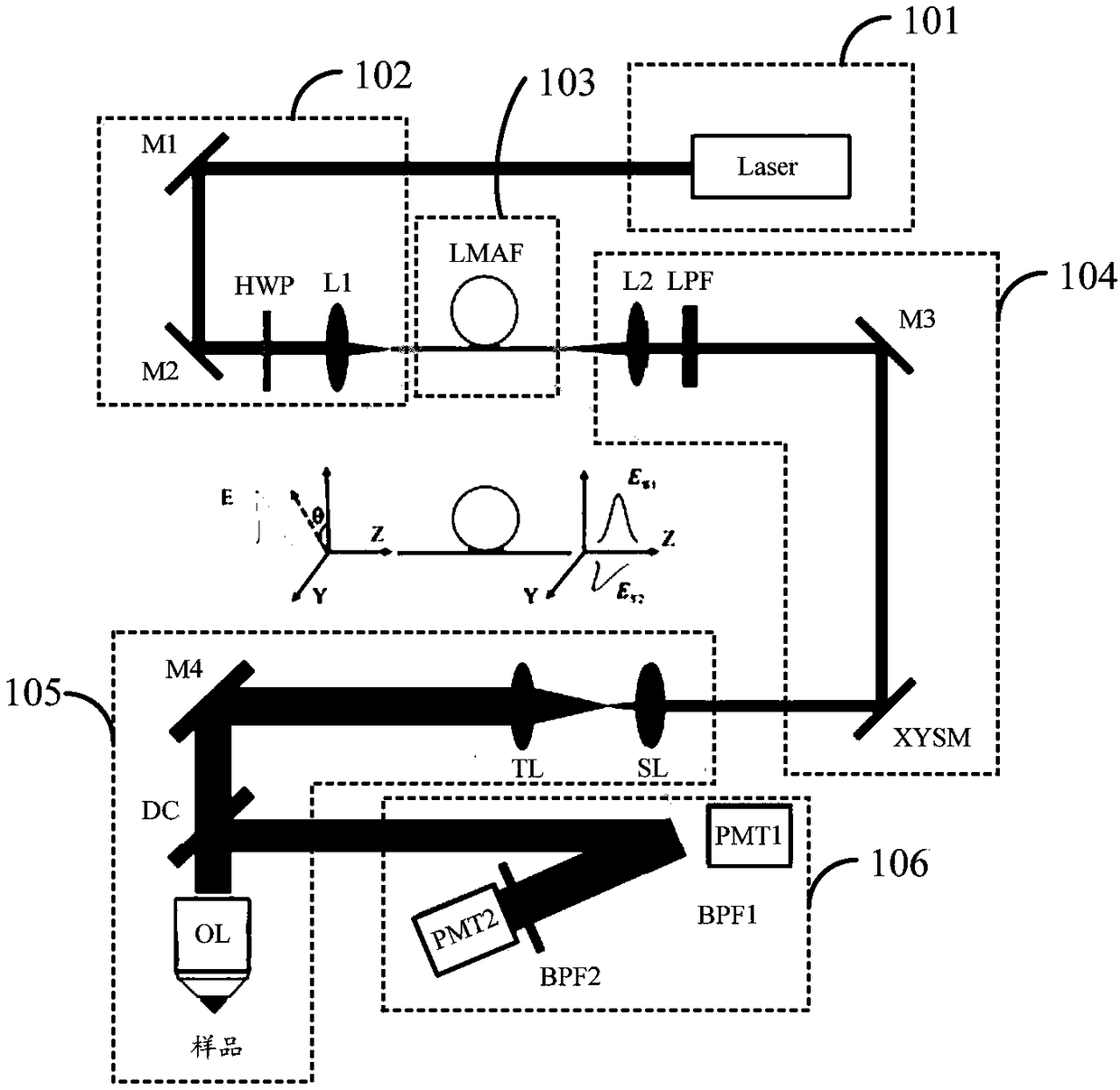
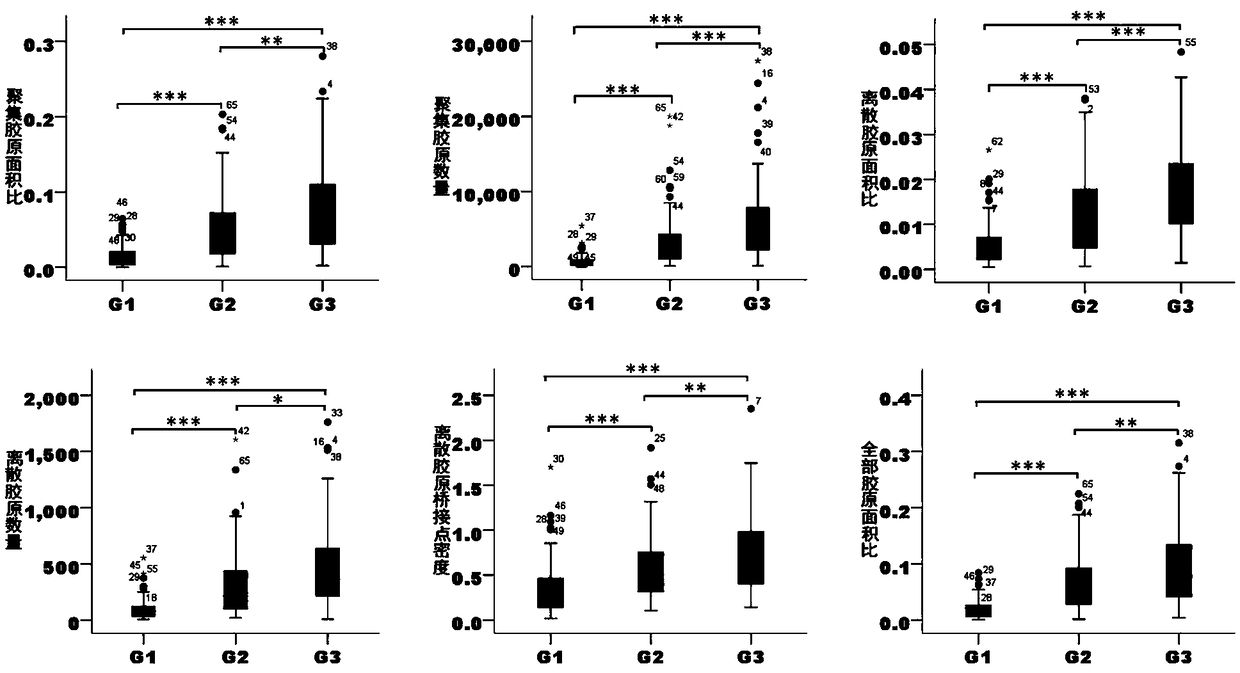
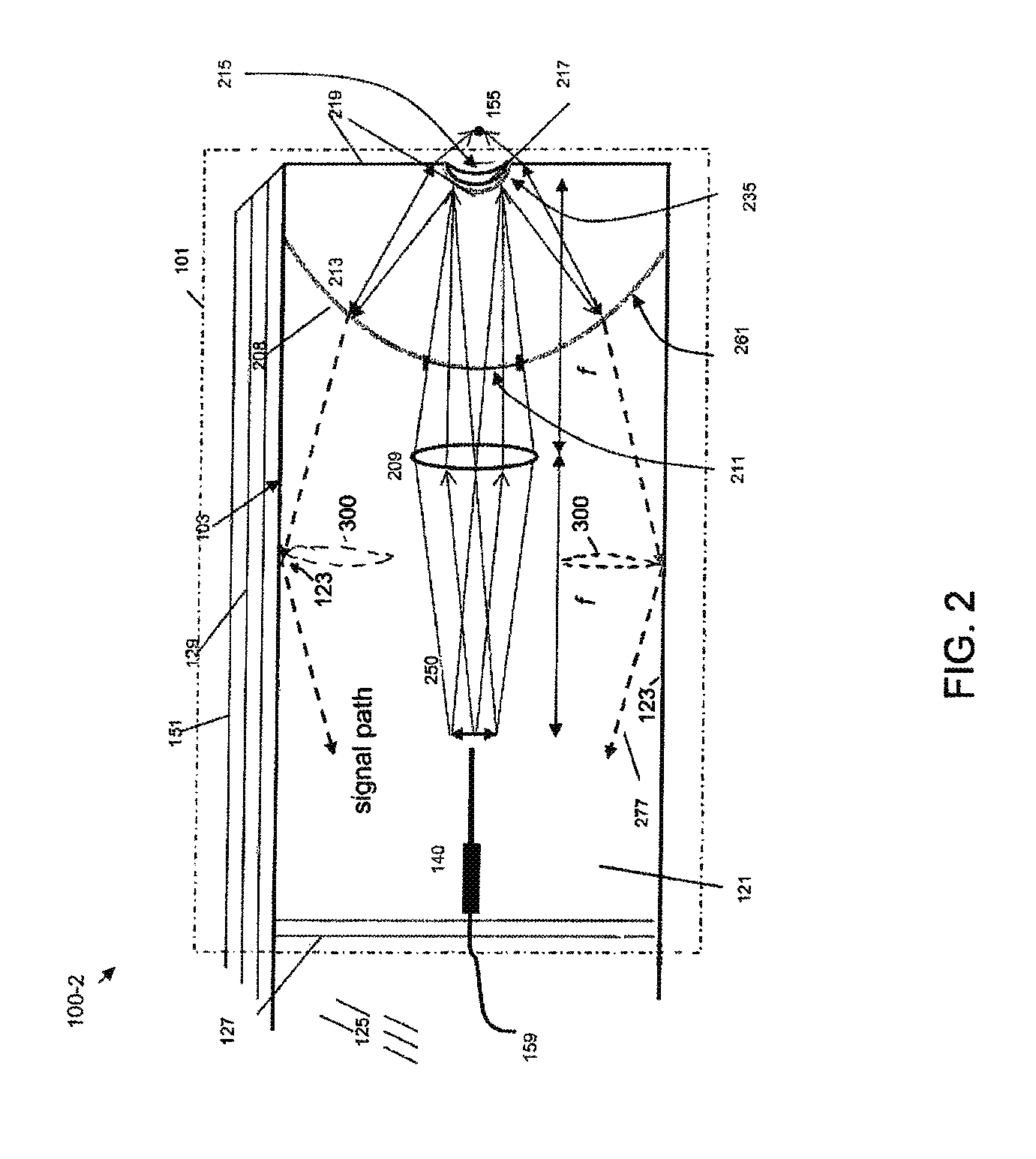
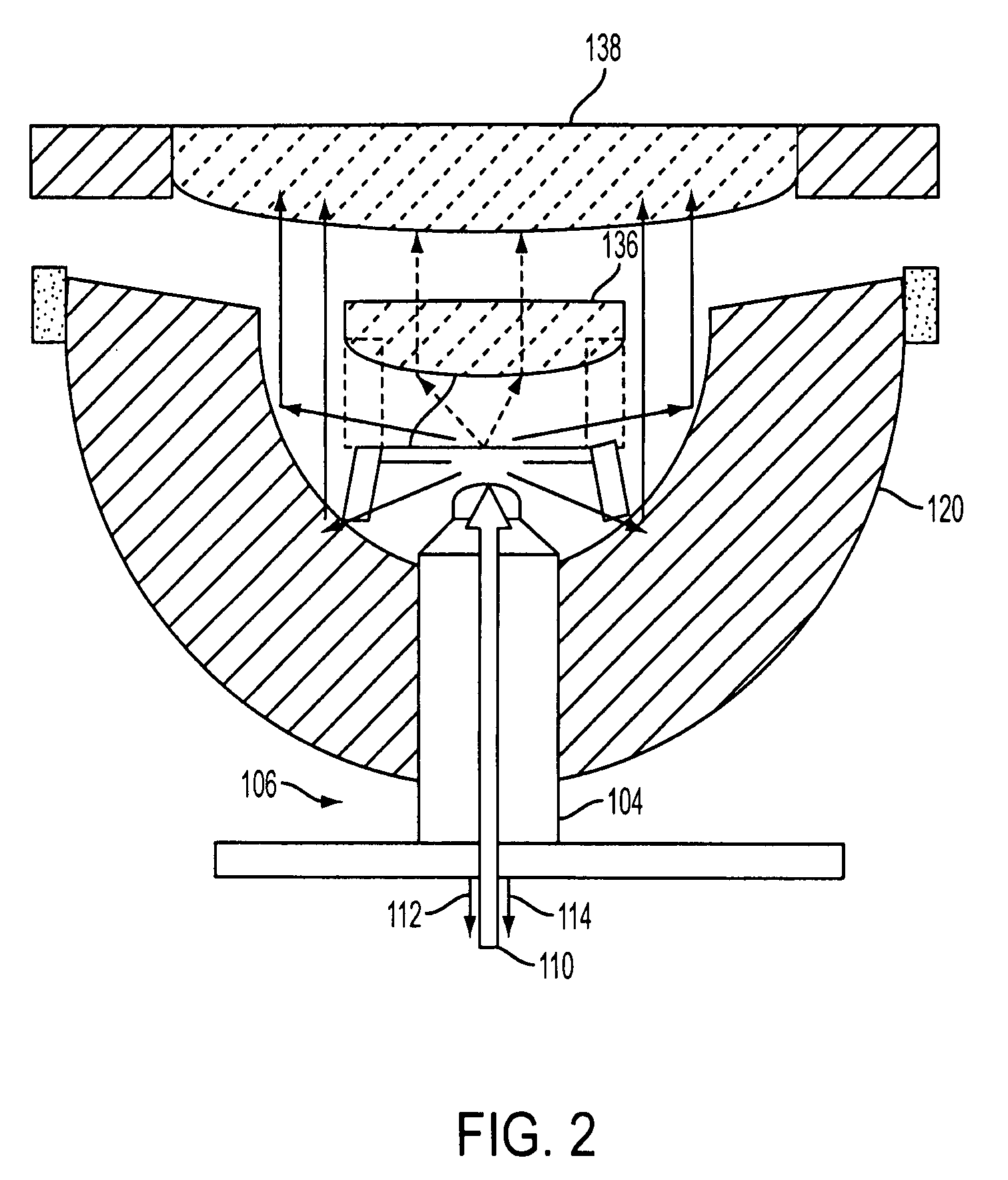
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Multi photon microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
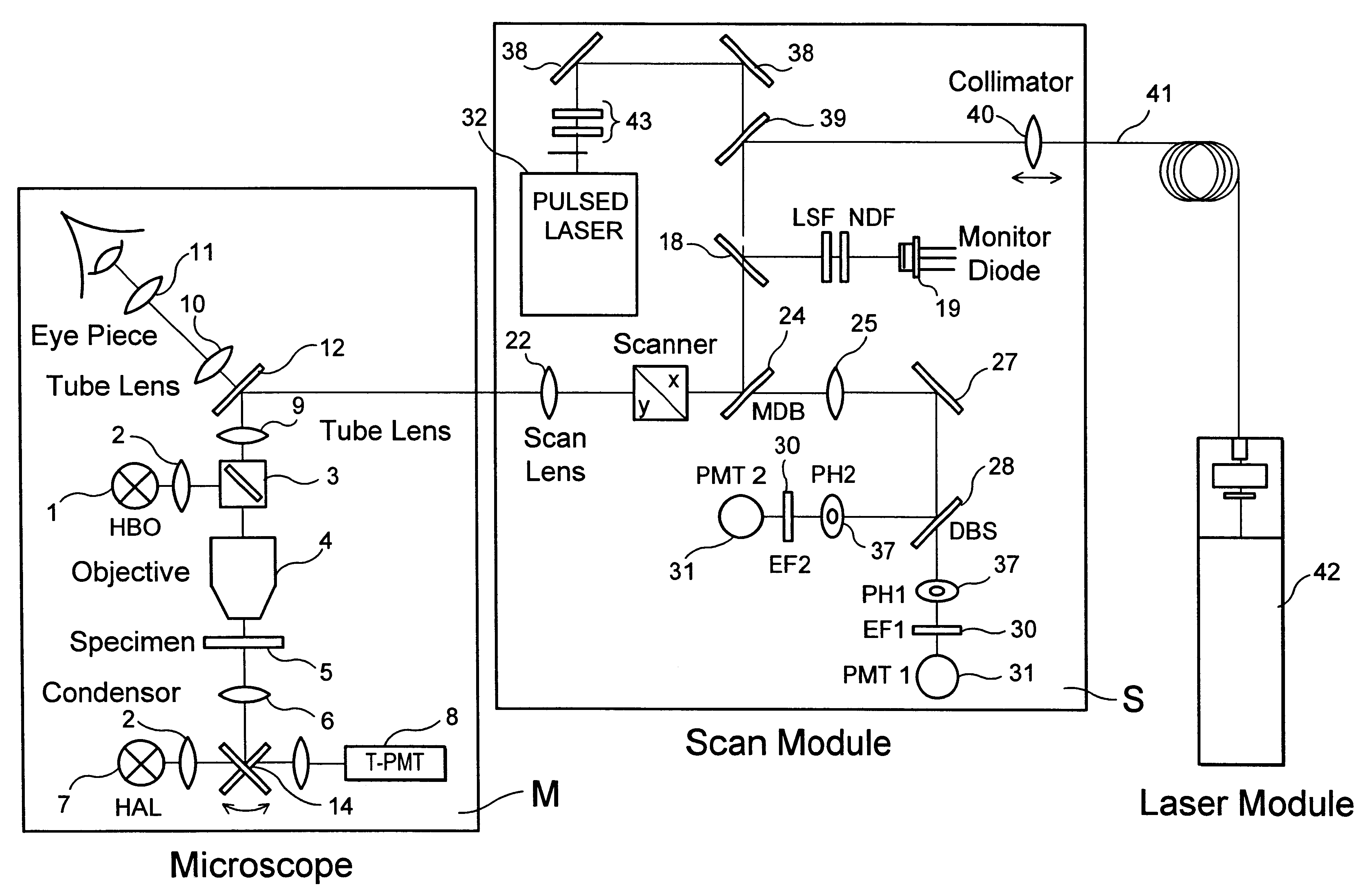
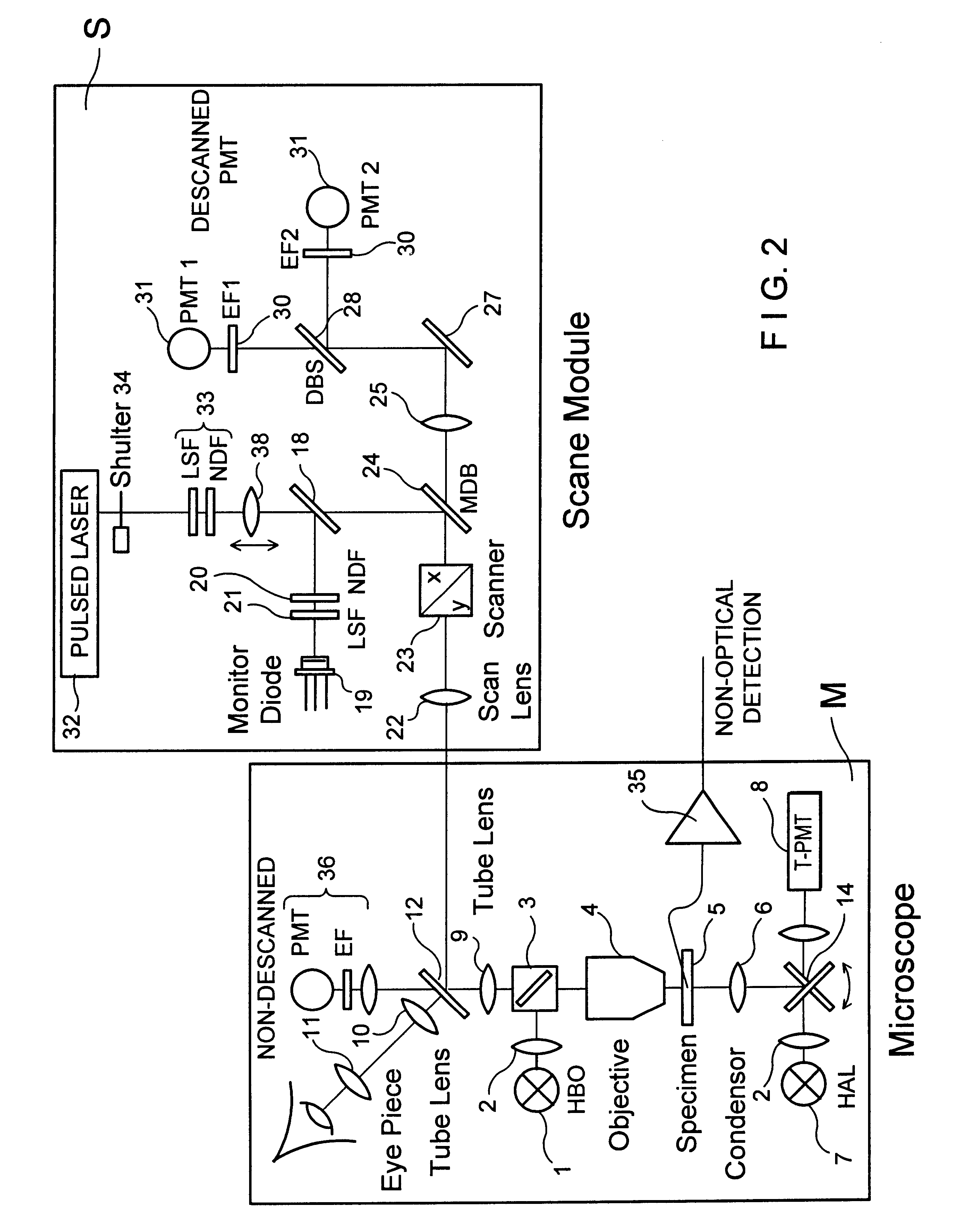
Highly compact laser scanning microscope with integrated short-pulse laser
InactiveUS6356088B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioAttenuation bandwidthMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationScanning probe techniquesLaser scanning microscopeDirect coupling
The invention describes a highly compact laser scanning microscope with integrated short-pulse laser. Direct coupling or a fiber coupling of the short-pulse laser with the laser scanning microscope is advantageously circumvented with this arrangement. This compact arrangement of the laser in the scan module of the laser scanning microscope can be used in a particularly advantageous manner, for example, in multiphoton microscopy for three-dimensionally resolved microscopic analysis, e.g., of biological specimens. Because of the inherent depth discrimination of the multiphoton technique, confocal pinholes can be entirely omitted in the detection beam path. Accordingly, the microscope system can be realized in a very simple manner with respect to engineering and is particularly simple to handle with respect to application. Through the use of a short-pulse laser system in which a plurality of wavelengths are available simultaneously, diverse applications can be realized in one and the same compact microscope system.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
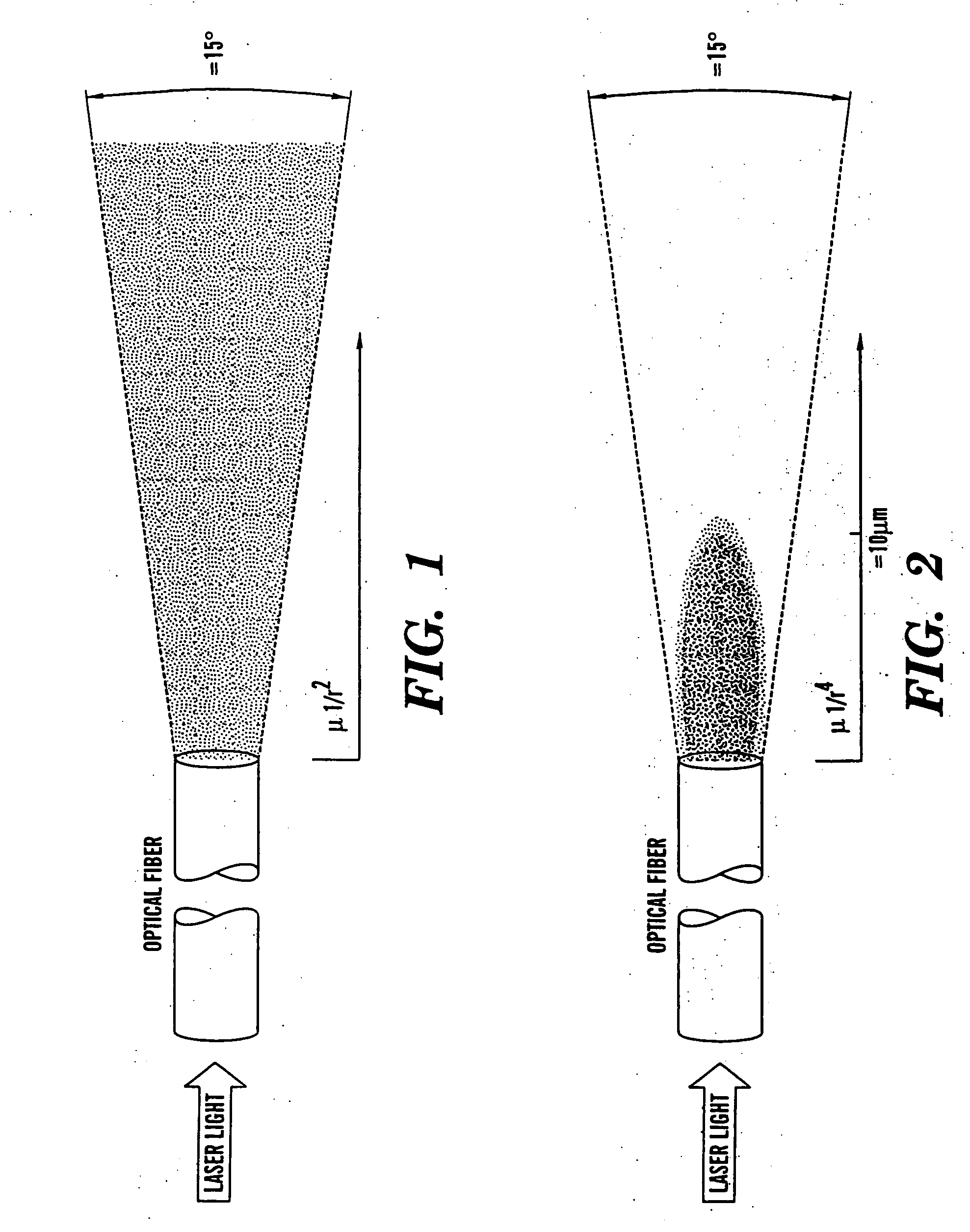
Optical fiber delivery and collection system for biological applications such as multiphoton microscopy, spectroscopy, and endoscopy
InactiveUS20050043636A1Improve spatial resolutionEfficient disseminationCladded optical fibreDiagnostics using lightCollection systemSpectroscopy
The present invention is directed to a method of applying radiation through an optical fiber for detecting disease within a plant or animal or other penetrable tissue, or imaging a particular tissue of a plant or animal. In addition, fluorescence and nonlinear scattering signals can be detected and localized within a subject by such application of radiation through an optical fiber. The radiation is effective to promote simultaneous multiphoton excitation. The optical fibers are used alone to examine internal regions of tissue, in conjunction with an optical biopsy needle to evaluate sub-surface tissue, or with an endoscope to evaluate tissue within body cavities. The present invention also relates to a device for coupling in radiation from an ultrashort mode-locked laser into the beam path of a microscope.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Method and system for wide-field multi-photon microscopy having a confocal excitation plane
InactiveUS20080116392A1Shorten Image Acquisition TimeScanning of the excitation light source over the specimen can be reduced or eliminatedPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansWide fieldLight beam
A wide field microscope includes a stage configured to hold a specimen having a fluorescent material therein, and a multi-photon excitation light source configured to produce excitation light having a single photon energy less than an absorption energy required for single photon excitation of said fluorescent material. A beam expansion unit is optically coupled to the light source and configured to expand the excitation light with reduced pulse spreading characteristics, and an infinity corrected objective optically coupled to the expansion unit and configured to focus the excitation light onto the specimen such that multi-photon excitation of the fluorescent material simultaneously occurs over a predetermined area of the specimen. A focus lens is configured to focus emission light emitted from said predetermined area of the specimen onto at least two pixels of an image detector simultaneously.
Owner:CELLOPTIC
Multi-path, multi-magnification, non-confocal fluorescence emission endoscopy apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20120140301A1Convenient treatmentAccurate identificationMicroscopesTelescopesOptical scannersMagnification
An optical scanner, scanner apparatus, or scanner assembly, which may be particularly advantageous for use in a multiphoton microscope, includes a first drivable bending component, a second drivable bending component mounted perpendicularly to the first component, and at least one optical waveguide coupled one or both of the first and second bending components, wherein the at least one optical waveguide provides both a propagation path for a multiphoton excitation radiation delivery between a light source and a target and a multiphoton-induced emission radiation delivery between the target and a detector. A GRIN relay lens. A multiphoton microscope incorporating the scanner and the GRIN relay lens.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Broadly tunable optical parametric oscillator
ActiveUS20110180729A1Color/spectral properties measurementsOptical devices for laserPicosecond laserLength wave
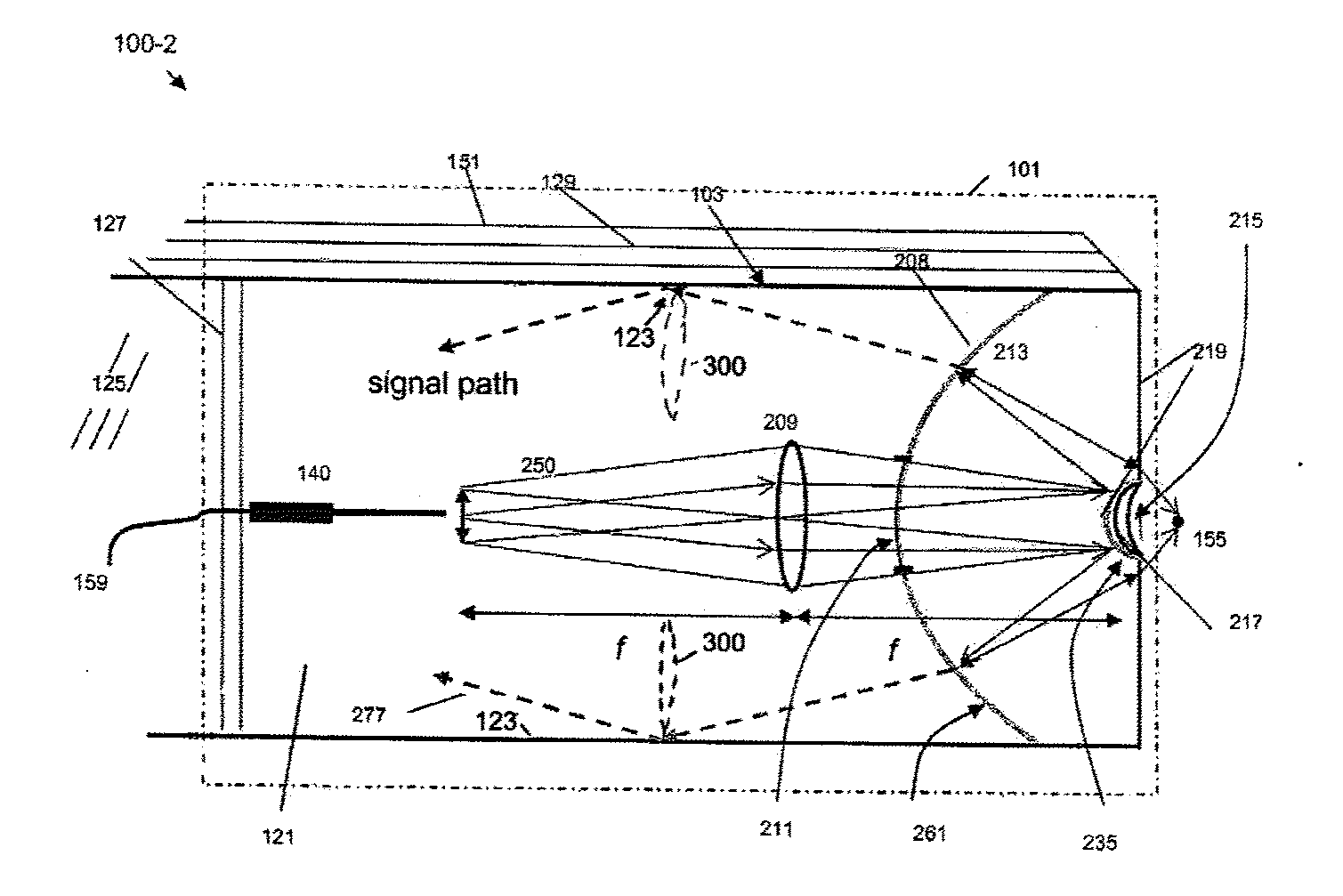
A novel broadly tunable optical parametric oscillator is described for use in numerous applications including multi-photon microscopy. The optical parametric oscillator includes at least one sub-picosecond laser pump source configured to output a pump signal having a wavelength of about 650 nm or less and at least one type II optical parametric oscillator in optical communication with the pump source and configured to generate a single widely tunable pulsed optical signal. In one application, an optical system is in optical communication with the optical parametric oscillator and configured to direct at least a portion of the optical signal to a specimen, and at least one analyzing device is configured to receive a signal from the specimen in response to the optical signal.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
Method and system for wide-field multi-photon microscopy having a confocal excitation plane
ActiveUS20050259319A1Shorten Image Acquisition TimeScanning of the excitation light source over the specimen can be reduced or eliminatedPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersEyepieceImage plane
According to one aspect of the invention, a wide-field microscope includes a stage configured to hold a specimen having a fluorescent material therein, and a multi-photon excitation light source configured to produce a substantially parallel beam of excitation light having a single photon energy less than an absorption energy required for single photon excitation of the fluorescent material. An infinity corrected objective is optically coupled to the multi-photon excitation light source and configured to focus the substantially parallel beam of excitation light onto the specimen such that multi-photon excitation of the fluorescent material simultaneously occurs over a predetermined area of the specimen. A focus lens is configured to focus emission light emitted from the predetermined area of the specimen onto at least two pixels of an image detector simultaneously. A focus lens is configured to focus emission light emitted from the predetermined area of the specimen onto an image plane, such that the image plane can be viewed through a binocular eyepiece or an imaging array detector.
Owner:CELLOPTIC
Method for depth resolved wavefront sensing, depth resolved wavefront sensors and method and apparatus for optical imaging
ActiveUS8451452B2Less sensitive to reflectionAll optics layout more compactInterferometersUsing optical meansWavefront sensorWavefront aberration
Methods and devices are disclosed for acquiring depth resolved aberration information using principles of low coherence interferometry and perform coherence gated wavefront sensing (CG-WFS). The wavefront aberrations is collected using spectral domain low coherence interferometry (SD-LCI) or time domain low coherence interferometry (TD-LCI) principles. When using SD-LCI, chromatic aberrations can also be evaluated. Methods and devices are disclosed in using a wavefront corrector to compensate for the aberration information provided by CG-WFS, in a combined imaging system, that can use one or more channels from the class of (i) optical coherence tomography (OCT), (ii) scanning laser ophthalmoscopy, (iii) microscopy, such as confocal or phase microscopy, (iv) multiphoton microscopy, such as harmonic generation and multiphoton absorption. For some implementations, simultaneous and dynamic aberration measurements / correction with the imaging process is achieved. The methods and devices disclosed can provide wavefront sensing in the presence of stray reflections from optical interfaces.
Owner:PODOLEANU ADRIAN +1
Method and system for wide-field multi-photon microscopy having a confocal excitation plane
ActiveUS7170675B2Scanning of the excitation light source over the specimen can be reduced or eliminatedShorten Image Acquisition TimePhotometryLuminescent dosimetersEyepieceImage plane
According to one aspect of the invention, a wide-field microscope includes a stage configured to hold a specimen having a fluorescent material therein, and a multi-photon excitation light source configured to produce a substantially parallel beam of excitation light having a single photon energy less than an absorption energy required for single photon excitation of the fluorescent material. An infinity corrected objective is optically coupled to the multi-photon excitation light source and configured to focus the substantially parallel beam of excitation light onto the specimen such that multi-photon excitation of the fluorescent material simultaneously occurs over a predetermined area of the specimen. A focus lens is configured to focus emission light emitted from the predetermined area of the specimen onto at least two pixels of an image detector simultaneously. A focus lens is configured to focus emission light emitted from the predetermined area of the specimen onto an image plane, such that the image plane can be viewed through a binocular eyepiece or an imaging array detector.
Owner:CELLOPTIC
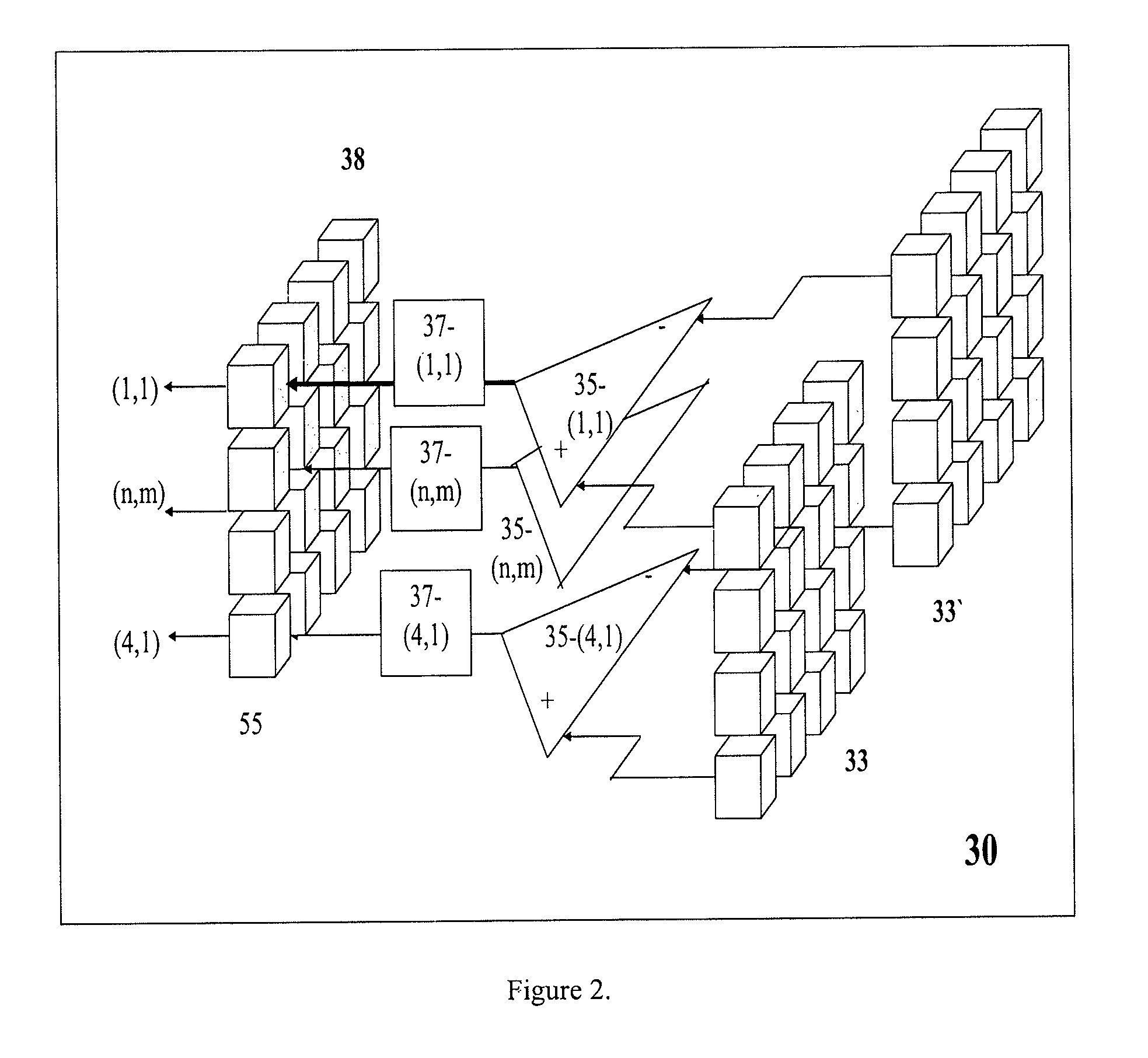
Apparatus for improving detection efficiency of multiphoton microscopy systems by focus compensation, pupil image division, and parallel pupil rearrangement
ActiveUS20090236549A1Photometry using reference valueRaman/scattering spectroscopyBeam splitterFluorescence
Disclosed is an apparatus for division and rearrangement of light from a source object. The apparatus splits the light from the source object, or image of the source object, and recombines it in a parallel, fashion to increase the efficiency of multiphoton microscopy in general and harmonic or fluorescence emission microscopy in particular. The apparatus includes a beam splitter configured to split a light beam into at least two independent light paths to yield a first light path and a second light path; a first beam focuser configured to direct and focus the first light path onto a focal plane; and a second beam focuser configured to direct and focus the second light path onto the same or different focal plane to which the first light path is focused; and wherein the first and second light paths may be superimposed upon one another at a common focal plane or directed independently to different positions.
Owner:PRAIRIE TECH
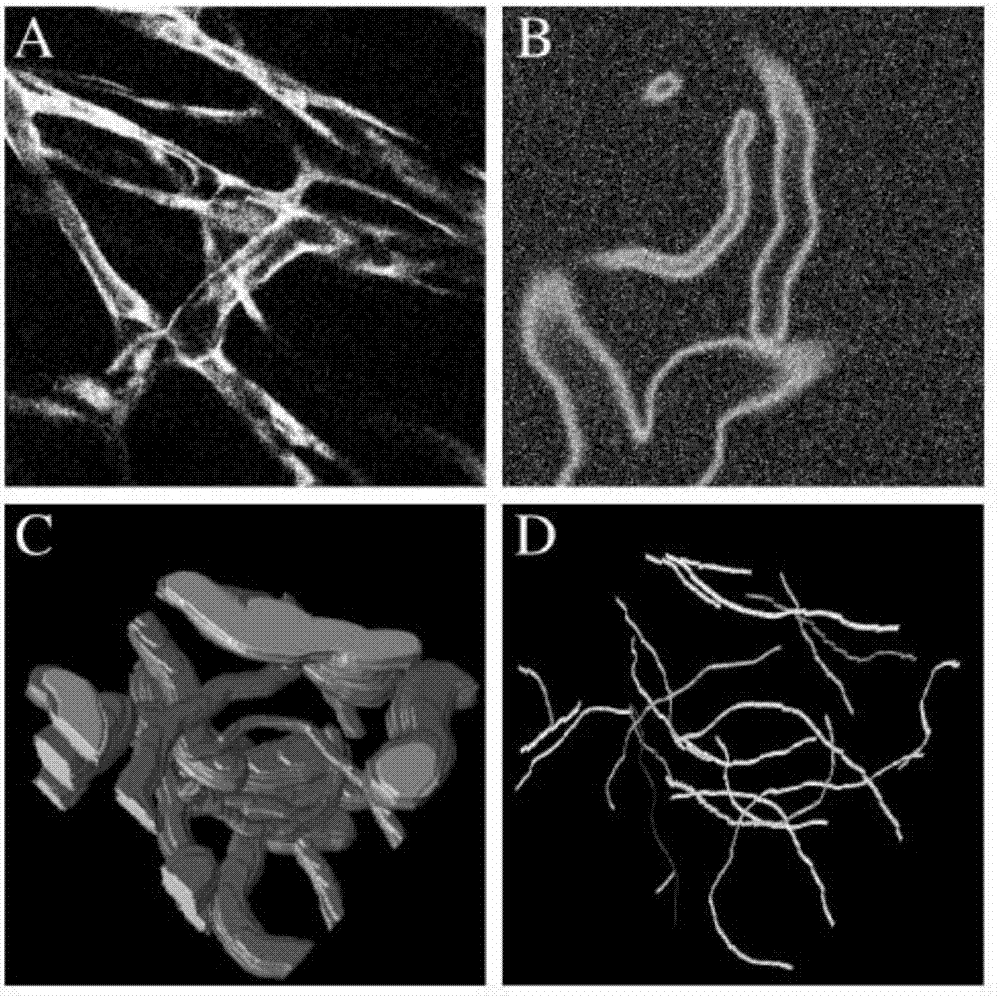
3D vascular structure extraction method based on convolutional cycle network
The invention provides a 3D vascular structure extraction method based on a convolutional cycle network. Main contents comprise experiment data, integration data, a convolutional neural network (CNN) framework and a convolutional long-term and short-period memory unit (ConvLSTM). The method comprises the following steps that clinic data and synthesis data are used to carry out experiment; actual data adopts a high-resolution fluorescence multiphoton microscope; in a mice, abdominal cavity model imaging is performed to acquire an image so as to describe a vascular system; a noise is added to simulate an actual condition; a CNN network and a convolutional LSTM network are combined; the convolutional long-term and short-period memory unit uses a deep configuration and shallow configuration combination and a training network and uses a weighted binary system cross entropy loss to test a training result. In the invention, from a complex microscope image, a real 3D vascular structure can be extracted, convolution complexity in three dimensions is reduced, a number of model parameters is greatly decreased, a wide view is possessed, and abundant characteristics can be extracted.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
Optical fiber delivery and collection method for biological applications such as multiphoton microscopy, spectroscopy, and endoscopy
InactiveUS7702381B2Efficient collectionRapid in vitro screeningCladded optical fibreDiagnostics using lightDiseaseSpectroscopy
The present invention is directed to a method of applying radiation through an optical fiber for detecting disease within a plant or animal or other penetrable tissue, or imaging a particular tissue of a plant or animal. In addition, fluorescence and nonlinear scattering signals can be detected and localized within a subject by such application of radiation through an optical fiber. The radiation is effective to promote simultaneous multiphoton excitation. The optical fibers are used alone to examine internal regions of tissue, in conjunction with an optical biopsy needle to evaluate sub-surface tissue, or with an endoscope to evaluate tissue within body cavities. The present invention also relates to a device for coupling in radiation from an ultrashort mode-locked laser into the beam path of a microscope.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Microscope system and method
ActiveUS7698000B2Eliminating orComputer controlMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical axisImaging lens
An optical system and method are presented for use in a multi-photon microscope. The system comprises an imaging lens arrangement, and a pulse manipulator arrangement. The pulse manipulator arrangement comprises a temporal pulse manipulator unit which is accommodated in an optical path of an input pulse of an initial profile, and is configured to affect trajectories of light components of the input pulse impinging thereon so as to direct the light components towards an optical axis of the lens arrangement along different optical paths, said temporal light manipulator unit being accommodated in a front focal plane of the imaging lens arrangement, thereby enabling to restore the input pulse profile at an imaging plane.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Time lapse observation method, and time lapse observation apparatus and multiphoton microscope used therefor
InactiveUS20130063584A1Television system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisReference Region
Time lapse observation method includes: before a process to obtain a first time lapse image, capturing an image of a reference area on a sample being a partial area of a target area or an area in a vicinity of the target area being a smaller area than the target area to obtain a reference image; storing a position of a capturing area in capturing the reference image as a reference position; before a process to obtain the time lapse image performed, setting a position of the capturing area sequentially at different positions in the optical axis direction of an objective including the reference position and capturing an image at each of the positions to obtain comparison target images; and matching the capturing area with the target area, based on a comparison result of the reference image and the comparison target images.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Systems and methods to reduce scattering in temporal focusing multiphoton microscopy
ActiveUS20200342205A1Enhance the imageInhibition effectSamplingSurgeryHigh resolution imageMaterials science
Systems and methods herein provide improved, high-throughput multiphoton imaging of thick samples with reduced emission scattering. The systems and methods use structured illumination to modify the excitation light. A reconstruction process can be applied to the resulting images to recover image information free of scattering. The disclosed systems and methods provide high throughput, high signal-to-noise ratio, and high resolution images that are depth selective.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Multi-photon microscope having an excitation-beam array
ActiveUS20150157210A1Reduce complexityLow costMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionOptoelectronicsPhoton
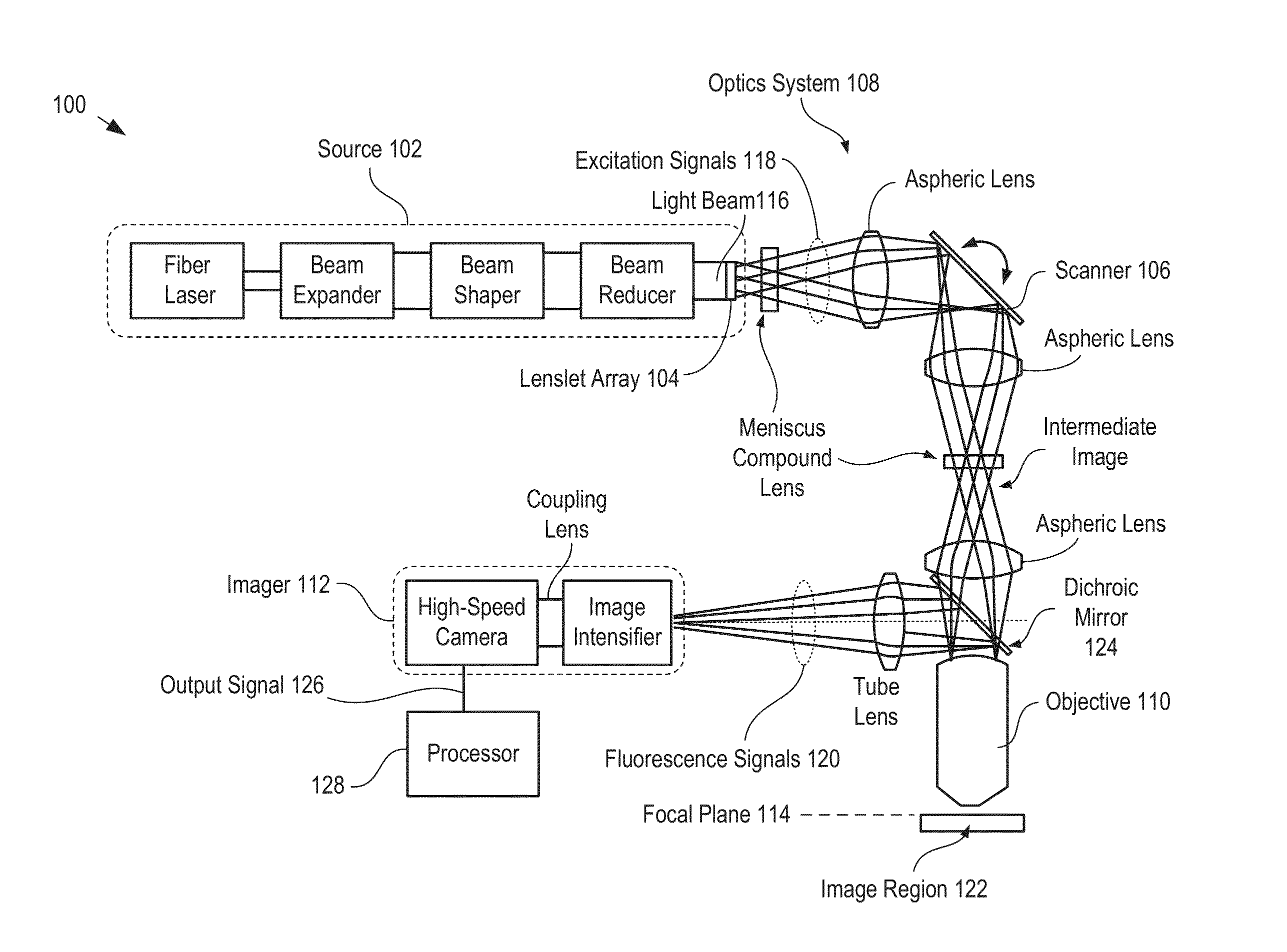
A two-photon imaging system capable of imaging of an image region in real time is presented. The imaging system comprises a source of excitation light that provides the excitation light as a plurality of laser beamlets. The plurality of laser beamlets is collectively scanned by a single-axis scanner along a first direction in the focal plane of the image region and oriented such that neither the rows nor columns are aligned with the first direction. As a result, each laser beamlet scans a different sub-region of the image region and the plurality of sub-regions are simultaneously scanned. As a result, the entirety of the image region is scanned in the same amount of time required to scan one image sub-region.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
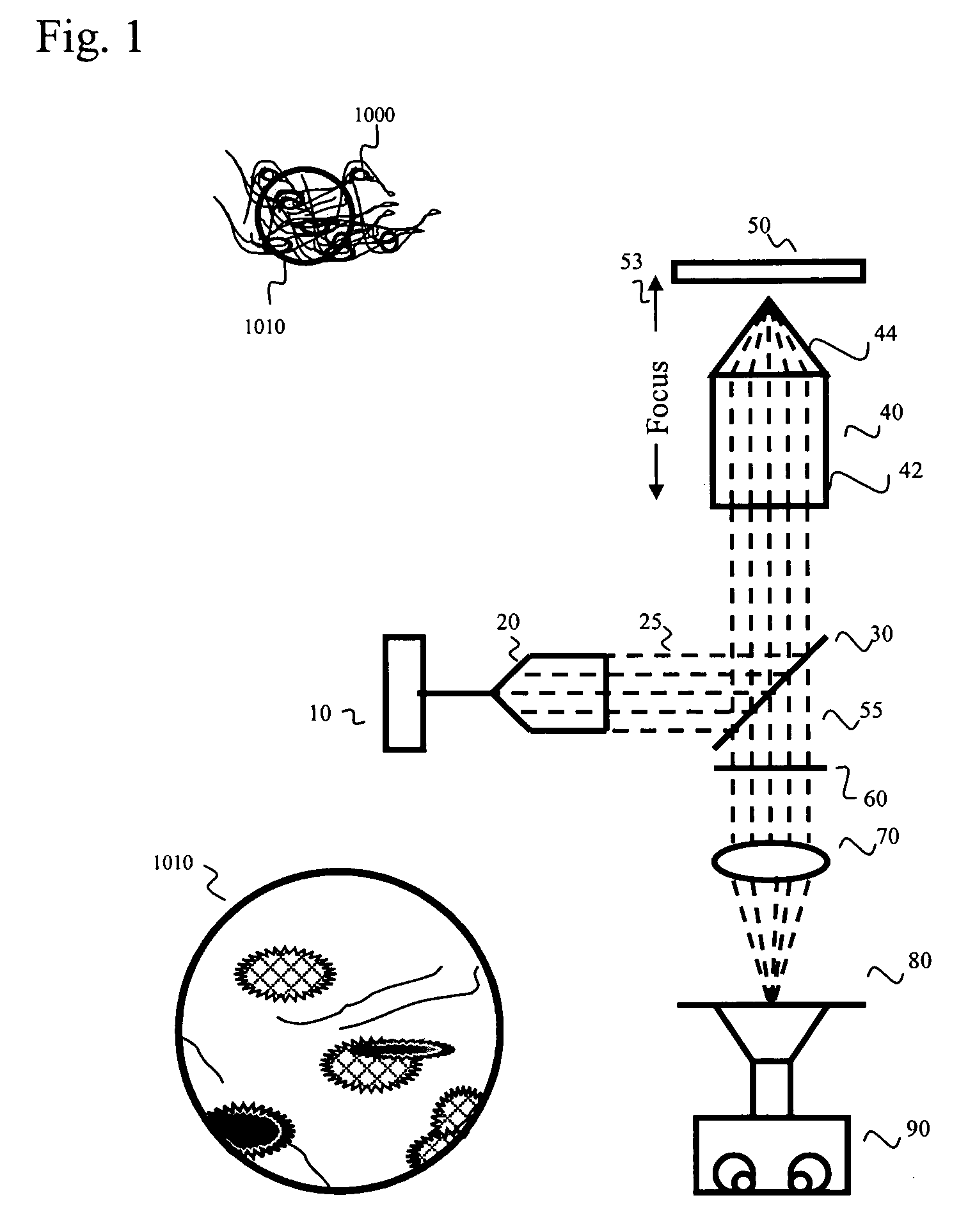
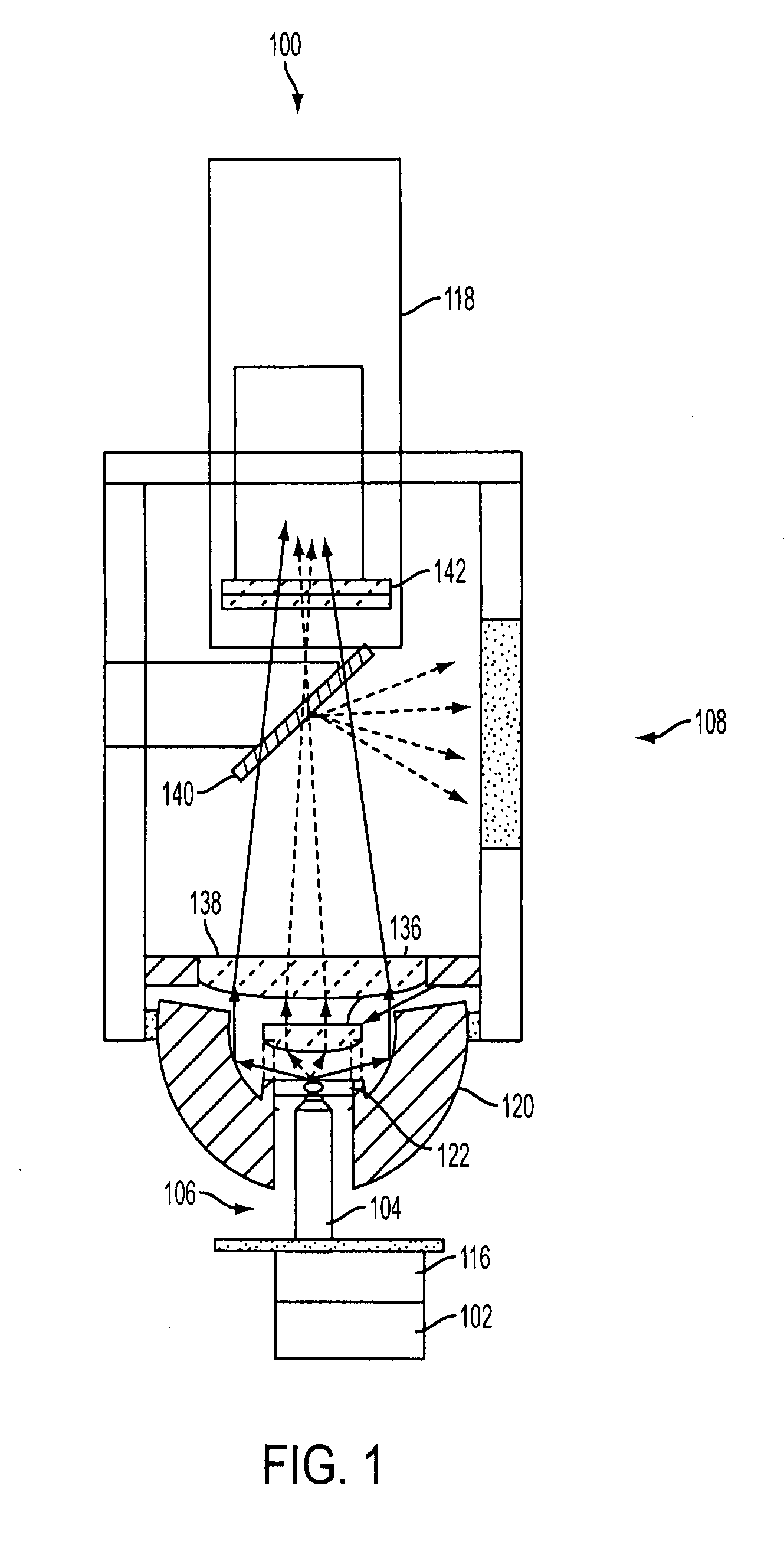
Wide-area fluorescence detection system for multi-photon microscopy
ActiveUS20080063345A1Improve light collectionPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersWide areaOptical property
A multi-photon microscope has an illumination source, an objective lens unit arranged in an optical path of the illumination source, a first light collection system arranged to collect a first portion of light emitted from a sample when the sample is illuminated by light from the illumination source, and a second light collection system arranged to collect a second portion of light emitted from the sample when the sample is illuminated by light from the illumination source. The first portion of light when collected by the first light collection system and the second portion of light when collected by the second light collection system, together provide a means of collecting as much light from as many angles as possible emanating from an emitting point source. This collection scheme has the potential to approach the total emission collection of light from an emitting point source depending on the optical properties of the sample being imaged.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Imaging platform based on nonlinear optical microscopy for rapid scanning large areas of tissue
ActiveUS20180106729A1Facilitate early diagnosisLow costDianostics using fluorescence emissionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationFluorescenceWater immersion
A multiphoton microscope based on two-photon excited fluorescence and second-harmonic generation that images FOVs of about 0.8 mm2 (without stitching adjacent FOVs) at speeds of 10 frames / second (800×800 pixels) with lateral and axial resolutions of 0.5 μm and 2.5 μm, respectively. The scan head of the instrument includes a fast galvanometric scanner, relay optics, a beam expander and a high NA objective lens. The system is based on a 25×, 1.05 NA water immersion lens, which features a long working distance of 1 mm. A proper tailoring of the beam expander, which consists of the scan and tube lens elements, enables scaling of the FOV. The system and method also include a flat wavefront of the beam, minimum field curvature, and suppressed spherical aberrations. All aberrations in focus are below the Marechal criterion of 0.07λ rms for diffraction-limited performance.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Apparatus for improving detection efficiency of multiphoton microscopy systems by focus compensation, pupil image division, and parallel pupil rearrangement
ActiveUS7943889B2Photometry using reference valueRaman/scattering spectroscopyBeam splitterFluorescence
Disclosed is an apparatus for division and rearrangement of light from a source object. The apparatus splits the light from the source object, or image of the source object, and recombines it in a parallel, fashion to increase the efficiency of multiphoton microscopy in general and harmonic or fluorescence emission microscopy in particular. The apparatus includes a beam splitter configured to split a light beam into at least two independent light paths to yield a first light path and a second light path; a first beam focuser configured to direct and focus the first light path onto a focal plane; and a second beam focuser configured to direct and focus the second light path onto the same or different focal plane to which the first light path is focused; and wherein the first and second light paths may be superimposed upon one another at a common focal plane or directed independently to different positions.
Owner:PRAIRIE TECH
A convolution neural network method for differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma
InactiveCN109214433AAvoid the shortcomings of strong observationAvoid missed diagnosisCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setOncology
The invention relates to a method for distinguishing differentiation grade of liver cancer by convolution neural network. The method comprises the following steps: step S1, preparing data: acquiring MPM images of liver cancer through a multi-photon microscope; 2, enlarging the MPM image data set of the liver cancer: adjusting the pixel of the original pixel size of 512x512 collected in the step S1, rotating the image horizontally, rotating vertically symmetrically, cutting and the like, so as to obtain the image number of the training set to be 16 times of the original image number; S3, designing a convolution neural network to obtain the differentiation result of the differentiation grade: designing the structure of the convolution neural network. The convolution neural network consists of eight layers: the first layer to the fifth layer is called convolution layer, which is used to extract the detailed features from the image; layer 6 to layer 8 are three fully connected layers, andafter layer 8, the probability of differentiation grade of liver cancer image is output. The invention can effectively overcome the shortcomings of time-consuming, missed diagnosis and strong subjectivity in the current clinical biopsy technology.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Plane-projection multi-photon microscopy
ActiveUS20120182413A1Uniform sizeLarge numerical apertureColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsWide fieldLaser light
A novel method and system for conducting wide-field multi-photon microscopy through plane-projection are provided. It has been discovered that the limitations of conventional temporal-focusing techniques, such as single excitation wavelength and low acquisition rates can be resolved utilizing a novel optical set-up in which an optical diffuser is used as the scatterer. The use of such an optical arrangement enables temporal focusing regardless of the central wavelength of laser pukes. In addition, the optical sectioning possible using the disclosed microscopy is comparable to confocal microscopy, and can be robustly achieved by both moderate and high NA objectives at 100-fs puke width. Moreover, the multi-photon excitation efficiency of the disclosed system can be enhanced by lowering the repetition rate of the ultrafast laser light source at constant pulse width and average power.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
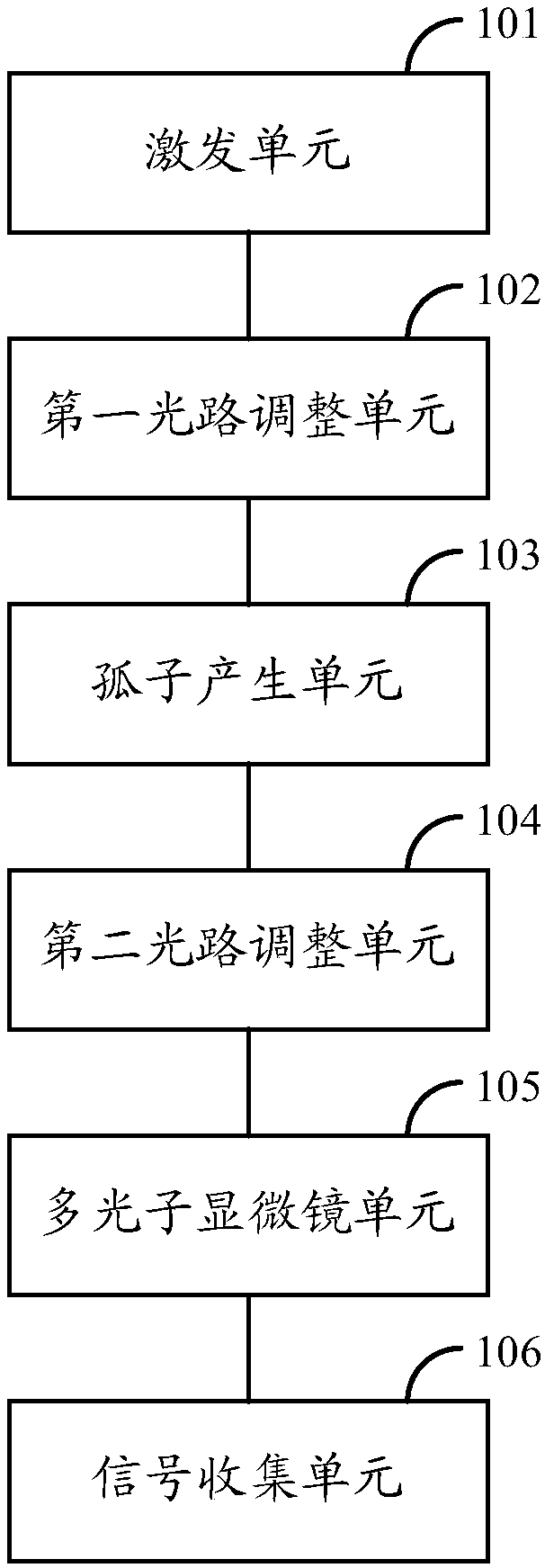
Self-reference measuring device for axial chromatic aberration of multiphoton microscope
InactiveCN108469412AEliminate mechanical errorsColor/spectral properties measurementsPerformed ImagingPhoton
The present invention is applicable to the field of optoelectronic technology, and provides a self-reference measuring device; the self-reference measuring device comprises an excitation unit, a firstoptical path adjusting unit, a soliton generating unit, a second optical path adjusting unit and a multiphoton microscope unit. The excitation unit is used for generating pump light with a preset wavelength and allowing the pump light to enter the first optical path adjusting unit; the first optical path adjusting unit is used for adjusting the polarization state of the pump light and allowing the pump light to enter the soliton generating unit, the the soliton generating unit is used to generate a laser pulse according to the pump light and allow the laser pulse to enter the second optical path adjusting unit; the second optical path adjusting unit is configured to process the laser pulse and allow the laser pulse to enter the multiphoton microscope unit, and the multiphoton microscope unit is used for measuring axial chromatic aberration based on imaging of a sample and transmitting harmonic signals to a signal collection unit for collection. The self-reference measuring device doesnot require a mechanical displacement platform to repeat scanning all the time, thereby eliminating mechanical errors introduced by the displacement platform when monochromatic excitation light repeatedly scanns.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Large-view-field microscope objective lens
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical microscopic imaging, and particularly discloses a large-view-field microscope objective lens. The objective lens comprises a scanner and a plurality of lenses. A back focal plane calculated by the objective lens according to excitation light wavelength is positioned outside an objective lens body. When the scanner is a single single-axis scanner or a single double-axis scanner, the single single-axis scanner or the single double-axis scanner is positioned on the rear focal plane of the objective lens. When the scanners are two single-axisscanners in one group, the rear focal plane of the objective lens is positioned in the middle of the two single-axis scanners in one group. According to the invention, the design concepts that the diameter of an incident light beam is kept unchanged, the field angle is increased and the rear focal plane of the objective lens is externally arranged are adopted, and the high-numerical-aperture large-field imaging microscope objective lens with low cost and small size is provided for a standard desk type multi-photon microscope.
Owner:苏州溢博伦光电仪器有限公司
Lightguides to simplify total emission detection for multiphoton microscopy
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method for discriminating liver cancer differentiation grades by using multiphoton imaging technology
InactiveCN108426862AOvercoming time consumingOvercome missed diagnosisPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by material excitationStatistical analysisWilms' tumor
The invention relates to a method for discriminating liver cancer differentiation grades by using a multiphoton imaging technology. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out quick freezing film shooting processing on a fresh liver cancer specimen subjected to surgical excision or puncture sampling; secondly, obtaining a collagen fiber MPM image inside a tumor by multiphoton microscopic imaging, processing the image, extracting features and then carrying out statistical analysis and discrimination by using Mann-Whitney inspection and Boxplot. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the multiphoton microscopic imaging and an image processing algorithm are utilized to be combined with a statistical analysis method for evaluating different differentiation grades of liver cancer; liver cancer differentiation grade data obtained by a label-free quick discrimination method are compared with pathologist diagnostic result data so as to achieve the aim of objectively evaluating the liver cancer differentiation grades; and the defects of time consumption, missed diagnosis and high subjectivity of a current clinical biopsy technique are effectively overcome.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Multi-path, multi-magnification, non-confocal fluorescence emission endoscopy apparatus and methods
ActiveUS8705184B2Efficient collectionGuaranteed normal transmissionMicroscopesTelescopesOptical scannersWaveguide
An optical scanner, scanner apparatus, or scanner assembly, which may be particularly advantageous for use in a multiphoton microscope, includes a first drivable bending component, a second drivable bending component mounted perpendicularly to the first component, and at least one optical waveguide coupled one or both of the first and second bending components, wherein the at least one optical waveguide provides both a propagation path for a multiphoton excitation radiation delivery between a light source and a target and a multiphoton-induced emission radiation delivery between the target and a detector. A GRIN relay lens. A multiphoton microscope incorporating the scanner and the GRIN relay lens.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Nonlinear optical device, multiphoton microscope, and endoscope
ActiveUS20120238820A1High peak powerGenerate efficientlyLaser detailsSurgeryHigh peakGroup velocity dispersion
Provided is a nonlinear optical device capable of alleviating, without the need for a complicated compensation mechanism, temporal broadening and the waveform distortion resulting from a group-velocity dispersion slope, to thereby irradiate an object with short optical pulses having high peak power. The nonlinear optical device includes a short optical pulse source (10) for generating short optical pulses and a short optical pulse delivery system (20) for delivering the short optical pulses generated from the short optical pulse source to an object, in which there is generated substantially no nonlinear optical effect and there is substantially no amount of group-velocity dispersion, the short optical pulse source generates short optical pulses, and the short optical pulses have a spectral width (full width at half maximum) λFWHM satisfying λ1<λFWHM<λ2.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Wide-area fluorescence detection system for multi-photon microscopy
ActiveUS7667210B2Improve light collectionPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersOptical propertyFluorescence
A multi-photon microscope has an illumination source, an objective lens unit arranged in an optical path of the illumination source, a first light collection system arranged to collect a first portion of light emitted from a sample when the sample is illuminated by light from the illumination source, and a second light collection system arranged to collect a second portion of light emitted from the sample when the sample is illuminated by light from the illumination source. The first portion of light when collected by the first light collection system and the second portion of light when collected by the second light collection system, together provide a means of collecting as much light from as many angles as possible emanating from an emitting point source. This collection scheme has the potential to approach the total emission collection of light from an emitting point source depending on the optical properties of the sample being imaged.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Multi-photon microscopy, imaging method using time-gated detection thereof
PendingUS20220146427A1Improve imaging effectHigh peak powerMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescencePhotodetectorEngineering
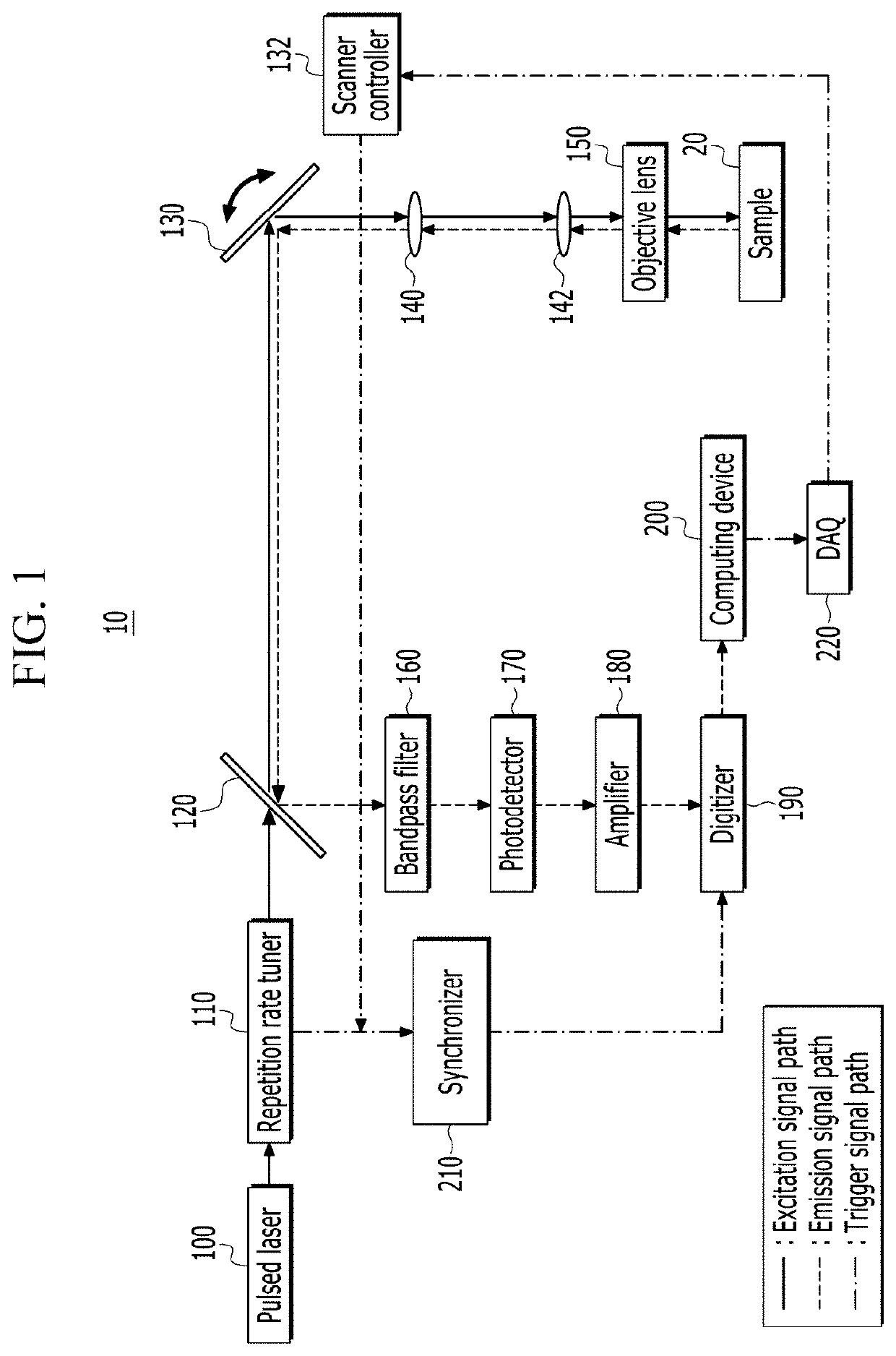
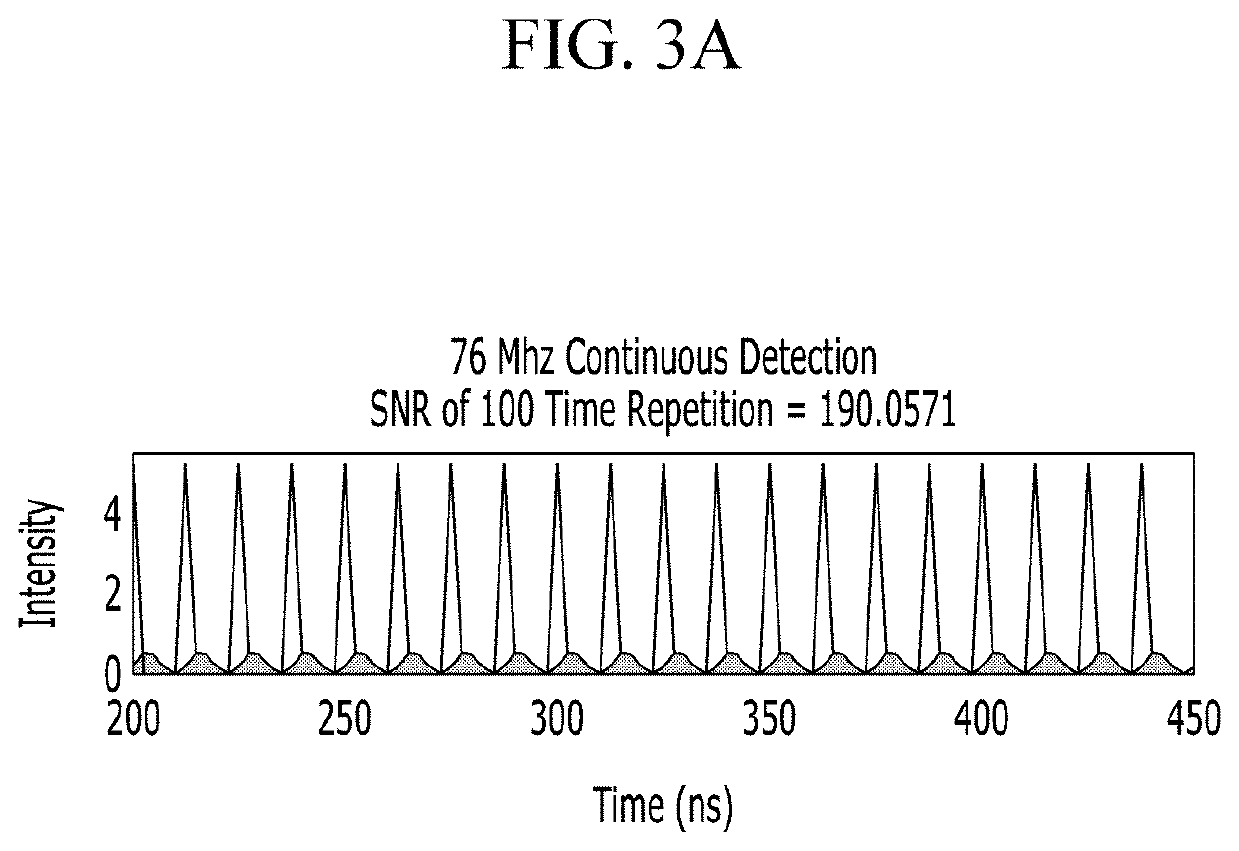
The multi-photon microscope comprises a repetition rate tuner that lowers an optical pulse train emitted from a pulsed laser to a repetition rate for time-gated detection, a scanner that scans the optical pulse train transmitted from the repetition rate tuner in x-axis and y-axis directions, an objective lens that irradiates an optical signal scanned by the scanner to the sample and acquires a fluorescence signal emitted from the excited fluorescent material, a photodetector that photoelectrically converts the fluorescence signal acquired by the objective lens, an amplifier that converts a current signal output from the photodetector into a voltage signal, a digitizer that samples the voltage signal output from the amplifier, and a computing device that separates sampling data output from the digitizer with a detection window set in time domain, and generates an image based on the sampling data separated by the detection window.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
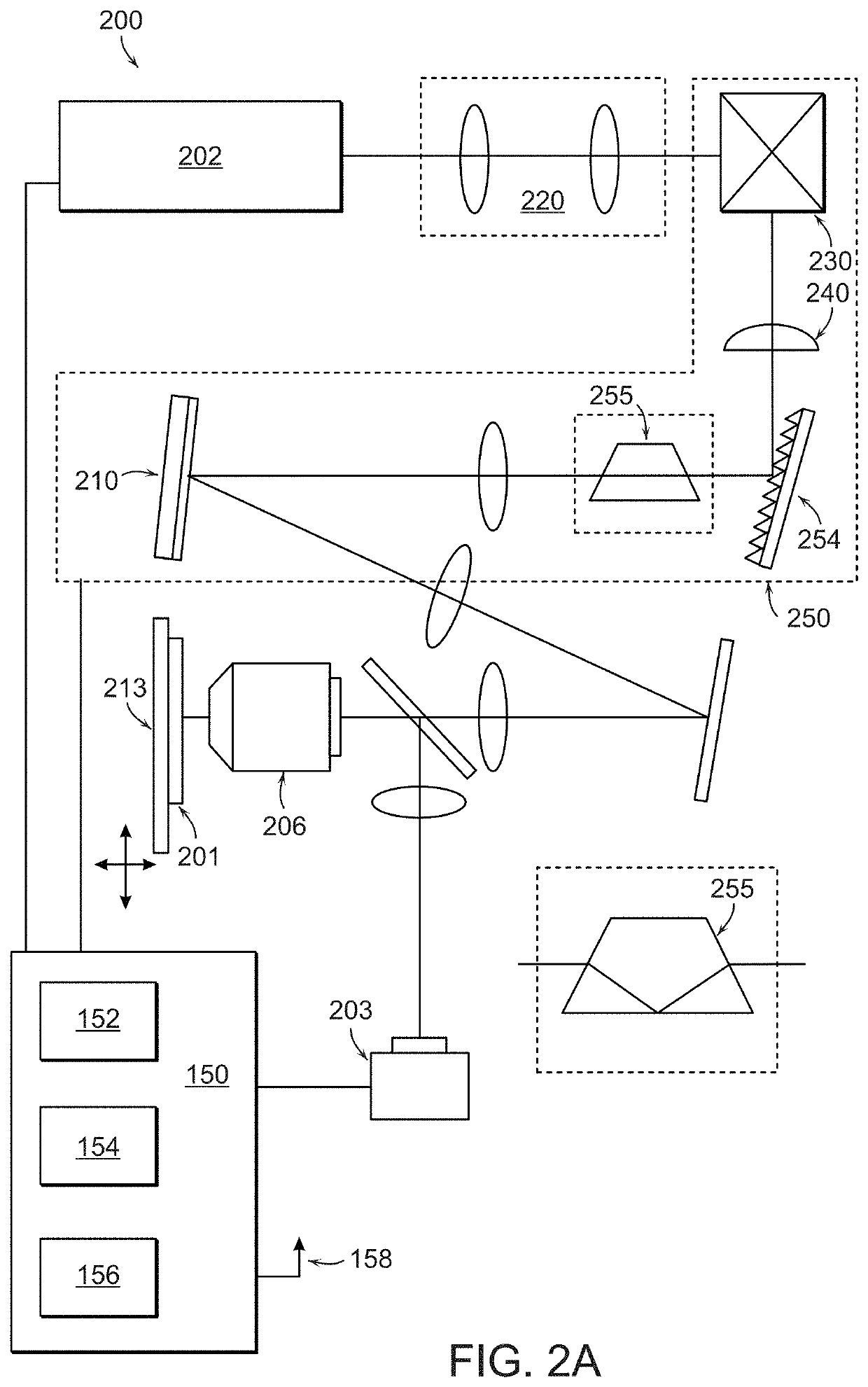
Dynamic focus and zoom system for use with wide-field, confocal and multiphoton microscopes
A dynamic focus and zoom system for use with wide-field, confocal and multiphoton microscopes having first, second and third MEMS mirrors situated within a housing. First and second fixed lenses form an optical relay. A prism / mirror is situated proximate to a first portal in the housing and is aligned linearly with the optical relay and a first MEMS mirror. The second MEMS mirror is proximate to and at a ninety-degree angle relative to the first MEMS mirror, which is at a forty-five-degree angle to the second fixed lens. The second MEMS mirror, third fixed lens and third MEMS mirror are aligned linearly, with the third fixed lens situated between the second and third MEMS mirrors. The third MEMS mirror is proximate to a second portal in the housing. The third MEMS mirror is situated adjacent to the prism / mirror.
Owner:AGILE FOCUS DESIGNS LLC
All-protein implantable, resorbable reflectors
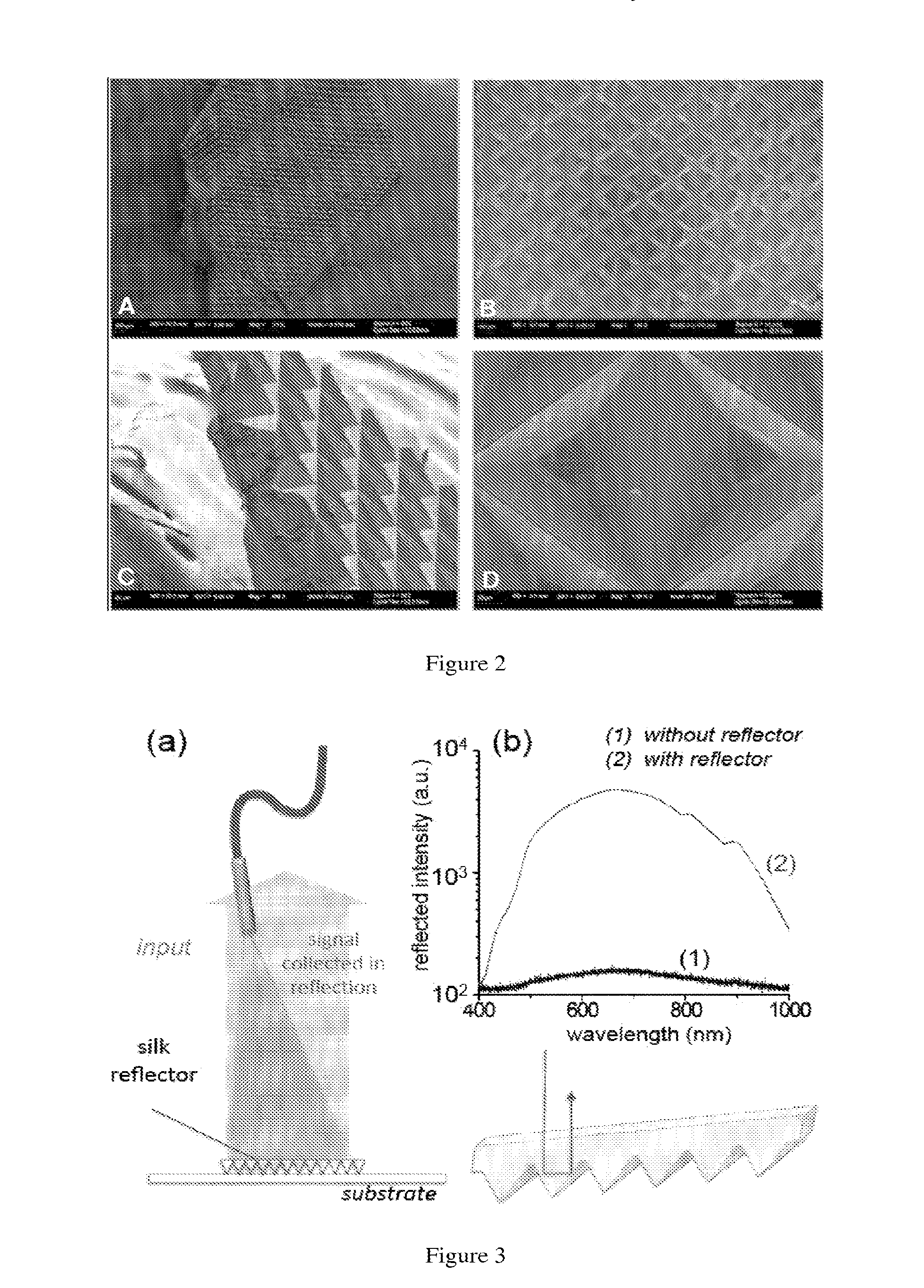
The invention provides for compositions and process for fabricating an optical reflector constructed from biocompatible and bioresorbable silk fibroin proteins. For example, the silk retroreflectors may be built based on millimeter size microprism arrays to rotate the image plane of imaged cortical layers, thus enhancing the amount of photons that are detectable in the reflected direction when inserted in a sample to be analyzed, and ultimately increasing in contrast ratio in multiphoton microscopy. Such device can be used as a label-free, biocompatible, bioresorbable, implantable device for various applications ranging from medical imaging / diagnostics, drug / therapeutic delivery, to food chain safety and environmental monitoring.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com