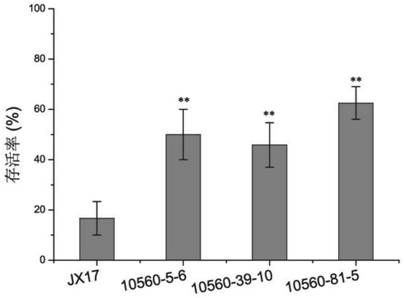
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69 results about "Genomic engineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compositions and methods directed to CRISPR/Cas genomic engineering systems
The invention relates to engineered CRISPR / Cas9 systems for genomic modification in mammalian cells. The present specification describes the design and testing of a polynucleotide encoding the Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes) Cas9 protein, where the nucleotide sequence has been optimized for expression in mammalian cells. The specification also describes all-in-one systems for RNA-guided genome engineering in mammalian cells, including human cells.
Owner:SYST BIOSCI
Processes and host cells for genome, pathway, and biomolecular engineering
ActiveUS20160186168A1High energy valueIncrease probabilityBacteriaUnicellular algaeBiotechnologyGenomic engineering
Owner:ENEVOLV
Method for synthesizing L-theanine through enzyme process
ActiveCN103409475AMake up for the shortcomings of poor stabilityHigh activityFermentationEscherichia coliChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing L-theanine through an enzyme process, and belongs to the biotechnical field. The method is characterized in that a gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase gene is obtained through chemical synthesis, a gene engineering bacterium over-expressing gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase is constructed by treating Escherichia coli as a host bacterium, glutamine and ethylamine hydrochloride having different concentrations are acted by a recombinase, and theanine is efficiently produced at a temperature of 37-50DEG C under a pH value of 9.5-10.5. The enzyme source preparation process has the advantages of simplicity, low cost, and large enzyme amount, and the theanine production method has the advantages of simplicity, high conversion rate, high output, short time and the like, and is in favor of the industrialized amplification production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
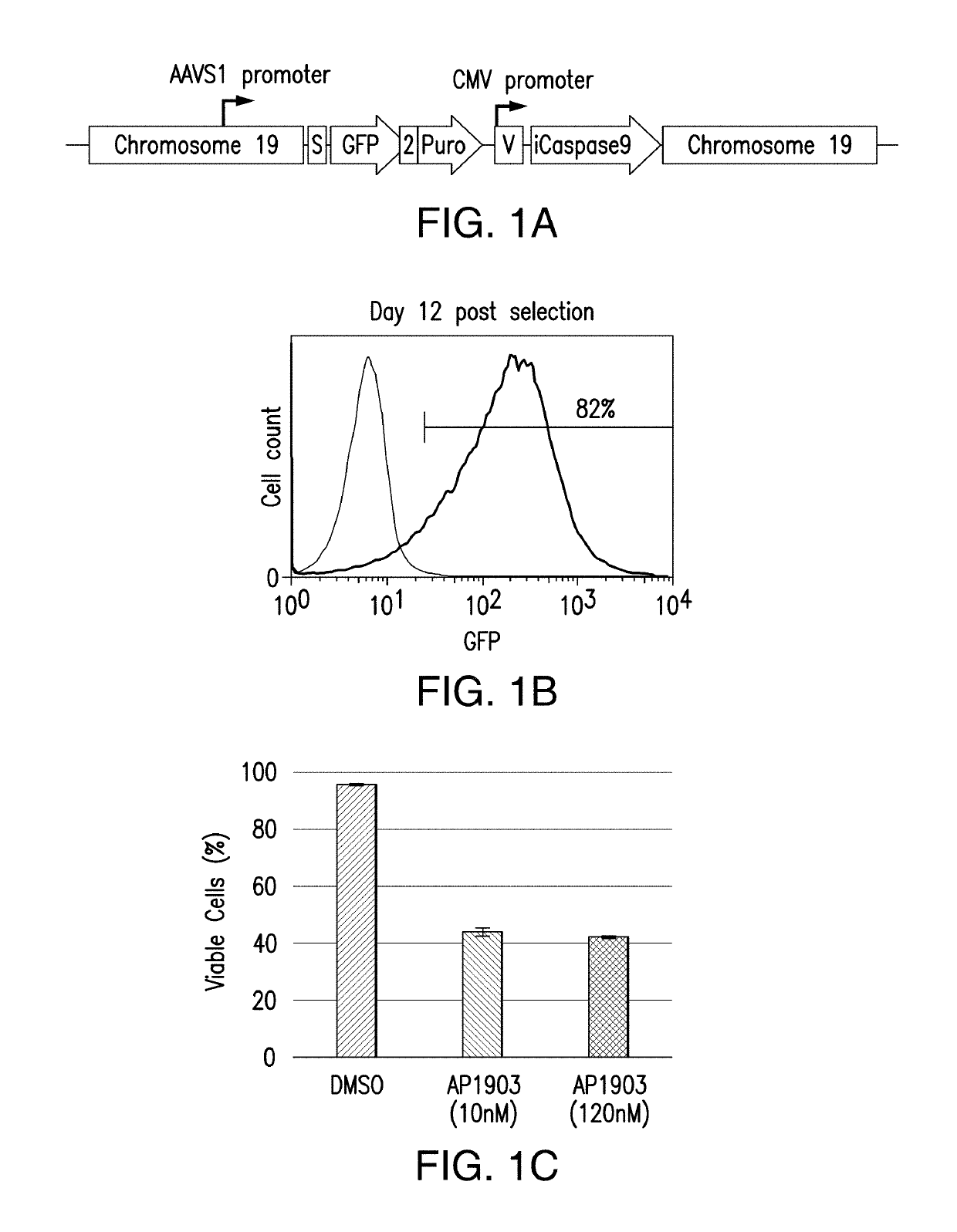
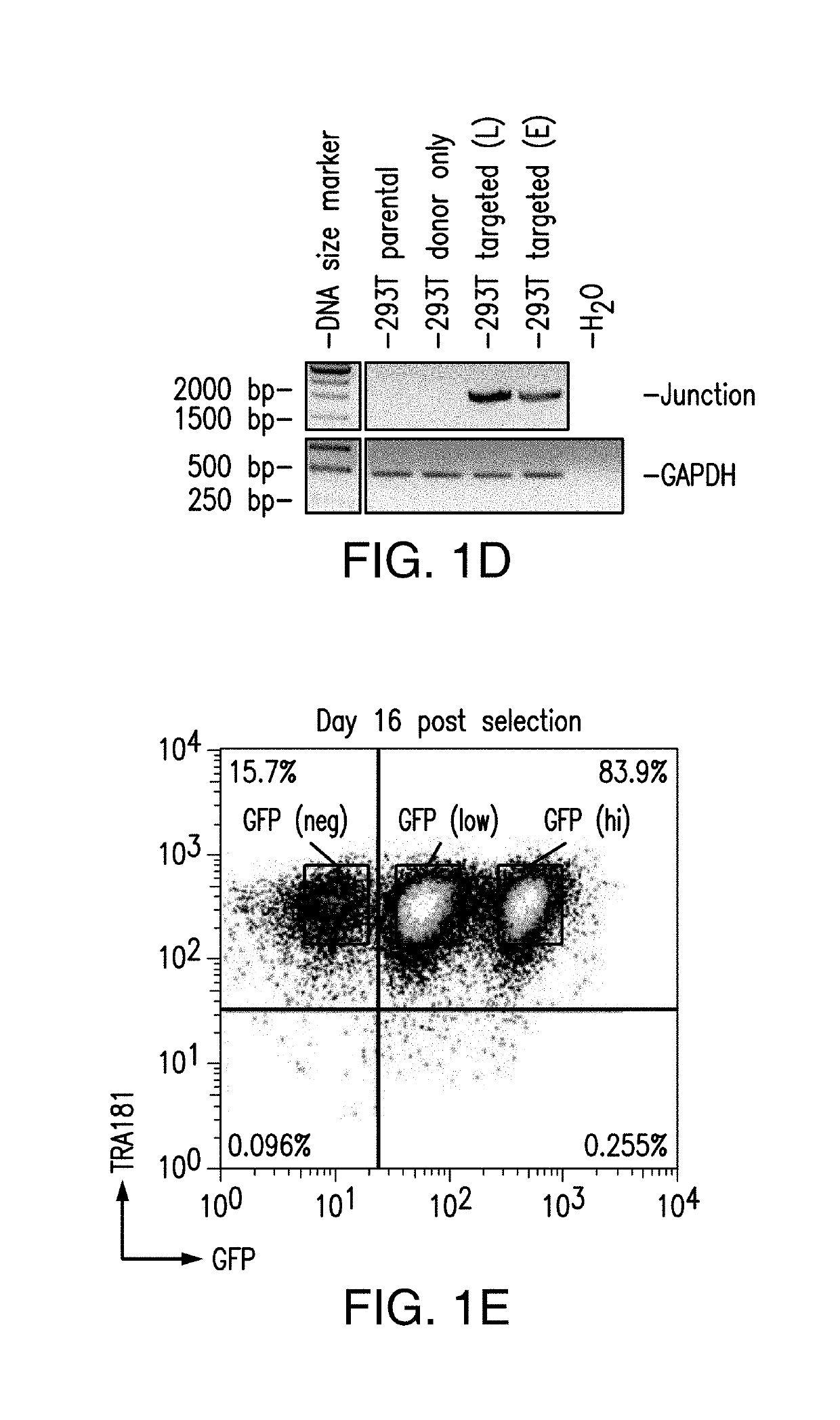
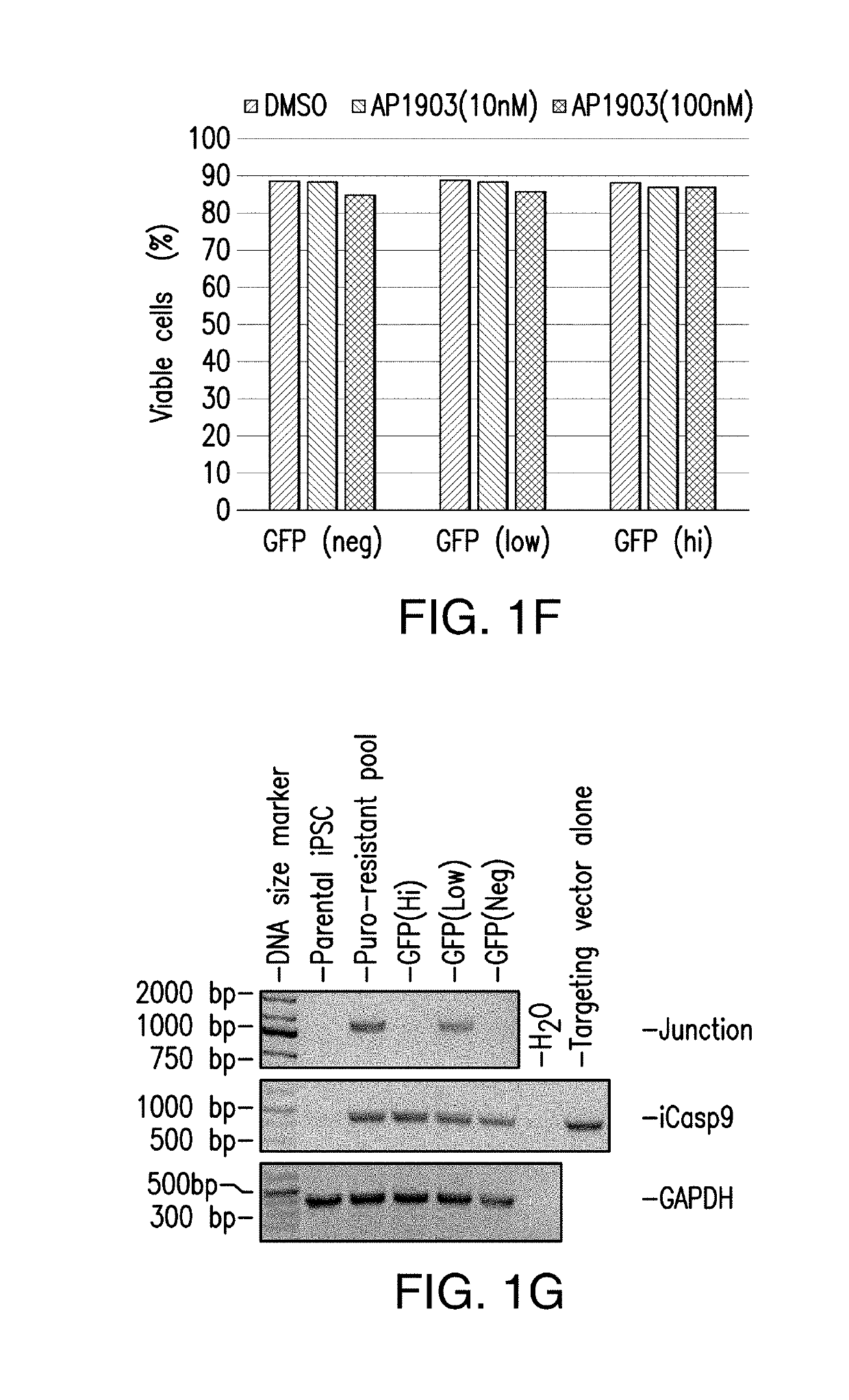
Genomic engineering of pluripotent cells
ActiveUS20180155717A1Improve durabilityImprove the immunityHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAGenomic engineeringPolynucleotide
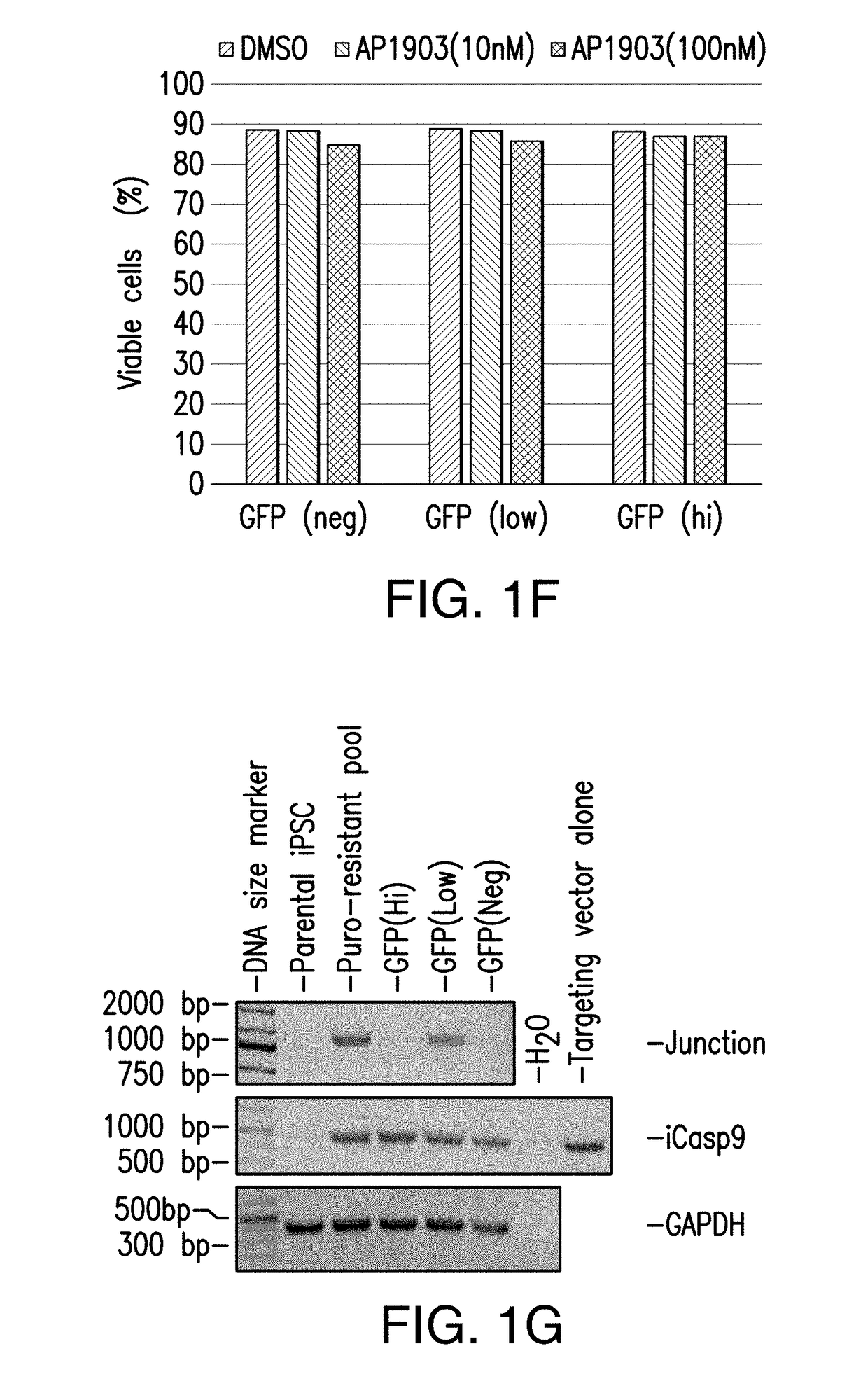
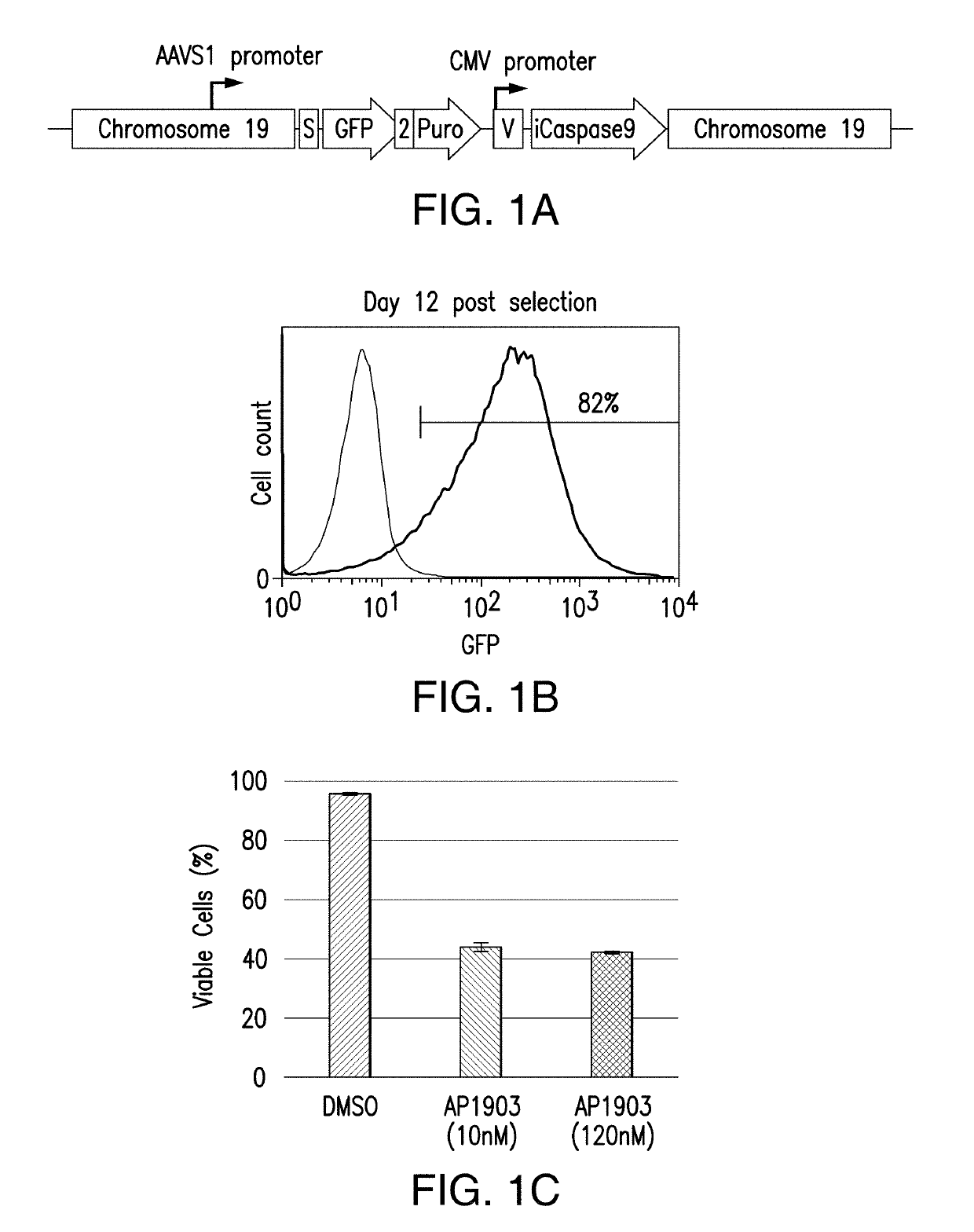
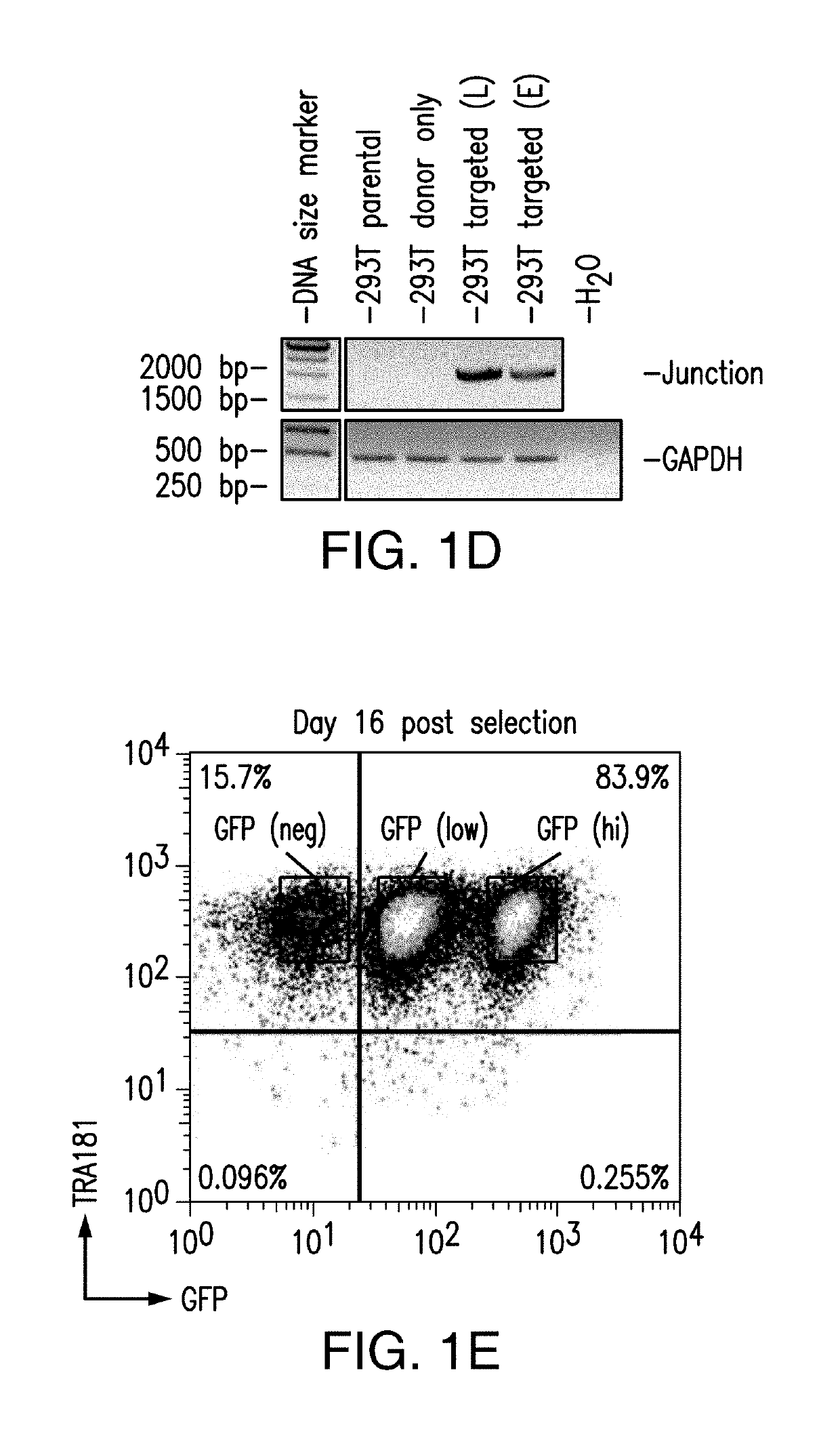
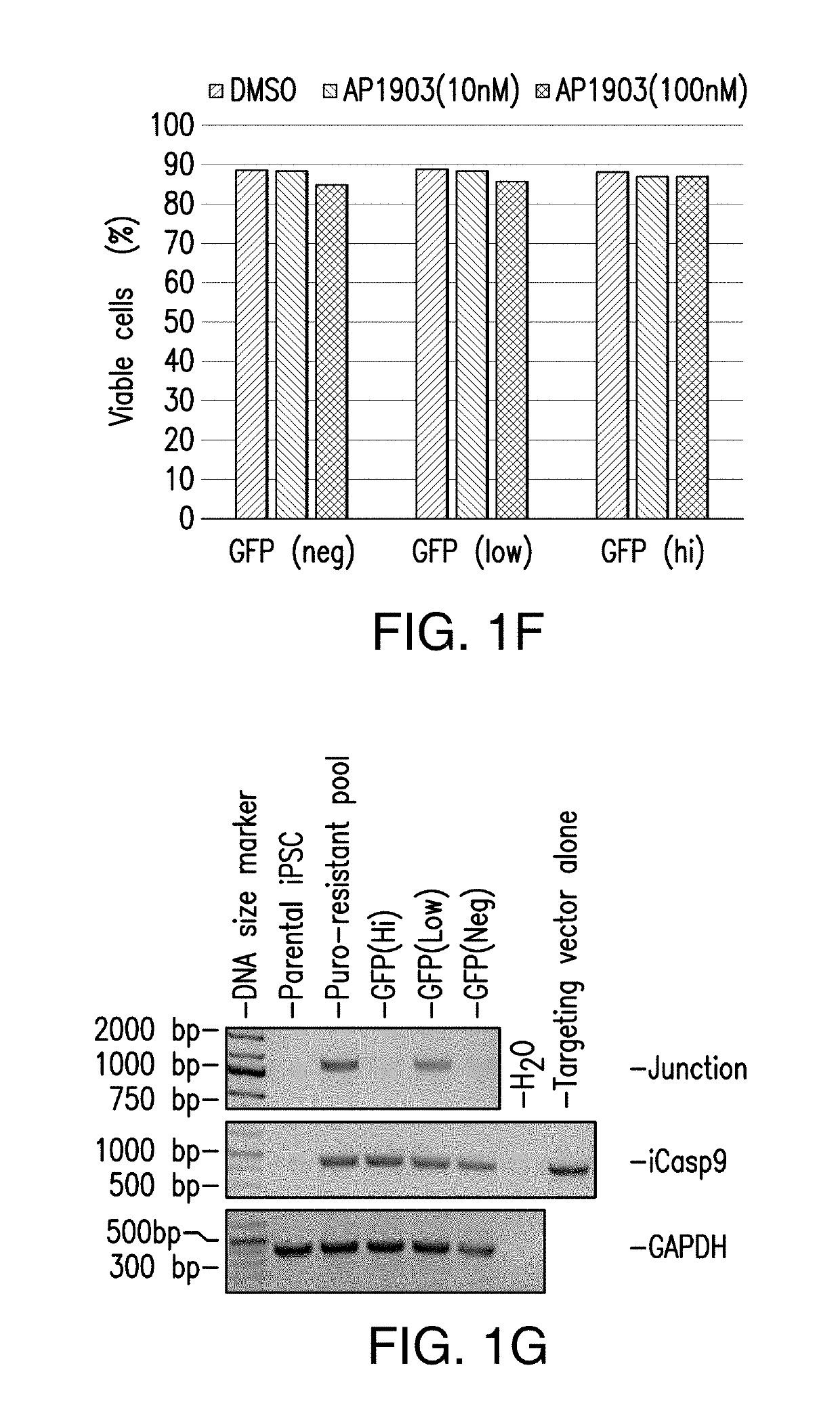
Provided are methods and compositions for obtaining genome-engineered iPSCs, and derivative cells with stable and functional genome editing at selected sites. Also provided are cell populations or clonal cell lines derived from genome-engineered iPSCs, which comprise targeted integration of one or more exogenous polynucleotides, and / or in / dels in one or more selected endogenous genes.
Owner:FATE THERAPEUTICS
Genomic engineering of pluripotent cells
ActiveUS10287606B2Improve durabilityImprove the immunityHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAGenomic engineeringPolynucleotide
Provided are methods and compositions for obtaining genome-engineered iPSCs, and derivative cells with stable and functional genome editing at selected sites. Also provided are cell populations or clonal cell lines derived from genome-engineered iPSCs, which comprise targeted integration of one or more exogenous polynucleotides, and / or in / dels in one or more selected endogenous genes.
Owner:FATE THERAPEUTICS
Genomic engineering of pluripotent cells
ActiveUS20190271005A1Increase resistanceMaintain pluripotencyHydrolasesAntineoplastic agentsGenomic engineeringPolynucleotide
Provided are methods and compositions for obtaining genome-engineered iPSCs, and derivative cells with stable and functional genome editing at selected sites. Also provided are cell populations or clonal cell lines derived from genome-engineered iPSCs, which comprise targeted integration of one or more exogenous polynucleotides, and / or in / dels in one or more selected endogenous genes.
Owner:FATE THERAPEUTICS
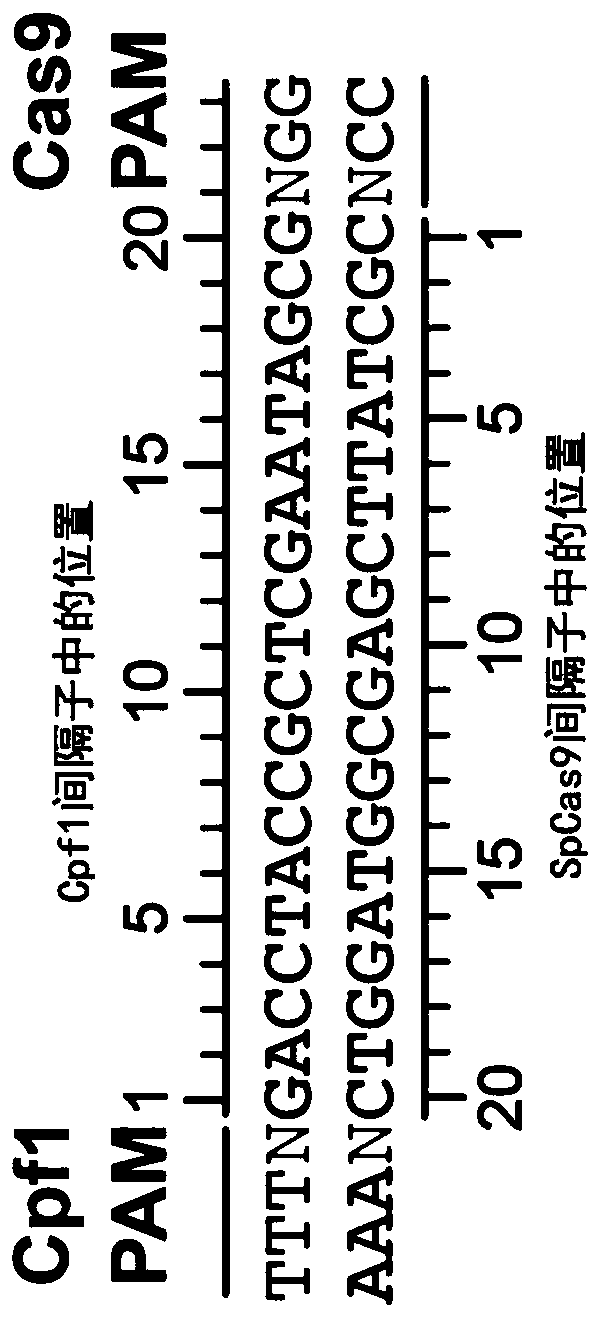
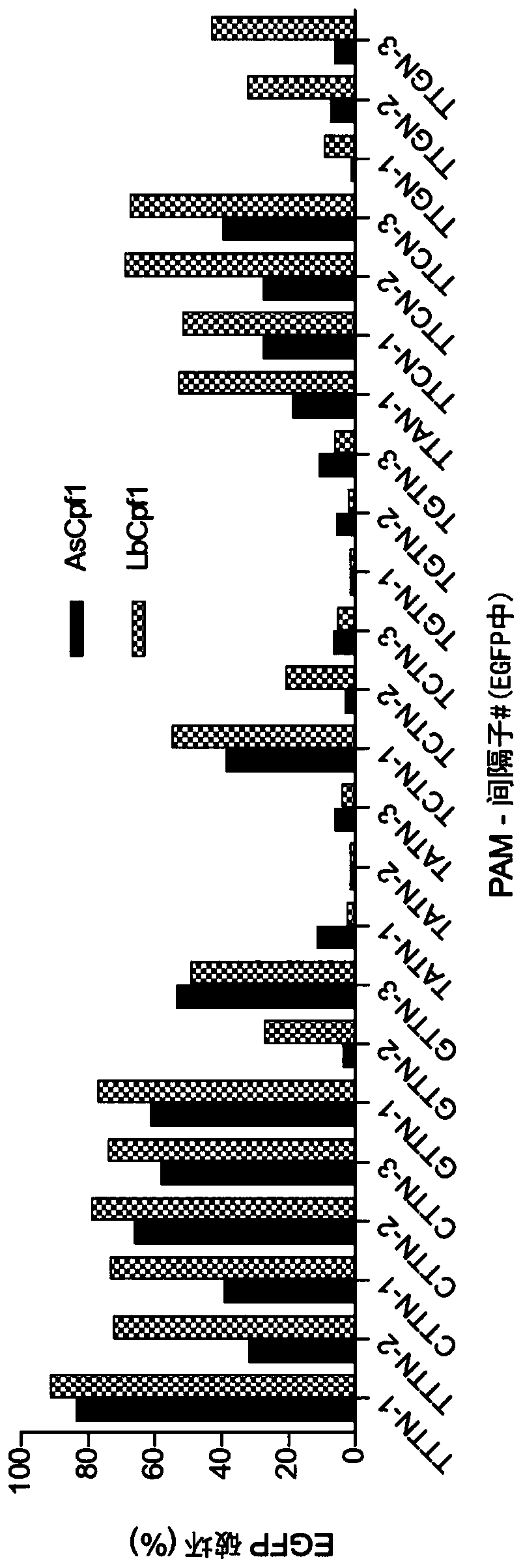
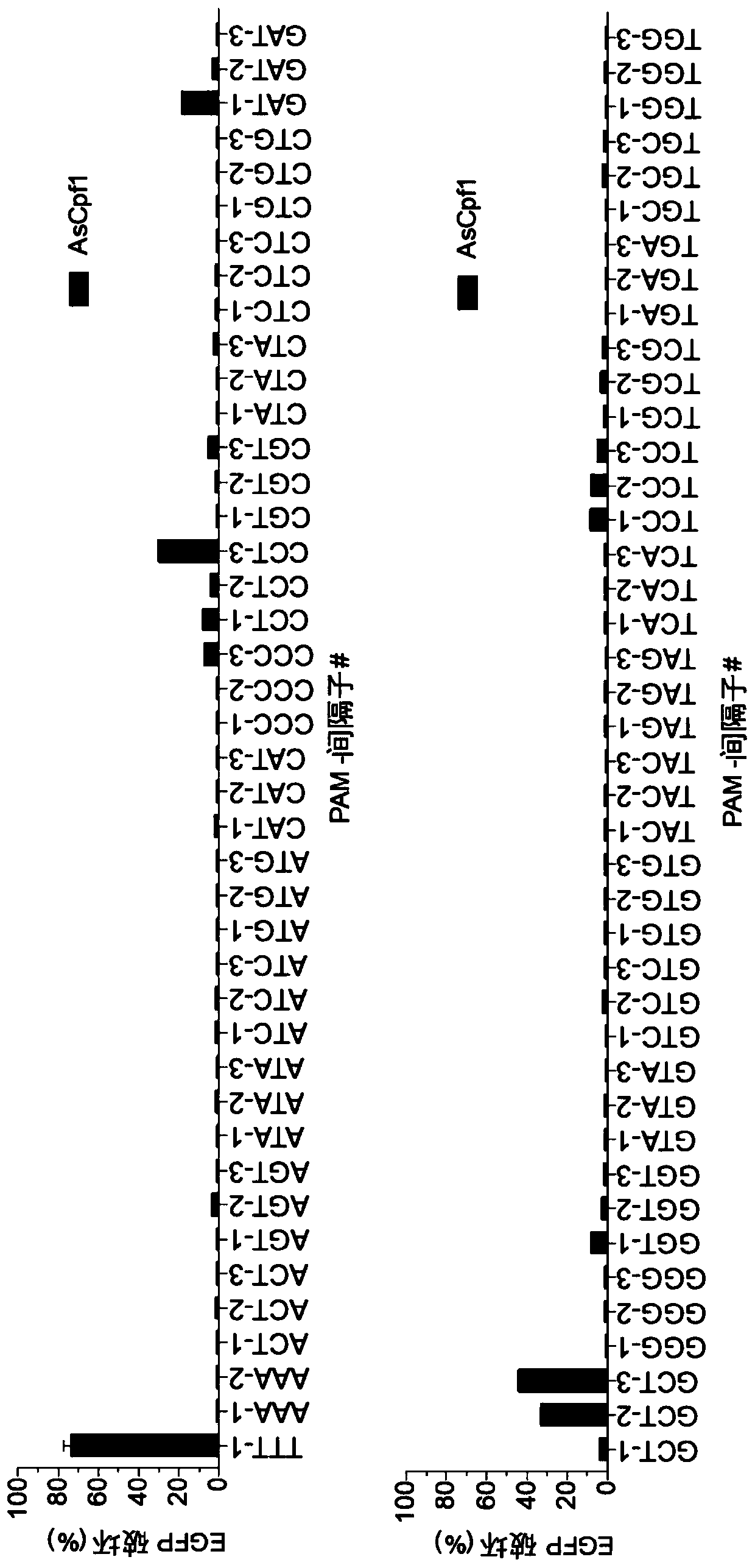
Variants of cpf1 (cas12a) with altered pam specificity
Engineered CRISPR from Prevotella and Francisella 1 (Cpf1) nucleases with improved targeting range and enhanced on-target activity, and their use in genomic engineering, epigenomic engineering, base editing, genome targeting, genome editing, and in vitro diagnostics.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Preparation and application of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase mutant
ActiveCN108034645AIncrease productionSimple purificationFermentationGlycosyltransferasesEnzymeMutant
The invention relates to preparation and application of a cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase mutant, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The amino acid of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase is subjected to mutation; the enzyme activity of the obtained mutant can reach 2.5 times of that of wild enzyme; the purification of the obtained cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase mutant is simple; the industrial production can be realized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of heat-resistant beta-glucosidase in preparation of gentiooligosaccharide
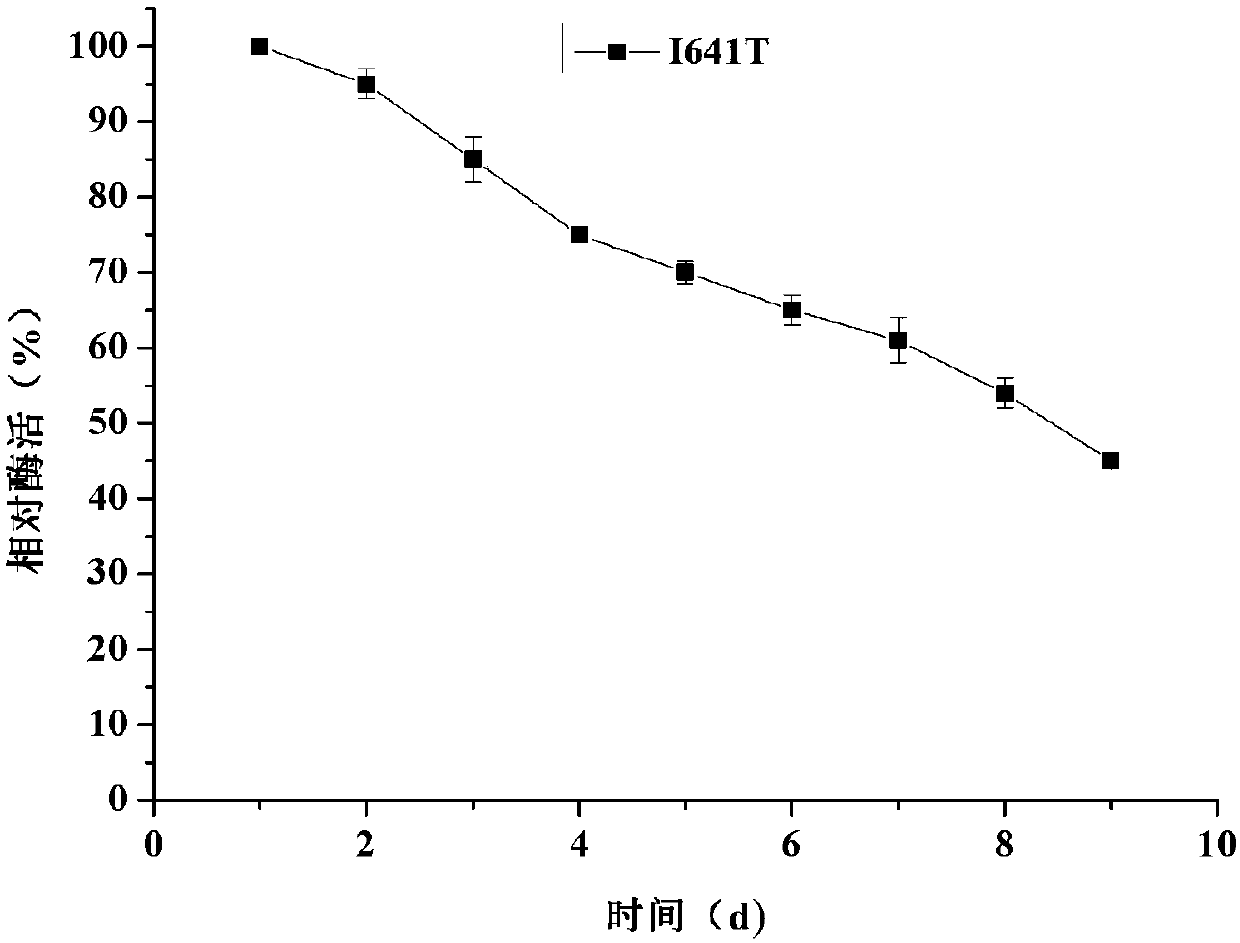
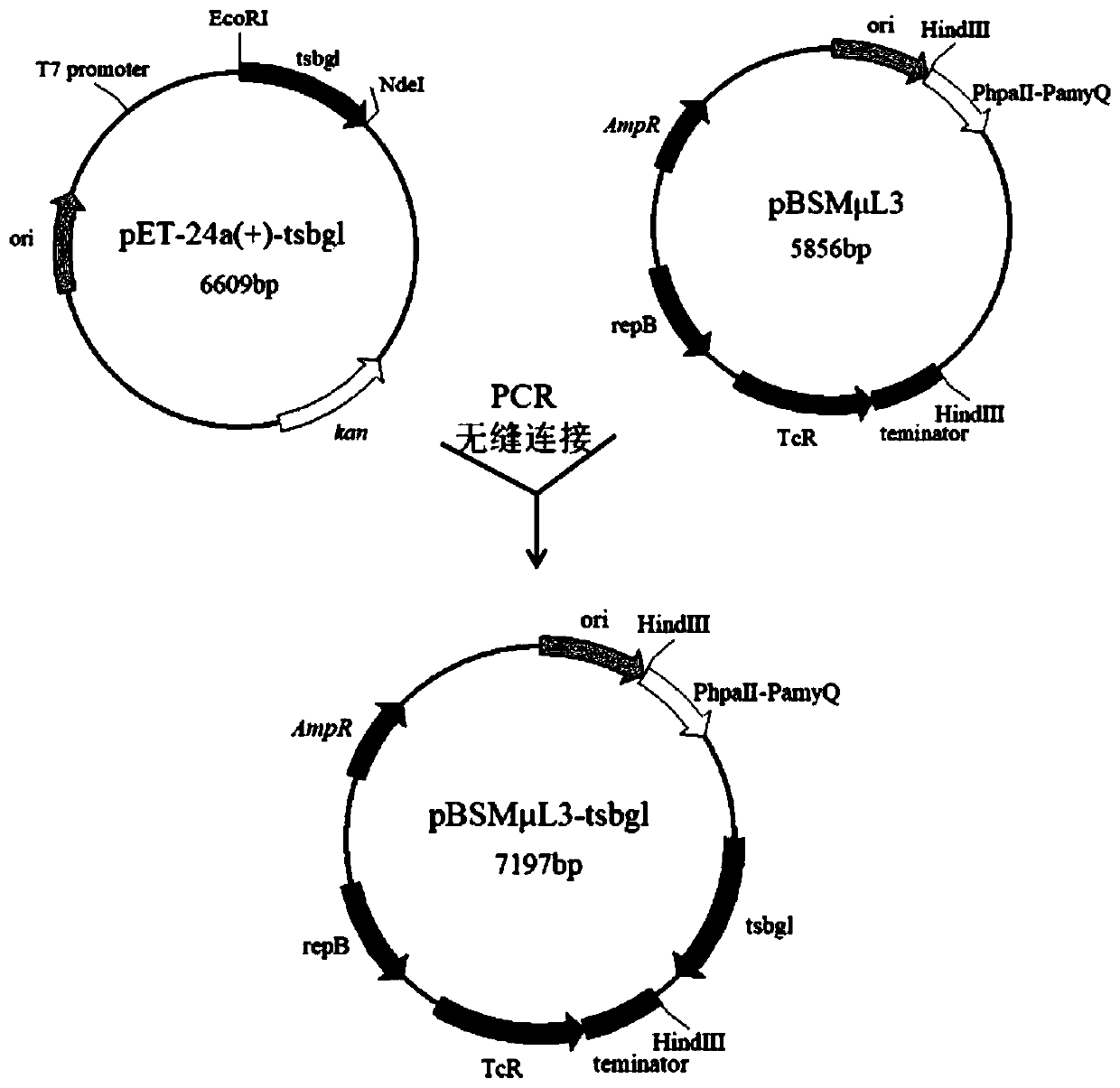
ActiveCN111411117AIncrease productionImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlgluceraseGenomic engineering
The invention discloses an application of heat-resistant beta-glucosidase in preparation of gentiooligosaccharide and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. A beta-glucosidase TSBGl gene from Thermotoga sp.KOL6 takes Bacillus subtilis WSH11 as an expression host, and high-efficiency expression of the tsbgl gene in bacillus subtilis is achieved. The optimum temperatureof the beta-glucosidase TSBGl is 90 DEG C, the optimum pH is 6.0, and the beta-glucosidase TSBGl has relatively high thermostability at 90 DEG C. The beta-glucosidase is added to a reaction system employing 1200 g / L of glucose as a substrate, enzyme reaction is carried out under the conditions of pH 6.0 and 90 DEG C, and the yield of the gentiooligosaccharide reaches 178.2 g / L. The beta-glucosidase meets the requirements for foods and other industrial applications and can be applied to industrial production of the gentiooligosaccharide.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Keratinase mutant with improved catalytic performance and application
InactiveCN109593746AImprove thermal stabilitySuitable for industrial mass productionBacteriaHydrolasesMulti siteWater baths
The invention discloses a keratinase mutant with improved catalytic performance and an application, belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and provides recombinant keratinase constructed on the basis of leading peptide engineering and multi-site saturated mutation and a leading peptide engineering method. A recombination strain M7 shows high keratinase catalytic potential, enzyme activity is remarkably improved from 179 U / mL to 1114 U / mL, the optimal reaction temperature is 40 DEG C, the optimal reaction pH is 10.0, over 80% enzyme activity is retained after water bath processing is performed for 90 min at 40 DEG C, heat stability is better, and the keratinase mutant is suitable for industrial large-scale production. Besides, the method for modifying protease with the leading peptide engineering can be a universal way for modifying industrial enzyme with the self-shearing characteristic.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
HTP genomic engineering platform for improving escherichia coli
PendingCN110945125AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationEscherichia coliGenomic engineering
The present disclosure provides a HTP genomic engineering platform for improving escherichia coli. that is computationally driven and integrates molecular biology, automation, and advanced machine learning protocols. The integrative platform utilizes a suite of HTP molecular tool sets to create HTP genetic design libraries, which are derived from, inter alia, scientific insight and iterative pattern recognition.
Owner:ZYMERGEN INC
Acid amylase AMYA4 and gene and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to acid amylase AMYA4 and gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the acid amylase AMYA4 is expressed as SEQ ID NO.1. The optimal pH value of the AmyA4 is 4.2, the optimal temperature is 75 DEG C, and the AmyA4 has high activity at the temperature of between 55 and 75 DEG C and has strong raw starch degrading capability at the same time. The zymology properties meet the process requirement for preparing sugar by a double-enzyme method, so the acid amylase has great application potential. In the process for preparing sugar by simulating the double-enzyme method, no matter paste starch or raw starch is used as a substrate, the starch can reach good hydrolysis rate under the action of matching commercial saccharifying enzyme, so the AmyA4 has huge application potential.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Negative regulator gene of streptomyces roseofulvus as well as preparation method and application thereof
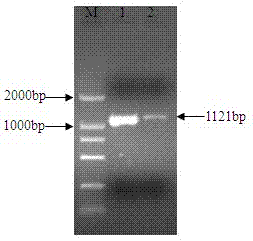
The invention relates to an nsdBmgh gene of Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63 as well as a preparation method and application thereof. In the invention, primers Ns8F and Ns8R are designed by utilizing an important negative regulator gene nsdB sequence in a Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) antibiotic metabolic pathway, and genomic DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63 is amplified to obtain a 1121bp segment; and two ends of a target sequence are extended by utilizing a primer anchoring polymerase chain reaction) (NPA-PCR ) method by a non-specific primer, thus obtaining the nsdBmgh gene of Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63. The preparation of the nsdBmgh gene provides an important basis for further researching and verifying the Streptomyces roseoflavus antibiotic metabolic pathway and regulatory mechanism, and establishes an important base for obtaining high-yield antibiotic gene engineering strains.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
A htp engineering platform
ActiveUS20210261949A1Improving phenotypic performanceHeating or cooling apparatusBiostatisticsMicroorganismBiochemical engineering
The present disclosure provides a HTP microbial genomic engineering platform that is computationally driven and integrates molecular biology, automation, and advanced machine learning protocols. This integrative platform utilizes a suite of HTP molecular tool sets to create HTP genetic design libraries, which are derived from, inter alia, scientific insight and iterative pattern recognition. The HTP genomic engineering platform described herein is microbial strain host agnostic and therefore can be implemented across taxa. Furthermore, the disclosed platform can be implemented to modulate or improve any microbial host parameter of interest.
Owner:ZYMERGEN INC
1,3-1,4-beta-glucanase mutant
ActiveCN105671022AImprove thermal stabilityMaintain catalytic activityBacteriaWort preparationGlucanaseMutase
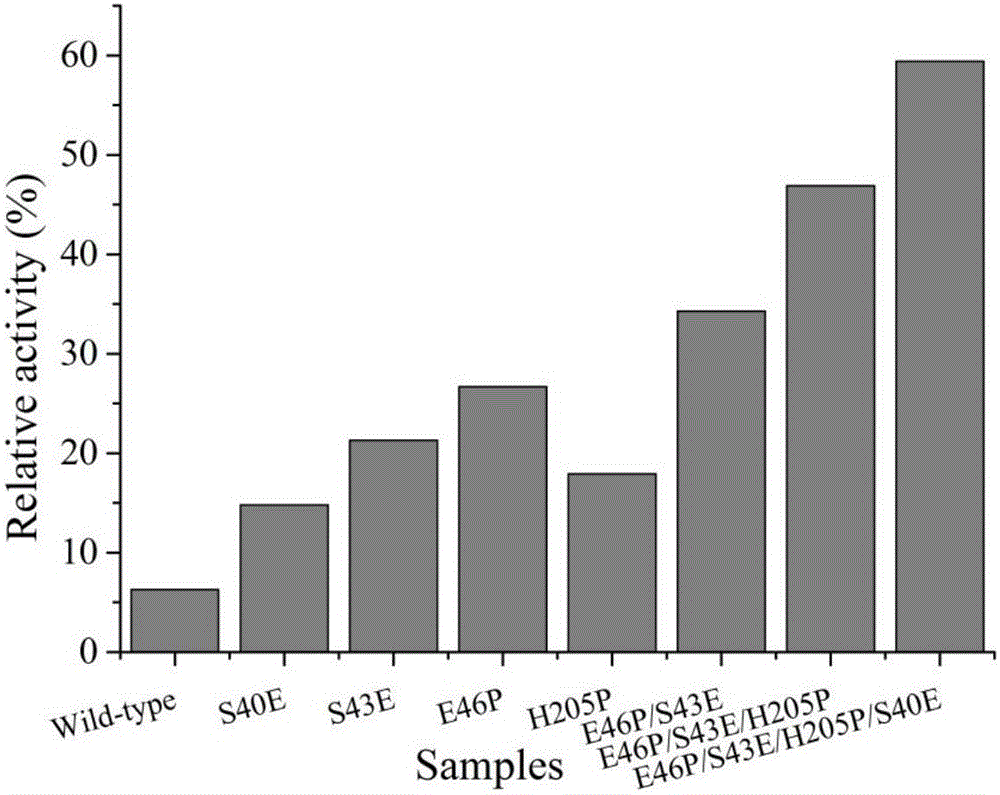
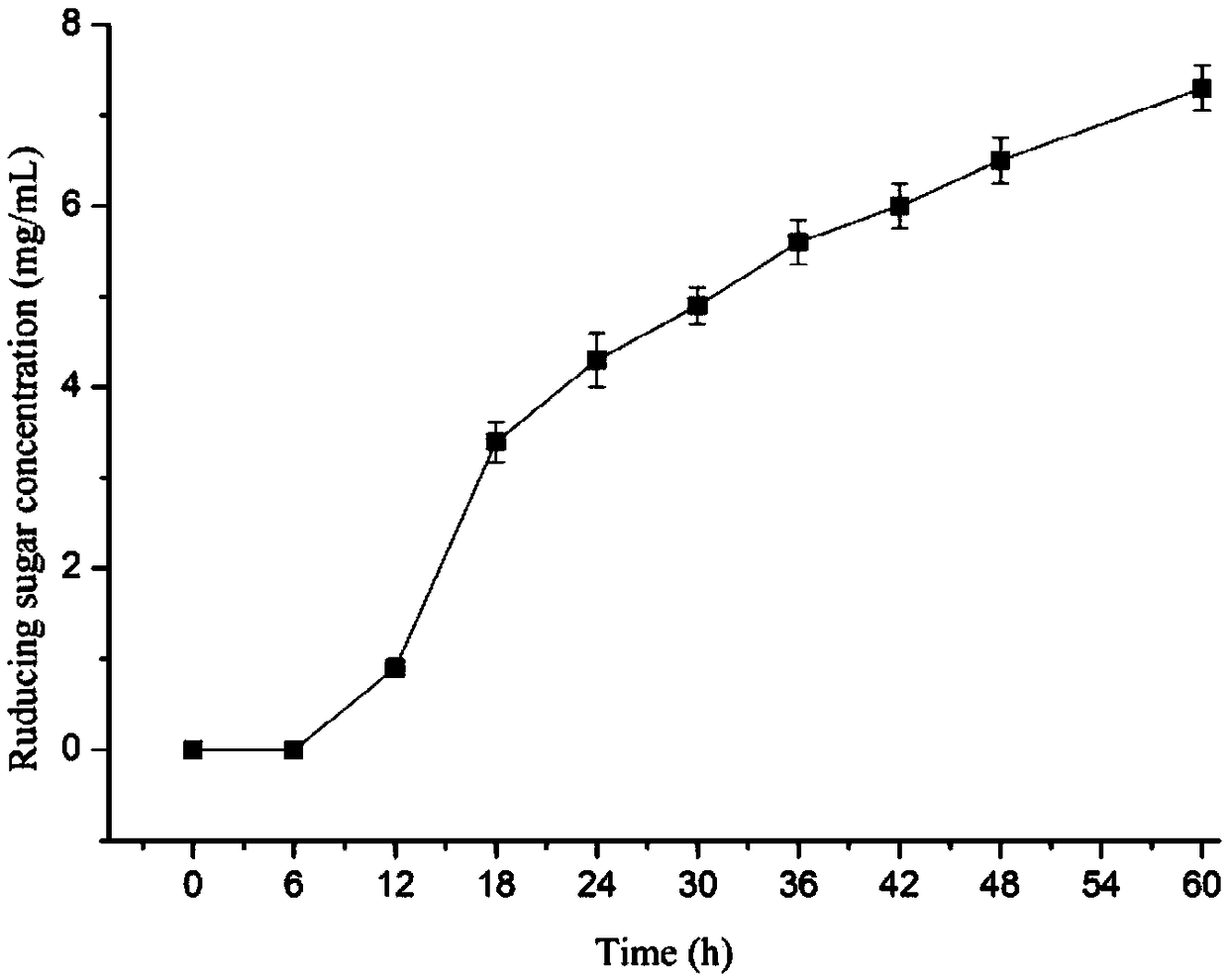
The invention discloses a 1,3-1,4-beta-glucanase mutant and belongs to the field of gene engineering and enzyme engineering.40-bit serine and 43-bit serine, 46-bit glutamic acid and 205-bit histidine of 1,3-1,4-beta-glucanase from bacillus terquilensis CGX 5-1 are mutated into glutamic acid, glutamic acid, praline and praline respectively through an iterative saturation mutation method, and finally four strains of single mutants and three strains of compound mutants are obtained.Seven strains of mutate enzyme all represent better heat stability, and particularly S40E / S43E / E46P / H205P mutate enzyme has extremely good heat stability.Compared with wild enzyme, the mutate enzyme can be used in the industry more easily.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Expansion protein and xylanase fusion protein, coding gene and applications thereof
ActiveCN108570107AHigher than vitalityEasy to removeAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEnzymesCelluloseXylanase
The invention discloses an expansion protein and xylanase fusion protein, a coding gene and applications thereof, wherein the expansion protein and xylanase fusion protein comprises an expansion protein EXCL and xylanase XYN, the EXCL is located at the N terminal of the fusion protein, XYN is located at the C terminal of the fusion protein, the amino acid sequence of the expansion protein EXCL isrepresented by SEQ ID NO:2, and the amino acid sequence of the xylanase XYN is represented by SEQ ID NO:4. The invention further provides a preferred method for inserting a linker peptide into the fusion protein. According to the present invention, the expansion protein and xylanase fusion enzyme is constructed by using the gene engineering technology, wherein the enzyme activity is increased by 1.3 times compared to the natural xylanase, and the obtained product can adsorb lignocellulose.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
Compositions and methods of improving specificity in genomic engineering using rna-guided endonucleases
Disclosed herein are optimized guide RNAs (gRNAs) and methods of designing and using said optimized gRNAs that have increased target binding specificity and reduced off-target binding.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Microbial strain improvement by a htp genomic engineering platform
ActiveCN111223527AIncrease productionImprove productivitySequence analysisInstrumentsMicroorganismBiochemical engineering
The invention relates to a microbial strain improvement by a HTP genomic engineering platform. The present disclosure provides a HTP microbial genomic engineering platform that is computationally driven and integrates molecular biology, automation, and advanced machine learning protocols. This integrative platform utilizes a suite of HTP molecular tool sets to create HTP genetic design libraries,which are derived from, inter alia, scientific insight and iterative pattern recognition. The HTP genomic engineering platform described herein is microbial strain host agnostic and therefore can be implemented across taxa. Furthermore, the disclosed platform can be implemented to modulate or improve any microbial host parameter of interest.
Owner:ZYMERGEN INC
Microbial strain improvement by a htp genomic engineering platform
ActiveCN108027849AIncrease productionImprove productivitySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsMicroorganismBiochemical engineering
The present disclosure provides a HTP microbial genomic engineering platform that is computationally driven and integrates molecular biology automation and advanced machine learning protocols. This integrative platform utilizes a suite of HTP molecular tool sets to create HTP genetic design libraries which are derived from inter alia scientific insight and iterative pattern recognition. The HTP genomic engineering platform described herein is microbial strain host agnostic and therefore can be implemented across taxa. Furthermore the disclosed platform can be implemented to modulate or improveany microbial host parameter of interest.
Owner:ZYMERGEN INC
High throughput transposon mutagenesis
InactiveUS20200102554A1Fast and efficient identificationImproved host phenotypeDNA preparationTransposon mutagenesisMicroorganism
The present disclosure is directed to a method of high-throughput (HTP) microbial genomic engineering, which utilizes in vivo transposon mutagenesis to develop strain libraries for the perturbation of microbial phenotypes.
Owner:ZYMERGEN INC
Method for preparing gentiooligosaccharide by using beta-1,6-glucanase and application of method
ActiveCN111593034AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesAlgluceraseGlucanase
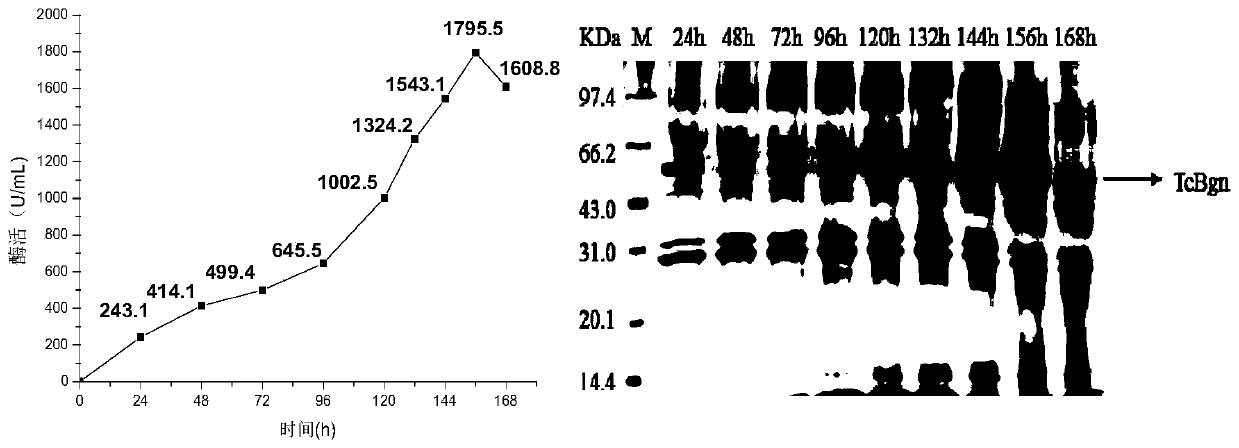
The invention relates to a method for preparing gentiooligosaccharide by using beta-1,6-glucanase and an application of the method and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering. The invention firstly provides beta-1,6-glucanase TcBgn with transglycosylation activity on gentiobiose, the beta-1,6-glucanase TcBgn can transform glucose into gentiooligosaccharide under the condition of relatively small additive amount of enzyme, and the transformation rate is high, so that the production cost can be significantly reduced. The gentiooligosaccharide is prepared by double-enzyme compounding of the beta-1,6-glucanase and beta-glucosidase, and the glucose is transformed into the gentiobiose and gentianose by using a double-enzyme compounded system, so that the transformation rate is high, and the proportion of the gentianose in a product is significantly improved. Therefore, the method for preparing the gentiooligosaccharide by a single enzyme of the beta-1,6-glucanase or double-enzyme compounding has good industrial application value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Processes and host cells for genome, pathway, and biomolecular engineering
ActiveUS9944925B2Increase probabilityIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiofuelsBiotechnologyGenomic engineering
Owner:ENEVOLV
Cas9-scForkI fusion protein and application thereof
InactiveCN104531633AFlexible designHigh cutting activityHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenomic engineeringGene Modification
The invention discloses a Cas9-scForkI fusion protein and application thereof, and belongs to the field of molecular biology. According to the Cas9-scForkI fusion protein and application, an inactivate Cas9 protein is transformed through a genetic engineering method; (G4S)10, namely (Gly-Gly-Gly-Gly-Ser)10, serves as a linker to be used for connecting two ForkIs; the ForkIs and the inactivate Cas9 are fused into Cas9-scForkI; and according to the Cas9-scForkI fusion protein, genomic editing can be carried out through sequence specificity. When the Cas9-scForkI fusion protein is used for drug screening or gene modification, more safety is obtained; and the fusion protein can further be used for gene treatment. Compared with the prior art, the design is more flexible; the cutting activation is higher; the input efficiency is higher when the fusion protein serves as a gene; and the fusion protein can be used for gene modification or gene treatment.
Owner:SUZHOU KECHUANG BIOTECH
Phenylpyruvic acid reductase sourced from lactobacillus plantarum and application thereof
InactiveCN107164341AImprove conversion efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacilliProtein
The invention discloses a phenylpyruvic acid reductase sourced from lactobacillus plantarum and an application thereof and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. In the invention, for the first time, the phenylpyruvic acid reductase, which has the activity of catalyzing phenylpyruvic acid to generate phenyllactic acid, is screened and produced. The invention belongs to the fields of gene engineering and protein expression. The enzyme is successfully cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 and is applied to production of the phenyllactic acid through whole-cell catalysis of phenylpyruvic acid. After the catalytic reaction is carried out for 5 h, conversion of the substrate reaches 98.38% and ee value reaches 99.9%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nitrile hydratase mutant and application thereof
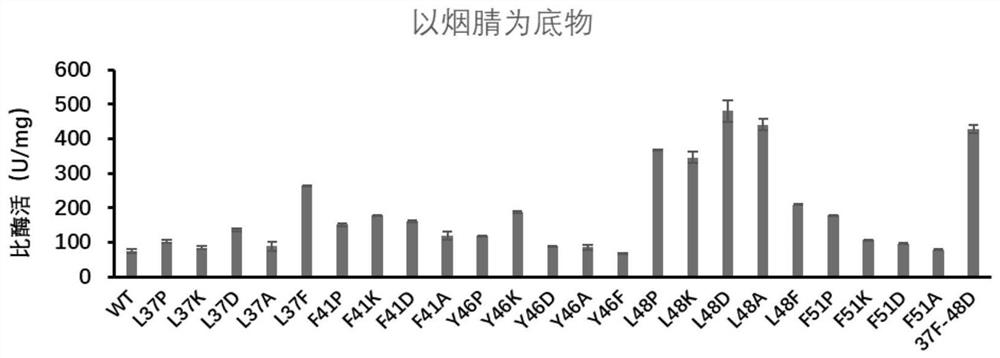
ActiveCN112322606AImprove thermal stabilityImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPyrazineGenomic engineering
The invention discloses a nitrile hydratase mutant and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. The half-life period of the nitrile hydratase mutantStr.t NHase-betaL48D at the temperature of 65 DEG C is about 43 minutes, and the thermal stability is remarkably improved compared with the thermal stability of other NHase enzymes. By adopting the technical scheme, the substrate tolerance of reaction taking nitrile compounds such as nicotinonitrile, acrylonitrile, benzonitrile, 2-cyanopyrazine nitrile, isobutyronitrile, n-valeronitrile and cinnamonitrile as substrates is obviously improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of rice gene OsNF-YC5 in improving salt tolerance of rice
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and rice molecular breeding, and particularly relates to application of a rice gene OsNF-YC5 in improving salt tolerance of rice. The rice gene OsNF-YC5 is knocked out or the expression of the rice gene OsNF-YC5 is down-regulated, so that the salt tolerance of the rice is improved, or a rice variety with high salt toleranceis bred; and the genomic DNA sequence of the rice gene OsNF-YC5 is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. According to the application, the gene OsNF-YC5 can be knocked out or the expression of the gene OsNF-YC5 is down-regulated by genetic engineering means such as a CRISPR gene targeting editing technology, and a rice mutant with the down-regulated expression or function deletion of the gene is obtained, so that the tolerance of high salt stress is remarkably improved, and as a result, the gene can be applied to breeding of salt-tolerant rice varieties.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
A high-throughput (HTP) genomic engineering platform for improving saccharopolyspora spinosa
PendingCN110914425AShorten the timeBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionEngineeringGenus Saccharopolyspora
The present disclosure provides a HTP microbial genomic engineering platform for Saccharopolyspora spp. that is computationally driven and integrates molecular biology, automation, and advanced machine learning protocols. This integrative platform utilizes a suite of HTP molecular tool sets to create HTP genetic design libraries, which are derived from, inter alia, scientific insight and iterativepattern recognition.
Owner:ZYMERGEN INC
Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria for producing campesterol and construction method
The invention discloses saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria for producing campesterol and a construction method, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and bioengineering. An expression cassette element of 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase is introduced into a yeast cell body, and is integrated into a yeast genome by utilizing a CRISPR / Cas9 gene operating system, C-22 sterol desaturase is knocked out, competition of an ergosterol branch path is relieved, and yeast synthesis from glucose to campesterol is realized. The method is simple in process, green and environment-friendly, and can be used for producing campesterol through fermentation. The yield of campesterol prepared by adopting the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain BY4742-delta erg5-TEF1p-dhcr7-ADH1t provided BY the invention can reach 253.35mg / L in a shake flask stage, and the horizontal yield of a fermentation tank can reach 916.88mg / L, which is increased by 2.6 times compared with the yield of campesterol in the shake flask stage of the strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for improving thermal stability of aspergillus niger xylanase through N-glycosylation modification
The invention discloses a method for improving thermal stability of aspergillus niger xylanase through N-glycosylation modification, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. Through enzymatic property determination, the half-life period t1 / 250 DEG C of the mutant enzyme T59N is prolonged to 340 min, the enzyme activity of the mutant enzyme A55N / D57S / T59N is not reduced after the mutant enzyme A55N / D57S / T59N is incubated for 500 min at 50 DEG C, and only the loss of the enzyme activity is 25.6% after the mutant enzyme A55N / D57S / T59N is incubated for 1260 min. The specific enzyme activity of the mutant enzyme A55N / D57S / T59N is 290.5 U / mg and is improved by 70.4% compared with that of xynA, the mutant enzyme is very stable when the pH value is 2.0-9.0, 70% or above of enzyme activity can still be kept after incubation for 1 h, and the method has a wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Novel glycosphingolipid endoglycosidase, and gene engineering preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a method for realizing the engineering expression of glycosyl endoglycosidase EGCase I. The method can realize the effective soluble expression of the EGCase I and maintain excellent hydrolysis and transglycosylation activity; a novel EGCase I mutant enzyme developed on the basis of the method has a broad substrate spectrum, and also has the activity of glycosidase synthetase; and the obtained glycosphingolipid endoglycosidase is very suitable for being applied to the analysis and the synthesis of industrial glycosphingolipids.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com