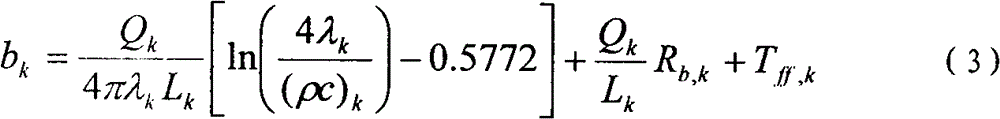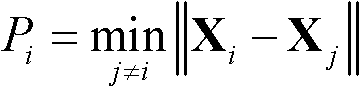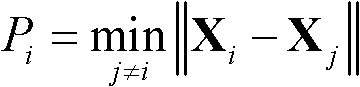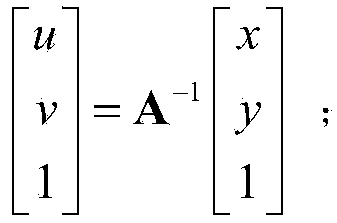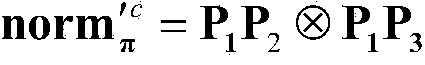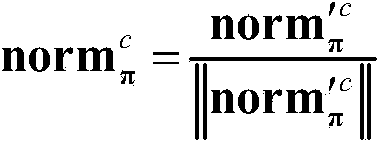Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
412 results about "Ground testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
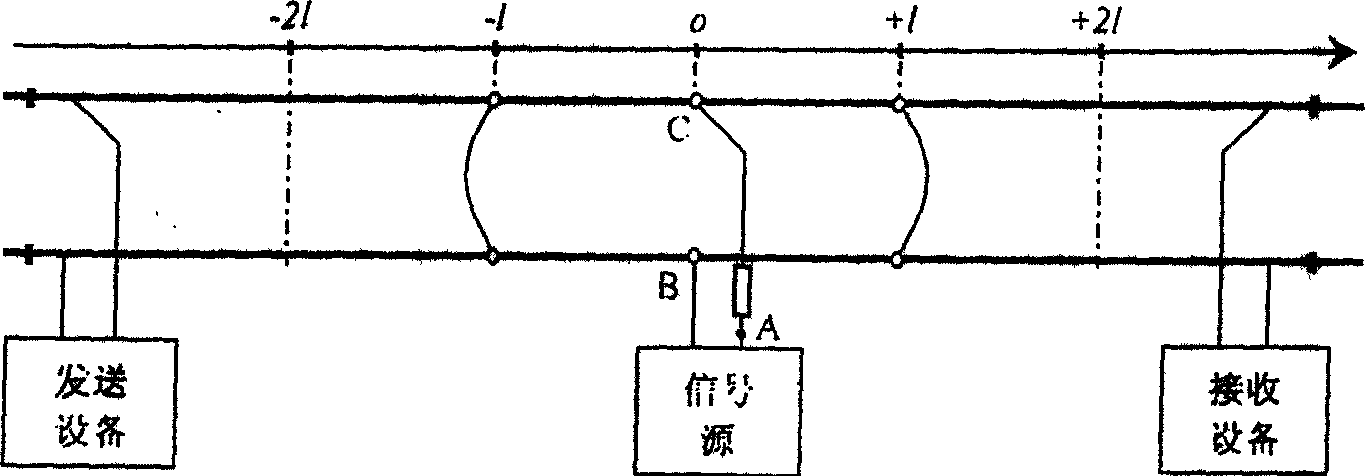
A ground test is usually performed on electrical wires to ensure that they are able to resist current overload. Grounding makes sure that electricity doesn't build up and cause damage to wiring, outlets and devices that use current. It diffuses excess electricity away from the device or system into the ground.
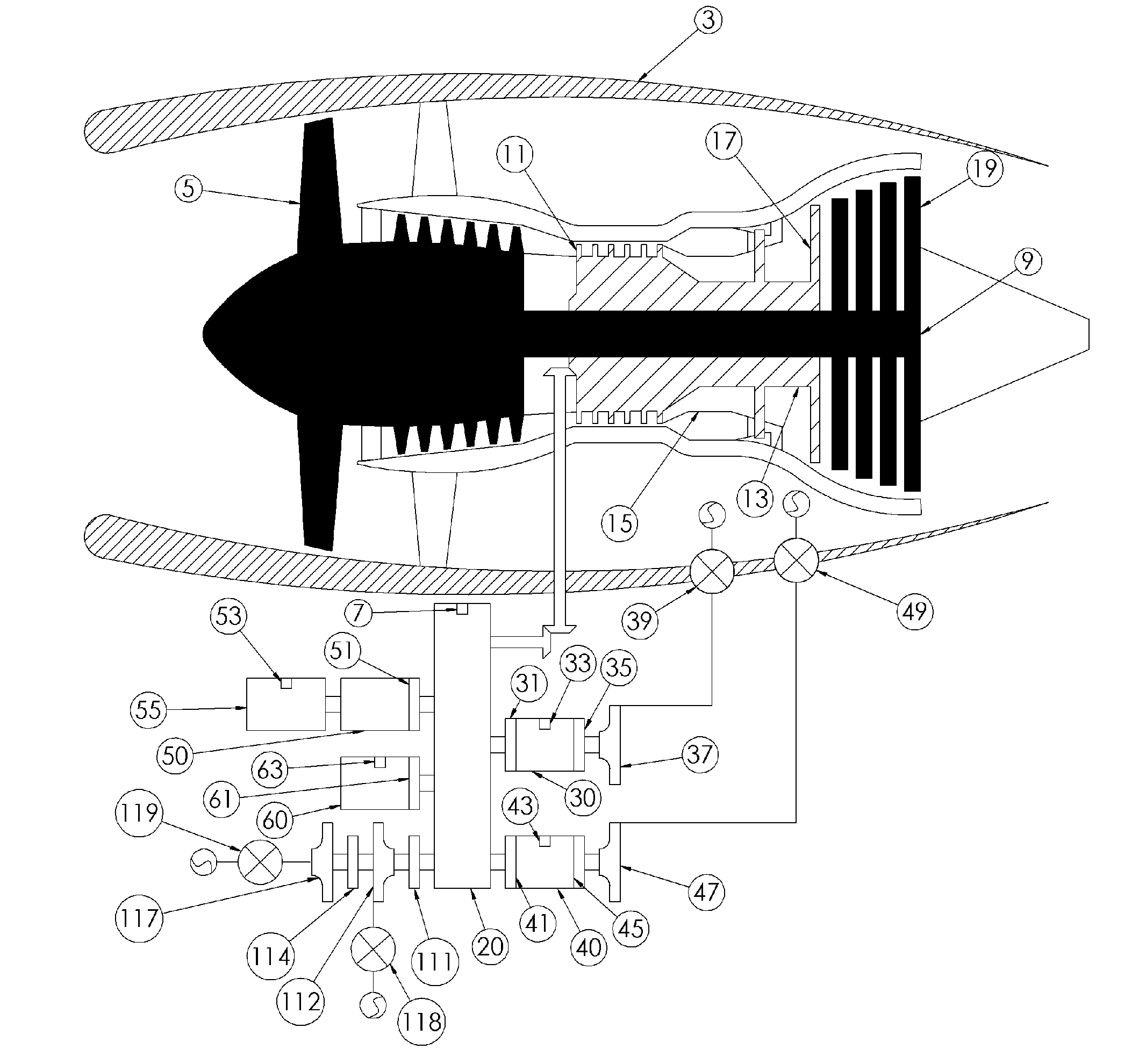
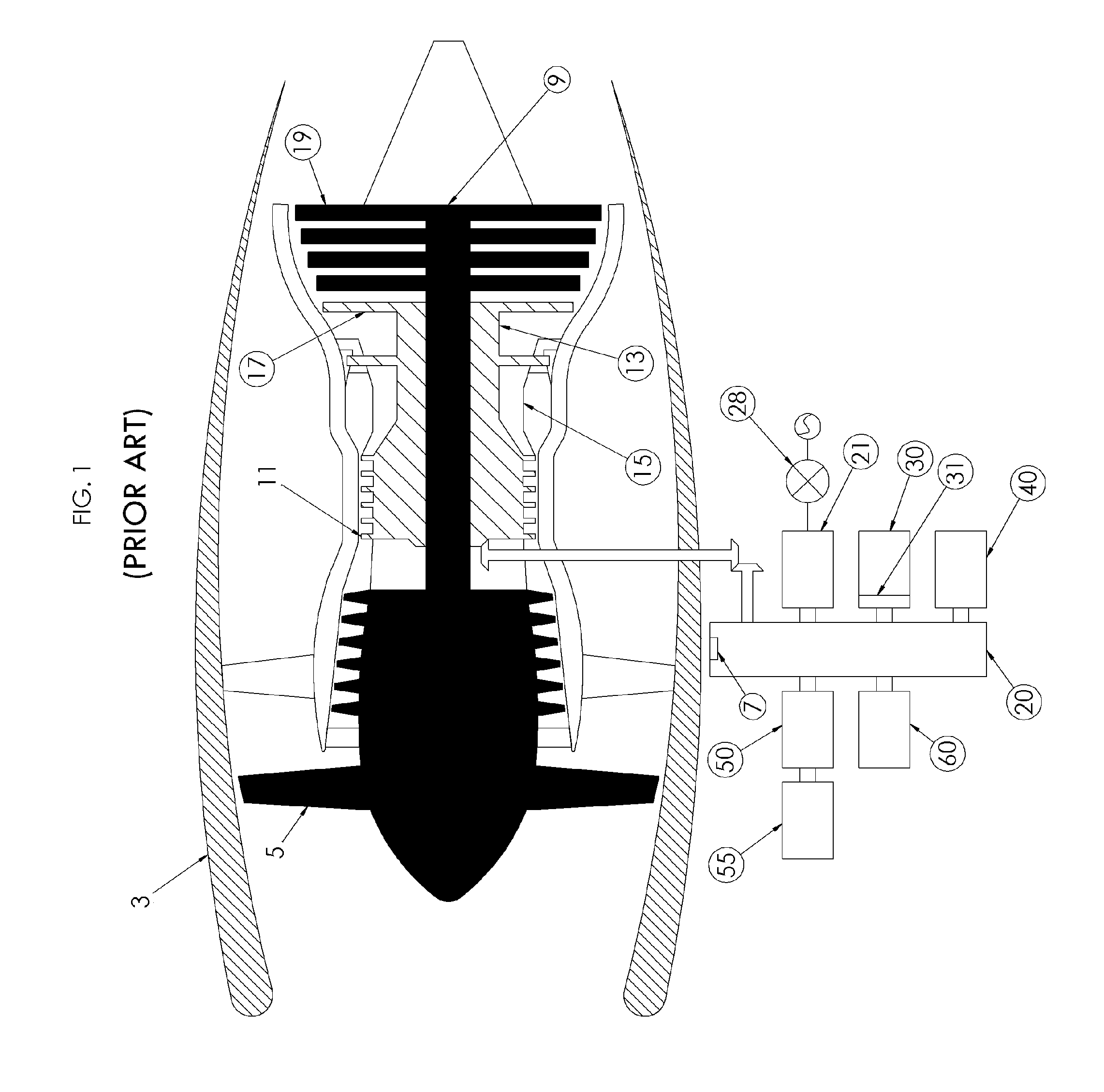
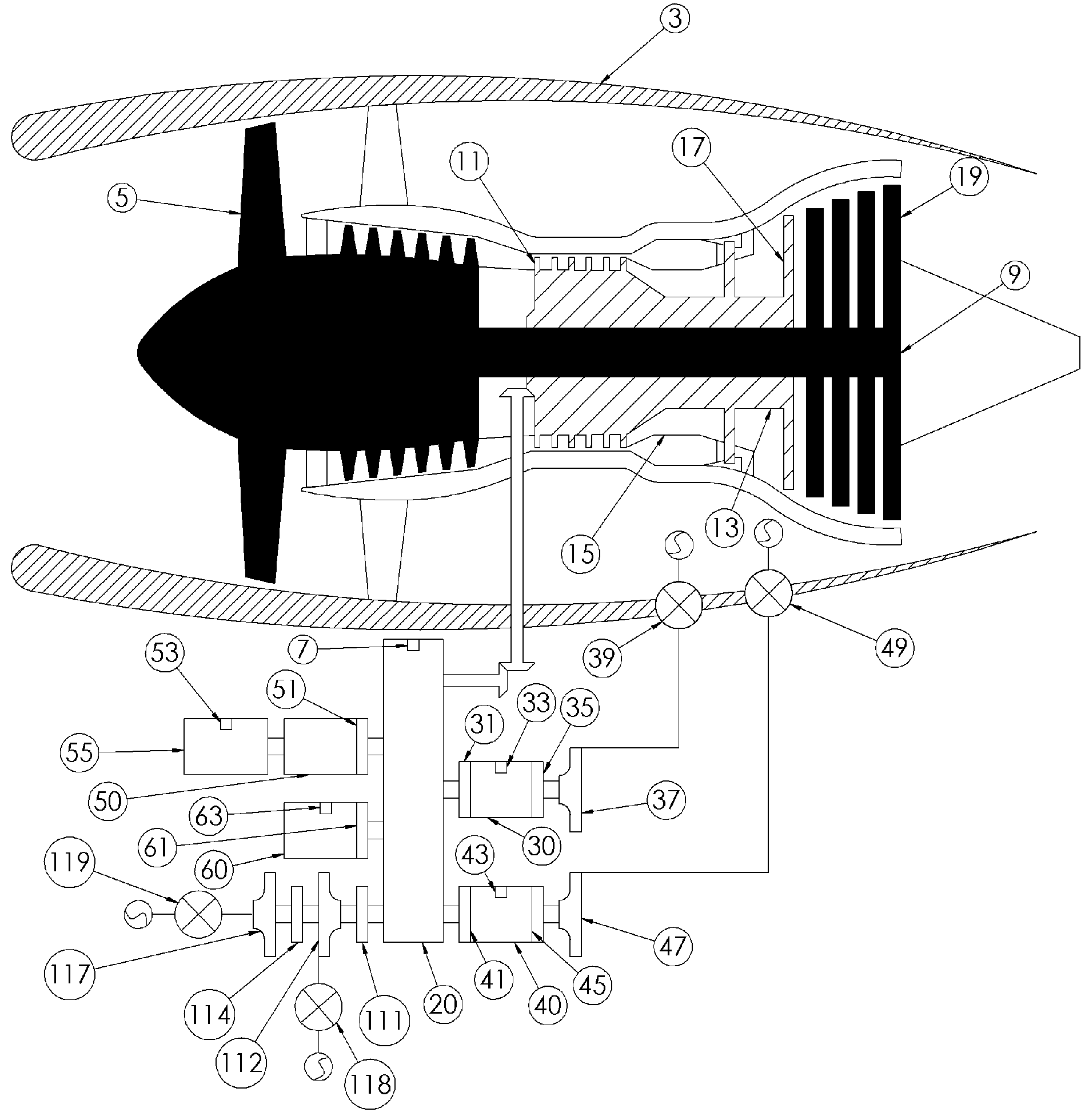
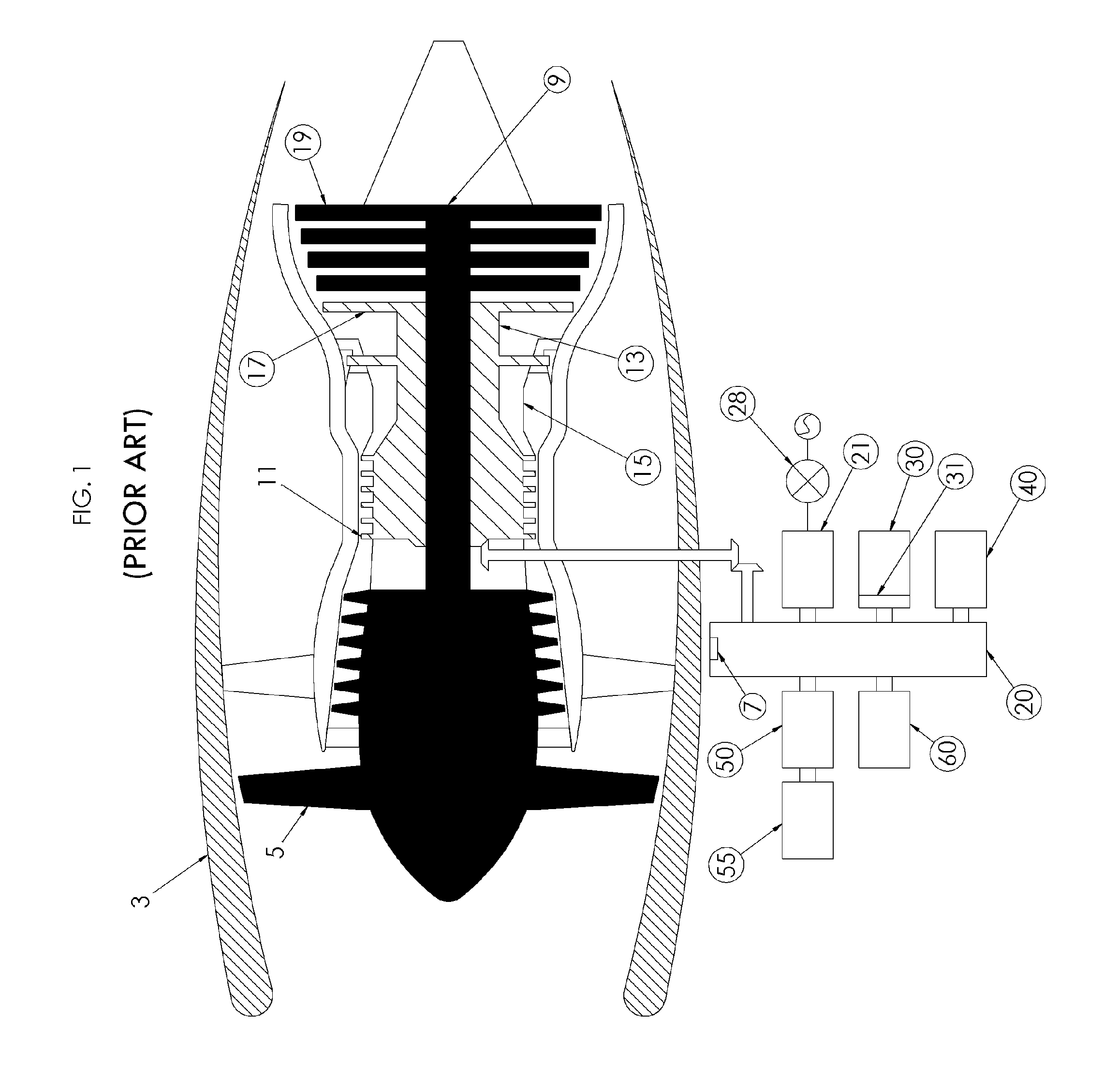
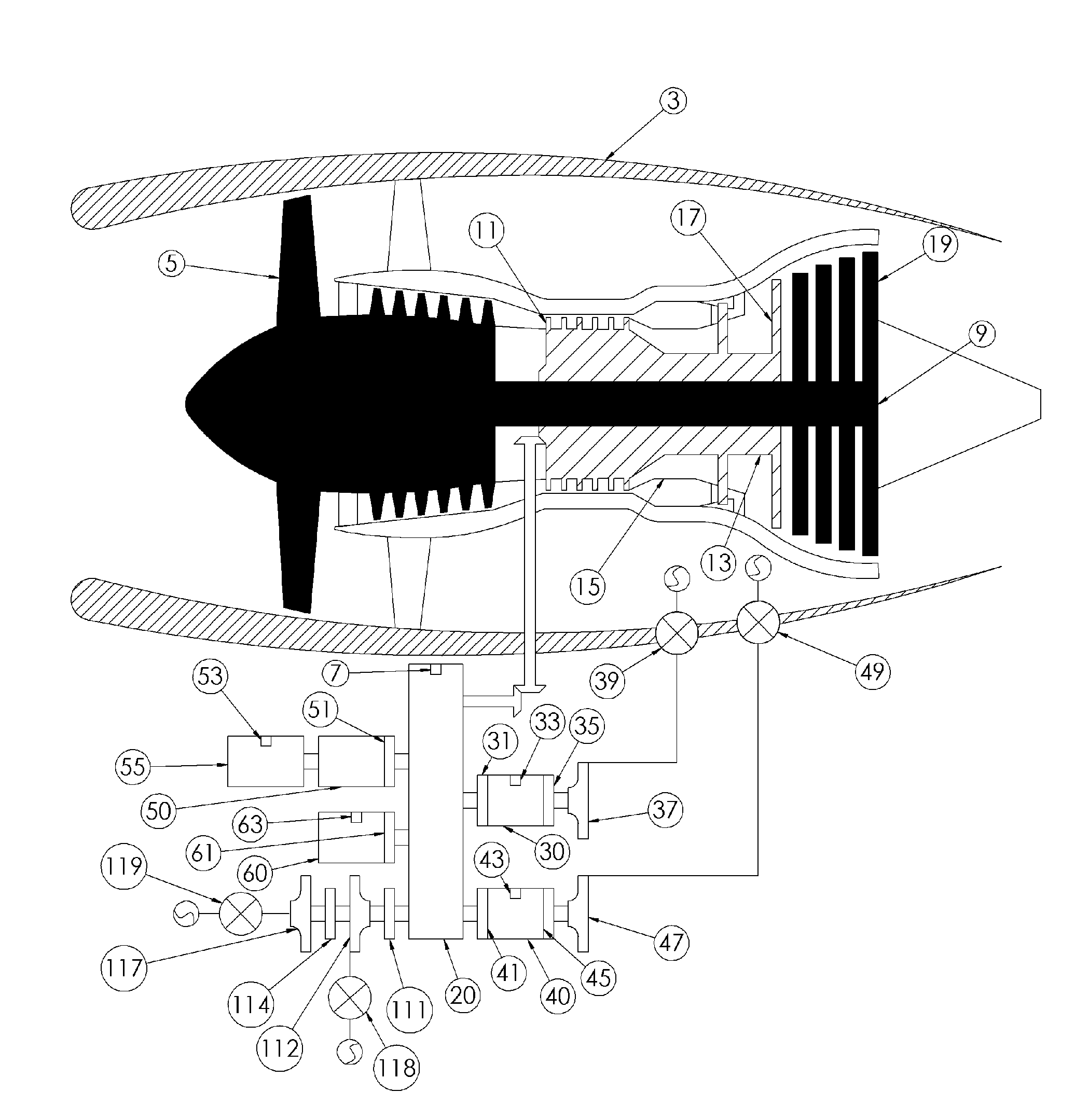
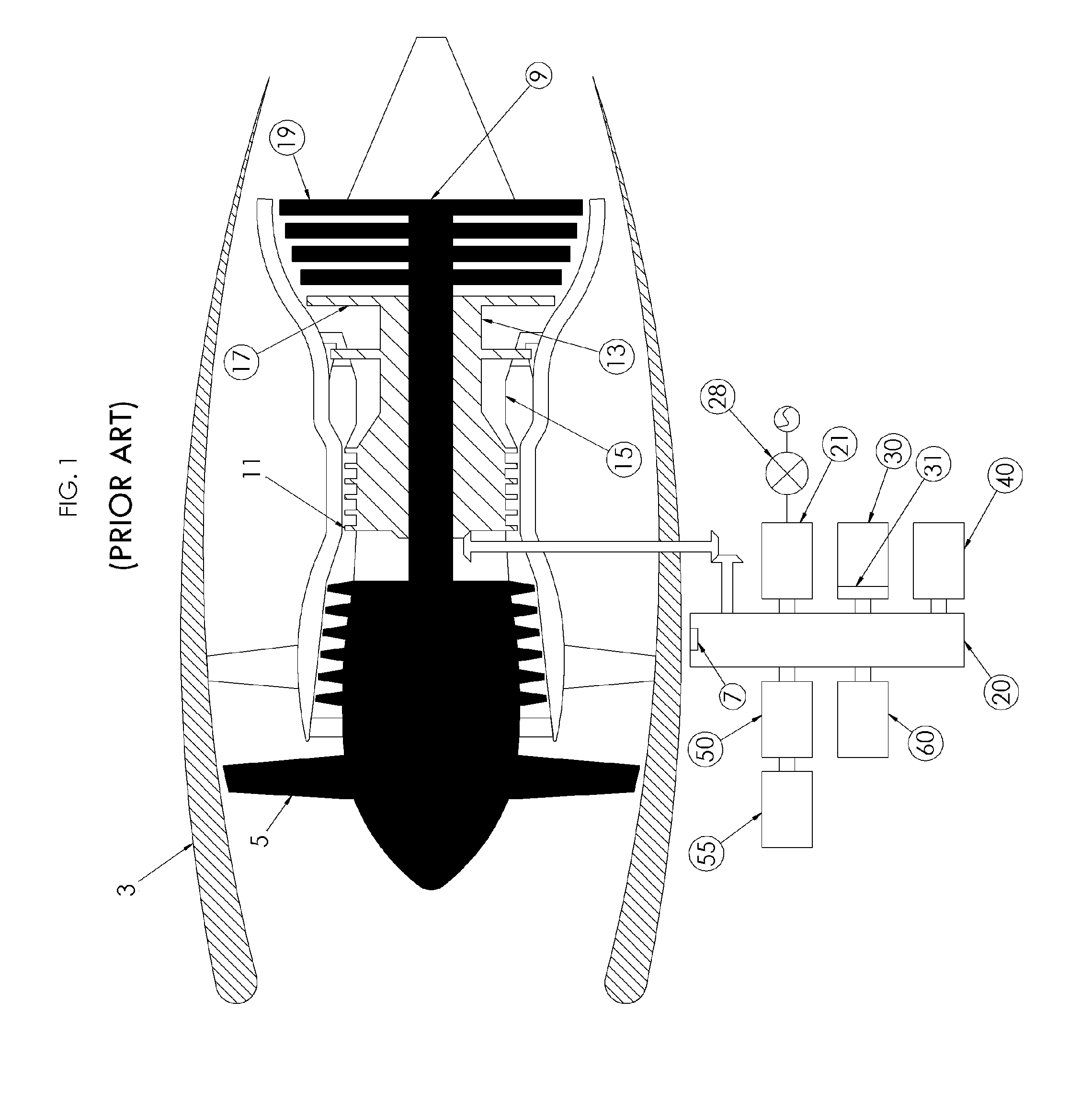
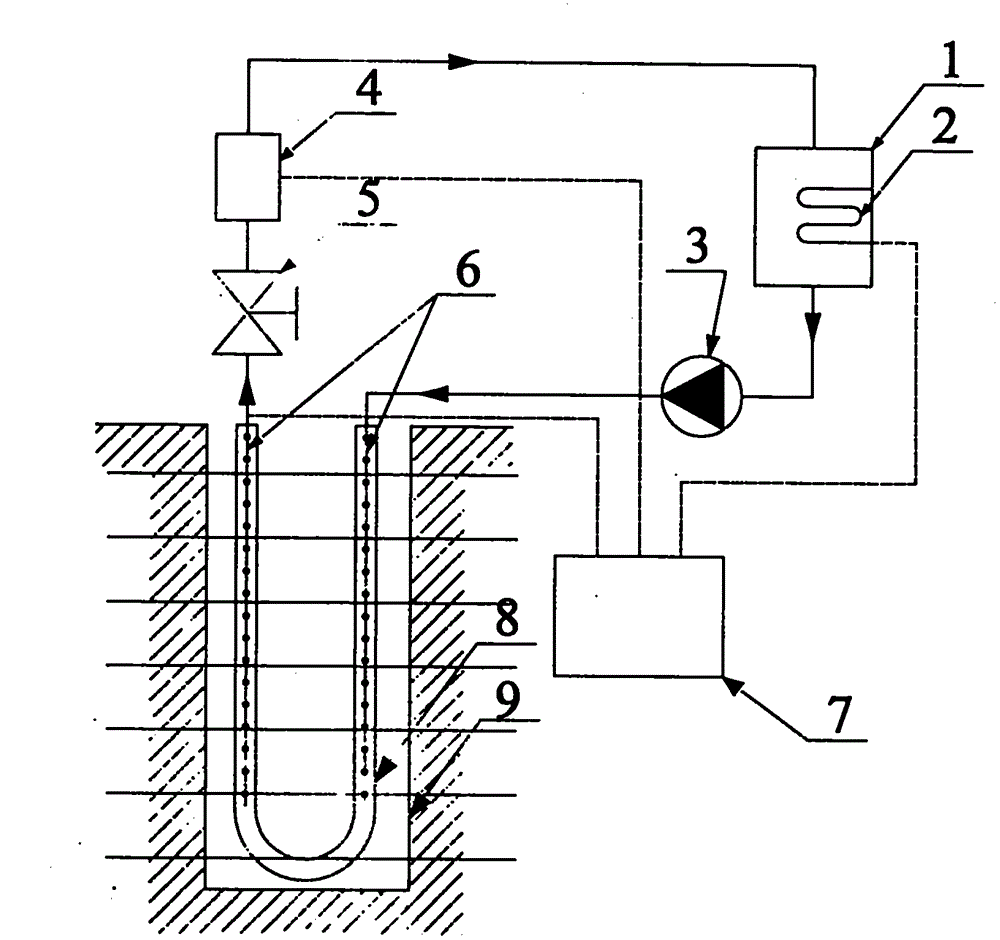
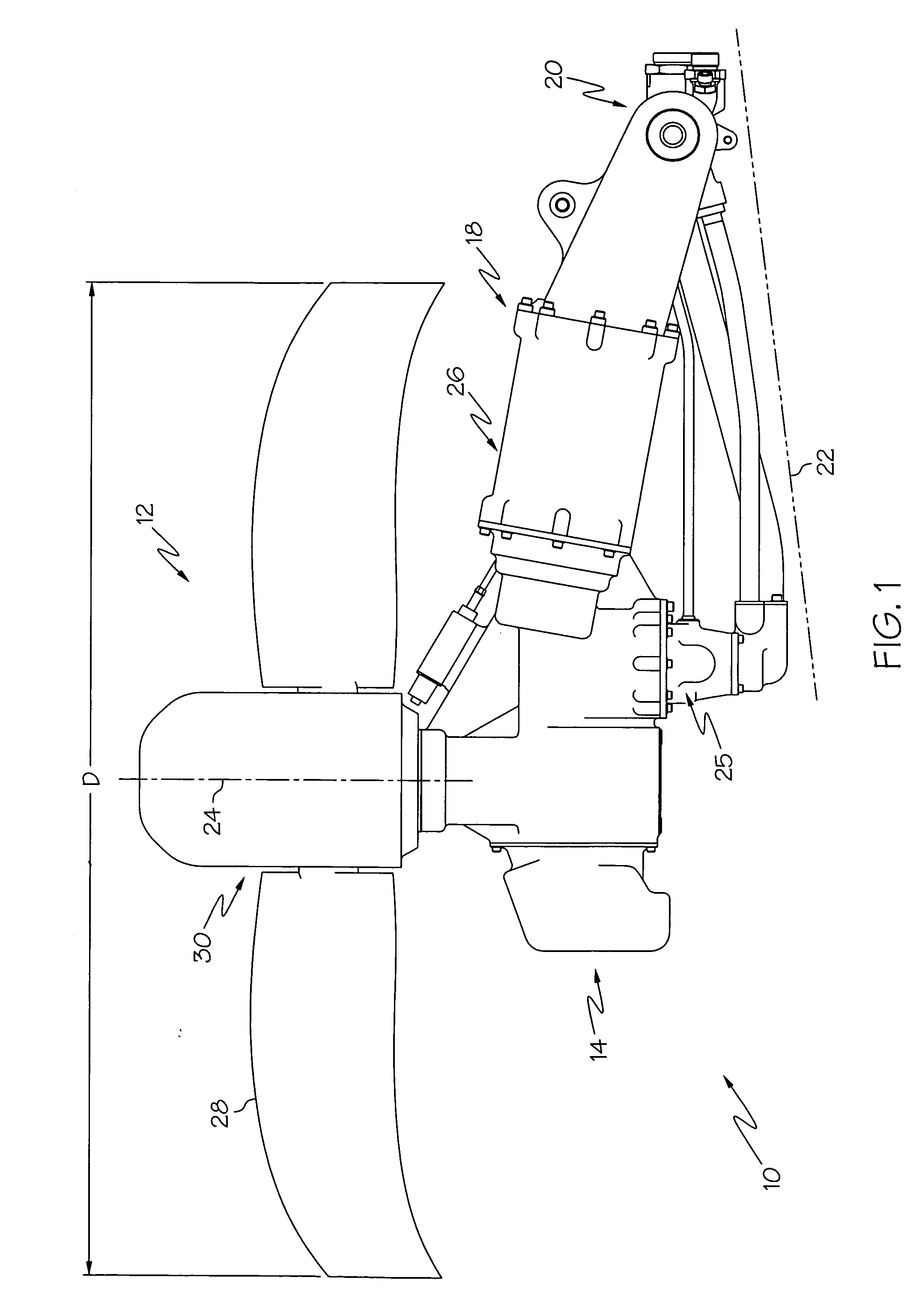
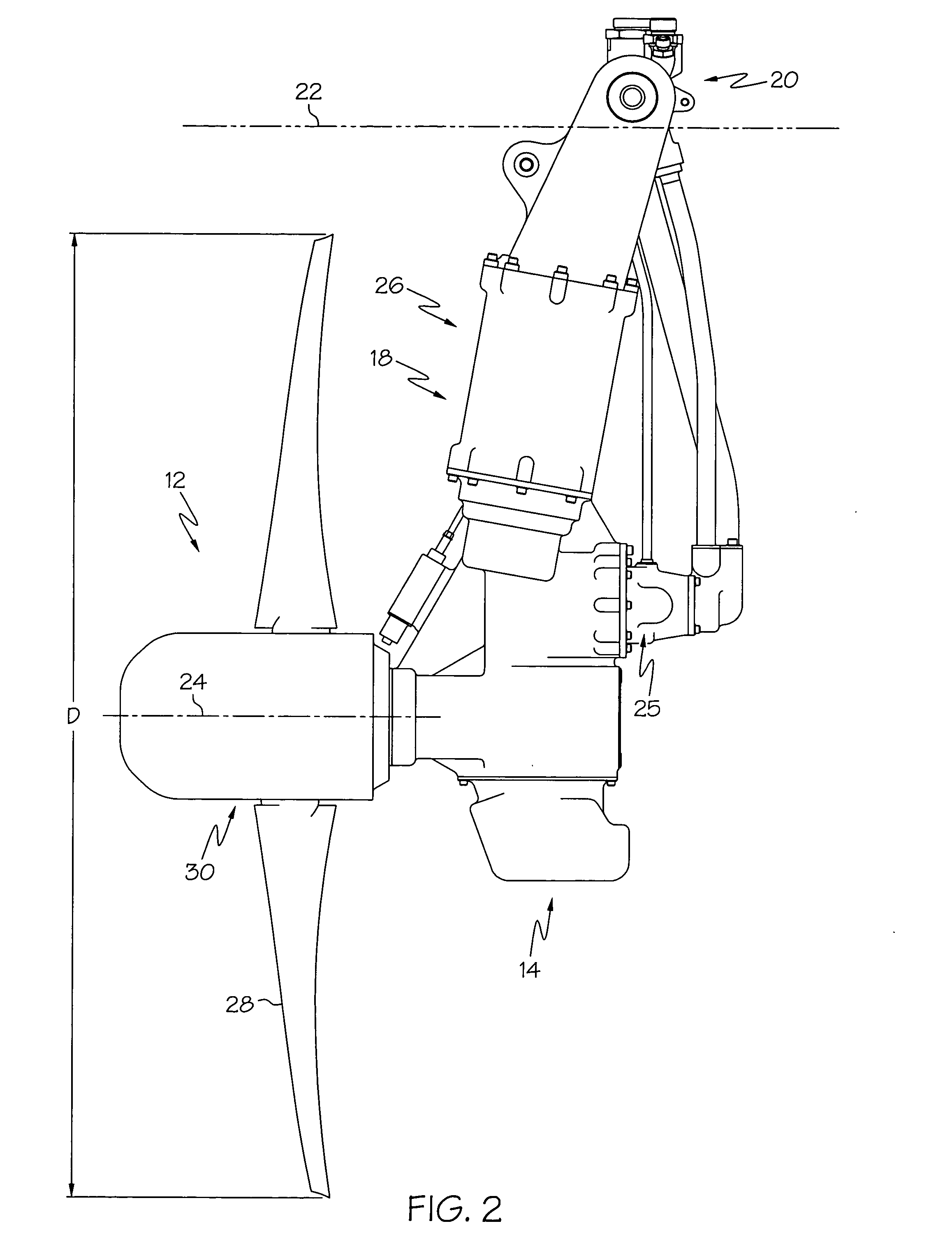
Aircraft with disengageable engine and auxiliary power unit components
InactiveUS20060260323A1Avoid damageSufficient torqueEngine fuctionsGas turbine plantsFlight vehicleGround testing
Several improvements to an aircraft turbine engine and Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) are disclosed, as well as methods of using these improvements in routine and emergency aircraft operations. The improvements comprise the addition of cockpit-controllable clutches that can be used to independently disconnect the engine's integrated drive generator (IDG), engine driven pump (EDP), fuel pump, and oil pump from the engine gearbox. These engine components may then be connected to air turbines by the use of additional clutches and then powered by the turbines. Similar arrangements are provided for the APU components. Cranking pads, attached to various engine and APU components, are disclosed to provide a means for externally powering the components for testing purposes and to assist with engine and APU start. Detailed methods are disclosed to use the new components for routine ground-testing and maintenance and for the enhancement of flight safety, minimization of engine component damage, and extension of engine-out flying range in the case of an emergency in-flight engine shutdown.
Owner:MOULEBHAR DJAMAL
Aircraft with disengageable engine and auxiliary power unit components
InactiveUS7805947B2Performed easily and efficientlyIncrease speedEngine fuctionsGas turbine plantsAuxiliary power unitGround testing
Several improvements to an aircraft turbine engine and Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) are disclosed, as well as methods of using these improvements in routine and emergency aircraft operations. The improvements comprise the addition of cockpit-controllable clutches that can be used to independently disconnect the engine's integrated drive generator (IDG), engine driven pump (EDP), fuel pump, and oil pump from the engine gearbox. These engine components may then be connected to air turbines by the use of additional clutches and then powered by the turbines. Similar arrangements are provided for the APU components. Cranking pads, attached to various engine and APU components, are disclosed to provide a means for externally powering the components for testing purposes and to assist with engine and APU start. Detailed methods are disclosed to use the new components for routine ground-testing and maintenance and for the enhancement of flight safety, minimization of engine component damage, and extension of engine-out flying range in the case of an emergency in-flight engine shutdown.
Owner:MOULEBHAR DJAMAL
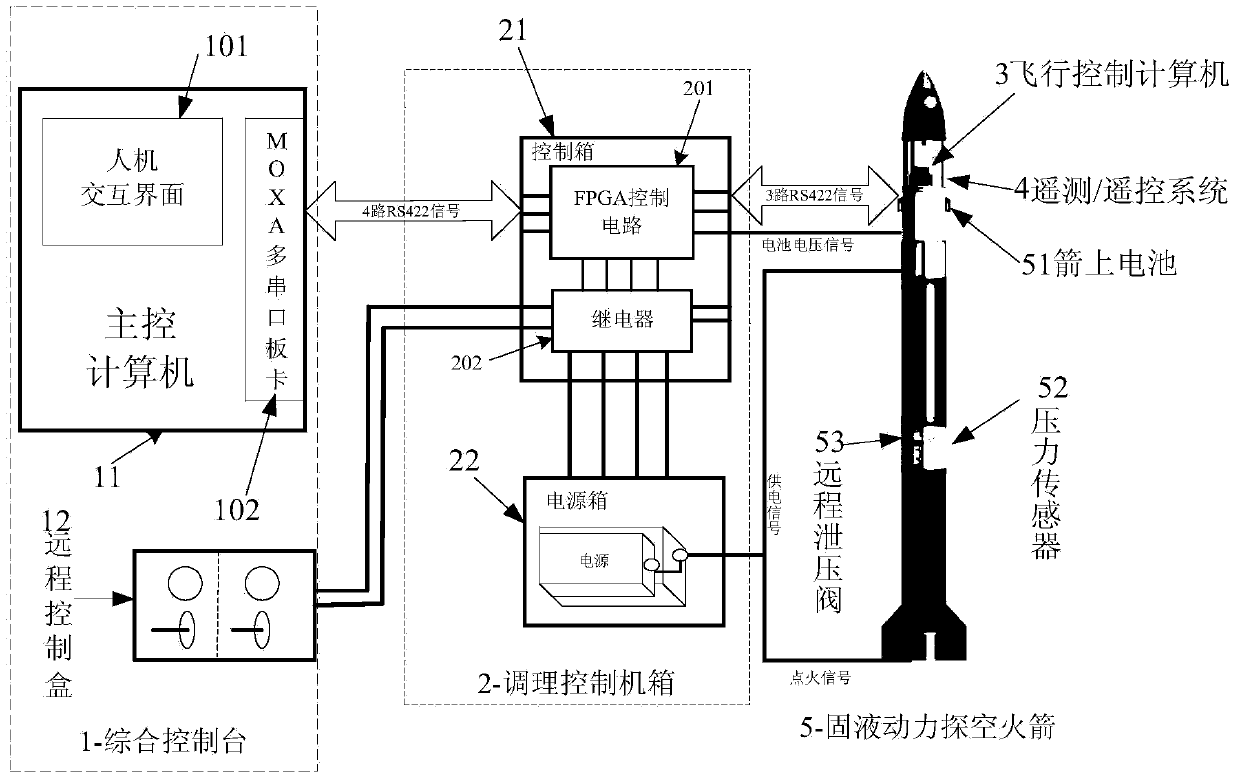
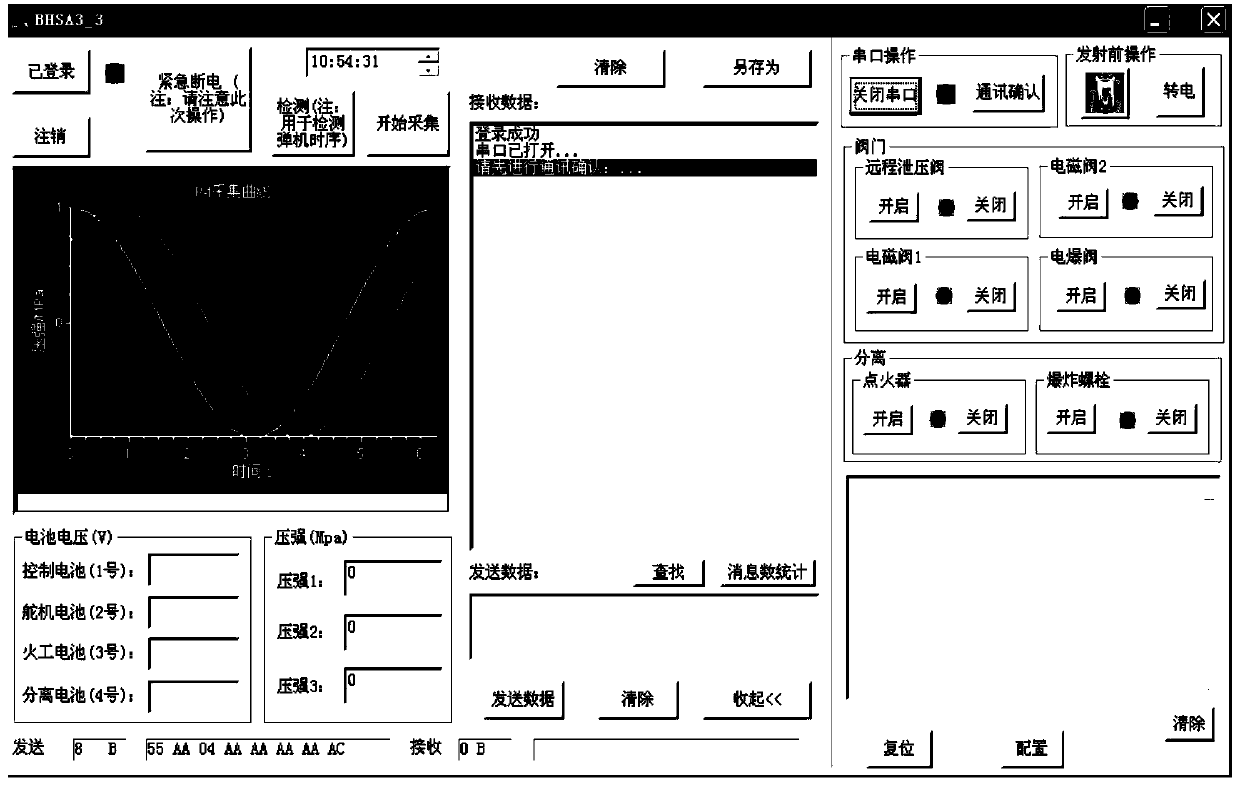
Solid-liquid power air vehicle ground test and launch control system of 422 bus
ActiveCN103558838ASafe and Efficient Ground Test Launch ControlRealize long-distance transmissionElectric testing/monitoringInteraction interfaceControl data
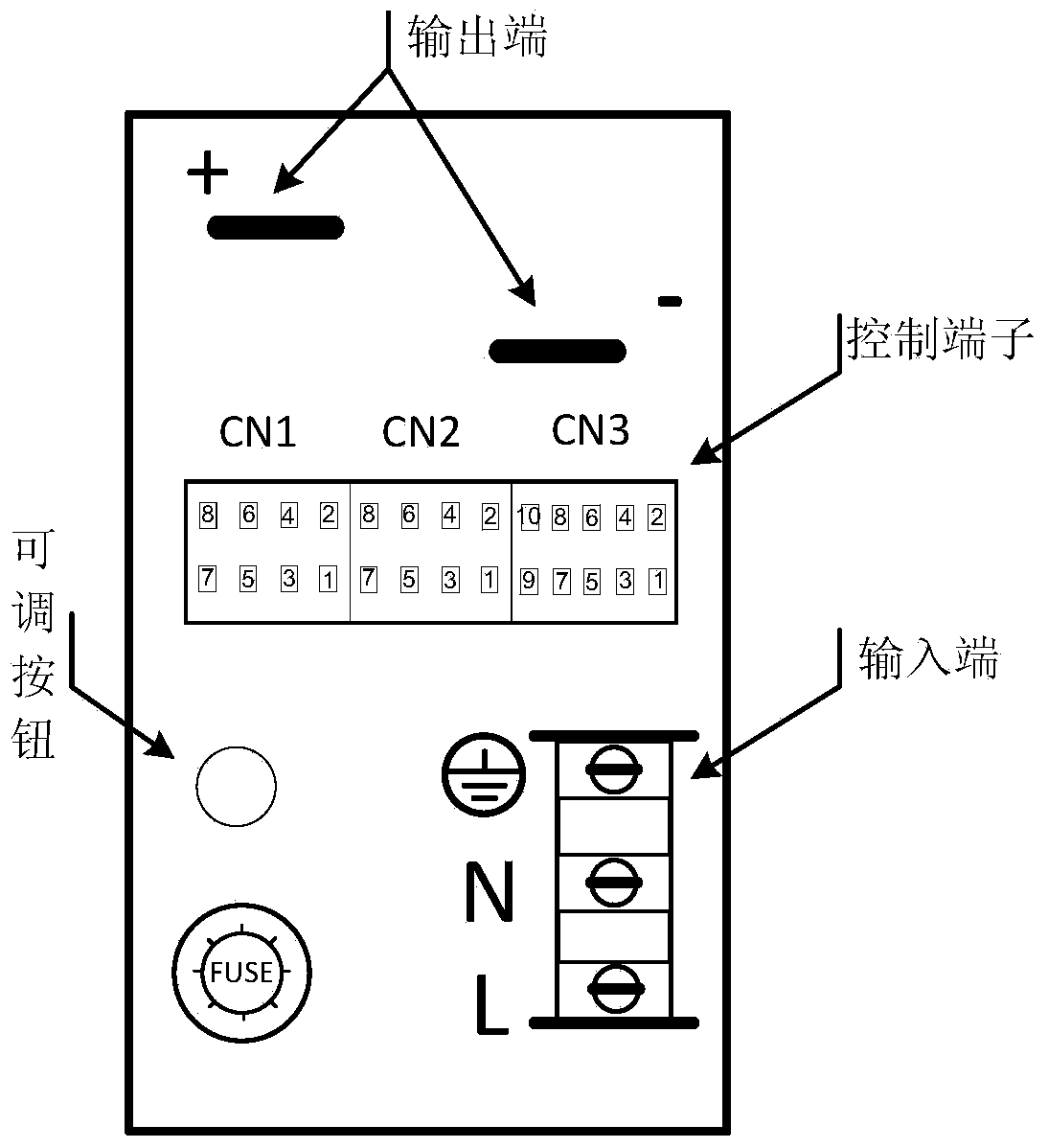
The invention relates to a solid-liquid power air vehicle ground test and launch control system of a 422 bus. The system comprises a ground integrated console, an adjusting control machine box, a flying control computer and a telemetering / telecontrol system. A main control computer of the ground integrated console uses a human-computer interaction interface, a CP-134U-I / DB9M board card of MOXA is used as a 422 node, orders are received and sent, and state information is displayed. The adjusting control machine box carries out ground and missile-borne power supply and distribution, signal forwarding, signal state monitoring and testing. The flying control computer receives orders sent by the main control computer and feeds the state information of an air vehicle back to the ground. According to the system, ground testing of the whole system, missile-borne system self detecting, result back transmitting, flying control data stapling, important parameter real-time detecting and system information back reading can be completed, and comprehensive monitoring of bus information, data real-time storage and displaying and safe protecting integration design are achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Ground testing system for on-track micro vibration of spacecraft
ActiveCN102650563AImprove the technical level of micro-vibration testMeet test verification requirementsVibration testingVibration measurementEngineering
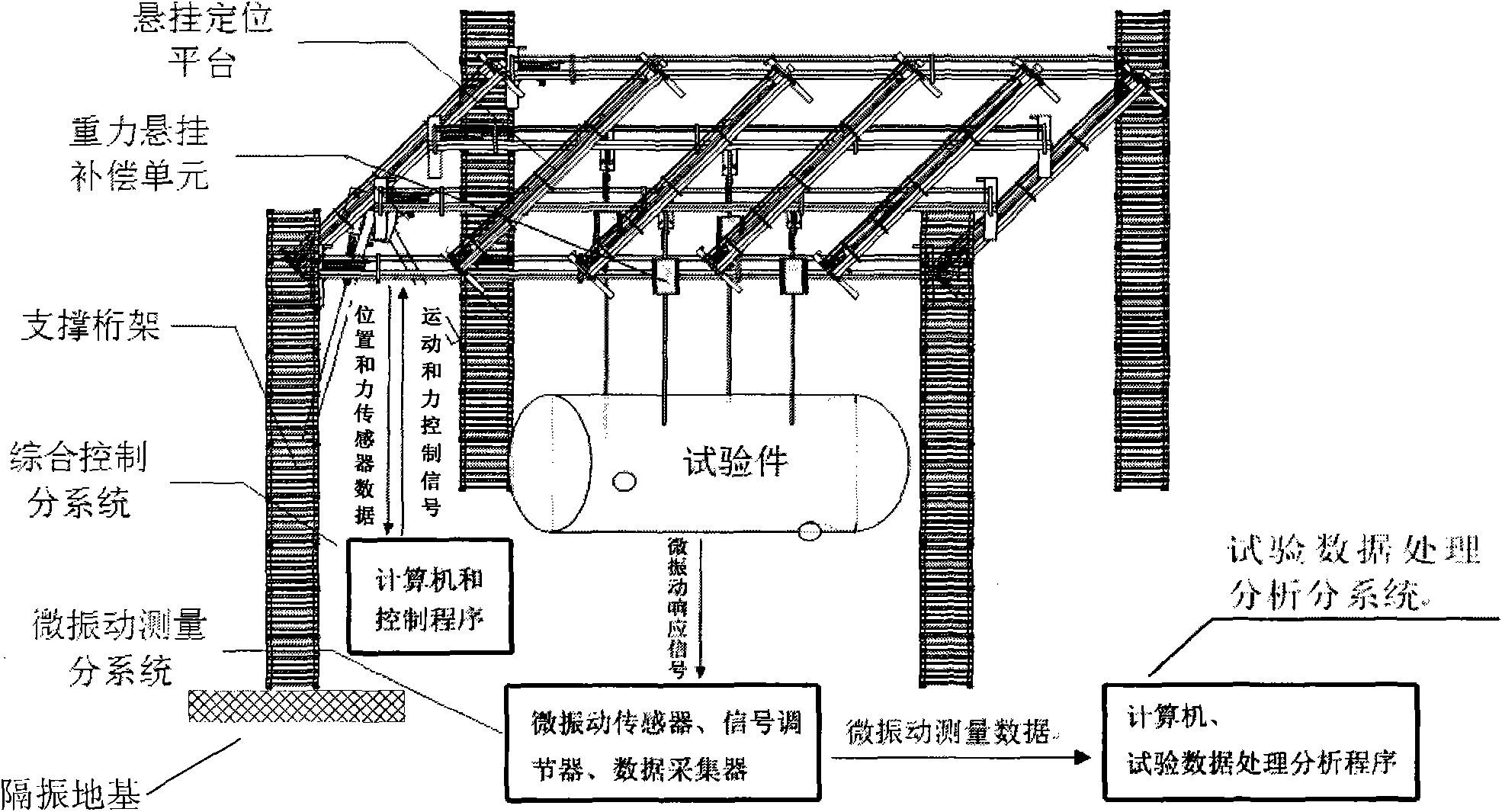
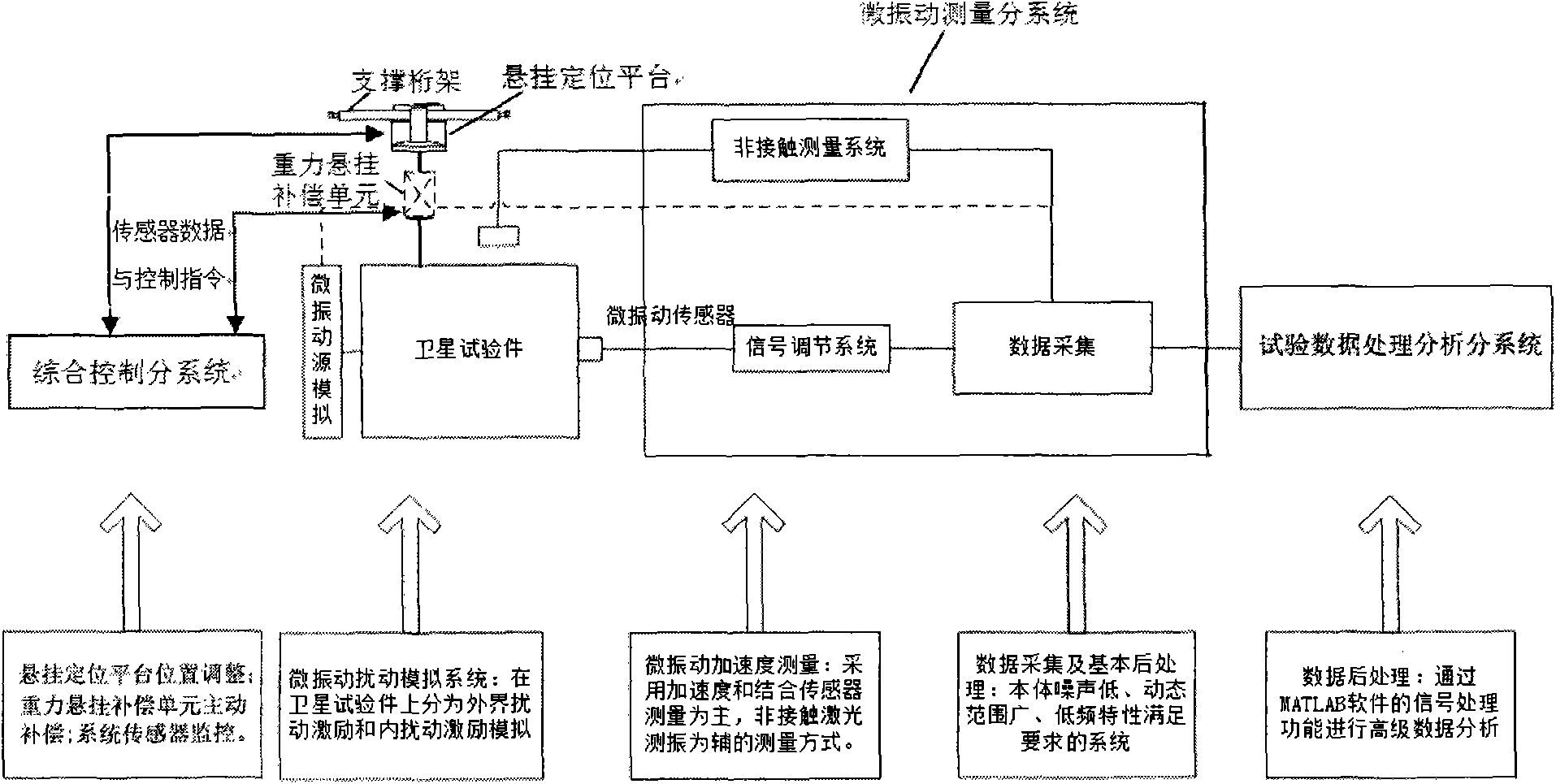
The invention discloses a ground testing system for on-track micro vibration of a spacecraft, which comprises a vibration isolating foundation, a supporting truss with a framework structure, a suspended positioning platform, a gravity suspended compensation unit, an integrated control subsystem, a micro vibration measurement subsystem and a test data processing and analyzing subsystem, wherein the vibration isolating foundation is connected with the ground, the supporting truss with the framework structure is fixedly supported on the vibration isolating foundation, the suspended positioning platform is supported on the supporting truss, the gravity suspended compensation unit is hung on the suspended positioning platform, and the integrated control subsystem is used for controlling the positioning and the fixation of the suspended positioning platform via coordination of sensors in various positions and performing the overall integrated control on the state of the system. By adopting the system, the ground simulation of the on-track micro vibration environment, the measurement of micro vibration and the data processing can be realized for the spacecraft at the system level and the component level, the technical level of testing the micro vibration of the spacecraft can be improved, and the demands for testing and verification of the on-track micro vibration environment in research on the spacecraft, particularly the high-precision satellite, can be satisfied.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
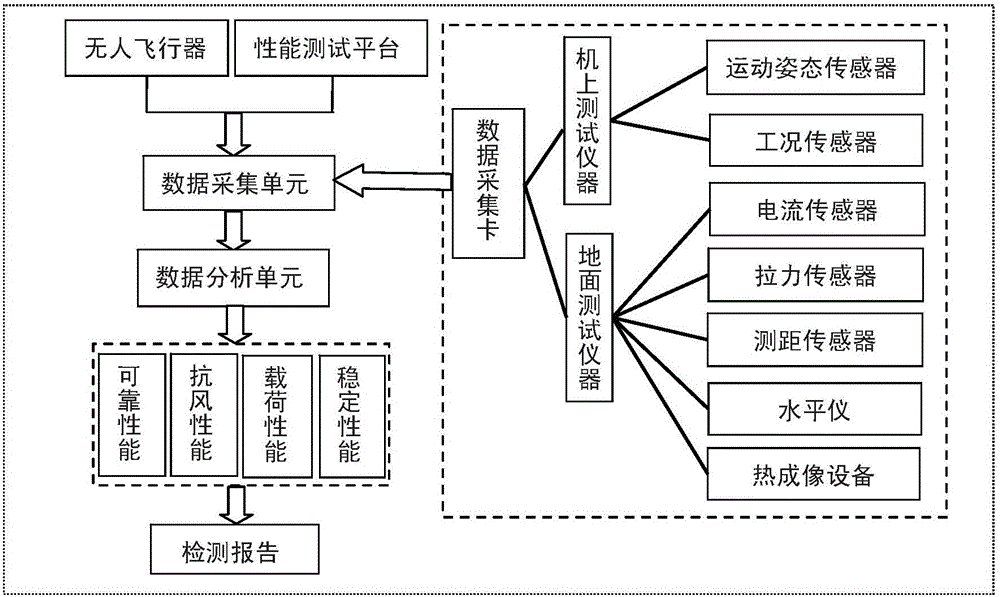
Performance test platform and method for multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN105083588AFlexible swingAccurate and reliable performance indicatorsAircraft components testingFlight vehicleEngineering
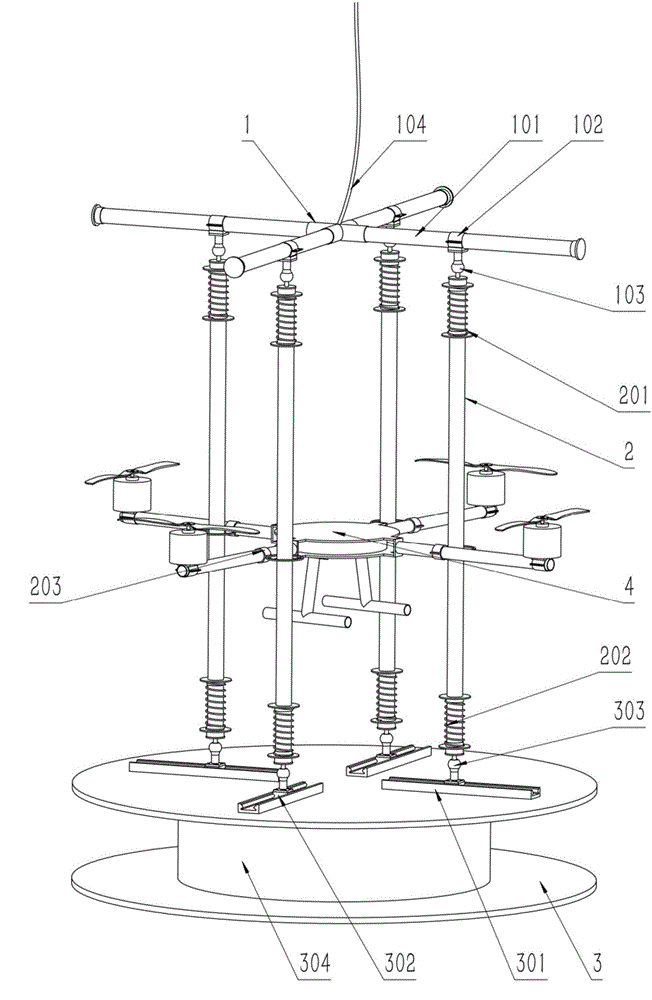
The invention discloses a performance test platform and method for a multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle. The test platform comprises a base, a stand column, a top frame, a performance test instrument and a calculation processing center; the bottom of the stand column is connected to the base through a ball-head universal bearing, and the top of the stand column is connected to the top frame through a ball-head universal bearing; the top frame is hung on an external rigid body through an elastic inhaul cable; a rack of the multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle is provided with a sleeving ring arranged on the stand column in a sleeving mode; the performance test instrument comprises an on-vehicle test instrument body which is arranged on the multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle and used for testing flight attitude information and work condition information of the multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle and a ground test instrument body which is arranged on the test platform and used for testing external response information of the multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle; the calculation processing center comprises a data collecting unit and a data analyzing unit. The test platform is simple in structure, good in flexibility and capable of accurately testing multiple performance indexes of the aerial vehicle.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
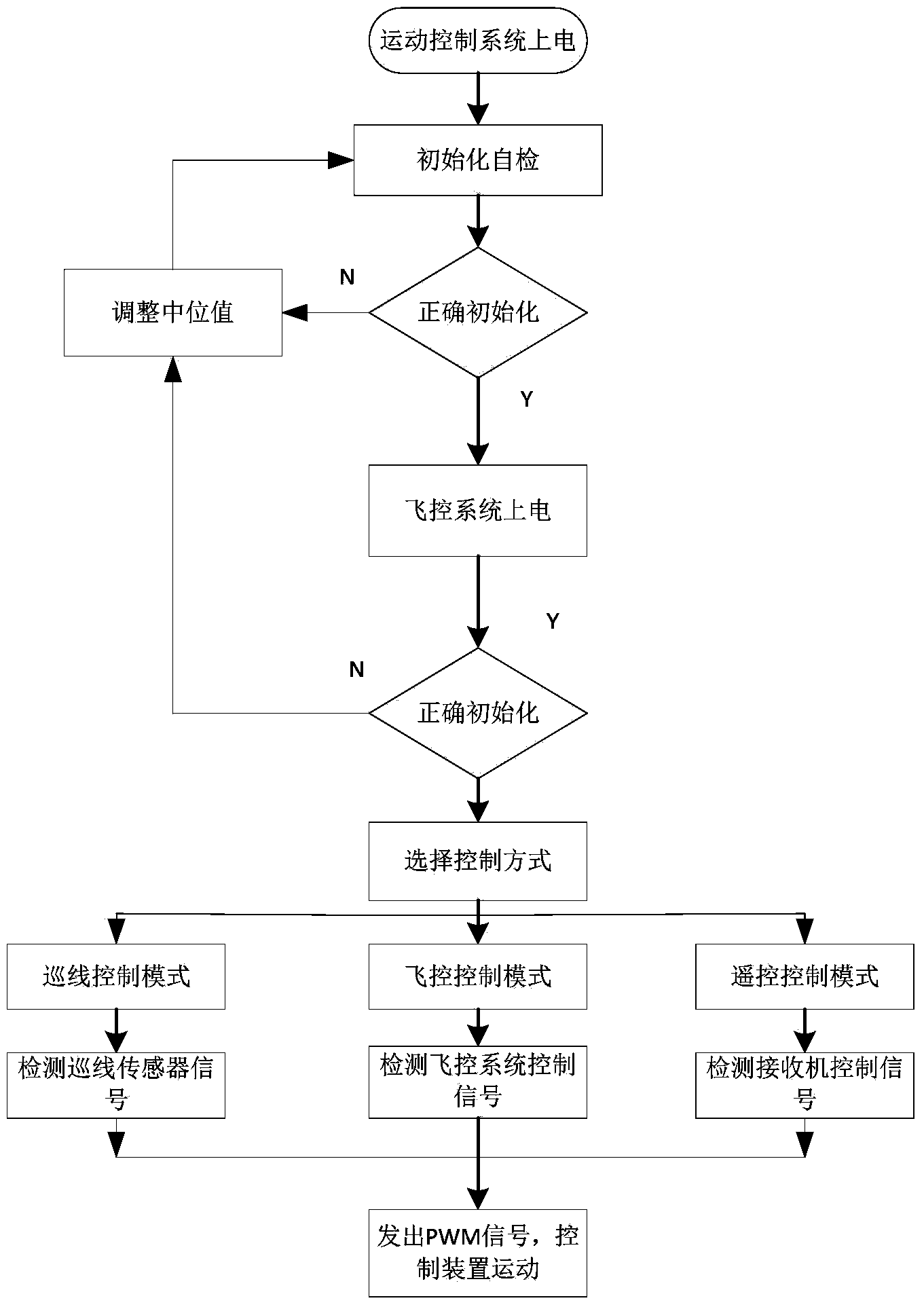
Ground test device used for flight control system and control method
ActiveCN103838152AReduce volumeEasy to testSimulator controlElectric testing/monitoringSystems designDriving mode
The invention discloses a ground test device used for a flight control system and a control method. The device comprises a carrying platform system, a motion control system, a flight control system, a remote controller, a receiver, a power supply system, a communication system and an upper computer, and the control method and a test method are included. Three working modes of the test device are achieved, one mode is that the test device moves under the control of the flight control system, one mode is that the test device moves under the control of the remote controller, and another mode is that the test device performs line-cruising motion. The three working modes can be conveniently switched. When the test device moves automatically under the control of the flight control system, a speed control loop and a direction control loop of the motion control system are used for making the test device visually simulate the motion, in an automatic drive mode, of an unmanned aerial vehicle and verifying algorithmic reasonability in the flight control system. Due to the fact that the three working modes are provided, the performance of the flight control system can be tested on the ground to a greater degree, system parameters can be effectively tested at the testing stage of flight control system designing, and reasonability and effectiveness of the control loops, a navigation algorithm and others can be verified.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Aircraft with disengageable auxiliary power unit components
InactiveUS20100300117A1Performed easily and efficientlyIncrease speedEngine fuctionsGas turbine plantsAuxiliary power unitGround testing
Owner:MOULEBHAR DJAMAL
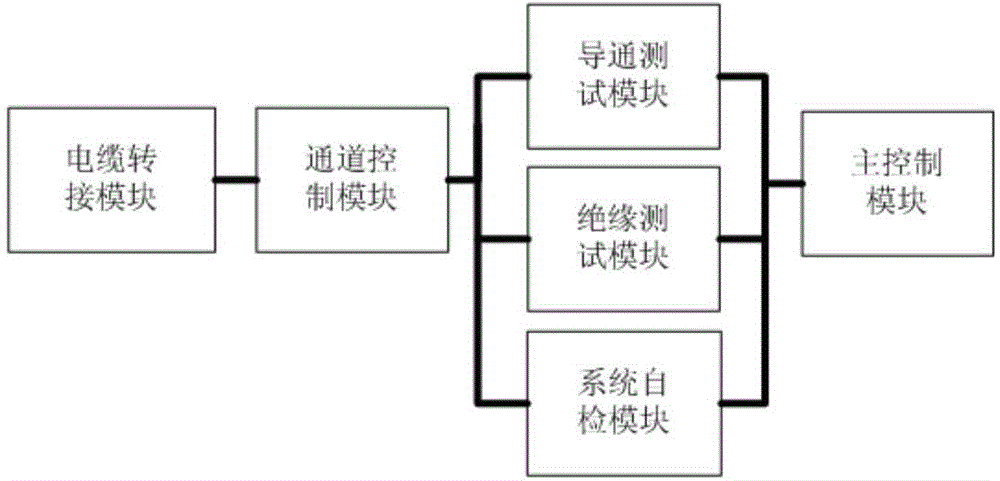
Cable testing system applied to minisatellite
ActiveCN104569730AReduce volumeFunction increaseTesting dielectric strengthTest efficiencyEngineering
The invention discloses a cable testing system applied to a minisatellite. The cable testing system comprises a cable adapter module, a channel control module, a conduction testing module, an insulation testing module and a system self-inspection module. Cables to be tested with different port types are connected to internal channels of the system through the cable adapter module, the channel control module controls connection and disconnection of the internal channels, the conduction testing module measures conduction resistance value among the channels, the insulation testing module measures insulation resistance value among the channels, and the system self-inspection module inspects and calibrates the system. The cable testing system solves the problems of low conduction insulation testing efficiency, poor accuracy, long period and high strength in low-frequency cables on satellites and ground testing low-frequency cables, quick testing of conduction insulation characteristics of the cables can be realized, and the cable testing system is applicable to the low-frequency cables on the satellites and the ground testing low-frequency cables.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
Test method and system of train pneumatic performance simulation test apparatus
InactiveCN101441138AIncrease authenticityStrong data authenticityAerodynamic testingRailway vehicle testingIn vehicleGround testing
The invention relates to a testing method and system for a train aerodynamic performance simulation testing device, which is used for testing various performance parameters of high-speed running train model in simulation test. The testing method comprises: arranging a train-carried data collection system in the train model, which is used for dynamic pressure tests of each testing point of the train model and tests of speed of the train model; arranging a ground data collection system on ground of the track, which is used for testing ground dynamic pressure and environmental parameters when the train model passes by the ground testing points. The invention is capable of real-timely recording dynamic change process of the train and ground air pressure, and accurately testing speed of the train model, thereby realizing tests of various test parameters such as dynamic pressure, speed, and the like, required for the simulation test, and obtaining test data of real-time and accurate train and ground dynamic pressure change data.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
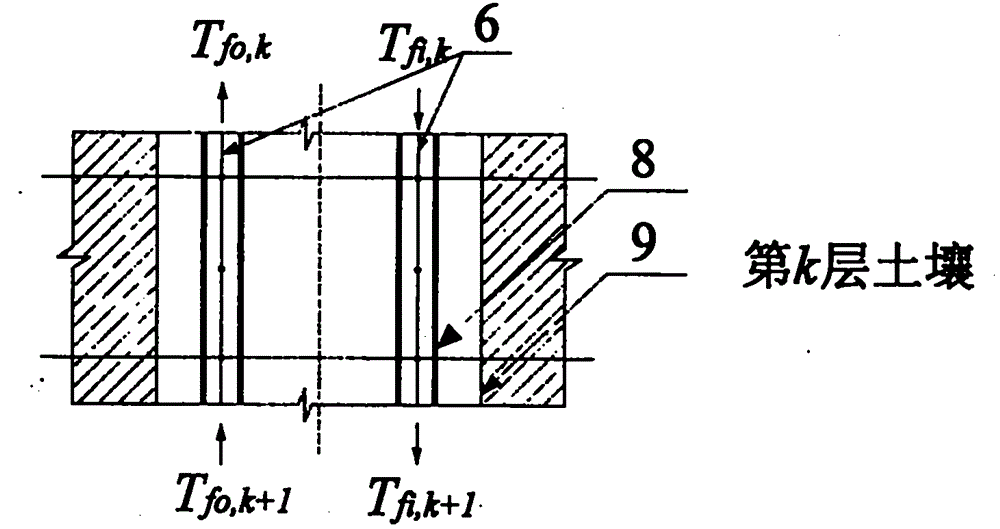
In-situ thermal response testing method of stratified thermal properties of underground rock and soil
InactiveCN102721722AAccurate dataHigh sensitivityMaterial heat developmentThermal response testGround testing
The invention relates to an in-situ thermal response testing method of stratified thermal properties of underground rock and soil. The invention relates to an in-situ thermal response testing device of the stratified thermal properties of the underground rock and soil. According to the in-situ thermal response testing device disclosed by the invention, a U-shaped pipe is buried, an optical fiber temperature sensor is inserted into two branch pipes of the U-shaped pipe, the U-shaped pipe is connected with an inlet and outlet of a circulating water pipeline of a ground testing device, water temperatures in the two branch pipes, namely the water inlet branch pipe and the water outlet branch pipe of the U-shaped pipe in different depth layers are respectively measured, the power of a heater is kept constant, and measured data of the water temperatures and the flow rates of circulating water in the two branch pipes of the U-shaped pipe in different depth layers at different times, as well as the corresponding heating power of the heater is recorded, so that a heat conduction coefficient, volume specific heat and a drilling thermal resistance value of soil in each layer can be obtained. According to the in-situ thermal response testing device disclosed by the invention, the defects that the distribution of the thermal properties of the rock and soil in different depths can not be obtained, the testing precision can not be improved, an optimal design method of the underground buried pipe can not be improved and the like in the prior art can be solved; furthermore, values of the thermal properties of the underground rock and soil, the types of the rock and soil, the contents of underground water and the seepage situations in the different depths can be obtained, and the in-situ thermal response testing device further has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong anti-interference property, corrosion resistance, small installation size, no requirements on a power supply and low testing cost.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
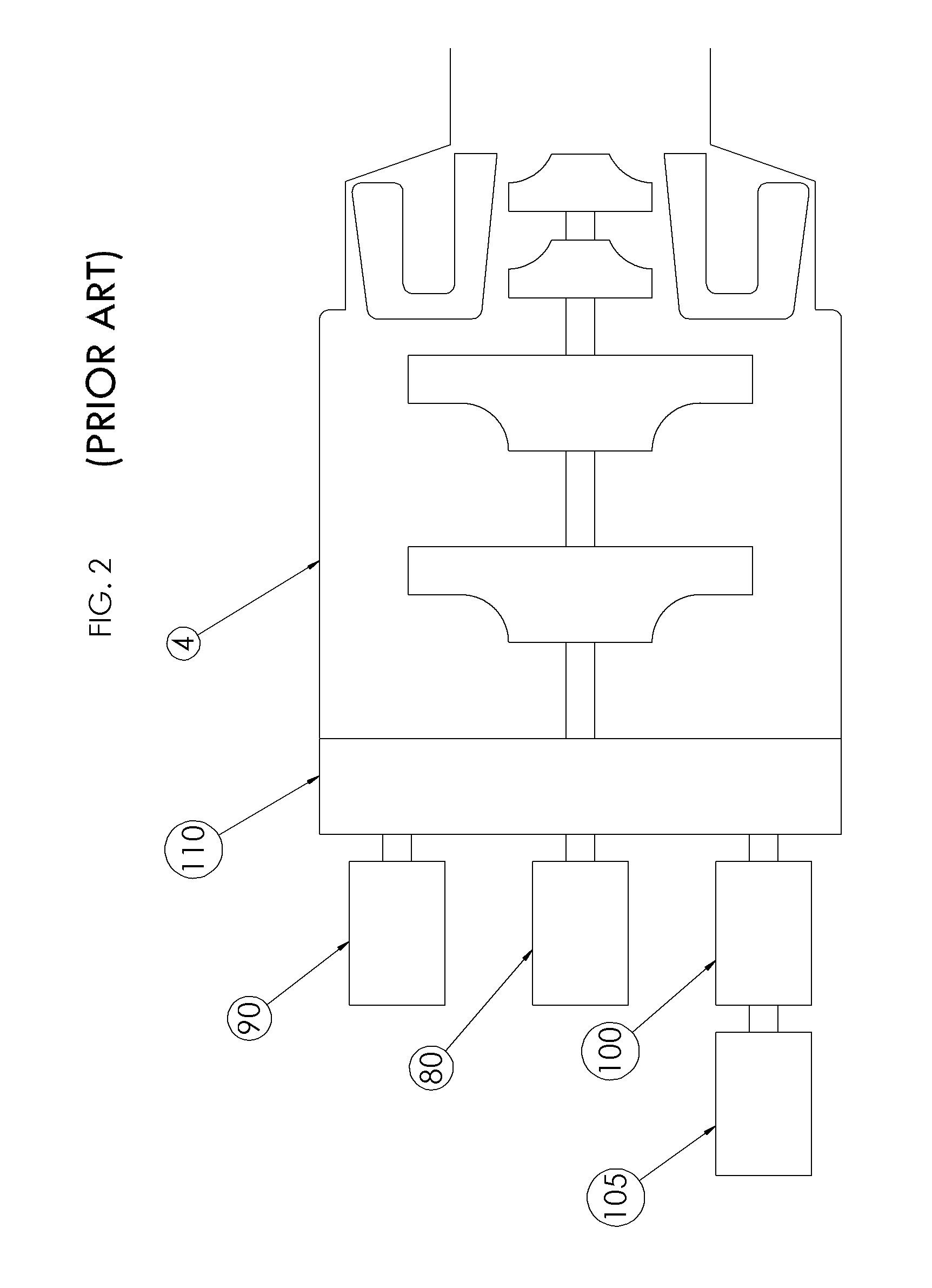
Ram air turbine with compound geartrain gearbox
An emergency power system may provide hydraulic and electrical power to an aircraft in the event of a failure of the aircraft's primary control power system. The system may be constructed as a ram air turbine in which a single ram air fan may drive both a hydraulic pump and an electrical generator. A unique gearbox may incorporate compound gearing to permit the pump and the generator to be driven at different speeds. Thus the pump and the generator may be driven at their respective optimum speeds. The pump and the generator may be detachably mounted on a gearbox that supports the ram air fan. The detachable mounting of the pump and generator may accommodate ease of maintenance of these items. The gearbox may be provided with a ground testing port through which rotational testing force may be introduced to a shaft that supports the ram air fan. This may permit ground level testing of the system. Ground level testing may reduce a need to perform periodic in-flight testing of the system.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Collision avoiding method for ground testing system of satellite formation flying
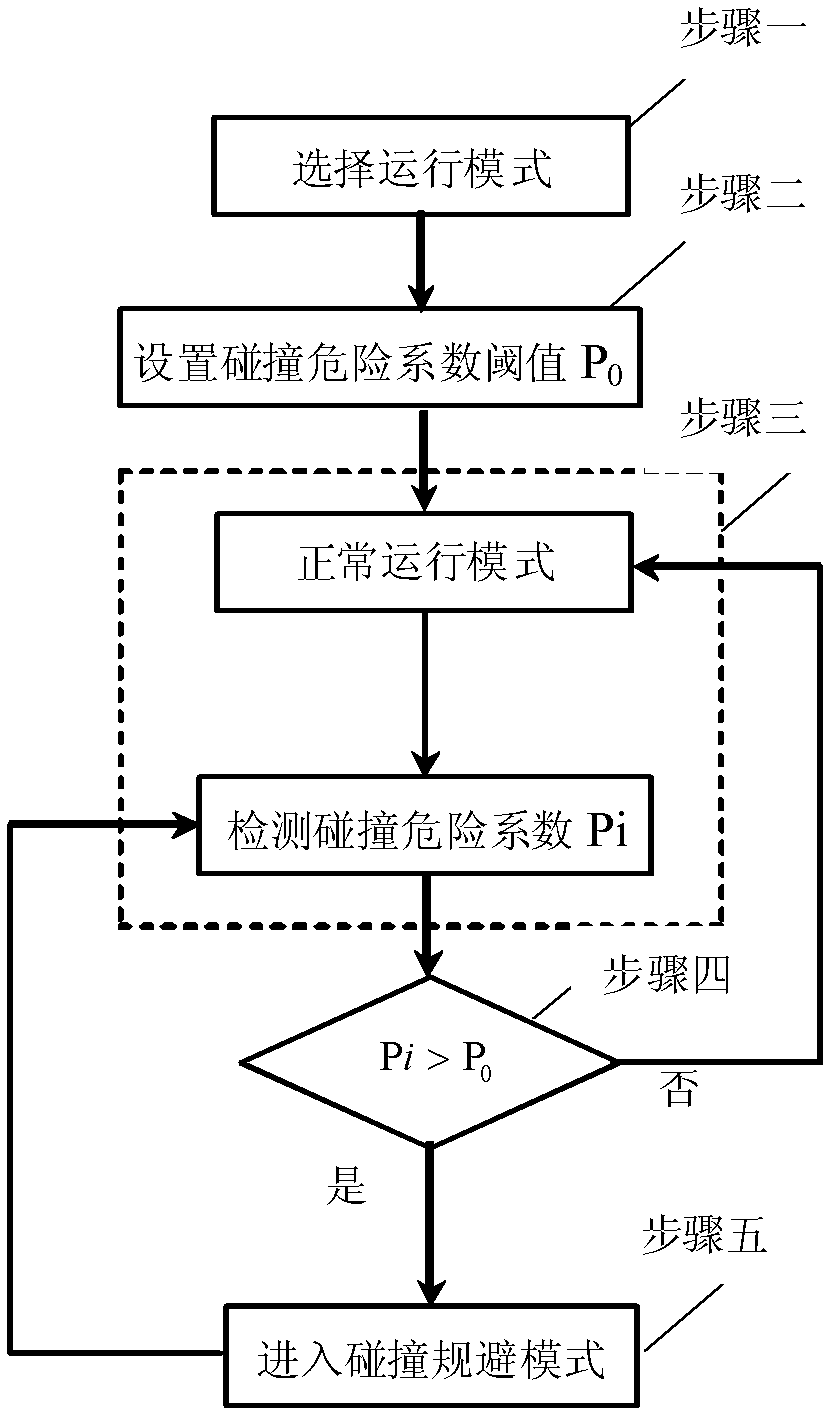
InactiveCN102541070AAvoid collisionAvoid safe operationSimulator controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsPotential fieldGround testing
A collision avoiding method for a ground testing system of satellite formation flying solves the problem that collision of simulation satellites cannot be avoided due to intersection of tracks and the fact that the simulation satellites move according to respective dynamic theory in satellite formation flying. The method specifically includes steps of: 1 choosing a moving mode; 2 setting a collision danger coefficient threshold P0; 3 choosing a normal moving mode, calculating collision danger coefficient Pi in each control period, and detecting the collision danger coefficient Pi; 4 judging Pi>P0; and 5 entering a collision avoiding mode, obtaining control force Fi of the ith simulation satellite according to artificial potential field, controlling the ith simulation satellite through the control force Fi to achieve collision avoiding, detecting the collision danger coefficient Pi and returning to step 3. The collision avoiding method is suitable for the field of ground testing systems of satellite formation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
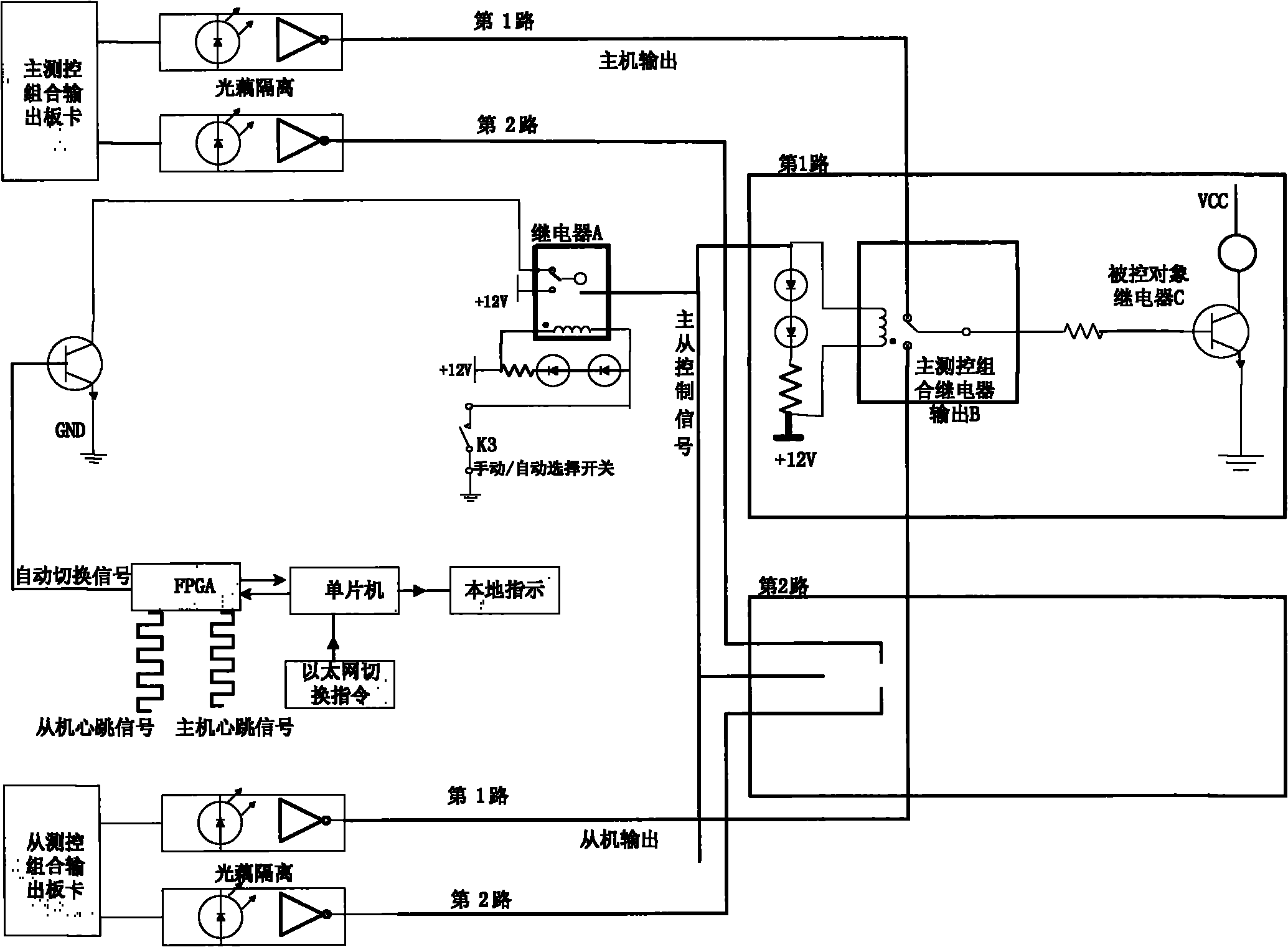
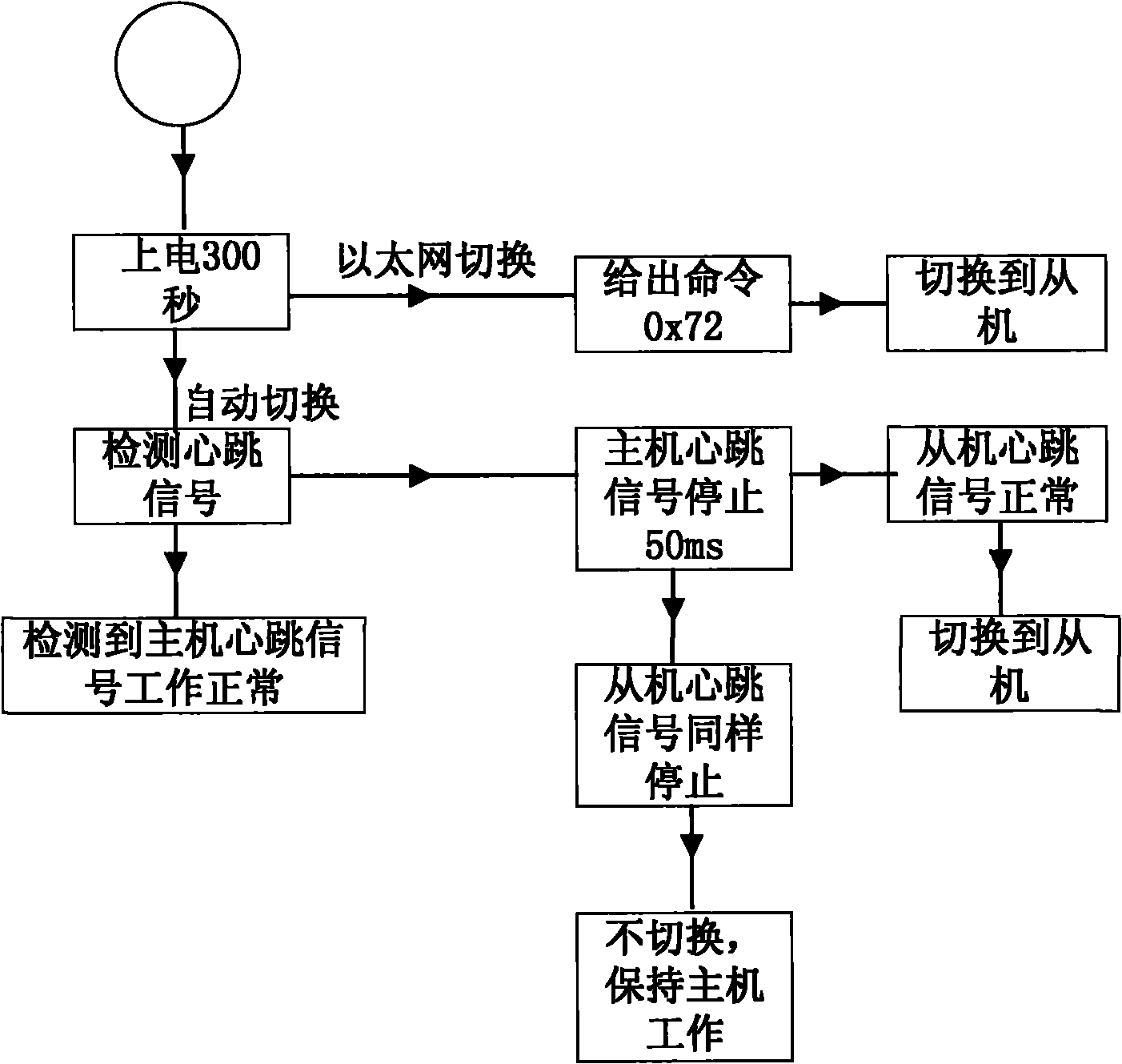
Redundancy switching circuit used for ground test launch and control system of carrier rocket
ActiveCN101782754AImprove reliabilityClear mechanismProgramme controlComputer controlRocketGround testing
The invention relates to a redundancy switching circuit used for a ground test launch and control system of a carrier rocket, which mainly comprises an FPGA module, a singlechip, a switching relay and a manual transfer switch, wherein the FPGA module realizes an automatic switching function and an Ethernet switching function, and the switching priority level of the Ethernet is high; the singlechip receives the interface signal of the Ethernet, transmits the signal to the FPGA module, meanwhile receives the master-slave machine working condition from the FPGA module and carries out real-time display; an amplifying circuit receives the output signal of the FPGA module and carries out power amplification; the relay receives the drive signal of the amplifying circuit and executes action; and the manual transfer switch is used for the manual switching involved by people under an emergency state, and the priority level of manual switching is the highest. The invention ensures that the test launch and control system is not disturbed when in outputting, thereby ensuring the reliability and the safety of the whole test launch and control system. The invention solves the problem that a rocket is unattended before being launched because of low reliability of general test launch and control equipment, thereby meeting the demands of high reliability and safety of the carrier rocket on the ground test launch and control system.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ASTRONAUTICAL SYST ENG
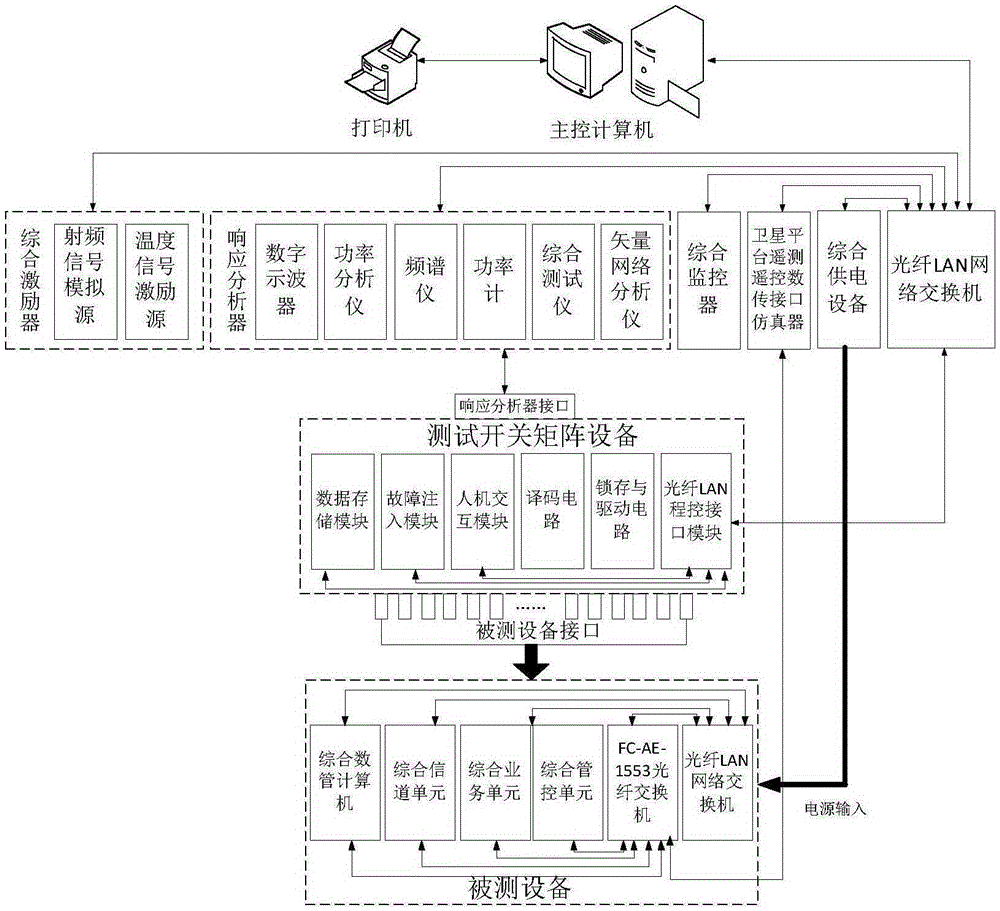
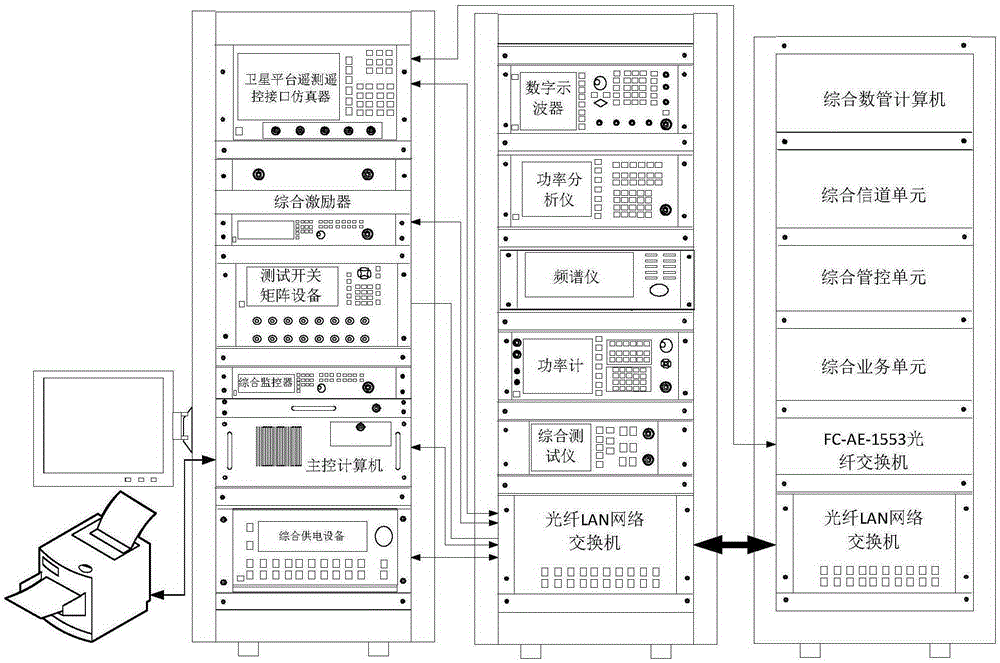
Automatic ground testing system of spaceborne electronic equipment
Disclosed in the invention is an automatic ground testing system of spaceborne electronic equipment. The invention aims at providing an automatic ground testing system having advantages of high integration, reliability, and extensibility, high comprehensive degree, and good capability of reduction of equipment and interfaces. According to the technical scheme, tested equipment, an integrated exciter, and a response analyzer are connected by testing switch matrix equipment; and one end surface of the testing switch matrix equipment faces the integrated exciter or the response analyzer and the other end surface faces the tested equipment. Loading and measurement of different parameters are carried out by switching connectors at different positions of the testing switch matrix equipment. A main control computer carries out data interaction with the integrated exciter, the response analyzer, the testing switch matrix equipment, integrated power supply equipment, and an integrated monitor by a fiber LAN switched network; analysis and testing data are outputted in a report mode; and instructions and remote telemetering information of the integrated monitor, an integrated channel unit, an integrated service unit, and an integrated management and control unit are transmitted by the fiber LAN switched network.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
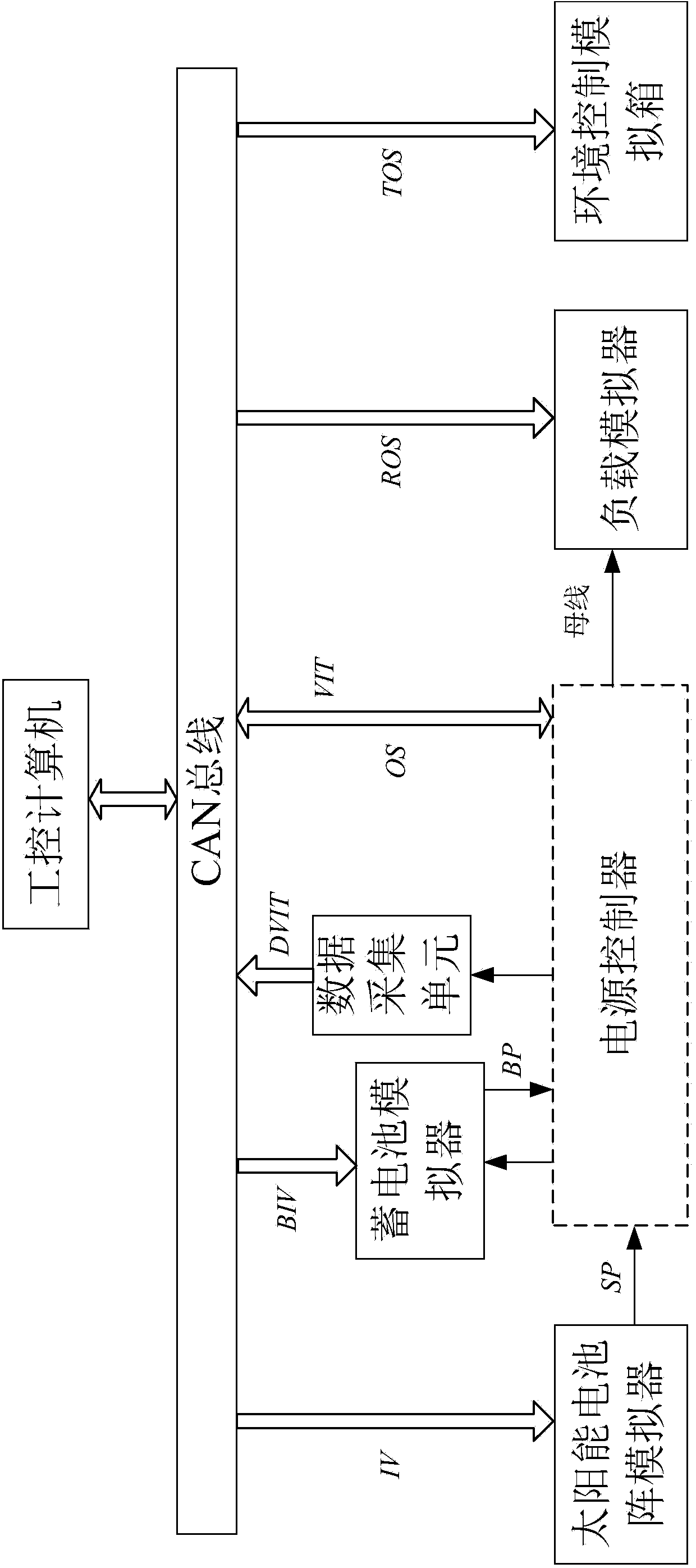
Ground testing system suitable for power source controller of stratospheric airship
ActiveCN104375502AImplement performance testingImplement functional testingElectric testing/monitoringTest efficiencyPower controller
The invention discloses a ground testing system suitable for a power source controller of a stratospheric airship. The ground testing system is applied to the development and test processes of the power source controller of the stratospheric airship. The ground testing system is composed of an industrial personal computer, a CAN bus, a data collecting unit, a solar battery array simulator, a storage battery simulator, a load simulator and an environment control simulation box. The CAN bus is adopted for communicating with the power source controller of the stratospheric airship, and combined with the industrial control computer and the data collecting unit, and testing on the function and the performance of the power source controller is finished under signals issued by the industrial control computer. The designed ground testing system reduces the testing cost and improves the testing efficiency.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mo/Ag laminated metal matrix composite for solar cell interconnected sheet and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN102169912AElectric discharge tubesFinal product manufactureGround testingBiological activation
The invention relates to a Mo / Ag laminated metal matrix composite for solar cell interconnected sheets and a preparation process thereof. By employing a vacuum metal plasma implantation technology, the invention comprises the steps of implanting metallic elements according to certain energy and dosage into molybdenum foil interconnected sheet materials processed by burnishing, degreasing and acidpickling activation; plating silver on the surface of molybdenum foils by a non-cyanide electroplating method; and conducting high temperature annealing under the protection of argon so that the metallic element of silver diffuses and penetrates into the molybdenum foils to form a metallurgical binding with Mo / Ag interfaces and finally to obtain the Mo / Ag laminated metal matrix composite having high interfacial binding strength and high welding strength. The welding (interfacial) strength of the composite reaches 460gf by single-point resistance spot welding. According to the invention, the Mo / Ag laminated metal matrix composite is prepared without adding an intermediate metal layer and cyanide electroplated silver. The ground testing is conducted and the performance requirement is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Automatic ground testing and relative camera pose estimation method in depth image
ActiveCN104361575AAccurate detectionNo human intervention requiredImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudEstimation methods
The invention discloses an automatic ground testing and relative camera pose estimation method in a depth image. The method includes the steps: calibrating the depth image; computing a point cloud coordinate of each point in the depth image depth under a depth camera coordinate system per pixel; consistently extracting the ground based on random sampling; extracting ground normal vectors; computing the point cloud coordinates under a world coordinate system. Manual intervention is not required, and ground testing can be performed fully automatically; compared with an image color information based method, the method based on three-dimensional depth information has the advantages that ground testing is more accurate, and height of each pixel in a scene can be restored. In addition, by the method, current depth camera pose and scene height solving can be completed with only one image without depending on historical information.
Owner:HUNAN SURE SECURE INTELLIGENCE CO LTD
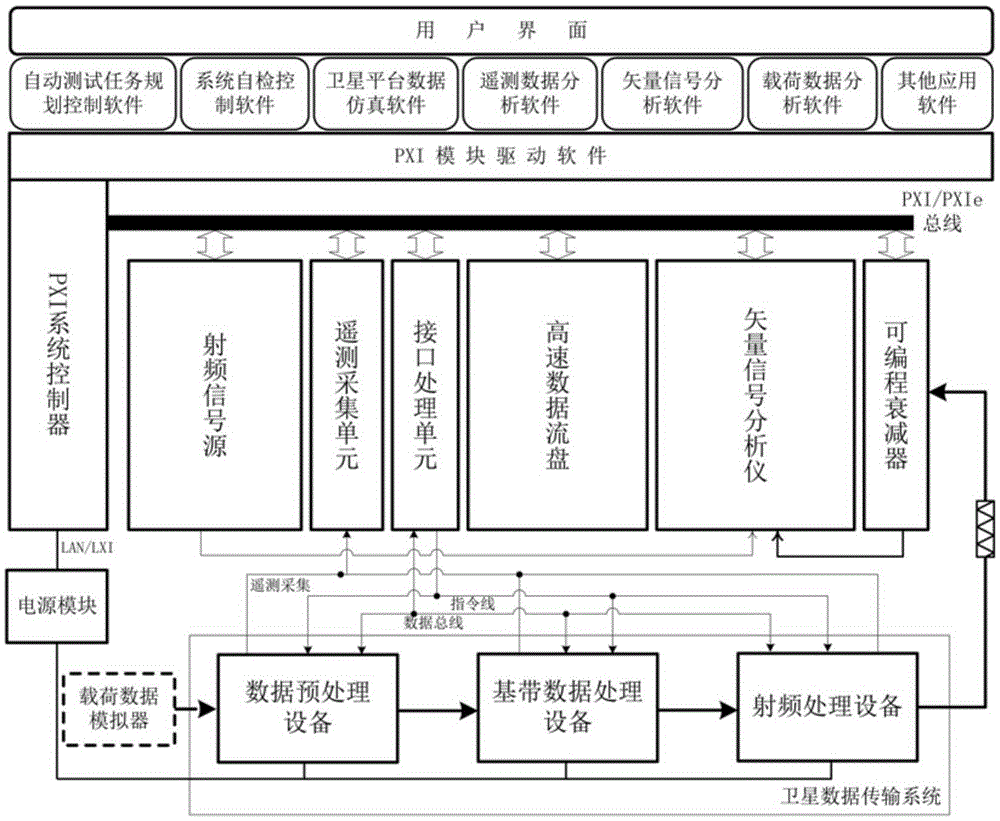
Remote sensing satellite data transmission product automatic testing system and method
InactiveCN105306156AOvercome difficultyOvercome the cycleTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionOperational systemStructure of Management Information
The invention provides a remote sensing satellite data transmission product automatic testing system and method. The remote sensing satellite data transmission product automatic testing system comprises a PXI system controller which provides a real-time operating system for a whole PXI platform; a PXI module set which is connected with a PXI bus and provides a direct interface for a tested product; a PXI case which provides a stable mechanically structured platform and a reliable power supply and heat radiation system for the PXI system; and a piece of testing system software which cooperates with the PXI module set to realize corresponding functions and provides an interacting interface for a user. Based on universal PXI architecture design, the remote sensing satellite data transmission product automatic testing system overcomes the disadvantages of huge device scale, high construction difficulty and long period of an existing remote sensing satellite data transmission ground testing system.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Monitoring system for rail transit bow net operating condition
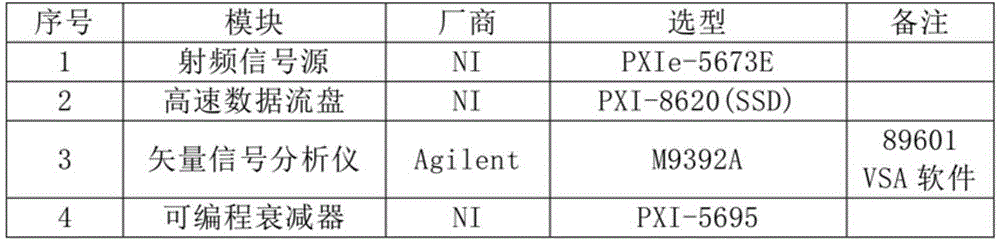
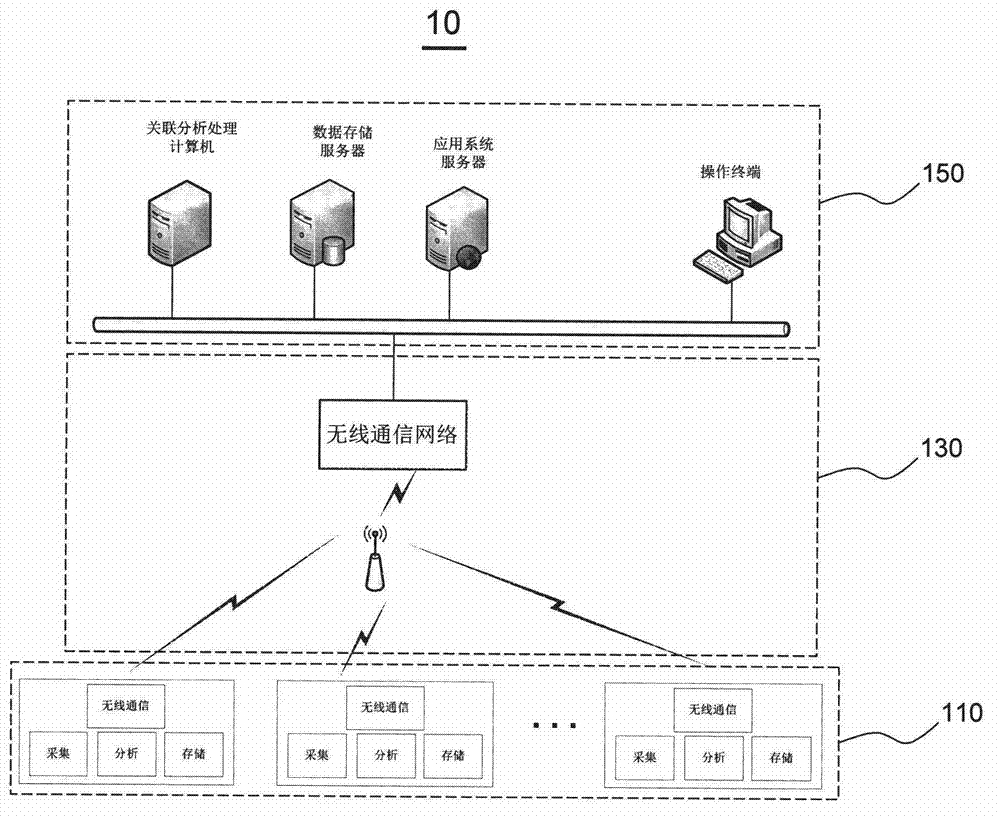
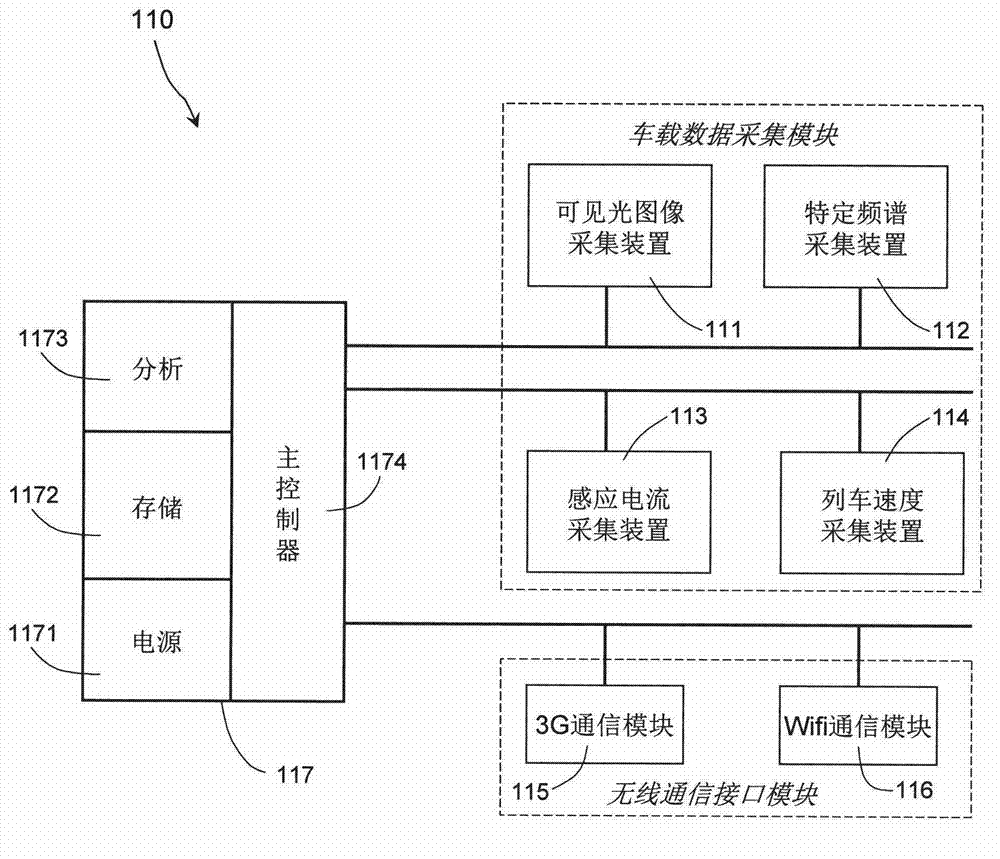
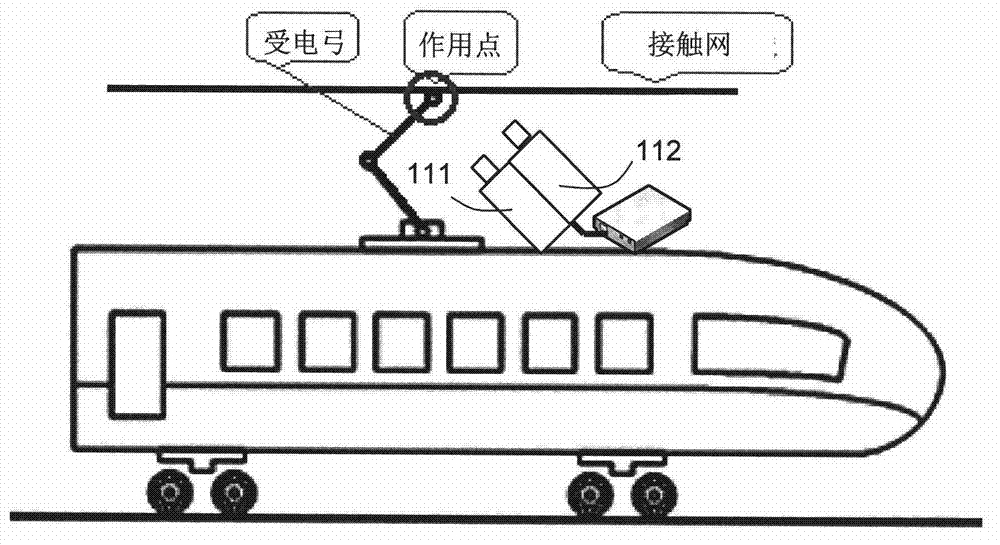
ActiveCN103115647ARealize fault warningImprove the efficiency of condition monitoringTesting dielectric strengthTransmission systemsData acquisitionMonitoring system
The invention provides a monitoring system for rail transit bow net operating condition, and belongs to technical field of rail transit detection. The monitoring system comprises a vehicle-mounted terminal, a ground testing center and a data communication network used for data transmission of the vehicle-mounted terminal and the ground testing center. The vehicle-mounted terminal comprises a vehicle-mounted data acquisition module, and a vehicle-mounted analyzing and warning module. The vehicle-mounted data acquisition module is used for acquiring bow net operating information from a bow net system to monitor bow net operating condition of the bow net system and acquiring general information of train operation. The vehicle-mounted analyzing and warning module is used for storing bow net operating condition and general information of train operation, and performing online analyzing and processing based on images and general information of train operation so as to judge whether operating condition is abnormal or not and send warning messages when operating condition is judged to be abnormal. The ground testing center performs association analyzing processing to bow net operating condition according to images and train operation general information from one or a plurality of vehicle-mounted terminals.
Owner:赵乎
Portable lightning current generating device and method for grounding device impact impedance testing
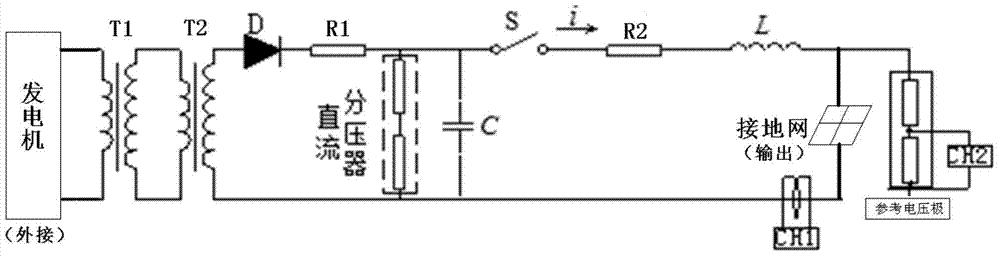
ActiveCN104714067AImprove work efficiencyEasy to carryTesting dielectric strengthElectrical measurement instrument detailsVoltage referenceEngineering
The invention discloses a portable lightning current generating device and method for grounding device impact impedance testing. The device comprises a power generator and a lightning current generator main loop test box. A rectifying silicon stack D, a charging resistor R1 and a direct-current voltage divider are connected in series to the output end of a boosting transformer T2. An energy-storage capacitor C is connected in parallel to the direct-current voltage divider. One end of a discharging switch S is connected with a positive electrode of the energy-storage capacitor C. The other end of the discharging switch S is connected with an adjustable wave modulated resistor R2. The other end of the adjustable wave modulated resistor R2 is connected with one end of an adjustable wave modulated inductor L. The other end of the adjustable wave modulated inductor L is connected with a grounding grid to be tested through a grounding testing current injection point. A grounding testing reverse current electrode and a reference voltage electrode are arranged on the periphery of the grounding grid to be tested. The ground testing reverse current electrode is connected to a negative electrode of the energy-storage capacitor C of a lightning current generator main loop. The device can simulate inductive effect and soil spark discharging effect really, and impact grounding resistance can be tested really.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
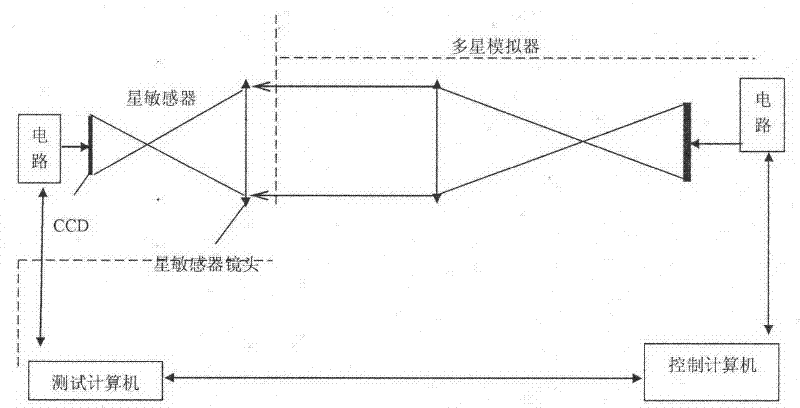
A ground test method for star sensor
The invention provides a ground testing method of a star sensor. The method comprises the following steps of: adjusting the star sensor by using a theodolite so that the Z axis of the star sensor points to true north and the Y axis of the star sensor vertically faces towards zenith; receiving a quaternion of the star sensor under an inertial coordinate system; converting the posture of the star sensor into a quaternion under a WGS84 coordinate system; converting the quaternion under the WGS84 coordinate system of the star sensor into a three-axis Euler angle; continuously operating the star sensor for 30 minutes, storing the difference between a roll angle and the local longitude and the difference between a drift angle and the local latitude in real time, and counting precisions of the roll angle and the drift angle; and storing the difference between a pitch angle and the local longitude in real time, and counting the precision of the pitch angle. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the testing process is simple; any special equipment is unnecessary; the method is not only used for testing the precision of the three-axis Euler angle of the star sensor but also used for completely testing the three-axis polarity of the star sensor; and in addition, only when the time precision satisfies requirements, the method is also used for testing the absolute longitude of the star sensor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
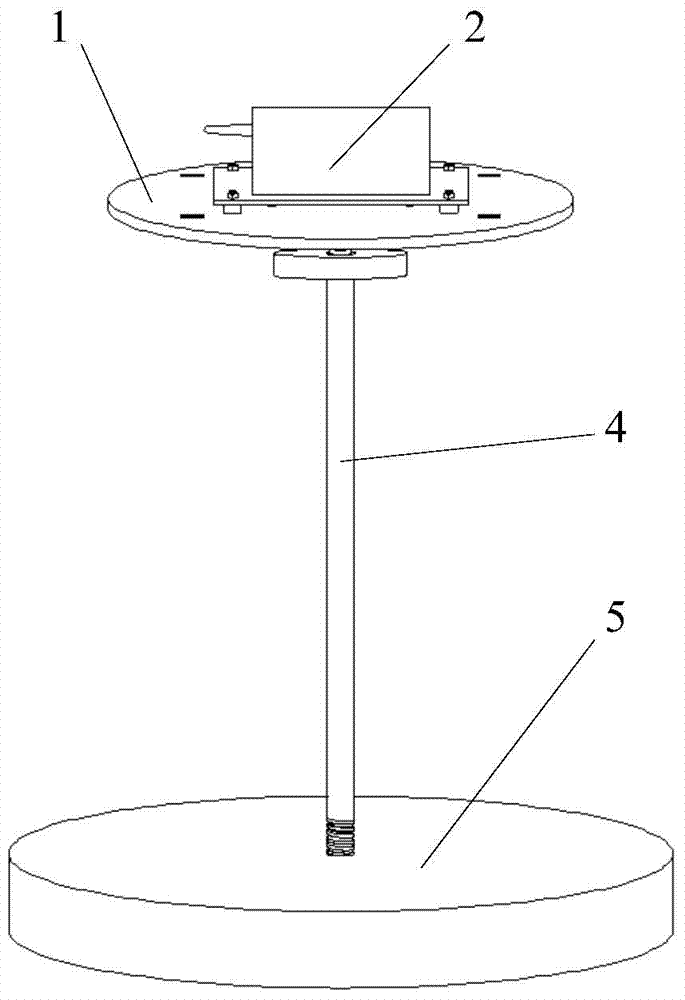
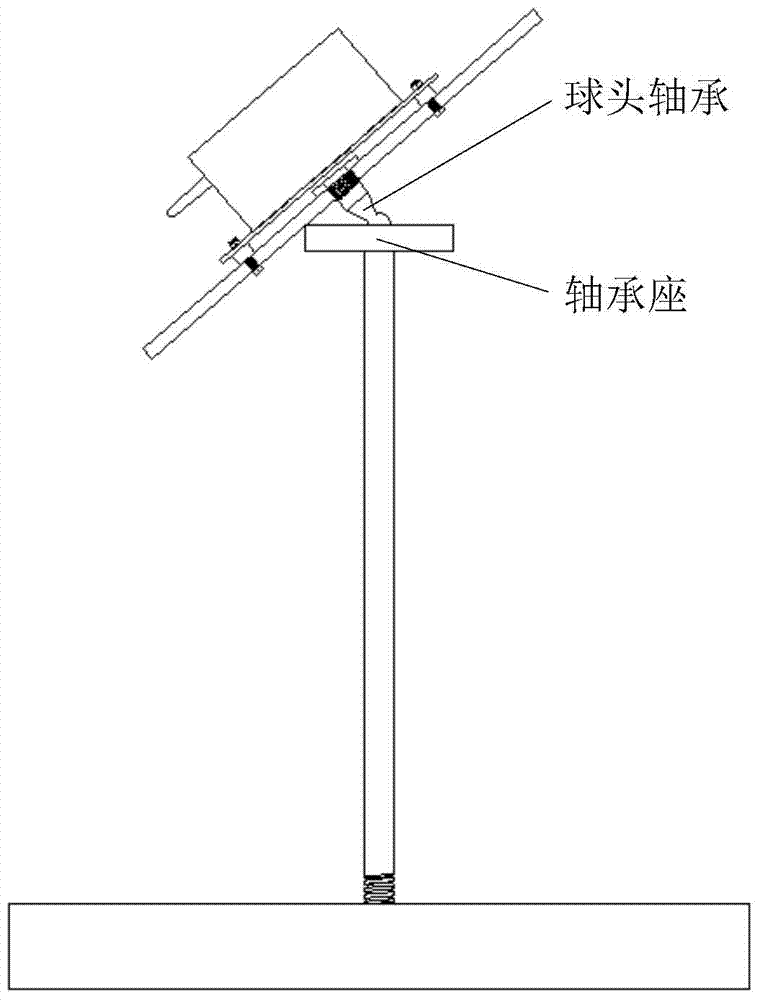
Unmanned helicopter ground testing console and application method thereof
ActiveCN104494840ADetermine the amount of adjustmentReduce the number of debuggingAircraft components testingComputer moduleEngineering
The invention relates to an unmanned helicopter ground testing console and an application method thereof. The testing console comprises an unmanned helicopter mounting disc, a data acquiring module, a support rod and a base; if an undercarriage is relatively short, an independent data acquiring module mounting disc is arranged between the unmanned helicopter mounting disc and the support rod. The support rod and the unmanned helicopter mounting disc / the data acquiring module mounting disc are connected by an universal rotating mechanism; and a removable hoop is arranged for keeping the mounting disc horizontal in the detaching of an unmanned helicopter. The testing console and the application method thereof are used for solving the problems of higher requirement of a PID parameter testing mode of traditional unmanned helicopter autostability equipment for the control skill of control staff, lower safety in the testing process and difficult guarantee of the precision degree of testing results. The testing console has such advantages as simple structure and convenience for use, disassembly, storage and carrying; and correspondingly, the application method is clear in process, is convenient for operation, and can largely shorten the PID parameter adjusting time.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
Spacecraft equipment ground testing system and method
ActiveCN101866178AWhether the verification is successfulElectric testing/monitoringSensing dataElectricity
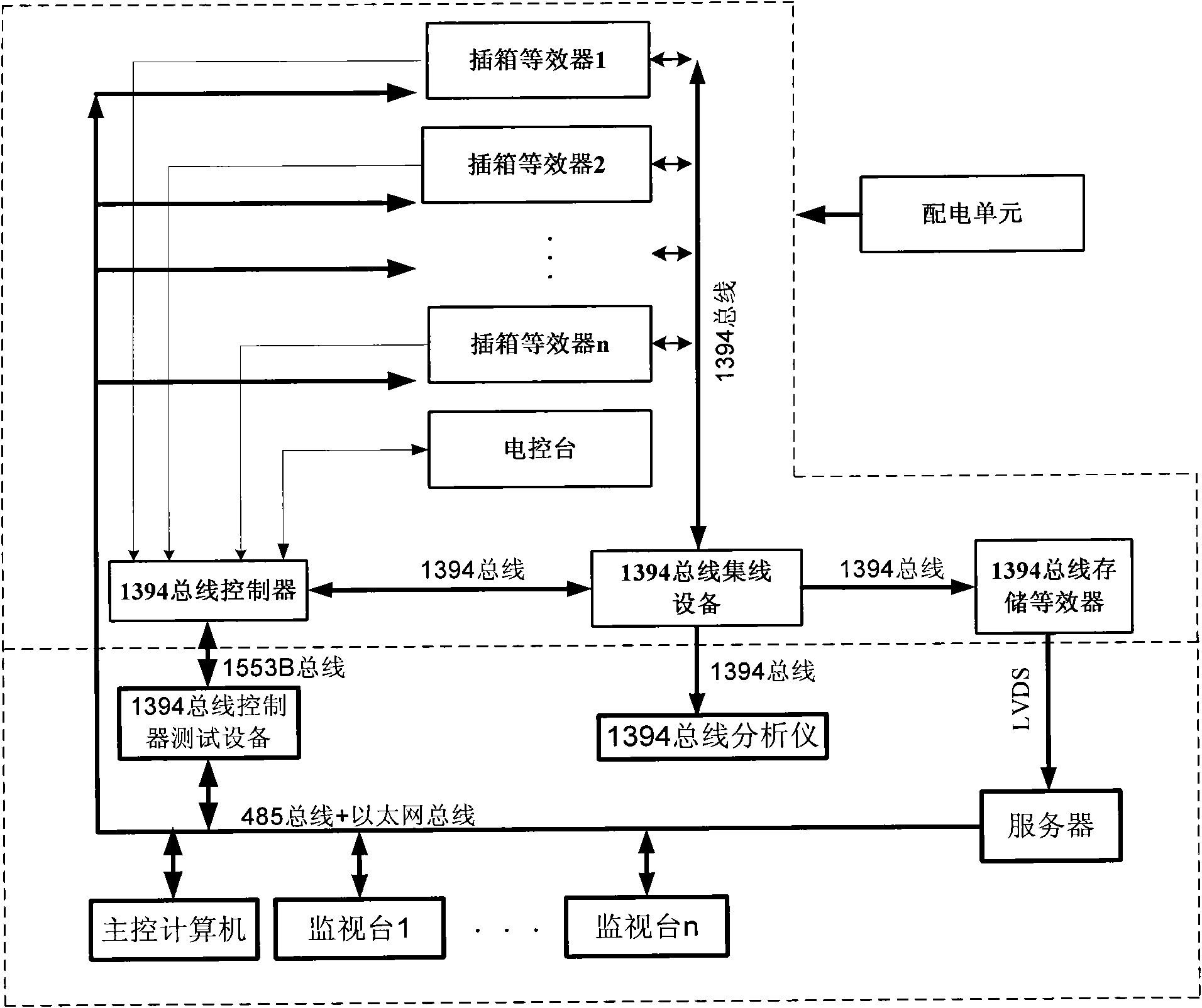
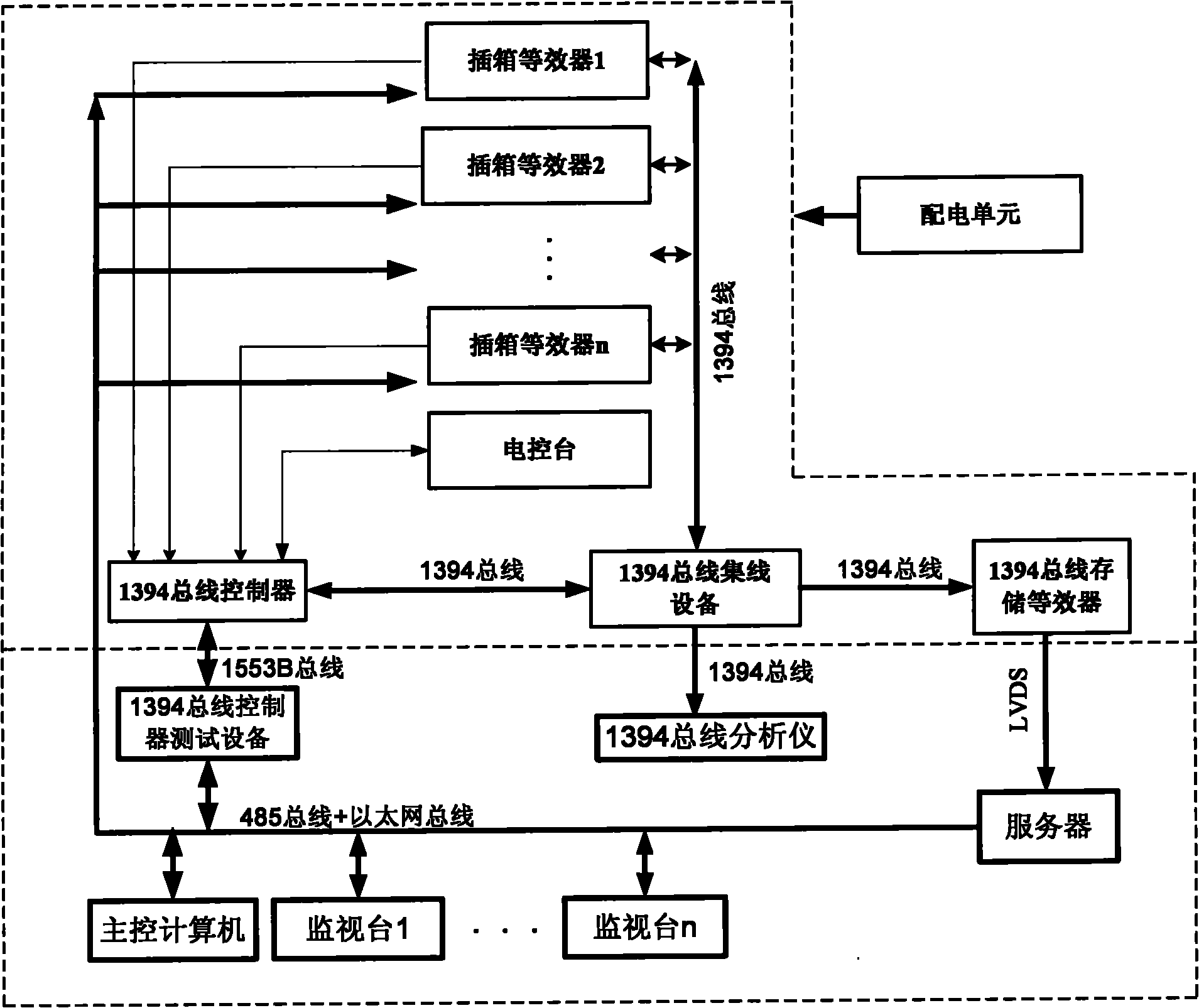
The invention discloses a spacecraft equipment ground testing system and a method. An electrical interface, a mechanical interface and a wiring method provided by a cabinet are the same with the actual interface and wiring on a spacecraft; replaceable equipment in the system is arranged in the cabinet; a main control computer power up plug-in box equivalent devices by sending a switch instruction; after power-up, a 1394 bus controller collects the remote sensing data all the plug-in box equivalent devices and sends the data to the main control computer; the main control computer sets a data transmission method of the plug-in box equivalent devices through the 1394 bus controller, sets the transmission contents of the plug-in box equivalent devices through a network bus, and the plug-in box equivalent devices output 1394 data according to the settings; and a monitoring station compares the data output by the plug-in box equivalent devices and a sample packet, and judges if the 1394 transmission is normal. The invention designs the cabinet to stimulate the space limitation, the electrical interface and the mechanical interface on the spacecraft so as to provide a high- simulation test environment for ground joint trial.
Owner:NO 513 INST THE FIFTH INST OF CHINA AEROSPACE SCI & TECH
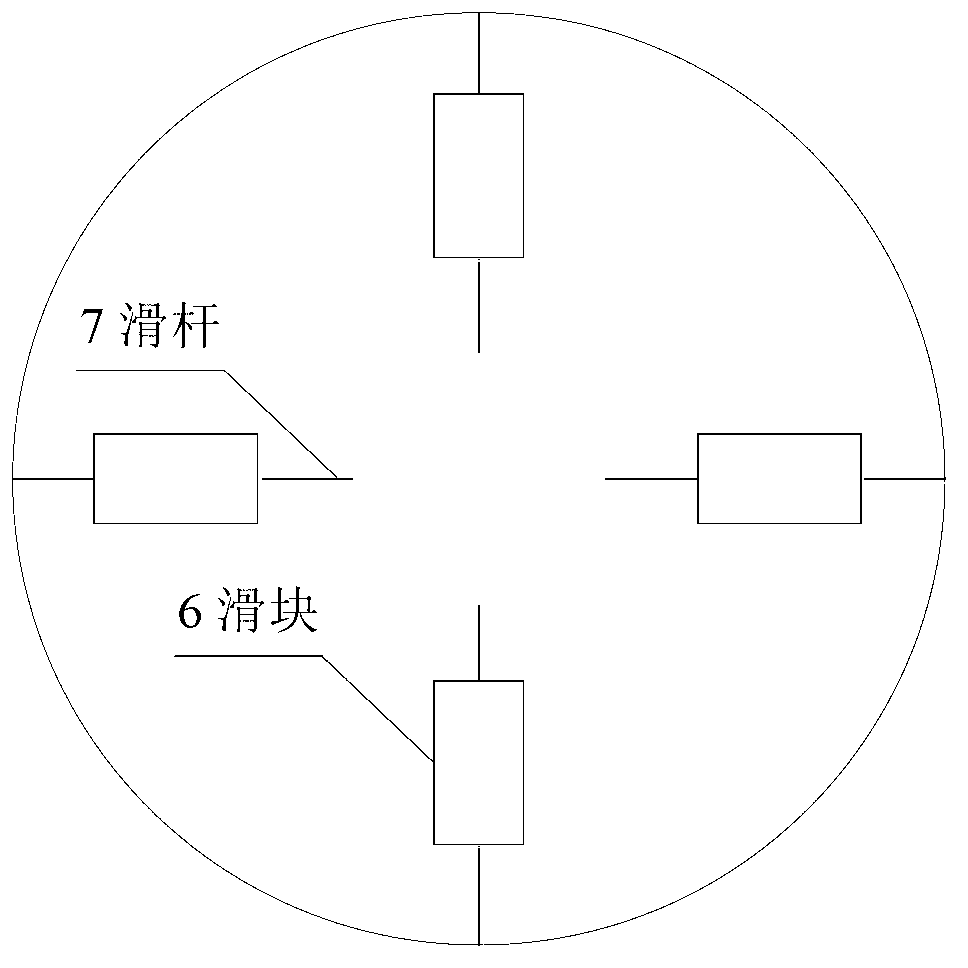
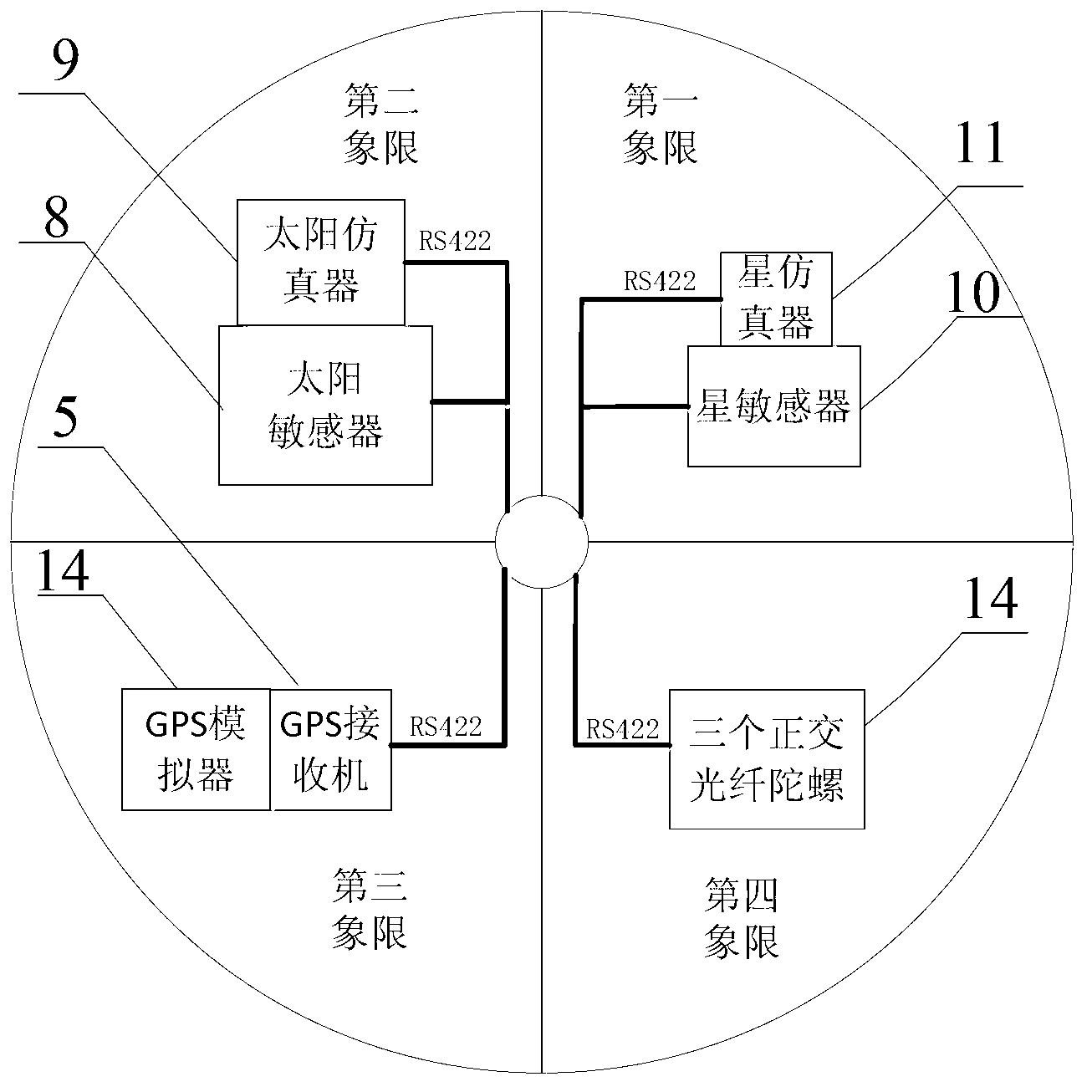
Satellite multiple attitude control mode test system based on double gimbal control moment gyroscope (DGCMG) structure
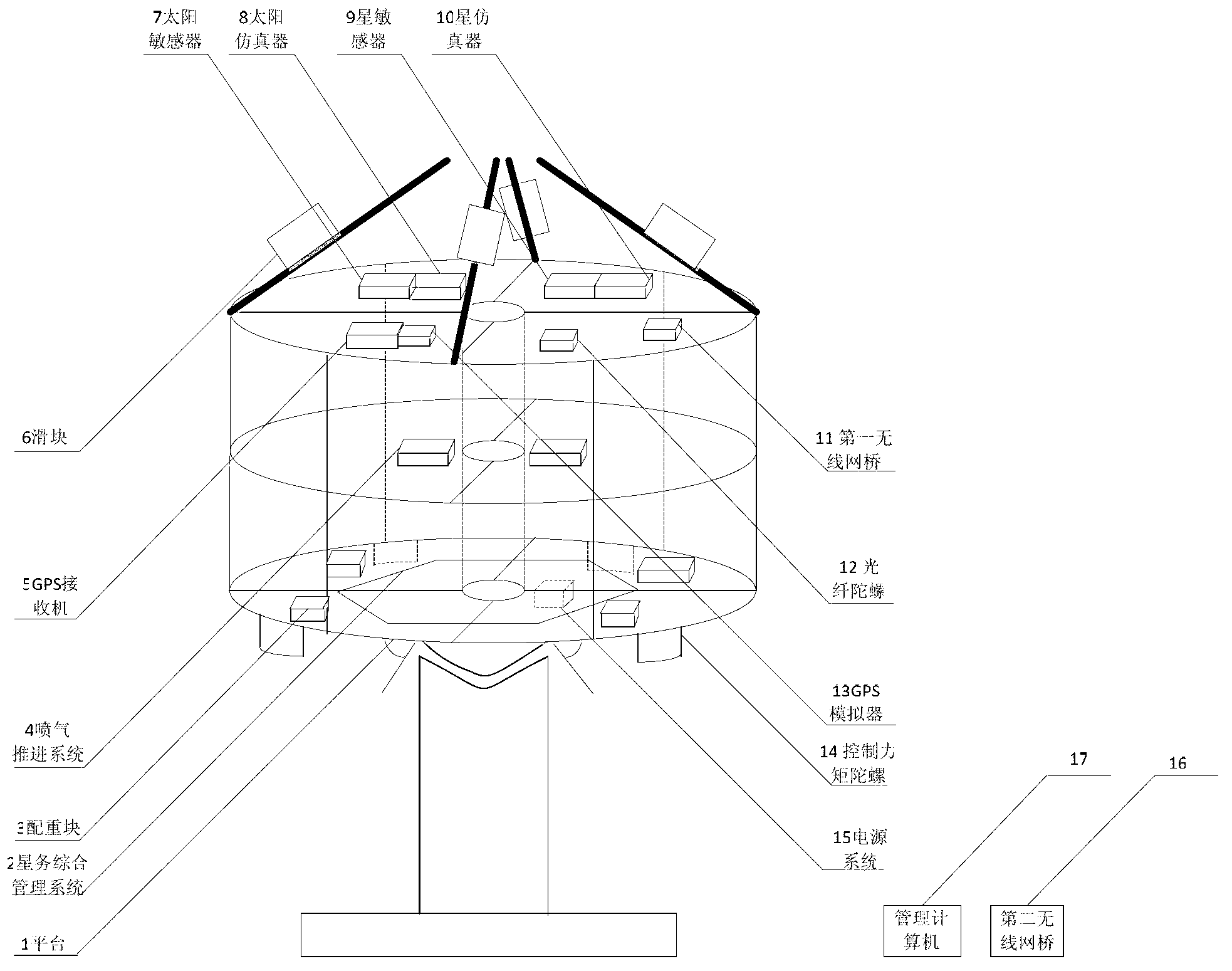
The invention relates to a satellite multiple attitude control mode test system based on a double gimbal control moment gyroscope (DGCMG) structure. Performance of three satellite attitude control systems which are based on a DGCMG, a single gimbal control moment gyroscope (CMG) and a flywheel is tested and verified through a DGCMG actuating mechanism. The satellite multiple attitude control mode test system based on the DGCMG structure comprises a platform system, the satellite attitude control system, a space environment simulation system and a ground station system. The platform system is composed of a tri-axial air bearing table, a satellite service comprehensive management system, a power source and a wireless bridge and used for simulating satellite dynamic characteristics and information management. The satellite attitude control system is composed of a jet propulsion system, the DGCMG, a fiber-optic gyroscope, a star sensor, a sun sensor and a global position system (GPS) receiver and used for determination of an attitude and an orbit and control of a satellite platform. The space environment simulation system is composed of a GPS simulator, a sliding block which is of a pyramidal structure, a sun simulator and a star simulator and used for simulating space interference torque, and part performance of a GPS satellite and a celestial body. The satellite multiple attitude control mode test system based on the DGCMG structure can provide ground testing and verification for multiple attitudes of a satellite.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
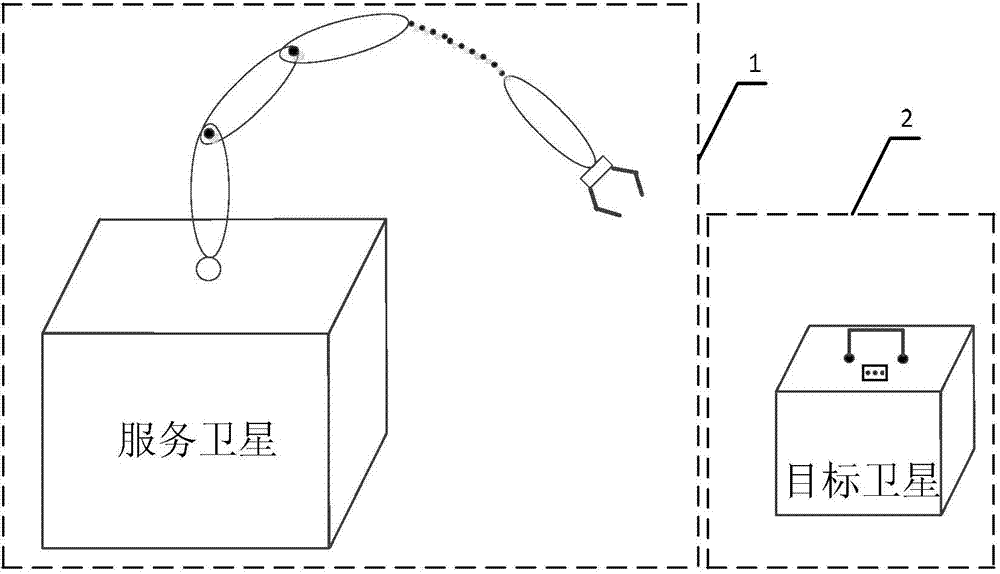
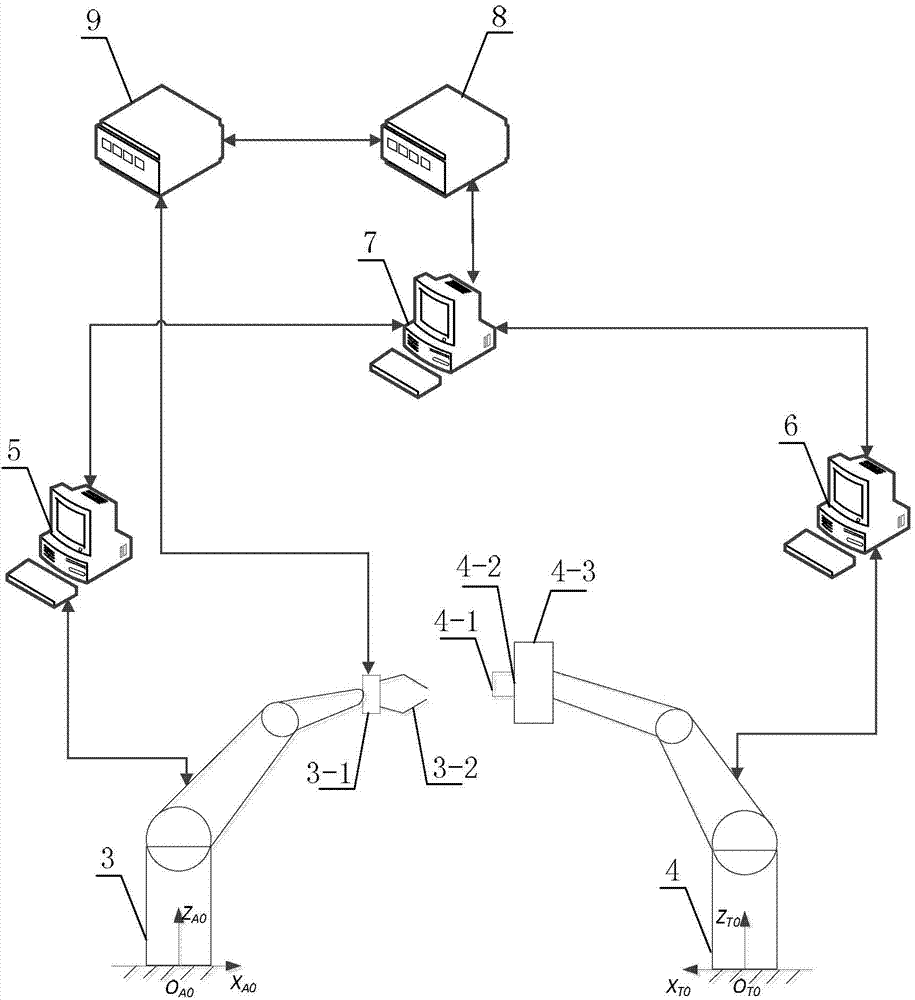
Ground-based simulation system for space robot visual servo to capture moving target and simulation method
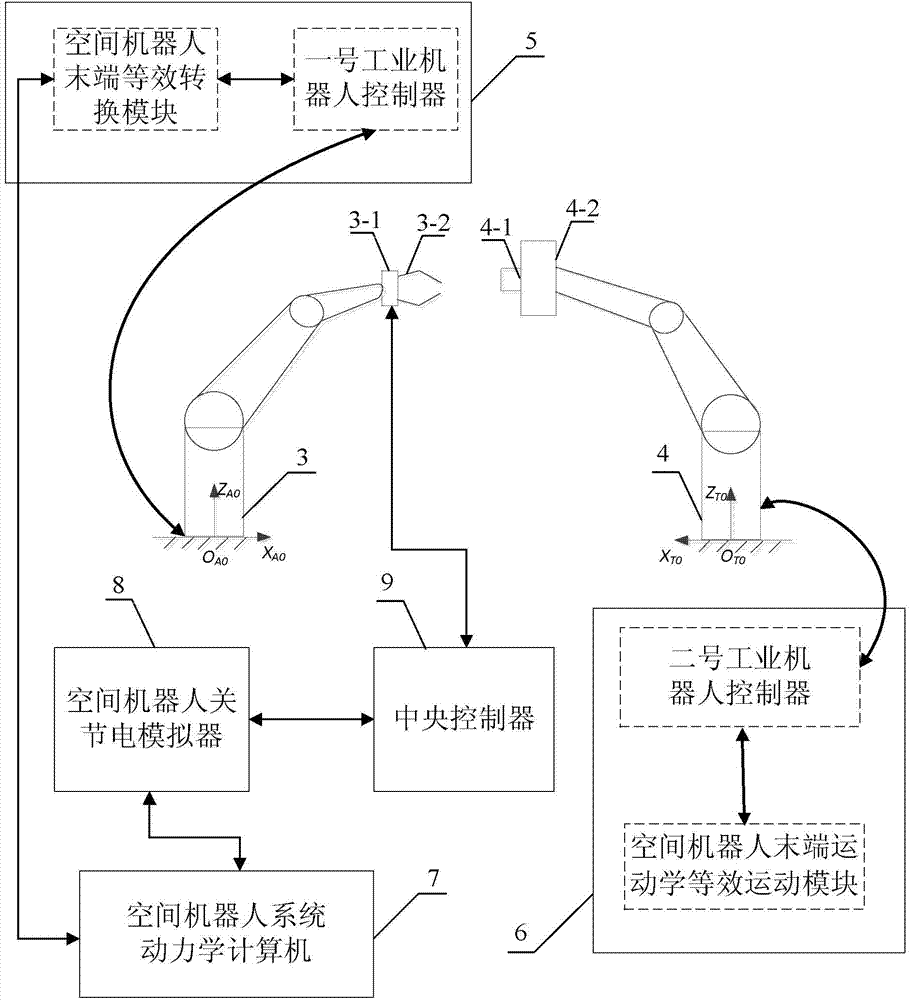
ActiveCN103926845AVerify reliabilityVerify Contact Status VerificationSimulator controlThree-dimensional spaceGround testing
The invention provides a ground-based simulation system for a space robot visual servo to capture a moving target and a simulation method and relates to the ground verification technology that the space robot visual servo captures the moving target in space. The ground-based simulation system for the space robot visual servo to capture the moving target and the simulation method aim at solving the problem that an existing ground testing system can not simulate the situation that the space robot visual servo captures a moving target satellite in a three-dimensional space. The method includes the steps of obtaining joint movement information according to the relative pose relation between a capture paw and a capture handle, obtaining control moments of all joints according to the joint movement information, calculating base pose information and joint angle information, calculating the base pose information and the joint angle information to obtain equivalent industrial robot joint angle instructions and then controlling a first industrial robot. The ground-based simulation system can be used for simulating the process that the space robot visual servo captures the moving target in the three-dimensional space and base disturbance conditions, and verifying the reliability of a route planning algorithm of the space robot visual servo. The ground-based simulation system is applicable to ground verification of the space robot visual servo to capture the moving target.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
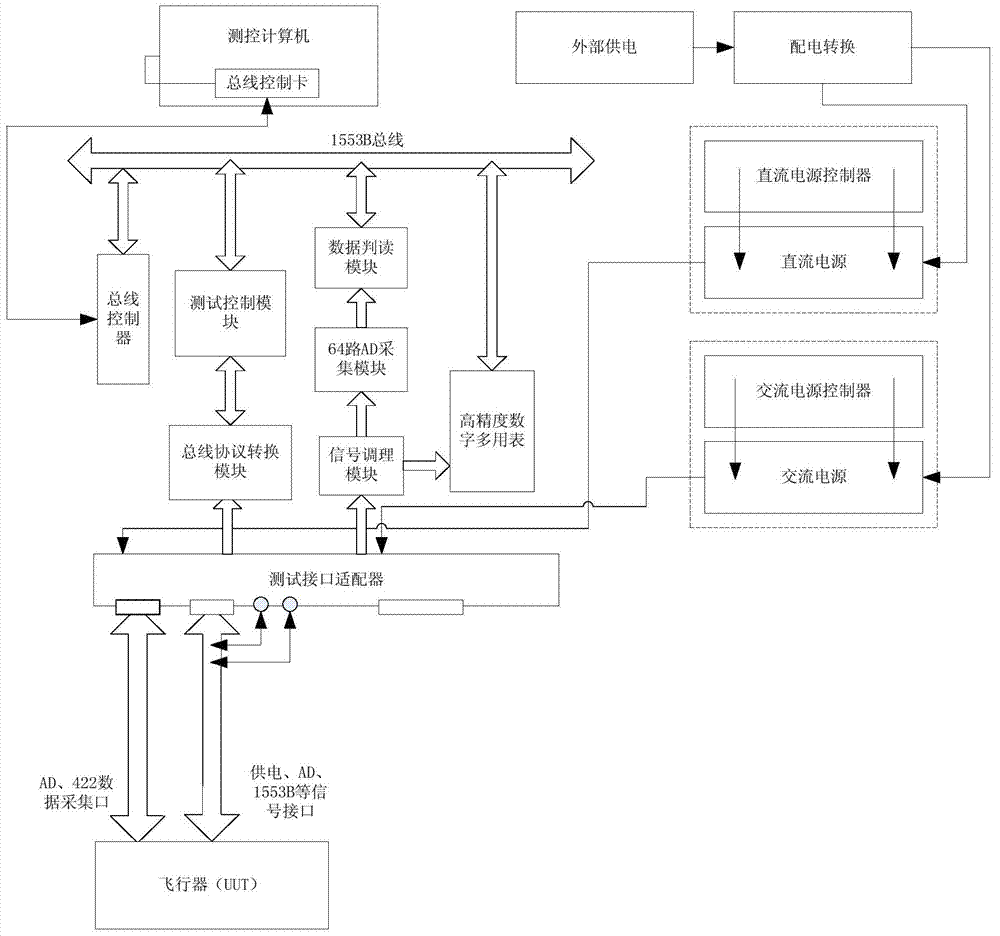
Air vehicle integrated testing system based on 1553B bus
ActiveCN103592908AAchieve high integrationAdd test functionTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlAC - Alternating currentSignal conditioning
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF LAUNCH VEHICLE TECH
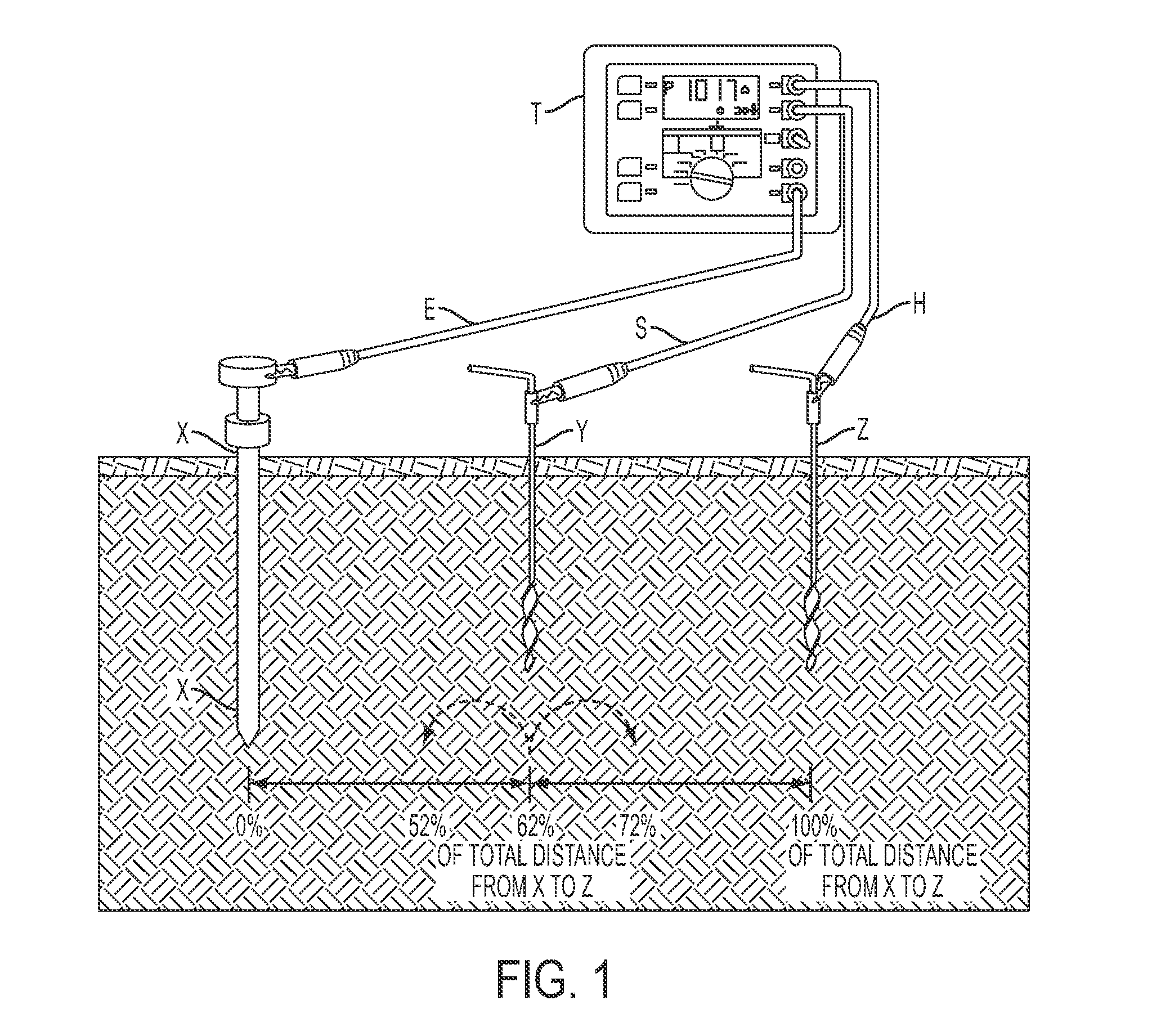
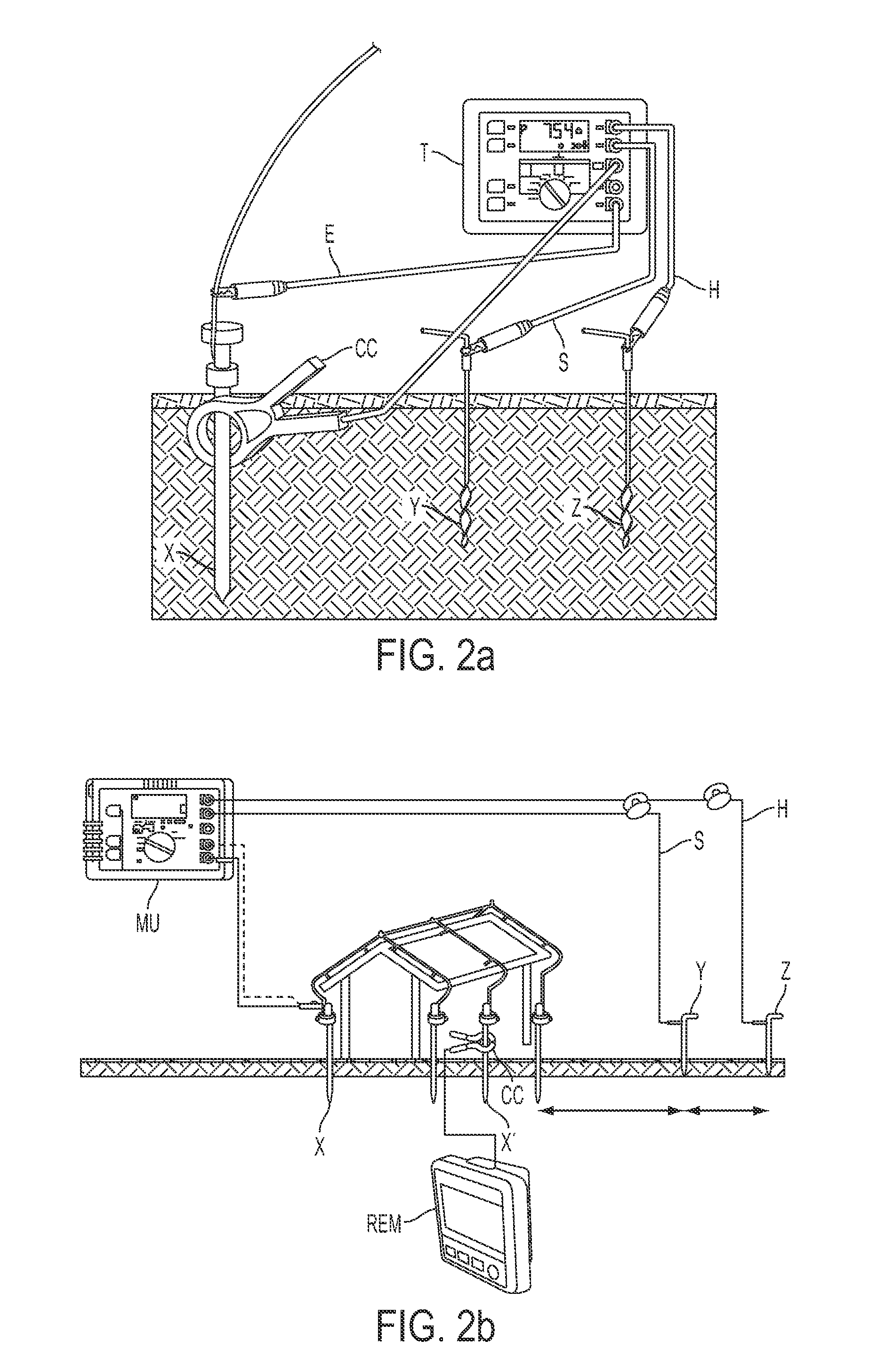
Track circuit primary parameter high-precision rapid ground measuring method and measuring apparatus thereof
InactiveCN1528629AEasy to testQuick testResistance/reactance/impedenceVehicle route interaction devicesReal-time clockExternal storage
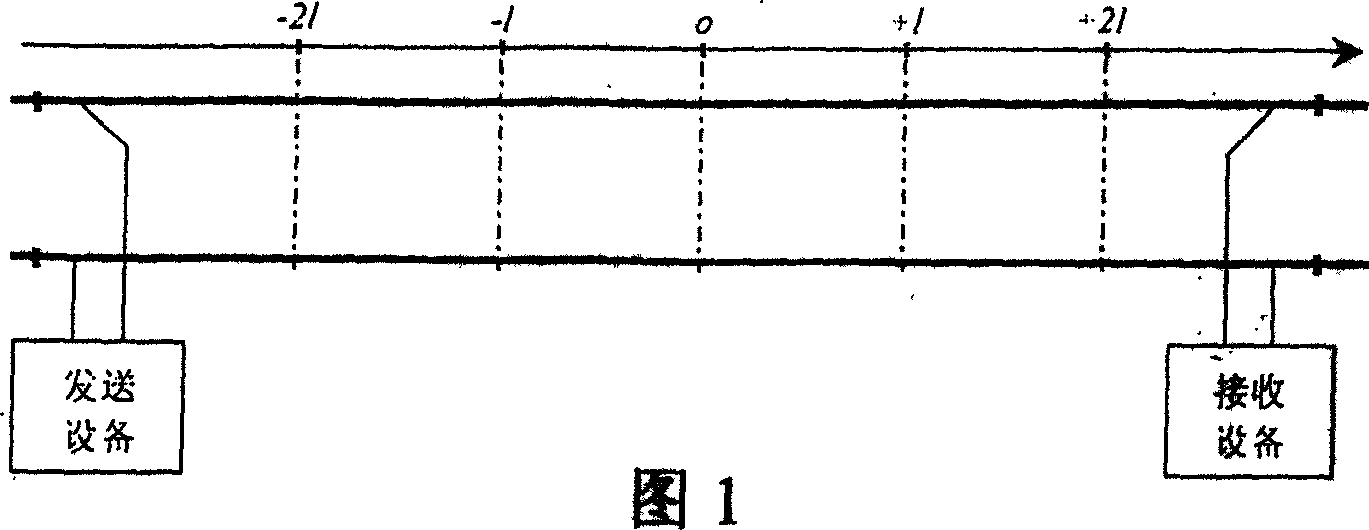
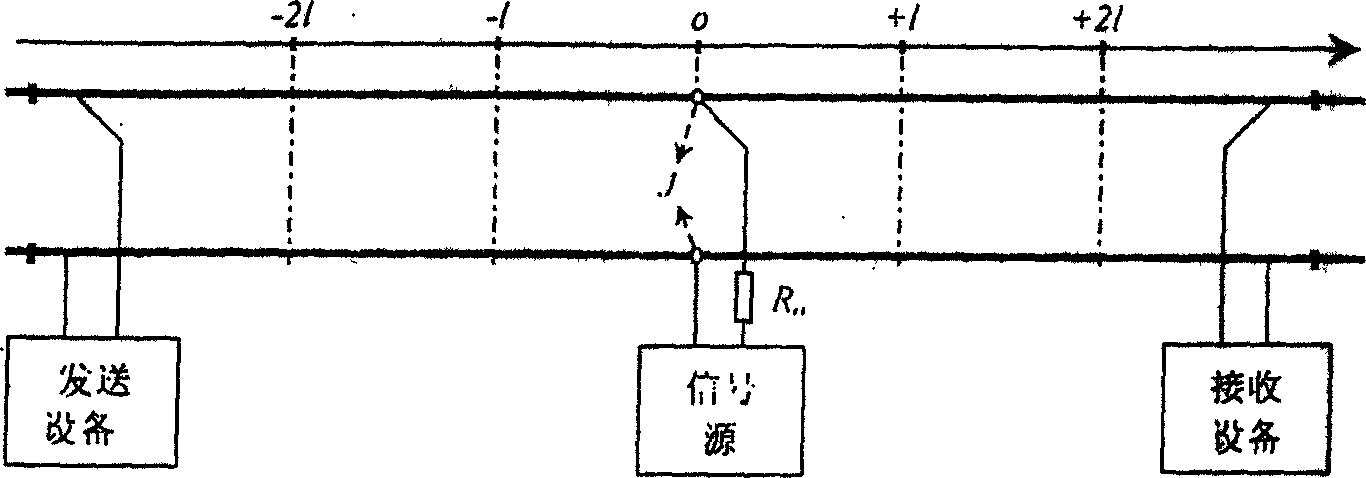
The invention relates to a rail-circuit primary-parameter high-precision quick ground testing method and device, transmitting signal between rails and adopting two-end short circuit by short circuit line to make it, during testing, only testing six scalar voltage values, and then simply calculating to obtain the rail impedance and road residue impedance of the line. The testing device includes microprocessor, analogue quantity collecting channel, signal output channel, external memory and real time clock, and man-machine interface. It is simple and practical, high-precision, and wide-applied range, and has very small effect on train working. It does not need extra protective measures.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
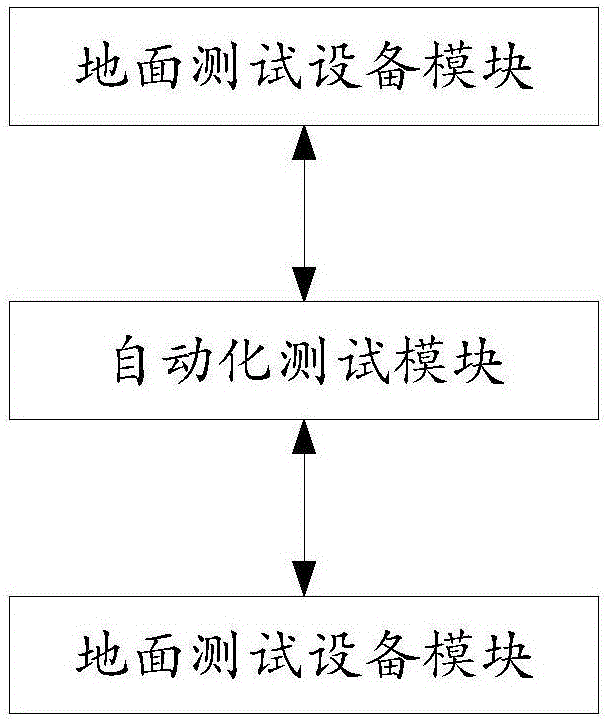
Parallel and automatic integrated testing system for satellites
ActiveCN106314825AImplement parallel designImplementAircraft components testingInformatizationCombined test
The invention relates to a parallel and automatic integrated testing system for satellites. The parallel and automatic integrated testing system comprises a ground testing equipment module, an automatic testing module and a data storage management module, wherein the data storage management module is connected with the automatic testing module through a data communication protocol for both-way communication, and the automatic testing module is connected with the ground testing equipment module through the data communication protocol for both-way communication. The parallel and automatic integrated testing system for the satellites realizes integration of integrated testing management, design, implementation and application for the satellites, improves the systematization, informatization and automation of satellite testing work, and can effectively increase the testing efficiency, effectively control quality risks in a testing process, increase the application analysis value of testing data and realize substantial saving of labor cost and management cost. The system is quite applicable to batch satellite testing, and parallel design and implementation on various layers of the integrated testing system for the satellites are realized.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG DEV LTD
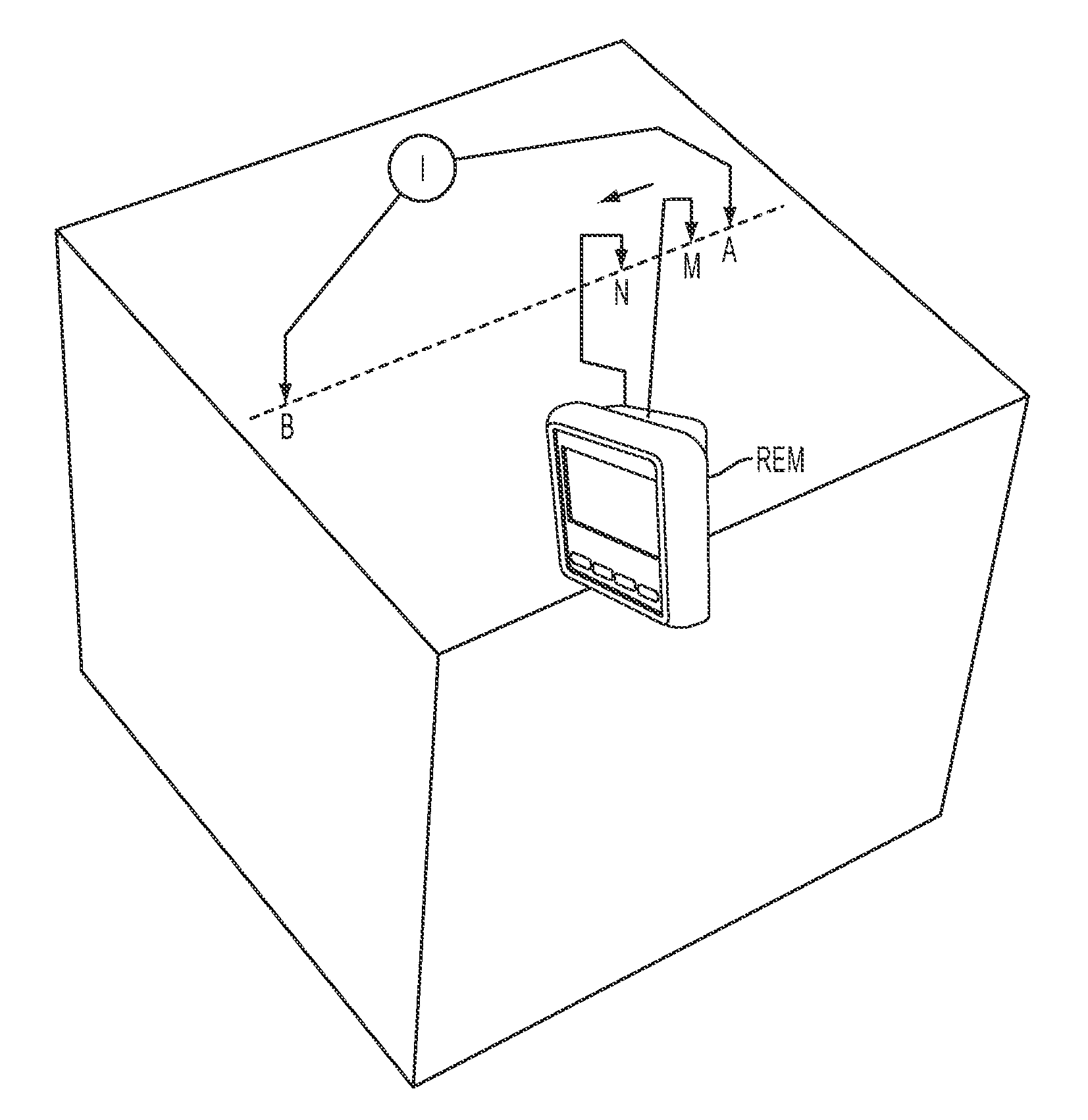
Earth ground tester with remote control
ActiveUS8390299B2Optimize dataElectronic circuit testingEarth resistance measurementsTelecommunications linkDisplay device
A testing device which may be used to conduct ground resistance and soil resistivity measurements. The testing device comprises both a main unit and a remote unit adapted to communicate with one another via a communication link. After setting the testing device up according to the desired measurement technique, the procedure may be carried out, and the resulting measurement values are subsequently displayed on the remote unit. This allows a single operator to perform measurements while standing directly adjacent to an electrode, which is, for example, placed at a large distance from the main unit and / or other electrodes. This relieves the operator from constantly having to walk back and forth placing electrodes in different positions, and also obviates the need to return to the main unit of the testing device to consult a display and / or change parameters or settings.
Owner:JOHN FLUKE MFG CO INC
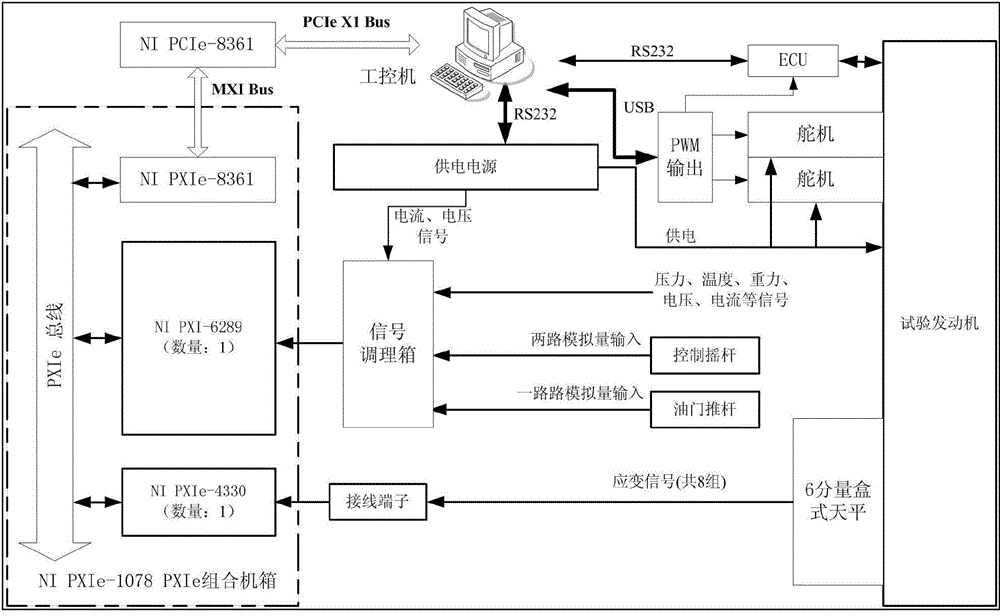
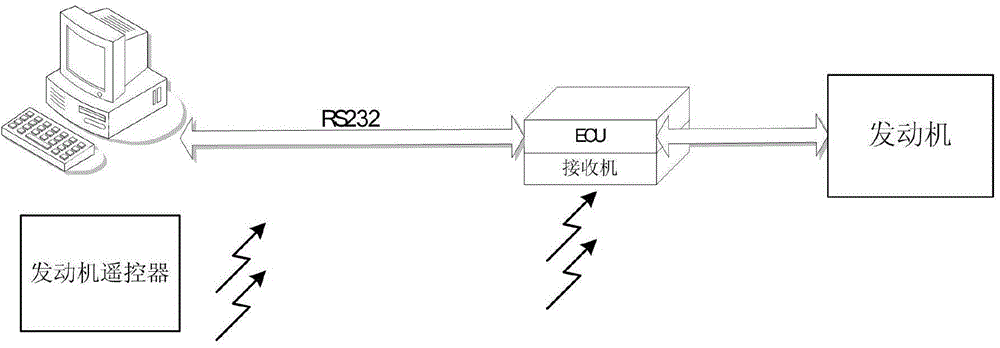
Miniature turbojet aero-engine ground measurement and control system
The invention discloses a miniature turbojet aero-engine ground measurement and control system. An engine has an electrical control unit, the tail of the engine is provided with an exhaust nozzle, the system includes an industrial control computer connected to the electrical control unit; and a data acquisition unit which includes a wind tunnel strain balance arranged under an engine base and a first data acquisition card which collects and measures balance signals of the wind tunnel strain balance which are generated when the engine rotates, and also includes two control rockers and a second data acquisition card which collects and measures two paths of voltage output signals of the two control rockers which are generated at current positions, wherein the first data acquisition card and the second data acquisition card are in communication connection with the industrial control computer; and an execution unit which includes two steering engines and a steering engine control module, wherein the two steering engines are connected to the exhaust nozzle, and the engine control module is connected to the industrial control computer. The system provided by the invention can comprehensively satisfy ground testing, rotating speed control and exhaust nozzle angle control of a miniature turbojet aero-engine.
Owner:SICHUAN MULTI IDEA M&C TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com