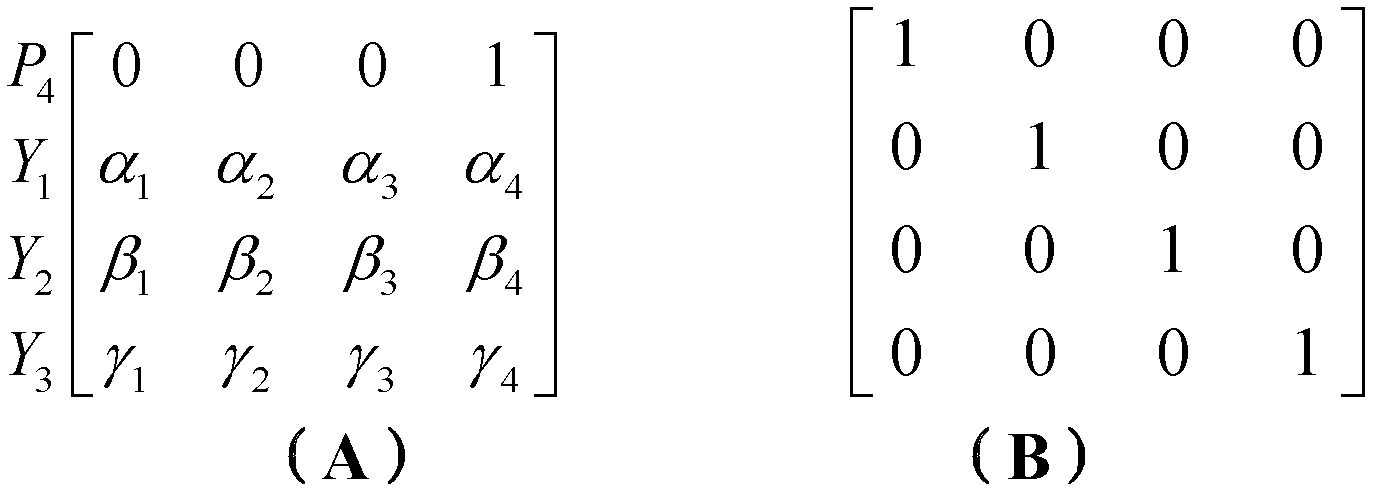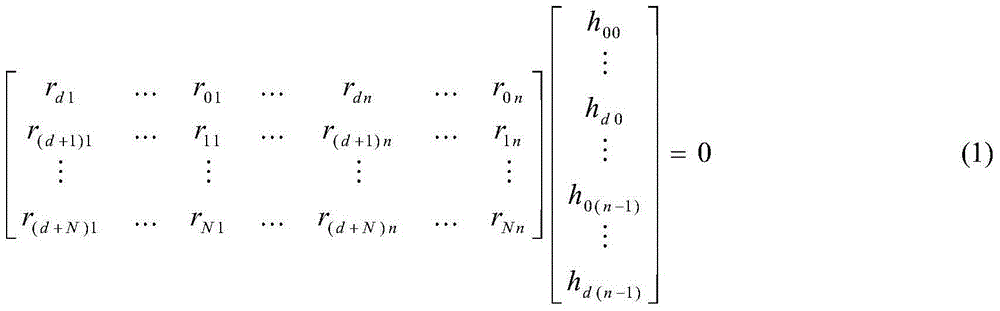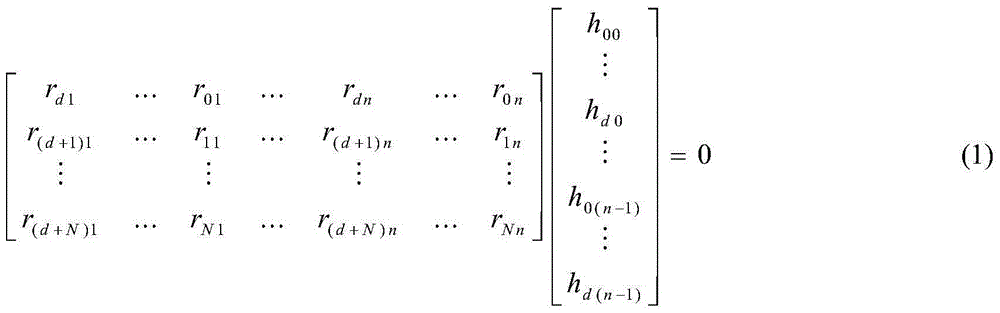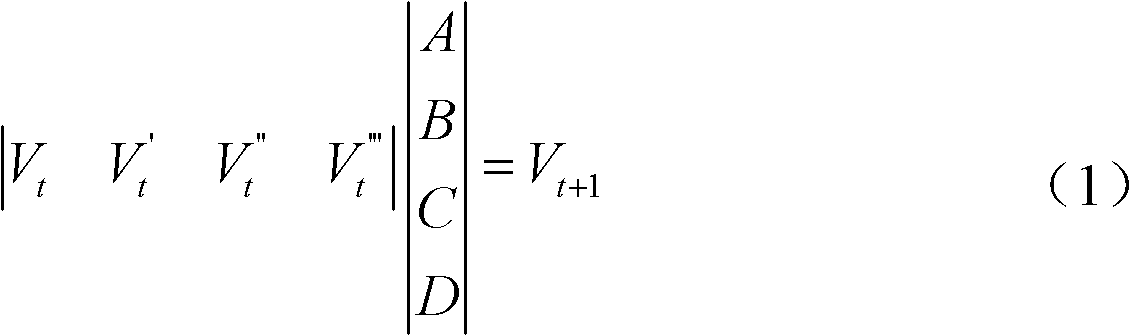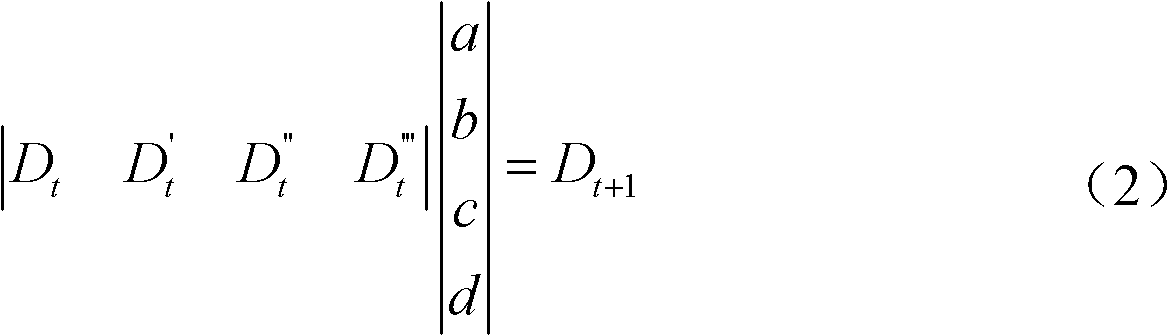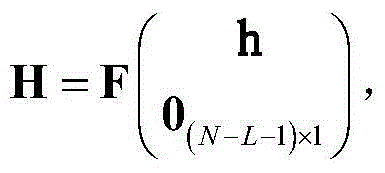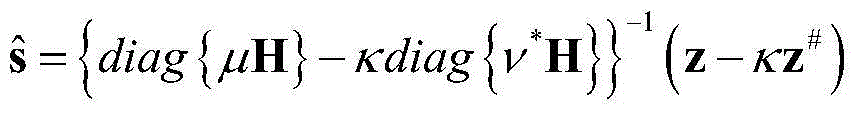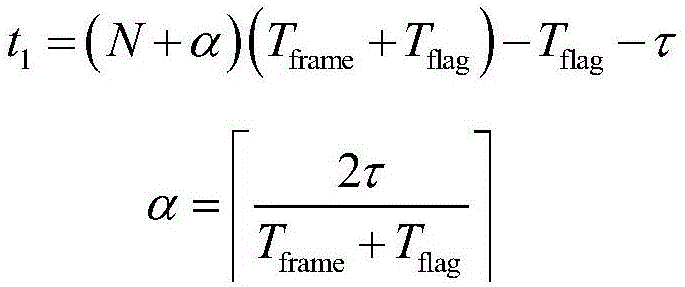Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
130 results about "Gaussian elimination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
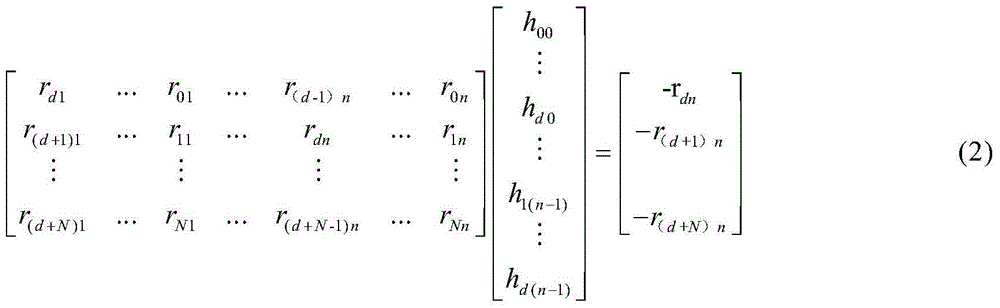
Gaussian elimination, also known as row reduction, is an algorithm in linear algebra for solving a system of linear equations. It is usually understood as a sequence of operations performed on the corresponding matrix of coefficients. This method can also be used to find the rank of a matrix, to calculate the determinant of a matrix, and to calculate the inverse of an invertible square matrix. The method is named after Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855), building on methods of linear reduction done by Chinese mathematicians circa 179 AD.
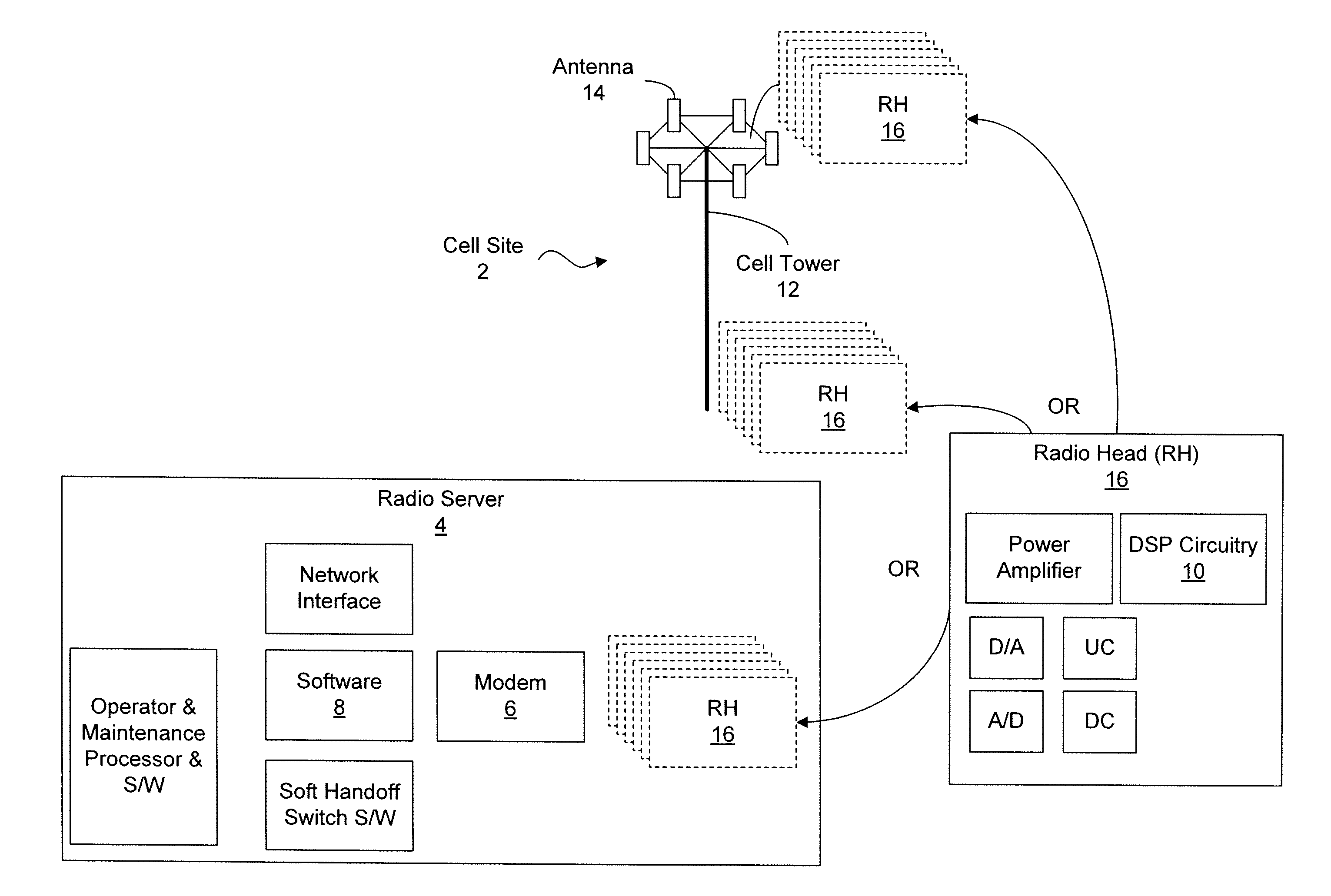
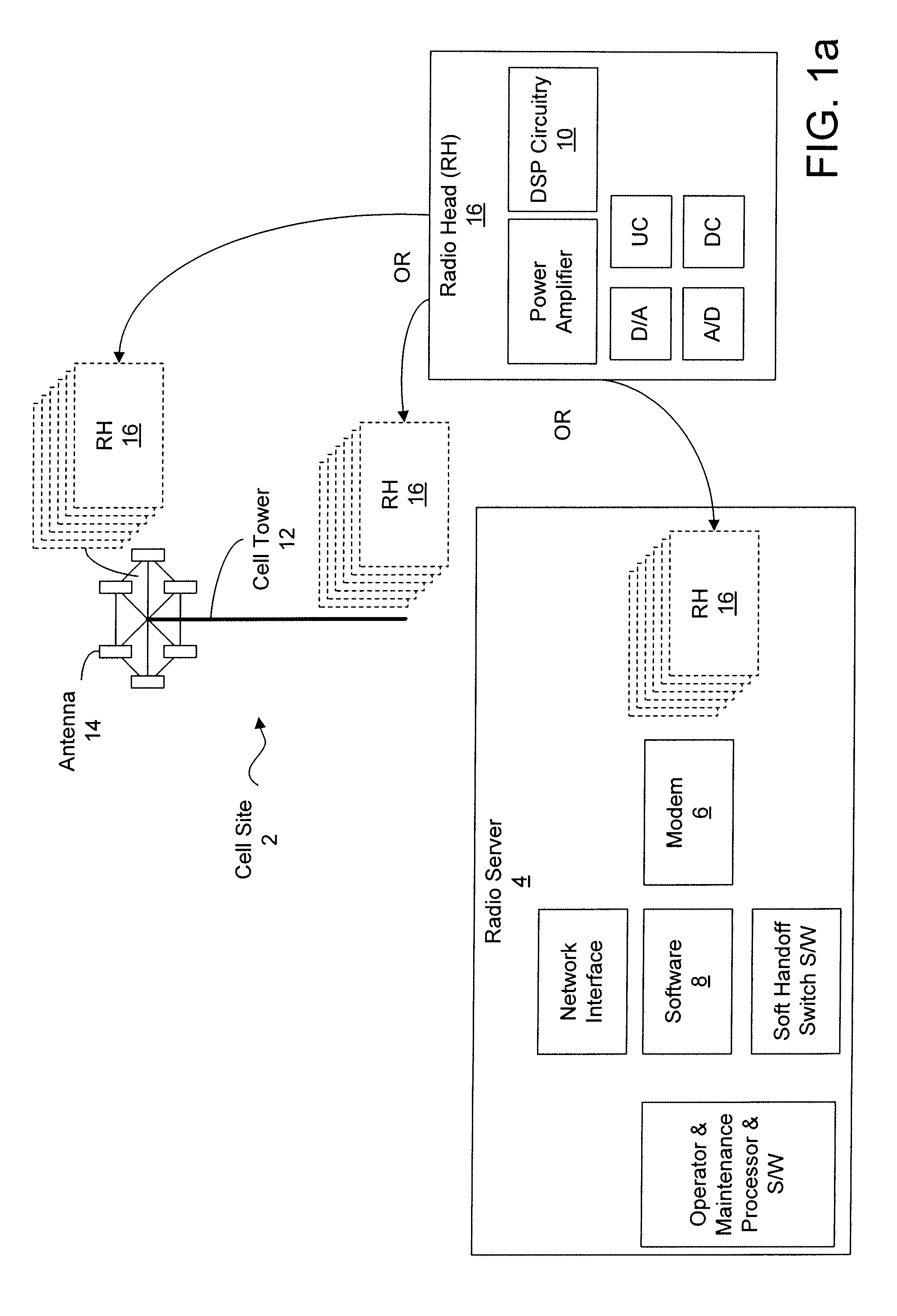
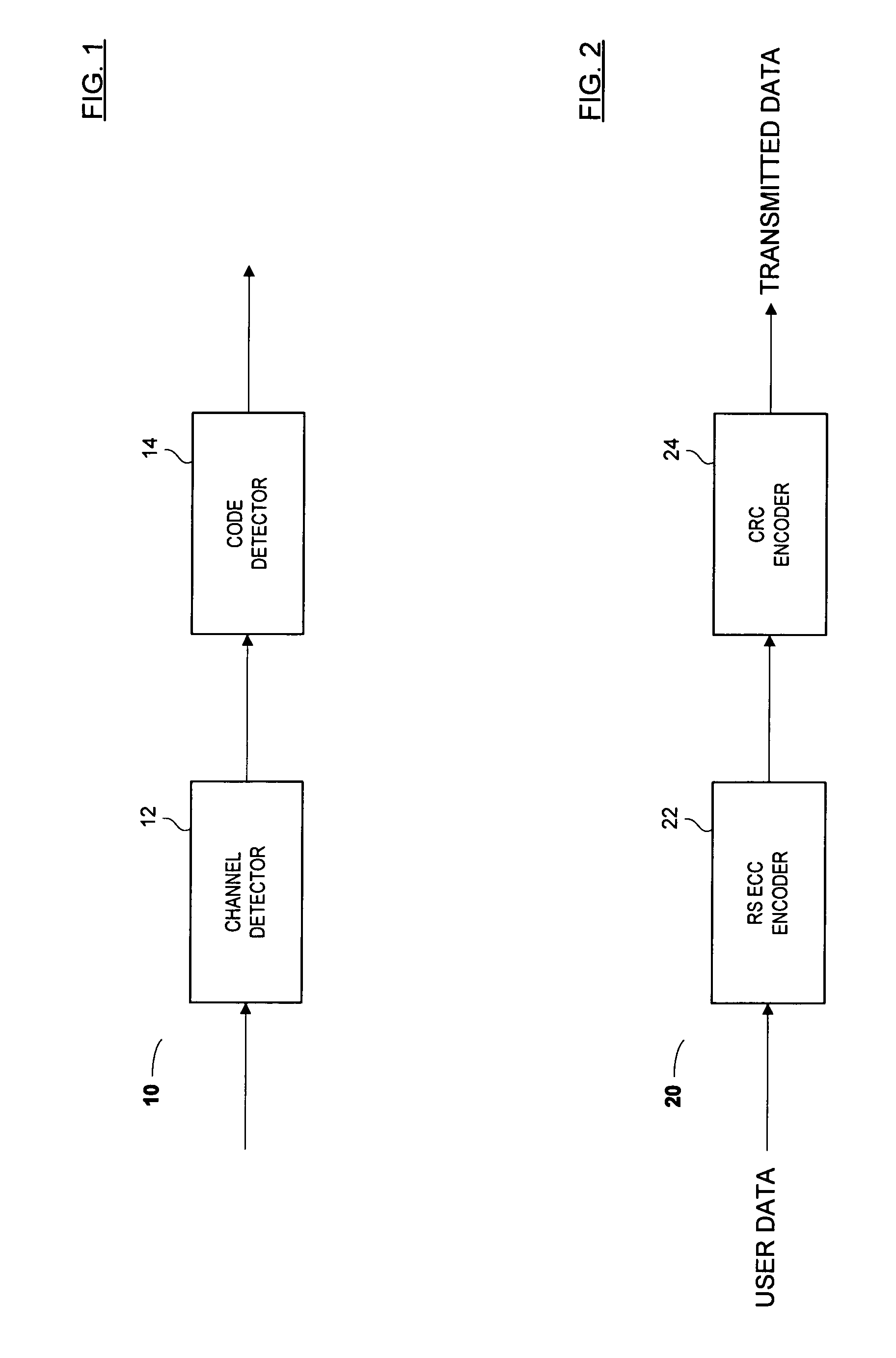
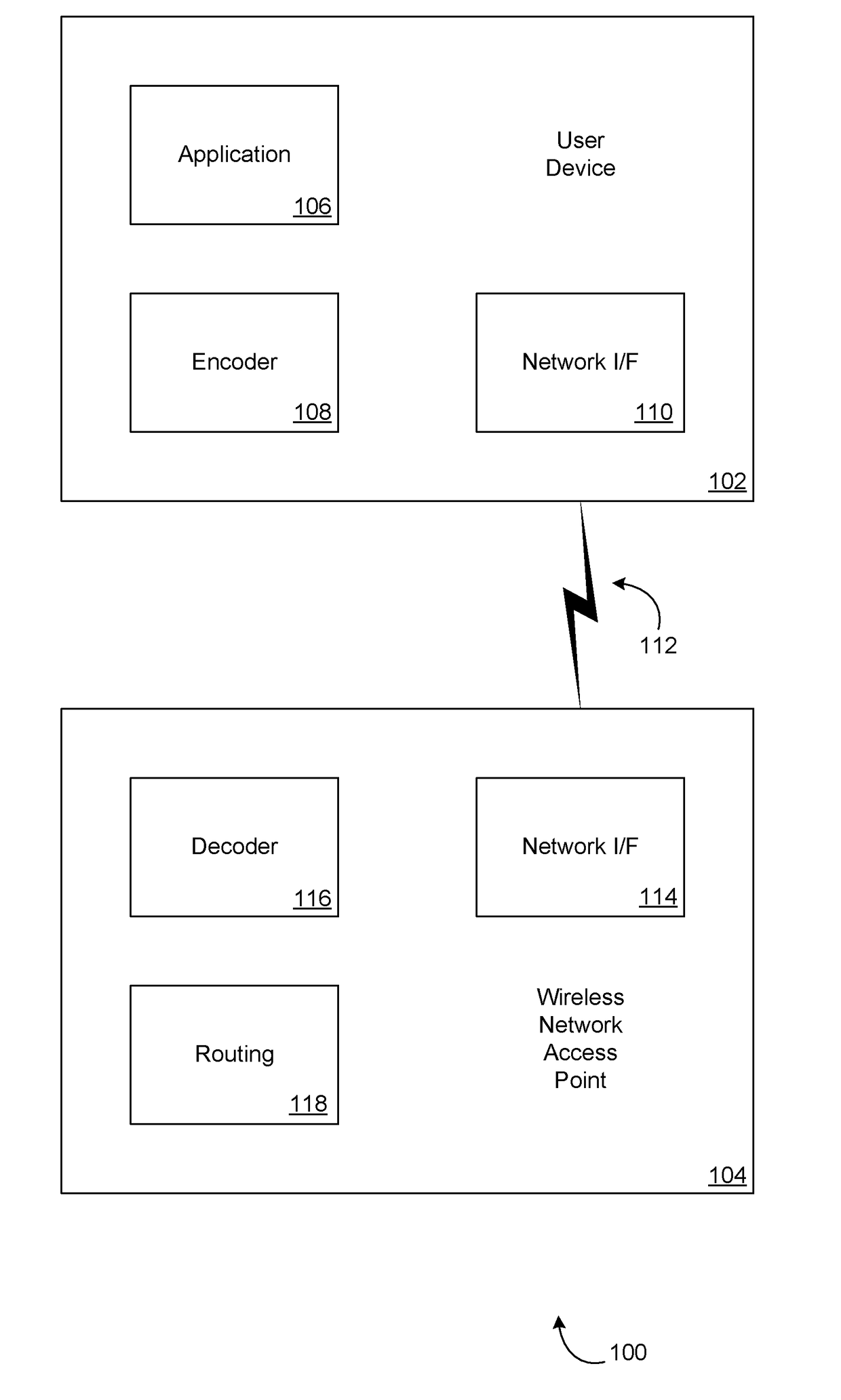
Dynamic digital pre-distortion system
ActiveUS20080260066A1Simplify reduce numberImprove efficiencyTransmitters monitoringPower managementAudio power amplifierLinear filter
A Dynamic Digital Pre-Distortion (DDPD) system is disclosed to rapidly correct power amplifier (PA) non-linearity and memory effects. To perform pre-distortion, a DDPD engine predistorts an input signal in order to cancel PA nonlinearities as the signal is amplified by the PA. The DDPD engine is implemented as a composite of one linear filter and N-1 high order term linear filters. The bank of linear filters have programmable complex coefficients. To compute the coefficients, samples from the transmit path and a feedback path are captured, and covariance matrices A and B are computed using optimized hardware. After the covariance matrices are computed, Gaussian elimination processing may be employed to compute the coefficients. Mathematical and hardware optimizations may be employed to simplify and reduce the number of multiplication operands and other operations, which can enable the DDPD system to fit within a single chip.
Owner:MICROELECTRONICS TECH INC
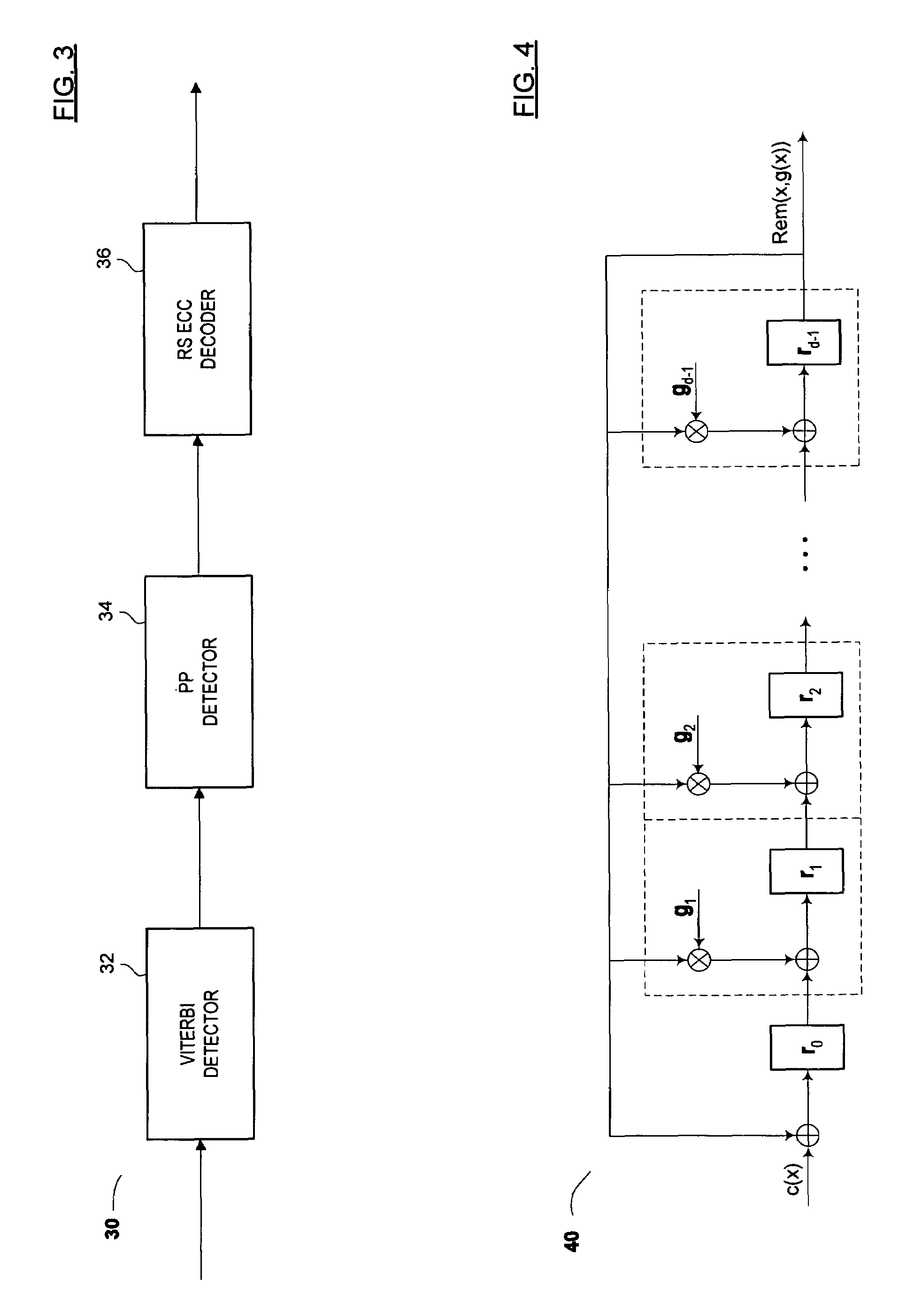
Methods and algorithms for joint channel-code decoding of linear block codes
ActiveUS7571372B1Facilitates PP implementationNot set it lowCode conversionRecord information storageError checkAlgorithm
Circuits, architectures, methods and algorithms for joint channel-code decoding of linear block codes, and more particularly, for identifying and correcting one or more errors in a code word and / or for encoding CRC (or parity) information. In one aspect, the invention focuses on use of (i) remainders, syndromes or other polynomials and (ii) Gaussian elimination to determine and correct errors. Although this approach may be suboptimal, the present error checking and / or detection scheme involves simpler computations and / or manipulations than conventional schemes, and is generally easier to implement logically. Since the complexity of parity-based error correction schemes increases disproportionately to the number of potential error events, the present invention meets a long-felt need for a scheme to manage error detection and / or correction in systems (such as magnetic recording applications) where there may be a relatively large number of likely error events, thereby advantageously improving reliability and / or performance in channel communications.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Support reaction type wind-tunnel balance shafting static calibration method
ActiveCN101419118ASimplify static calibration deviceSimple calculationAerodynamic testingGaussian eliminationEngineering
The invention relates to a method for statically calibrating a body axial system of a bearing reaction wind tunnel balance, wherein a loading device is arranged on a connecting end of a supporting rod of the wind tunnel balance, and the displacement of the loading device of the wind tunnel balance is measured through a laser displacement sensor which is arranged on a rigid support; after the wind tunnel balance is loaded, the reading of the laser displacement sensor is acquired, and the displacement of the loading device of the wind tunnel balance and the displacement of various loading points are calculated; the load exerted is subjected to translation and synthesized on an origin of a coordinate system of a body axle, and the bearing reaction generated on the wind tunnel balance by a base on the origin of the coordinate system of the body axle is solved and taken as the load of the body axial system of the wind tunnel balance; and a static calibration formula of the wind tunnel balances is solved through the least square method and the Gaussian elimination method by combination of the increment of outputted voltage signals before and after loading of all the wind tunnel balances and the loads of body axial systems. The static calibration method can simplify a static calibration device of the wind tunnel balance, not only does not need to use a complex offset-type or single-vector motion mechanism but also does not need to be limited by the performance of a reference balance, and is simple to calculate due to fixed position of the body axial system of the wind tunnel balance compared with the displacement method of a measuring and loading device.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Dynamic digital pre-distortion system
ActiveUS8005162B2Simplify reduce numberAvoid missing signalTransmitters monitoringPower managementAudio power amplifierMemory effect
A Dynamic Digital Pre-Distortion (DDPD) system is disclosed to rapidly correct power amplifier (PA) non-linearity and memory effects. To perform pre-distortion, a DDPD engine predistorts an input signal in order to cancel PA nonlinearities as the signal is amplified by the PA. The DDPD engine is implemented as a composite of one linear filter and N−1 high order term linear filters. The bank of linear filters have programmable complex coefficients. To compute the coefficients, samples from the transmit path and a feedback path are captured, and covariance matrices A and B are computed using optimized hardware. After the covariance matrices are computed, Gaussian elimination processing may be employed to compute the coefficients. Mathematical and hardware optimizations may be employed to simplify and reduce the number of multiplication operands and other operations, which can enable the DDPD system to fit within a single chip.
Owner:MICROELECTRONICS TECH INC
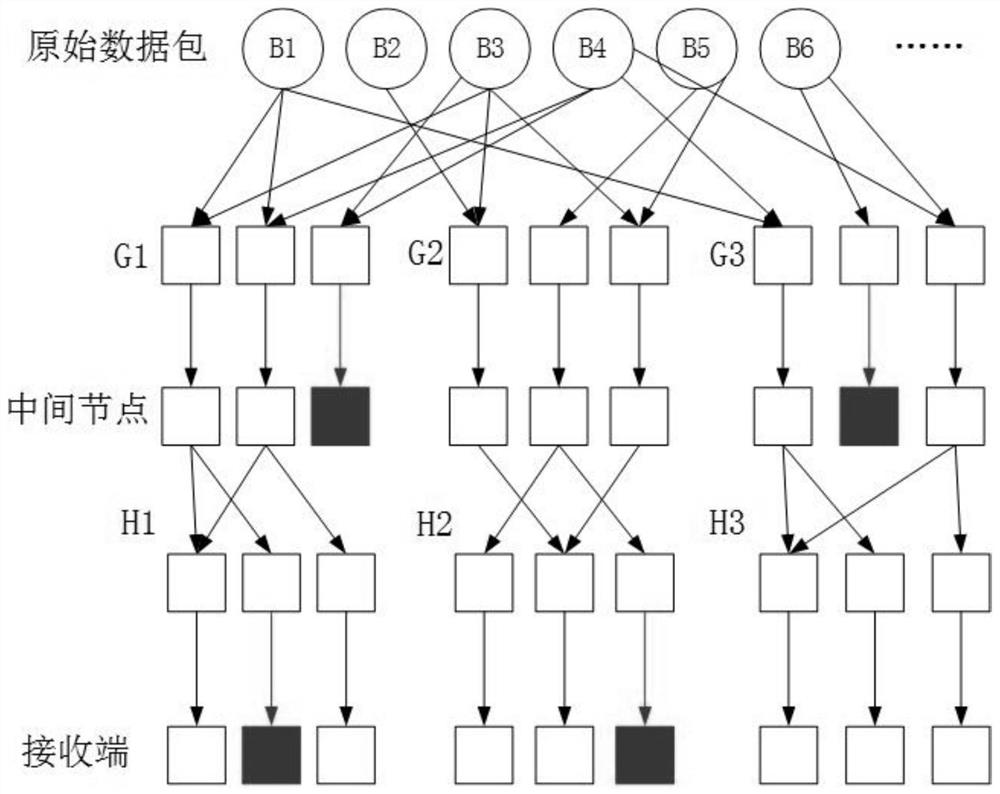
Wireless reliable broadcasting method based on random linear network code
InactiveCN102638331AReduce complexityImprove retransmission performanceError prevention/detection by transmission repeatOriginal dataWireless broadcast
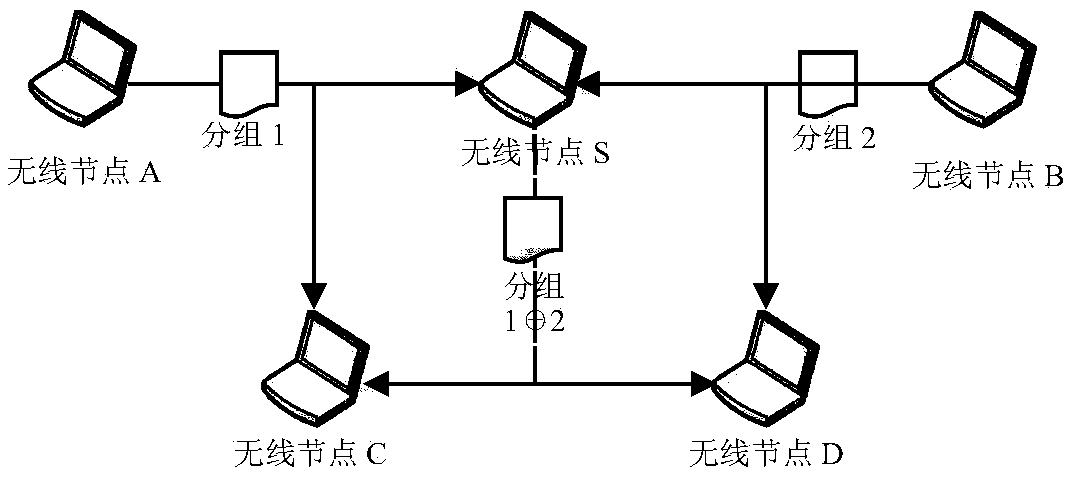
The invention relates to a wireless reliable broadcasting method based on a random linear network code. The wireless reliable broadcasting method comprises two stages: broadcasting an original data packet and retransmitting a coding packet, namely, performing a linear network code on a lost data packet, and retransmitting the coding packet; and respectively solving each lost original data packet by utilizing a Gaussian elimination method after each receiving node receives the coding packets with the preset amount. The method in the invention can be used for overcoming the defect that a traditional retransmission method is not suitable for point-to-multipoint broadcasting scene and also prevents limitation that performance is not stable and system expense is large in the retransmission method based on XOR (exclusive OR) coding, according to the wireless reliable broadcasting method based on the random linear network code, disclosed by the invention, linear network code and retransmission is carried out on the lost original data packet of each receiving node through lower coding algorithm complexity and system expense; and the receiving node can be used for solving the original data packet from the coding packet by utilizing a solution of a linear equation system, and the retransmission performance of wireless broadcast is modified, and the average retransmission times is reduced. The wireless reliable broadcasting method disclosed by the invention is stable, is not influenced by data package loss distribution and has good promotion application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for recovery of lost and/or corrupted data
ActiveUS20090292966A1Quality improvementReduce operational burdenCode conversionError correction/detection using block codesTriangulationParity-check matrix
A method for recovery of lost and / or corrupted data transmitted from a transmitter device to a receiver device. The data is coded by an encoder connected to the transmitter device. The data is transmitted from the transmitter device to the receiver device via a transmission system and is decoded by means of a decoder connected to the receiver device. This is performed through application of a low density parity check method, wherein lost and / or corrupted data is restored during decoding. The decoding is performed by solving the equation system of the parity check matrix H. The parity check matrix H is brought into a triangular form by column and / or row permutations. Columns of a sub-matrix B of the matrix H which impede the triangulation process are shifted into a sub-matrix P of the matrix H so that the triangulation process can be continued until the matrix H except for the sub-matrix P has been completely brought into a triangular form. The Gaussian elimination method is applied to a part of the sub-matrix P. The selection of the column or columns of the sub-matrix B which are to be shifted into the sub-matrix P is performed on the basis of the weight of the column which corresponds to the number of non-zero-entries in the column, and / or on the basis of the weight of the rows of the sub-matrix B connected to the column.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
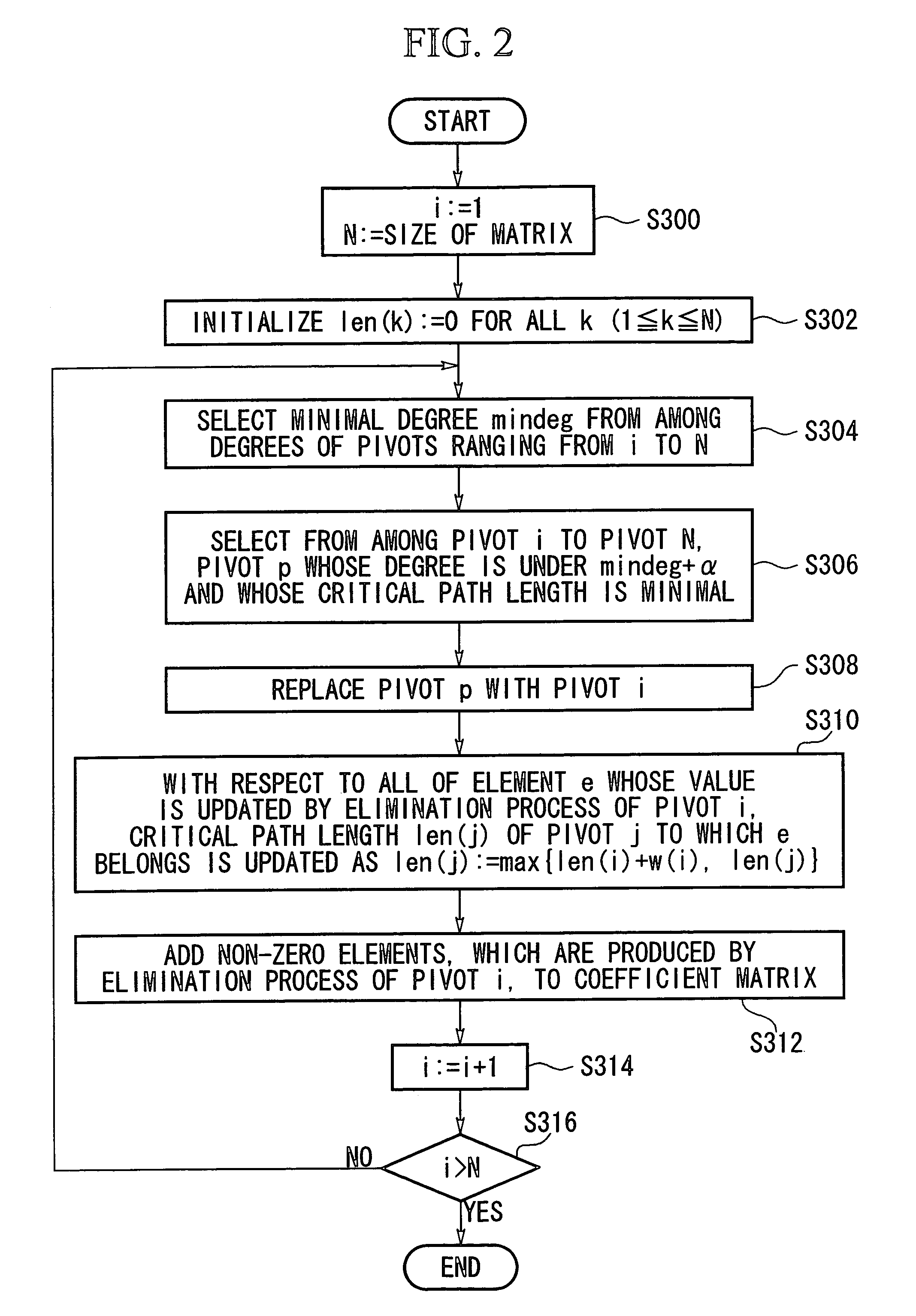
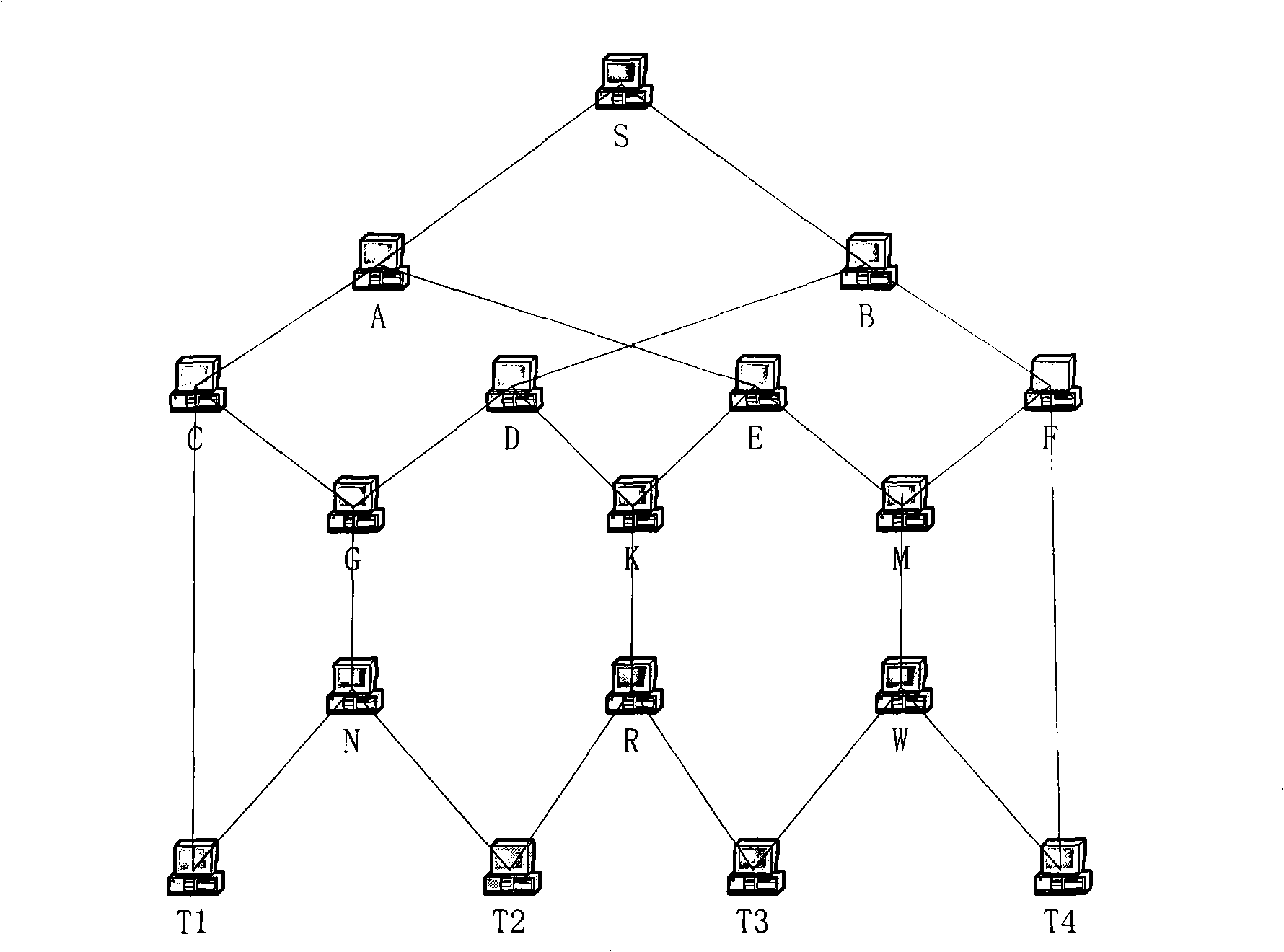
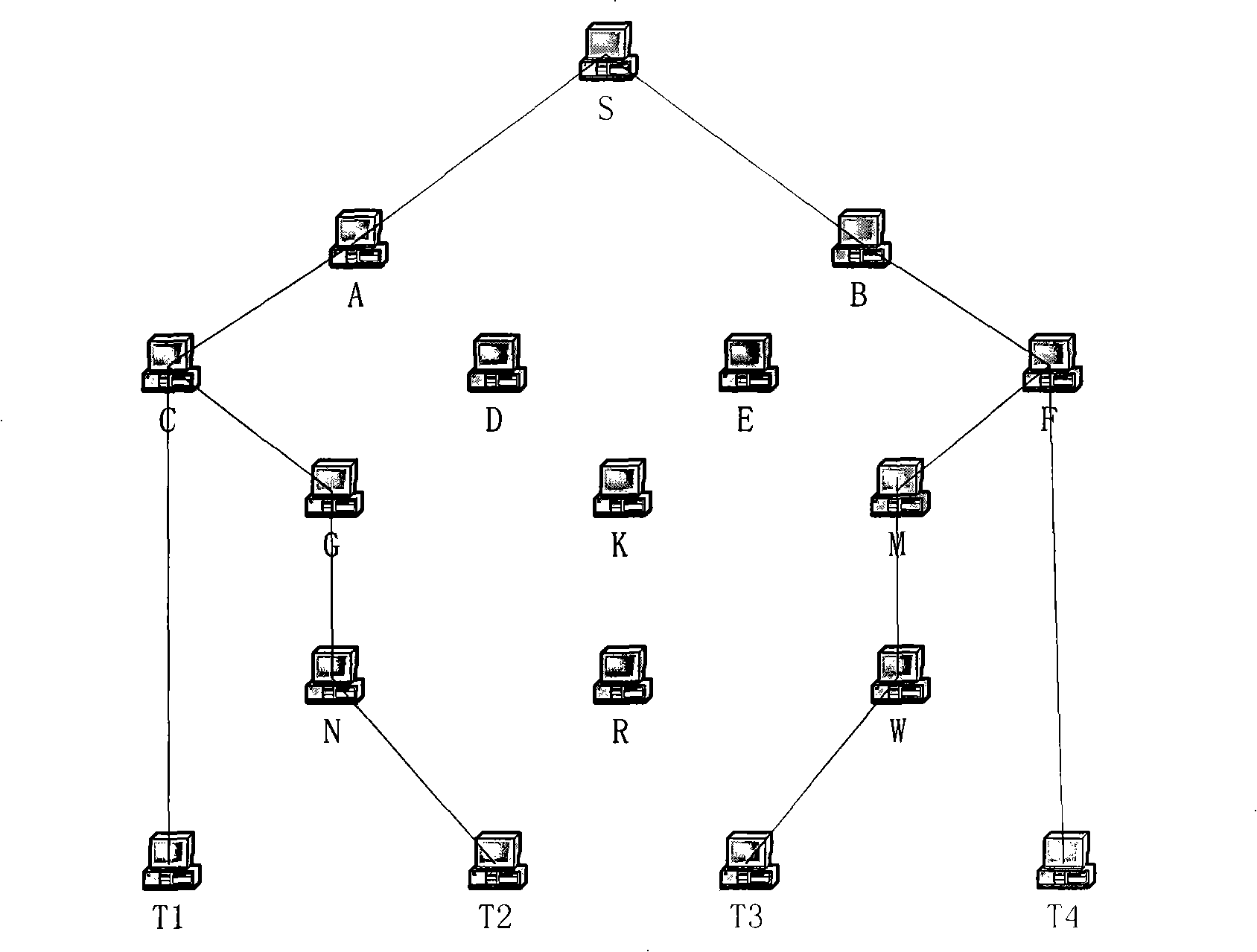
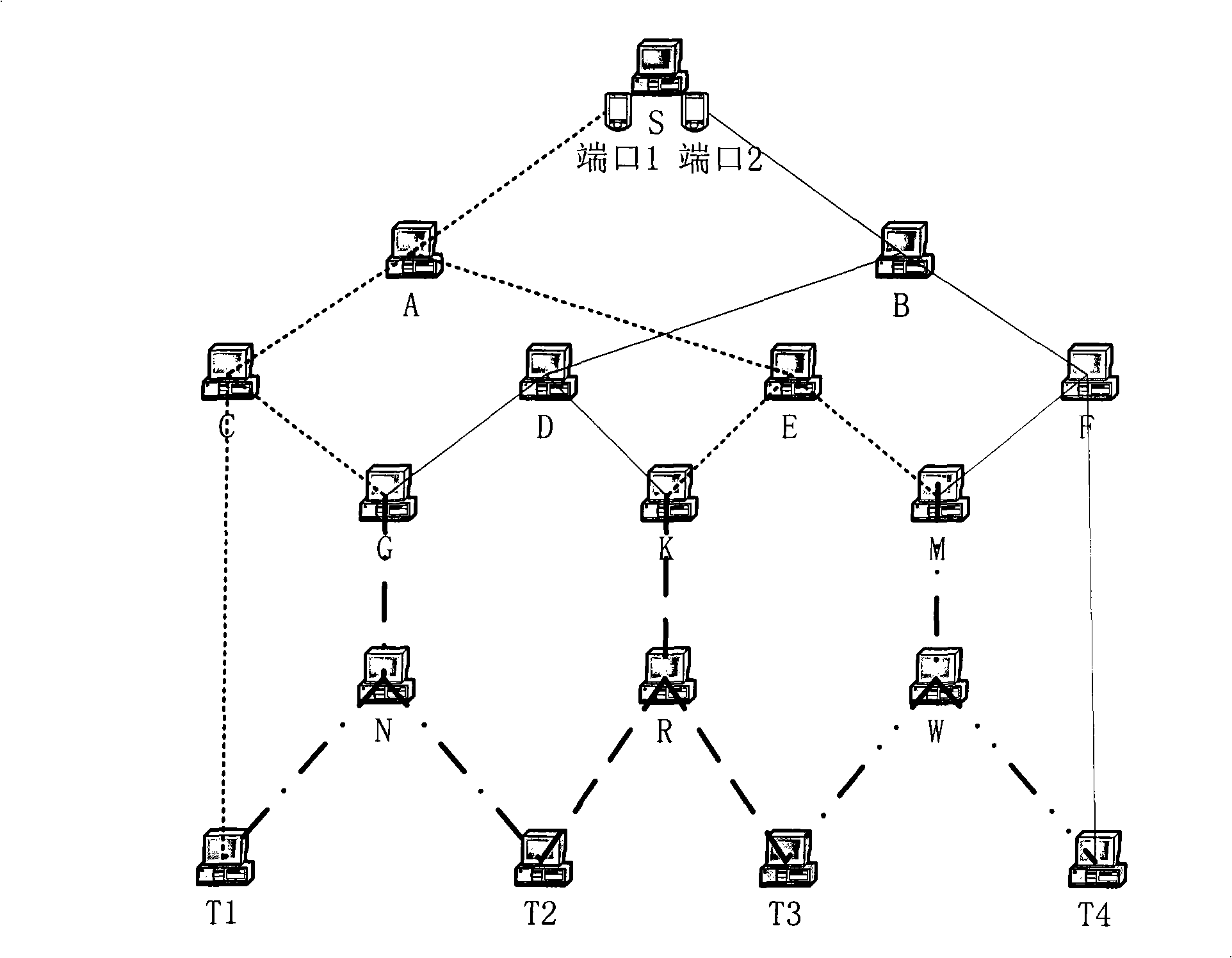
Method and apparatus for matrix reordering and electronic circuit simulation
InactiveUS7089159B2High-speed performanceImprove high-speed performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAnalogue computers for electric apparatusPath lengthSimultaneous equations
A matrix reordering method performs reordering of elements of a coefficient matrix created based on coefficients of linear simultaneous equations whose solutions are to be produced by parallel processing of processors of a computer in accordance with Gaussian elimination. Herein, degrees corresponding to numbers of non-zero elements are calculated with respect to all pivots included in the coefficient matrix. Then, a first pivot whose degree is under a threshold (mindeg+α) is selected from among the pivots of the coefficient matrix, while a second pivot whose critical path length is minimum is also selected from among the pivots of the coefficient matrix. Replacement of elements is performed between the first pivot and second pivot to complete reordering with respect to the first pivot. In addition, non-zero elements, which are newly produced by the Gaussian elimination of the first pivot, are added to the coefficient matrix. If a degree or a parameter of the first pivot is under a threshold (β), reordering is performed on a partial matrix whose elements are not eliminated and are selected from among the elements of the coefficient matrix in accordance with the nested dissection method, so that non-zero elements, which are newly produced by the Gaussian elimination of the partial matrix, are added to the coefficient matrix. Because the critical path length can be reduced as compared with conventional techniques, it is possible to considerably reduce a total processing time of the parallel processing to secure high-speed performance of the Gaussian elimination.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Method for distributing ascent type encode vector in multicast network
InactiveCN101409602AIncrease the probability of successful decodingReduce sizeSpecial service provision for substationError preventionNetwork codeMulticast network
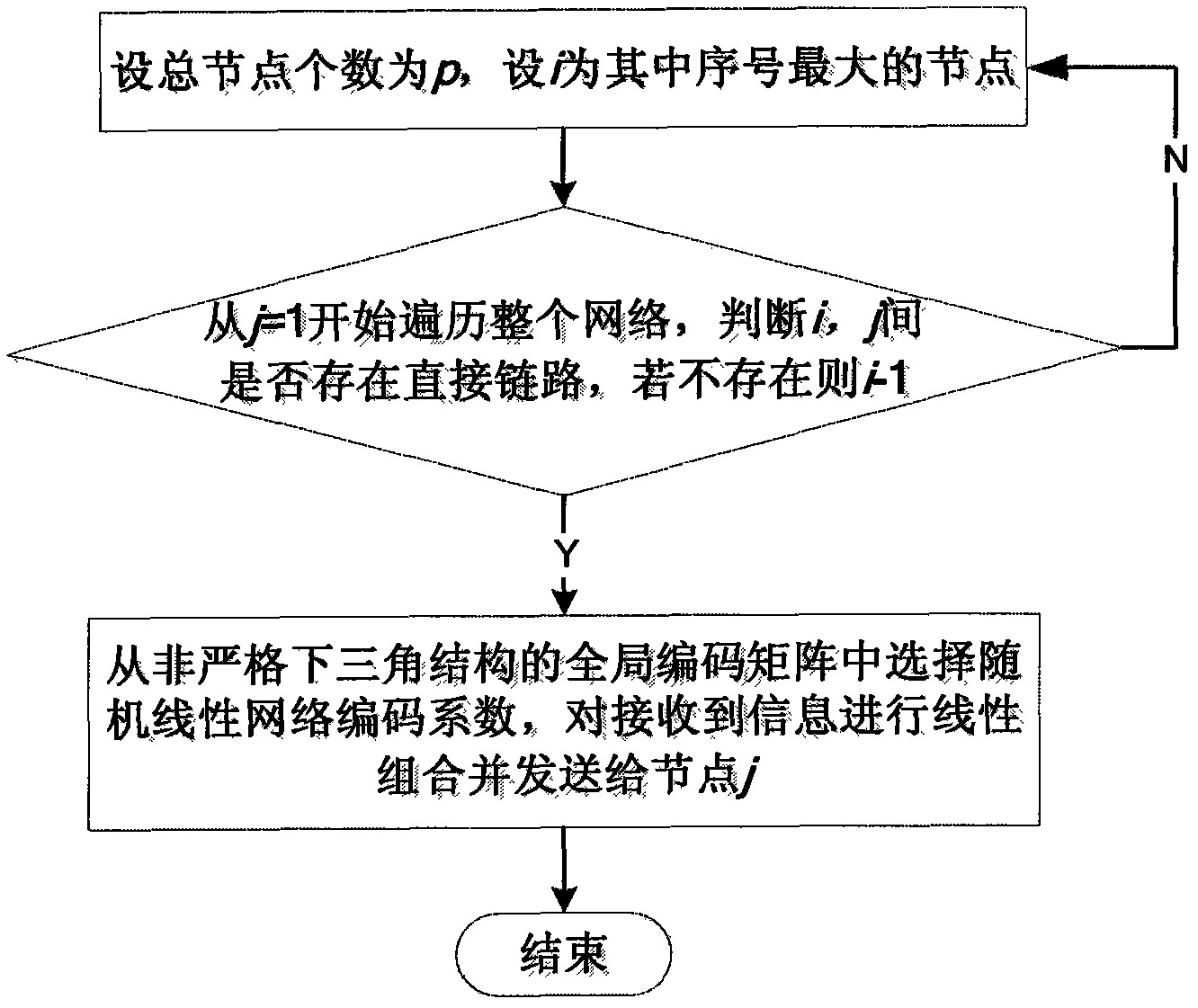
The invention discloses a method for distributing upstream going coding vectors in a multicast network, comprising: linearity unrelatable global coding vectors are distributed from the beginning of a grogram and gradually transmitted to a source node, and decoding matrix is ensured to have full rank at a destination node; namely, the linearity unrelatable global coding vectors are distributed for all the destination nodes and then transmitted towards upstream, and local coding vectors are calculated and recorded according to a certain regulation at the coding nodes. A congregation of the global coding vectors is maintained at the source node, and all the coding vectors are respectively recorded at one port of a buffer of the coding vector. When the data is transmitted, the message sent by the source node is firstly multiplied by the global coding vectors at all the ports of the buffer, and then is transmitted towards the downstream. After receiving the message, the destination nodes transfer the decoding matrix to decode by adopting Gaussian elimination method. The invention is applicable to the method for distributing the coding vectors in topology of the known network and the unknown network, so as to increase the decoding probability of the success for receiving node in the multicast network based on the network code, reduce the size of alphabet needed by decoding and lower the complexity of the network code.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Parameter blind identification method of puncturing turbo code component coder
InactiveCN104683072AReduce operational complexityRealize parameter blind identificationError preventionInformation processingLinear matrix
The invention relates to a parameter blind identification method of a puncturing turbo code component coder, belonging to the technical field of the code identification in a communication system. The method comprises the steps of multiplexing a puncturing turbo code information bit and a verification bit to form a puncturing convolutional code, carrying out statistics and analysis for the code length and a code word starting point of the puncturing convolutional code by virtue of a linear matrix analysis method, identifying a verification matrix of the component coder by utilizing partial Walsh-Hadamard conversion, obtaining a puncturing mode and generating a matrix further by virtue of a Gaussian elimination method, carrying out the blind identification on the parameters of the puncturing turbo code component coder, and verifying the accuracy of the identified parameters. By adopting the method, the operation complexity of identifying the component coder parameter can be alleviated, the identification efficiency and the identification reliability can be improved, and the method is applicable to the fields of the intelligent communication, information processing and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Message coding for ncma-based multiple access networks
ActiveUS20170064701A1Spread the wordDifferent from numberCode conversionCoding detailsAccess networkFountain code
Computationally efficient message encoding and decoding schemes for NCMA-based multiple access networks are enabled. Belief propagation decoding of fountain codes designed for NCMA-based multiple access networks may be enhanced using Gaussian elimination. Networks utilizing a network-coded slotted ALOHA protocol can benefit in particular. In such cases, Gaussian elimination may be applied locally to solve the linear system associated with each timeslot, and belief propagation decoding may be applied between the linear systems obtained over different timeslots. The computational complexity of such an approach may be of the same order as a conventional belief propagation decoding algorithm. The fountain code degree distribution may be tuned to optimize for different numbers of expected channel users.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method and device for detecting signals in multi-input and multi-output system
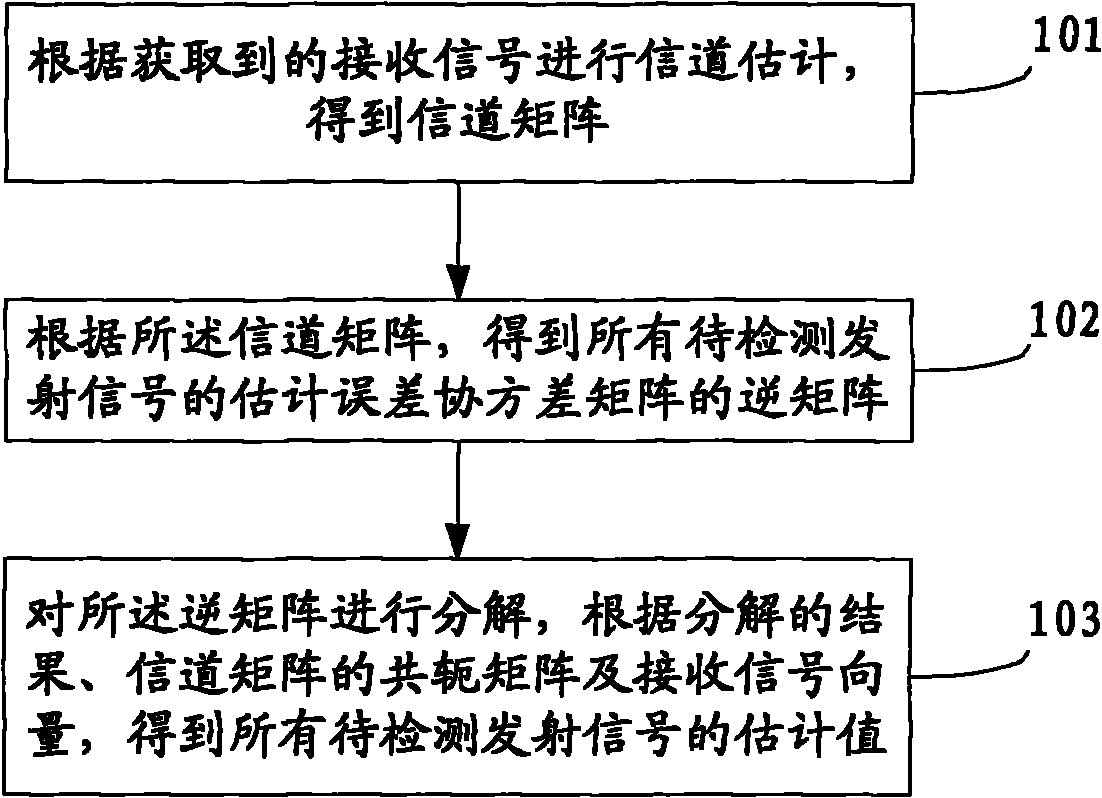
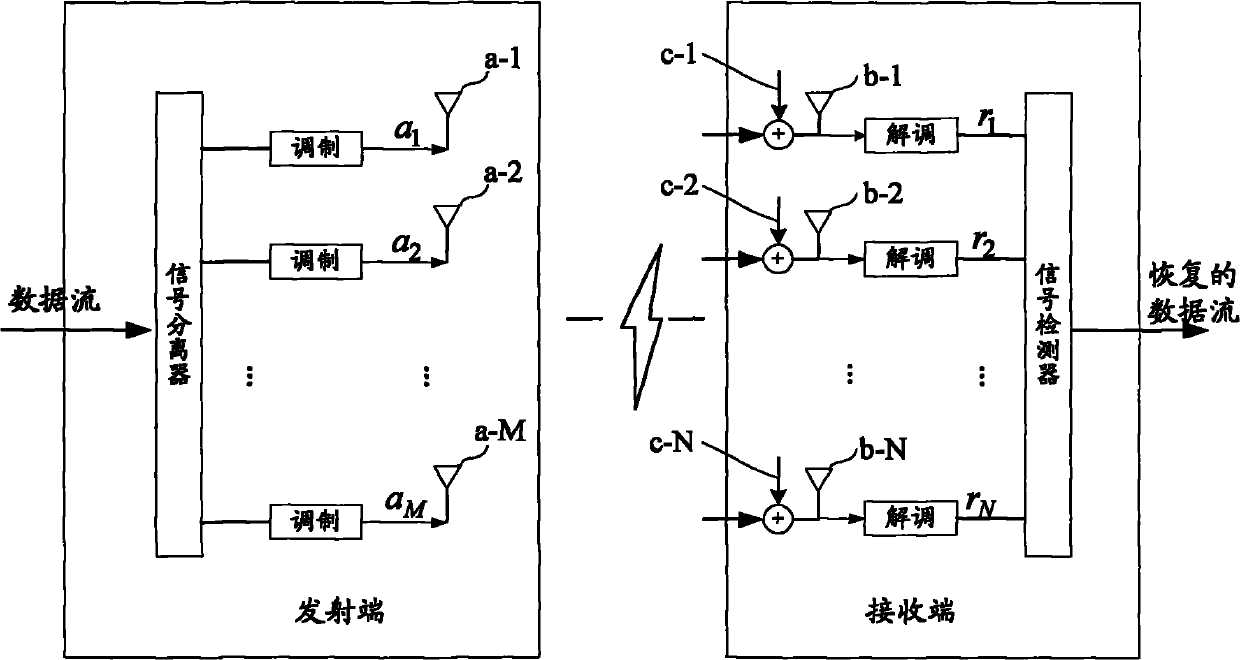
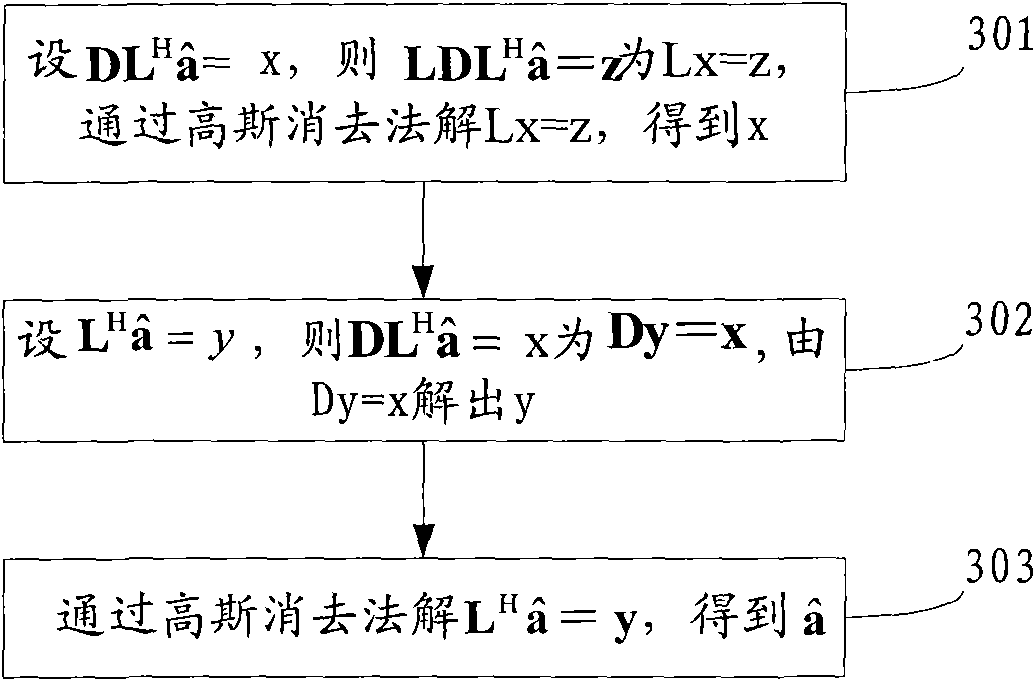
ActiveCN101998440AReduce computational complexityImplement signal detectionBaseband system detailsTransmission monitoringMulti inputComputation complexity
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting signals in a multi-input and multi-output system, which belongs to the field of communication. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out channel estimation according to obtained receiving signals to obtain a channel matrix H; obtaining an inverse matrix R of an estimation error covariance matrix Q of all emitting signals to be detected according to the channel matrix H; decomposing the inverse matrix R of the estimation error covariance matrix Q; and obtaining the estimation value of all emitting signals to be detected according to the decomposing results, a conjugate matrix HH of the channel matrix H and the receiving signal vector r. The device comprises a channel estimation module, a calculating module, a decomposing module and a detection module. Through decomposing the inverse matrix R of the estimation error covariance matrix Q and adopting a Gaussian elimination method, the invention realizes the signal detection, avoids the matrix inversion during the signal detection, and reduces the calculation complexity during the signal detection.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Sliding-window-based network coding method
InactiveCN105515728AReduce complexitySmall scaleCode conversionCoding detailsSlide windowNetwork code
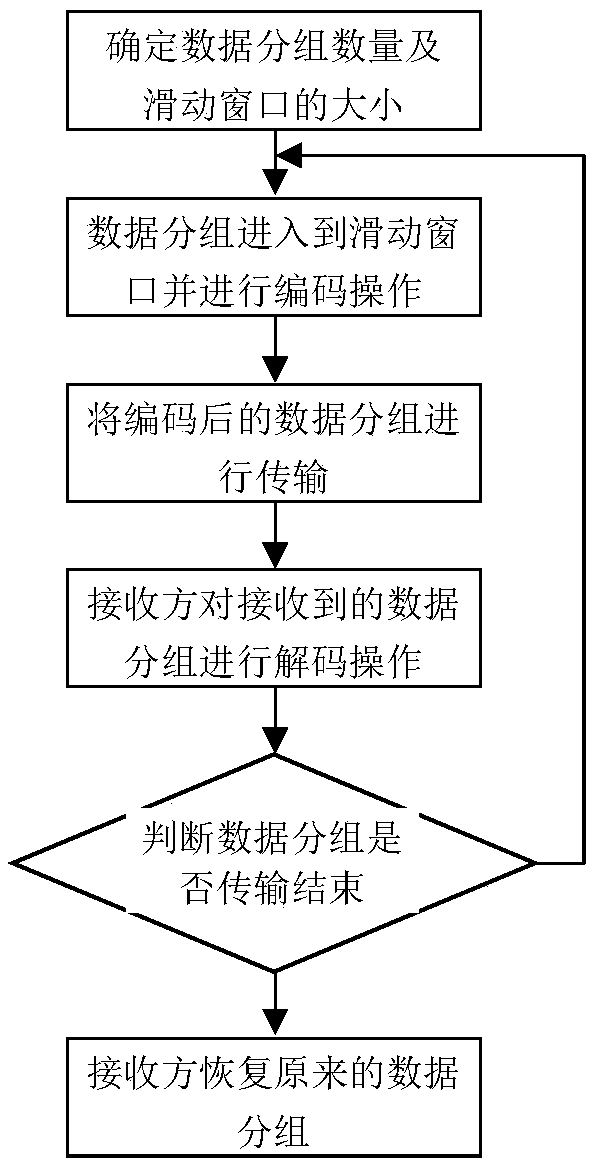
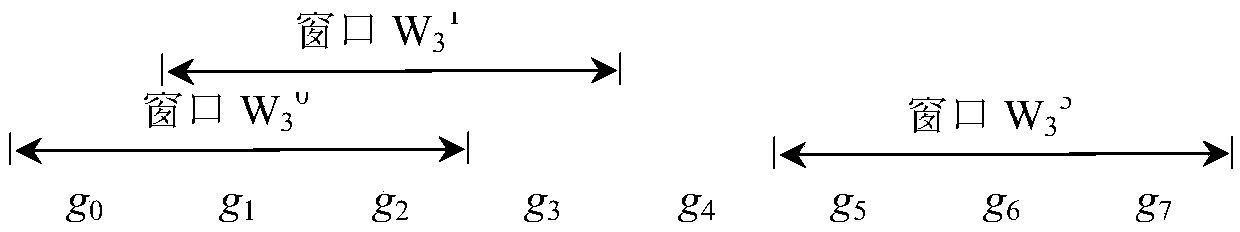
Disclosed in the invention is a sliding-window-based network coding method. The method comprises: the number N of to-be-sent data groups and a size W of a sliding window are determined; a source node carries out coding on the to-be-sent data groups according to the determined size of the sliding window and an intermediate node carries out coding again on the received coded groups and transmits the processed coded groups; and then a destination node carries out decoding on the received coded groups by using an exchange Gaussian elimination method and recovers the decoded data groups. According to the invention, the size of the sliding window is determined and only the data groups in the sliding window are coded, thereby improving reliability of the network coding and substantially reducing the decoding complexity. Therefore, the rapid network coding is realized; and the data throughout of the network is maximized, thereby extending the network lifetime.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF ECONOMICS
Method and apparatus for solving systems of linear inequalities
InactiveUS6950844B2Reduced interval widthReduce widthComplex mathematical operationsComputation using denominational number representationNonlinear systems of equationsInterval matrix
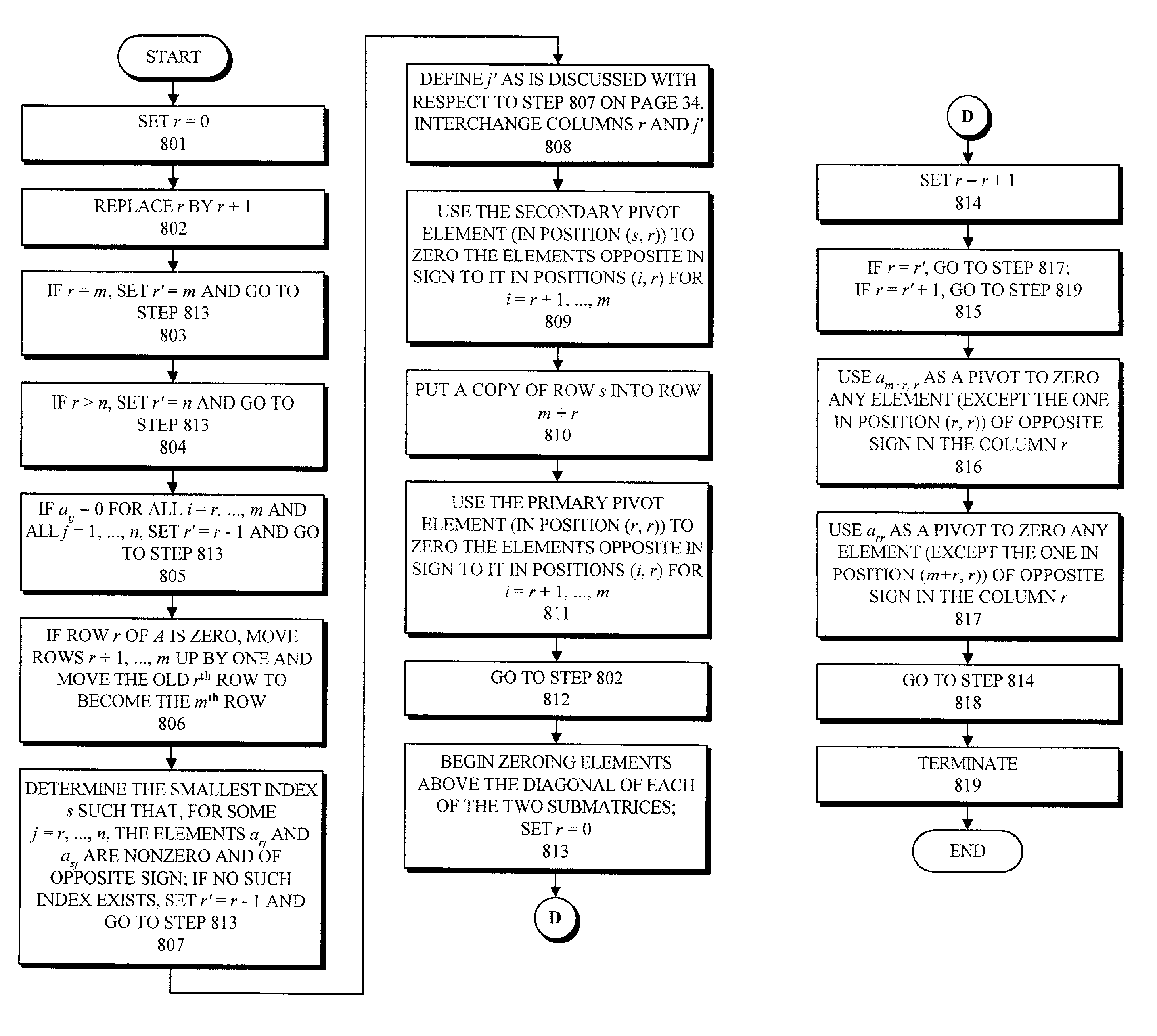
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that performs a procedure to solve a system of linear inequalities. During operation, the system receives a representation of the system of linear inequalities Ax≦b, wherein Ax≦b can be a linearized form of a system of nonlinear equations. Within this representation, A is an interval matrix with m rows corresponding to m inequalities, and with n columns corresponding to n variables, the vector x includes n variable components, and the vector b includes m scalar interval components. The system solves the system of linear inequalities Ax≦b by performing a Gaussian elimination process using only positive multipliers so as not to change the sense of any inequality. For a given column j in A, performing the Gaussian elimination process involves attempting to select a primary pivot row r including a primary pivot element, arj, which does not contain zero, and attempting to select a secondary pivot row s including a secondary pivot element, asj, which does not contain zero and is opposite in sign to arj. If r and s are successfully selected, the system uses the secondary pivot element asj to zero elements opposite in sign to it in the same column of A, except for the primary pivot element arj. The system also adds a copy s′ of the secondary pivot row s to the matrix A, thereby increasing the number of rows in the matrix A. Next, the system uses the primary pivot element are to zero elements opposite in sign to it in the same column of A, except for the copy of the secondary pivot element as′j in row s′.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
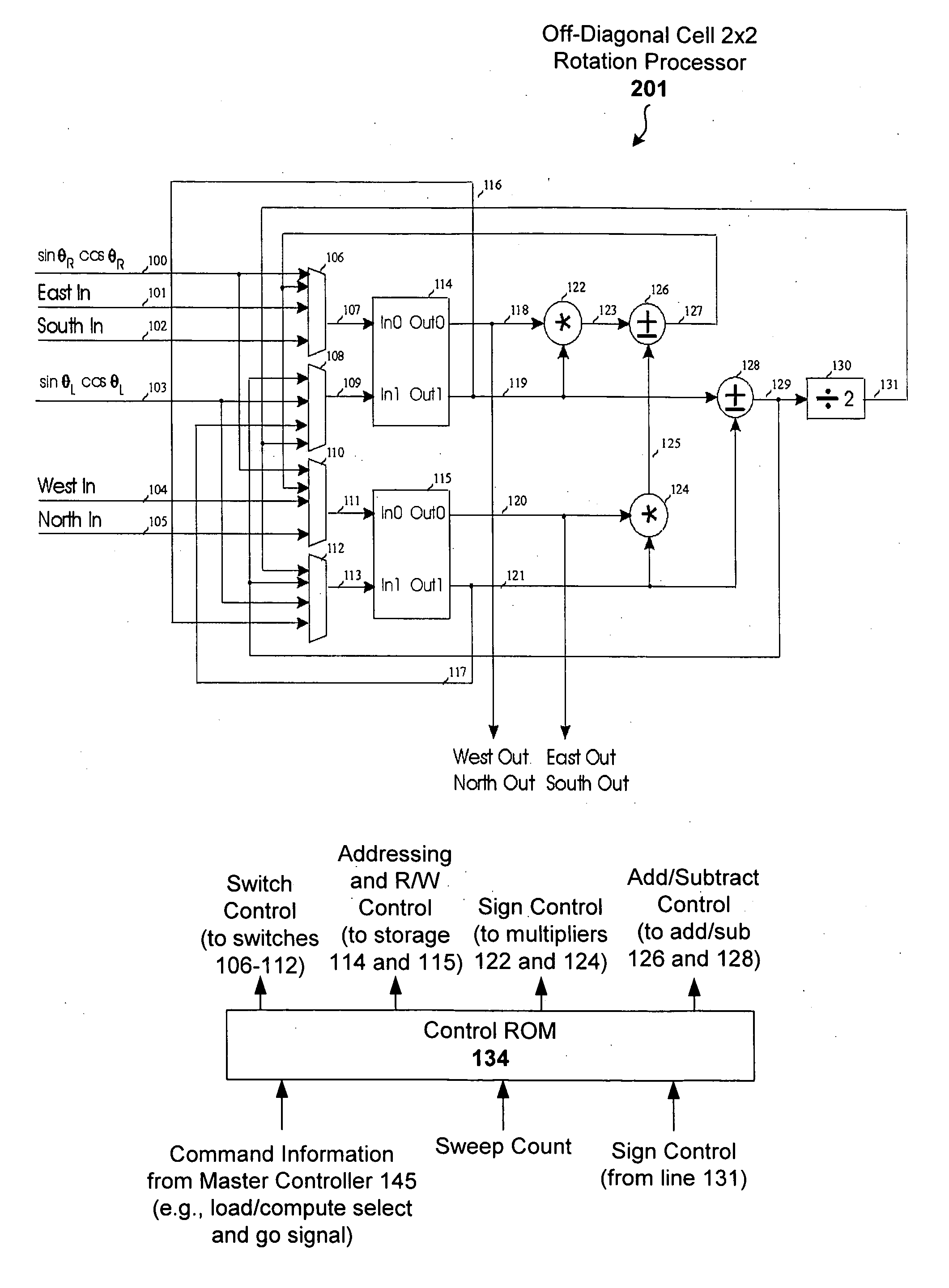
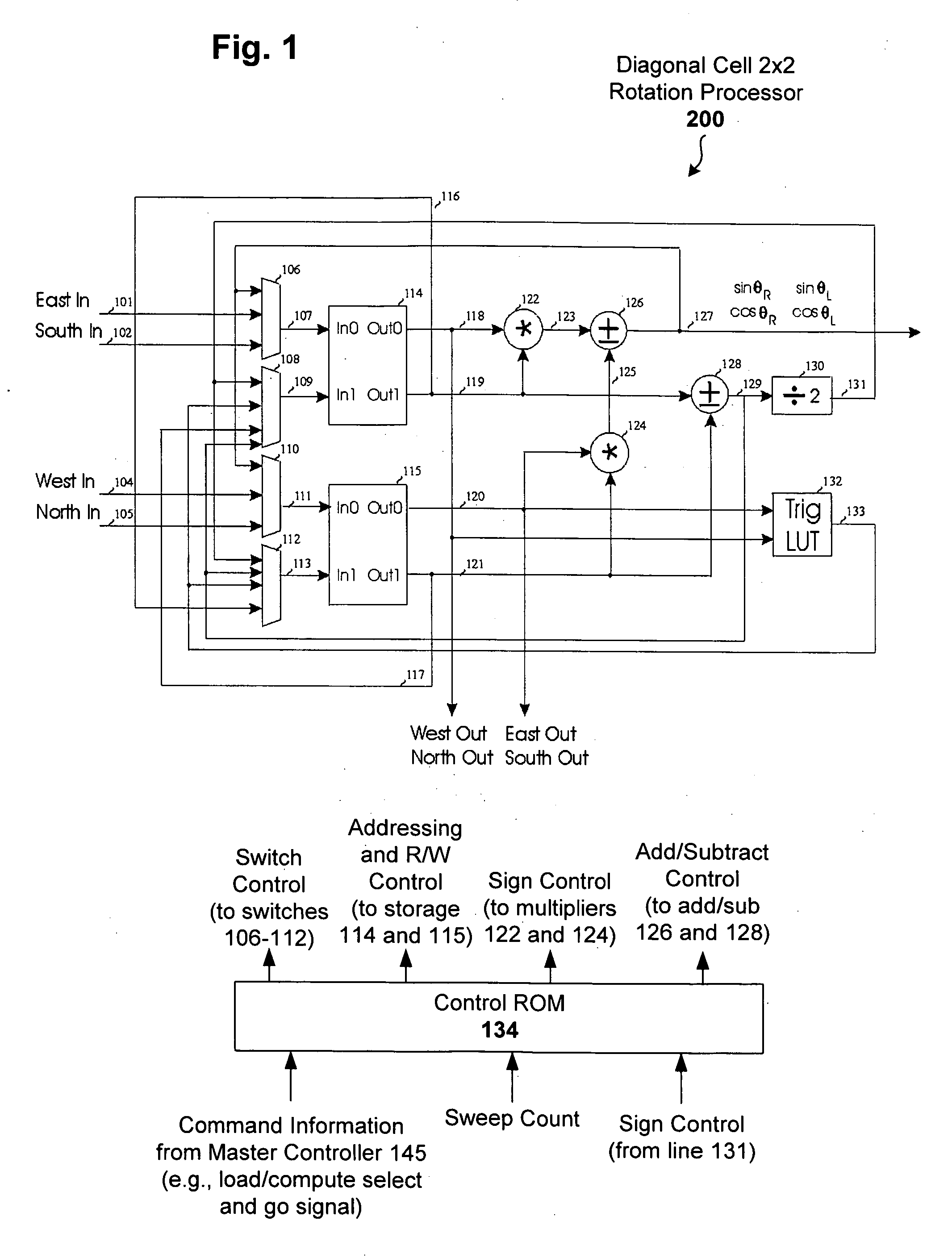
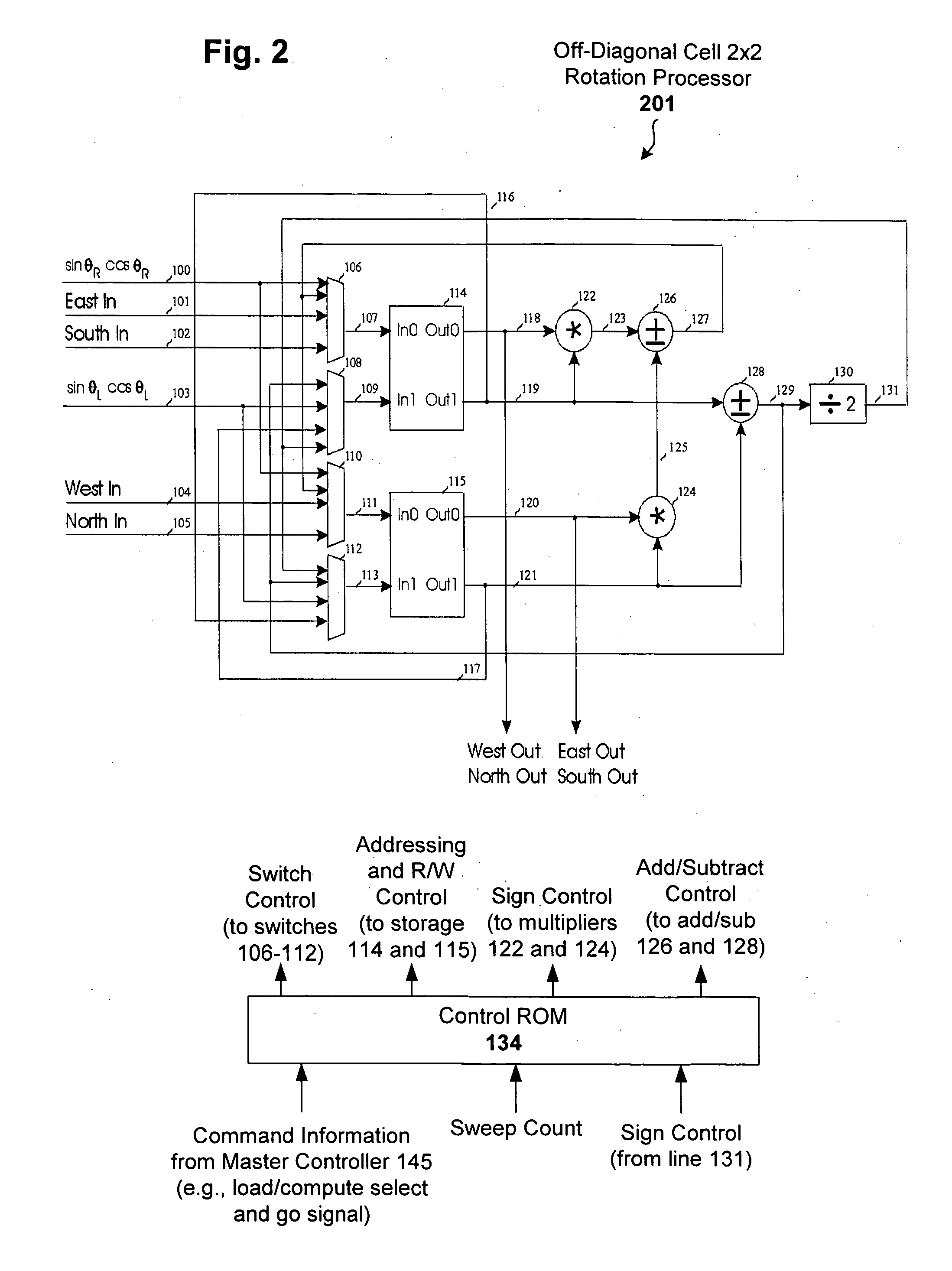
Scalable 2X2 rotation processor for singular value decomposition
InactiveUS20060173948A1Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsSingular value decompositionFeature vector
A two-plane rotation (TPR) approach to Gaussian elimination (Jacobi) is used for computational efficiency in determining rotation parameters. A rotation processor is constructed using the TPR approach to perform singular value decomposition (SVD) on two by two matrices yielding both eigenvalues and left and right eigenvectors. The rotation processor can then be replicated and interconnected to achieve higher dimensioned matrices. For higher dimensional matrices, the rotation processors on the diagonal solve the 2×2 rotation angles, broadcast the results to off-diagonal processors, whereby all processors perform matrix rotations in parallel.
Owner:FRANTORF INVESTMENTS
Method for quickly solving nodal impedance matrix of power system
The invention provides a method for quickly solving a nodal impedance matrix of a power system, and relates to the field of analytical computation of the power system. The method mainly comprises the following steps of inputting data of a nodal admittance matrix Y; establishing an augmented matrix B by the nodal admittance matrix Y and an identity matrix E together; normalizing the augmented matrix B and carrying out a Gauss-Jordan elimination method on the augmented matrix B for n times; obtaining an inverse matrix Z. At present, traditional methods for solving the nodal impedance matrix comprise an LDU (Logic Data Unit) triangular decomposition method and a Gauss elimination method, and compared with the two traditional methods, the novel method for quickly solving the nodal impedance matrix by utilizing the Gauss-Jordan elimination method, provided by the invention, has the advantages that the principle is simple and easy to understand, the computation time is reduced, the programming is convenient, and the like; compared with the traditional LDU triangular decomposition method and the Gauss elimination method, by utilizing the method for verifying systems such as an IEEE-57 node, an IEEE-118 node and an IEEE-300 node, the computation speeds can be respectively increased by about 25%-50%.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Channel coding method adopting layered low density check code
InactiveCN1564466AGuaranteed sparsityImprove decoding performanceData representation error detection/correctionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresTheoretical computer scienceLow-density parity-check code
Check matrix of check code in low density is divided into three layers. Each layer is created by circular shifting first row. Check matrix built based on structure in three layers is transformed to corresponding generator matrix through Gaussian elimination. Generator matrix is utilized to generate code words of encoder, and check matrix is utilized to decode procedure of decoder. The invented method reduces hardware complexity of encoder and decoder.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for solving node impedance matrix of electric system on basis of Gaussian elimination method of sparse symmetric matrix technology
InactiveCN104714928AReduce invalid calculationsReduce calculationComplex mathematical operationsNODALElectric power system
The invention belongs to the field of power system analysis and computing and discloses a method for solving a node impedance matrix of an electric system on the basis of a Gaussian elimination method of a sparse symmetric matrix technology. The method mainly comprises the following steps that a node admittance matrix Y is formed; the matrix Y and a matrix En form an augmented matrix Bn=[YEn]; elimination is carried out on the matrix Bn according to the spare symmetry to obtain Bn(n-1)'=[Y(n-1)'En(n-1)']; according to Y(n-1)'Zn=En(n-1)', sparseness and symmetry, elements above and on the left of a diagonal element Znn of a matrix Zn are solved; a matrix Y(k-1)' is obtained according to the Y(n-1)'; elements above and on the left of a diagonal element Zkk of the matrix Zk are obtained according to Y(k-1)'Zk=Ek(k-1)', sparseness and symmetry. By the utilization of the symmetric sparseness, all invalid computation of the previous generation process is avoided, and computation of about 50% of nonzero elements is reduced; by the utilization of the characteristics of the E matrix element structure and the sparseness of upper triangle elements, the elements of the matrix Zk are obtained in a back substitution mode according to a symmetry mode, and back substitution computation is greatly accelerated. The method can check IEEE-30, -57 and -118 node systems and the like, and the computation speed for the IEEE-118 node system can be improved by 96-97% compared with a traditional Gaussian elimination method and an LDU triangular decomposition method.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
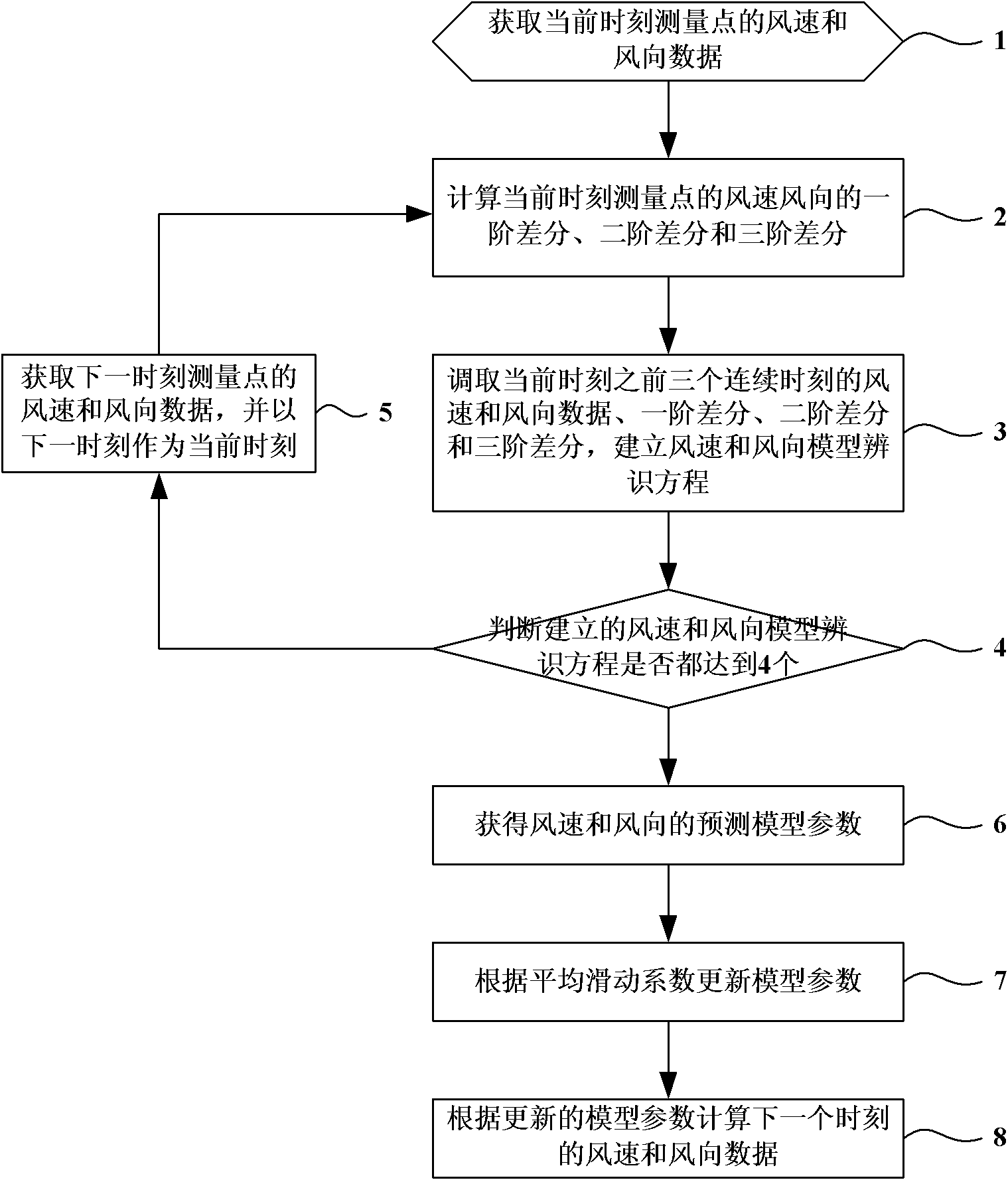
Railway wind disaster prevention prediction method
InactiveCN102122004AAble to learnImprove accuracyWeather condition predictionICT adaptationQuaternionMeasurement point
The invention discloses a railway wind disaster prevention prediction method in the technical fields of railway disaster prevention alarming and monitoring. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring wind speed and wind direction data of a current moment measuring point; calculating the first-order difference, the second-order difference and the third-order difference of the wind speed and wind direction data of the current moment measuring point; retrieving the wind speed and wind direction data, the first-order difference, the second-order difference and the third-order difference of three continuous moments before the current moment and establishing an identification equation of a wind speed and wind direction model; establishing a quaternion first-order equation set according to the identification equation of the wind speed and wind direction model and acquiring the model parameters of the wind speed and the wind direction through a Gaussian elimination method; updating the model parameters according to an average sliding coefficient; and calculating the wind speed and wind direction data of the next moment according to the updated model parameters. The invention improves the prediction accuracy and the accuracy of a prediction result.
Owner:BEIJING JIAXUN FEIHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Coding resource adaptive scheduling algorithm in distributed network
InactiveCN101764675AImplement codec operationsError preventionBroadcast service distributionNetwork codeMulticast network
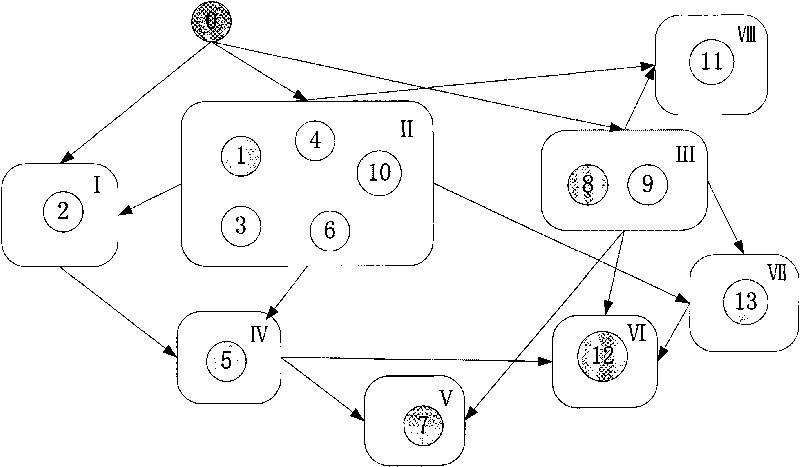
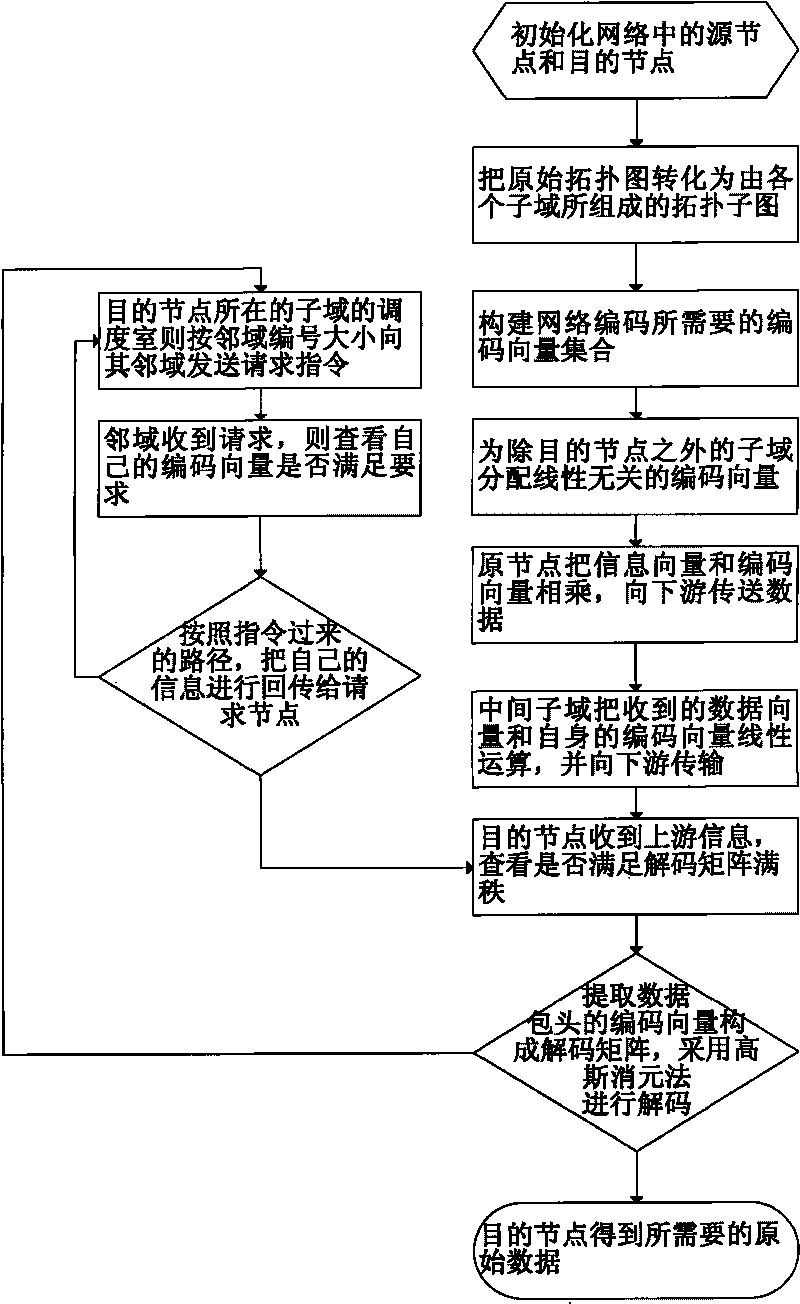
The invention discloses a coding resource adaptive scheduling algorithm in a multicast network, comprising: dividing the subdomain of network topology which is needed to be processed by coding multicast, and then according to the different demands of a destination node, adopting scheduling algorithm for scheduling and configuring network resource especially coding vector resource in real time; after all information transmitted by an upstream link circuit is collected by the destination node, extracting coding vector of data header to form decoding matrix; and adopting Gaussian elimination method for decoding, and obtaining the needed primary data. The method can lead network coding resource to be configured according to the need, ensures a target end to receive the needed coding information at the most rapid speed, and decodes in time. In addition, nodes are allowed to take part in or exit from multicast at any time, so that distributed network coding multicast can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Efficient coding design method based on BATS code in multi-hop transmission system
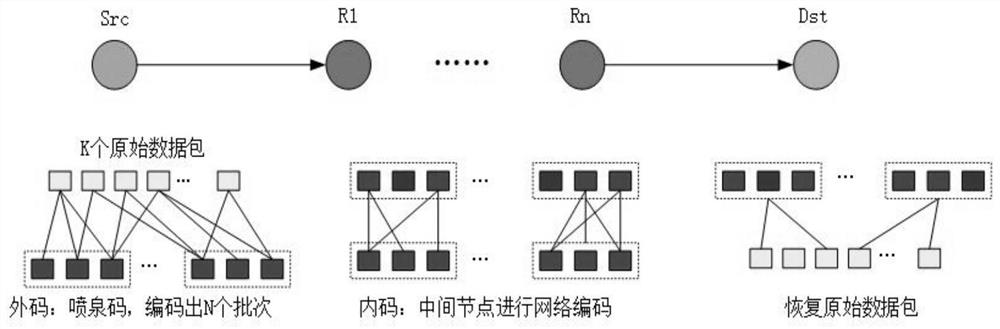
InactiveCN111917512AImprove transmission efficiencyReduce coding redundancyChannel coding adaptationForward error control useOriginal dataTrunking
The invention discloses an efficient coding design method based on a BATS code in a multi-hop transmission system. The efficient coding design method comprises the following steps: 1) dividing an original file into K original data packets with equal length; 2) at a transmitter end, performing outer code encoding of the BATS code on the k equilong original data packets by adopting an efficient encoding design scheme of the BATS code to obtain encoded packets; 3) sending the encoded packets obtained in the step 2) to a relay node through a wireless channel; 4) enabling the relay node to receivethe encoded packets, and codes the encoded packets belonging to the same batch by using BATS intra-code coding to obtain recoded encoded packets; 5) enabling the relay node to send re-coded packets tothe next relay node; and 6) enabling a receiver to find the encoded packets belonging to the same batch, perform iterative decoding on the coded packets of the same batch, and performs Gaussian elimination decoding on the coded packets of the same batch to obtain the original data packets. The invention can reduce the coding redundancy in multi-hop network transmission and improve the transmission efficiency of the data packets.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Blind identification method for (n, 1 and m) convolutional code with error codes
InactiveCN103401650AStorage simplificationReduce storageError preventionFault toleranceGaussian elimination
A blind identification method for an (n, 1 and m) convolutional code with error codes belongs to the technical field of blind identification of channel codes and comprises the following steps: after to-be-identified data is read by a computer, an identification matrix is established; row simplification is performed to the matrix through the method of gaussian elimination; the code length and the starting point are identified according to the simplification results; n paths of data are combined in pairs; the multinomials of a (2,1 and m) convolutional code are identified through a method of solving an equation set by a Hadamard matrix; and the result obtained through identification is updated to a final generator matrix according to the relation of the multinomials. The method has the advantages that storage of high-order Hadamard is simplified, the storage capacity of data in the operation process of a computer is reduced, the processing procedure of obtaining multinomials of the (n, 1 and m) convolutional code through the (2, 1 and m) convolutional code is introduced in detail, a parallel computing part is added, the treatment process of a program is accelerated, and the fault tolerance is good.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for blind identification of (n, k and m) system convolutional code
InactiveCN103401569AImplement programming operationsEasy to implementError correction/detection using convolutional codesMain diagonalRegular pattern
A method for blind identification of an (n, k and m) system convolutional code belongs to the technical field of blind identification of channel codes and comprises the following steps: after to-be-identified data is read by a computer, an identification matrix with the row number of 180 and the line number of 170 is established; row simplification is performed to the matrix through the method of gaussian elimination; for the simplified matrix, the code length, the information bit length and the data starting point are identified according to the arrangement rule of elements 0 and elements 1 in the main diagonal of the matrix, and then an appearing regular matrix is found according to the positions of obtained regular elements; the regular matrix is extracted from the simplified identification matrix to obtain a check matrix; a generator matrix is obtained through extraction according to the relation between the check matrix and the generator matrix. A specific implementation process of blind identification of the (n, k and m) system convolutional code is given in the method, so that programming operation can be realized advantageously, the identification speed is high, and the method is simple. The identification rate can reach 100% under the condition that no error code exists in the (n, k and m) system convolutional code.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Hardware Acceleration for Batched Sparse Codes
ActiveUS20170195914A1Effectively offload computationally intensive overheadEffectively offload computationally intensive overheadsNetwork traffic/resource managementChannel coding adaptationComputer hardwareData stream
Hardware acceleration for batched sparse (BATS) codes is enabled. Hardware implementation of some timing-critical procedures can effectively offload computationally intensive overheads, for example, finite field arithmetic, Gaussian elimination, and belief propagation (BP) calculations, and this can be done without direct mapping of software codes to a hardware implementation. Suitable acceleration hardware may include pipelined multipliers configured to multiply input data with coefficients of a matrix associated with a random linear network code in a pipelined manner, addition components configured to add multiplier output to feedback data, and switches to direct data flows to and from memory components such that valid result data is not overwritten and such that feedback data corresponds to most recent valid result data. Acceleration hardware components (e.g., number and configuration) may be dynamically adjusted to modify BATS code parameters and adapt to changing network conditions.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
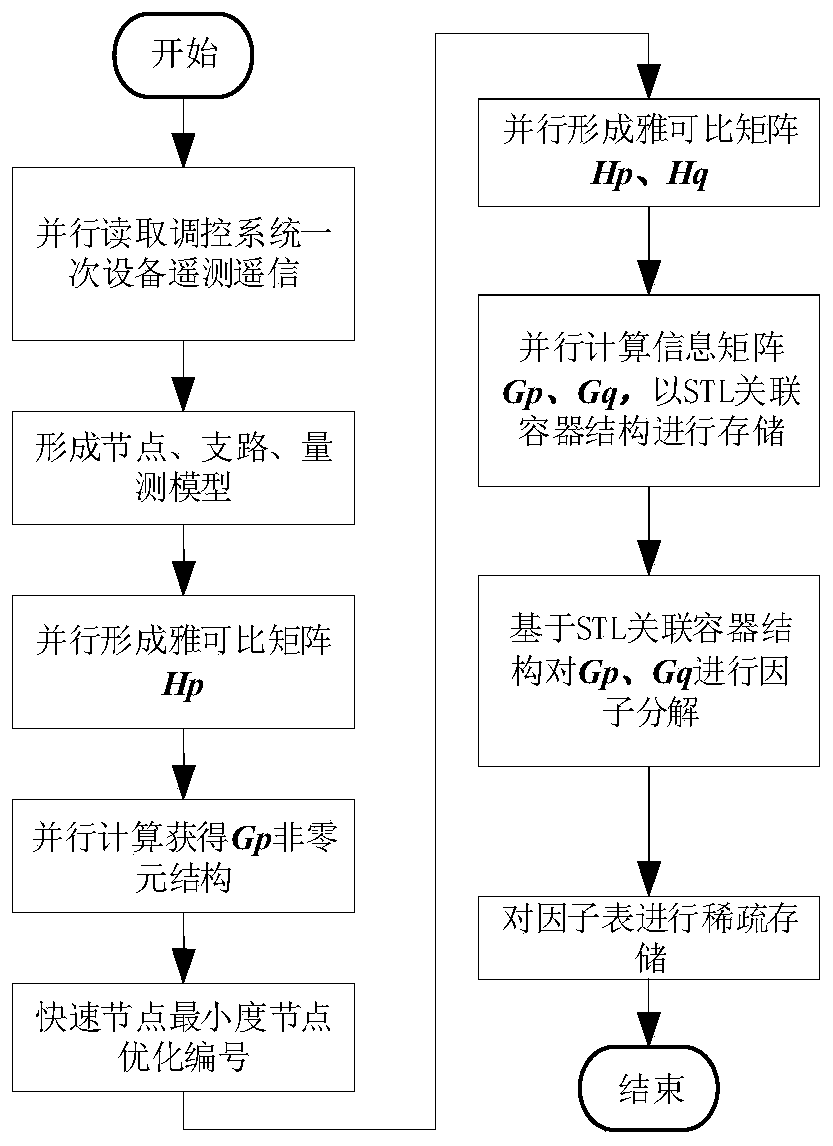
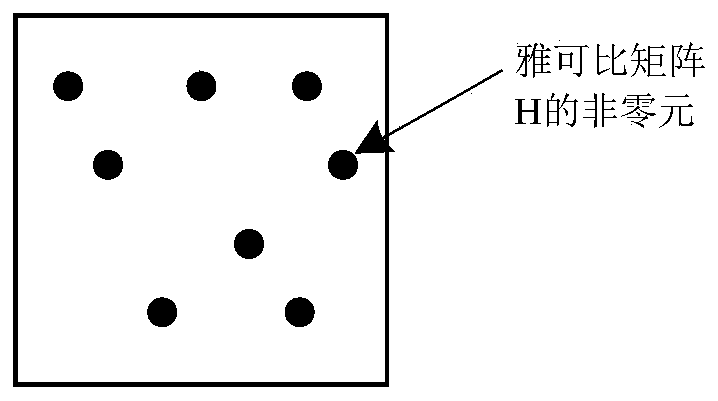
Power system state estimation method and system based on information matrix sparse solution
ActiveCN111062610AImprove computing efficiencyReduce the numberResourcesComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmElectric power system
The invention discloses a power system state estimation method and system. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring telemetering and telesignaling data of primary equipment of a power system in real time; constructing a power system node branch model; determining non-zero element distribution of the active jacobian matrix according to the node branch model, and determining non-zero element distribution of the active information matrix; performing node optimization numbering based on active information matrix non-zero element distribution; calculating an active Jacobian matrix and areactive Jacobian matrix according to the new node sequence to obtain a new active information matrix and a reactive information matrix, and performing factorization by adopting a Gaussian eliminationmethod to obtain an active information matrix factor table and a reactive information matrix factor table; and performing power system state estimation based on the active information matrix factor table and the reactive information matrix factor table. When the method is used for solving the information matrix and estimating the state of the power system, the memory operation in the solving process can be reduced, the calculation load is reduced, and the calculation efficiency of power grid state estimation is improved.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +4
Lower triangular Cholesky decomposition-based ambiguity correlation-lowering method
The invention discloses a lower triangular Cholesky decomposition-based ambiguity correlation-lowering method and belongs to the satellite navigation and positioning technical field. According to themethod, LDL<T> decomposition is performed on an ambiguity variance-covariance matrix, so that a unit lower triangular matrix L and diagonal matrix D can be obtained; Gaussian elimination and conditional variances are adopted to exchange two integer transformation processes, so that the correlation of the off-diagonal elements of the lower triangular matrix L can be lowered, and therefore, elementsin the diagonal matrix D are sorted in an ascending order as much as possible; and finally, ambiguity search can be carried out to realize ellipsoid shape transformation, and the number of redundantinteger candidate nodes contained in a search space can be decreased, search time can be reduced, and ambiguity resolution efficiency can be improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Reliable video transmission method and device based on network coding
InactiveCN102065289AImprove throughputImprove anti-packet loss performanceError preventionTelevision systemsComputer hardwarePacket loss
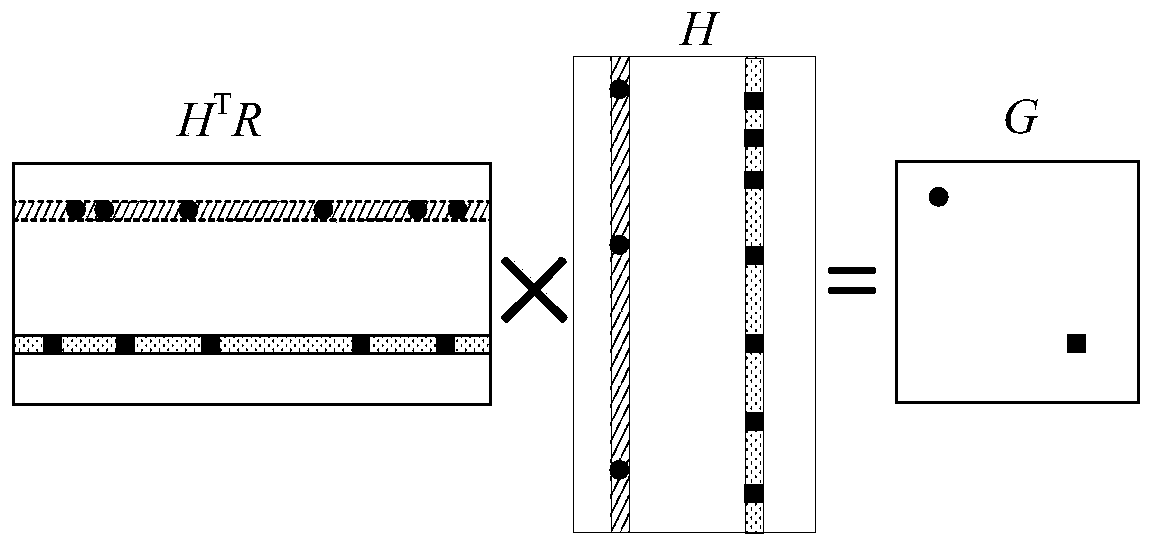
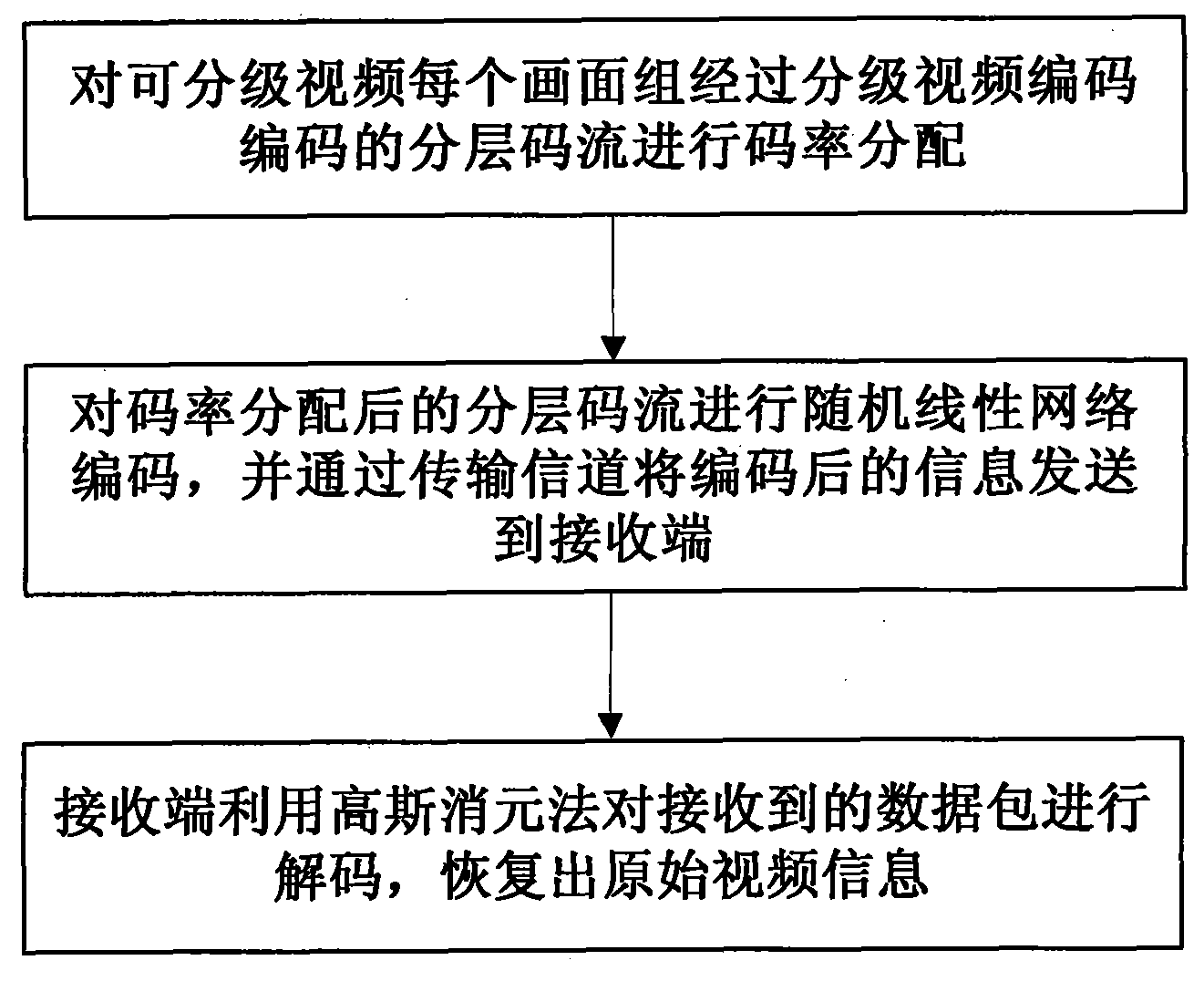
The invention discloses a reliable video transmission method based on network coding to mainly solve the problem of lower video reconstruction quality of a receiving end caused by packet loss or error codes in a general video transmission method. The reliable video transmission method based on network coding comprises the following steps of: adding corresponding redundant information to a layered code stream used for performing the scalable video coding for each picture group of original video information, and packing the layered code stream to complete code rate distribution; performing the random linear network coding on data packets subjected to code rate distribution by using a designed global coding matrix with a nonstringent lower triangular structure; and transmitting coded information to the receiving end through a transmission channel, and decoding a network coding code stream at the receiving end by using a Gaussian elimination method, and restoring the original video information. The reliable video transmission method based on network coding has the advantages of improving the problem of lower video reconstruction quality of the receiving end caused by packet loss and time delay in the transmission process, and realizing the unequal error protection of an H. 264 / SVC (scalable video coding) code stream and the high-reliability video multicast.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Channel coding method for low-density checking code
InactiveCN1614896AImprove decoding performanceOvercome code lengthError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceGaussian elimination
The method includes following steps: the check matrix of low density check code is mapped into a geometrical body; the check matrix is built into four layers by using different threading method; each layer relates to a threading method in geometrical body; the check matrix built with four layer structure is converted into generator matrix by using Gaussian elimination method or triangularization method; the generator matrix is used in generating code word of code device. The check matrix is used in decode procedure of decoder.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Compensation method for IQ imbalance existing in OFDM system receiver
InactiveCN104486285AReduce lossesReduce computational complexityMulti-frequency code systemsComputation complexityGaussian elimination
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Erasure correcting decoding method and system of LDPC code
InactiveCN104052499AImprove reception success rateReduce reception wait timeError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsDecoding methodsNumber times
The invention discloses an erasure correcting decoding method and system of an LDPC code. The method includes the steps that (S1) known information in a codon is put into a verification equation set to obtain residual verification equation sets; (S2) equations with only one unknown variable are found in the residual verification equation sets, and the unknown variables are solved and put into the residual verification equation set to be updated; (S3) the step (S2) is repeated, if all unknown variables are recovered, decoding is successful, and if not all the variables are recovered, the step (S4) is carried out; (S4) sub equation sets in the residual verification equation sets are searched for, if only one unknown variable occurs in the sub equation sets once and other unknown variables occur even number times, the sub equation sets are added, so that the unknown variable which occurs only once is solved, the residual verification equation sets are updated, and the step (S3) is carried out until all the unknown variables are recovered. According to the erasure correcting decoding method and system of the LDPC code, guessing and Gaussian elimination do not need to be carried out, and decoding performance of the LDPC code can be improved when the LDPC code is transmitted on a deletion channel.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
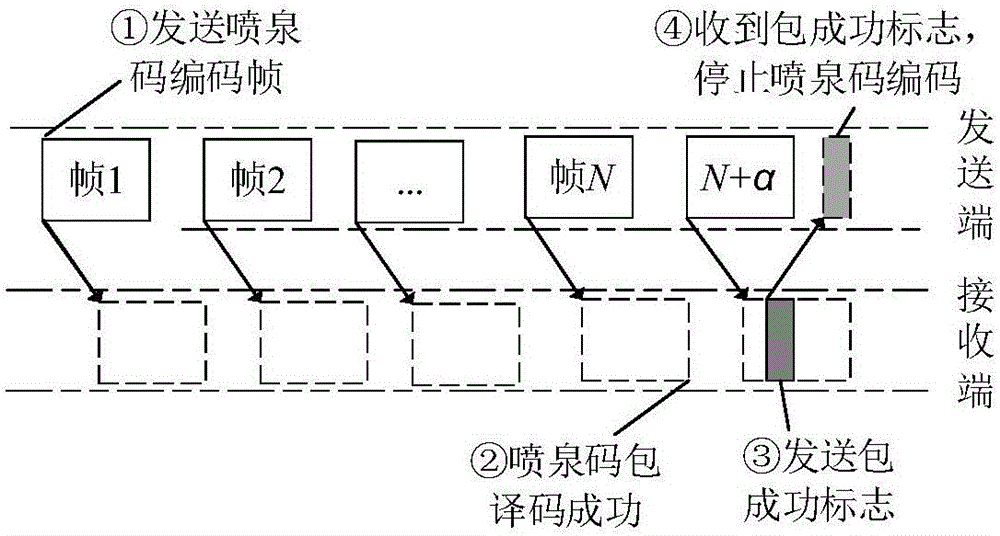
Method for decoding fountain code and underwater acoustic communication transmission method of fountain code
ActiveCN107181533AReduce Decoding LatencyLow Redundancy Frame RatioTransmitted data organisation to avoid errorsDecoding methodsFountain code
The invention provides a method for decoding a fountain code. The method comprises: when a receiving terminal receives an nth generation vector Gn and code vector Tn that are transmitted by a transmitting terminal, a generation matrix G<(j)> with j as an order and a matrix formed by generation vectors Gn are processed by using a gaussian elimination method to obtain an intermediate matrix G'; if the order of the G increases by being compared with the order of the G<(j)>, a relation, expressed by a formula: G<(j+1)>=G', is met; a coding matrix T(j) and a matrix formed by coding vectors Tn are processed by using a gaussian elimination method to obtain coding matrix T<(j+1)>; and the steps are repeated until the order j of the generation matrix is equal to the number K of sending data blocks and an information matrix is T<(K)> and decoding is completed. With the decoding method, the decoding delay can be reduced; and a low redundant frame proportion can be kept. On the basis of the decoding method, the invention also provides an underwater acoustic communication transmission method of a fountain code. With the transmission method, the influence on the channel utilization rate by the feedback information transmission time can be eliminated and the channel utilization rate can be improved.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com