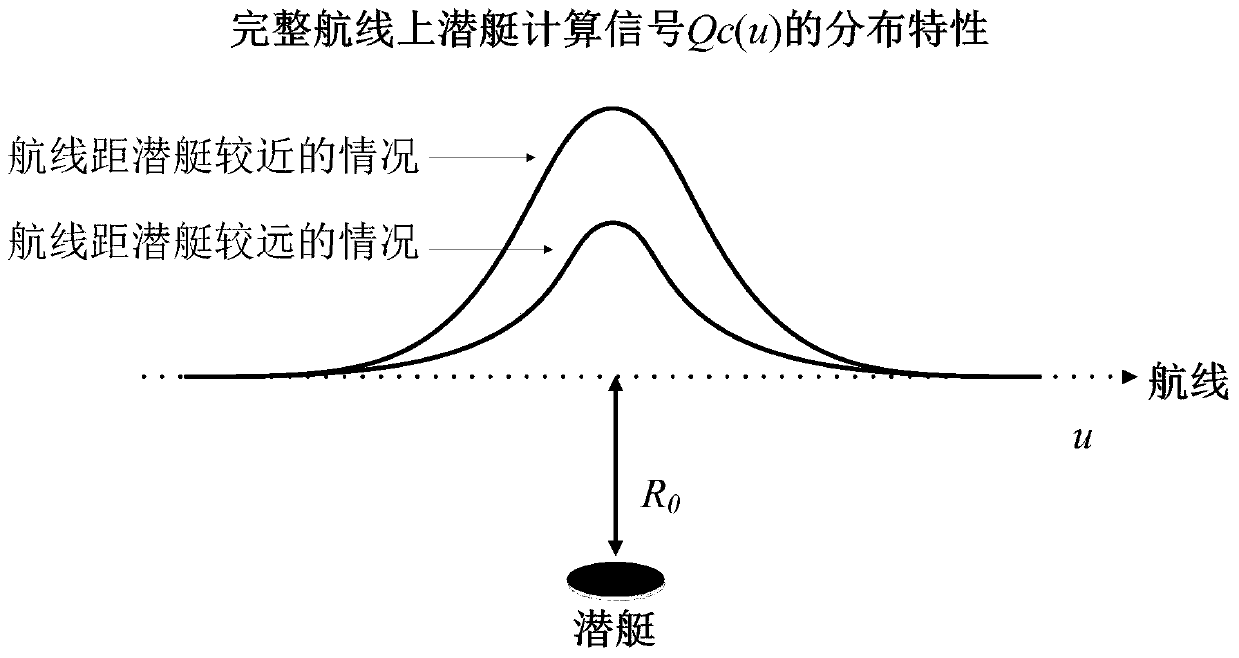
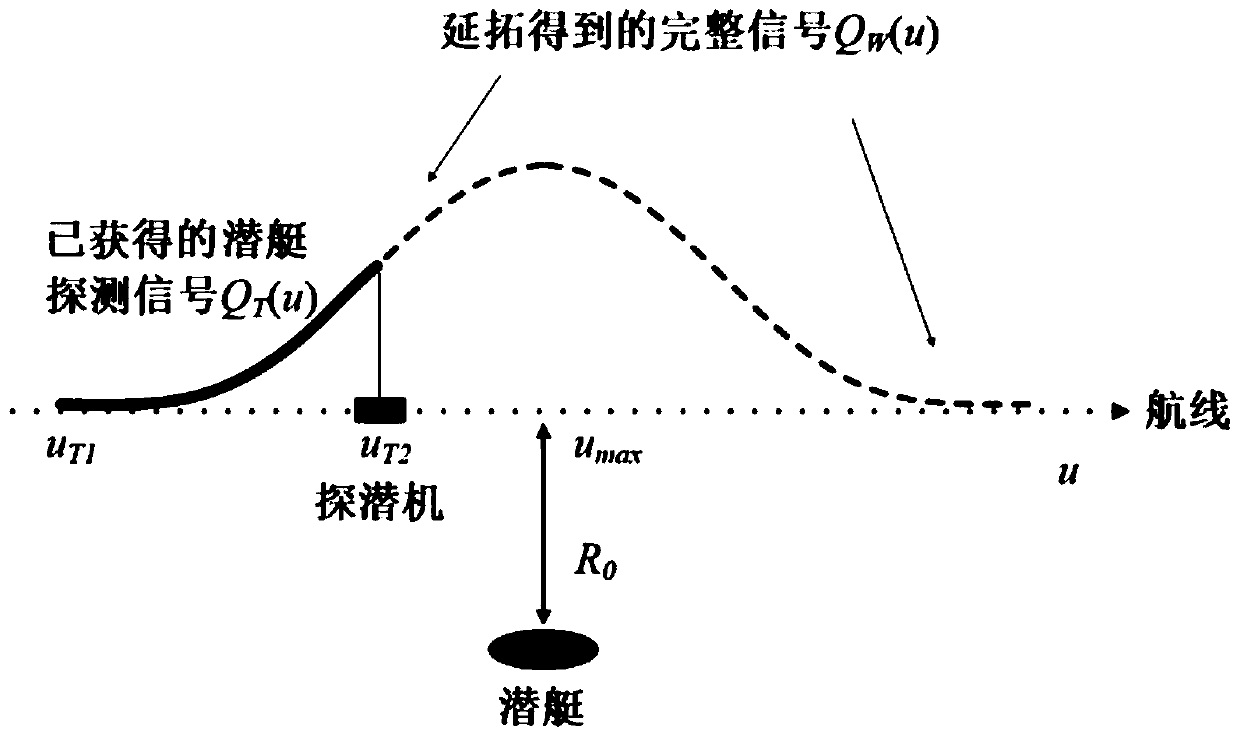
Antisubmarine detection machine navigation method based on magnetic signal continuation algorithm for submarine detection
InactiveCN109739263AAchieve positioningFly fastNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in three dimensionsOrthogonal basisContinuation algorithm
The invention provides anantisubmarine detection machine navigation method based on magnetic signal continuation algorithm for submarine detection, and belongs to the field of the submarine detectionor antisubmarine detection machines and antisubmarine detection indicators. The antisubmarine detection machine navigation method comprises the steps that firstly a magnetized submarine is equivalentto a magnetic doublet, and submarine signals of a present complete ship route represented by a combination of orthogonal basis functions are acquired; an antisubmarine detection indicator composed ofthree single-direction vector magnetic-field measuring probes is mounted on the antisubmarine detection machine in an orthogonality mode; on the present ship route, submarine detected signals are acquired using the antisubmarine detection indicator, prolongation is conducted on the submarine detected signals, thus the prolonged submarine signals of the present complete ship route are acquired, orientation of the submarine is calculated, and the present ship route of theantisubmarine detection machine is further updated; and the process is repeated until the antisubmarine detection machine is located over the submarine, and the navigation ends. According to the antisubmarine detection machine navigation method based on the magnetic signal continuation algorithm for the submarine detection,real-time location is conducted on the submarine through the antisubmarine detection machine, thus the route is continuously corrected, and the antisubmarine detection machinedirectly flies to the submarine, flying distance of the antisubmarine detection machine is greatly reduced, and submarine detection time is shortened.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
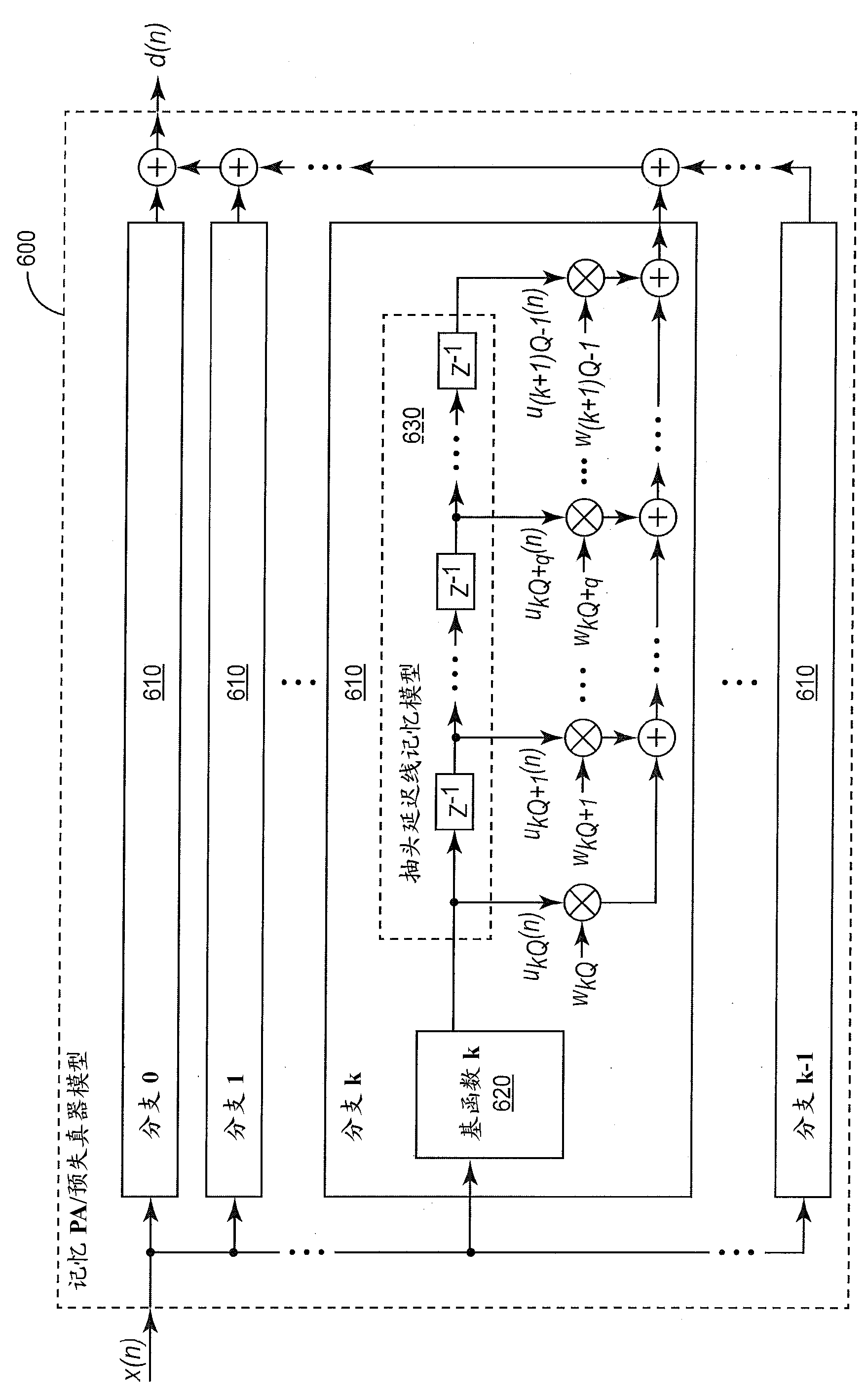
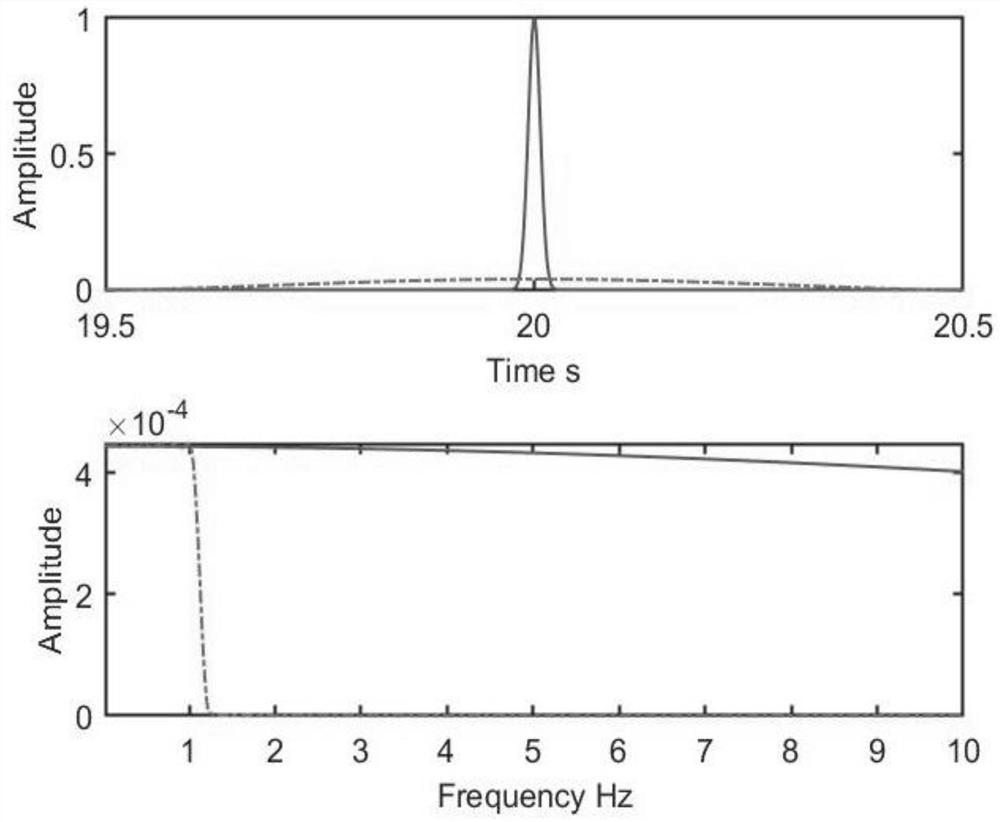
Orthogonal basis function set for ditigal predistorter
ActiveCN103299542AGood for evaluationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationAlgorithmOrthonormal basis functions
A predistorter applies a distortion function to an input signal to predistort the input signal. The output of the distortion function is modeled as the sum of the output signals from the orthogonal basis functions weighted by corresponding weighting coefficients. Techniques are described for orthogonalizing the basis function output signals depending on the distribution of the input signal.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Passive magnetic signal optimization extraction and detection method for high sampling rate
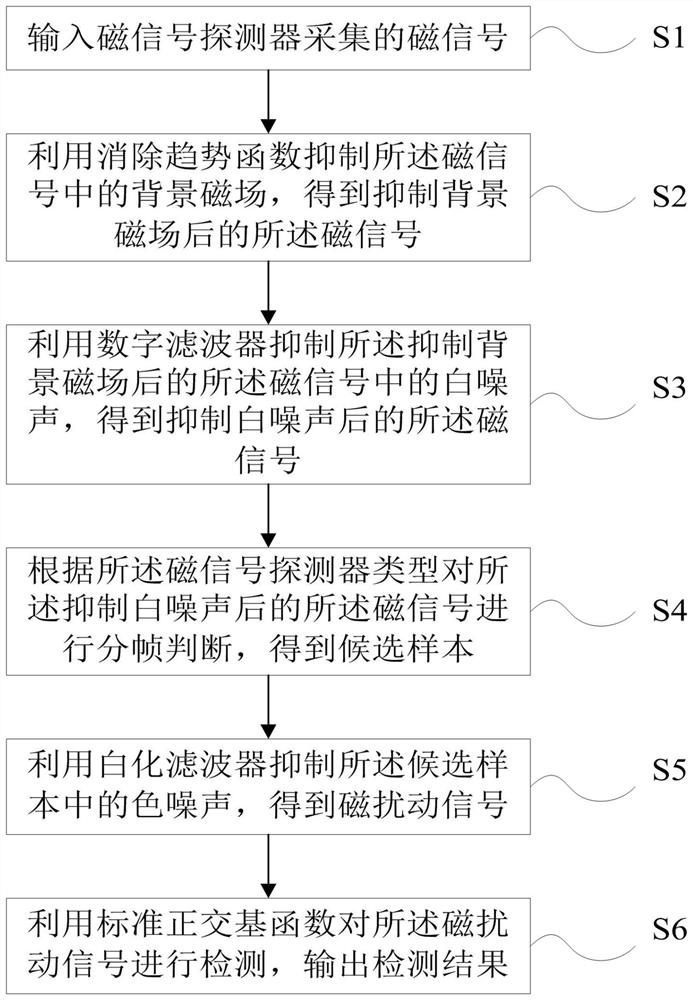
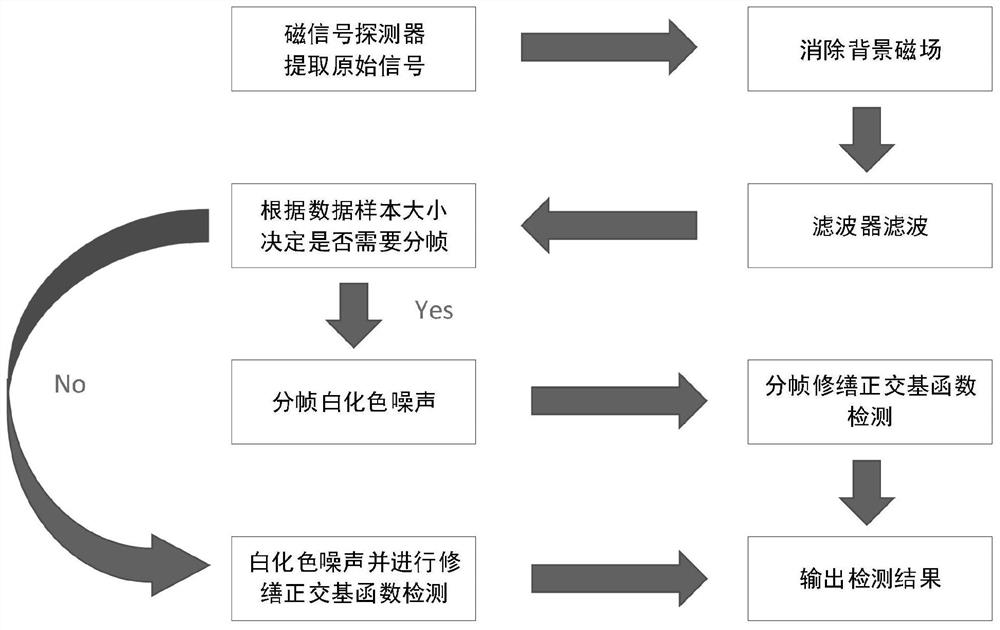
ActiveCN113655529AImprove reliabilityImprove effectivenessElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationMagnetic disturbanceComputational physics
The invention discloses a passive magnetic signal optimization extraction and detection method for a high sampling rate. The method comprises the following steps: S1, inputting a magnetic signal collected by a magnetic signal detector; S2, suppressing a background magnetic field in the magnetic signal by using an elimination trend function to obtain a magnetic signal after the background magnetic field is suppressed; S3, suppressing white noise in the magnetic signal after the background magnetic field is suppressed by using a digital filter, and obtaining a magnetic signal after the white noise is suppressed; S4, according to the type of the magnetic signal detector, performing framing judgment on the magnetic signal after white noise suppression to obtain candidate samples; S5, inhibiting color noise in the candidate sample by using a whitening filter to obtain a magnetic disturbance signal; and S6, detecting the magnetic disturbance signal by using a standard orthogonal basis function, and outputting a detection result. Compared with the prior art, after the optimized extraction technology designed by the invention is adopted, the target identification distance and the target identification precision are effectively improved, and the result has relatively high reliability and effectiveness.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +2
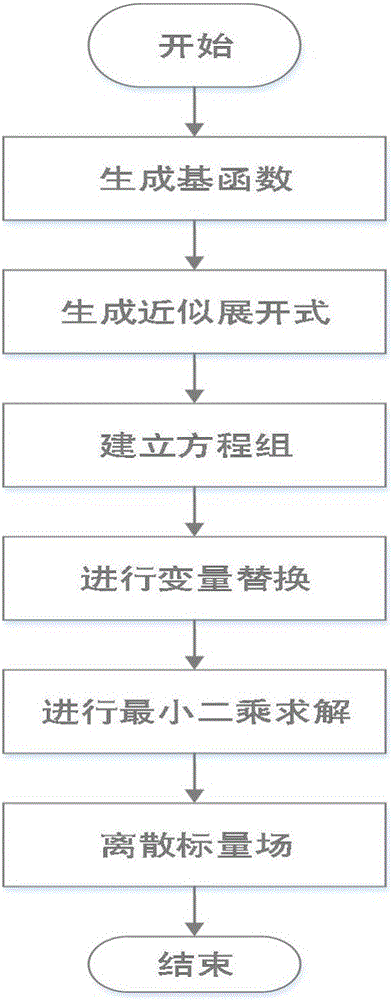
Universal right-angle geometric scalar field reconstruction method
InactiveCN106095727AImprove adaptabilityReduce the impact of reconstruction accuracyComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmScalar field
Provided is a universal right-angle geometric scalar field reconstruction method. The method comprises the steps that 1, an orthogonal basis function is determined according to the primary function type and order needed by a user; 2, a to-be-solved continuous cylindrical geometric scalar field is approximatively expanded according to the orthogonal basis function obtained in the step 1; 3, an underdetermined linear algebraic equation system about an underdetermined coefficient is set up through all known information; 4, on the basis of variable substitution, a least square method is used for solving the underdetermined linear algebraic equation system, the least square solution of the underdetermined linear algebraic equation system is obtained to serve as a scalar field expansion coefficient, the scalar field expansion coefficient is substituted into a scalar field expansion equation, and a continuous scalar field can be obtained; 5, according to the obtained continuous scalar field, designated discrete information of the scalar field is obtained through further discretizing; the undetermined scalar field is expanded through the orthogonal basis function, an expansion function is constructed through variants and orders, the least square method is used for solving, the influence of selection of an expansion basis function on reconstruction precision is effectively reduced, the requirement for the reconstruction condition number is reduced, meanwhile multiple kinds of discrete information can be processed, and the adaptability of the method to different problems is effectively improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
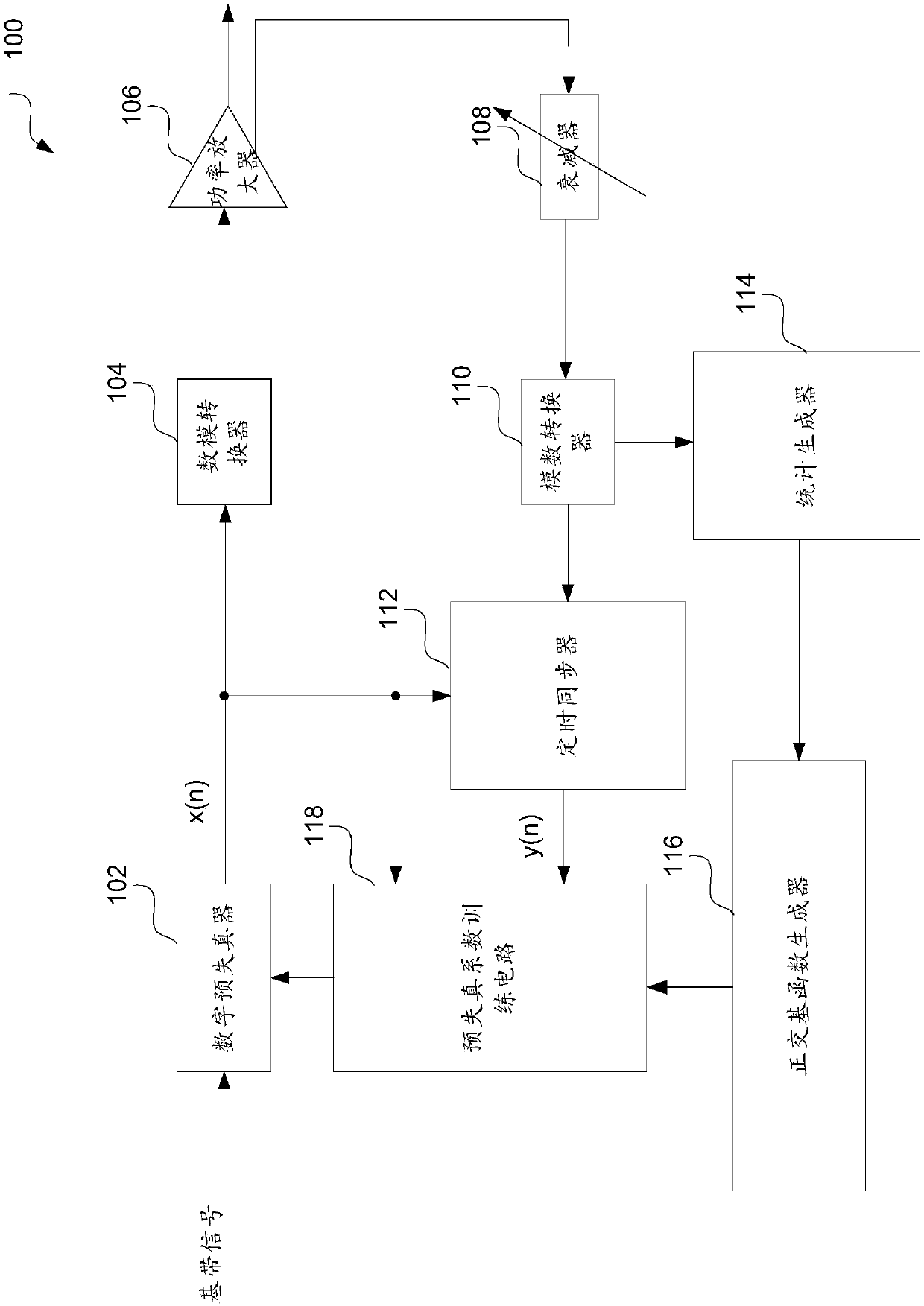
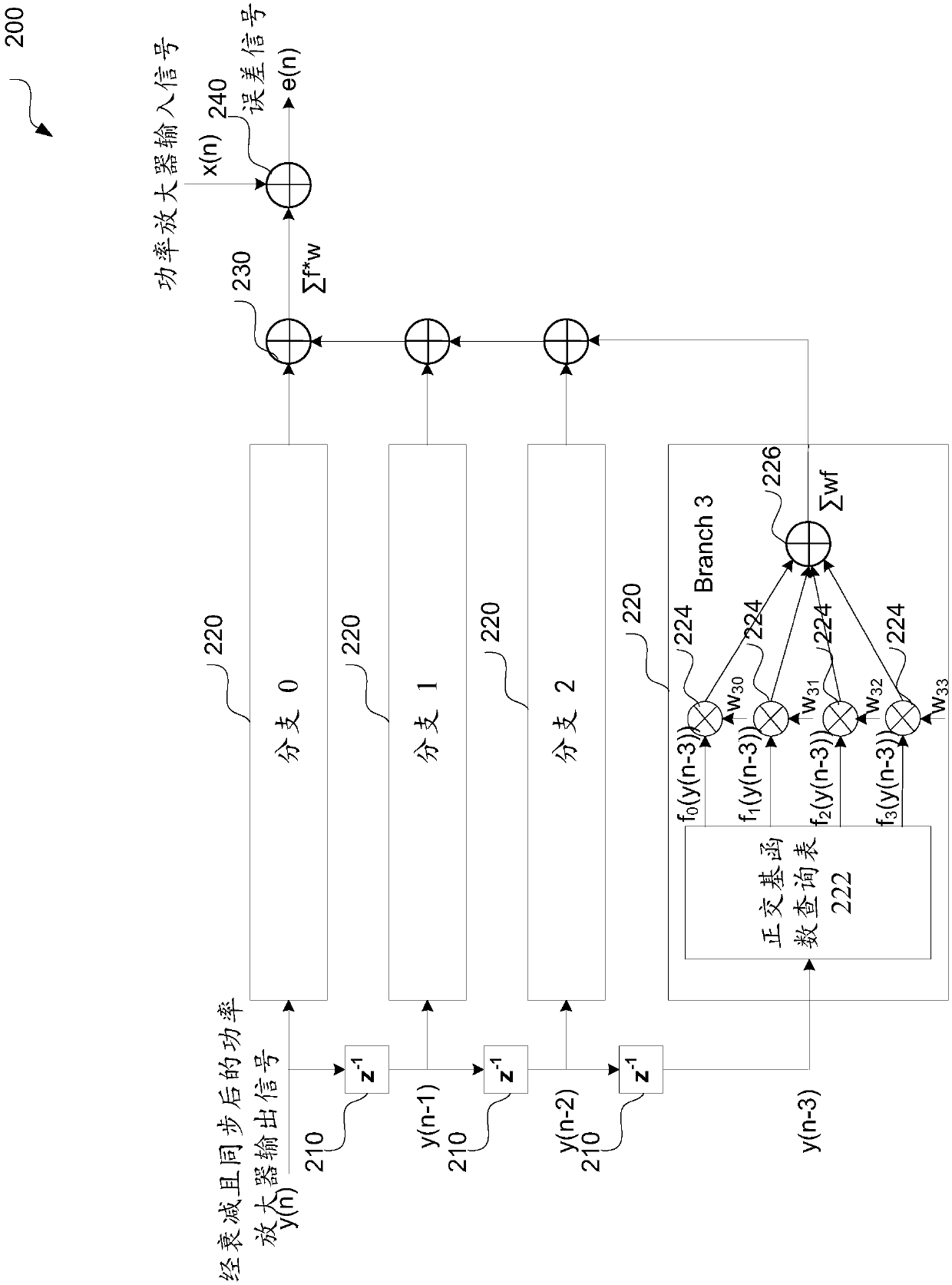
Circuit and method for predistortion
ActiveCN107786174AAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersDigital down converterAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a circuit and method for predistortion. The circuit comprises a digital predistorter configured to modify an input baseband signal via a predistortion coefficient to generate amodified digital signal; a digital analog converter configured to convert the modified digital signal to generate an analog signal; a power amplifier configured to amplify the digital signal to generate an amplified signal; an attenuator configured to attenuate the amplified signal to generate an attenuated signal; an analog-digital converter configured to generate an attenuated digital signal; atiming synchronizer configured to synchronize the attenuated digital signal and the modified digital signal to generate synchronous amplified signals; a statistic generator configured to generate a probability density function of multiple samples of the input baseband signal; an orthogonal basis function generator configured to generate a group of normalized orthogonal basis functions; and a predistortion coefficient training circuit configured to generate updated predistortion coefficients.
Owner:SINO WEALTH ELECTRONICS
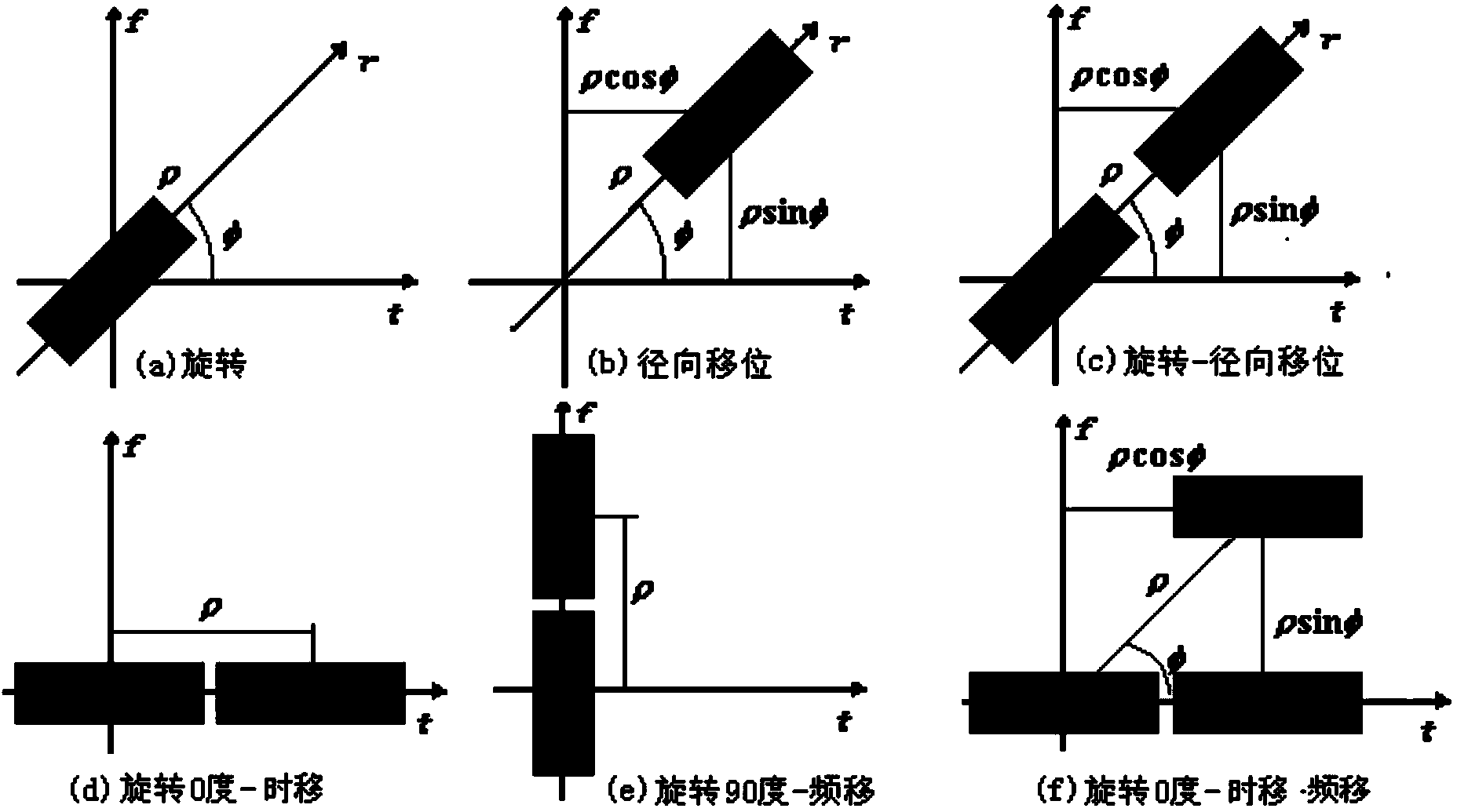
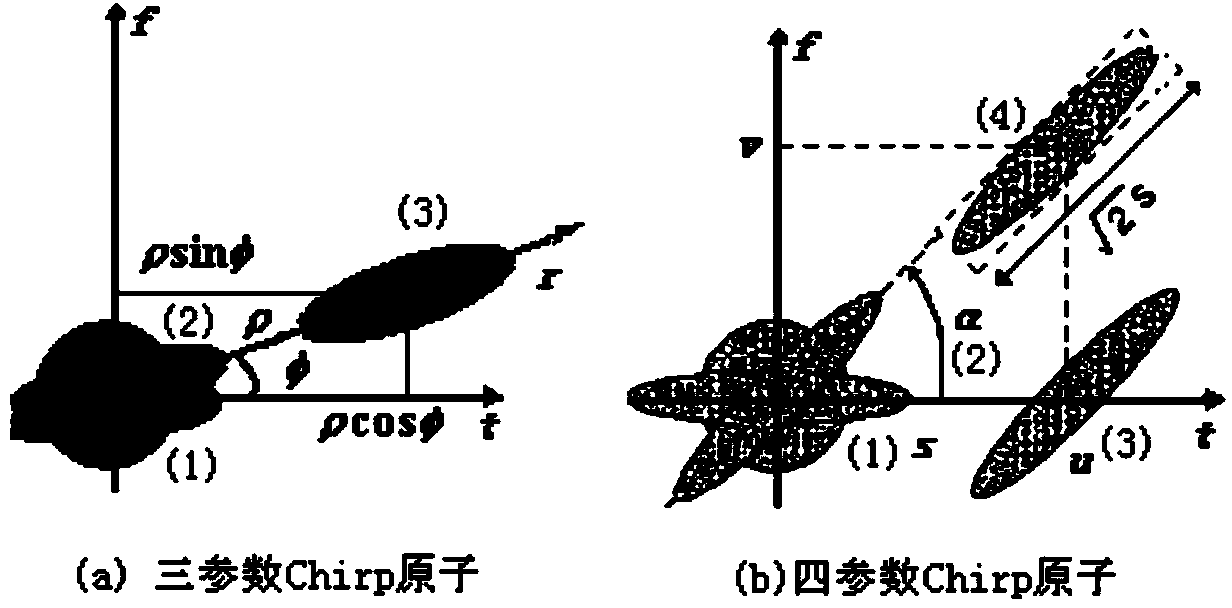
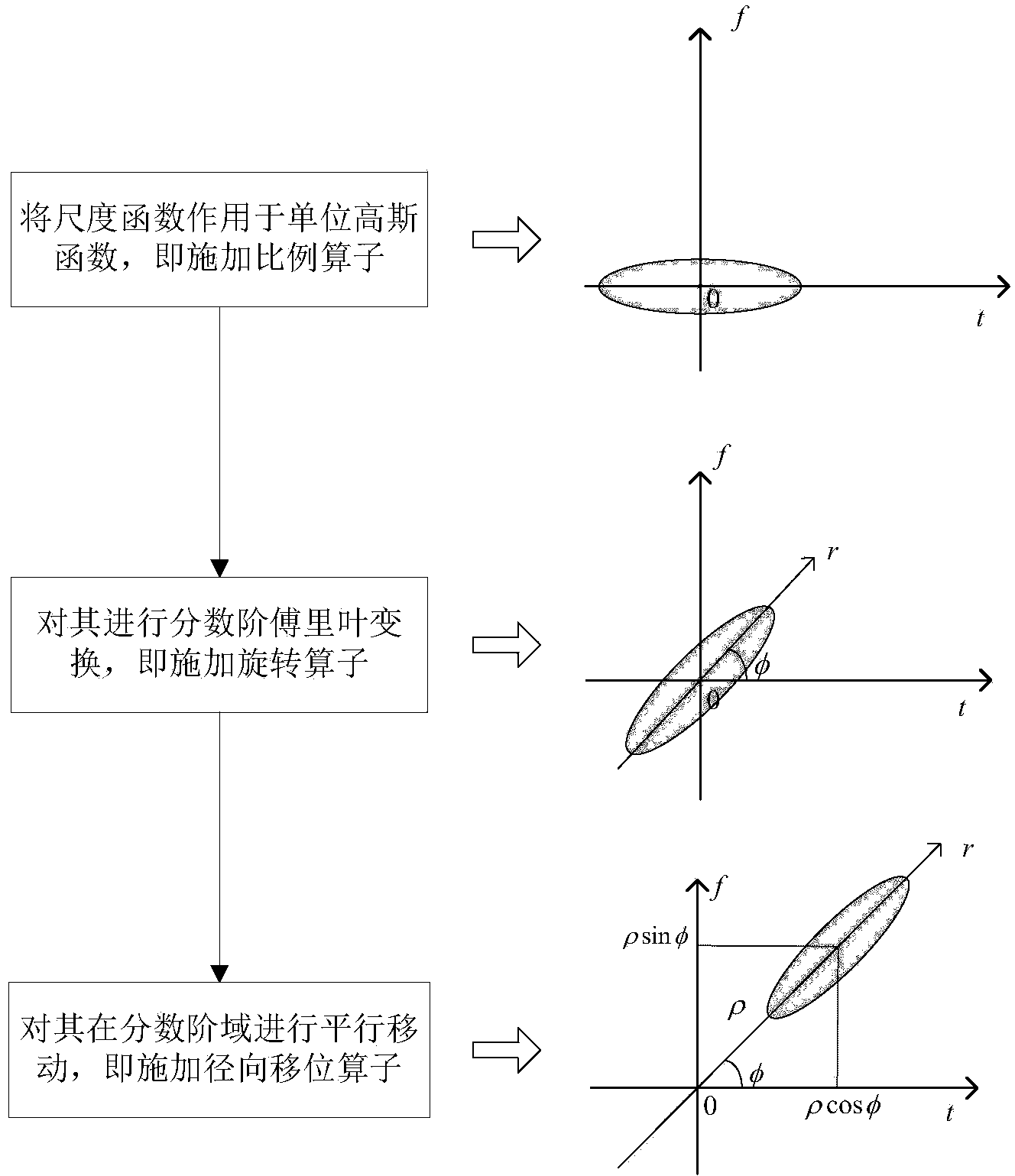
Method of Chirp time-frequency atoms denoted with three parameters
The invention discloses a simplified representation method of Chirp time-frequency atoms in self-adaption signal decomposition. For representation of time-frequency characteristics of non-stationary signals, time-frequency atoms of a better local time-frequency structure are used for replacing orthogonal basis functions, and linear combination of the best time-frequency atoms is used for representing signals. The time-frequency atoms are obtained through calculation by applying various operators on basic functions, the more operators applied on the basic functions, the more parameters the time-frequency atoms obtain, the stronger local capacity of the time-frequency atoms matching or approaching signals, while the harder the finding of optimal time-frequency atoms. The Chirp time-frequency atoms can well match frequency linear variation elements in the signals and approach nonlinear frequency variation elements. The Chirp time-frequency atoms are commonly represented by 4 parameters of proportion, time shift, frequency shift and linear frequency modulation. The simplified representation method of the Chirp time-frequency atoms in the self-adaption signal decomposition introduces revolve-radial shift operators and composition operators through fractional order Fourier transform to obtain the Chirp time-frequency atoms represented by the three parameters of proportion, revolve and radial shift. According to the simplified representation method of the Chirp time-frequency atoms in the self-adaption signal decomposition, advantages of more concise representation, more definite physical significance of each parameter, great time reduction for searching the optimal time-frequency atoms can be obtained.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
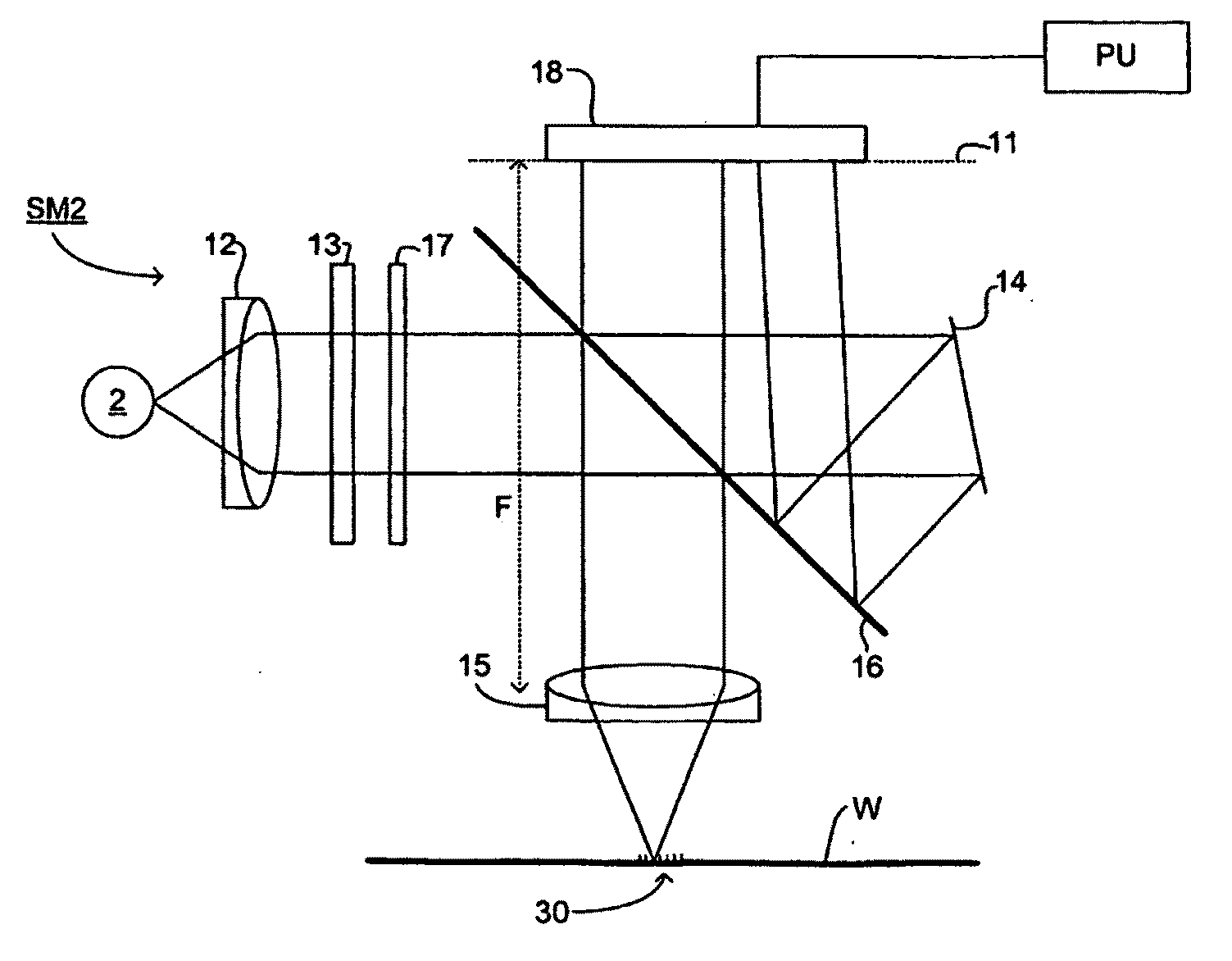
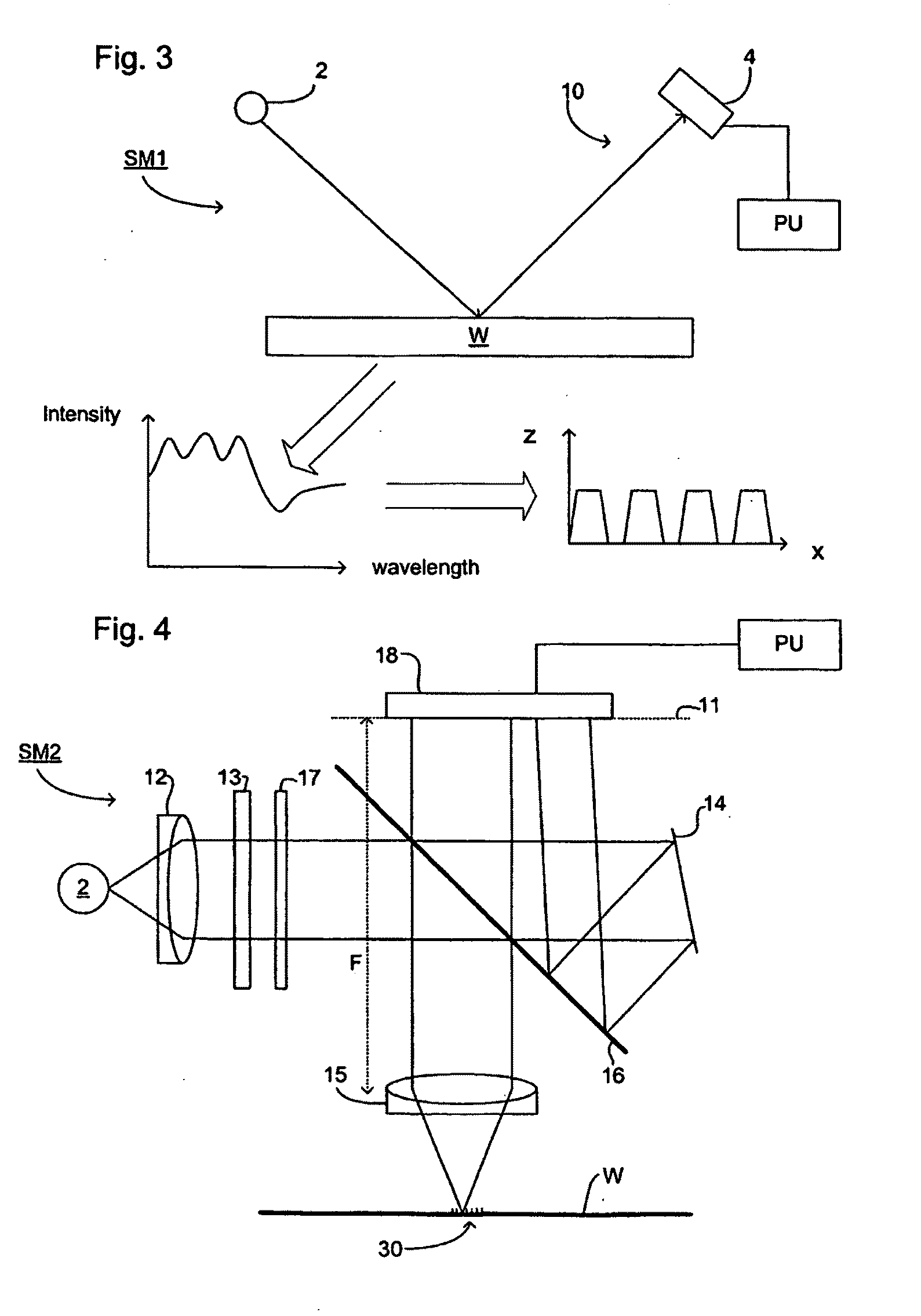
Lithographic System, Lithographic Method And Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20110299050A1Reduction in accuracyEfficient executionPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingScatterometerPupil
A lithographic system includes a lithographic apparatus and a scatterometer. In an embodiment, the lithographic apparatus includes an illumination optical system arranged to illuminate a pattern and a projection optical system arranged to project an image of the pattern on to a substrate. In an embodiment, the scatterometer includes a measurement system arranged to direct a beam of radiation onto a target pattern on said substrate and to obtain an image of a pupil plane representative of radiation scattered from the target pattern. A computational arrangement represents the pupil plane by moment functions calculated from a pair of orthogonal basis function and correlates the moment function to lithographic feature parameters to build a lithographic system identification. A control arrangement uses the system identification to control subsequent lithographic processes performed by the lithographic apparatus.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
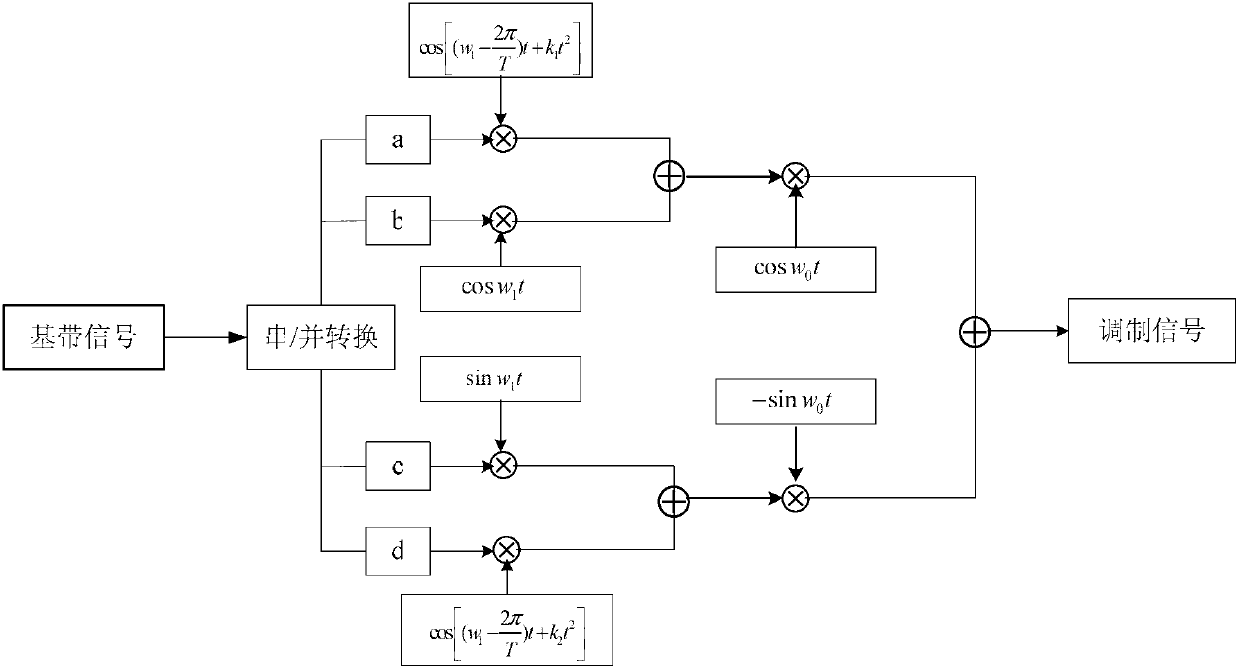
Modulation and demodulation method of wave form synergy signal based on frequency domain and fractional Fourier domain orthogonal basis function
A modulation and demodulation method of a wave form synergy signal based on a frequency domain and a fractional Fourier domain orthogonal basis function relates to a signal modulation and demodulation method, and aims at solving the problem that a modulation and demodulation method of an existing quaternary phase shift keying (QPSK) signal is low in efficiency. Modulation and demodulation are achieved by a way of wave form synergy of a chirp signal and a sine and cosine signal, and therefore the modulation and demodulation method of the wave form synergy signal based on the frequency domain and the fractional Fourier domain orthogonal basis function is a novel modulation and demodulation method. In addition, two branches of chirp signals are respectively added to an I branch and a Q branch modulated by the existing QPSK signal and are used as carrier waves to respectively modulate one branch of baseband signal, so that existing two-way modulation is added up to four-way modulation, and at the demodulation end, filter waves are combined and matched by using a frequency domain template and a fraction domain template, and eight integrators are designed, and finally filtering results are combined so as to judge the information bit. The modulation and demodulation method is appropriate for the wireless communication field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Apparatus and method for pH control in wastewater treatment plants and other systems
A method includes obtaining (4002) a nonlinear model (3124) that represents a pH of a material (3104) in a process to be controlled. The model is generated using an orthonormal basis function and an ordinal spline basis function. The method also includes performing (4004) non-linear model predictive control of the process using the model. The method could also include generating the model using the orthonormal basis function and the ordinal spline basis function. This could include identifying a distribution (3300) of knots and multiple ordinal spline functions, where each ordinal spline function is associated with one of the knots. The ordinal spline basis function can be generated using at least one of the ordinal spline functions.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com