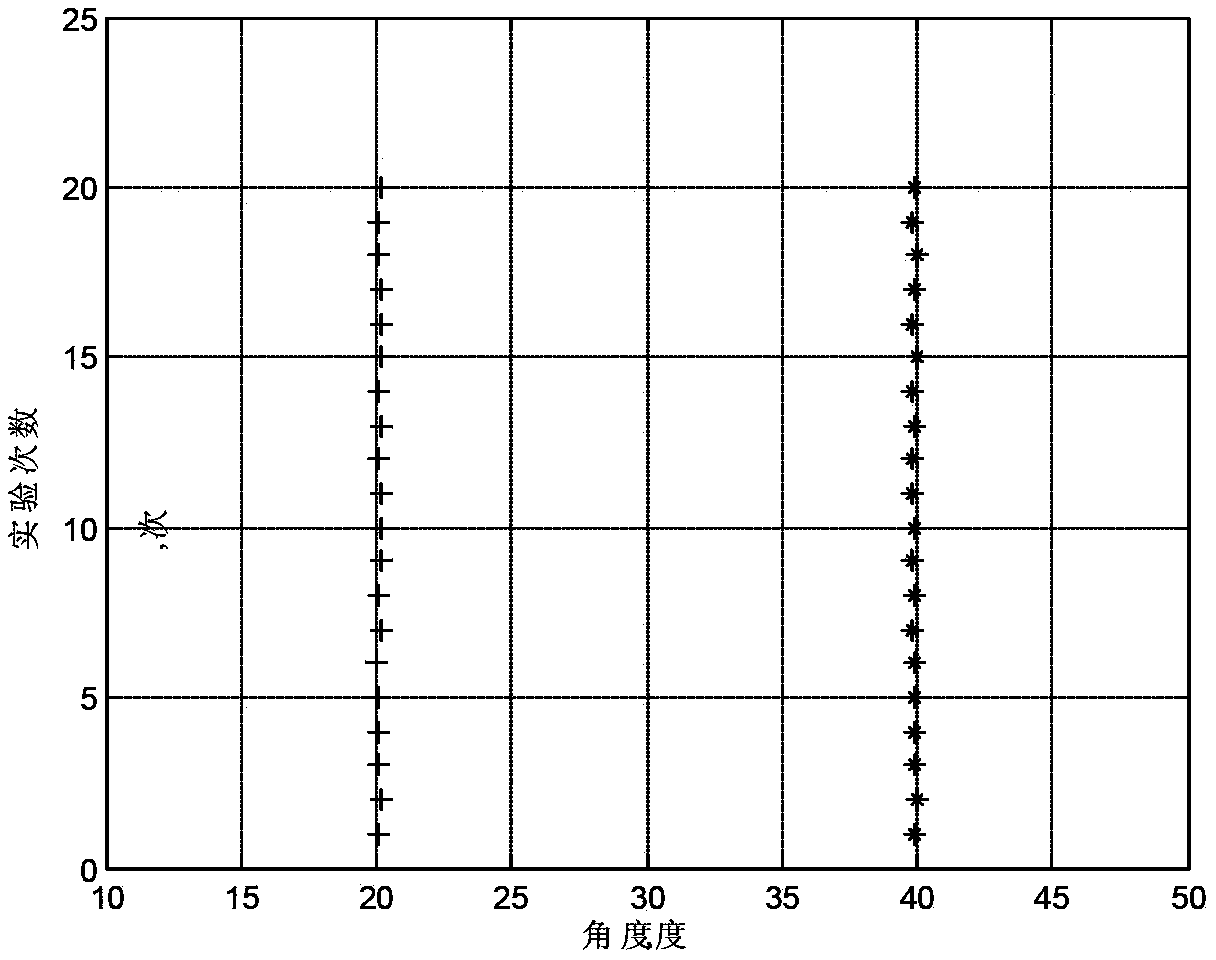
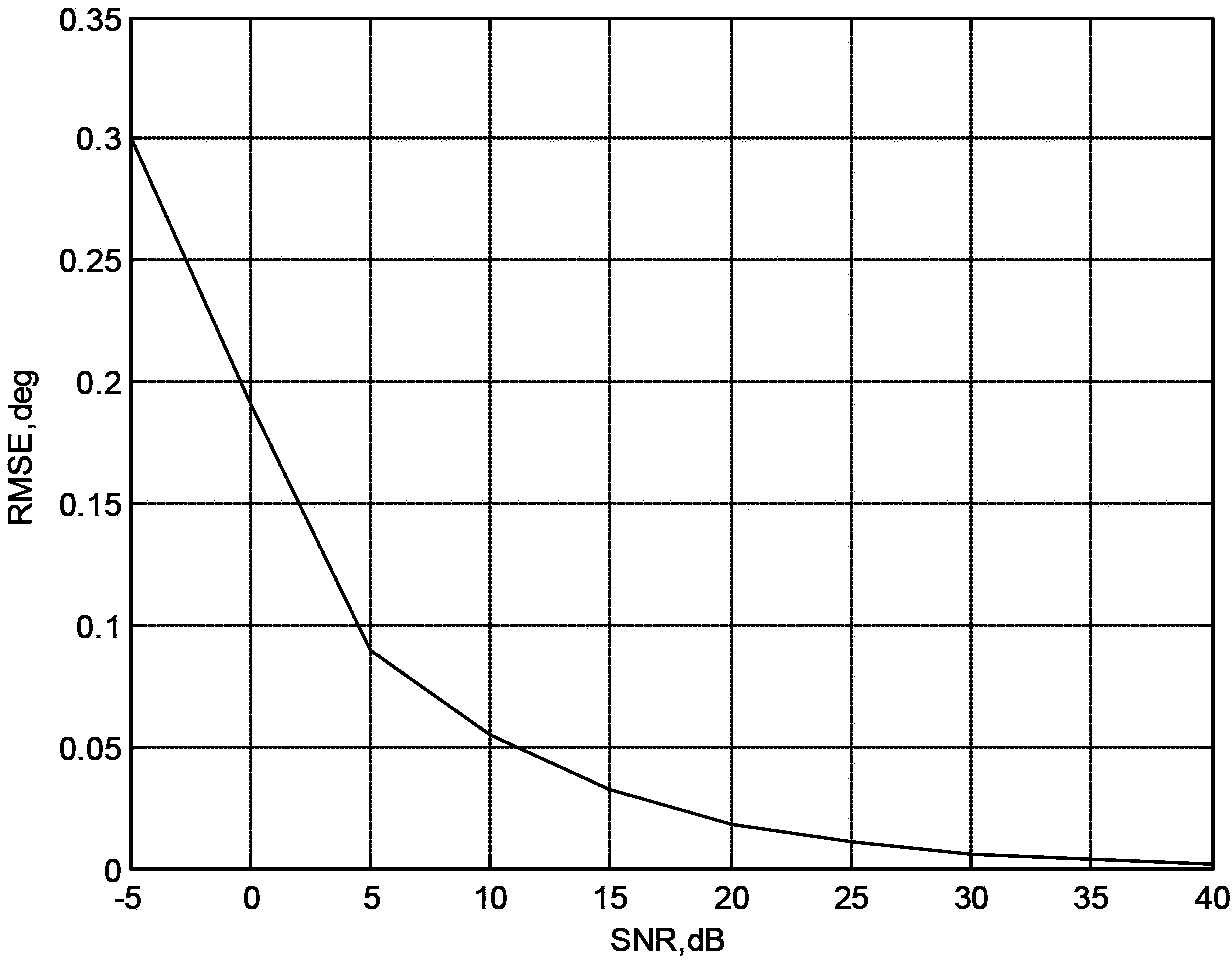
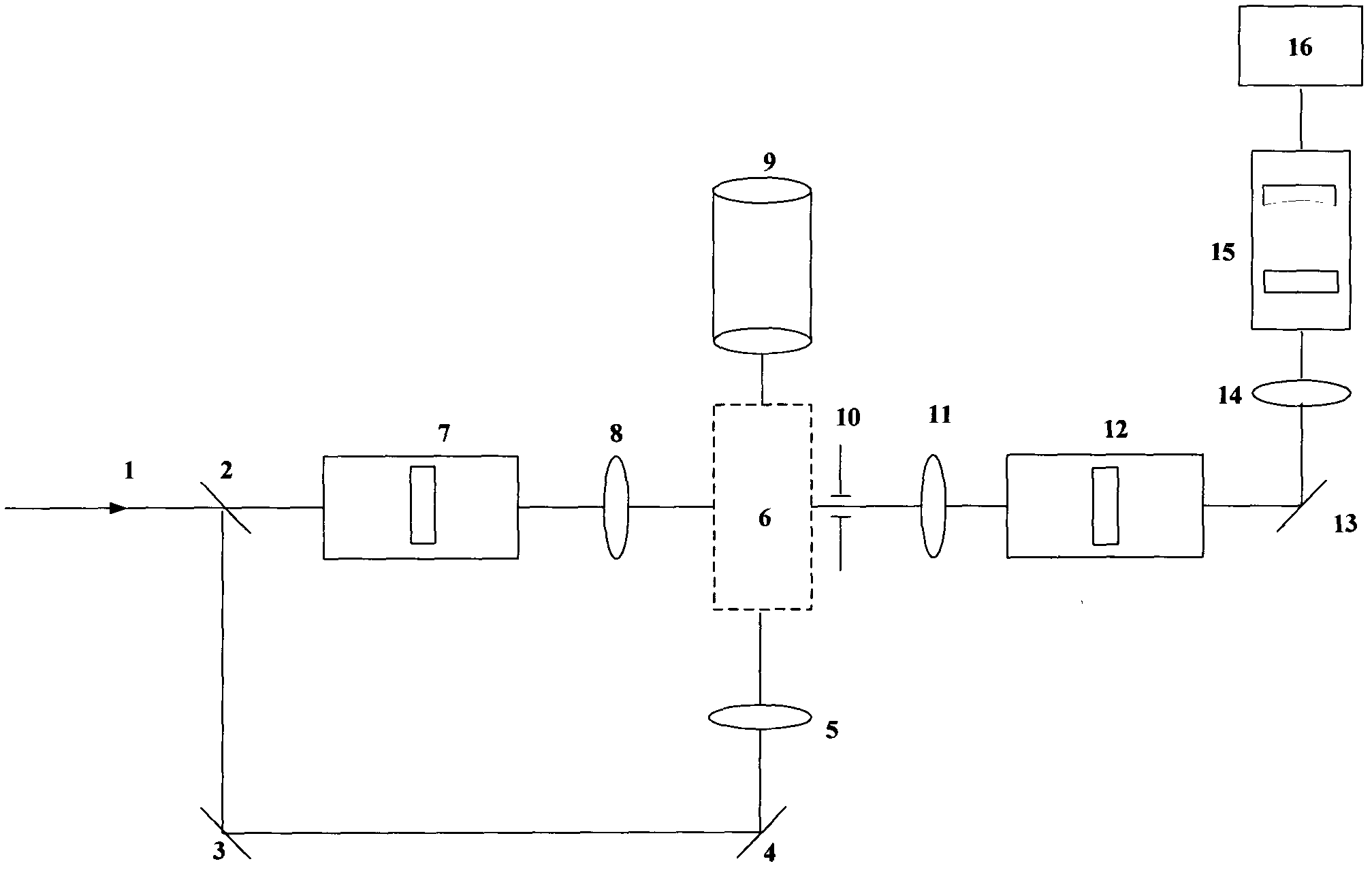
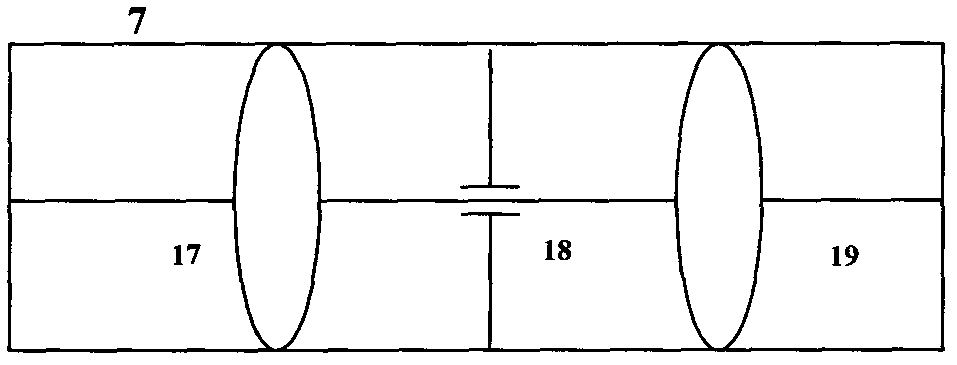
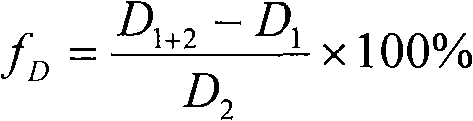Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
158 results about "Spectral function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An inversion method for laser radar data of atmospheric particulate matter particle size spectrum spatial and temporal distribution
ActiveCN103234877AAchieving Simultaneous ExtractionGet Optical PropertiesParticle size analysisParticulatesExtinction
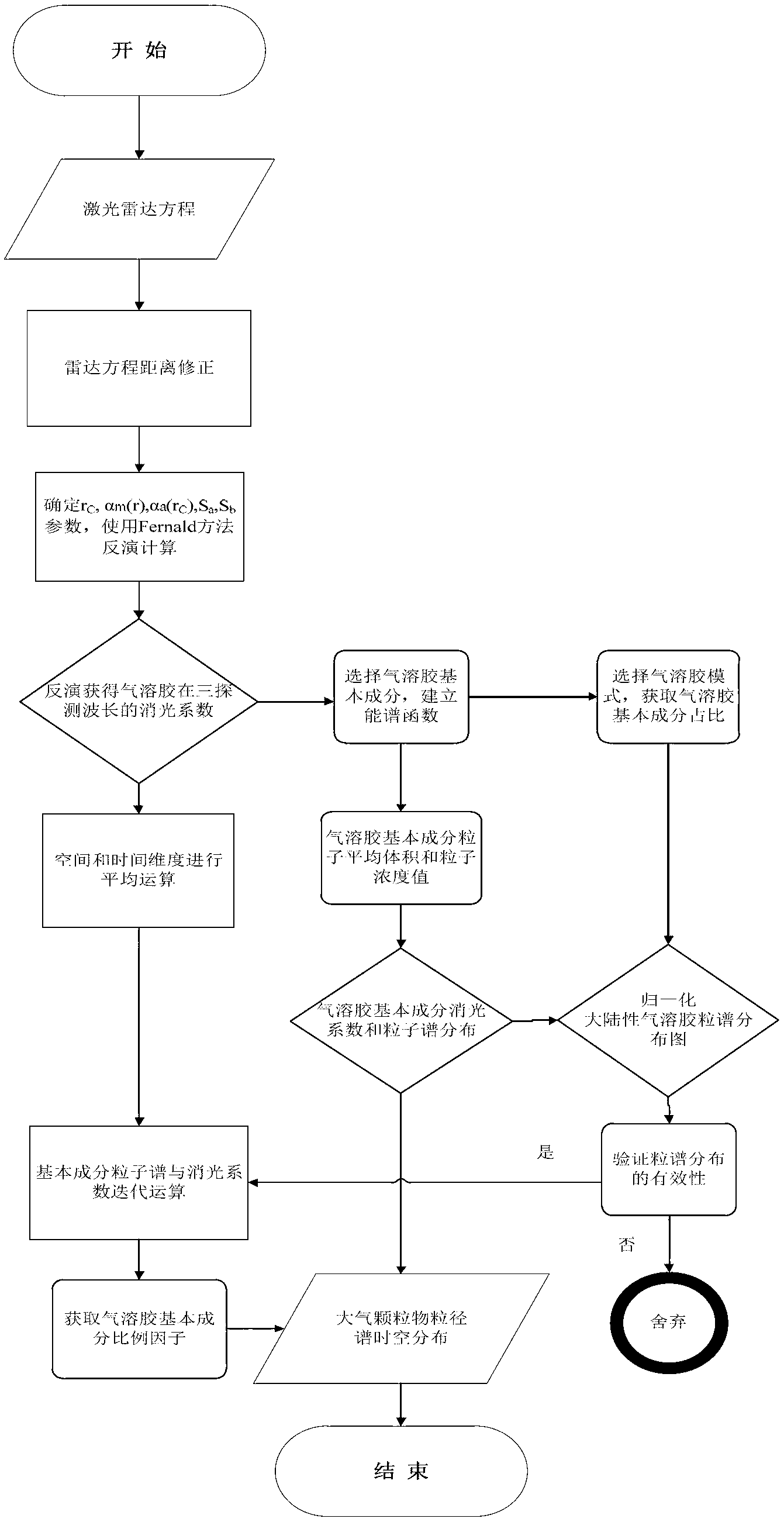
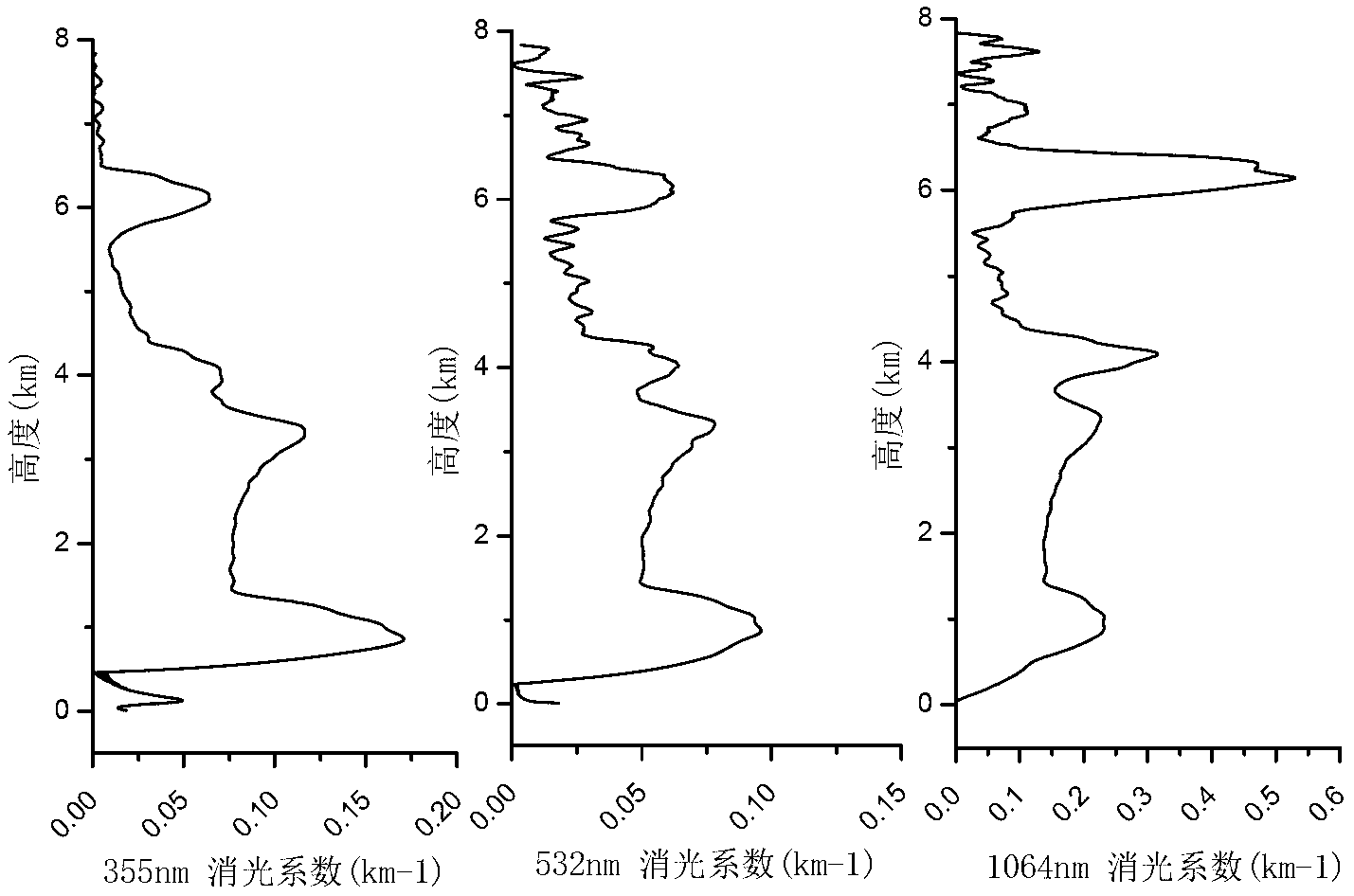
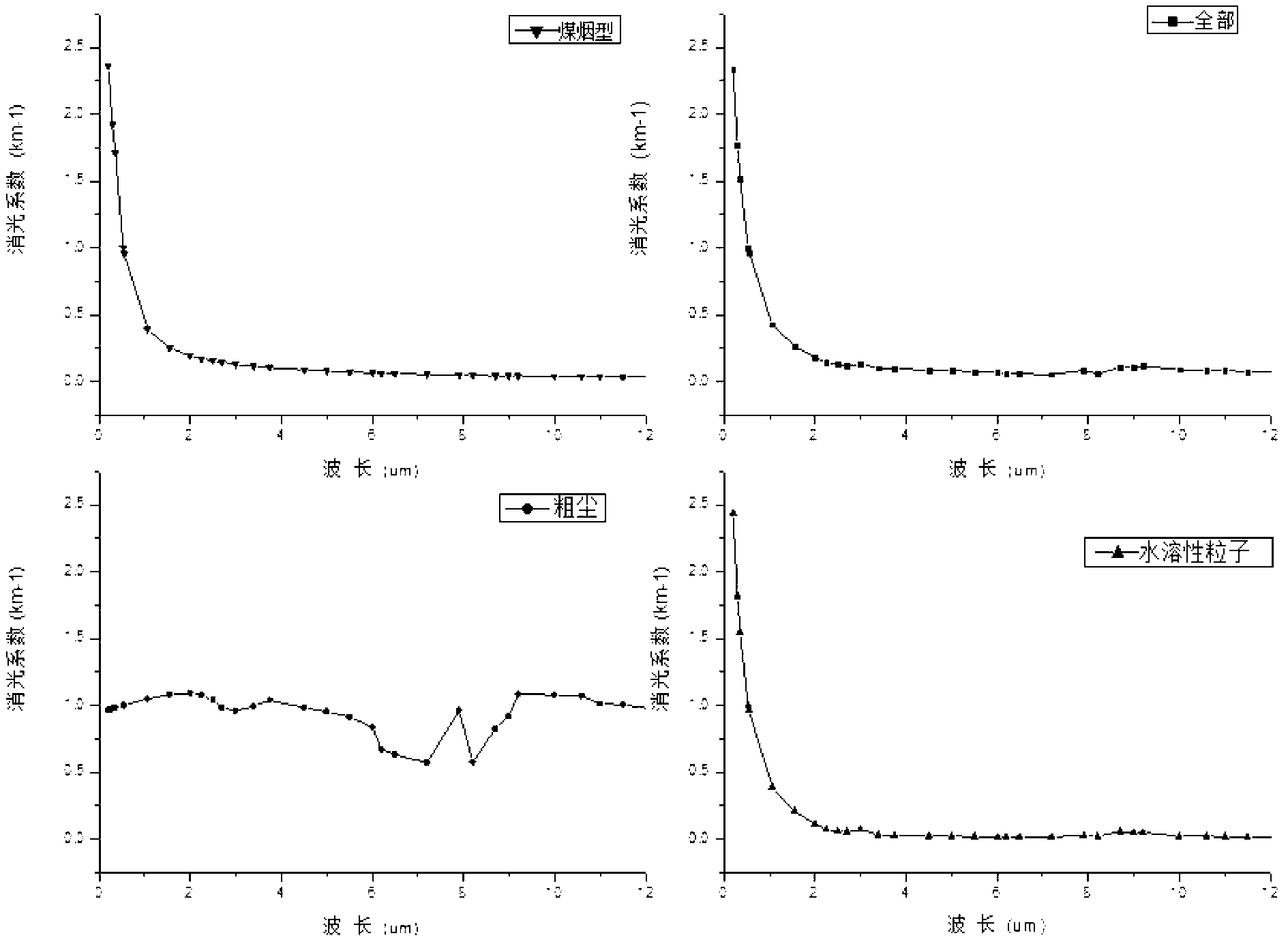
The present invention discloses an inversion method for laser radar data of atmospheric particulate matter particle size spectrum spatial and temporal distribution. The method comprises: by measuring back scattered echo signal of atmospheric particulate matters via laser radar, accurately inverting to obtain extinction coefficients of atmospheric particulate matters in three wavelengths of infrared, visible and ultraviolet bands at different heights from the ground; building lognormal distribution spectral functions of four aerosol components and parameters thereof, for obtaining refractive indexes at different bands of different aerosols and the mixing ratio of the four aerosol components in different aerosol modes; obtaining the particle size spectrum normalized at 0.55 micron of the extinction coefficient of each aerosol basic component, and comparing with a standard spectrum for authentication; and finally performing iterative calculation to the extinction coefficient spectrums obtained by laser radar surveying to obtain the aerosol mixed volume ratio of each height, thus obtaining atmospheric particulate matter particle size distribution of different heights at different times. According to the inversion method of the invention, valid data are provided for analysis and study of particle properties and variation patterns, especially, an effective means for spatial and temporal change detection for the particle-size spectrum of the atmospheric particulate matters is provided, and active three-dimensional telemetry technology suitable for atmospheric particulate matter particle size distribution is established.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
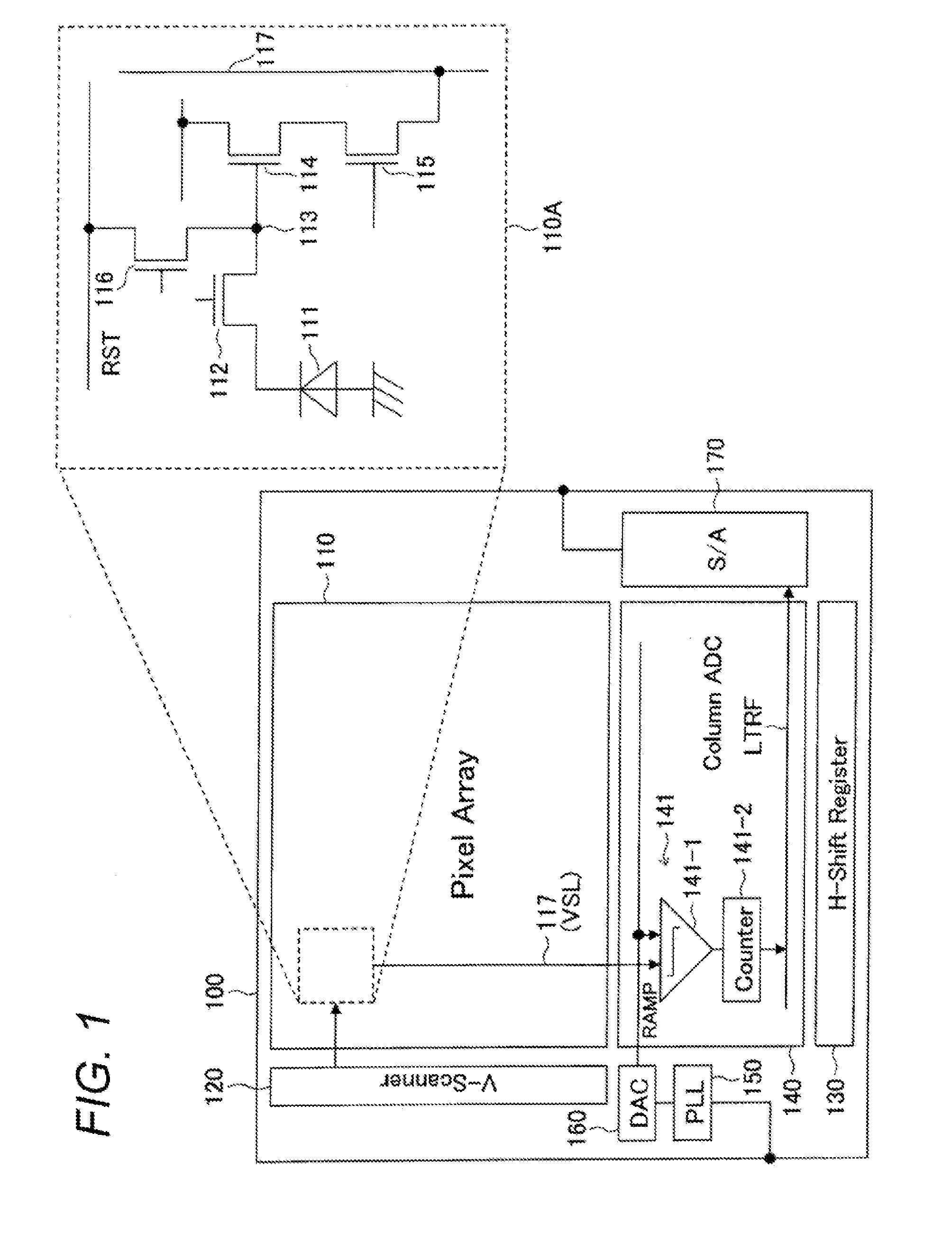
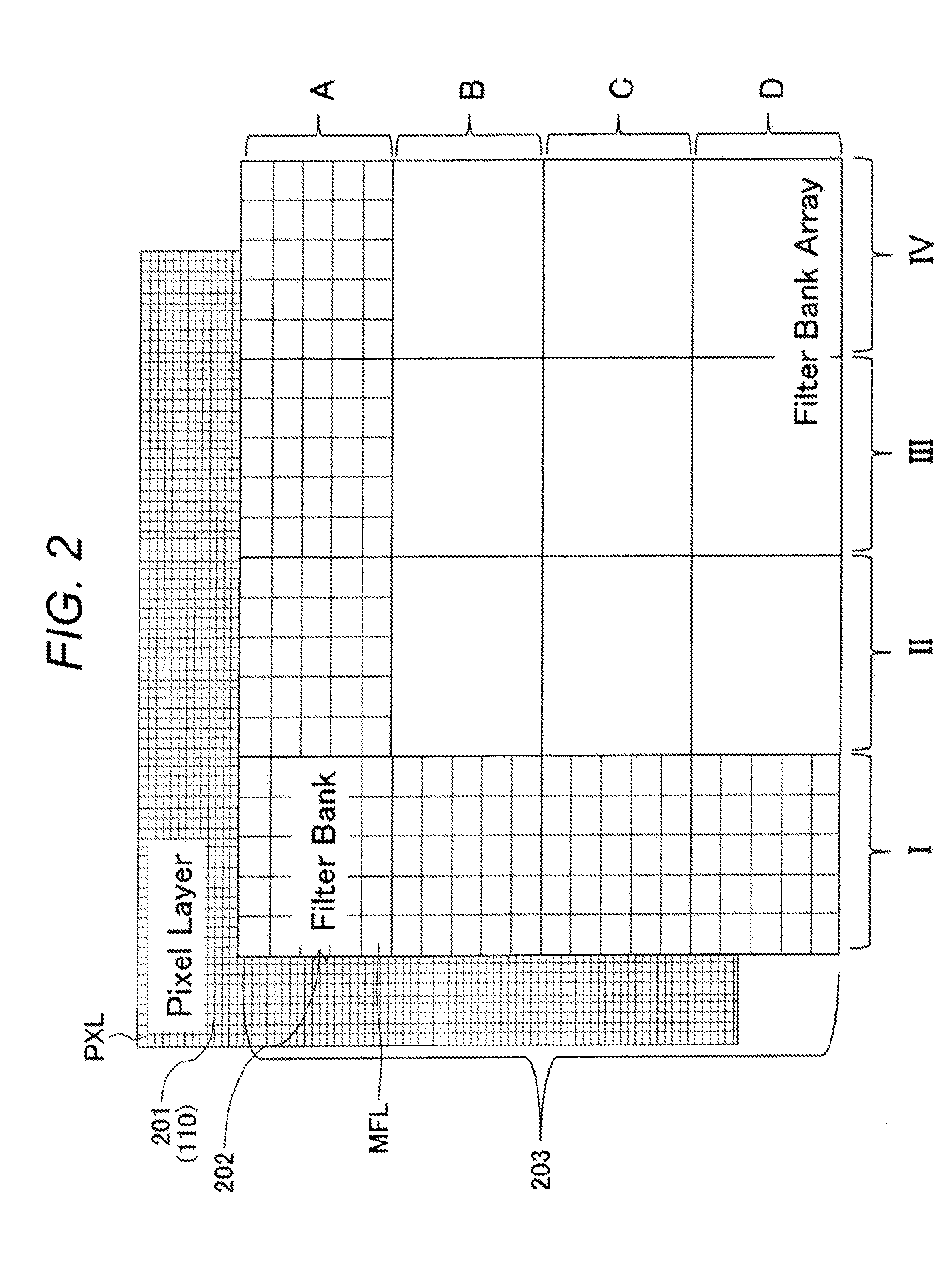
Solid-state image sensor, and imaging system
ActiveUS20140146207A1High sensitivityHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsHigh spatial resolutionImage resolution
The present technology relates to solid-state image sensor and an imaging system which are capable of providing a solid-state image sensor and an imaging system which are capable of realizing a spectroscopic / imaging device for visible / near-infrared light having a high sensitivity and high wavelength resolution, and of achieving two-dimensional spectrum mapping with high spatial resolution. There are provided a two-dimensional pixel array, and a plurality of types of filters that are arranged facing a pixel region of the two-dimensional pixel array, the filters each including a spectrum function and a periodic fine pattern shorter than a wavelength to be detected, wherein each of the filters forms a unit which is larger than the photoelectric conversion device of each pixel on the two-dimensional pixel array, where one type of filter is arranged for a plurality of adjacent photoelectric conversion device groups, wherein the plurality of types of filters are arranged for adjacent unit groups to form a filter bank, and wherein the filter banks are arranged in a unit of N×M, where N and M are integers of one or more, facing the pixel region of the two-dimensional pixel array.
Owner:SONY CORP
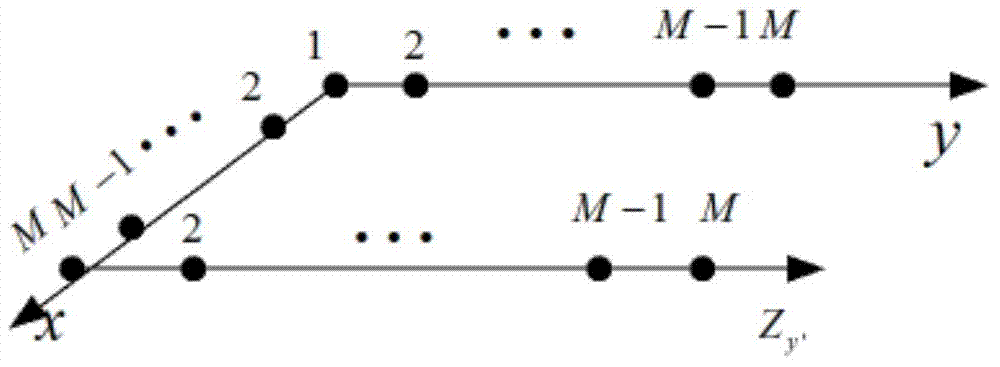
Virtual array DOA estimation method based on L type array
InactiveCN104730491AReduce complexityLarge apertureDirection/deviation determination systemsDecompositionSignal subspace
The invention discloses a virtual array DOA estimation method based on an L type array. The method comprises the steps that 1, based on the shift invariant property, a subarray Zx and a subarray Zy of the L type array horizontally shift to obtain a virtual array Zx' and a virtual array Zy', rotation invariance of two sub signals is formed due to the shift invariant property of the subarrays, and the virtual subarray signals are equal to the L type subarray Zx and L type subarray Zy input signals multiplied by a twiddle factor respectively; 2, the output of the four subarrays are combined to form a virtual array output signal Z (t); 3, the signal subspace and the noise subspace can be described by decomposing the features of covariance matrixes output by the array, mutual correlation processing is carried out on the array output signal Z(t) to obtain Rzz, and eigenvalue decomposition is carried out to obtain signal subspaces; 4, the twiddle factor is solved through linear operation, and the signal wave arrival direction can be obtained through the diagonal element of the twiddle factor. According to the virtual array DOA estimation method, no spectral function needs to be calculated, the phenomenon that the wave arrival direction is indirectly calculated without searching for the peak value is avoided, the complexity is lowered, the equipment complexity and cost are reduced, and the positioning precision is high.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
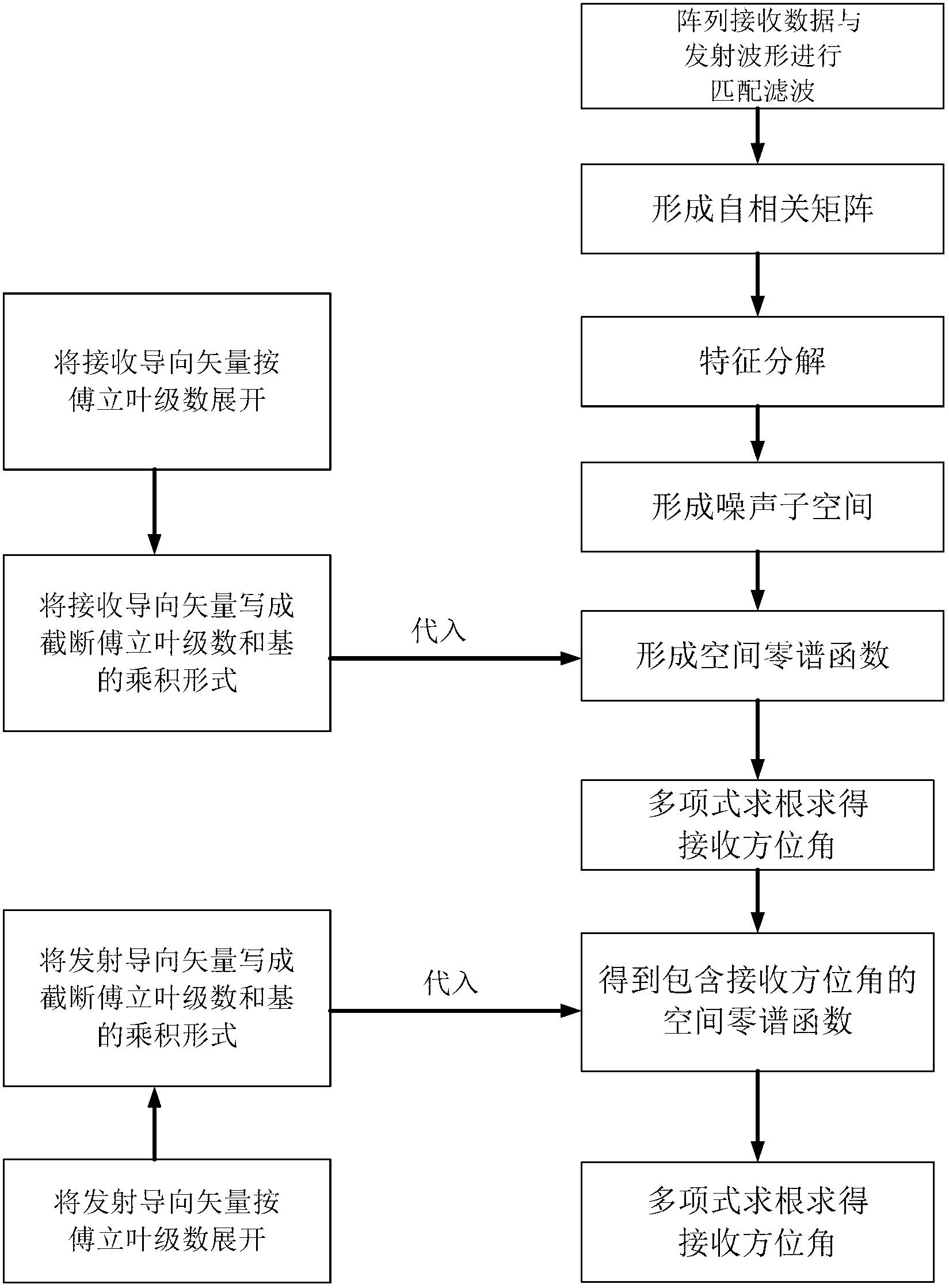
Estimating method of direction of arrival of bistatic MIMO (Multi-Input Multi-Output) radar based on circular array
InactiveCN102707264AReduce computationQuick calculationWave based measurement systemsMulti inputAngle of departure
The invention discloses an estimating method of direction of arrival of a bistatic MIMO (Multi-Input Multi-Output) radar based on a circular array, and mainly solves the problems that in the prior art, calculation is large and the direction of arrival of the circular array cannot be estimated. The realizing process comprises the steps of: 1, obtaining a cut-off Fourier coefficient of a steering vector of the array, and replacing the steering vector by the product of the Fourier coefficient and a base; 2, performing matched filtering for received data by the array to form an autocorrelation matrix and performing characteristic-decomposition for the matrix; 3, selecting a characteristic vector to form a noise sub space and obtaining a spatial zero-spectral function; 4, introducing the steering vector received to the spatial zero-spectral function, and solving an acceptance angle by polynomial rooting; and 5, introducing the acceptance angle received to the spatial zero-spectral function and solving an angle of departure by polynomial rooting. According to the estimating method of direction of arrival of the bistatic MIMO radar based on the circular array, the polynomial rooting method can be adopted to estimate the direction of arrival of the manifold MIMO radar of the circular array, spectrum peak search is avoided, calculation is low, and the estimating method of direction of arrival of the bistatic MIMO radar based on the circular array can be applied to estimating the direction of arrival of the bistatic MIMO radar.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
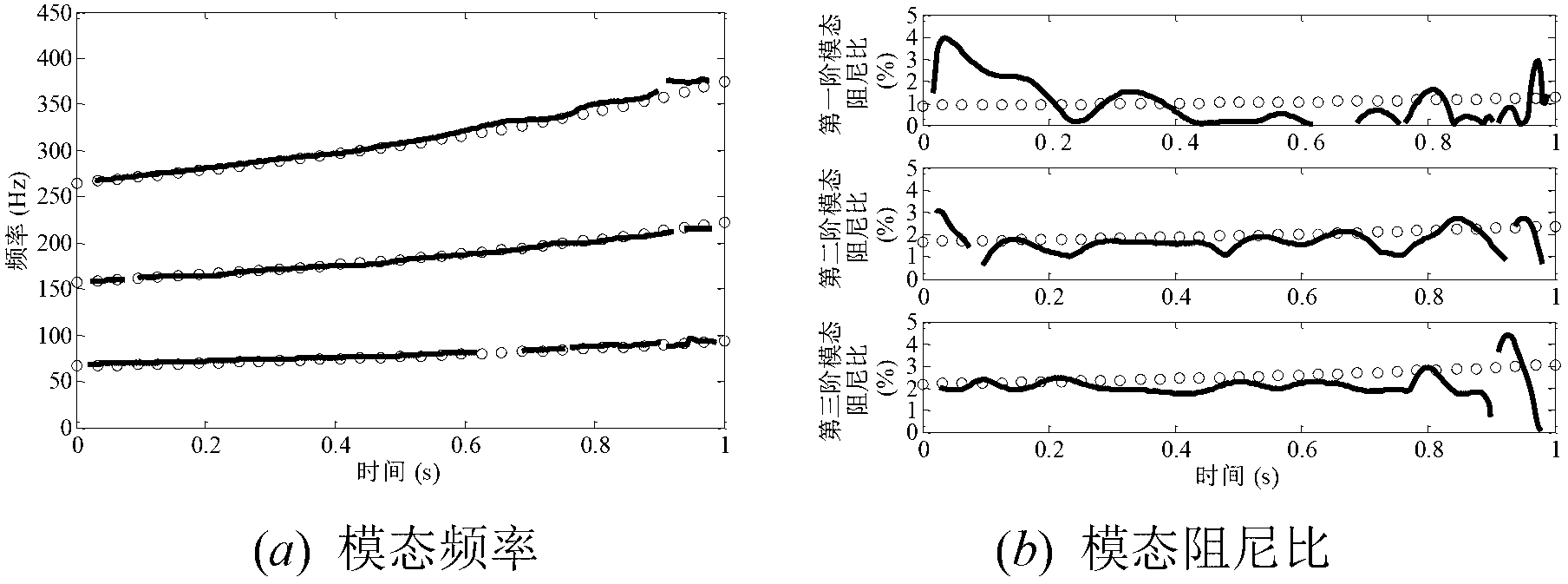
Time frequency domain time varying structure modal parameter identification method based on time varying common demominator model
ActiveCN102982196AReduce engagementEasy to useSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainStructural dynamics
The invention relates to a time frequency domain time varying structure modal parameter identification method based on a time varying common demominator model and belongs to the technical field of structural dynamics. Firstly, structural dynamics response signals measured and obtained by aircraft or spacecraft structures with the time varying characteristics under the work situations are analyzed in a time frequency mode to obtain a time relative power spectral function of non-parametric evaluation corresponding to time varying structures. Then, the time varying common demominator model is used as a parametric model of the time varying structural dynamics to evaluate to-be-evaluated parameters of the time varying common demominator model through a least squares methods of the time domain. Finally, the evaluated to-be-evaluated parameters of the time varying common demominator model is utilized to calculate the model frequency and the model damping ratio corresponding to the time varying common demominator model. The time frequency domain time varying structure modal parameter identification method based on the time varying common demominator model is suitable for model parameters recognition of time varying structure in the field of aircraft and spacecraft engineering application and has the advantages of being simple and convenient to use. Furthermore, users are low in participation degree.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for estimating direction of arrival of MIMO radar based on nested array
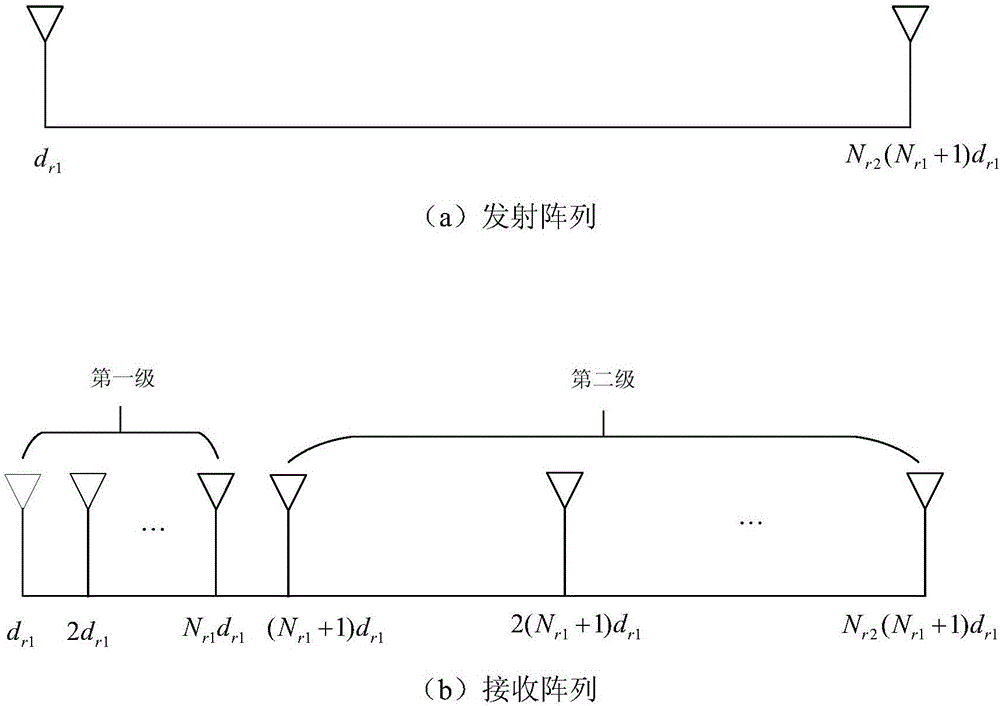
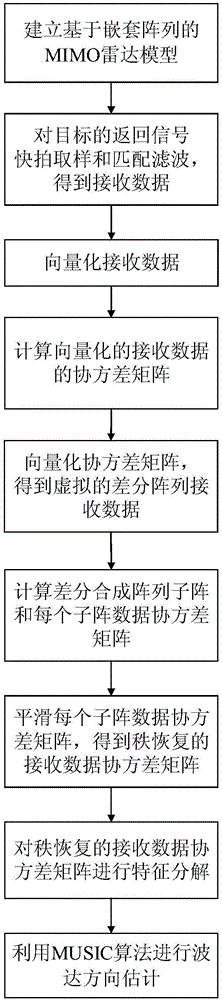
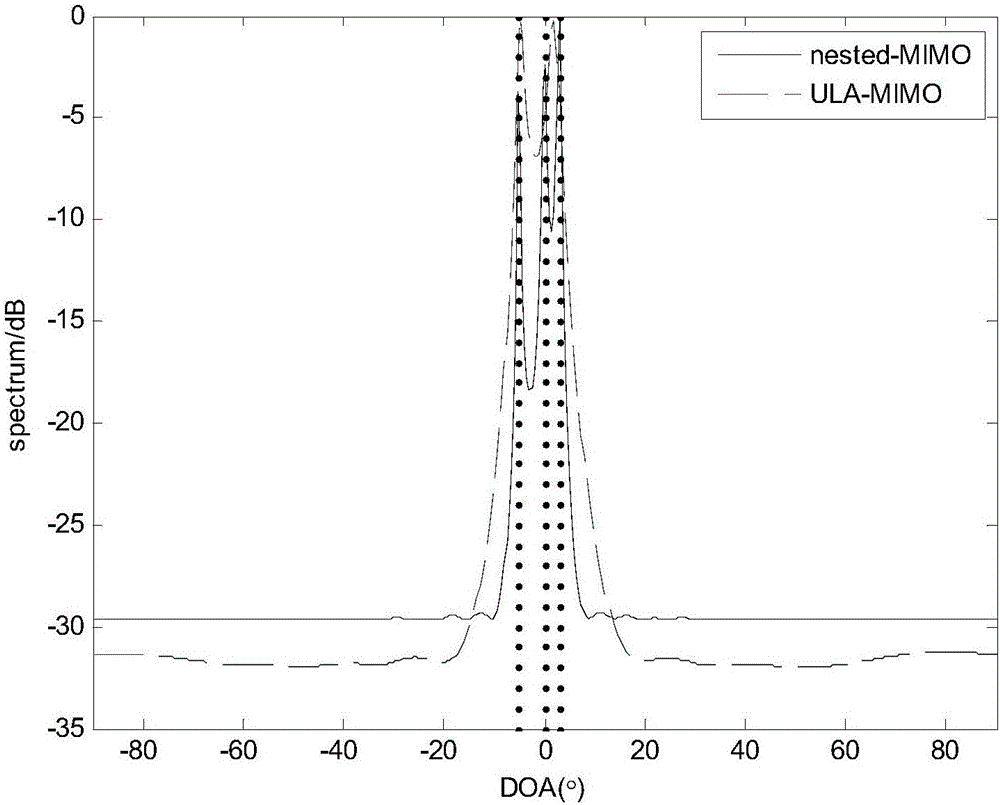
ActiveCN106707257AEasy to implementIncrease freedomWave based measurement systemsRadarImage resolution
The invention discloses a method for estimating the direction of arrival of MIMO radar based on a nested array, which mainly solves a problem that the early radar is low in resolution for the direction of arrival and small in number of recognized signal sources. Implementation of the method comprises the steps of 1) building a nested array based MIMO radar model, and acquiring a target return signal; 2) performing snapshot sampling, matched filtering and vectorization on the target return signal in sequence, and acquiring vectorized receiving data y; 3) estimating a covariance matrix Ryy of the receiving data y, and performing vectorization on the covariance matrix Ryy to acquire an observation vector z; 4) removing repeated elements of the observation vector z to acquire virtual differential array receiving data z1; 5) dividing the virtual differential array receiving data z1 into N1 pieces of subarray receiving data, and acquiring a rank-recovery receiving data covariance matrix Rss; 6) performing eigenvalue decomposition on the rank-recovery receiving data covariance matrix Rss to acquire a noise subspace EN; and 7) acquiring the direction of arrival according to a spectral function formed by the noise subspace EN. The method disclosed by the invention improves the degree of freedom and the resolution of an MIMO radar system, and can be applied to radar target orientation detection.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A single dipole polarization sensitive array dimensionality reduction DOA estimation method in a multipath interference environment
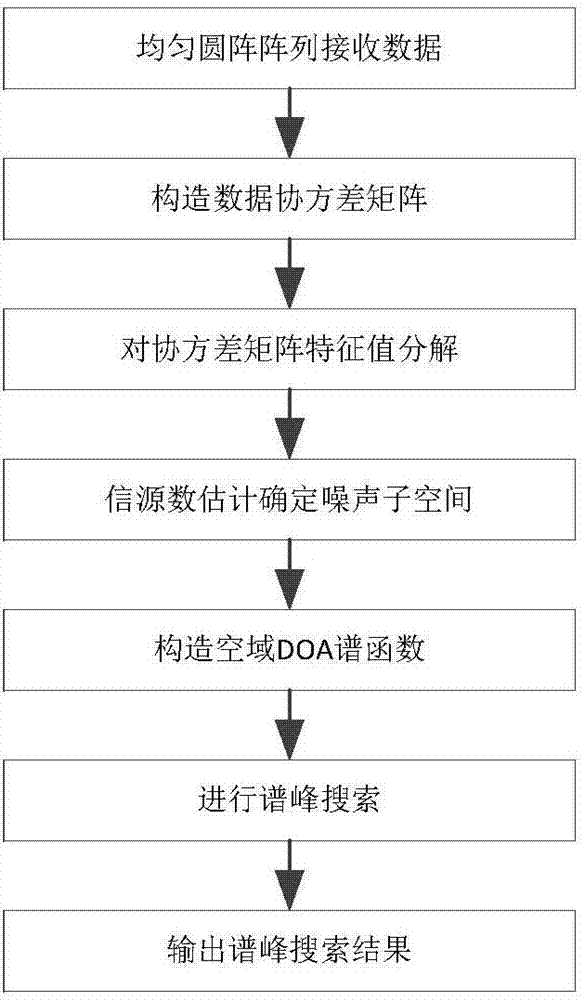
ActiveCN107015191AFast executionFully receivedRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsElevation angleMultipath interference
The invention provides a single dipole polarization sensitive array dimensionality reduction DOA estimation method in a multipath interference environment. The array employs single dipoles concurrent with the edge of a circumference to from a uniform circular array structure, can simultaneously perform azimuth angle and elevation angle two-dimensional estimation and can effectively fight multi-path interferences to realize mathematical modeling of narrowband signals received by a uniform circular array concurrent array; then according to a matrix rank loss principle, the four-dimensional spectral function of the polarization MUSIC (multiple signal classification) algorithm is subjected to dimensionality reduction processing to construct a spatial spectral function so as to realize the fast search of spatial two-dimensional angles. Compared with polarization sensitive array DOA and polarization parameter combined estimation methods, the dimensionality reduction DOA estimation method of the invention can realize rapid estimation of signal source angles under the condition of not increasing hardware demands, receive and utilize the polarization characteristics of signal sources and interference sources to effectively distinguish objects and interferences to realize object estimation in a complex environment and has a certain engineering application value.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
OFDM-based high-resolution radar communication integration waveform optimization method
ActiveCN105137410ARealize transmissionIncrease data rateWave based measurement systemsMultiple signal classificationAmbiguity
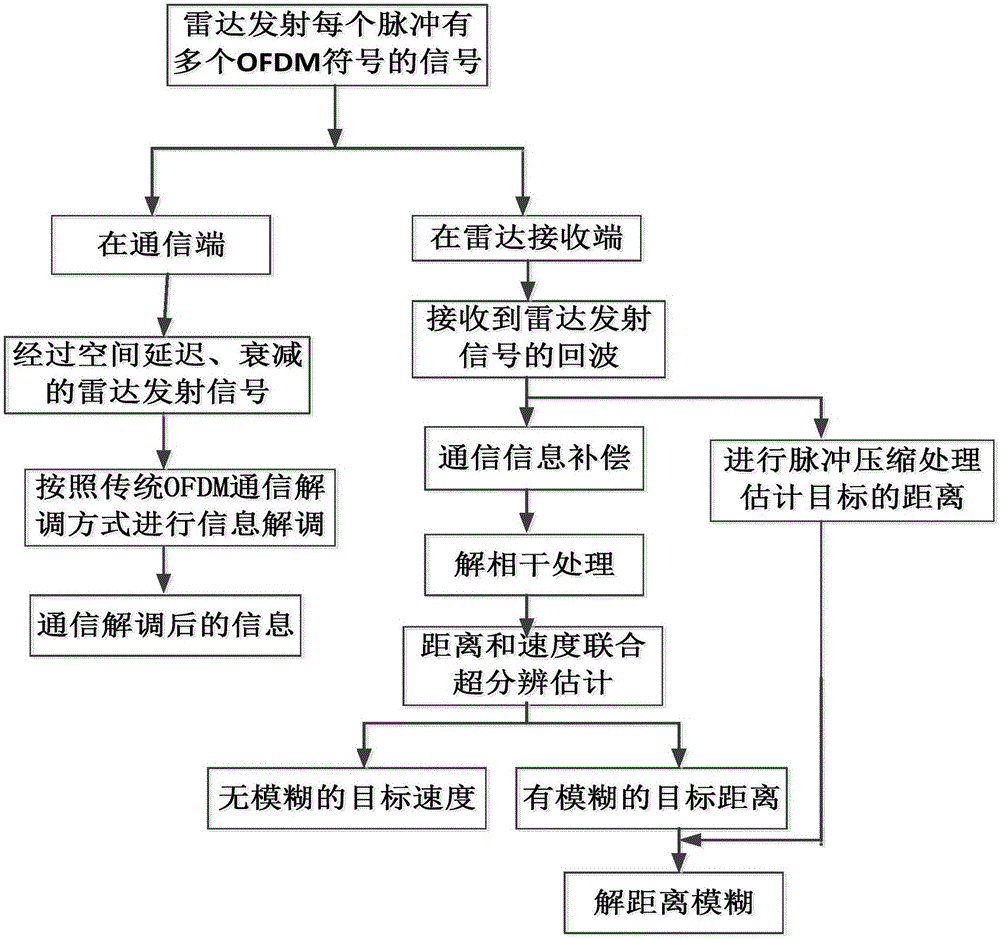
The invention discloses an OFDM-based high-resolution radar communication integration waveform optimization method. The method comprises steps: a radar transmission end adopts a pulse transmission mode to obtain a signal transmitted by a radar transmission end, the signal is transmitted to a communication end and a radar receiving end respectively, information demodulation is carried out after the signal arrives at the communication end, a signal after information demodulation is obtained, pulse compression processing and communication information compensation are respectively carried out on an echo signal for the signal received by the radar receiving end, a target estimation range corresponding to a target and an echo signal after communication information compensation are obtained respectively, decorrelation processing is carried out on the echo signal, an average value for multiple time sub arrays is obtained, MUSIC algorithm is used for calculating a spectral function related to a target range and a target speed in the average value, a target range with range ambiguity and a target speed without ambiguity corresponding to the target are further obtained, range ambiguity solution processing is carried out on the target range with range ambiguity, and a real target range corresponding to the target is obtained.
Owner:昆山煜壶信息技术有限公司
Method for detecting printing color by using complex frequency spectrum color feature numerical values
ActiveCN102092206ASolve balance problemsSolving Tonal LinearizationColor measuring devicesDuplicating/marking methodsPattern recognitionFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a method for detecting a printing color by using complex frequency spectrum color feature numerical values, comprising the following steps of: measuring the color of a printing matter through a visible spectrophotometer to obtain a spectrum function, and then calculating according to a complex frequency spectrum chromatic diagram and a color feature numerical value calculating method to obtain the complex frequency spectrum color feature numerical values such as a complex frequency spectrum color phase value H, a complex frequency spectrum brightness value L and the like; detecting a product color feature numerical value in real time in the printing and producing processes, and carrying out holographic detection and adjustment on the color and the contrast of the printing matter by utilizing the relation between brightness and the thickness of an ink layer, the relation between a color phase of a secondary color and color strength, the relation between gray level and the balance of three colors, i.e. yellow, pinkish red and green and the linear relation between comprehensive brightness and a dot area rate. Compared with the traditional detecting method, the method for detecting the printing color by using the complex frequency spectrum color feature numerical values has obvious advantages on the aspects such as data intuition, operability of method, effectiveness in use, economical efficiency of instruments, universality in popularization and the like, and particularly solves the problem that the two traditional indexes, i.e. three-color gray level balance and contrast linearization, are still judged mainly depending on vision and adjusted depending on experience.
Owner:庞多益 +1
Cross spectral function-based operational modal analysis experiment method and apparatus
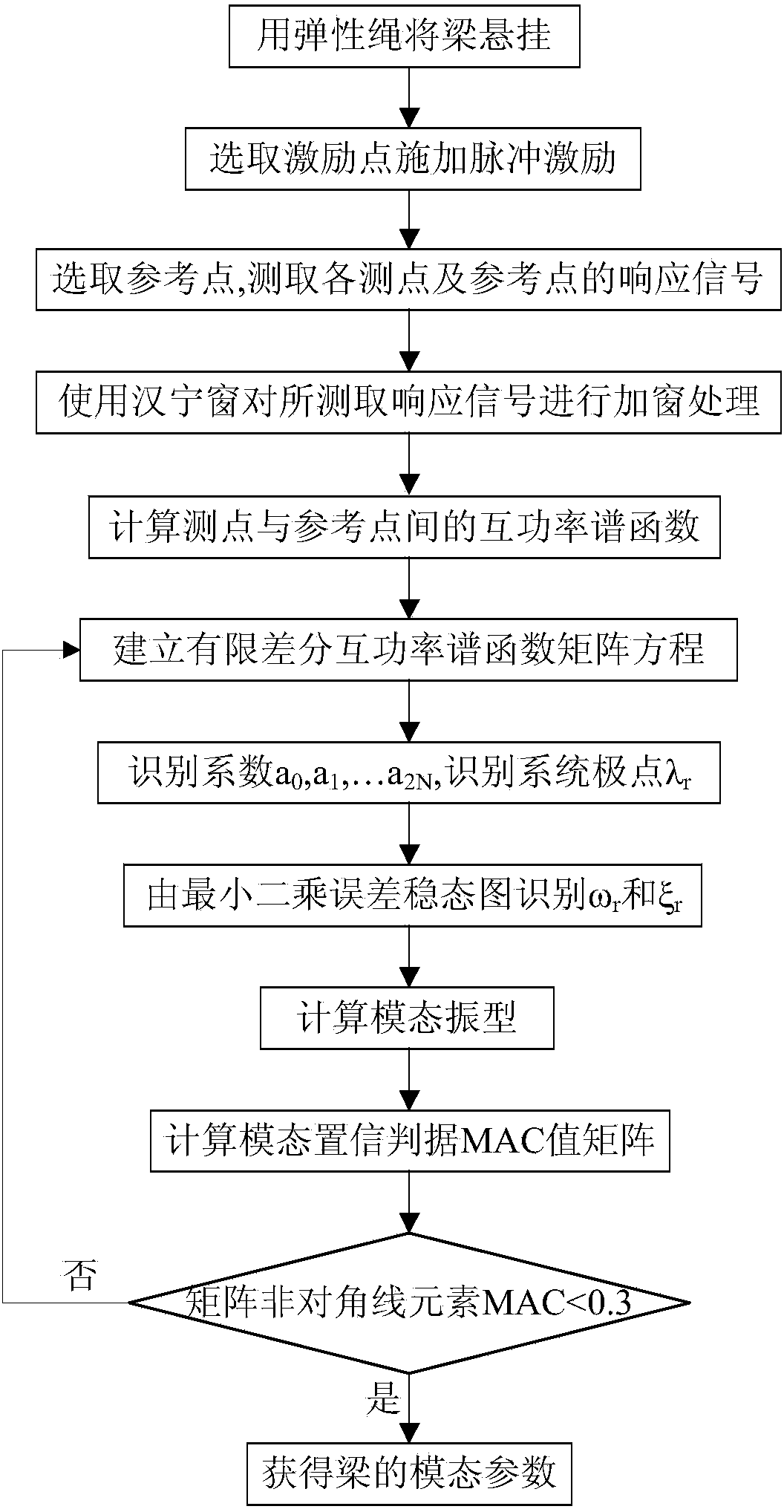
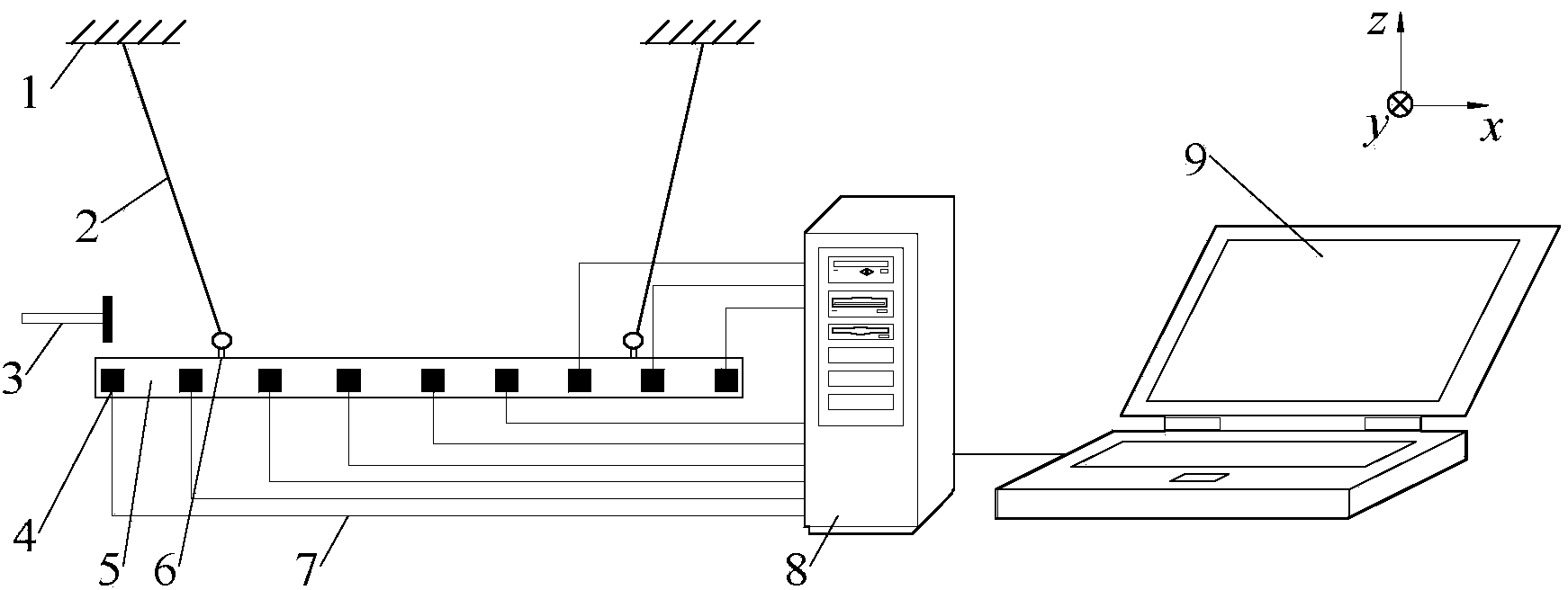
ActiveCN104165742AEasy to analyzeConvenient and fast dynamic characteristic analysisSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementVibration testingTest efficiencySpectral function
The invention relates to a cross spectral function-based operational modal analysis experiment method. The method comprises the following steps that: (1), a beam is suspended by elastic ropes and a steel hammer is used for exerting pulsed excitation on the beam at a selected excitation point; (2), response signals generated by a reference point and a response point after the pulsed excitation are collected; (3), band-pass filtering is carried out on the collected signals; (4), a cross-power spectral function between the reference point and the response point is calculated and a matrix equation formed by data of the cross-power spectral function at different sampling moments is constructed; (5), a coefficient matrix is calculated by using the matrix equation so as to obtain a system pole; (6), a modal shape matrix and a modal participation factor matrix are identified; and (7), modal assurance criterion matrix value calculation is carried out; and when the modal assurance criterion value is in a preset reasonable range, a modal parameter of the beam is obtained. In addition, the invention also provides a cross spectral function-based operational modal analysis experiment apparatus. According to the invention, the experiment intensity and time are reduced; and the test efficiency as well as the learning effect of students is also substantially improved.
Owner:杭州肯上信息科技有限公司
Three-dimensional ocean wave analogy method based on ocean wave spectrum
The invention discloses a three-dimensional ocean wave analogy method based on an ocean wave spectrum. The three-dimensional ocean wave analogy method based on an ocean wave spectrum includes confirming an observation time t and obtaining an ocean wave height at the moment, taking a relative calm moment of the ocean surface before the observation time t as an observation time 0 and obtaining an ocean wave height at the moment, deducing a relative correlation function of ocean waves based on considering the formation time history of the ocean waves and obtaining an attenuation weight function of the ocean waves through calculation, multiplying the ocean wave height of the observation time 0 by the attenuation weight function and superposing the result to the ocean wave height of the observation time t thus reflecting the influence of a previous moment ocean wave on the ocean wave of an observation time, changing an angle initial phase of an orientation spectral function of superposed ocean waves to imitate the changes of wind directions. Repeat the steps of the three-time dimensional ocean wave analogy method, and ocean superpositions of a plurality of moments are obtained and finally the imitation of ocean waves is obtained. The three-dimensional ocean wave analogy method based on ocean wave spectrum utilizes the steps to imitate the ocean waves. The imitated effect of the ocean waves is less in distortion compared with the prior art and fits with real ocean waves.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Broadband signal source positioning method based on subspace weight sparse recovery
The invention discloses a broadband signal source positioning method based on subspace weight sparse recovery. The method comprises steps that multiple broadband signals having unknown correlation in the space are irradiated to a linear sensor array formed by multiple isotropy sensors, and a complex observation matrix is acquired according to the linear sensor array; a target signal arrival angle is estimated under a compression sensing framework according to the complex observation matrix to carry out reconstruction to acquire a first signal model; truncated singular value decomposition of the complex observation matrix is carried out to construct a weight matrix; a weight vector is calculated according to the weight matrix; dimensional reduction is carried out according to the first signal model to acquire a second signal model; the second signal model is optimized to acquire a third presentation form of the target signal under the compression sensing framework; a spectral function is calculated according to the third presentation form of the target signal under the compression sensing framework to acquire an estimate of the target signal arrival angle. The method is advantaged in that decorrelation capability of a compression sensing algorithm and estimation precision of an MUSIC algorithm are realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
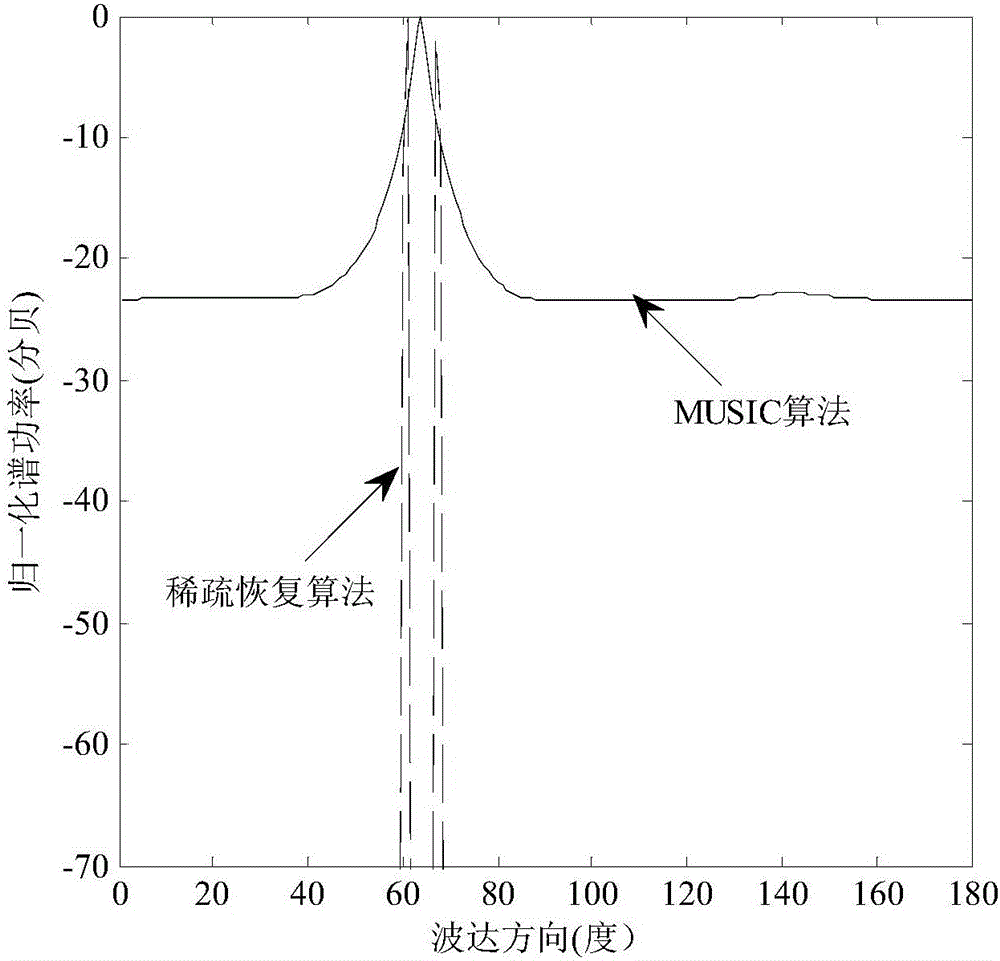
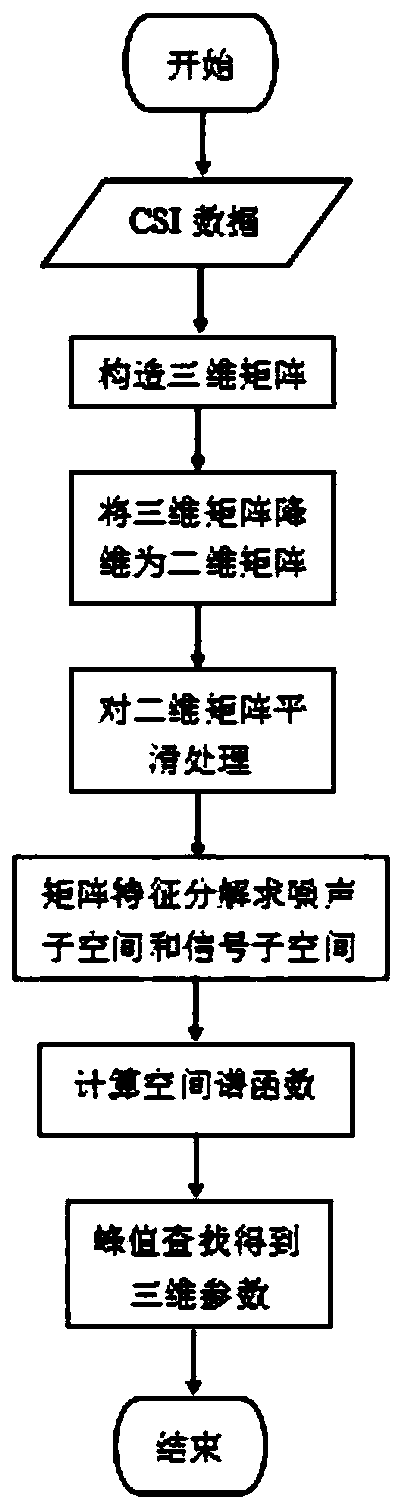
Three-dimensional joint estimation method based on Wi-Fi channel state information
ActiveCN109738861AGuaranteed irrelevanceImprove Joint Estimation AccuracyPosition fixationDecompositionSignal subspace
The invention provides a three-dimensional joint estimation method based on Wi-Fi channel state information (CSI). Firstly, in order to overcome the limitation of the number of antennas and the channel bandwidth to a two-dimensional joint estimation model, the obtained channel state information forms a three-dimensional matrix from three dimensions of subcarriers, the antennas and data packets; secondly, dimensional reduction processing is performed on the three-dimensional matrix, and smooth processing between the subcarriers, the antennas and the data packets is performed on the basis; and finally, signal subspace decomposition and noise subspace decomposition are performed on the smoothed matrix to construct a spectral function. Based on the spectral function, three-dimensional joint search of an angle of arrival (AoA), time of flight (ToF) and doppler frequency shift (DFS) is performed. A designed three-dimensional joint estimation algorithm can still achieve high estimation precision under the conditions of a small number of antennas and a narrow channel bandwidth, and provides a theoretical basis for application such as accurate indoor tracking and positioning.
Owner:重庆派明科技有限公司
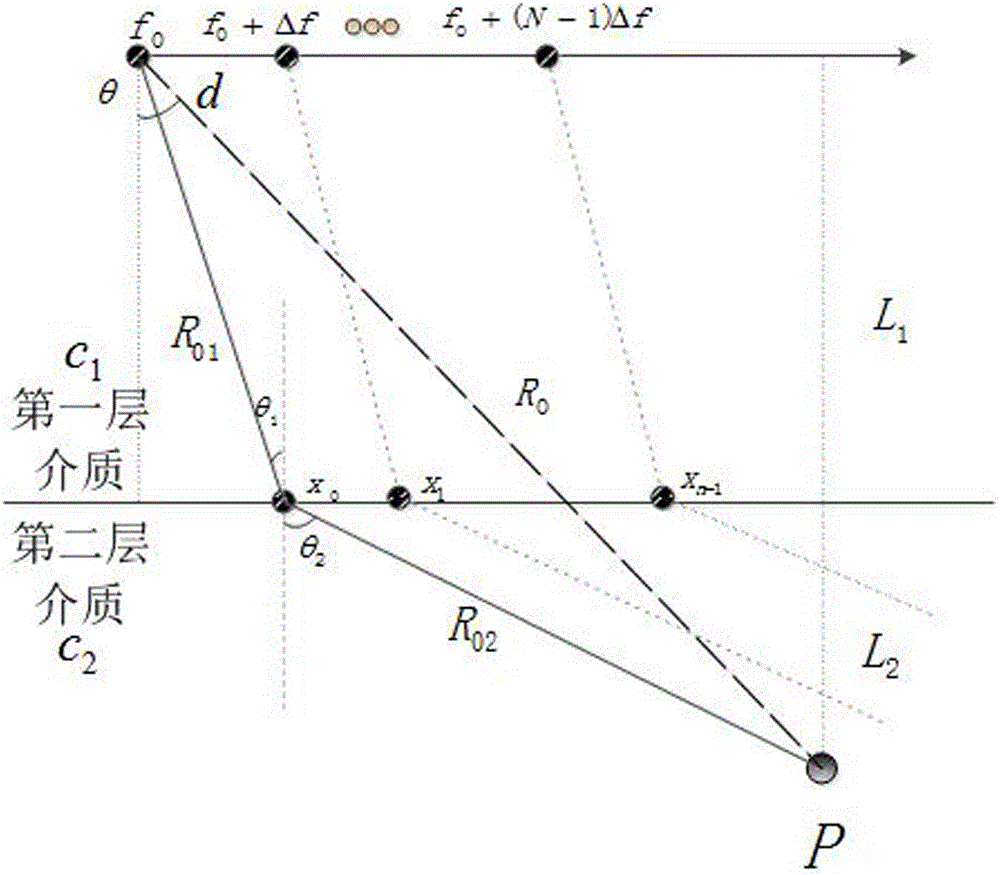
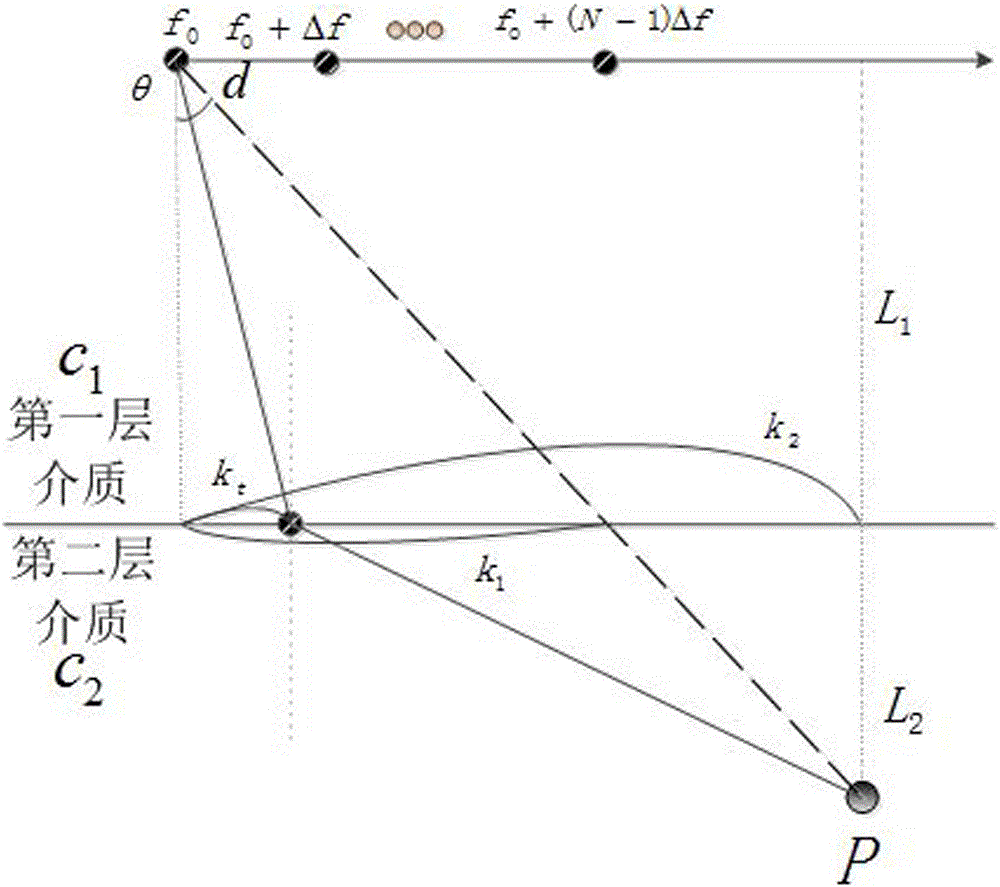
MUSIC algorithm based frequency diverse array two-layer medium target positioning method
ActiveCN106772337AAchieve signal echo distanceAchieving angular decouplingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDecompositionMultiple signal classification
The invention discloses a MUSIC algorithm based frequency diverse array two-layer medium target positioning method, which is characterized in that a transmitting-receiving beam direction pattern of a frequency diverse array of the two-layer medium is derived through determining a propagation path of electromagnetic waves in a two-layer medium; received echo waves are enabled to contain decoupled distance and angle information through two groups of different frequency deviations, and an estimated value of an echo signal covariance matrix is acquired according to snapshot data of L echo signals; eigenvalue decomposition is performed on the acquired estimated value, eigenvalues which are equal to the number of target sources K and corresponding eigenvectors are regarded as a signal subspace according to the size of eigenvalues, and the left 2N-K eigenvalues and eigenvectors are regarded to be a noise subspace; and a spectral function is constructed according to the noise subspace, and point-by-point computation is performed on distance and angle variations so as to find the wave crest and estimate the target location. The method disclosed by the invention realizes positioning for a shielded target in a multi-layer medium under a single transmitting single receiving mechanism of each array element of RDA radar by using a MUSIC algorithm.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system sampling frequency shift blind estimation method under multipath fading channel
InactiveCN103095638AImprove estimation performanceImprove performanceMulti-frequency code systemsSampling frequency offsetPhase shifted
An orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system sampling frequency shift blind estimation method under a multipath fading channel includes: according to features of stable circulation of OFDM signals with relevant pilot frequency, an improved spectral function overcomes fading brought by sampling frequency shift and data influenced by the multipath fading channel to estimate relative value points and estimate the sampling frequency shift according to cyclic spectrum value phase shift amount at a estimated value point. The OFDM system sampling frequency shift blind estimation method under the multipath fading channel can overcome influence of frequency shift, white gaussian noise and the multipath fading channel, makes full use of data by using jump transformation, and greatly improves estimate performance of sampling frequency shift of the OFDM system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multi-objective angle ambiguity resolving method based on rotating interferometer
ActiveCN108254718AAchieve resolutionSolve the direction finding ambiguity problemPosition fixationPhase differenceDecomposition
The invention discloses a multi-objective angle ambiguity resolving method based on a rotating interferometer. The multi-objective angle ambiguity resolving method mainly solves the problem that two-dimensional angle estimation of multi-objective signal sources working at the same frequency and same time cannot be solved in the prior art. The multi-objective angle ambiguity resolving method is implemented by the steps of: acquiring a phase difference matrix between array elements of a multichannel rotating interferometer; acquiring interference data matrixes received by the multichannel rotating interferometer at different moment during the rotation process; performing forward spatial smoothing processing on the data matrixes, and calculating smoothed signal autocorrelation matrixes; performing eigenvalue decomposition on the autocorrelation matrixes, calculating a spectral function, and acquiring an angle ambiguity curve distribution diagram through spectrum peak searching; and projecting angle ambiguity curves into a parameter space, and accumulating parameters to obtain two-dimensional angle estimation of different objectives. The multi-objective angle ambiguity resolving methodcan simultaneously resolve ambiguity of two-dimensional angles of different objectives, calculates unambiguous two-dimensional angle information of each objective, and is used for estimating two-dimensional angles of satellite-borne rotating interferometers in space electronic reconnaissance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multipath utilization-based beam forming method
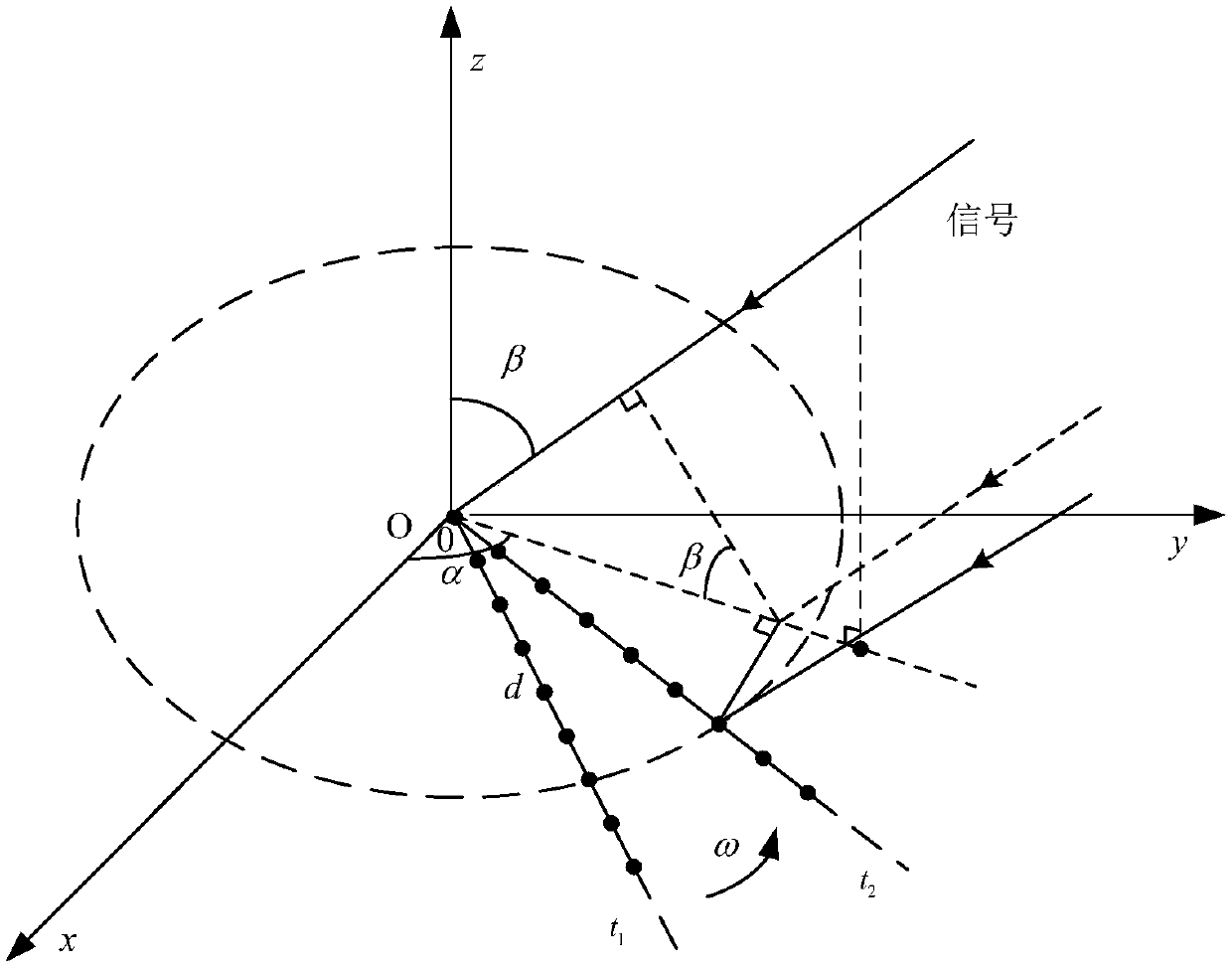
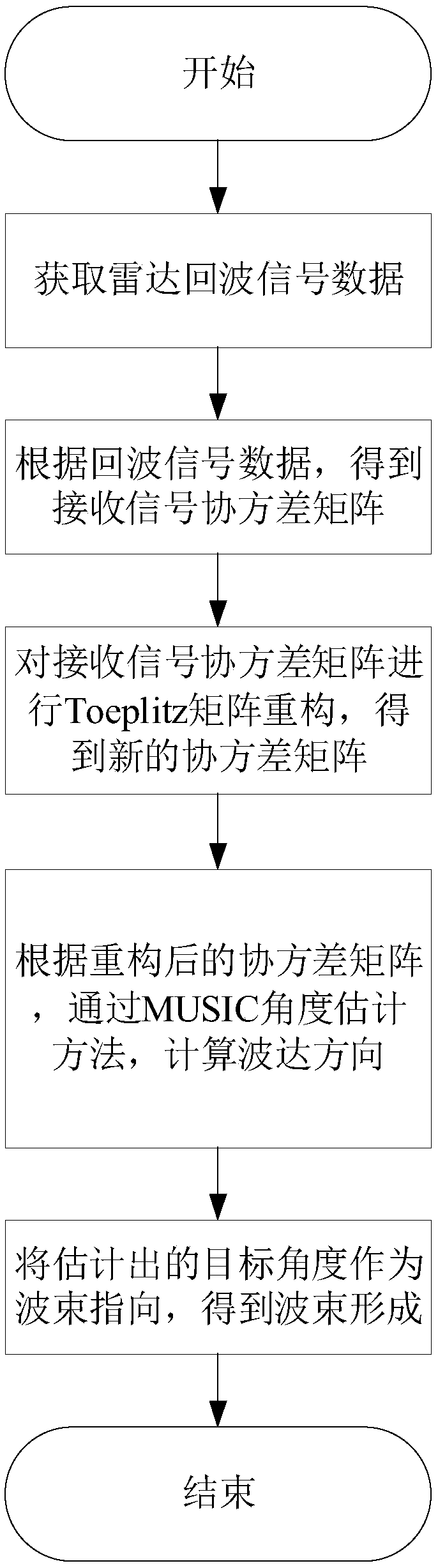
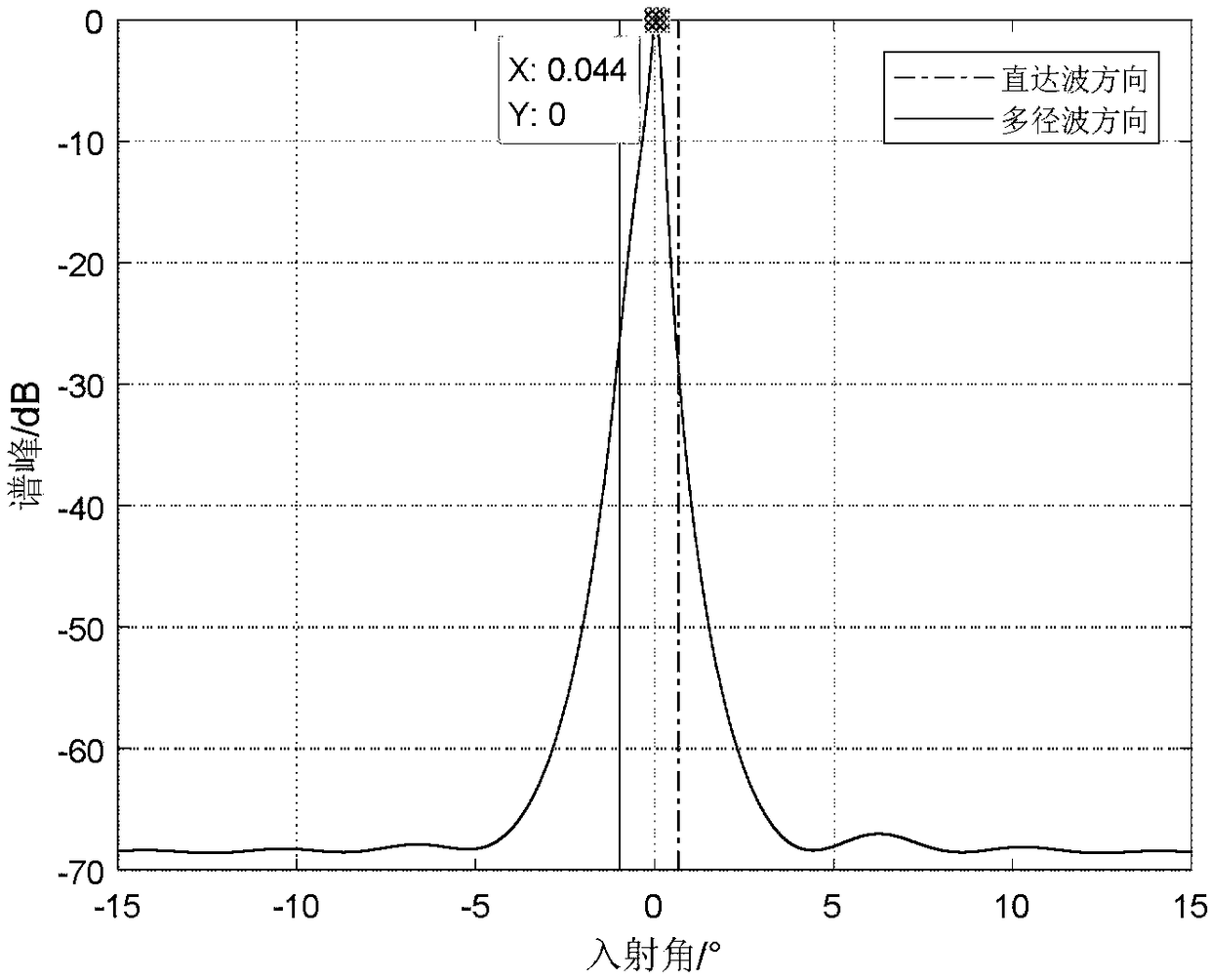
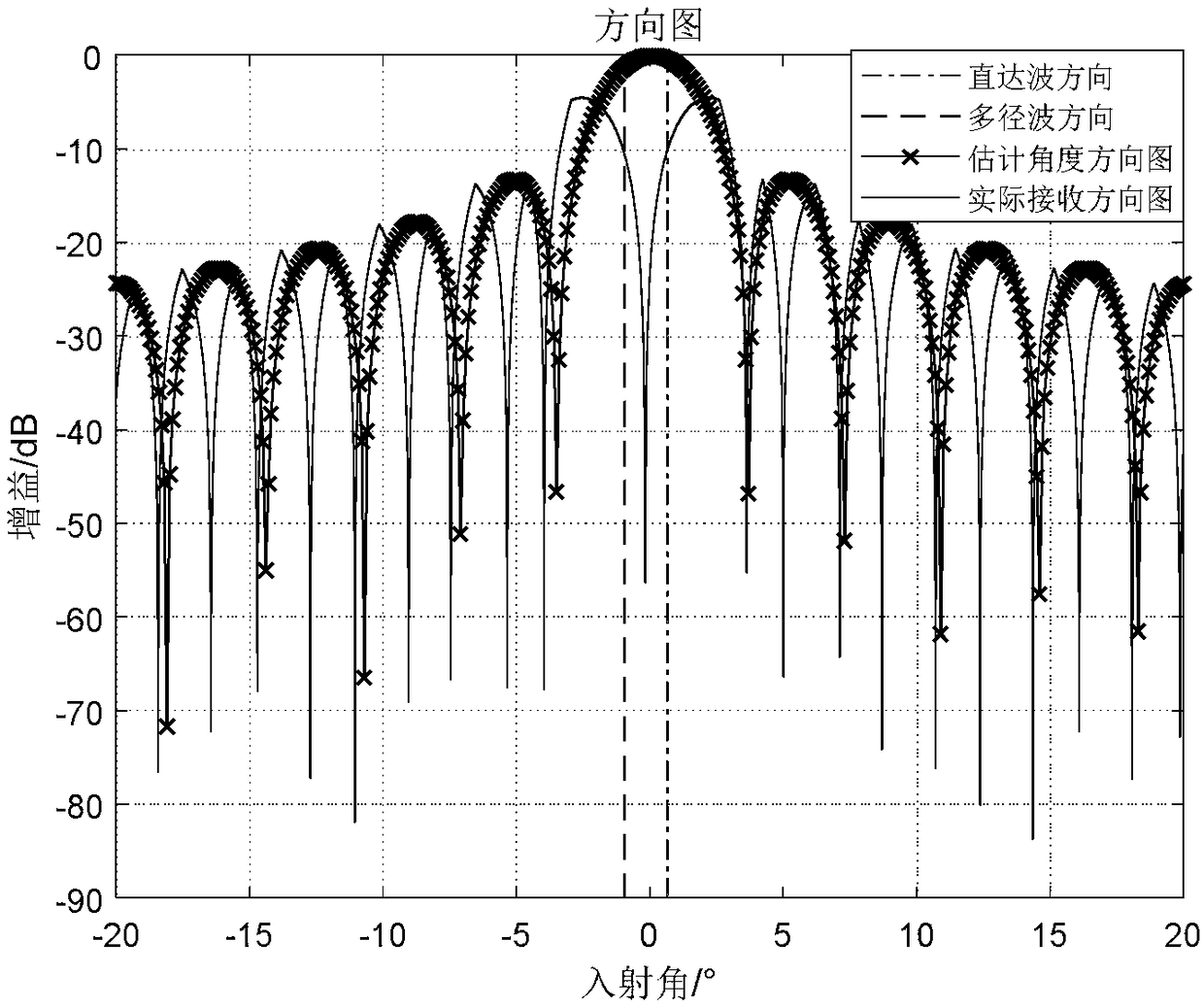
ActiveCN109407055AThe target search range is accurateNarrow searchWave based measurement systemsDecompositionRadar
The invention discloses a multipath utilization-based beam forming method. With the method adopted, the problem that multipath coherent signals cannot be effectively received in a low-altitude multipath environment in the prior art can be solved. The implementation process of the method includes the following steps that: an array radar acquires echo signal data, and solves a received signal covariance matrix Rxx; Toeplitz covariance matrix reconstruction is performed on the received signal covariance matrix, so that a new covariance matrix R is obtained; eigenvalue decomposition is performed on the reconstructed variance matrix, so that a noise subspace EN is obtained; a spatial spectral function S(theta) is formed according to the noise subspace; an angle corresponding to the peak value point of a spectral peak is found according to the spatial spectral function, namely the angle of a target is estimated; and with the estimated target angle adopted as a beam direction, beamforming isperformed. According to the method of the invention, with the estimated target angle adopted as the beam direction, beamforming is performed, and therefore, the multipath coherent information can be effectively utilized to improve the signal multi-noise ratio of echo signals. The method can be used for the effective reception of multipath coherent signals in a low-altitude multipath environment.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
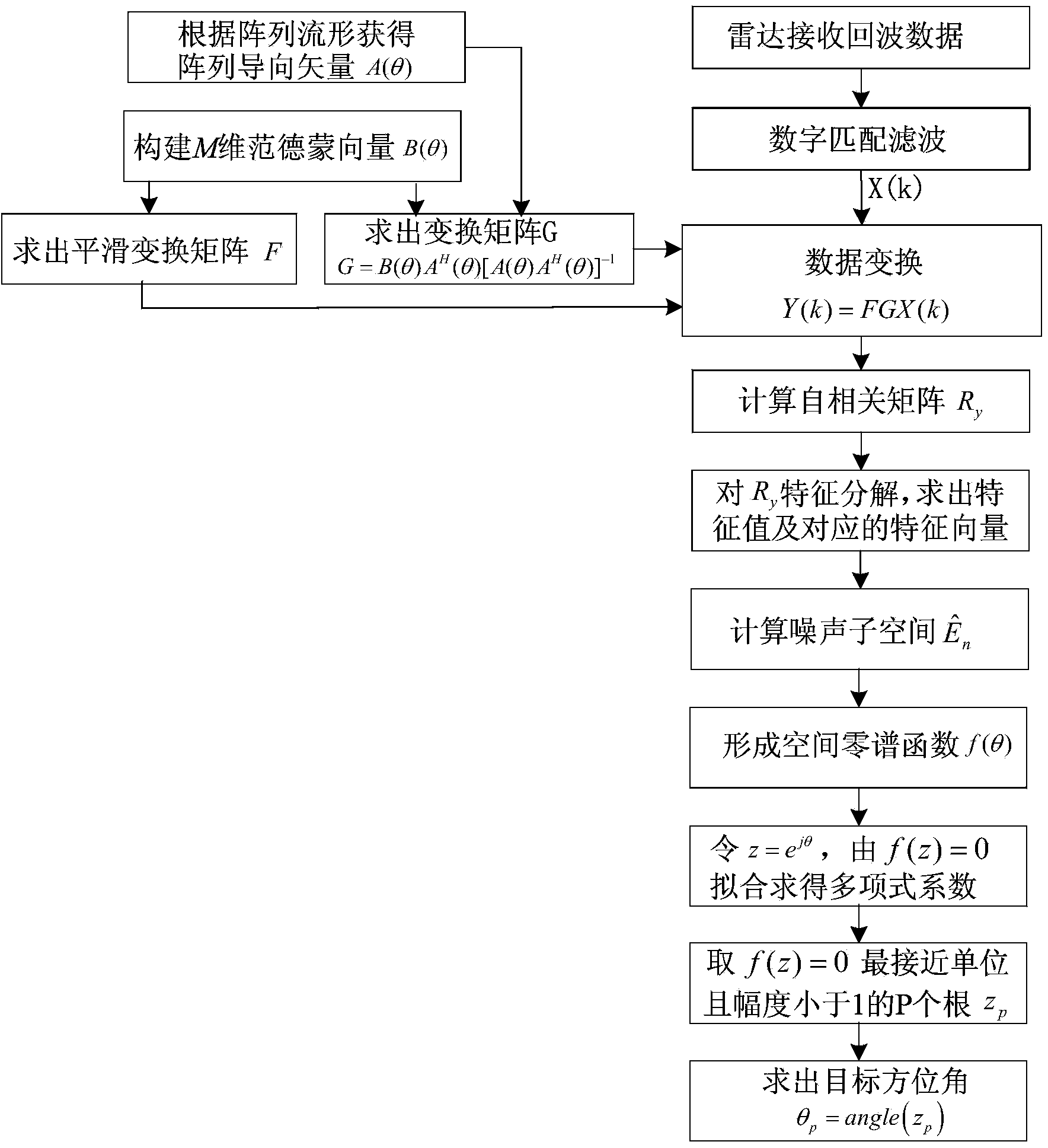
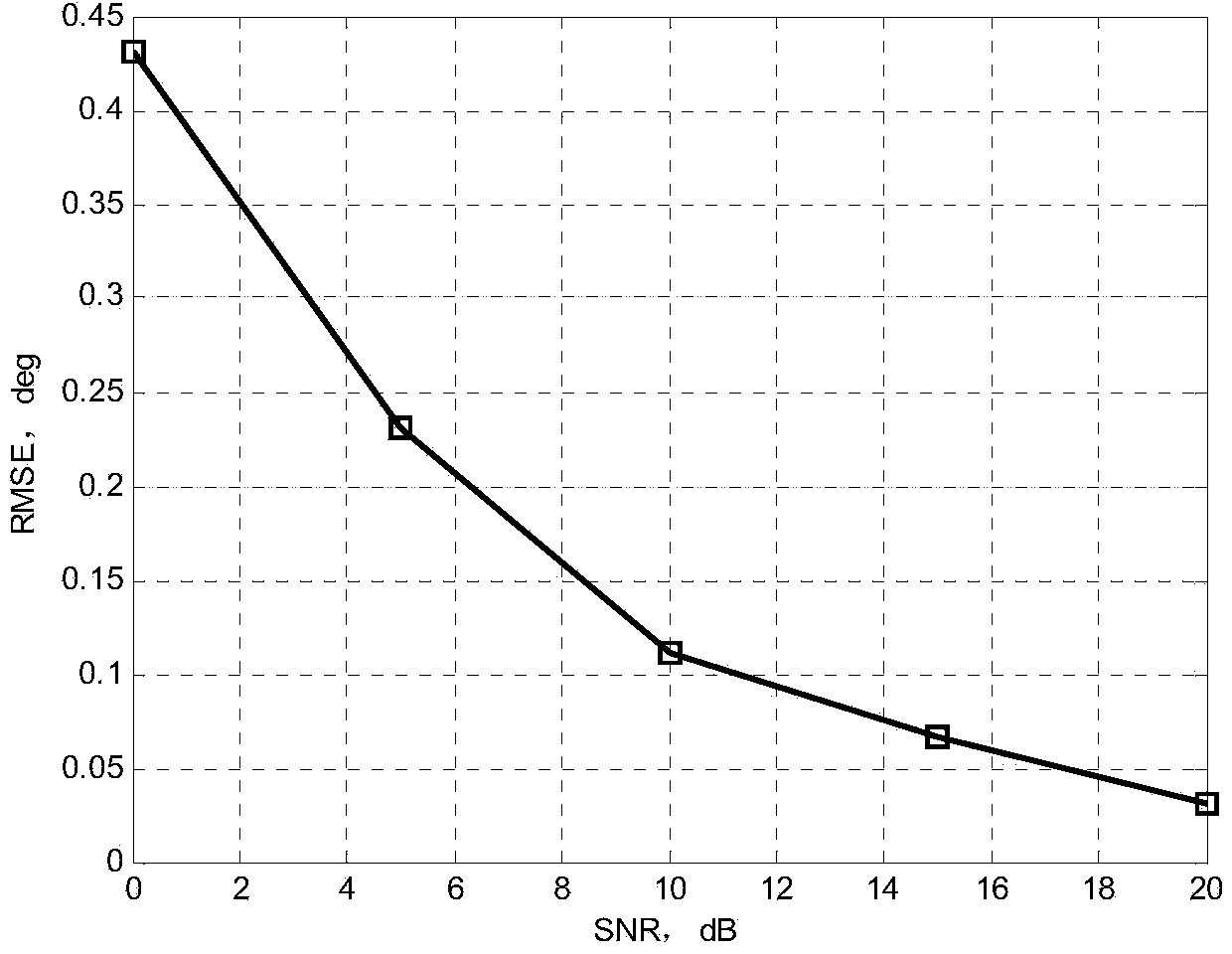
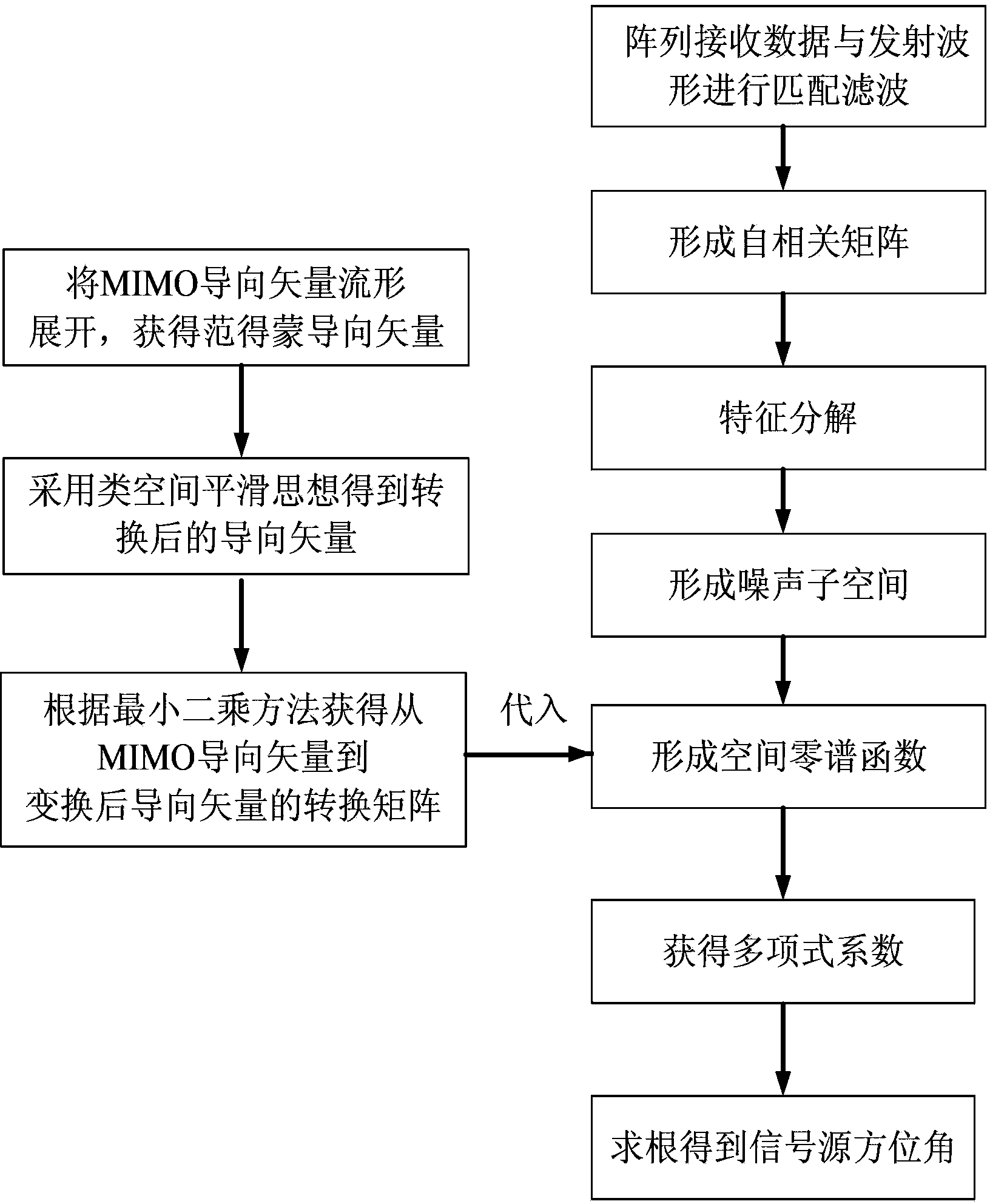
Method for direction of arrival estimation of coherent source of single-base MIMO radar
The invention belongs to the technical field of radars and discloses a method for direction of arrival estimation of a coherent source of a single-base MIMO radar. The method can be used for goal orientation and tracking of the single-base MIMO radar with any array manifold. The method is implemented in the following steps: step 1, a guiding vector of the single-base MIMO radar is written according to the array manifold; step 2, an M-dimension Vandermonde vector is set, and a transfer matrix G is obtained; step 3, a transformed guiding vector is obtained through a smooth transformation matrix F; step 4, matched filtering is conducted on received data of the MIMO radar, the received data obtained after matched filtering are recorded as X(k), transformed data Y(k)=FGX(k) are obtained through the transfer matrix G and the smooth transformation matrix F, and then an autocorrelation matrix is formed; step 5, eigen-decomposition is conducted on the autocorrelation matrix, and then a noise subspace is formed; step 6, a space zero spectral function is formed through the noise subspace; step 7, the polynomial rooting method is adopted to obtain a target azimuth angle.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Infrared spectrum characteristic extraction method for high-precision discriminating variety, producing area and growth mode of traditional Chinese medicinal materials
ActiveCN101498661ARapid determination of authenticityRapid mass determinationColor/spectral properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorInfrared
The invention discloses a method for extracting the characteristics of infrared spectrums for highly precisely distinguishing the varieties, the producing areas and the growth patterns of Chinese herbal medicine, which comprises the steps of obtaining the infrared spectrums of the Chinese herbal medicine samples of different varieties, preprocessing the infrared spectrums, classifying the Chinese herbal medicine samples according to the producing areas and the growth patterns thereof, calculating the spectral functions on differences of the Chinese herbal medicine samples of same and different varieties, obtaining the characteristic vectors of multiple Chinese herbal medicine samples, reducing the dimensionalities of the characteristic vectors and optimizing the distribution of the characteristic vectors so as to extract the characteristics of the infrared spectrums.
Owner:HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIV
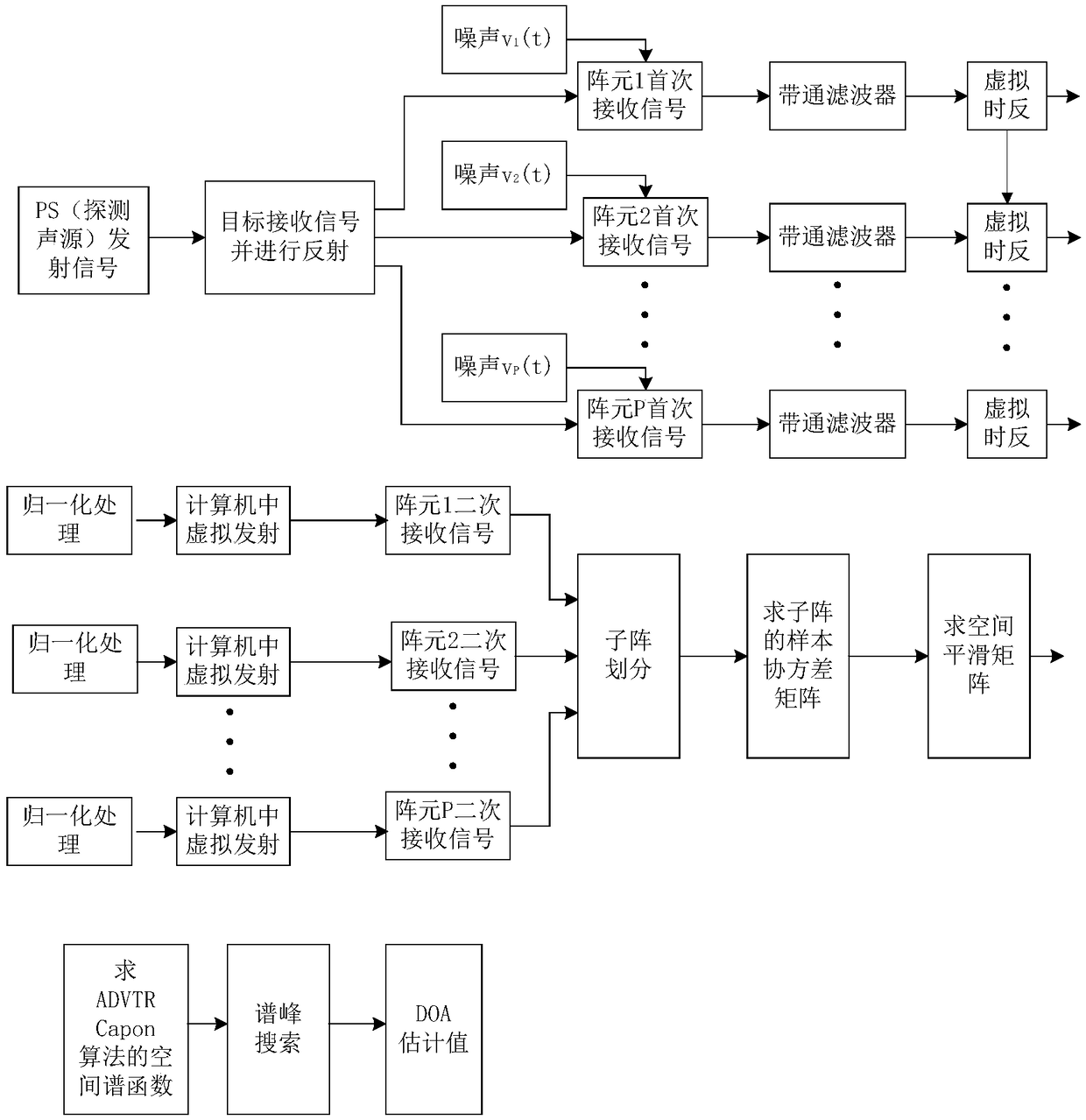
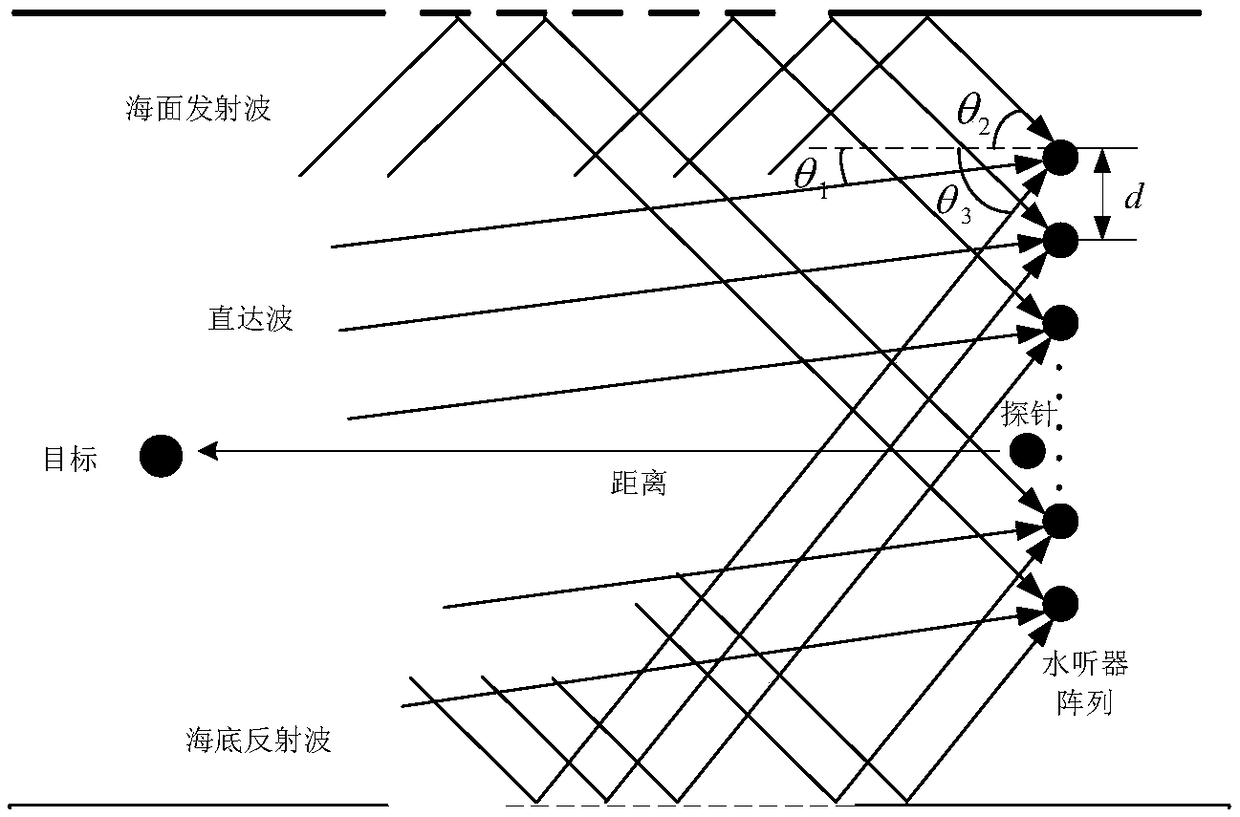
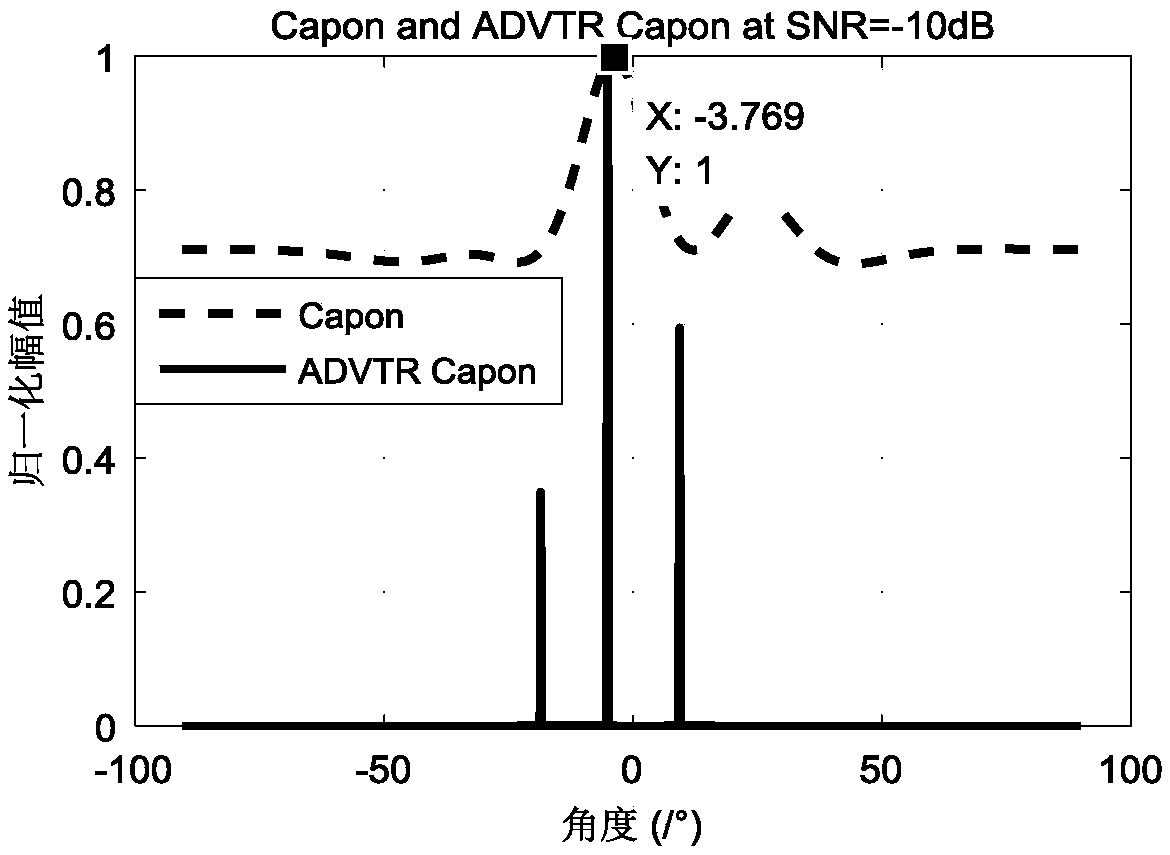
Underwater target DOA estimation method based on active virtual time reversal method
InactiveCN108845309ASmall energy attenuationImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPeak valueArray element
The invention provides an underwater target DOA (Directional of Arrival) estimation method based on an active virtual time reversal method. In a uniform linear array of a hydrophone, a detection acoustic source sends a signal, and a target receives the signal and reflects the signal. Each array element of the uniform linear array receives the signal and virtual time reversal is realized in a computer after filtering. After normalization processing, the time reversal signals are virtually transmitted to a channel as secondary transmission signals in the computer. Spatial smoothing is performedon secondary receiving signals and a covariance matrix of each sub-array is obtained respectively. A spatial spectral function of a Capon algorithm based on ADVTR (Active Detection on Virtual Time Reversal) is calculated and spectral peak searching is performed, and a spectral peak value is used as a DOA estimation value of the target. The invention reduces the energy attenuation of signals, improves the signal-to-noise ratio of the receiving signals, and can be directly extended to two or more targets.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
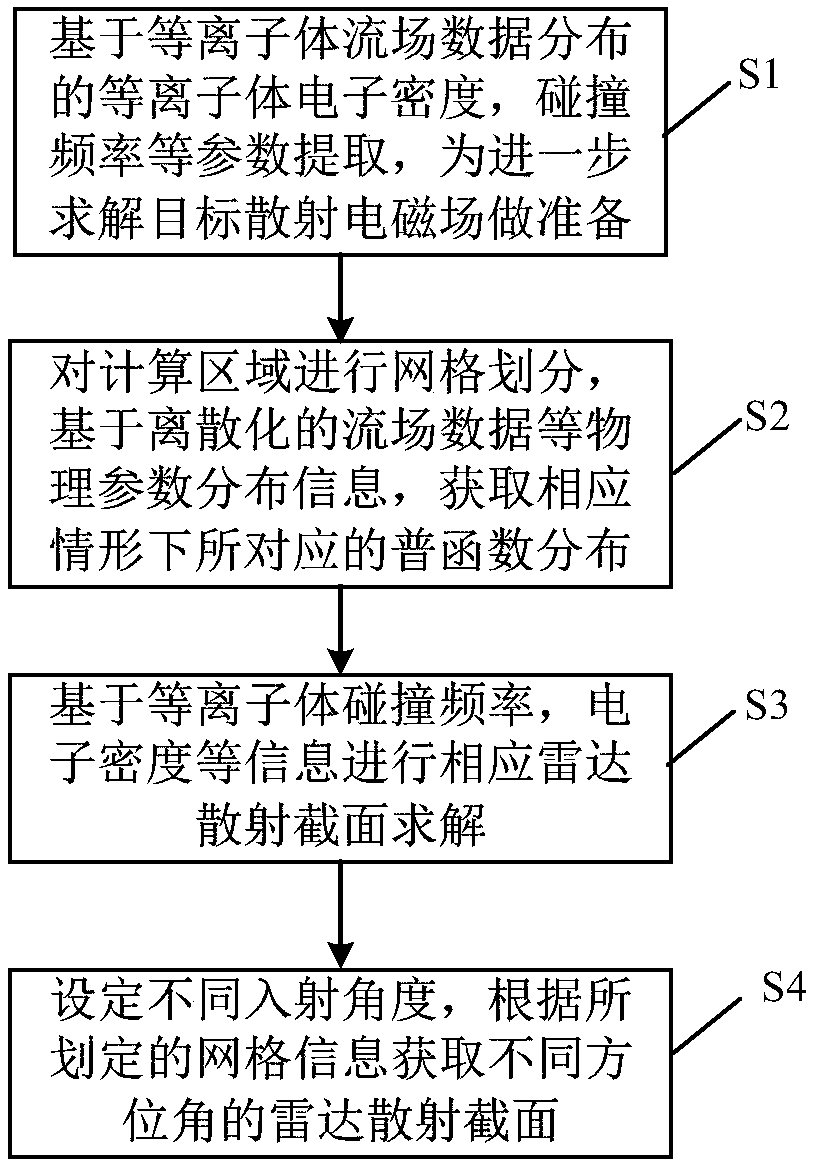
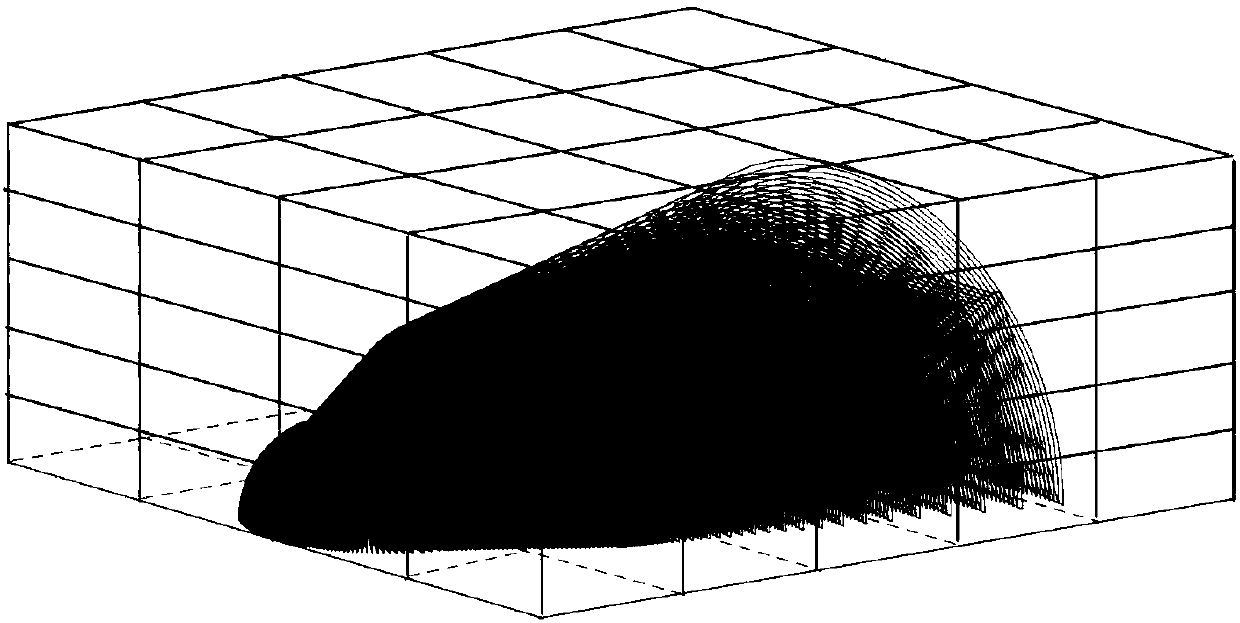
Rapid calculation method of radar scattering cross section of hypersonic speed aircraft
ActiveCN108152799ASmall amount of calculationIncrease calculation rateWave based measurement systemsScattering cross-sectionPlasma electron
The invention provides a rapid calculation method of the radar scattering cross section of a hypersonic speed aircraft. The method comprises that S1) on the basis of distribution characteristic of surrounding plasmas in the moving state of the aircraft, a physical field parameter including the plasma electron density and collision frequency and based on plasma flow field data is extracted; S2) a calculation area is divided according to grids, and on the basis of discrete information, a spectral function distribution model corresponding to a corresponding motion state is obtained; S3) the corresponding radar scattering cross section is solved on the basis of the physical field parameter of plasma flow field data distribution; and S4) different incident angles are set, and the radar scattering cross sections of different azimuths are obtained according to the divided grid information. The method has the advantages of being simple, rapid and equivalent.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Estimation method for arriving direction of monostatic MIMO radar based on random array manifolds
The invention discloses an estimation method for the arriving direction of a monostatic MIMO radar based on random array manifolds. The method mainly solves the problems that an existing technology is only suitable for linear arrays and large in calculated quantity. The method comprises the steps that 1) the guide vector quantity of the monostatic MIMO radar is written according to the array manifolds; 2) manifold spreading is carried out on the guide vector quantity of the MIMO radar to obtain the Vandermonde guide vector quantity, guide vector quantity transfer is conducted by means of a spatial smoothing thought, and a transfer matrix from the MIMO guide vector quantity to the guide vector quantity after transfer is evaluated; 3) a receiving array and a transmitted waveform are utilized to carry out matched filtering to form an autocorrelation matrix; 4) characteristic decomposition is conducted on the autocorrelation matrix to obtain an eigenvalue and an eigenvector, and the eigenvector is selected to form a noise subspace; 5) the noise subspace is used for forming a space zero spectral function, and a polynomial rooting method is adopted to obtain an azimuth angle. The method can achieve quick estimation on the arriving direction of the monostatic MIMO radar based on the random array manifolds, is small in operation quantity, and can be used for target locating and radar tracking.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method of evaluating inhibition of CCOS (computer controlled optical surfacing) process on errors under different frequencies
The invention relates to a method of evaluating the inhibition of CCOS (computer controlled optical surfacing) process on errors under different frequencies. The method includes the steps of S1, building a formula (1), PSDaft=(1-H)(1-H)<*>*PSDbef, for smoothing spectral function H, PSDaft and PSDbef according to the power spectral density functions PSDbef and PSDaft before and after optical element polishing, with (1-H)<*> being a conjugate to (1-H) and the symbol * being an operator used for obtaining the conjugate; S2, subjecting the formula (1) to bilateral modulo operation according to complex operation algorithms to obtain a power spectral density function expression (2), PSDaft=|(1-H)|2*PSDbef, for polished surface shape data; S3, solving the formula (2) according to |H|<1 due to the fact that the smoothing spectral function H is for Fourier transform after function normalization is removed, thus establishing a smoothing spectral function H formula (3); expressing the inhibition of the PCCOS process on errors under different frequencies as a frequency normalization function, calculating smoothing spectral function curves according to the PSDbef and PSDaft obtained before and after polishing, and evaluating the magnitude of the inhibition of the CCOS process on the errors under different frequencies according to values of the smoothing spectral function curves.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Temperature measuring device based on high-pressure gas Rayleigh-Brillouin scattering spectrum
InactiveCN102589714AImprove reliabilityHigh precisionSpectrum investigationPyrometry using electric radation detectorsSpectral functionHigh pressure
The invention relates to a temperature measuring device based on high-pressure gas Rayleigh-Brillouin scattering spectrum. The device can probe the Brillouin frequency shifting rate in the Rayleigh-Brillouin scattering spectrum at different pressures to measure acoustic velocity at different pressures so as to achieve temperature retrieval. 355nm single-die laser enters the high pressure gas to mutually interact with various gas molecules in the gas; the scattering signal passes through an F-P scanning interferometer and is received by a photon detector, therefore, the Rayleigh-Brillouin scattering spectrum of the high pressure gas can be obtained. According to the temperature measuring device, the precise measurement on the gas temperature at different pressures is achieved through analysis and calculation of the spectral function.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Single dipole polarization sensitive rotation array DOA and polarization parameter joint estimation method
InactiveCN106990386AAchieving Joint EstimationSmall scaleRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsEstimation methodsSpectral function
The invention is to provide a single dipole polarization sensitive rotation array DOA and polarization parameter joint estimation method. The method is characterized by, to begin with, carrying out mathematical modeling on an array receiving signal of a polarization sensitive rotation array; and then, modifying an expression of a steering vector in a spectral function of a MUSIC algorithm, thereby realizing joint estimation of incident signal DOA and polarization parameters by utilizing the MUSIC algorithm. The rotation array not only can be constructed by utilizing the single dipole polarization sensitive rotation array, but also can be constructed by utilizing any polarization sensitive antenna unit or combination, and has high portability. The array can effectively reduce the number of channels of the system, and greatly reduces cost of the system; and with fewer array elements, the problem of channel inconsistency due to larger number of array elements can be prevented effectively.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
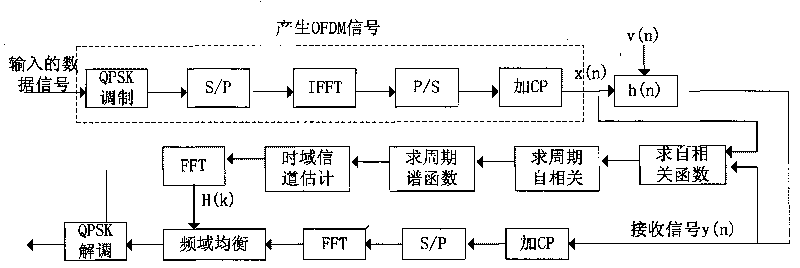
Blind channel estimation method based on cyclostationarity of OFDM signals
InactiveCN101729479AReduce the numberImprove accuracyBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumResource utilization
The invention discloses a blind channel estimation method based on the cyclostationarity of OFDM signals, which has the advantages that the two methods are used for analyzing the z transformation of the time delay variable Tau in the periodic spectral function of OFDM-received signals based on one fixed cycle frequency and realizing the accurate estimation of the channel information through selecting two different related values of the z transformation of the delay variable Tau, finally using the information containing the channel amplitude and the minimum phase and combining the current least square method. The two methods only use the spectral information of one cycle frequency, so that the number of the cycle frequencies is reduced and the spectral resource utilization rate is effectively improved, thereby improving the accuracy of the channel estimation. By the emulation verification, the performance of the method is obviously superior to that of the traditional blind channel estimation method.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
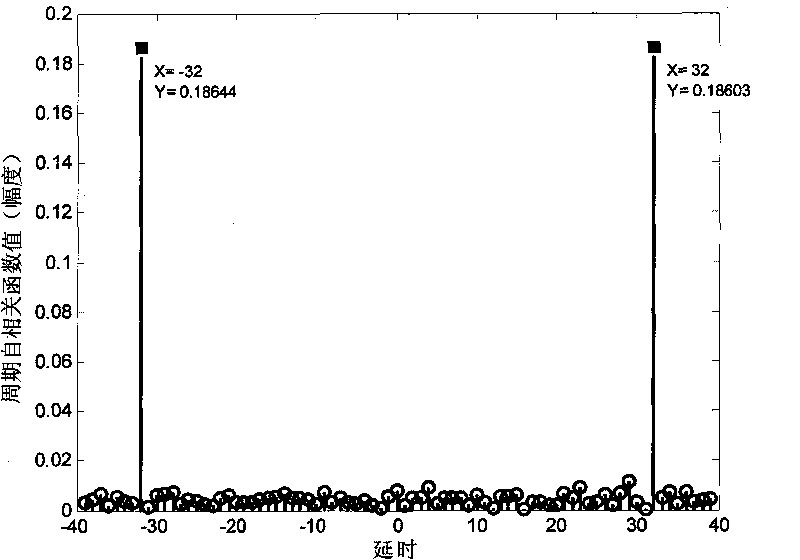
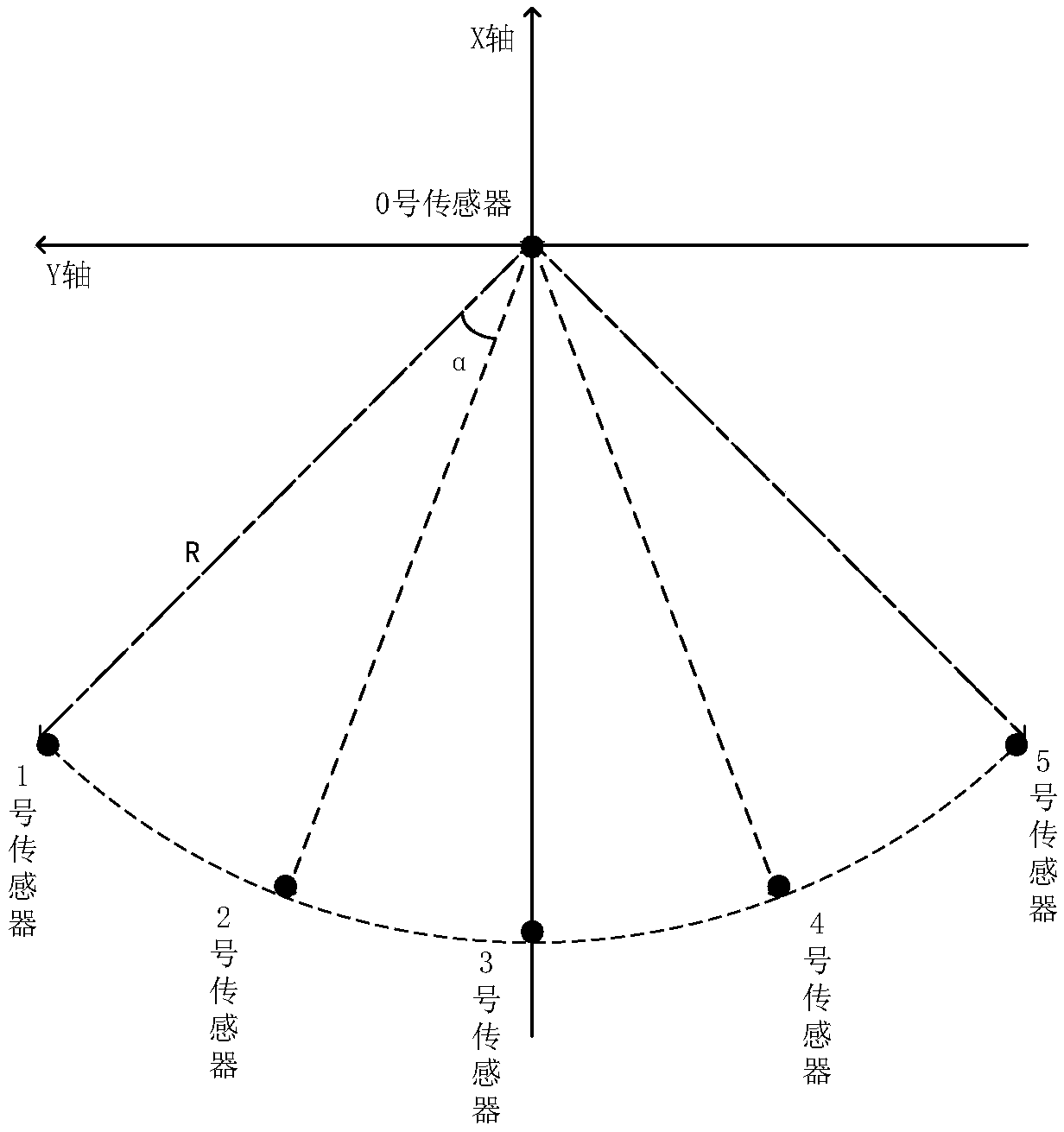
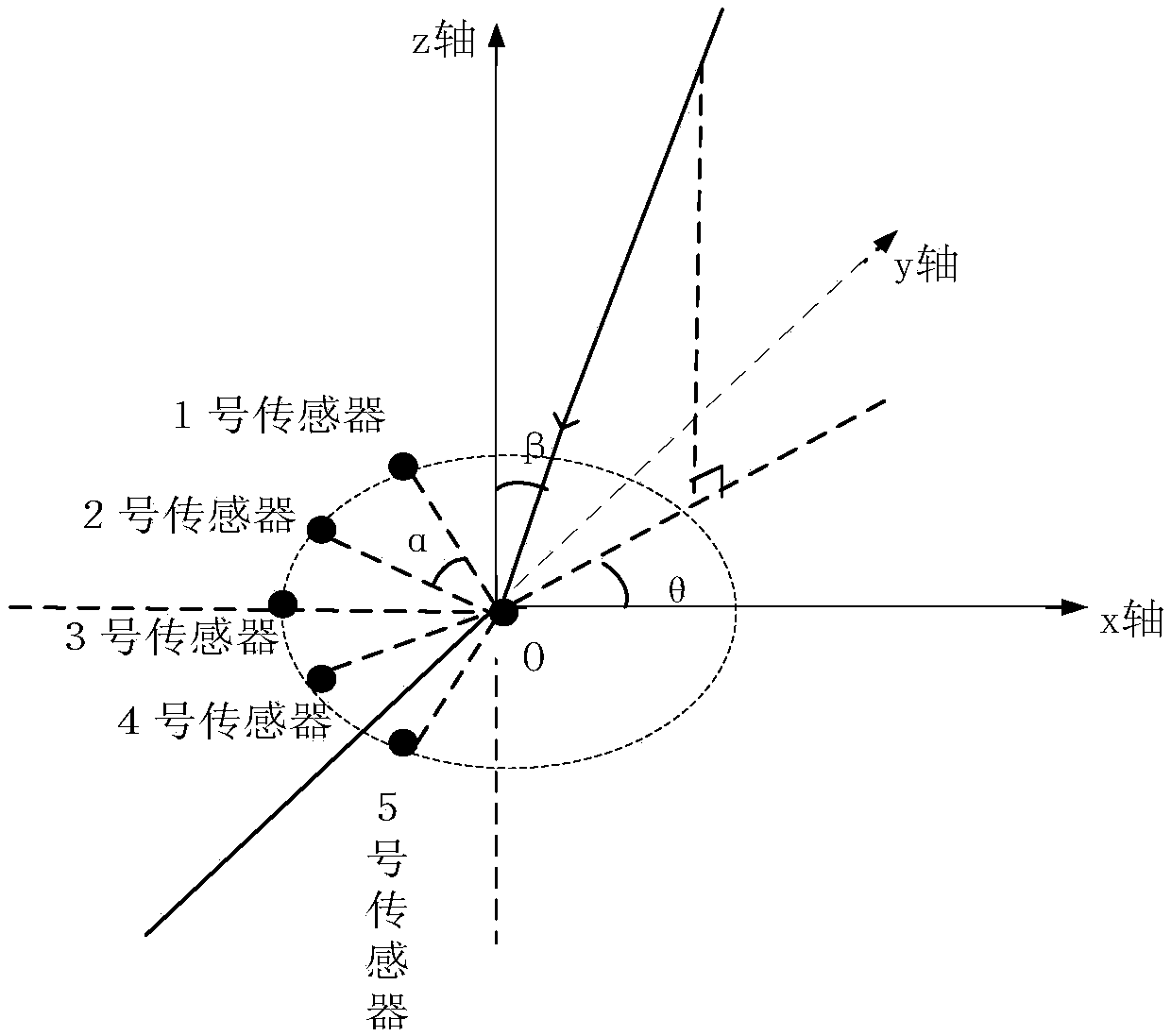
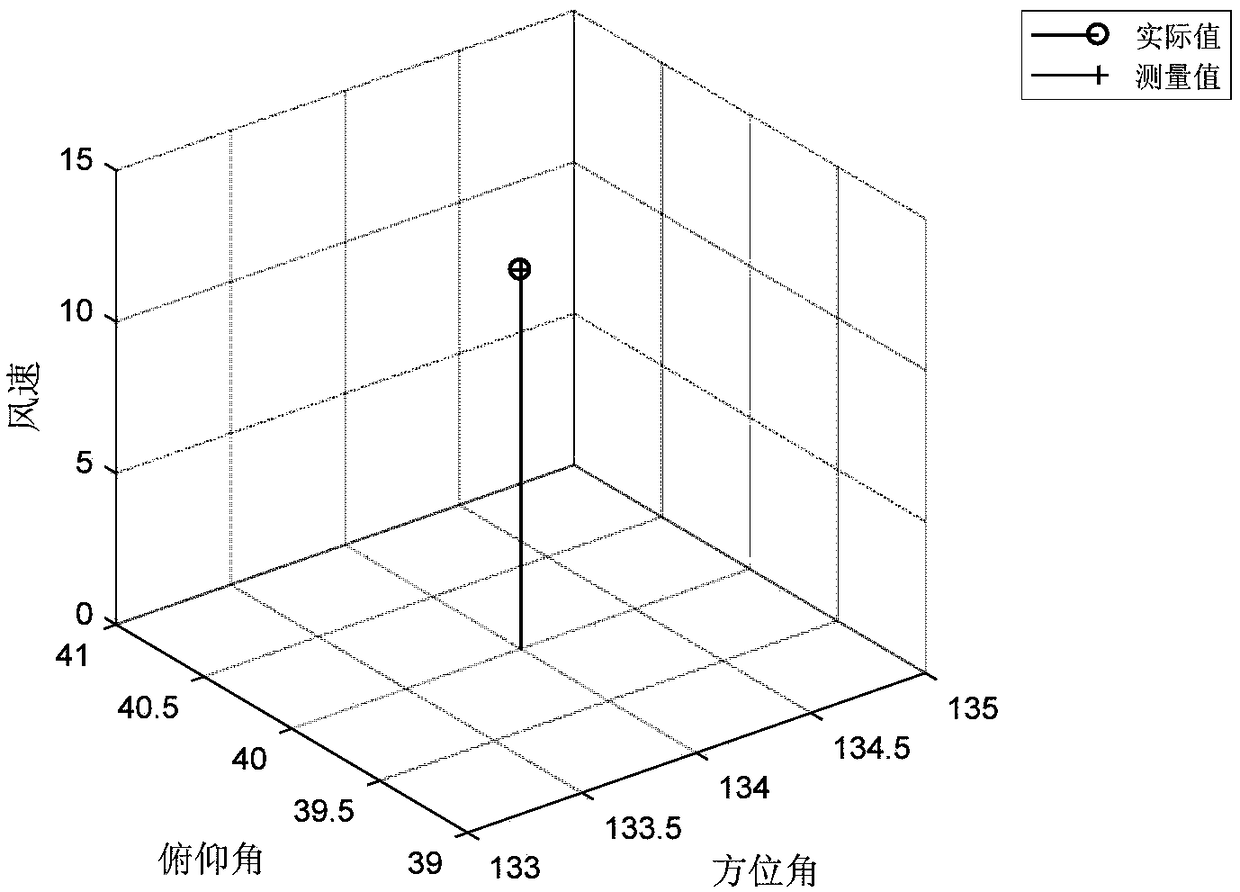
Three-dimensional wind speed and direction measuring method based on multiple signal classification algorithm
InactiveCN109188019AEfficient measurementAccurate measurementIndication/recording movementFluid speed measurementSensor arrayAlgorithm
The invention proposes a three-dimensional wind speed and direction measuring method based on a multiple signal classification algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: arranging ultrasonicsensors in a certain manner, and establishing an appropriate mathematical relationship between the speed, pitch angle and azimuth information of wind in a three-dimensional space; calculating time delay information when each sensor receives the information; and using the multiple signal classification algorithm to carry out subspace classification on a covariance matrix of information data received by a sensor array, calculating a spectral function and searching for a spectral peak value to obtain information about the speed, azimuth and pitch angle of the wind, so that the wind in the three-dimensional space can be accurately measured. The three-dimensional wind speed and direction measuring method based on the multiple signal classification algorithm provided by the invention does not rely on a time difference that an actual signal arrives at each sensor in the case of downwind and headwind, but uses a mathematical relationship between a wind vector and each sensor to calculate thedelay of an emission signal arriving at each receiving sensor. The method is simple to implement, does not require timing, and is less influenced by human and environmental factors.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
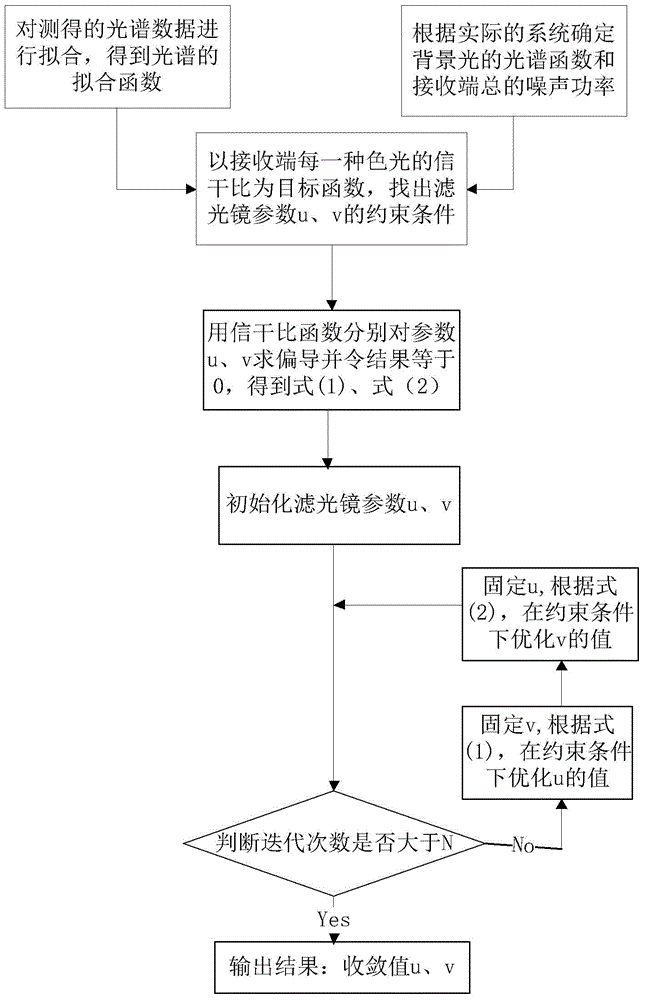
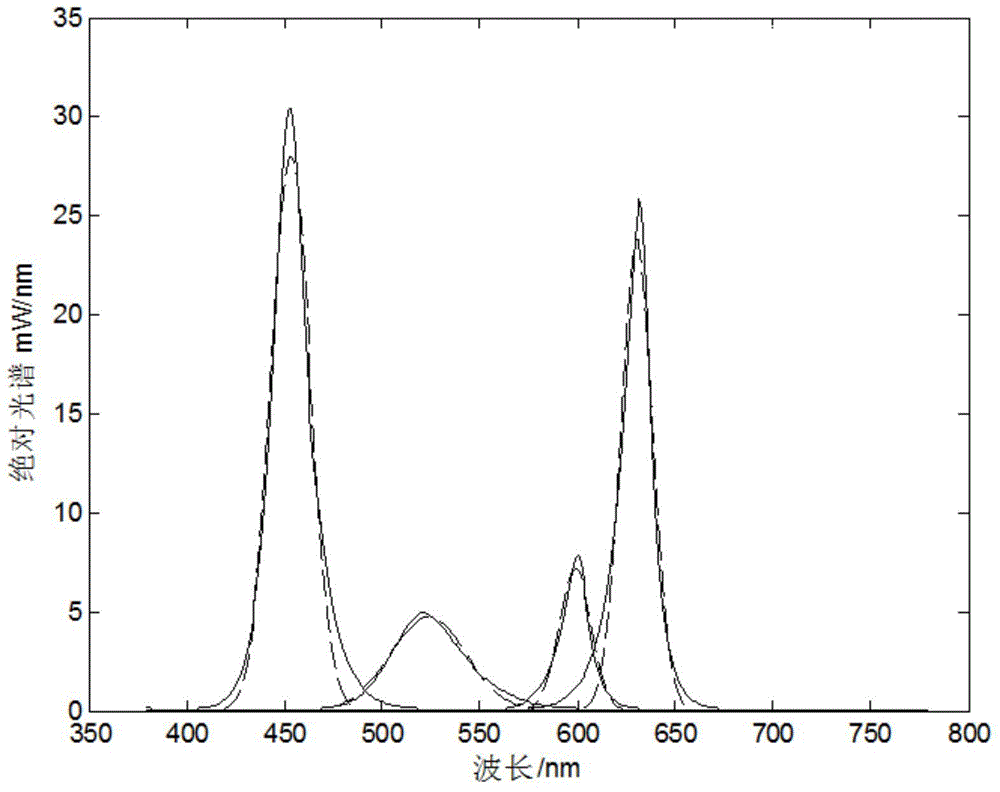
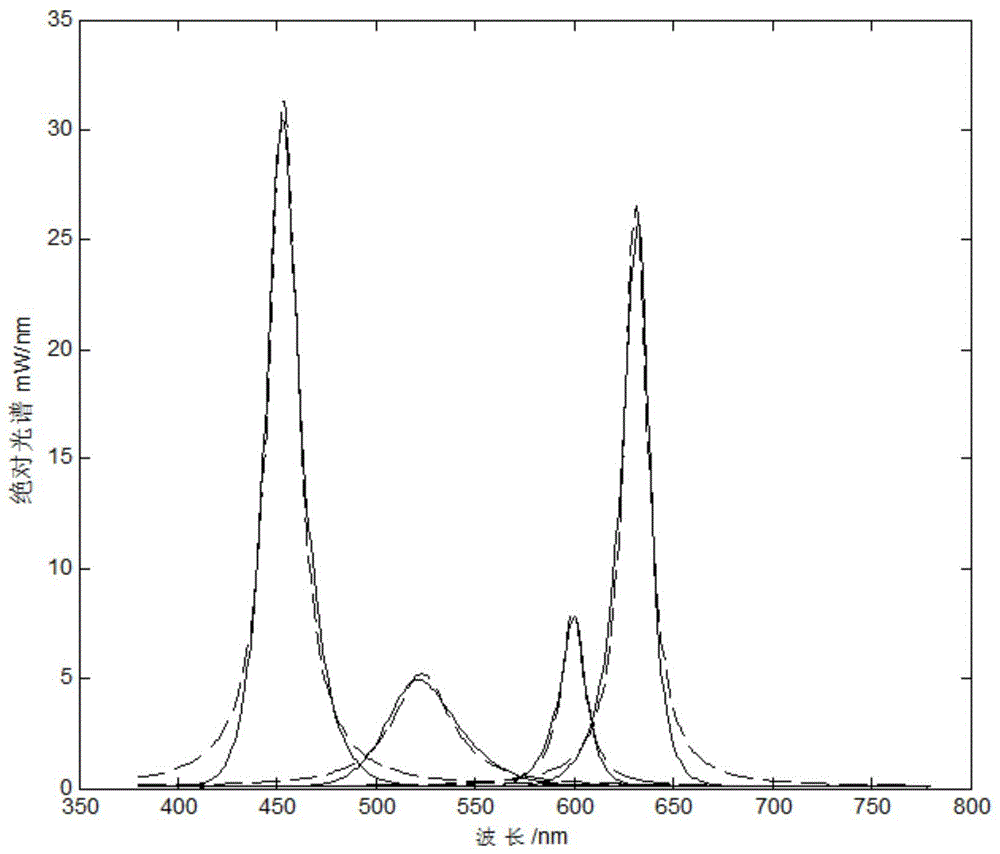
Filter parameter optimization method based on visible light communication
ActiveCN104993867AReduce cross-interferenceExcellent filter parametersClose-range type systemsElectromagnetic receiversSpectral fittingVisible light communication
The invention provides a filter parameter optimization method based on visible light communication, comprising: firstly utilizing a spectrometer to detect the spectrum data of each monochromatic light, and employing a gauss or Lorentzen function for fitting to obtain a spectral fitting function; in dependence on a real system, determining the spectral function of a bias light and the total noise power of a receiving terminal; using the signal to interference ratio of each color light at the receiving terminal as an objective function, and meanwhile determining constraint conditions of filter parameters; first using a signal to interference ratio function to solve the partial derivative of each variable, and setting a partial derivative result to be zero, then fixing a variable, and optimizing another variable under the constraint conditions, and successively performing rounds of iteration to obtain the optimal solution of the filter parameters; and respectively solving objective functions of color lights to obtain the optimal value of parameters of each colored filter. The method is suitable for a plurality of filters, has a fast convergence rate in operation, and can better reduce interference among light colors.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
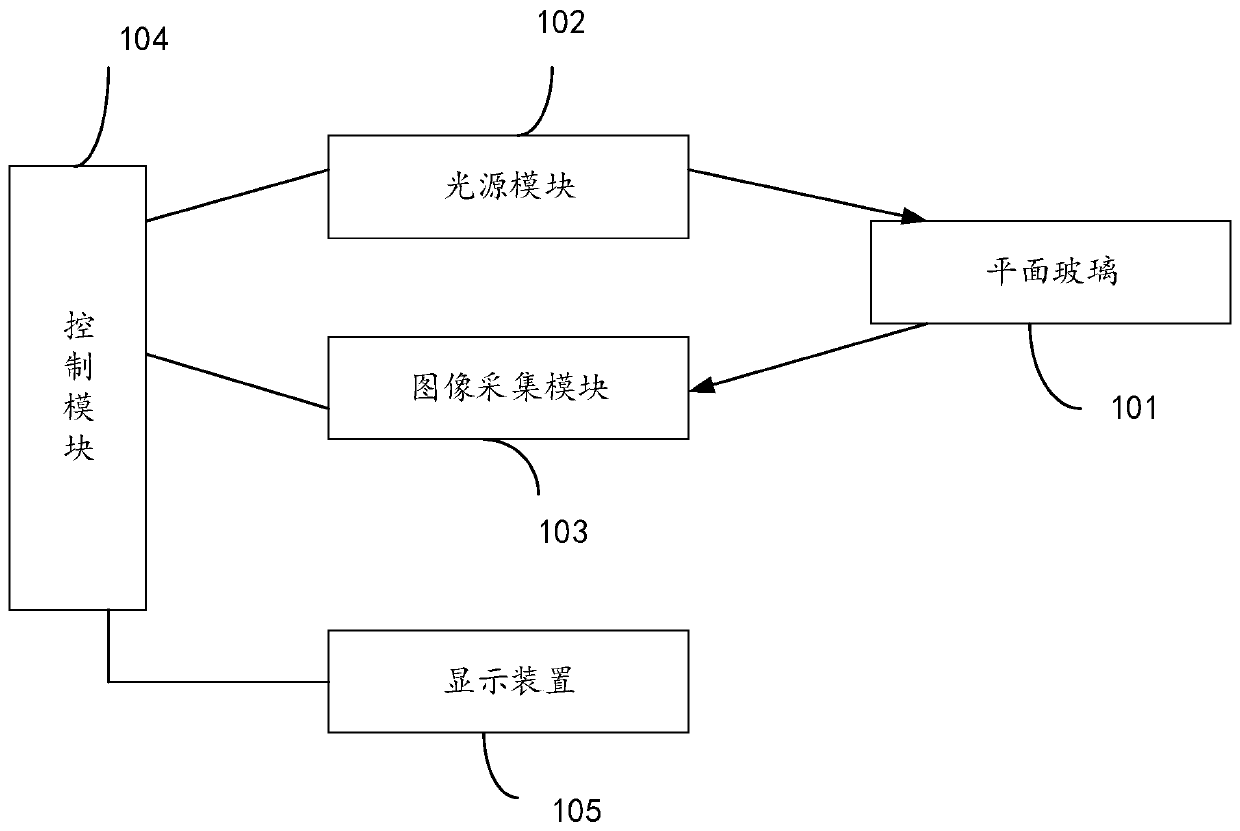
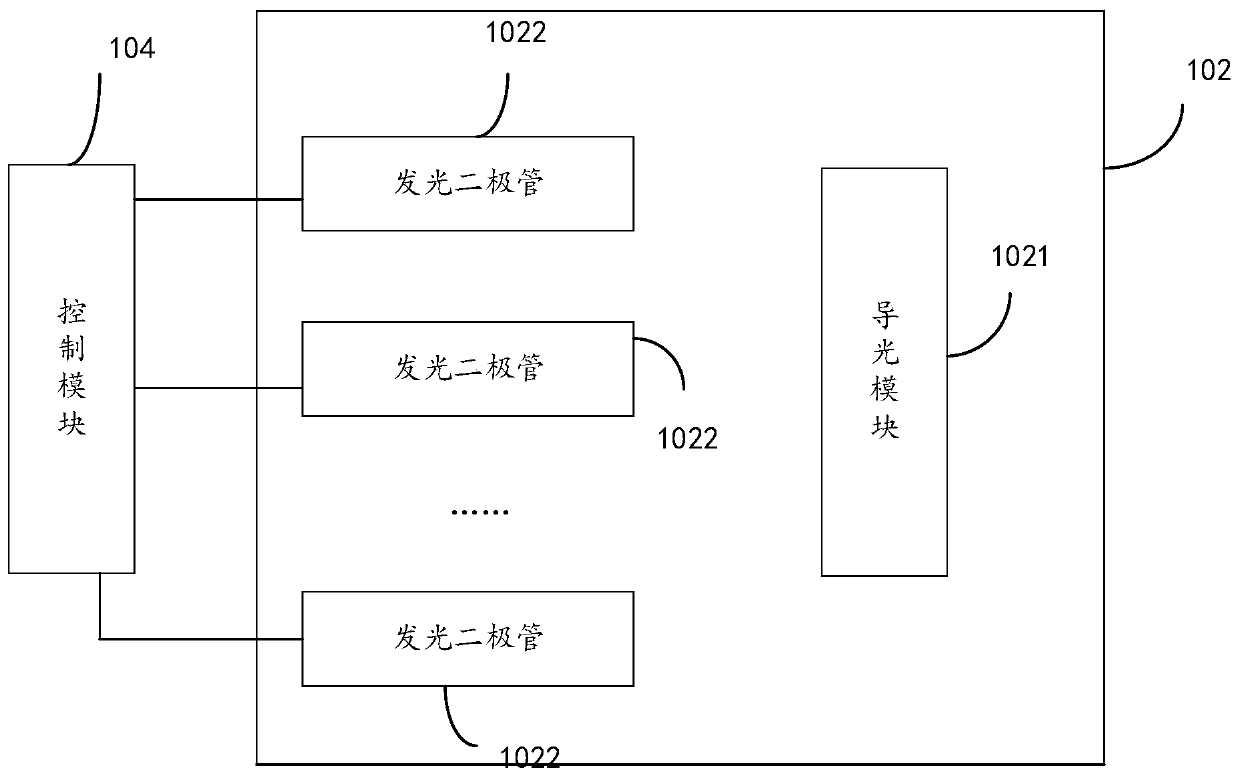
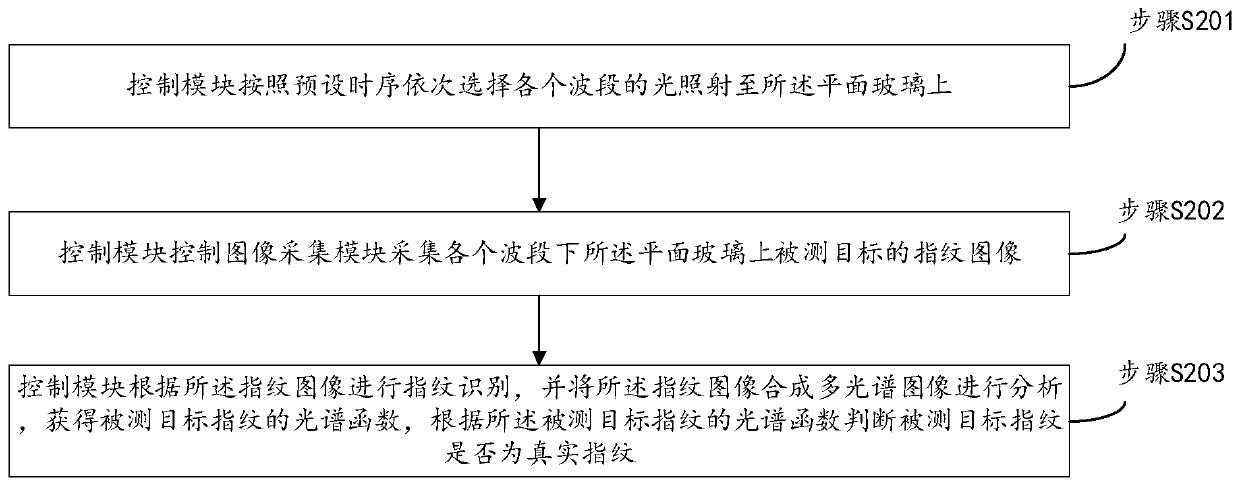
Multispectral living fingerprint identification equipment and identification method
ActiveCN110046564AEffective Liveness DetectionImprove detection accuracyMatching and classificationDetecting live finger characterSpectral functionMultispectral image
The invention provides multispectral living fingerprint identification equipment and an identification method. The equipment comprises plain glass, a light source module, an image acquisition module and a control module, the light source module is used for providing light of multiple different wave bands. The control module is used for sequentially selecting light of each wave band according to apreset time sequence and irradiating the light to the plain glass; the image acquisition module is used for acquiring a fingerprint image of a tested target on the plain glass under each wave band andsending the fingerprint image to the control module; the control module is also used for carrying out fingerprint identification according to the fingerprint image, synthesizing the fingerprint imageinto a multispectral image, analyzing the multispectral image to obtain a spectral function of the detected target fingerprint, and judging whether the detected target fingerprint is a real fingerprint or not according to the spectral function of the detected target fingerprint. The equipment can effectively carry out living body detection on fingerprints, and is high in detection precision and high in accuracy.
Owner:深圳市合飞科技有限公司
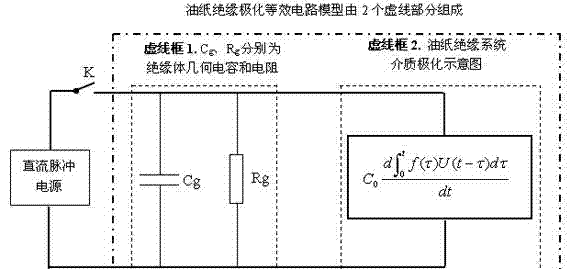
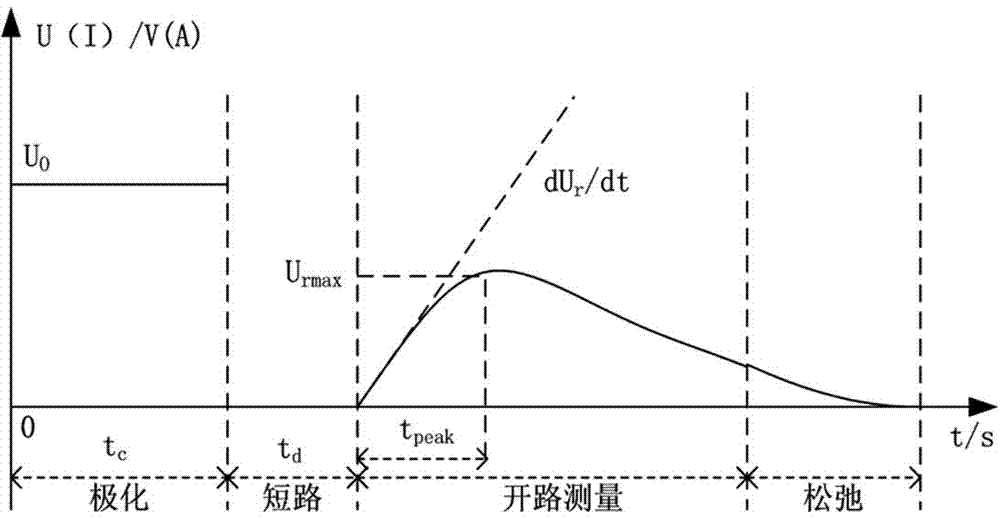
Method for judging number of energy storage elements and number of relaxation response branch circuits in oiled paper insulation equivalent circuit
InactiveCN103698664AReliable and Powerful Analytical ToolsTesting dielectric strengthCapacitanceDecomposition
The invention provides a method for judging the number of energy storage elements and the number of relaxation response branch circuits in an oiled paper insulation equivalent circuit. The method comprises the following steps: m spectral lines can be separated after successive differential spectral decomposition is carried out on the spectral lines of a return voltage differential time domain spectral function of oiled paper insulation equipment by a time domain dielectric spectral decomposition method, and the number of the energy storage elements (polarized capacitors) of the dielectric polarization equivalent circuit of the oiled paper insulation equipment can be judged as m; the number of the relaxation response branch circuits in the equivalent circuit in a black box is N, wherein N=m-1. A blank in the research field of studying oiled paper insulation aging through an extended Debye model is filled by the judging method provided by the invention, and a reliable and powerful analysis means is provided for construction of the oiled paper insulation relaxation response equivalent circuit, in-depth investigation of insulation aging and the like in future.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com