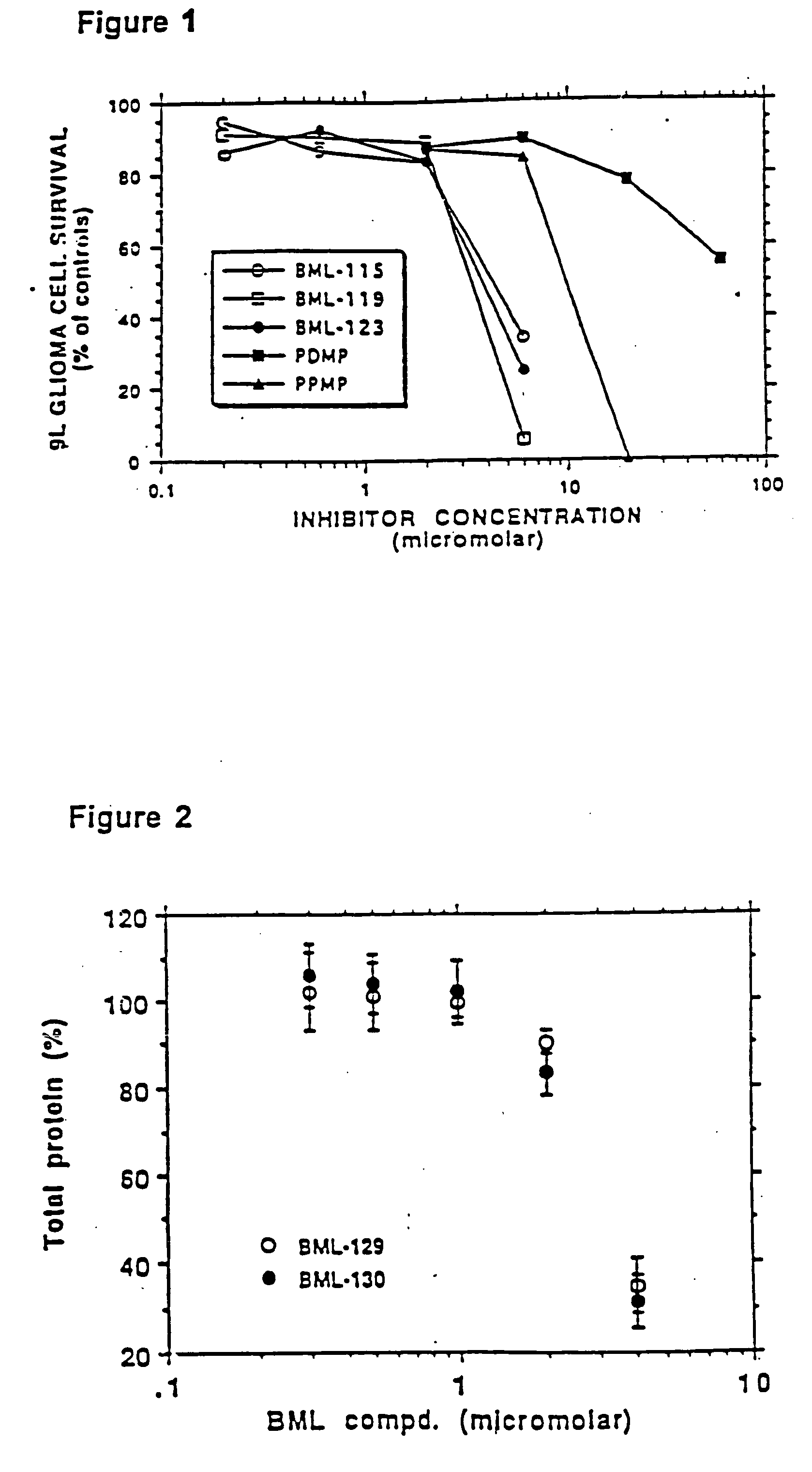
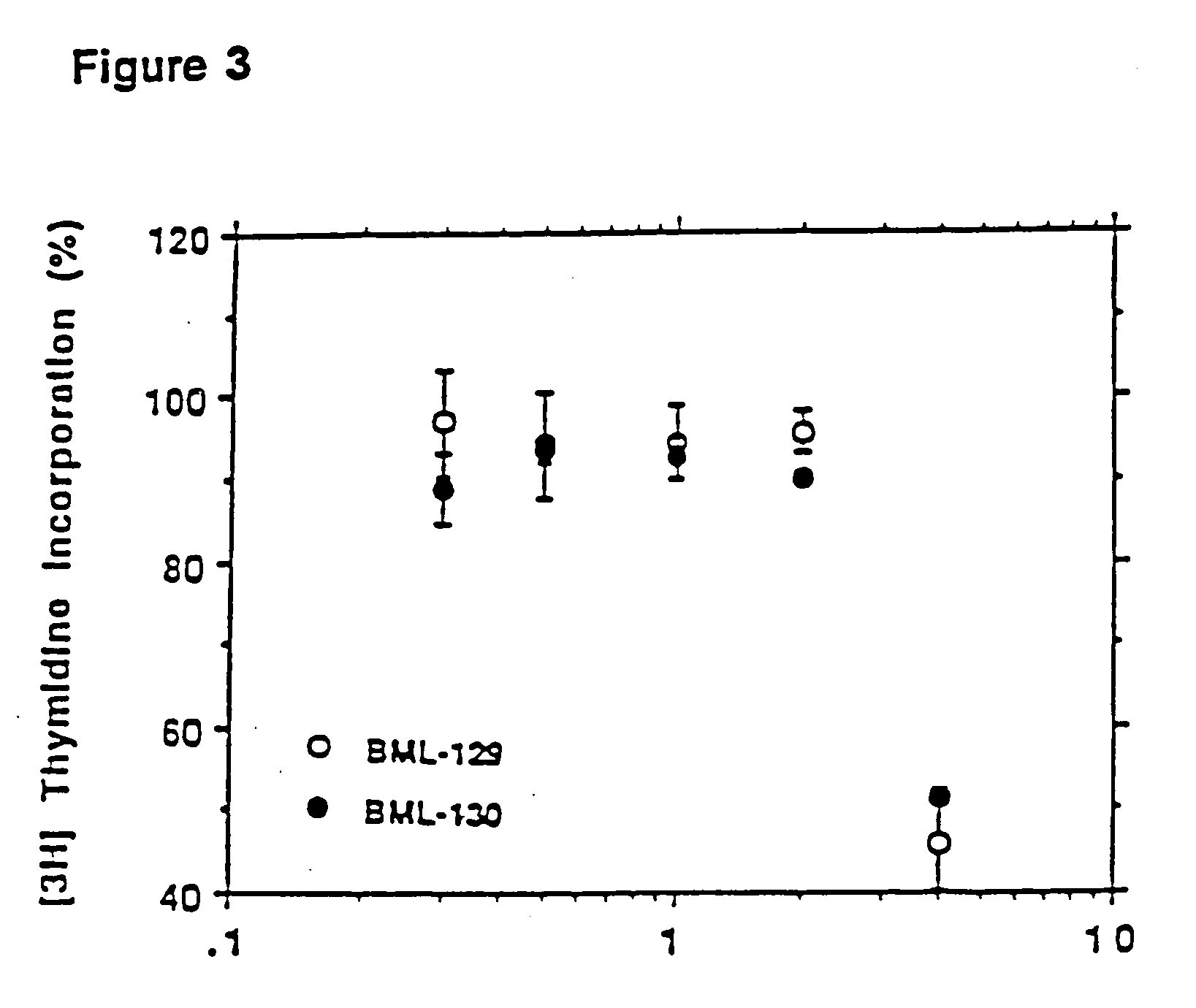
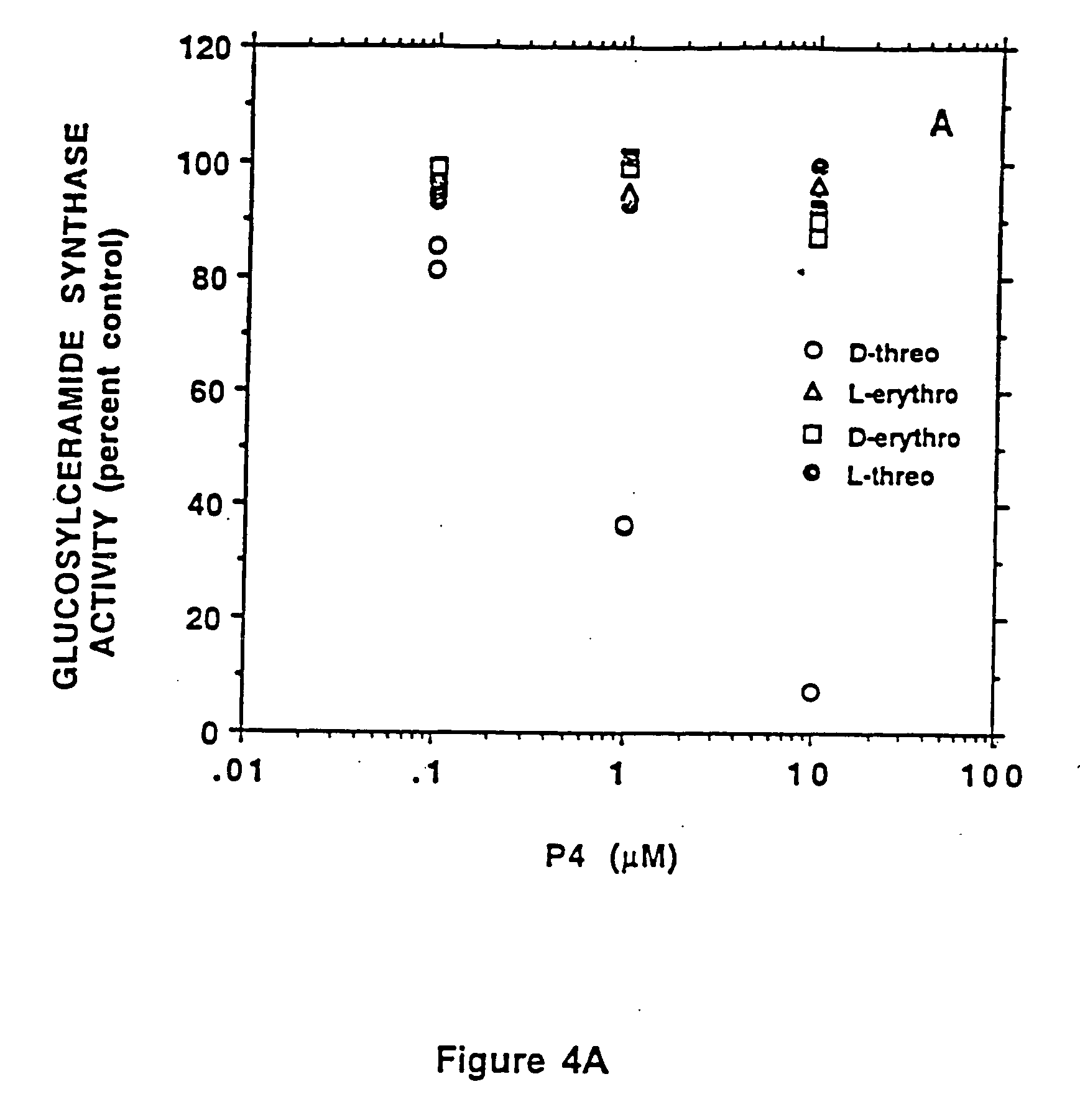
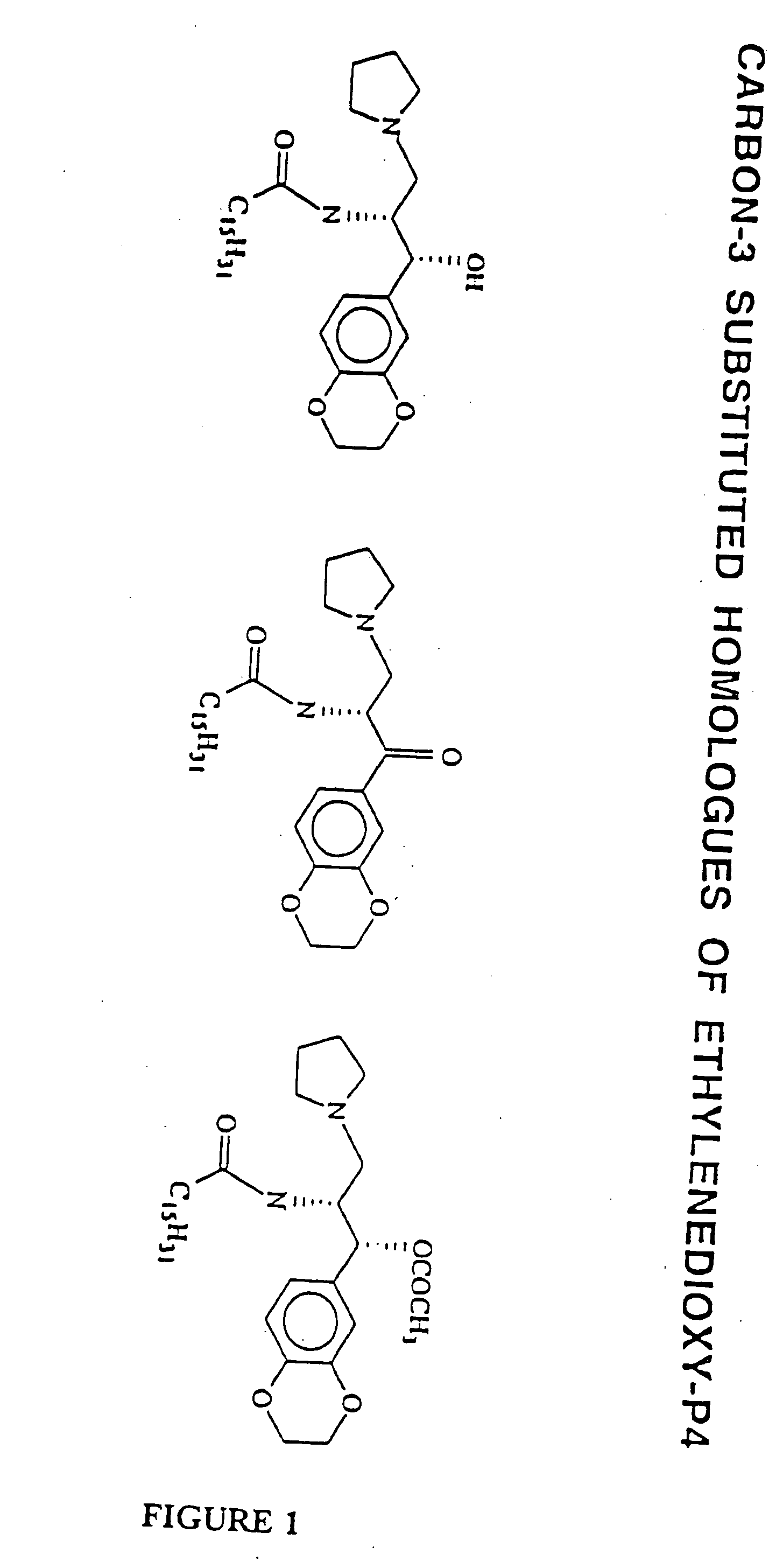
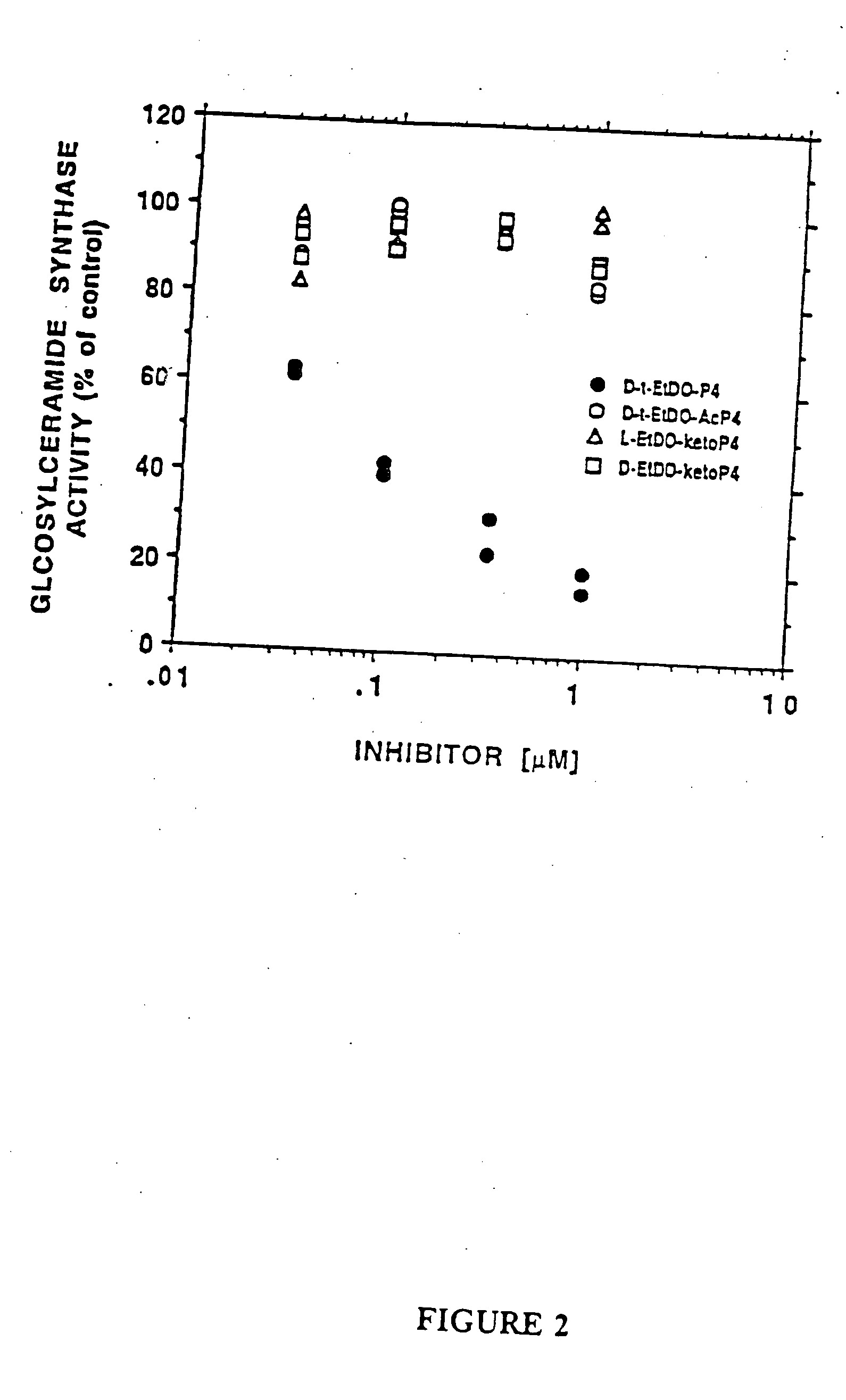
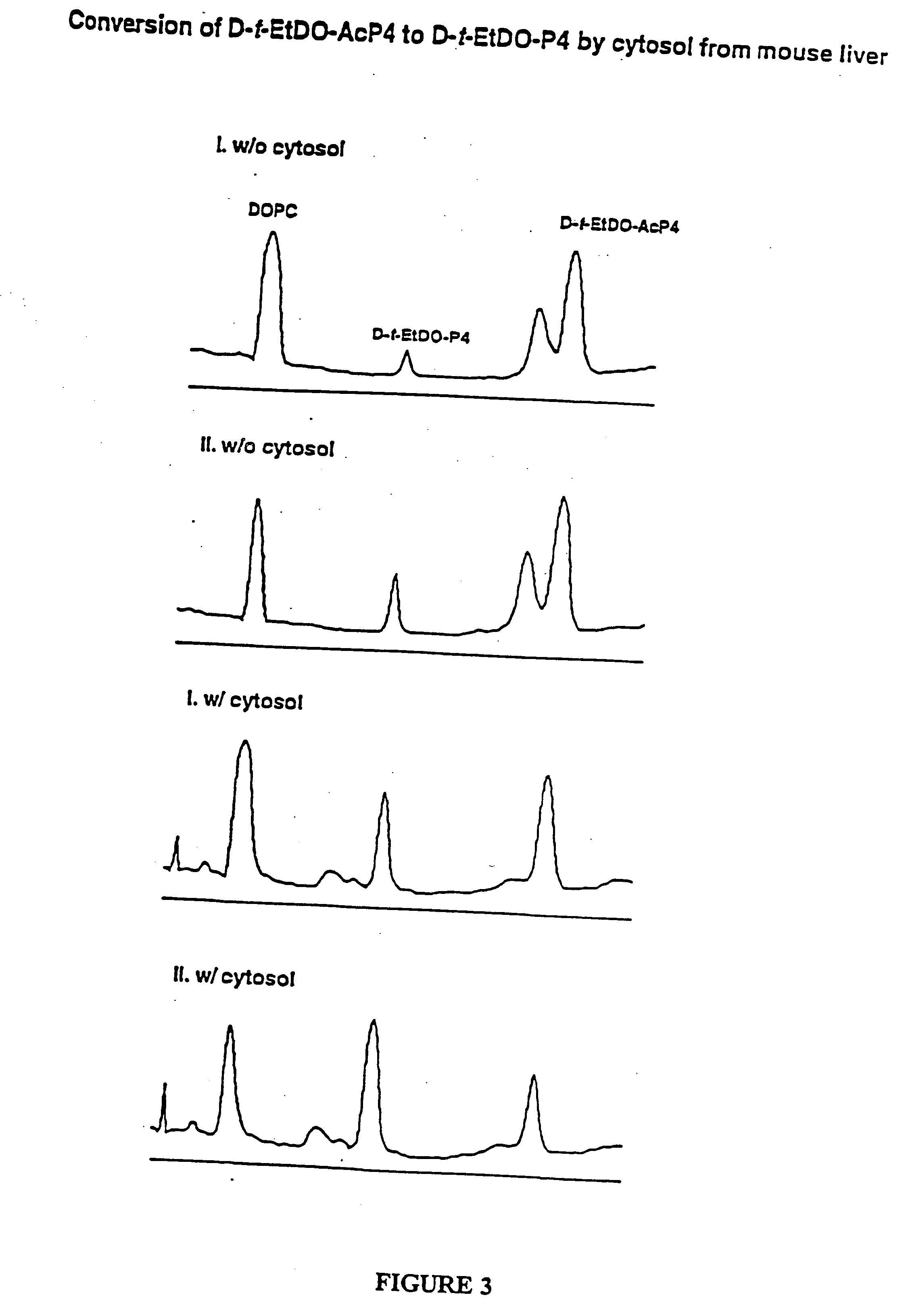
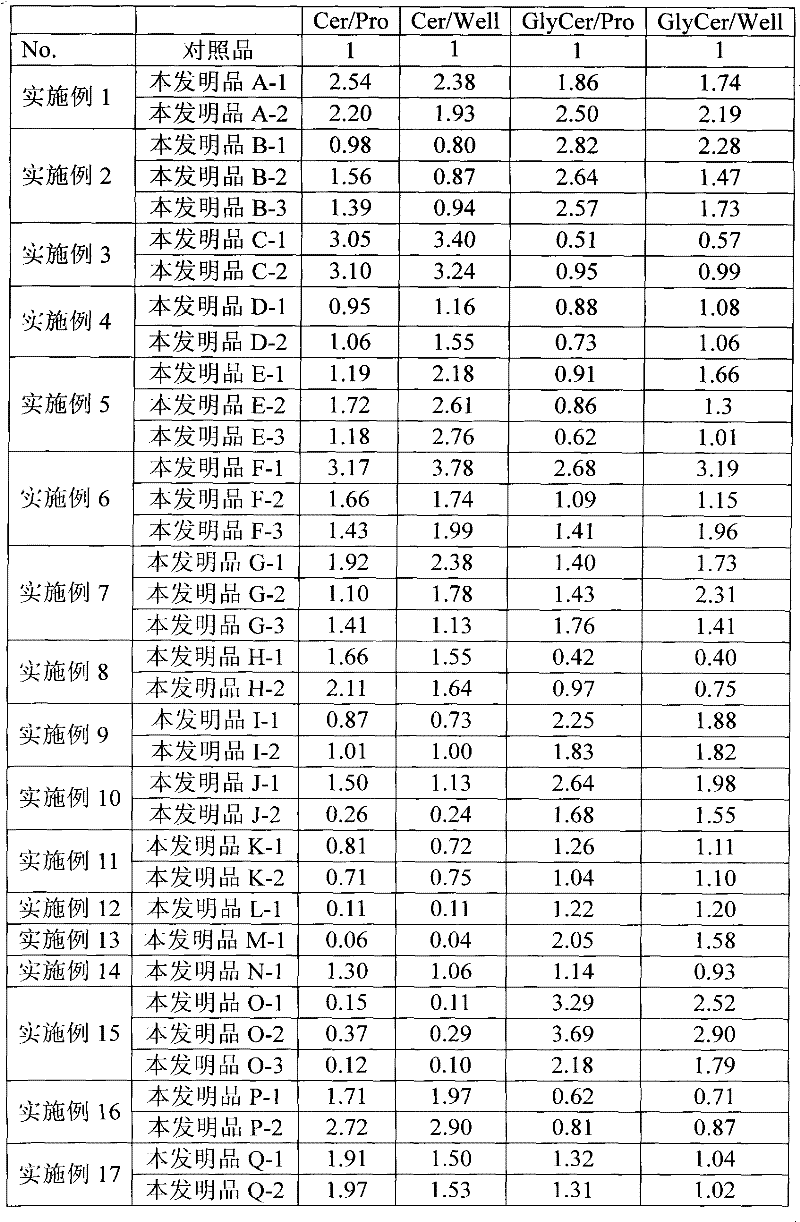
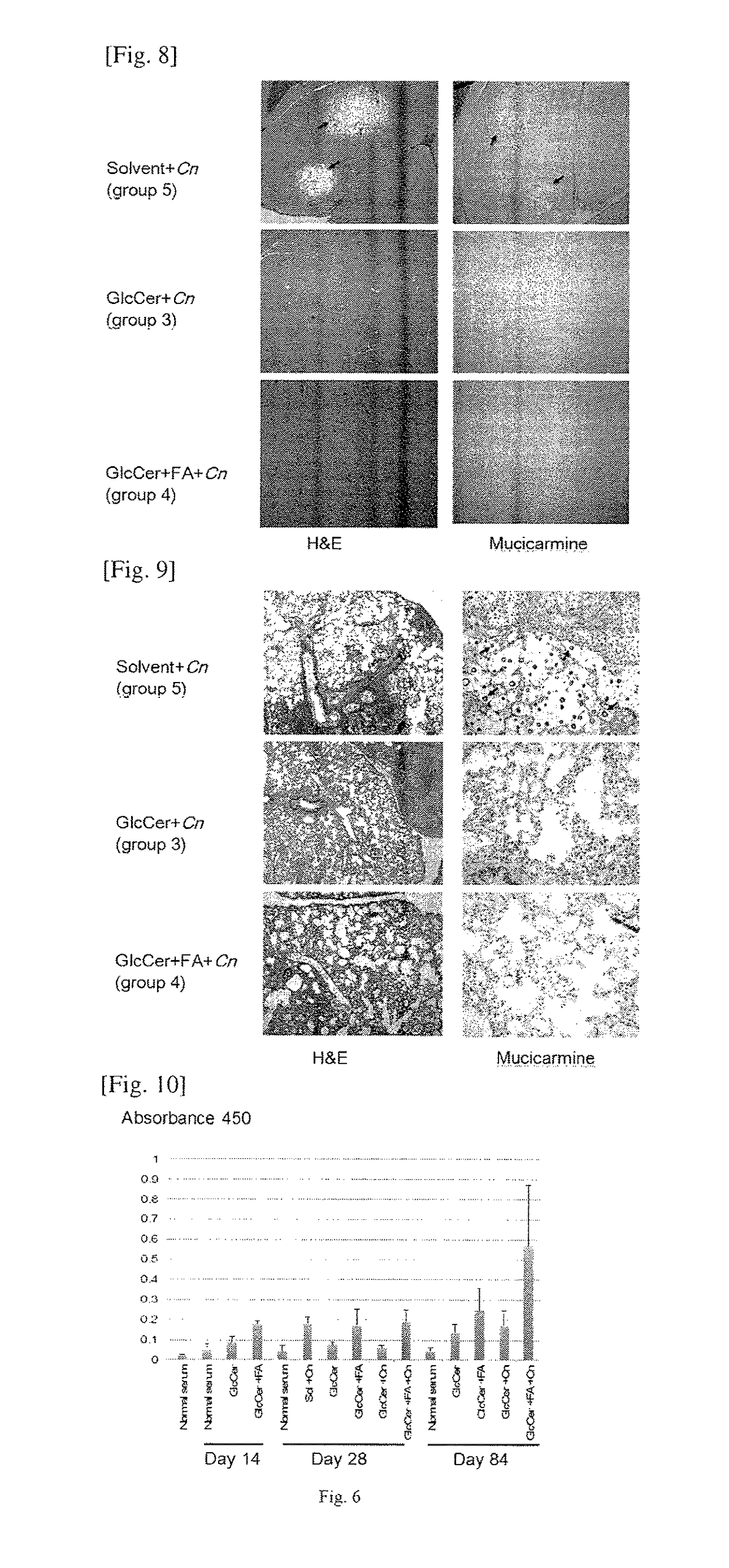
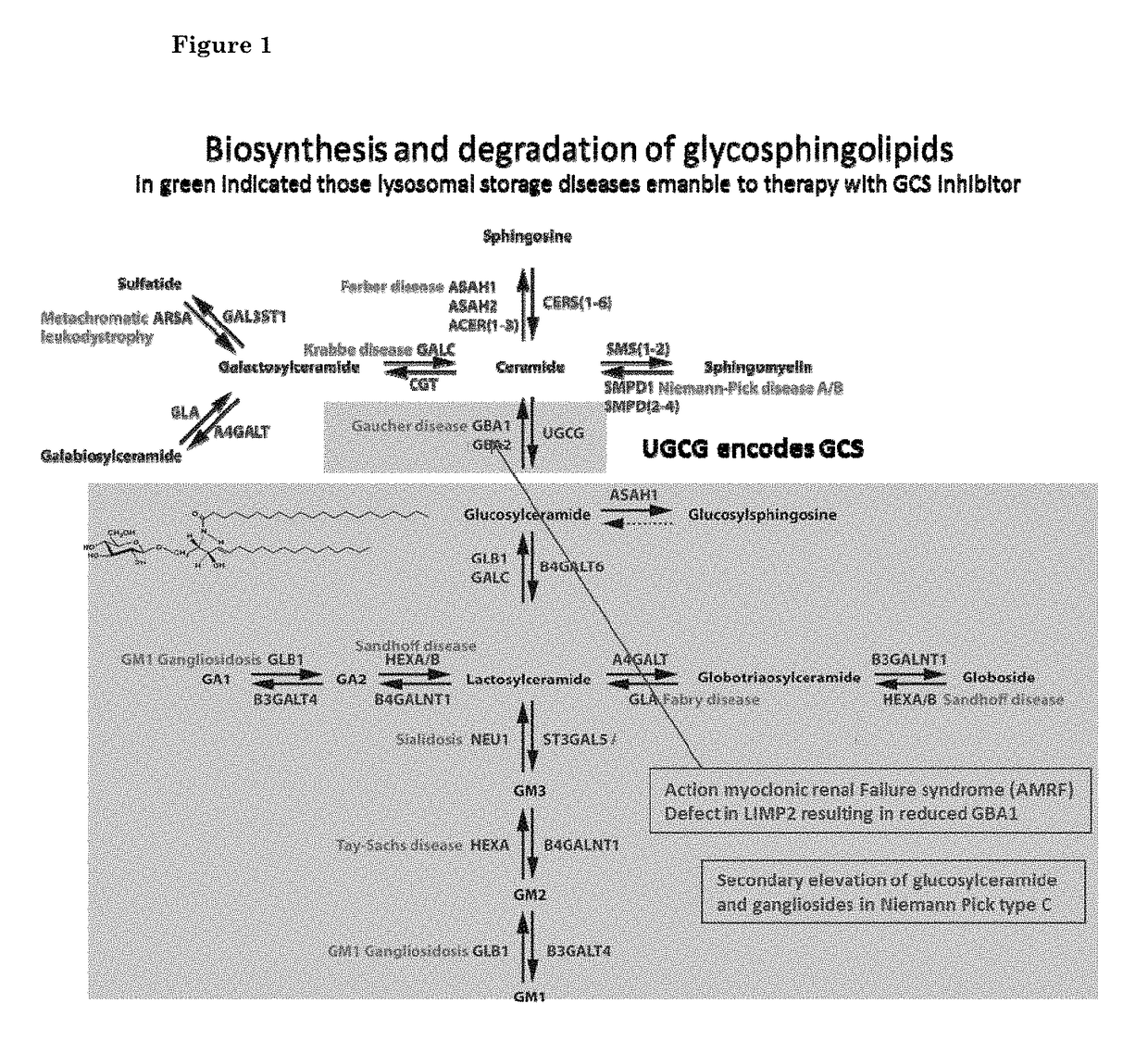
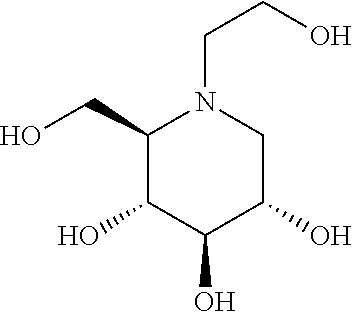
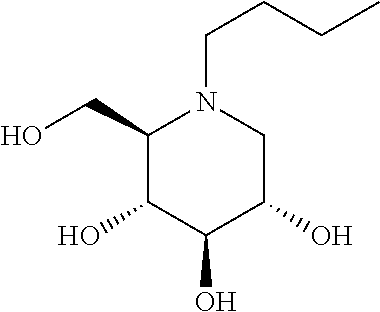
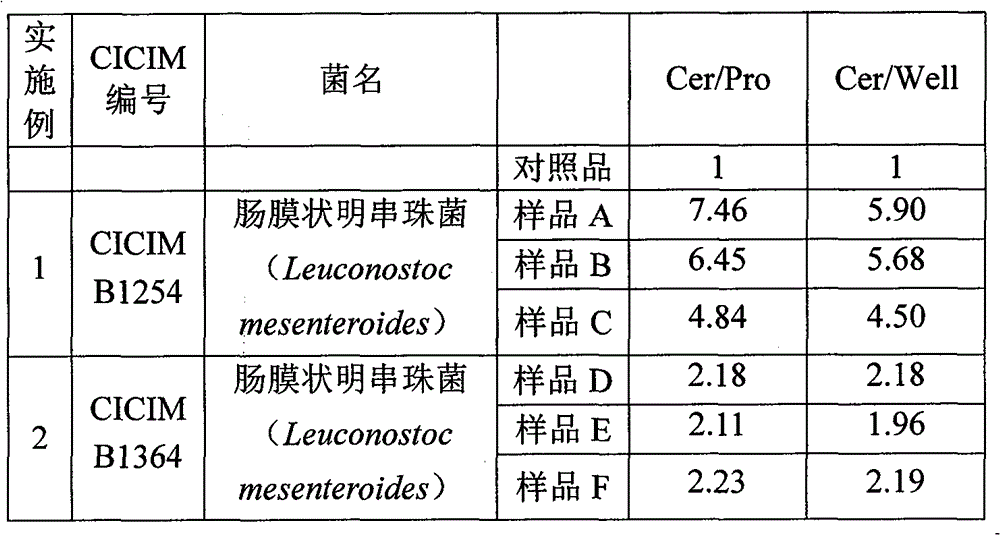
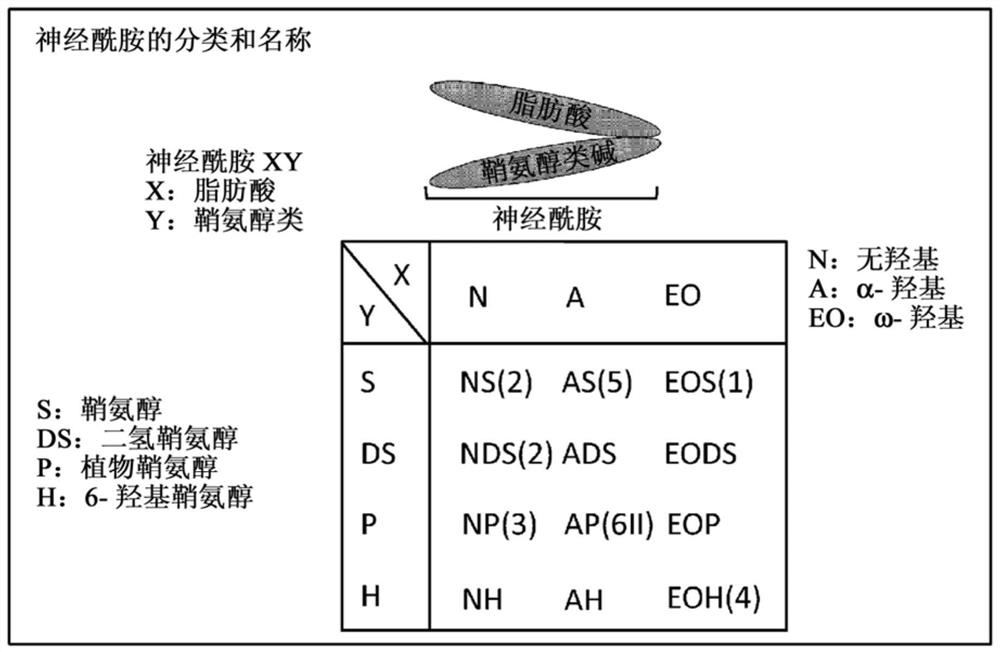
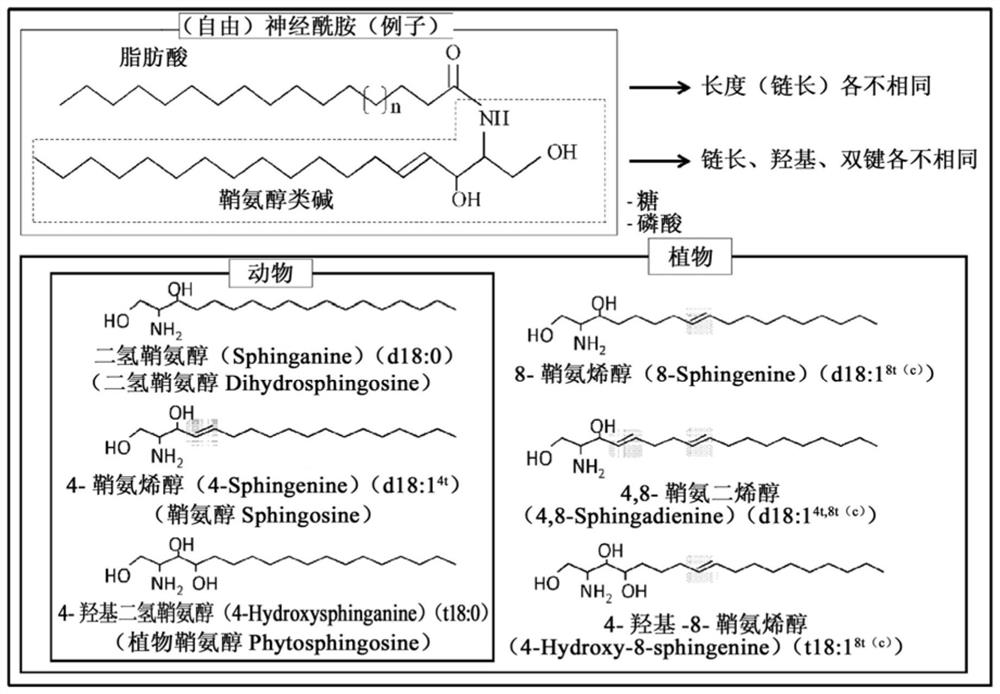
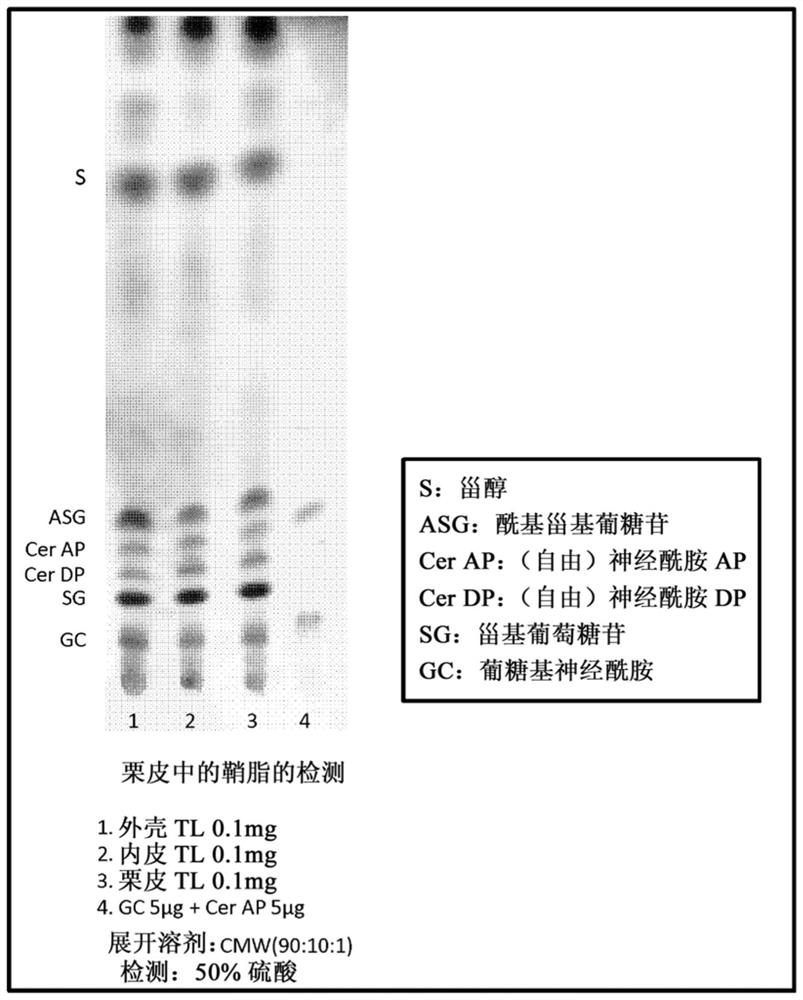
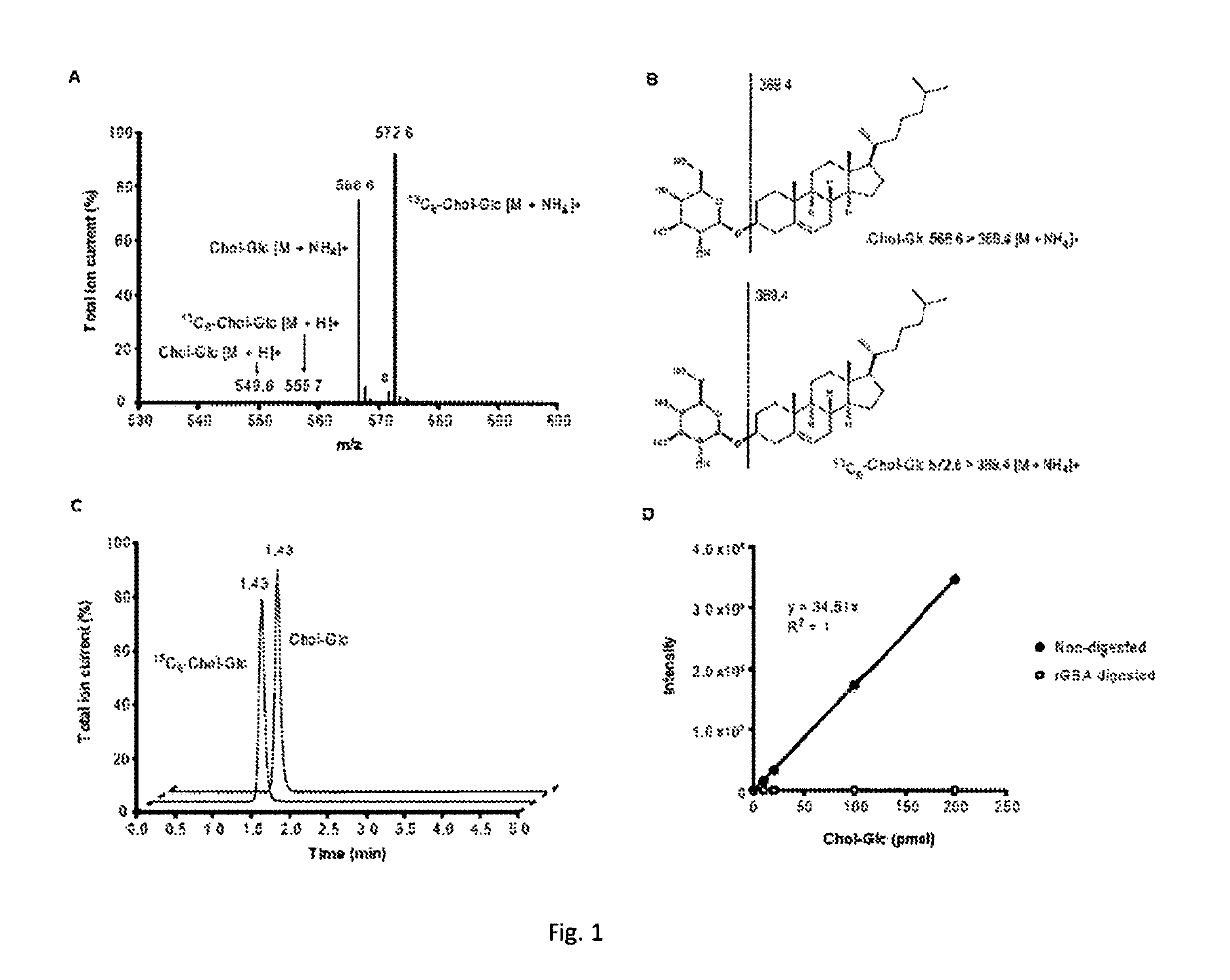
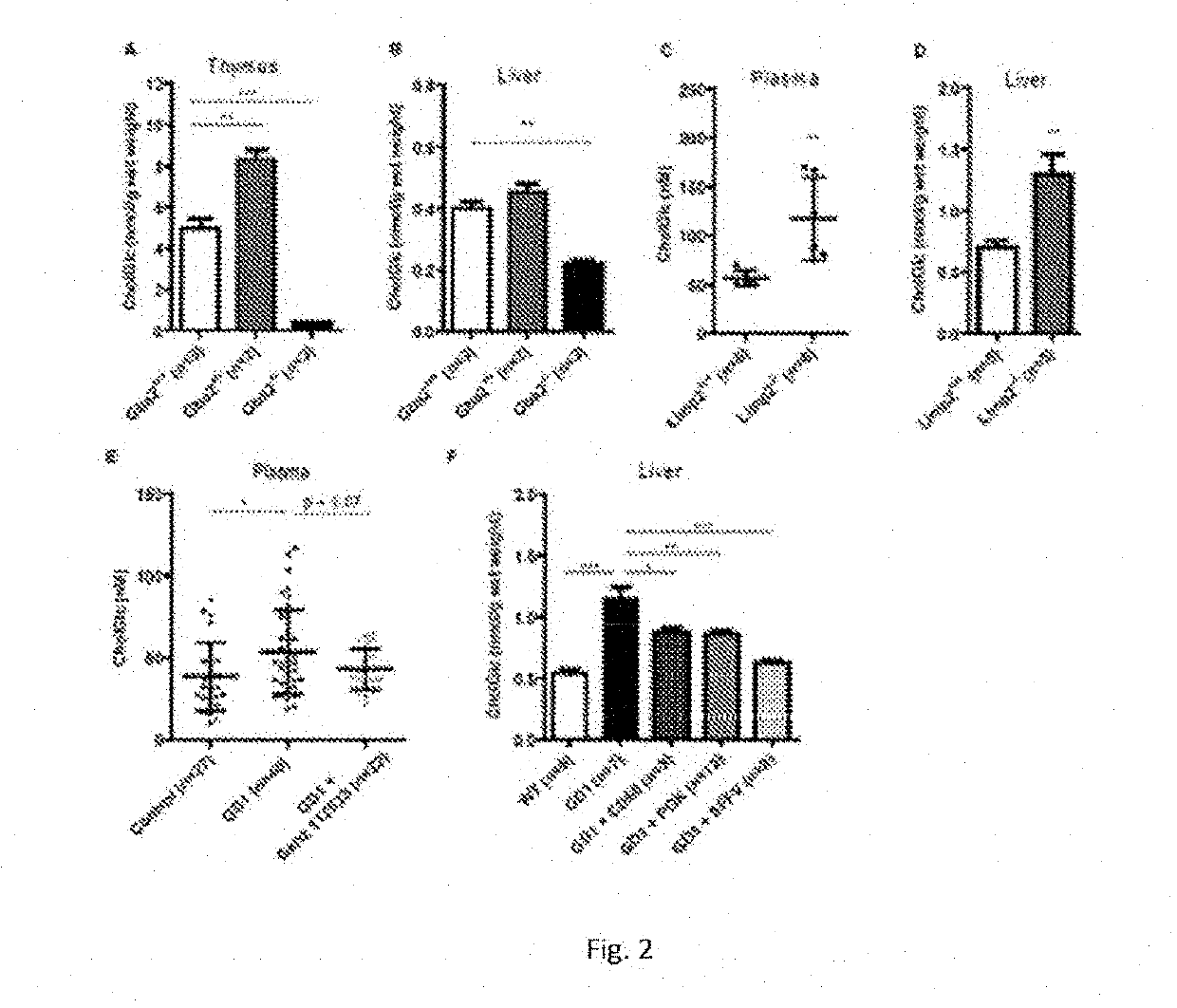
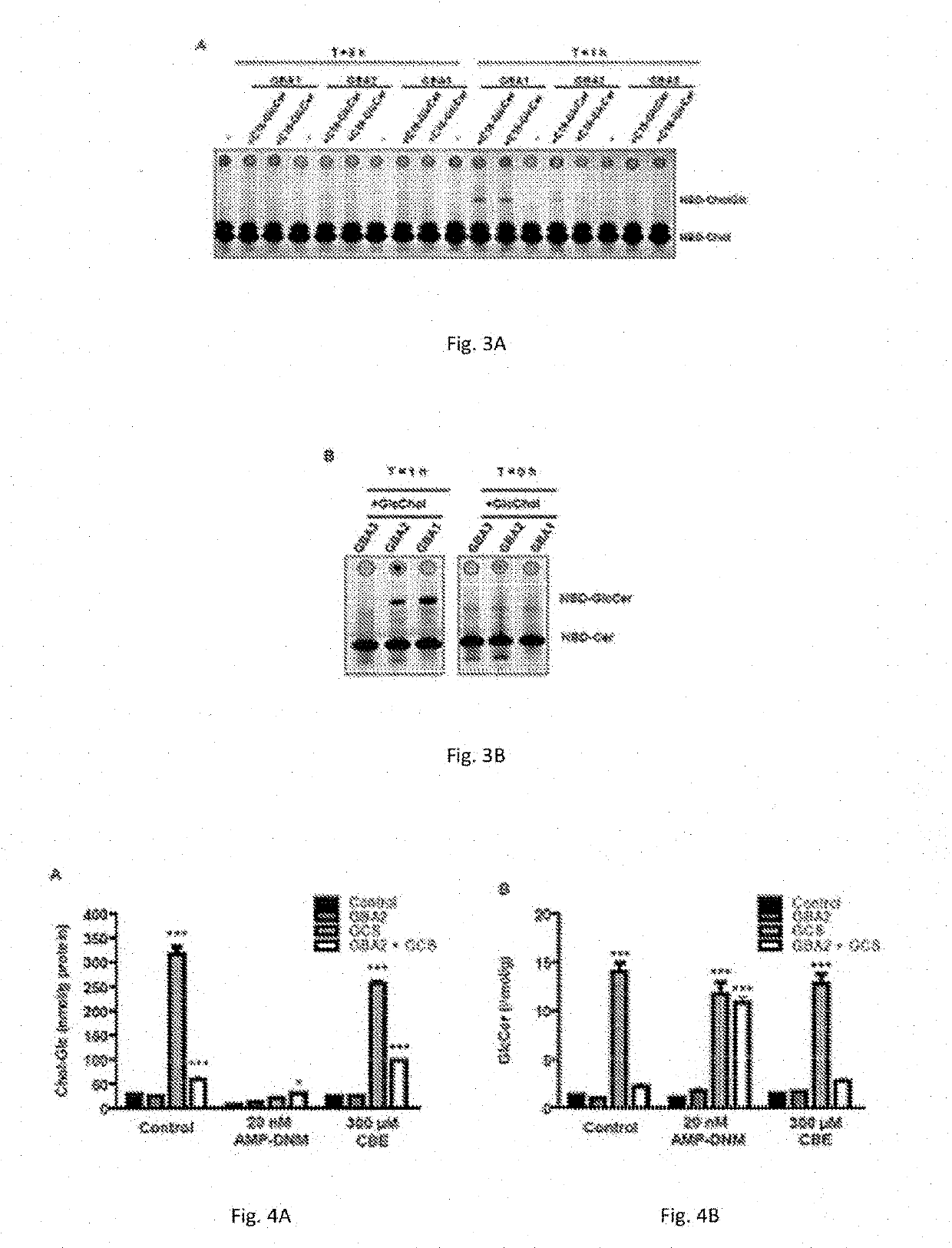
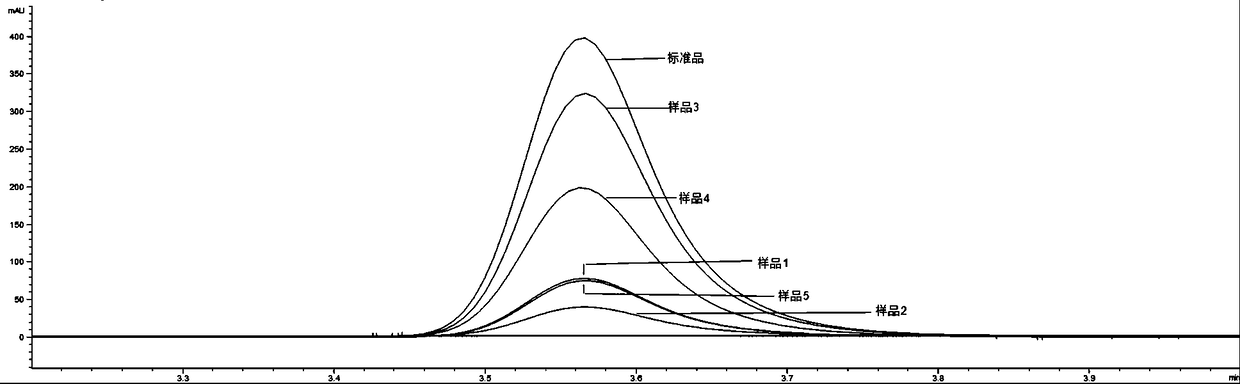
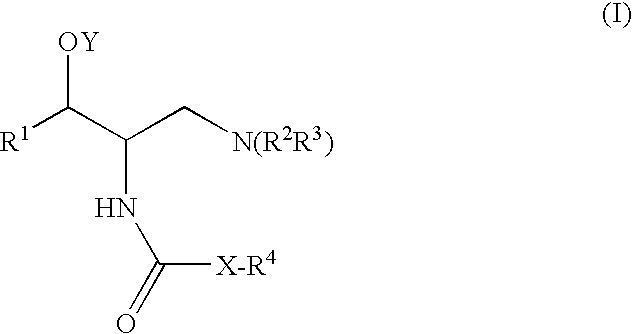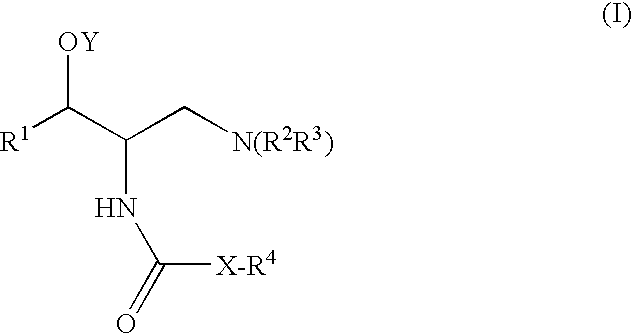Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Glucosylceramides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
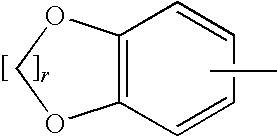
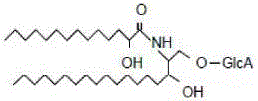
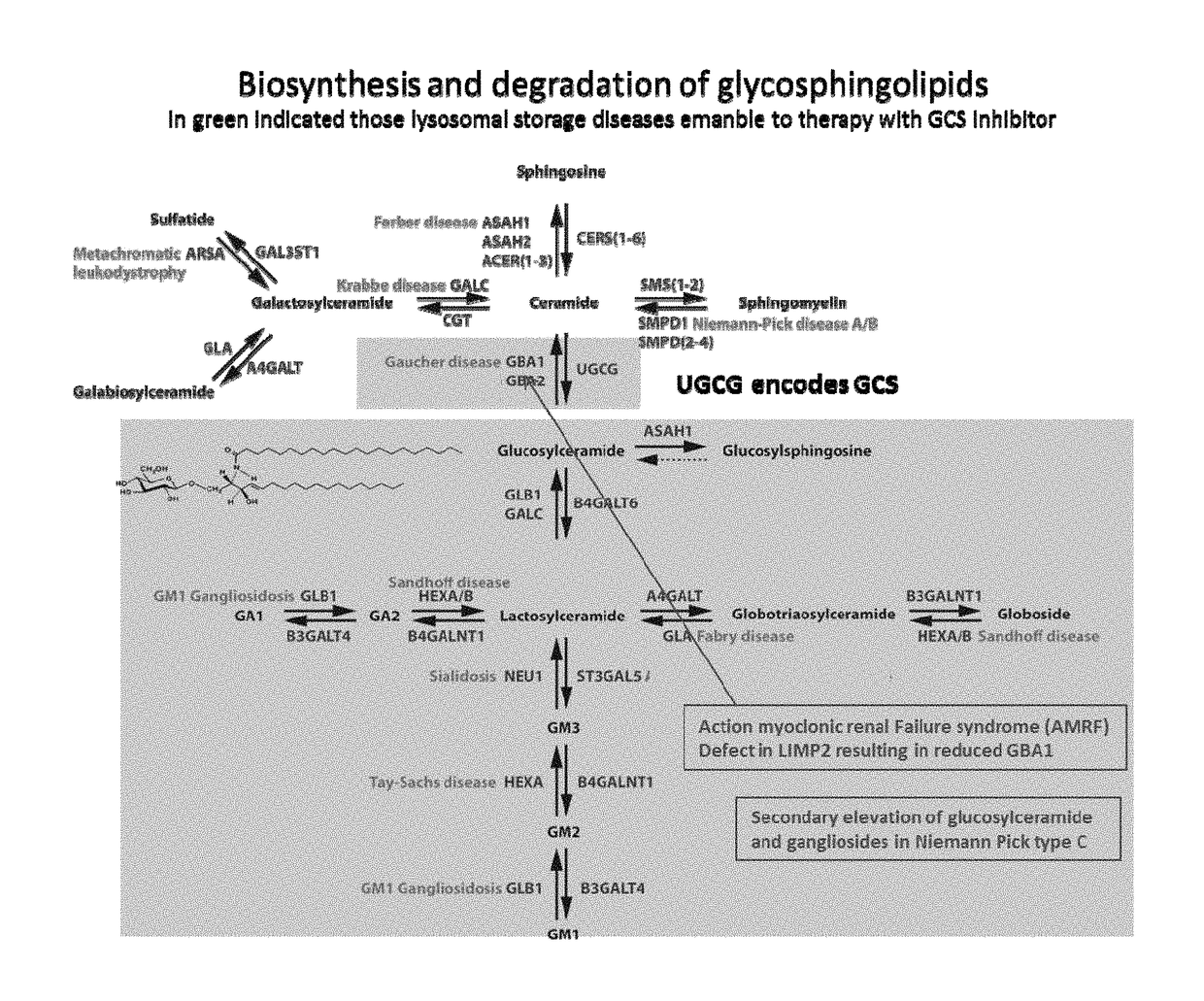
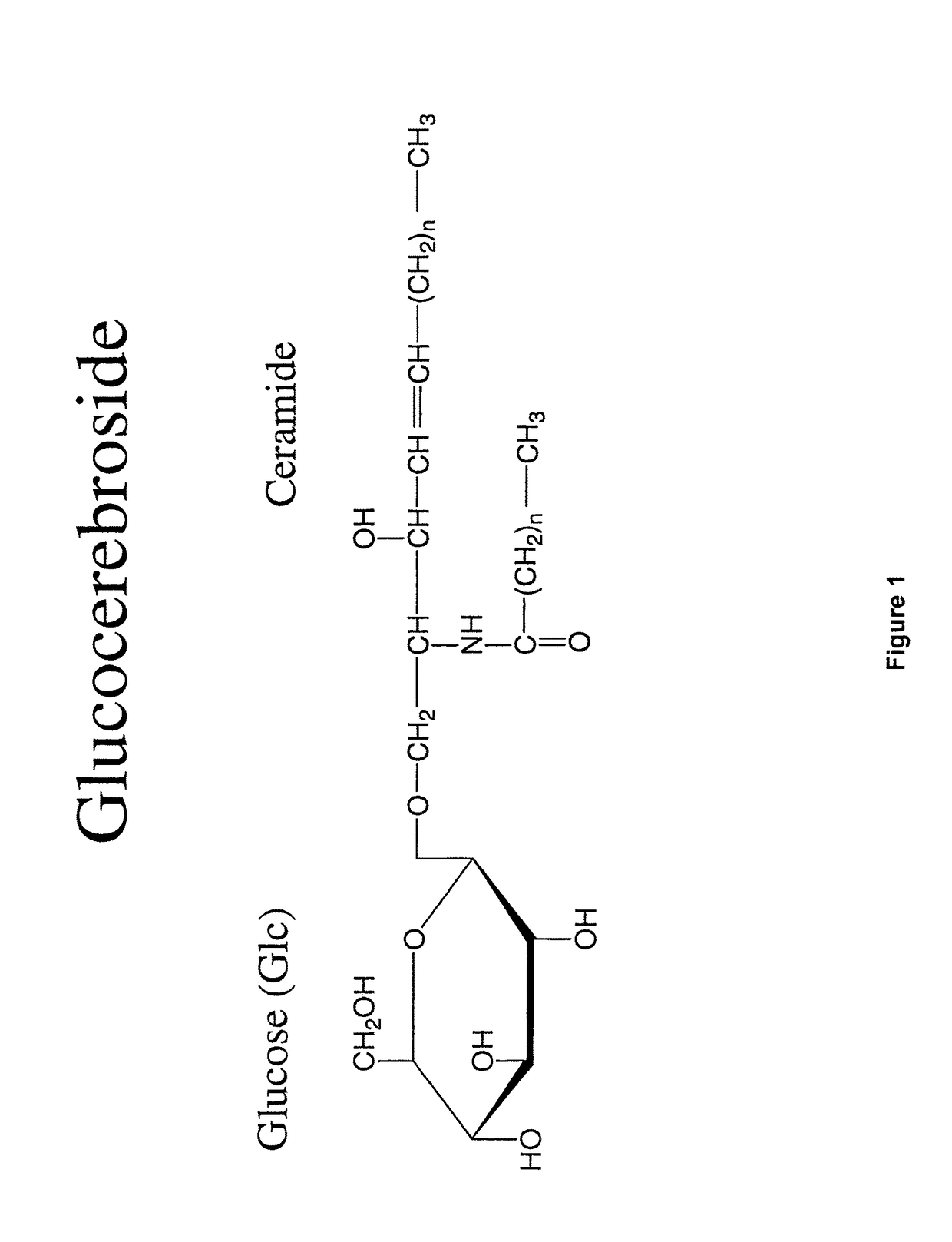
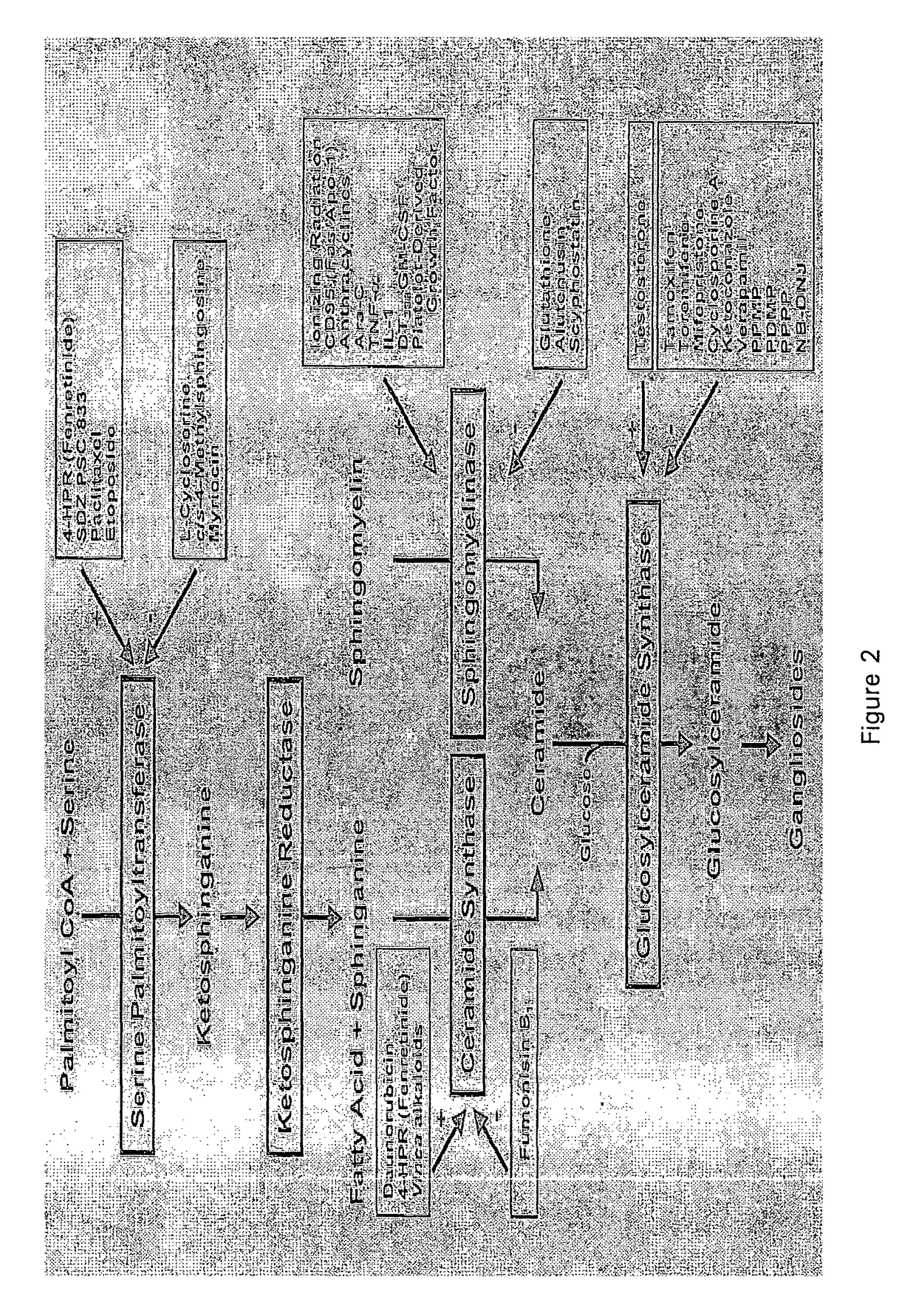
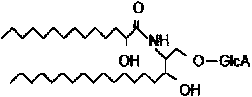
Cerebrosides which contain as their polar head group a glucose moiety bound in glycosidic linkage to the hydroxyl group of ceramides. Their accumulation in tissue, due to a defect in beta-glucosidase, is the cause of Gaucher's disease.
Amino ceramide-like compounds and therapeutic methods of use
InactiveUS20050049235A1Lower Level RequirementsSolve low usageAntibacterial agentsBiocideGlycosphingolipidGlcCer synthase
The present invention provides amino ceramide-like compounds which inhibit glucosyl ceramide (GlyCer) formation by inhibiting the enzyme GlyCer synthase, thereby lowering the level of glycosphingolipids. The compounds of the present invention have improved GlcCer synthase inhibition activity and are therefore useful in therapeutic methods for treating various conditions and diseases associated with altered glycosphingolipid levels.
Owner:GENZYME CORP +1
Amino ceramide-like compounds and therapeutic methods of use
InactiveUS20060217560A1Lower Level RequirementsImprove concentrationOrganic chemistryGlycosphingolipidGlycolipid
Novel prodrugs of amino ceramide-like compounds are provided which inhibit glucosyl ceramide (GlcCer) formation by inhibiting the enzyme GlcCer synthase, thereby lowering the level of glycosphingolipids. The compounds of the present invention have improved GlcCer synthase inhibition activity and are therefore highly useful in therapeutic methods for treating various conditions and diseases associated with altered glycosphingolipid levels.
Owner:SHAYMAN JAMES A
2-acylaminopropoanol-type glucosylceramide synthase inhibitors
InactiveUS20100256216A1High metabolic stabilityInhibit synthesisBiocideOrganic chemistryStructural formulaGlycolipid
A compound is represented by Structural Formula (I): or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. A pharmaceutical composition comprises a compound represented by Structural Formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. A method of treating a subject in need thereof comprises administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a compound represented by Structural Formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The subject has type 2 diabetes; renal hypertrophy or hyperplasia associated with diabetic nephropathy; Tay-Sachs; Gaucher's; or Fabry's disease. Methods of decreasing plasma TNF-α, lowering blood glucose levels, decreasing glycated hemoglobin levels, inhibiting glucosylceramide synthase, and lowering glycosphingolipid concentrations in a subject in need thereof respectively comprise administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a compound represented by Structural Formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Amino ceramide-like compounds and therapeutic methods of use
InactiveUS20050239862A1Lower Level RequirementsSolve low usageBiocideOrganic chemistryGlycosphingolipidCompound (substance)
Novel amino ceramide-like compounds (1) are provided which inhibit glucosyl ceramide (GlcCer) formation by inhibiting the enzyme GlcCer synthase, thereby lowering the level of glycosphingolipids. The compounds of the present invention have improved GlcCer synthase inhibition activity and are therefore highly useful in therapeutic methods for treating various conditions and diseases associated with altered glycosphingolipid levels.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Pharmaceutical formulations employing short-chain sphingolipids and their use
This invention pertains to pharmaceutical formulations which comprise (i) a drug (e.g., an amphiphilic drug) (e.g., an anthracycline) (e.g., doxorubicin) and (ii) a short-chain sphingolipid (e.g., a short-chain glycosphingolipid or a short-chain sphingomyelin) (e.g., N-octanoyl-glucosylceramide, referred to as C8-GlcCer) (e.g., N-hexanoyl-sphingomyelin, referred to herein as C6-SM), and which provide improved drug delivery and efficacy. The short-chain sphingolipidis selected from compounds of the following formula: wherein: R1 is independently: an O-linked saccharide group; or an O-linked polyhydric alcohol group; or: R1 is independently: an O-linked (optionally N-(C1-4alkyl)-substituted amino)-C1-6alkyl-phosphate group; or an O-linked (polyhydric alcohol-substituted)-C1-6alkyl-phosphate group; R2 is independently C3-9alkyl, and is independently unsubstituted or substituted; R3 is independently C7-19alkyl, and is independently unsubstituted or substituted; R4 is independently —H, —OH, or —O—C1-4alkyl; RN is independently —H or C1-4alkyl; the bond marked with an alpha (α) is independently a single bond or a double bond; if the bond marked with an alpha (α) is a double bond, then R5 is —H; if the bond marked with an alpha (α) is a single bond, then R5 is —H or —OH; the carbon atom marked (*) is independently in an R-configuration or an S-configuration; the carbon atom marked (**) is independently in an R-configuration or an S-configuration; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, esters, ethers, chemically protected forms thereof. In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical formulation is a liposomal pharmaceutical formulation prepared using a mixture of lipids comprising, at least, vesicle-forming lipids (e.g., phospholipids) (e.g., phosphatidylcholines) (e.g., fully hydrogenated soy phosphatidylcholine (HSPC)) (e.g., dipalmitoyl-phosphatidylcholine (DPPC)) and said short-chain sphingolipid, and optionally cholesterol and optionally a vesicle-forming lipid which is derivatized with a polymer chain (e.g., a phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) which is derivatized with polyethyleneglycol (PEG)) (e.g., N-(carbonyl-methoxypolyethylene glycol 2000)-1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine sodium salt (MPEG2000-DSPE). The present invention also pertains to methods for the preparation and use of such formulations.
Owner:NETHERLANDS CANCER INST
Β glycolipids as immuno-modulators
The invention relates to the use of β-glycolipids as immunomodulators. More particularly, the invention relates to the use of β-glycolipids, preferably, β-lactosyl-ceramide, β-glucosylceramide, β-galactosyl-ceramide, ceramid and β-lactosyl-ceramide, as well as any mixture or combination thereof for the treatment of immune related disorders. The present invention further relates to a process for the modulation of the Th1 / Th2 cell balance toward anti-inflammatory cytokine producing cells, in a subject suffering from an immune related disorder. Therapeutic compositions and method for the preparation of these compositions are also provided.
Owner:ENZO THERAPEUTICS ENZO BIOCHEM
Method for preparing D-glucosylceramide by using soy sauce filter residue
ActiveCN106434825AIncrease contentWith process extraction valueMicroorganism based processesFermentationRational useResource utilization
The invention relates to a method for preparing D-glucosylceramide by using a soy sauce filter residue, and is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: activating strains: A, respectively inoculating 100 mL of an activation culture medium with an sphingomonas strain and a yarrowia lipolytica strain; B, carrying out aerobic fermentation culture of the sphingomonas strain activated culture liquid P and the yarrowia lipolytica strain activated culture liquid Q obtained in the step A for 36-72 h, to obtain a composite strain fermentation liquid; C, mixing the composite strain fermentation liquid with the soy sauce filter residue, adding the mixture into a compound fermentation tank, carrying out static culture, and culturing for 48-96 h at the temperature of 25-30 DEG C, to obtain a strain cell-rich filter residue; and carrying out high pressure homogenization for 2 times, to obtain a wall-broken cell homogenate; and D, mixing the wall-broken cell homogenate with an ethanol solution, filtering to obtain a precipitate, and thus obtaining a D-glucosylceramide extract. Through rational use of the soy sauce filter residue, the waste can be turned into treasure, soy sauce industries are facilitated to improve economic benefits, and the resource utilization of the soy sauce filter residue and the development of high-value by-products are greatly improved.
Owner:PROYA COSMETICS
Ceramide and/or glucosylceramide generating accelerant or humectant
InactiveCN104337731AIncreased production of ceramidesIncreased/or ability to glucosylceramideCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBLACK TEA EXTRACTAccelerant
The invention provides a geramide and / or glucosylceramide generating accelerant or humectant. The geramide and / or glucosylceramide generating accelerant or humectant takes black tea extracts selected from more than one of black brick tea, compressed tea after fermentation and Pu'er tea as effective components.
Owner:KAO CORP
Combination Therapy of Beta-Glycolipids and Antibodies for the Treatment of Immune-Related Disorders
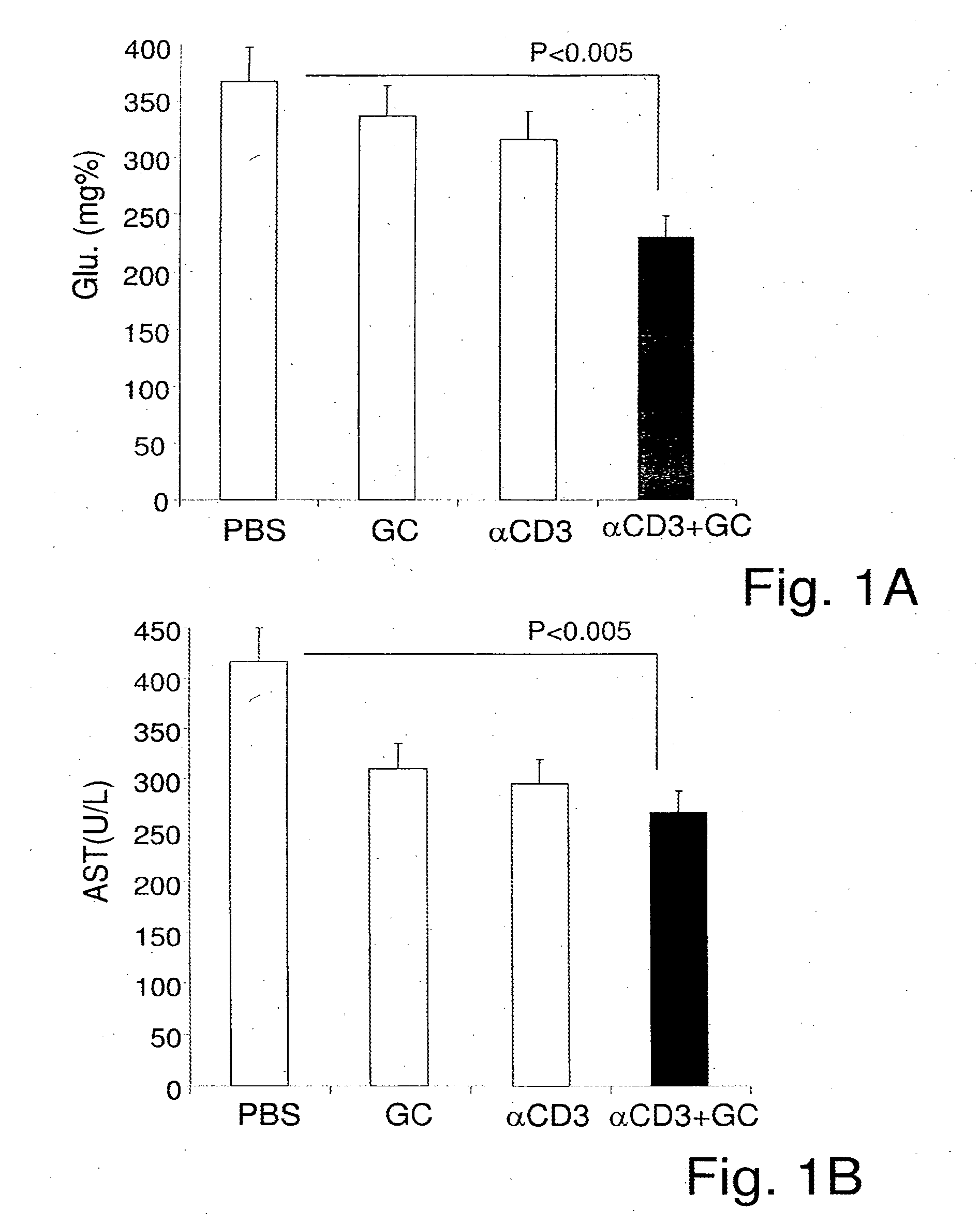
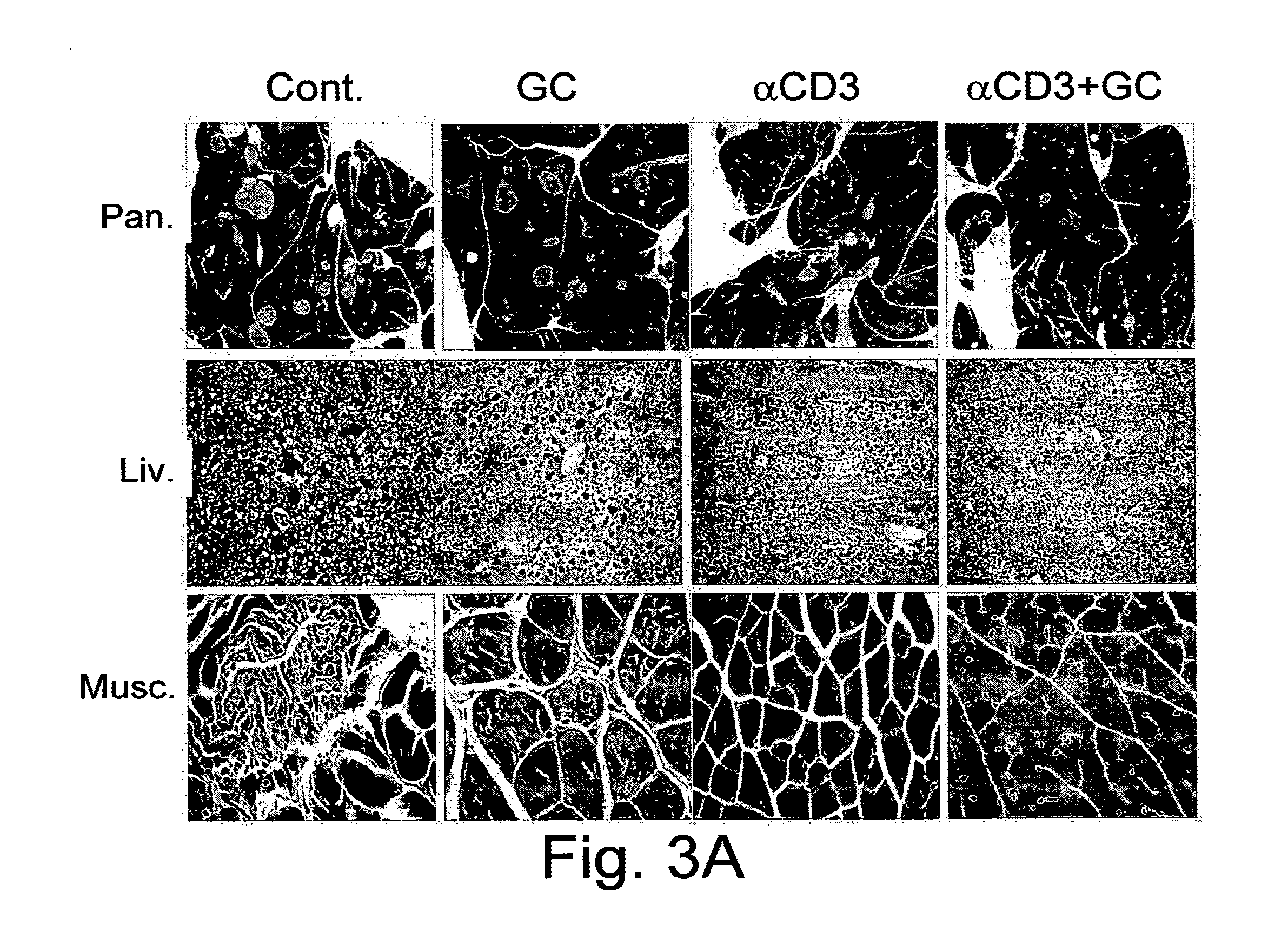
The present invention relates to a combination therapy for the treatment of immune-related disorders. More particularly, the invention relates to oral or mucosal synergistic compositions combining beta-glycolipids, preferably, β-glycosphin-golipids with immunoglobulin molecules specific for at least one antigen derived from a component of the immune system, specifically an anti-CD3 antibody. The invention further provides methods kits and uses of the combined compositions of the invention for immune-modulation and thereby for the treatment of immune-related disorders. In a preferred embodiment, anti-CD3 antibody (OKT3) is orally administered in combination with β-glucosylceramide (also known as glycocerebroside) in an animal model of type 2 diabetes.
Owner:HADASIT MEDICAL RES SERVICES & DEVMENT +1
Manufacturing method of ceramide generation accelerator and/or glucosylceramide generation accelerator
InactiveCN102465151AGood moisturizing effectLow costCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsMicroorganismBiotechnology
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a ceramide generation accelerator and / or a glucosylceramide generation accelerator, wherein Candida microorganisms are cultured in a culture medium containing beam dregs and saccharides, and the ceramide generation accelerator and / or the glucosylceramide generation accelerator are / is obtained from an obtained supernatant. According to the manufacturing method disclosed by the invention, by utilization of specific microorganisms and byproducts, namely the bean dregs, of the food processing industry and the like as a main raw material of the culture medium, the ceramide generation accelerator and / or the glucosylceramide generation accelerator can be acquired at low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:KAO CORP
Preparation method for producing promoter by ceramide and/or glucosylceramide
InactiveCN103060385AIncreased ability to produce ceramide/glucosylceramideGood moisturizing effectCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyGlucosylceramides
The invention provides a preparation method for producing promoter by ceramide and / or glucosylceramide, wherein a microbe of Yarrowia is cultured in a medium containing bean dregs and carbohydrate, and ceramide and / or glucosylceramide is obtained in a clear liquid to generate the promoter. According to the preparation method of the invention, the specific microbe is used, the by-product bean dregs in a food processing industry can be taken as a main raw material of the medium, thereby the promoter generated by the ceramide and and / or glucosylceramide can be obtained with low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:KAO CORP
Lysosomal storage disorder biomarkers and methods of use thereof
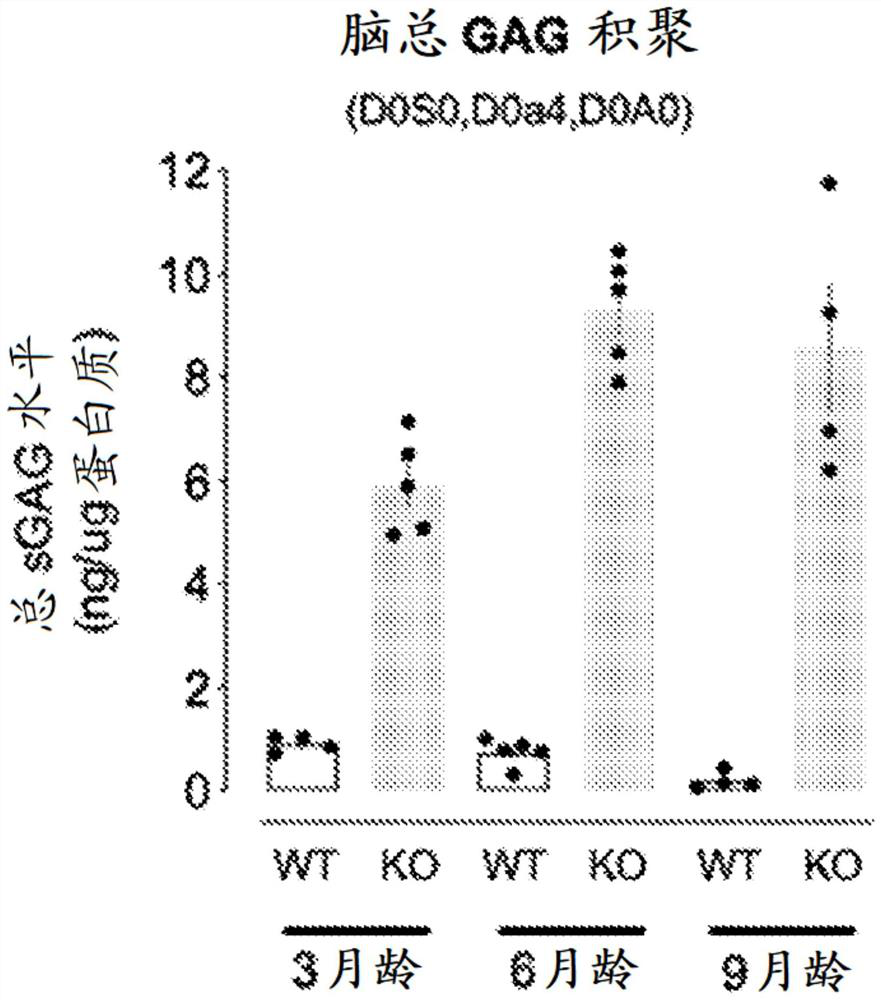
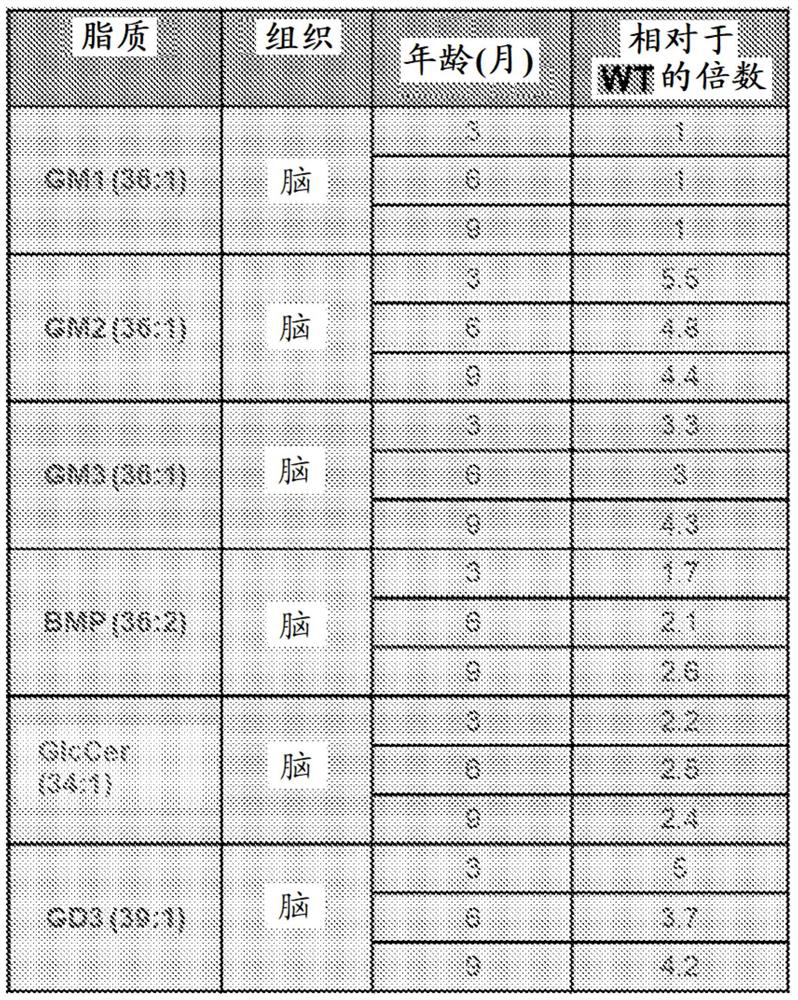
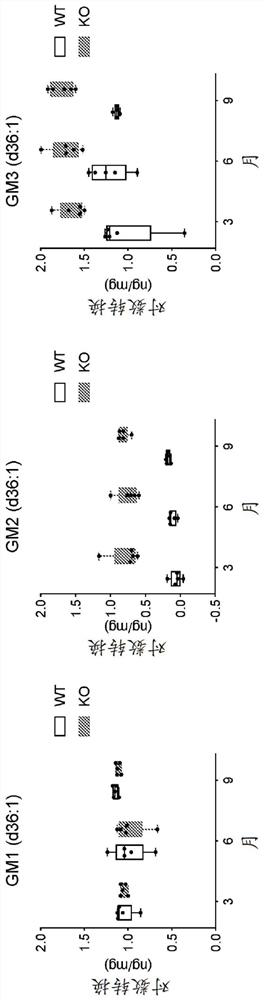
Certain embodiments provide a method of detecting one or more biomarkers in a subject having a lysosomal storage disorder, and the method comprises the steps: 1) measuring the concentration of a combination of two or more lipids in a sample from the subject, wherein the combination of lipids is selected from the group consisting of: a) a bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate (BMP); b) a GM2 ganglioside and / or a GM3 ganglioside; c) a GD3 ganglioside; d) a GD1a / b ganglioside; and e) a glucosylceramide (GlcCer); 2) measuring the concentration of GlcCer in a sample from the subject; 3) measuring the concentration of neurofilament light chain (Nf-L) in a sample from the subject; and / or 4) measuring the concentration of soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (sTREM2) in a sample from the subject.
Owner:DENALI THERAPEUTICS INC
Manufacturing method of ceramide generation accelerator
InactiveCN102465150AIncreased ability to produce ceramide/glucosylceramideGood moisturizing effectCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a ceramide generation accelerator and / or a glucosylceramide generation accelerator, wherein Pichia microorganisms are cultured in a culture medium containing beam dregs and saccharides, and the ceramide generation accelerator and / or the glucosylceramide generation accelerator are / is obtained from an obtained supernatant. According to the manufacturing method disclosed by the invention, by utilization of easily obtainable substances as the culture medium and specific microorganisms, the ceramide generation accelerator and / or the glucosylceramide generation accelerator can be acquired at low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:KAO CORP
Method for utilizing extraction residue of yeast extract
InactiveUS20140228305A1Less contaminantLittle riskBiocideCosmetic preparationsYeast extractChemistry
To produce a glucosylceramide composition suitable for a functional food or a medicinal product, having stable quality, and cleared of contaminants such as sterol glycosides. An objective is to produce a glucosylceramide composition at low cost from a raw material which is safe, has been eaten by human beings, and is readily available. A glucosylceramide-containing composition is produced by extraction from a raw material of a yeast residue in an organic solvent, such as an alcohol, the yeast residue being obtained after extraction of yeast extract from Torula yeast or the like.
Owner:KOHJIN CO LTD
Method for preparing Eliglustat
ActiveCN108822072AFix build issuesRaw materials are easy to getOrganic chemistryDiseaseStaudinger reaction
The invention discloses a method for preparing Eliglustat. The Eliglustat is an effective specific glucosylceramide systhase inhibitor, which can be used for treating type-I Gaucher disease. The invention provides the synthetic method of Eliglustat, which comprises the following steps: 1,4-benzdioxan-6-formaldehyde and a chiral ligand are subjected to an adiastereoselectivity Aldol reaction, and then subjected to a reduction reaction, replacement and a Staudinger reaction, and an amidation reaction to obtain Eliglustat. The method has the advantages of easy acquisition of raw material, simpleoperation, high product yield and purity, and easy industrial large production.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
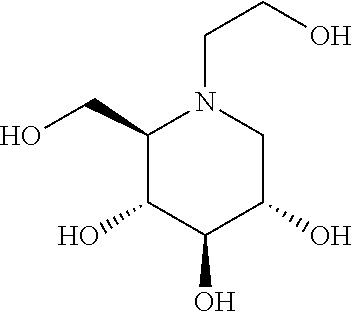
N-(5-((aryl or heteroaryl)methyloxy)pentyl)-substituted iminosugars as inhibitors of glucosylceramide synthase
Deoxynojirimycin and deoxygalactonojirimycin derivatives according to the present invention are N-alkylated D-galacto, D-gluco- or L-ido-deoxynojirimycin with a linear methyloxypentyl group bearing various sidegroups and a non-fused bicyclic aromatic group (“X”) on the methyloxy-carbon. These compounds display an increased inhibitory potency towards GCS, and / or an increased inhibitory potency towards GBA2, and / or a decreased inhibitory potency towards GBA1, relative to known deoxynojirimycin derivatives of the same (D-gluco, L-ido or D-galacto) configuration. Therefore, compounds of the present invention are effective in the treatment of diseases which are associated with an irregular level of cytosolic or lysosomal glucosylceramide and / or higher glycosphingolipids, such as a lysosomal storage disorder, such as Gaucher disease, Fabry disease, Tay-Sachs disease, Sandhoff disease, GM1 gangliosidosis, Sialidosis, Niemann Pick disease type C and AMRF, or a symptom of one of the diseases collectively classed as metabolic syndrome, such as obesity, insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, polycystic kidney disease, type II diabetes and chronic inflammation, or a neurodenegerative disorder, such as Parkinson disease or Lewy-body dementia.
Owner:LEIDEN UNIVERSITY +1
Fungal glucosylceramide as a vaccine for fungal infections
InactiveUS20170224790A1Improve protectionReduce transmissionOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsFungal diseaseAdjuvant
The present invention features compositions that include a fungal glucosylceramide (GlcCer) purified from a non-pathogenic fungus (e.g., Candida utilis) and, optionally, an adjuvant. The invention also features methods of treating a patient who has a fungal disease and methods of preventing a fungal disease in a subject by administration of these compositions. Also within the scope of the invention are methods of formulating a fungal vaccine by: (a) providing a fungal glucosylceramide isolated from a non-pathogenic fungus; and (b) combining the fungal glucosylceramide with an adjuvant in a physiologically acceptable excipient.
Owner:KOHJIN CO LTD +1
N-(5-((aryl or heteroaryl)methyloxy)pentyl)-substituted iminosugars as inhibitors of glucosylceramide synthase
Deoxynojirimycin and deoxygalactonojirimycin derivatives according to the present invention are N-alkylated D-galacto, D-gluco- or L-ido-deoxynojirimycin with a linear methyloxypentyl group bearing various sidegroups and a non-fused bicyclic aromatic group (“X”) on the methyloxy-carbon. These compounds display an increased inhibitory potency towards GCS, and / or an increased inhibitory potency towards GBA2, and / or a decreased inhibitory potency towards GBA1, relative to known deoxynojirimycin derivatives of the same (D-gluco, L-ido or D-galacto) configuration. Therefore, compounds of the present invention are effective in the treatment of diseases which are associated with an irregular level of cytosolic or lysosomal glucosylceramide and / or higher glycosphingolipids, such as a lysosomal storage disorder, such as Gaucher disease, Fabry disease, Tay-Sachs disease, Sandhoff disease, GM1 gangliosidosis, Sialidosis, Niemann Pick disease type C and AMRF, or a symptom of one of the diseases collectively classed as metabolic syndrome, such as obesity, insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, polycystic kidney disease, type II diabetes and chronic inflammation, or a neurodenegerative disorder, such as Parkinson disease or Lewy-body dementia.
Owner:LEIDEN UNIVERSITY +1
Preparation method of promoter for producing ceramide and/or glucosylceramide
InactiveCN102477446AIncreased ability to produce ceramide/glucosylceramideGood moisturizing effectCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyDebaryomyces
The invention provides a preparation method of a promoter for producing ceramide and / or glucosylceramide, wherein debaryomyces microbes are cultured in a culture medium containing bean dregs and saccharides, and the promoter for producing ceramide and / or glucosylceramide is obtained from the supernatant. According to the preparation method of the invention, special microbes are used, and bean dregs which are by products in food processing industry are used as a main raw material of the culture medium; therefore the promoter for producing ceramide and / or glucosylceramide is obtained with low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:KAO CORP
Preparation method of promoter for producing ceramide and/or glucosylceramide
InactiveCN102477446BGood moisturizing effectLow costCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyDebaryomyces
The invention provides a preparation method of a promoter for producing ceramide and / or glucosylceramide, wherein debaryomyces microbes are cultured in a culture medium containing bean dregs and saccharides, and the promoter for producing ceramide and / or glucosylceramide is obtained from the supernatant. According to the preparation method of the invention, special microbes are used, and bean dregs which are by products in food processing industry are used as a main raw material of the culture medium; therefore the promoter for producing ceramide and / or glucosylceramide is obtained with low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:KAO CORP
Beautifying, whitening and spot-fading health-care product
The invention discloses a beautifying, whitening and spot-fading health-care product. The product comprises, by mass, 2-4 parts of grape polyphenols, 10-14 parts of hawthorn fruits, 3-5 parts of vitamin C, 3-7 parts of vitamin E, 1 part of procyanidine, 2 parts of beta-carotene, 2-4 parts of active iron, 15-20 parts of pectin, 2-5 parts of protein, 5-8 parts of provitamin A, 2-4 parts of mucoprotein, 3-6 parts of glucosylceramide, 5-6 parts of tranexamic acid, 7-9 parts of natural astaxanthin, 3-5 parts of vitamin C (VC), 3-5 parts of calcium pantothenate, 2-4 parts of L-vitamin C, 2-3 parts of arbutin, 4-6 parts of L-serine and 3-7 parts of hyaluronic acid. The product has the advantages that through the tranexamic acid, melanin and pigmented spots are prevented from being formed, the melanin transmission path is blocked, the skin of a user is whiter, and spots are faded; the glucosylceramide can make the skin of the user bright, and the health-care and whitening effects are better.
Owner:庞文
Manufacturing method of ceramide production accelerating agent
InactiveCN102559767BGood moisturizing effectCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsMicroorganismMicrobiology
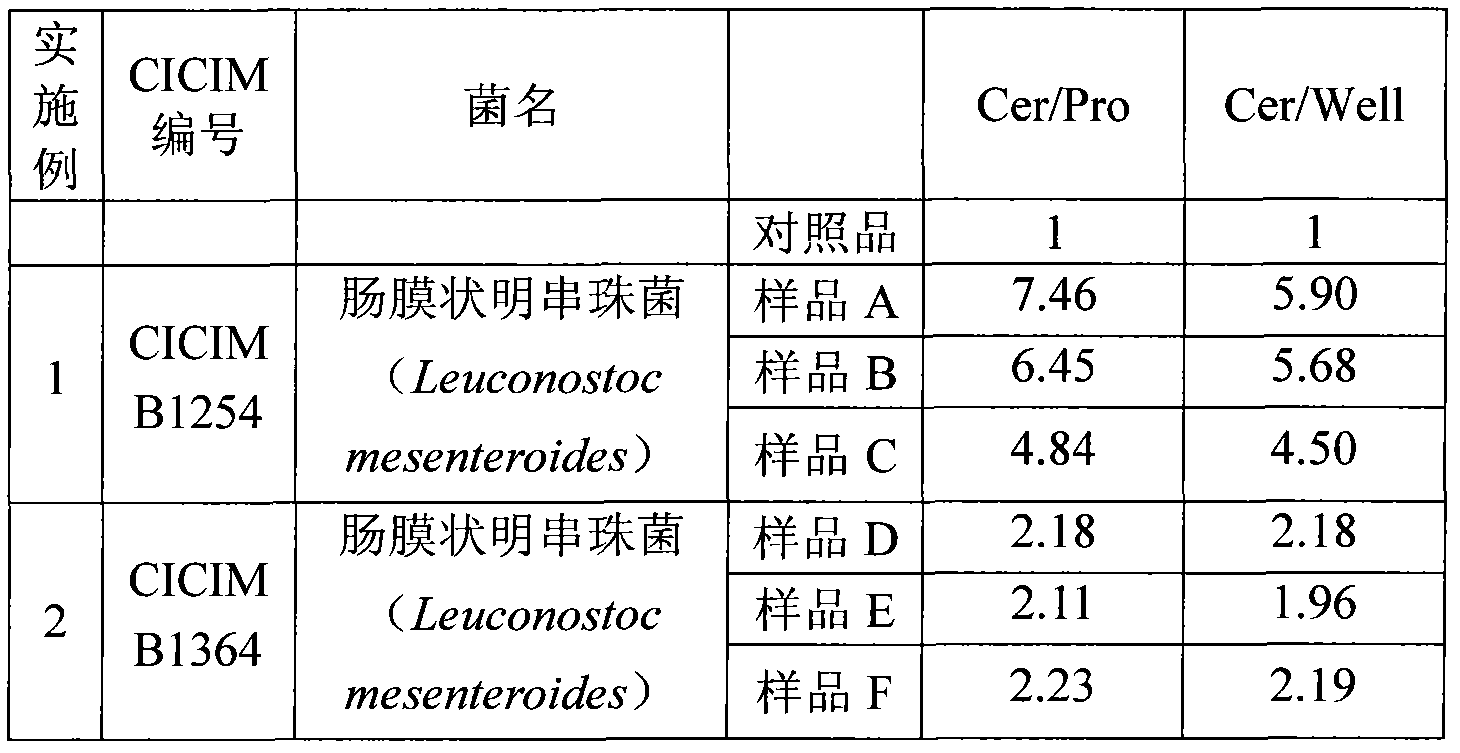
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a ceramide production accelerating agent and / or a glucosylceramide ceramide production accelerating agent. The method comprises the following steps of: culturing a microorganism of Leuconstoc in a culture medium containing bean dregs and saccharides, and obtaining the ceramide production accelerating agent and / or the glucosylceramide ceramide production accelerating agent from supernate. According to the manufacturing method provided by the invention, the ceramide production accelerating agent and / or the glucosylceramide ceramide production accelerating agent can be efficiently obtained at low cost through utilizing an easily obtained substance as the culture medium and utilizing a specific microorganism.
Owner:KAO CORP
Chestnut Bark Extract
ActiveCN109562054BFunction increaseGood moisturizing effectCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsUltraviolet absorbanceOrganic chemistry
Provided are a method for efficiently producing free ceramide (especially human-type free ceramide) and the like. The extract obtained from chestnut bark contains relatively abundant free ceramides and glucosylceramides, which is useful. In addition, chestnut bark acetone extract has ultraviolet absorption and ultraviolet wavelength conversion actions, which is useful.
Owner:SATICINE MEDICAL CO LTD
Method for screening antifungal substance acting on glucosylceramide as target
InactiveCN102586394BSimplify the screening processReliable resultsFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementAntifungalFungal disease
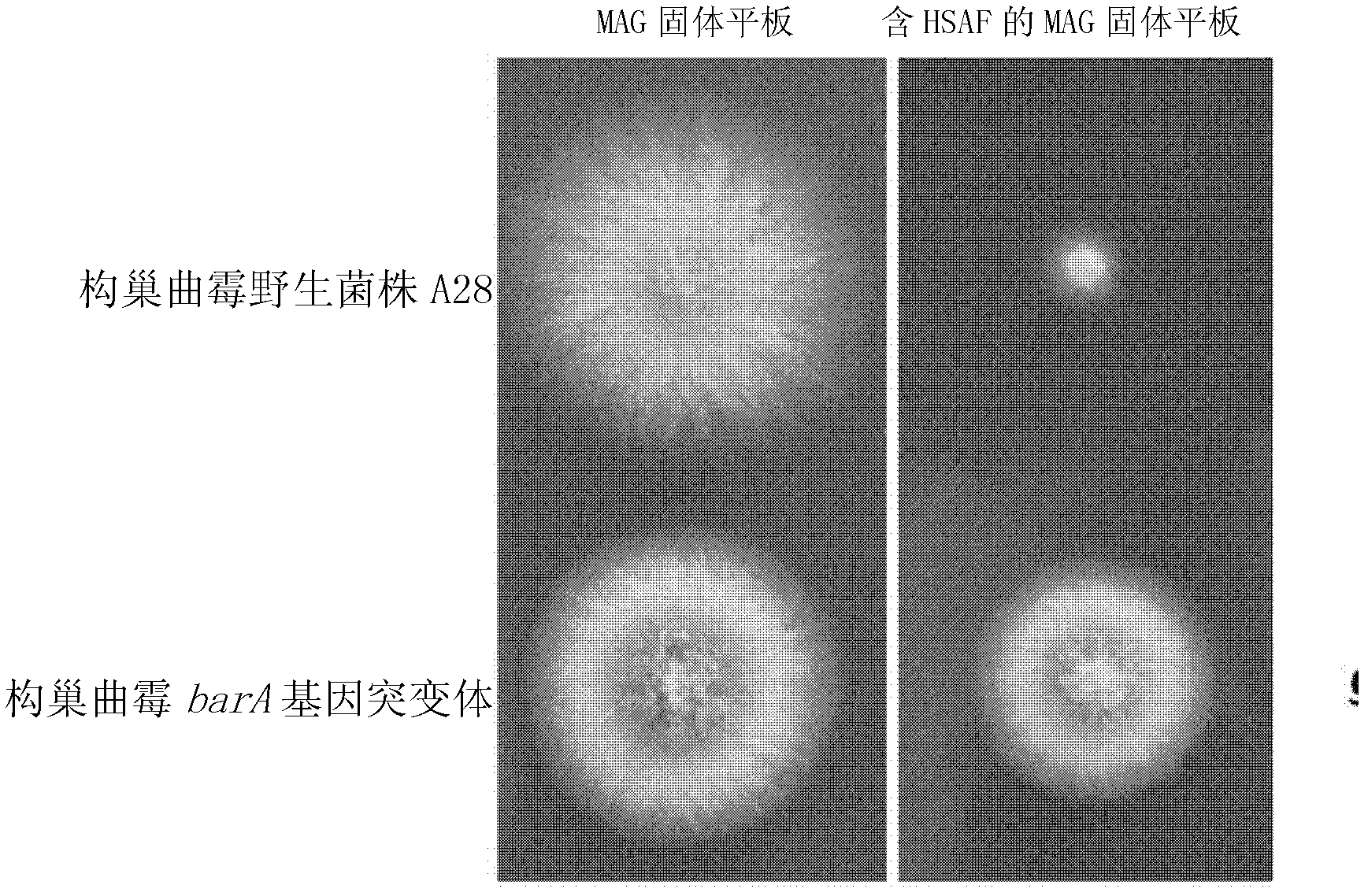
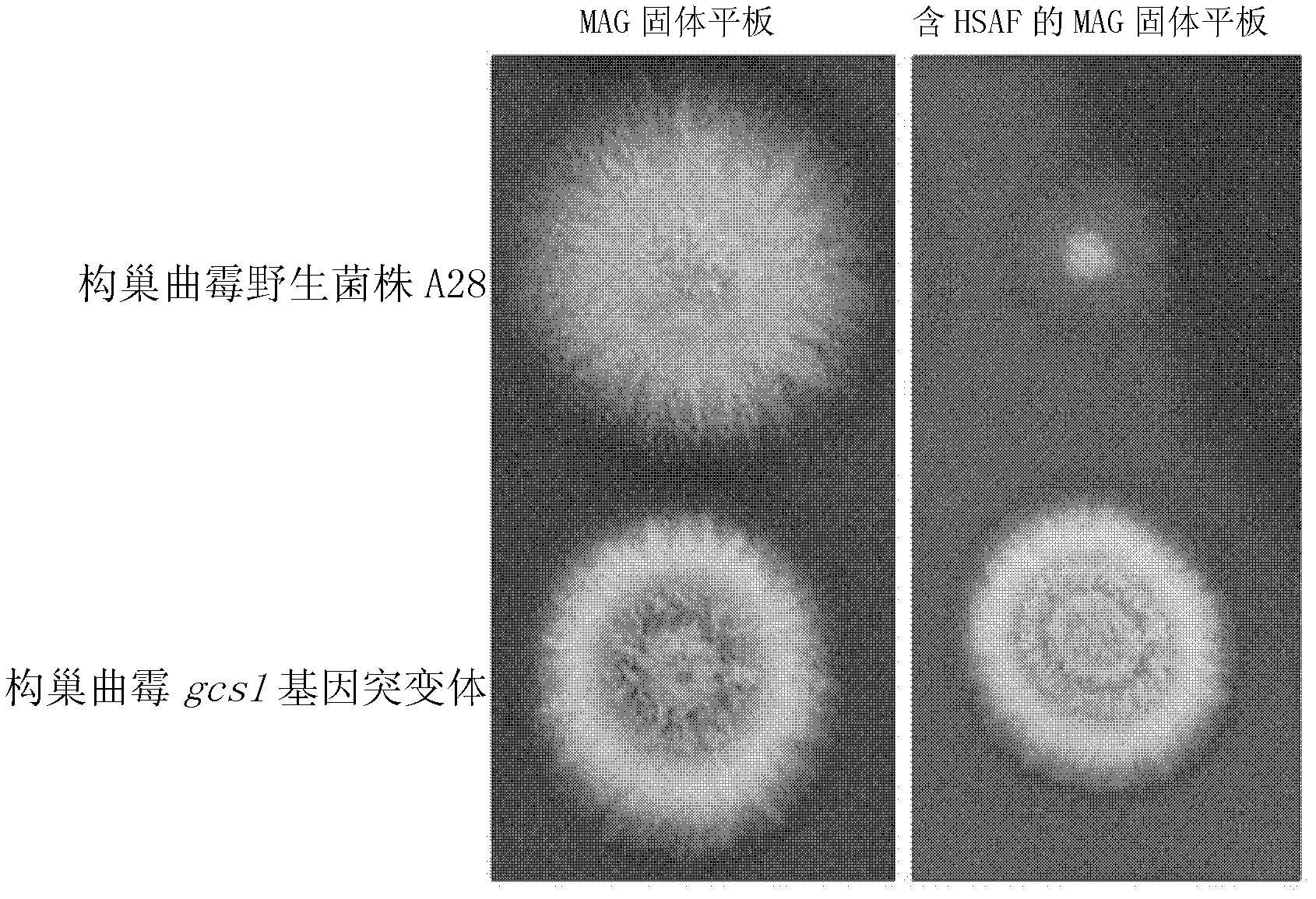
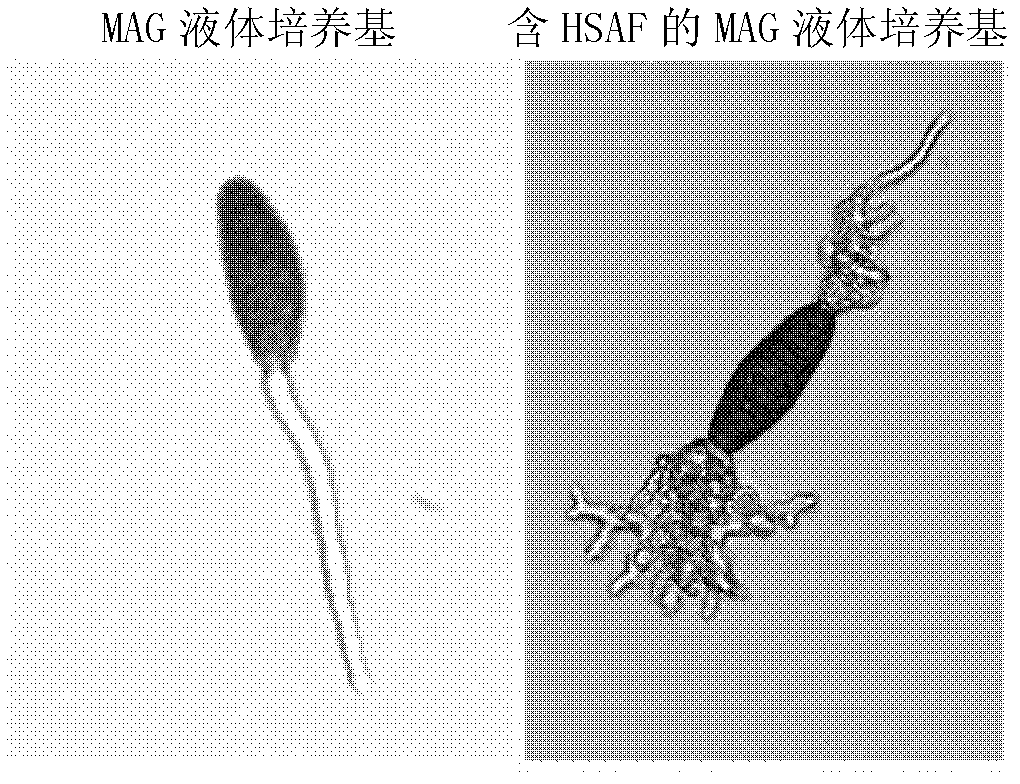
The invention discloses a method for screening an antifungal substance acting on glucosylceramide as a target. The method provided by the invention includes the following steps: a wild fungus strain and a mutant strain are respectively cultured on solid plates containing a substance to be assayed, and if the growth of the mutant strain on the plate is better than the growth of the wild fungus strain on the plate, the substance to be assayed is a candidate antifungal substance or a candidate substance containing the antifungal substance; and the target of the antifungal substance is glucosylceramide. The method established by the invention has the advantages that: the target is specific, moreover, the method integrates in vivo screening and activity assay, whether the substance is the antifungal substance targeting glucosylceramide can be judged only according to the difference between the sensitivities of the mutant strain and the wide strain on the antifungal substance, the screening process is simpler, and can save time and labor, and the result is more accurate and reliable. The method has a great application prospect in the screening and development of green control agents for fungal diseases.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Manufacturing method of ceramide production accelerating agent
InactiveCN102559767AGood moisturizing effectCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a ceramide production accelerating agent and / or a glucosylceramide ceramide production accelerating agent. The method comprises the following steps of: culturing a microorganism of Leuconstoc in a culture medium containing bean dregs and saccharides, and obtaining the ceramide production accelerating agent and / or the glucosylceramide ceramide production accelerating agent from supernate. According to the manufacturing method provided by the invention, the ceramide production accelerating agent and / or the glucosylceramide ceramide production accelerating agent can be efficiently obtained at low cost through utilizing an easily obtained substance as the culture medium and utilizing a specific microorganism.
Owner:KAO CORP
Glucocerebroside treatment of liver disorders
The present invention provides a method for the treatment of immune mediated or immune related diseases or disorders, infectious diseases, metabolic disorders and cancer in mammalian subjects. This method comprises the administration of a naturally occurring, mammalian intermediary metabolite or T cell receptor ligand, preferably a glucosylceramide, to a mammalian subject. In a preferred embodiment, such mammalian subjects are human beings.
Owner:ENZO THERAPEUTICS
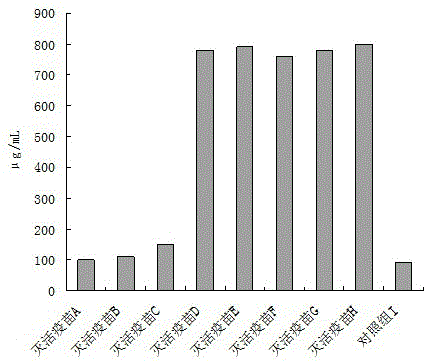
Porcine epidemic diarrhea inactivated vaccine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104383528BEnhance immune responseImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsAdditive ingredientDiarrhea
The invention provides a PED (Porcine Epedemic Diarrhea) inactivated vaccine and a preparation method thereof and relates to the field of biopharmacy. The PED inactivated vaccine comprises inactivated PEDV (Porcine Epedemic Diarrhea Virus), and is characterized in that the PED inactivated vaccine comprises 0.05-10 mg / mL Beta-glucosylceramide, 0.1-21 mg / mL monophosphoryl lipid A, 1.5-125 mg / mL muramyl dipeptide and 0.7-4.5 mg / mL Beta-glucan. According to the ingredients of the PED inactivated vaccine, Beta-glucosylceramide, monophosphoryl phosphoryl lipid A, muramyl dipeptide and Beta-glucan have the synergistic effect, the immune response of animals to antigens in the vaccine is significantly improved, the immune window phase is shortened, the antibody production duration of the animal body is obviously prolonged, the serum antibody level is improved, and the level of total intestinal mucosa secretory antibodies (the total SIgA) is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
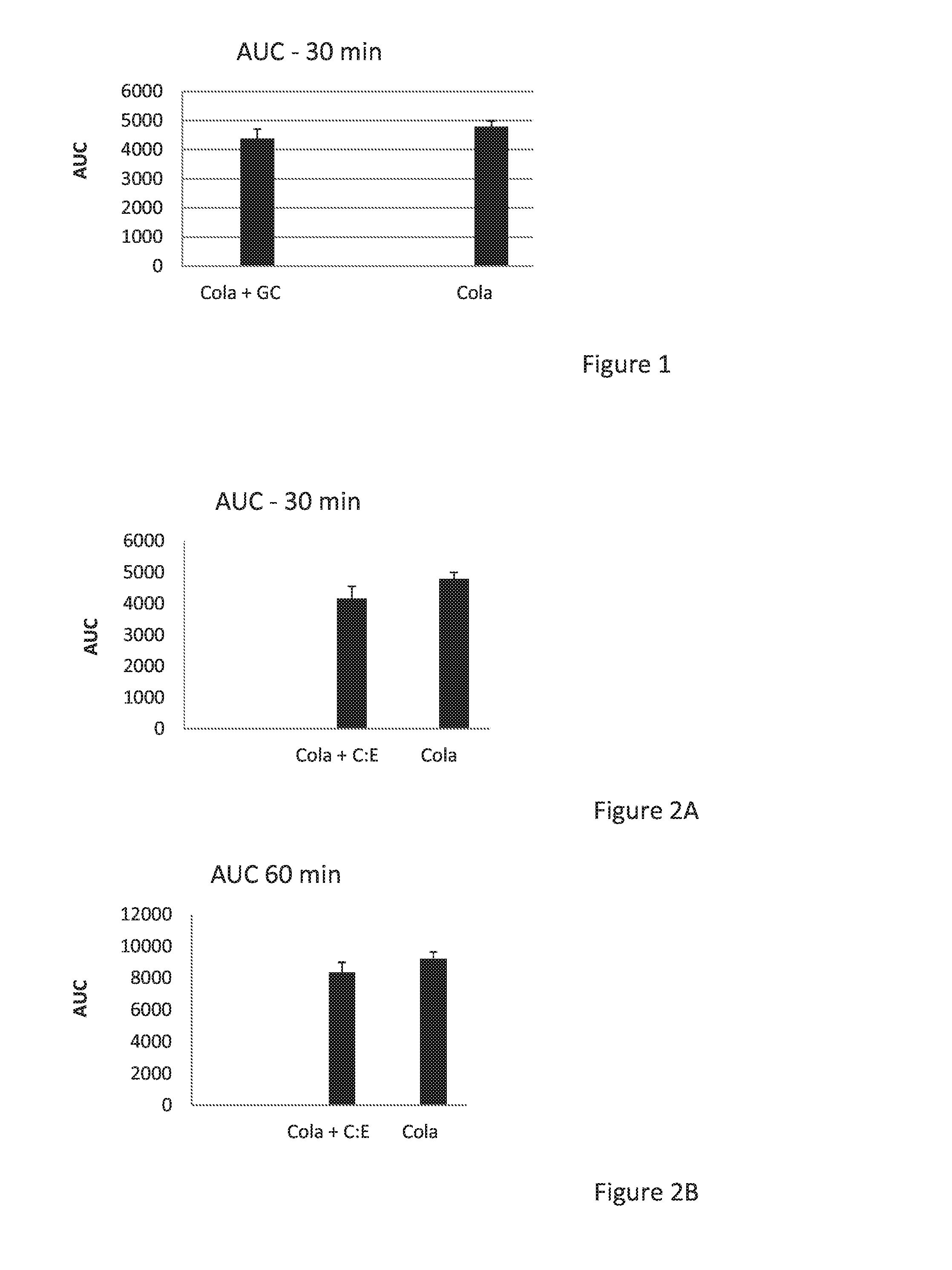
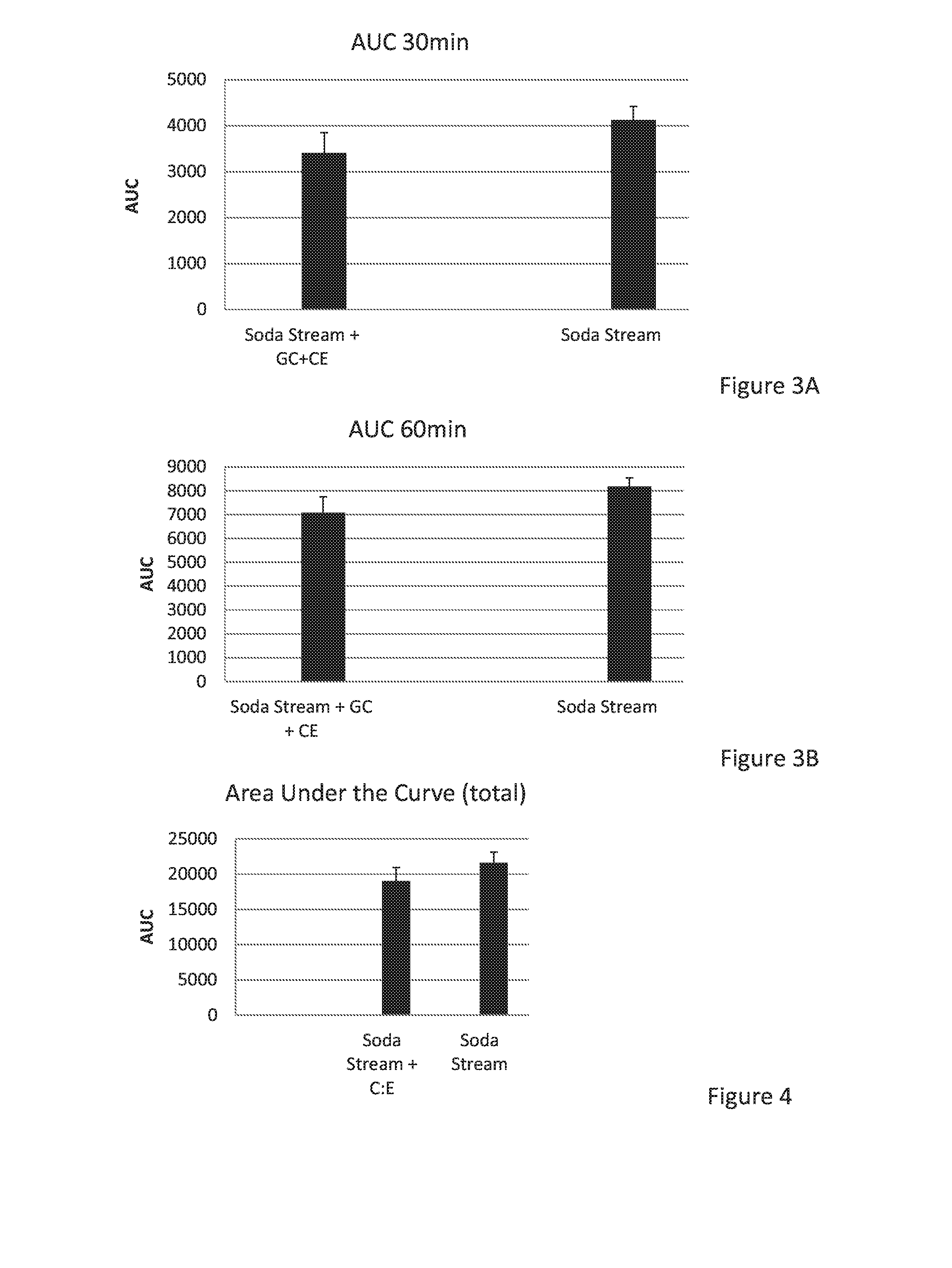
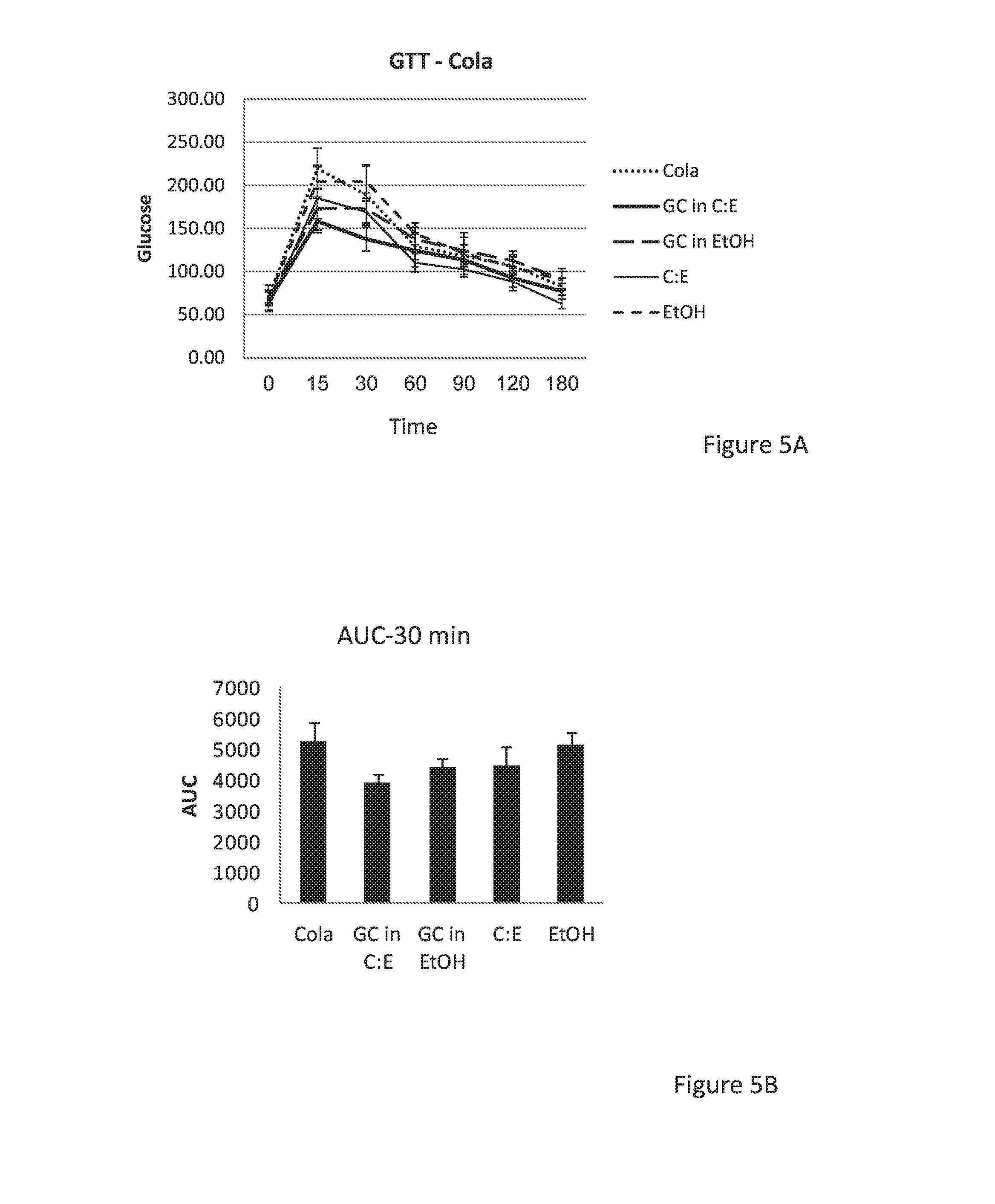
Combination of beta-glucosylceramide and polyethoxylated castor oil and other adjuvants for controling blood sugar levels, immunoprotection and hepatoprotection
InactiveUS20170035791A1Control blood sugar levelsReduce degradationMetabolism disorderDigestive systemAdjuvantPolyethylene glycol
The disclosure relates to compositions and methods for adding beta glucosylceramide and / or Cremophor EL (CE), or an adjuvant selected from polyethylene glycol and beta cyclo dextrin or any type of beta or alpha glucosylceramide with / without CE, or CE alone, to drinks or foods to serve as liver protectors, sugar protectors, and anti inflammatory protectors.
Owner:NATURAL SHIELD ISRAEL 2016 LTD
Glycosylated metabolites
The invention provides means and methods for detecting a glycosylated metabolite in a sample comprising adding to the sample a compound comprising a labelled glycosyl group coupled via an O-glycosidic bond to an aglycon with a specific structural formula wherein the glycosyl group comprises at least one isotope and / or a side chain being a label for detection, and wherein the sample is screened for the presence of a glycosylated metabolite with the glycosyl group other than a glucosylceramide. The invention further provides a method of treating a disorder caused by accumulation of a glycosylated metabolite other than glucosylceramide in a subject comprising administering to the subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a glucosylceramide synthase (GCS) inhibitor.
Owner:LEIDEN UNIVERSITY
A kind of method utilizing soy sauce filter residue to prepare d-glucosylceramide
ActiveCN106434825BIncrease contentWith process extraction valueMicroorganism based processesFermentationRational useResource utilization
The invention relates to a method for preparing D-glucosylceramide by using a soy sauce filter residue, and is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: activating strains: A, respectively inoculating 100 mL of an activation culture medium with an sphingomonas strain and a yarrowia lipolytica strain; B, carrying out aerobic fermentation culture of the sphingomonas strain activated culture liquid P and the yarrowia lipolytica strain activated culture liquid Q obtained in the step A for 36-72 h, to obtain a composite strain fermentation liquid; C, mixing the composite strain fermentation liquid with the soy sauce filter residue, adding the mixture into a compound fermentation tank, carrying out static culture, and culturing for 48-96 h at the temperature of 25-30 DEG C, to obtain a strain cell-rich filter residue; and carrying out high pressure homogenization for 2 times, to obtain a wall-broken cell homogenate; and D, mixing the wall-broken cell homogenate with an ethanol solution, filtering to obtain a precipitate, and thus obtaining a D-glucosylceramide extract. Through rational use of the soy sauce filter residue, the waste can be turned into treasure, soy sauce industries are facilitated to improve economic benefits, and the resource utilization of the soy sauce filter residue and the development of high-value by-products are greatly improved.
Owner:PROYA COSMETICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com