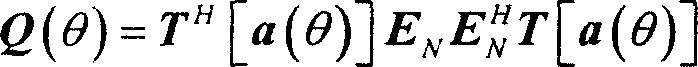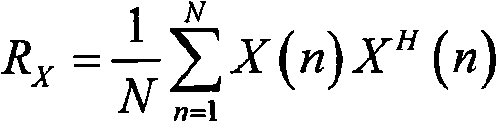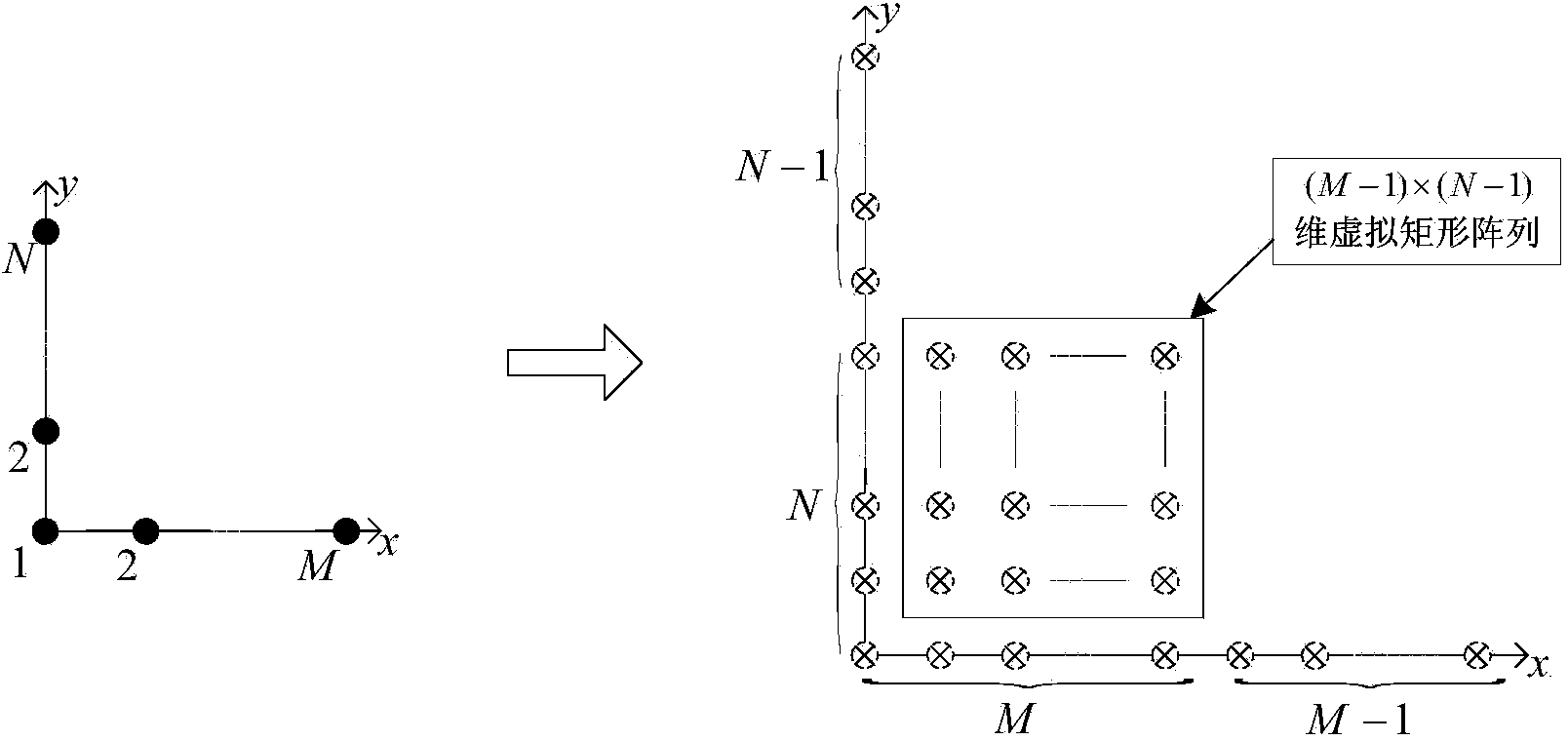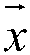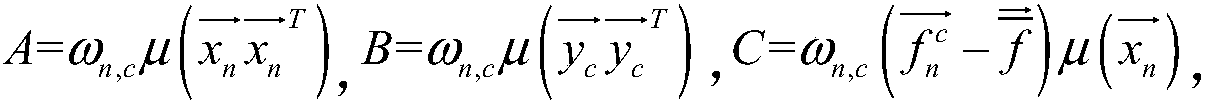Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
376 results about "Eigendecomposition of a matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
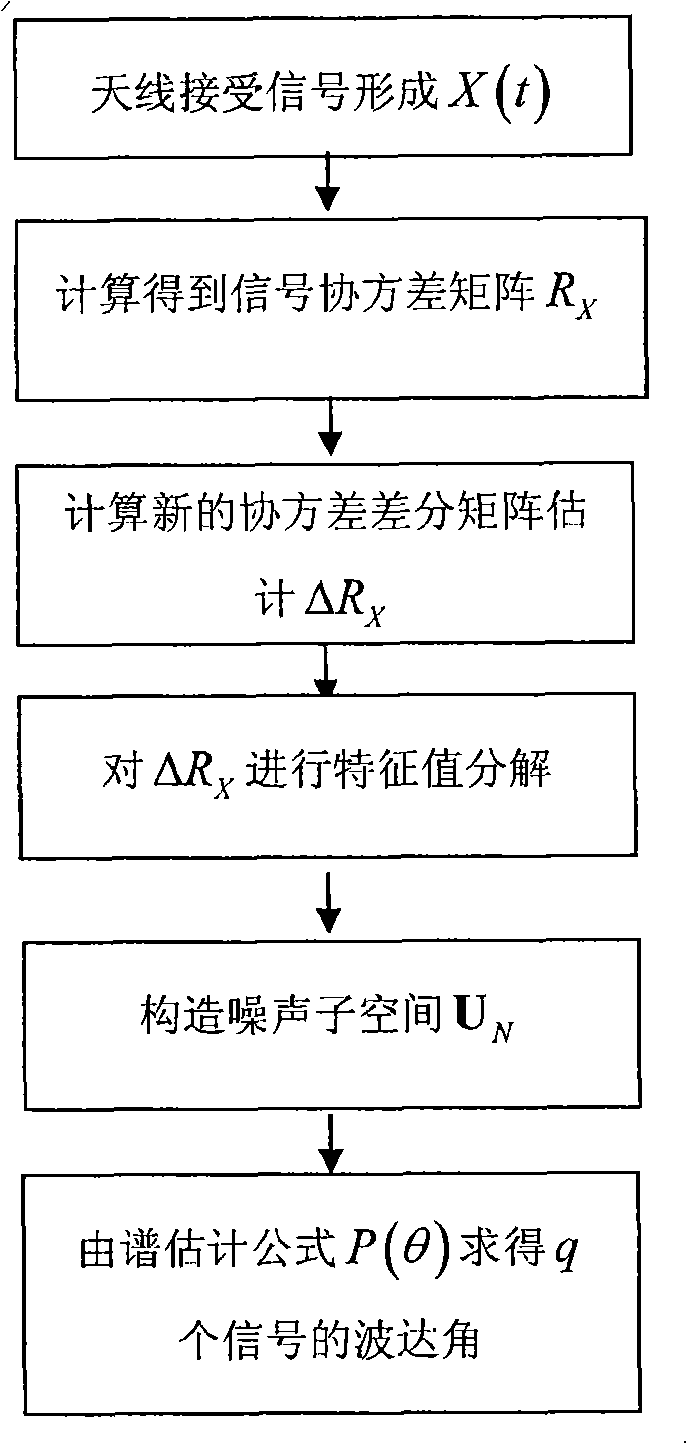
In linear algebra, eigendecomposition or sometimes spectral decomposition is the factorization of a matrix into a canonical form, whereby the matrix is represented in terms of its eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Only diagonalizable matrices can be factorized in this way.
Partially supervised machine learning of data classification based on local-neighborhood Laplacian Eigenmaps
InactiveUS20060235812A1FastEasily extended into SSII algorithmDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setDecomposition
A local-neighborhood Laplacian Eigenmap (LNLE) algorithm is provided for methods and systems for semi-supervised learning on manifolds of data points in a high-dimensional space. In one embodiment, an LNLE based method includes building an adjacency graph over a dataset of labelled and unlabelled points. The adjacency graph is then used for finding a set of local neighbors with respect to an unlabelled data point to be classified. An eigen decomposition of the local subgraph provides a smooth function over the subgraph. The smooth function can be evaluated and based on the function evaluation the unclassified data point can be labelled. In one embodiment, a transductive inference (TI) algorithmic approach is provided. In another embodiment, a semi-supervised inductive inference (SSII) algorithmic approach is provided for classification of subsequent data points. A confidence determination can be provided based on a number of labeled data points within the local neighborhood. Experimental results comparing LNLE and simple LE approaches are presented.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
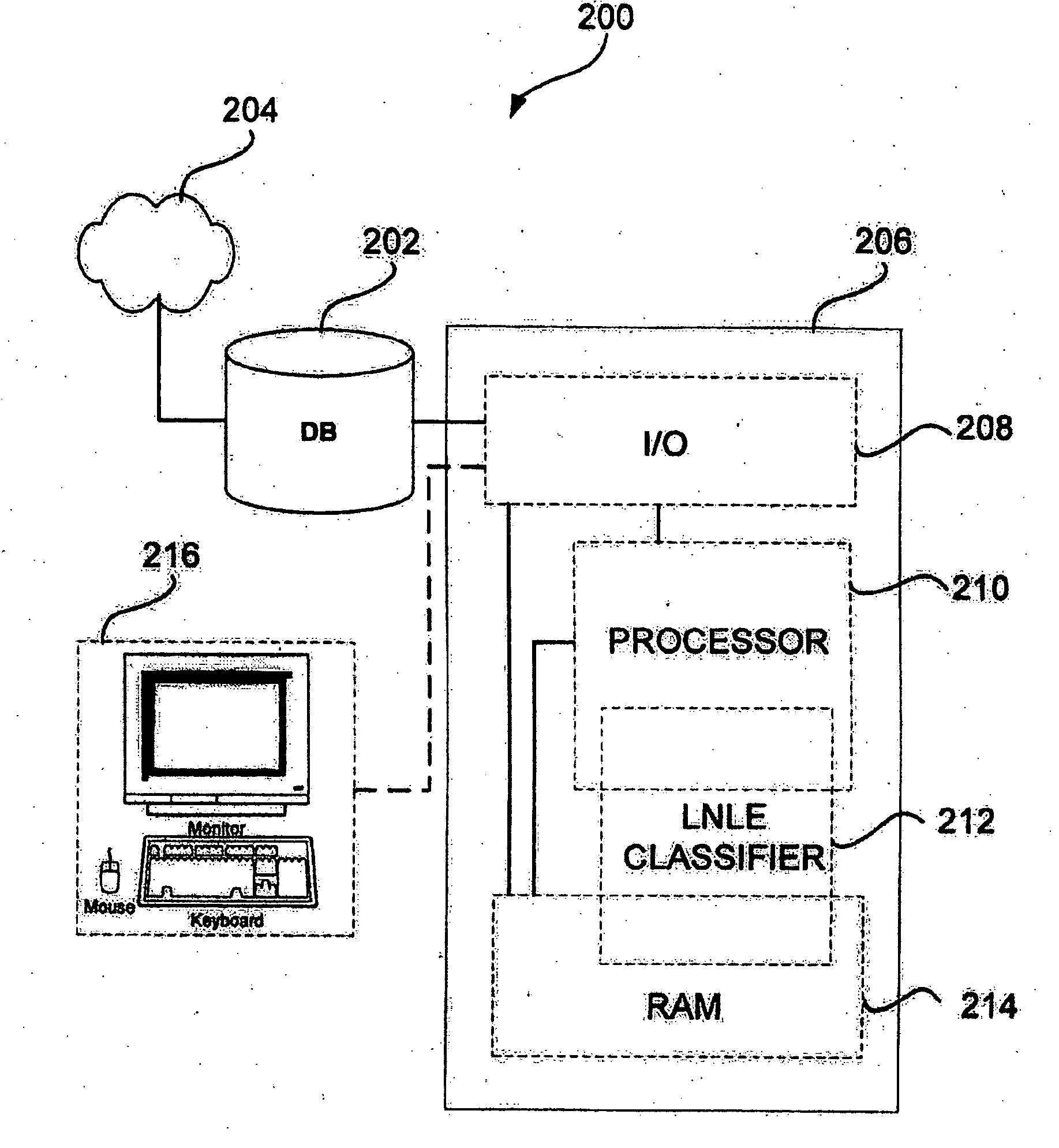
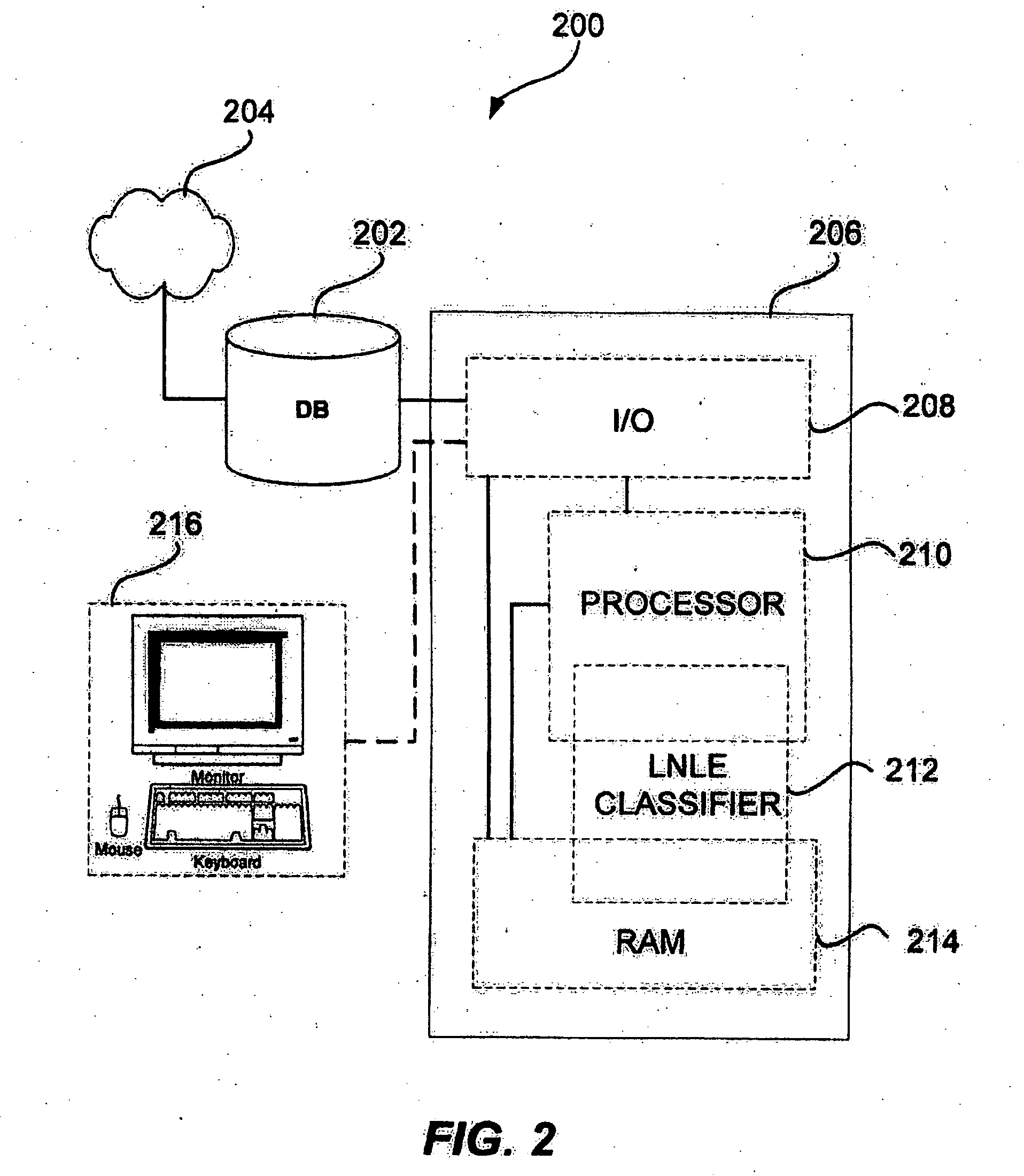
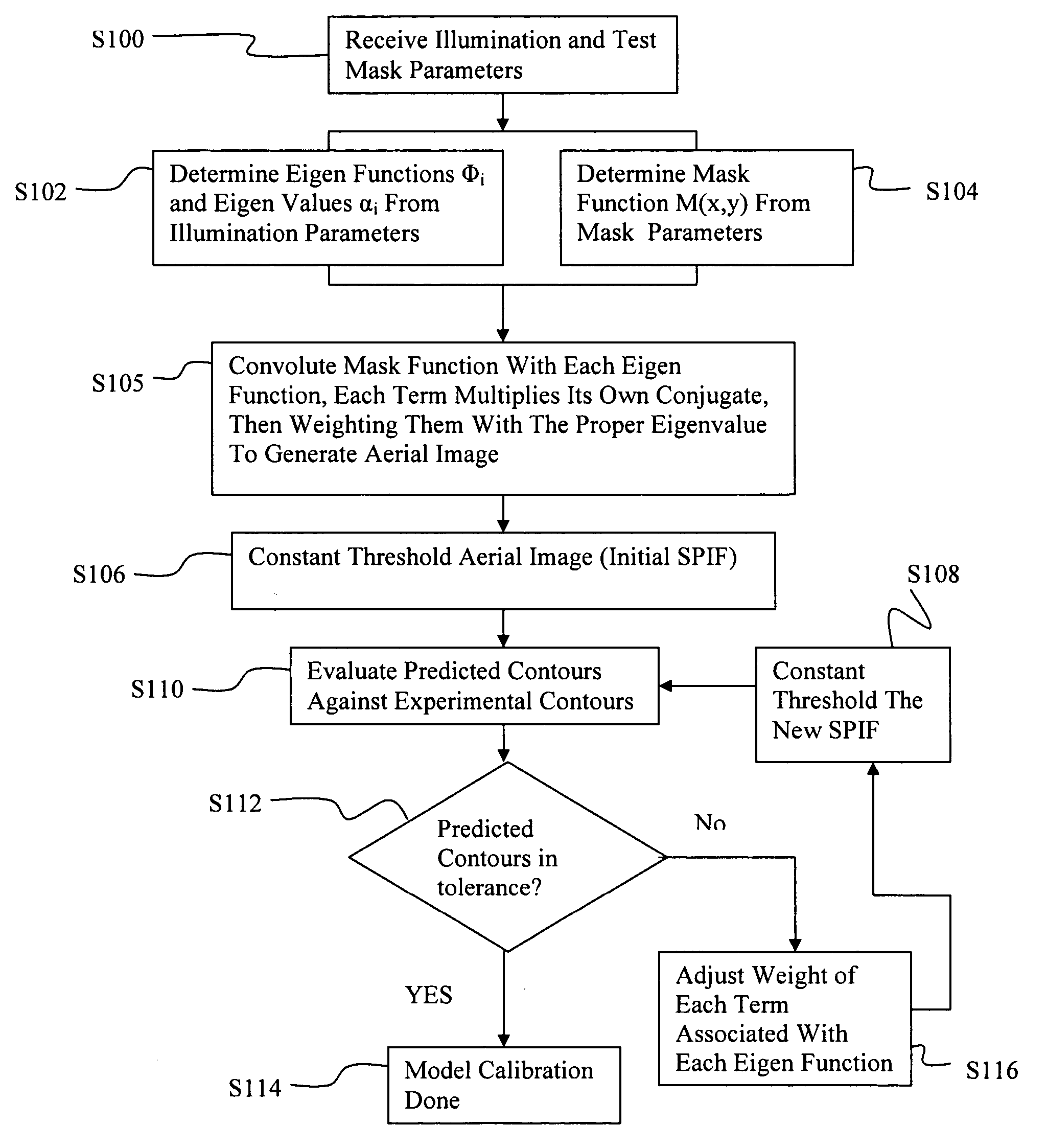
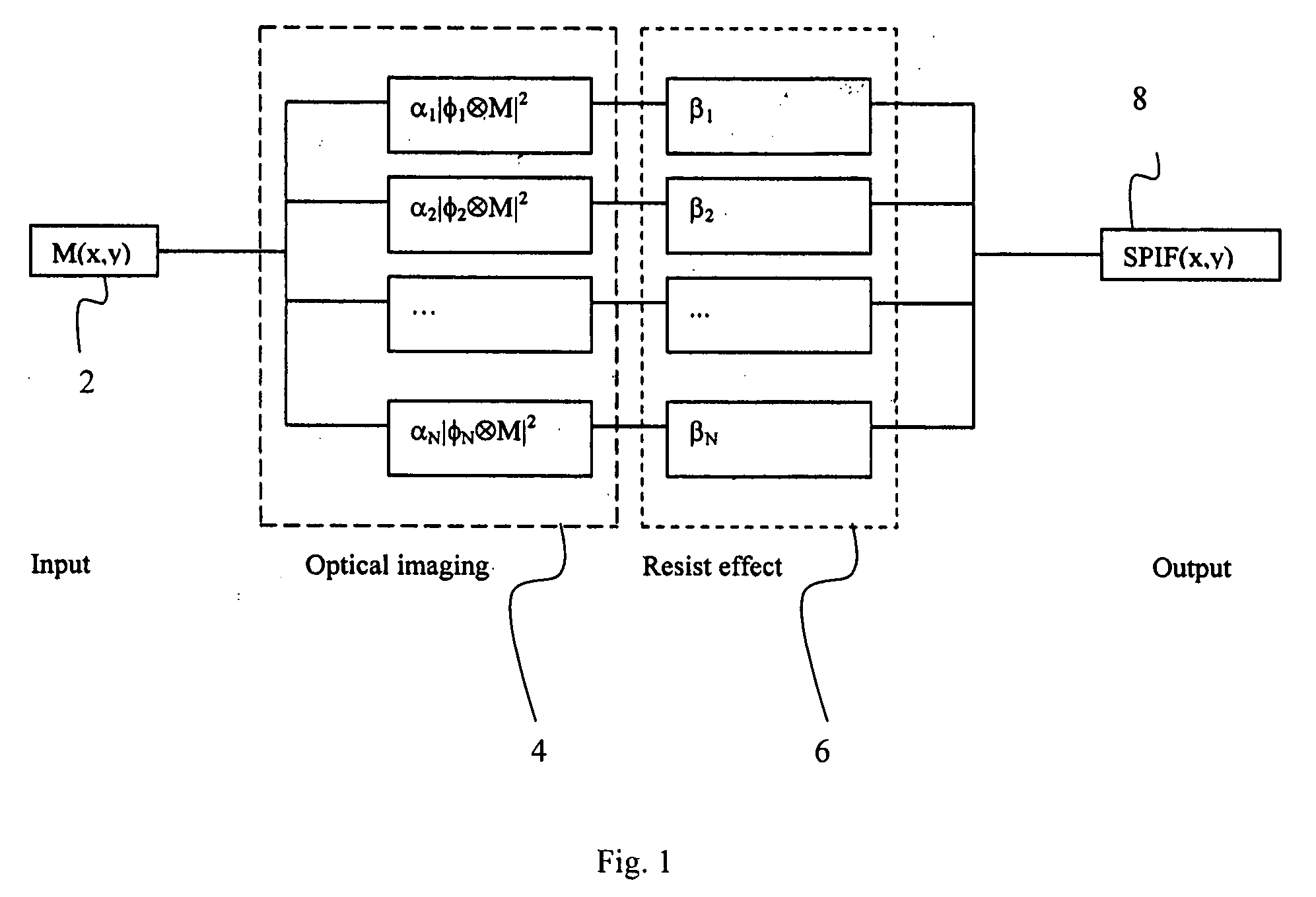
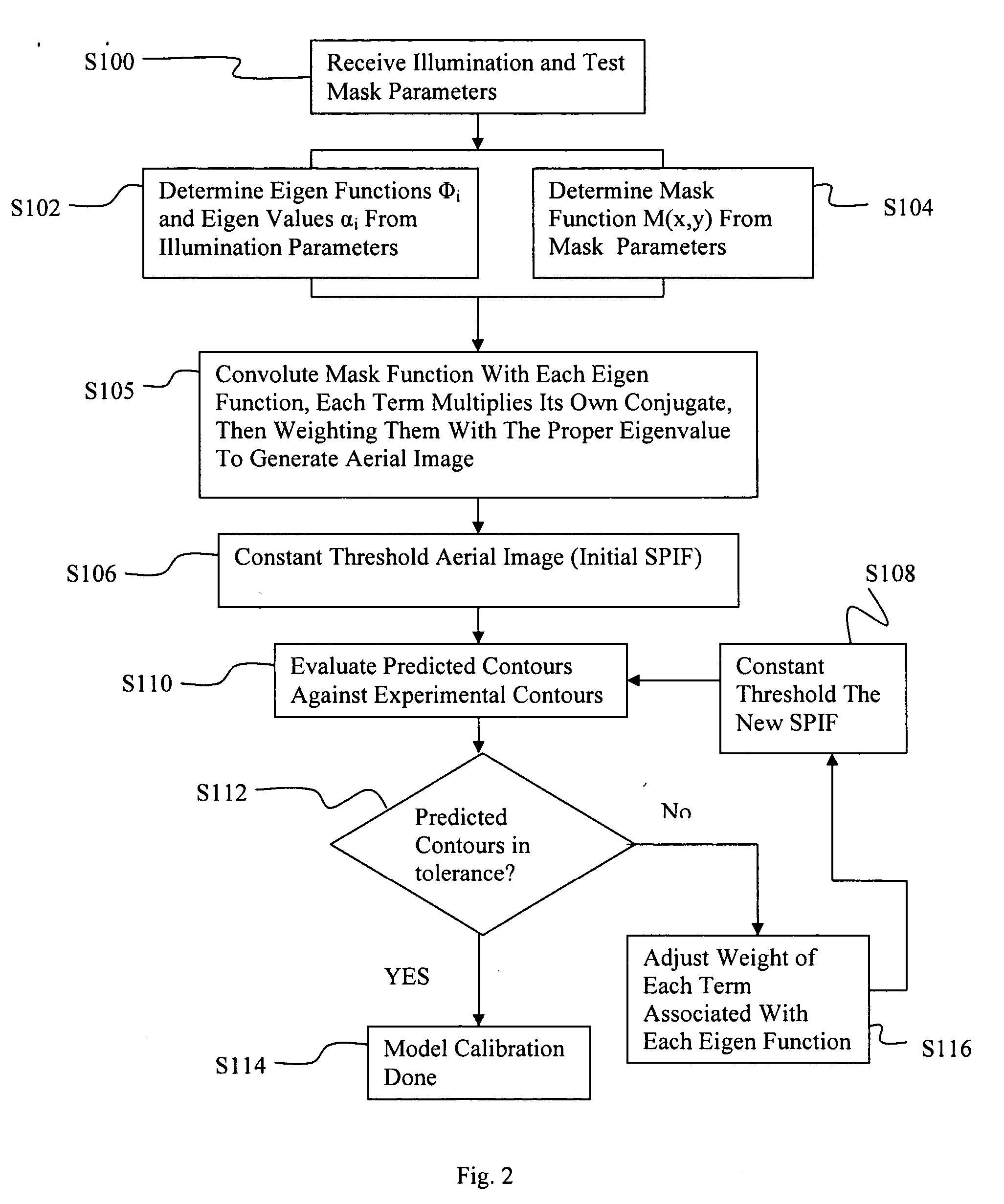
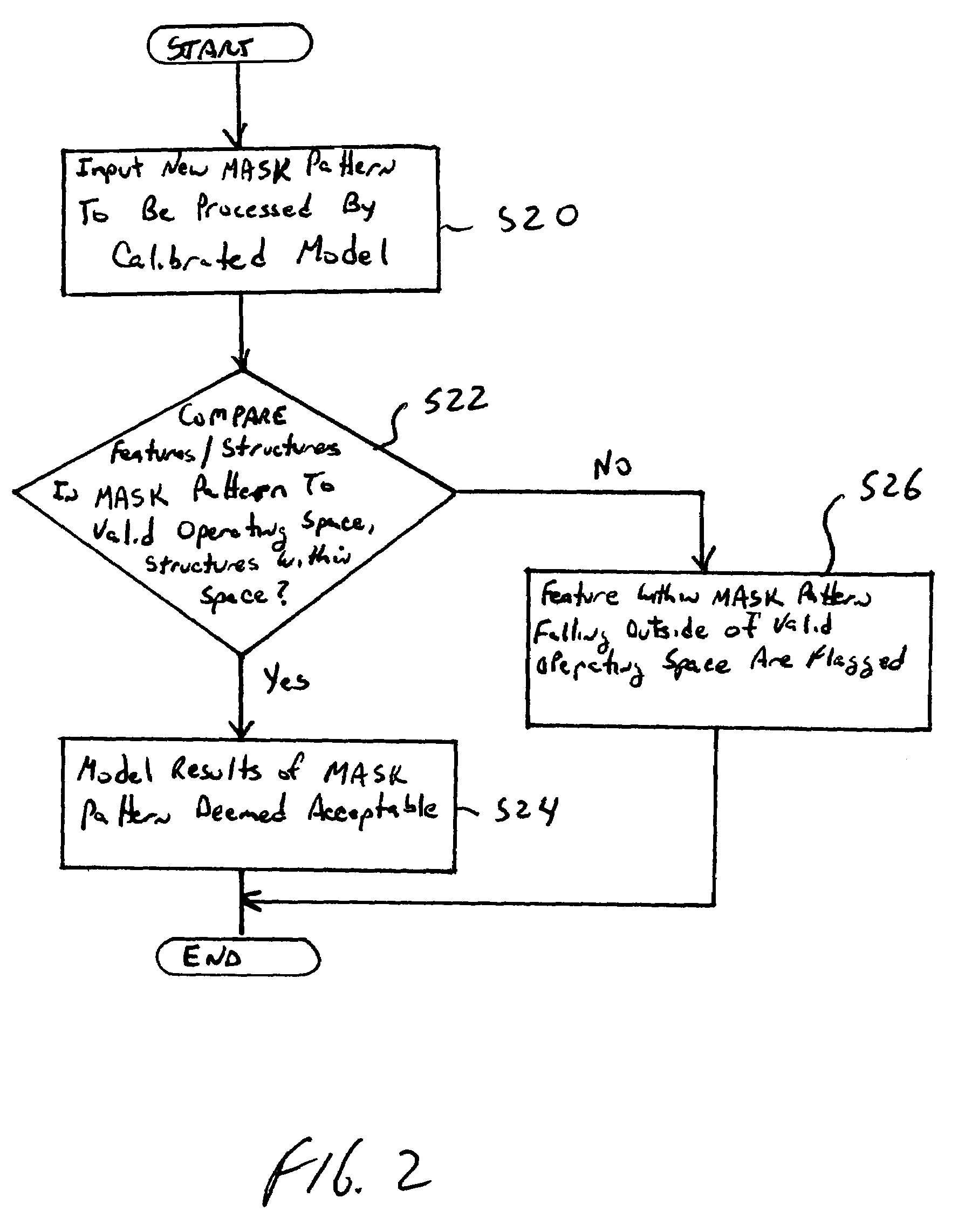
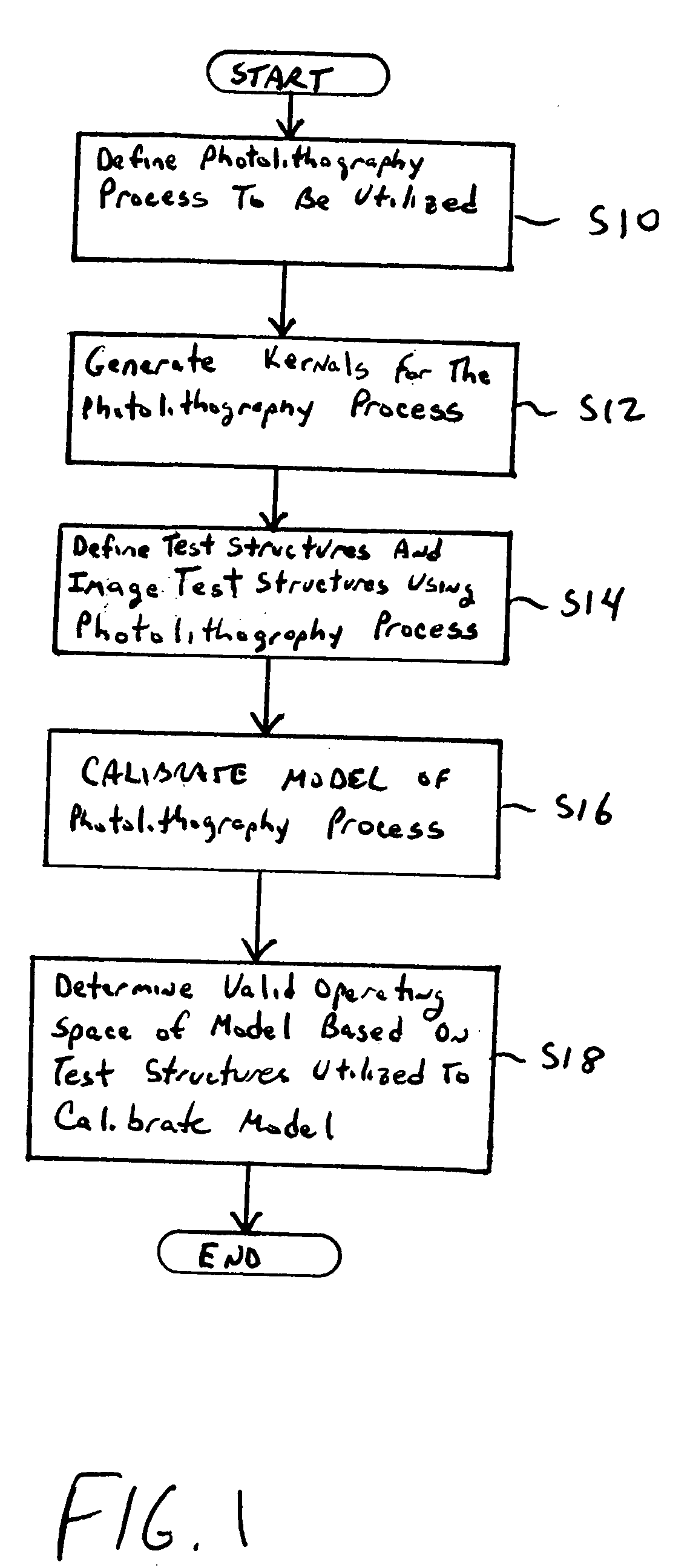
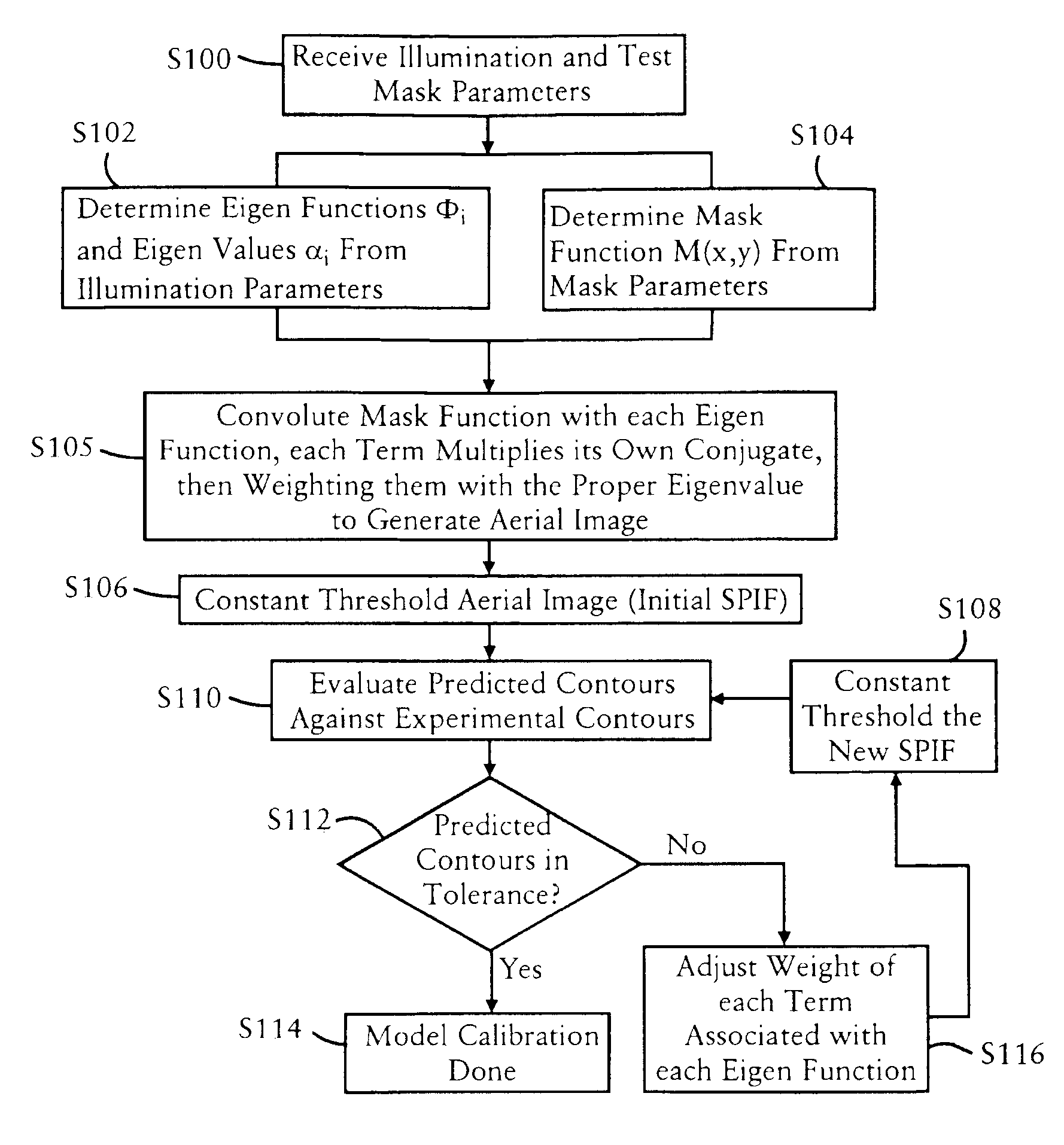
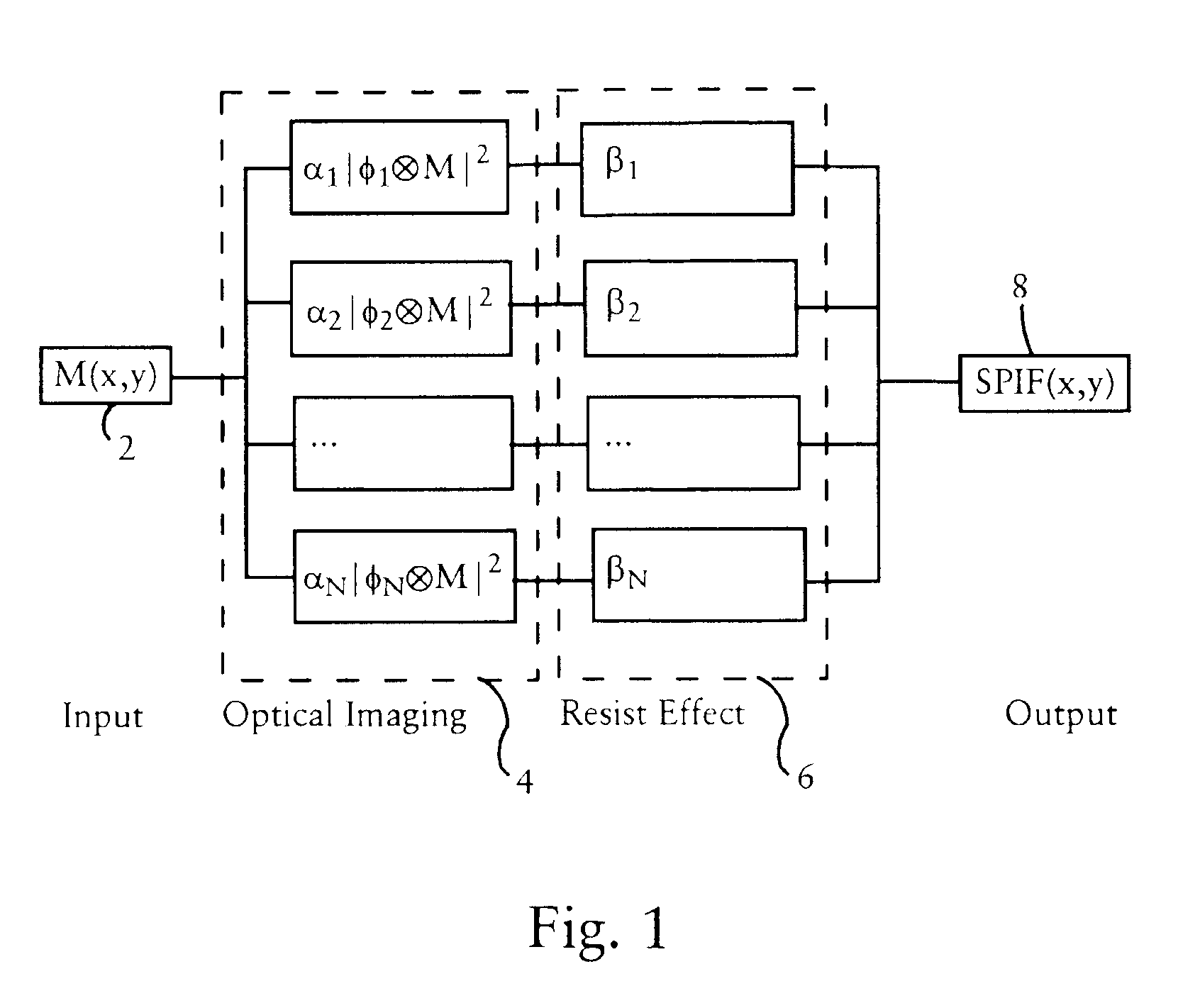
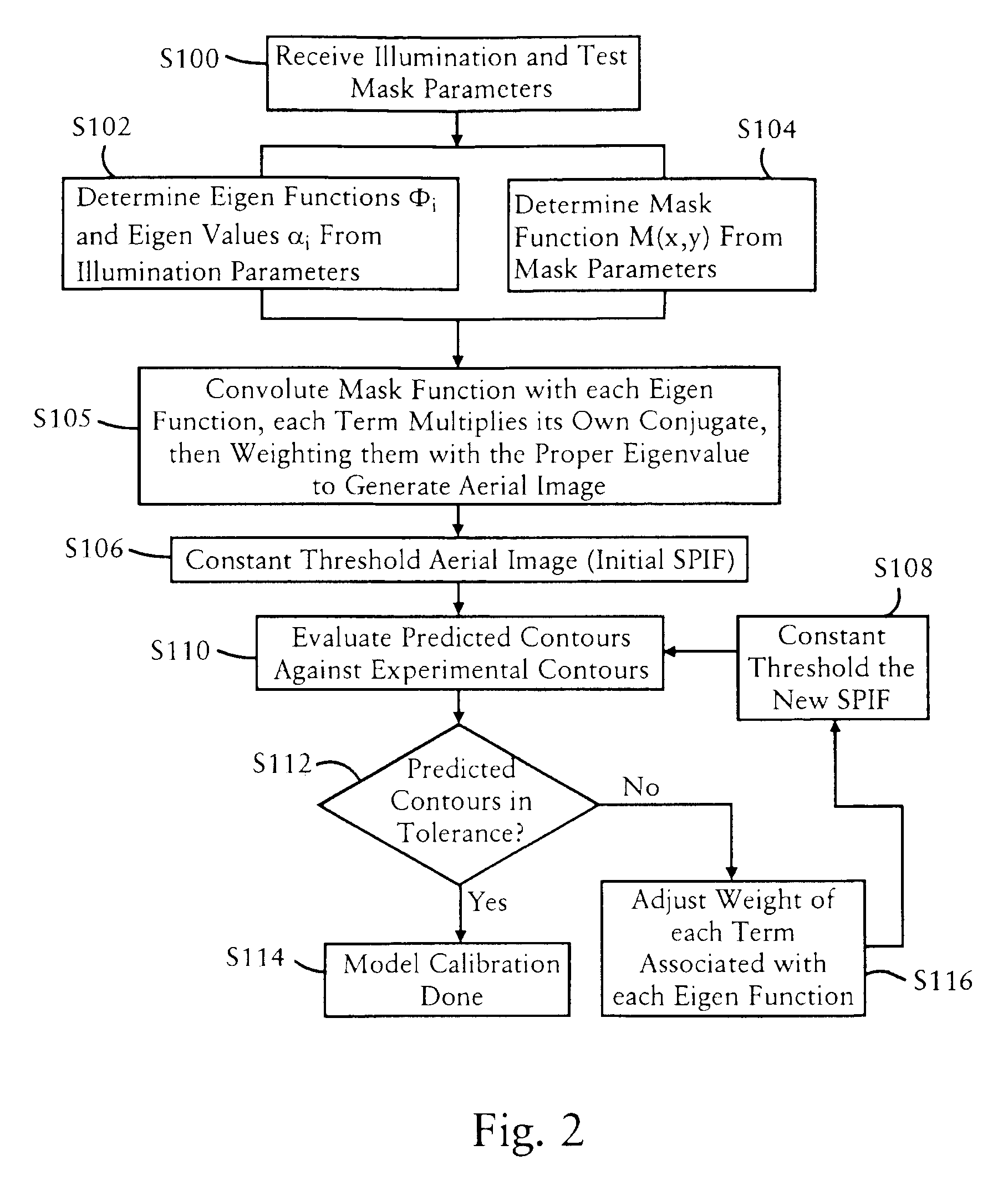
Eigen decomposition based OPC model
InactiveUS20050149902A1Minimal human interventionMinimal interventionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionResistPupil function
Model OPC is developed based on eigen decomposition of an aerial image expected to be produced by a mask pattern on a surface of a resist. With the eigen decomposition method the aerial image intensity distribution around a point (x, y) is accurately described in the model. A scalar approach may be used in the eigen decomposition model which treats the light wave through the mask as a scalar quantity. A eigen decomposition alternatively may use a vector approach which utilizes a vector to describe the light wave and the pupil function. A predicted SPIF may be generated from the aerial image which may be used to verify the mask modeling process by comparing the predicted SPIF to an experimentally determined SPIF. The model OPC, once calibrated, may be used to evaluate performance of a mask and refine features of the mask.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
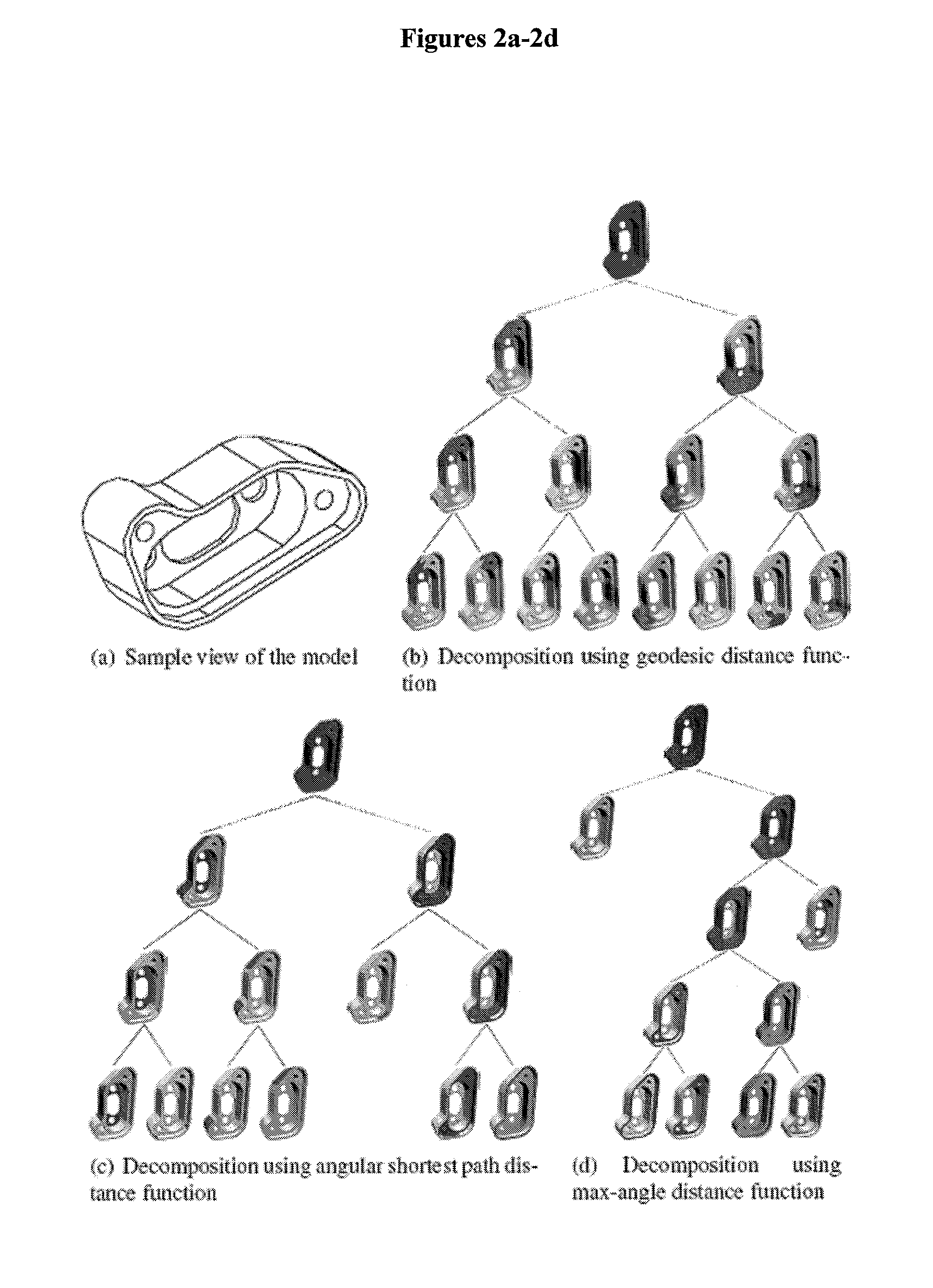
Multi-scale segmentation and partial matching 3D models
ActiveUS20080215510A1Improve performance consistencyConsistency in its performanceDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsViewpointsDecomposition
A scale-Space feature extraction technique is based on recursive decomposition of polyhedral surfaces into surface patches. The experimental results show that this technique can be used to perform matching based on local model structure. Scale-space techniques can be parameterized to generate decompositions that correspond to manufacturing, assembly or surface features relevant to mechanical design. One application of these techniques is to support matching and content-based retrieval of solid models. Scale-space technique can extract features that are invariant with respect to the global structure of the model as well as small perturbations that 3D laser scanning may introduce. A new distance function defined on triangles instead of points is introduced. This technique offers a new way to control the feature decomposition process, which results in extraction of features that are more meaningful from an engineering viewpoint. The technique is computationally practical for use in indexing large models.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
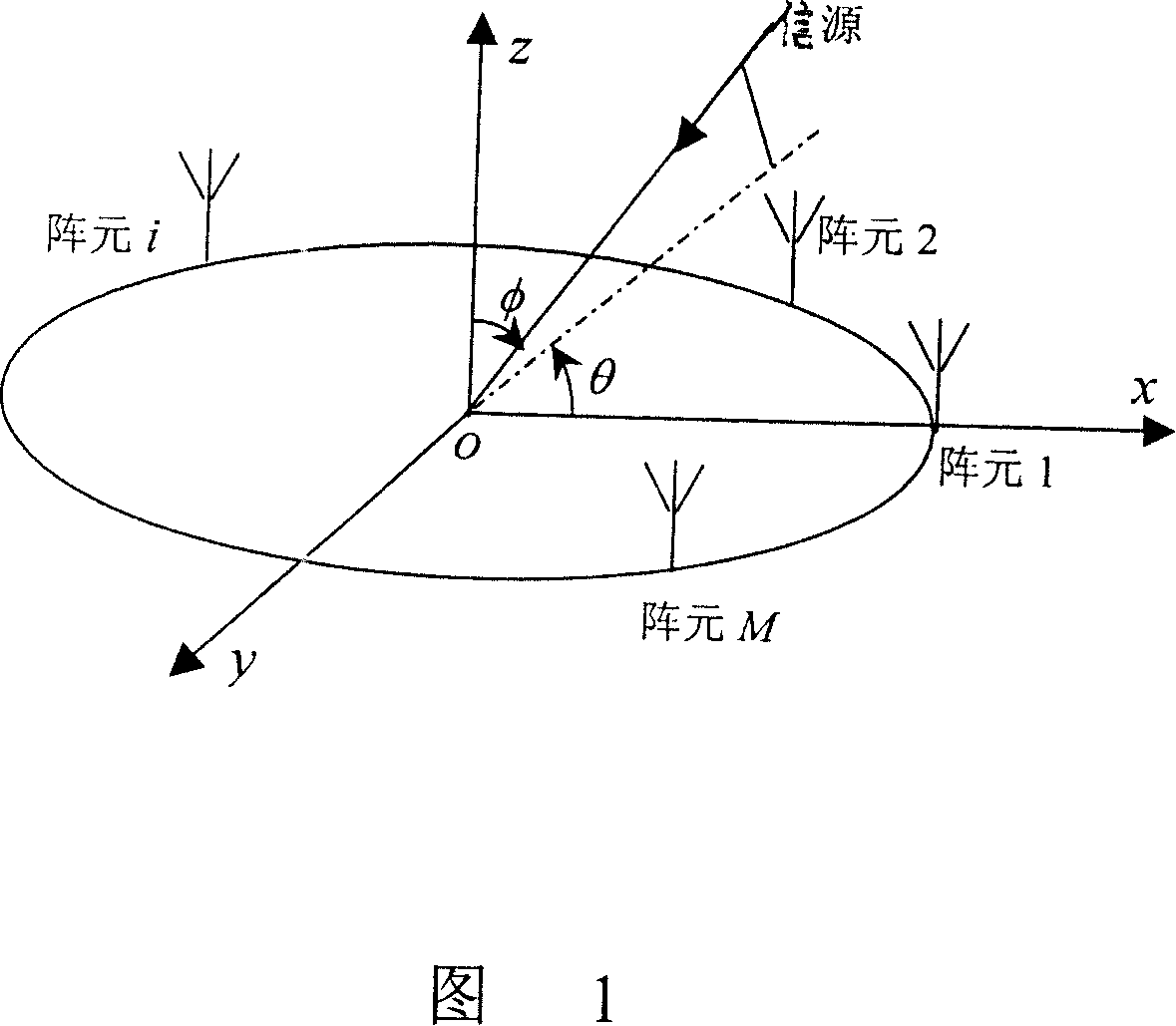
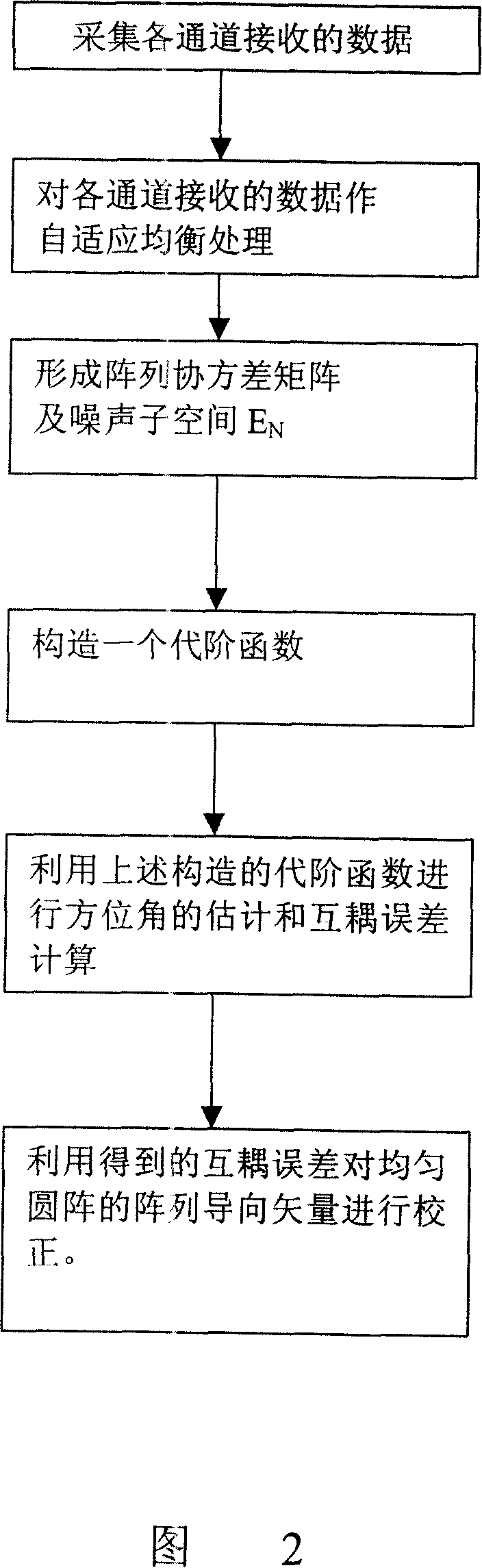
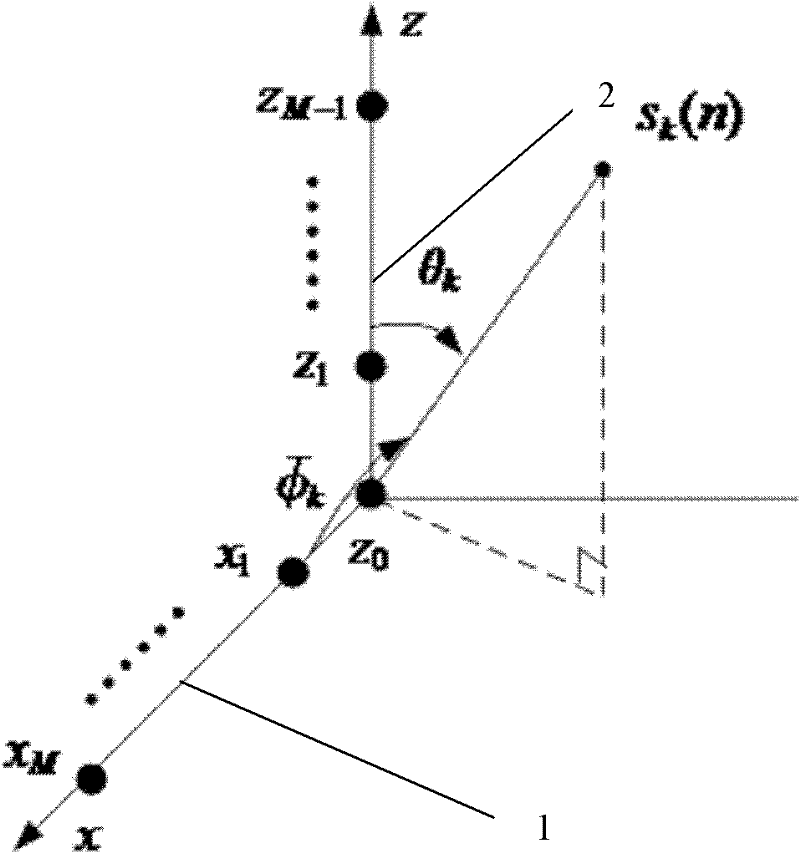
Array mutual coupling calibration and source direction estimation method suitable for uniform circular array
InactiveCN101149429ASolve a large amount of computationGood adhesionDirection findersEuclidean vectorCovariance matrix
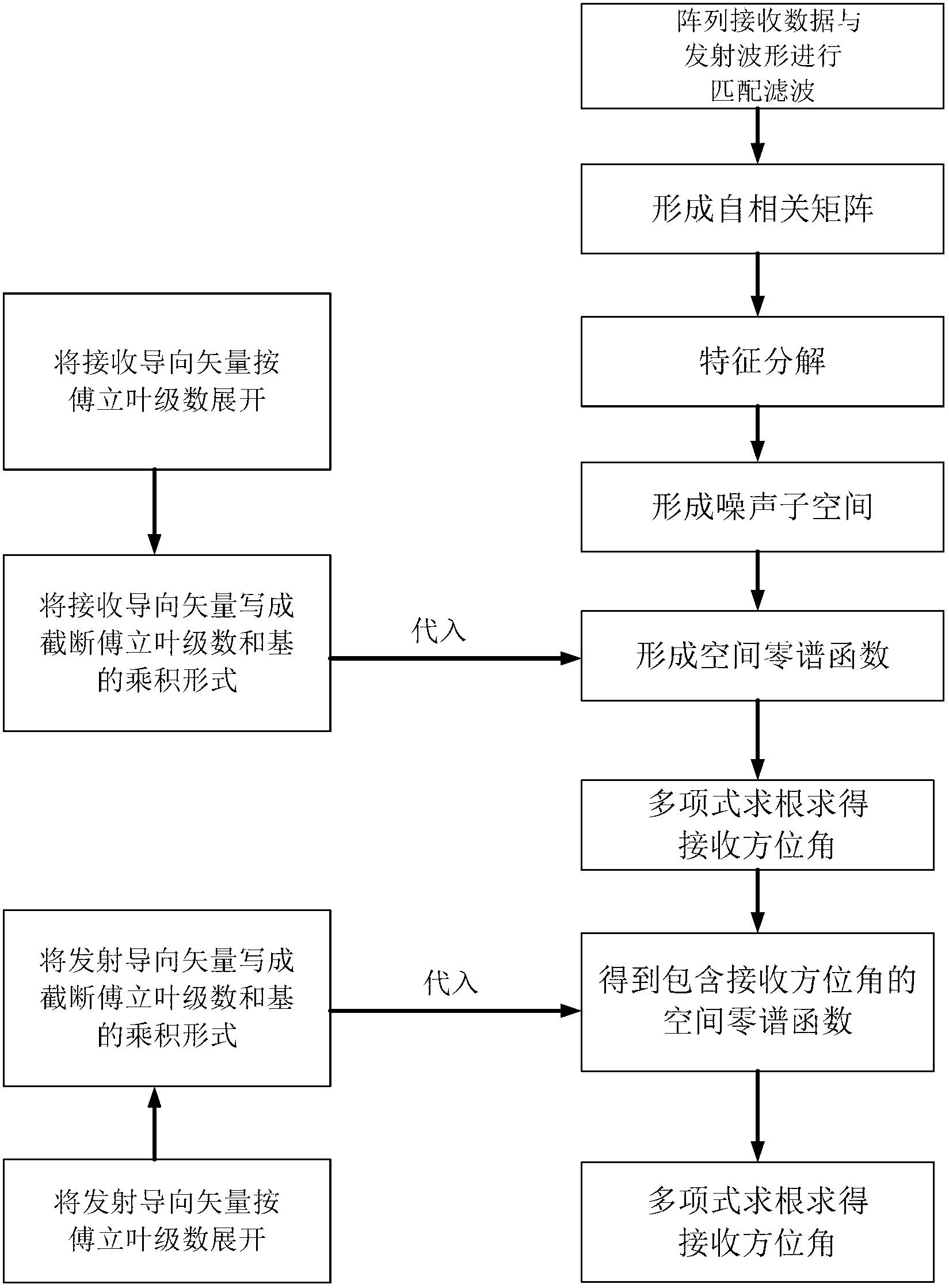
This invention relates to an array cross coupling proofreading and information source direction measuring method for homogeneous round array. This method uses array information disposing technique to estimate round array cross coupling error and information source AOA at the same time. Approaches are as follows: First collects data from each channel and saves it to the system memory. Then the data needs to be adaptive equalizing disposed. Next range the disposed data to a covariance matrix and disassemble it according to their character. After this can get noise subspace consisted of small characterized vector. By using subspace construction expense function, the azimuth angle and cross coupling errors can be figured out. Finally through the complexor from cross coupling error to homogeneous round array, finish the proofreading. This invention can universally apply to cross coupling proofreading and information source direction measuring in radar and communicating field. It is worth to wildly apply.
Owner:中国人民解放军空军工程大学导弹学院 +1
Virtual array DOA estimation method based on L type array
InactiveCN104730491AReduce complexityLarge apertureDirection/deviation determination systemsDecompositionSignal subspace
The invention discloses a virtual array DOA estimation method based on an L type array. The method comprises the steps that 1, based on the shift invariant property, a subarray Zx and a subarray Zy of the L type array horizontally shift to obtain a virtual array Zx' and a virtual array Zy', rotation invariance of two sub signals is formed due to the shift invariant property of the subarrays, and the virtual subarray signals are equal to the L type subarray Zx and L type subarray Zy input signals multiplied by a twiddle factor respectively; 2, the output of the four subarrays are combined to form a virtual array output signal Z (t); 3, the signal subspace and the noise subspace can be described by decomposing the features of covariance matrixes output by the array, mutual correlation processing is carried out on the array output signal Z(t) to obtain Rzz, and eigenvalue decomposition is carried out to obtain signal subspaces; 4, the twiddle factor is solved through linear operation, and the signal wave arrival direction can be obtained through the diagonal element of the twiddle factor. According to the virtual array DOA estimation method, no spectral function needs to be calculated, the phenomenon that the wave arrival direction is indirectly calculated without searching for the peak value is avoided, the complexity is lowered, the equipment complexity and cost are reduced, and the positioning precision is high.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method for estimating parameters of space stretching electromagnetic vector sensor array
InactiveCN103941221AReduce difficultyReduce complexityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSignal subspaceDomain combination
The invention provides a method for estimating parameters of a space stretching electromagnetic vector sensor array. The method comprises the steps of receiving K unrelated incoming signals through a receiving array, and constructing guide vectors of the incoming signals corresponding to the array; expressing the guide vectors of the incoming signals as a product of a spatial domain function array and a polarizational domain function vector; computing a covariance matrix of the received data; analyzing features of the covariance matrix of the received data to obtain signal subspace and noise subspace; constructing a multi-signal classified MUSIC spatial-polarizational domain combination zero spectrum function, and maximizing the spatial-polarizational domain combination zero spectrum function; performing MUSIC dimension reduction process to separate a spatial domain spectrum and a polarizational domain spectrum by means of the self-conjugate moment Rayleigh-Ritz entropy theorem, performing traversal search within value ranges of variables and estimating signal parameters. By means of the method, four-dimensional MUSIC search is transformed into two-dimensional spatial domain search and two-dimensional polarizational domain search, and therefore, calculated quantity is decreased.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
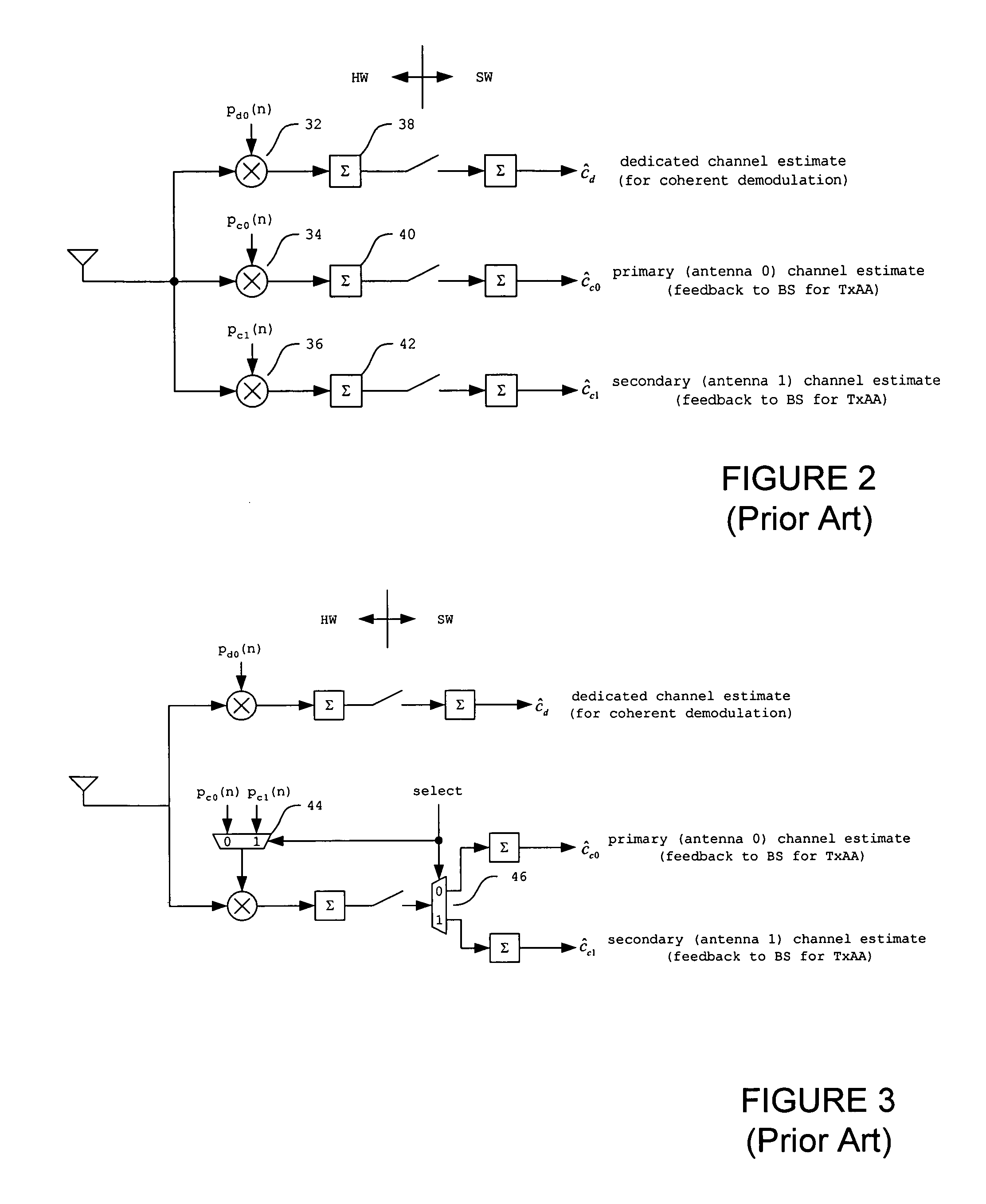
Method and apparatus for improving transmit antenna weight tracking using channel correlations in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS7236538B1Improves weight vector trackingDiversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPhase correlationGradient estimation
A novel method and apparatus for improving transmit antenna weight tracking using channel vector element to element correlations in a wireless communication system is disclosed. The present channel autocorrelation tracking technique utilizes the observation that tracking can be improved when a channel gain vector contains correlated elements. In a first embodiment of the autocorrelation tracking technique, the present invention extracts a coarse gradient estimate by utilizing a perturbation vector autocorrelation matrix estimate and a perturbation autocorrelation matrix to update TxAA weight vectors accordingly. In a second embodiment of the channel autocorrelation tracking technique, the present invention extracts a coarse gradient estimate by utilizing eigendecompositions, perturbation vector autocorrelation matrix estimates, and perturbation autocorrelation matrices to update TxAA weight vectors accordingly. In a third embodiment of the channel autocorrelation tracking technique, the present invention reduces the phase change that can occur at receivers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
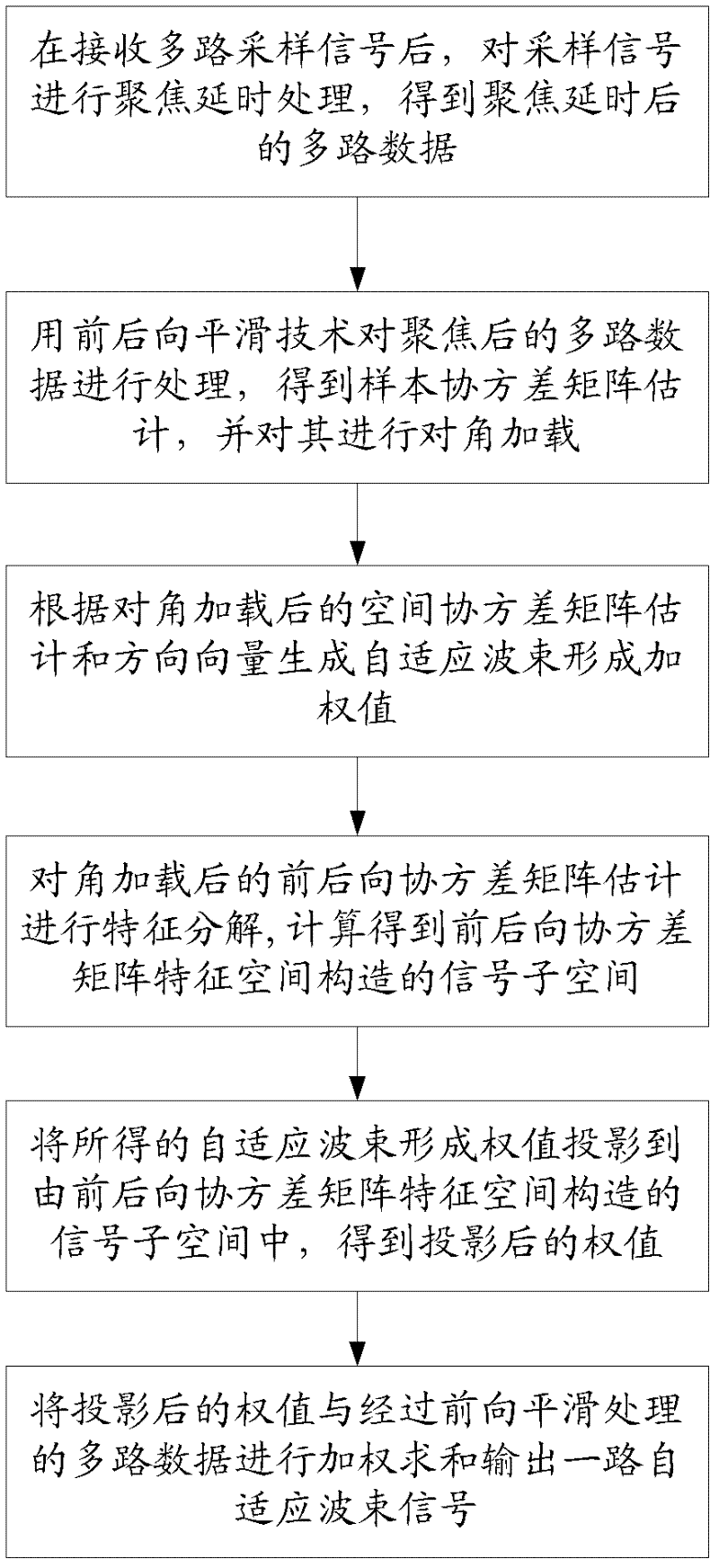
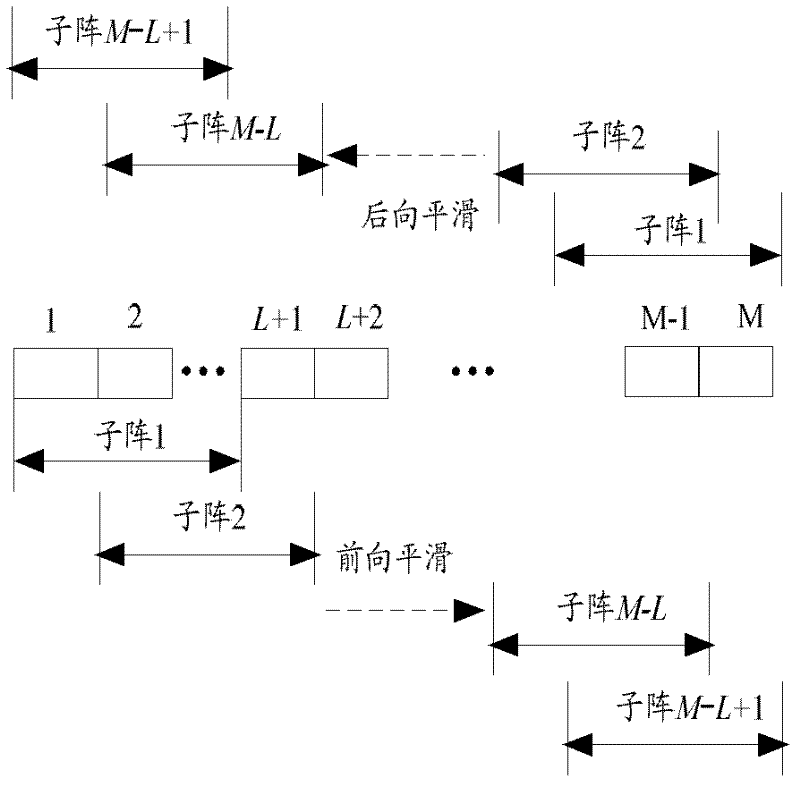
Characteristic space-based backward and forward adaptive wave beam forming method
ActiveCN102499712AImprove robustnessIncrease contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsSonificationDecomposition
The invention discloses a characteristic space-based backward and forward adaptive wave beam forming method, and relates to the technical field of medical ultrasonic imaging. The method comprises the following steps of: performing focusing delay processing and backward and forward smoothing on a plurality of paths of sampled signals of a received array to obtain a sample covariance matrix estimate; performing diagonal loading on the sample covariance matrix estimate and then combining with a direction vector to calculate an adaptive wave beam forming weight; performing characteristic decomposition on the backward and forward covariance matrix estimate after the diagonal loading to construct a signal subspace; projecting the adaptive wave beam forming weight into the signal subspace to obtain a new adaptive wave beam forming weight; and finally, performing weighted summation on a plurality of paths of data subjected to the backward and forward smoothing by the new adaptive wave beam forming weight so as to obtain a path of adaptive wave beam signal. By using the method, the problems of improving the image resolution and contrast, being sensitive to the direction error and the like existing in the conventional adaptive wave beam forming algorithm are solved, and the overall quality of the ultrasonic imaging is comprehensively improved.
Owner:STATE GRID EAST INNER MONGOLIA ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD MAINTENANCE BRANCH +1
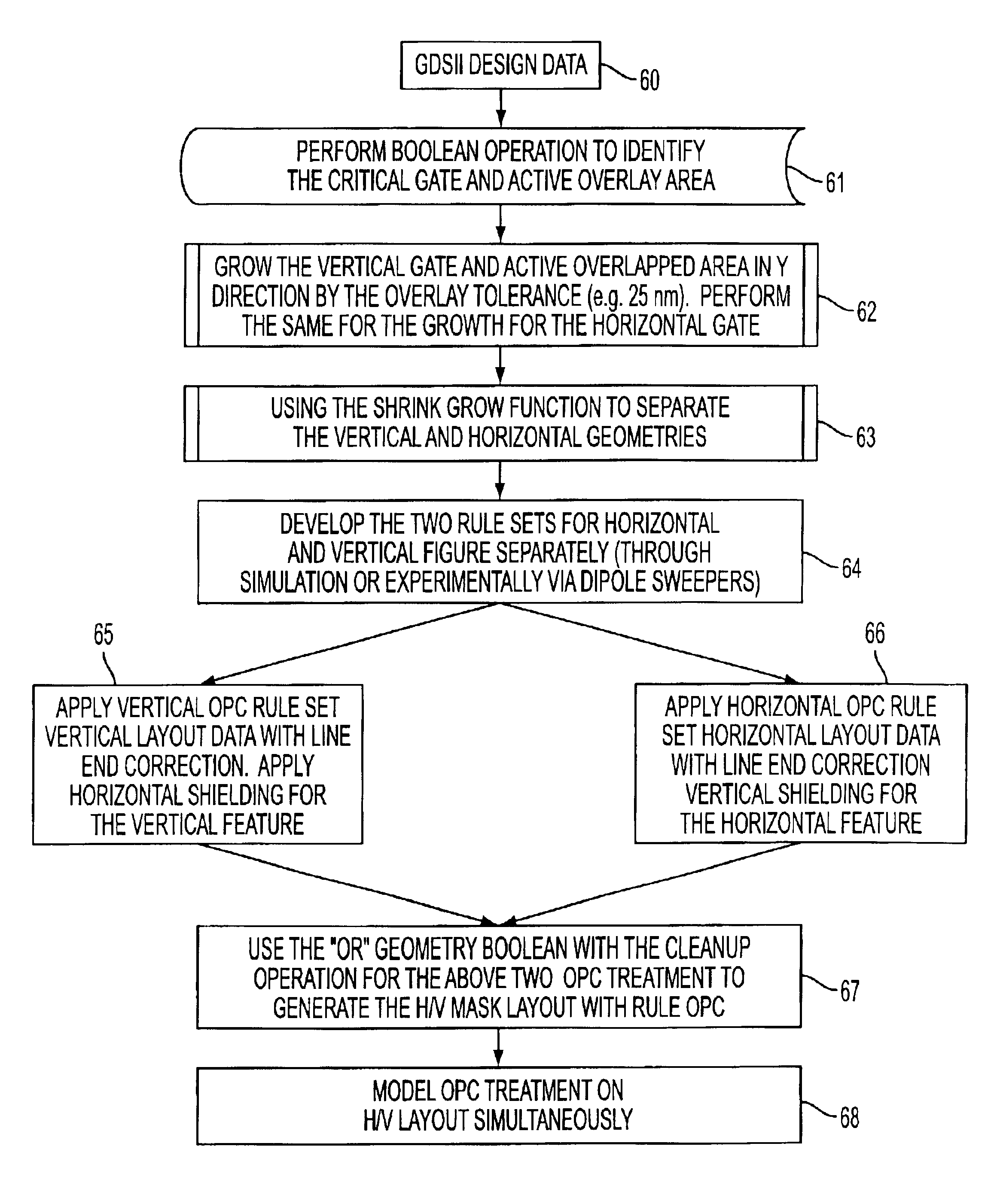
Method and apparatus for performing rule-based gate shrink utilizing dipole illumination
ActiveUS6915505B2Reduction of gate lengthShorten the lengthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPhysicsDipole
A method of printing a gate pattern on a substrate comprising the steps of: identifying at least one area in the pattern in which one of the gate features overlays one of the active regions; reducing a width dimension of the one of the gate features at the location which the one of the gate features overlays the one of the active regions; extracting the gate features from the pattern; decomposing the gate features into a vertical component mask and a horizontal component mask; and illuminating the vertical component mask and the horizontal component mask utilizing dipole illumination.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Brain cognitive state judgment method based on polyteny principal component analysis
InactiveCN103116764AGood recognition and classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixDecomposition
The invention discloses a brain cognitive state judgment method based on polyteny principal component analysis (PCA). The method includes the following steps of firstly, inputting sample sets, and processing input data; secondly, calculating characteristic decomposition of training sample sets, determining an optimal feature transformation transformational matrix, and projecting training samples into tensor characteristic subspace to obtain feature tensor sets of the training sets; thirdly, vectorizing lower dimension feature tensor data which are subjected to dimensionality reduction as input of linear discriminant analysis (LDA), determining an LDA optimal projection matrix, and projecting the vectorized lower dimension feature tensor data into LDA feature subspace for further extracting discriminant feature vectors of the training sets; and fourthly, classifying features, subjecting the discriminant feature vectors obtained by projection of training images and test images to feature matching, and further classifying the features . According to the brain cognitive state judgment method, PCA is utilized to directly perform dimensionality reduction and feature extraction to multi-level tensor data, the defect that structures and correlation of original image data are destroyed and redundancy and structures in the original images can not be completely maintained due to the fact that traditional PCA simply performs dimensionality reduction is overcome, and space structure information of functional magnetic resonance image (fMRI) imaging data is kept.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Estimating method of direction of arrival of bistatic MIMO (Multi-Input Multi-Output) radar based on circular array
InactiveCN102707264AReduce computationQuick calculationWave based measurement systemsMulti inputAngle of departure
The invention discloses an estimating method of direction of arrival of a bistatic MIMO (Multi-Input Multi-Output) radar based on a circular array, and mainly solves the problems that in the prior art, calculation is large and the direction of arrival of the circular array cannot be estimated. The realizing process comprises the steps of: 1, obtaining a cut-off Fourier coefficient of a steering vector of the array, and replacing the steering vector by the product of the Fourier coefficient and a base; 2, performing matched filtering for received data by the array to form an autocorrelation matrix and performing characteristic-decomposition for the matrix; 3, selecting a characteristic vector to form a noise sub space and obtaining a spatial zero-spectral function; 4, introducing the steering vector received to the spatial zero-spectral function, and solving an acceptance angle by polynomial rooting; and 5, introducing the acceptance angle received to the spatial zero-spectral function and solving an angle of departure by polynomial rooting. According to the estimating method of direction of arrival of the bistatic MIMO radar based on the circular array, the polynomial rooting method can be adopted to estimate the direction of arrival of the manifold MIMO radar of the circular array, spectrum peak search is avoided, calculation is low, and the estimating method of direction of arrival of the bistatic MIMO radar based on the circular array can be applied to estimating the direction of arrival of the bistatic MIMO radar.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
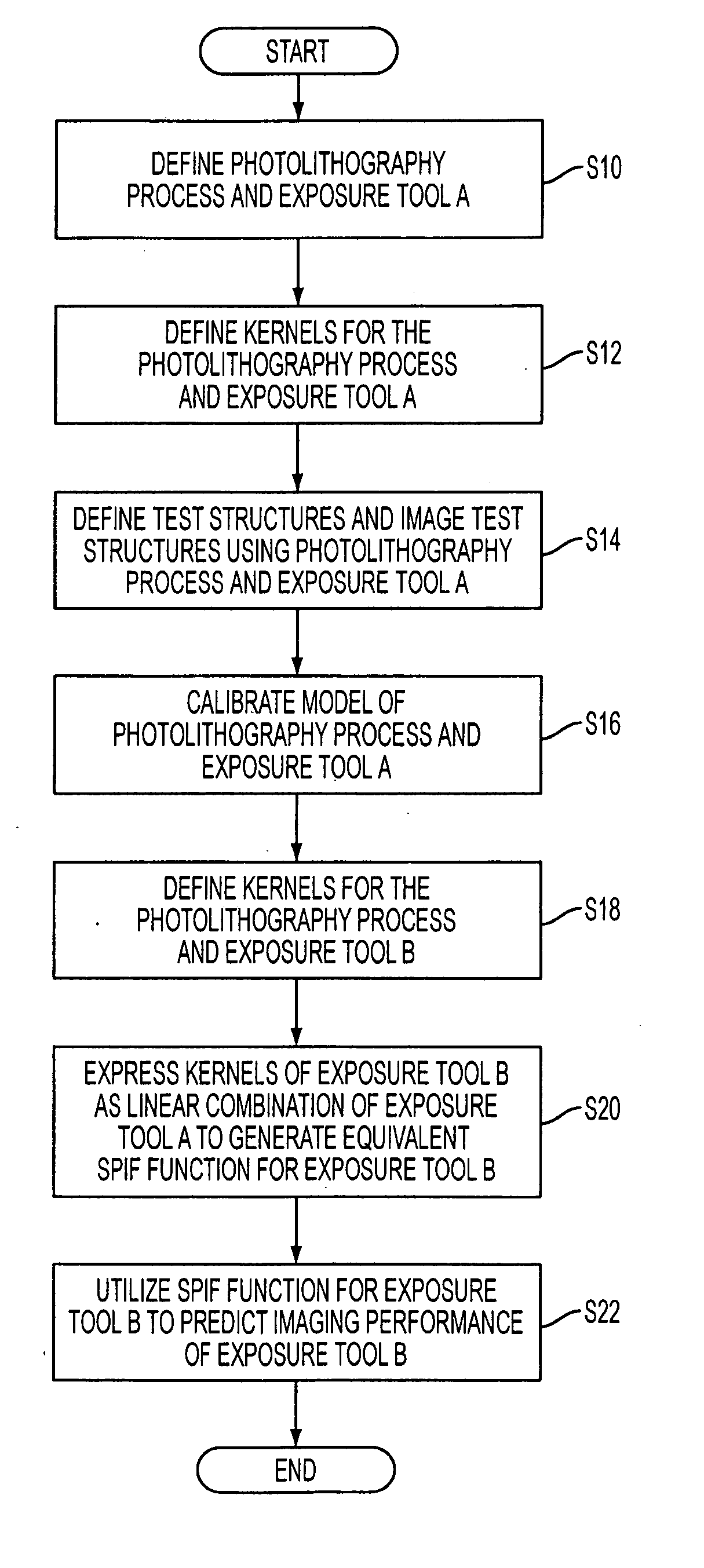
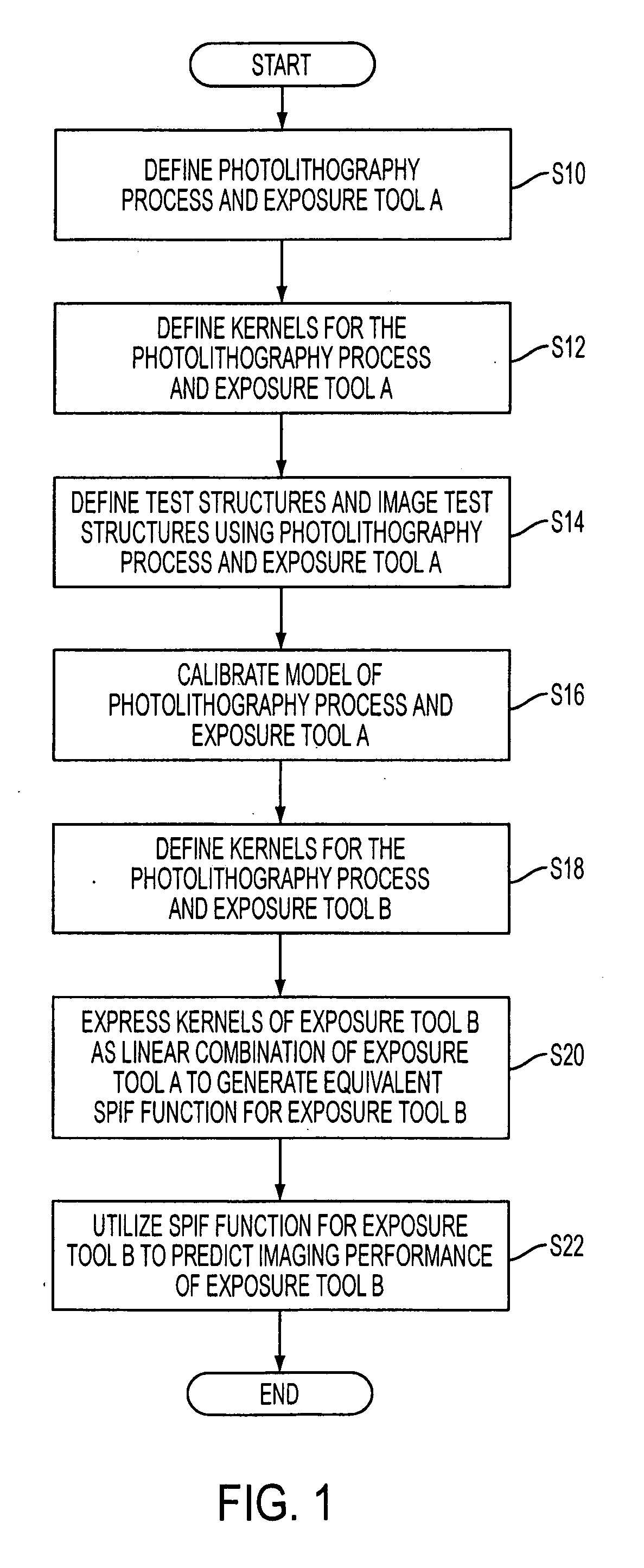
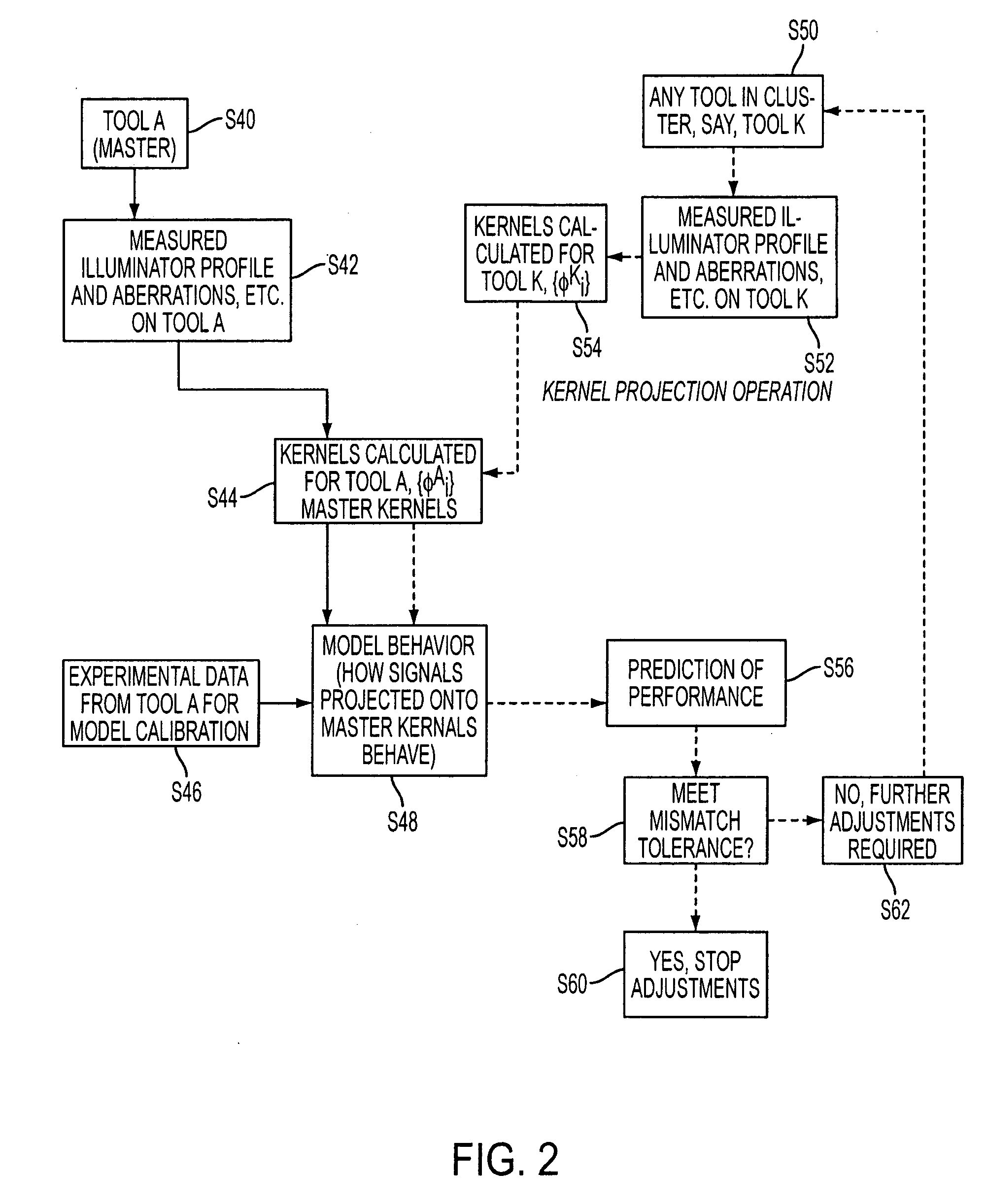
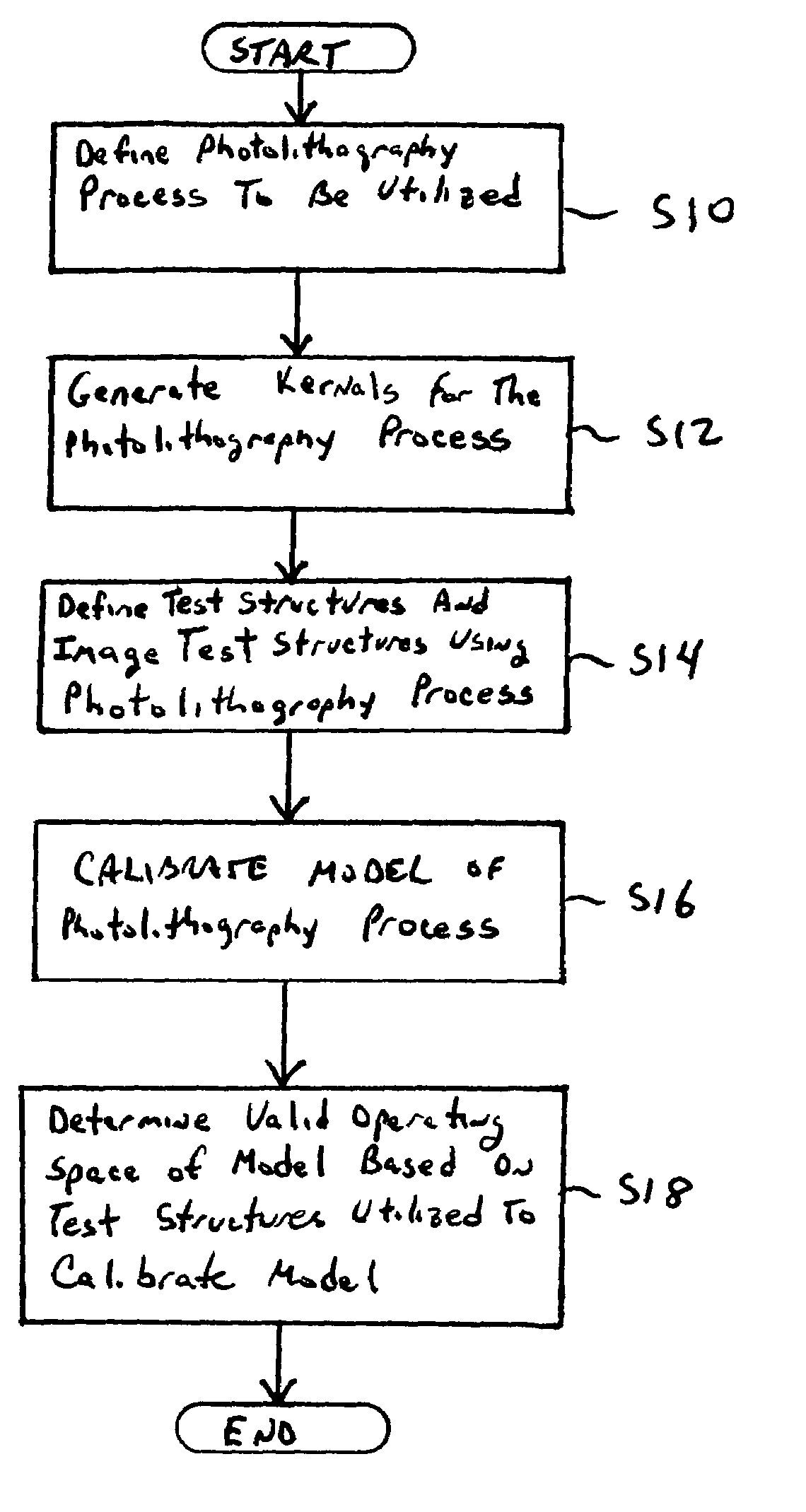
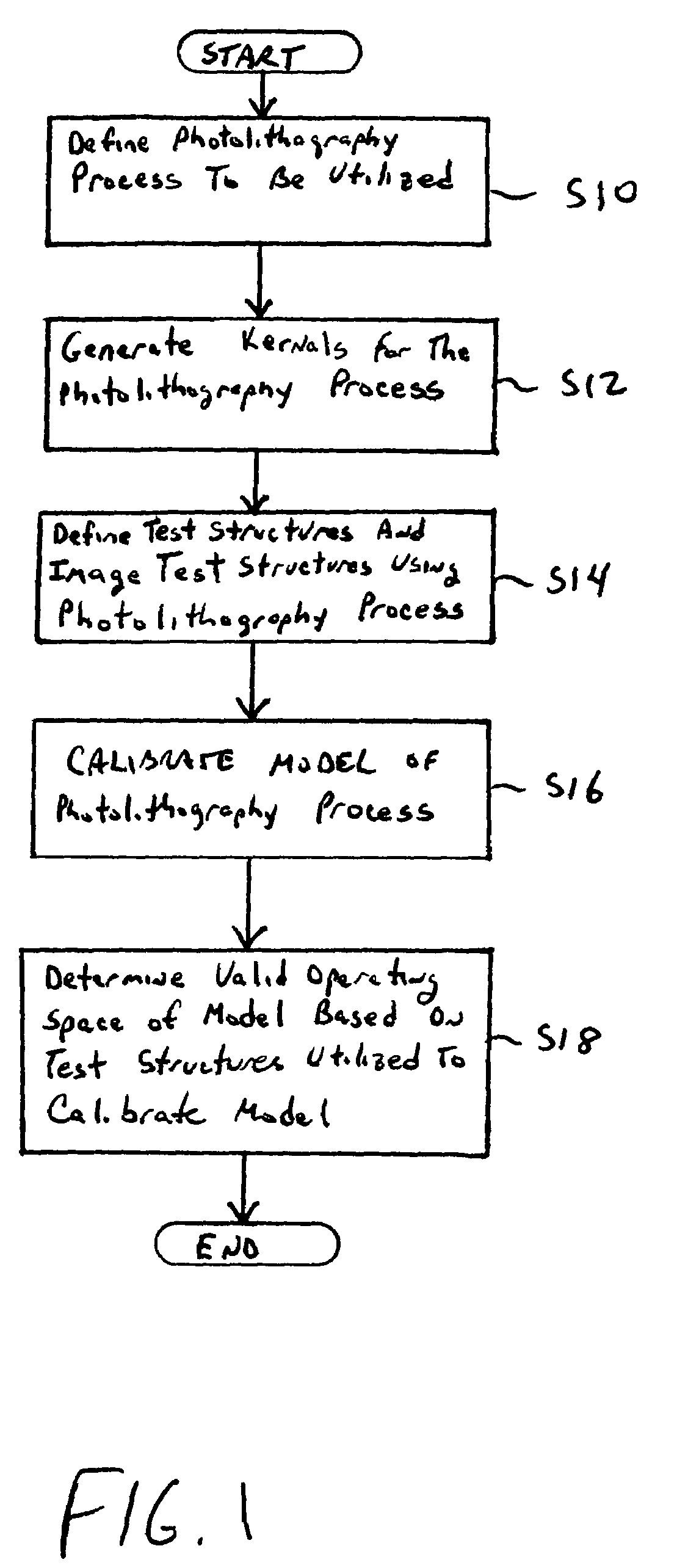
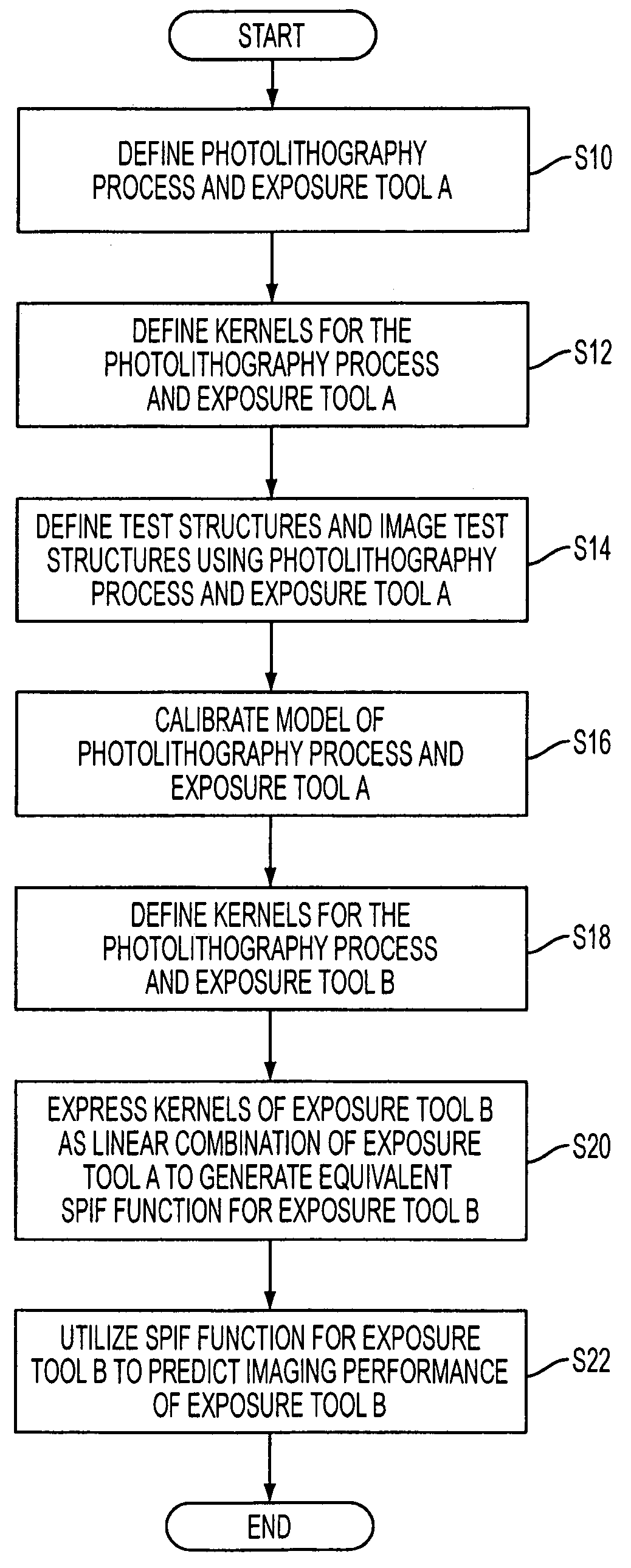
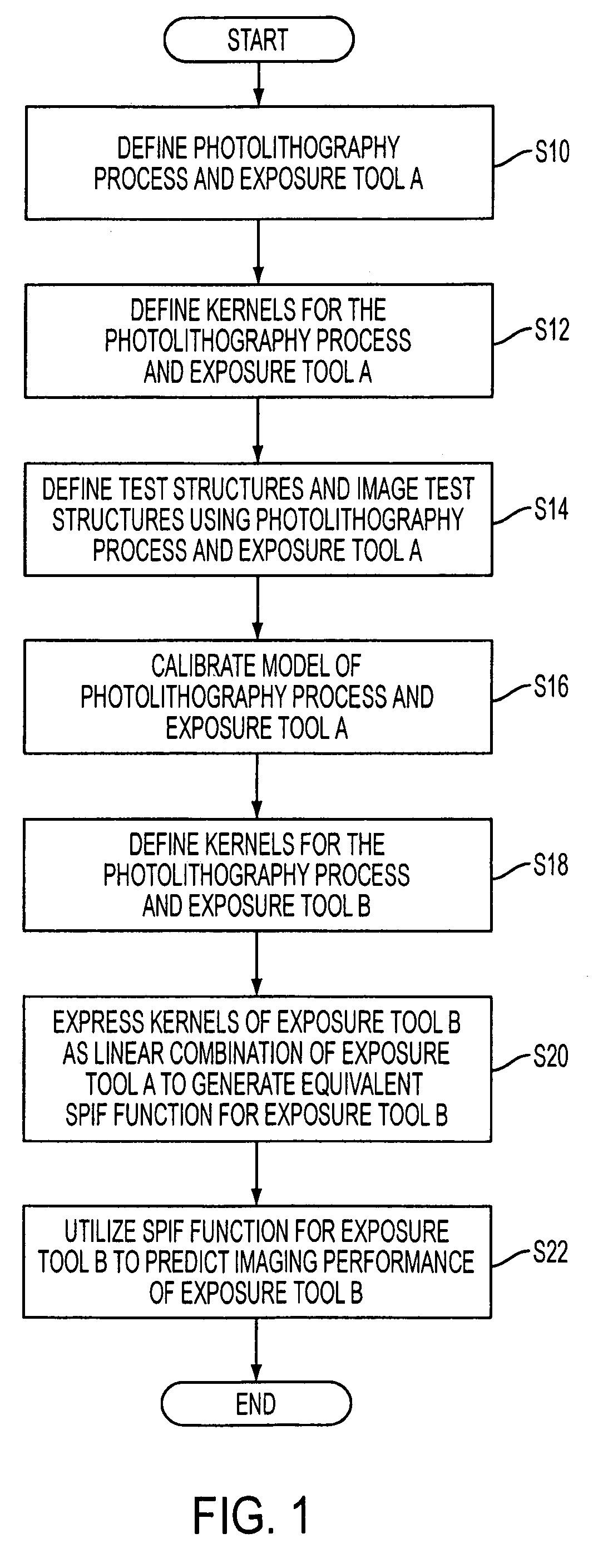
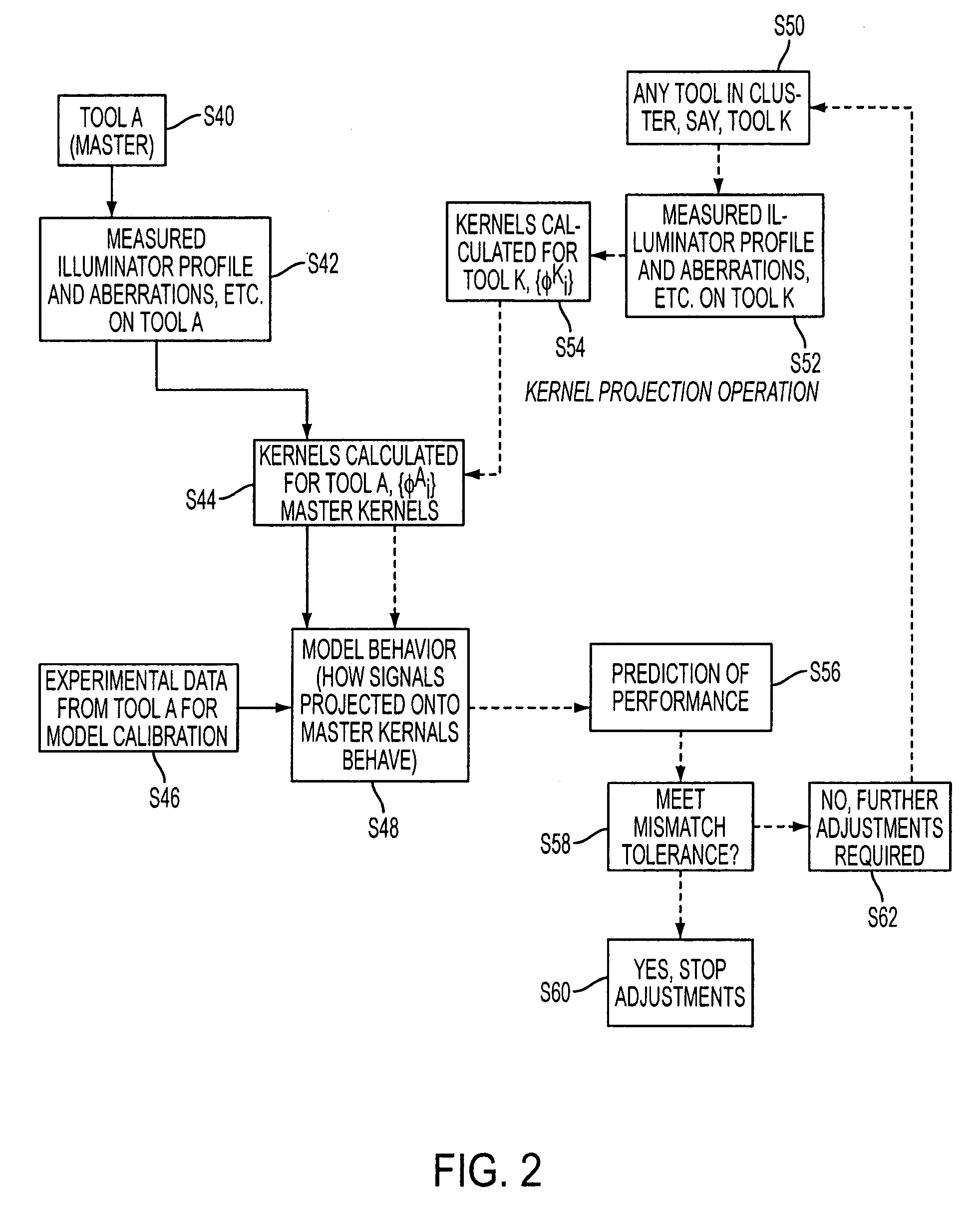
Method of predicting and minimizing model OPC deviation due to mix/match of exposure tools using a calibrated eigen decomposition model
ActiveUS20050179886A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusDecompositionLinearity
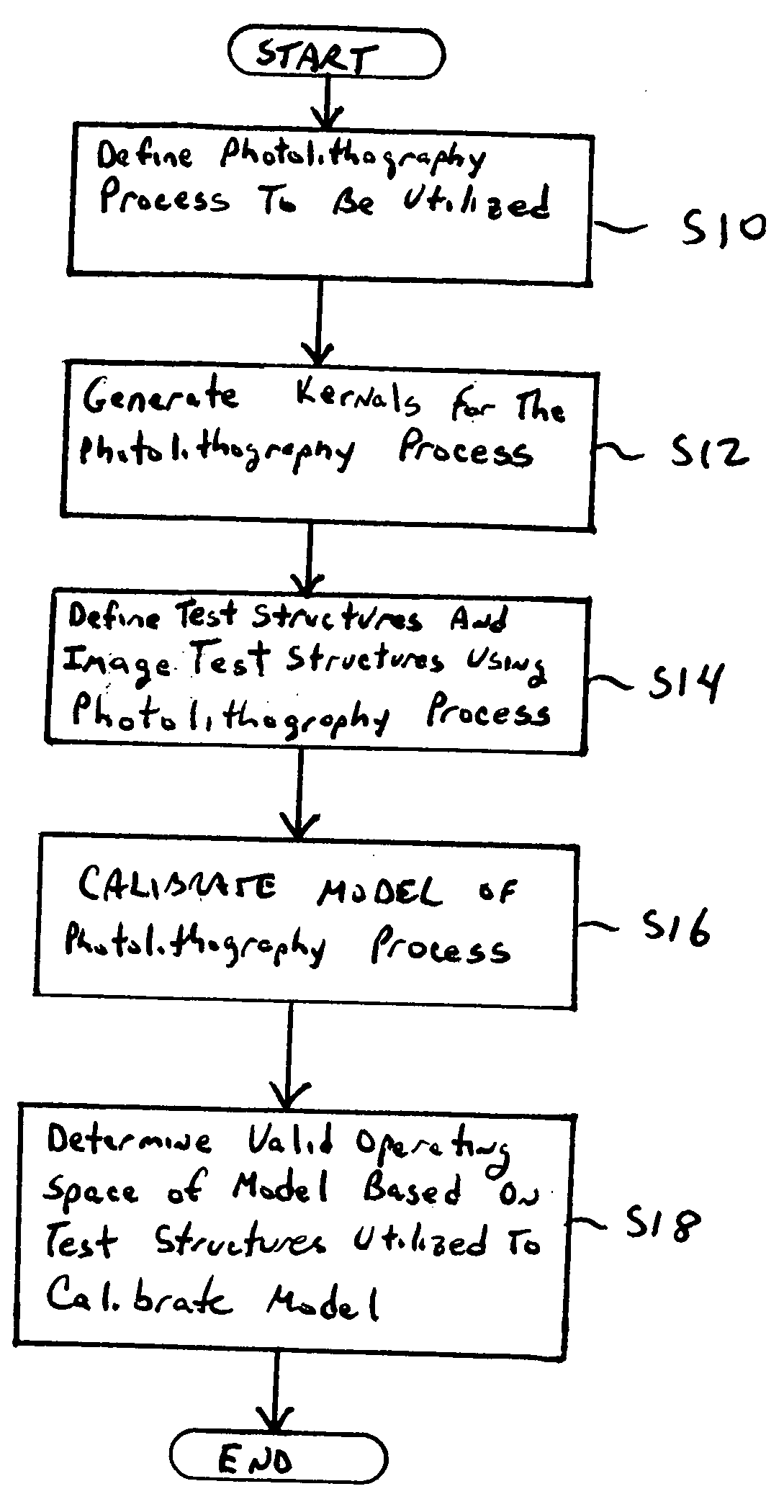
A method for generating models for simulating the imaging performance of a plurality of exposure tools. The method includes the steps of: generating a calibrated model for a first exposure tool capable of estimating an image to be produced by the first exposure tool for a given photolithography process, where the calibrated model includes a first set of basis functions; generating a model of a second exposure tool capable of estimating an image to be produced by the second exposure tool for the photolithography process, where the model includes a second set of basis functions; and representing the second set of basis functions as a linear combination of the first set of basis functions so as to generate an equivalent model function corresponding to the second exposure tool, where the equivalent model function produces a simulated image corresponding to the image generated by the second exposure tool for the photolithography process.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
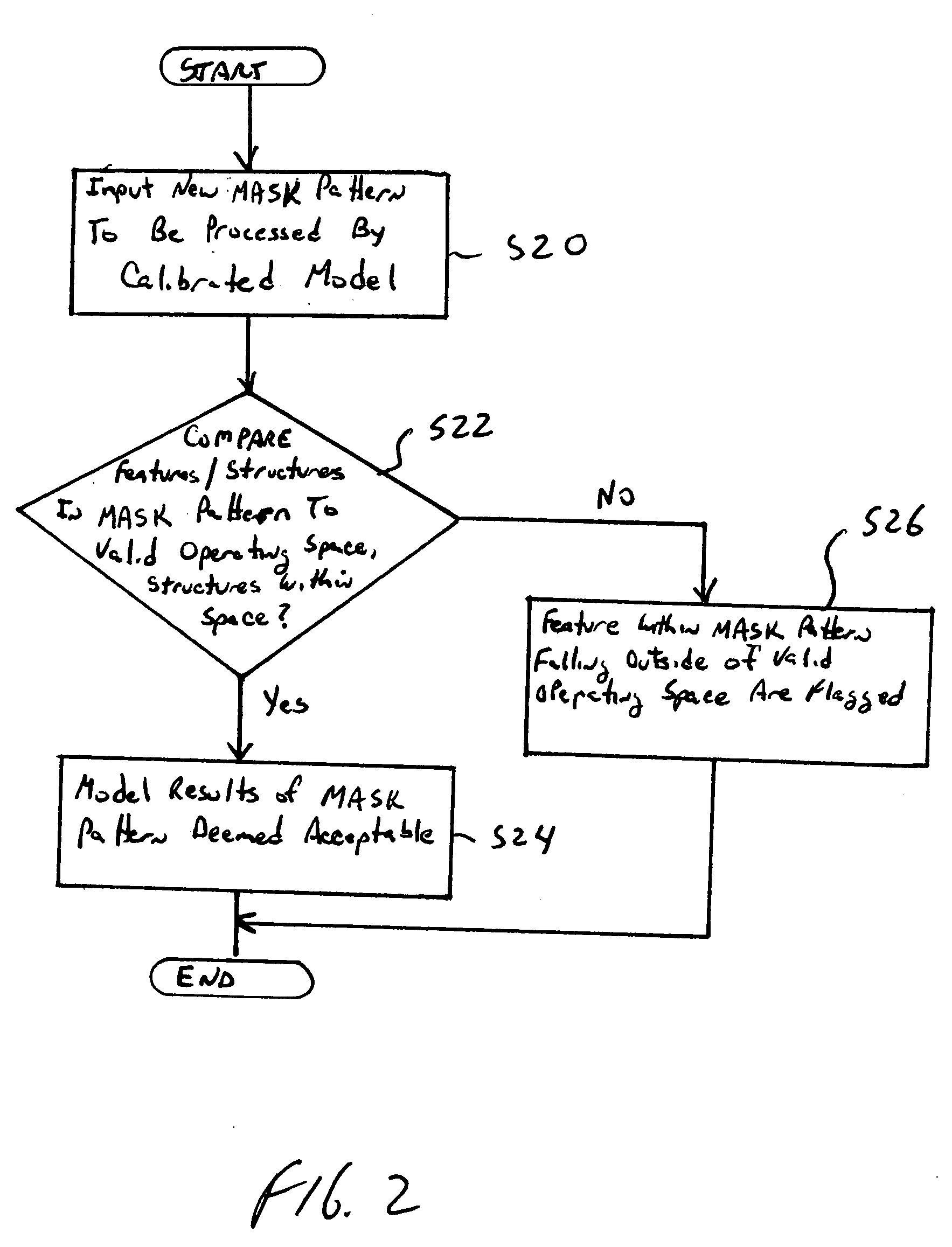
Method of manufacturing reliability checking and verification for lithography process using a calibrated eigen decomposition model
ActiveUS7342646B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionLithography processDecomposition
A method for modeling a photolithography process which includes the steps of generating a calibrated model of the photolithography process capable of estimating an image to be produced by the photolithography process when utilized to image a mask pattern containing a plurality features; and determining an operational window of the calibrated model, which defines whether or not the calibrated model can accurately estimate the image to be produced by a given feature in the mask pattern.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Sparse L-shaped array and two-dimensional DOA estimation method thereof
InactiveCN106054123ASmall amount of calculationThe parameters are accurateRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsCross correlation matrixDecomposition
The invention discloses a sparse L-shaped array and a two-dimensional DOA estimation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of wireless mobile communication. The sparse L-shaped array comprises a first subarray formed by a sparse uniform linear array, the array element space of which is equal to the wavelength, and an auxiliary array element, and a second subarray formed by an arbitrary sparse linear array, the minimum array element space of which is smaller than or equal to a half wavelength. The shared array element of the two linear arrays is a reference array element, and the distance between the auxiliary array element and the reference array element is the half wavelength. The two-dimensional DOA estimation method is characterized by, to begin with, calculating an autocorrelation matrix according to received data of the second subarray, carrying out characteristic decomposition on the autocorrelation matrix and then, estimating a corresponding second angle, and carrying out calculation to obtain an information source autocorrelation matrix based on the second angle; and obtaining an array manifold matrix of the first subarray according to a cross-correlation matrix of the received data of the two subarrays and the information source autocorrelation matrix, thereby finishing estimation of a first angle corresponding to the first subarray, and obtaining the two-dimensional DOA. Complexity is low, and DOA estimation precision is high.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method of predicting and minimizing model OPC deviation due to mix/match of exposure tools using a calibrated Eigen decomposition model
ActiveUS7242459B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusDecompositionComputer science
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
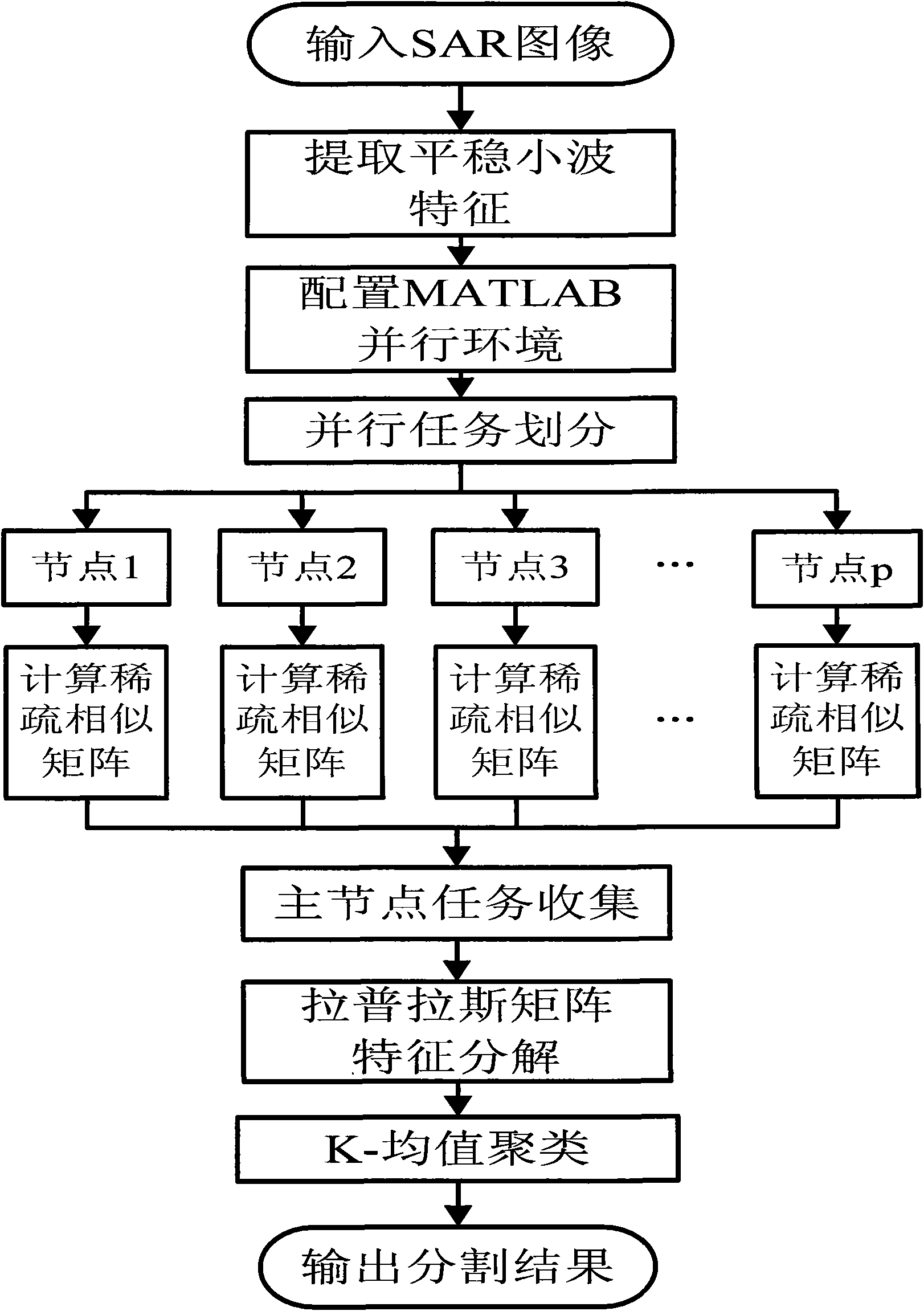
SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image segmentation method based on parallel sparse spectral clustering
InactiveCN101853491ASolve the problem of excessive calculationOvercome limitationsImage enhancementScene recognitionDecompositionSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses an SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image segmentation method based on parallel sparse spectral clustering, relating to the technical field of image processing and mainly solving the problem of limitation of segmentation application of large-scale SAR images in the traditional spectral clustering technology. The SAR image segmentation method comprises the steps of: 1, extracting features of an SAR image to be segmented; 2, configuring an MATLAB (matrix laboratory) parallel computing environment; 3, allocating tasks all to processor nodes and computing partitioned sparse similar matrixes; 4, collecting computing results by a parallel task dispatcher and merging into an integral sparse similar matrix; 5, resolving a Laplacian matrix and carrying out feature decomposition; 6, carrying out K-means clustering on a feature vector matrix subjected to normalization; and 7, outputting a segmentation result of the SAR image. The invention can effectively overcome the bottleneck problem in computation and storage space of the traditional spectral clustering technology, has remarkable segmentation effect on large-scale SAR images, and is suitable for SAR image target detection and target identification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
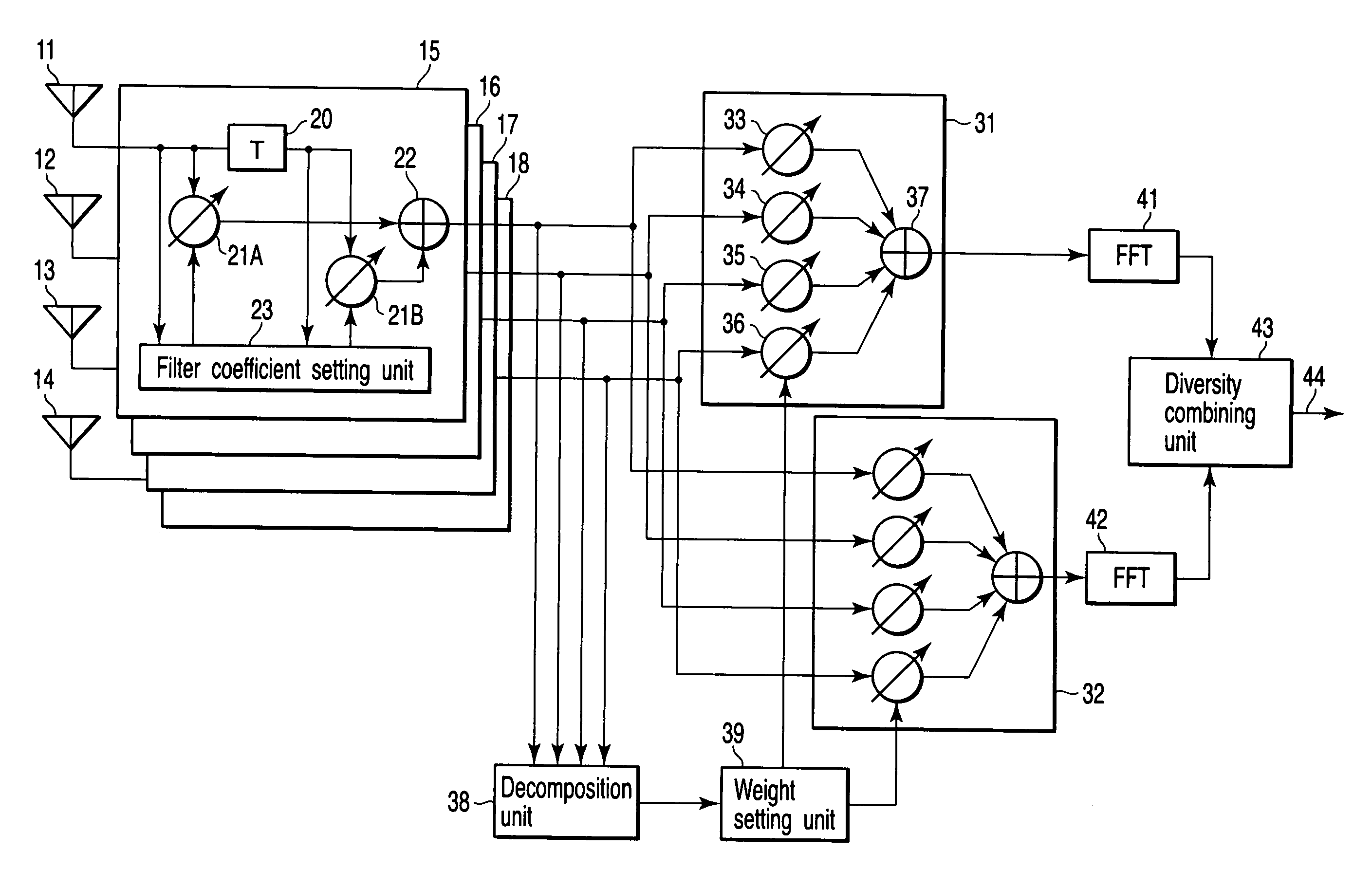
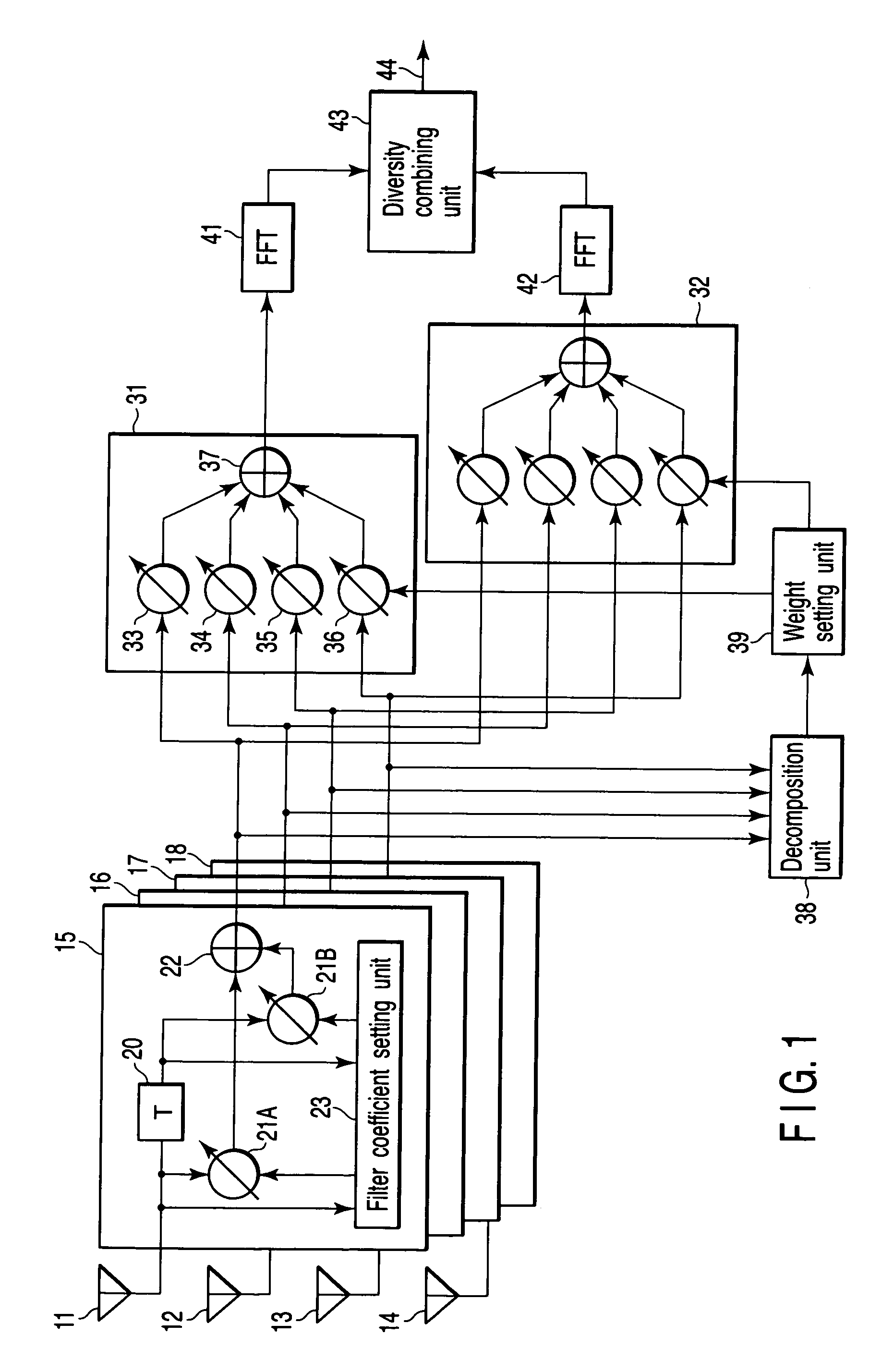
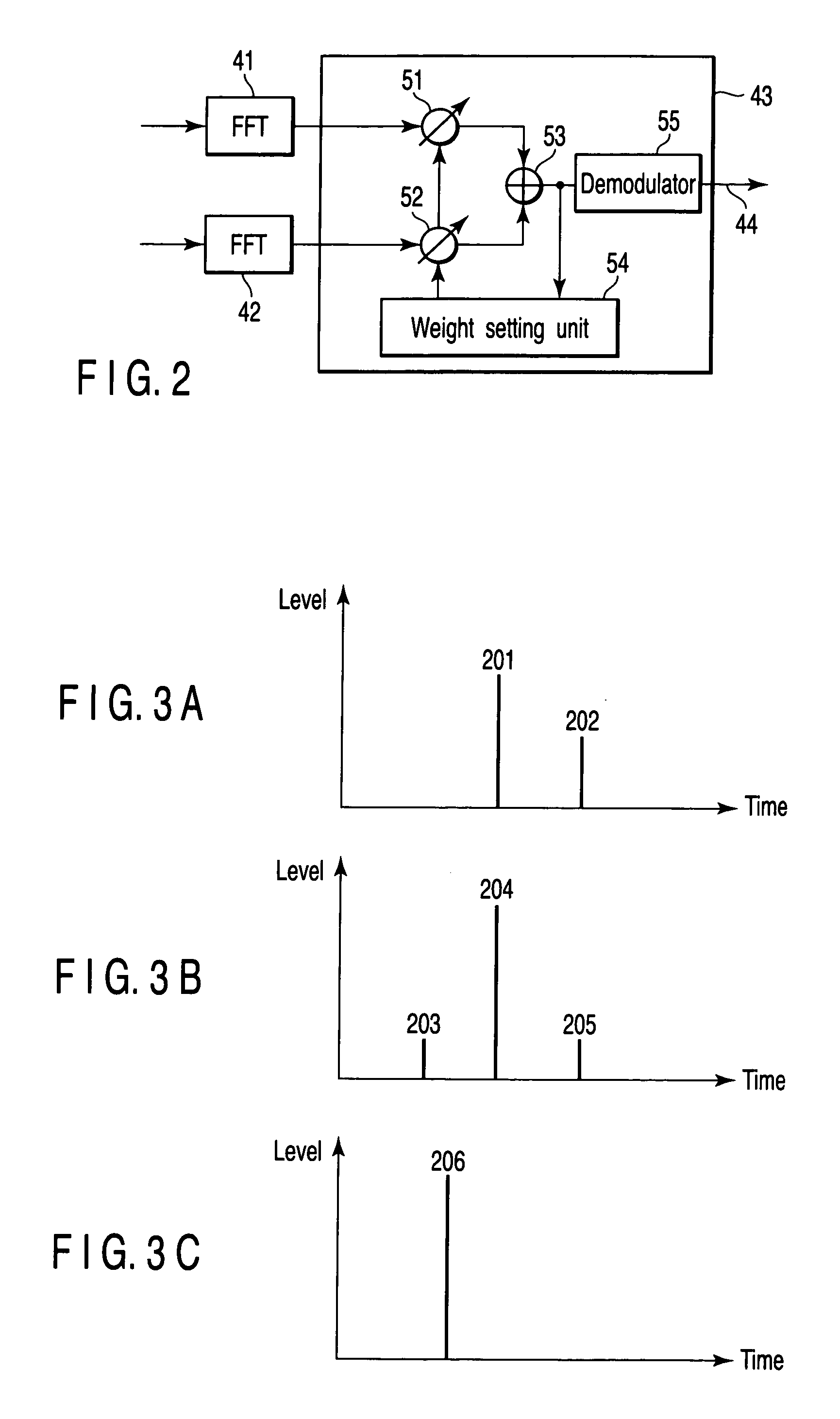
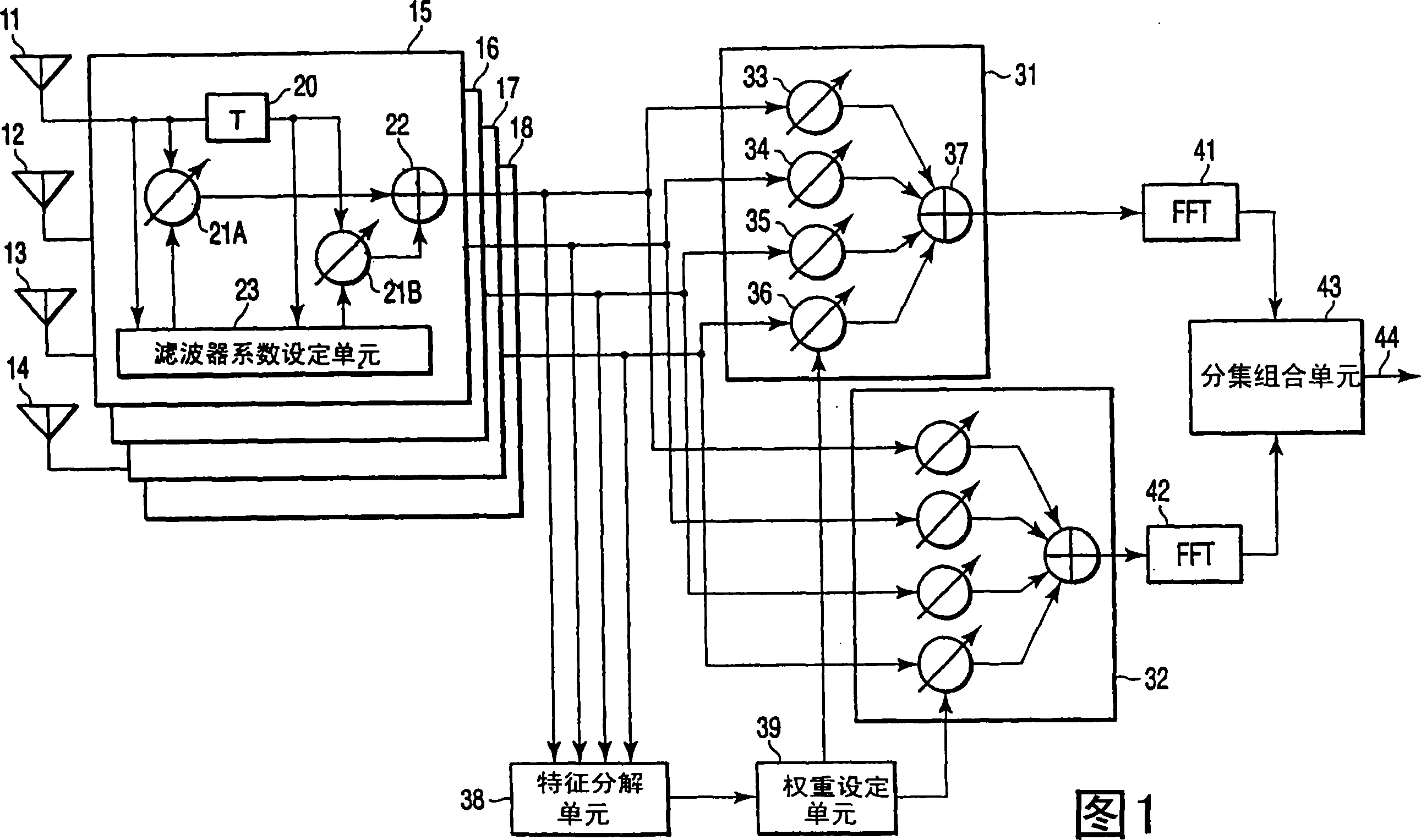
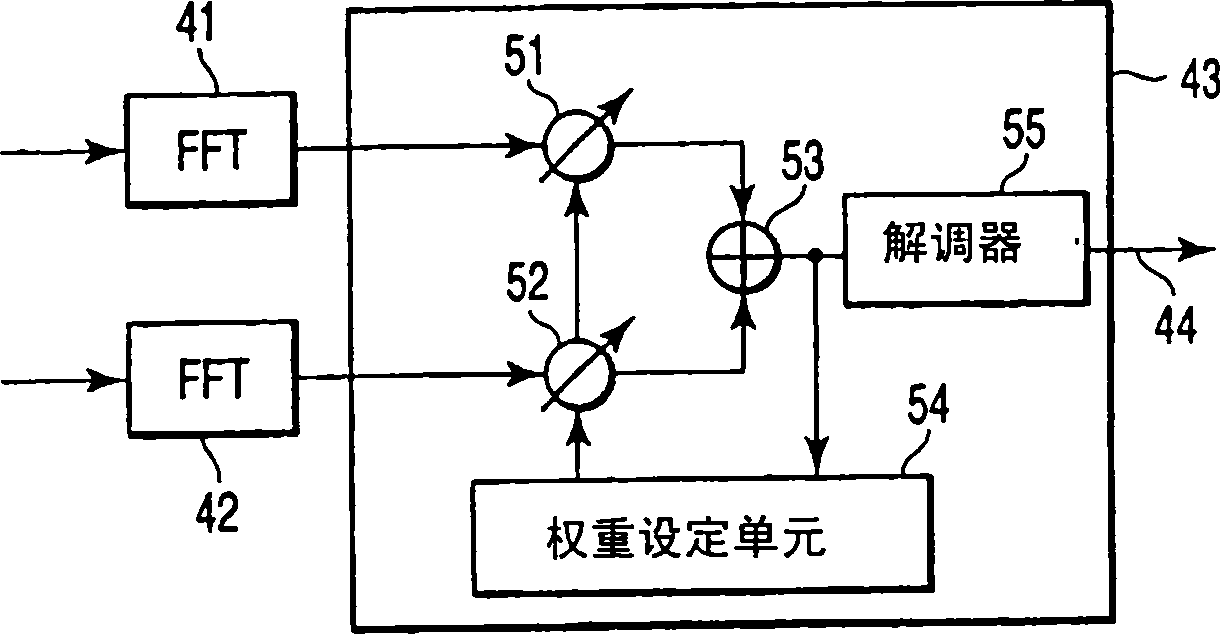
Diversity receiver device
InactiveUS20060294170A1Reduce delay spreadReduce spreadModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionDelay spreadFeature vector
A diversity receiver device includes N antennas to receive OFDM signals, N digital filters to filter the signals received by the N antennas in order to reduce delay spread, K (K≦N) beamforming units configured to subject the filtered signals to a beamforming process by using combining weights, an eigen-decomposition unit configured to subject the filtered signals to eigen-decomposition to generate N eigenvalues, a weight setting unit configured to select K eigenvalues in descending order from the generated N eigenvalues in order to set eigenvectors corresponding to the K eigenvalues to the beamforming units as the combing weight, respectively, K FFT units configured to subject the output signals of the beamforming units to fast Fourier transformation to output FFT signals, and a diversity combining unit configured to combine the FFT signals.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Multi- baseline interference synthetic aperture radar interference phase unwrapping method
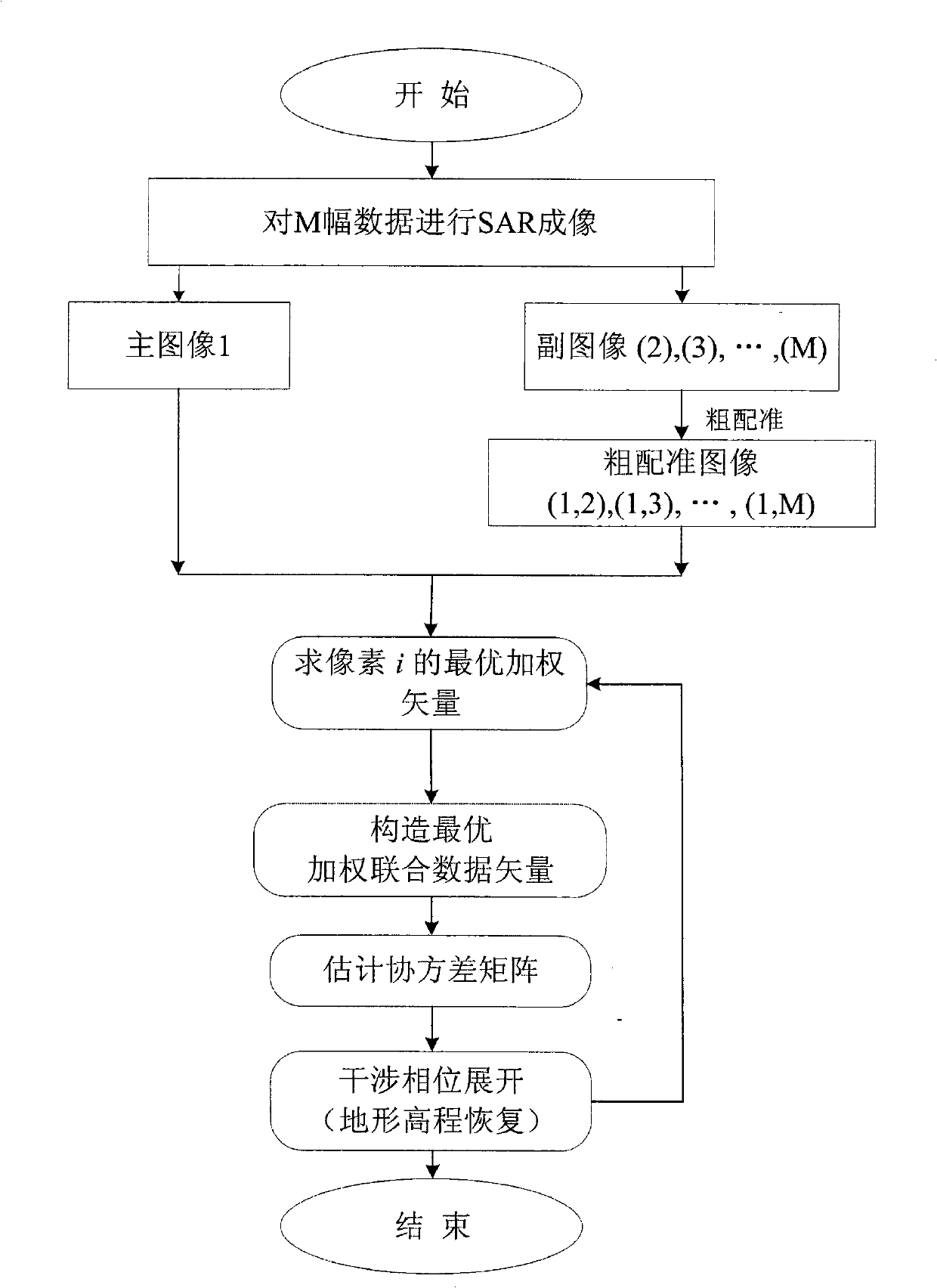
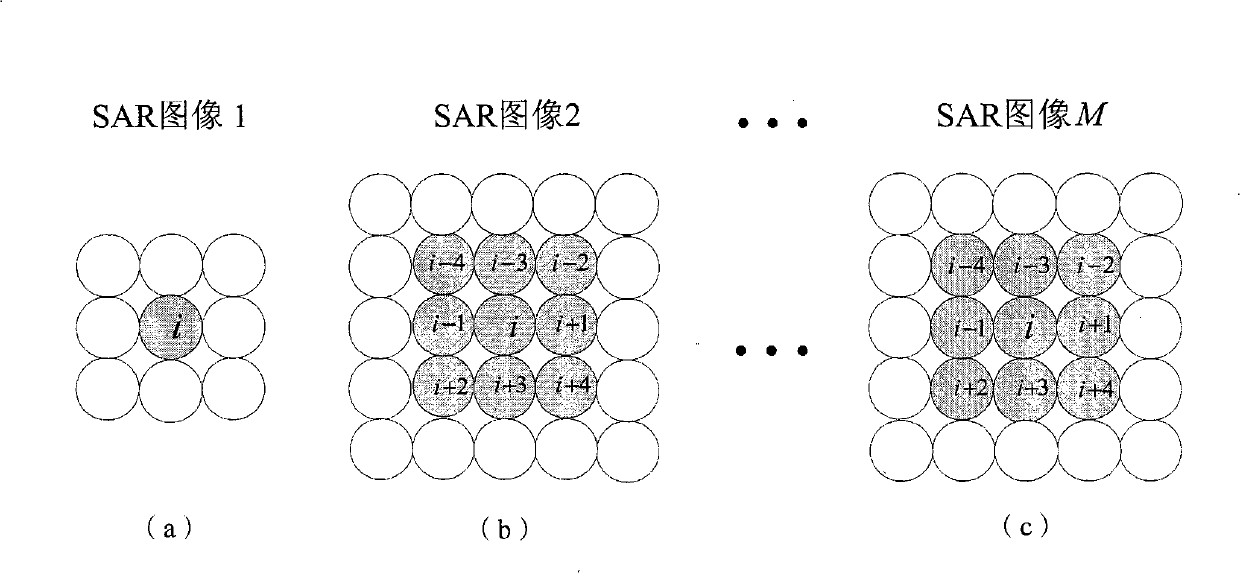
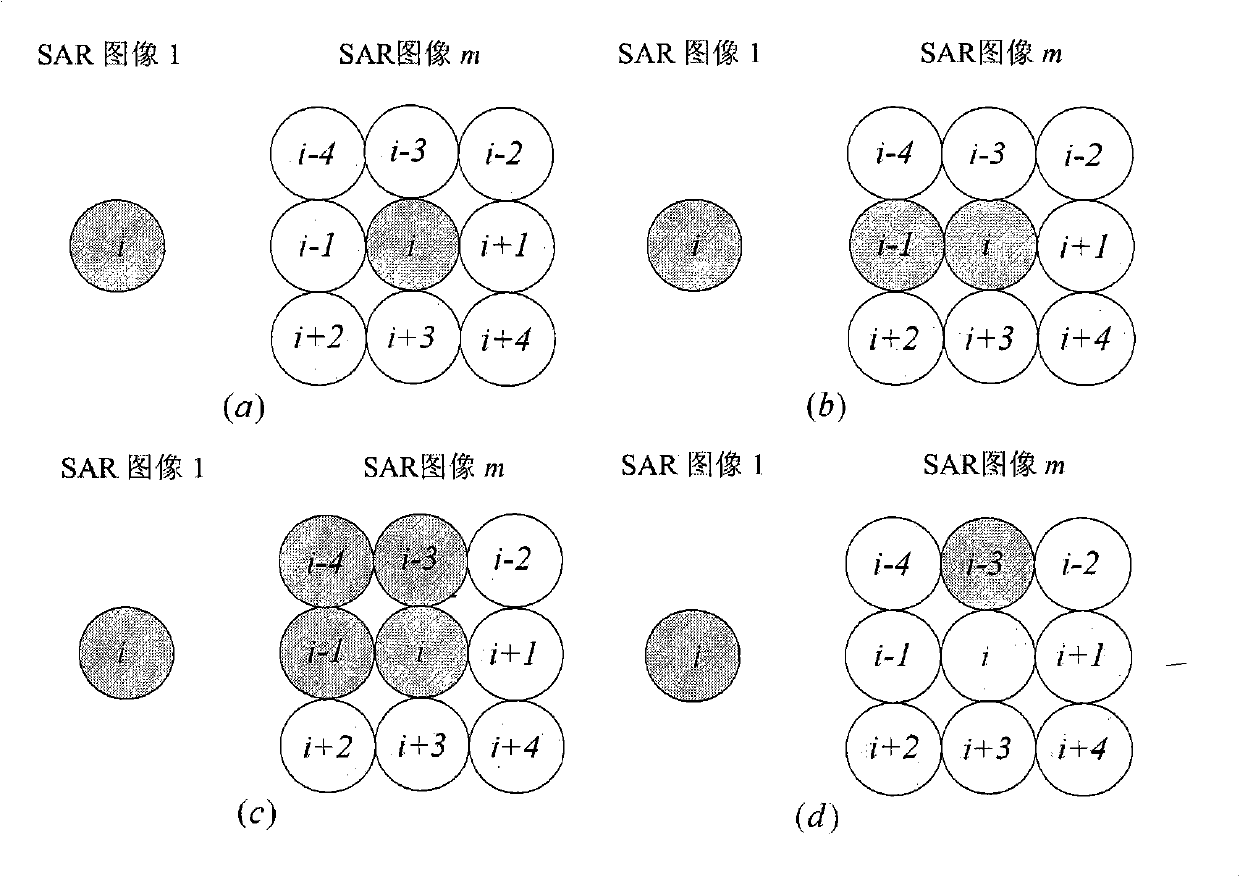
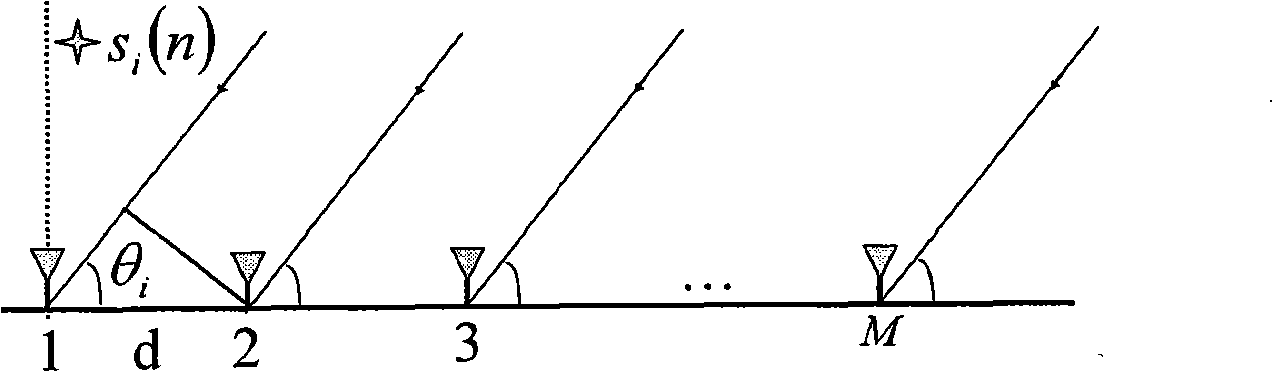
InactiveCN101339245AAccurate Dimension EstimationPrecise expansionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTerrainInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses an expansion method of an interference phase of multi-baseline interference synthetic aperture radar. The process is that a SAR imaging processing is carried out respectively to M echo data received by a satellite; any one of the images after the SAR imaging processing is selected as a main image; by using the main image as a reference, a rough registration is carried out respectively to other images through a correlation method so as to obtain M-1 roughly-registered SAR images; A roughly-registered SAR image is used for constructing an optimum weighted joint data vector jx (i, w); a covariance matrix Cov (i, w) is estimated according to the optimum weighted joint data vector and resolved characteristically so as to obtain a cost function; the interference phase phi corresponding to the minimum value of the output power of the cost function is used as the deployment result of the interference phase; the above-mentioned relevant process is repeated respectively to each of pixels to obtain the expansion result of the interference phase of the entire image. The expansion method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of small calculating amount and accurate expansion of the interference phase when the SAR image registration accuracy is bad, thereby being used for the reconstruction of a ground three-dimensional terrain with high resolution and high precision and the detection of a ground moving target.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for estimating signal wave direction
InactiveCN101325807ARemove estimated effectsReduce arityDiversity/multi-antenna systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSignal waveEstimation methods
The invention provides a signal DOA estimation method. The method supposes that an unknown noise covariance matrix has a symmetrical Toeplitz matrix character; according to the difference conception of the traditional covariance matrix, an imaginary number j is introduced so that the newly constructed covariance matrix changes into a central Hermitian matrix, thereby, the character decomposition can obtain the same DOA as the incident signal numbers. The method greatly reduces the number of the antenna array element required by estimating the signal wave arrival direction, and a wave crest is only formed in the wave arrival direction of the real signal. The method can reduce cost greatly in the practical application.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Low-complexity space target two-dimensional angle estimation method of L-shaped array MIMO radar
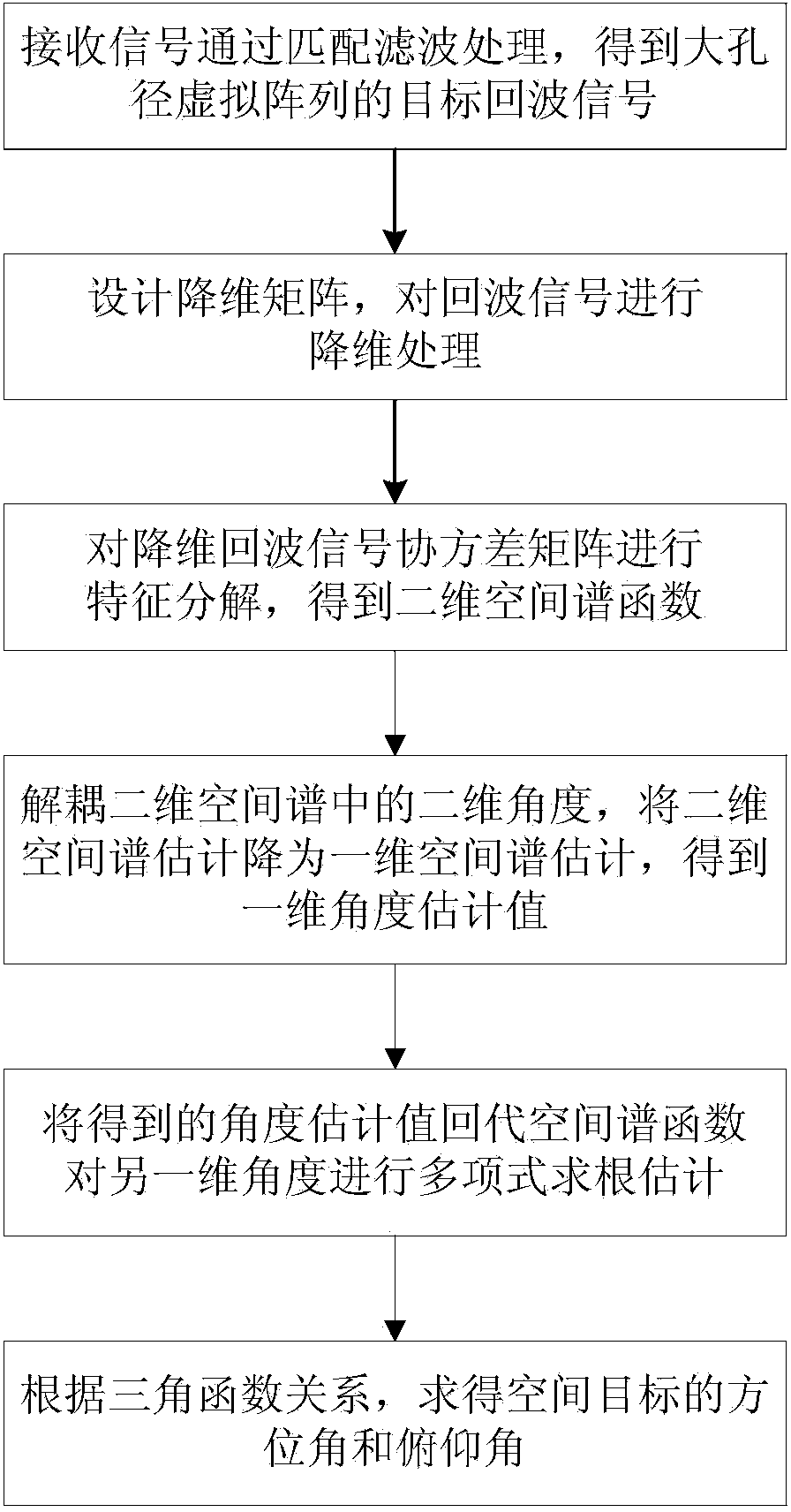
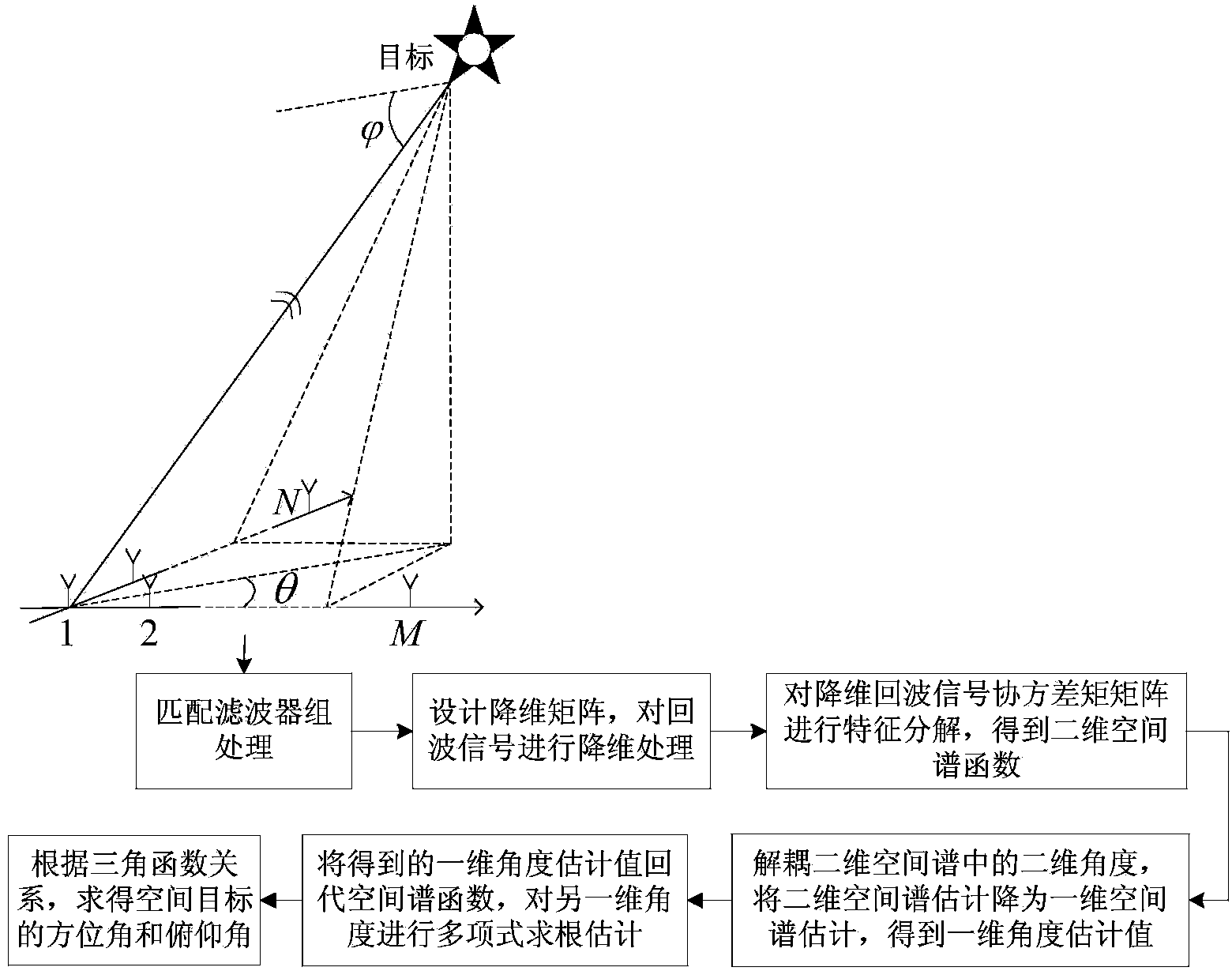
ActiveCN103901417ARealize two-dimensional positioningReduce operational complexityWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsDecomposition
The invention aims to provide a low-complexity space target two-dimensional angle estimation method of L-shaped array MIMO radar. The method comprises the following steps that an L-shaped array is composed of two uniform linear arrays perpendicular to each other, the distance between every two adjacent array elements is a half of a wavelength, one linear array has M array elements, the other linear array has N array elements, all the array elements are receiving and sending co-located array elements, orthogonal narrow-band signals are sent, received signals are processed by means of matched filtering, and echo signals of a large-aperture virtual array are obtained; a dimensionality reduction array is designed, and dimensionality reduction is conducted on the echo signals; characteristic decomposition is conducted on a covariance matrix of dimensionality reduction signals, and a two-dimensional space spectrum function is obtained; a two-dimensional angle in the two-dimensional space spectrum function is decoupled, and space spectrum estimation is conducted on the angle of one dimension; an obtained space spectrum estimated value is substituted into the space spectrum function, and polynomial rooting estimation is conducted on the angle of the other dimension; according to the relation of trigonometrical functions, the azimuth angle and pitching angle of a target are obtained. The method greatly reduces computational complexity of algorithm, and is beneficial to real-time processing of a radar system.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Multi-target location method of bistatic common-address multi-input-multi-output radar
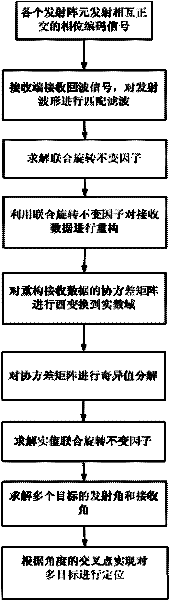
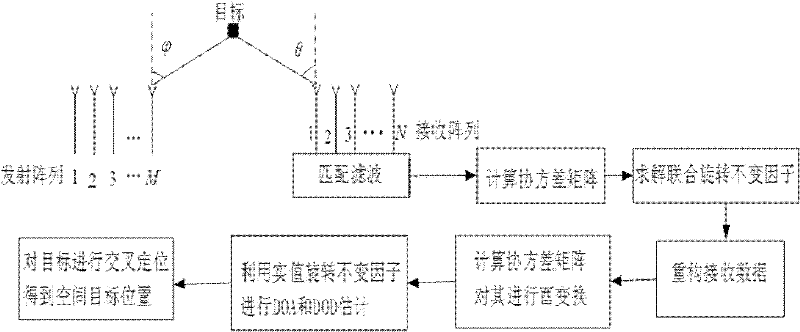
InactiveCN102213761AHigh precisionAvoid simultaneous application to the transmitterRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSingular value decompositionDomain name
The invention provides a multi-target location method of a bistatic common-address multi-input-multi-output radar. The method comprises the following steps of: transmitting mutual orthogonal phase coded signals by M transmitting array elements; receiving the phase coded signals by N receiving array elements; performing matching filtering on the received phase coded signals by a matching filter ofeach receiver which is used for receiving the array elements; reconfiguring covariance matrix of signal data subjected to matching filtering; performing unitary transformation on the reconfigured covariance matrix to obtain the covariance matrix of a real number field; performing singular value decomposition on the covariance matrix of the real number field; estimating emission angles and acceptance angles of a plurality of objects by utilizing actual value combination spinning invariant factor; and realizing multi-target location according to a cross point of the two angles to obtain the position of a space object. According to the method, the combination spinning invariant factor is adopted to reconfigure the receiving data so as to improve the estimation performance of an object; and the covariance matrix of the real number field is obtained through unitary transformation, and characteristic decomposition is performed on the covariance matrix of the real number field so as to be favorable for real-time processing and realization on hardware.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method of manufacturing reliability checking and verification for lithography process using a calibrated eigen decomposition model
ActiveUS20050210437A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionLithography processDecomposition
A method for modeling a photolithography process which includes the steps of generating a calibrated model of the photolithography process capable of estimating an image to be produced by the photolithography process when utilized to image a mask pattern containing a plurality features; and determining an operational window of the calibrated model, which defines whether or not the calibrated model can accurately estimate the image to be produced by a given feature in the mask pattern.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
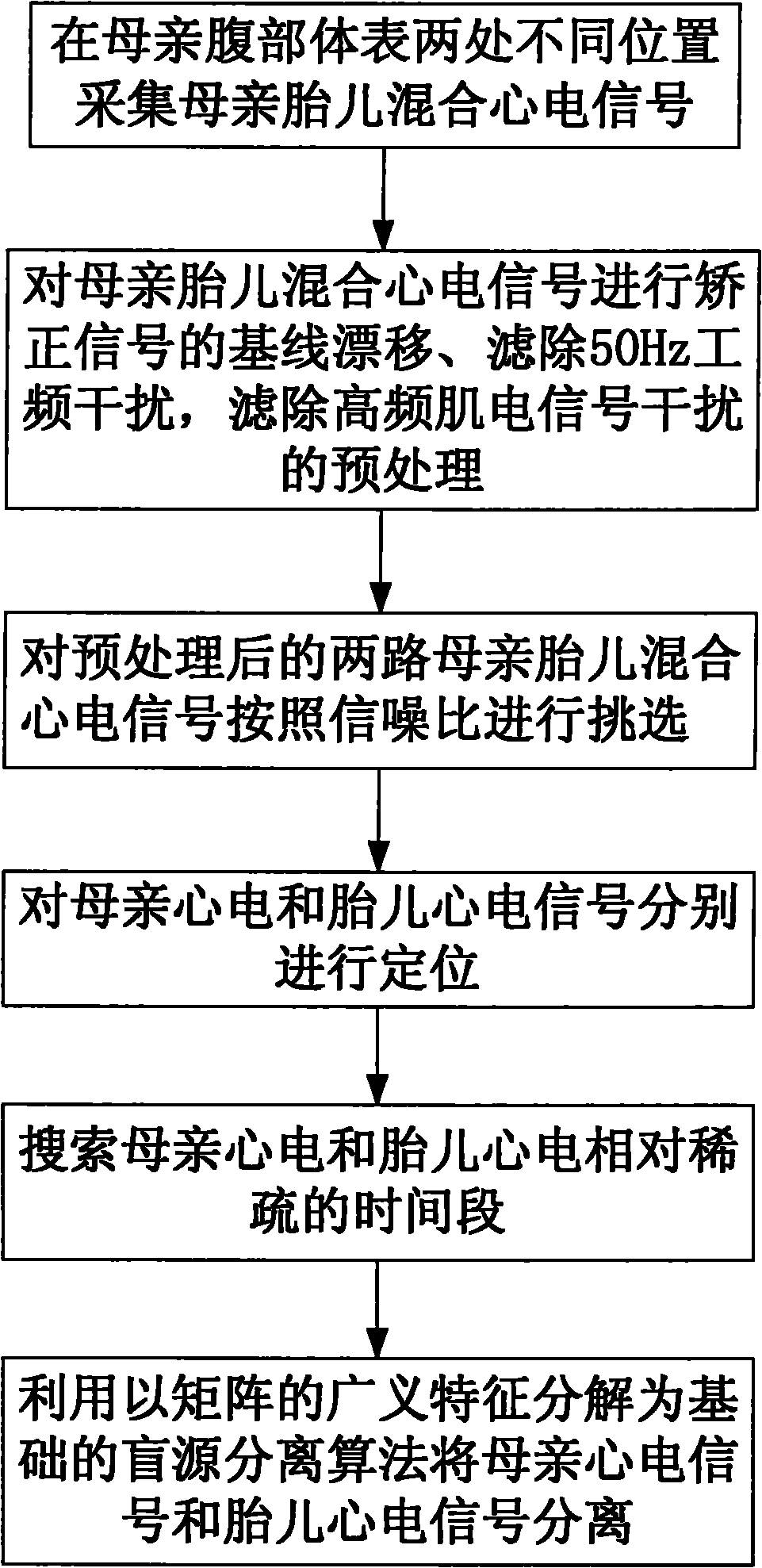
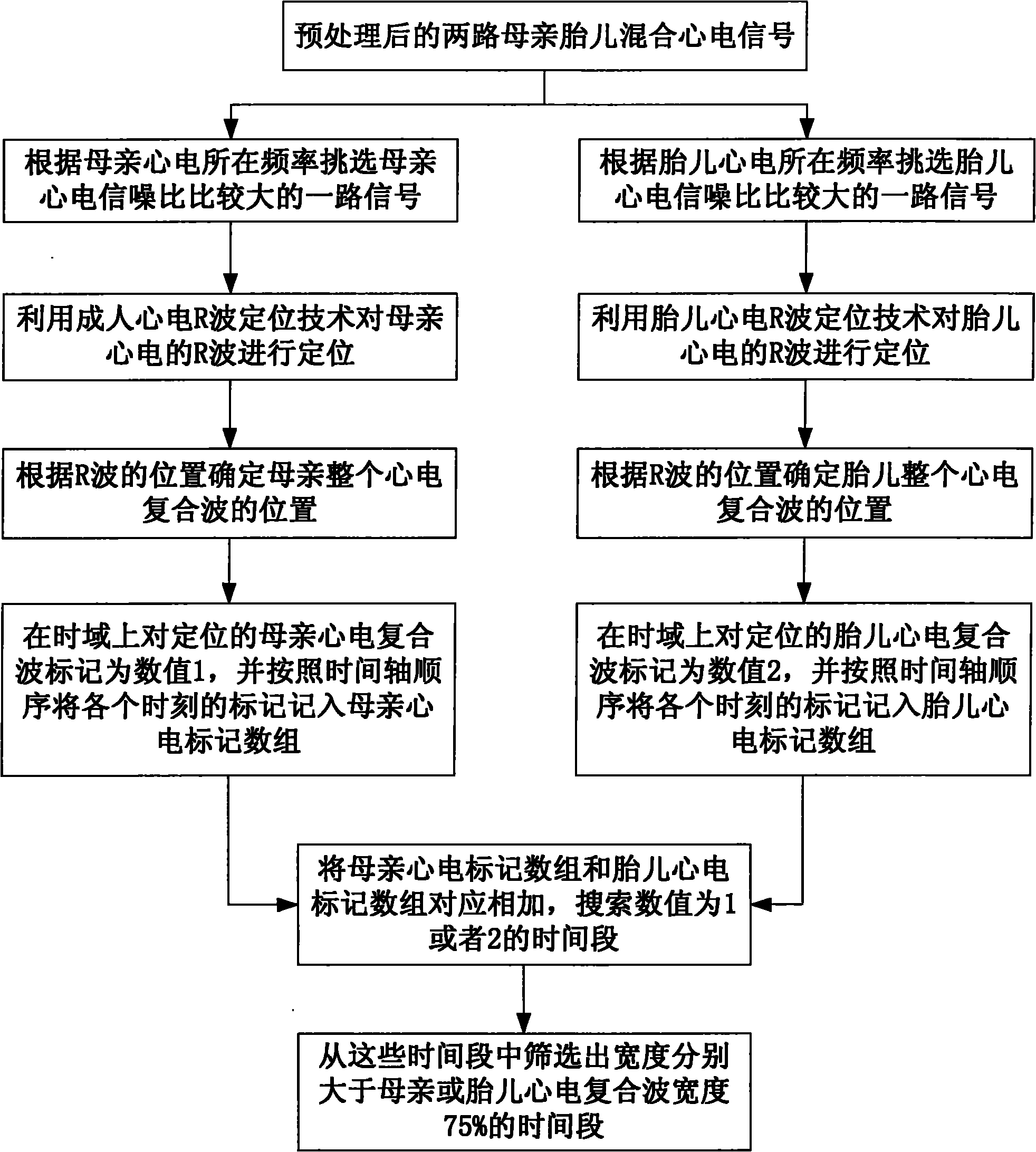
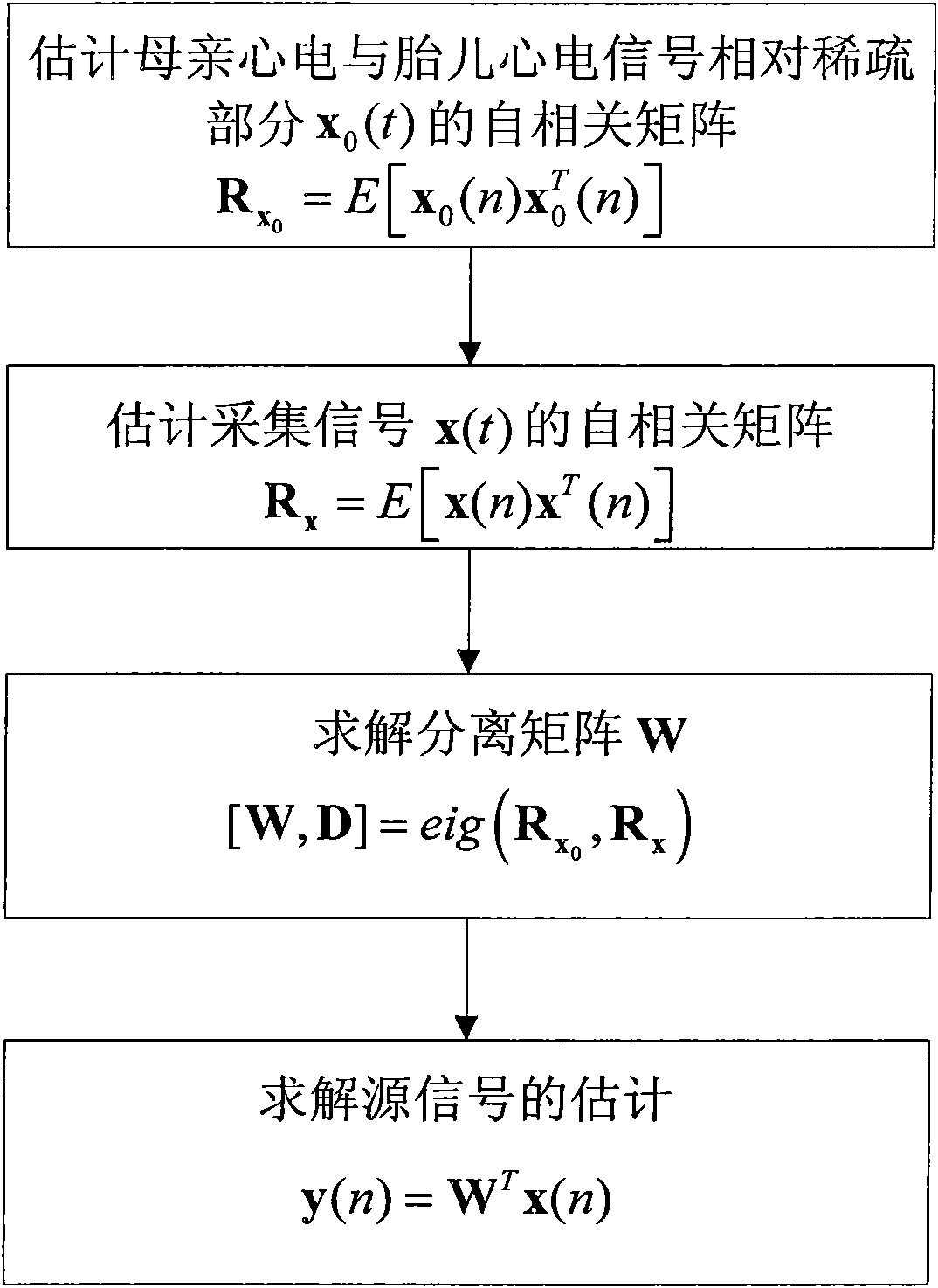
Fetus electrocardio blind separation method based on relative sparsity of time domain of source signal
InactiveCN101972145ASolve problems that overlap and are difficult to separateEfficient and accurate extractionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalMedical diagnosis
The invention provides a fetus electrocardio blind separation method based on the relative sparsity of time domains of source signals, comprising the following steps of: firstly acquiring mutually overlaid mother-fetus mixed electrocardiosignals of mother and fetus electrocardio in two paths from the body surface of the abdomen of a mother; then carrying out pretreatment on the acquired mother-fetus mixed electrocardiosignals, wherein the pretreatment includes the steps of: correcting the baseline drift of the mother-fetus mixed electrocardiosignals, and filtering the interference of power frequency of 50 Hz, the interference of high-frequency myoelectric signals, and the like; respectively positioning the mother electrocardiosignal and the fetus electrocardiosignal in the pretreated mother-fetus mixed electrocardiosignals; then searching relatively sparse time slices of the mother electrocardio and the fetus electrocardio; and finally separating the mother electrocardiosignal from the fetus electrocardiosignal by utilizing a basic blind source separation algorithm resolved through the general features of a matrix. The invention solves the problem that the time domains and frequency domains of the mother electrocardiosignal and the fetus electrocardiosignal are mutually overlaid and difficult to separate and can efficiently and accurately extract the fetus electrocardiosignal used for medical diagnosis.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
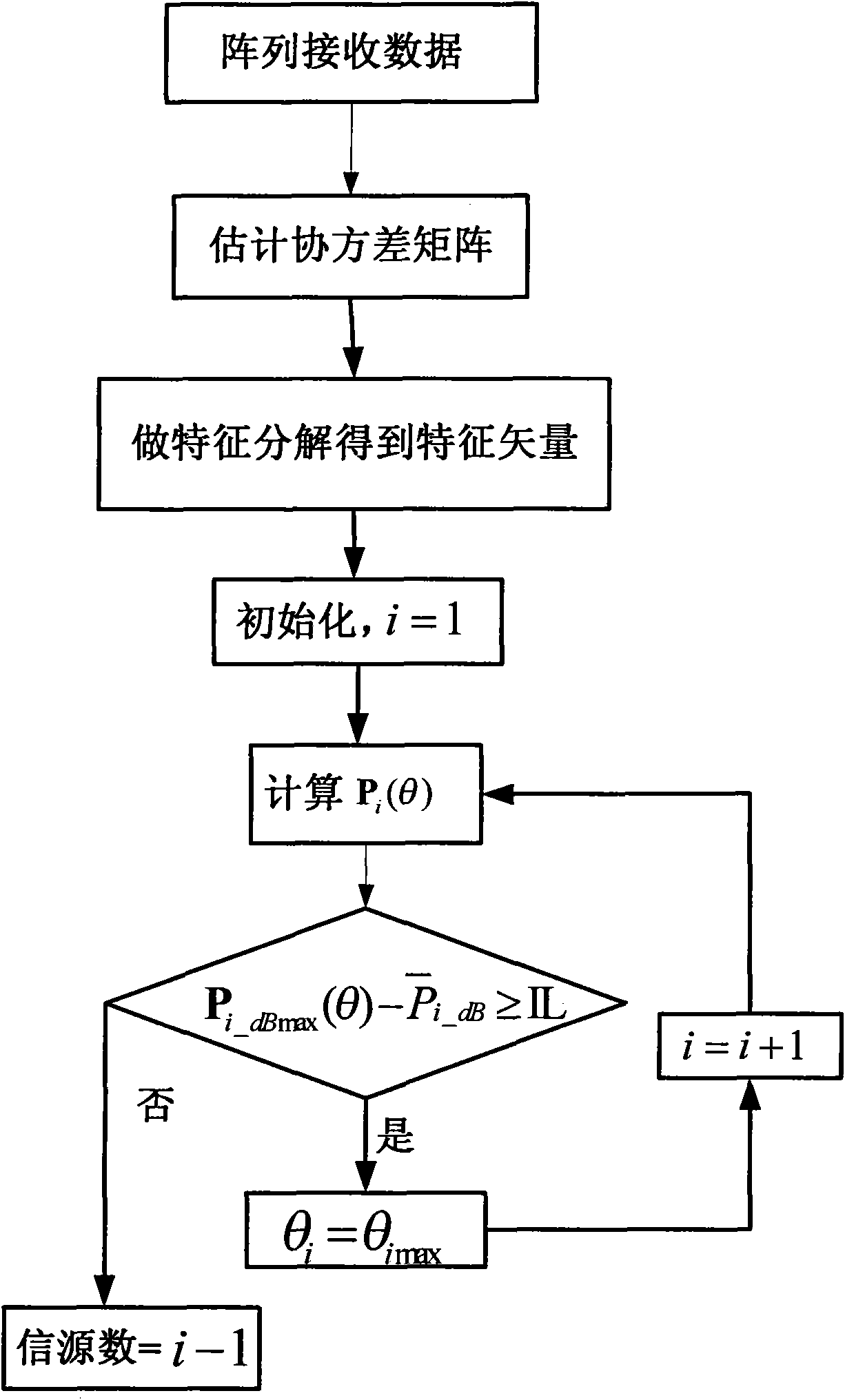
Method for estimating direction of arrival and information source number of strong and weak signals
ActiveCN101795150ASimple calculationReduce computationSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionRadarDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for estimating a direction of arrival and an information source number of strong and weak signals, which mainly solves the problem that the conventional method cannot accurately estimate the direction of arrival of the strong and weak signals when the information source number is unknown. The method comprises the following implementing processes: estimating a covariance matrix according to array receiving data; performing characteristic decomposition on the covariance matrix to acquire characteristic values arranged in a descending order and corresponding characteristic vectors; calculating spatial spectrums of characteristic beams in turn from the first characteristic vector; and estimating the direction of arrival and the information source number of each signal by comparing the difference between a maximum value of the spatial spectrums and an average value outside a main lobe beam width with a set threshold value. The method is simple and practical, can accurately estimate the direction of arrival and the information source number of the strong and weak signals when a plurality of strong and weak signals are coexistent, and can be used for extracting information or suppressing interference in numerous fields of radar, communication, navigation, measurement and control and electronic reconnaissance.
Owner:XIAN DAHENG TIANCHENG IT CO LTD
Eigen decomposition based OPC model
InactiveUS7398508B2Minimal interventionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionResistPUPILLARY FUNCTIONS
Model OPC is developed based on eigen decomposition of an aerial image expected to be produced by a mask pattern on a surface of a resist. With the eigen decomposition method the aerial image intensity distribution around a point (x, y) is accurately described in the model. A scalar approach may be used in the eigen decomposition model which treats the light wave through the mask as a scalar quantity. A eigen decomposition alternatively may use a vector approach which utilizes a vector to describe the light wave and the pupil function. A predicted SPIF may be generated from the aerial image which may be used to verify the mask modeling process by comparing the predicted SPIF to an experimentally determined SPIF. The model OPC, once calibrated, may be used to evaluate performance of a mask and refine features of the mask.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Face image age estimation method, device and terminal equipment
ActiveCN107169454AImprove robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsTerminal equipmentComputer vision
The invention belongs to the technical field of convolutional neural networks, and provides a face image age estimation method, device and terminal equipment. The method includes building a convolutional neural network model including a potential factorization layer; initializing the convolutional neural network model; inputting preprocessed images to the initialized convolutional neural network model, and training the initialized convolutional neural network model through a counterpropagation method based on an age loss function according to the preprocessed images; and inputting a face image to be detected to the trained convolutional neural network model, and outputting the age of the face in the face image to be detected. The potential factorization layer decomposes features of the image into components related with age which need to be obtained and related components unrelated with age, so training and detection can be performed based on the components related with age, so that the convolutional neural network model has relatively good robustness.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device for estimating two-dimensional direction of arrival (DOA) of coherent signals based on L array and method thereof
InactiveCN102253363ARadio wave finder detailsRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsCross correlation matrixDecomposition
The invention provides a device for estimating two-dimensional direction of arrival (DOA) of coherent signals based on an L array and a method thereof. The method is characterized by carrying out communication connection on a longitudinal x-direction equidistant linear subarray antenna, a vertical z-direction equidistant linear subarray antenna, an instantaneous correlation computation device, an instantaneous correlation matrix computation device, a linear operation sub-estimation device, a DOA estimation device and a DOA angle pairing device, utilizing a subarray averaging technology to carry out decorrelation on the incident signals, simultaneously implementing linear operation on cross-correlation matrices of L array received data to obtain null space, firstly estimating an angle of pitch and an azimuth angle respectively, then paring the angle of pitch and the azimuth angle and finally obtaining the azimuth angle according to the geometrical relationship, and the method dispenses with eigen-decomposition and has high computation efficiency.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
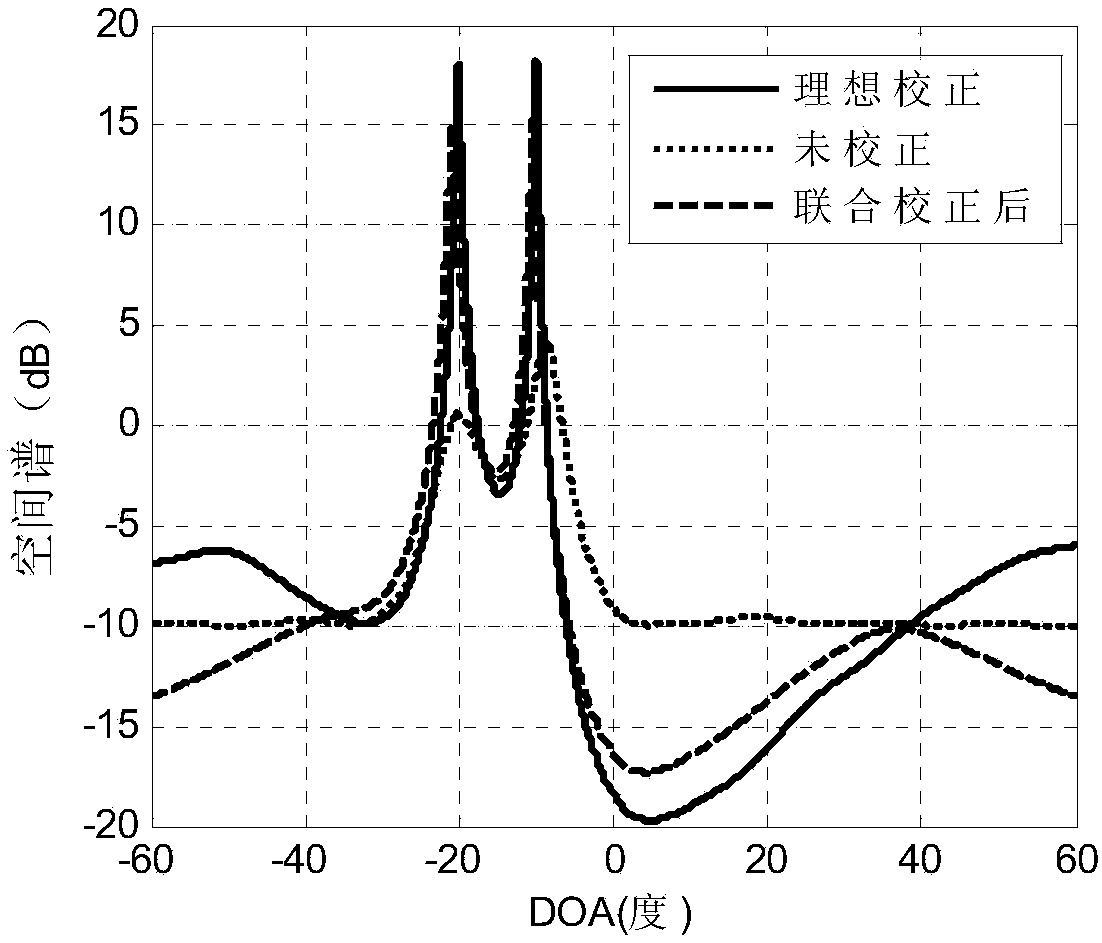
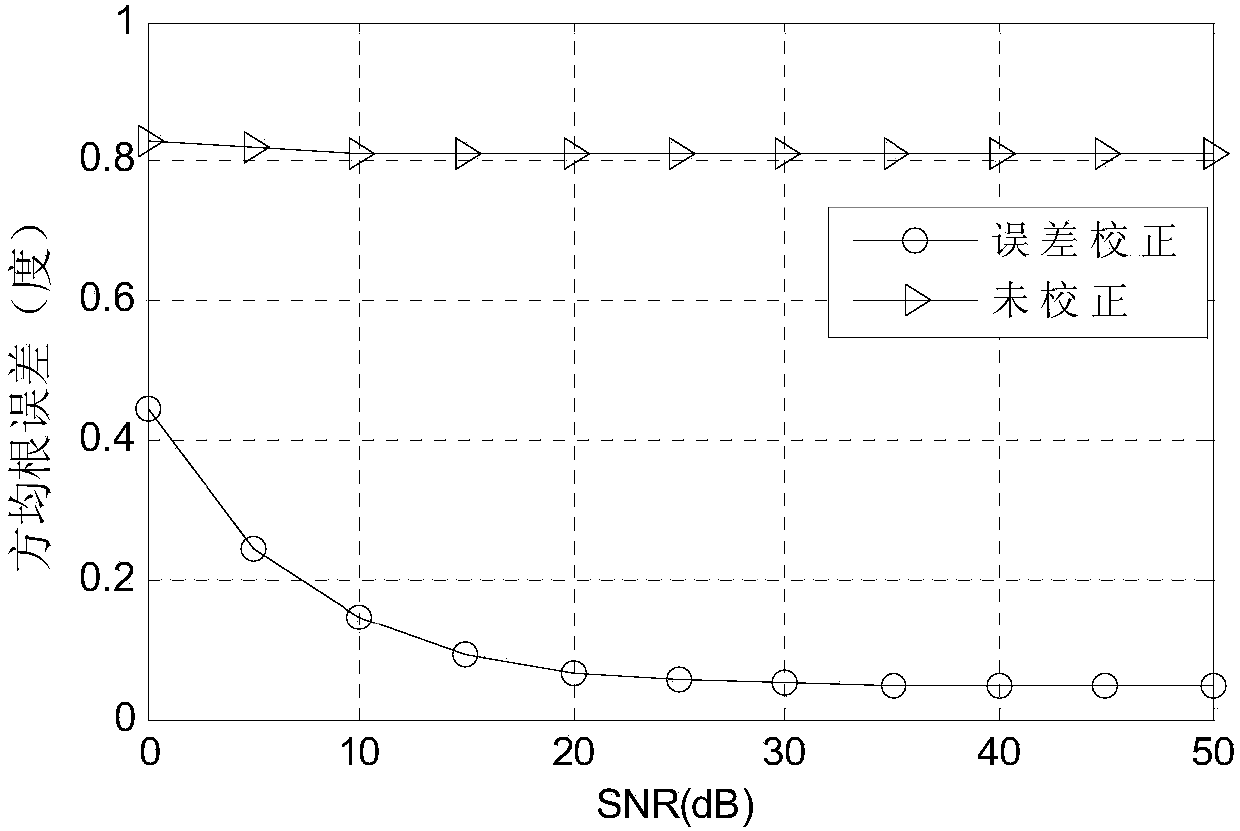
Method of correcting various array errors in wave-reaching direction estimation
InactiveCN107037397AReduce mistakesReduce complexityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsError processingEstimation methods
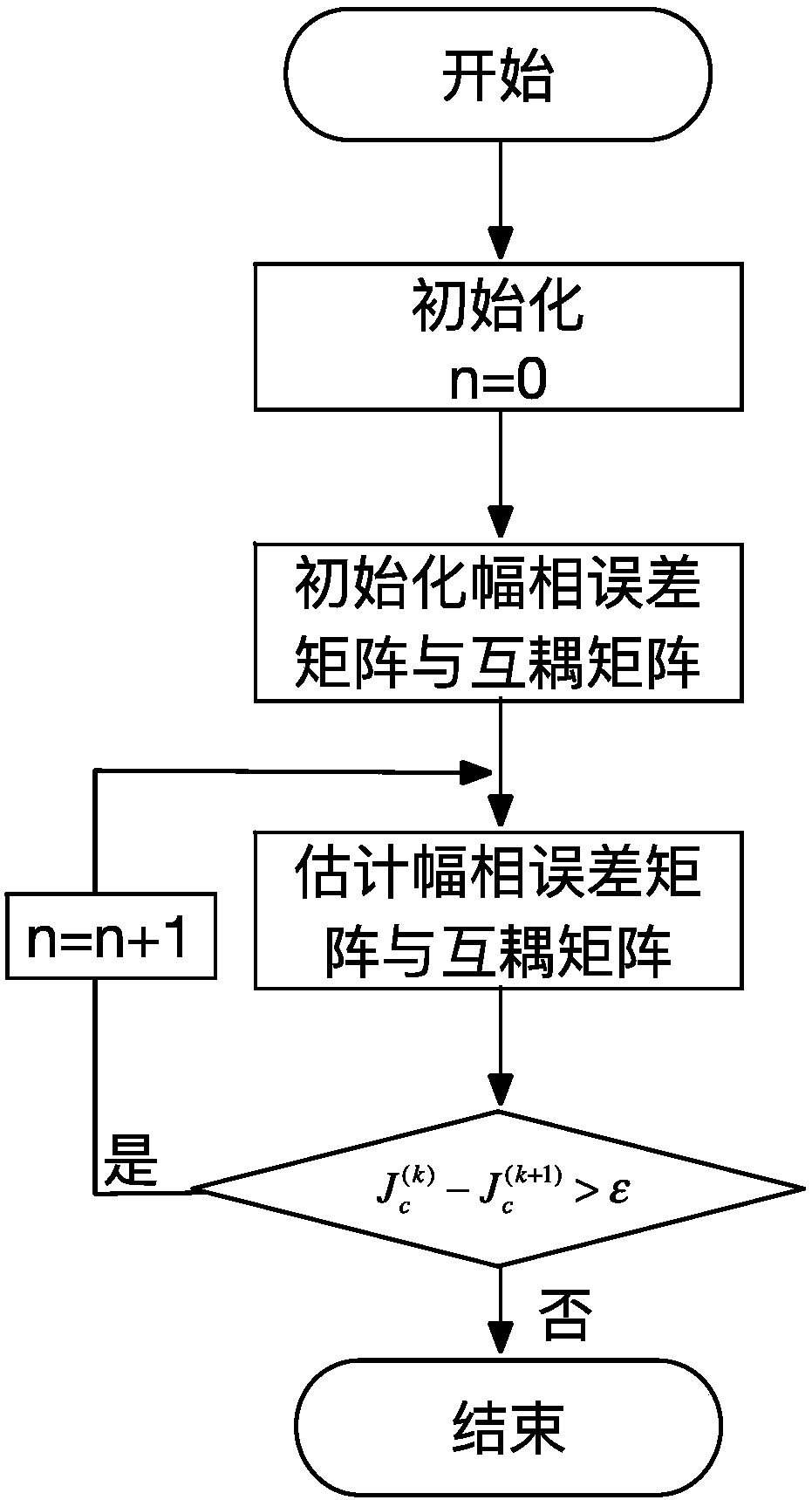
The invention relates to an error estimation method in wave-reaching direction estimation and in particular to a method of correcting various array errors in wave-reaching direction estimation. In order to overcome the defects that the processing speed is relatively low and the complexity is relatively high as an existing array error processing method always corrects one error, the invention provides the method of correcting various array errors in wave-reaching direction estimation. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring an amplitude and phase error matrix and a cross coupling array; obtaining a characteristic decomposition covariance matrix, a noise sub-spatial matrix and an estimation matrix according to a MUSIC algorithm; defining a spatial spectrum; searching for DOA estimation of N peak values in the spatial spectrum; solving an estimated value of an amplitude and phase inconsistency error matrix; solving an estimated value of the cross coupling matrix; calculating a cost function; giving a threshold, and if the difference between the adjacent iterated cost functions twice is greater than the threshold, performing continuous iteration; and if not, escaping circulation to obtain a to-be-estimated parameter. The method provided by the invention is suitable for estimating the wave-reaching direction in the presence of the array error.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Diversity receiver device
A diversity receiver device includes N antennas to receive OFDM signals, N digital filters to filter the signals received by the N antennas in order to reduce delay spread, K (K<=N) beamforming units configured to subject the filtered signals to a beamforming process by using combining weights, an eigen-decomposition unit configured to subject the filtered signals to eigen-decomposition to generate N eigenvalues, a weight setting unit configured to select K eigenvalues in descending order from the generated N eigenvalues in order to set eigenvectors corresponding to the K eigenvalues to the beamforming units as the combing weight, respectively, K FFT units configured to subject the output signals of the beamforming units to fast Fourier transformation to output FFT signals, and a diversity combining unit configured to combine the FFT signals.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Personal music recommendation mapping
InactiveUS20100328312A1Digital data information retrievalDrawing from basic elementsGraphicsData set
Scale free network datasets, such as music tracks, playlists and other media item recommendations are analyzed and presented in a graphic map display (FIG. 1) for visualization, preferably in an interactive environment (FIG. 2). A plotting and visualization system generally comprises a network extraction routine, coupled with a high performance eigendecomposition (map layout calculation) algorithm, and a novel visualization interaction methodology.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com