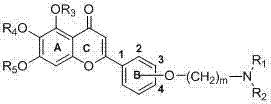
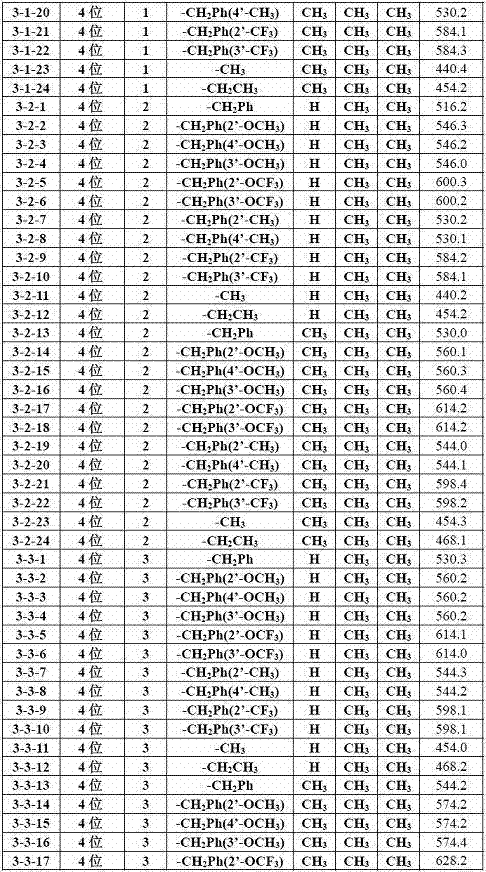
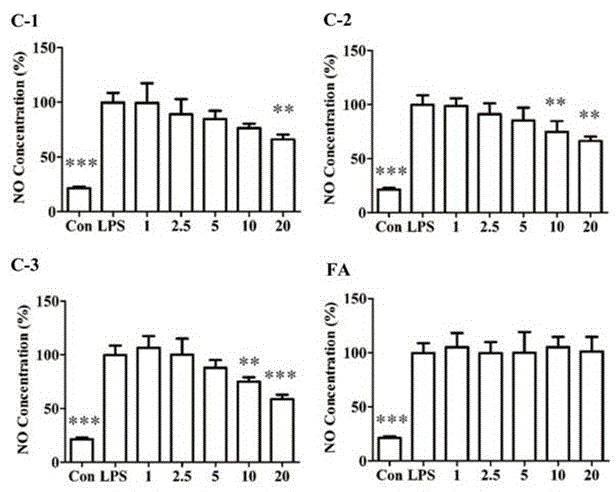
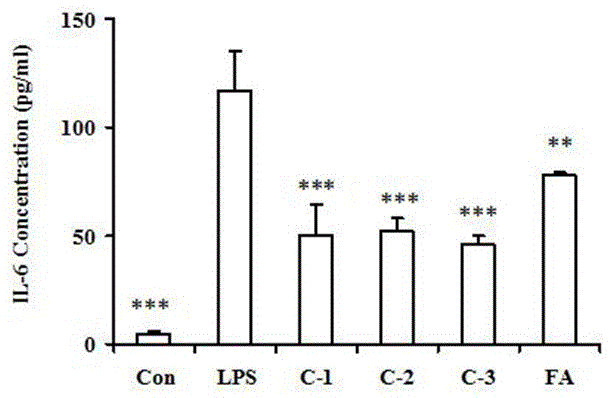
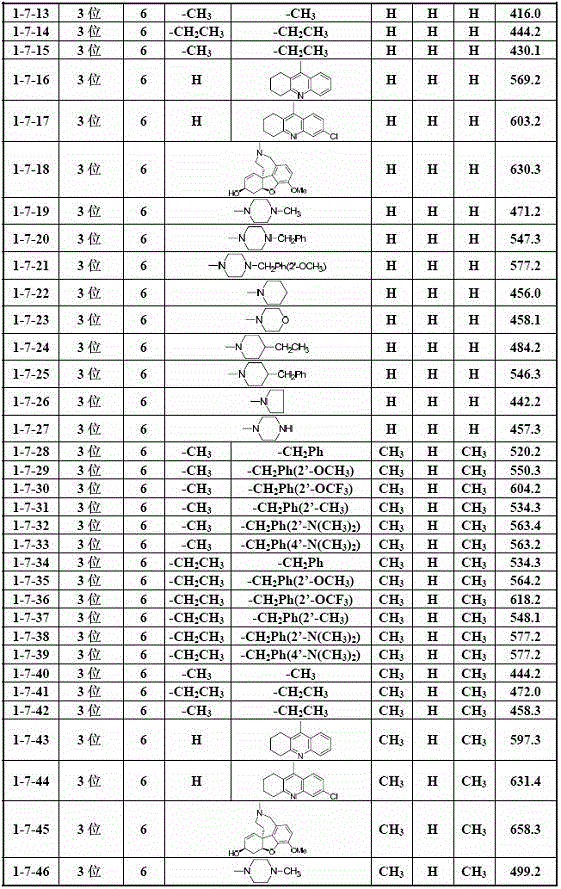
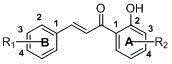
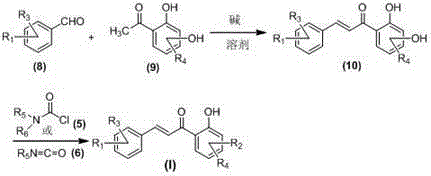
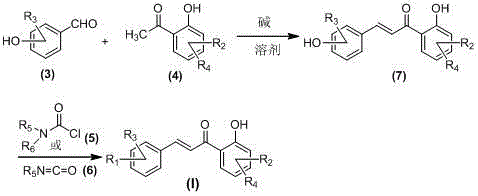
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
465 results about "Ischemic vascular dementia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vascular dementia can be caused by ischemic or hemorrhagic infarcts affecting multiple brain areas, including the anterior cerebral artery territory, the parietal lobes, or the cingulate gyrus. On rare occasion, infarcts in the hippocampus or thalamus are the cause of dementia.
Aminoindan derivatives
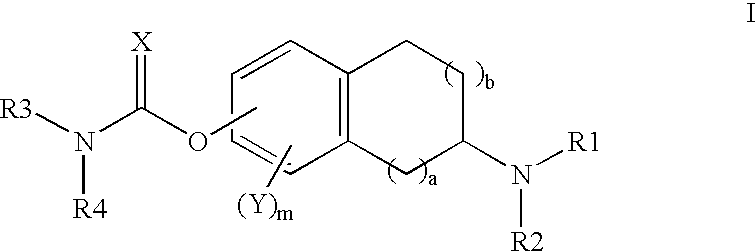
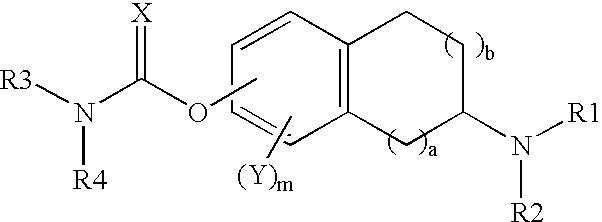
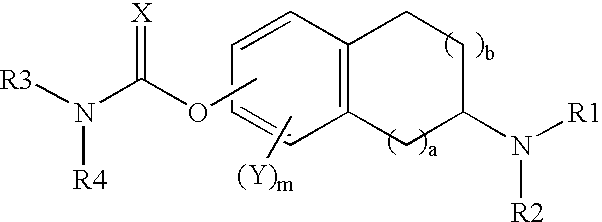
This invention is directed to compounds of the following formula:wherein when a is 0, b is 1 or 2; when a is 1, b is 1, m is from 0-3, X is 0 or S, Y is halogeno, R1 is hydrogen C1-4 alkyl, R2 is hydrogen, C1-4 alkyl, or optionally substituted propargyl and R1 and R4 are each independently hydrogen, C1-6 alkyl, C6-12 aryl, C6-12 aralkyl each optionally substituted.This invention is also directed to the use of these compounds for treating depression, Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD), Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), Tourette's Syndrome. Alzheimer's Disease and other dementia's such as senile dementia, dementia of the Parkinson's type, vascular dementia and Lewy body dementia.This invention is further directed to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of the above-defined compounds and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
Methods of treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases and disorders
The present invention provides compostions and methods useful for treating and preventing neurodegenerative disease and neurologically related disorders by inhibition of Lp-PLA2. The compositions and methods are useful for treating and preventing diseases and disorders with abnormal blood brain barrier (BBB) function, for example neurodegenerative diseases with a permeable BBB, such as but not limited to, Alzheimer's Disease, Huntington's Disease, Parkinson's Disease and Vascular Dementia.
Owner:UNIV OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF NEW JERSEY +1
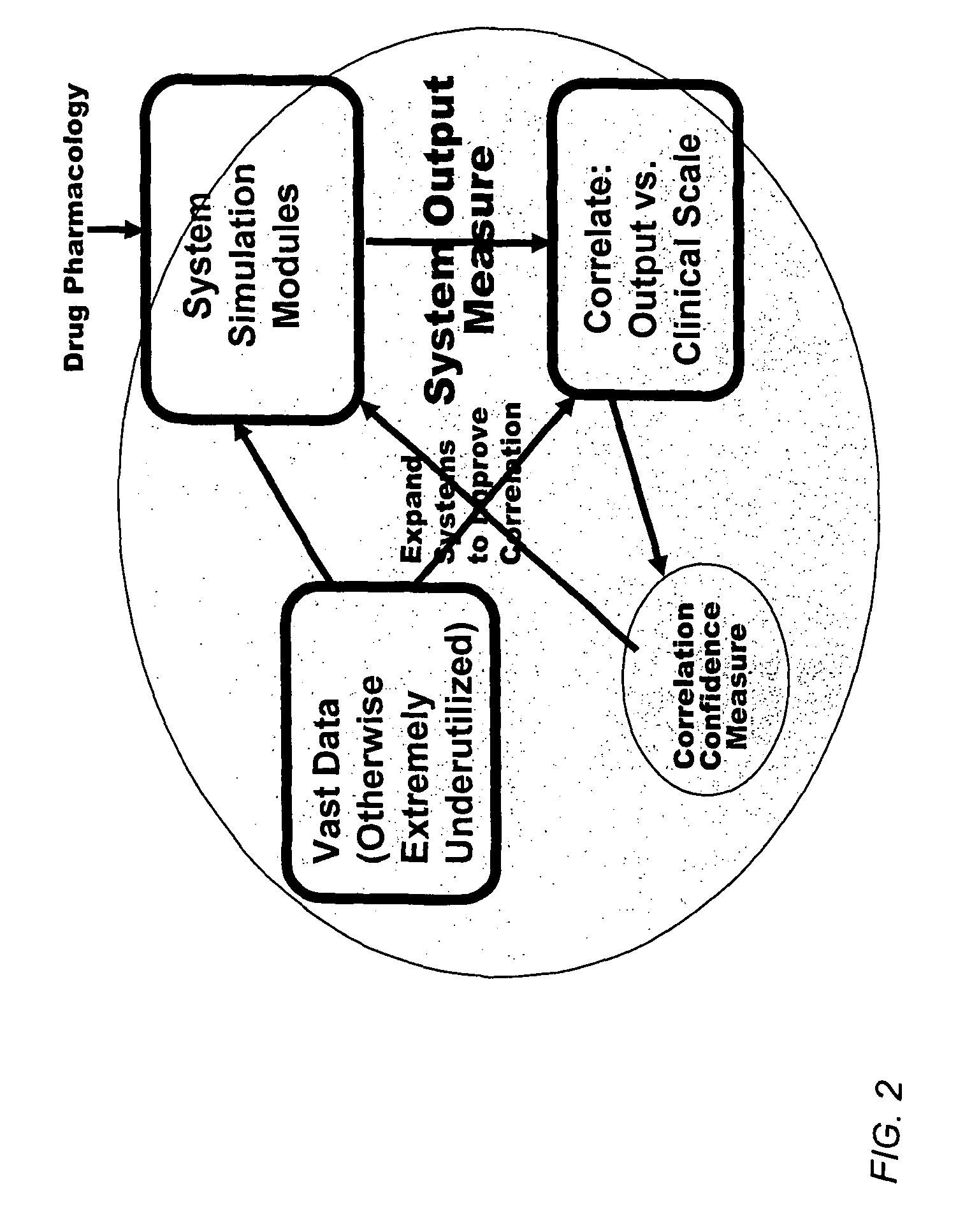
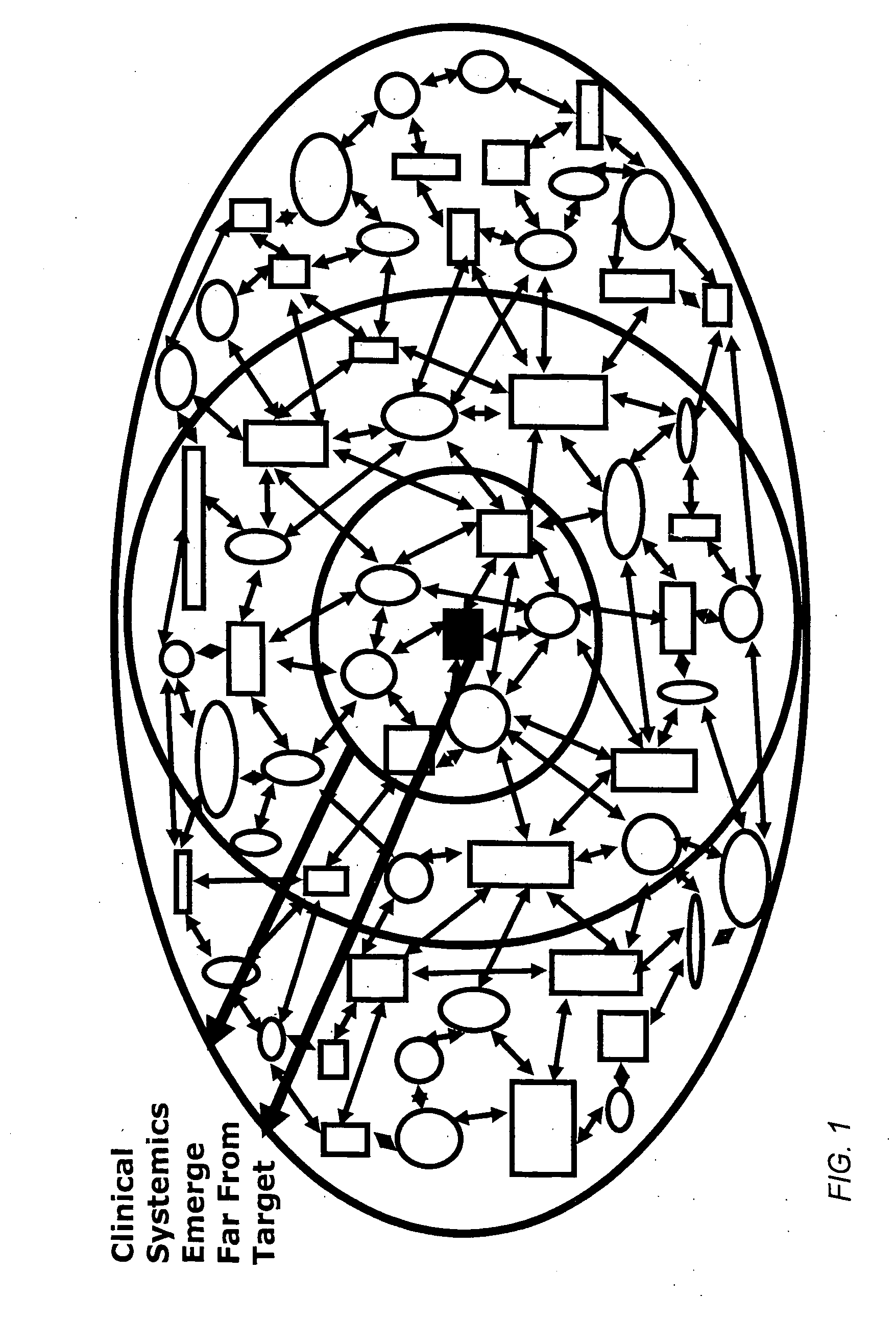
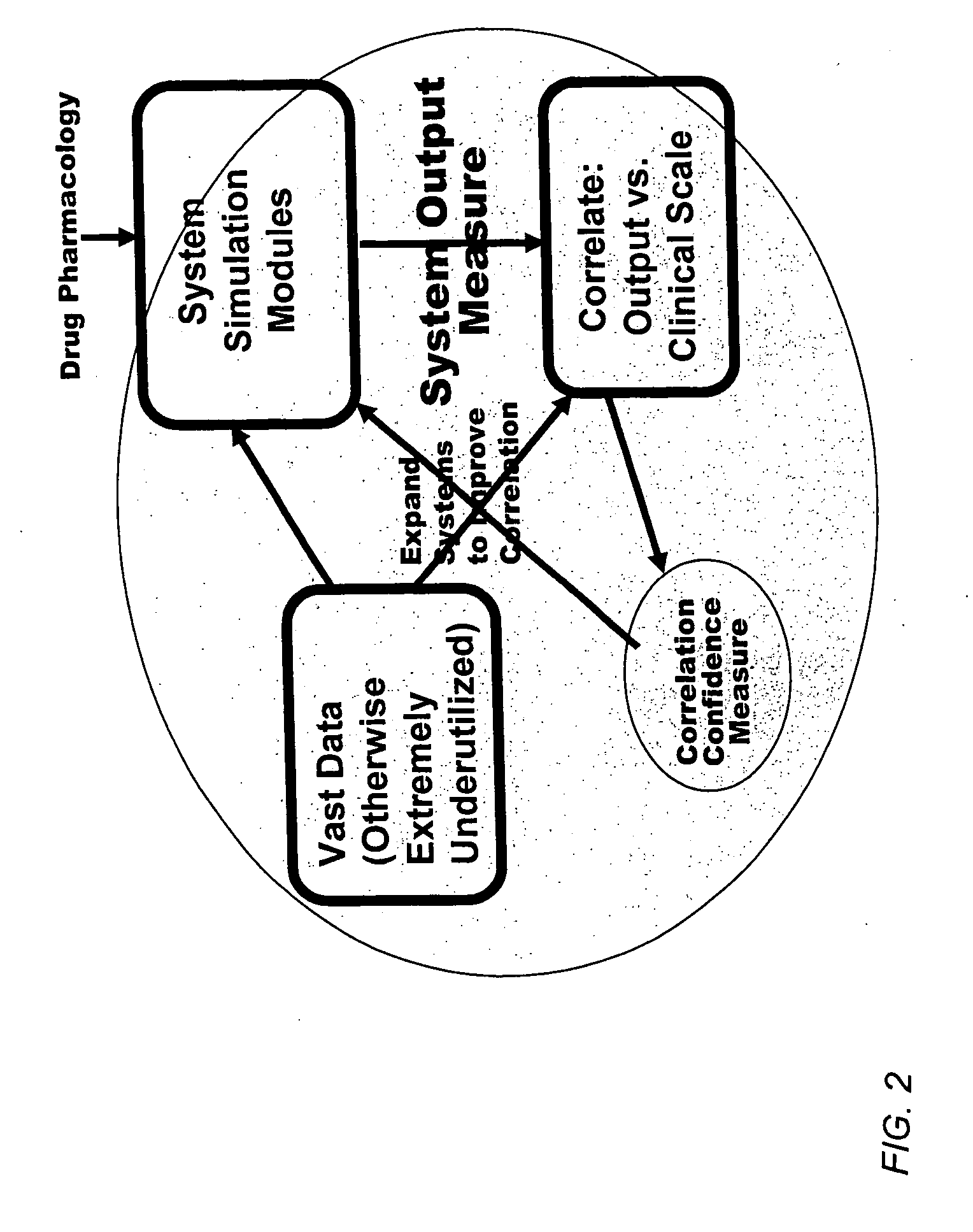
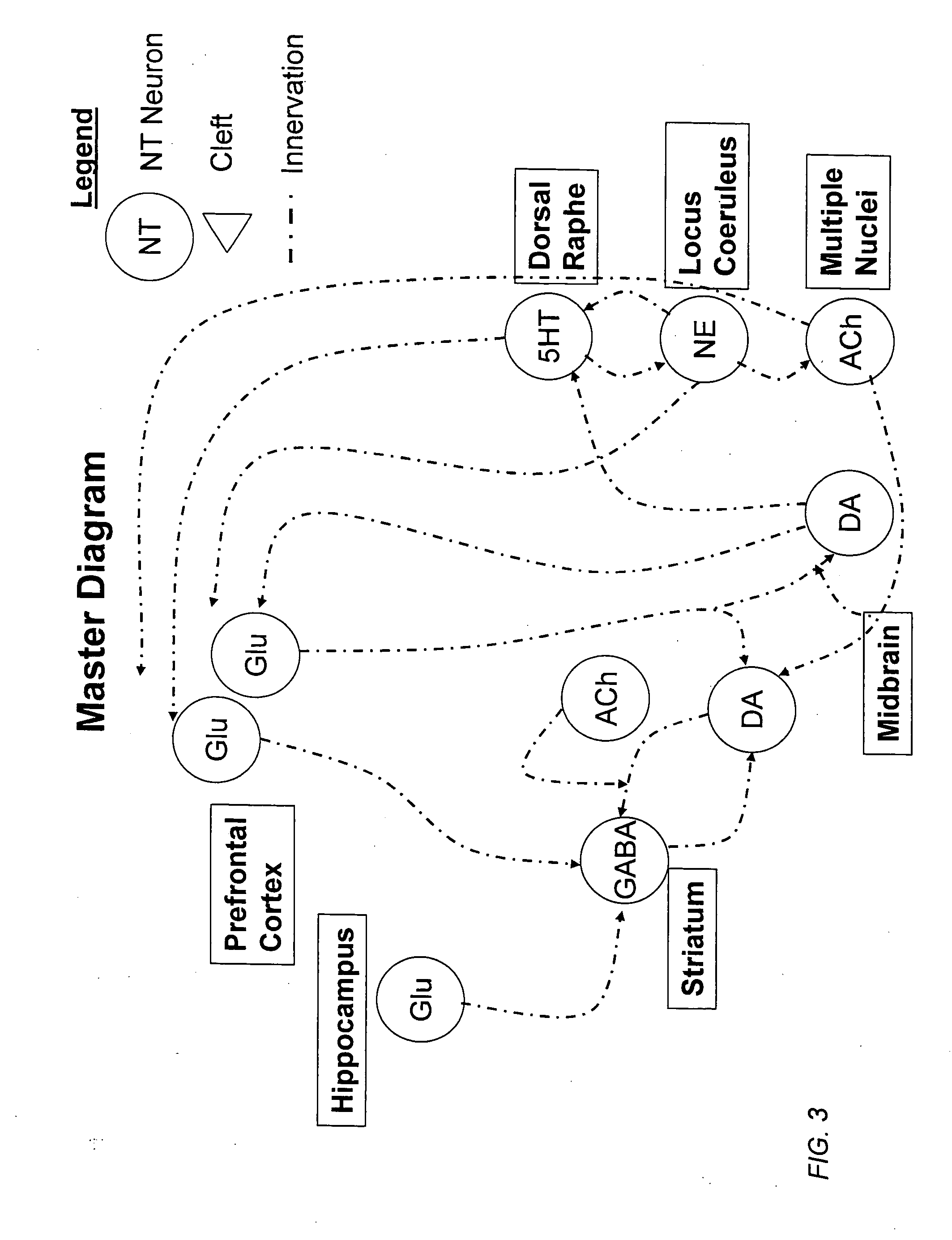
Method and apparatus for computer modeling of the interaction between and among cortical and subcortical areas in the human brain for the purpose of predicting the effect of drugs in psychiatric and cognitive diseases
ActiveUS8150629B2Easy to set upImprove clinical outcomesMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesSubstance abuserAmygdala
Computer modeling of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, for example in a normal and a pathological state resembling schizophrenia which pathological state has inputs representing the effects of a drug(s), for the purpose of using the outputs to predict the effect of drugs in psychiatric and cognitive diseases on one or more clinical scales. Diseases that can be modeled include psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depression, ADHD, autism, obsessive-compulsive disorder, substance abuse and cognitive deficits therein and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Mild Cognitive impairment, Parkinson's disease, stroke, vascular dementia, Huntington's disease, epilepsy and Down syndrome. The computer model preferably uses the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, to define the biological processes related to the biological state of the generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala and cortex, as well as certain mathematical relationships related to interactions among biological variables associated with the biological processes.
Owner:CERTARA USA INC
Methods to facilitate transmission of large molecules across the blood-brain, blood-eye, and blood-nerve barriers
InactiveUS7629311B2Reduce deliveryImprove efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderTrendelenburg positionGolimumab
A method for delivering a biologic to a human with Alzheimer's-related dementia, comprising administering the biologic parenterally into the perispinal space of the human without direct intrathecal injection, and thereafter positioning the human's head below the horizontal. The method further includes delivering a TNF antagonist to the brain of a human for treating mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer's related dementia, or vascular dementia, comprising administering the TNF antagonist golimumab parenterally into the perispinal space of the human without direct intrathecal injection, and thereafter positioning the human in a Trendelenburg position, for delivery of the golimumab to the brain via the human's vertebral venous system.
Owner:EDWARD LEWIS TOBINICK M D
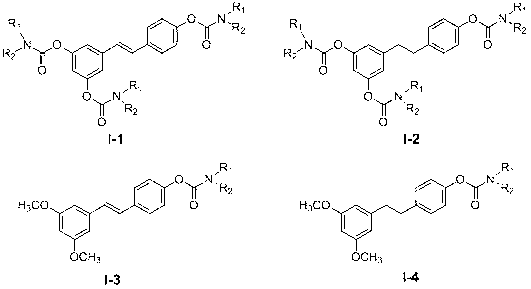
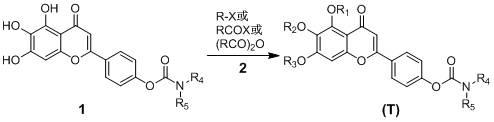
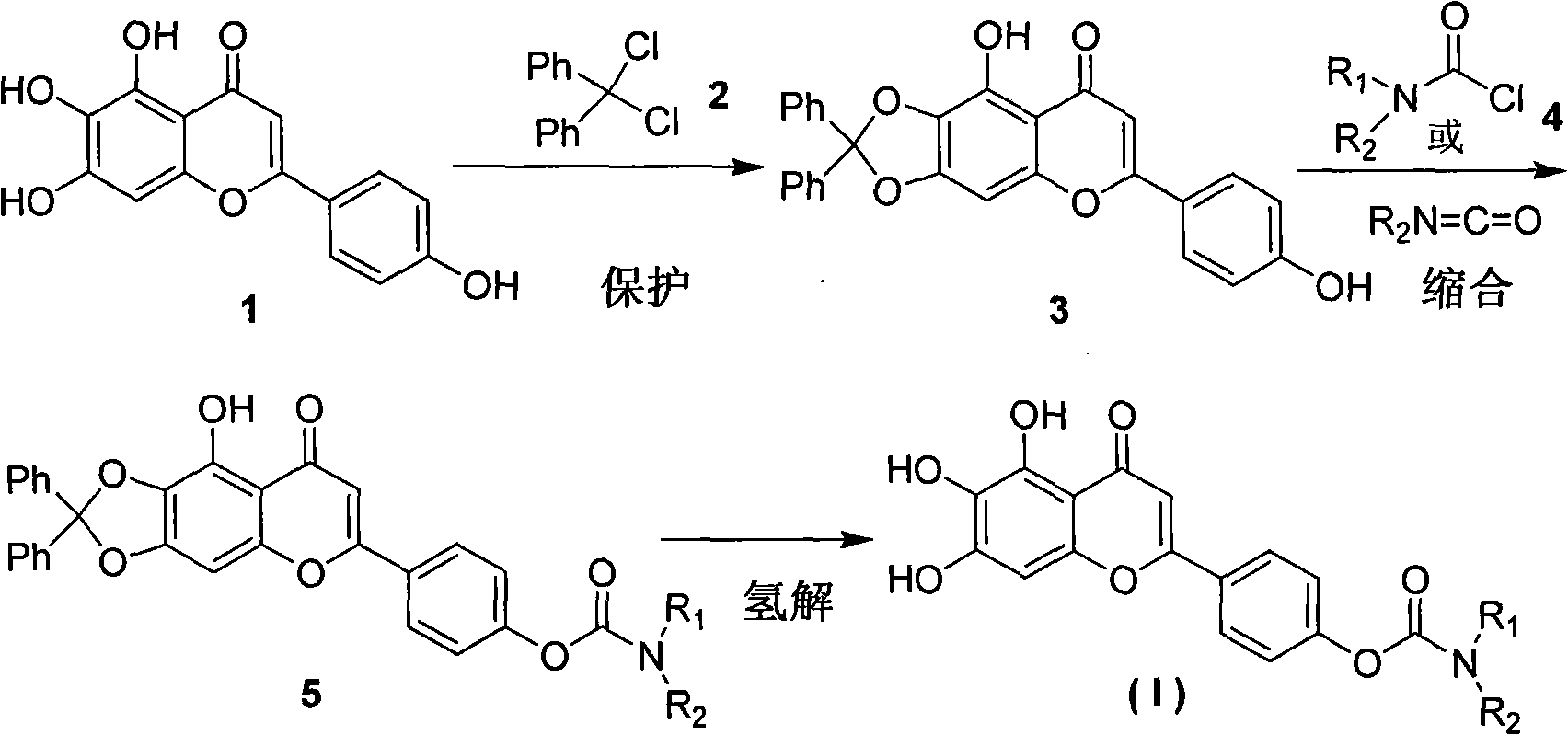
Carbamate compounds, preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses novel carbamate compounds (I-1 to I-4) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, a preparation method of the compounds, and application of the compounds in preparation of medicines for preventing neurodegenerative diseases, including but not limited to vascular dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) related cretinism, multiple sclerosis, progressive lateral spinal sclerosis, neuropathic pain, glaucoma and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
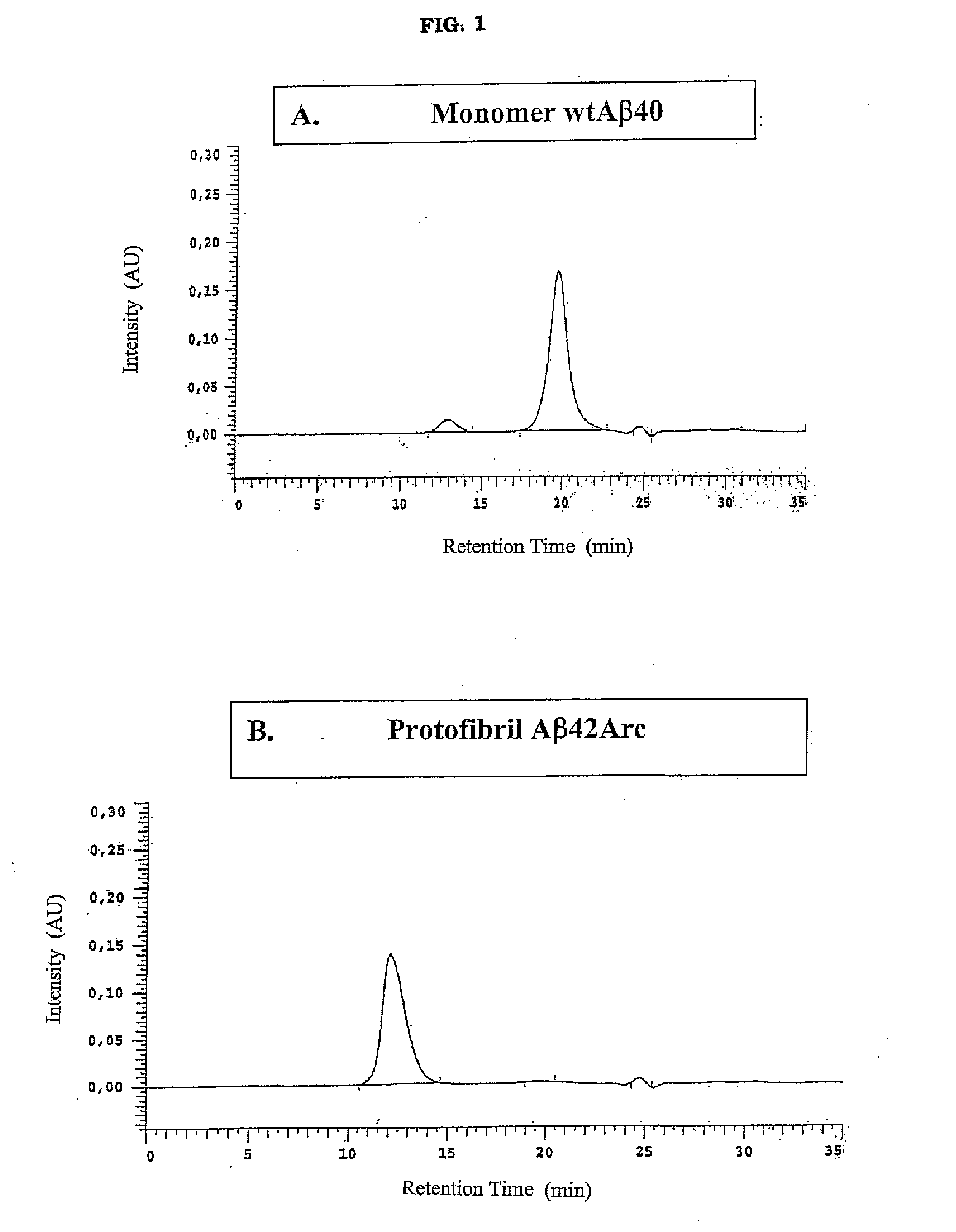
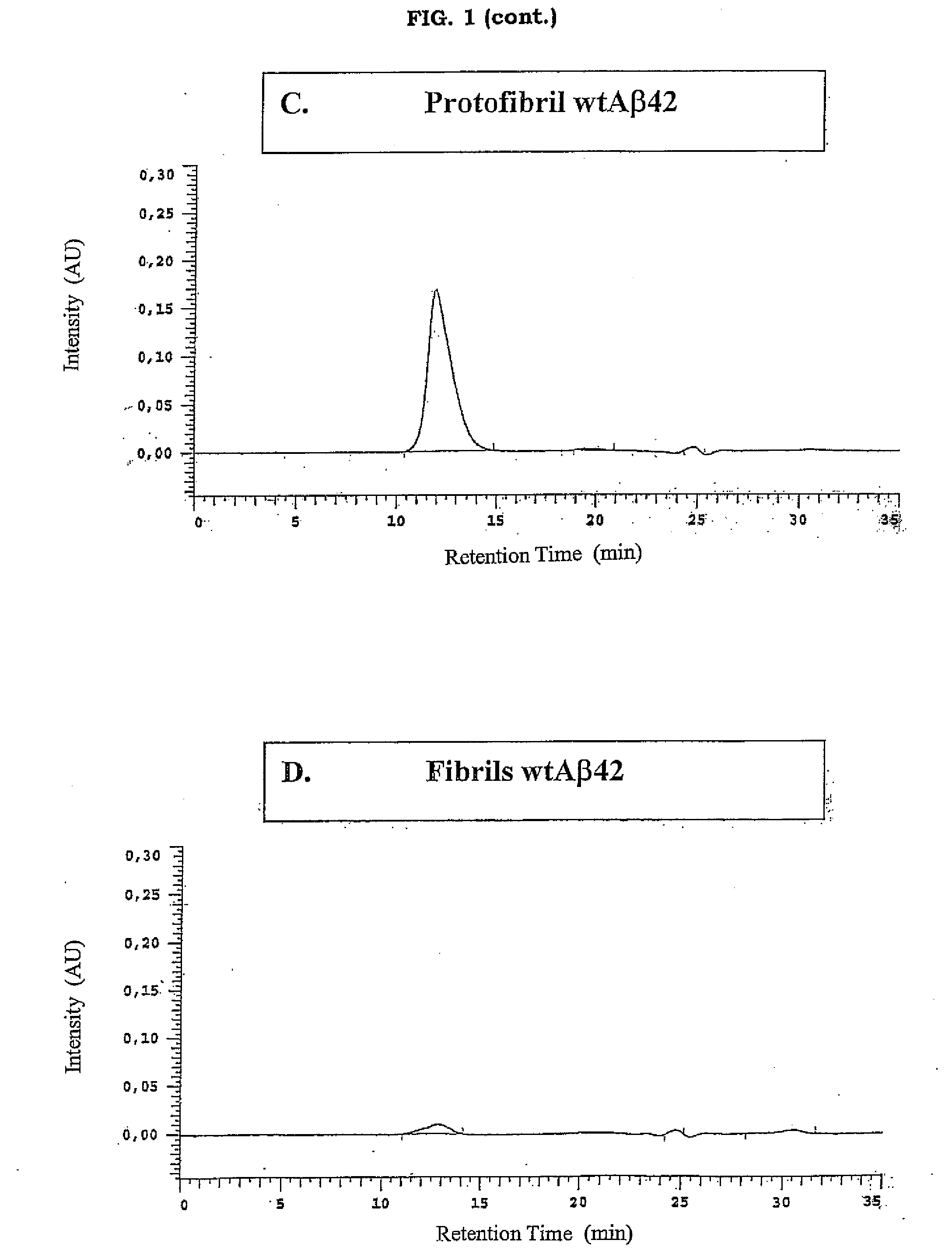
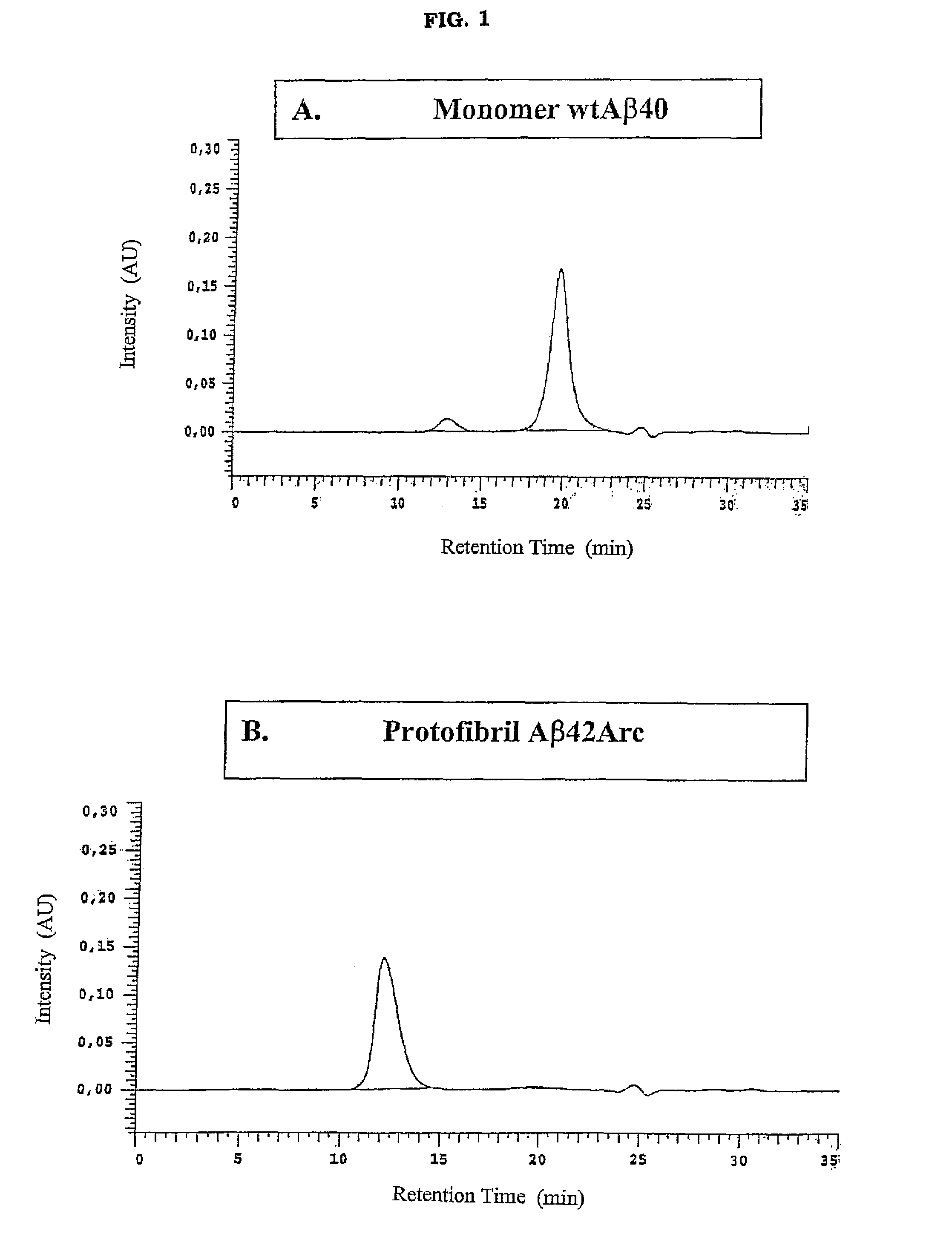
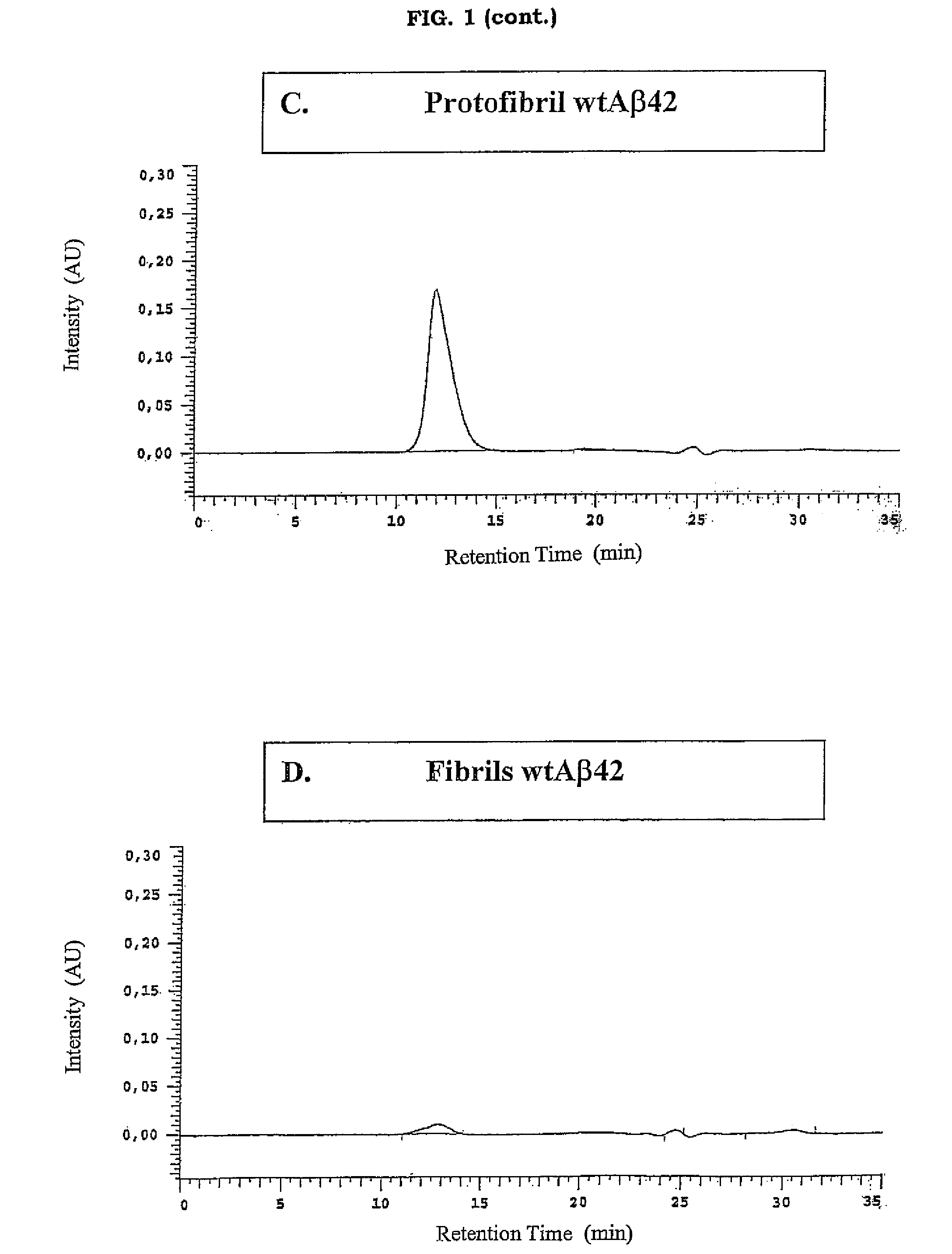
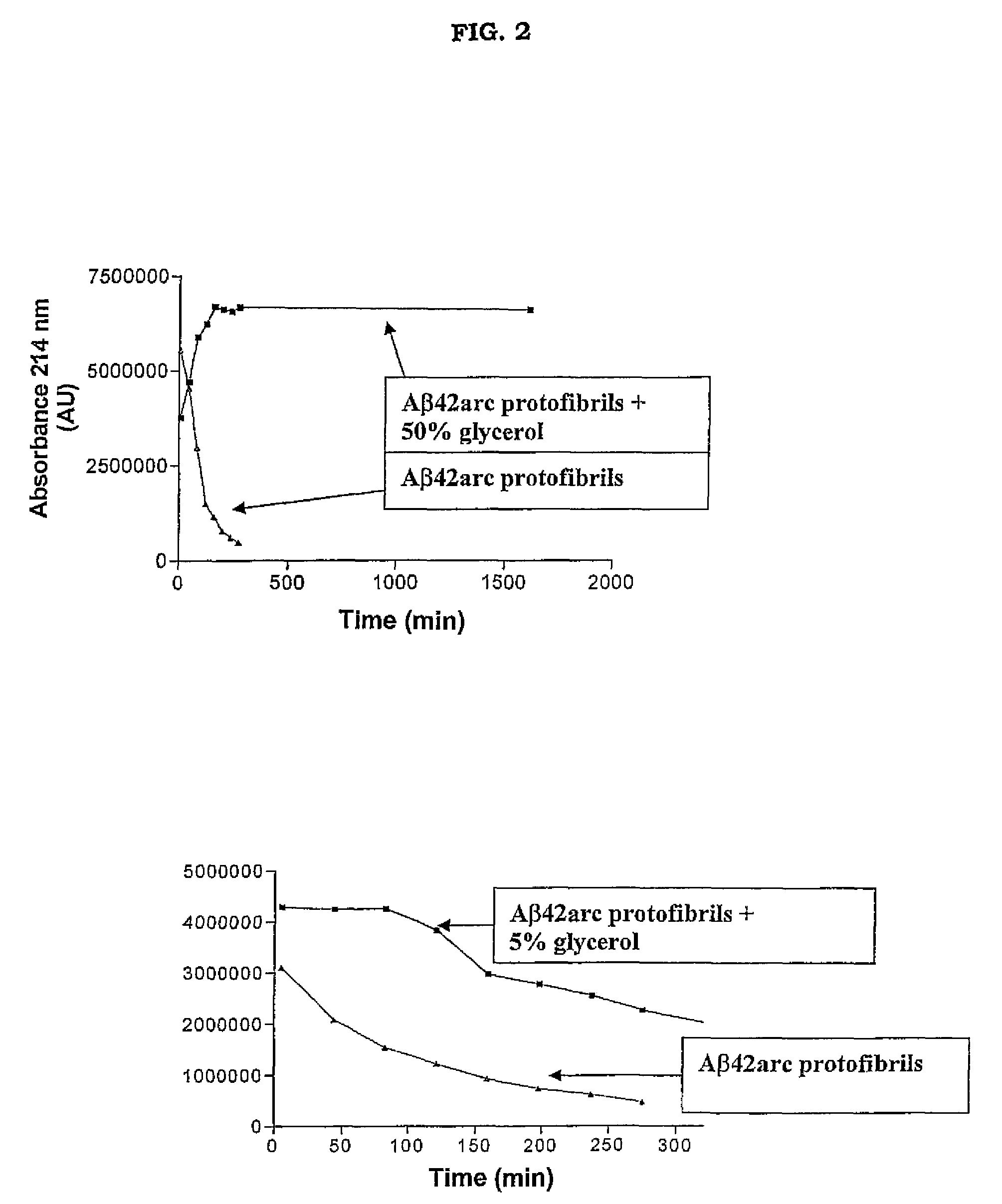
Antibodies Specific For Soluble Amyloid Beta Peptide Protofibrils and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20090155246A1Avoid side effectsModulating levelNervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigenAmyloid beta
The invention pertains to the development of antibodies that specifically bind amyloid beta protein (Abeta) in its protofibril conformation. The invention also comprises methods of using anti-Abeta protofibril antibodies to diagnose or treat Alzheimer's disease, Down's syndrome Lewybody dementia, vascular dementia, and other neurodegenerative disorders. Furthermore, the invention pertains to the use of anti-Abeta protofibril antibodies to screen and identify substances that will modulate protofibril activity or formation in vitro or in vivo. The invention also pertains to methods for synthesising pure Abeta protofibril antigens as well as to a method for stabilising Abeta protofibrils antigens as well as to a method for stabilising Abeta protofibrils.
Owner:BIOARCTIC NEUROSCI AB
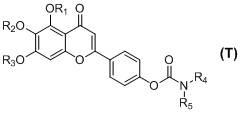
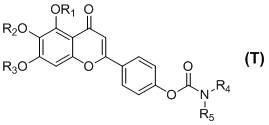
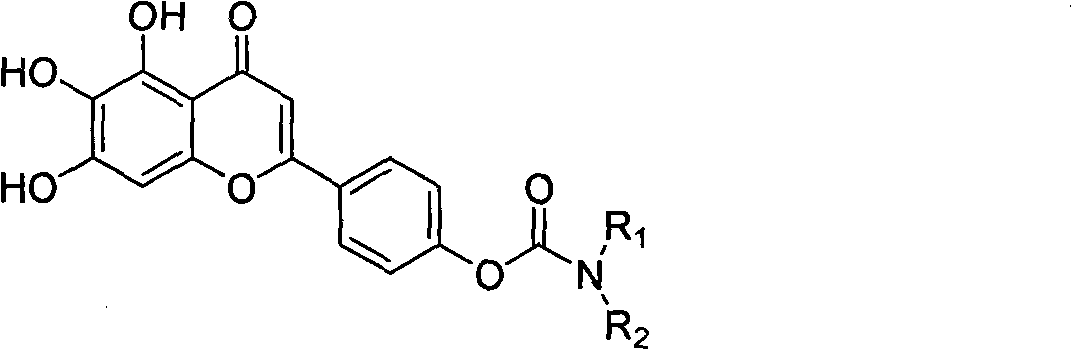
Scutellarin carbamate derivative, preparation method and use thereof
The invention discloses a 4'-carbamate derivative of scutellarin shown in formula (I), a preparation method of the compound and application of the compound in preparing medicines for preventing and / or treating various symptoms and diseases caused by acetyl cholinesterase and / or mediated by free radicals, such as vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease. In the formula, each of R1, R2 and R3 independently represents H, C1-C12 alkyl or R6CO, wherein R6 represents C1-C12 alkyl, but R1, R2 and R3 are not H at the same time; each of R4 and R5 independently represents H, C1-C12 alkyl, C1-C6 fatty alcohol, or an ester formed by the C1-C6 fatty alcohol and C1-C6 carboxylic acid, the C1-C6 carboxylic acid, or an ester formed by the C1-C6 carboxylic acid and the C1-C6 fatty alcohol; or R4NR5 represents a morpholine ring, a piperidine ring, a 4-benzyl piperidine ring, a piperazine ring, the piperazine ring with the 4-position substituted by C1-C12 alkyl, or a tetrahydropyrrole ring.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Methods to facilitate transmission of large molecules across the blood-brain, blood-eye, and blood-nerve barriers
InactiveUS20070196375A1Reduction in rate of progressHalt in progression of illnessOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSpinal cordTnf antagonists
A method for delivering a biologic to a human with Alzheimer's-related dementia, comprising administering the biologic parenterally into the perispinal space of the human without direct intrathecal injection, and thereafter positioning the human's head below the horizontal. The method further includes delivering a TNF antagonist to the brain of a human for treating mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer's related dementia, or vascular dementia, comprising administering the TNF antagonist golimumab parenterally into the perispinal space of the human without direct intrathecal injection, and thereafter positioning the human in a Trendelenburg position, for delivery of the golimumab to the brain via the human's vertebral venous system.
Owner:EDWARD LEWIS TOBINICK M D
Antibodies specific for soluble amyloid beta peptide protofibrils and uses thereof
ActiveUS8106164B2Avoid side effectsModulating levelNervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigenAmyloid beta
Owner:BIOARCTIC NEUROSCI AB
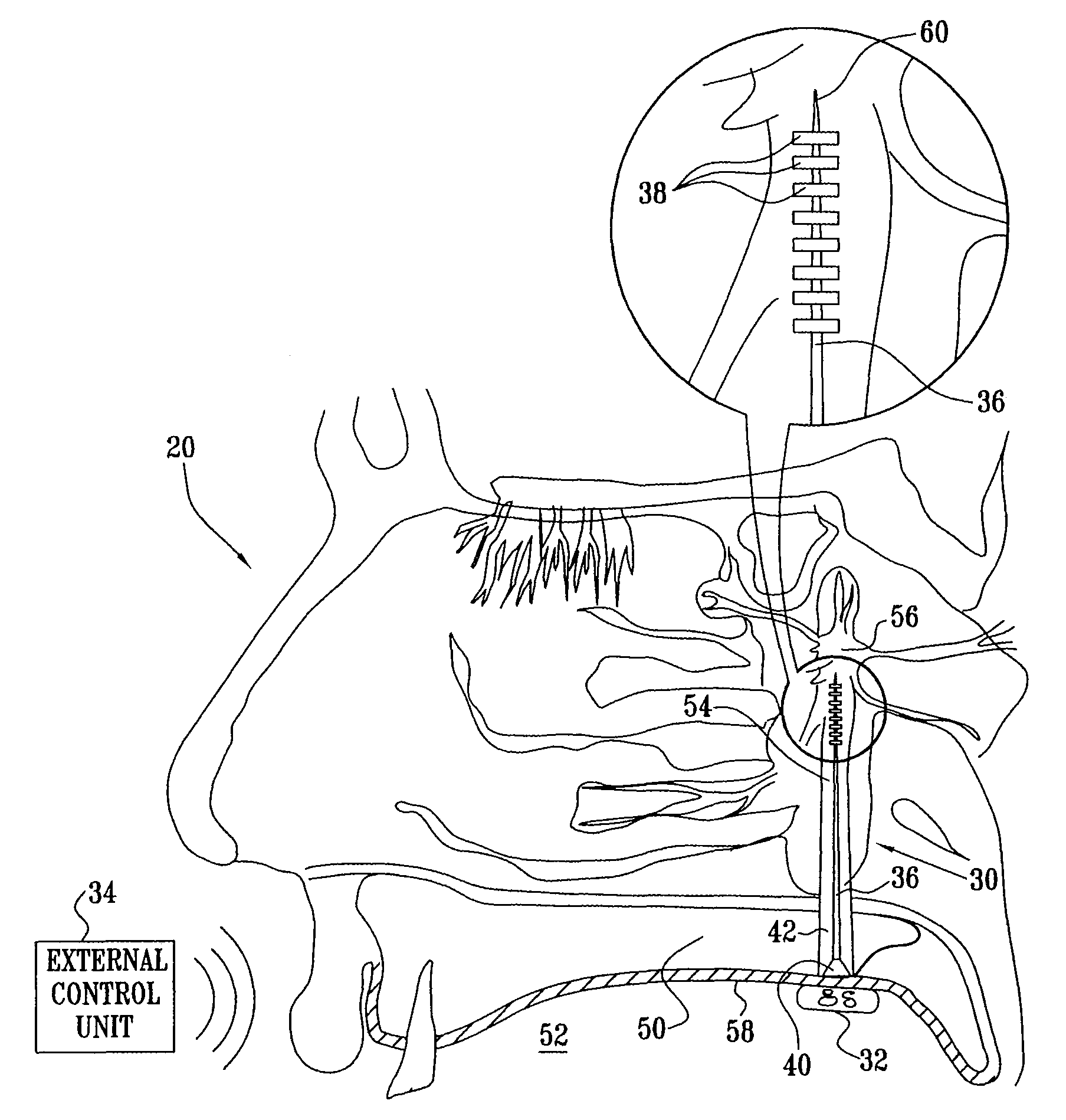
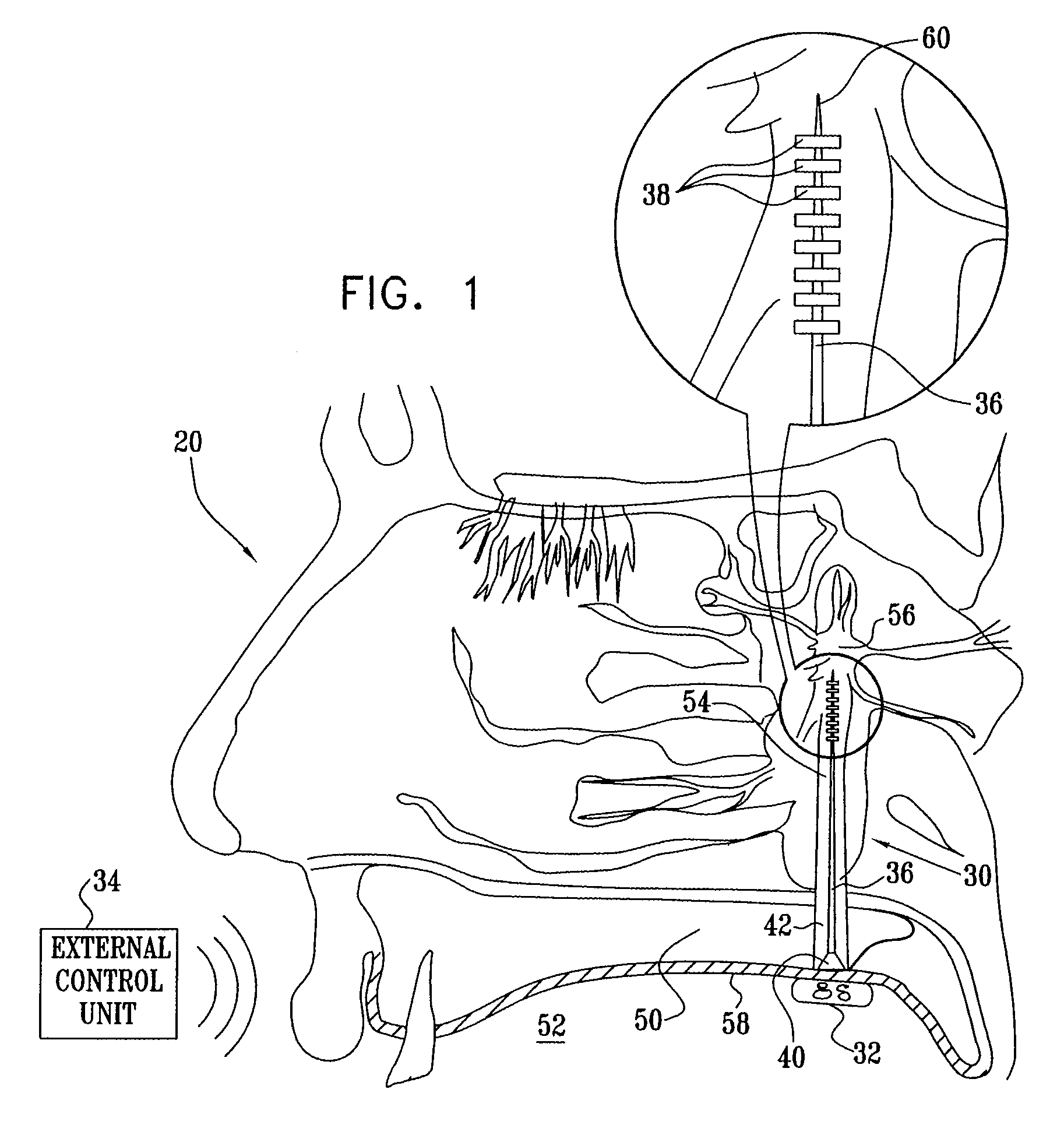
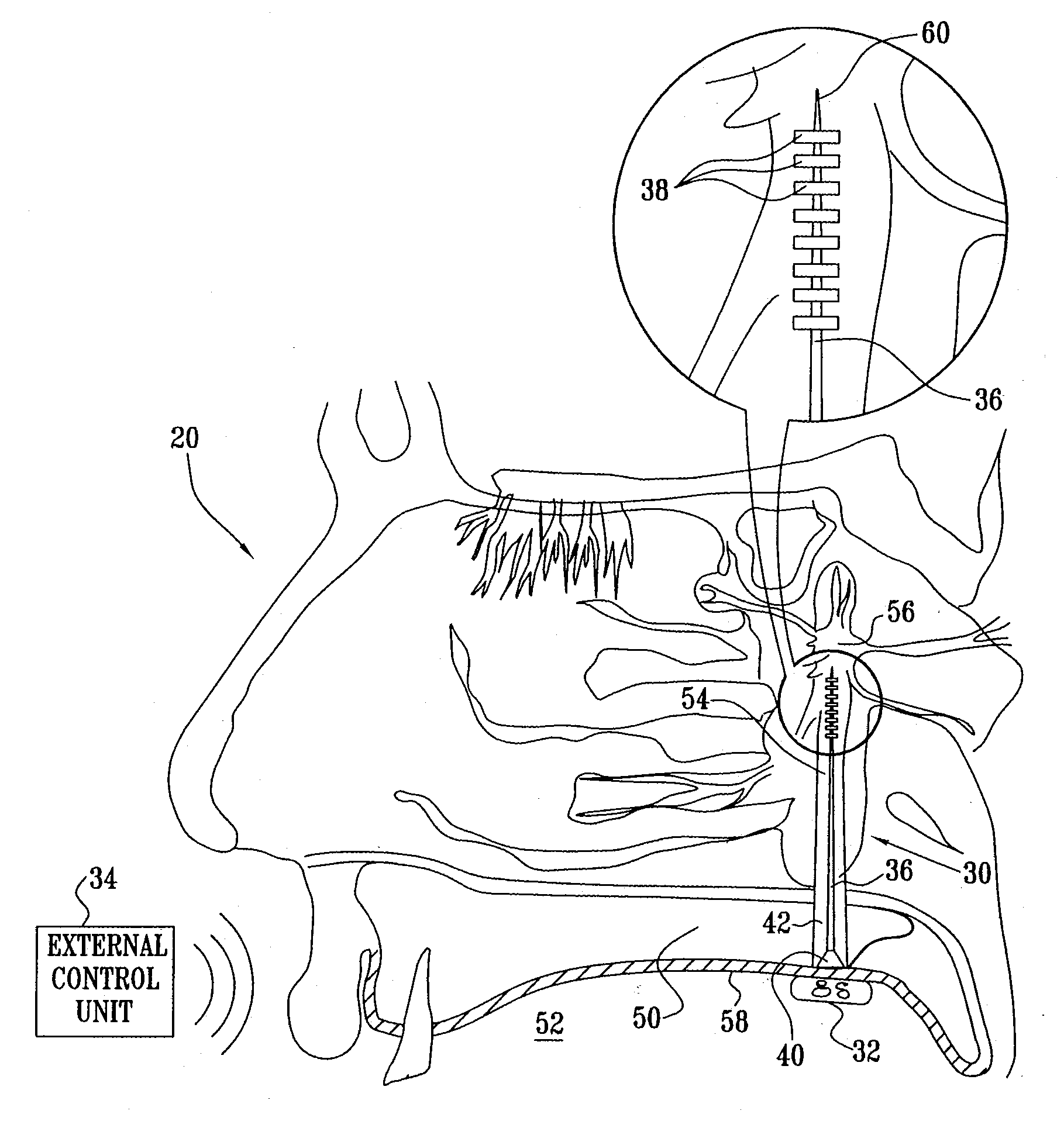
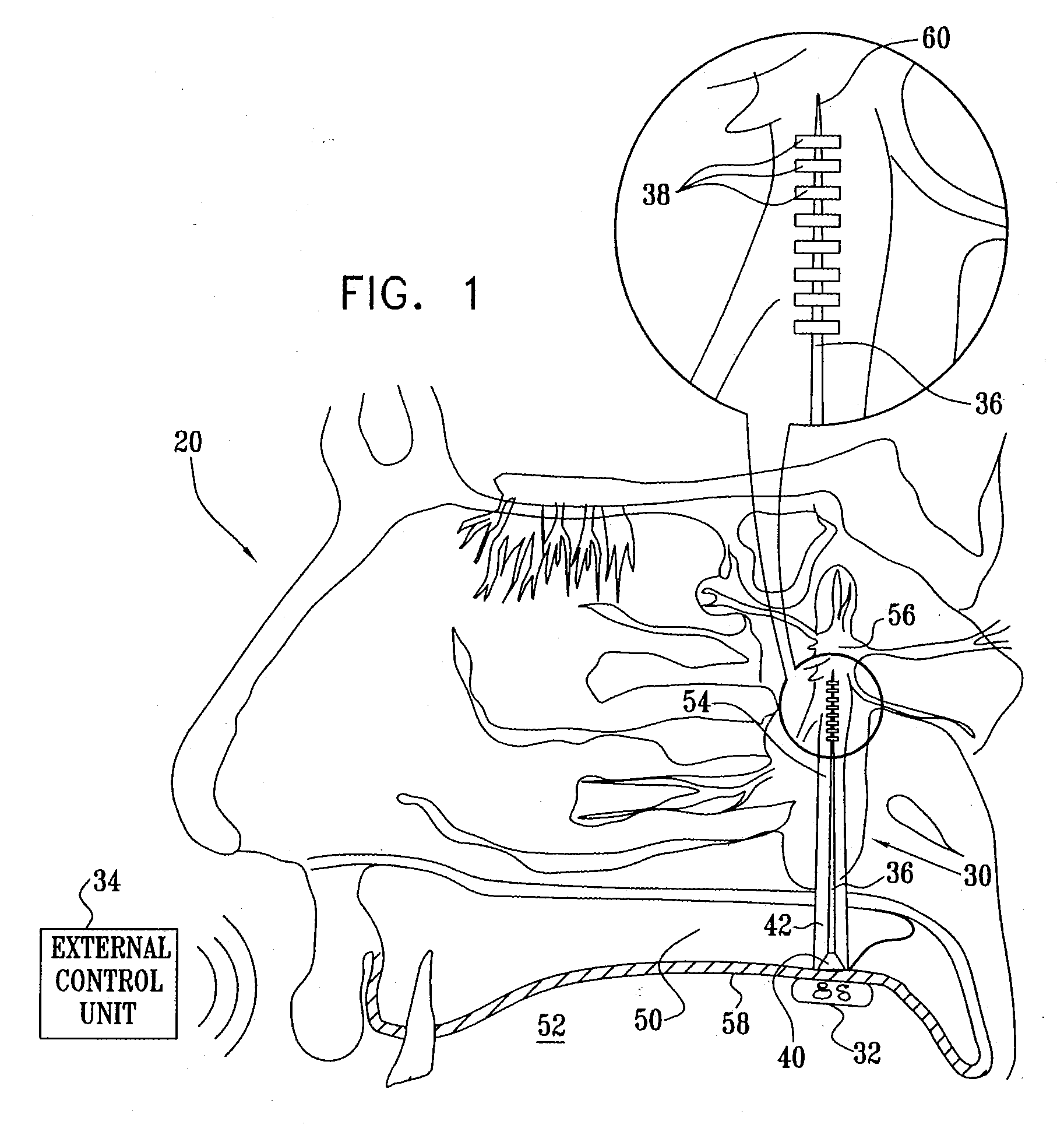
Long-term SPG stimulation therapy for prevention of vascular dementia
ActiveUS7860569B2Reduce riskReduce development riskSpinal electrodesHead electrodesDeep petrosal nerveMedicine
A method is provided that includes identifying that a subject is at risk of suffering from vascular dementia (VaD). Responsively to the identifying, a risk of development of the VaD is reduced by applying electrical stimulation to a site of the subject selected from the group consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG), a greater palatine nerve, a lesser palatine nerve, a sphenopalatine nerve, a communicating branch between a maxillary nerve and an SPG, an otic ganglion, an afferent fiber going into the otic ganglion, an efferent fiber going out of the otic ganglion, an infraorbital nerve, a vidian nerve, a greater superficial petrosal nerve, and a lesser deep petrosal nerve; and configuring the stimulation to induce at least one neuroprotective occurrence selected from the group consisting of: an increase in cerebral blood flow of the subject, and a release of one or more neuroprotective substances. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
Method and apparatus for computer modeling of the interaction between and among cortical and subcortical areas in the human brain for the purpose of predicting the effect of drugs in psychiatric & cognitive diseases
ActiveUS20070106479A1Easy to set upImprove clinical outcomesMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesSubstance abuserHuntingtons chorea
Computer modeling of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, for example in a normal and a pathological state resembling schizophrenia which pathological state has inputs representing the effects of a drug(s), for the purpose of using the outputs to predict the effect of drugs in psychiatric and cognitive diseases. A method is provided for developing a computer model of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain which comprises the steps of identifying data relating to a biological state of a generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala and cortex; identifying biological processes related to the data, these identified biological processes defining at least one portion of the biological state of the generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala, and cortex; and combining the biological processes to form a simulation of the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain. Diseases that can be modeled include psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depression, ADHD, autism, obsessive-compulsive disorder, substance abuse and cognitive deficits therein and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Mild Cognitive impairment, Parkinson's disease, stroke, vascular dementia, Huntington's disease, epilepsy and Down syndrome. A resulting computer model is of the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, comprising code to define the biological processes related to the biological state of the generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala and cortex, and code to define the mathematical relationships related to interactions among biological variables associated with the biological processes. At least two of the biological processes are associated with the mathematical relationships. A combination of the code to define the biological processes and the code to define the mathematical relationships define a simulation of the biological state of the interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain. Computer executable software code is provided comprised of code to define biological processes related to a biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain including code to define mathematical relations associated with the biological processes. A computer model of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain is provided, comprising a computer-readable memory storing codes and a processor coupled to the computer-readable memory, the processor configured to execute the codes. The memory comprises code to define biological processes related to the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, and code to define mathematical relationships related to interactions among biological variables associated with the biological processes.
Owner:CERTARA USA INC
Method for Quantitative Diagnosis of Cerebrovascular, Neurovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases via Computation of a CO2 Vasomotor Reactivity Index based on a Nonlinear Predictive Model
InactiveUS20140278285A1Sensitive and reliableMedical simulationHealth-index calculationComputational modelComputer aid
The present invention relates generally to a method for computer-aided quantitative diagnosis of cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases (such as Alzheimer's, vascular dementia, mild cognitive impairment, transient ischemia, stroke etc.) via a vasomotor reactivity index (VMRI) which is computed on the basis of a computational model of the dynamic nonlinear inter-relationships between beat-to-beat time-series measurements of cerebral blood flow velocity, arterial blood pressure and end-tidal CO2. This model is obtained by means of a method pioneered by the inventors and may incorporate additional physiological measurements from human subjects. Its purpose is to provide useful information to physicians involved in the diagnosis and treatment of cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases with a significant neurovascular component by offering quantitative means of assessment of the effects of the disease or medication on cerebral vasomotor reactivity. Initial results from clinical data have corroborated the diagnostic potential of this approach.
Owner:MARMARELIS VASILIS Z +2
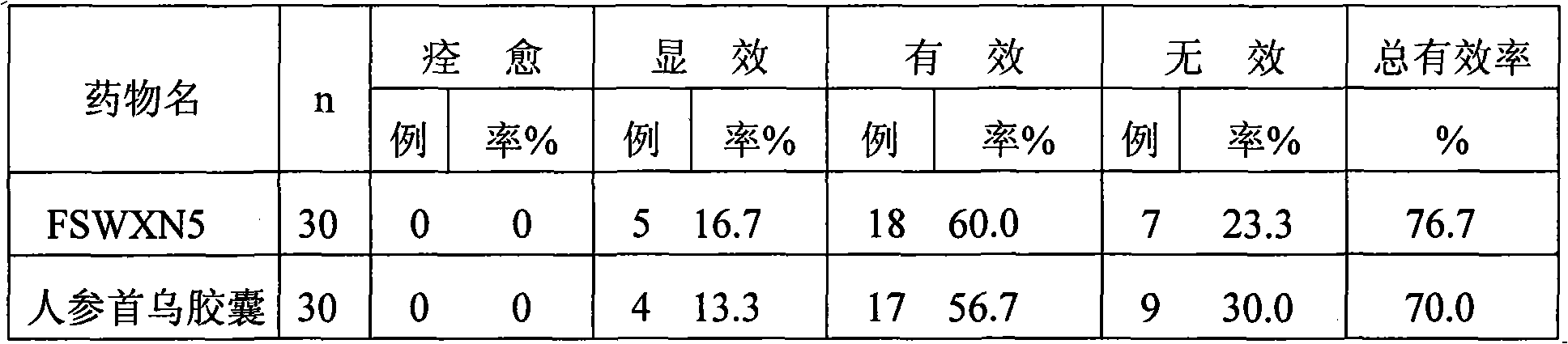
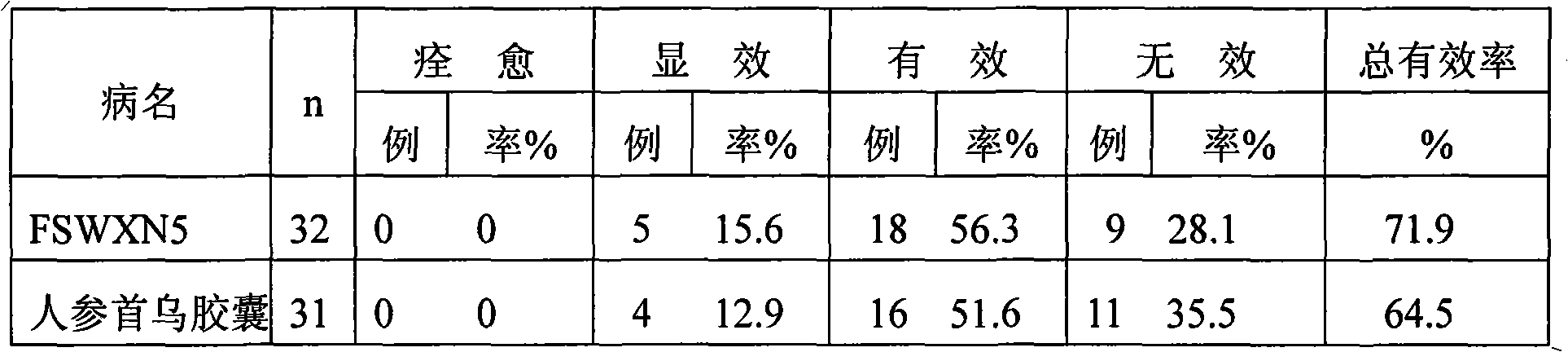
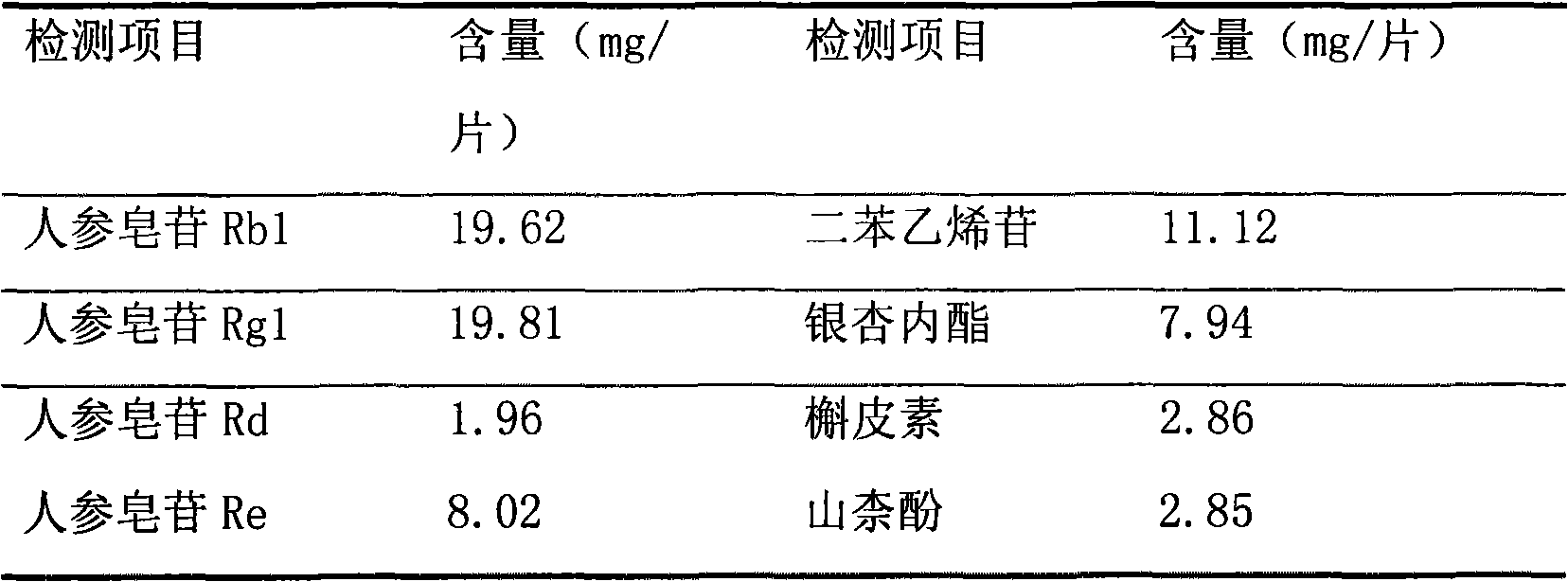
Composition of traditional Chinese medicine effective constituent for preventing and treating diseased associated with cerebral ischemia injury
ActiveCN101357136AAvoid gatheringPrevent thrombosisOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderSequelaAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a composite of active ingredients of Chinese herb medicine used for preventing the damage of cerebral ischemia and relevant diseases, in particular to a preparation which is prepared by the active ingredients of the Chinese herb medicine; the preparation is prepared by the active ingredients of the Chinese herb medicine and the conventional preparation technique which is used by carriers permitted by pharmacy, and comprises the following components with the parts by weight: 2 to 10 parts of ginsenoside Rb, 2 to 10 parts of ginsenoside Rg1, 1 to 5 parts of ginsenoside Rd, 1 to 5 parts of ginsenoside Re, 2 to 10 parts of stilbene glycoside, 1 to 5 parts of ginkgolide and 1 to 5 parts of flavonoid mixture which consists of kaempferol and quercetin with the weight rate to be 1:1. The invention has the advantages that the defects that in the traditional compounded Chinese medicine, the composition is complex, the product quality is not controlled effectively and the curative effect is not stable are overcome, has clear ingredients, definite effect, stable quality and obvious control effect on ischemic stroke, sequela, cerebral arteriosclerosis and vascular dementia, can improve the functions of motor nerve, and learning and memory of the patients, has low toxicity and simple preparation method without obvious side effect and is suitable for industrial mass production.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
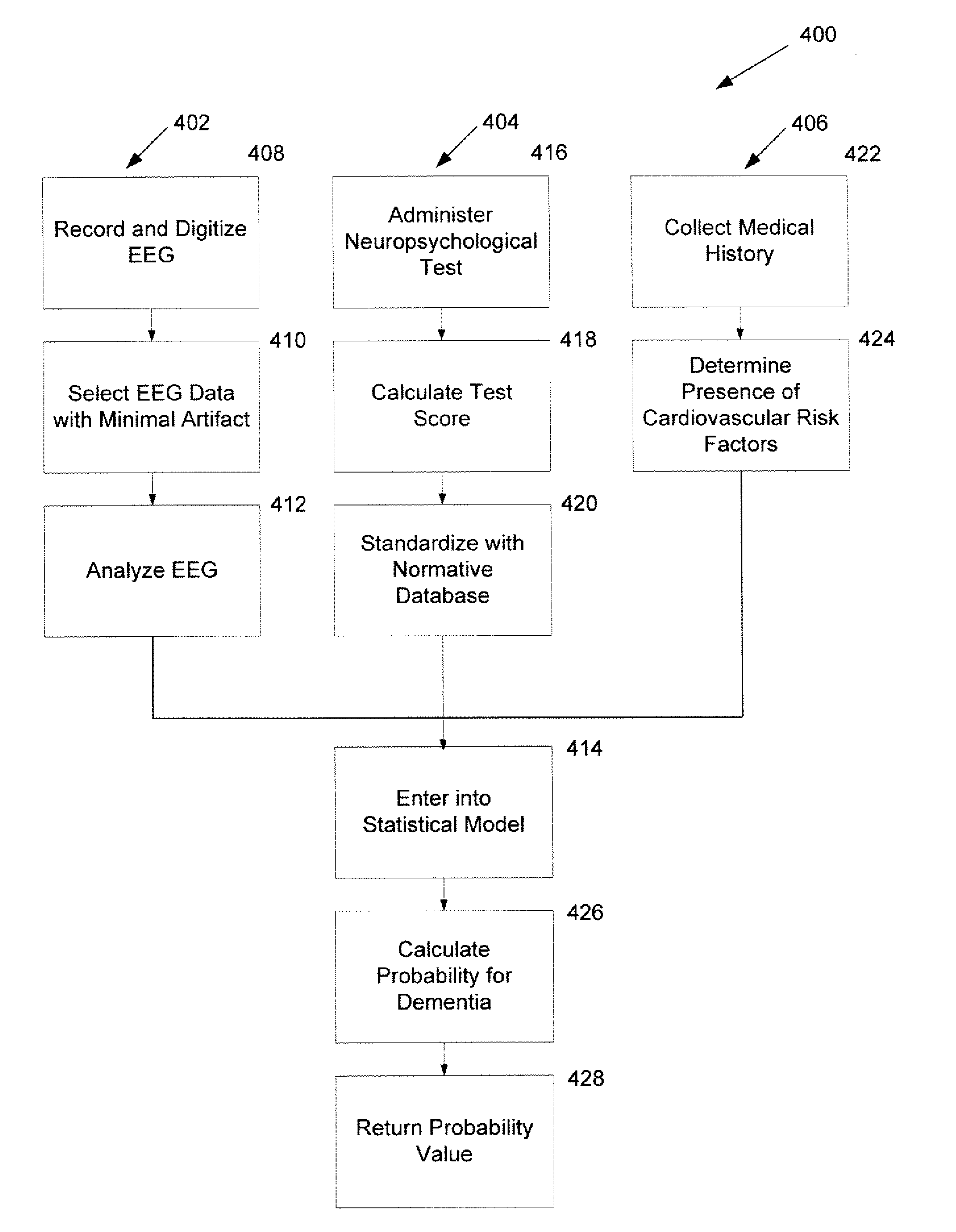
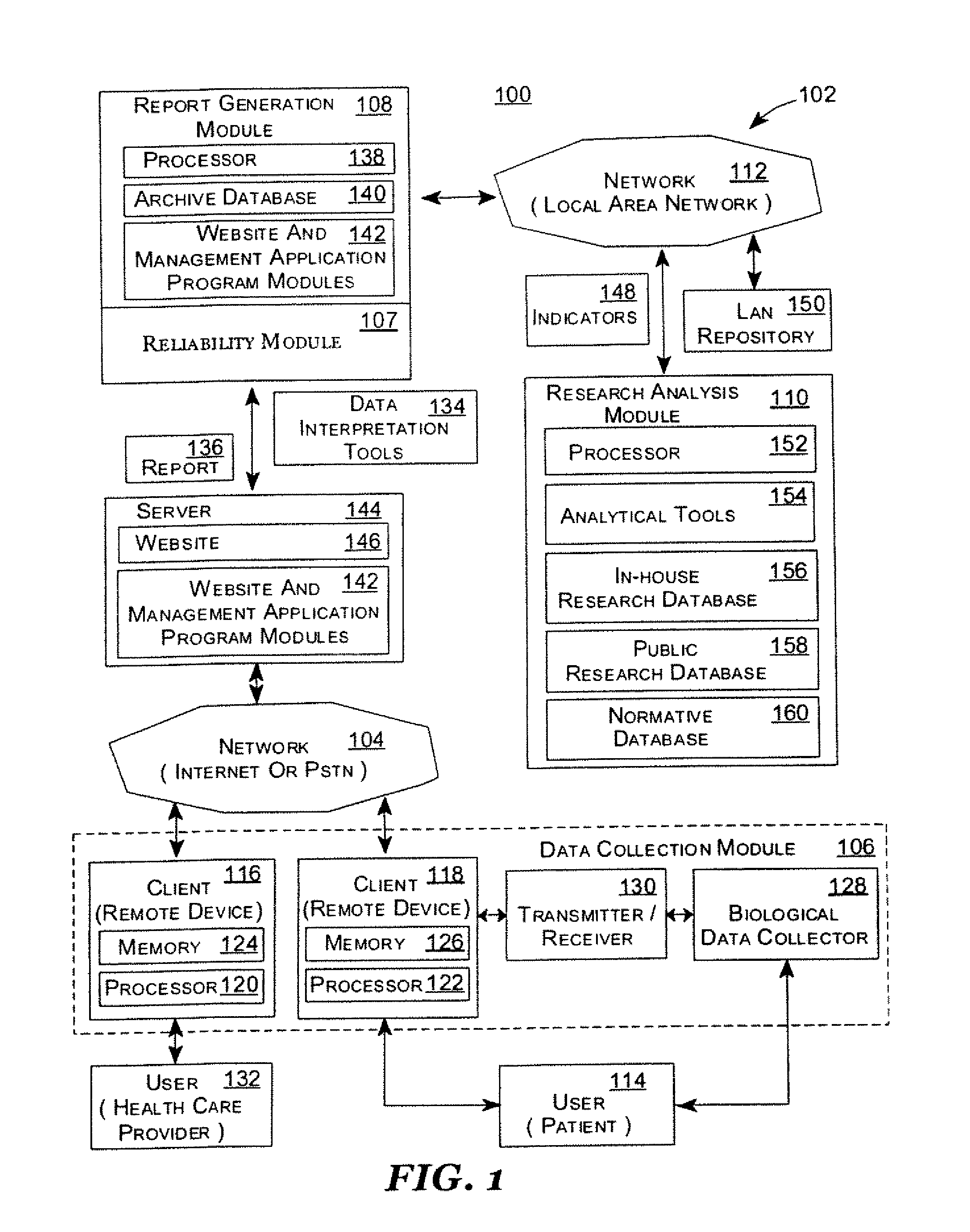
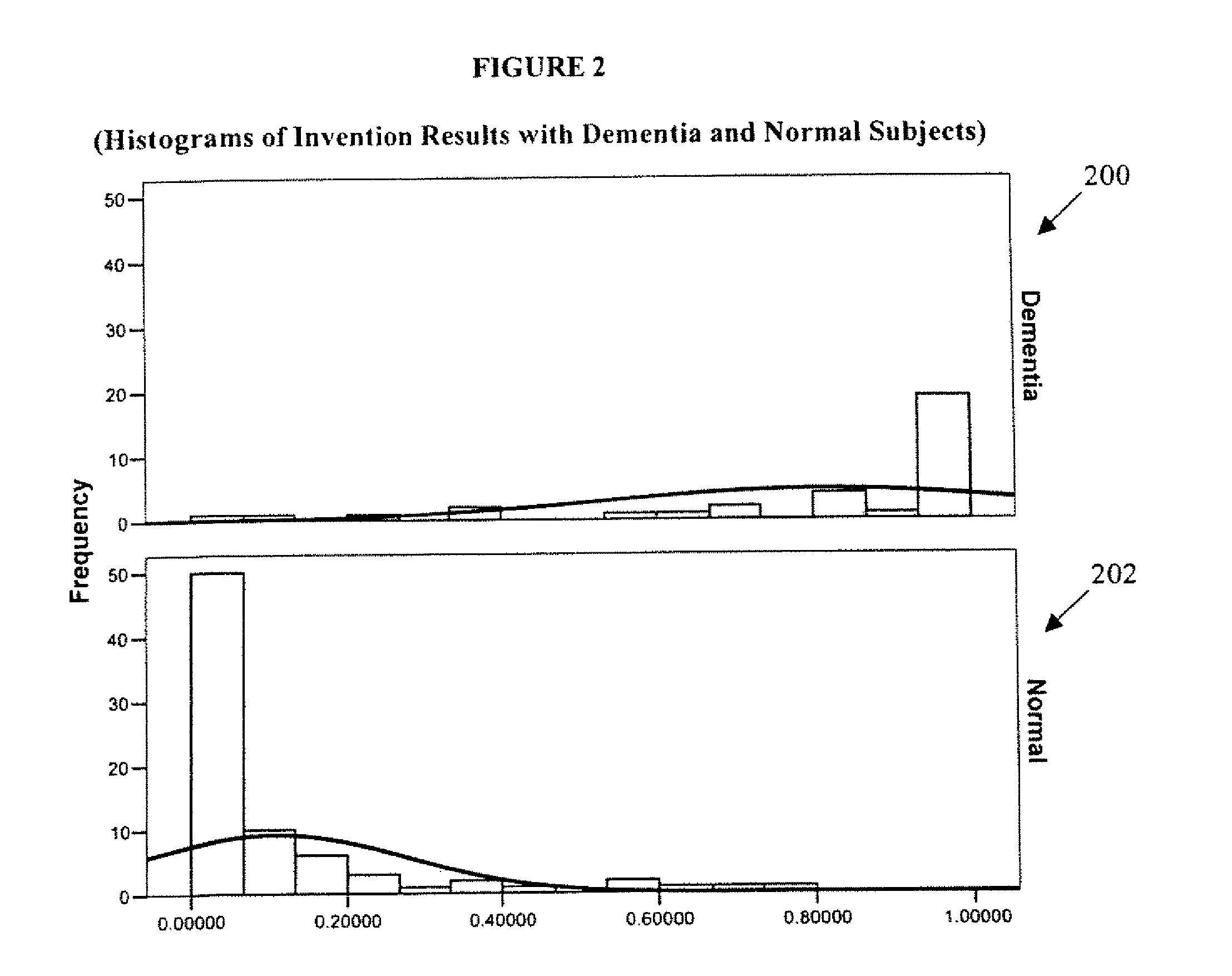
Systems and Methods for Analyzing and Assessing Dementia and Dementia-Type Disorders
InactiveUS20070299360A1High sensitivityStrong specificityElectroencephalographyMedical automated diagnosisMixed dementiaElectroencephalography
Embodiments of the invention can provide systems and methods for analyzing and assessing dementia and dementia-type disorders by integrating the use of electroencephalography (EEG), neuropsychological or cognitive testing data, and cardiovascular risk factor data. Embodiments of the invention can provide systems and methods for early detection of dementia, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), vascular dementia (VAD), mixed dementia (AD and VAD), MCI, and other dementia-type disorders. Embodiments of the invention can provide some or all of the following improvements over conventional systems and methods, including: (1) Increased sensitivity, specificity, and overall accuracy; (2) Detection of AD, VAD and mixed dementia; and (3) Accurate detection of mild dementia and some cases of mild cognitive impairment in addition to the detection of moderate to severe dementia.
Owner:LEXICOR MEDICAL TECH
Long-term spg stimulation therapy for prevention of vascular dementia
ActiveUS20090105783A1Preventing dementiaPreventing CBF deteriorationSpinal electrodesHead electrodesDeep petrosal nerveMedicine
A method is provided that includes identifying that a subject is at risk of suffering from vascular dementia (VaD). Responsively to the identifying, a risk of development of the VaD is reduced by applying electrical stimulation to a site of the subject selected from the group consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG), a greater palatine nerve, a lesser palatine nerve, a sphenopalatine nerve, a communicating branch between a maxillary nerve and an SPG, an otic ganglion, an afferent fiber going into the otic ganglion, an efferent fiber going out of the otic ganglion, an infraorbital nerve, a vidian nerve, a greater superficial petrosal nerve, and a lesser deep petrosal nerve; and configuring the stimulation to induce at least one neuroprotective occurrence selected from the group consisting of: an increase in cerebral blood flow of the subject, and a release of one or more neuroprotective substances. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
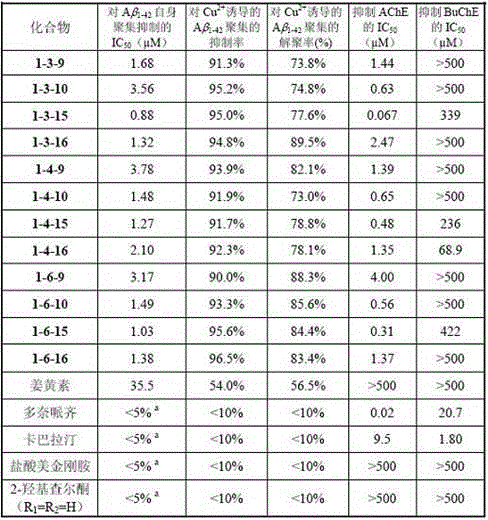
2-hydroxyl chalcone compound as well as preparation method and purpose thereof
ActiveCN105481706AEnhanced inhibitory effectStrong inhibitory activitySenses disorderNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaNeuro-degenerative disease
The invention discloses a novel 2-hydroxyl chalcone compound (I), as well as pharmacy acceptable salt, preparation method, medical composition, and purpose thereof in preparing medicines for treating and / or preventing neurodegenerative diseases including but not limited to vascular dementia, Alzheimer's diseases, Parkinson's diseases, Huntington's diseases, dementia relevant to HIV, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, neuropathic pain, glaucoma and the like (As shown in the description.).
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Flavone alkylamine compounds as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a type of novel flavone alkylamine compounds with the formula (I) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, a preparation method, a pharmaceutical composition and application in preparation of medicines for treating and / or preventiung neurodegeneration related diseases. The diseases comprise but are not limited to vascular dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, HIV related dementia, multiple sclerosis, progressive lateral sclerosis, neuropathic pain, glaucoma and other neurodegeneration diseases.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Application of ferulic acid derivative as neuroprotective drug
InactiveCN104958287AReduce inflammatory damageReduce free radical damageOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNeuroprotective DrugsNerve cells
The invention relates to application of a ferulic acid derivative to preparation of drugs for treating and / or preventing neurodegenerative diseases related to nerve cell injury. The neurodegenerative diseases includes but not limited Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, diabetic neuropathy, ischemia stroke and hemorrhagic stroke.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
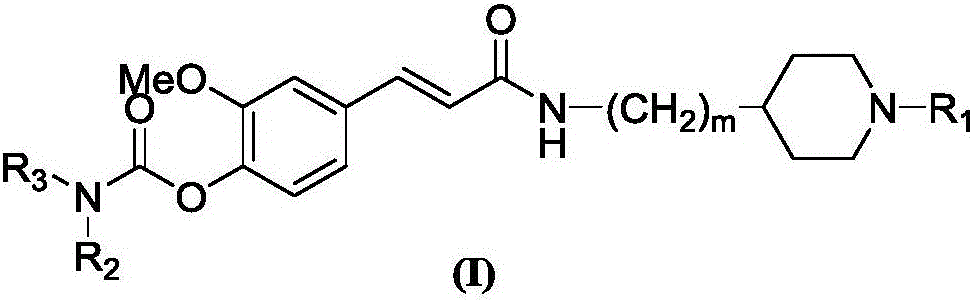
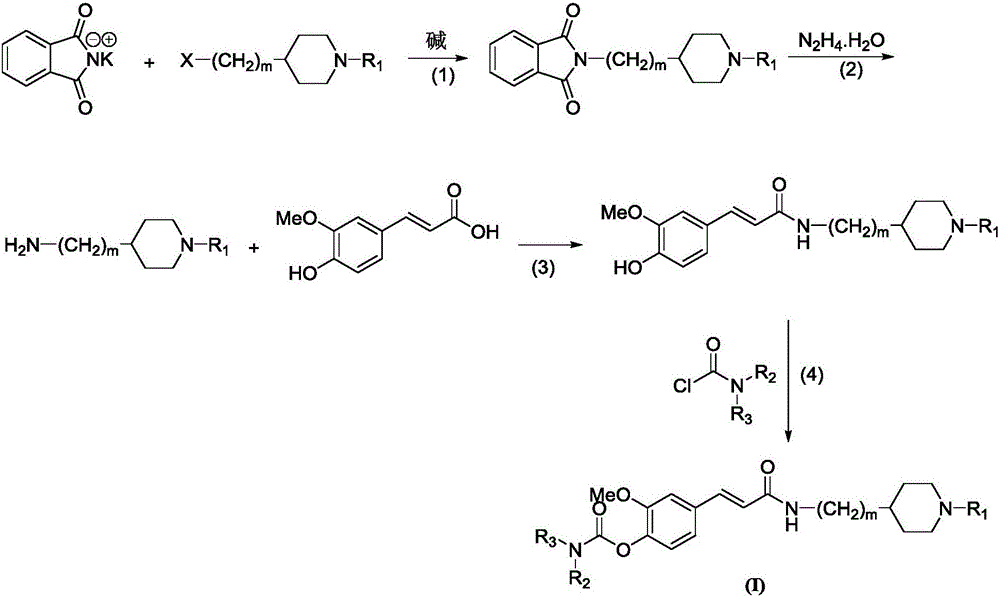
4-carbamate-3-methoxy cinnamic acid cyclamine alkyl amide compound, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105837497AEasy to prepareGood repeatabilitySenses disorderNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaSide effect
The invention discloses a 4-carbamate-3-methoxy cinnamic acid cyclamine alkyl amide compound, and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound prepared in the invention has low toxic and side effect, and can treat neurodegenerative diseases including, but not limited to, vascular dementia, the Alzheimer's disease, the Parkinson's disease, the Huntington's disease, HIV-associated dementia, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, neuropathic pain, glaucoma and the like.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
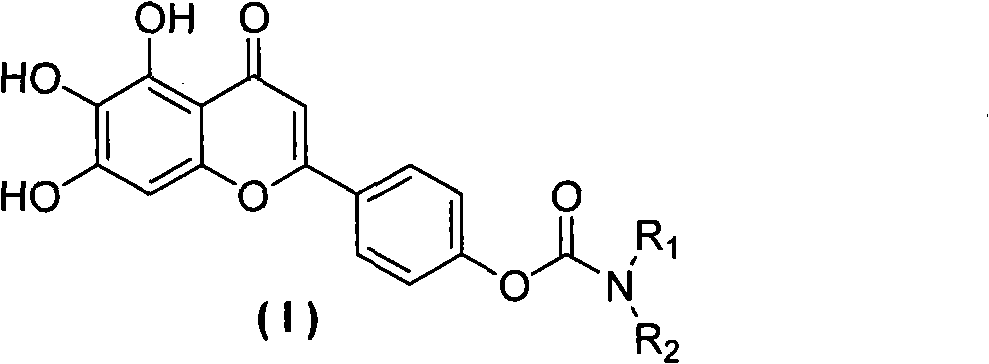
Scutellarein carbamate derivates, preparation method and application thereof
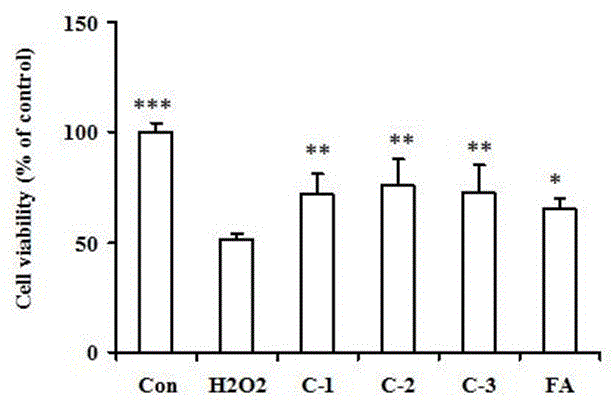
The invention relates to a novel scutellarin aglycon 4 (1)-position carbamate derivant (1), a preparation method and the application thereof. A pharmacological experiment proves that the compounds have obvious inhibitory activity of acetylcholinesterase and have protective effect with different degrees on PC12 cell trauma induced by H2O2, so the compounds can be used for preparing the drugs for treating neurodegenerative diseases such as vascular dementia, AD (presenile dementia), etc.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
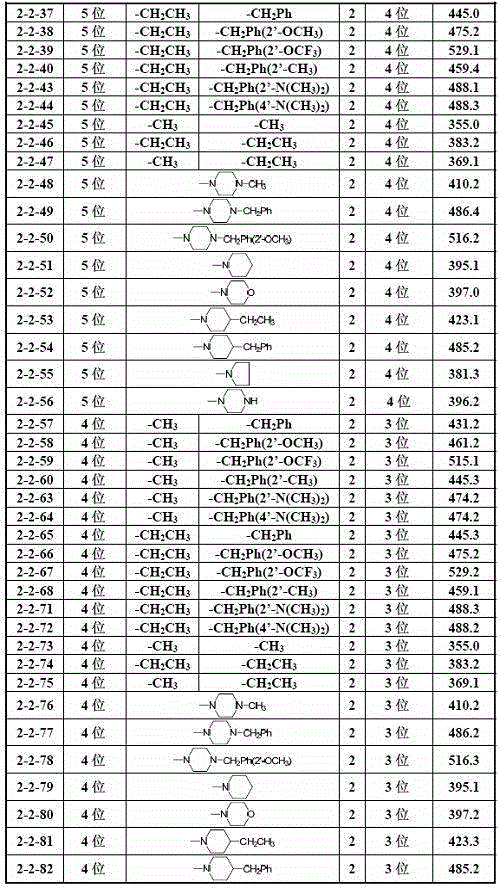
Preparation method and application of 9-bit substituent double-functional group berberine derivatives
InactiveCN102030746AStrong inhibitory activitySmall side effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseAcetylhomocholine
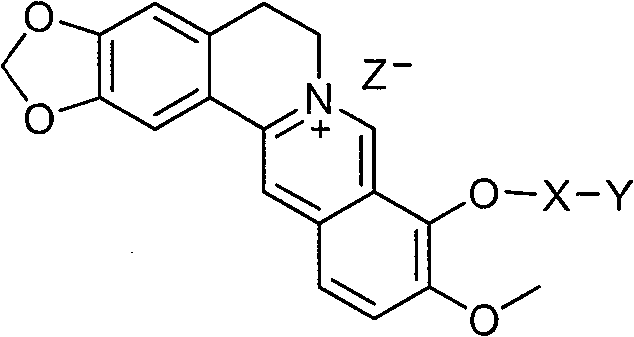
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of 9-bit substituent double-functional group berberine derivatives. In-vitro biological activity assay research shows that the 9-bit substituent double-functional group berberine derivatives provided by the invention has acetylcholinesterase inhibition activity higher than that of berberine serving as a leading compound, and also has higher inhibition activity on butyrylcholine esterase. After being further optimized and screened, the derivatives have favorable foreground of being developed into medicaments for treating diseases such as AD disease, vascular dementia, cognitive dysfunction and the like. The general formula of the derivatives is shown as the following formula, wherein X, Y and Z are defined in specifications.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
2-hydroxychalcone amine compounds, and preparation method and uses thereof
InactiveCN105439876AExtended incubation periodShorten the incubation periodSenses disorderNervous disorderPharmaceutical drugNeuro-degenerative disease
The invention discloses 2-hydroxychalcone amine compounds and pharmaceutically-acceptable salts, preparation method thereof, pharmaceutical composition, and uses for preparing medicines treating and / or preventing neurodegenerative related diseases, the diseases including but not limited to vascular dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntingdon's disease, HIV associated dementia, multiple sclerosis, progressive lateral sclerosis, neuropathic pain, glaucoma and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Application of sodium alginate oligose and derivative to treatment of vascular dementia
The invention relates to application of sodium alginate oligose and a derivative to treatment of vascular dementia. The sodium alginate oligose and the derivative of the sodium alginate oligose are particularly mannuronic acid oligose or mannuronic acid oligose with a carboxyl at a 1-position of a reducing end and the derivative or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, formed by connecting a beta-D-mannuronic acid through a 1,4-glucosidic bond.
Owner:GREEN VALLEY (SHANGHAI) PHARM CO LTD
Carbamate chalcone compound, preparation method therefor and use of carbamate chalcone compound
InactiveCN105481796AExtended incubation periodSenses disorderNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaCarbamate
The invention discloses a novel carbamate chalcone compound represented by a formula I shown in the description and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, a preparation method for the novel carbamate chalcone compound and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, a pharmaceutical composition and use of the pharmaceutical composition in the preparation of drugs for treating and / or preventing neurodegenerative related diseases, including, but not limited to neurodegenerative diseases such as vascular dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, HIV related cretinism, multiple sclerosis, progressive lateral spinal sclerosis, neuropathic pain and glaucoma.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
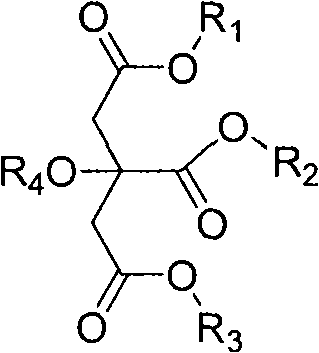
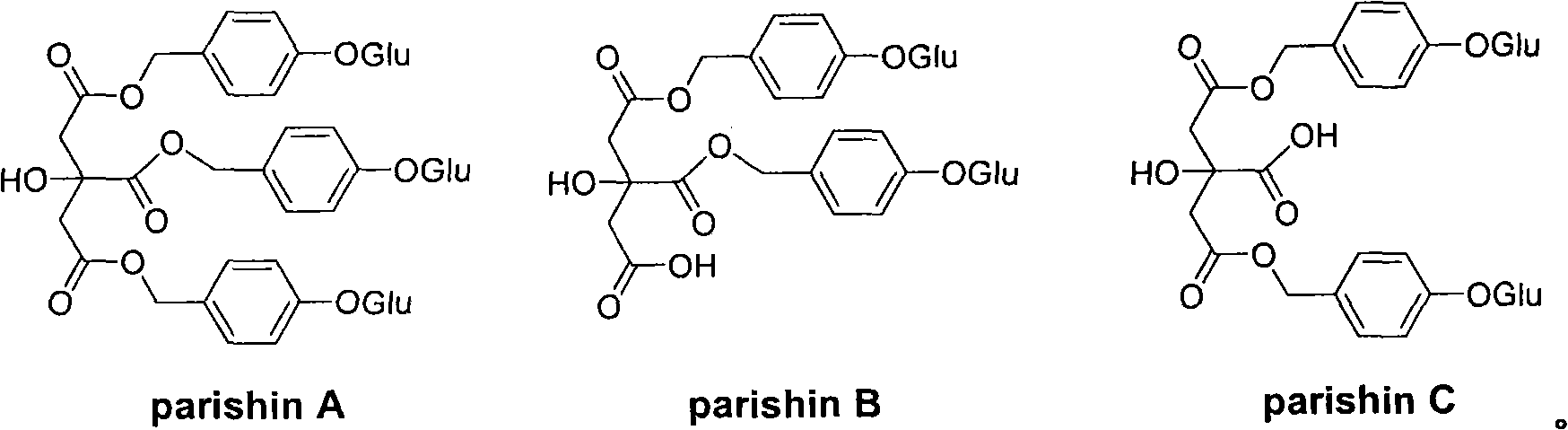
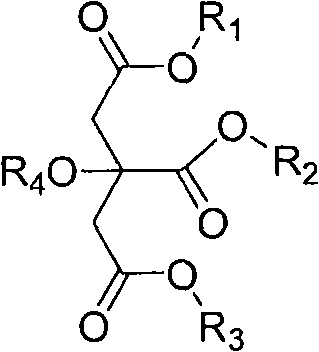
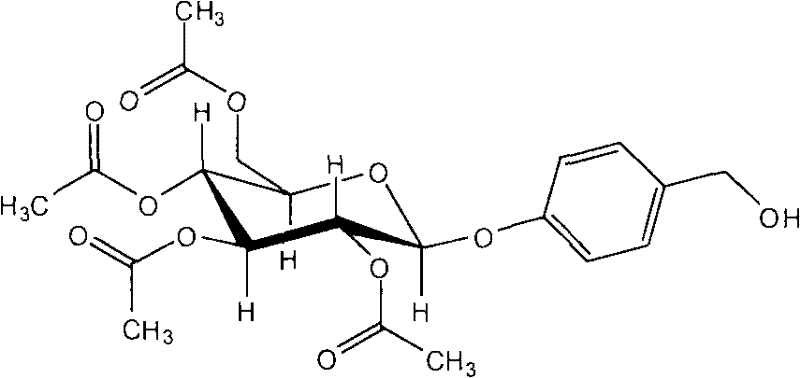
Gastrodiaelata Blume plant extract for preventing and treating vascular dementia and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to application of a Gastrodiaelata Blume plant extract containing parishin derivants on preparing a medicament for preventing and treating vascular dementia and other diseases. The invention also relates to a method for preparing the plant extract extracted and refined from Gastrodiaelata Blume plant, wherein active components are the parishin derivants, in particular to parishin A, B and C. The method adopts alcohol extraction; and an extract is refined and purified by a chromatogram method to obtain the plant extract with the content of the parishin derivants of 35 percent, in particular over 50 percent. A medicament preparation optimally selects injections, troches, capsules, soft capsules, oral liquid or dropping pills and the like.
Owner:北京协和制药二厂有限公司
Application of acetagastrodine in preparing medicines to prevent and treat vascular dementia (VD) and Alzheimer disease (AD)
Relating to the medicine field, the invention discloses the use of acetagastrodine in preparing medicines to prevent and treat vascular dementia and Alzheimer disease. The invention also provides a medicinal composition for preventing and treating senile dementia and its capsule as well as sustained release agent. Animal tests show that: acetagastrodine can substantially enhance the learning and memory abilities of rats with vascular dementia, reduce the activity of AchE in brains, enhance the vitality of ChAT in brains, and remarkably reduce Glu content; acetagastrodine has significant protective effect on damaged PC12 cells caused by H2O2 by enhancing the vitality of SOD and total ATP enzyme in PC12 cells and reducing the content of MDA and LD; acetagastrodine can substantially enhance the learning and memorizing abilities of AD model rats, enhance the CAT content in brains of the model rats, reduce the MAO vitality and simultaneously prevent the decrease of neurotransmitters. Acetagastrodine is better than gastrodin in terms of the treatment effects on VD and AD, and enjoys good clinical application prospect.
Owner:KPC PHARM INC
Oral Chinese medicinal preparation for treating vascular dementia
ActiveCN1657084AShort course of treatmentQuick effectNervous disorderUnknown materialsActive ingredientRhizome
An orally taken Chinese medicine for treating vascular dementia is prepared from fleece flower root, astragalus root, Chinese angelica root, Chuan-xiong rhizome and lucid ligustrum fruit.
Owner:SHANGHAI PHARMA GRP QINGDAO GROWFUL PHARMA CO LTD
Injection composition containing oxiracetam and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102552125AImprove stabilitySimple recipePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsChemical compositionOxiracetam
The invention provides an injection composition containing oxiracetam and a preparation method and an application thereof. The composition contains sodium hydroxide. The invention further provides a preparation method and an application of the medicinal composition. The composition is mainly used for improving memory and the memory learning function of a mentally retarded patient, and is suitablefor memory and amentia caused by symptoms such as mild or moderate vascular dementia, senile dementia, brain trauma and the like, or is taken as an auxiliary treatment medicament.
Owner:北京爱力佳医药科技有限公司
Phenethyl alcohol glycoside-containing callicarpa kochiana extractive and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101797307AHigh extraction rateSignificant efficacy in the treatment of Alzheimer's diseaseOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlcoholCallicarpa kochiana
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Use of stilbene glycoside in treating dementia
The present invention relates to stilbene glycosie compound and the use of its derivative and medicinal salt in preparing medicine for dementia, especially for Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia. Animal experiment proves that stilbene glycoside compound can resist brain cell damage caused by beta-amyloid protein and hydrogen peroxide, raise the memory capacity of mouse model with scopolaminedementia and A beta dementia and gerbille model with double-sided common carotid artery obstruction caused brain ischemia, inhibit the lipide peroxidation of brain tissue of mouse model with brain ischemia, strengthen the activity of its brain tissue SOD, and reduce the calcium ion density in its brain cells.
Owner:XUANWU HOSPITAL OF CAPITAL UNIV OF MEDICAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com