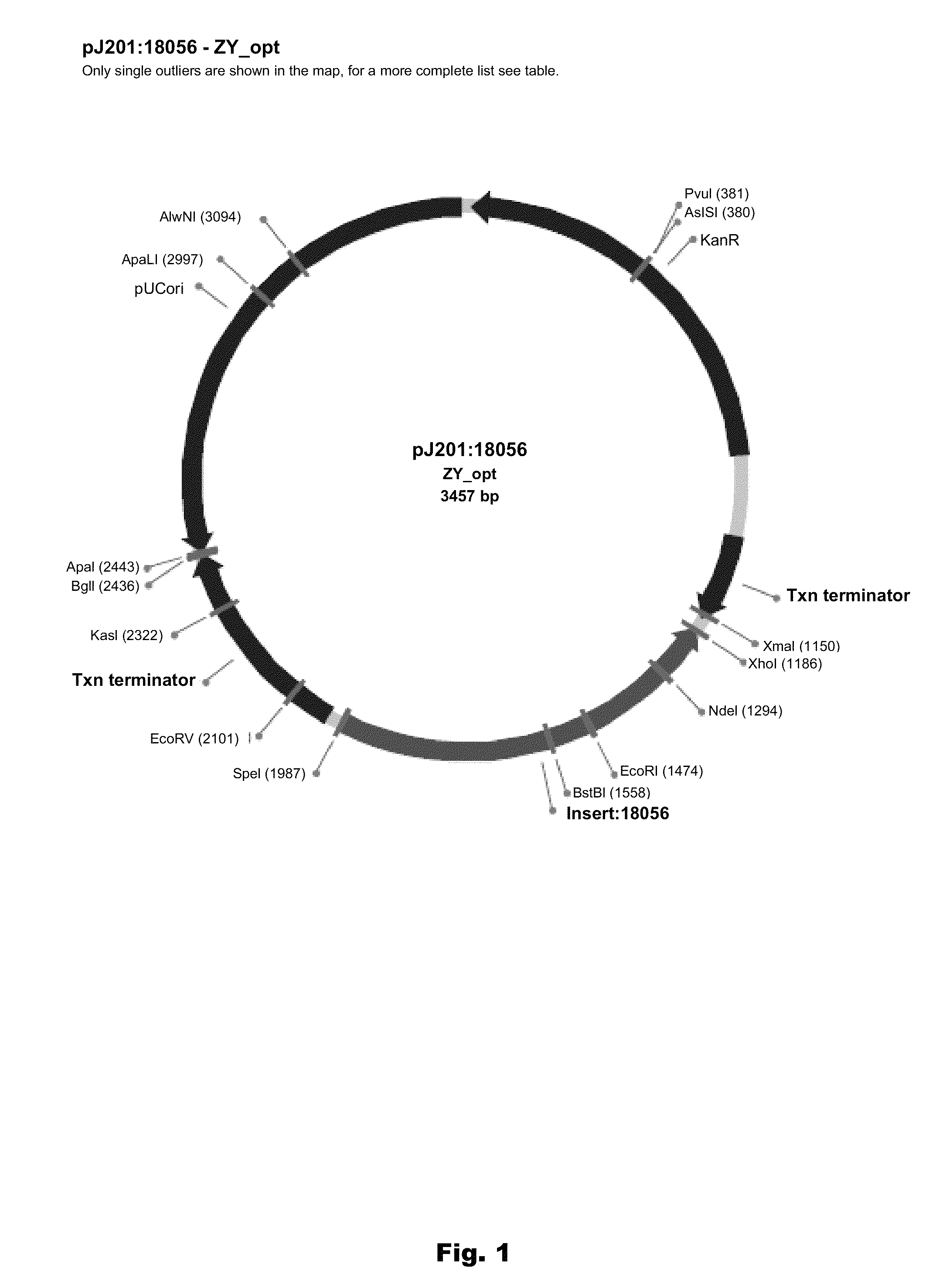
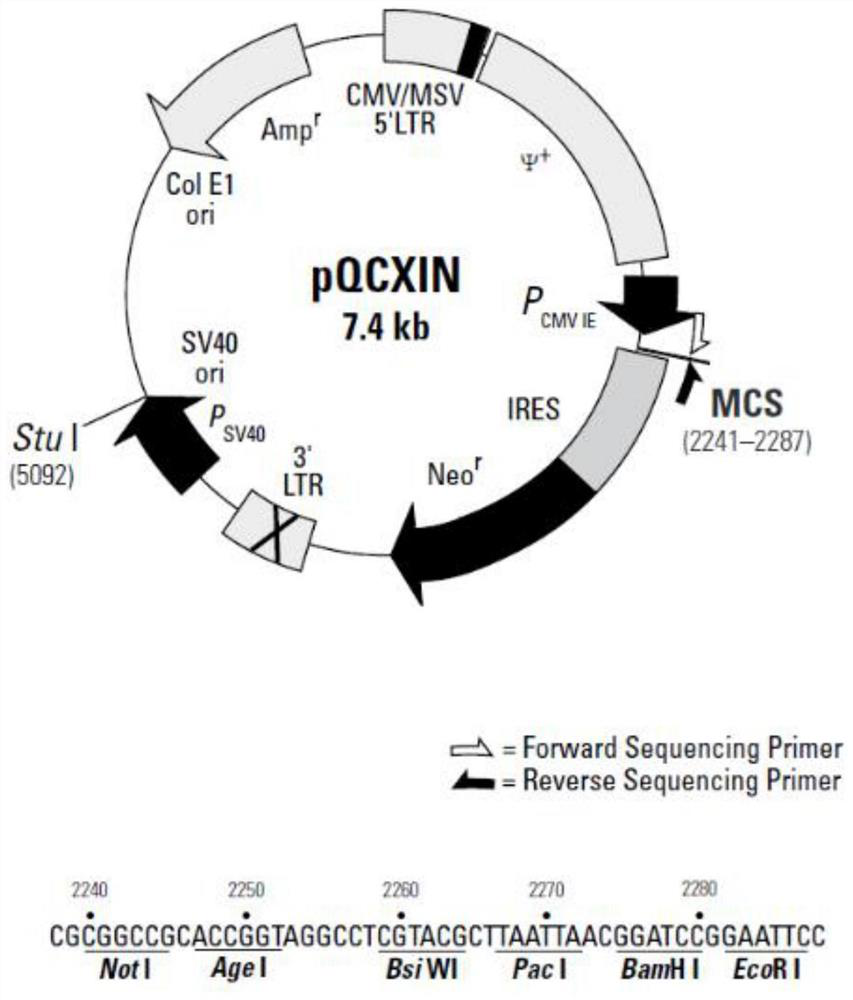
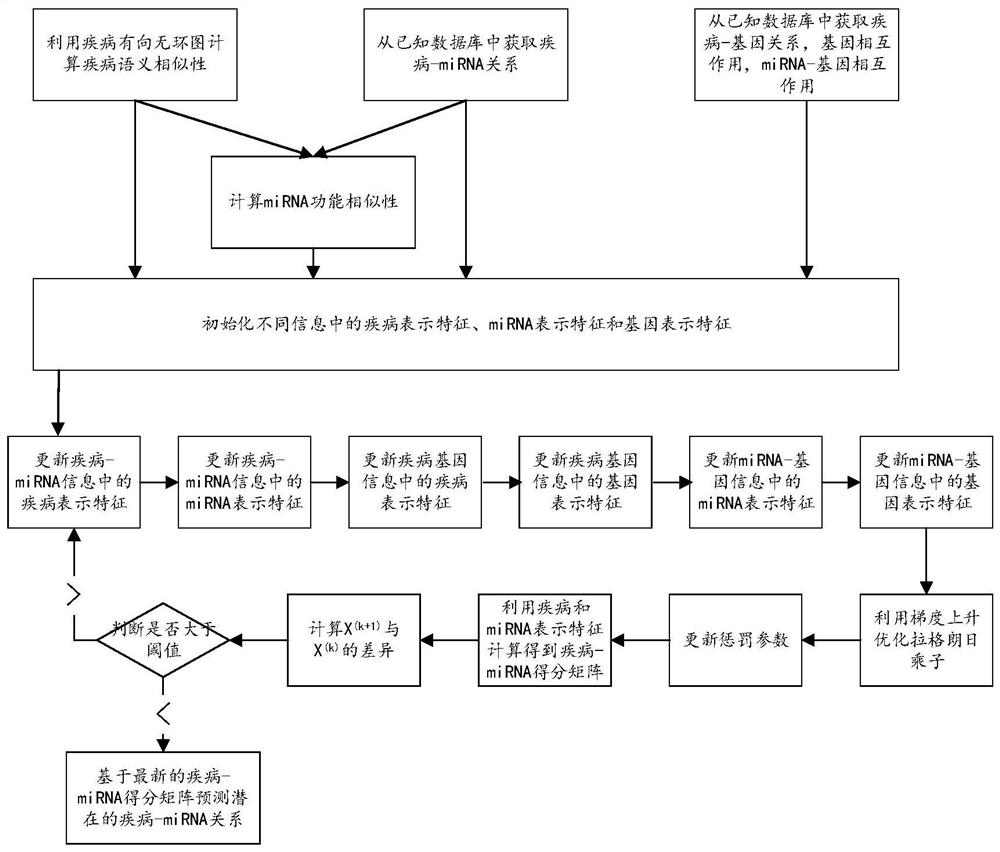
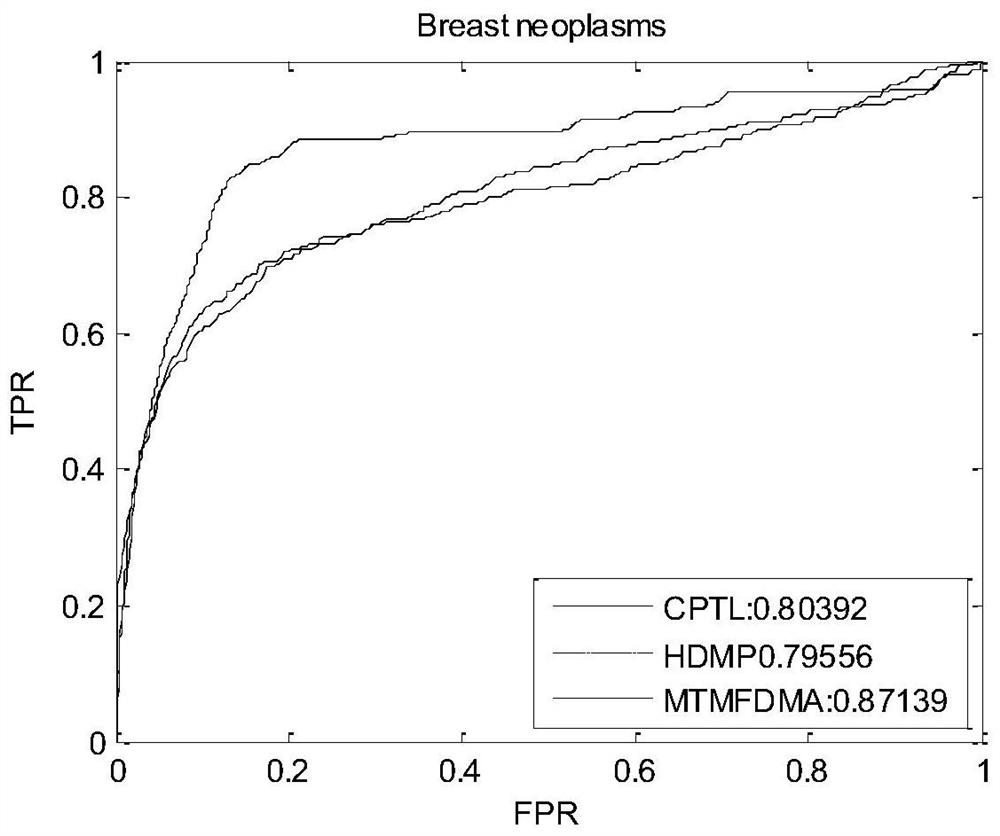
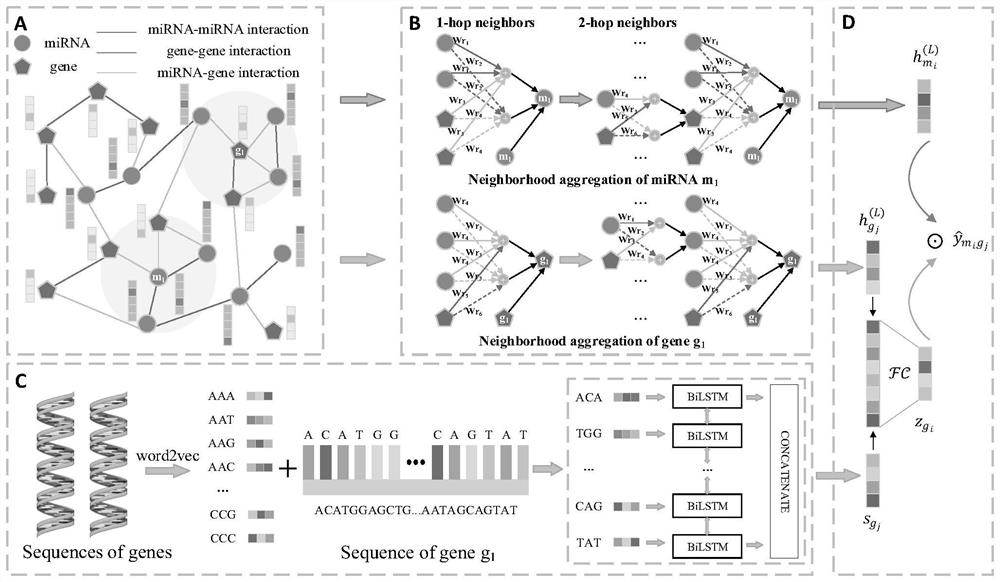
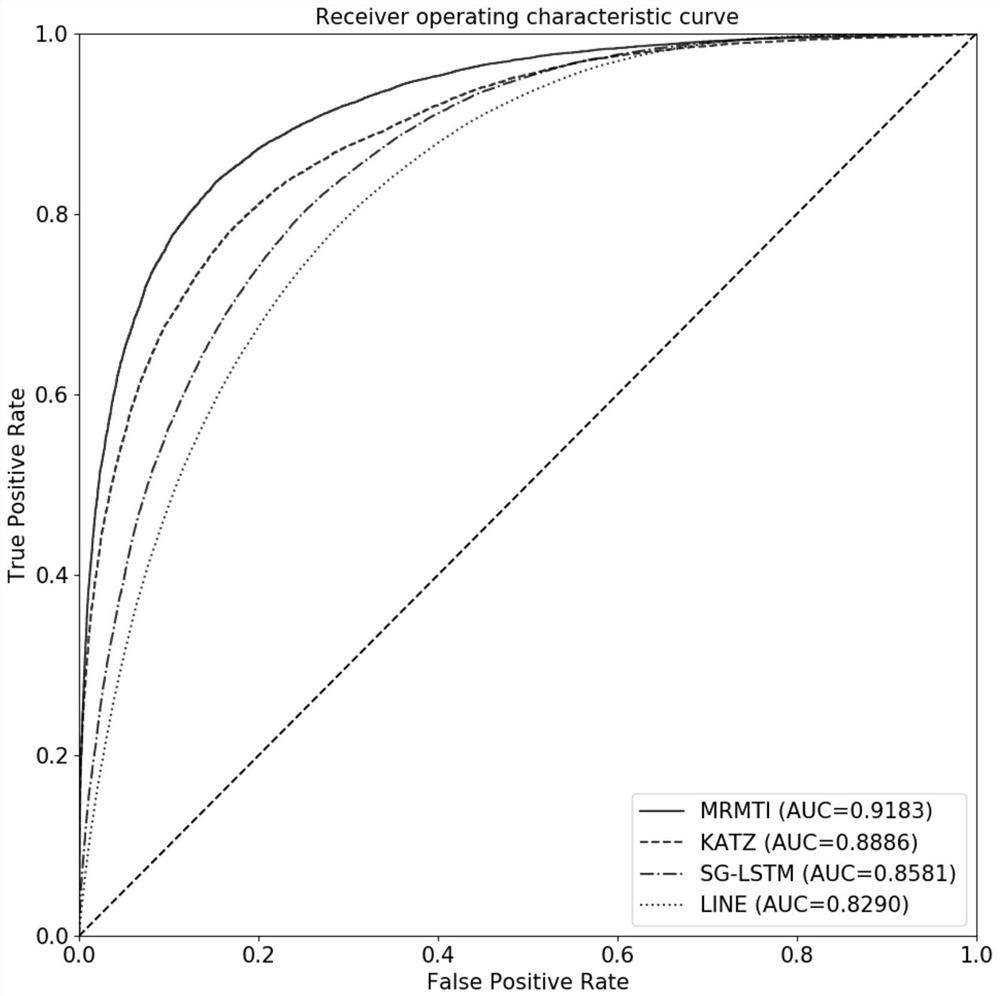
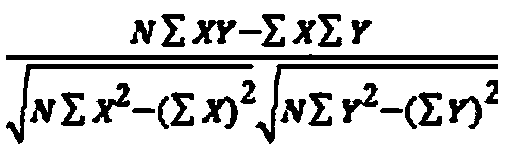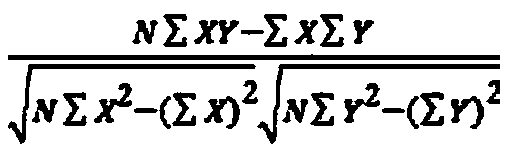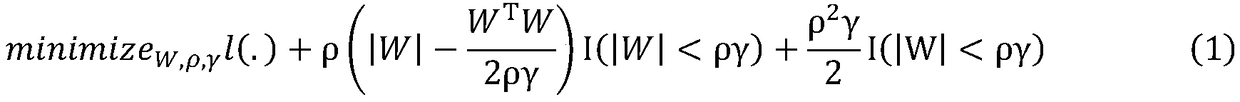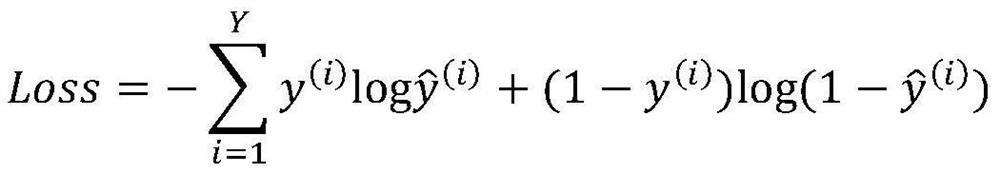Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49 results about "Gene interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gene interactions can result in the alteration or suppression of a phenotype. This can occur when an organism inherits two different dominant genes, for example, resulting in incomplete dominance.
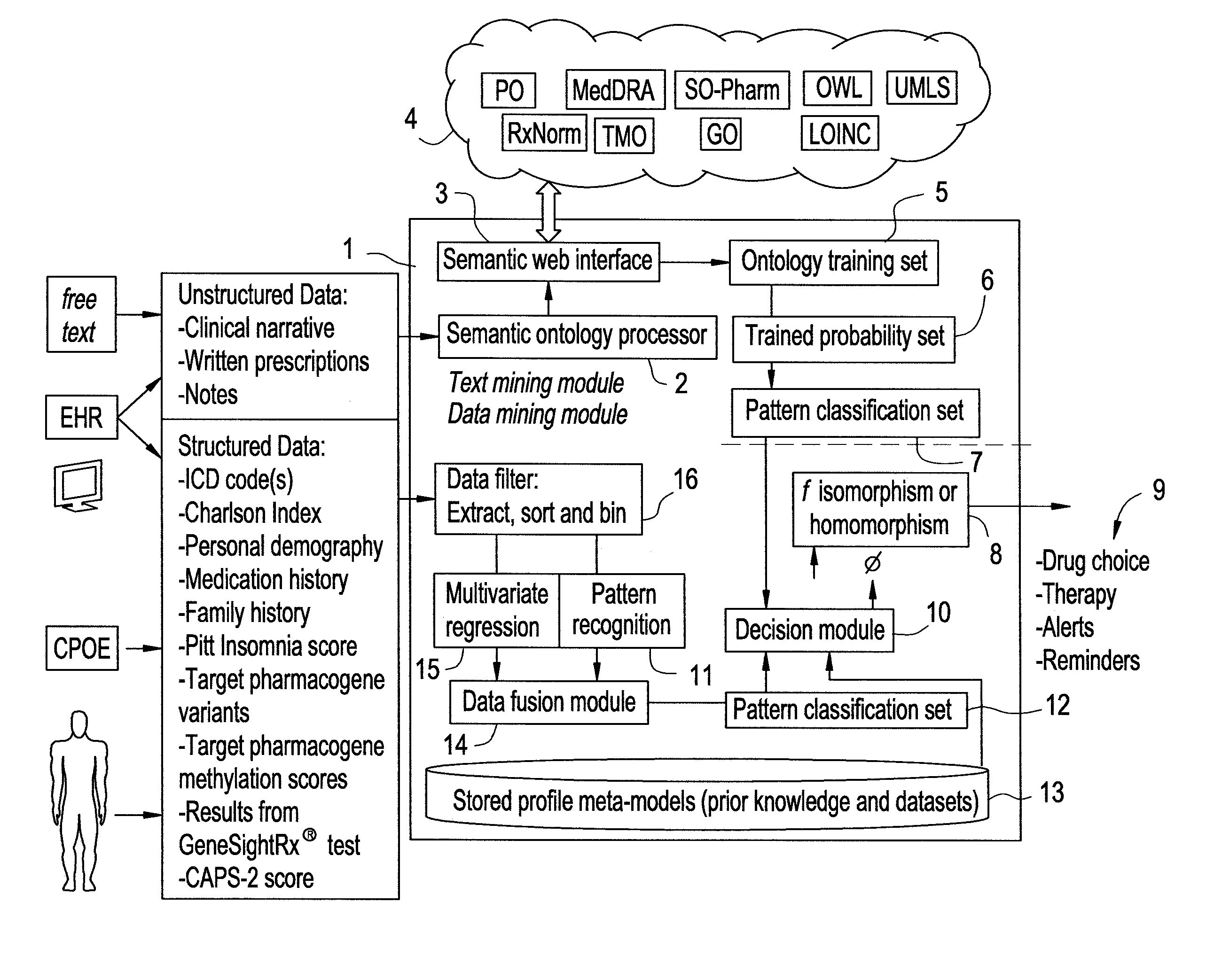
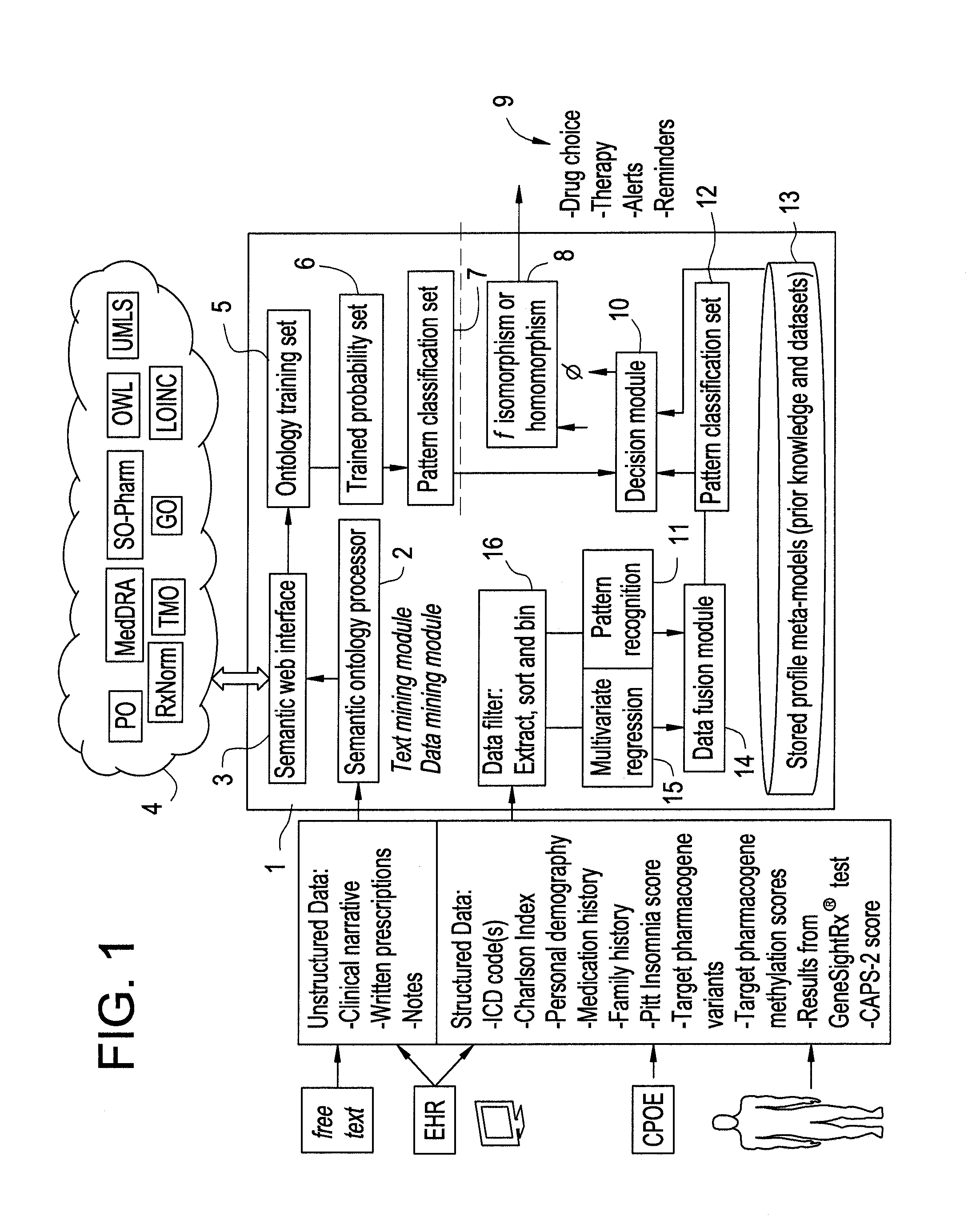
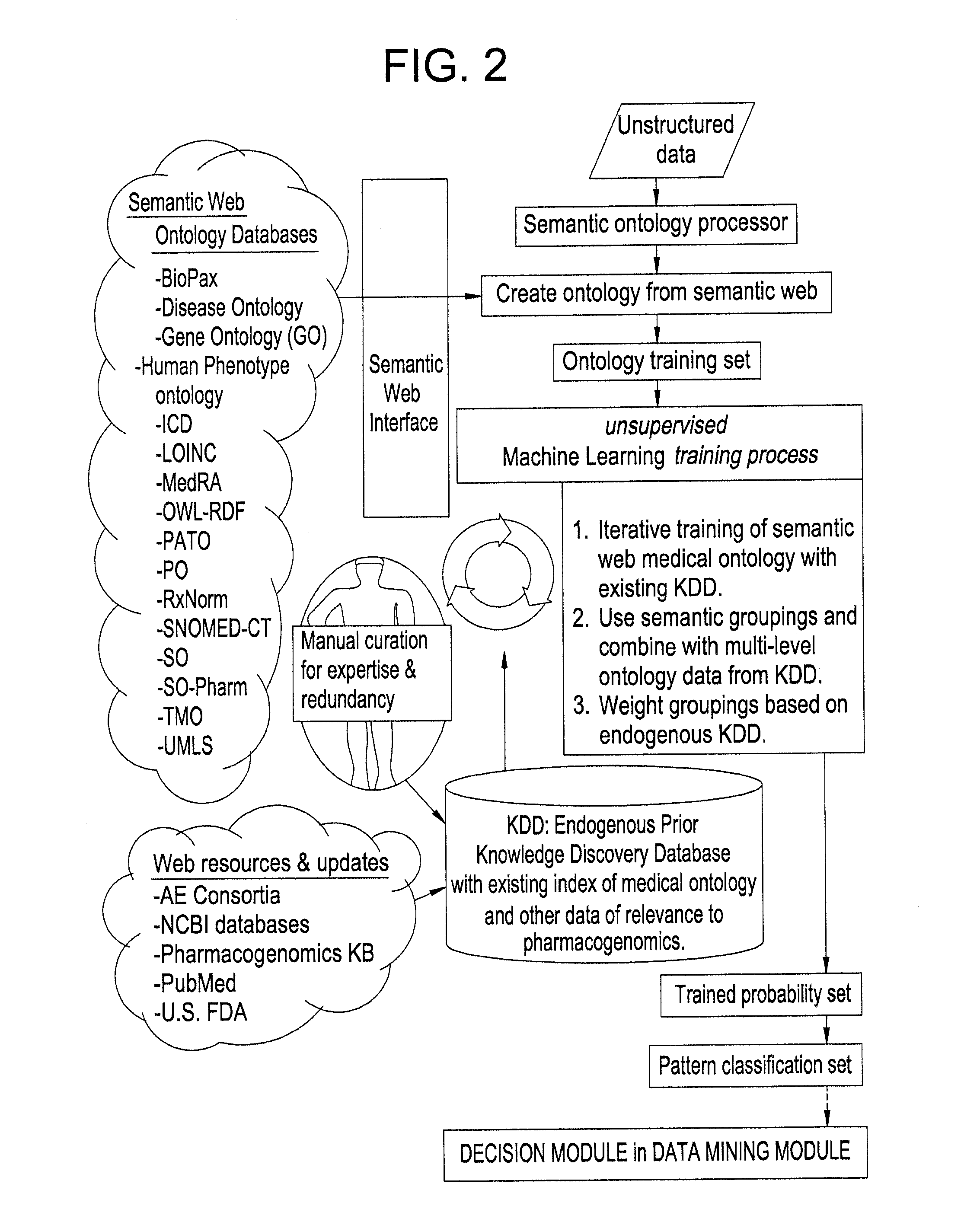
Systems and Methods for Pharmacogenomic Decision Support in Psychiatry
InactiveUS20140046696A1Medical simulationData processing applicationsClinical variablesDecision taking
The present invention provides methods and systems or apparatuses, to analyze multiple molecular and clinical variables from an individual diagnosed with a psychiatric disorder, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), in order to optimize medication selection for therapeutic response. Molecular co-variables include polymorphisms in genes including those involved in central control and mediation of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis (HPA) stress response, the density of methylation in regulatory regions of said polymorphic genes, polymorphisms in genes that encode cytochrome P450 enzymes responsible for drug metabolism, and drug-drug and drug-gene interactions. Clinical co-variables include but are not limited to the sex, age and ethnicity of that individual, medication history, family history, diagnostic codes, Pittsburgh insomnia rating score, and Charlson index score. The system makes a determination based on unstructured and structured data types derived from internal and external knowledge resources to determine psychotropic drug choice that best matches the molecular and clinical variation profile of an individual patient. The decision support system provides a therapeutic recommendation for a clinician based on the patient's variation profile.
Owner:ASSUREX HEALTH INC
Method for determining personalized nutrition and diet using nutrigenomics and physiological data
InactiveUS20100113892A1Reduce the possibilityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsNutritionNutrient ingestion
This invention relates generally to providing nutrigenomic information tailored to that of the customer so that the customer can make informed decisions regarding diet, exercise, risks of disease and other health issues that result in a healthier lifestyle and prolonged lifespan. In particular the invention provides systems for research and commercial purposes, particularly for research for improving dietary constituents, personalized nutrition and diets, and of nutrient-gene interactions involved in diseases. The invention further relates to a method for doing business encompassing establishing and running a nutrigenomic research super-market and providing validated nutrient intake data to health care practitioners.
Owner:KAPUT JAMES +1
System and method for reconstructing pathways in large genetic networks from genetic perturbations
InactiveUS20030023388A1Reduce research costsPrecise positioningDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsGraphicsGenetic network
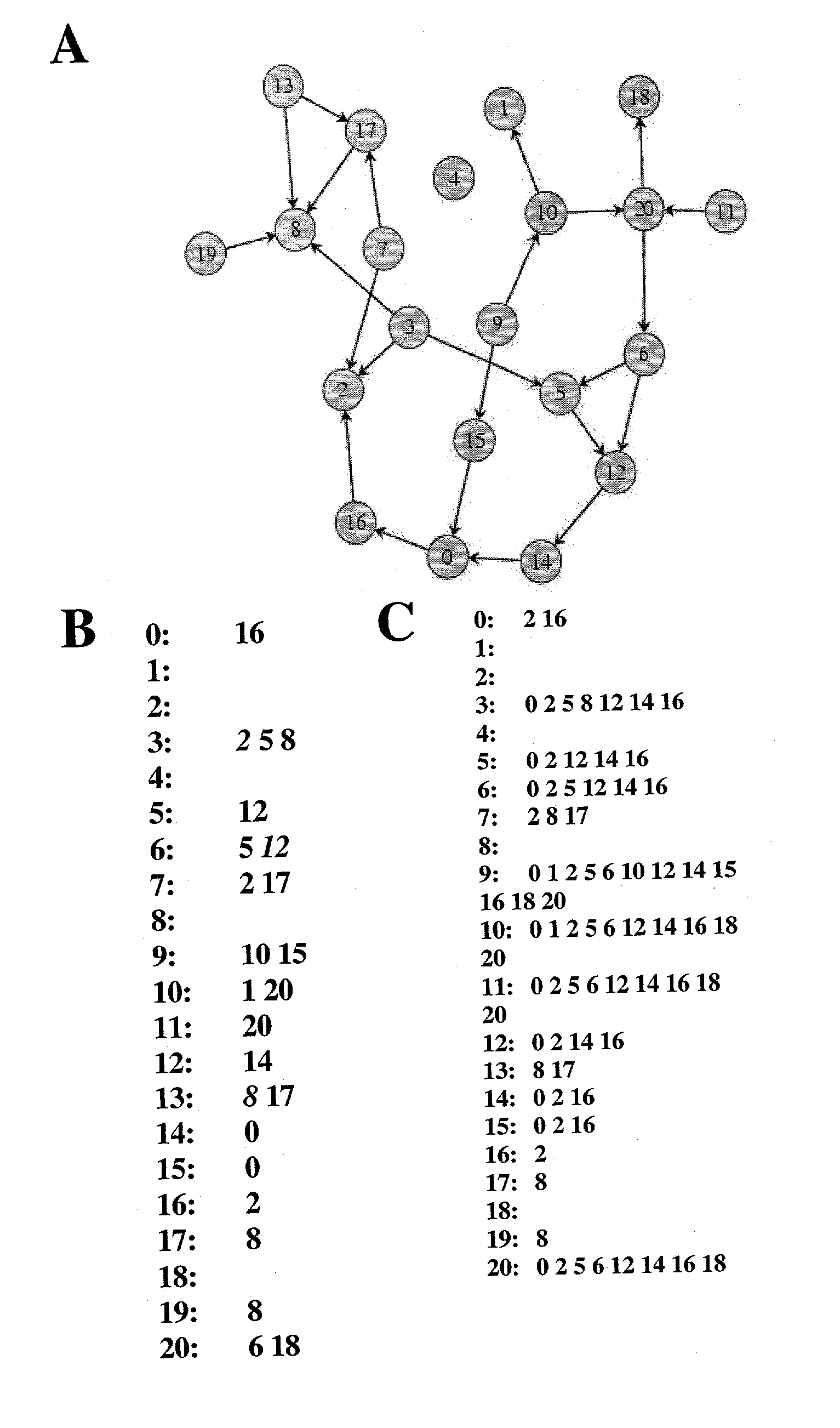
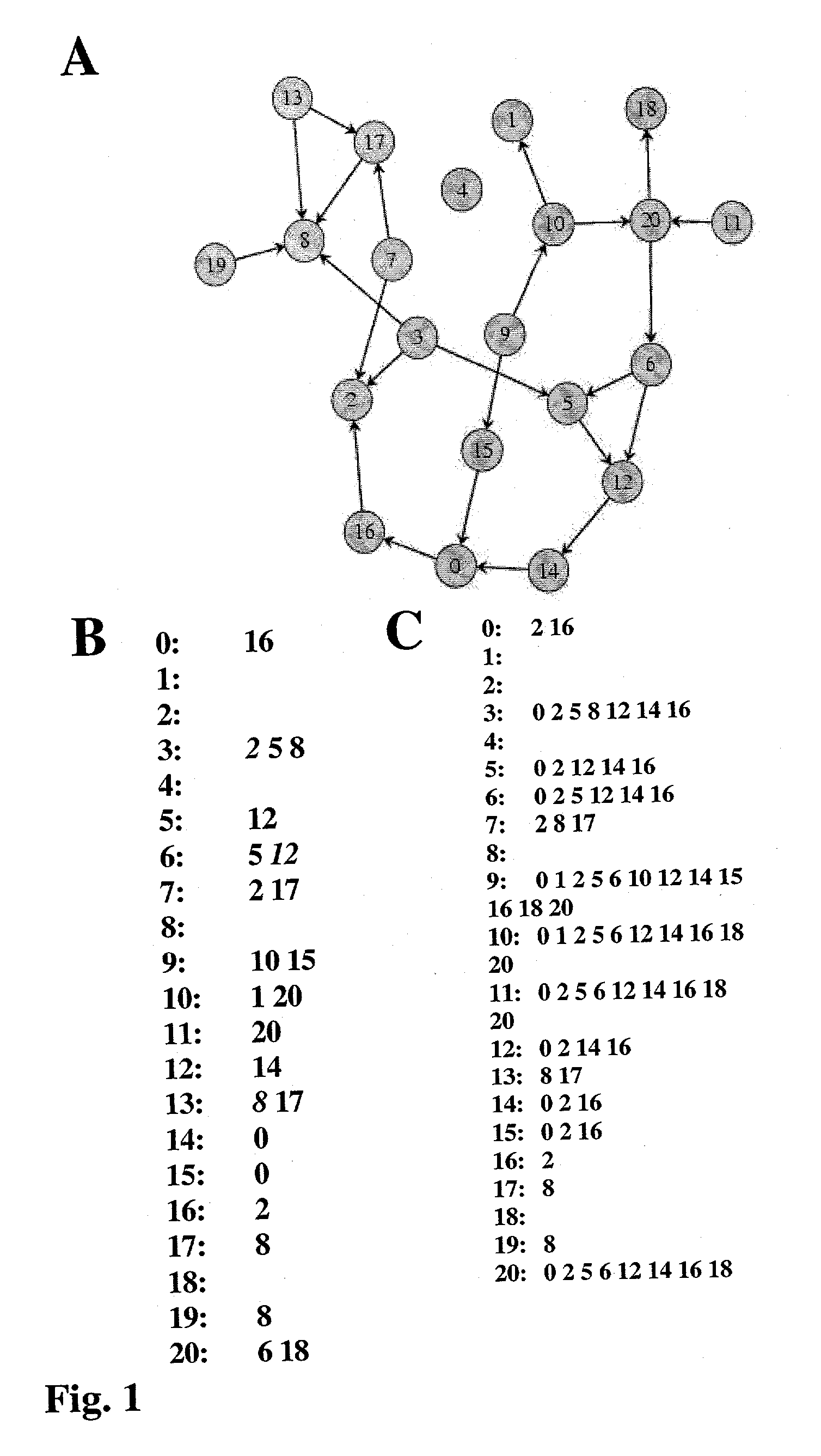
A system and method for reconstructing pathways in large genetic networks from genetic perturbations comprises an analysis method and system that applies a recursive algorithm for determining the path between every gene pair in an arbitrarily large genetic network from large-scale gene perturbation data and reconstructs all direct and indirect regulatory gene interactions in the network. Graph theory mathematics is applied to genetic network reconstruction in the following manner: Genetic perturbation data is used to identify all genes accessible from a perturbed gene to generate an accessibility list for the gene. Graph theory mathematics is applied to the accessibility list and its graph to determine a condensation of the graph as defined by the condensation's accessibility list. Graph theory mathematics is applied to the accessibility list, such as through a recursive algorithm performed on a desktop computer, to obtain an adjacency list for the gene that characterizes a genetic network.
Owner:STC UNM
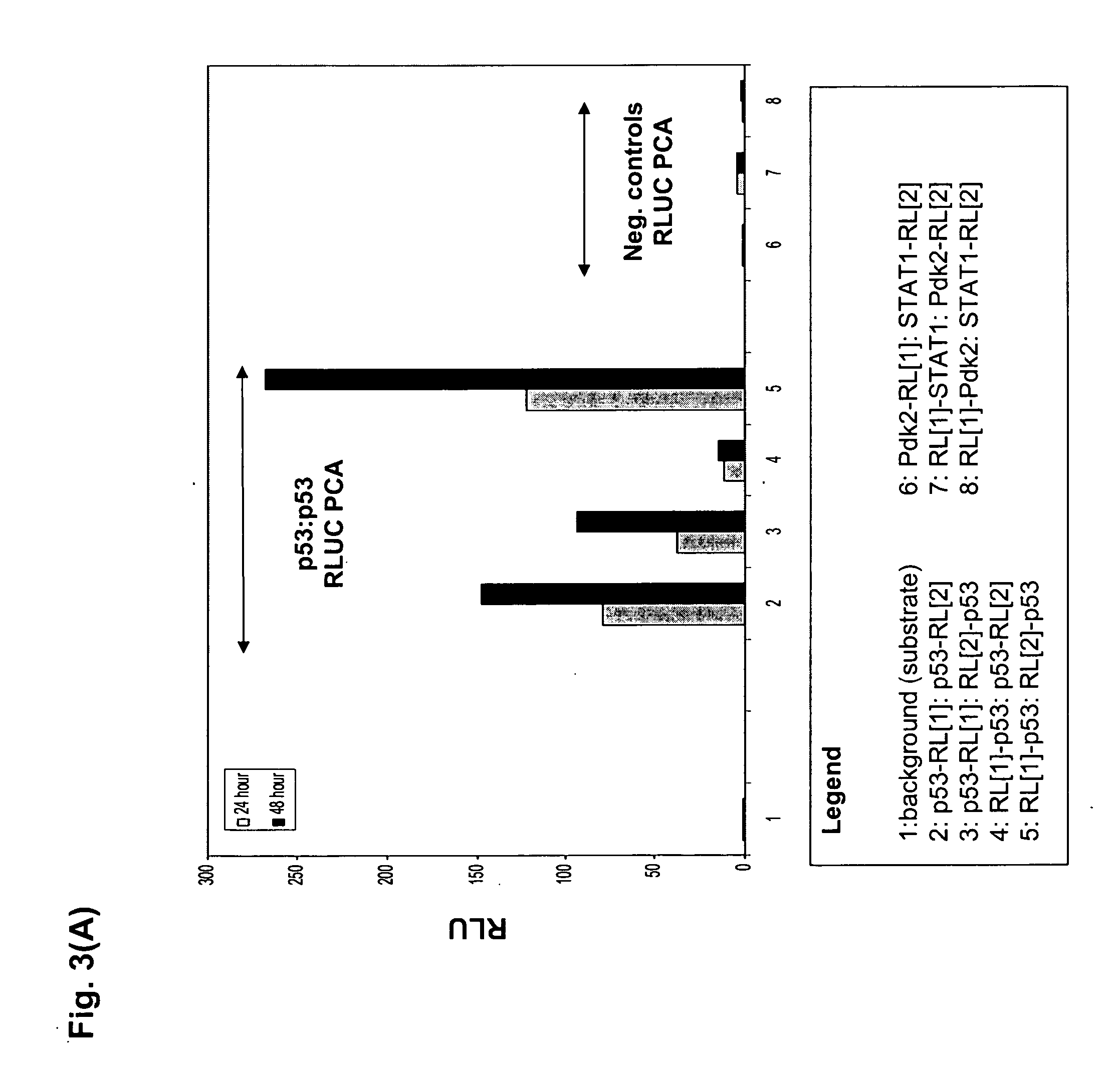
Protein fragment complementation assays for high-throughput and high-content screening
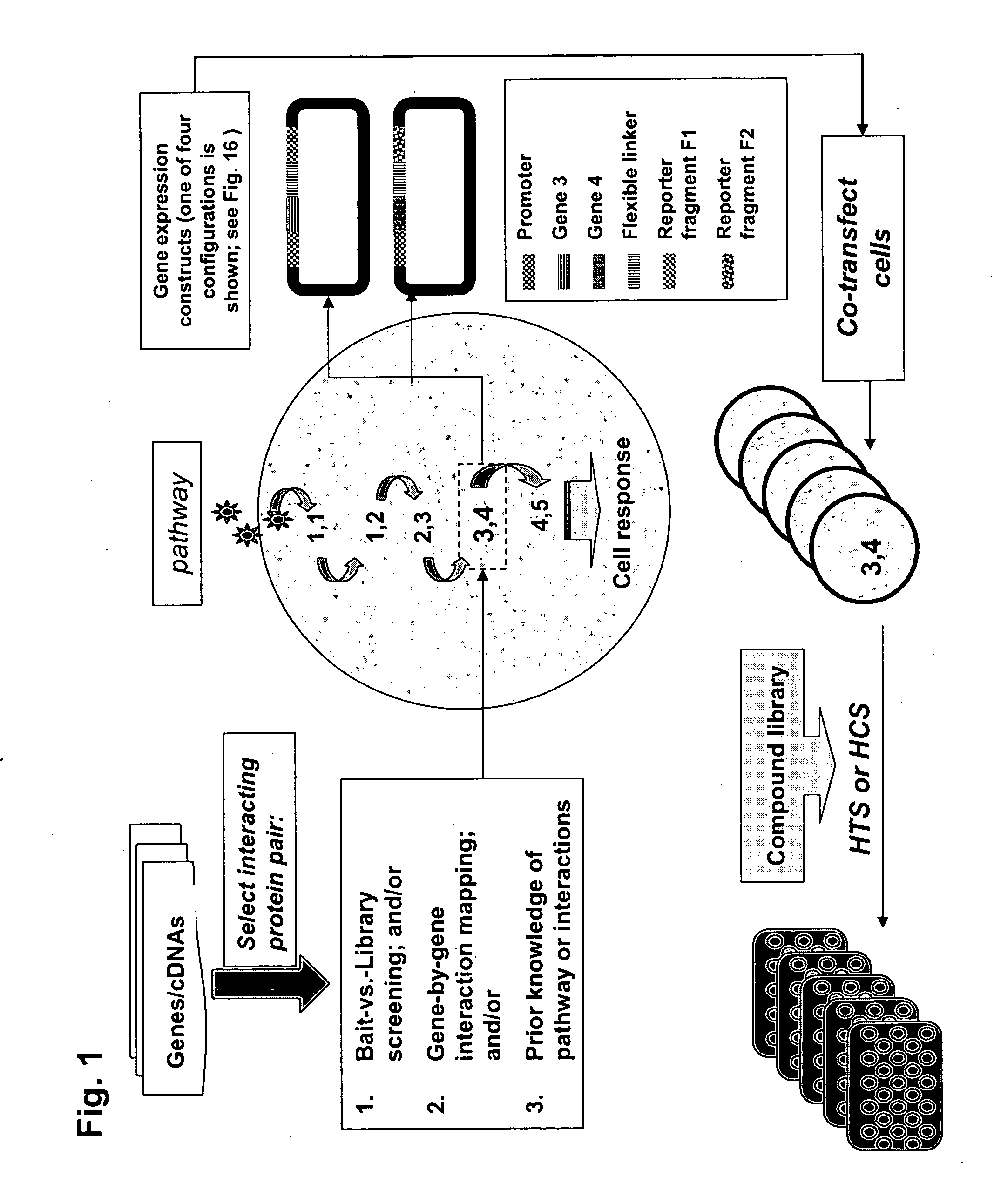
The present invention provides protein fragment complementation assays for drug discovery, in particular to identify compounds that activate or inhibit cellular pathways. Based on the selection of an interacting protein pair combined with an appropriate PCA reporter, the assays may be run in high-throughput or high-content mode and may be used in automated screening of libraries of compounds. The interacting pair may be selected by cDNA library screening; by gene-by-gene interaction mapping; or by prior knowledge of a pathway. Fluorescent and luminescent assays can be constructed using the methods provided herein. The selection of suitable PCA reporters for high-throughput or high-content (high-context) assay formats is described for a diversity of reporters, with particular detail provided for examples of monomeric enzymes and fluorescent proteins. Methods are described for constructing such assays for one or more steps in a biochemical pathway; testing the effects of compounds from combinatorial, natural product, peptide, antibody, nucleic acid or other diverse libraries on the protein or pathway(s) of interest; and using the results of the screening to identify specific compounds that activate or inhibit the protein or pathway(s) of interest. Single-color and multi-color assays are disclosed. Further disclosed are universal expression vectors with cassettes that allow the rapid construction of assays for a large and diverse number of gene / reporter combinations. The development of such assays is shown to be straightforward, providing for a broad, flexible and biologically relevant platform for drug discovery.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Protein fragment complementation assays for high-throughput and high-content screening
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
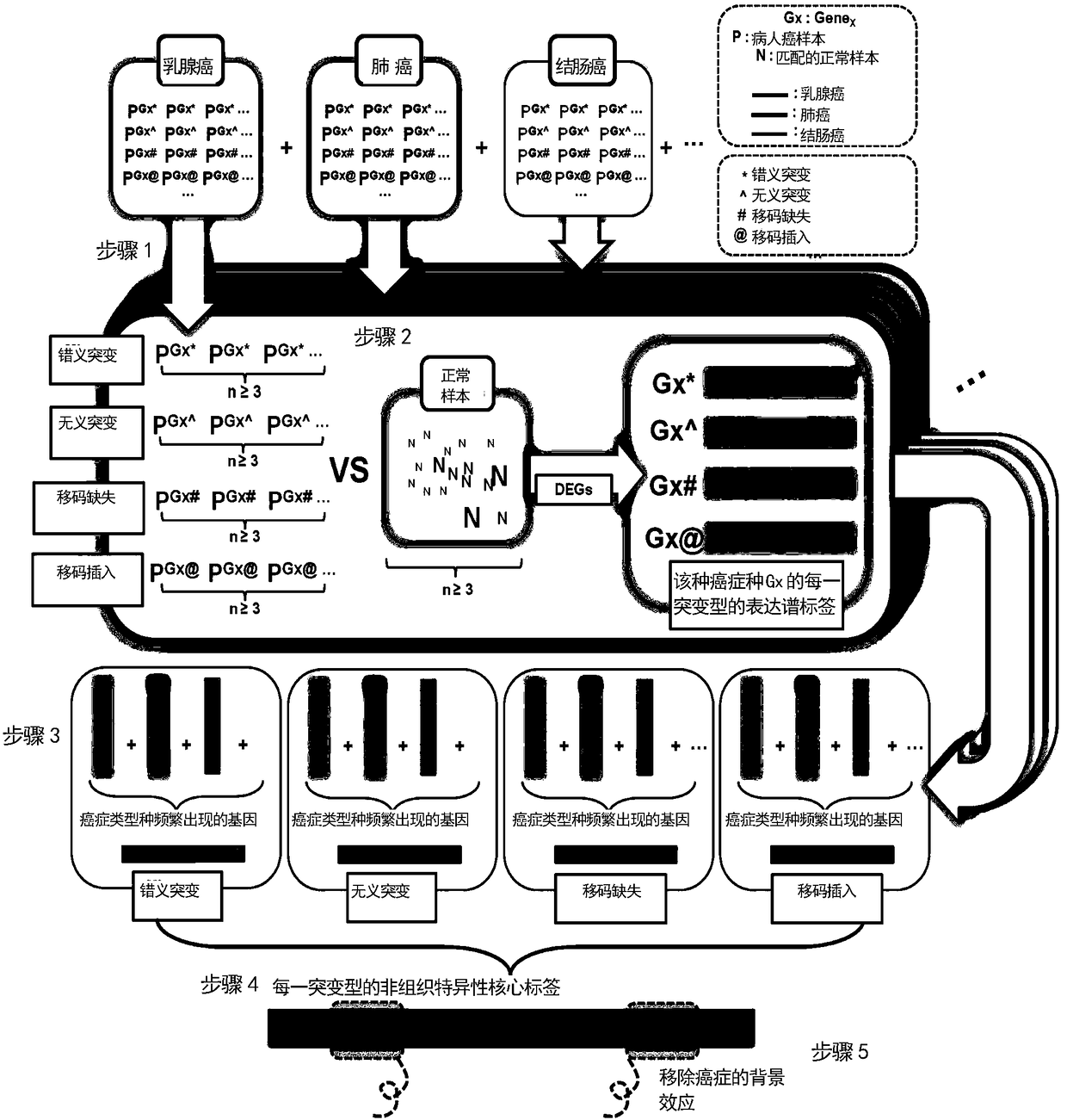
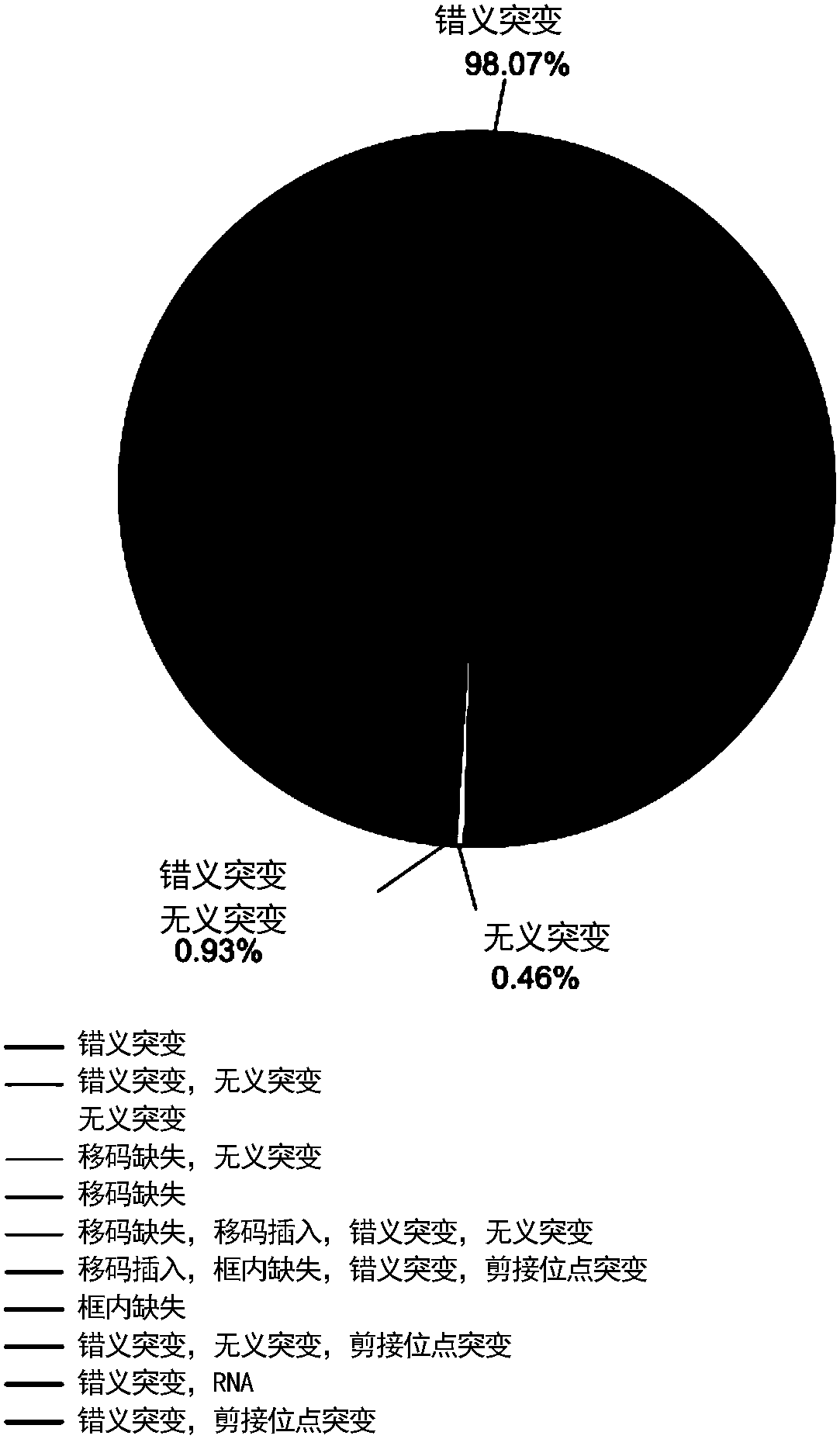
Cancer genome and non-specific gene tag-based large-scale drug relocation method
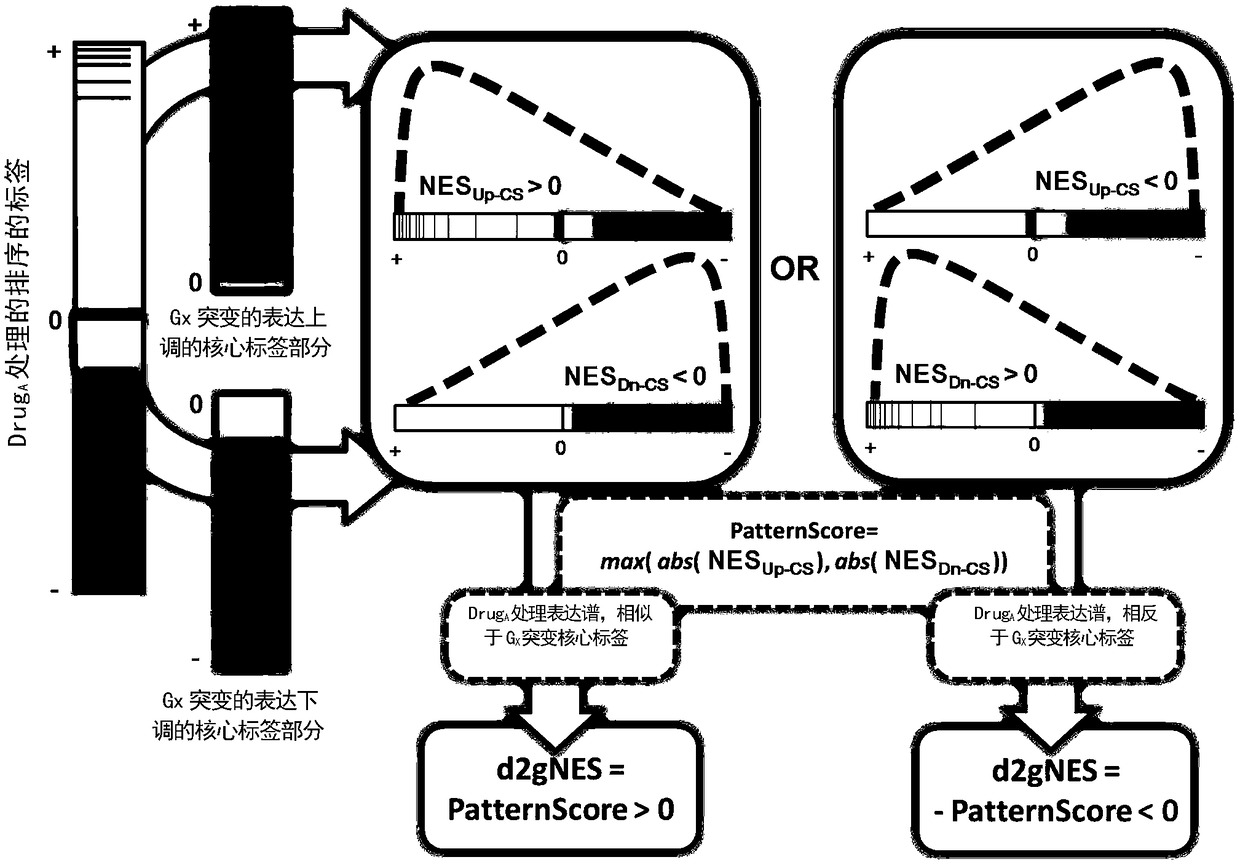
The invention relates to a cancer genome and non-specific gene tag-based large-scale drug relocation method, and discloses a method for expression profile core labels of single human coding gene mutations without organization resource backgrounds through integrating and analyzing large-scale transcriptome data in different cancer types for the first time. On the basis of core labels, the inventionprovides a drug relocation method which aims at the in-vivo environment, is not based on model animals or cells and is capable of comprehensively covering more than 8000 human genome potential targetgenes for the first time, and designs a quantitative index for measuring interaction specificity between drugs and target genes for the first time, so that a drug relocation analysis method for comprehensively analyzing human drug target genes in a large scale is realized and a new way is provided or drug target point design and human disease treatment.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cloning and transient expression method of persimmon deastringency related genes
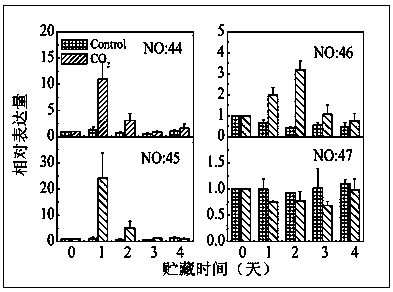
The invention provides a cloning and transient expression method of persimmon deastringency related genes. The method comprises: first acquiring gene 3'-terminal sequences, then employing 3' RACE (rapid amplication of cDNA ends) technology to acquire 3'-terminal sequences of ADH and PDC gene family members in persimmon fruits; adopting Q-PCR (quantitative polymerase chain reaction) technology to analyze the genetic expression of ADH and PDC gene family members in a persimmon fruit deastringency treatment; and conducting separation to obtain full-length sequences of ADH and PDC gene family members, then establishing a transient expression system of persimmon leaves. The method of the invention clones the persimmon deastringency related gene family members, analyze the expression patterns of the family members in the persimmon deastringency treatment, and finally verifies functions of the target genes through transient expression of the persimmon leaves. The invention clarifies the regulation mechanism for postharvest persimmon deastringency from the molecular mechanism aspective, and can be used for further functional verification (transgenosis, gene interaction and the like) study of the postharvest persimmon deastringency mechanism.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
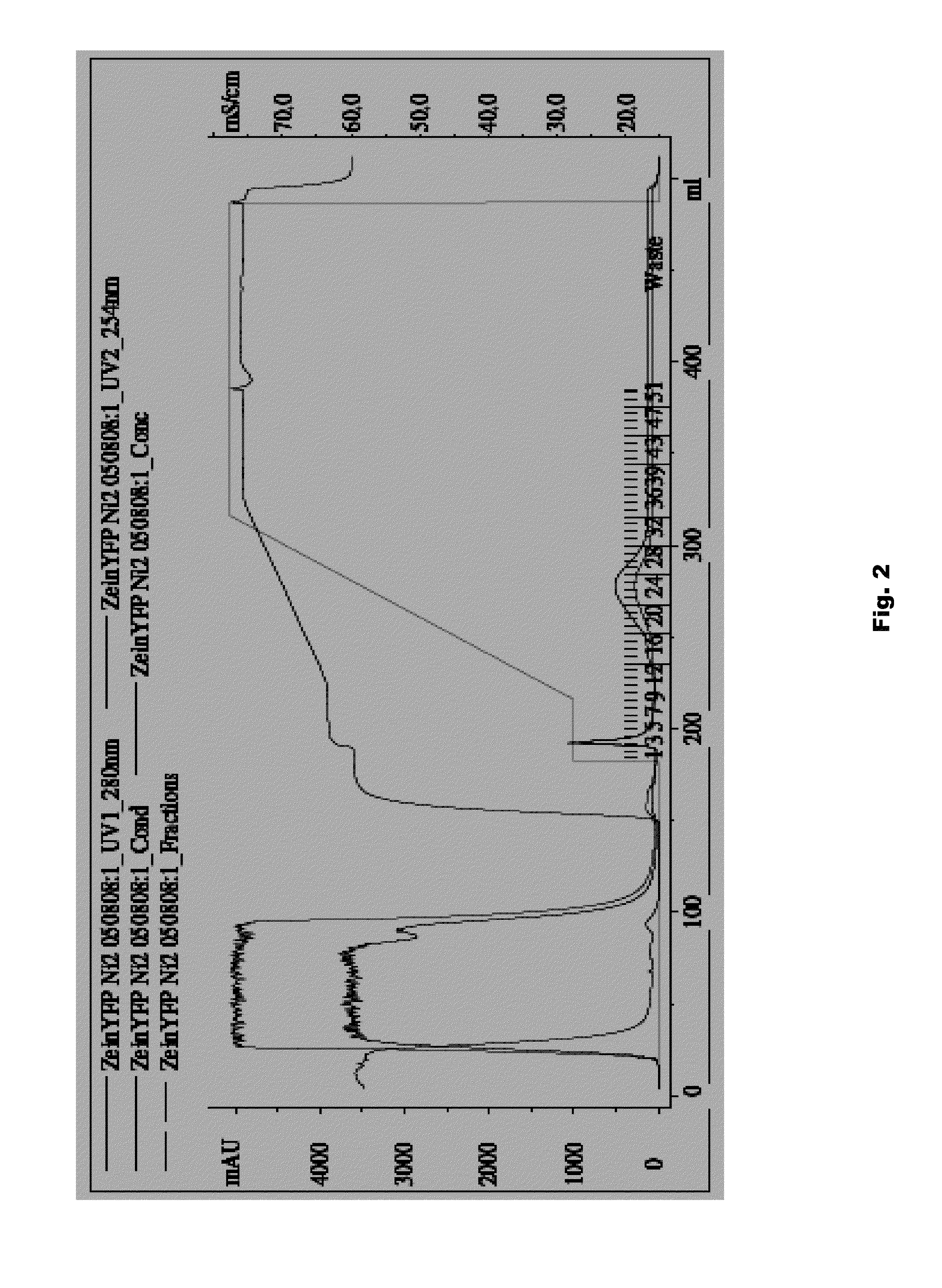
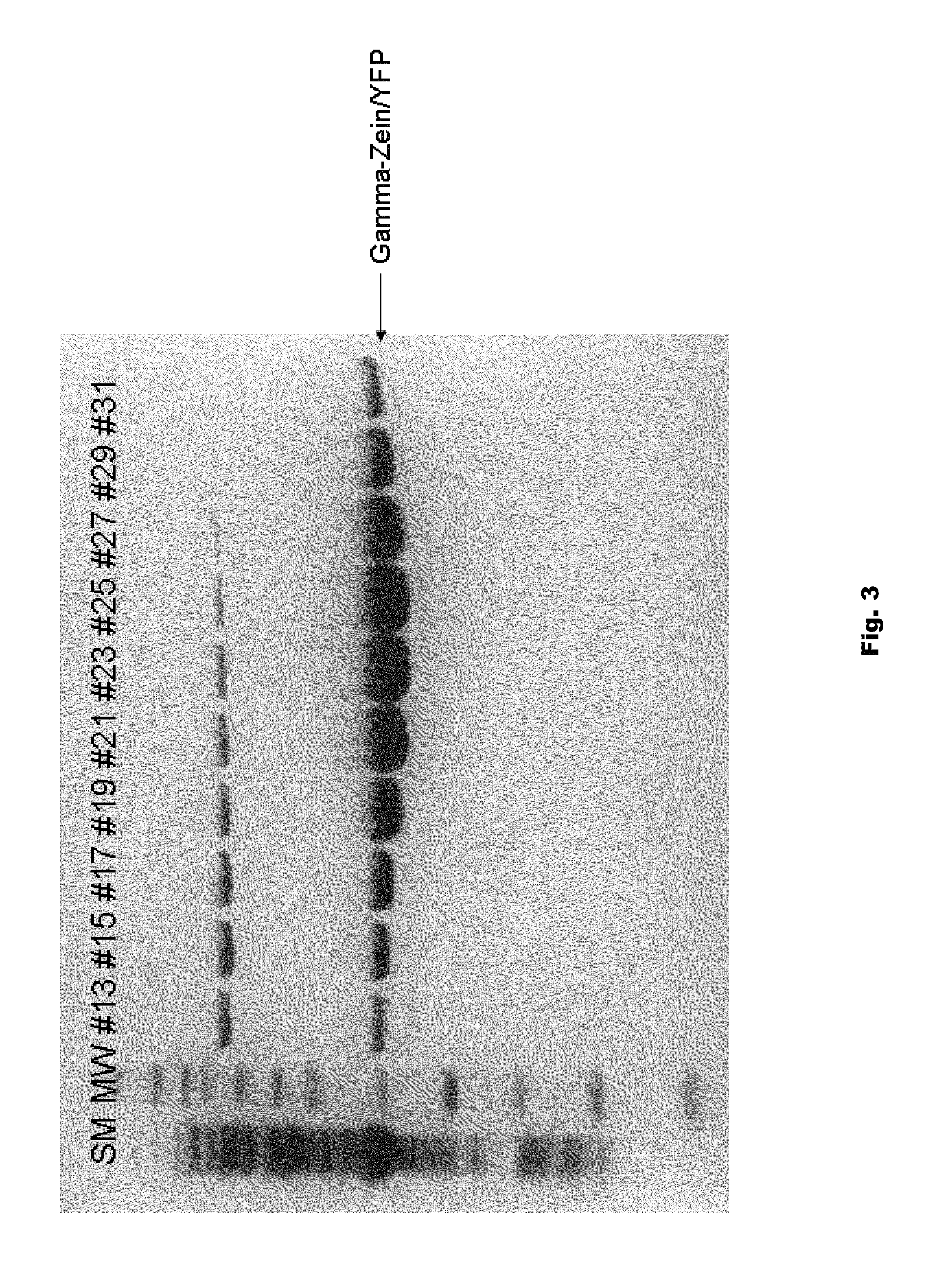
Plant peptide gamma-zein for delivery of biomolecules into plant cells
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Barcoded synthetic lethal screening to identify drug targets
InactiveUS20040121324A1Synthetic strongQuick convenient identificationFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementMutant cloneMedicine
The present invention relates to methods of using synthetic lethal screening techniques to identify drug targets. The methods of the present invention use "barcoded" libraries of cells, where the library consists of a collection of different mutant clones, each mutant clone bearing a knock-out mutation of a different gene. Each mutant clone has a unique DNA identifier tag, or "barcode," to allow for quick and convenient identification of the clone and its mutation. The use of such a library allows for rapid, quantitative, sensitive and simple identification of genes which interact with a mutated target gene. So identified genes are promising targets for drug screening.
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC +1
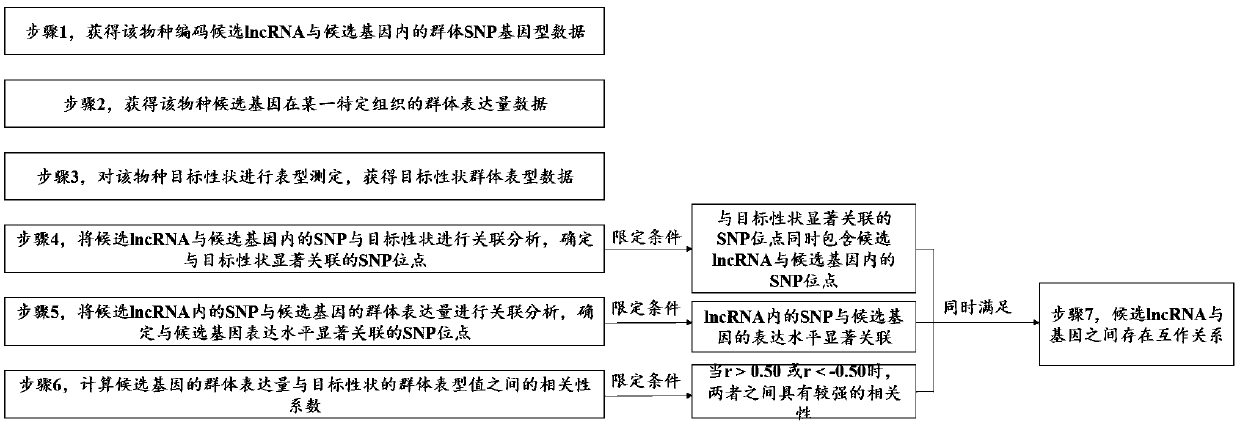
Method for identifying plant lncRNA and gene interaction
ActiveCN109545278AAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsDiameter at breast heightCorrelation analysis
The present invention provides a method for identifying plant lncRNA and gene interaction, and relates to the technical field of molecular genetics. The method comprises the following steps: population SNP genotype data of lncRNA and gene are obtained; population expression data of the gene in a studied tissue are obtained; target trait population phenotypic data are obtained; the population SNP genotype data and target trait population phenotypic data are subjected to correlation analysis; the population SNP genotype data and population expression data are subjected to correlation analysis; acorrelation coefficient r of the population SNP genotype data and target trait population phenotypic data is calculated; when three limit conditions are met at the same time, the lncRNA interacts with the gene to commonly affect phenotypic variation of plant target traits. The method is used to accurately detect interaction between populus tomentosa lncRNA LNC-0052611 and gene Pto-COMT25, and theinteraction affects the phenotypic variation of diameter at breast height of populus tomentosa.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Gene-gene interaction recognition method based on sparsity factor analysis
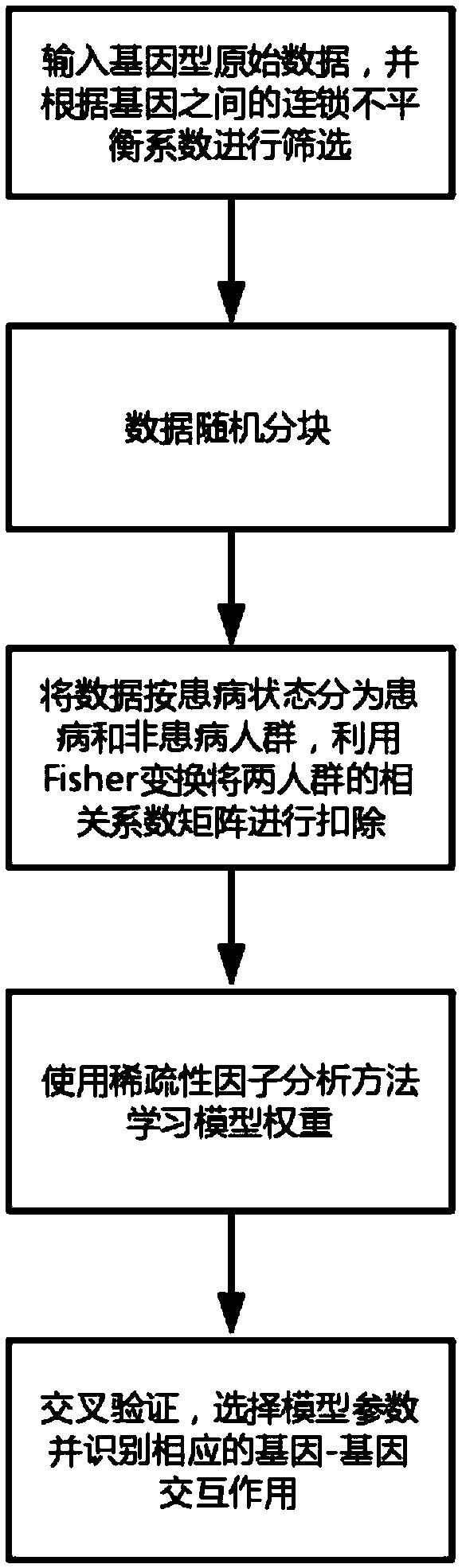
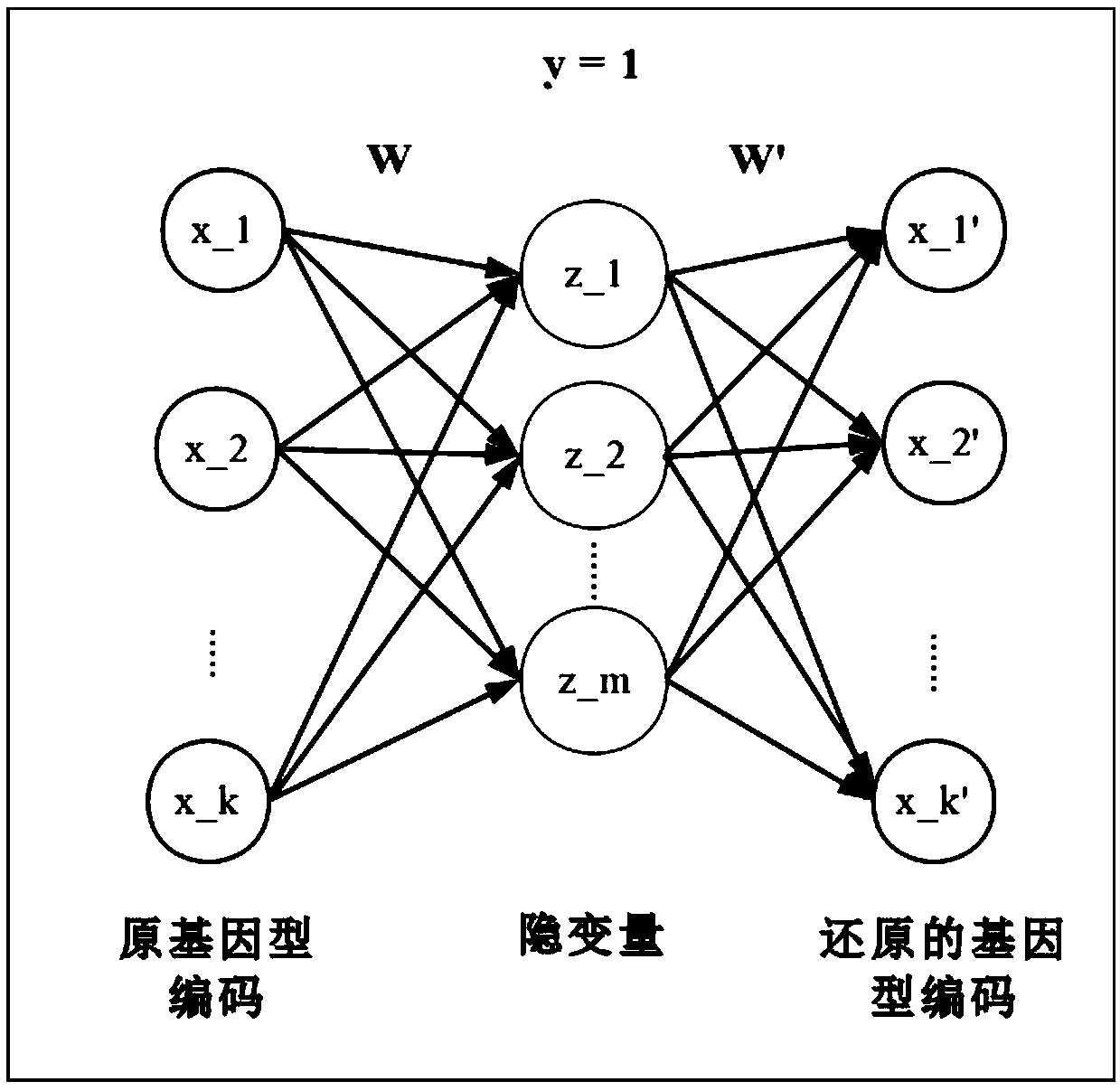
The invention discloses a gene-gene interaction recognition method based on the sparsity factor analysis (Sparse Factor Analysis for Epistasis, EPISFA). The method comprises the following steps of 1)entering genotype raw data and screening according to a linkage disequilibrium coefficient between genes; 2) randomly dividing the data into blocks; 3) dividing the data into diseased and non-diseasedgroups according to a disease state, calculating the correlation coefficient matrix of two groups, and using Fisher transform to deduct gene site correlation of the correlation coefficient matrix ofthe two groups; 4) learning model weights using a sparsity factor analysis method; 5) conducting cross-validation, selecting model parameters, and identifying corresponding gene-gene interaction. Experiments show that the statistical efficiency and computational efficiency of the method are both high and the method has good application prospects.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
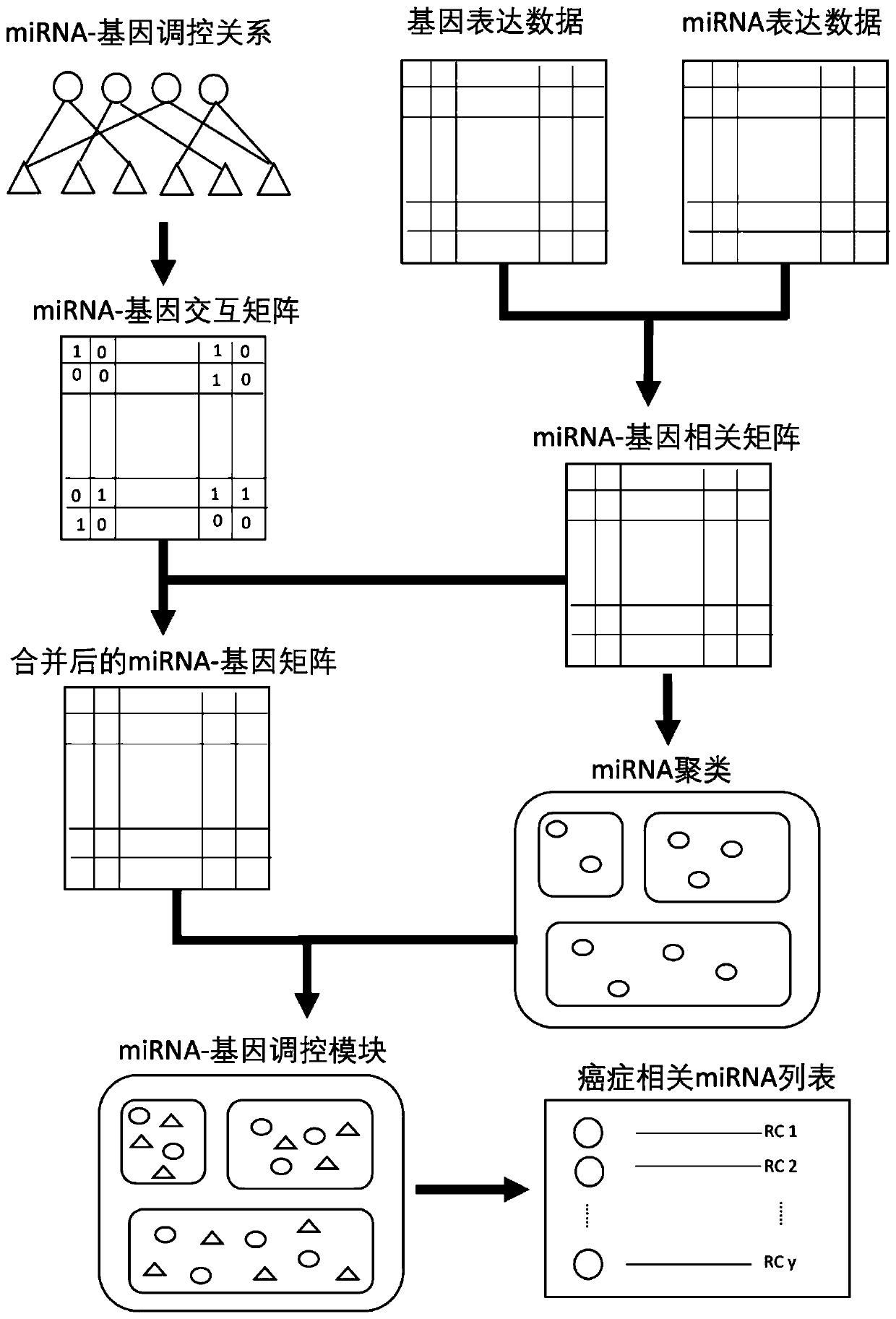
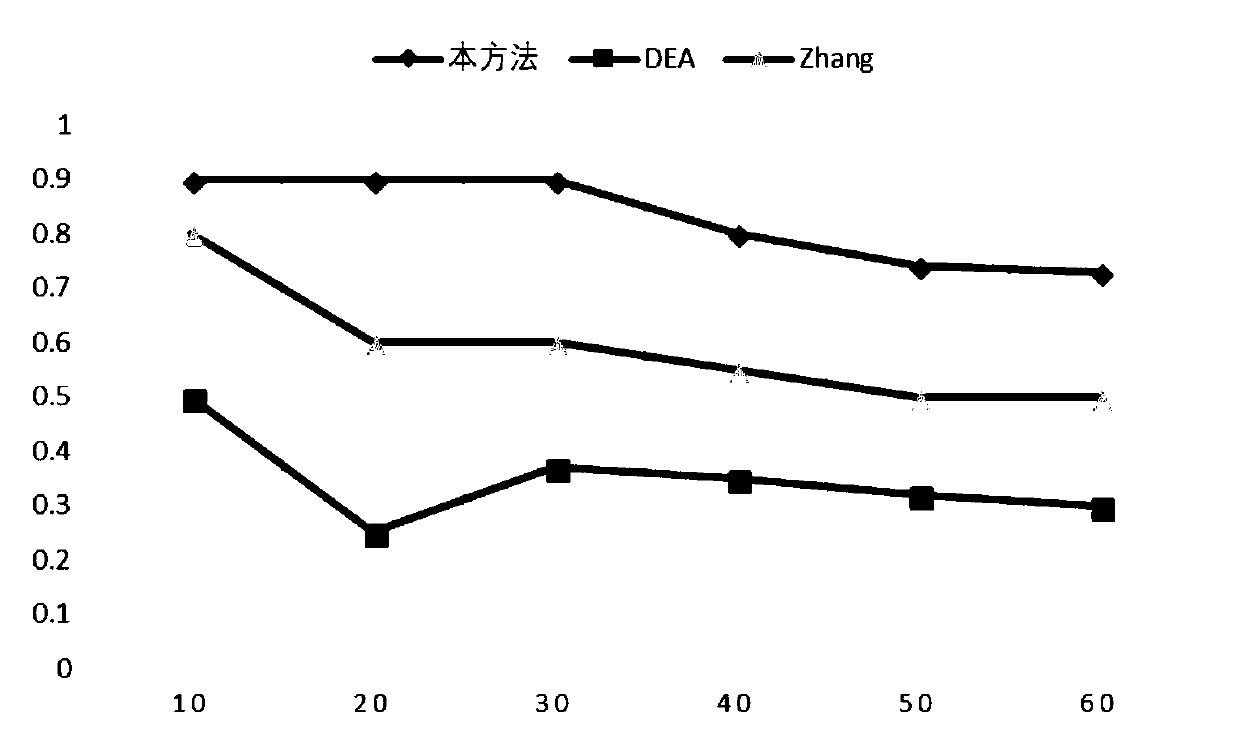
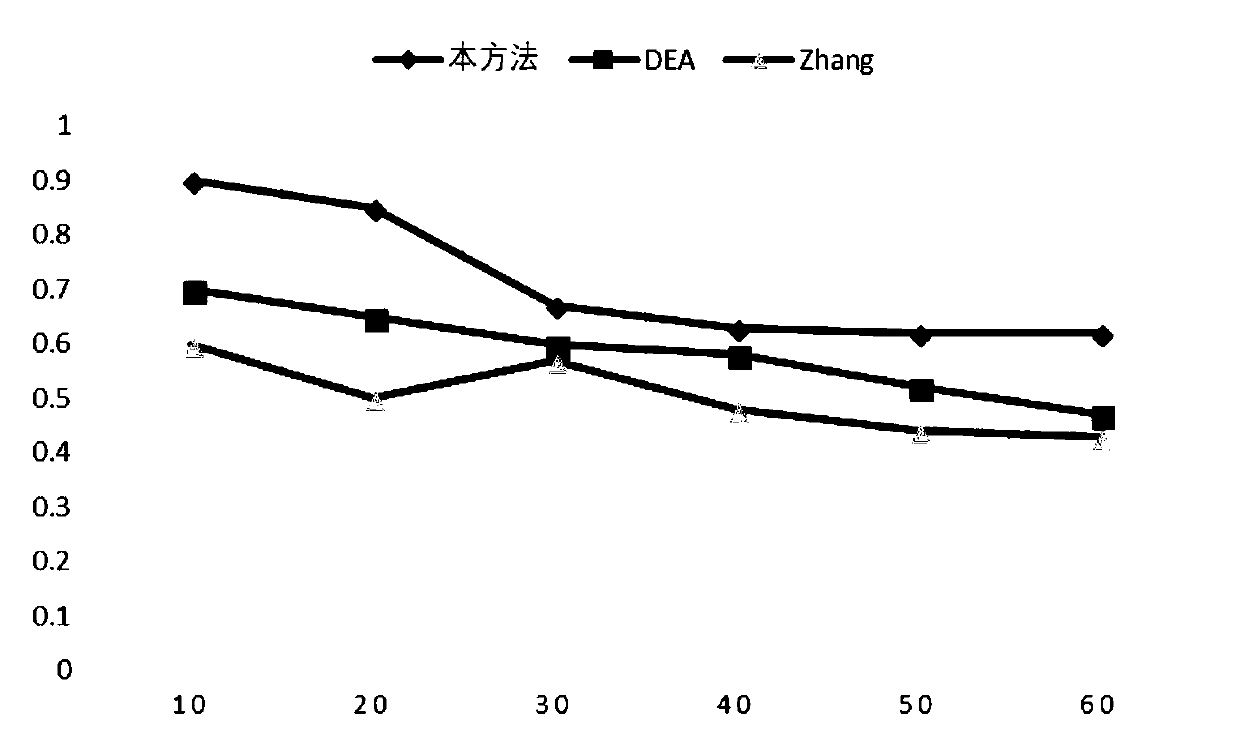
Cancer-related MicroRNA identification method based on miRNA-gene regulation module
The invention relates to data mining in bioinformatics, and particularly to a method for identifying the cancer-related miRNA through a miRNA-gene regulation module. The method comprises the steps ofperforming difference comparison of gene expression data; processing the gene expression data and miRNA expression data; constructing the miRNA-gene interaction matrix; calculating a miRNA-gene correlation coefficient, obtaining a miRNA-gene correlation matrix, performing fuzzy clustering on the miRNA; constructing a combined miRNA-gene interaction matrix and a miRNA-gene correlation matrix, calculating absolute average correlation degree of the gene with each miRNA, adding the gene into the miRNA according to absolute average correlation degree for constructing the miRNA-gene regulating module; calculating the correlation degree of the miRNA in each module, and ordering according to the correlation degree. The main process is presented in a graph 1. The method can be used for acquiring the cancer-related miRNA for searching the function and the mechanism in a cancer development and generating process, screening the miRNA biological mark in cancer early-period diagnosis, and acquiringtargets in targeted treatment of the cancer.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Application of KDM3B gene in mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation, proliferation and migration chemotaxis
ActiveCN111979184ASkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsSignaling networkDifferentially expressed genes
The invention relates to the technical field of bioengineering, in particular to application of a KDM3B gene in mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic / odontogenic differentiation, proliferation and migration chemotactic processes. It is found that the KDM3B gene has the effect of positively regulating the function of the mesenchymal stem cells, a basis is provided for application of KDM3B in the processof promoting osteogenic / odontogenic differentiation and proliferation and migration chemotaxis of the mesenchymal stem cells, and a pathway for mediating significant changes of the function of the differentially expressed gene is enriched based on a KEGG database. 14 significant pathways related to differential gene expression are identified in total, and the pathways play a key role in functionregulation of KDM3B. An interaction library based on remarkably regulated GOs and pathways is constructed through signal network analysis, so that 12 core genes are identified according to the degreeof gene interaction, and an important theoretical basis is laid for studying the reconstruction and regulation mechanism of tooth root regeneration seed cells.
Owner:BEIJING STOMATOLOGY HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
System and method for reconstructing pathways in large genetic networks from genetic perturbations
InactiveUS7124032B2Reduce research costsPrecise positioningBiological testingSystems biologyGraphicsGenetic network
A system and method for reconstructing pathways in large genetic networks from genetic perturbations comprises an analysis method and system that applies a recursive algorithm for determining the path between every gene pair in an arbitrarily large genetic network from large-scale gene perturbation data and reconstructs all direct and indirect regulatory gene interactions in the network. Graph theory mathematics is applied to genetic network reconstruction in the following manner: Genetic perturbation data is used to identify all genes accessible from a perturbed gene to generate an accessibility list for the gene. Graph theory mathematics is applied to the accessibility list and its graph to determine a condensation of the graph as defined by the condensation's accessibility list. Graph theory mathematics is applied to the accessibility list, such as through a recursive algorithm performed on a desktop computer, to obtain an adjacency list for the gene that characterizes a genetic network.
Owner:STC UNM
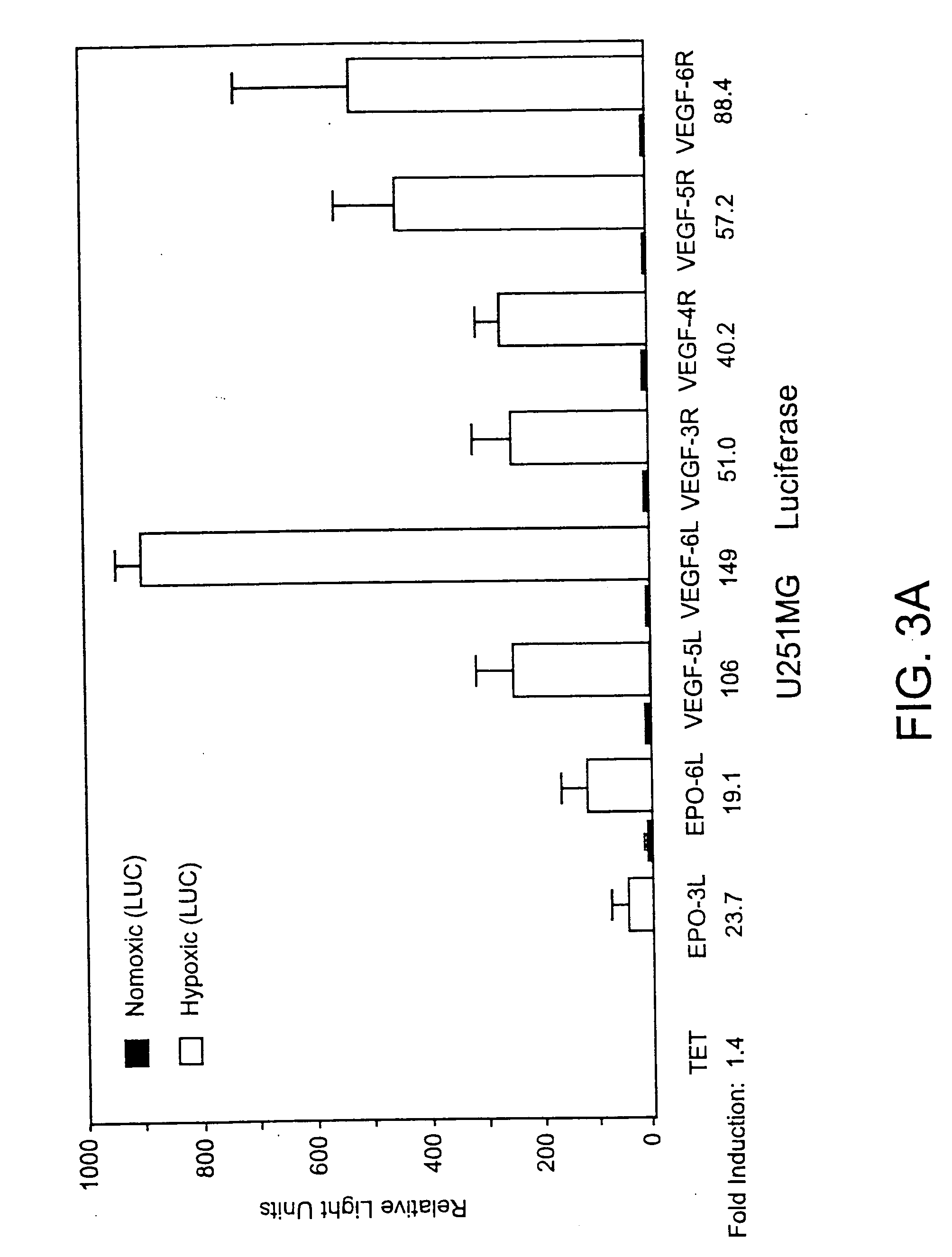
Viruses targeted to hypoxic cells and tissues
The present invention relates to compositions comprising a novel recombinant virus which replicates selectively in cells or tissues that are hypoxic or have an activated HIF pathway. The novel compositions of the invention comprise a recombinant virus genetically engineered to have a hypoxia / HIF-responsive element, or a multiplicity of such elements, operably linked to a promoter which is in turn operably linked to a nucleic acid(s) encoding a peptide(s) which regulates or modulates replication of the virus and / or encode a therapeutic molecule. The invention also includes constructs useful for screening of agents which interact with proteins or genes in the hypoxia-inducible pathway or are jointly translated under hypoxia and animal models useful for monitoring a variety of hypoxic conditions in a non-invasive manner.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
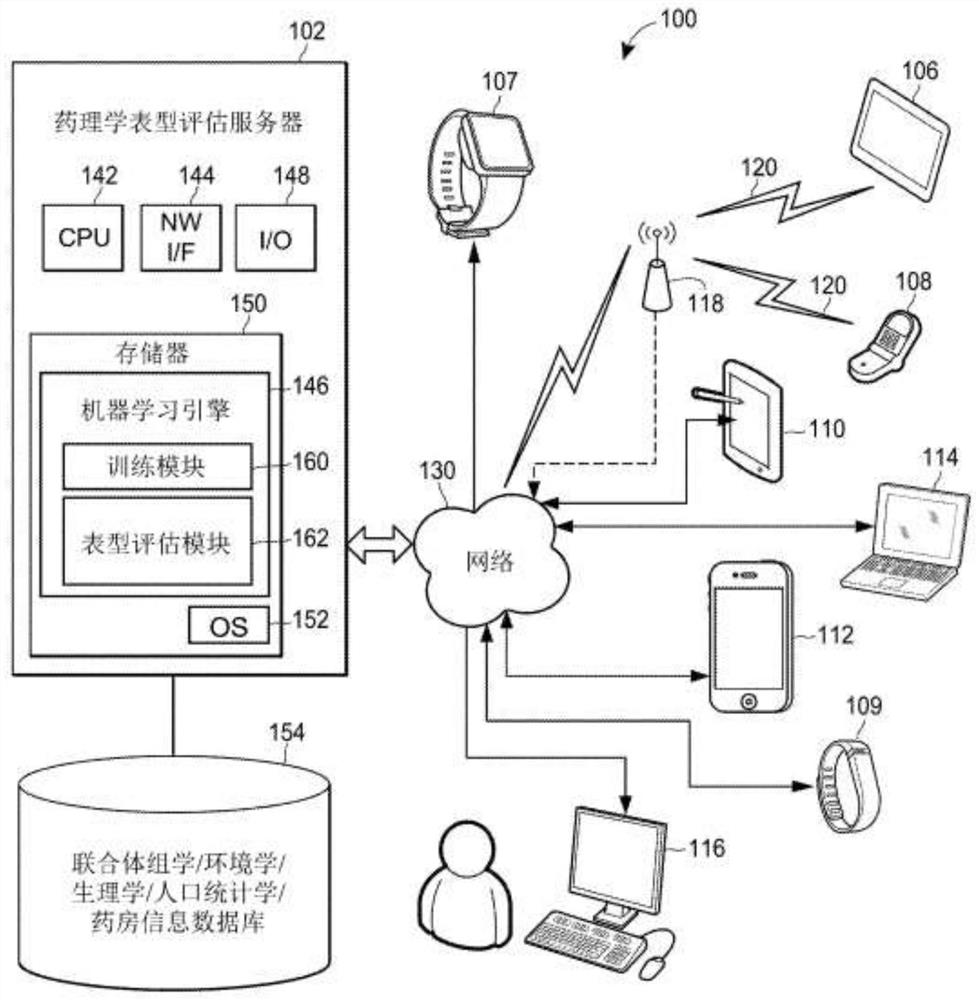
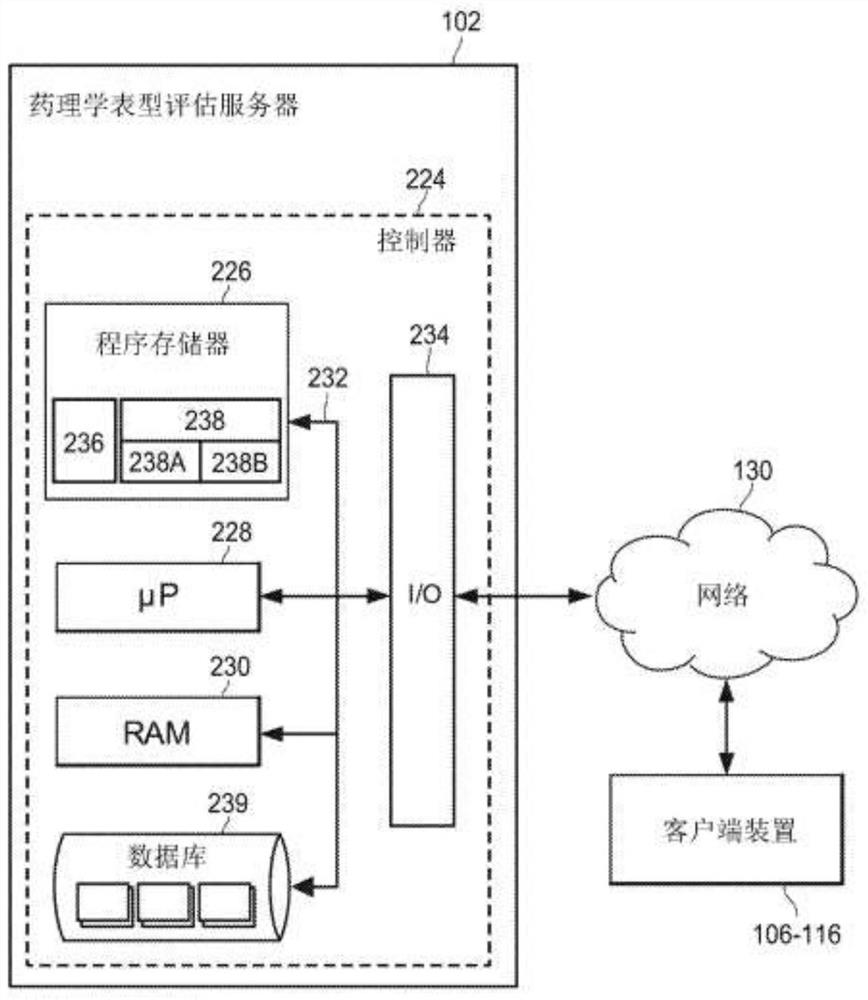
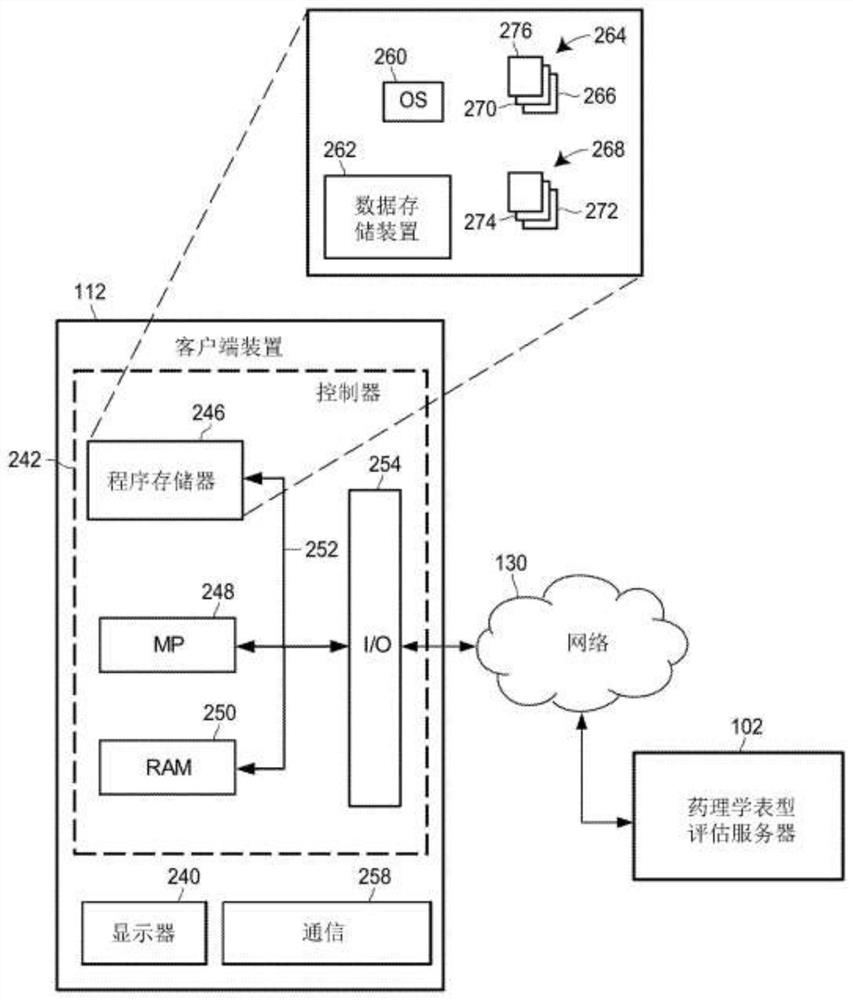
Individual and cohort pharmacological phenotype prediction platform
PendingCN111742370AIdentification is accurate and validMedical data miningHealth-index calculationSubstance abuserIdiopathic disease
For patients who exhibit or may exhibit primary or comorbid disease, pharmacological phenotypes may be predicted through the collection of panomic, physiomic, environmental, sociomic, demographic, andoutcome phenotype data over a period of time. A machine learning engine may generate a statistical model based on training data from training patients to predict pharmacological phenotypes, includingdrug response and dosing, drug adverse events, disease and comorbid disease risk, drug-gene, drug-drug, and polypharmacy interactions. Then the model may be applied to data for new patients to predict their pharmacological phenotypes, and enable decision making in clinical and research contexts, including drug selection and dosage, changes in drug regimens, polypharmacy optimization, monitoring,etc., to benefit from additional predictive power, resulting in adverse event and substance abuse avoidance, improved drug response, better patient outcomes, lower treatment costs, public health benefits, and increases in the effectiveness of research in pharmacology and other biomedical fields.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Analytic method for predicting body weight increase caused by treating schizophrenia through second-generation antipsychotic based on polygene combination interactive effect
ActiveCN110317868ARealize reasonable screeningImprove forecast accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsStatistical analysisOriginal data
The invention discloses an analysis method for predicting body weight increase caused by treating schizophrenia through a second-generation antipsychotic based on the polygene combination interactiveeffect. The method comprises the steps that a sample is prepared for collecting peripheral blood of a patient with body weight increase caused by treating schizophrenia through the second-generation antipsychotic, a hypotonic salt fractionation method is used for extracting a genome DNA sample; a MODLI-TOF flight mass spectrum detecting method is used for performing genetic typing of a 5-HT2CR gene, a histamine 1 receptor gene, an oxytocin gene, an NPY / R gene, a Leptin gene, an adiponectin gene, an FGF21 gene and a FGF23 gene; data analysis and extraction are performed, instrument original data is aligned, data with no noise interference for statistic analysis is obtained, a generalized multi-factor dimension reduction method is used for performing the quantitative trait gene-gene interaction effect, crossed verification is further applied, and the gene interaction effect is used for predicting body weight increase. By adopting the generalized multi-factor dimension reduction method, the continuous ending variable is processed, covariance is introduced, and the method has the advantages of greatly enlarging the application range and greatly increasing the prediction accuracy.
Owner:SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF XINJIANG MEDICAL UNIV
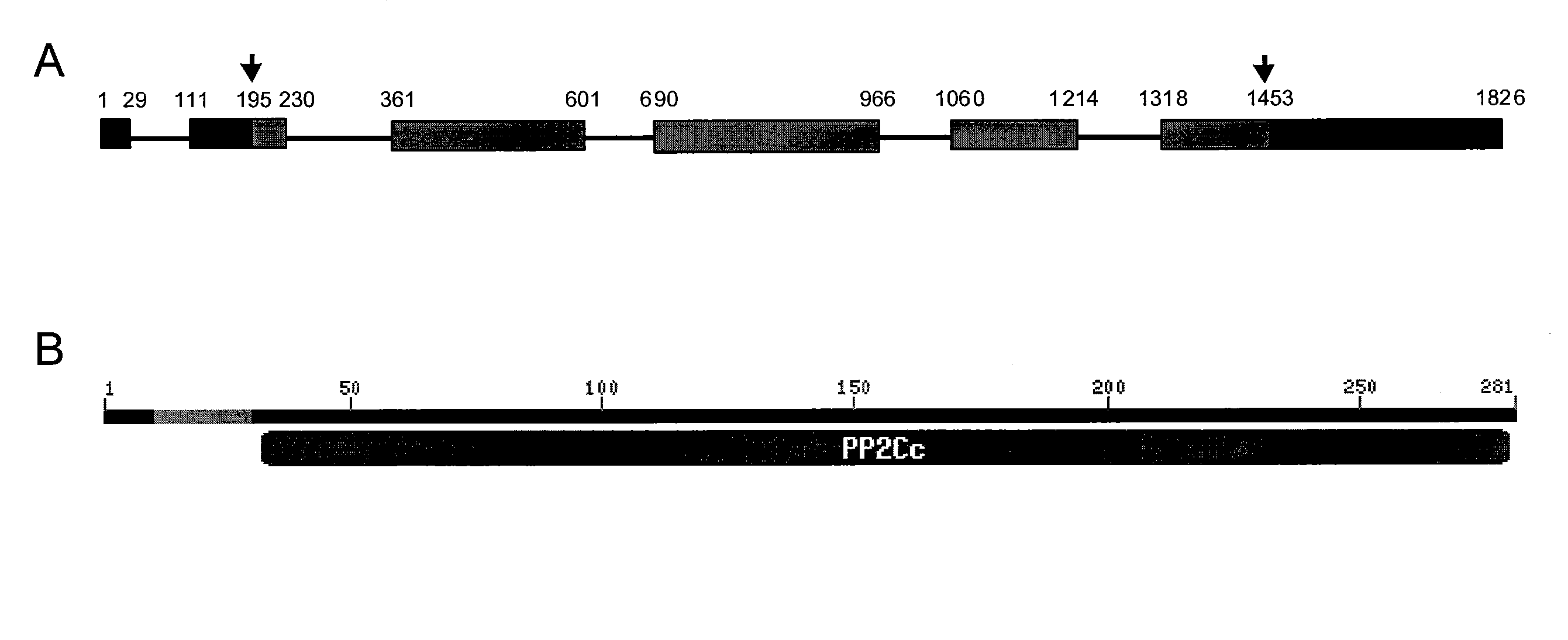
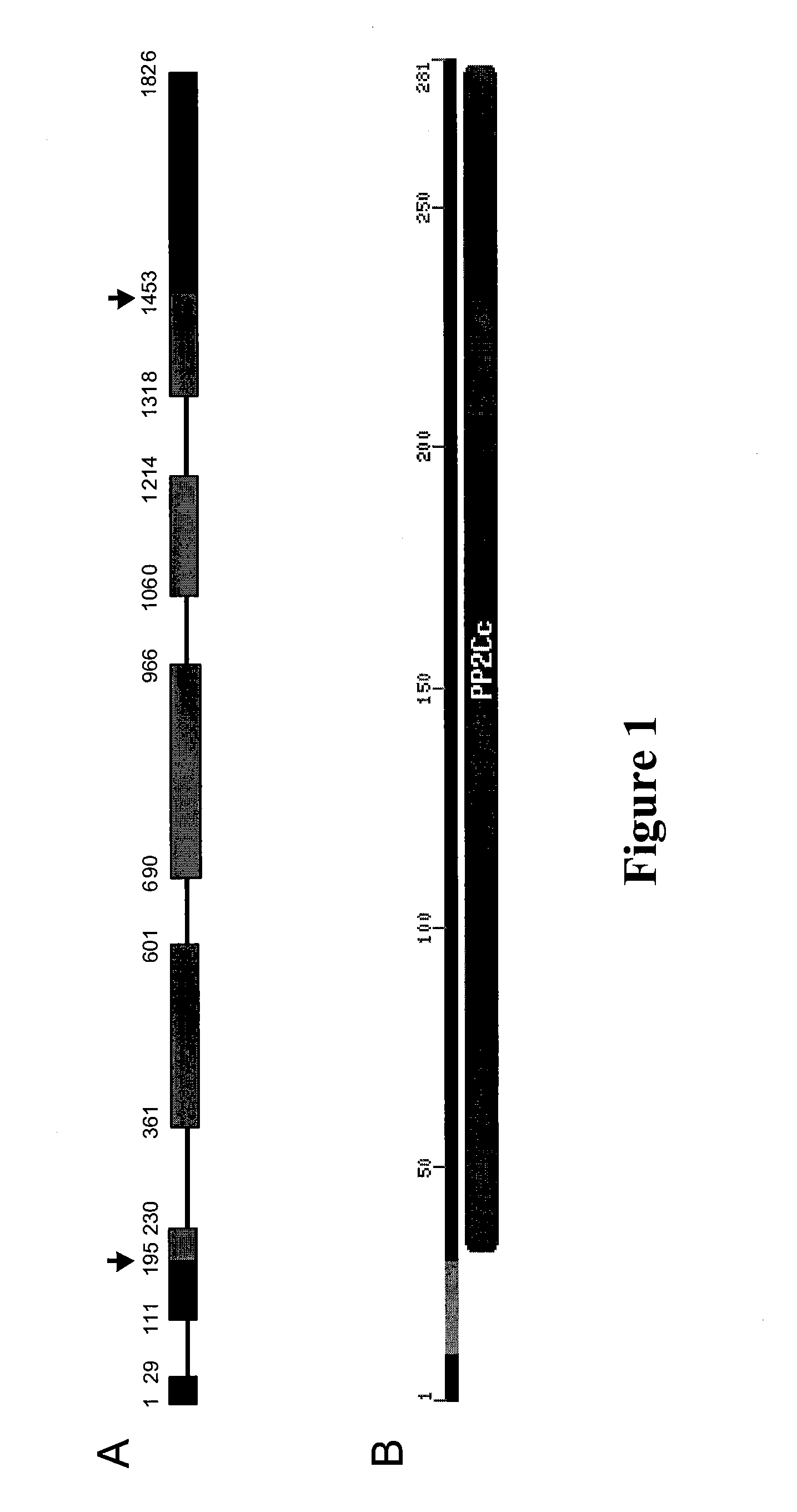
Plants with reduced expression of phosphatase type 2c gene for enhanced pathogen resistance
InactiveUS20070256193A1Improve disease resistanceTight regulationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationDiseaseR gene
The present invention relates to a method for down regulating an Arabidopsis protein phosphatase type 2C gene, referred to as “defense-associated protein phosphatase type 2C one” (DAPP1) that functions as a negative regulator of a plant defense pathway by contacting the gene or gene mRNA with an interfering nucleotide sequence that interacts with the gene and reducing expression thereof. Plants including such interfering nucleotide sequence exhibit increased disease resistance to pathogen even in the absence of R genes. Close homologs of DAPP1 exist in multiple crop species, and as such, the controlled down-regulation of homologous genes in a variety of crop species will enhance disease resistance of target crop species to pathogens.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
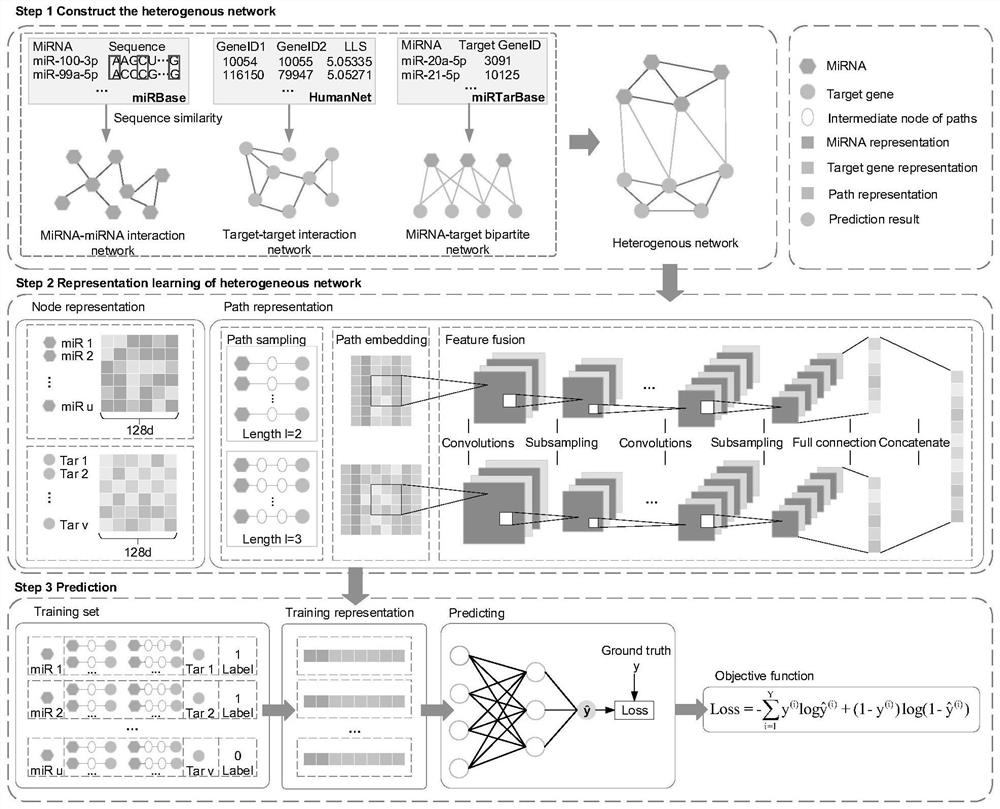
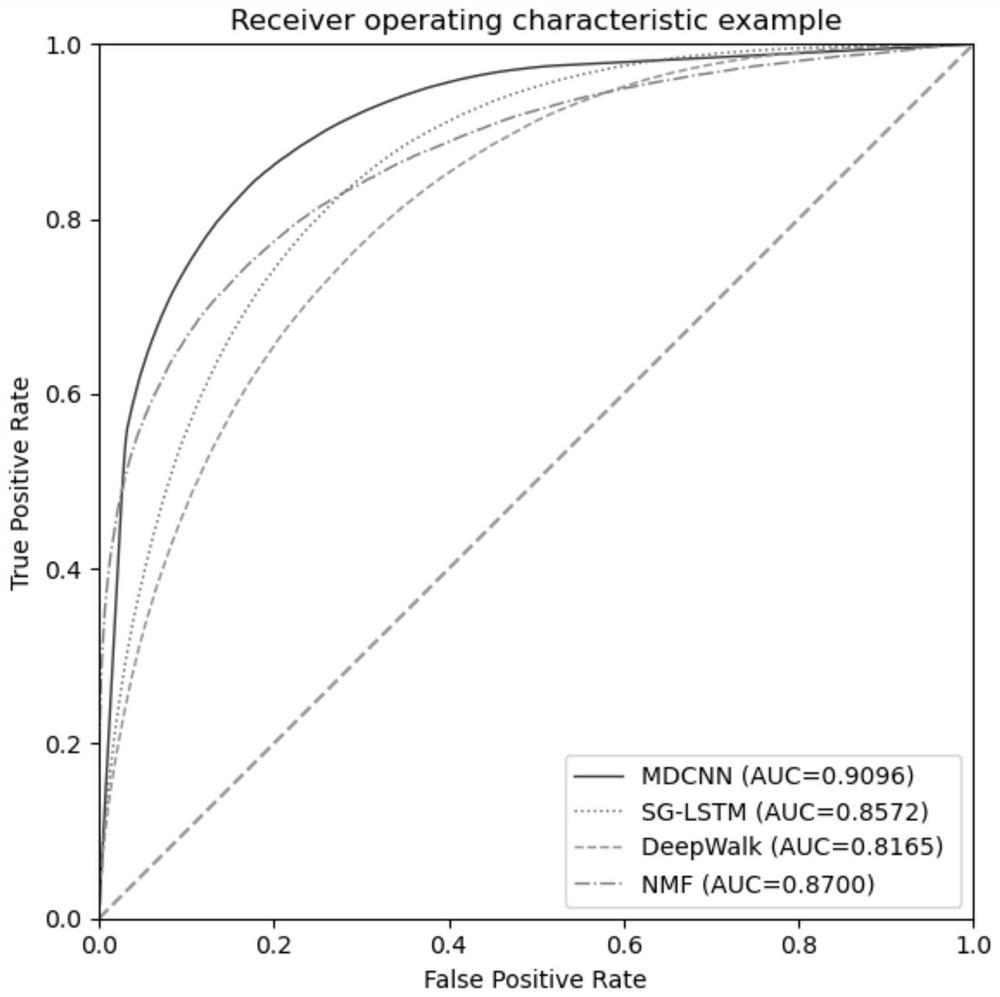
MiRNA-gene relationship prediction method and system based on deep learning heterogeneous information network
ActiveCN112951328ASimple structureSimple and fast operationBiostatisticsNeural architecturesInformation networksHeterogeneous network
The invention discloses a miRNA-gene relationship prediction method and system based on a deep learning heterogeneous information network. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a miRNA-gene heterogeneous information network; then collecting a path instance set between the miRNA-gene pair on the heterogeneous network by using a meta path, and capturing effective information of the path set by using a deep convolutional neural network; and finally, splicing miRNA embedding, gene embedding and path embedding, and predicting the interaction between miRNA and the gene through a multi-layer perceptron. According to the invention, the defect that the traditional machine learning needs to manually collect features is avoided, and the network node features are automatically learned by using a deep learning method in a form of network nodes. A contrast experiment result shows that the performance of the MDCNN is superior to that of other methods, and the potential miRNA-gene interaction can be accurately predicted.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for screening micro ribonucleic acid (microRNA) target gene based on natural language processing system
InactiveCN102375840AIdentification work is easySolve the problem of predicting too many and too many microRNA target genesSpecial data processing applicationsNODALResearch Object
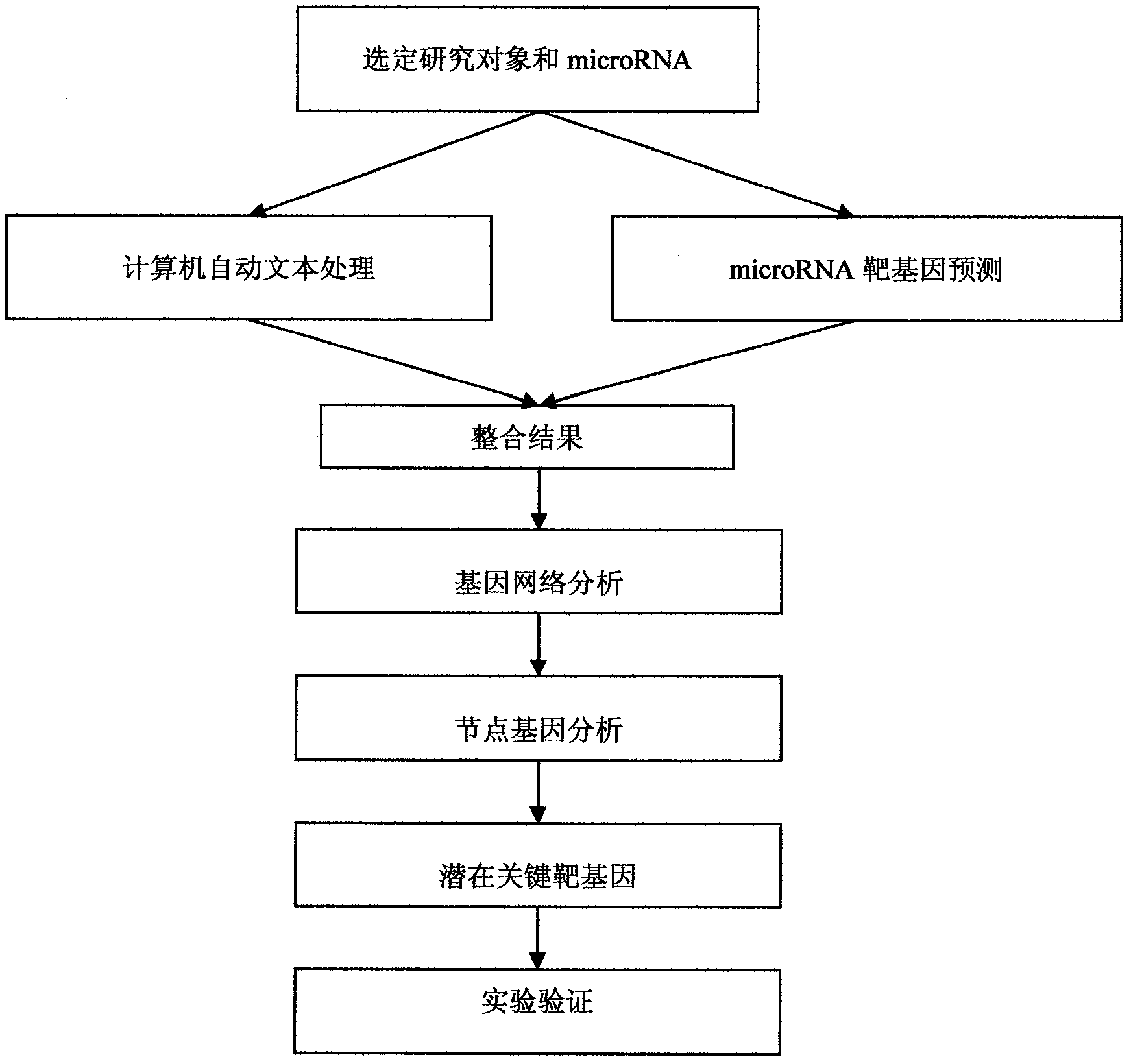
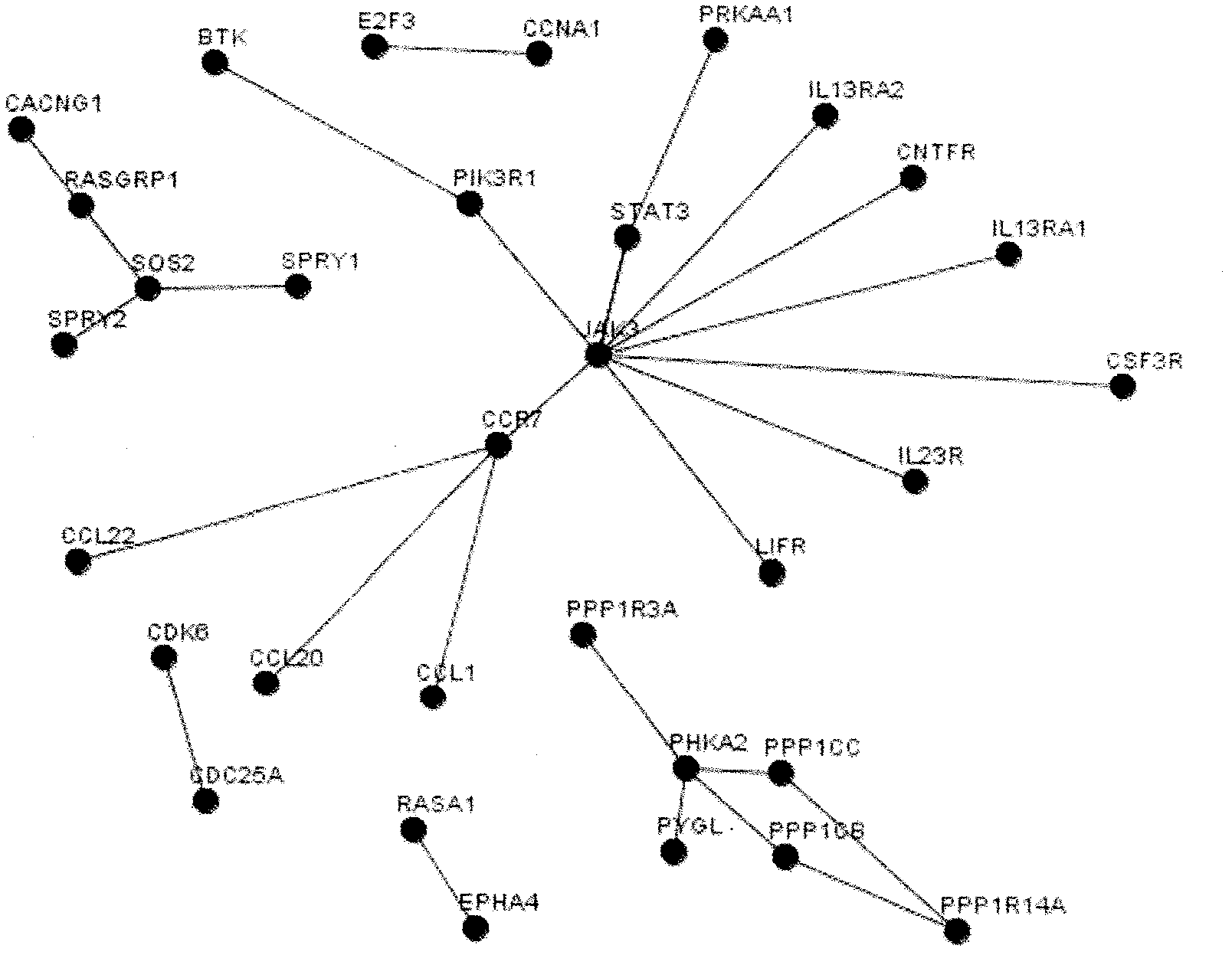
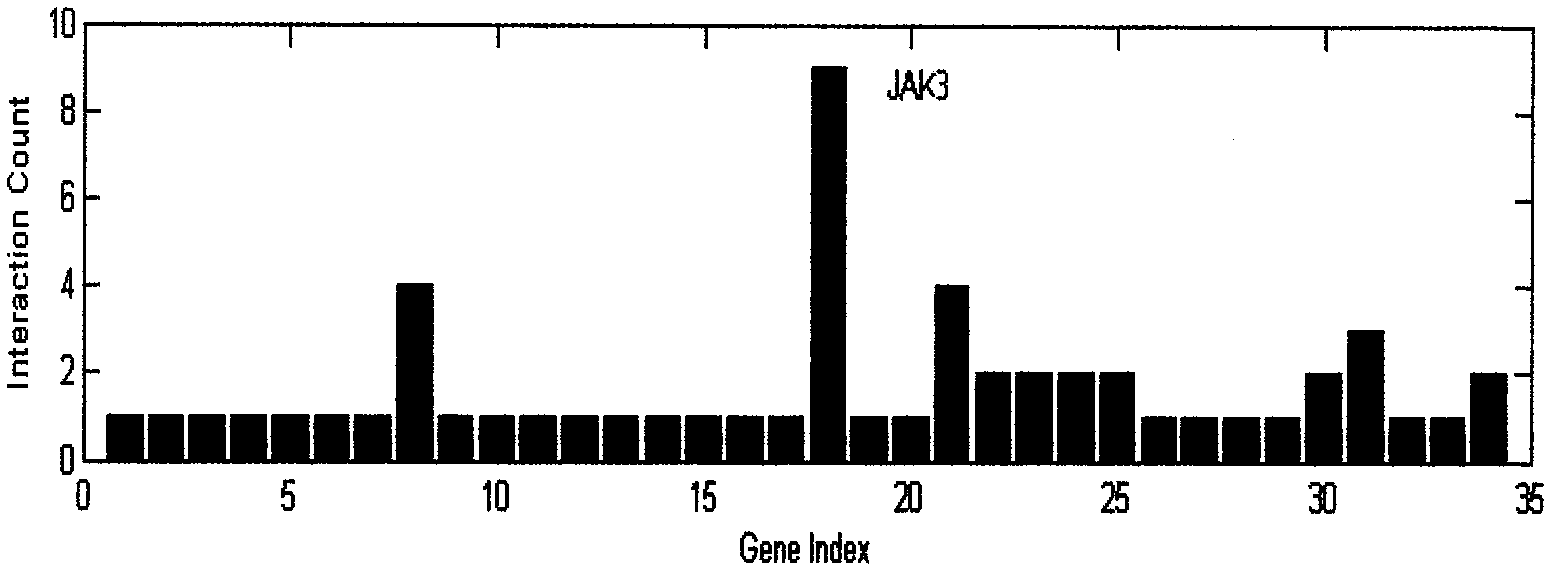
The invention discloses a bioinformatics method capable of screening a micro ribonucleic acid (microRNA) target gene from the existing literature by using a computer natural language processing system, which can eliminate complicated steps of a middle experiment and locking the target gene directly so as to bring convenience to further experiment verification. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: 1, selecting a specific development object and the microRNA; 2, introducing a literature excavation technology, and searching a relative gent; 3, performing target gene prediction on the microRNA, and settling into a list; 4, integrating gene lists in the steps 3 and 4, and constructing a gene interaction relationship network; 5, analyzing the connectivity of the gene in the step 4, searching a node gene, and screening a key target gene of the microRNA out; and 6, performing experiment verification.
Owner:浙江中医药大学附属第一医院
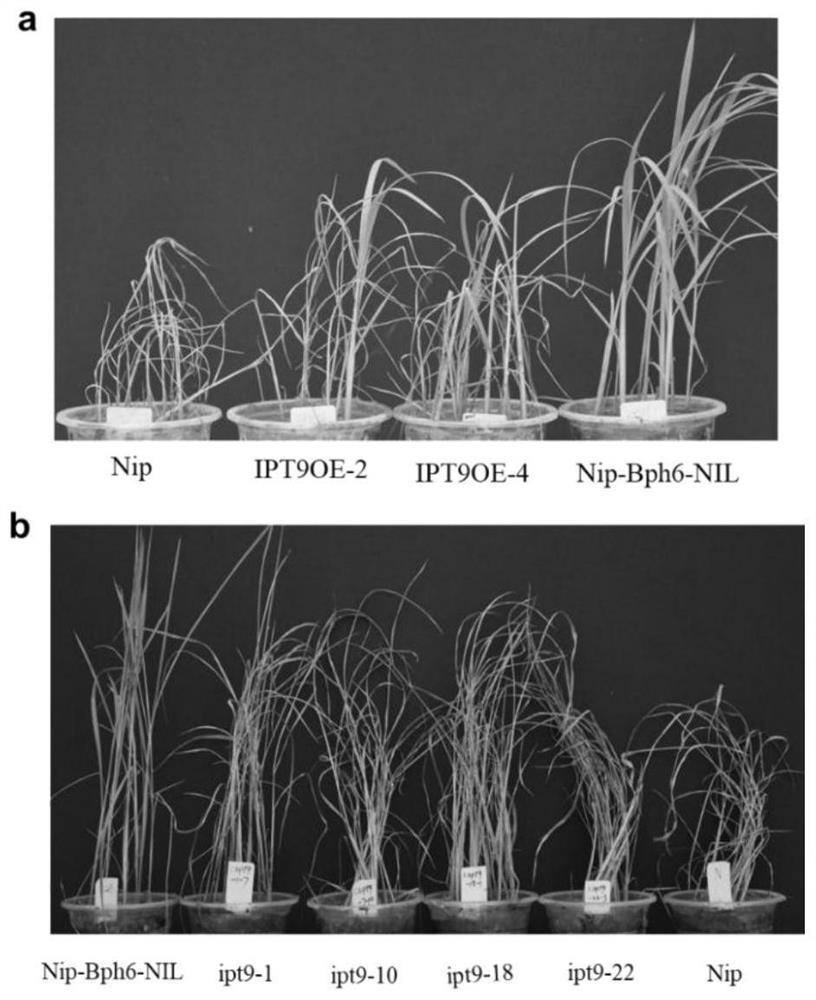
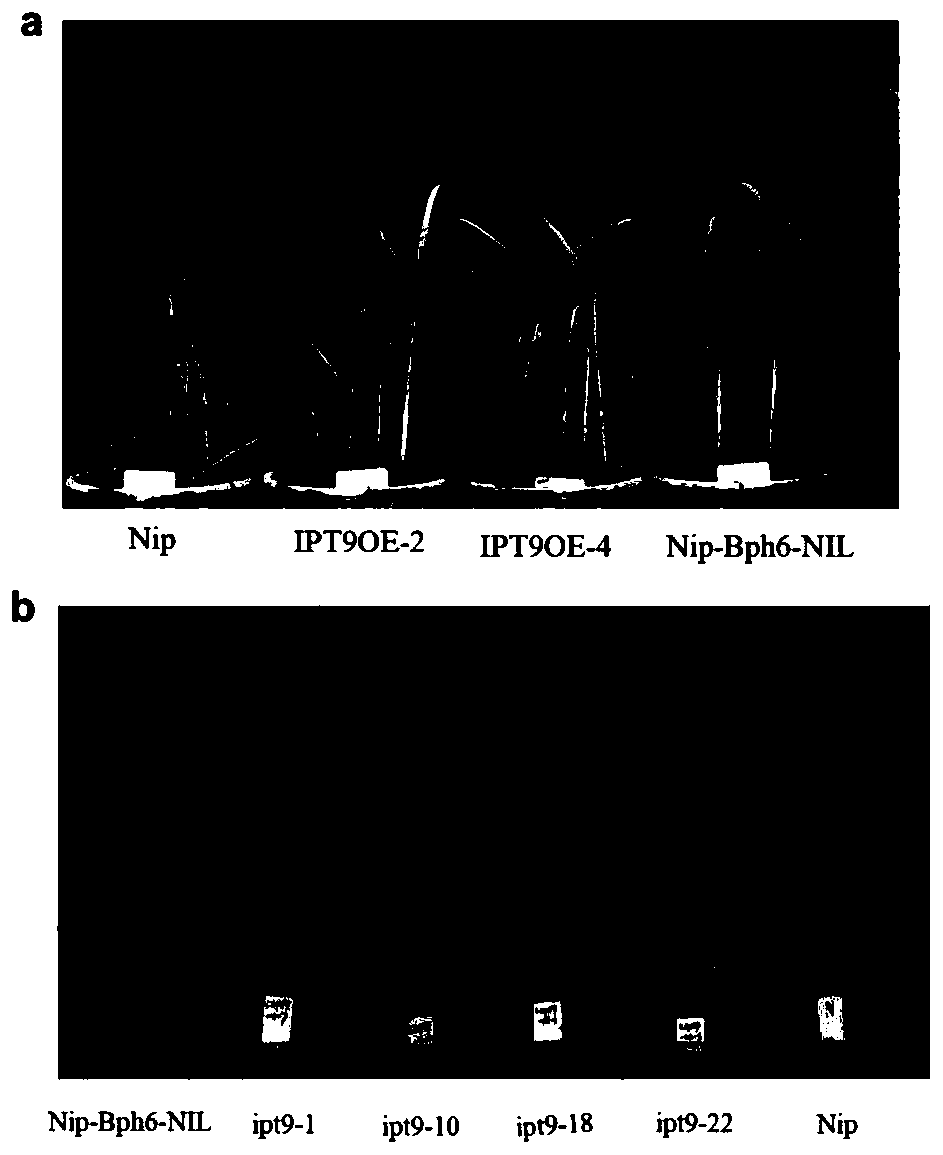
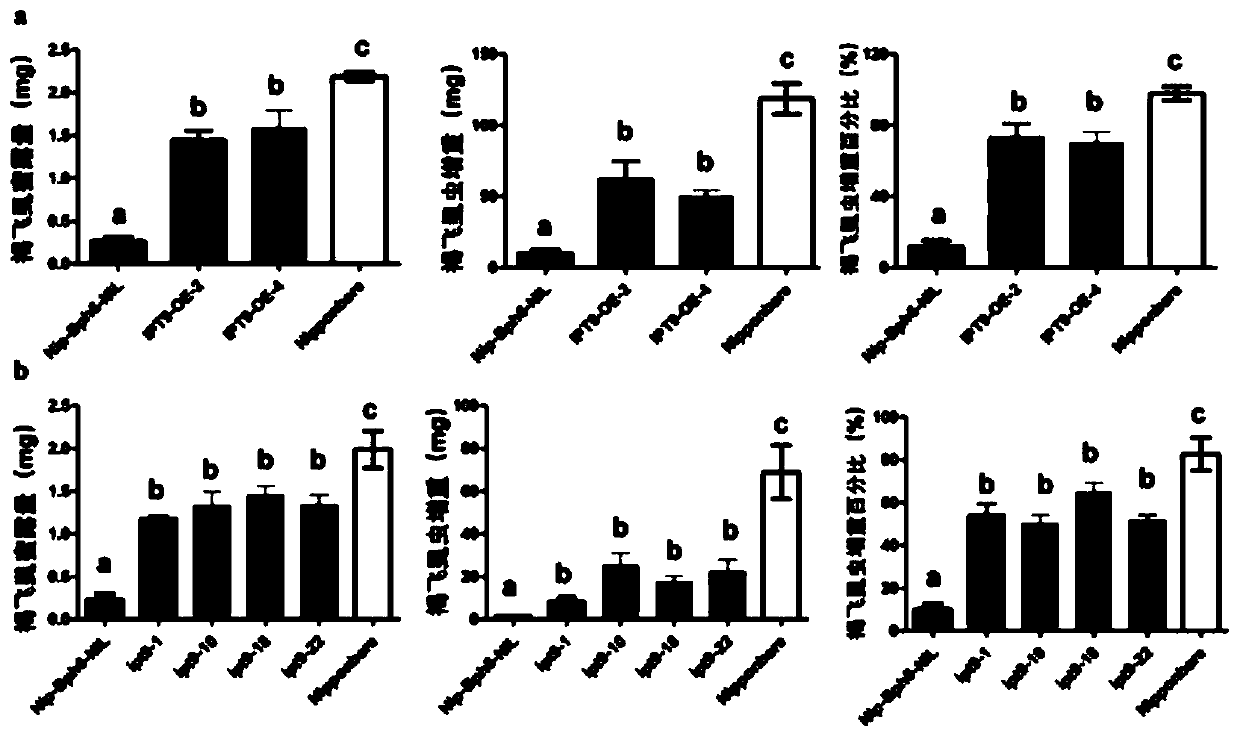
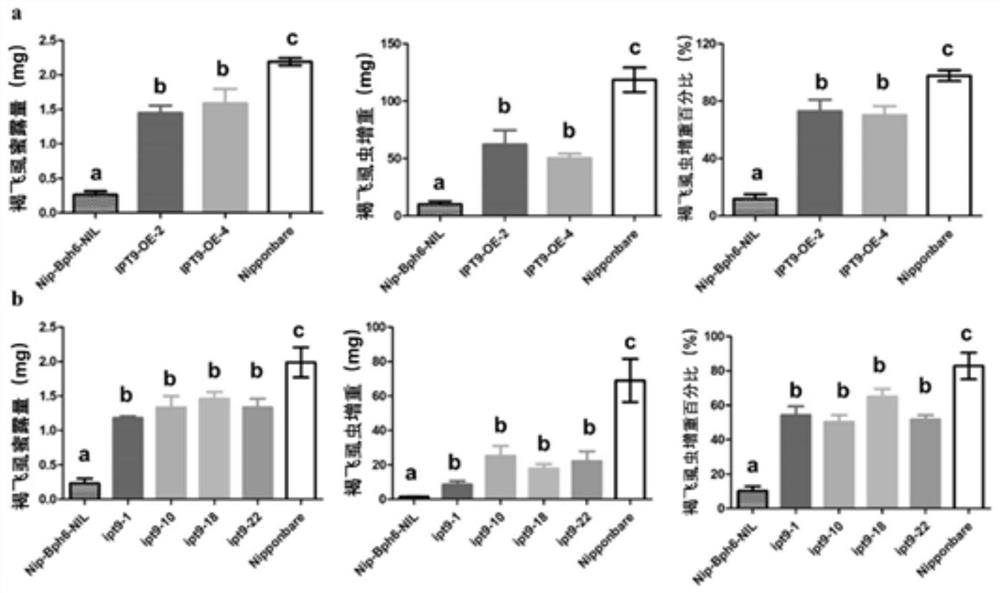
Application of rice tRNA isopentenyl transferase gene OsIPT9 in brown planthopper resistance of rice
The invention discloses an application of a rice tRNA isopentenyl transferase gene OsIPT9 in brown planthopper resistance of rice, which belong to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. TheOsIPT9 has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, the nucleotide sequence of the OsIPT9 is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2, and the ORF sequence of the OsIPT9 is as shown in SEQ ID No. 3. The OsIPT9 is transferred into Nipponbare which is sensitive to the brown planthopper through agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation, and the resistance of overexpressed plants to the brown planthopperis enhanced; meanwhile, in a resistant material NIP-Bph6-NIL, the OsIPT9 is knocked out by utilizing a CRISPR / Cas9 technology, so that the resistance of the plant to the brown planthopper is remarkably reduced. The gene disclosed by the invention provides a good theoretical basis for researching gene interaction between rice and brown planthopper, and has reference significance for researching gene molecular functions and breeding.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV +1
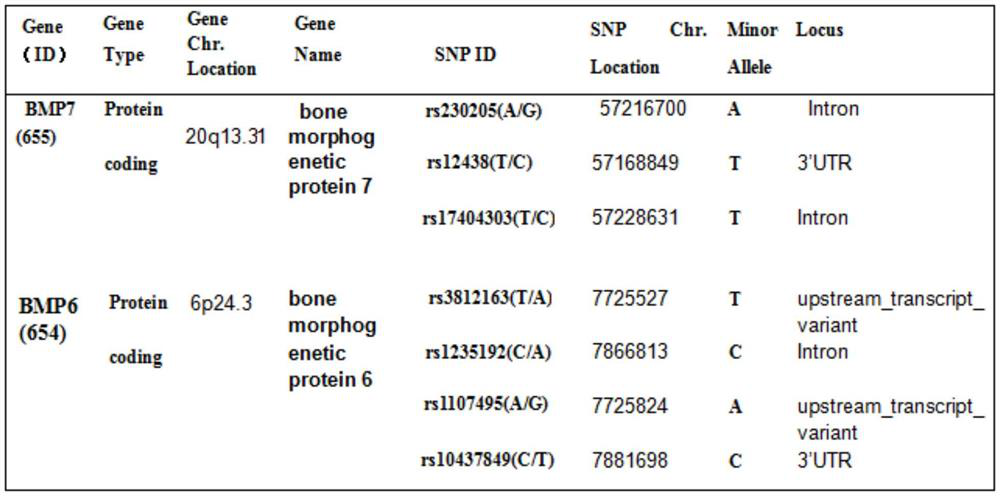
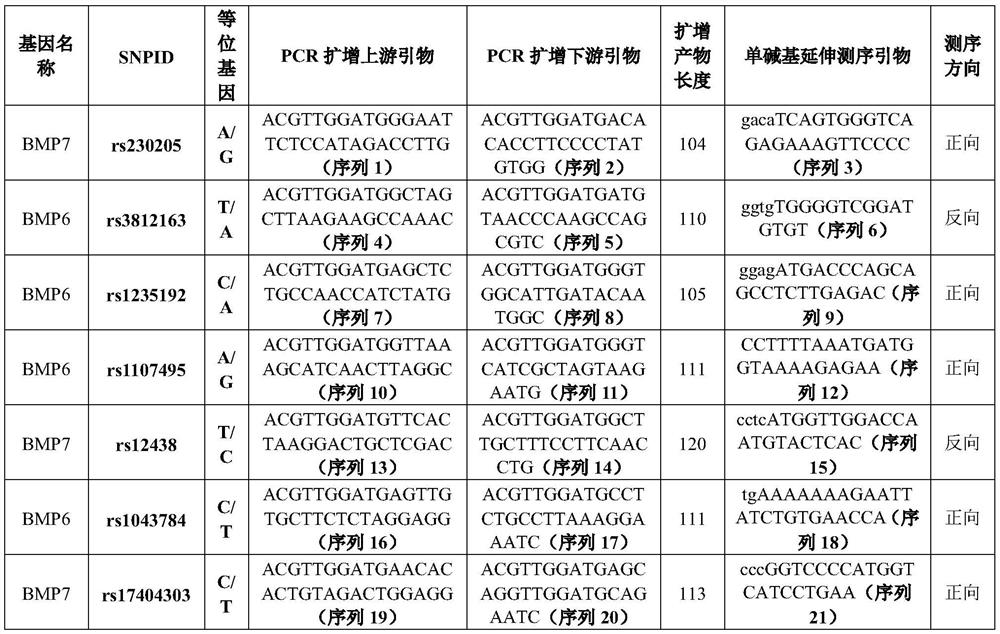
Single nucleotide polymorphic sites of BMP6 and BMP7 genes related to ONFH risk, combined detection substance and application
The invention provides application of BMP7 and BMP6 gene 7SNPs markers or a marker combination in ONFH molecular early warning, clinical molecular diagnosis and typing, and drug therapy targets. The pairwise interaction of 6SNPs is obviously related to the ONFH onset risk, and the risk correlation is partially or completely different from the action of the single SNP on the ONFH onset risk. the synergistic effect of a plurality of SNPs on the ONFH risk is found more clearly according to the result of the gene interaction, ONFH is further verified to be a complex disease caused by combination of a plurality of micro-effect genes, the combined effect of the molecular genetics sites is described, and the markers have important value for ONFH early-stage molecular early warning and molecular prevention and control strategy establishment.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
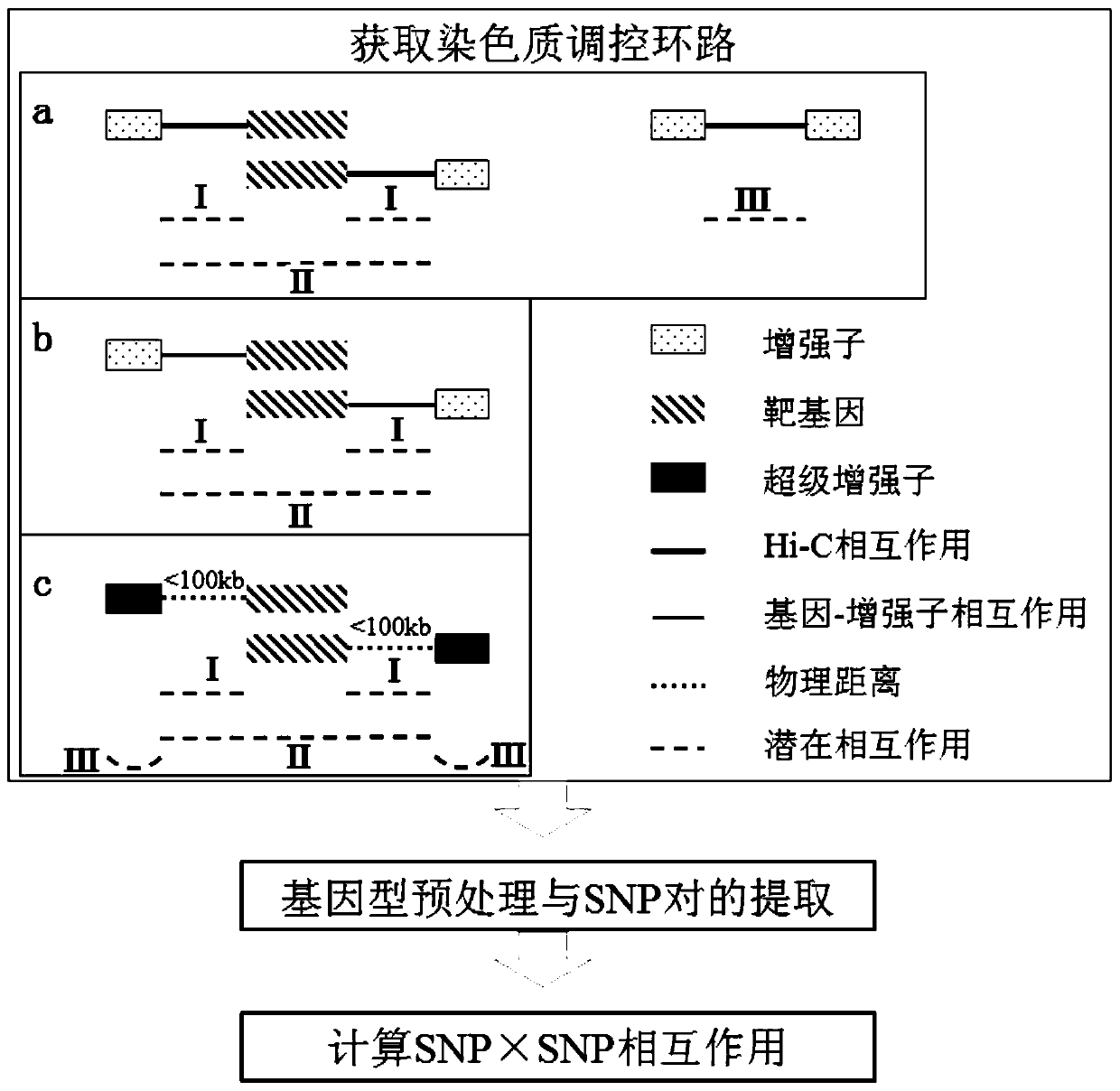
A method and system for detecting epistasis in complex diseases based on chromatin regulatory loops
ActiveCN108334749BQuick exploreAccurate explorationBiostatisticsProteomicsPharmaceutical drugGene interaction
The invention discloses a method and a system of detecting epistasis of a complex disease on the basis of chromatin regulation loops. Chromatin remote-interaction data and chromatin segmentation status data of cell lines related to the complex disease are collected and arranged; the above-mentioned data are utilized to establish the chromatin regulation loops; and SNP (Single nucleotide polymorphism) interaction which is in the regulation loops and can influence phenotypes of the complex disease is calculated. According to the method, the data of chromatin remote-interaction and the like are utilized to establish the chromatin regulation loops based on gene interaction, and the epistasis is calculated according to the chromatin regulation loops. Compared with the prior art, the method cangreatly decrease a calculation amount, can also reduce false negative results, thus rapidly and accurately explores SNP interaction related to the complex disease, and provides potential targets for subsequent drug design and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
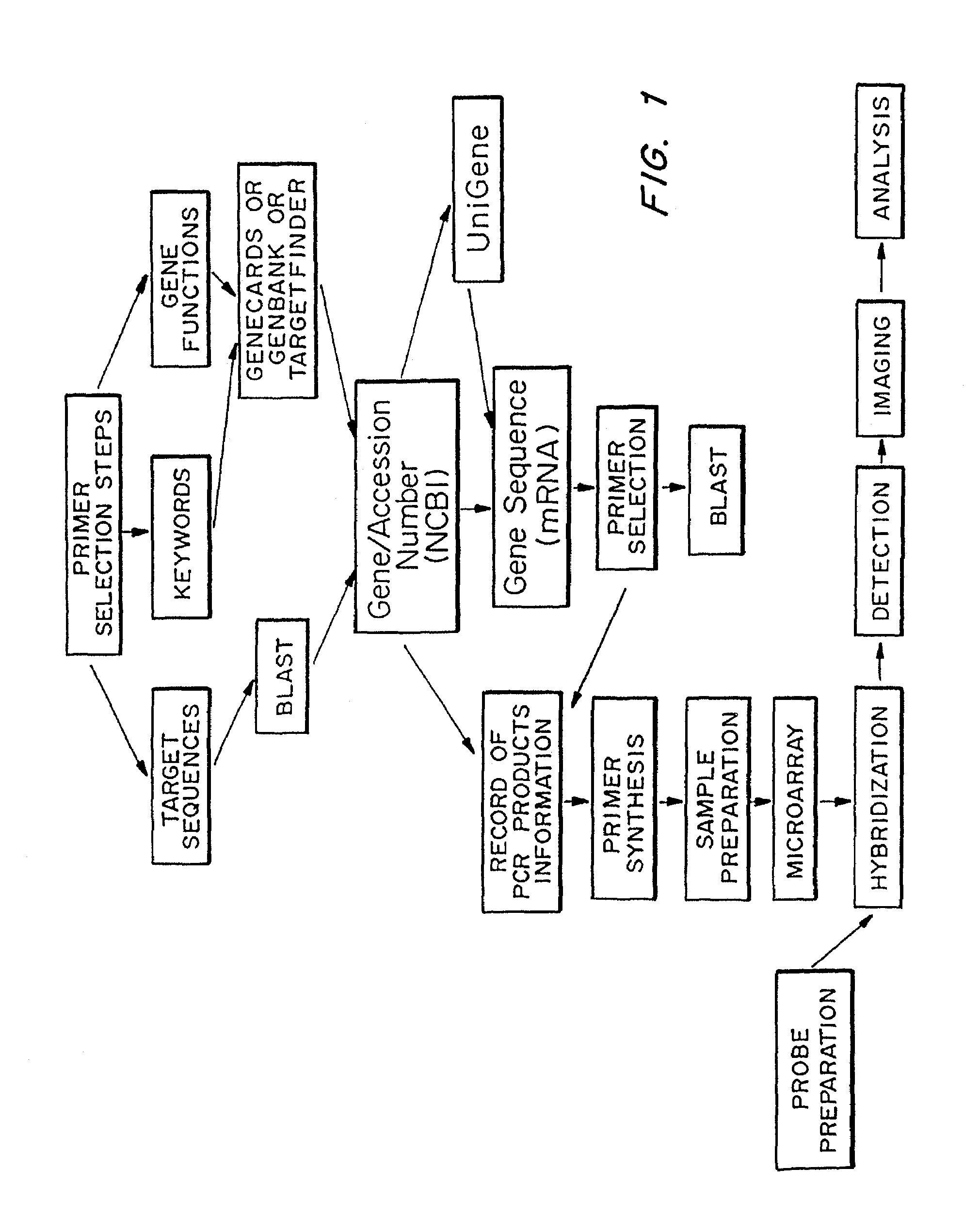
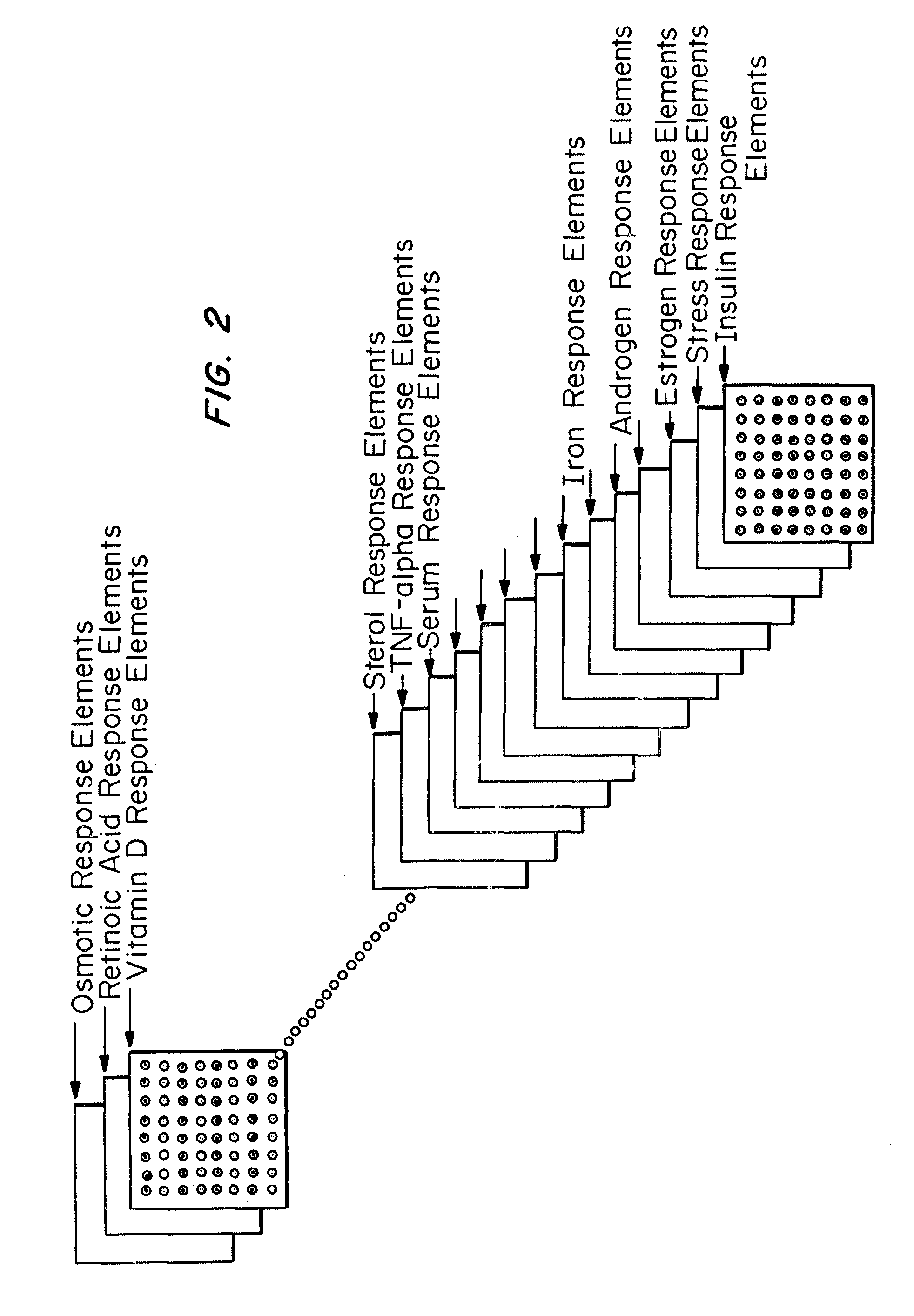
Microarrays to screen regulatory genes
Microarray technology allows the multiple parallel processing of information generated from matrices of huge numbers of loci on a solid substrate, which is useful in the gathering of gene signatures defining specific biological states. An approach has been developed to facilitate this process wherein genes of the same regulatory modality are selected. The transcriptional regulation of these genes is related to the same control element. Primers specific for the regulatory genes are selected, based on minimum cross-reactivity with other genes, using known gene data banks. PCR products of selected regions of known genes either binding to this sequence or whose expression is dependent on this binding, as well as genes interacting with the regulatable genes and control genes, referred to as “amplicons” or “gene cDNA fragments” of between about 450 and 1000 nucleotide bases in length, are obtained from a total RNA pool. These amplicons are arrayed on a nylon membrane or other appropriate microchip susbstrate, which is then used as a regulatory gene-specific microarray that is hybridized with sample. Sample will typically be the mRNA obtained from cells associated with a particular state (examples include age or exposure to conditions such as outspace, low gravity), disease (such as cancer or an infection), or disorder (such as a genetic defect or trauma). The transcriptionally regulated profile of regulatory gene-related genes specific to a given cultured cell sample is then determined using a software based analysis of the amount of hybridization which is detected. This information is useful in determining drug targets, markers associated with the disease state (either the presence or absence, or the extent of the disease), or the response of the disease state to drugs or other treatments.
Owner:LOUISVILLE RES FOUND UNIV OF
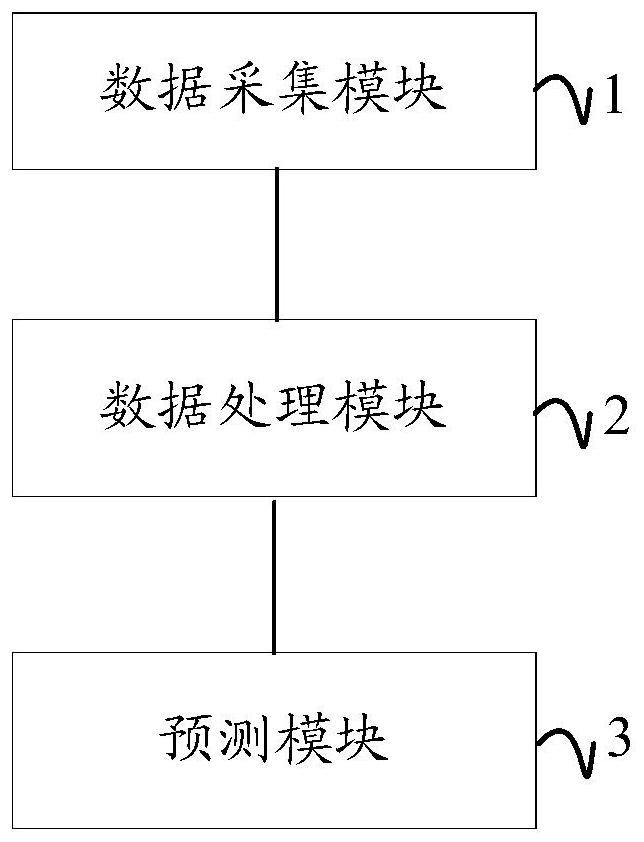
Disease-related miRNA prediction system
PendingCN112599202AImprove predictive performanceEffective predictionBiostatisticsMedical automated diagnosisInformation networksData acquisition
The invention discloses a disease-related miRNA prediction system. The disease-related miRNA prediction system comprises a data acquisition module, a data processing module and a prediction module. The data acquisition module is used for acquiring disease sample data, disease-miRNA relationship data, disease-gene relationship data, gene interaction data and miRNA-gene interaction data; the data processing module is used for constructing a miRNA-gene-disease heterogeneous information network according to the data acquired by the data acquisition module, and decomposing and processing the miRNA-gene-disease heterogeneous information network through a multi-task matrix to obtain final representation characteristics of diseases, genes and miRNA; and the prediction module is used for predictingthe miRNA related to the disease according to the final representation characteristics of the disease and the final representation characteristics of the miRNA. According to the invention, predictioncan be carried out by effectively combining gene information and known disease-related miRNA, and the prediction performance of the disease-related miRNA is improved.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Method and system for predicting interaction between miRNA and gene based on multi-relational graph convolutional network
PendingCN114093422ARich forecasting meansFully capture the structureNeural architecturesSequence analysisInformation networksHeterogeneous network
The invention discloses a method and a system for predicting interaction between miRNA and a gene based on a multi-relational graph convolutional network. The method comprises: constructing a heterogeneous information network of miRNA and genes, and learning network topology features of nodes by using a multi-relational graph convolutional network based on the heterogeneous network; meanwhile, capturing effective characteristics of the gene sequence by using a recurrent neural network; and finally, combining network topology characteristics with sequence characteristics, and calculating an association prediction score of the miRNA-gene pair by using the obtained miRNA and gene embedding. According to the method, manual feature construction is not needed in the implementation process, representation learning is combined, the advantages of the multi-relation graph convolutional network are fully utilized, effective gene sequence information is mined, and feature representation of miRNA and gene nodes is better captured. Experimental results show that the MRMTI is superior to other comparison methods in the aspect of association prediction of miRNA and genes, and has good prediction performance.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
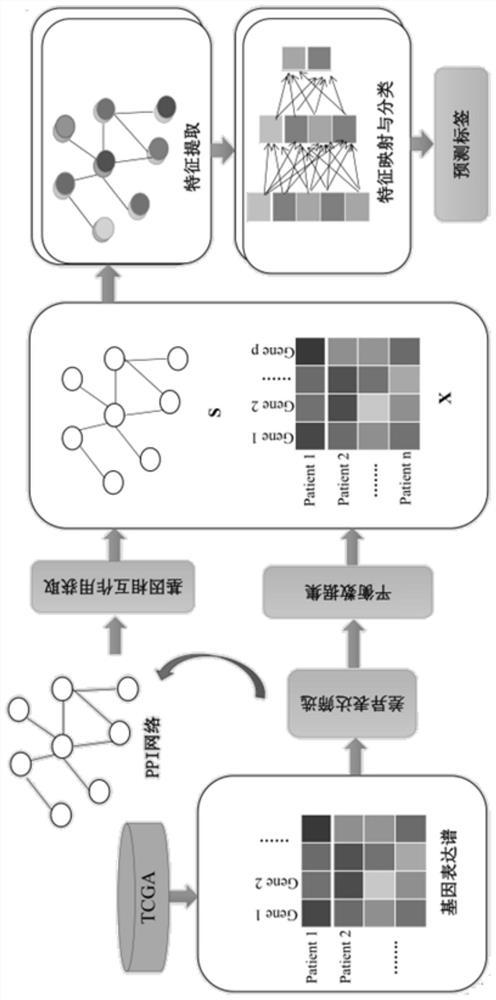
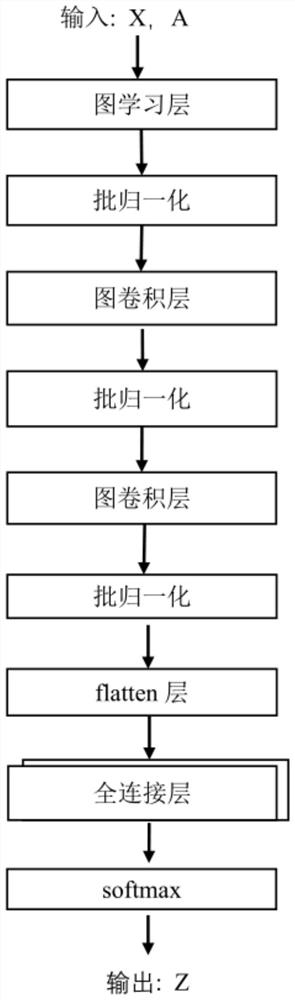
Distance metastasis identification method based on gene interaction mode optimization graph representation
The invention discloses a remote metastasis identification method based on gene interaction mode optimization graph representation. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing data; constructing and processing a protein-protein interaction network (PPI); dividing a training test set; constructing a glmGCN model expressed on the basis of a gene interaction mode optimization graph; using a ten-fold cross validation network model; and applying the model to a test set test. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the tumor metastasis is predicted under the GCN framework, more attention is paid to the gene-gene relation of the given initial graph in the field in the graph learning layer, and therefore more accurate prediction performance is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Cell metabolism reprogramming method and application thereof
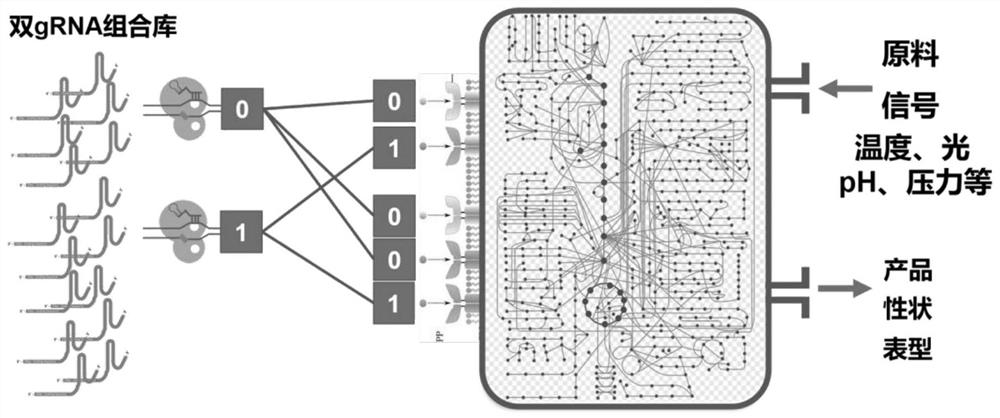
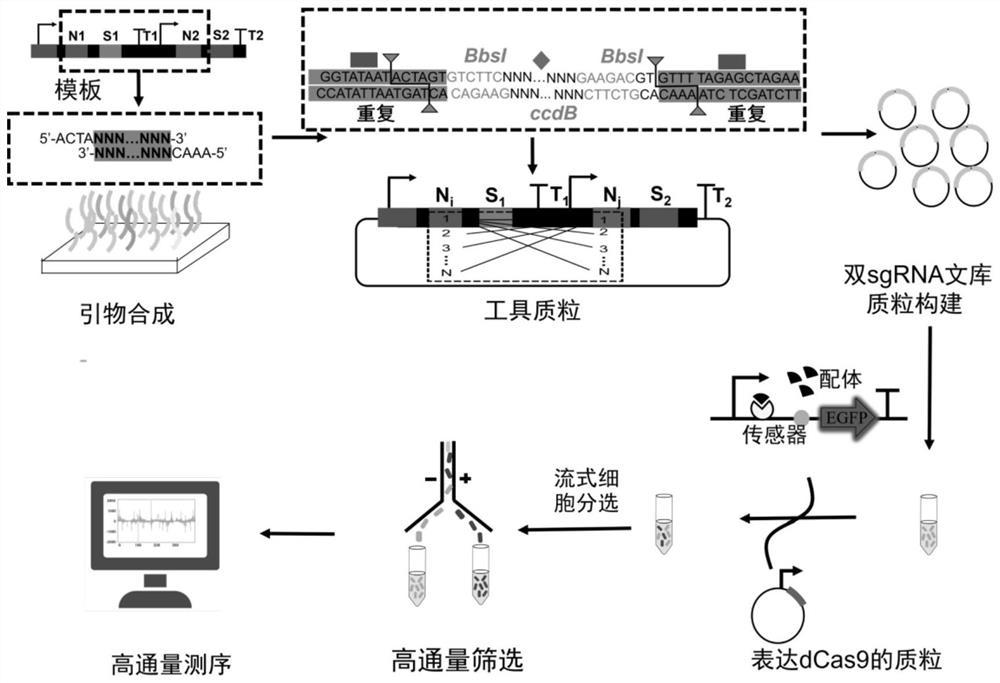
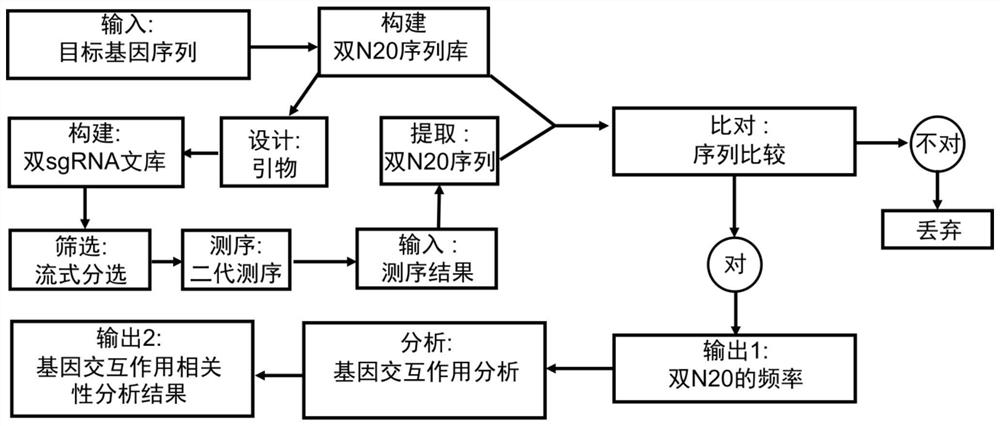
The invention discloses a cell metabolism reprogramming method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering.The cell metabolism reprogramming method utilizes sensitive nodes of a cell metabolism network to reprogram the metabolism network and mainly comprises the three parts of CRISPRi-based double-gene combination weakening, cell high-throughput screening and survival rate-based gene interaction analysis. The invention provides an intelligent metabolism reprogramming method which is novel, simple, efficient and low in cost, and can be widely used for operating a cell metabolism network.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
A method for cloning and transient expression of genes related to persimmon deastringency
The invention provides a cloning and transient expression method of persimmon deastringency related genes. The method comprises: first acquiring gene 3'-terminal sequences, then employing 3' RACE (rapid amplication of cDNA ends) technology to acquire 3'-terminal sequences of ADH and PDC gene family members in persimmon fruits; adopting Q-PCR (quantitative polymerase chain reaction) technology to analyze the genetic expression of ADH and PDC gene family members in a persimmon fruit deastringency treatment; and conducting separation to obtain full-length sequences of ADH and PDC gene family members, then establishing a transient expression system of persimmon leaves. The method of the invention clones the persimmon deastringency related gene family members, analyze the expression patterns of the family members in the persimmon deastringency treatment, and finally verifies functions of the target genes through transient expression of the persimmon leaves. The invention clarifies the regulation mechanism for postharvest persimmon deastringency from the molecular mechanism aspective, and can be used for further functional verification (transgenosis, gene interaction and the like) study of the postharvest persimmon deastringency mechanism.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Application of rice tRNA prenyltransferase gene osipt9 in resistance to brown planthopper in rice
The invention discloses the application of rice tRNA isopentenyl transferase gene OsIPT9 in rice resistance to brown planthopper. It belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering technology. OsIPT9 It has the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1, the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.2, and the ORF sequence shown in SEQ ID No.3. Through Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation, the OsIPT9 Transplanted into Nipponbare, which is susceptible to N. lugens, the overexpressed plants have enhanced resistance to N. lugens; at the same time, the resistant material NIP‑Bph6‑NIL was knocked out by CRISPR / Cas9 technology OsIPT9 , resulting in a significant down-regulation of plant resistance to N. lugens. The gene of the invention provides a good theoretical basis for studying the gene interaction between rice and brown planthopper, and has reference significance for studying gene molecular function and breeding.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com