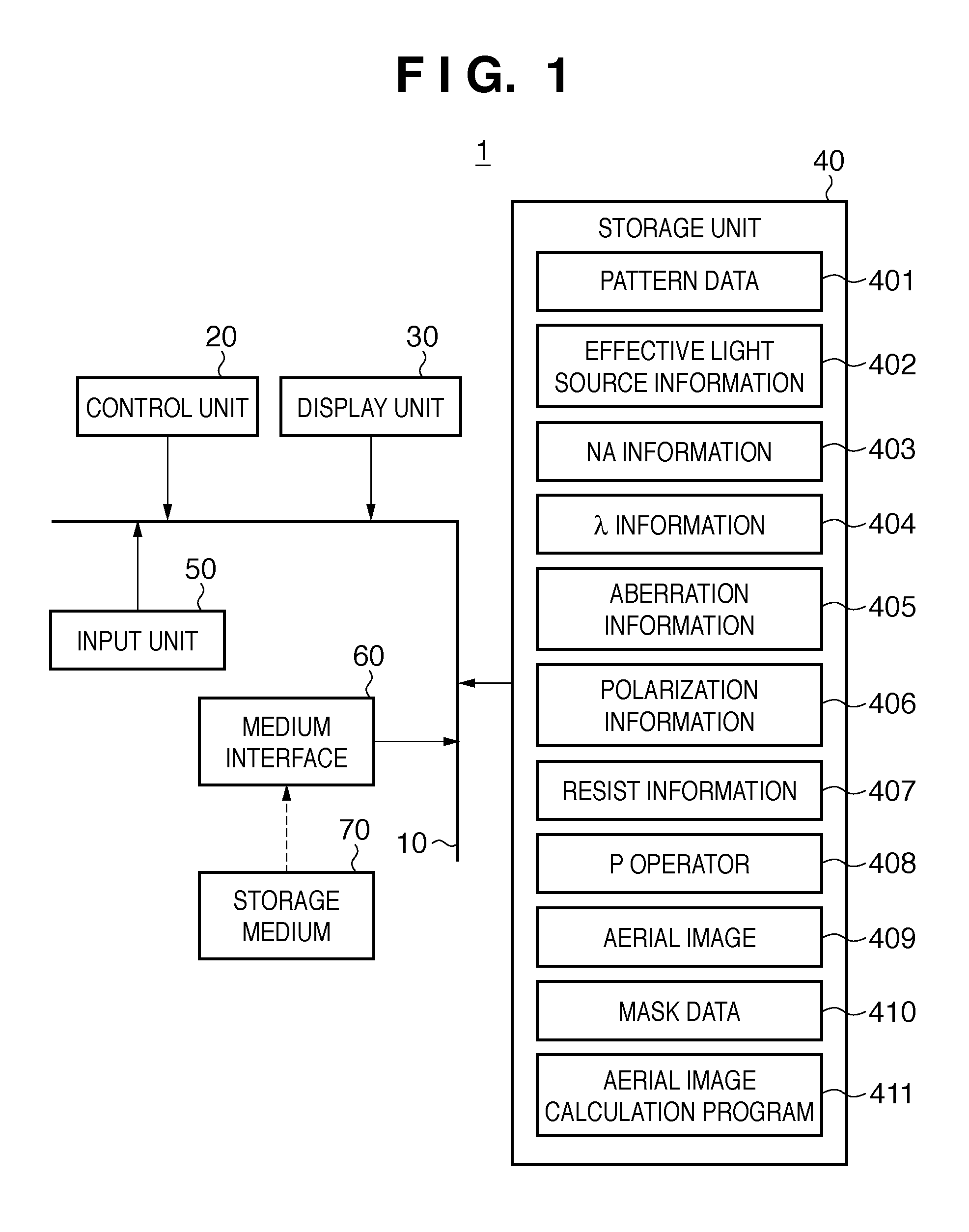
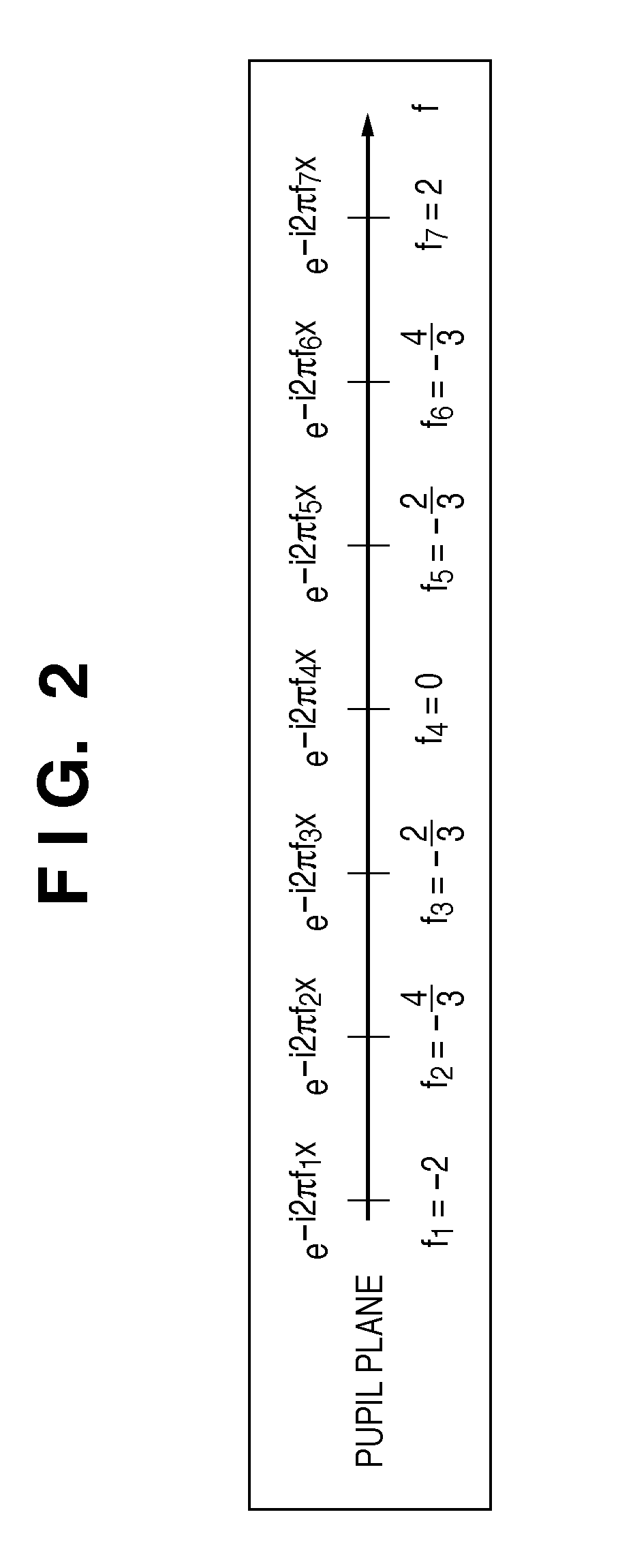
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Pupil function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
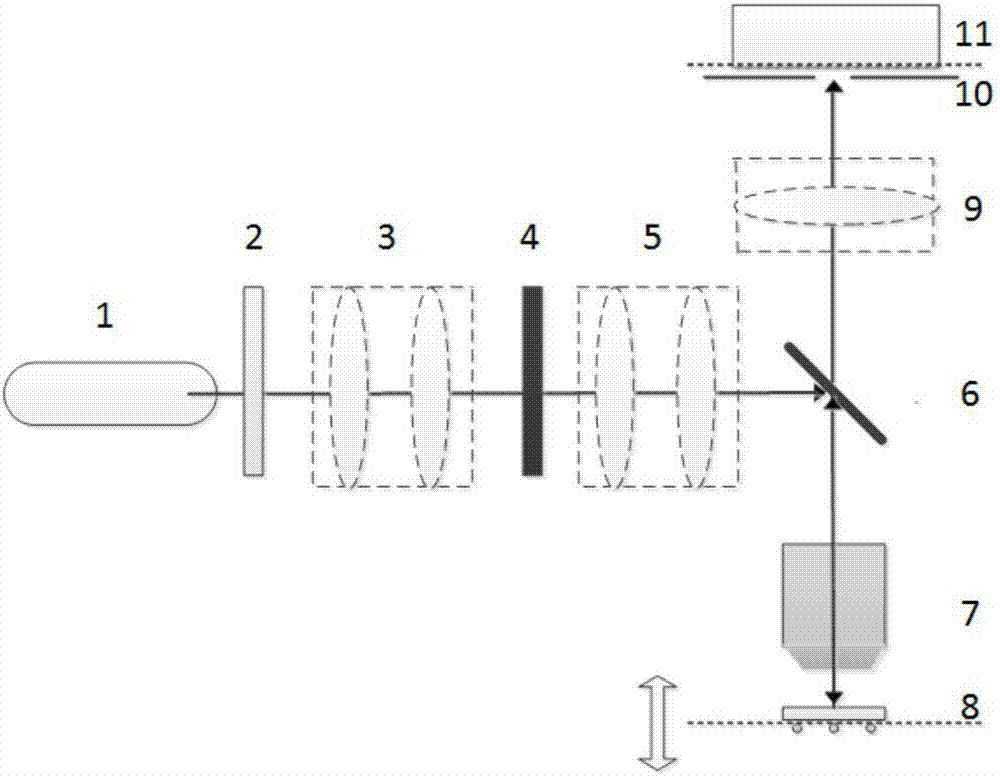
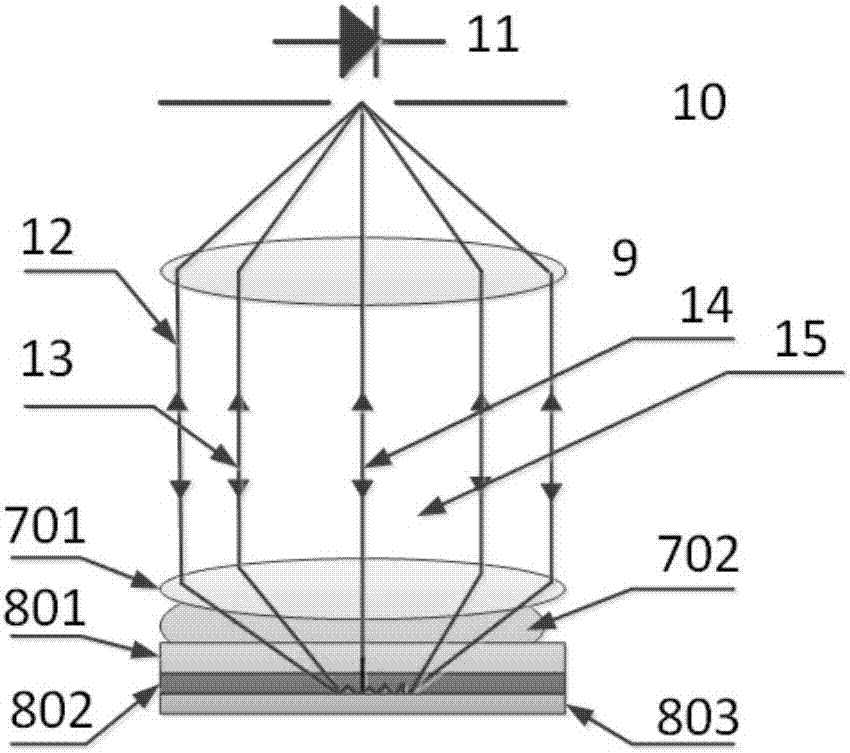
The pupil function or aperture function describes how a light wave is affected upon transmission through an optical imaging system such as a camera, microscope, or the human eye. More specifically, it is a complex function of the position in the pupil or aperture (often an iris) that indicates the relative change in amplitude and phase of the light wave. Sometimes this function is referred to as the generalized pupil function, in which case pupil function only indicates whether light is transmitted or not. Imperfections in the optics typically have a direct effect on the pupil function, it is therefore an important tool to study optical imaging systems and their performance.
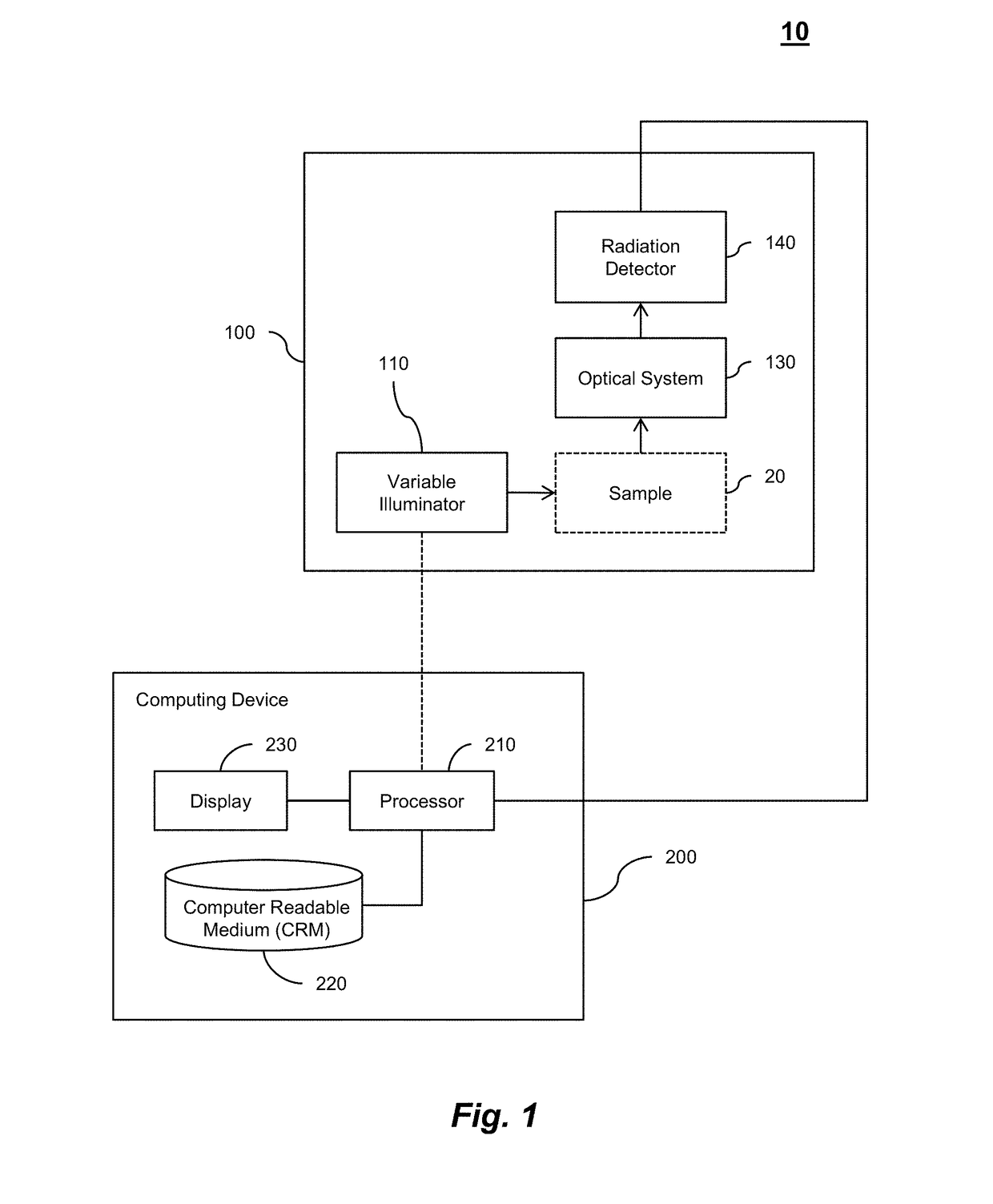
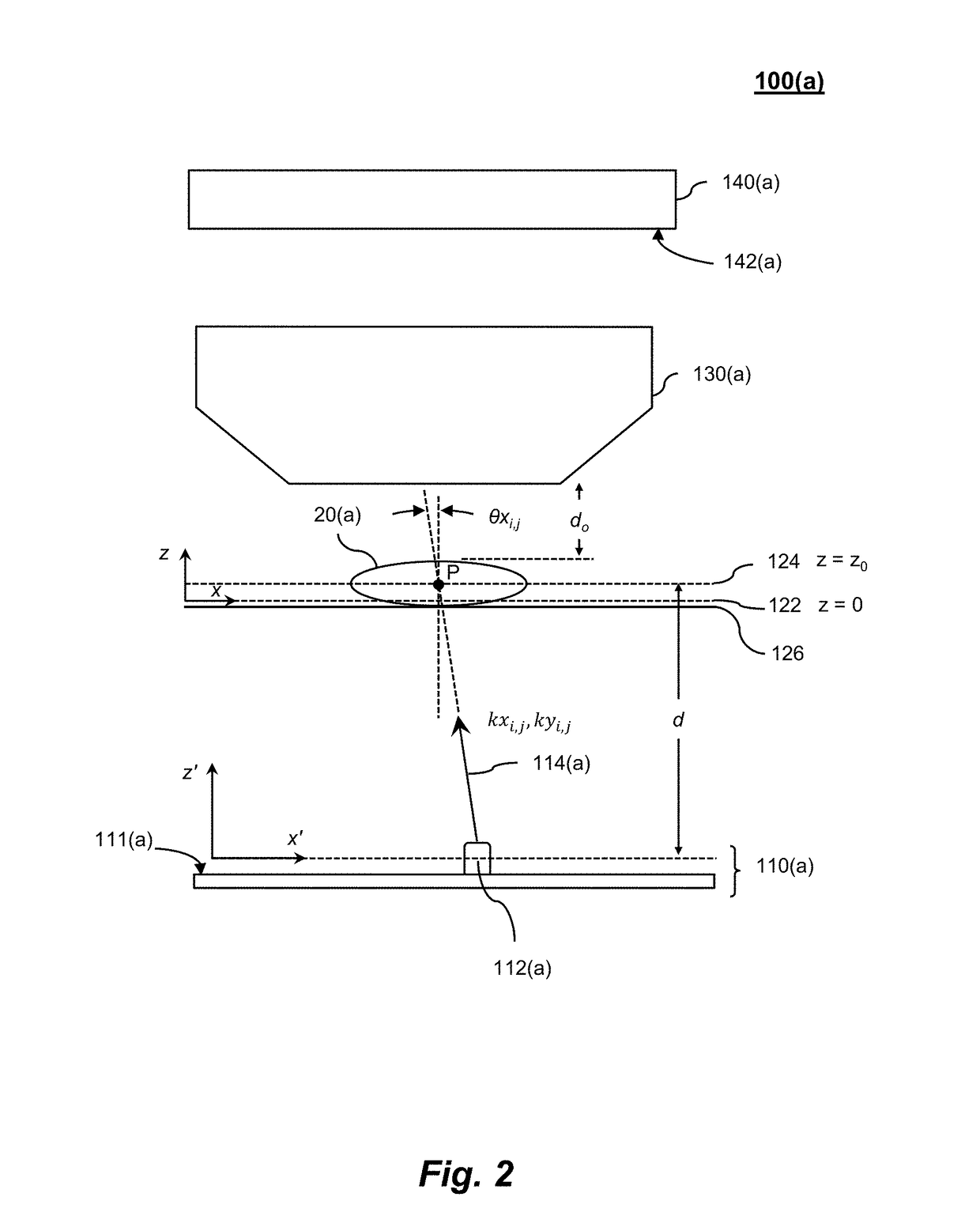
Embedded pupil function recovery for fourier ptychographic imaging devices
ActiveUS20150160450A1High resolutionColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsPupil functionEmbedded system
Certain aspects pertain to Fourier ptychographic imaging systems, devices, and methods that implement an embedded pupil function recovery
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Eigen decomposition based OPC model
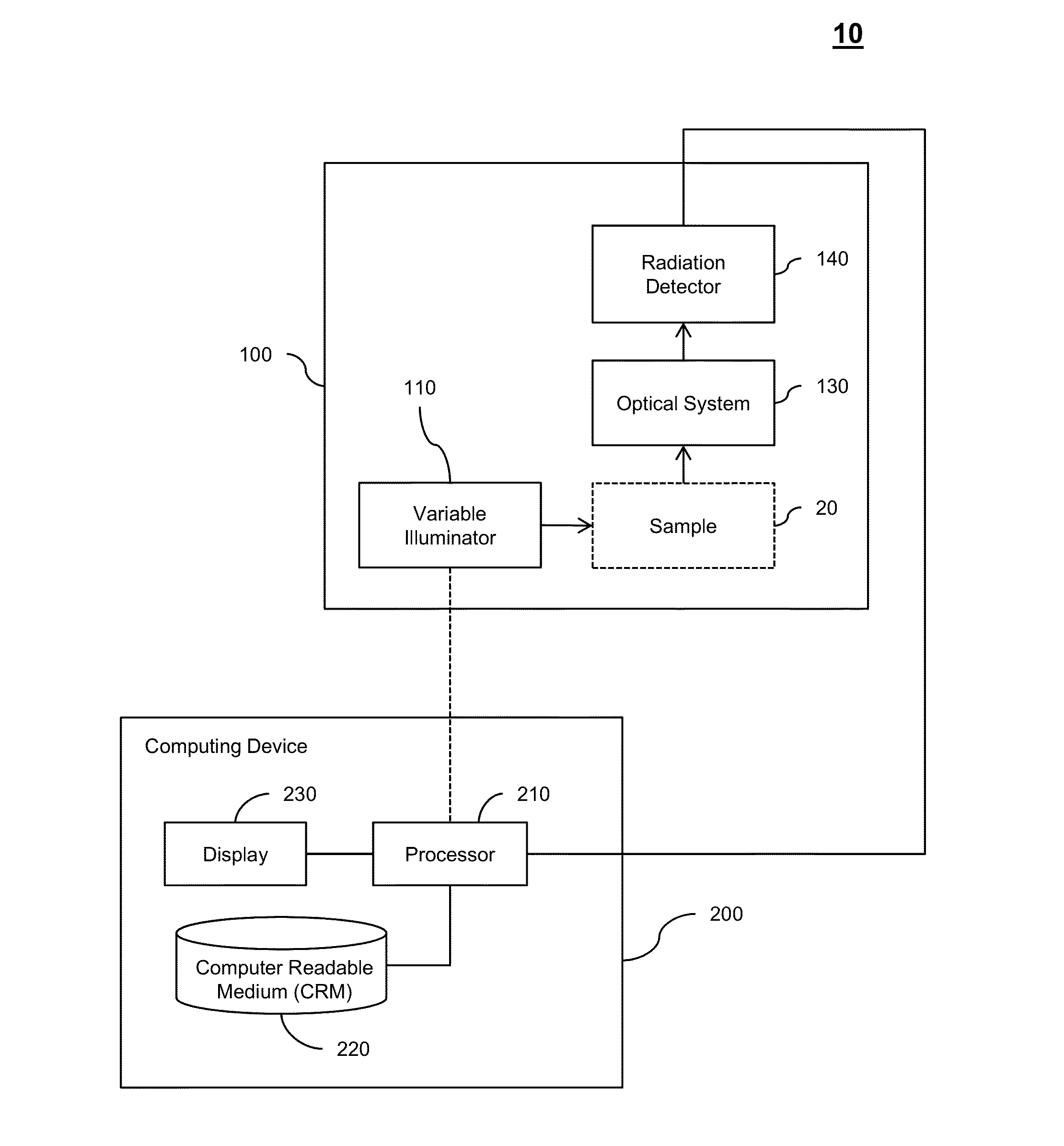
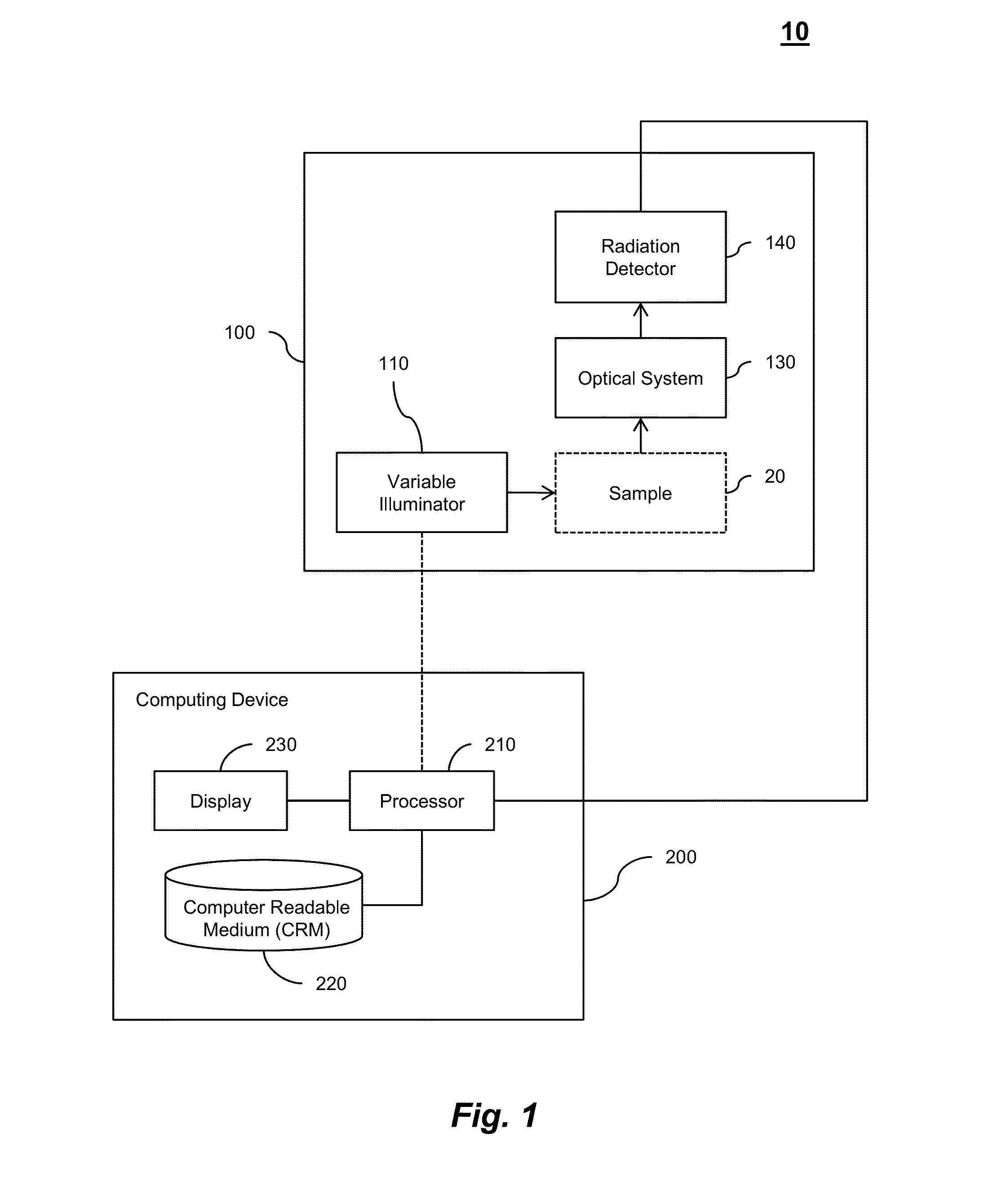
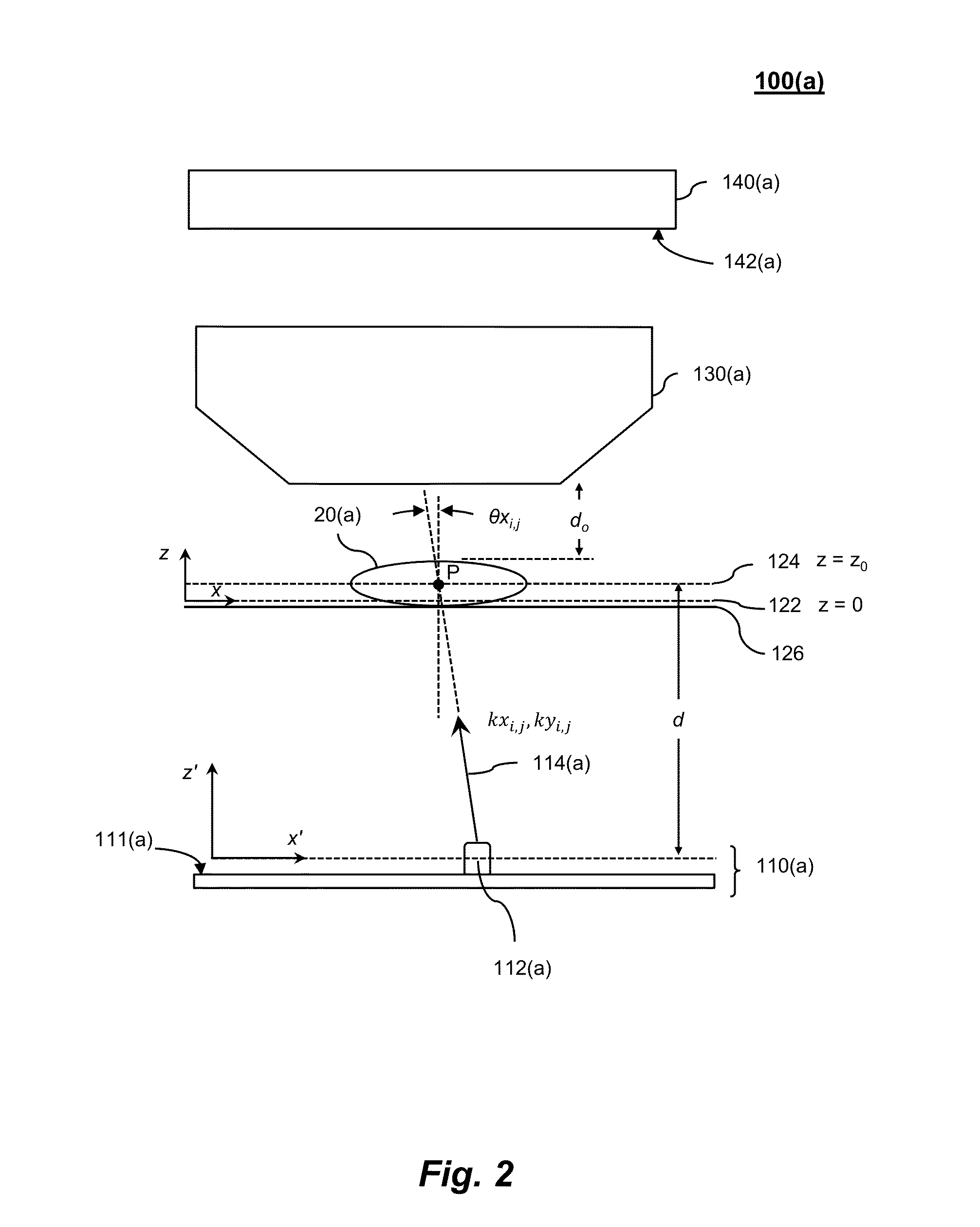
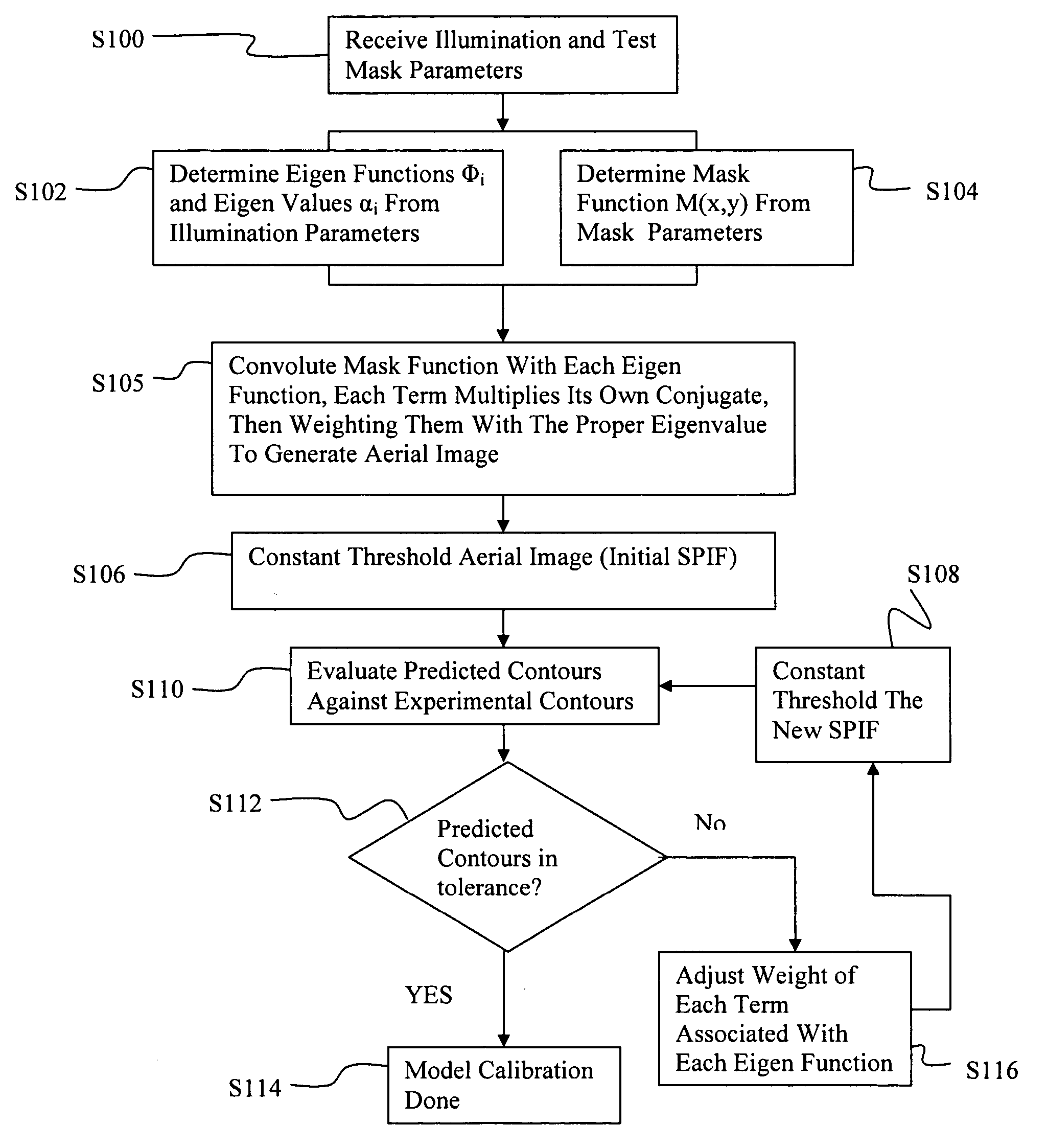
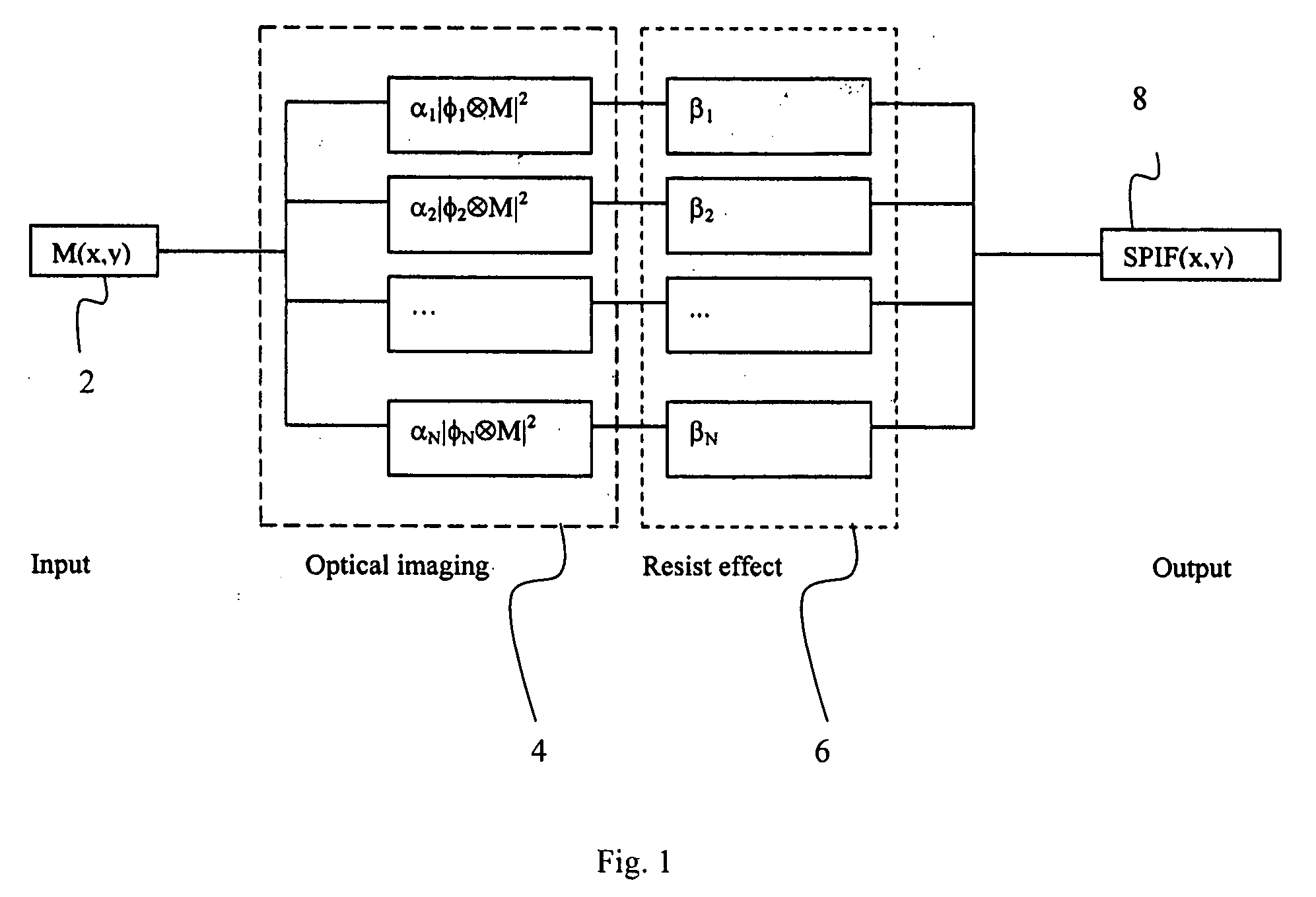
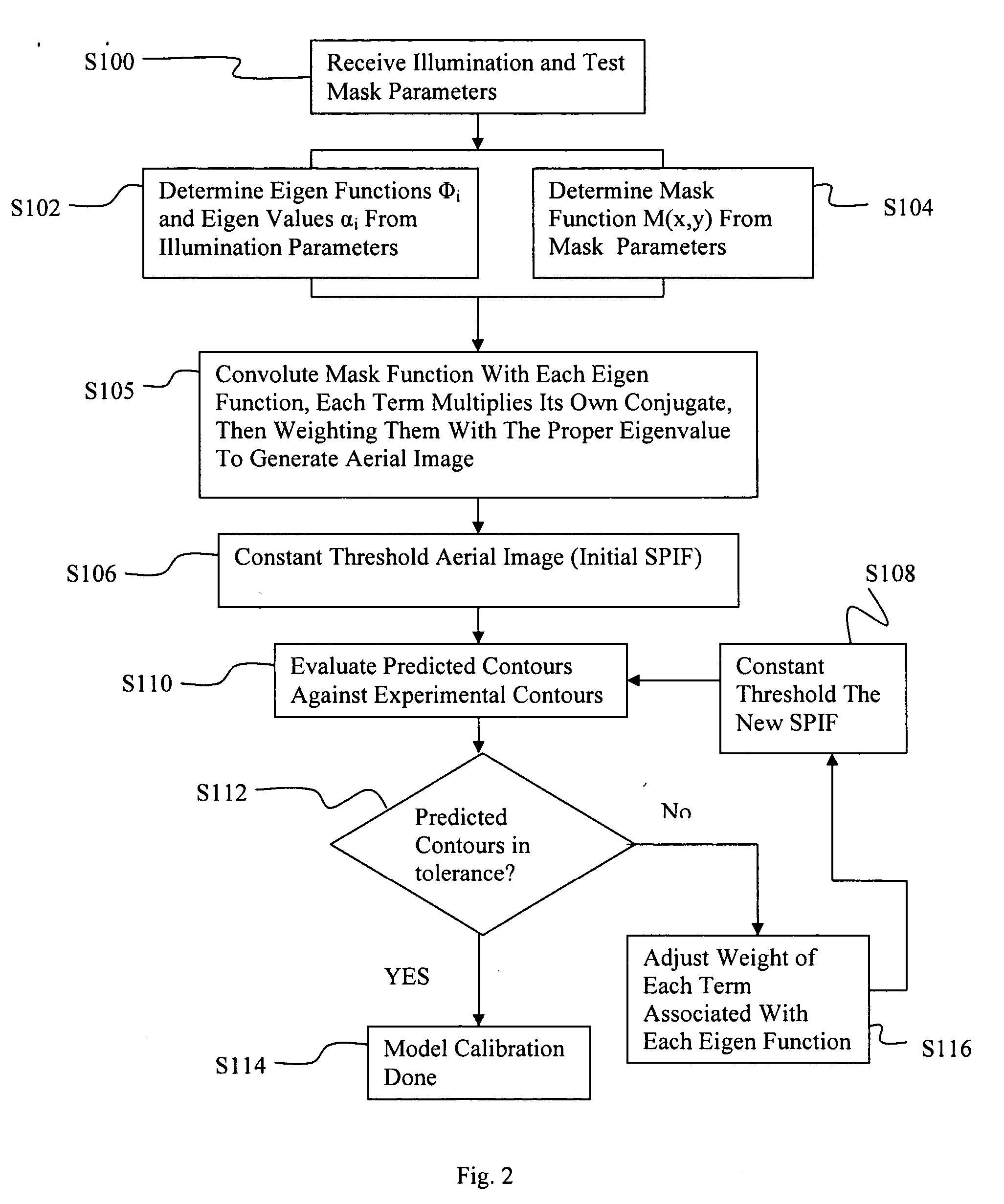
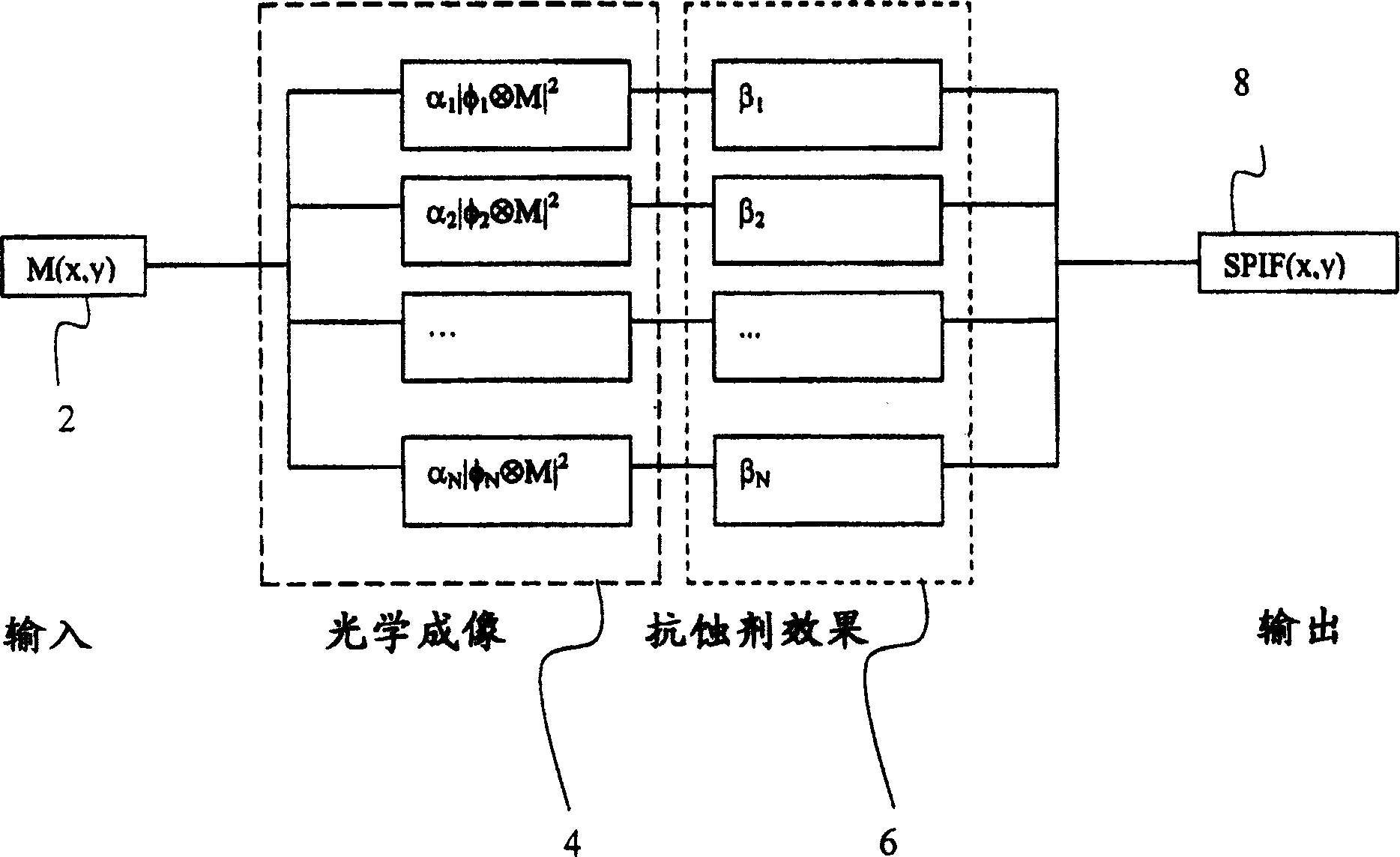
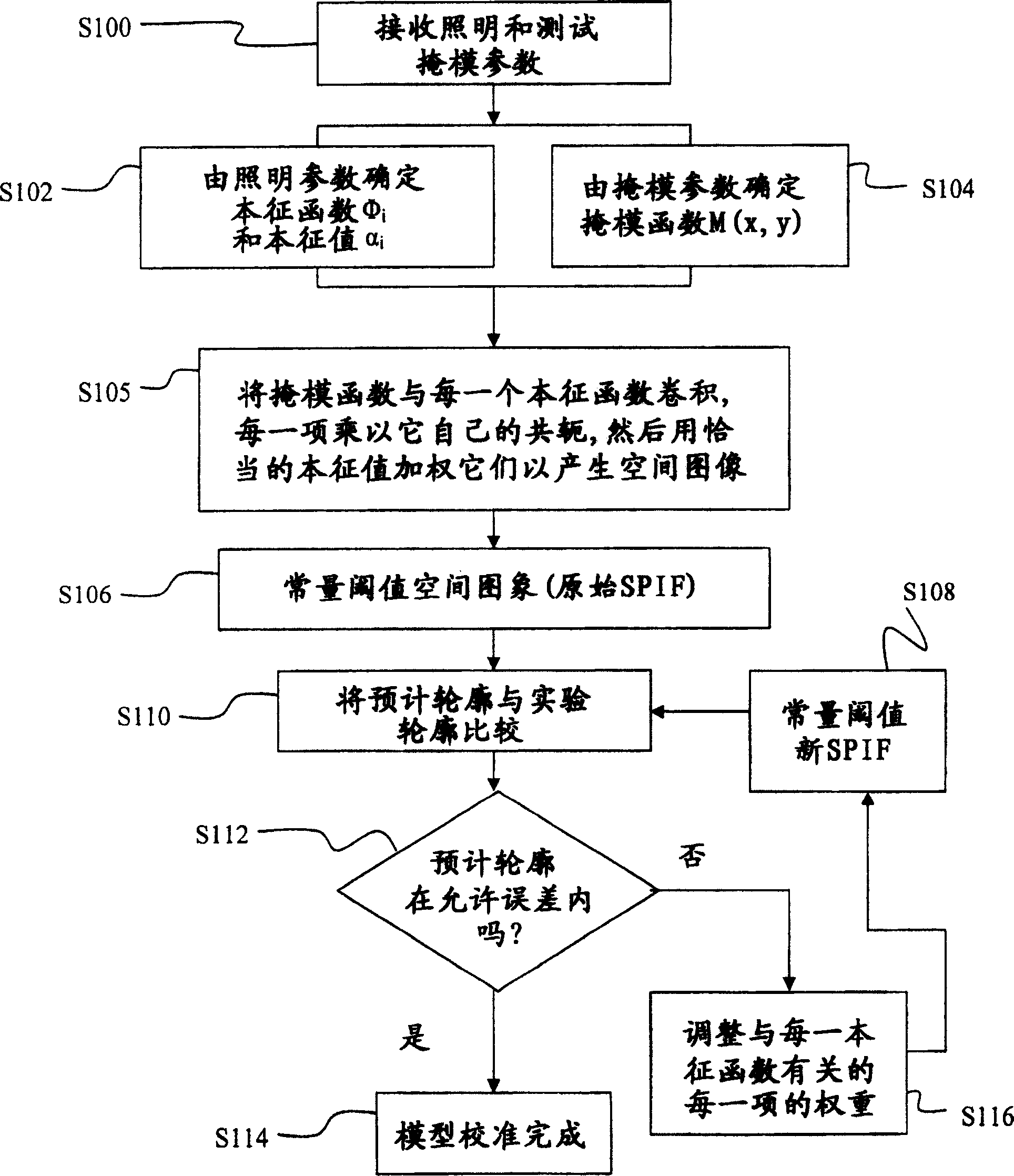
InactiveUS20050149902A1Minimal human interventionMinimal interventionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionResistPupil function
Model OPC is developed based on eigen decomposition of an aerial image expected to be produced by a mask pattern on a surface of a resist. With the eigen decomposition method the aerial image intensity distribution around a point (x, y) is accurately described in the model. A scalar approach may be used in the eigen decomposition model which treats the light wave through the mask as a scalar quantity. A eigen decomposition alternatively may use a vector approach which utilizes a vector to describe the light wave and the pupil function. A predicted SPIF may be generated from the aerial image which may be used to verify the mask modeling process by comparing the predicted SPIF to an experimentally determined SPIF. The model OPC, once calibrated, may be used to evaluate performance of a mask and refine features of the mask.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method for improving optical scanning holographic tomography effect
InactiveCN104159094ASmall viewing impactEvenly distributed noiseImage enhancementSteroscopic systemsOptical scanning holographyOptical tomography
The invention discloses a method for improving an optical scanning holographic tomography effect, and belongs to the field of optical tomography. The method can solve the defect in the conventional optical scanning technology that restored section images have louder out-of-focus noise, in real time. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing a random phase in the optics encryption technique, changing a certain pupil function in a conventional optical scanning holographic system into a stochastic phase pupil function, and equaling restore of out-of-focus layer images into decryption under the condition of mistakenly decrypting a secret key, thereby enabling the out-of-focus layer images overlaid on the restored section images to be gaussian white noise with statistical independence and greatly reducing the influence of the out-of-focus noise on the focus layer images. Meanwhile the out-of-focus noise can also be filtered through design of a gaussian filter, so that the longitudinal resolution of the system can be improved; besides, through the adoption of the method, the bandwidth of the optical transfer function is wider, and the transverse resolution of the restored section images can be higher.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Systems and methods for rendering a display to compensate for a viewer's visual impairment
A system and a method are provided for rendering on a display of an electronic device a pre-corrected image of an original image to compensate for a visual impairment of a user of the device, such that the pre-corrected image when displayed on the display would be perceived by the user to be in better optical focus than the user would perceive a display of the original image. The steps of the method implemented include receiving hardware characteristics of the display, receiving at least one parameter describing the visual impairment of the user, receiving at least one parameter describing the conditions under which the display is seen by the user, calculating a pupil function, calculating a Point Spread Function (PSF), calculating a pre-corrected image corresponding to at least a portion of the original image to compensate for the visual impairment of the user, and rendering on the display the pre-corrected image.
Owner:焦点再现
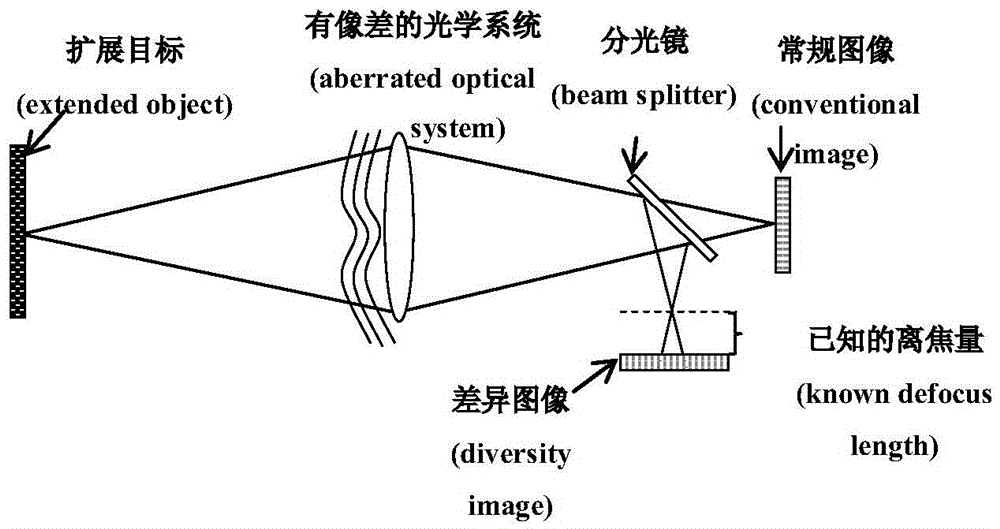
Method for detecting surface shape of large-aperture telescope by using phase diversity phase retrieval
InactiveCN105588519AReduce development costsSimplify hardware configurationUsing optical meansPupil functionDiffusion function
The invention relates to a method for detecting the surface shape of a large-aperture telescope by using phase diversity phase retrieval. The method comprises the following steps of: representing a 2-bit variable by using a 1-bit variable in order to representing an imaging relation of an optical system; expanding a wave aberration into a series, solving a transfer function by using self-correlation operation of a pupil function and changing a Zernike coefficient so as to obtain different transfer function calculating results, comparing the transfer function calculating results with a transfer function result acquired from the Fourier transform of a measured point spread function, using a minimum mean square error result as a solution; and solving an evaluation value E. The method for detecting the surface shape of a spherical mirror on the basis of phase diversity phase retrieval in a focal plane detector is low in development cost, simple in hardware, susceptible of influences of environment (especially vibration), and capable of dynamically detecting optical elements and systems.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Embedded pupil function recovery for fourier ptychographic imaging devices
Certain aspects pertain to Fourier ptychographic imaging systems, devices, and methods that implement an embedded pupil function recovery.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
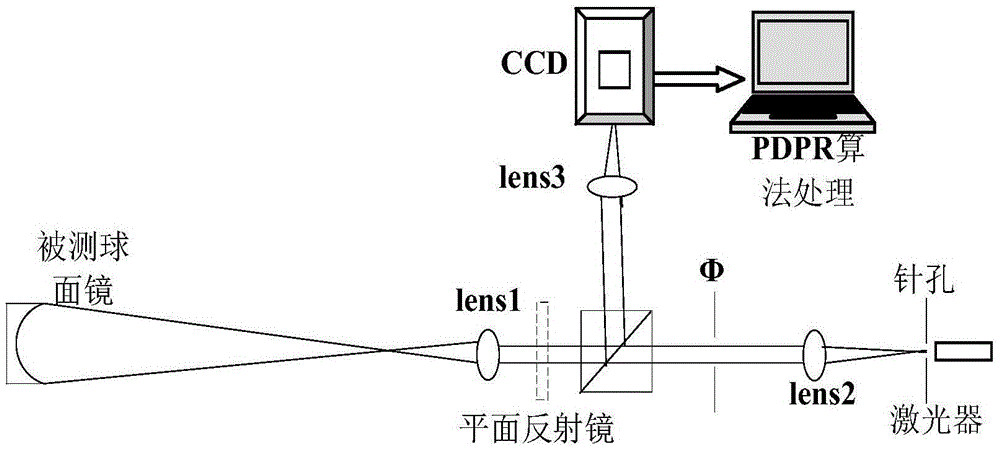
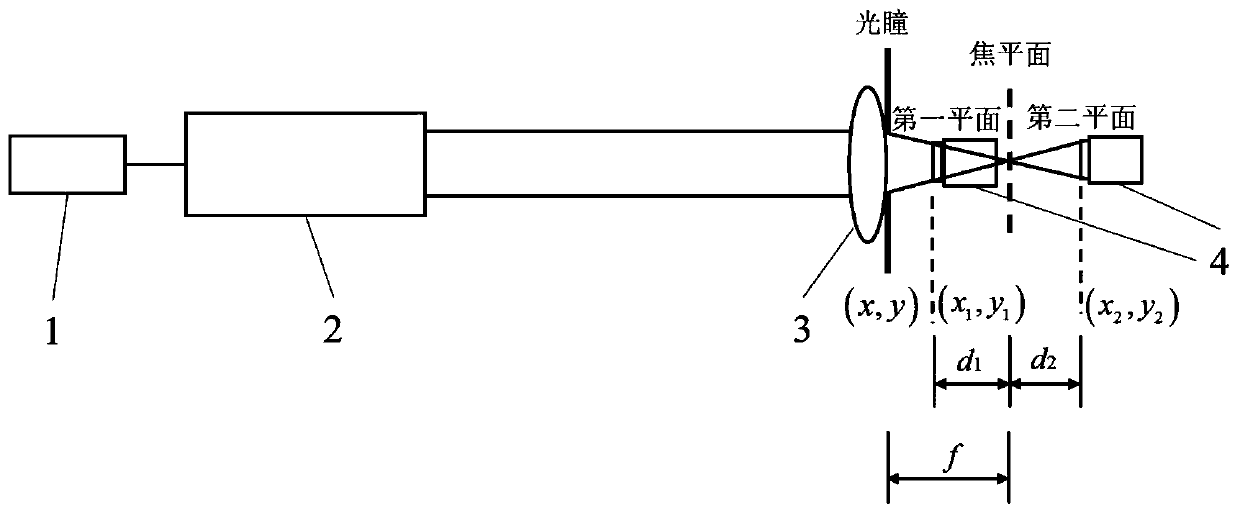
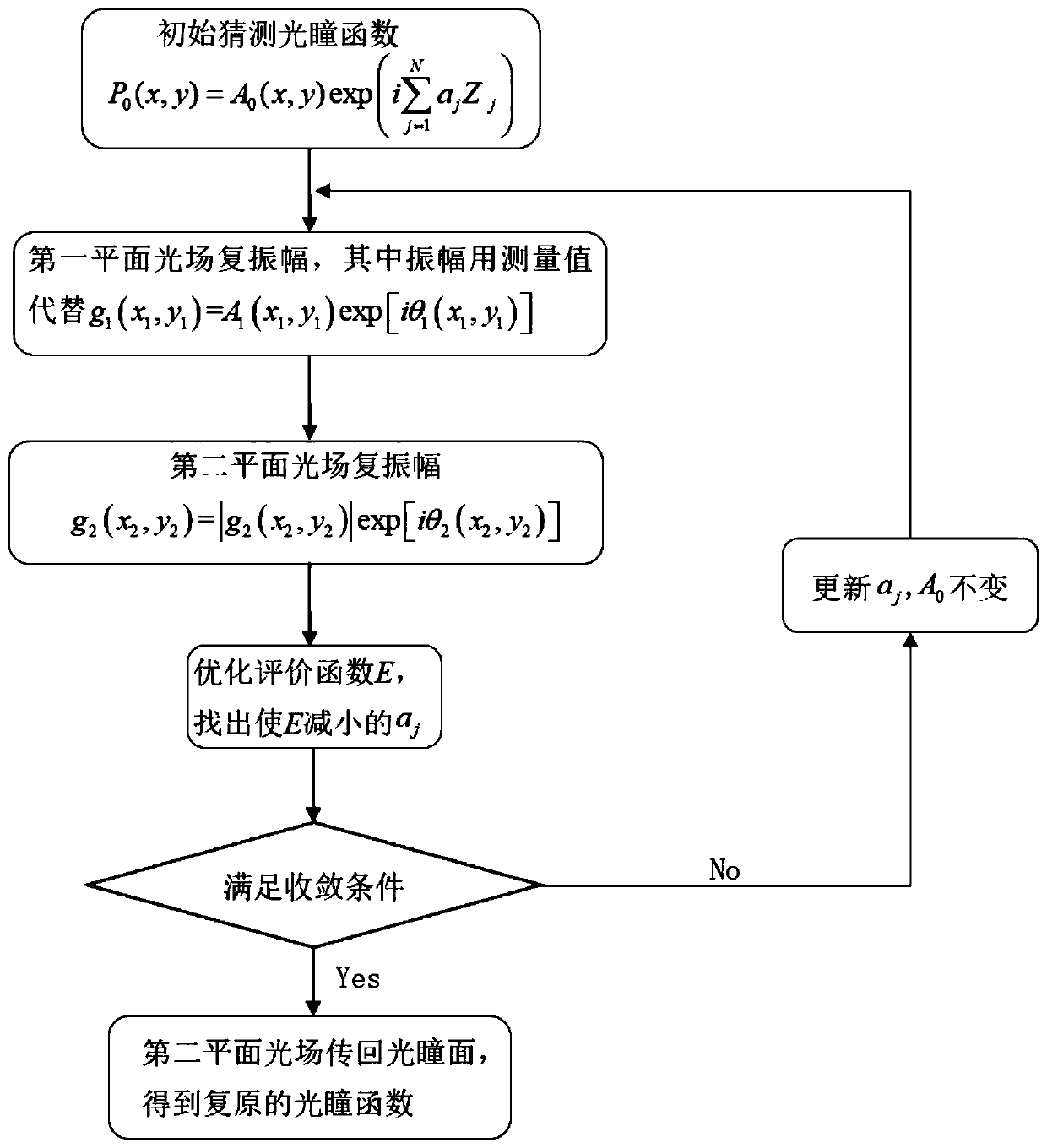
Single focal plane high-precision testing method for optical wavefront of optical imaging system
InactiveCN102252763ASolve for uniformitySolve the errorOptical measurementsPupil functionCalculation error
The invention discloses a single focal plane high-precision testing method for optical wavefront of an optical imaging system, relates to the technical field of optical testing, solves the problems that exit pupil amplitudes are not distributed uniformly and calculation errors are introduced by fast Fourier transform in the conventional phase retrieval algorithm, and provides the scheme for eliminating the influence of vibration in the process of image acquisition on detection accuracy. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a detection platform of the optical imaging system; detecting the position of the focal plane of a lens to be detected by using a detection device in the detection platform and acquiring an out-of-focus stellar image of the lens to be detected by the detection device; selecting effective data according to the acquired out-of-focus stellar image and calculating a pupil function of an optical system; and extracting the phase of the acquired pupil function to obtain the optical wavefront of the optical imaging system. The pupil function of the optical system is calculated by a Zernike multinomial, an extended Nijboer-Zernike multinomial, and a generalized inverse matrix. The single focal plane high-precision testing method is low in cost, and high in accuracy and is suitable for manufacturing enterprises, scientific research and detection units of the optical imaging system.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
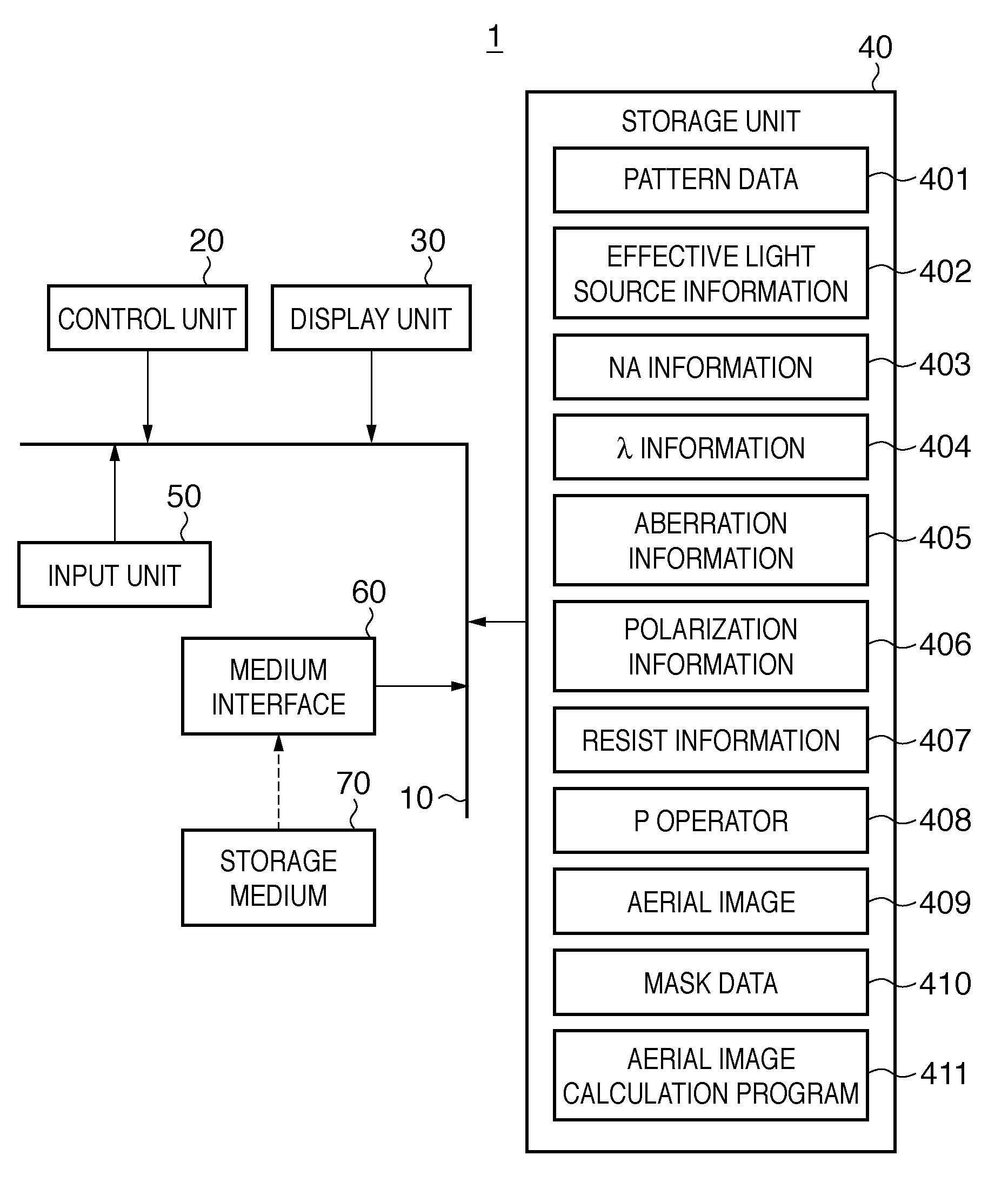
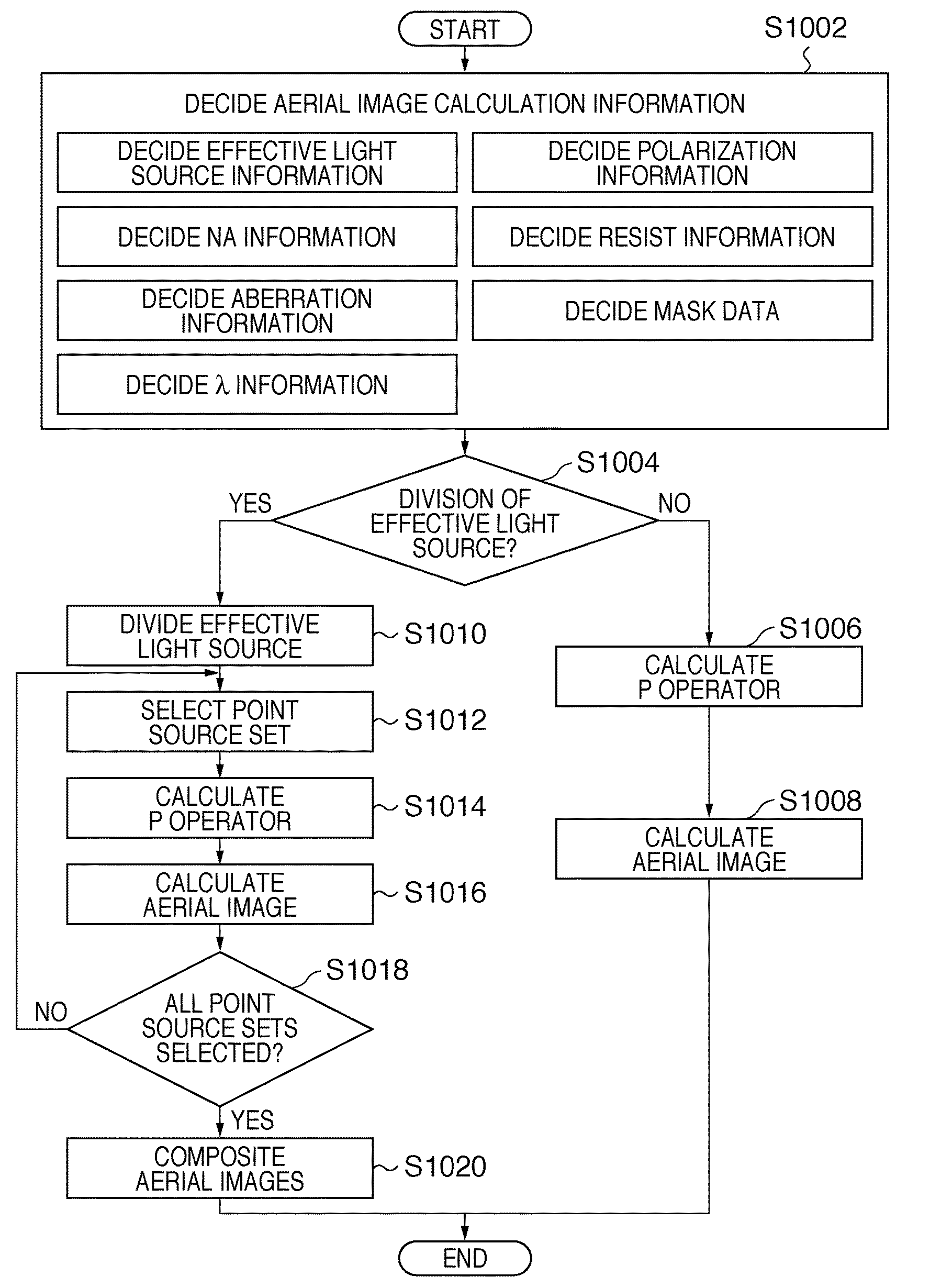
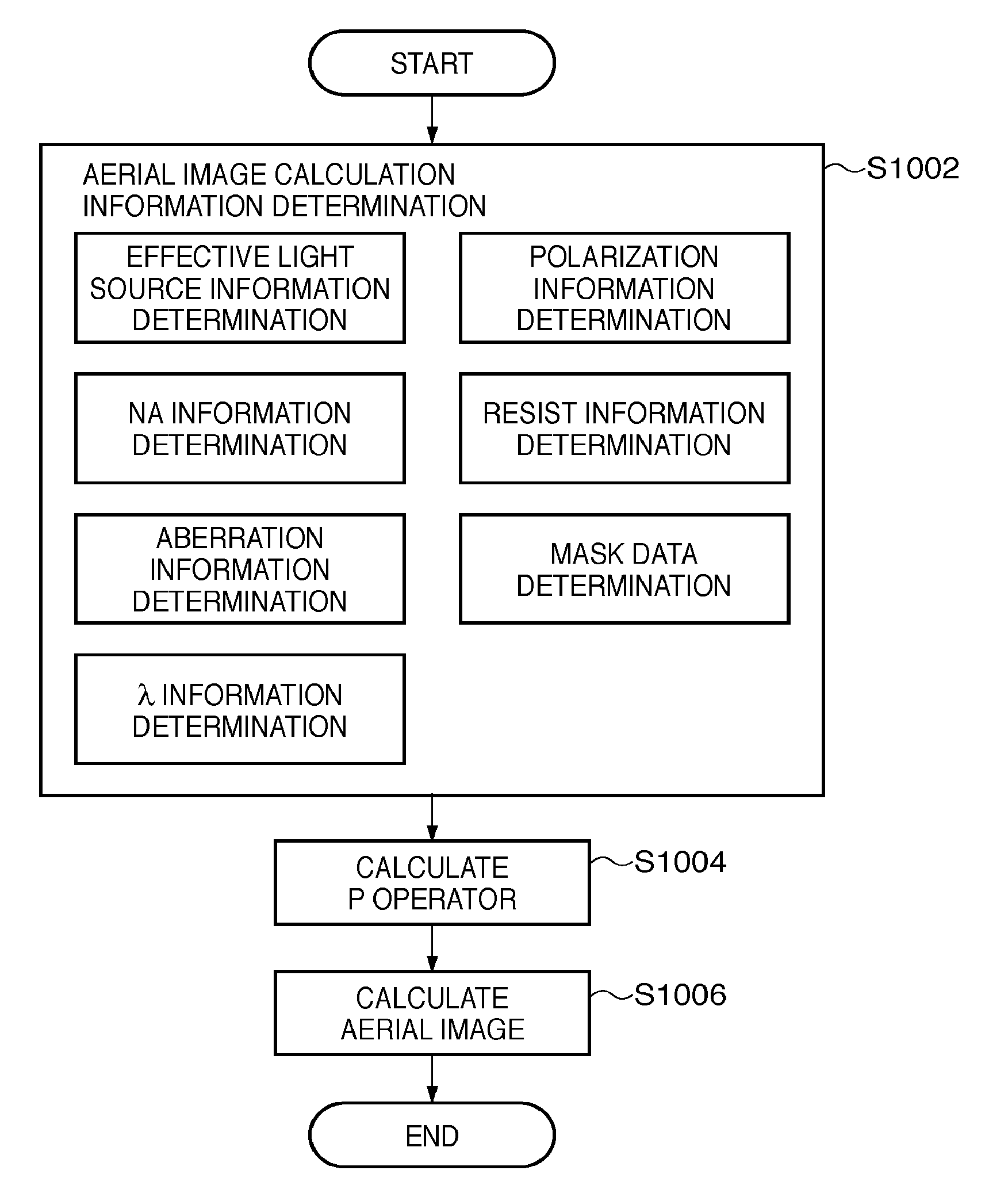
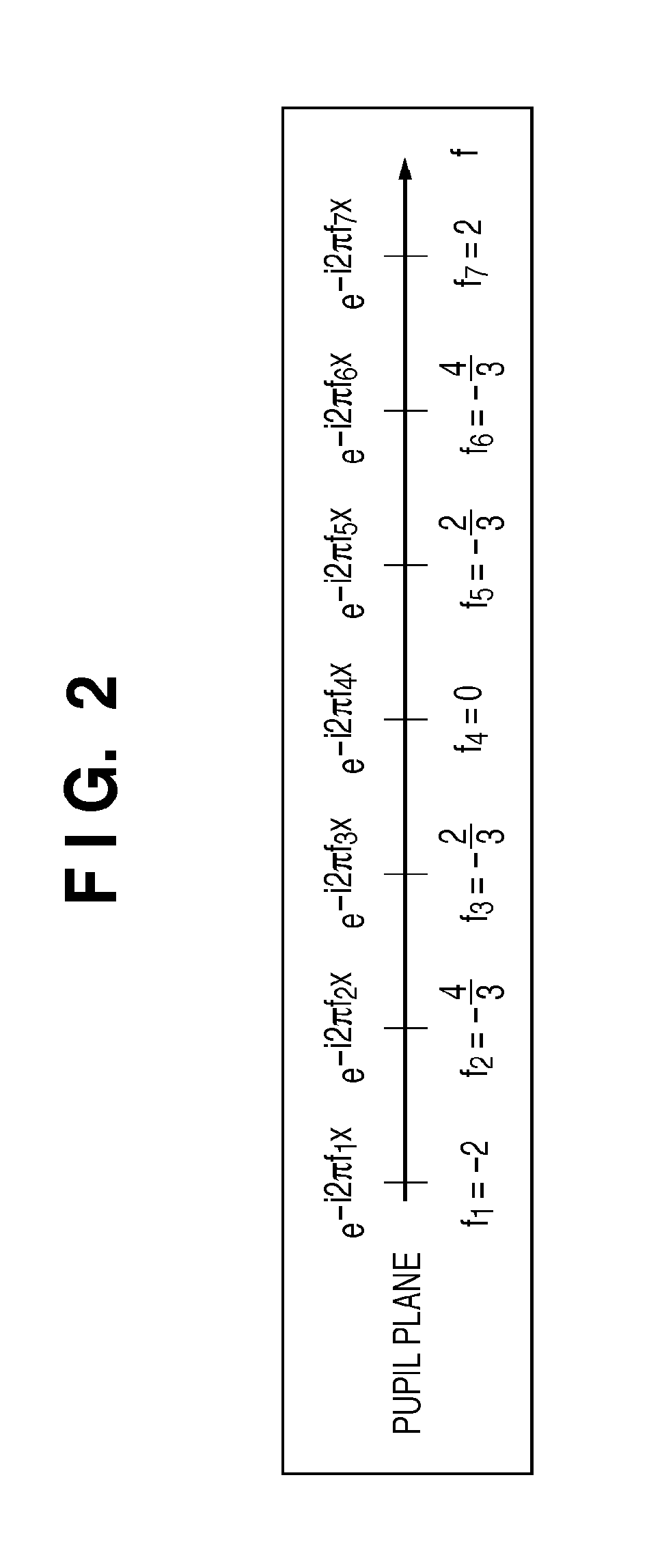
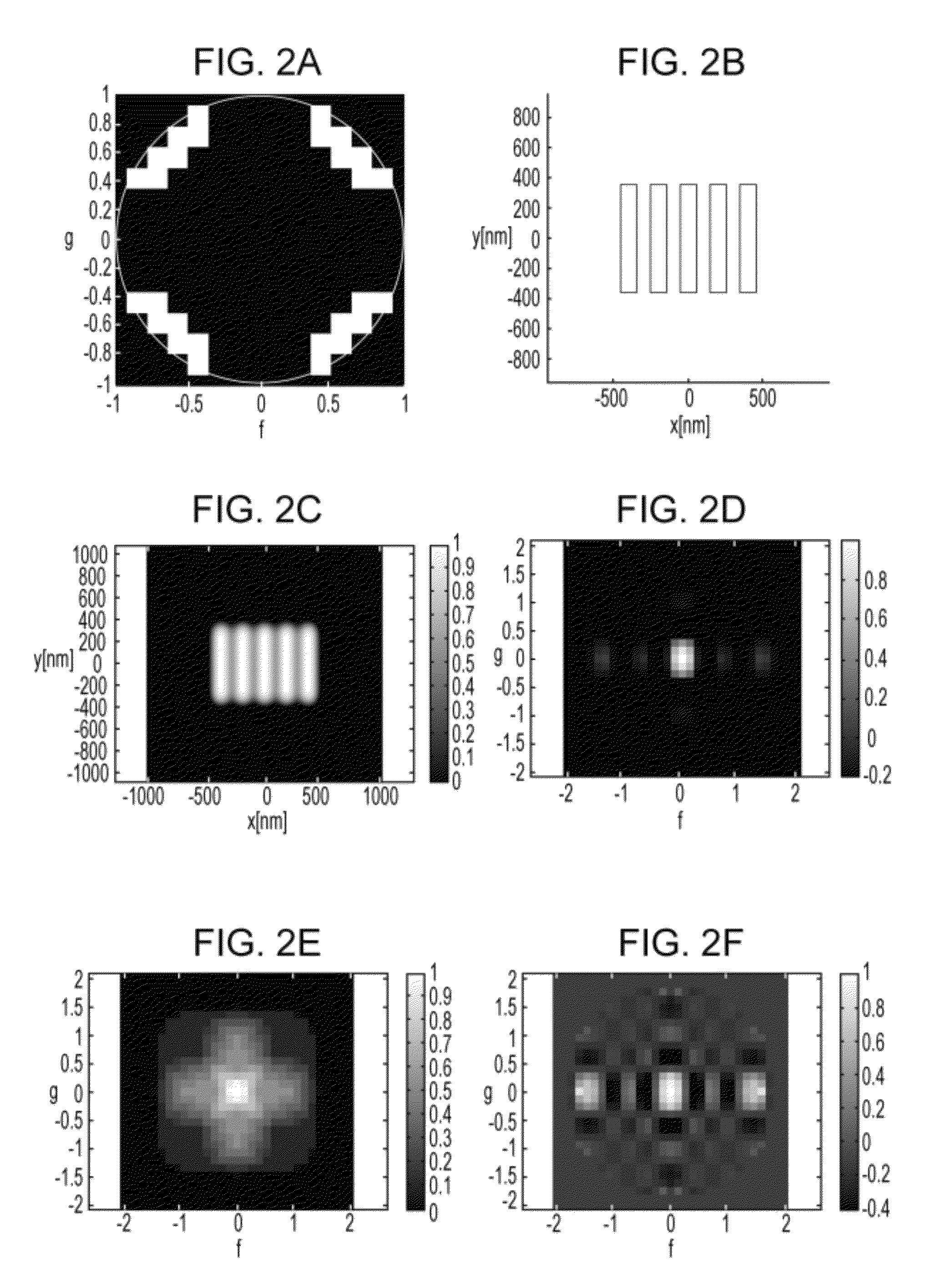
Calculation method, generation method, program, exposure method, and mask fabrication method
ActiveUS20090091736A1Short timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSingular value decompositionPupil function
The present invention provides a calculation method of calculating, by a computer, a light intensity distribution formed on an image plane of a projection optical system, comprising a step of dividing an effective light source formed on a pupil plane of the projection optical system into a plurality of point sources, a step of shifting a pupil function describing a pupil of the projection optical system for each of the plurality of point sources in accordance with positions thereof, thereby generating a plurality of shifted pupil functions, a step of defining a matrix including the plurality of pupil functions, a step of performing singular value decomposition of the matrix, thereby calculating an eigenvalue and an eigenfunction, and a step of calculating the light intensity distribution, based on a distribution of the light diffracted by the pattern of the mask, and the eigenvalue and the eigenfunction.
Owner:CANON KK
Eigen decomposition based OPC model
InactiveCN1661479ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionPUPILLARY FUNCTIONSPupil function
Model OPC is developed based on eigen function decomposition of an aerial image expected to be produced by a mask pattern on a surface of a resist. With the eigen function decomposition method the aerial image intensity distribution around a point (x,y) is accurately described in the model. A scalar approach may be used in the eigen function decomposition model which treats the light wave through the mask as a scalar quantity. A eigen function decomposition alternatively may use a vector approach which utilizes a vector to describe the light wave and the pupil function. A predicted SPIFF (system pseudo intensity function) may be generated from the aerial modelling may be used to verify the mask modelling process by comparing the predicted SPIFF to an experimentally determined SPIFF. The model OPC, once calibrated, may be used to evaluate performance of a mask and refine features of the mask.
Owner:ASML MASKTOOLS BV
Phase iteration minimization based Fourier ptychographic microscopy image reconstruction method
ActiveCN108550108AReconstructed intensity images are of good qualityGeometric image transformationPupil functionFrequency spectrum
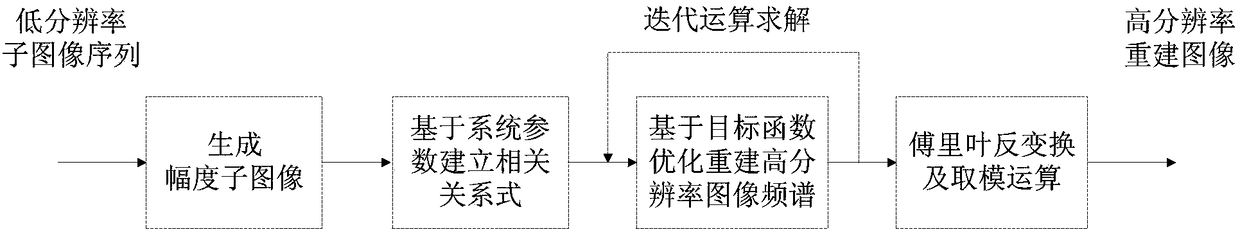
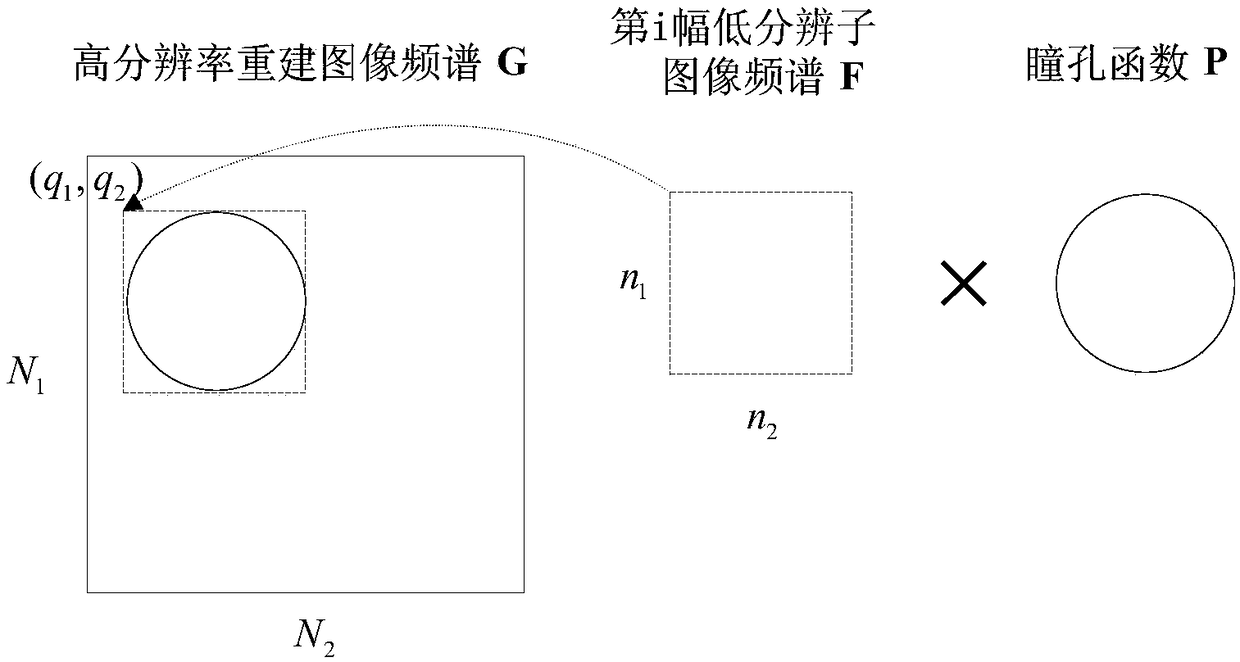
The invention belongs to the technical field of a Fourier ptychographic microscopy, and especially relates to a phase iteration minimization based Fourier laminate imaging image reconstruction method.The method includes the following steps: S1, generating a series of amplitude sub-images corresponding to low-resolution sub images; S2, obtaining reconstruction algorithm parameters, the parametersincluding the positions of frequency spectrums generated by each low-resolution sub image in high-resolution reconstruction spectrums, pupil functions, etc., and building the relation between the low-resolution sub images and high-resolution reconstruction images; S3, taking phase recovery as one of optimization targets, generating a target function for image reconstruction target optimization, performing solving through iterative minimization, and obtaining frequency spectrums of a high-resolution reconstruction image; and S4, performing Fourier inverse transformation on the frequency spectrums of the high-resolution reconstruction image, using the models of results as the images after high-resolution reconstruction. The method performs the high-resolution image reconstruction by using the low-resolution sub images with the same numbers, and therefore, better reconstruction intensity image quality can be achieved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
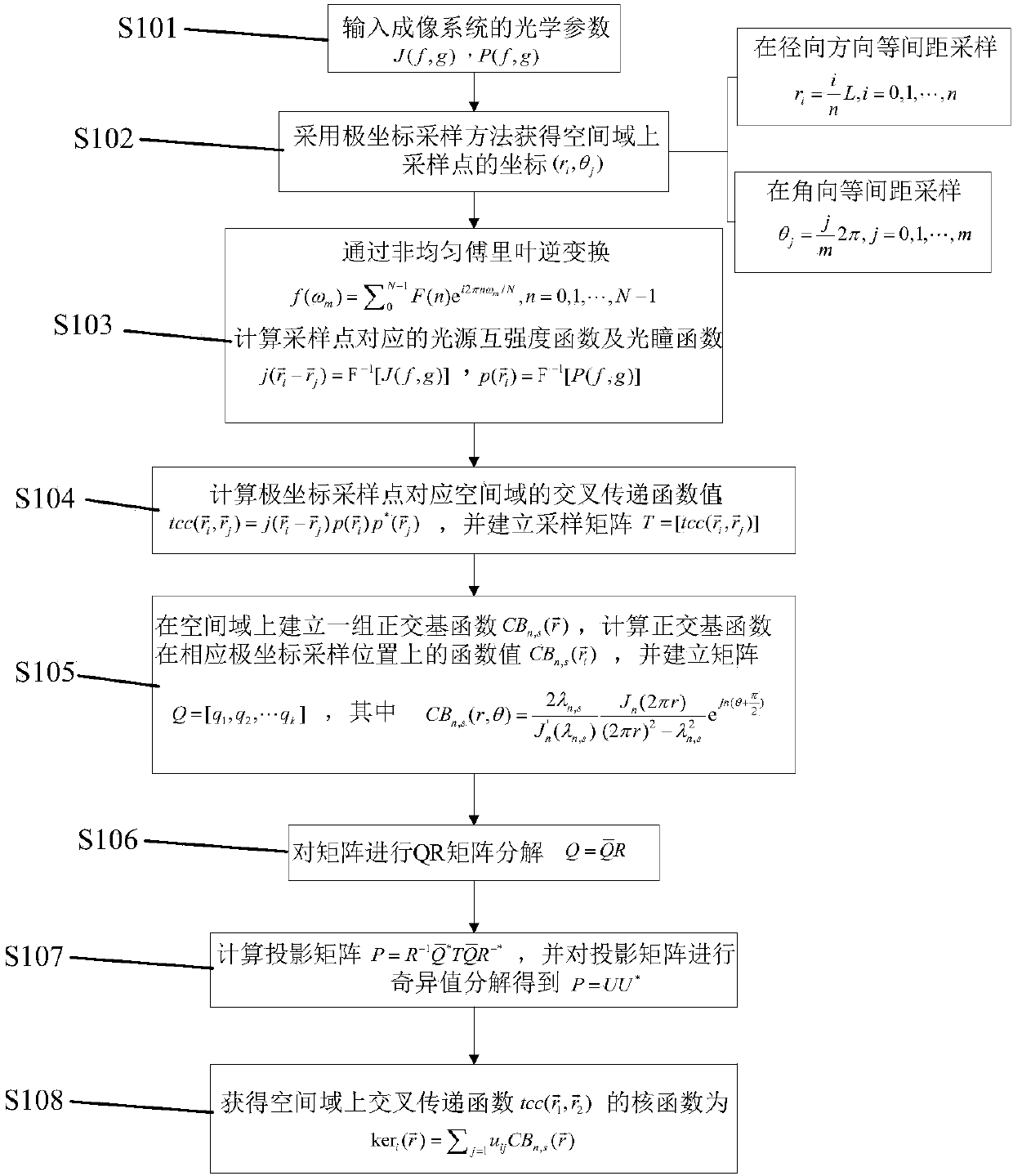
Polar coordinate sampling-based cross transfer function quick decomposition method
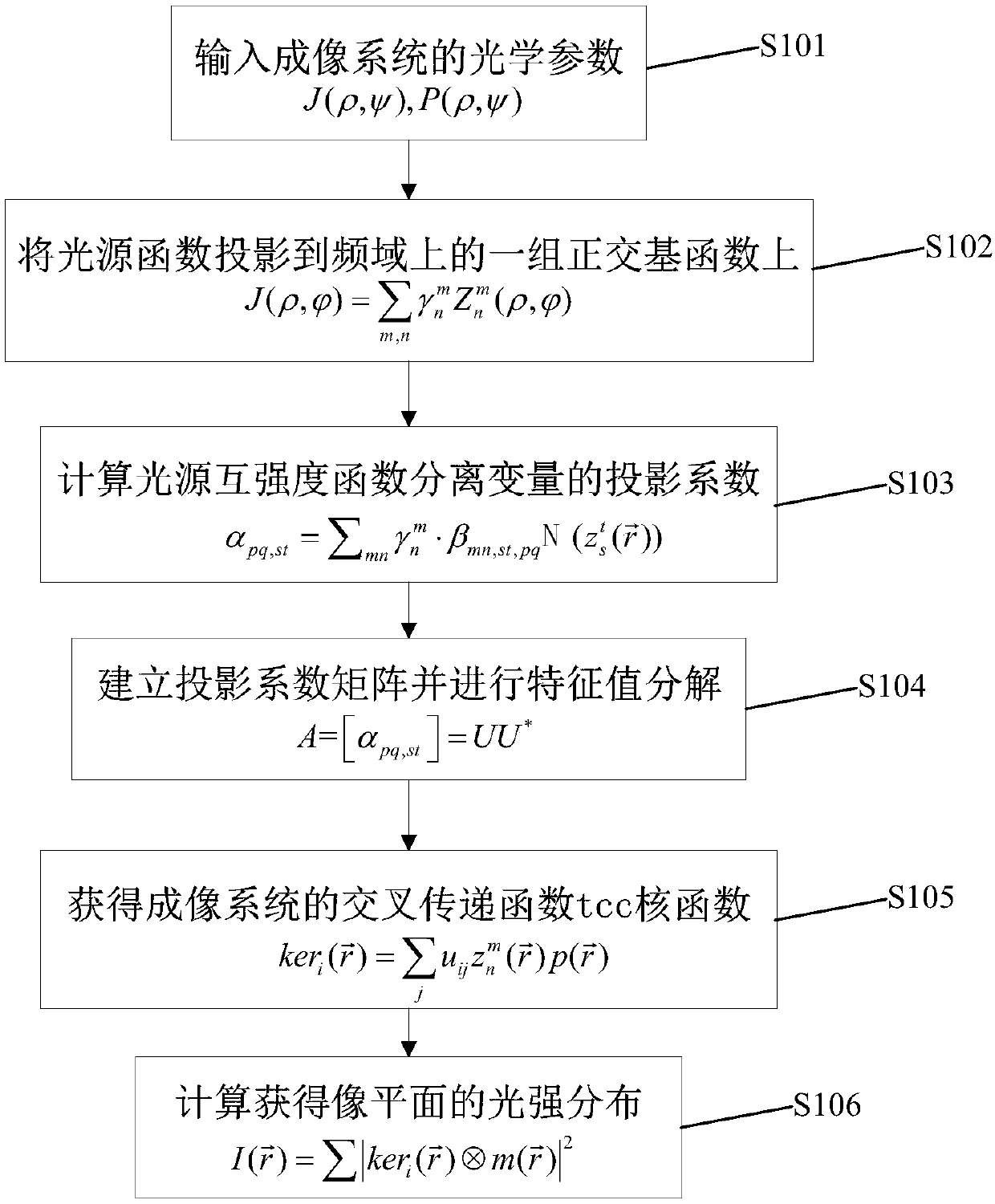
InactiveCN107644131APromote decompositionAchieve decompositionSpecial data processing applicationsSingular value decompositionMatrix decomposition
The invention discloses a polar coordinate sampling-based cross transfer function quick decomposition method. The method comprises the following steps of 1) obtaining optical parameters of an imagingsystem; 2) obtaining coordinates (ri, theta j) of sampling points on a spatial domain by adopting a polar coordinate sampling method; 3) calculating light source mutual intensity functions, defined inthe specification, and pupil functions, defined in the specification, corresponding to the sampling points through non-uniform inverse Fourier transform; 4) calculating a cross transfer function value, defined in the specification, of the spatial domain corresponding to the sampling points, and establishing a sampling matrix defined in the specification; 5) establishing a group of orthogonal basis functions defined in the specification, calculating function values, defined in the specification, of the orthogonal basis functions in corresponding polar coordinate sampling positions, and establishing a matrix Q=[q1, q2, ...qk]; 6) performing QR matrix decomposition, defined in the specification, on the matrix Q; 7) calculating a projection matrix and performing singular value decomposition on the projection matrix P to obtain P=UU*; 8) obtaining a kernel function, defined in the specification, of the cross transfer function, defined in the specification, on the spatial domain. Quick analysis can be performed to obtain the TCC kernel function, so that light intensity distribution calculation is quick and efficient, and actual photoetching process design demands are met.
Owner:SUZHOU COGENDA ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Calculation program, and exposure method for calculating light intensity distribution formed on image plane
ActiveUS8059262B2Short timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSingular value decompositionPupil function
The present invention provides a calculation method of calculating, by a computer, a light intensity distribution formed on an image plane of a projection optical system, comprising a step of dividing an effective light source formed on a pupil plane of the projection optical system into a plurality of point sources, a step of shifting a pupil function describing a pupil of the projection optical system for each of the plurality of point sources in accordance with positions thereof, thereby generating a plurality of shifted pupil functions, a step of defining a matrix including the plurality of pupil functions, a step of performing singular value decomposition of the matrix, thereby calculating an eigenvalue and an eigenfunction, and a step of calculating the light intensity distribution, based on a distribution of the light diffracted by the pattern of the mask, and the eigenvalue and the eigenfunction.
Owner:CANON KK
Computer readable storage medium including effective light source calculation program, and exposure method
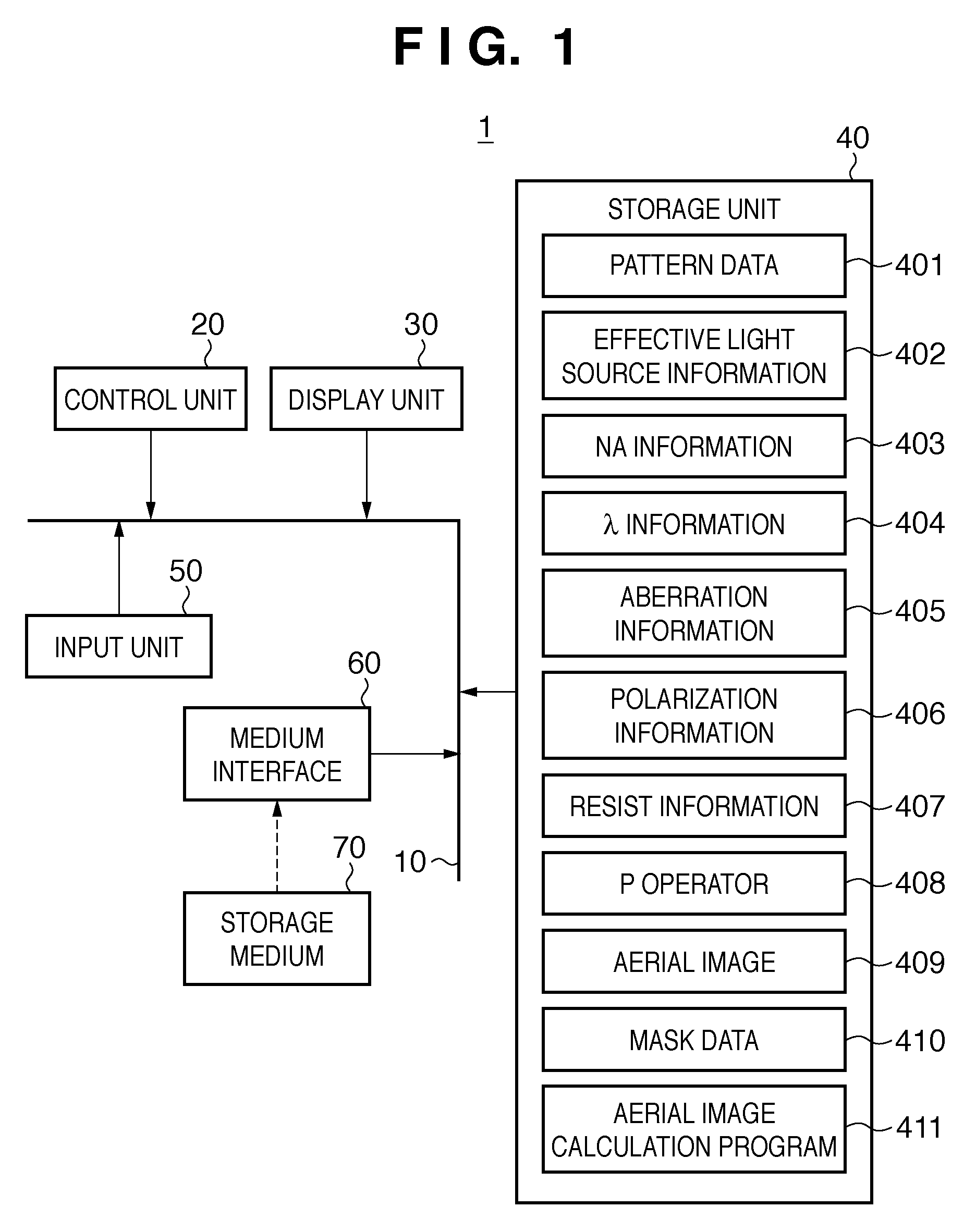
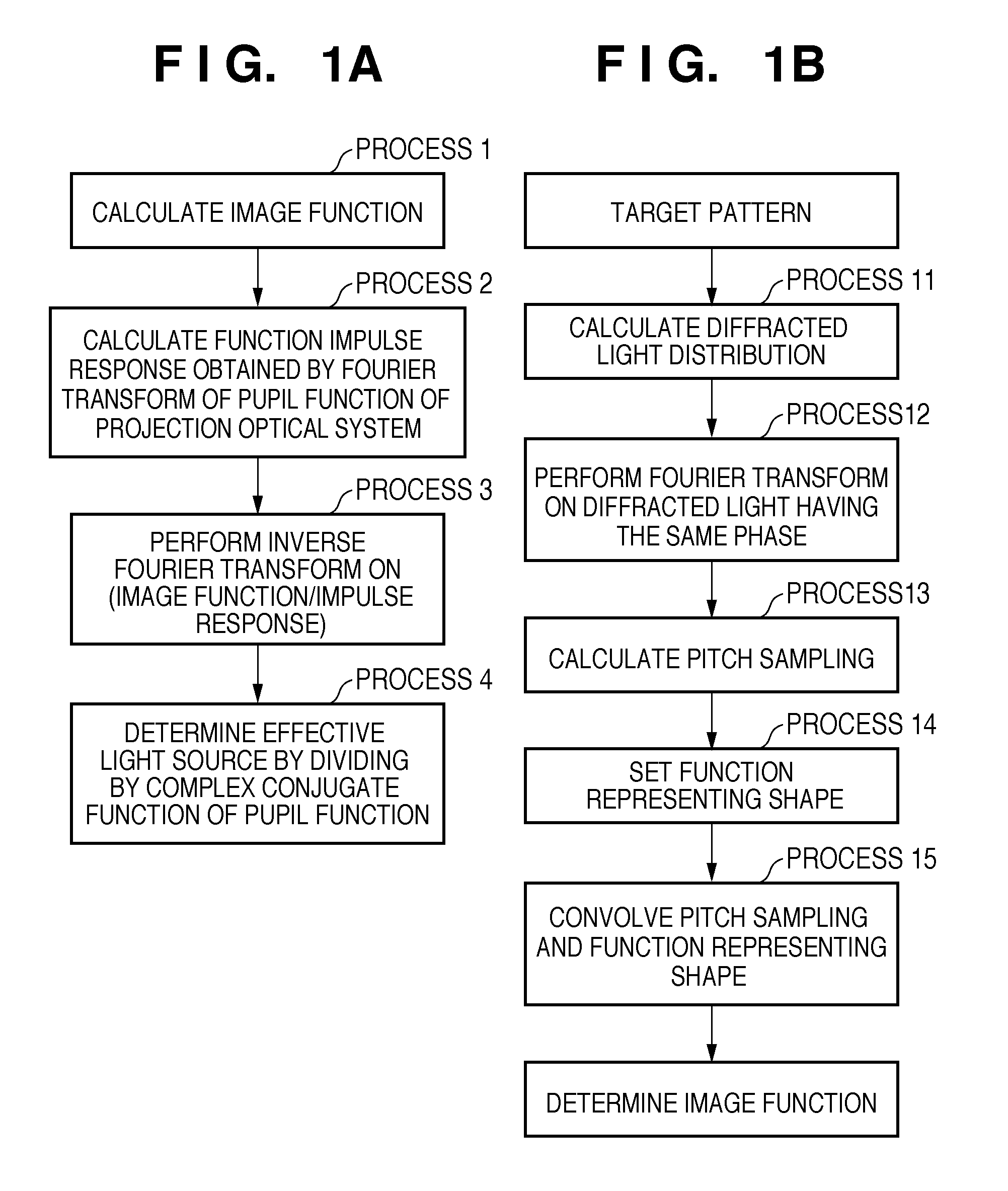
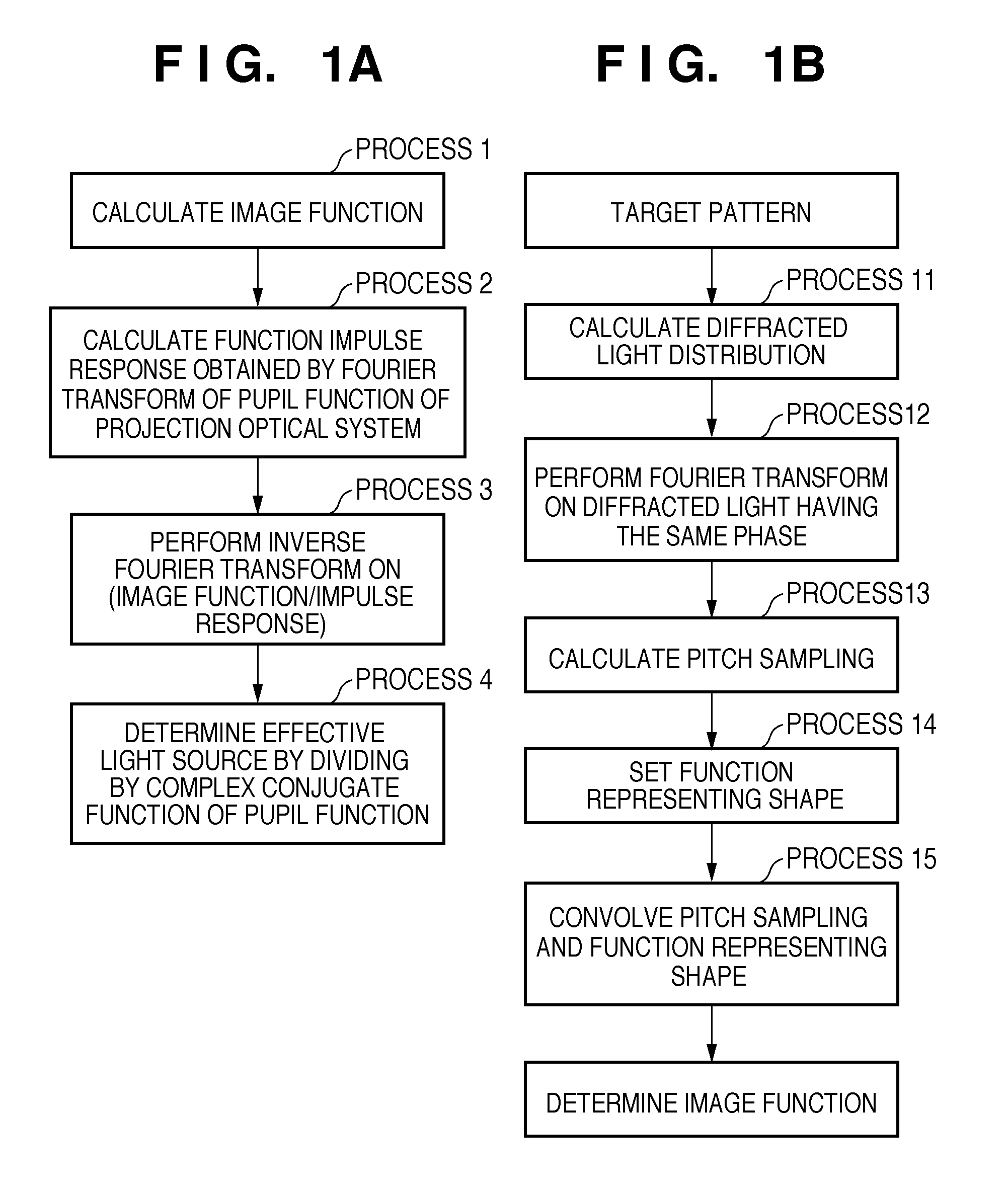
InactiveUS20110122394A1Reduce a decrease in image formation performancePhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingPupil functionImage fusion
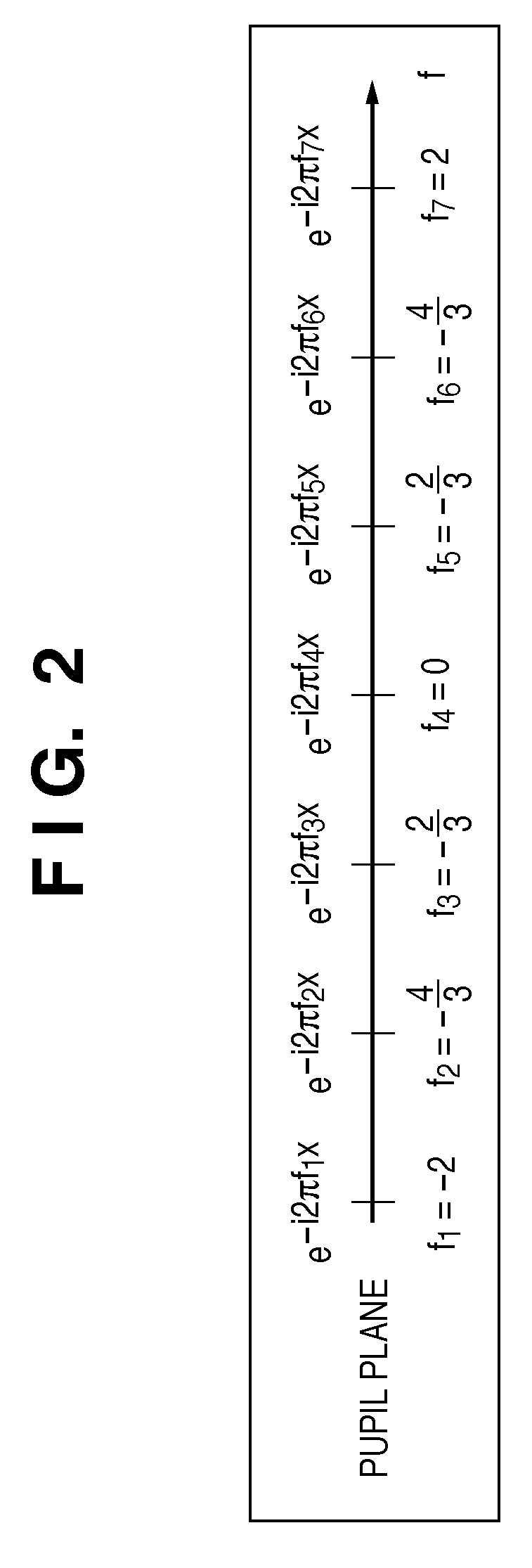
A storage medium includes a program which causes a computer to execute a method of calculating a light intensity distribution on a pupil plane of an illumination optical system. The method includes: determining an impulse response function of a projection optical system by performing Fourier transform on a pupil function of the projection optical system; setting a length to a second zero point of the impulse response function as a response length, extracting, from elements forming a target pattern, only elements inside am area within radius which is response length, and determining a function indicating the extracted pattern as an image function; and obtaining the light intensity distribution based on the pupil function, the determined impulse response function, and the determined image function.
Owner:CANON KK
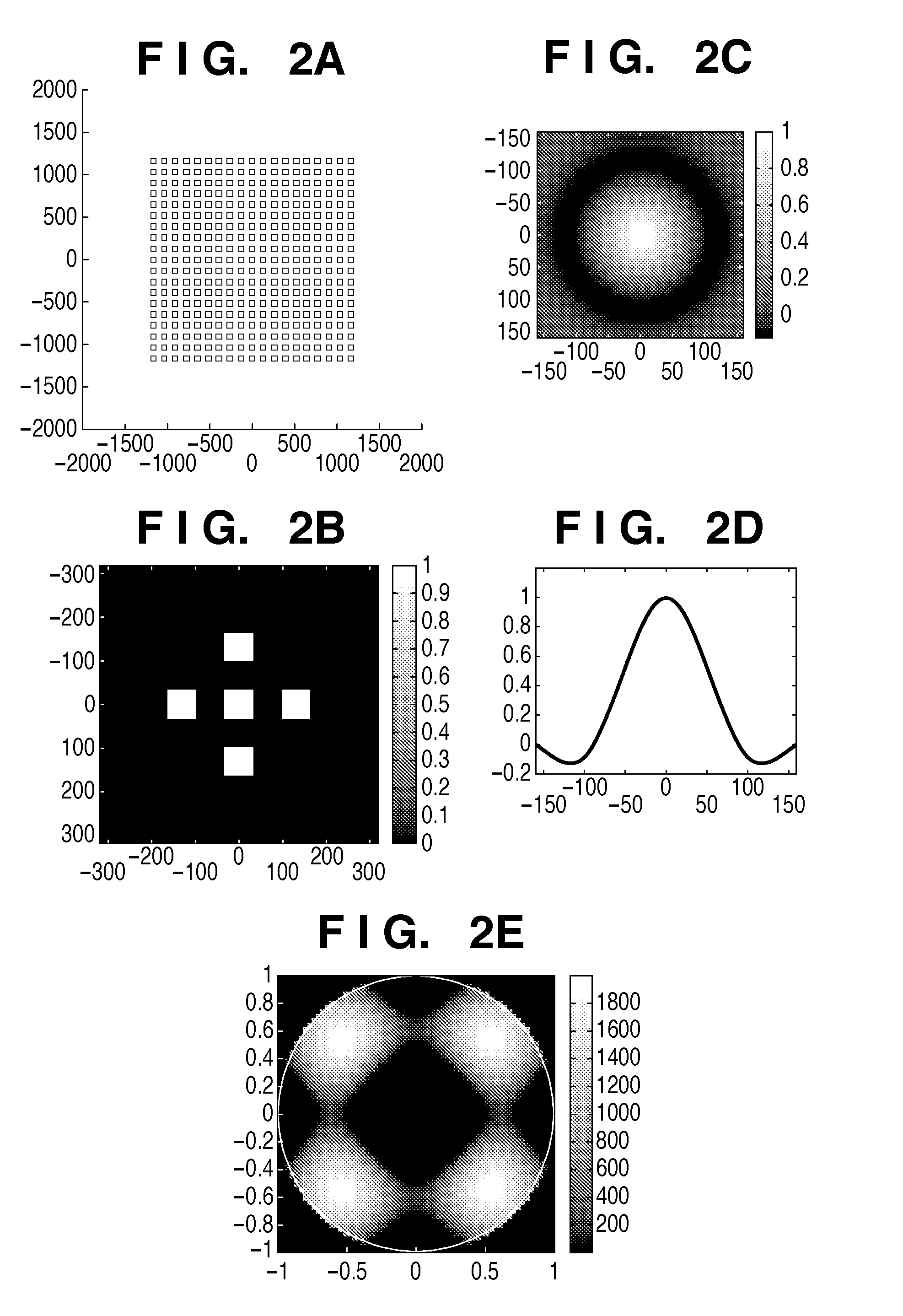
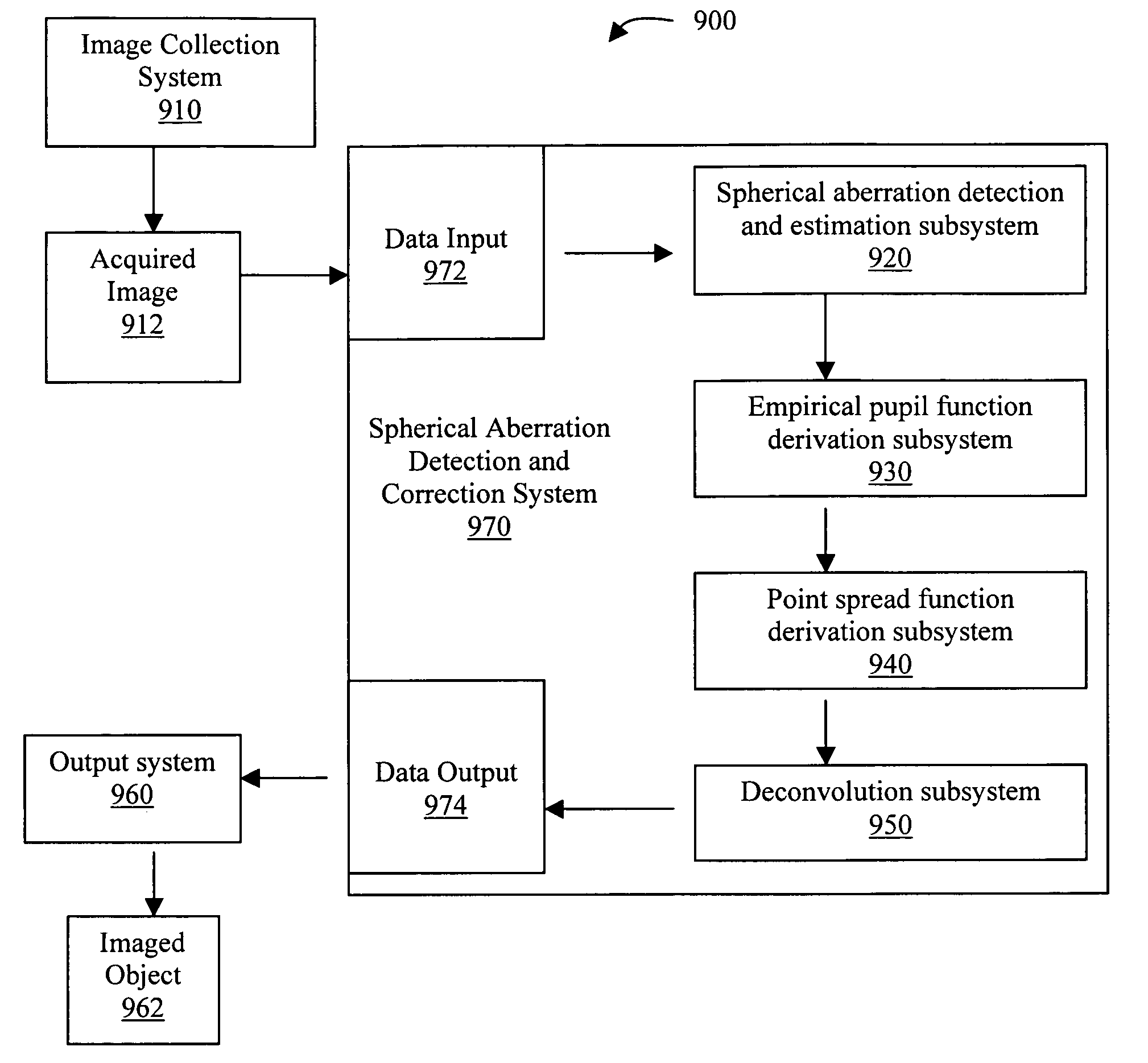
Methods, system, and program product for the detection and correction of spherical aberration
The present invention provides methods, a system, and a program product for the rapid detection and correction of spherical aberration in microscopy systems. More specifically, the present invention empirically derives a pupil function, adaptively corrects PSF parameters, and automatically detects the coefficient for spherical aberration. A first aspect of the invention provides a method for detecting and estimating spherical aberration in an acquired image obtained using an optical system, comprising the steps of deconvolving an image using each of a plurality of point spread functions, wherein each point spread function has a different spherical aberration value, calculating an image energy for each deconvolved image, and choosing as a spherical aberration coefficient the spherical aberration value corresponding to the deconvolved image having the lowest image energy, wherein a spherical aberration coefficient other than 0 indicates the presence of spherical aberration in the acquired image and its distance from 0 is an estimation of the degree and direction of spherical aberration.
Owner:MEDIA CYBERNETICS
Computer readable medium and exposure method
InactiveUS20100053580A1Short timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital computer detailsSingular value decompositionPupil function
A computer readable medium containing computer-executable instructions which cause a computer to execute processing steps that calculate a light intensity distribution formed on an image plane of a projection optical system. When executed, the medium causes a computer to execute the steps of dividing an effective light source into the plurality of areas, generating, for each of the plurality of areas, a plurality of shifted pupil functions by shifting a pupil function in accordance with a position of each of divided point sources, defining, for each of the plurality of areas, a matrix including the plurality of pupil functions, calculating, for each of the plurality of areas, eigenvalues and eigenfunctions by performing singular value decomposition of the matrix, and calculating, for each of the plurality of areas, the light intensity distribution based on a diffracted light distribution from the mask and the eigenvalues and the eigenfunctions.
Owner:CANON KK
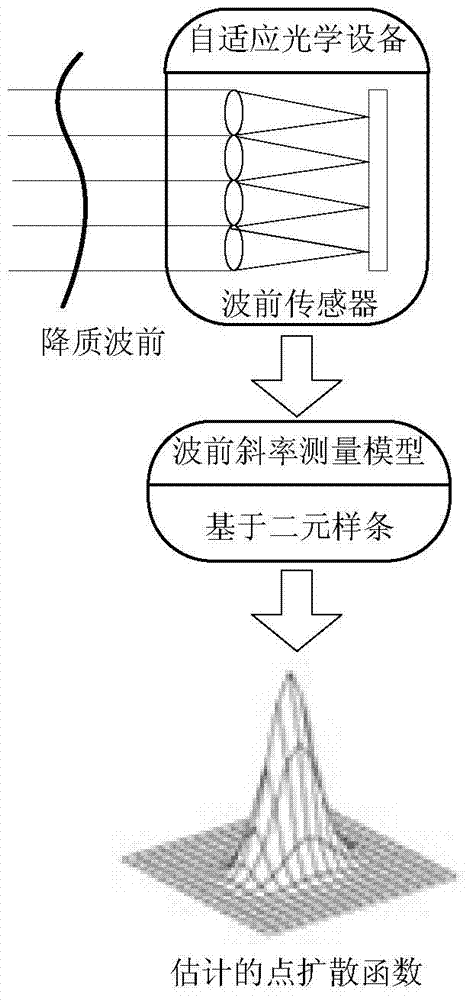
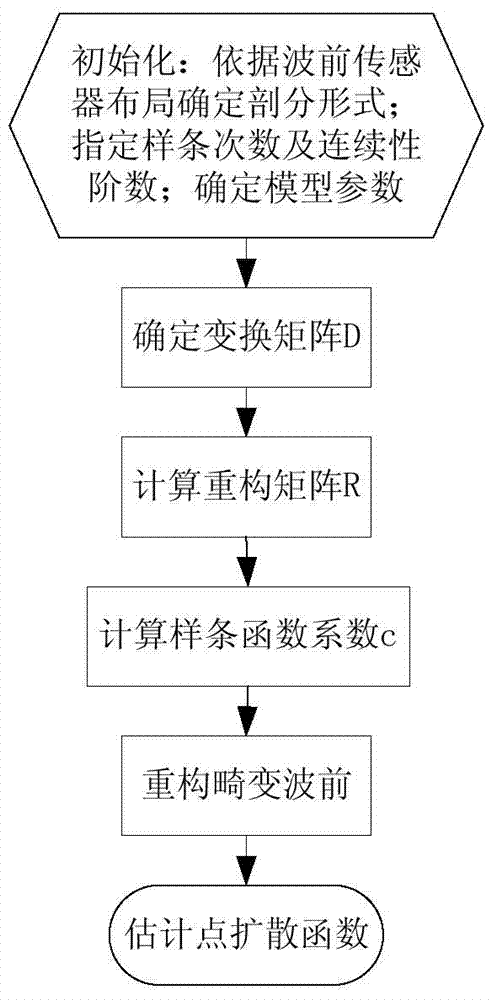
Point diffusion function estimation method in self-adaptive optical imaging
ActiveCN103714516AImprove estimation accuracyImproved accuracy of wavefront reconstructionImage enhancementPupil functionWavefront sensor
The invention discloses a point diffusion function estimation method in self-adaptive optical imaging. The invention is based on a B-network method for studying a multivariate spline. Firstly, a distorted wavefront which has gone through atmosphere quality degradation is approximately represented by a bivariate spline in terms of pure subdivision, thereby obtaining a mathematic relation between wavefront sensor gradient measurement data and a spline function coefficient; secondly, in combination with a smooth splicing condition of a spline function in terms of adjacent triangulation, the gradient measurement data is employed to estimate the spline function coefficient by virtue of restricting a least square estimation, thereby reconstructing the distorted wavefront; and finally, the obtained distorted wavefront is combined with a lens pupil function, thereby estimating and obtaining a instantaneous point diffusion function in imaging through atmosphere turbulence. Compared with a traditional Zernike mode point diffusion function estimation method, the point diffusion function estimation method of the invention overcomes the defect of imperfection of a transformation matrix rank and increases the estimation precision; and the point diffusion function estimation method of the invention is applicable to wavefront sensors with shielded centers and various geometric assignment situations of micro-lens arrays.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Calculation method, generation method, program, exposure method, and mask fabrication method
ActiveUS20120019805A1Short timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSingular value decompositionPupil function
The present invention provides a calculation method of calculating, by a computer, a light intensity distribution formed on an image plane of a projection optical system, comprising a step of dividing an effective light source formed on a pupil plane of the projection optical system into a plurality of point sources, a step of shifting a pupil function describing a pupil of the projection optical system for each of the plurality of point sources in accordance with positions thereof, thereby generating a plurality of shifted pupil functions, a step of defining a matrix including the plurality of pupil functions, a step of performing singular value decomposition of the matrix, thereby calculating an eigenvalue and an eigenfunction, and a step of calculating the light intensity distribution, based on a distribution of the light diffracted by the pattern of the mask, and the eigenvalue and the eigenfunction.
Owner:CANON KK
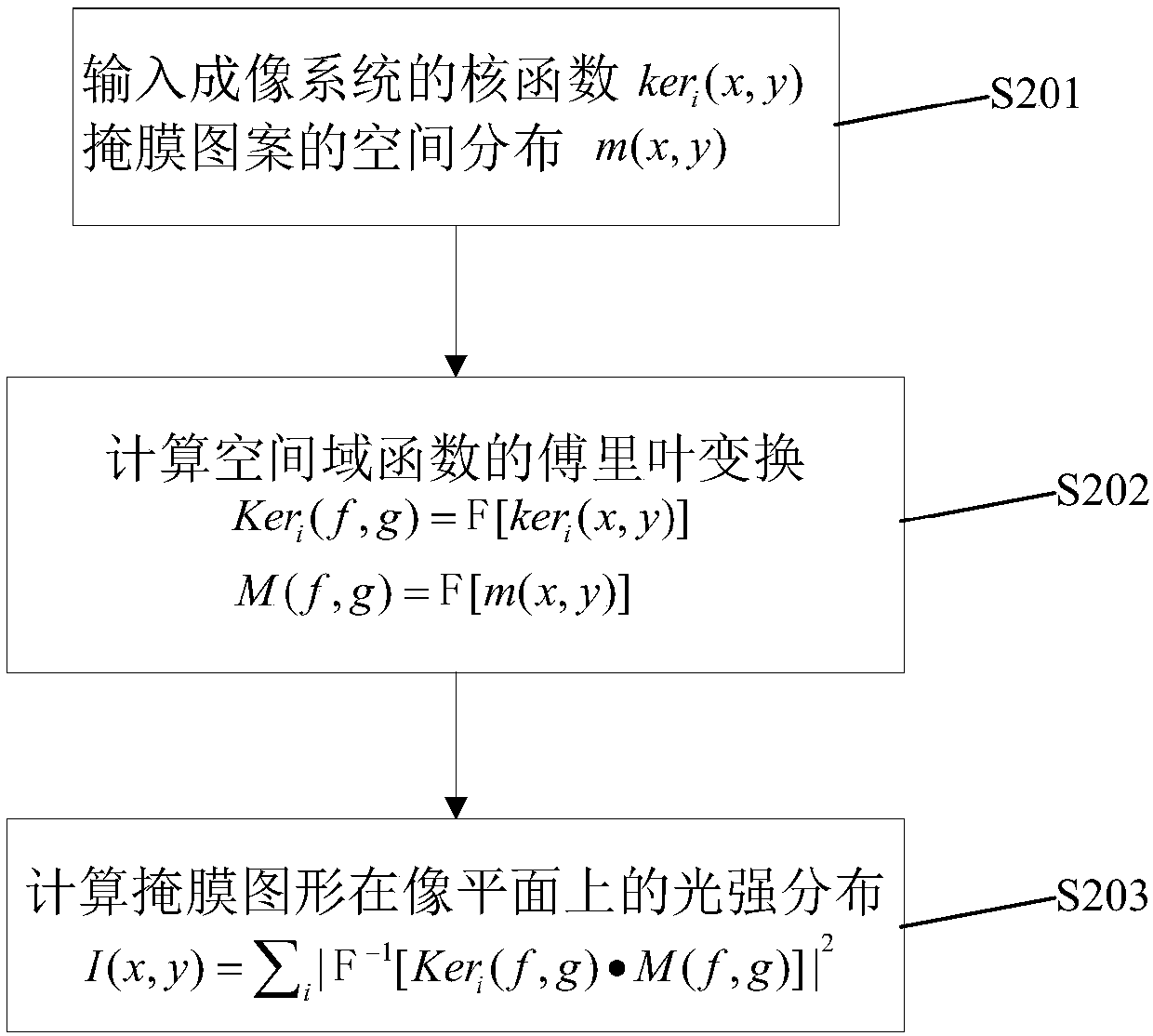
Rapid optical imaging calculation method based on light source mutual intensity function decomposition
InactiveCN107479335AQuick calculationEasy accessPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusHat matrixPupil function
The invention discloses a rapid optical imaging calculation method based on light source mutual intensity function decomposition. The rapid optical imaging calculation method comprises the following steps: 1) acquiring a light source function and a pupil function of an imaging system; 2) projecting the light source function to a group of orthogonal basis functions on a frequency domain; 3) solving a projection coefficient alpha pq,st of a base function corresponding to a light source mutual intensity function on a space domain; 4) establishing a positive definite projection matrix A=[alpha pq,st] by using the projection coefficient alpha pq,st, and performing feature vector decomposition A=UU*; 5) performing variables separation on the light source mutual intensity function, and establishing a kernel function of a cross transmission function on the space domain; and 6) calculating the convolution of the kernel function and a mask plate pattern, and acquiring an exposure pattern on an image plane. By adopting the method, Fourier function conversion pairs on a group of space domains and frequency domains are utilized, complex integral transformation is calculated according to convolution definition, then corresponding kernel functions are rapidly acquired, light intensity distribution can be rapidly and efficiently calculated, and thus actual photolithography process design requirements can be met.
Owner:SUZHOU COGENDA ELECTRONICS CO LTD
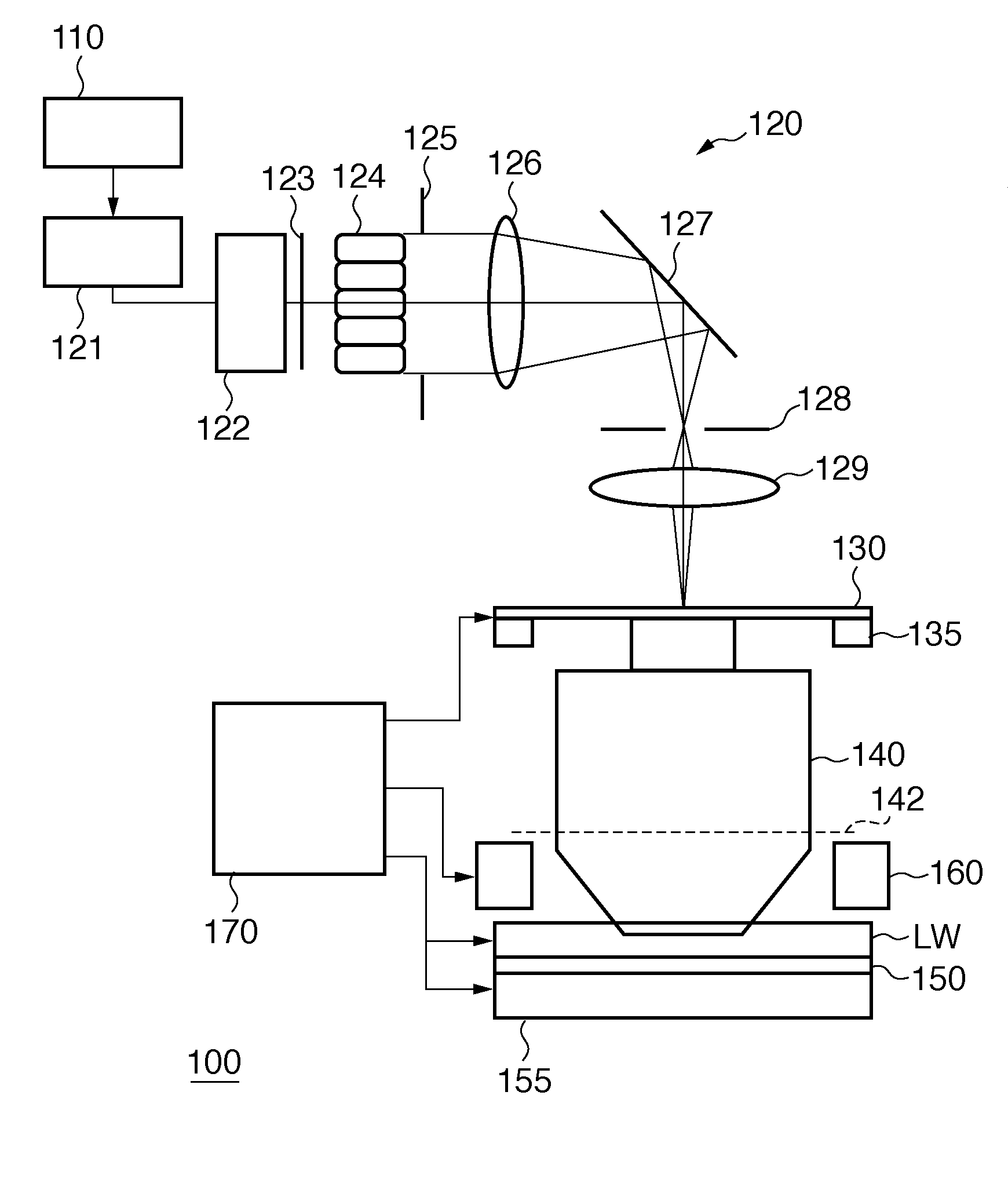
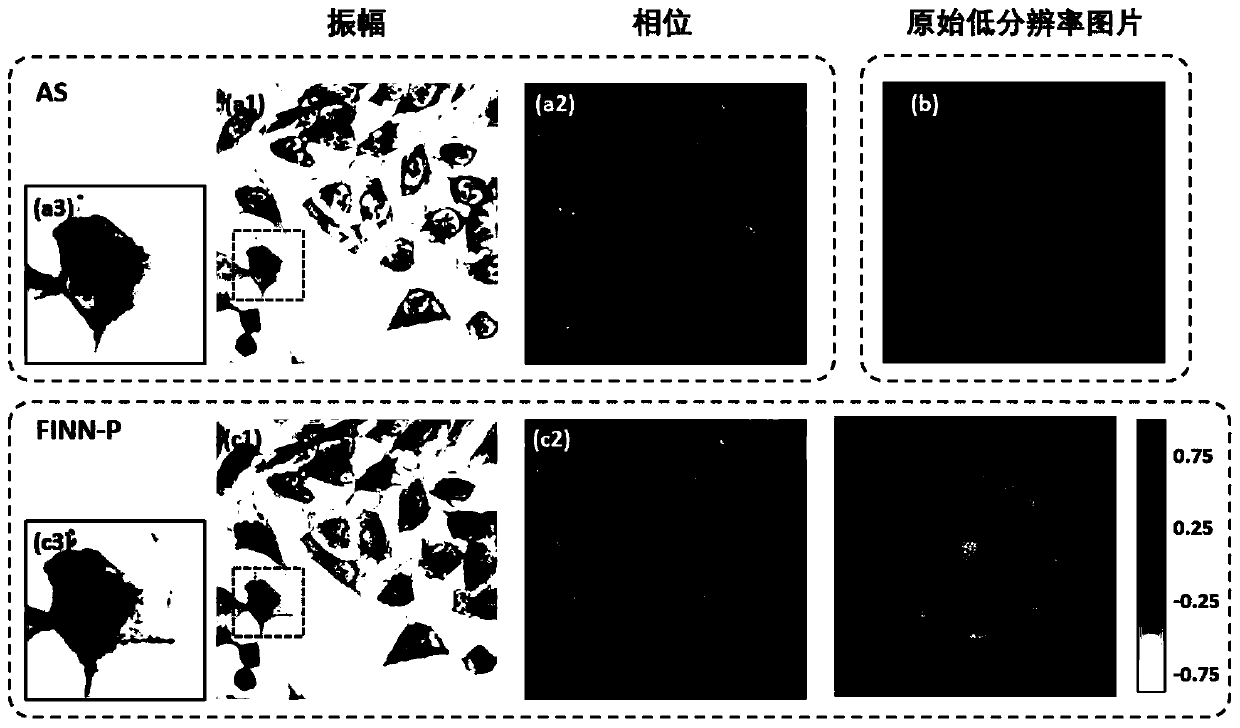
Fourier laminated microscope pupil recovery method based on neural network
The invention discloses a Fourier laminated microscope pupil recovery method based on a neural network in the field of computer imaging. The problem that the reconstruction precision of the existingFourier laminated imaging model is low under the influence of optical phase difference is solved. A neural network model is established based on a TensorFlow deep learning framework in combination with a forward imaging mode of an FPM system. The problem that the universality of a reconstruction model based on a deep convolutional neural network is poor is solved; a recovery process for a pupil function of the system is introduced, so that the influence of optical aberration in the system on a reconstruction result can be better suppressed, and a better result is obtained. According to the invention, the frequency spectrum and the pupil function of the sample are set as a trainable two-dimensional network layer in the network; complex amplitude information and a pupil function of a sampleare obtained at the same time by minimizing a loss function in the training process. The method has good universality and can still obtain a reconstruction result better than that of a traditional algorithm under the condition that aberration exists in the system.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
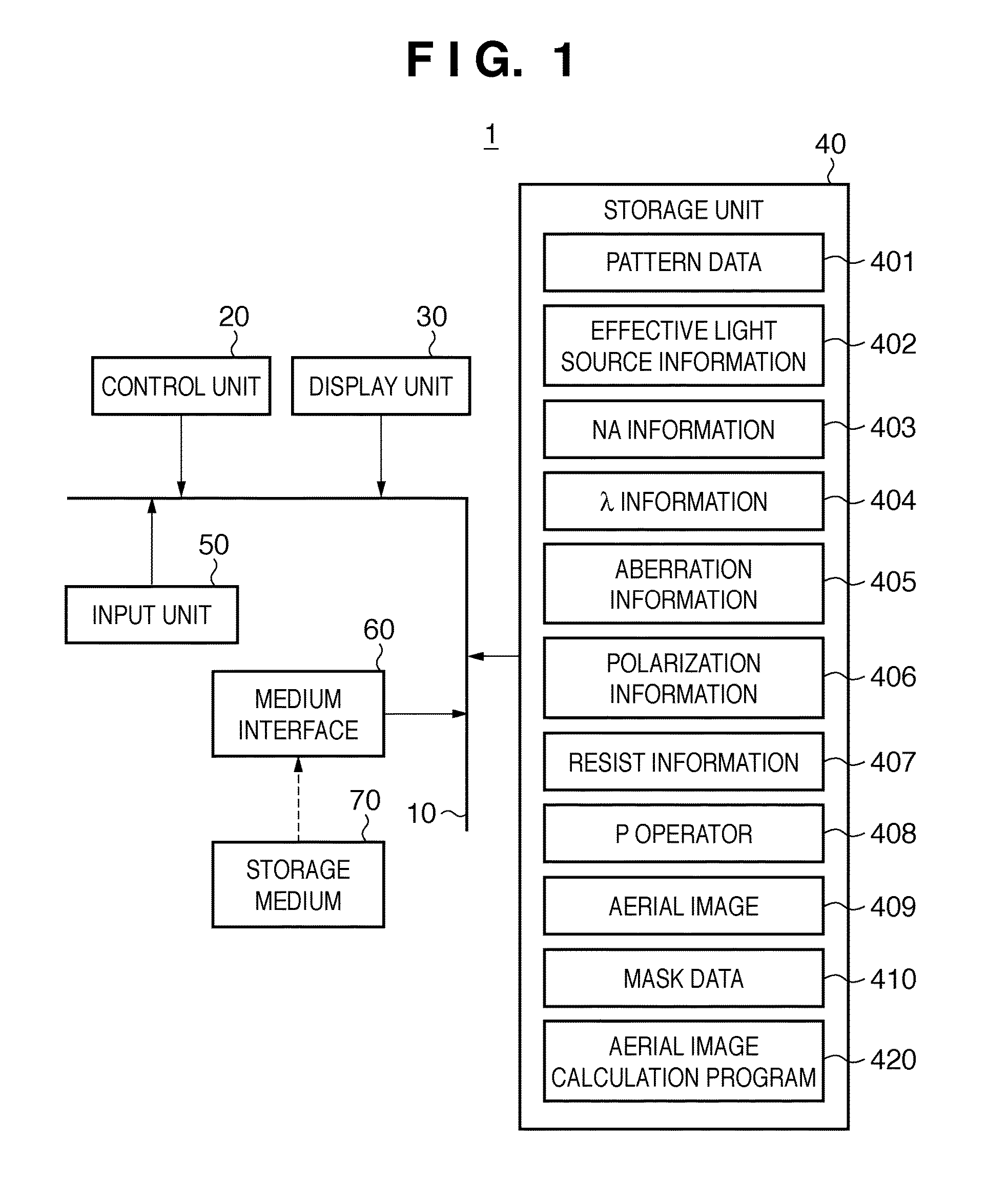
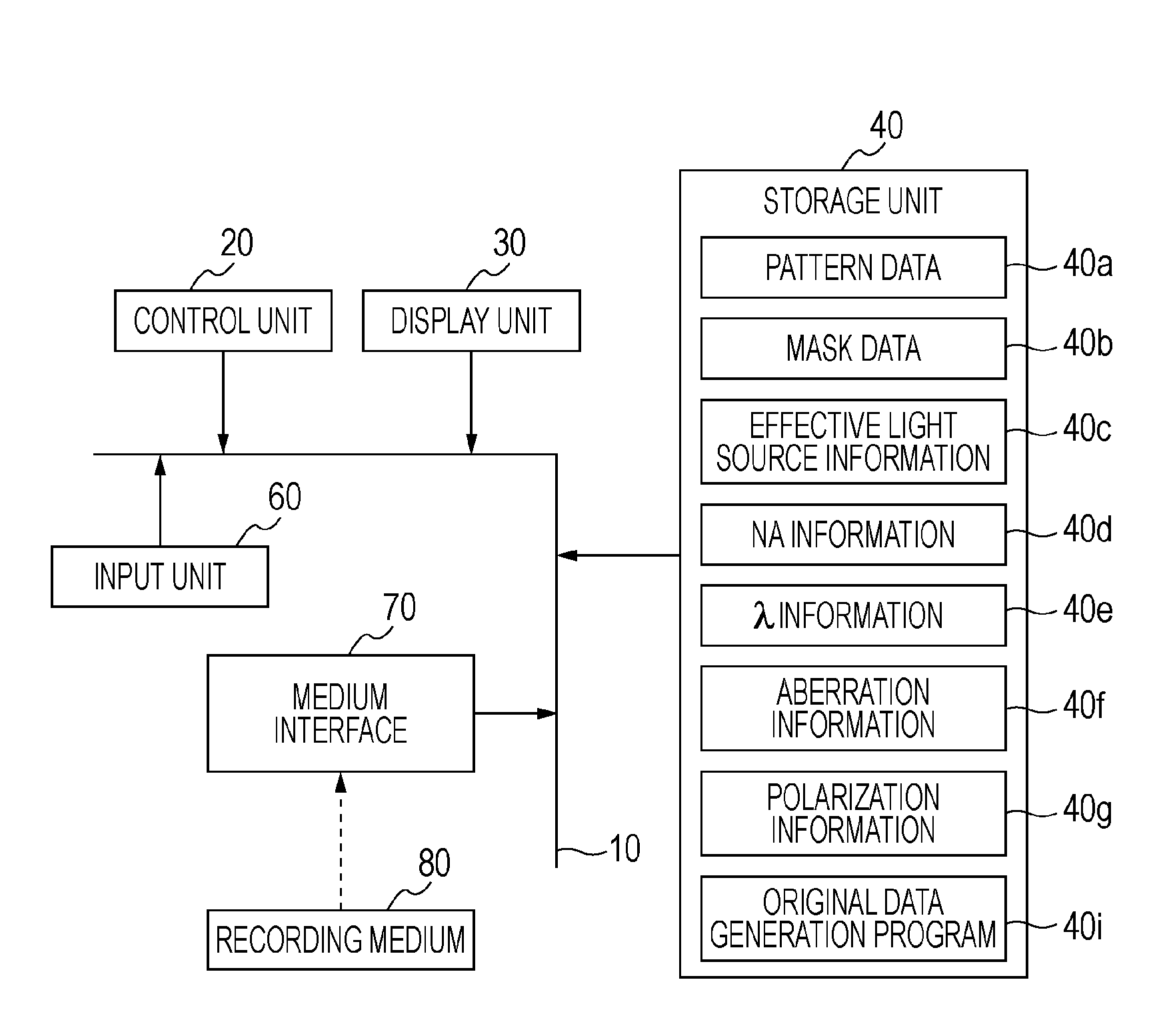
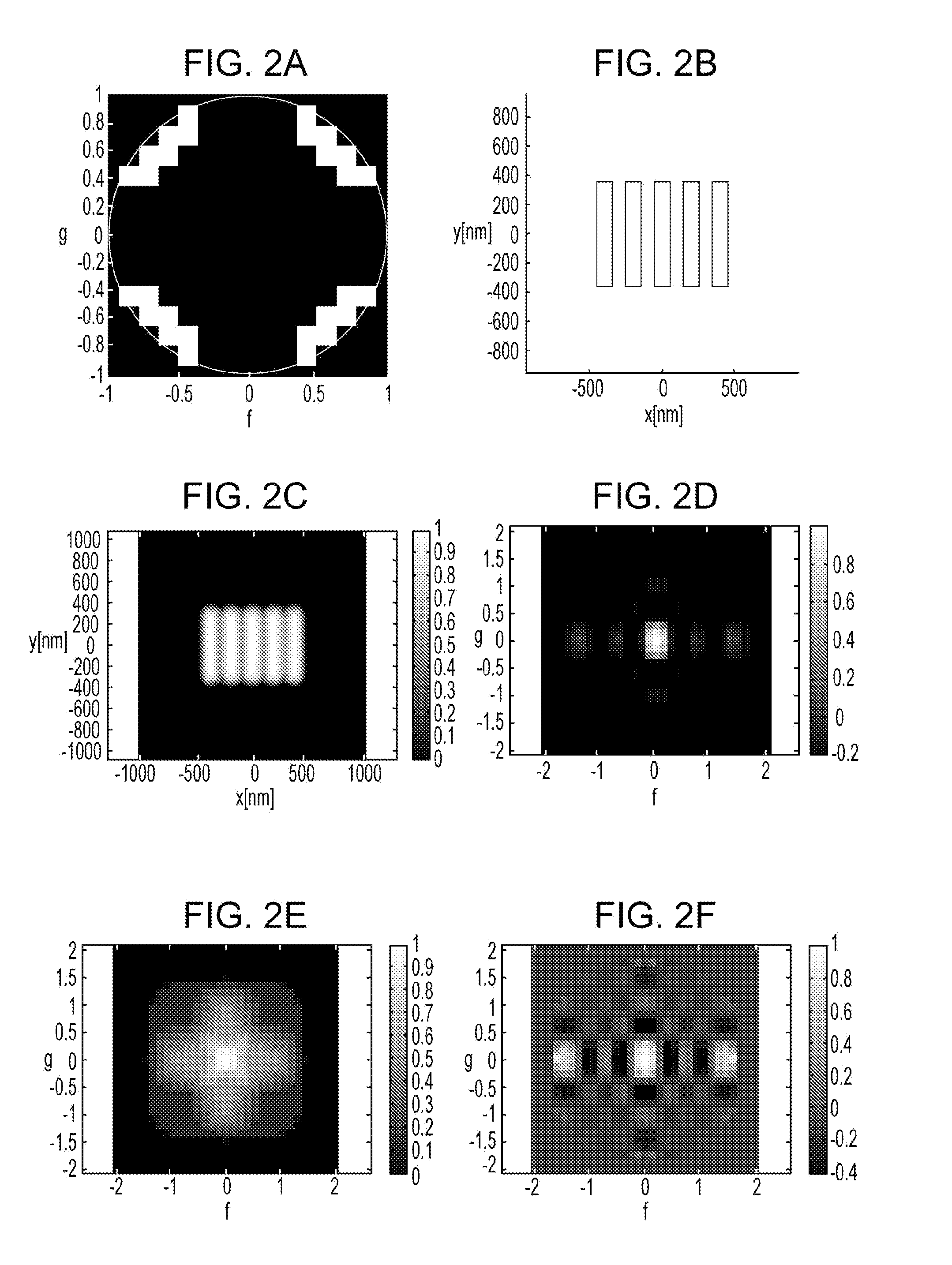
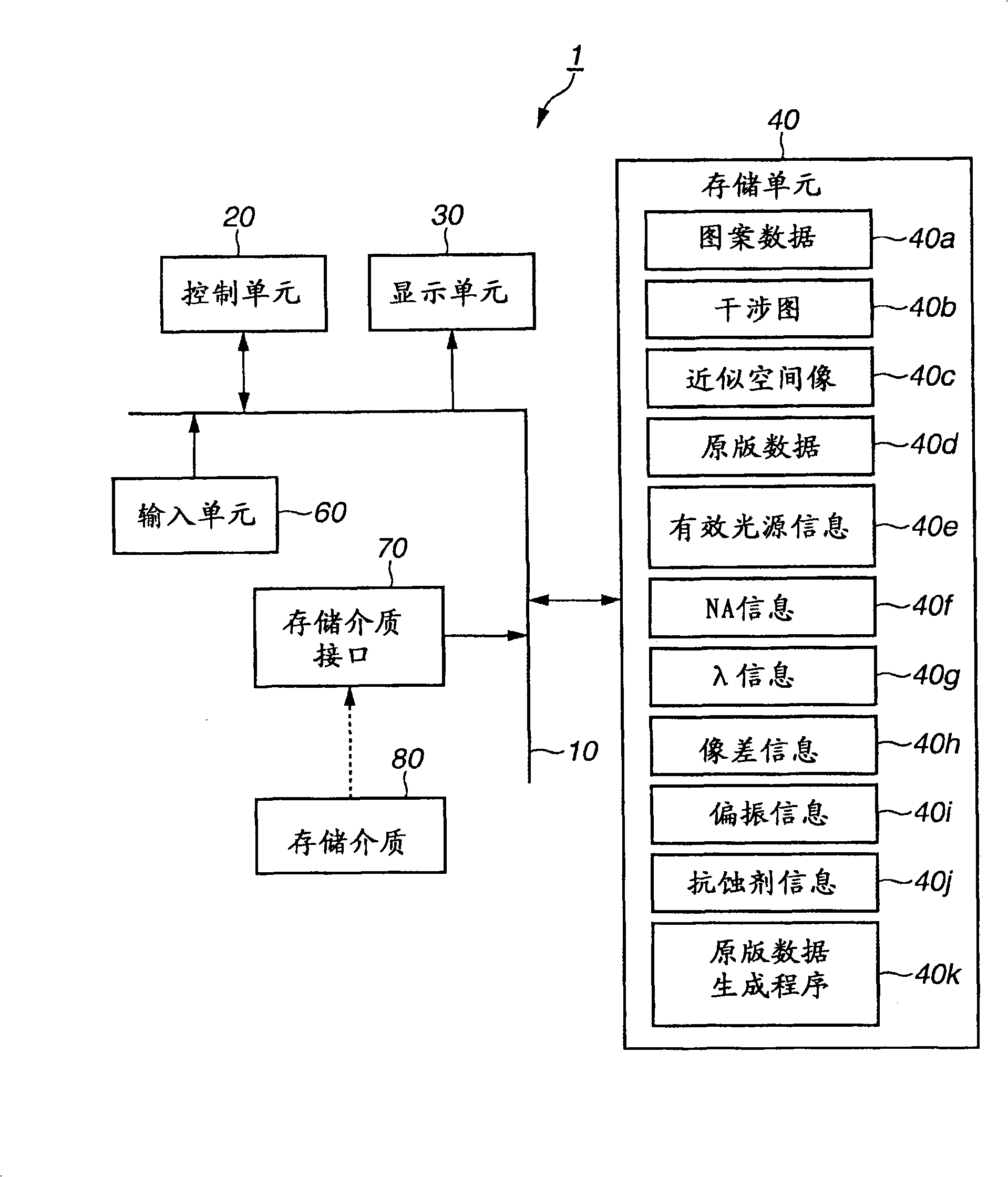
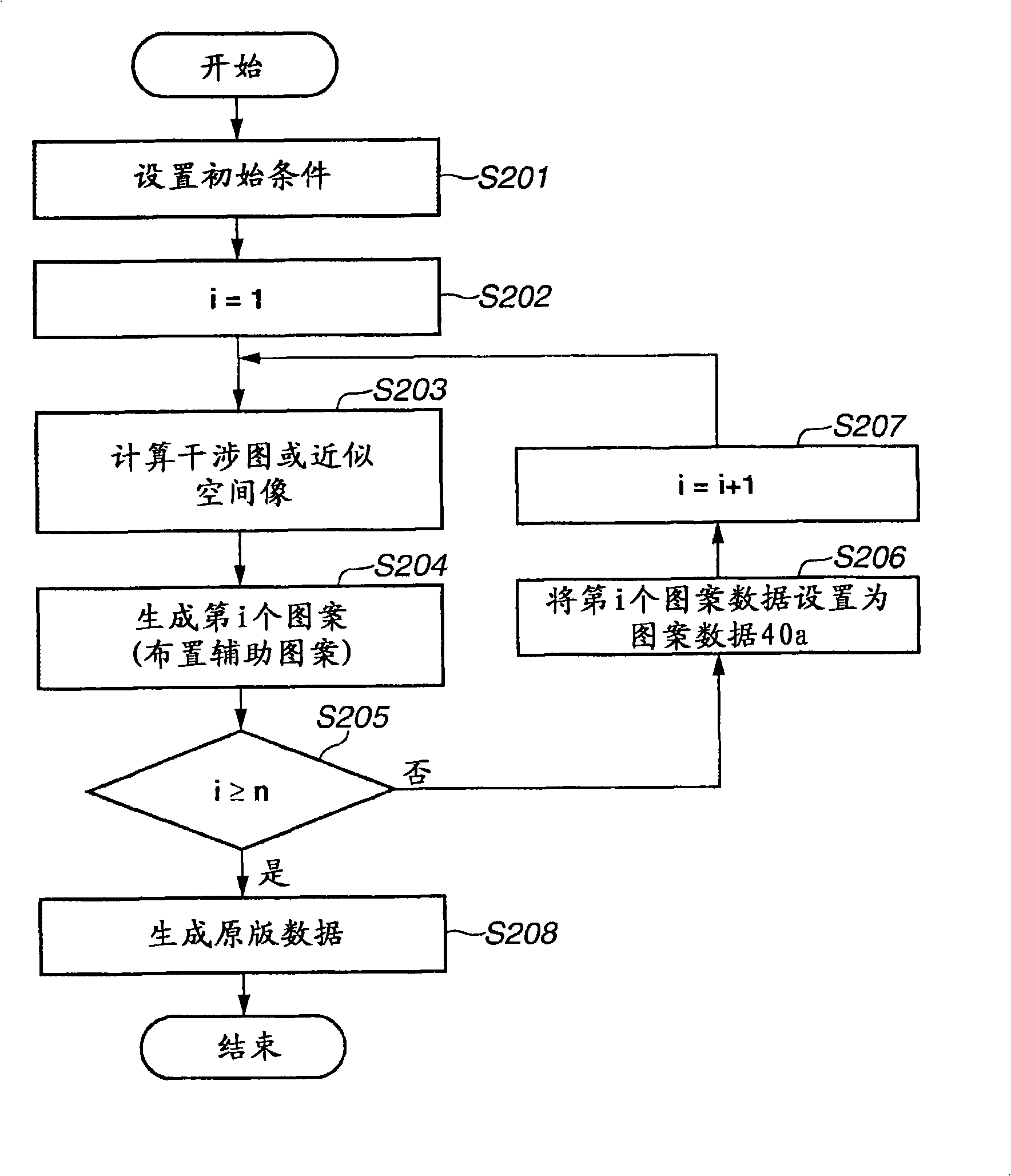
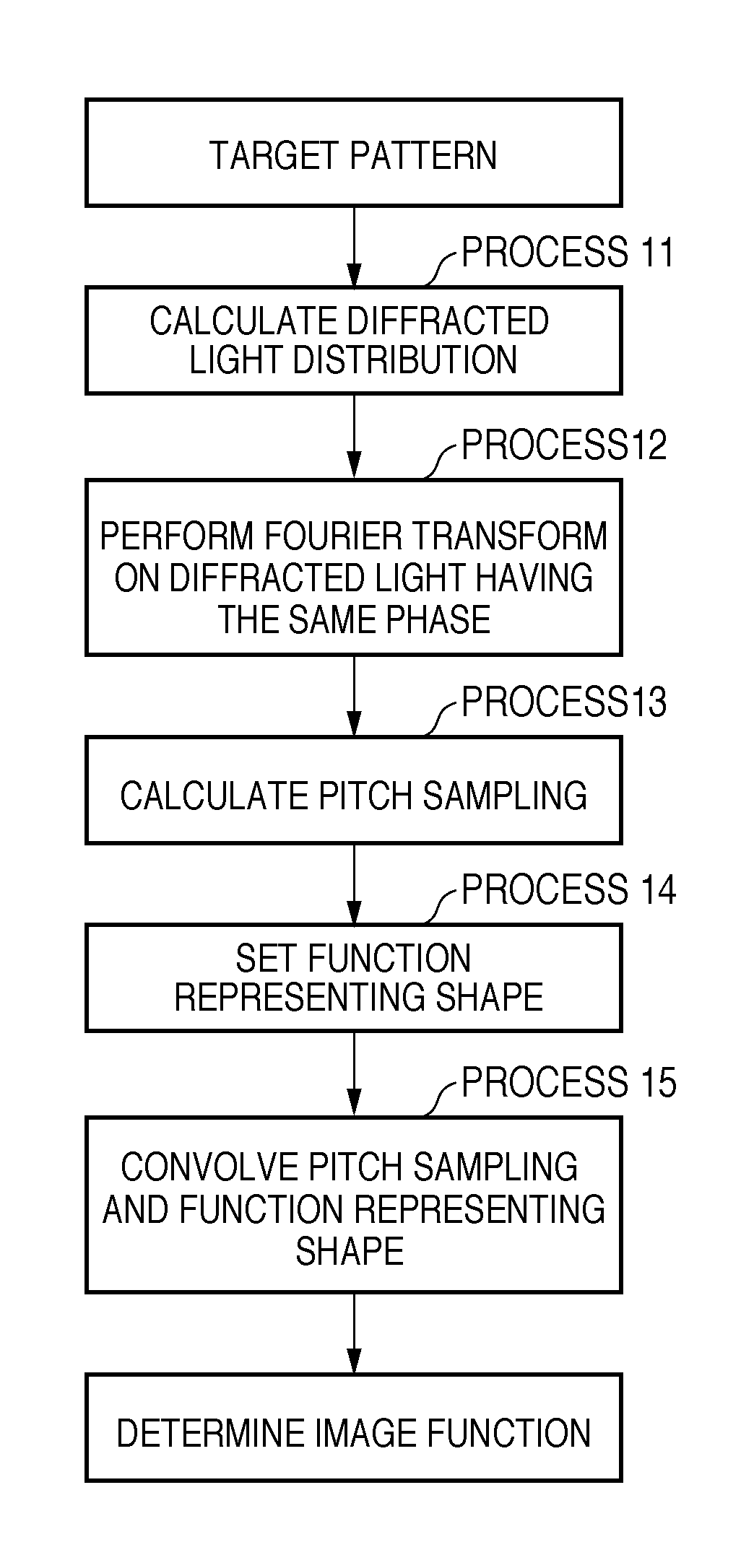
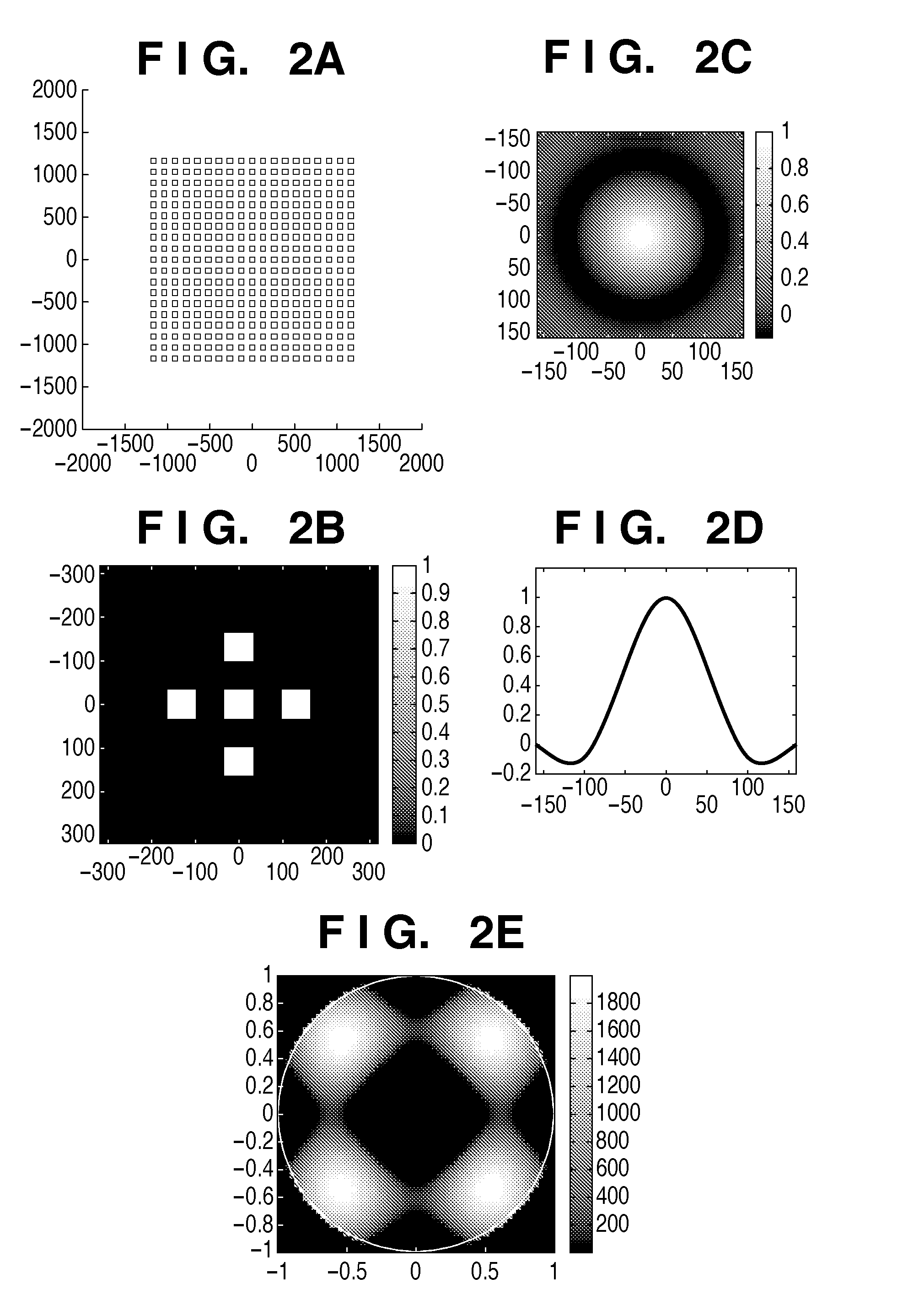
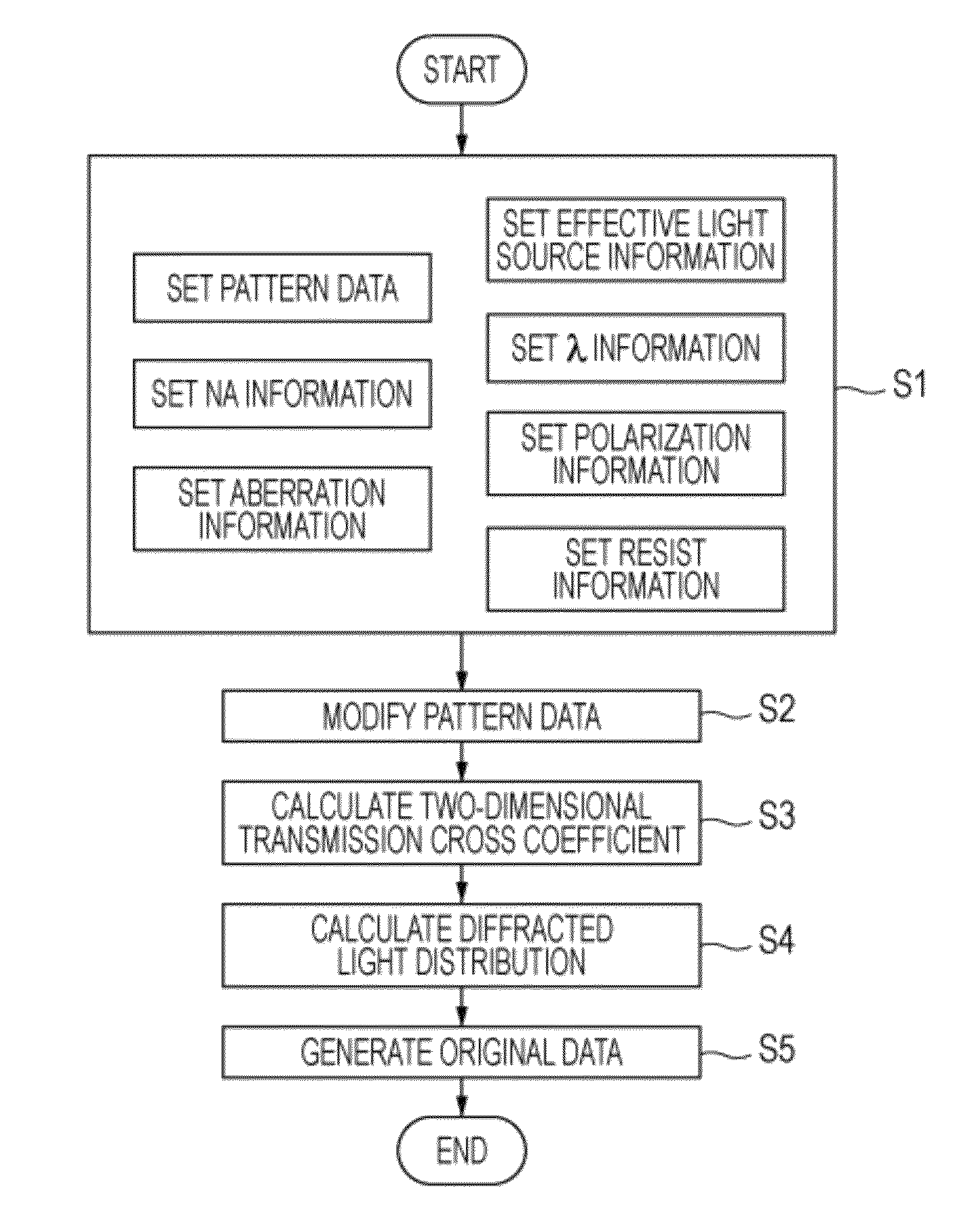
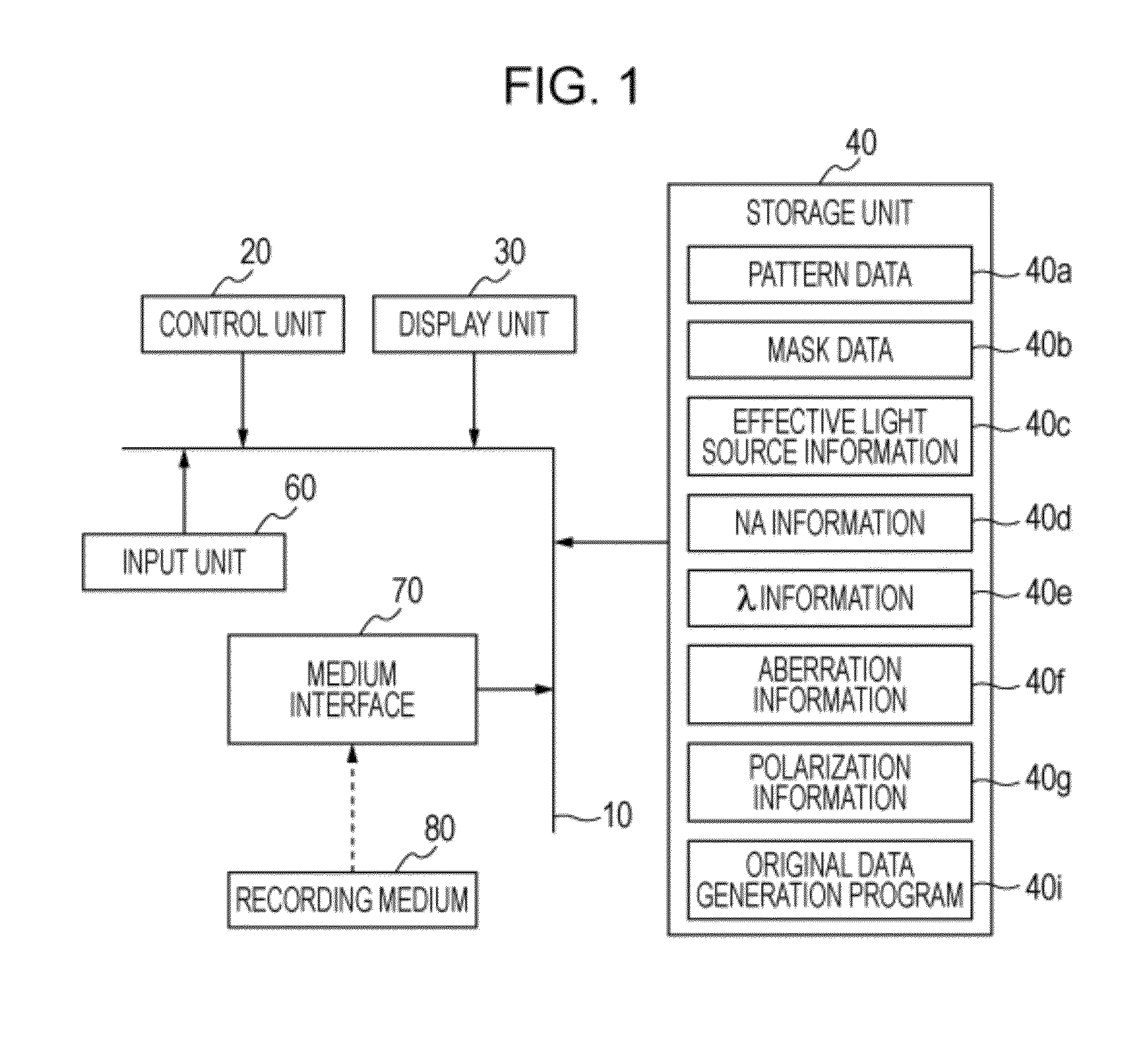
Recording medium storing original data generation program, original data generation method, original fabricating method, exposure method, and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20100037199A1Forming accuratelySmall amount of calculationPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPupil functionOriginal data
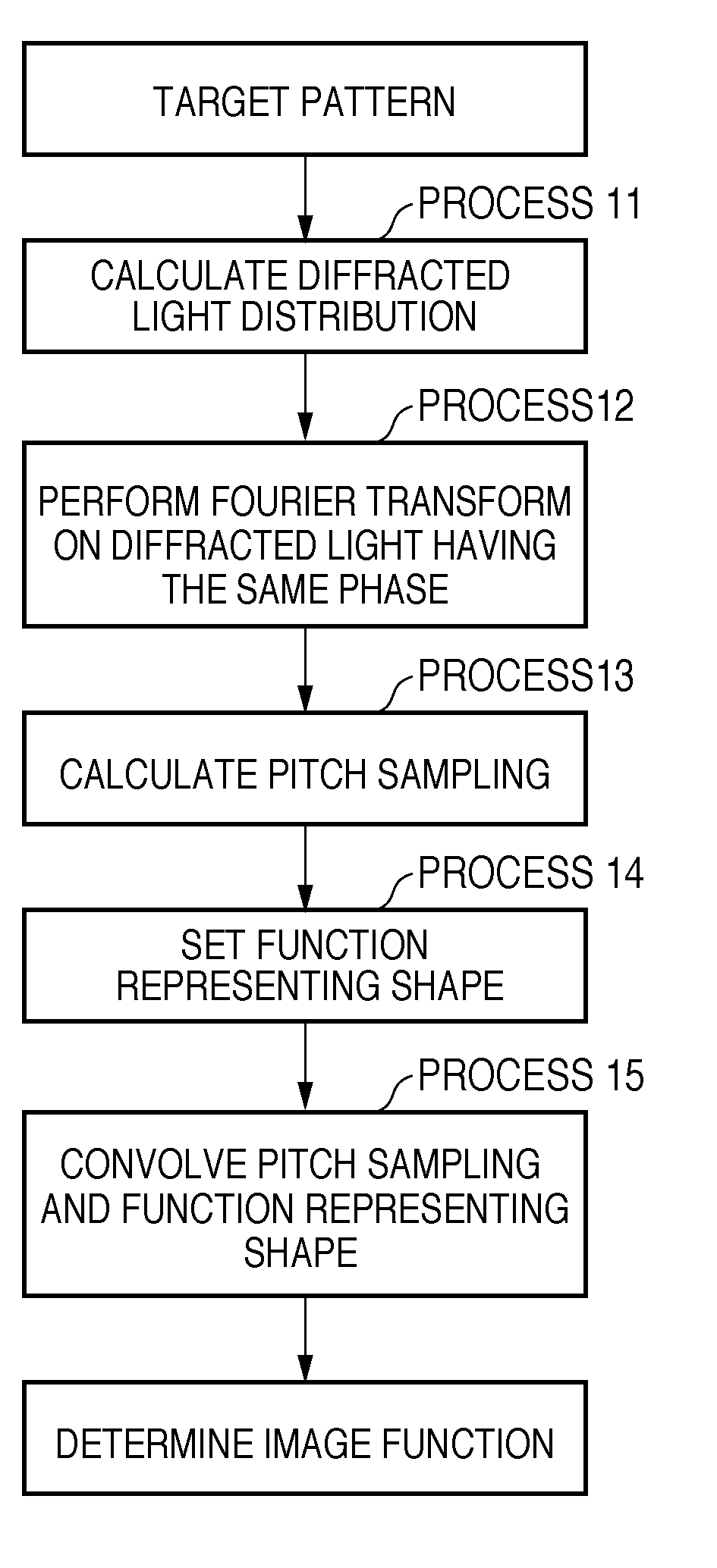
To calculate data of an original, a computer is caused to execute the following steps of converting data regarding an intended pattern to be formed on a substrate into frequency-domain data, calculating a two-dimensional transmission cross coefficient using a function representing an effective light source that an illumination device forms on a pupil plane of a projection optical system when the original is absent on an object plane of the projection optical system and using a pupil function of the projection optical system, calculating a diffracted light distribution from a pattern that is formed on the object plane using both the frequency-domain data and data of at least one component of the calculated two-dimensional transmission cross coefficient, and converting data of the calculated diffracted light distribution into spatial-domain data to determine the data of the original.
Owner:CANON KK
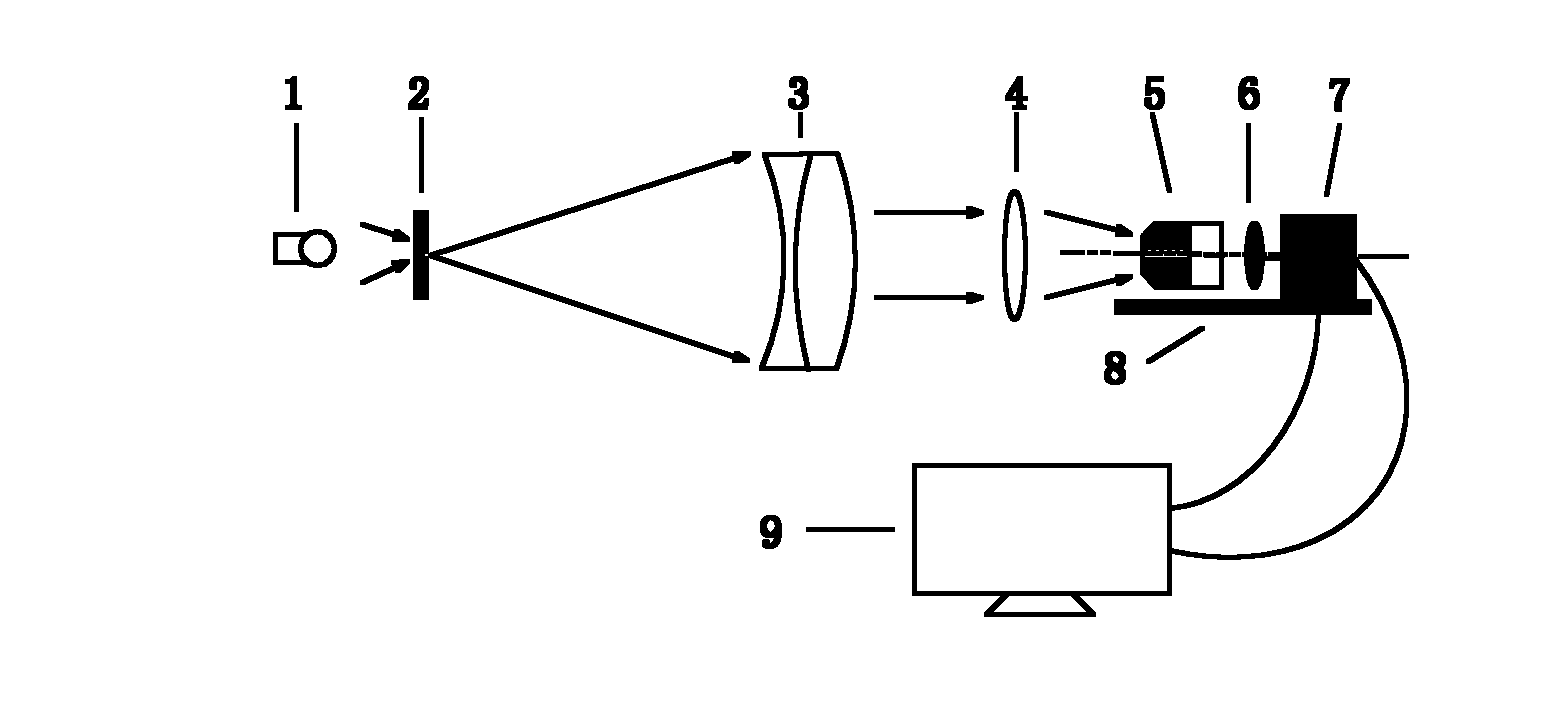
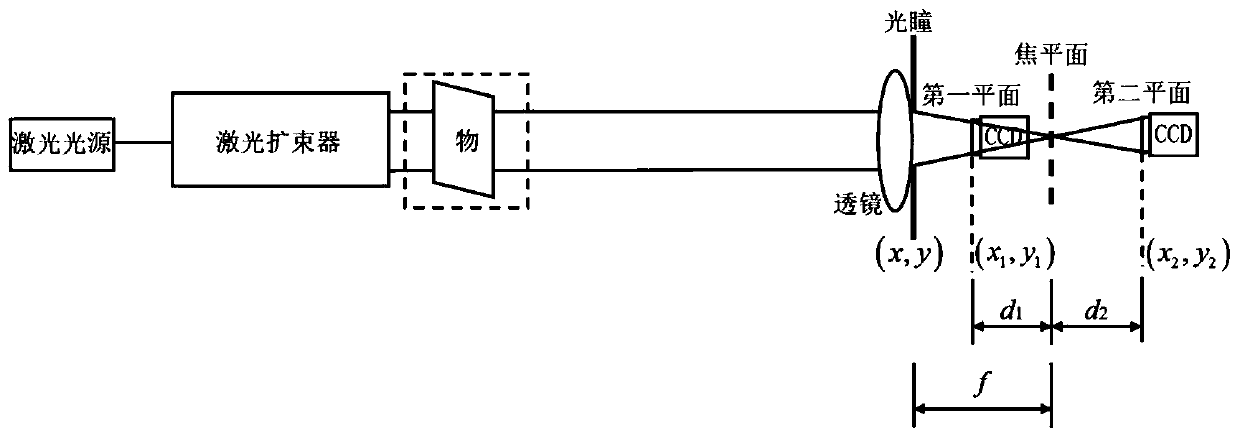
Single-lens calculation imaging method based on phase recovery
The invention discloses a single-lens calculation imaging method based on phase recovery. The method comprises the following steps: illuminating a lens by using parallel light without adding an imaging object, acquiring two diffraction patterns before or after focusing of the lens, and solving a pupil function of a system by using a phase recovery algorithm; solving an actual transfer function ofthe system according to the pupil function, and calculating an ideal transfer function of the system by using system focal length information; solving an aberration correction filter of the system byusing the actual transfer function and the ideal transfer function; carrying out approximate infinity imaging on an object in a system, collecting two images, and solving the complex amplitude of theclearest image by using a phase recovery algorithm, wherein one image is the clearest image which can be collected; and finally, performing aberration correction on the imaged image by using the solved aberration correction filter. The aberration of the imaging system is corrected by introducing the phase recovery algorithm, the problems that the imaging system is simple in structure and low in imaging quality when the aberration is large can be solved, and extra hardware equipment does not need to be added into the system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Apparatuses and methods using measurement of a flare generated in an optical system
InactiveUS20100002243A1Wide rangePhotomechanical apparatusUsing optical meansPupil functionTransmittance
The present invention provides a method including measuring a wavefront aberration of the optical system to be measured on a measurement surface, measuring a pupil transmittance distribution of the optical system determining a pupil function of the optical system based on the wavefront aberration and the pupil transmittance distribution, and performing imaging computation using the pupil function to obtain a light intensity distribution formed on an image plane of the optical system, and calculating a flare, generated in the optical system, from the light intensity distribution.
Owner:CANON KK
Mask pattern generation method and optical image calculation method
ActiveUS20150131066A1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusPupil functionPattern generation
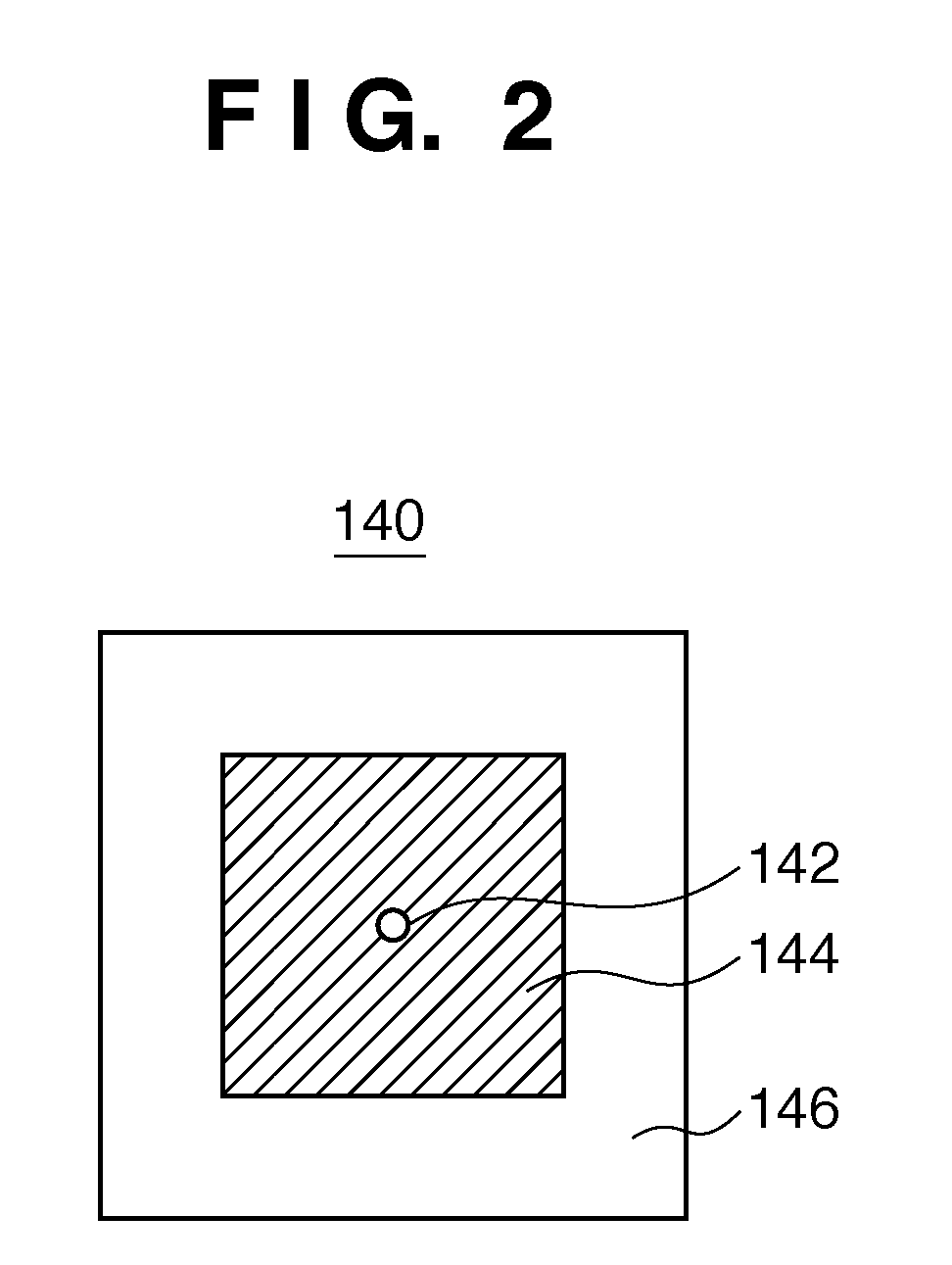
In a method for generating, with a computer, a pattern of a mask, a pattern on an object plane of a projection optical system is set, shifted plural pupil functions are generated, a matrix containing the generated plural pupil functions is defined, an image of the pattern on the object plane is calculated by generating a vector obtained by transposing and complex-conjugating a vector containing, as components, values of the pupil functions at origin coordinates on a pupil plane from among components of the matrix, and performing convolution integral between the pattern on the object plane and a Fourier transform of a product of the vector and the matrix, an assist pattern for the pattern on the object plane is generated using the calculated image, and a pattern of the mask including the pattern on the object plane and the assist pattern is generated.
Owner:CANON KK
Coaxial interference surface plasma microscopical method and coaxial interference surface plasma microscopical system based on pupil modulation
InactiveCN106872413ASimple structureLow costMaterial analysis by optical meansMicro nanoPupil function
The invention discloses a coaxial interference surface plasma microscopical method and a coaxial interference surface plasma microscopical system based on pupil modulation. The coaxial interference surface plasma microscopical system comprises a linear polarization illumination coherent light source, a beam expanding projecting apparatus, a spatial light modulator, a sample clamping and micro-nano mobile platform, a high numerical-aperture microobjective, an imaging lens group and an imaging optical path consisting of a confocal diaphragm and an image sensor which are sequentially arranged along an optical path. In an out-of-focus process of a sample, a confocal interference signal V(z) curve is detected on the image sensor conjugated with a focus plane of the microobjective; as a clear aperture of the system is limited, a caused edge interference effect and background noise have influence on a cycle of the V(z) curve. According to the coaxial interference surface plasma microscopical method and the coaxial interference surface plasma microscopical system disclosed by the invention, the influence on the cycle of the V(z) curve is eliminated by adopting a rear focus plane pupil function modulation mode. The system has the advantages of simplicity, low cost, high signal-noise ratio, capability of realizing high-resolution imaging and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Photomask data generation method, photomask generation method, exposure method, and device manufacturing method
ActiveCN101354529ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPupil functionOptic system
The present invention relates to a photomask data generation method, photomask generation method, exposure method, and device manufacturing method. A method for generating original plate data includes calculating a two-dimensional transmission cross coefficient based on a function indicating an intensity distribution of light formed on a pupil plane of a projection optical system with illumination light and a pupil function for the projection optical system, calculating an approximate aerial image obtained by approximating an aerial image on an image plane of the projection optical system by at least one component of a plurality of components of the aerial image based on the two-dimensional transmission cross coefficient and a first pattern on an object plane of the projection optical system, generating a further pattern having the first pattern on the object plane and auxiliary patterns based on the approximate aerial image, and generating original plate data including a pattern generated by repeating the calculating and generating processing by using the further pattern as the first pattern on the object plane.
Owner:CANON KK
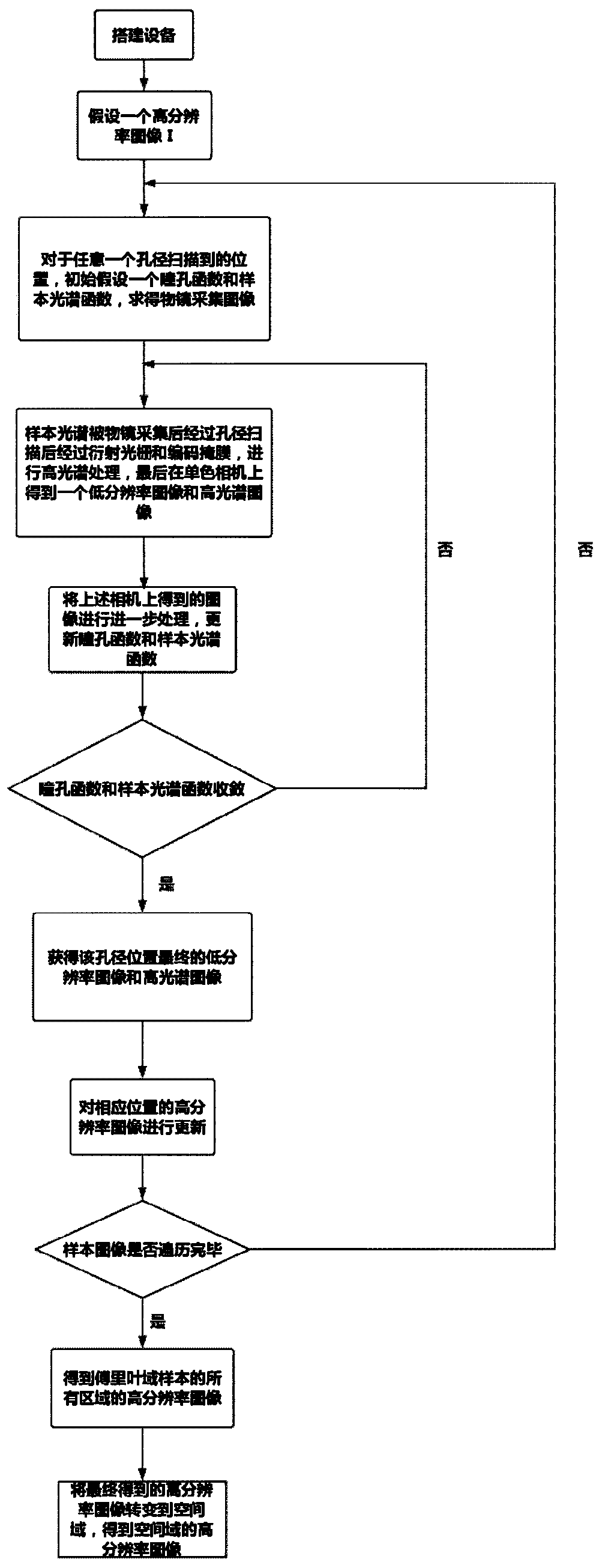
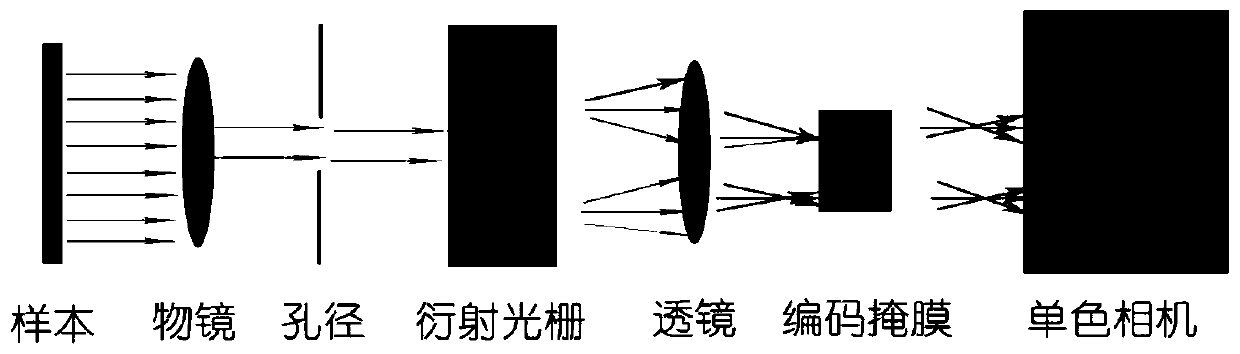
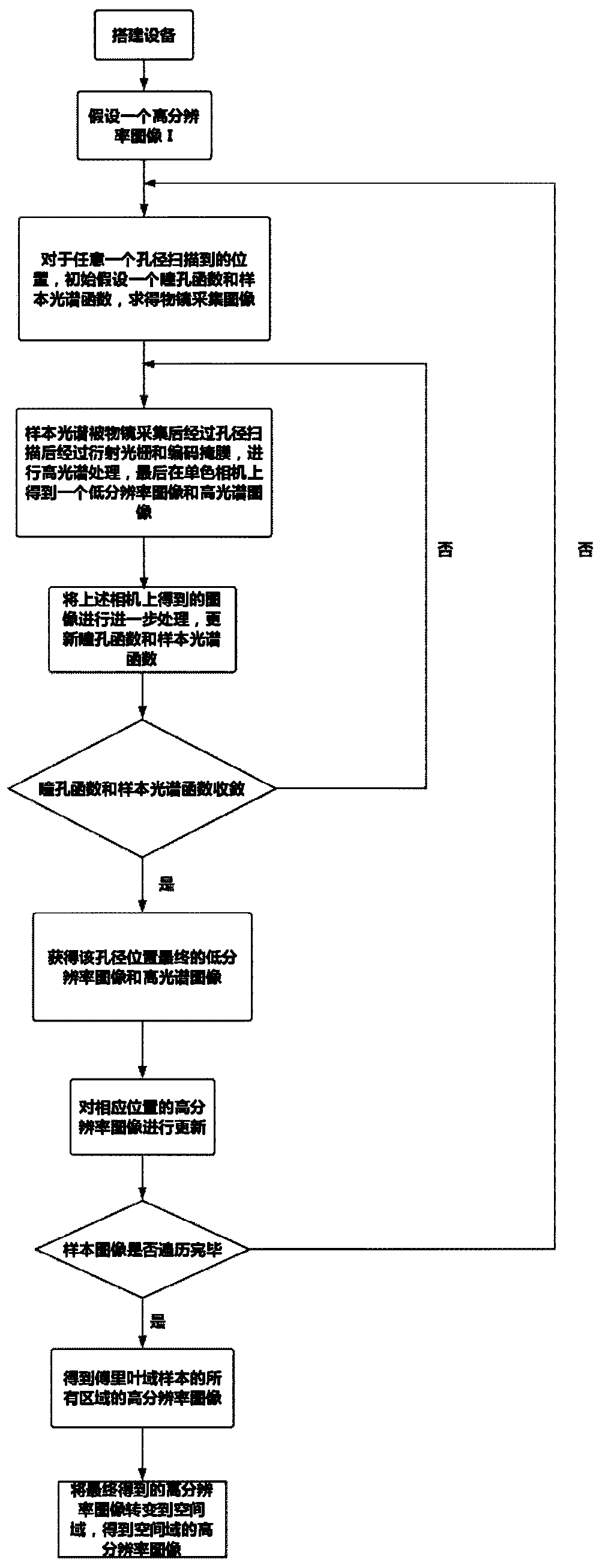
Multispectral laminated imaging method based on aperture scanning
ActiveCN111121969ARealize macroscopic imagingImprove image qualitySpectrum investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsPupil functionHigh resolution image
The invention relates to a multispectral laminated imaging method based on aperture scanning. An LED matrix is replaced by aperture scanning, single-beam light irradiation is adopted, light waves emitted from a sample pass through an aperture, low-resolution images from different positions of the sample are obtained through aperture cyclic scanning and hyperspectral processing, processing is carried out in a Fourier domain, and finally a high-resolution image of the sample is obtained. On the premise of realizing laminated imaging, the defects of an LED matrix are overcome. And the pupil function and the sample spectrum are iteratively updated, and the pupil function is converged, so that the resolution of the obtained imaging picture is higher. Hyperspectral imaging is introduced, and thenature of the sample is further understood through hyperspectral imaging, so that a clearer image is constructed, the sample can be analyzed more thoroughly, and conditions are provided for analyzingthe sample.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Pupil function synthetic aperture imaging method
InactiveCN102486578AReduce difficultyReduce the difficulty of adjustmentOptical elementsSynthetic aperture imagingPupil function
The invention relates to a pupil function synthetic aperture imaging method, which comprises the following steps of: 1) acquiring complex amplitude distribution of an image surface; and 2) acquiring a synthetic aperture image according to the complex amplitude distribution of the image surface. According to the pupil function synthetic aperture imaging method, the adjustment difficulty is reduced, and imaging flexibility is realized.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Computer readable storage medium including effective light source calculation program, and exposure method
InactiveUS8502962B2Reduce a decrease in image formation performancePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusPupil functionImage fusion
A storage medium includes a program which causes a computer to execute a method of calculating a light intensity distribution on a pupil plane of an illumination optical system. The method includes: determining an impulse response function of a projection optical system by performing Fourier transform on a pupil function of the projection optical system; setting a length to a second zero point of the impulse response function as a response length, extracting, from elements forming a target pattern, only elements inside am area within radius which is response length, and determining a function indicating the extracted pattern as an image function; and obtaining the light intensity distribution based on the pupil function, the determined impulse response function, and the determined image function.
Owner:CANON KK
Recording medium storing original data generation program, original data generation method, original fabricating method, exposure method, and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS8321815B2Small amount of calculationForming accuratelyPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPupil functionOriginal data
To calculate data of an original, a computer is caused to execute the following steps of converting data regarding an intended pattern to be formed on a substrate into frequency-domain data, calculating a two-dimensional transmission cross coefficient using a function representing an effective light source that an illumination device forms on a pupil plane of a projection optical system when the original is absent on an object plane of the projection optical system and using a pupil function of the projection optical system, calculating a diffracted light distribution from a pattern that is formed on the object plane using both the frequency-domain data and data of at least one component of the calculated two-dimensional transmission cross coefficient, and converting data of the calculated diffracted light distribution into spatial-domain data to determine the data of the original.
Owner:CANON KK
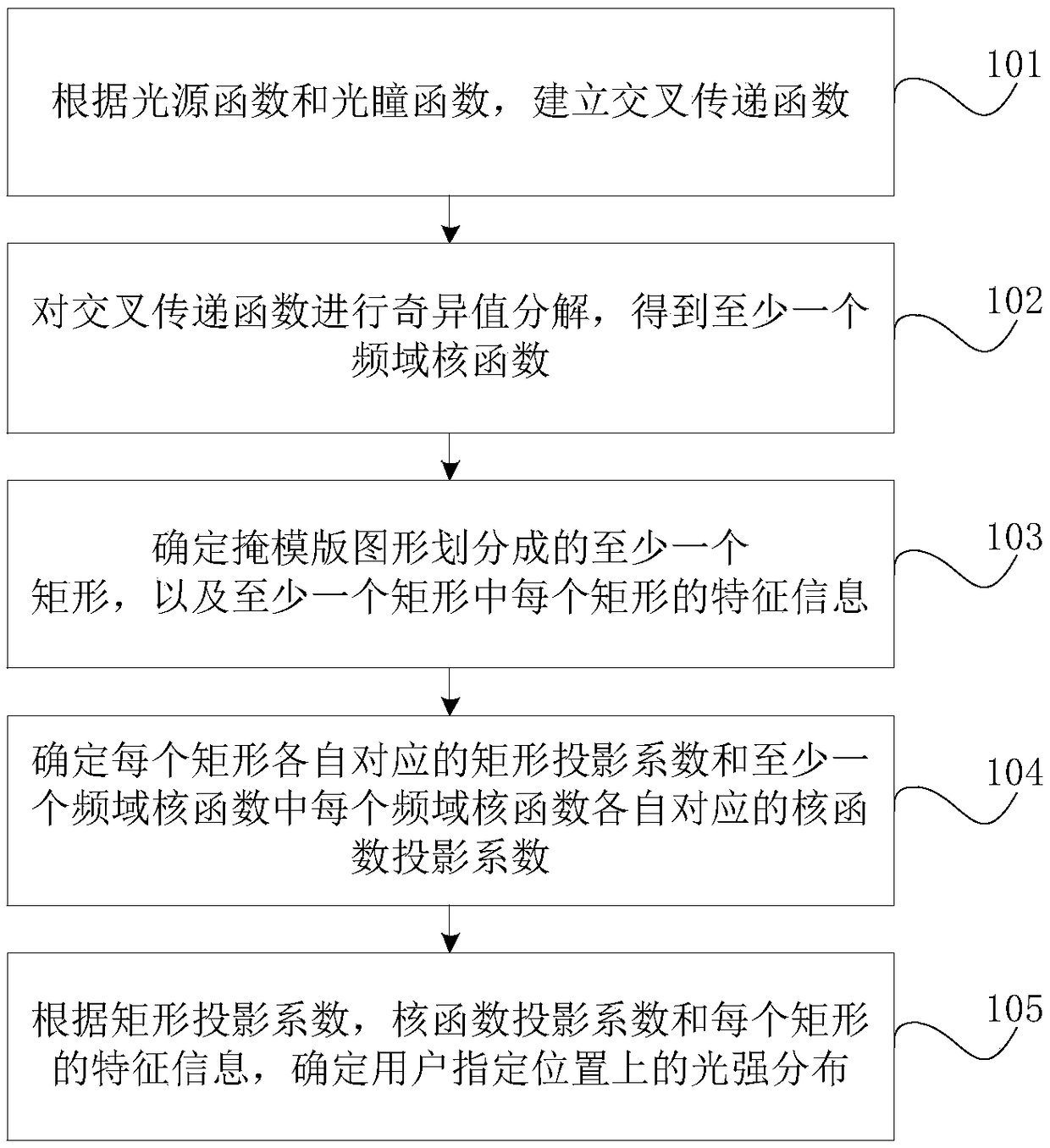
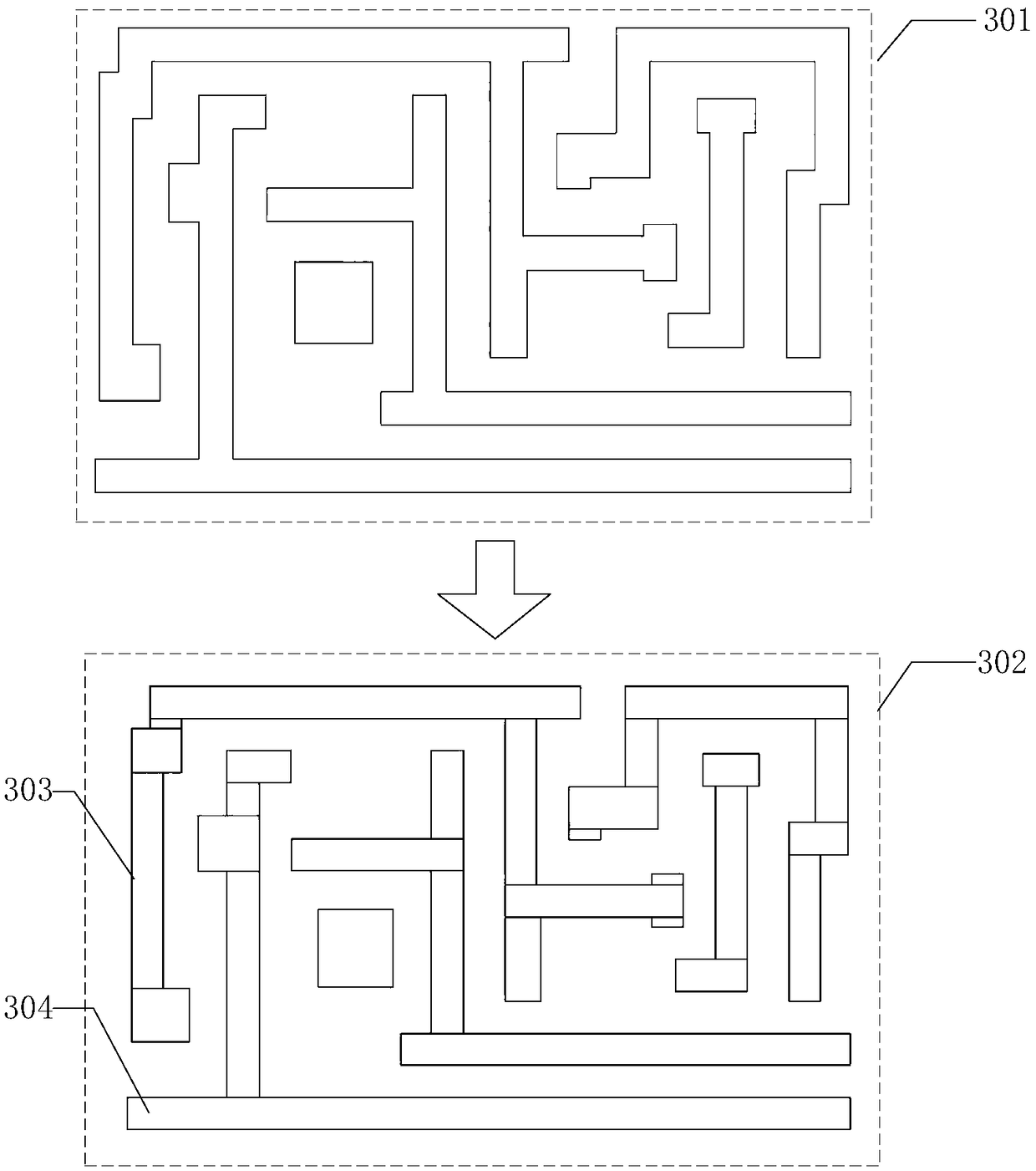
Method and device for quickly determining light intensity distribution based on mask graphics processing
ActiveCN109164683AQuick fixAvoid double countingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCAD circuit designSingular value decompositionGraphics
The present application discloses a light intensity distribution fast determination method and device based on mask graphics processing. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a cross transfer function according to a light source function and a pupil function; Performing singular value decomposition on the cross transfer function to obtain at least one frequency domain kernel function; Determining at least one rectangle into which the mask pattern is divided, and characteristic information of each rectangle in the at least one rectangle; Determining a rectangular projectioncoefficient corresponding to each rectangle and a kernel function projection coefficient corresponding to each kernel function in at least one frequency domain; According to the rectangular projectioncoefficients, the kernel projection coefficients and the characteristic information of each rectangle, the light intensity distribution at the specified position of the user is determined. In the present application, the light intensity distribution is quickly determined by the kernel function projection coefficient and the rectangular projection coefficient. Due to the existence of repetitive rectangles in the rectangles divided by the mask pattern, repetitive calculation can be avoided when calculating the rectangular projection coefficients, the calculation time can be reduced, and the lithographic efficiency can be improved.
Owner:MOYAN COMPUTATIONAL SCI NANJING PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com