Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
356 results about "Friction stir processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
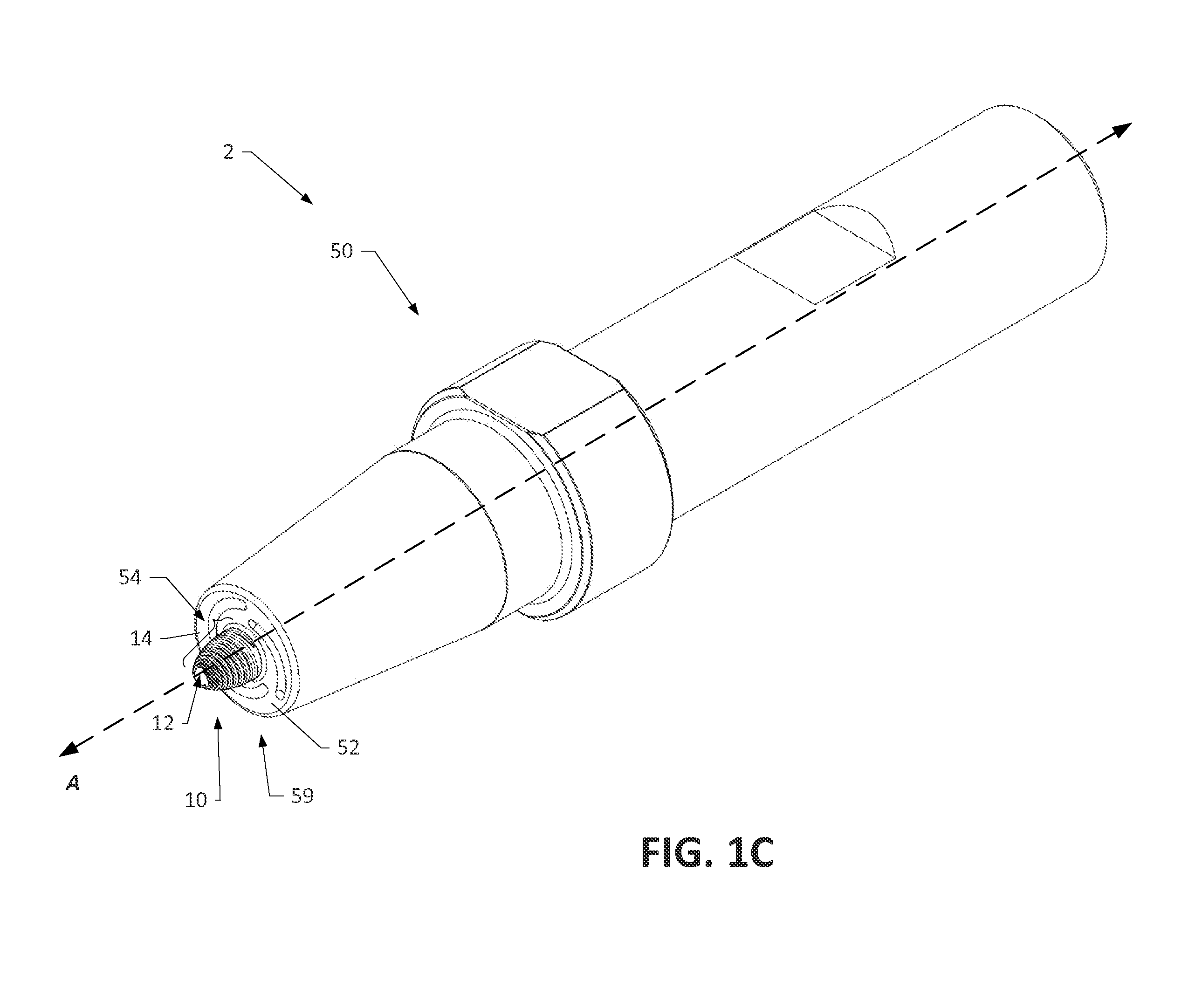
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
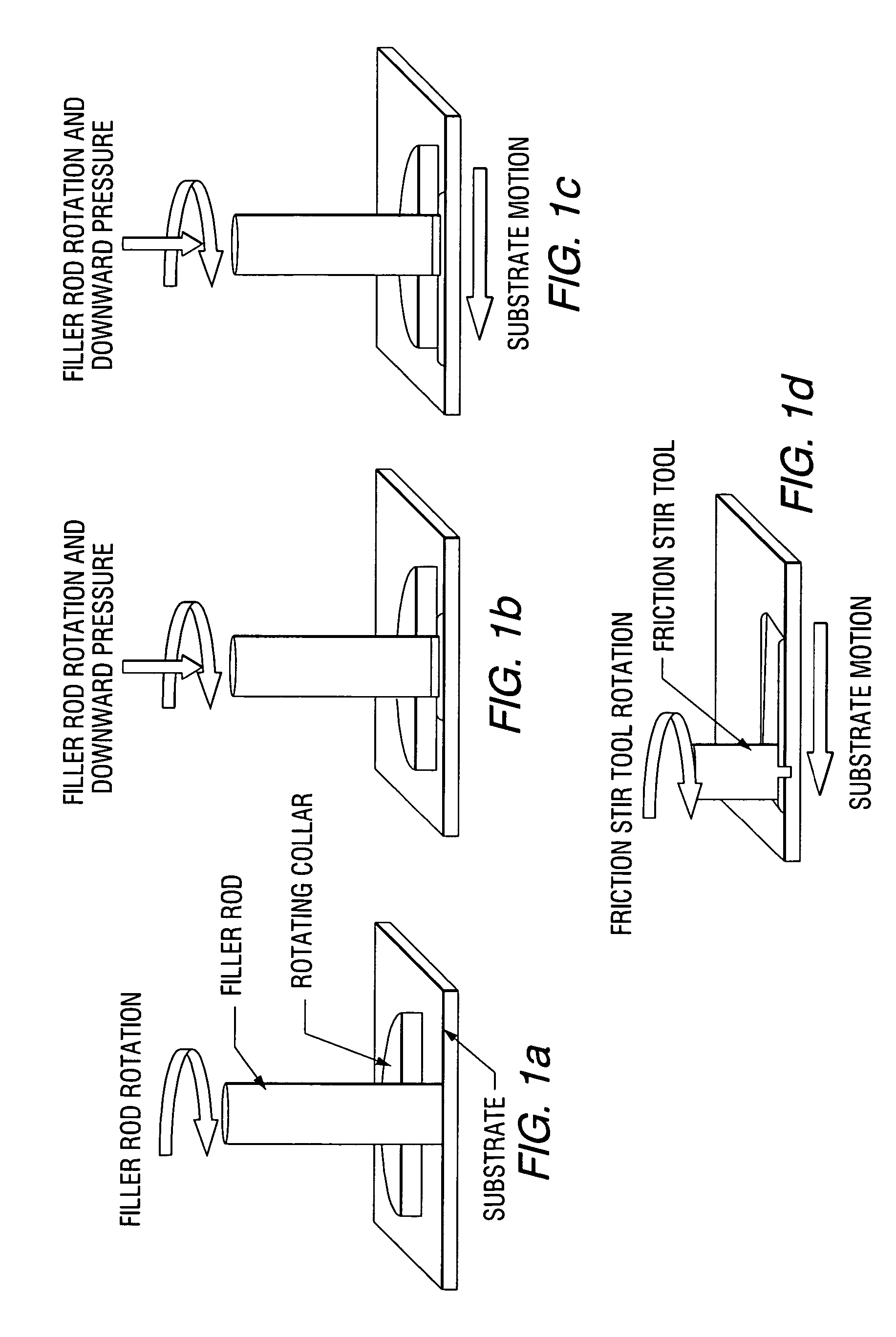
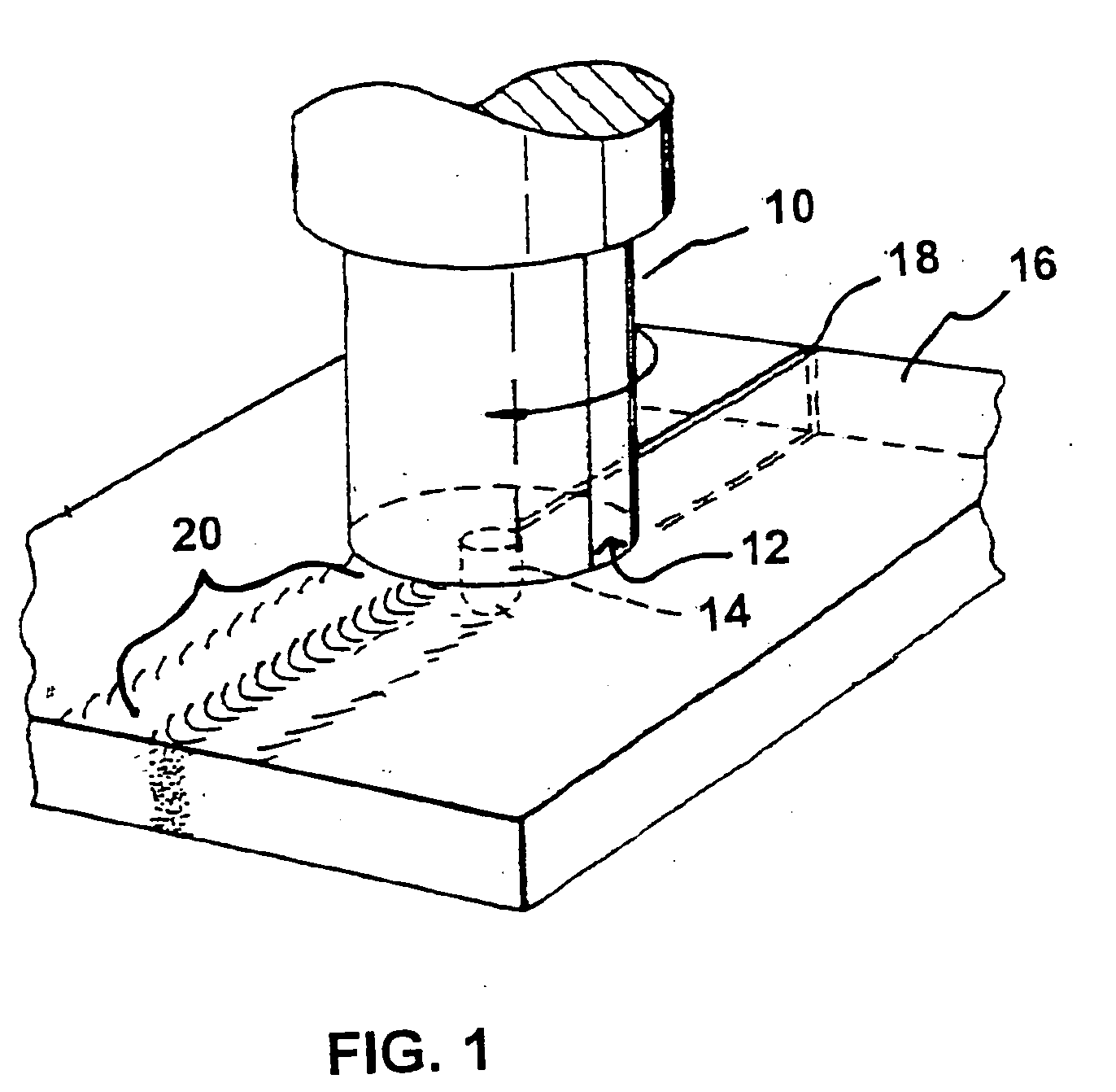
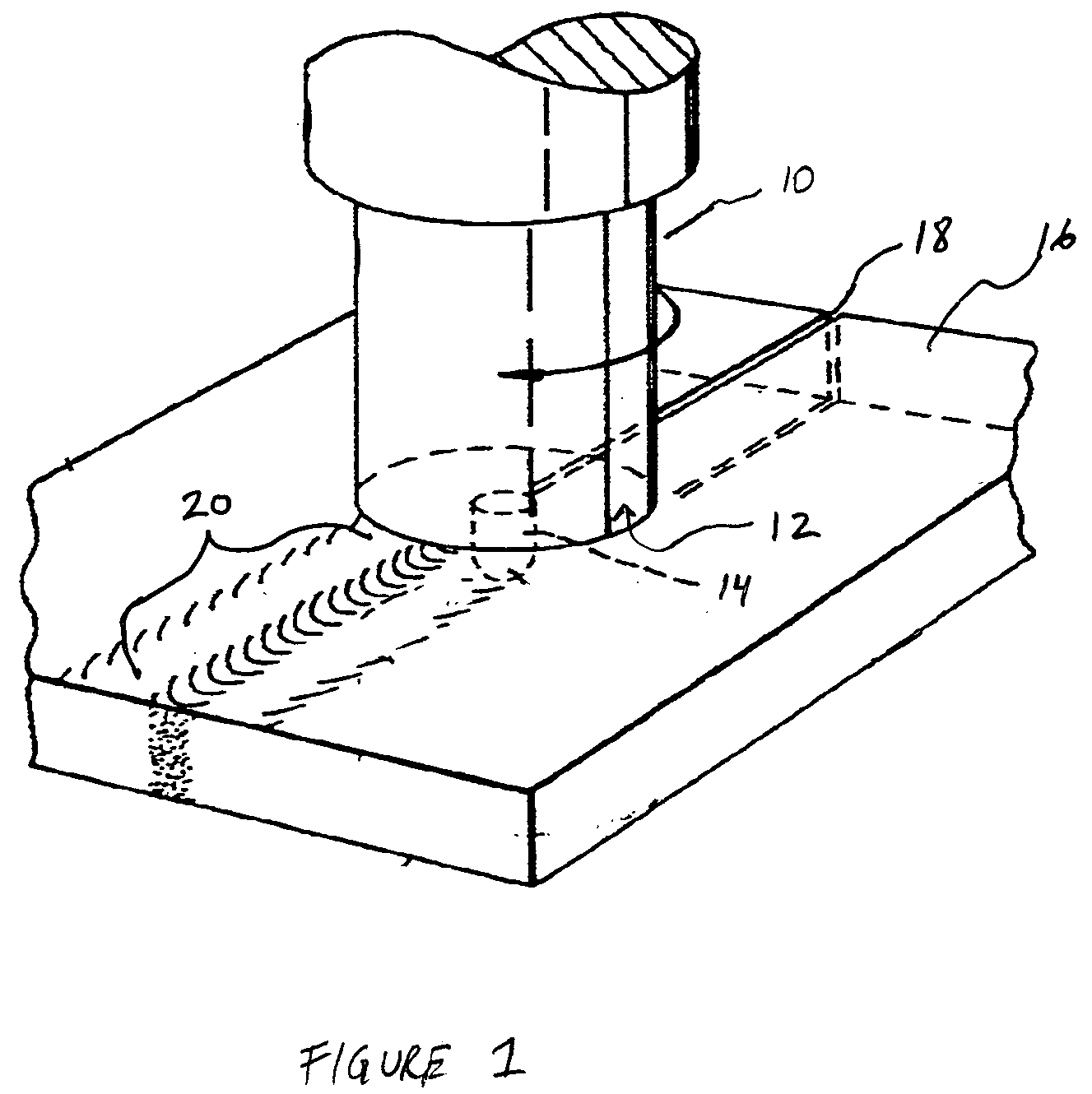
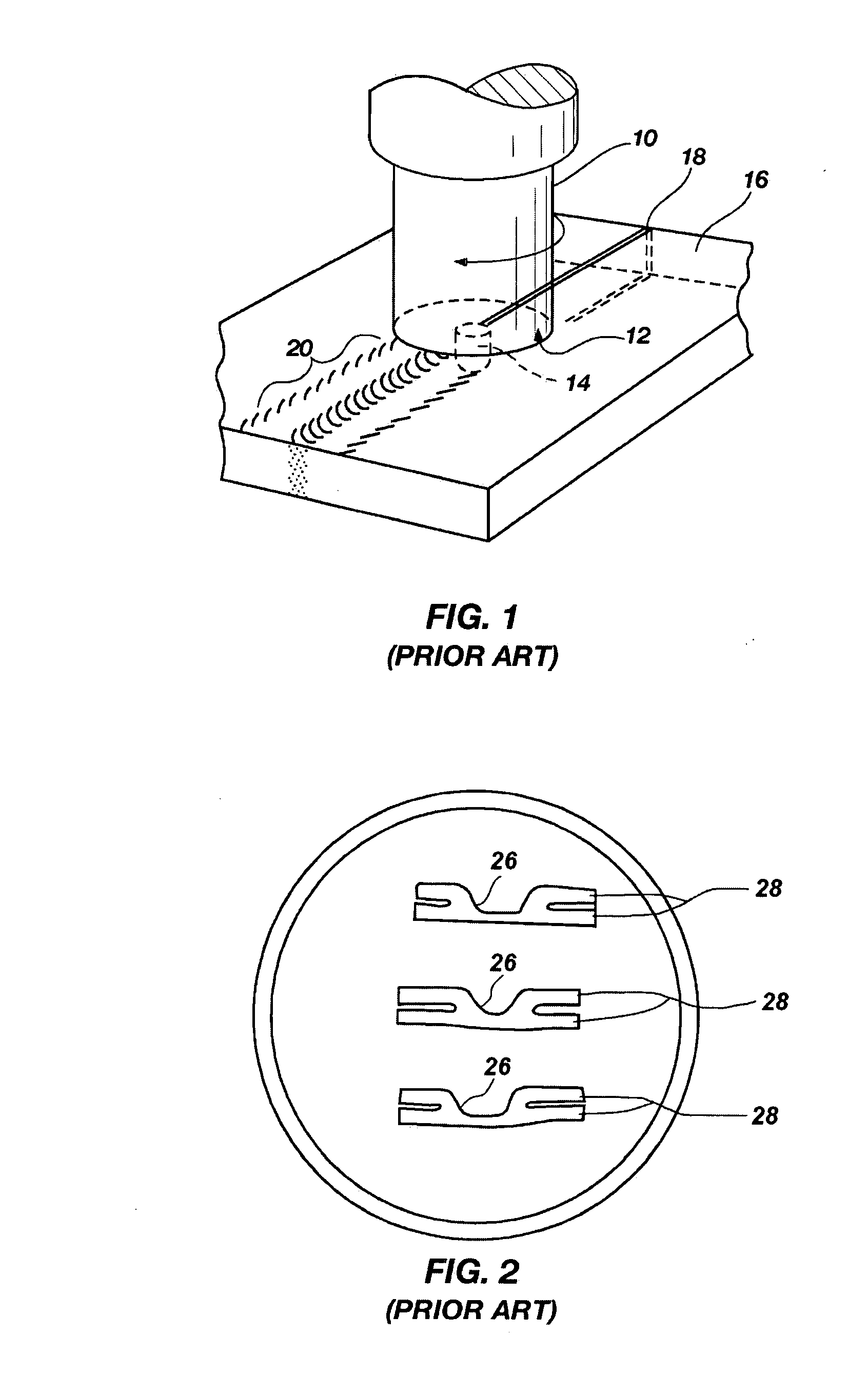
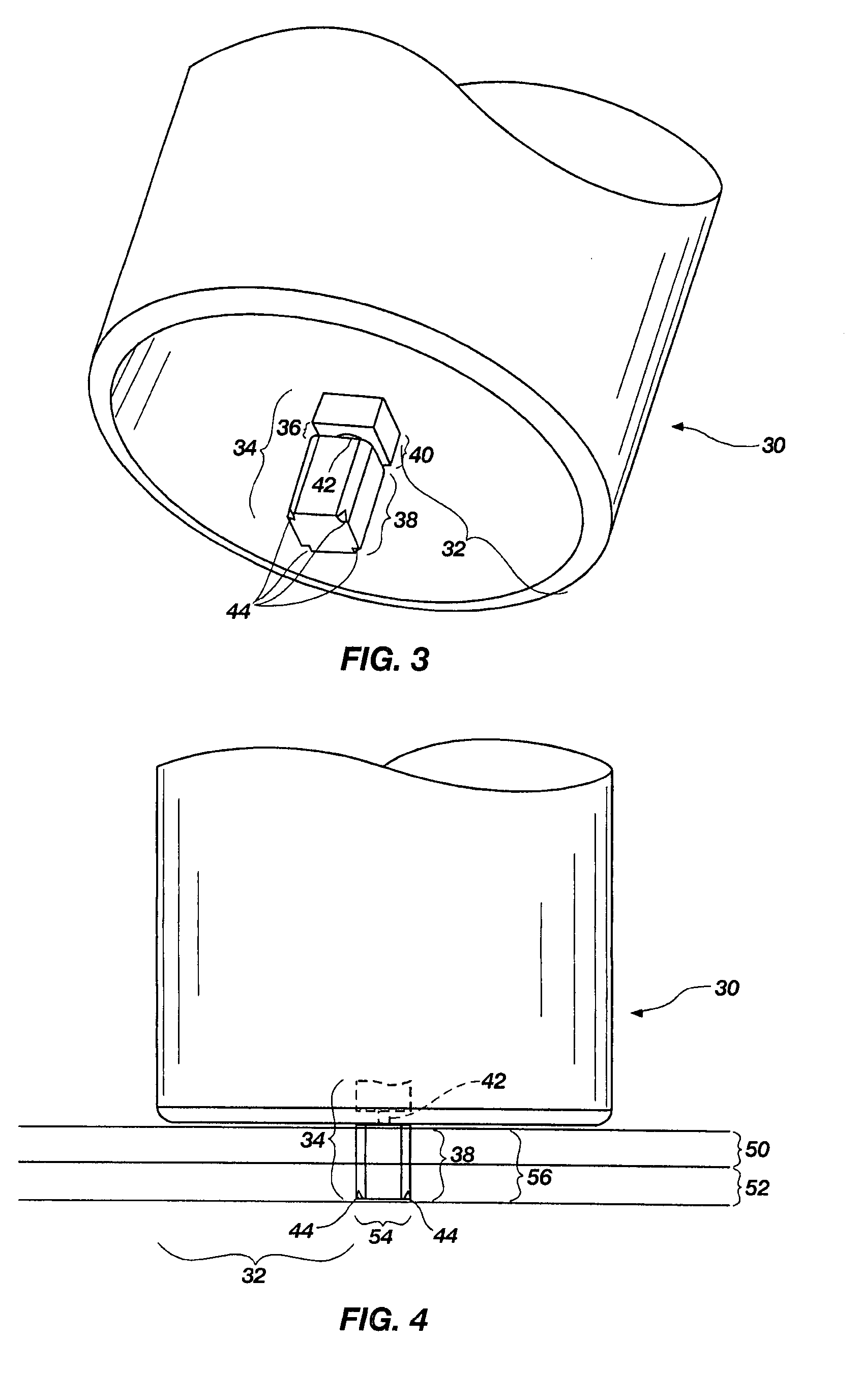
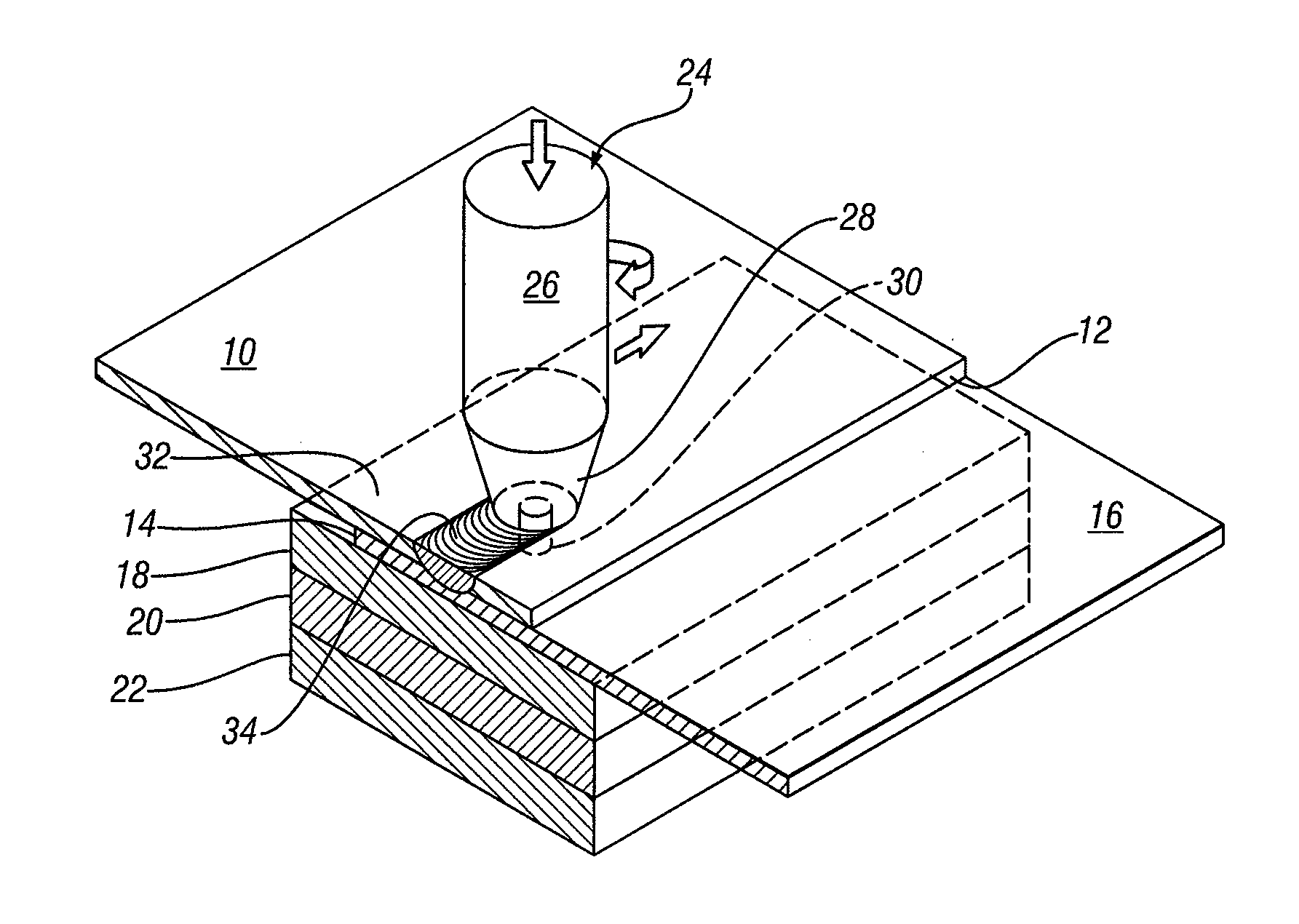
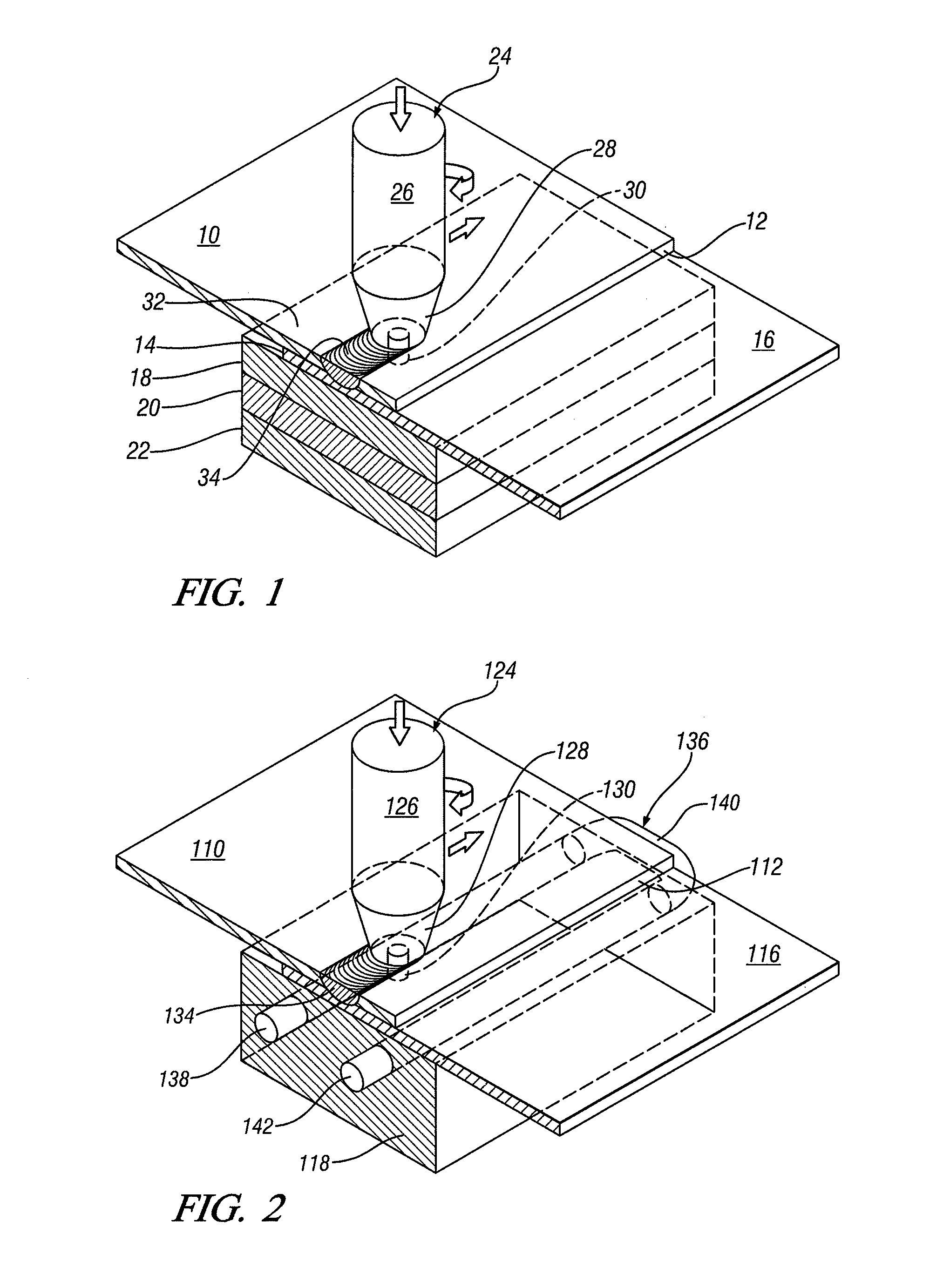
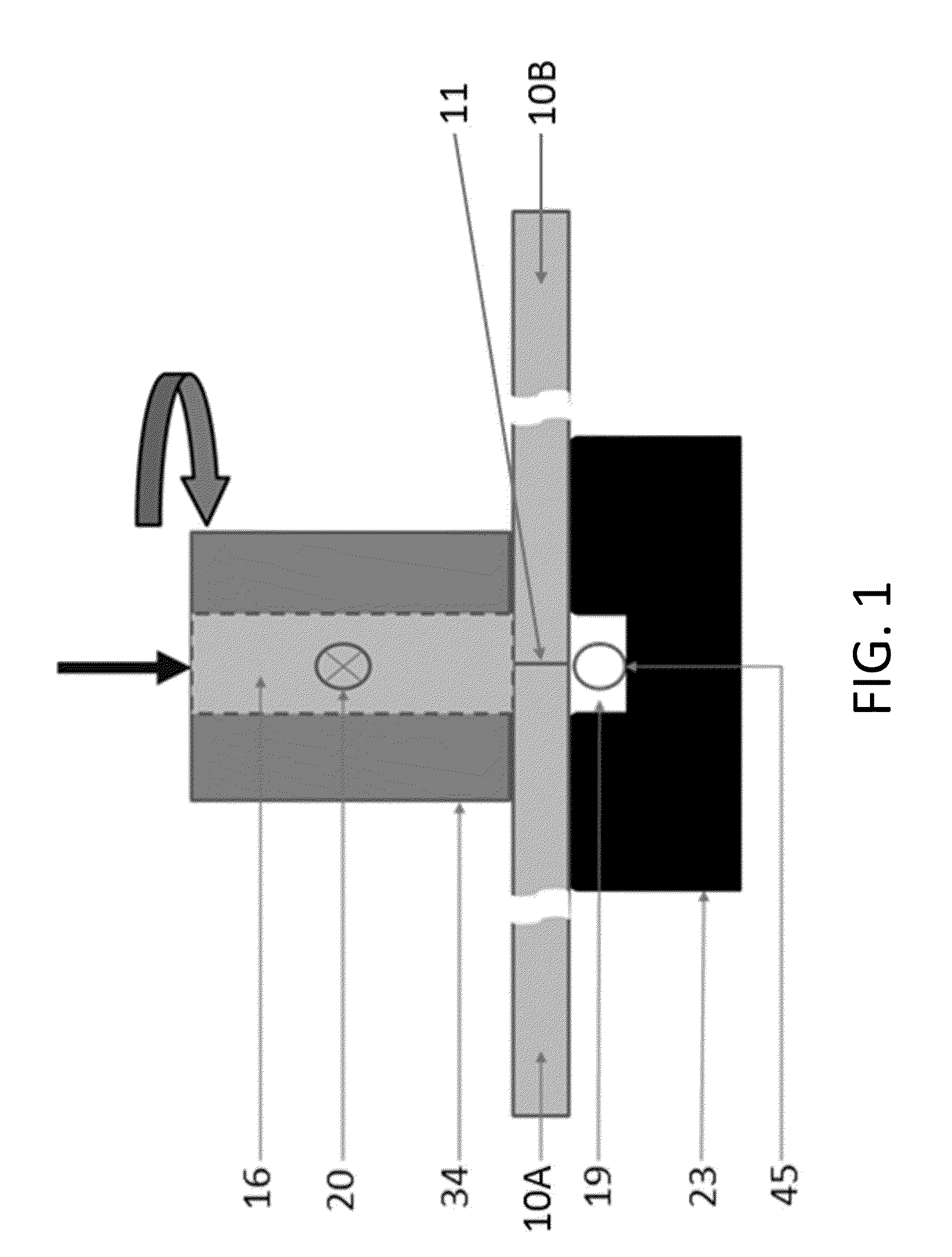
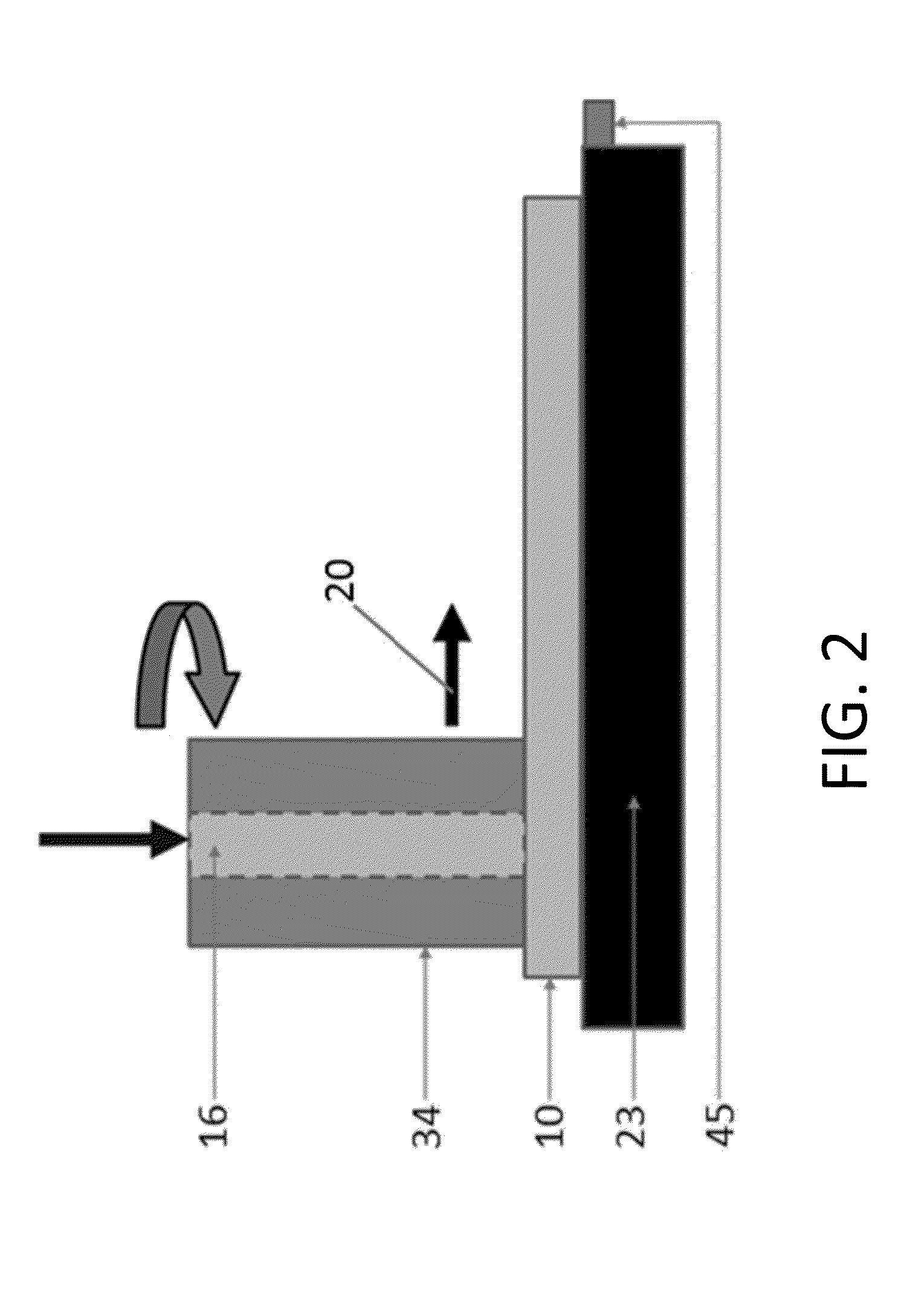
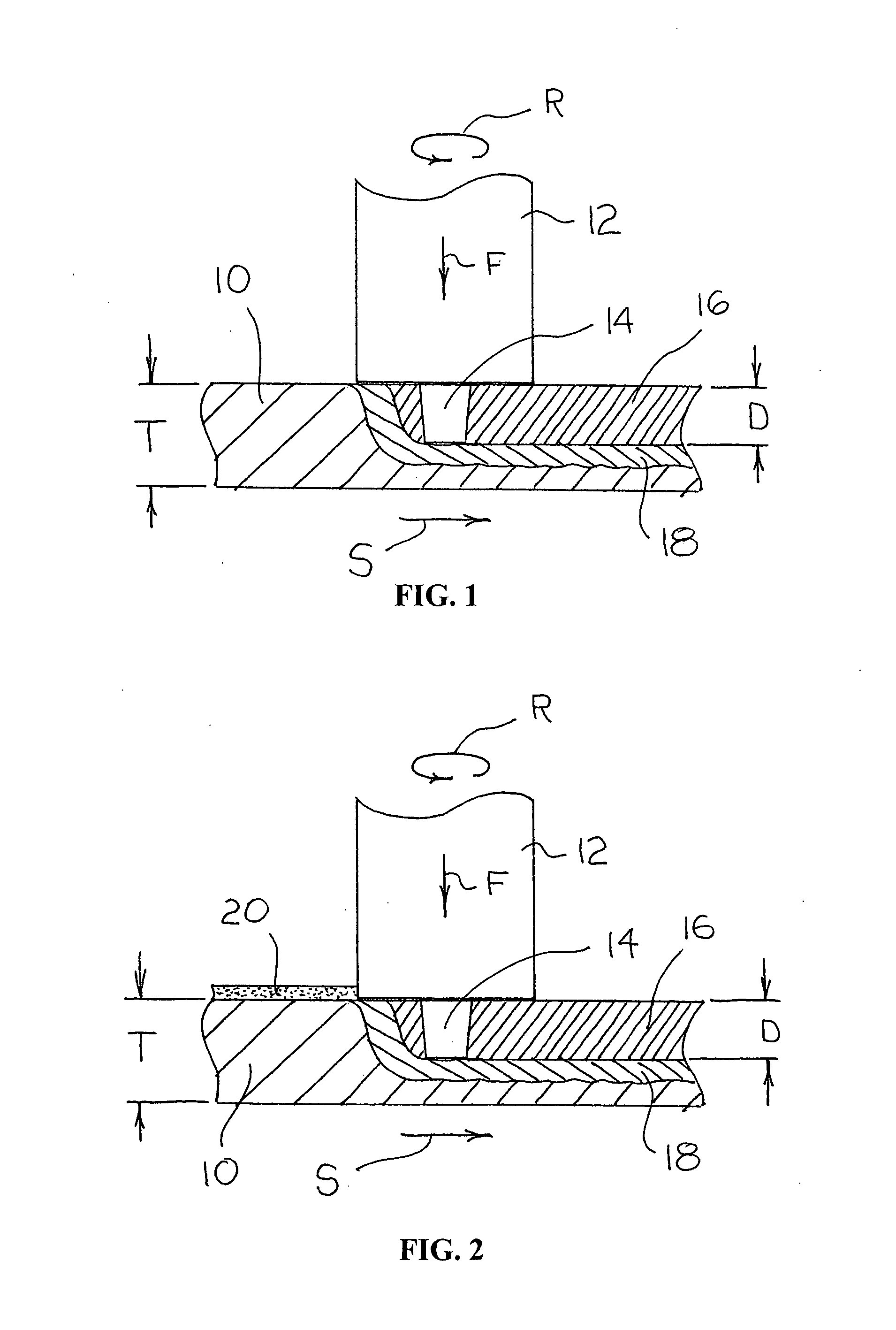
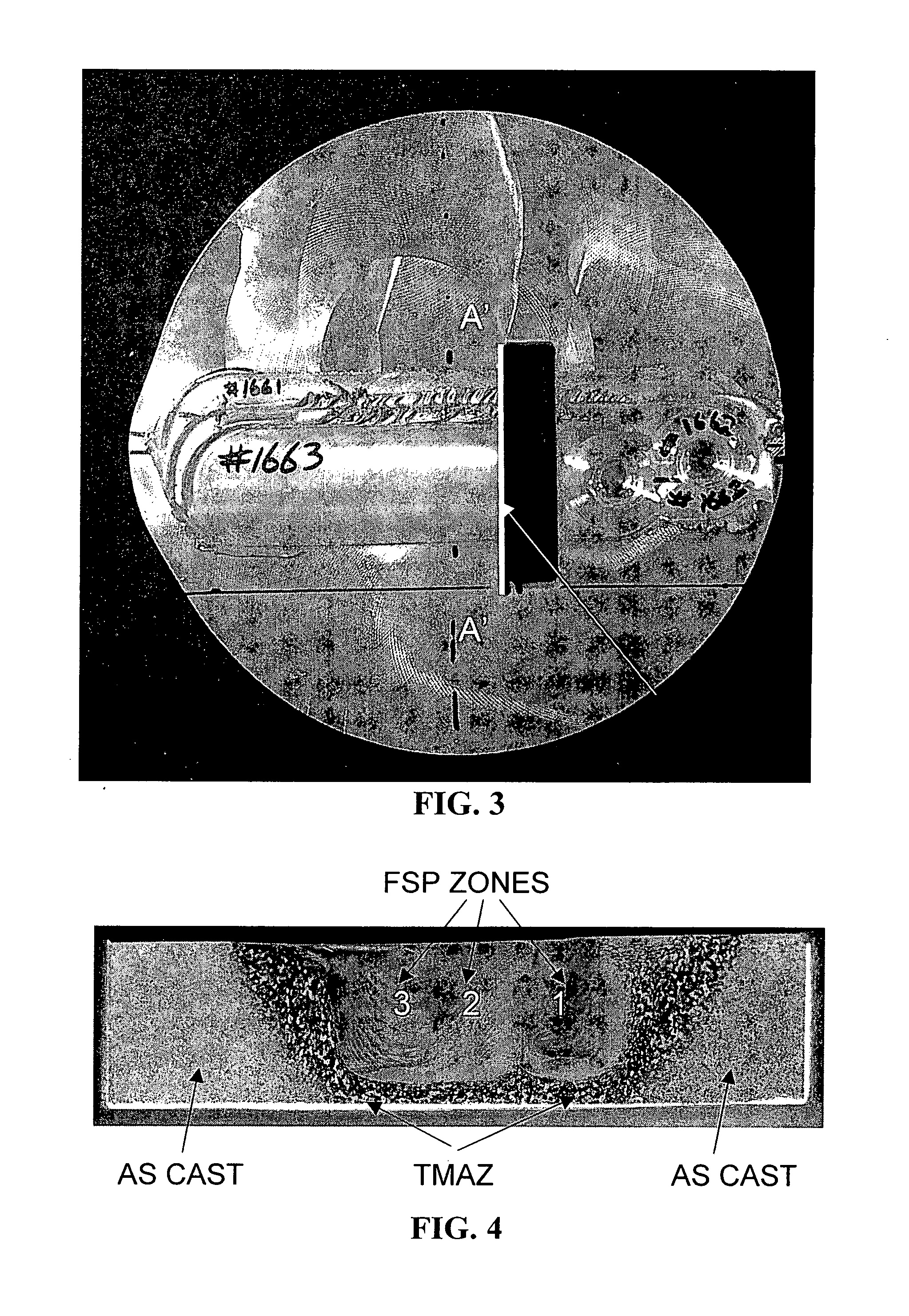
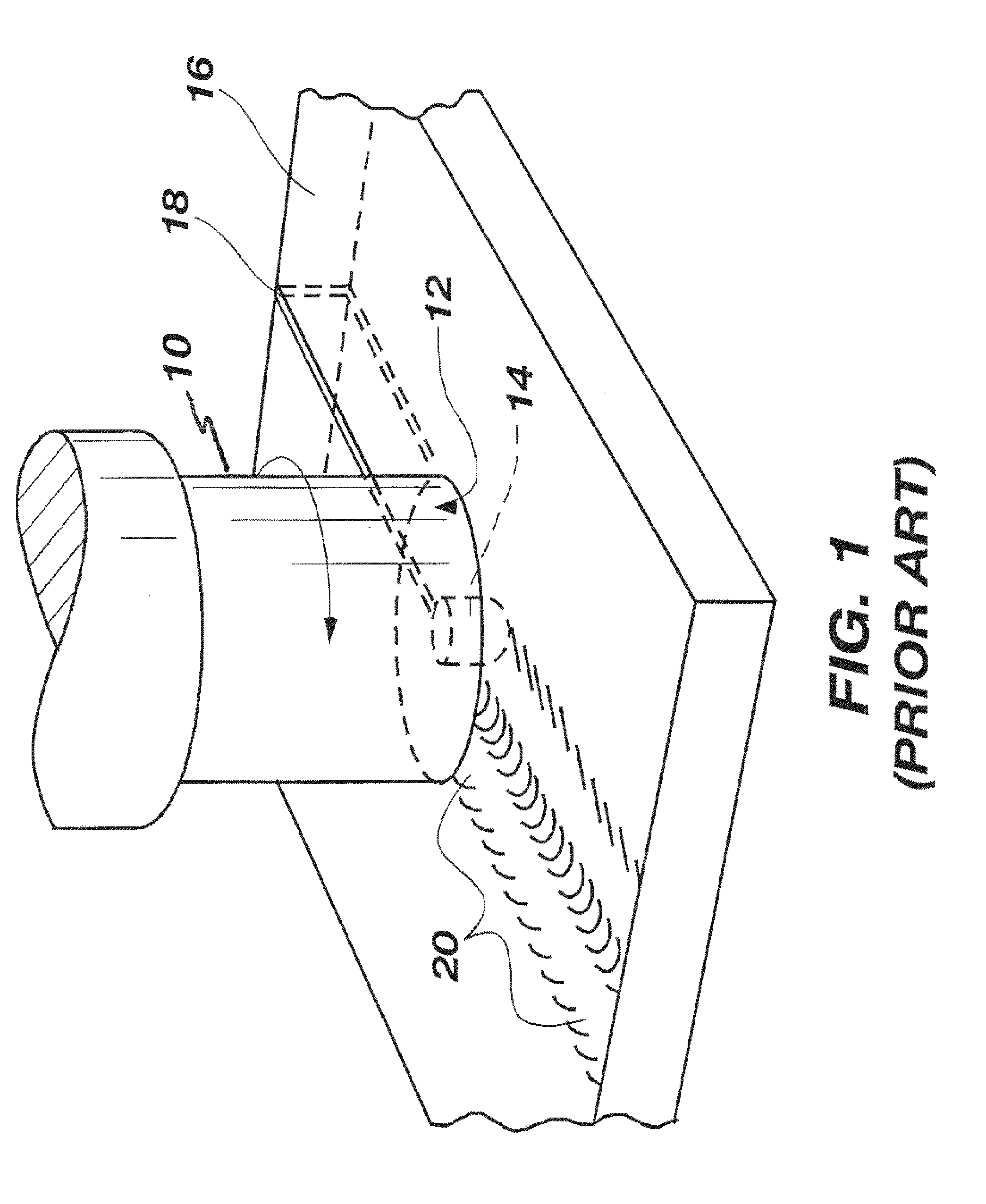
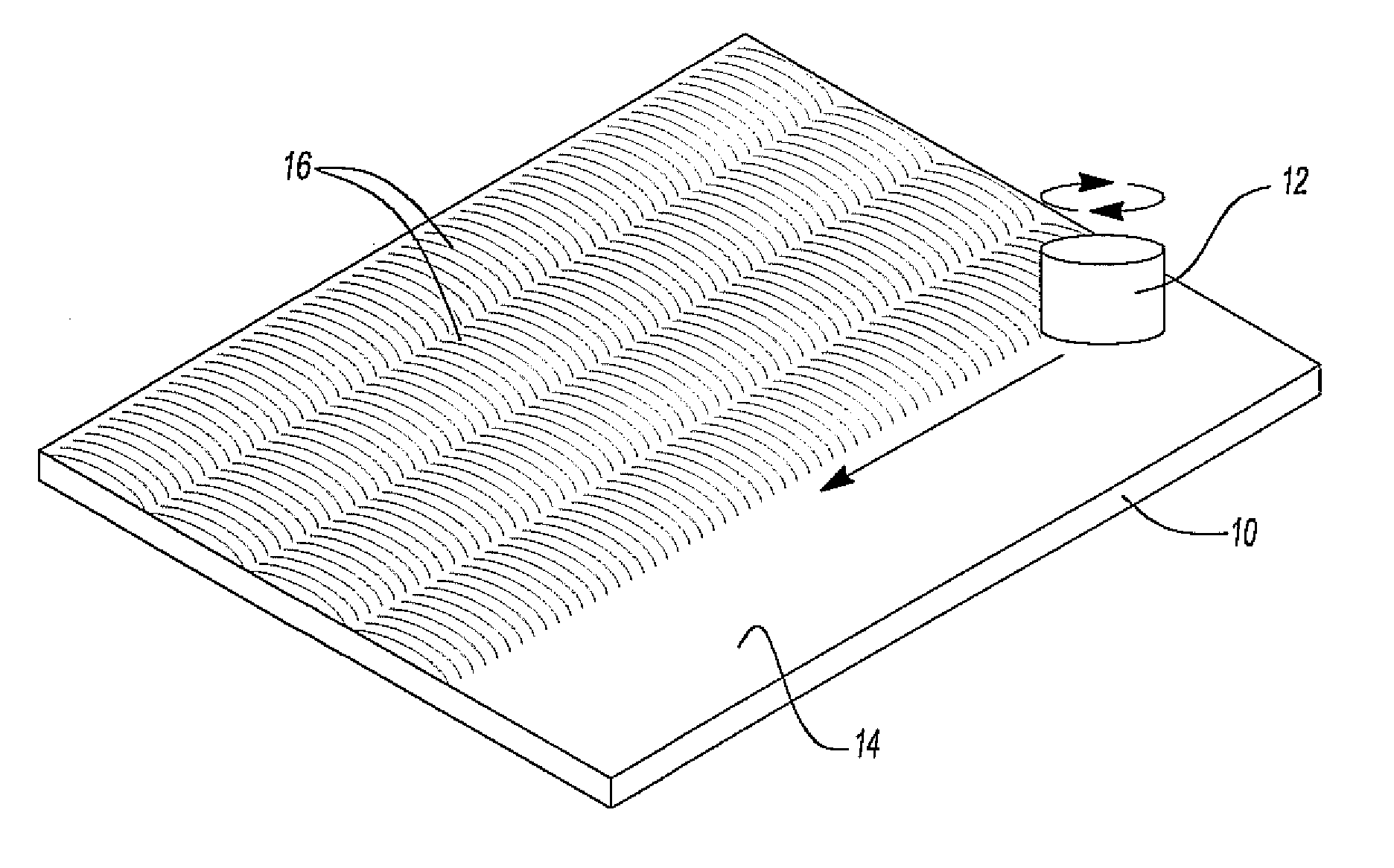
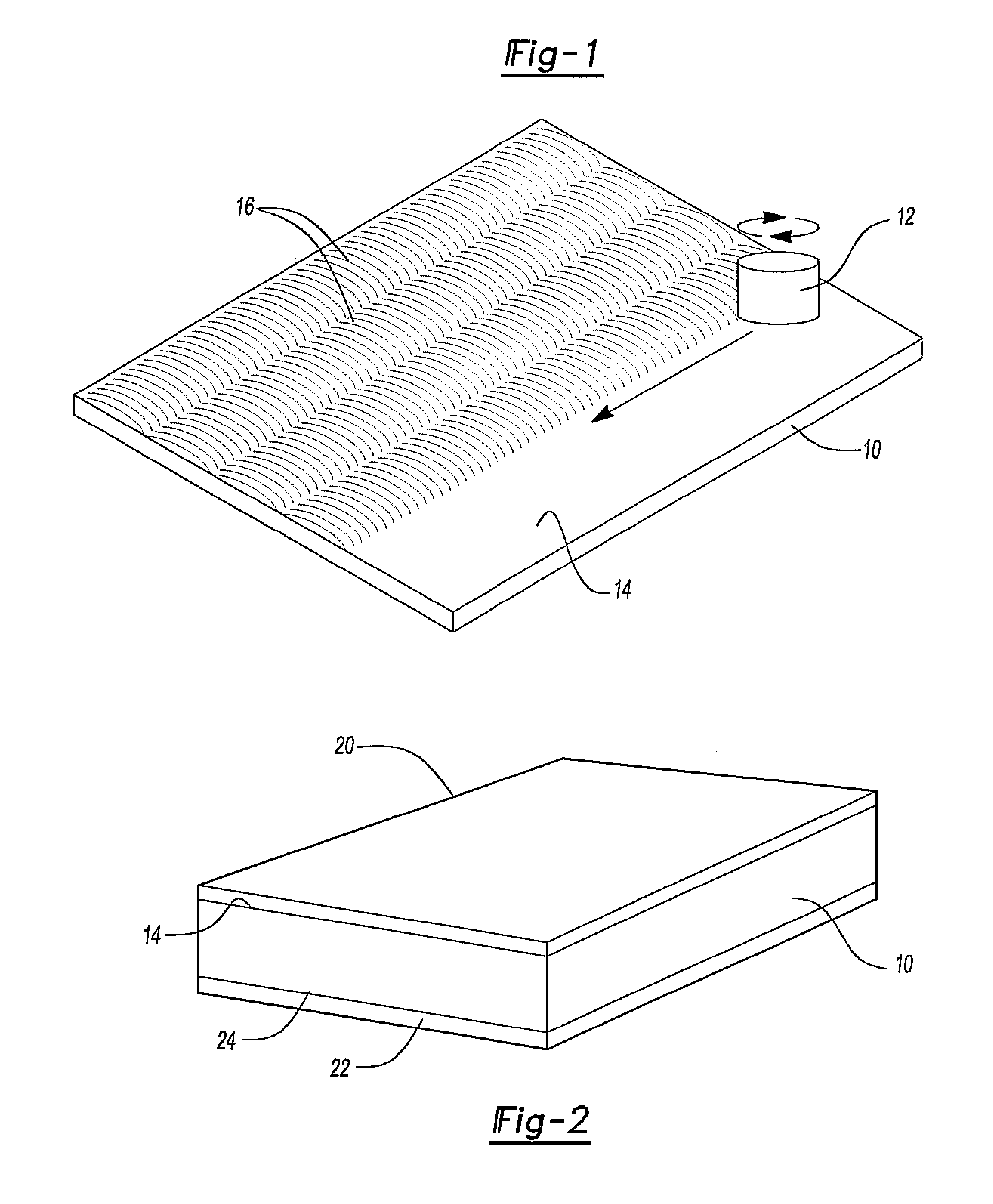
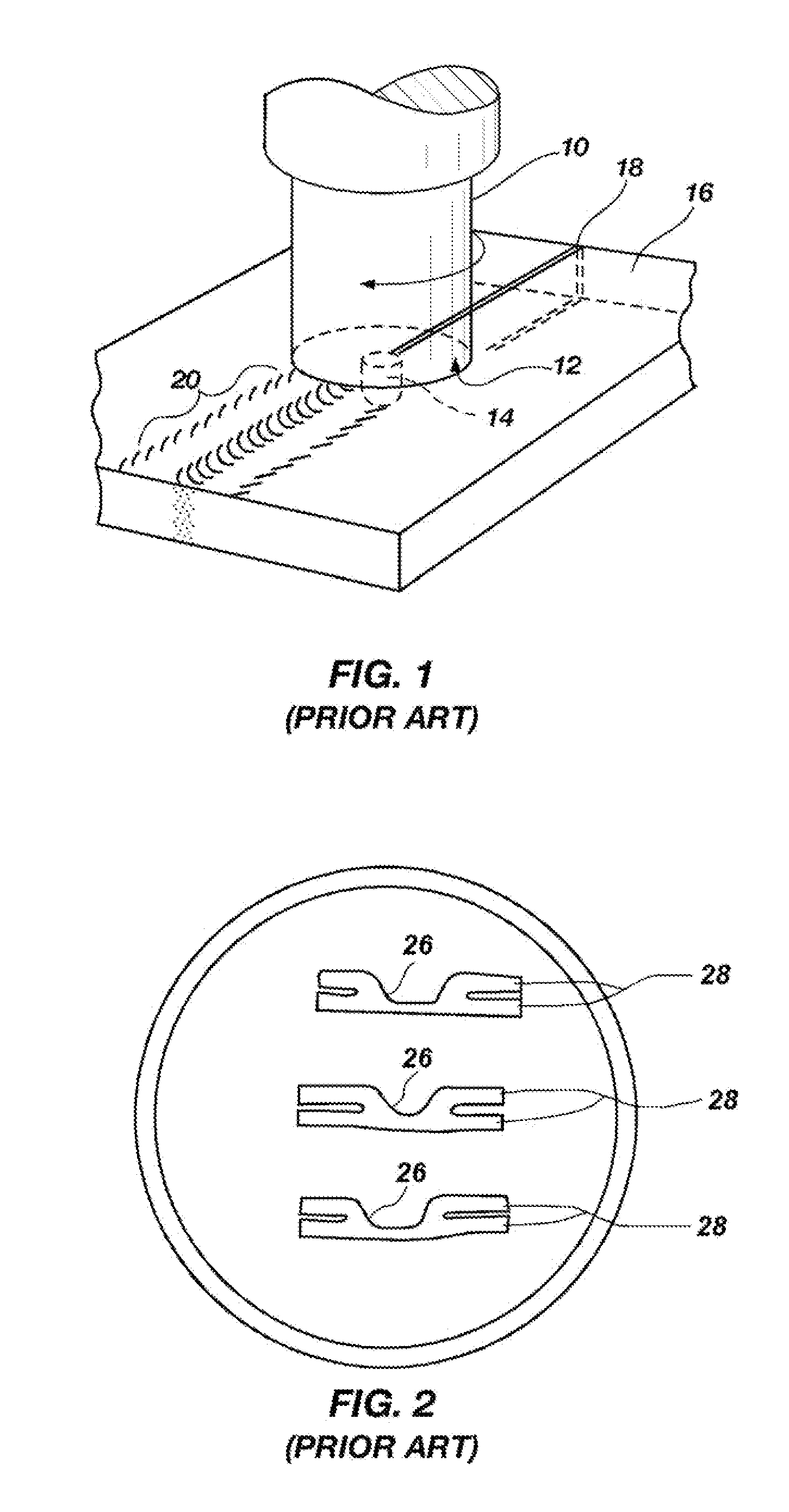
Friction stir processing (FSP) is a method of changing the properties of a metal through intense, localized plastic deformation. This deformation is produced by forcibly inserting a non-consumable tool into the workpiece, and revolving the tool in a stirring motion as it is pushed laterally through the workpiece. The precursor of this technique, friction stir welding, is used to join multiple pieces of metal without creating the heat affected zone typical of fusion welding.
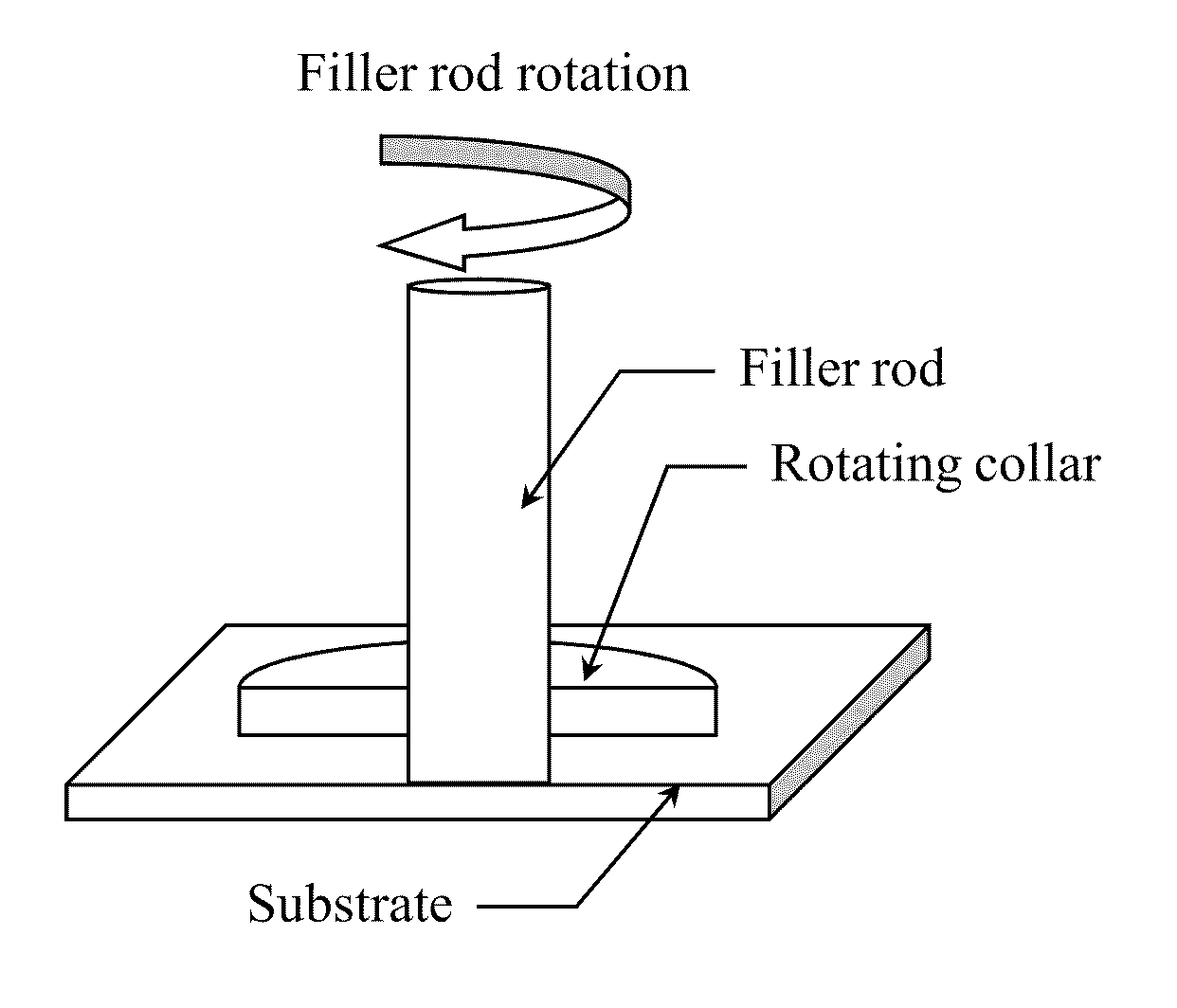
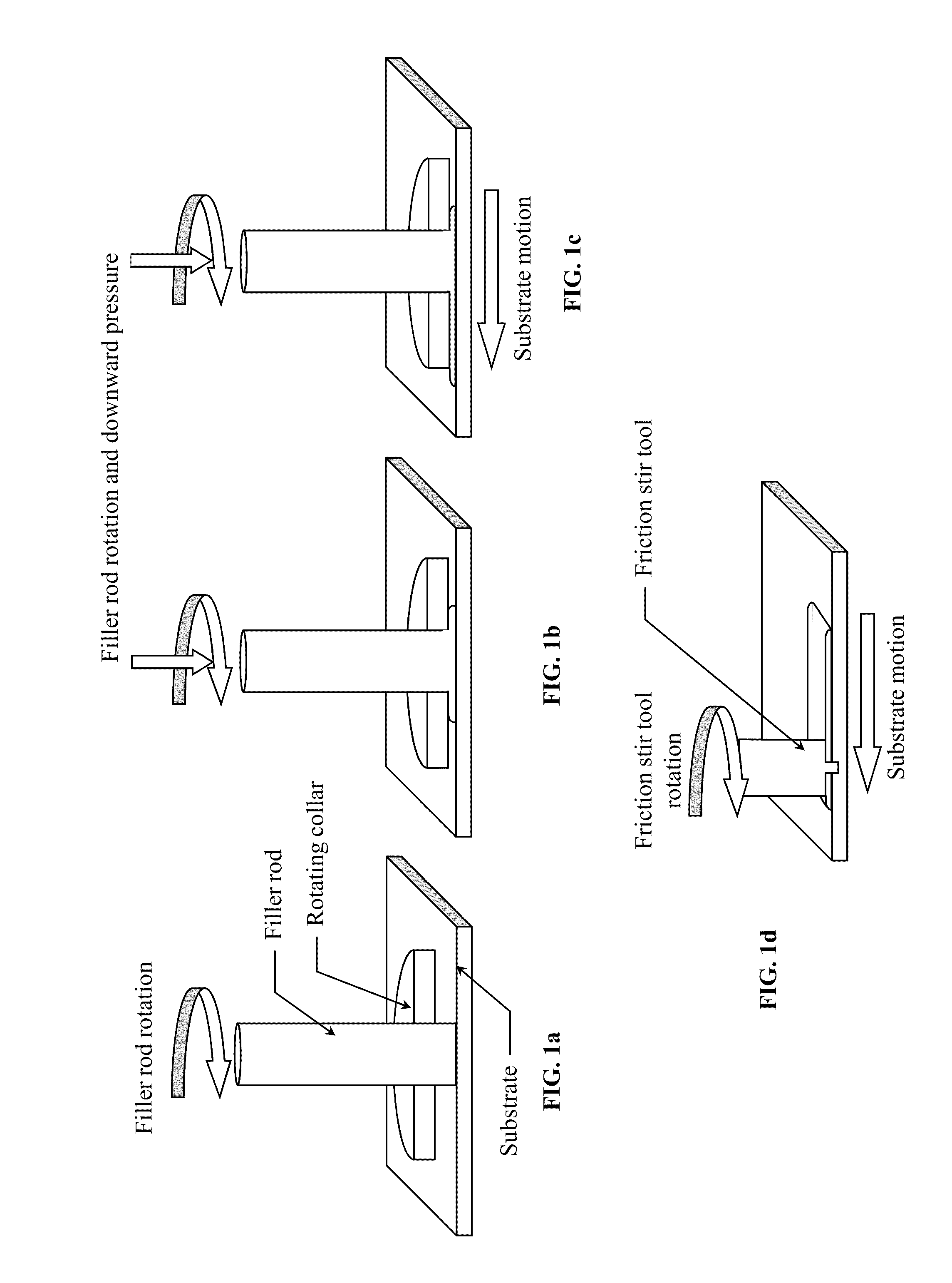
Friction stir fabrication
InactiveUS20080041921A1High bonding strengthHigh densityCooking-vessel materialsPressure inorganic powder coatingMetal matrix compositeFriction stir processing
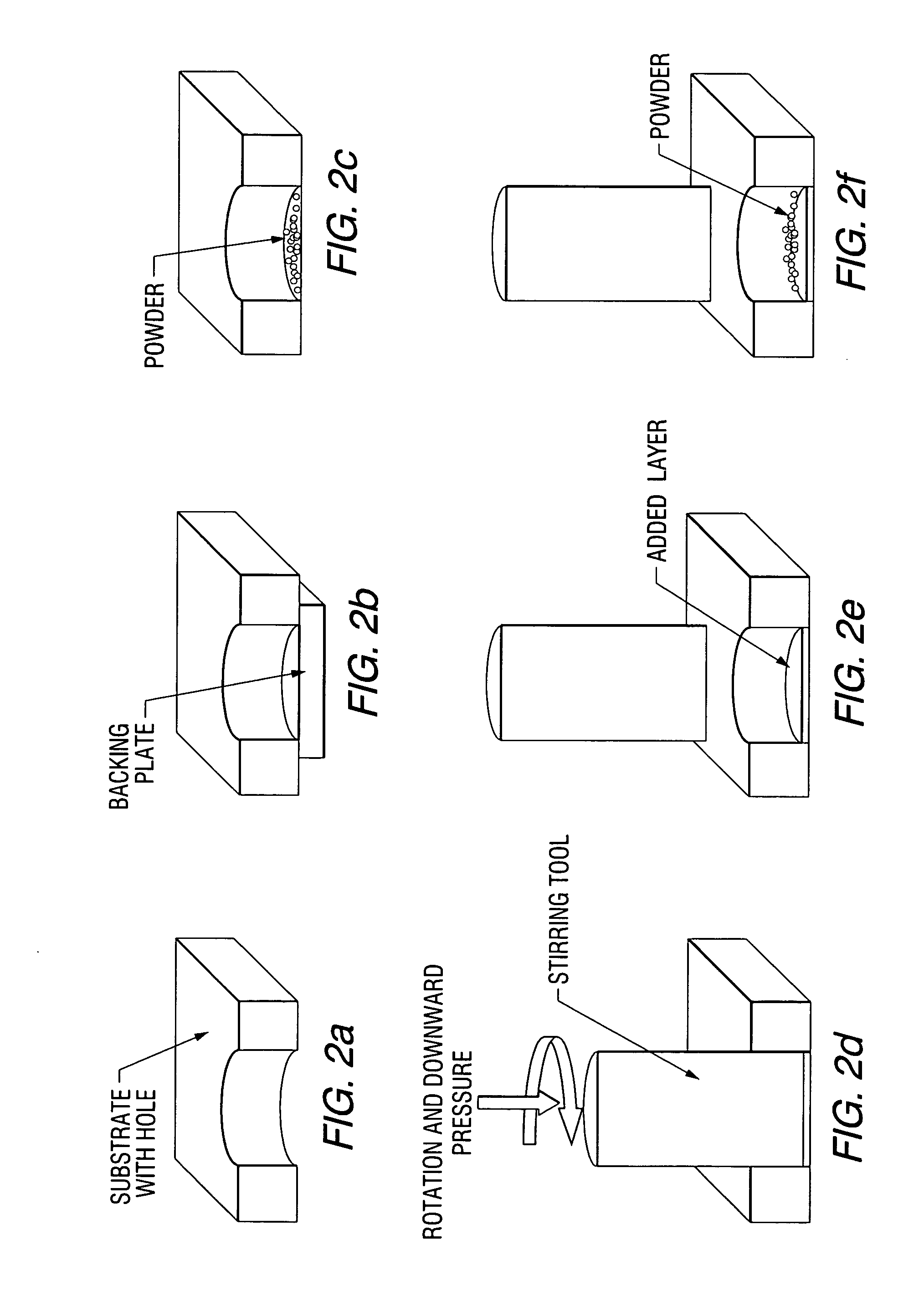
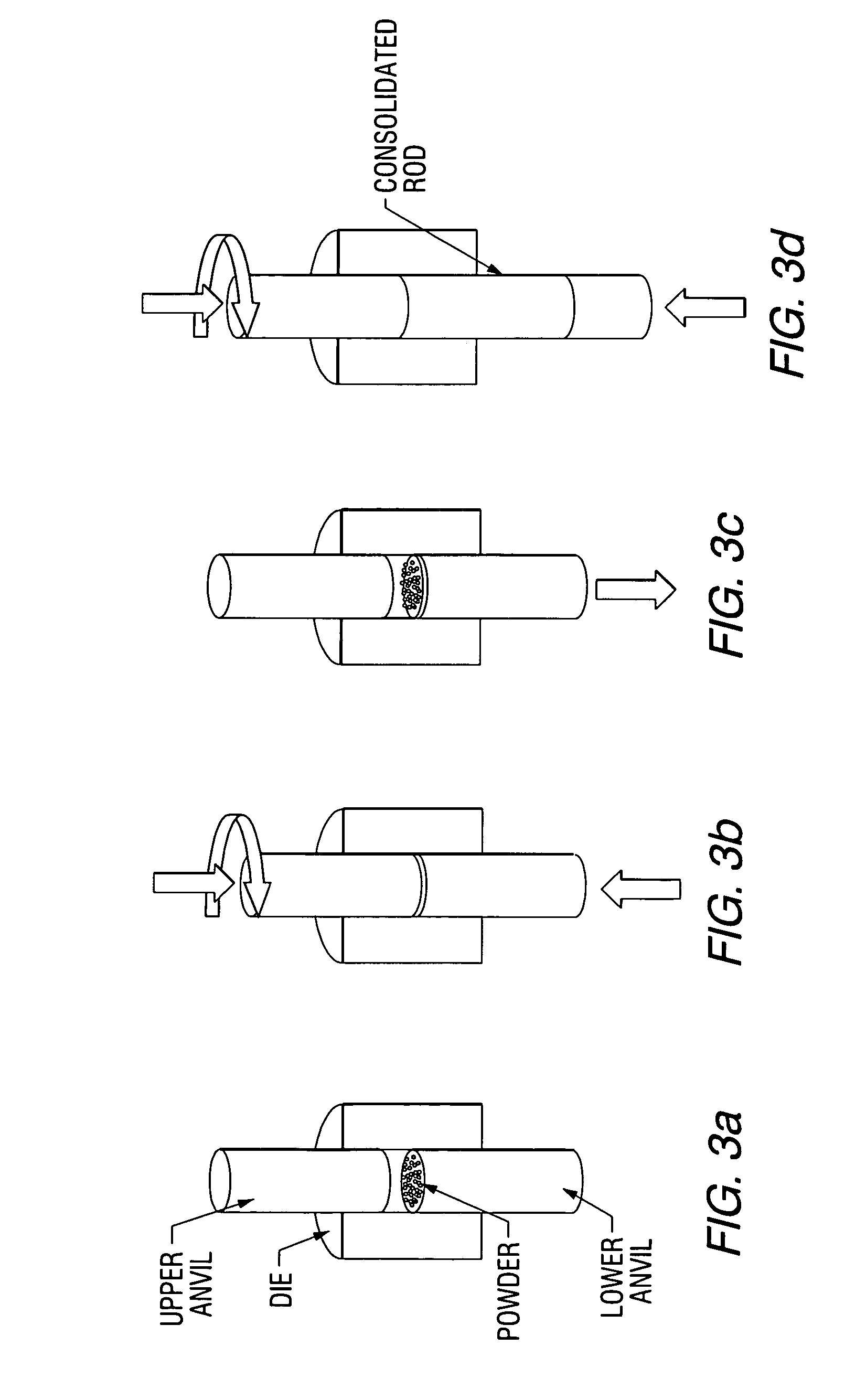
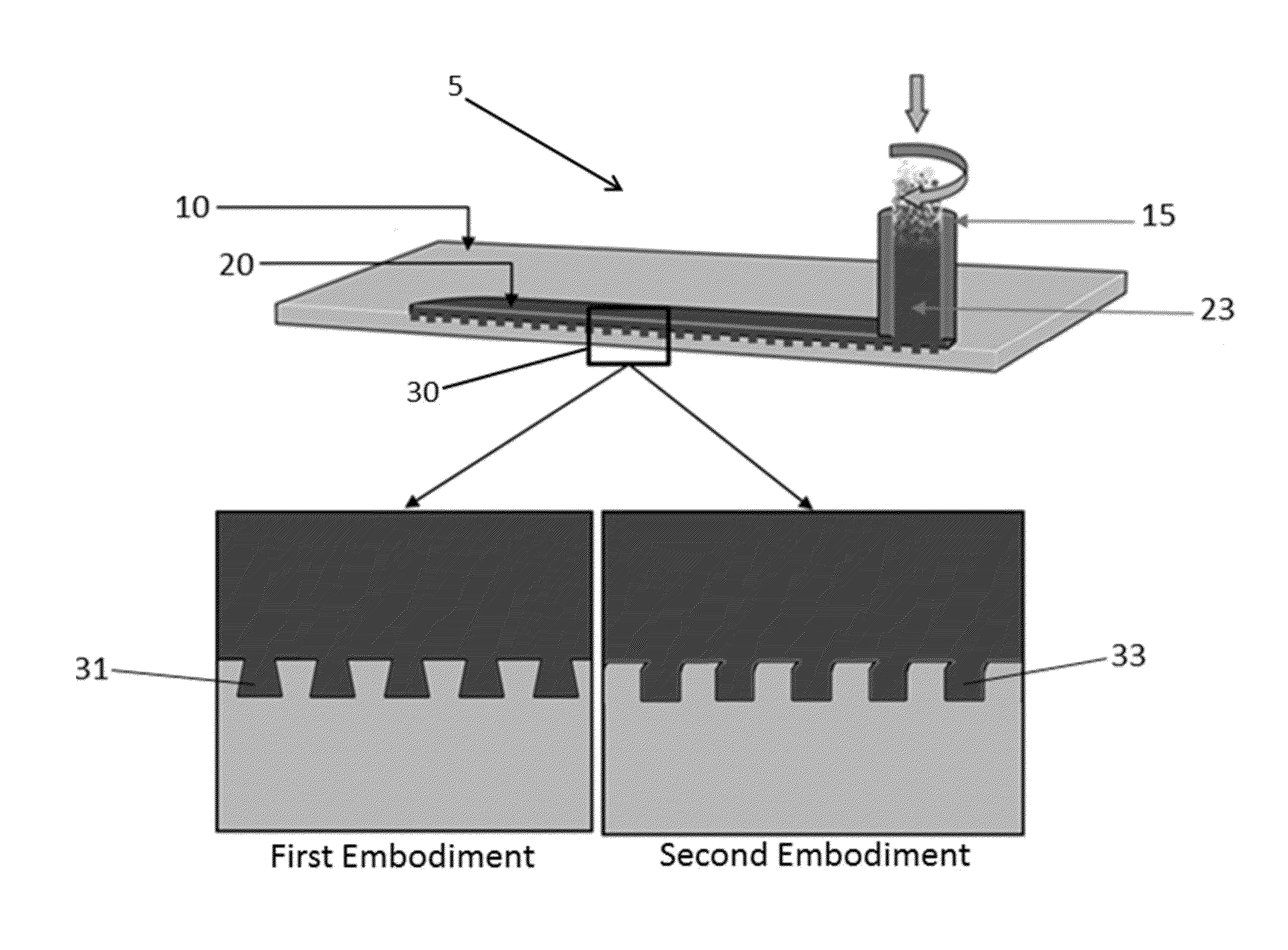
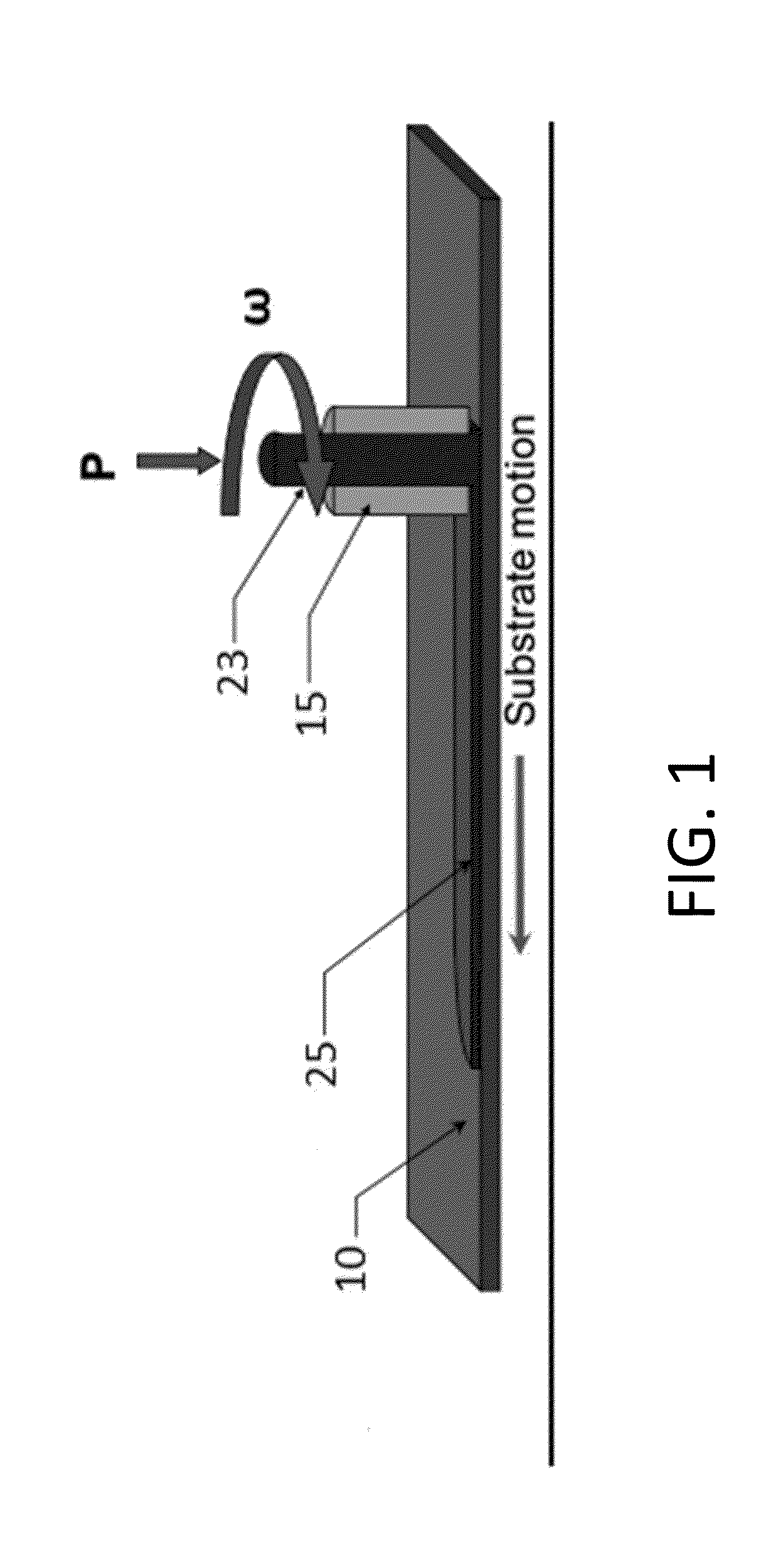
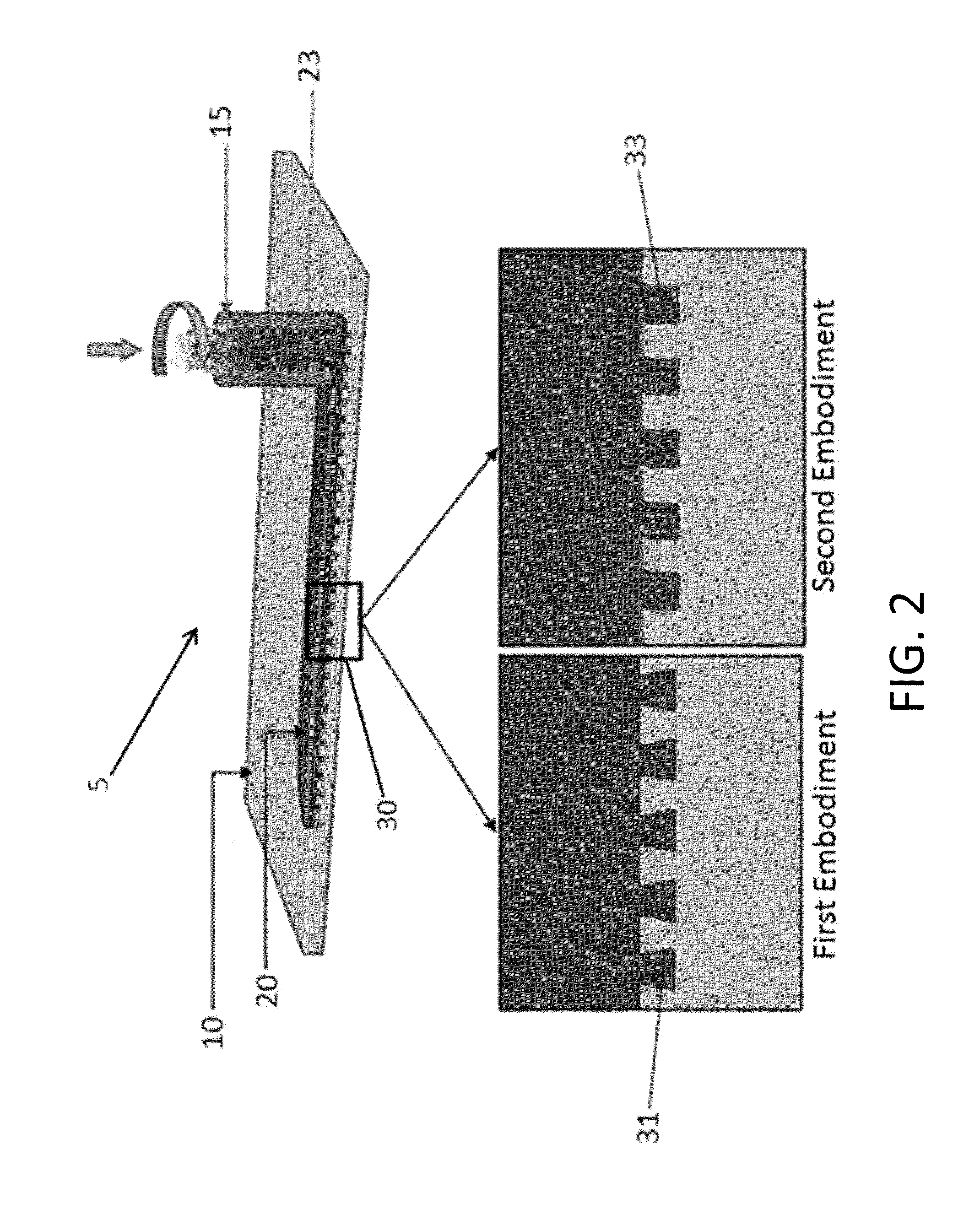
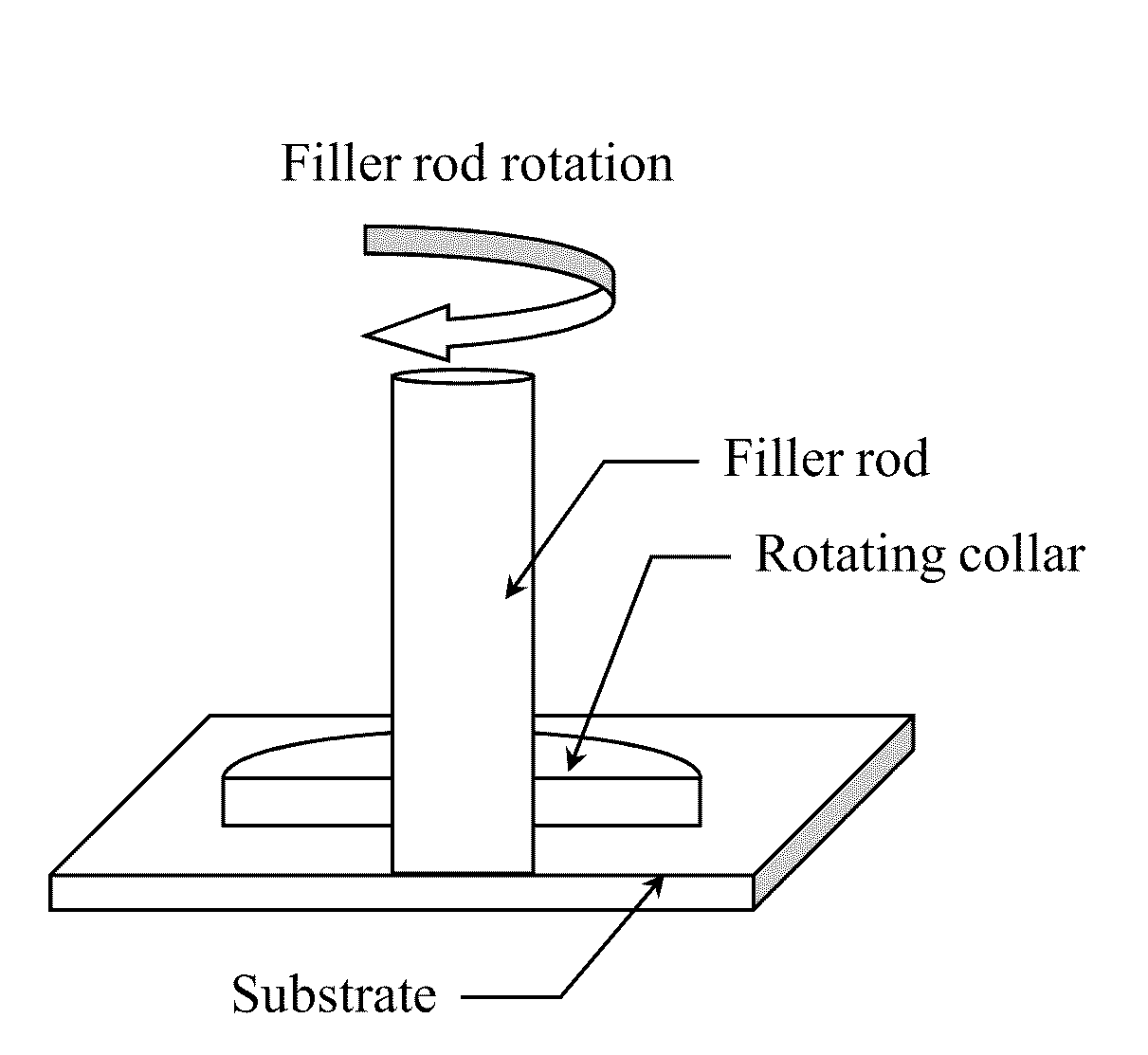
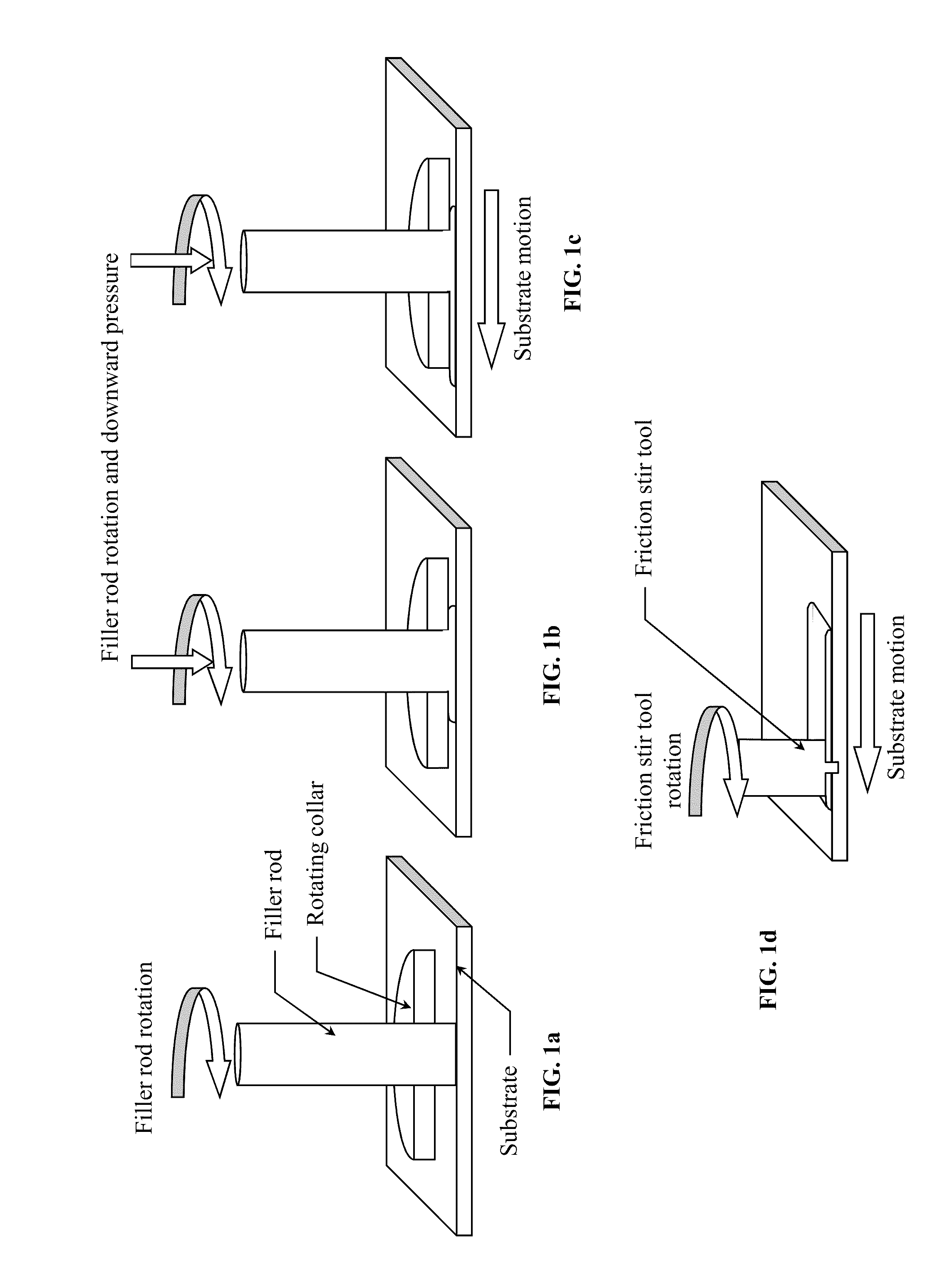
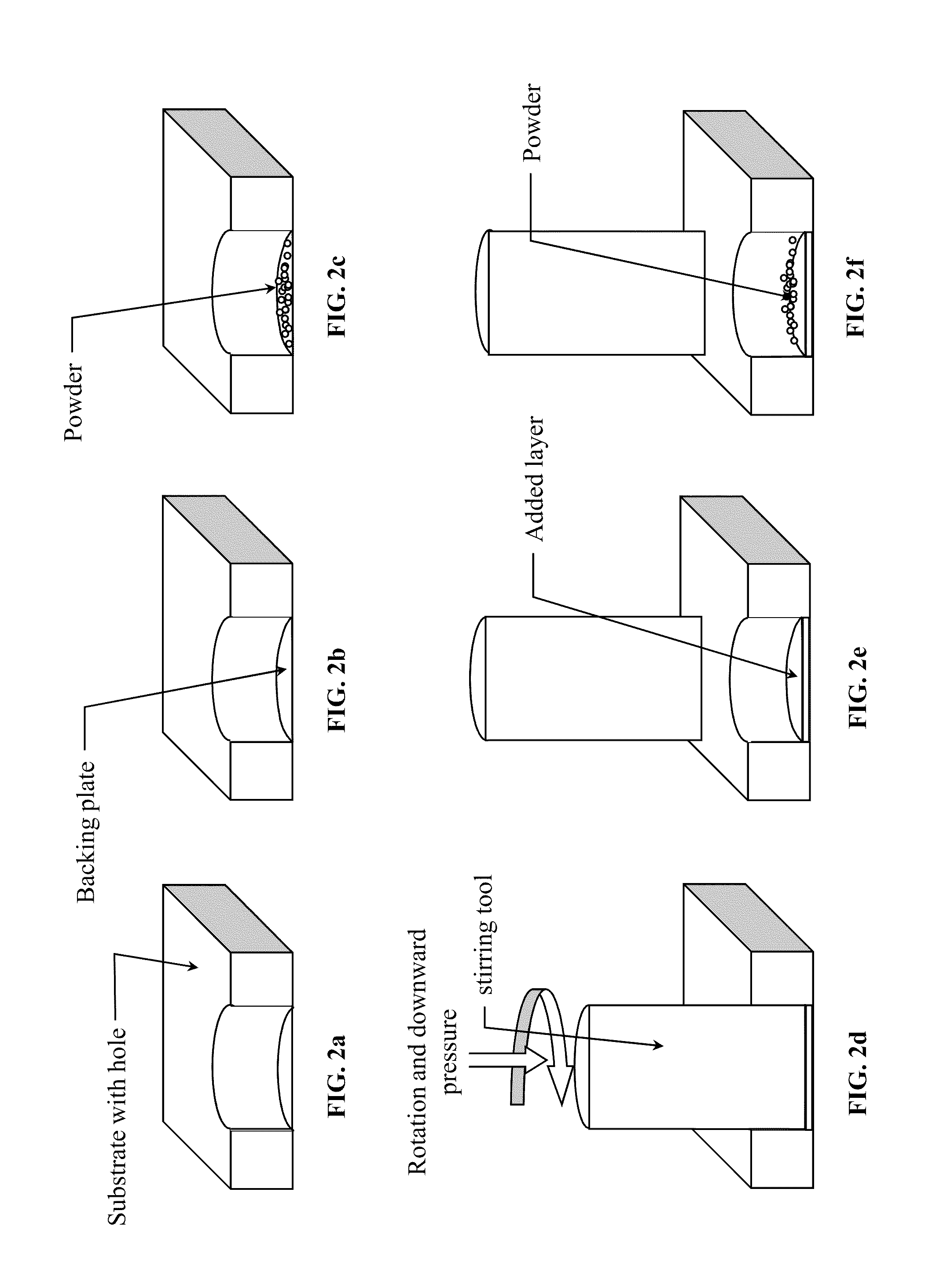
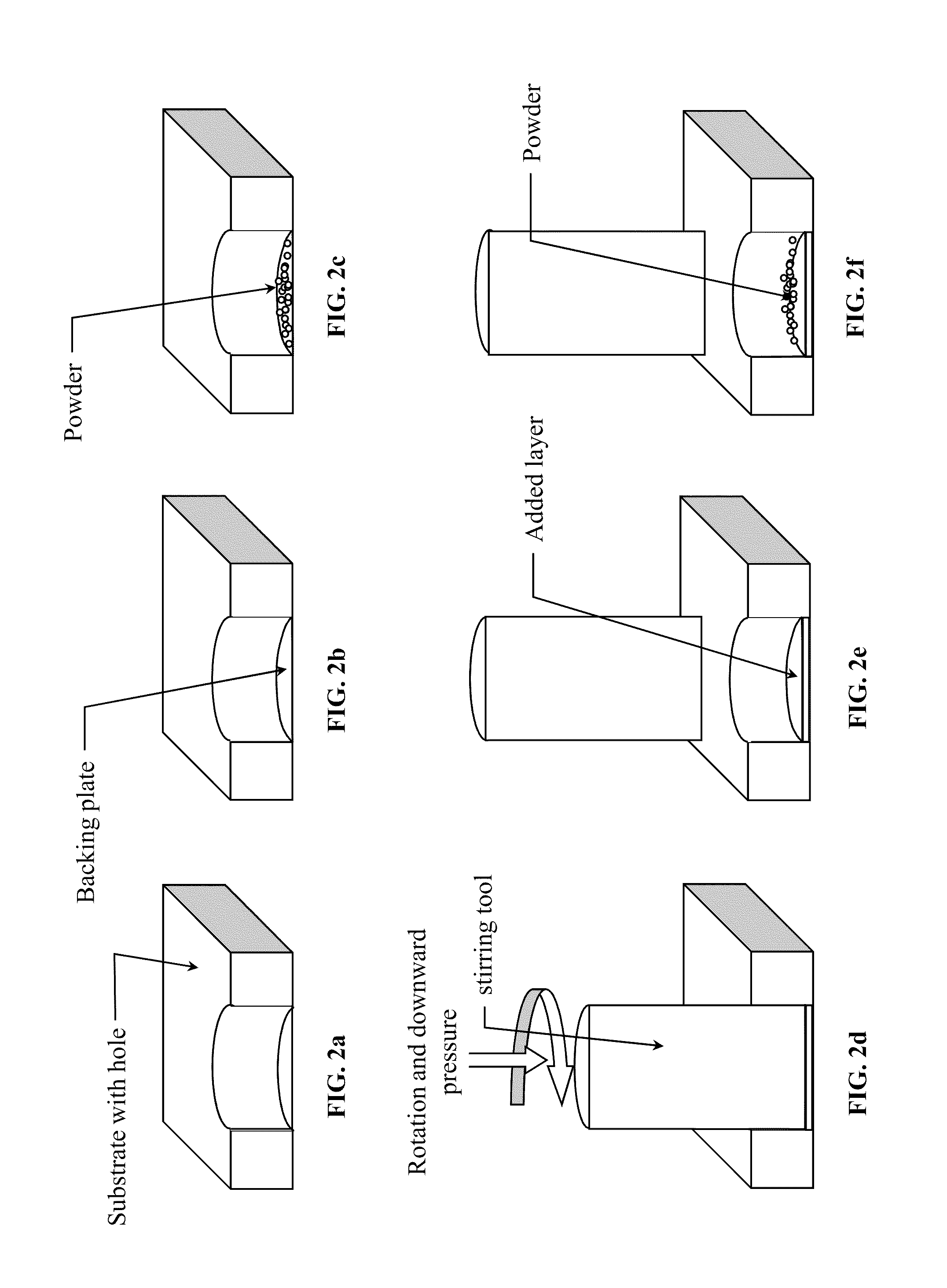
A low-temperature friction-based coating method termed friction stir fabrication (FSF) is disclosed, in which material is deposited onto a substrate and subsequently stirred into the substrate using friction stir processing to homogenize and refine the microstructure. This solid-state process is capable of depositing coatings, including nanocrystalline aluminum and / or metal matrix composites and the like, onto substrates such as aluminum at relatively low temperatures. A method of making rod stock for use in the FSF process is also disclosed.
Owner:MELD MFG CORP
Friction stirring and its application to drill bits, oil field and mining tools, and components in other industrial applications
InactiveUS20060049234A1Long life cycleImprove performanceWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesFriction stir processingFriction stir welding
Solid state processing is performed on a workpiece that operates alone or is a component of equipment used in various demanding, harsh and wearing environments in which failure of a product could compromise safety or the environment or otherwise result in significant cost for repair or replacement, wherein the solid state processing performed by using a tool capable of friction stir processing, friction stir mixing, or friction stir welding results in a workpiece that offers a longer life-cycle and / or improved performance and / or improved reliability as a result of the solid state processing.
Owner:MEGASTIR TECH
Solid state processing of materials through friction stir processing and friction stir mixing
InactiveUS20060032891A1Improve toughnessIncrease and decrease hardnessWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesCompressibilityFriction stir processing
Solid state processing is performed on a workpiece by using a tool capable of friction stir processing, friction stir mixing, or friction stir welding, wherein solid state processing modifies characteristics of a workpiece while substantially maintaining a solid phase in some embodiments, allowing some elements to pass through a liquid phase in other embodiments, and wherein modified characteristics of the material include, but are not limited to, microstructure, macrostructure, toughness, hardness, grain boundaries, grain size, the distribution of phases, ductility, superplasticity, change in nucleation site densities, compressibility, expandability, coefficient of friction, abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance, fatigue resistance, magnetic properties, strength, radiation absorption, and thermal conductivity.
Owner:ADVANCED METAL PROD INC +1
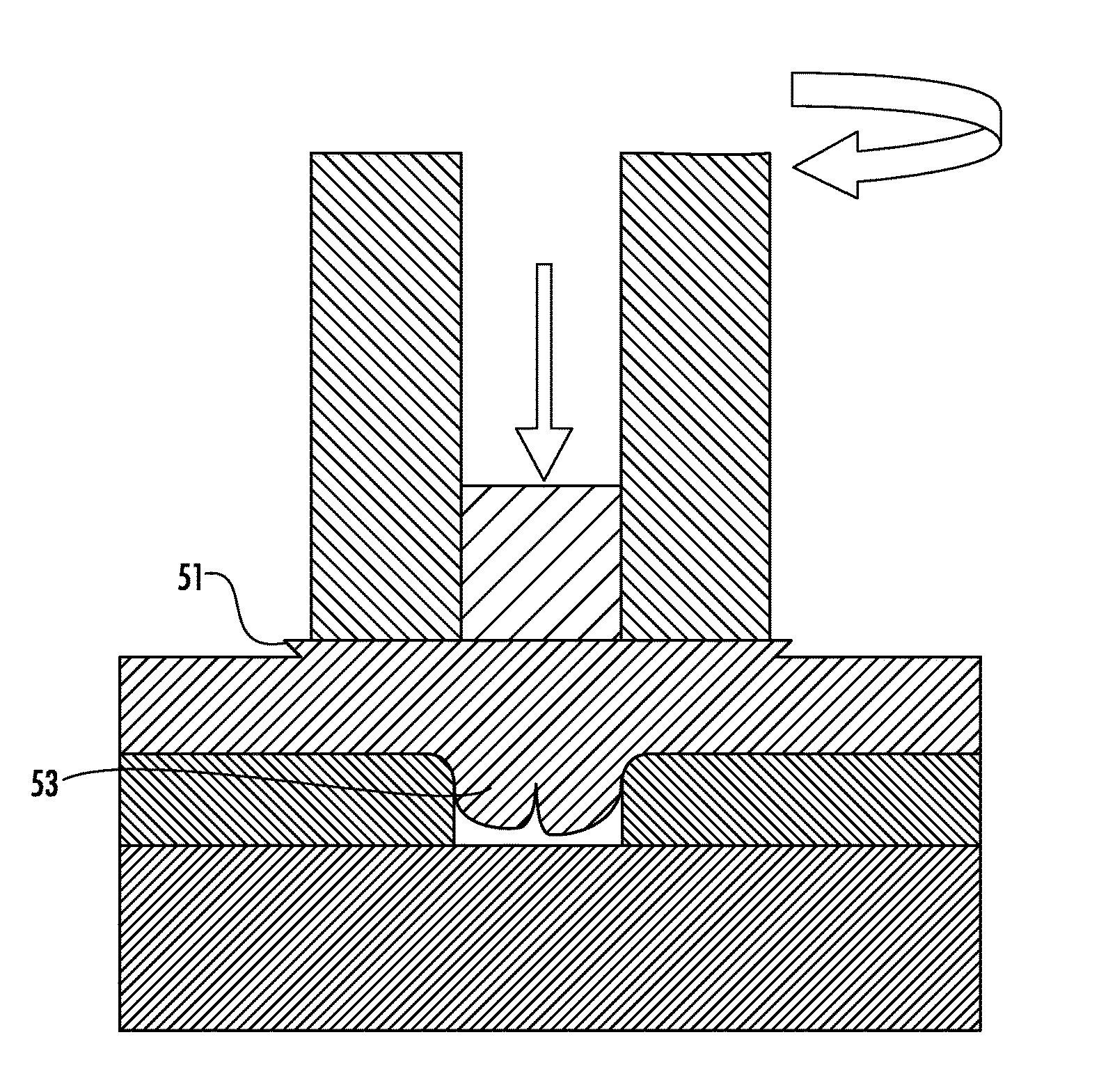
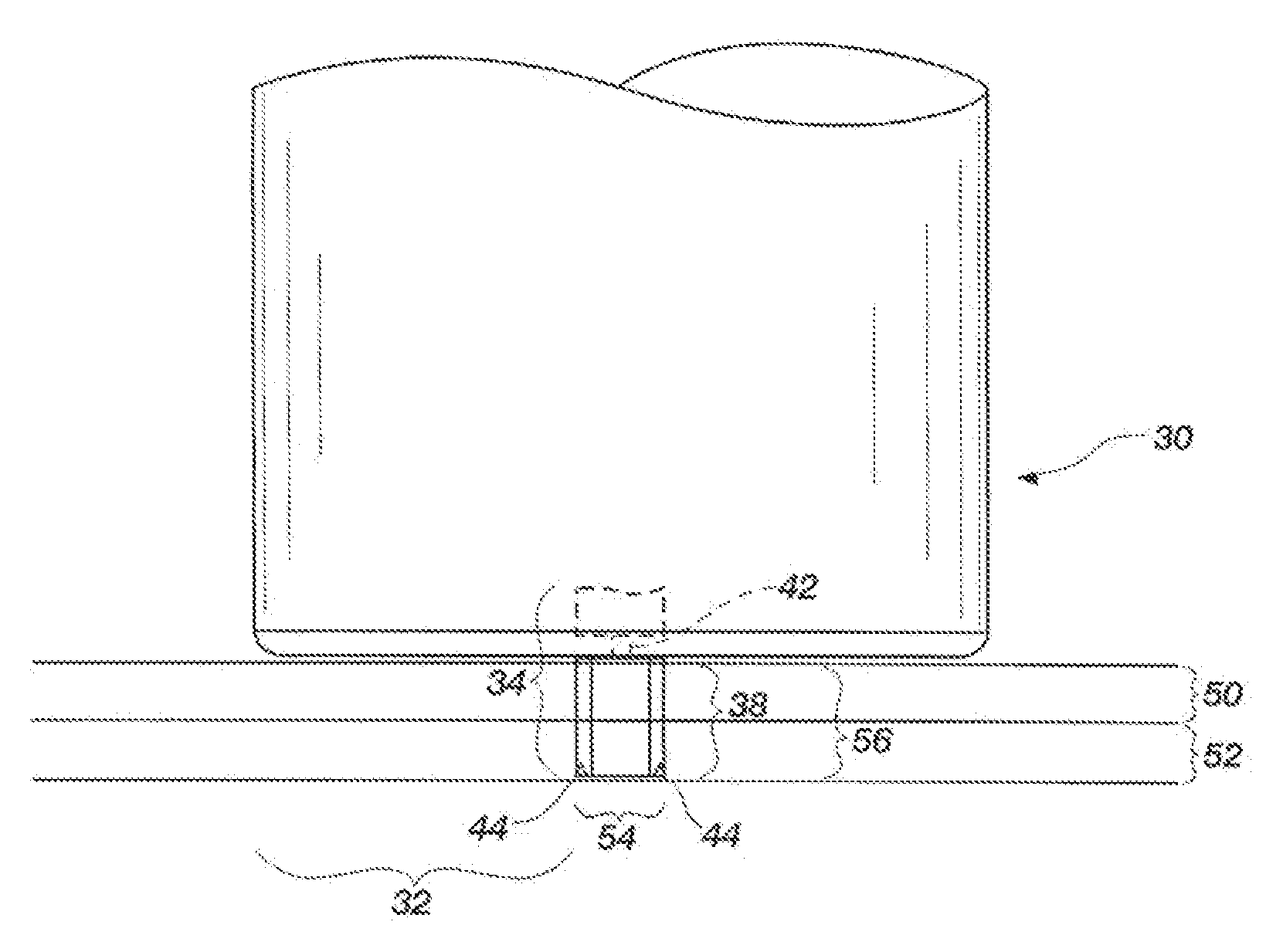
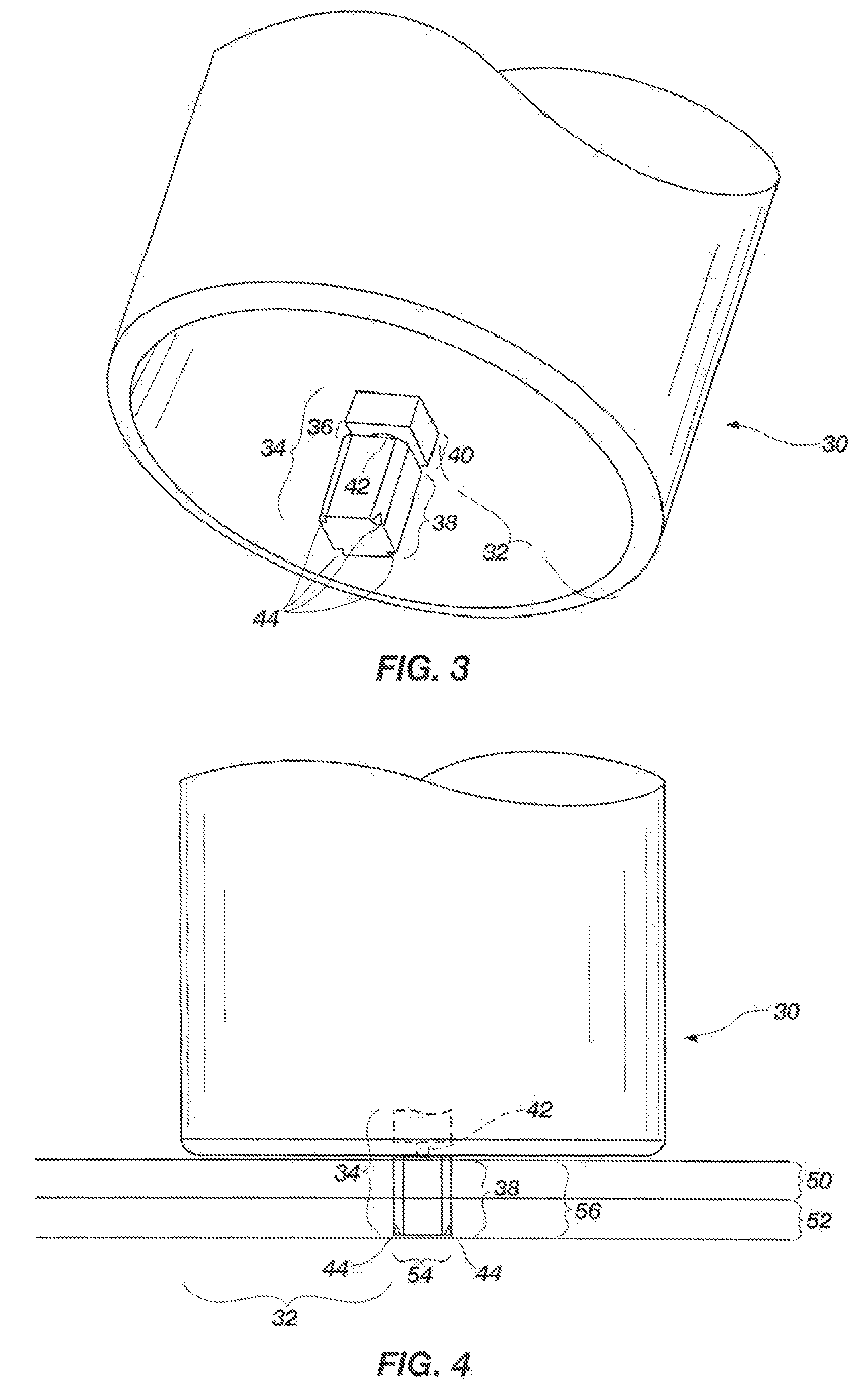
Apparatus for friction stir and friction stir processing
InactiveUS20090152328A1InhibitionWelding/cutting auxillary devicesPistonsEngineeringFriction stir processing
An apparatus for a friction stir and a friction stir processing of the present invention suppress an occurrence of a surface defect in an area processed by the friction stir. The apparatus for the friction stir includes a tool having a columnar tip-side part, a rotating unit for rotating the tool on a central axis, a first pressing unit for pressing a tip of the tool rotated by the rotating unit against a work, a jig having a tool insertion hole into which the tip-side part of the tool is inserted so that the tip-side part of the tool is encircled around the jig, a second pressing unit for slidably pressing the jig against the work, and a press control unit for controlling the first pressing unit so that the tip-side part of the tool is gradually pulled out of the work by the first pressing unit while moving the tool and the jig relative to the work, in a state that the tool is rotated by the rotating unit and the tip of the tool has been sunk into the work to a predetermined depth by the first pressing unit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
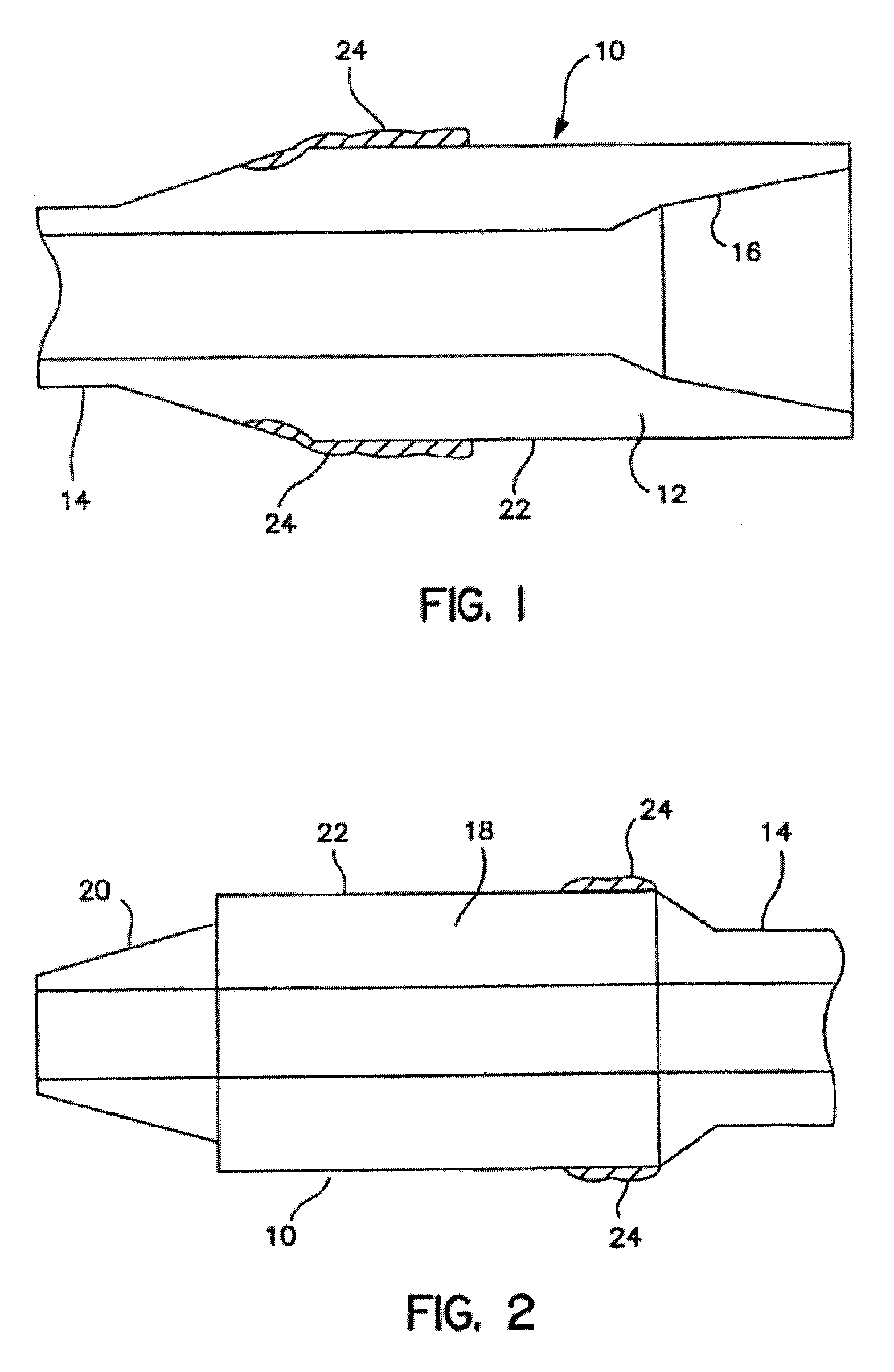
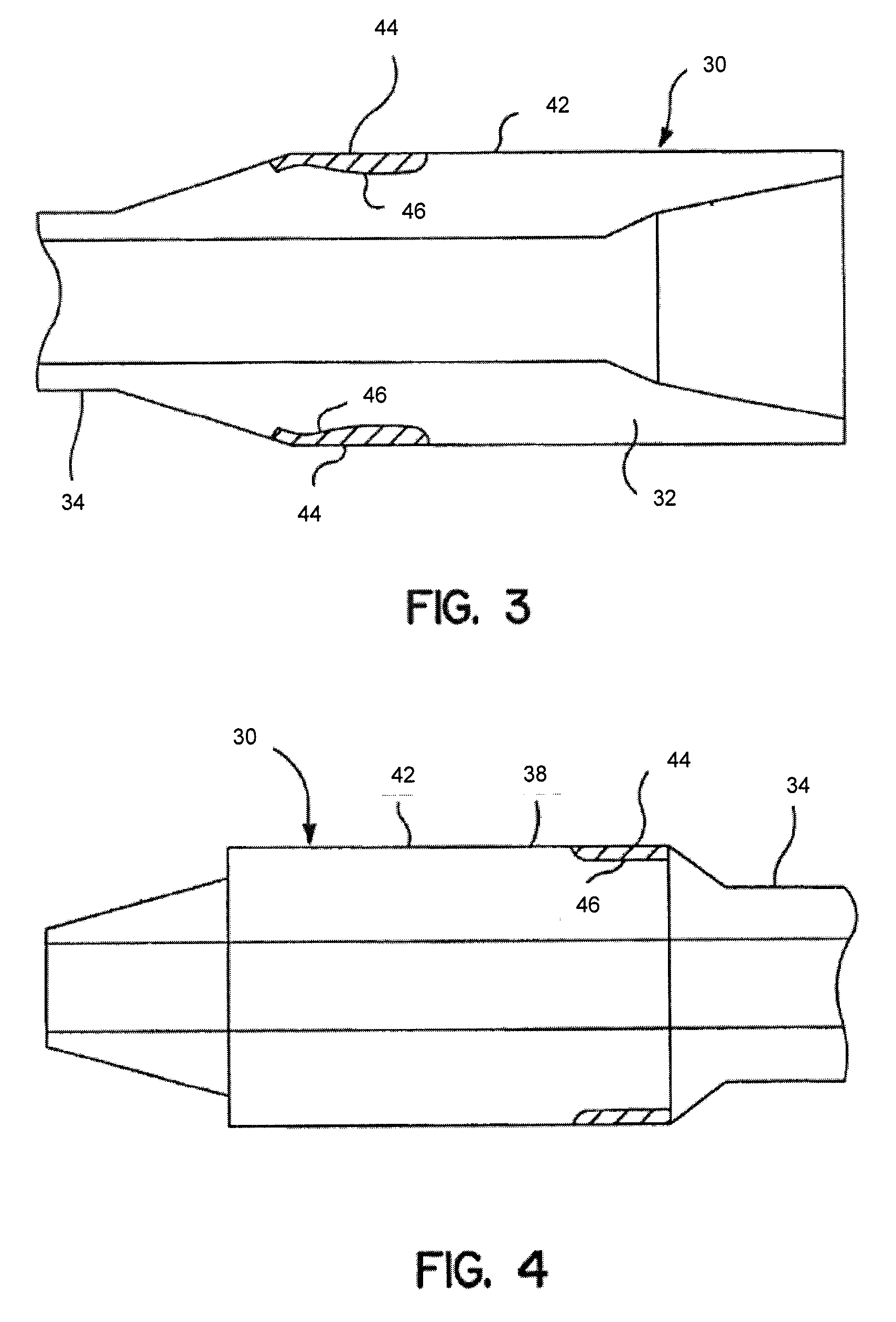
Three-body joining using friction stir processing techniques
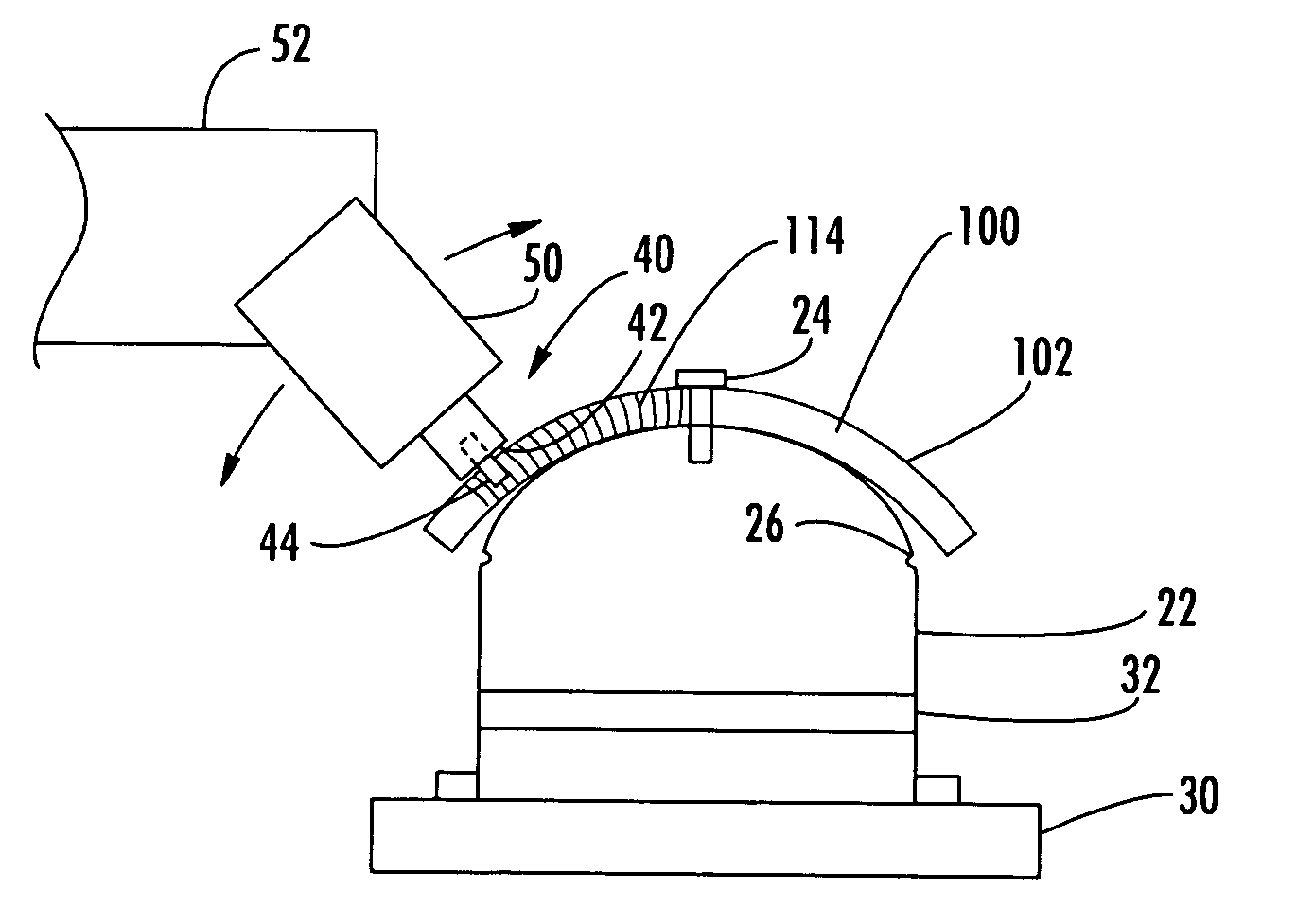
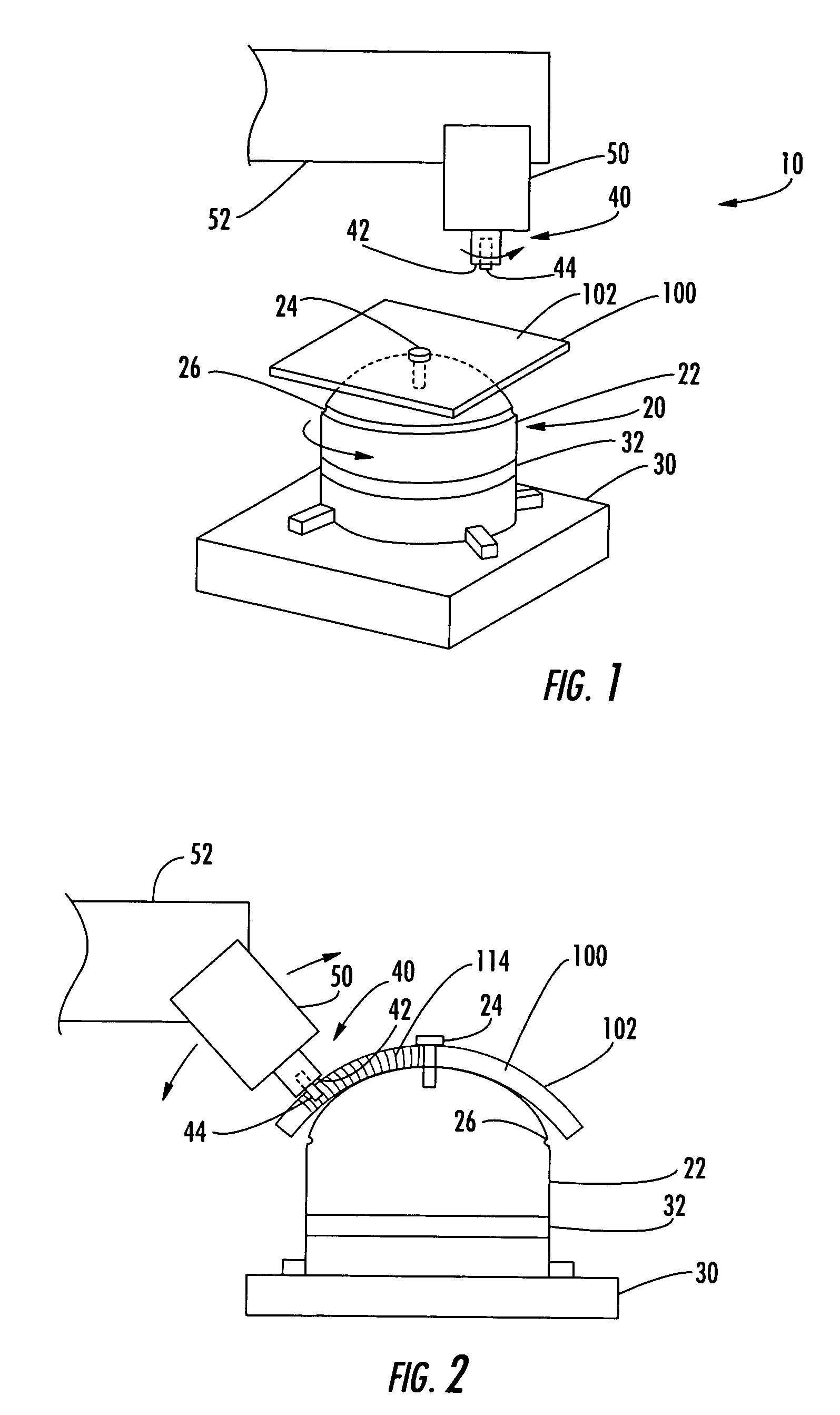
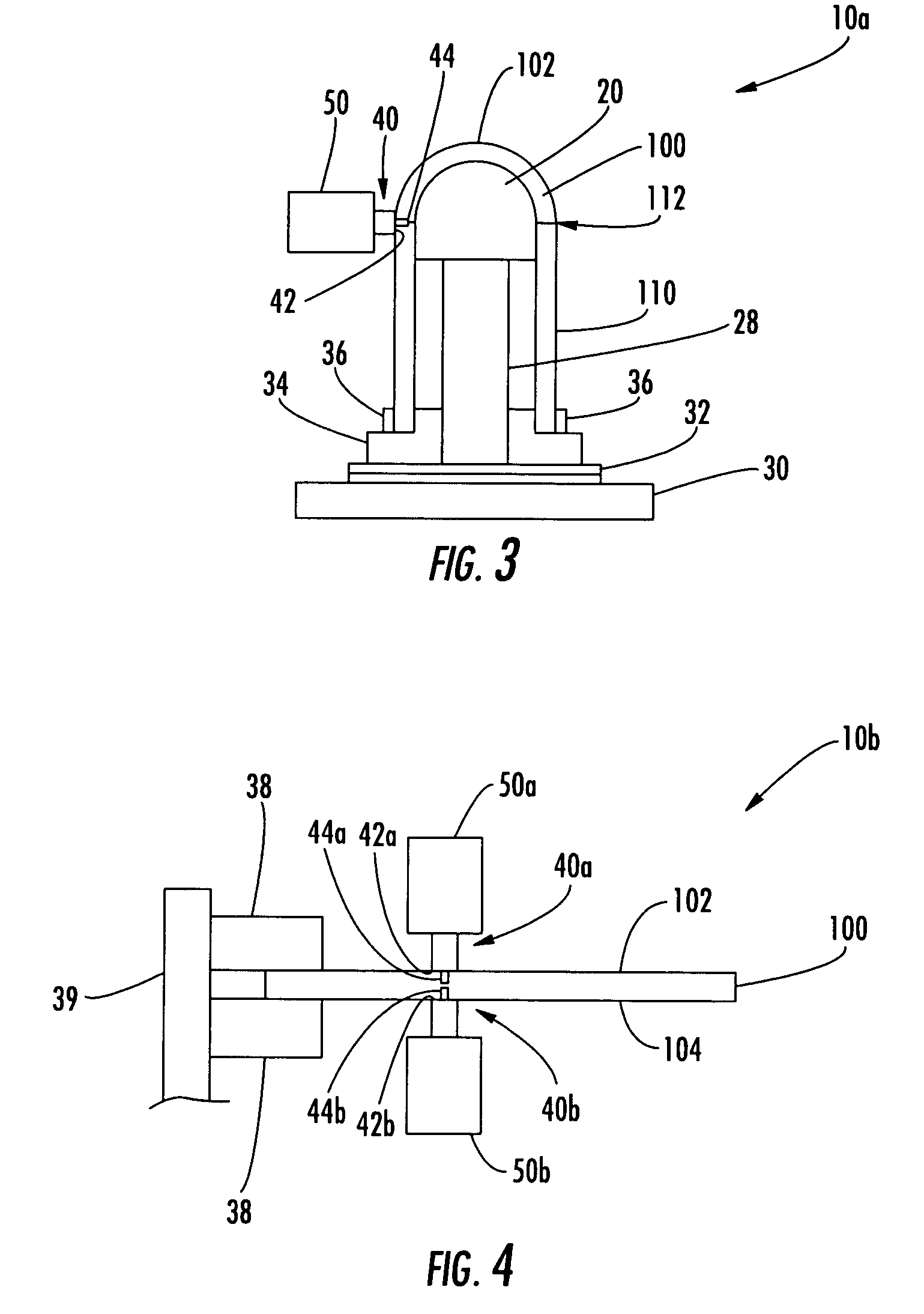
ActiveUS20080006678A1Increase rotation speedRotational speedWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesMechanical engineeringFriction stir processing
A friction stir tool is provided to perform friction stir riveting using a partially consumable pin, wherein the pin includes a cutting edge on a bottom surface thereof, wherein the tool is rotated at a first speed to enable cutting by the pin into a first material that is overlapping a second material, wherein after the pin has cut to a sufficient depth, the rotational speed of the tool is increased to thereby enable plasticization of the consumable pin, the first material, and the second material, wherein the tool is then rapidly decelerated until stopped, enabling diffusion bonding between the pin, the first material and the second material.
Owner:MAZAK CORP +1
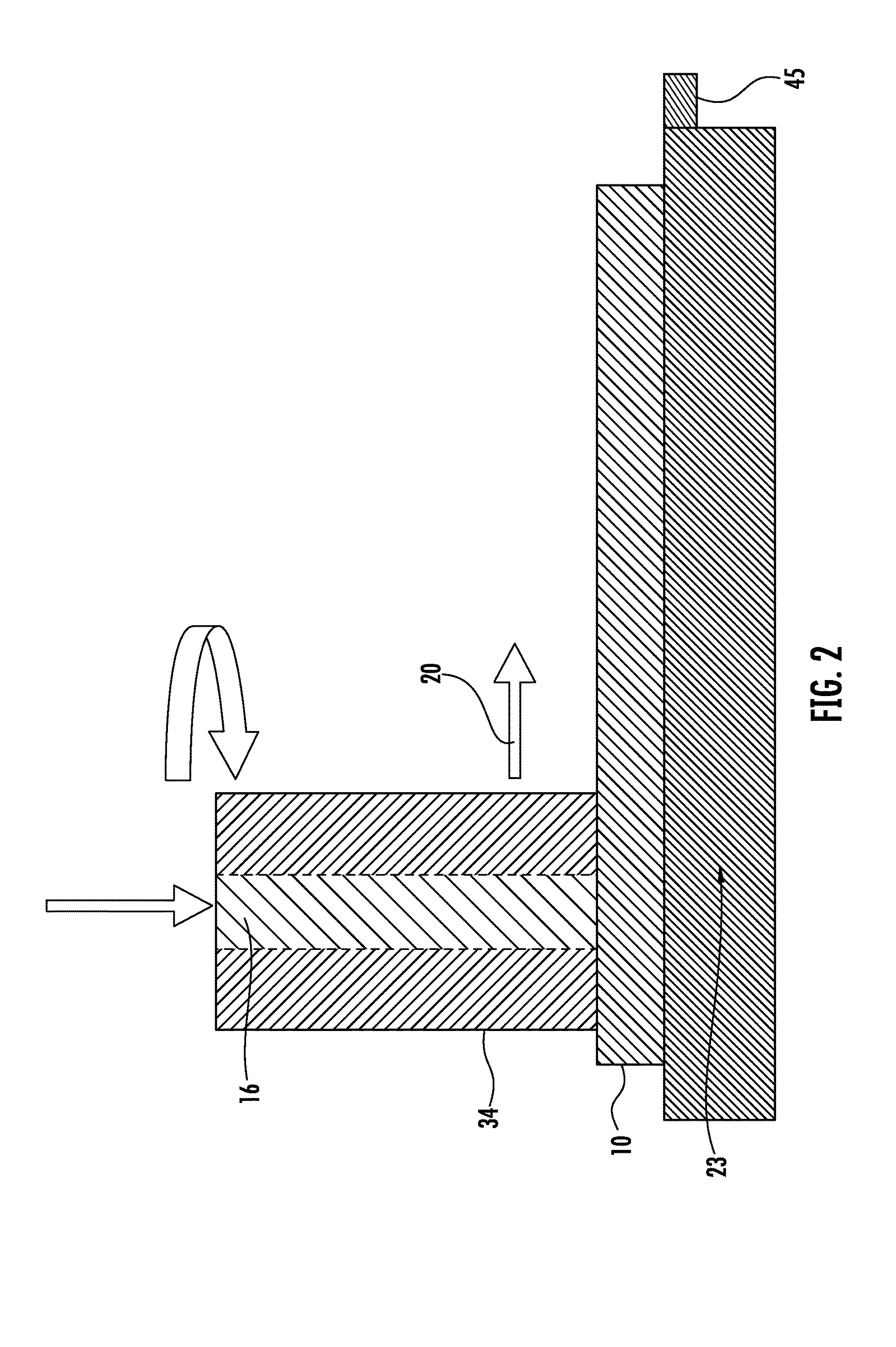
Reducing sheet distortion in friction stir processing
InactiveUS20090200359A1Lower yield strengthEnable unwanted deformationVehicle componentsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesFriction reductionSpot welding
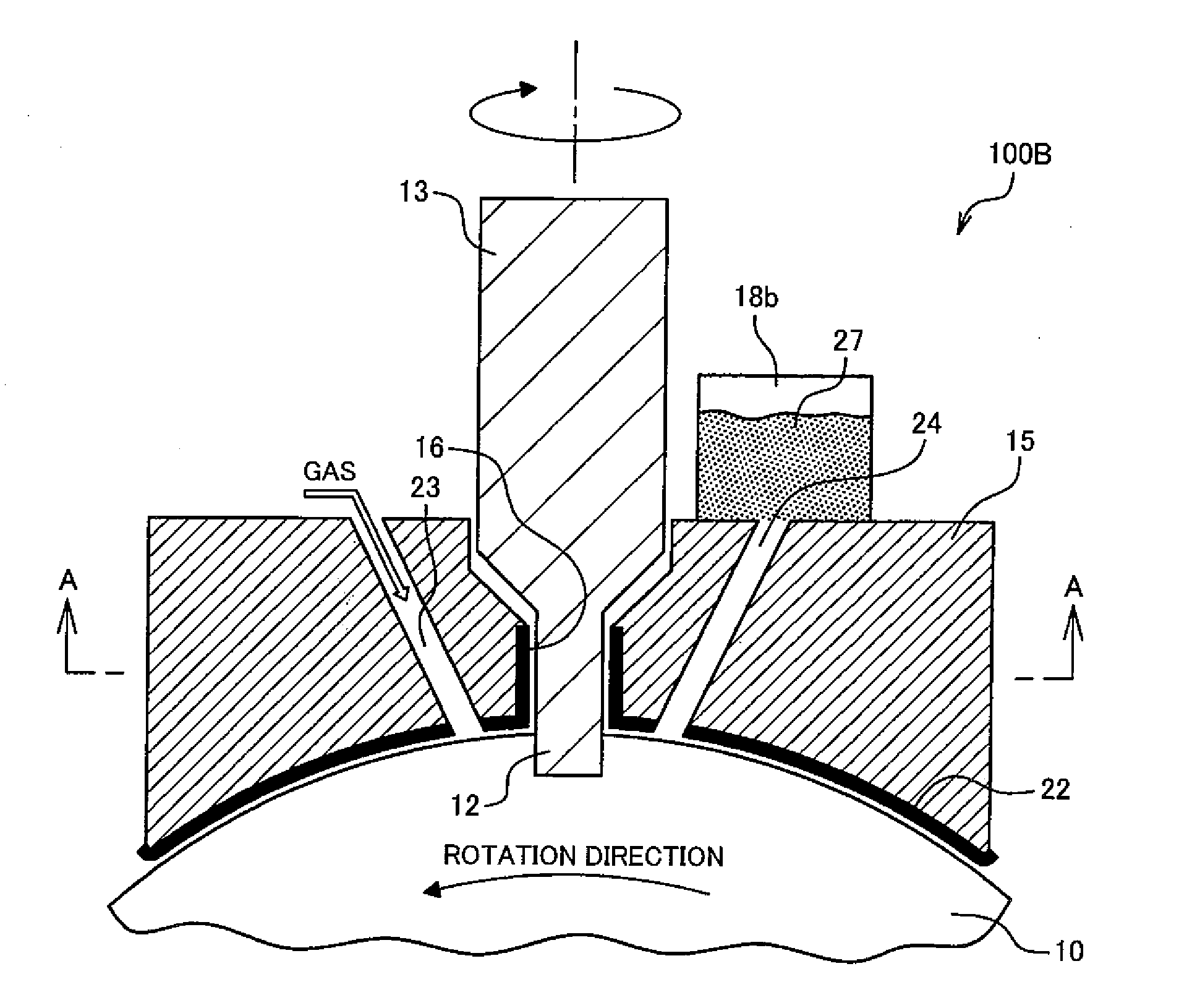
Local heat may be generated through surfaces of sheet metal workpieces by supporting the workpiece(s) on a hard surfaced anvil and engaging the opposite surface of the workpiece with a rotating, and optionally translating, friction stir tool that is pressed against the work surface. Advantages are realized in friction stir processing (e.g. seam or spot welding) of such sheet metal workpieces by using an anvil with appreciable thermal conductivity, or a liquid cooled anvil body, to suitably cool the site(s) of the workpiece engaged by the friction stir tool to minimize or eliminate distortion of the workpiece.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
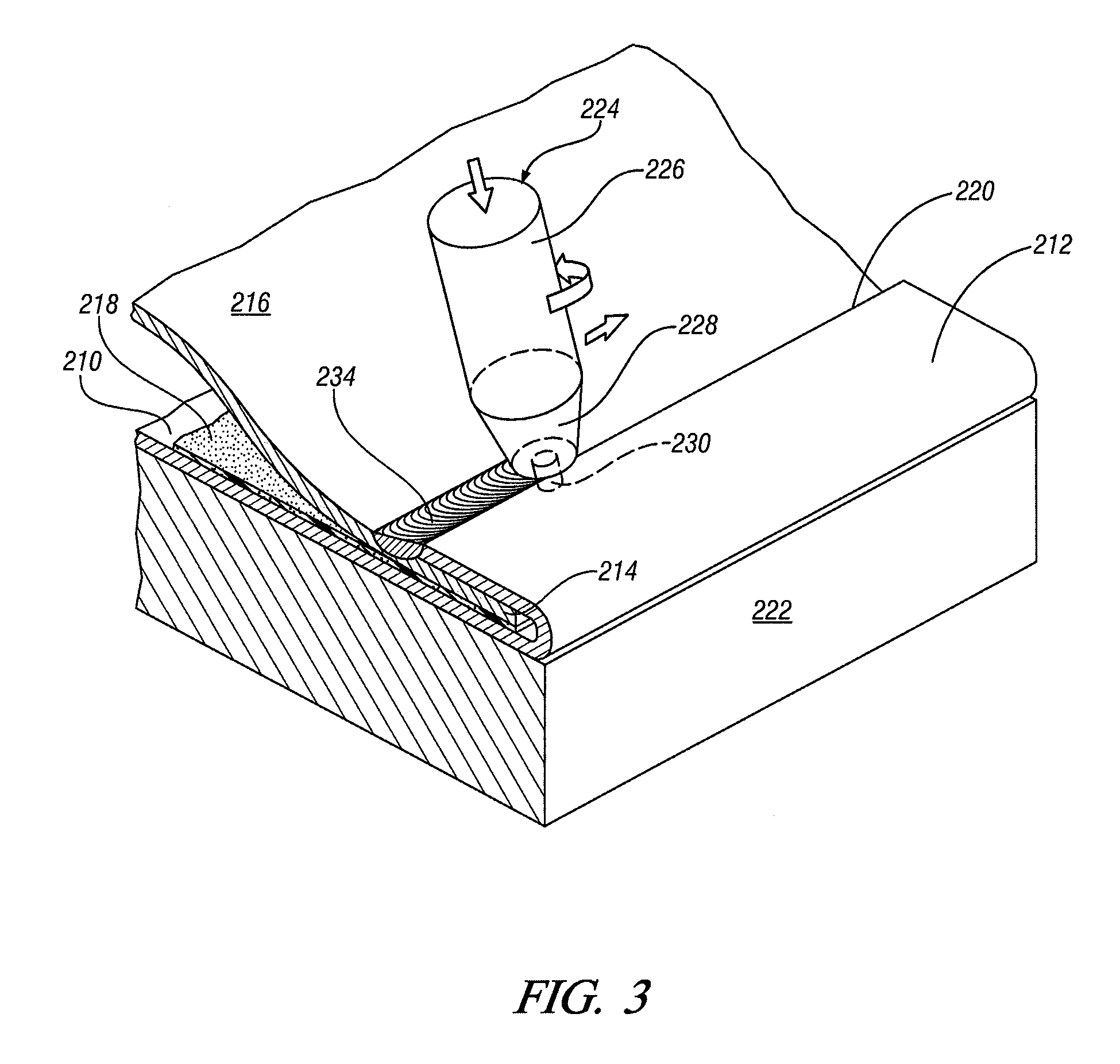
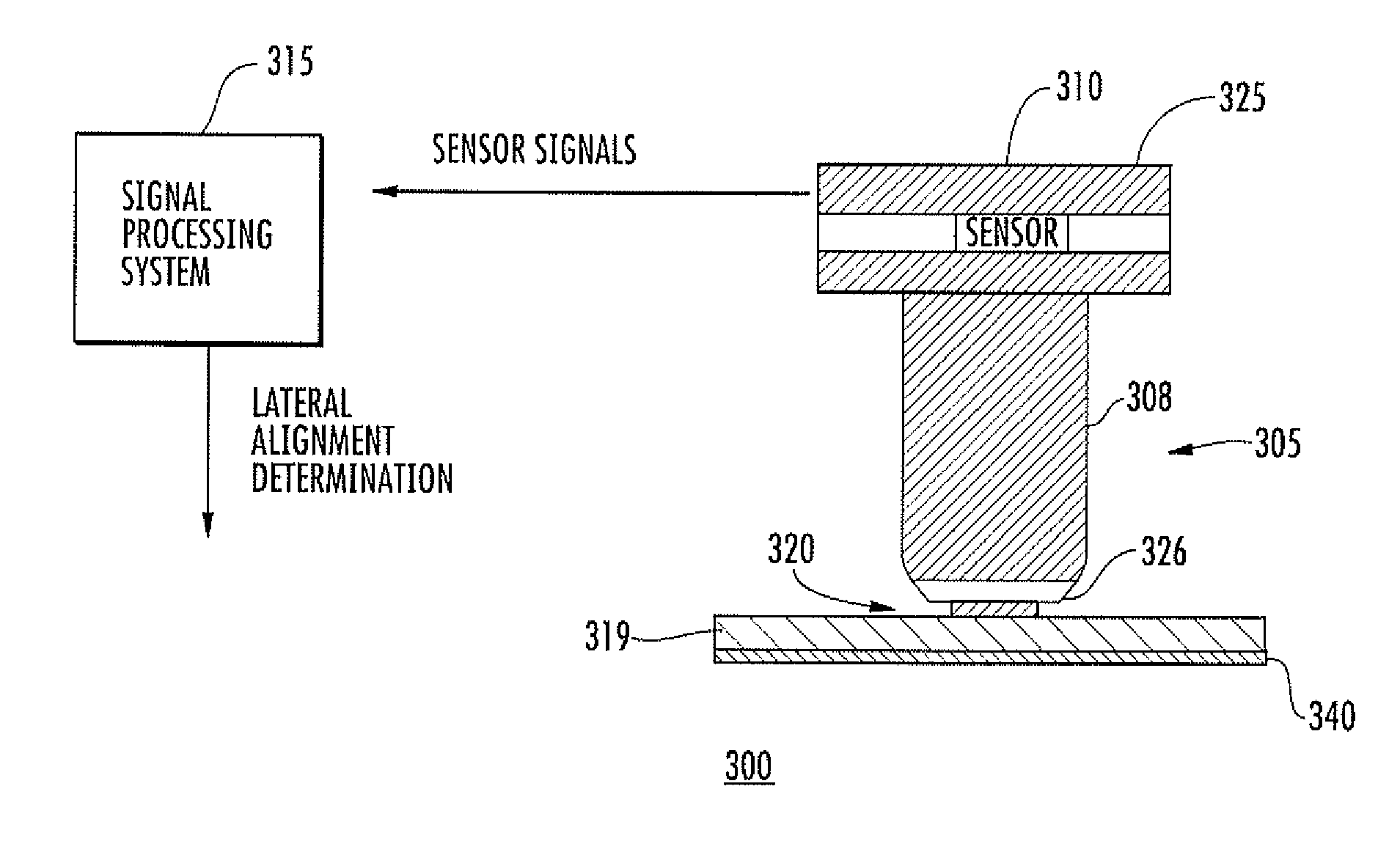
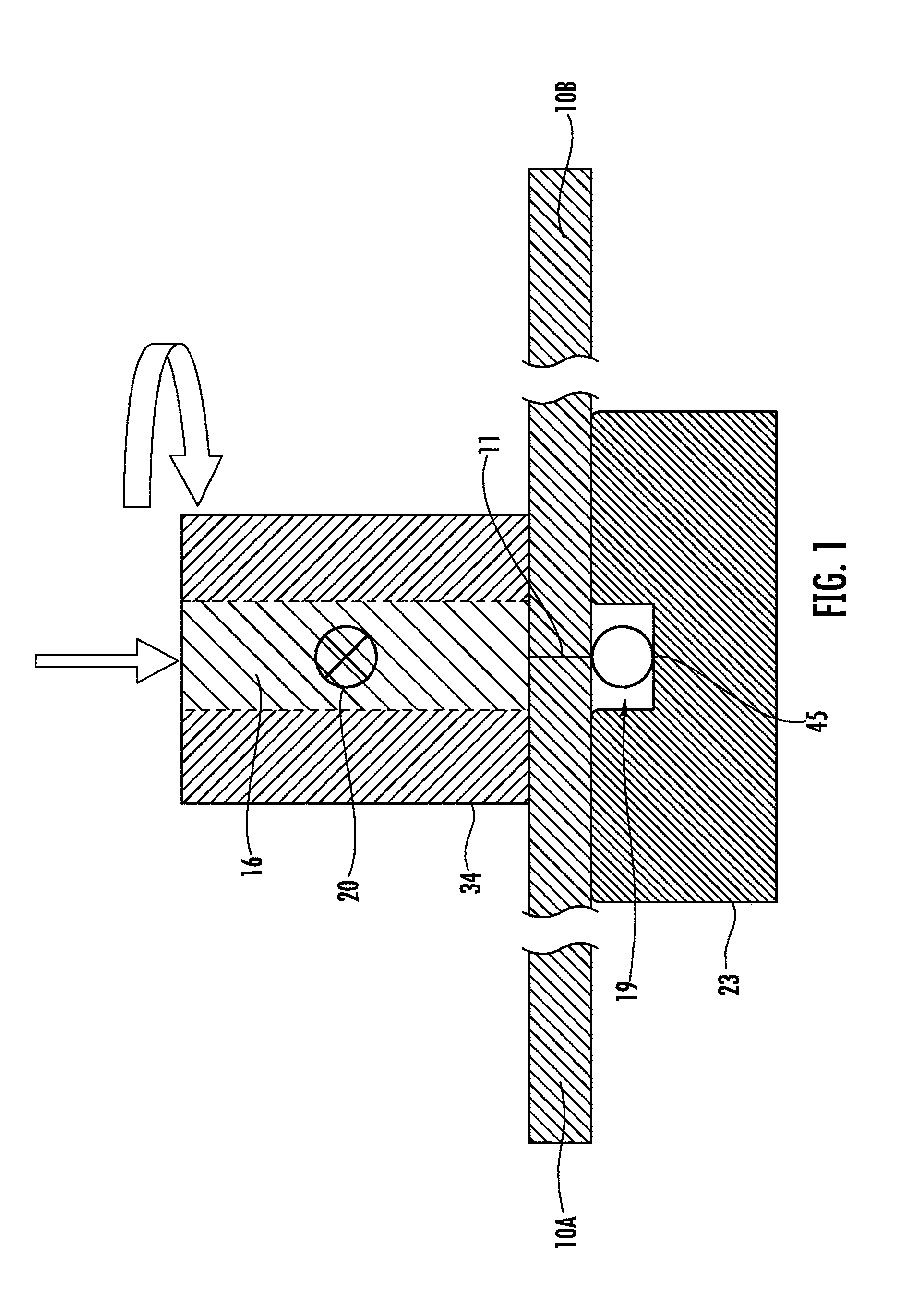
Lateral position detection for friction stir systems
InactiveUS20090294511A1Welding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesClosed loopEngineering
A friction stir system for processing at least a first workpiece includes a spindle actuator coupled to a rotary tool comprising a rotating member for contacting and processing the first workpiece. A detection system is provided for obtaining information related to a lateral alignment of the rotating member. The detection system comprises at least one sensor for measuring a force experienced by the rotary tool or a parameter related to the force experienced by the rotary tool during processing, wherein the sensor provides sensor signals. A signal processing system is coupled to receive and analyze the sensor signals and determine a lateral alignment of the rotating member relative to a selected lateral position, a selected path, or a direction to decrease a lateral distance relative to the selected lateral position or selected path. In one embodiment, the friction stir system can be embodied as a closed loop tracking system, such as a robot-based tracked friction stir welding (FSW) or friction stir processing (FSP) system.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Friction stirring of high softening temperature materials using new surface features on a tool
InactiveUS20060289608A1High melting pointCooking-vessel materialsWelding/cutting auxillary devicesSpot weldingFriction stir processing
A method of selecting a geometry for a friction stirring tool, said tool having a melting point that is higher than the workpiece material, wherein the tool is placed in motion against the workpiece to generate heat in the workpiece such that workpiece material is transported in surface features of the tool, and wherein surface features manage workpiece material flow around the tool, and wherein the tool can be used in friction stir processing, friction stir mixing, friction stir welding, and friction stir spot welding of high melting temperature materials or high softening temperature materials.
Owner:MAZAK CORP
Solid state joining using additive friction stir processing
ActiveUS20160175981A1Reduce breakageReduced tool wearAdditive manufacturing apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesFilling materialsFriction stir processing
Owner:MELD MFG CORP
Crack repair using friction stir welding on materials including metal matrix composites, ferrous alloys, non-ferrous alloys, and superalloys
InactiveUS20050061853A1Avoid loopholesWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesCrazingNuclear reactor
A system and method of using friction stir welding and friction stir processing to perform crack repair or preventative maintenance of various materials and structures, wherein the structures include pipeline, ships, and nuclear reactor containment vessels, wherein the friction stir welding and processing can be performed on various materials including metal matrix composites, ferrous alloys, non-ferrous alloys, and superalloys, and wherein the friction stir welding and processing can be performed remotely and in harsh environments such as underwater or in the presence of radiation.
Owner:BABB JONATHAN A +1
Method for preparing pre-coated aluminum and aluminum-alloy fasteners and components having high-shear strength and readily deformable regions
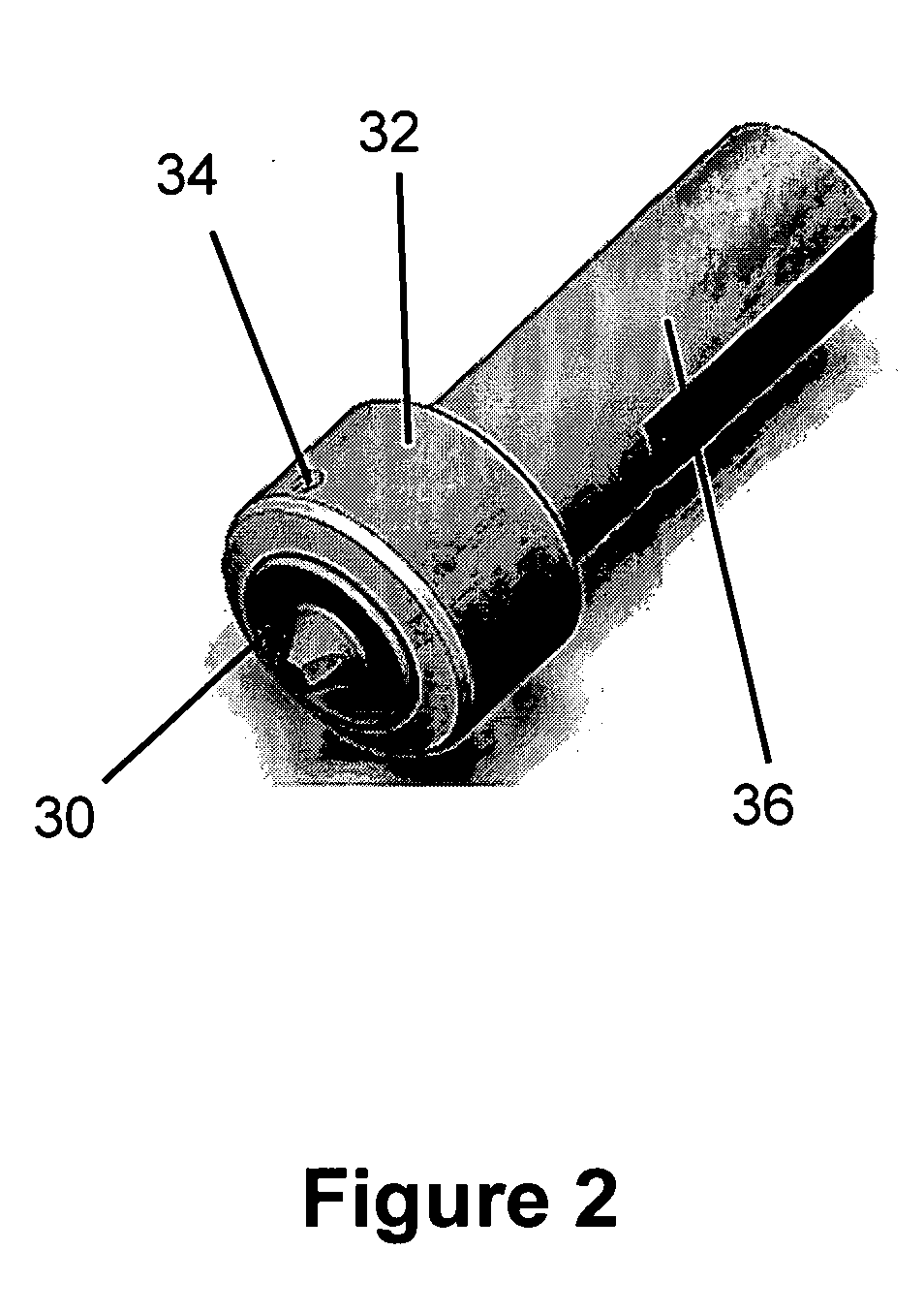
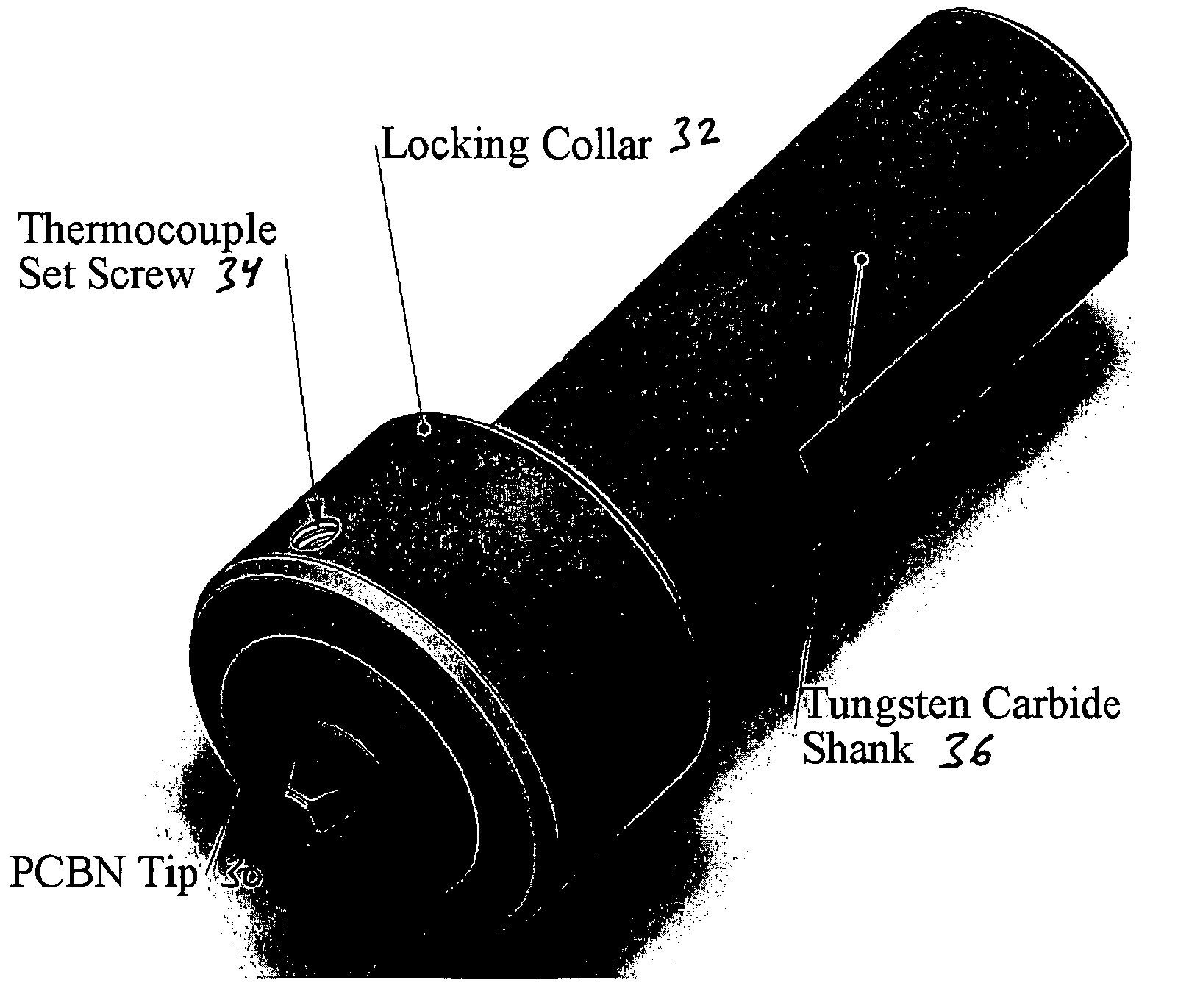
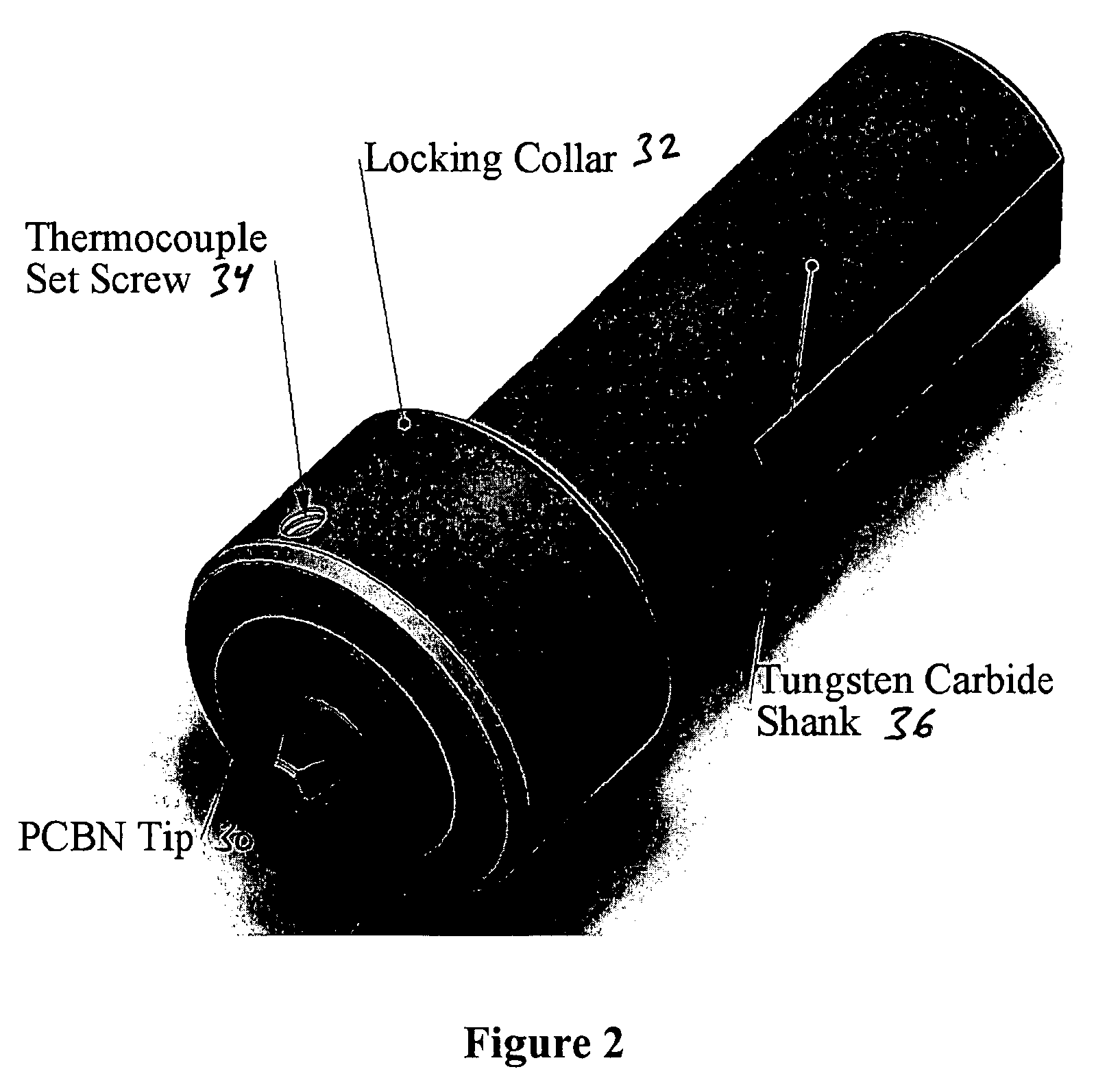
A fastener component is formed from aluminum or aluminum-alloy material having a head portion and an elongate shank portion, the shank portion having an end and intermediate or transition region. At least the shank portion of the fastener is cold-worked or heat-treated to an intermediate hardness stage, typically to a T6 condition. The intermediate region of the shank portion is further cold-worked to harden or strengthen the intermediate region of the shank portion with respect to the end of the shank, typically to a T8 condition. The aluminum or aluminum-alloy material of the component advantageously has ultra-fine grain size of less than about 5 microns. The ultra-fine grain size is advantageously obtained by friction stir processing (FSP) or equal angle extrusion (EAE).
Owner:THE BOEING CO
In-situ interlocking of metals using additive friction stir processing
ActiveUS20160175982A1Additive manufacturing apparatusVehicle componentsFilling materialsFriction stir processing
A method for joining materials using additive friction stir techniques is provided. The method joins a material to a substrate, especially where the material to be joined and the substrate are dissimilar metals. One such method comprises (a) providing a substrate with one or more grooves; (b) rotating and translating an additive friction-stir tool relative to the substrate; (c) feeding a filler material through the additive friction-stir tool; and (d) depositing the filler material into the one or more grooves of the substrate. Translation and rotation of the tool causes heating and plastic deformation of the filler material, which flows into the grooves of the substrate resulting in an interlocking bond between the substrate and filler material. In embodiments, the depositing of the filler material causes deformation of the grooves in the substrate and an interlocking configuration between the grooves of the substrate and the filler material results.
Owner:MELD MFG CORP
Stir processed cast aluminum-scandium structures and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20070297935A1Improve mechanical propertiesImprove corrosion resistanceAluminium compoundsGallium/indium/thallium compoundsFriction stir processingScandium
Friction stir processing is applied to an aluminum-scandium alloy workpiece in either a wrought or cast state including scandium-containing precipitates. The process selectively modifies the microstructure of the aluminum-scandium workpiece, for example, by reducing grain size and recrystallization of the substrate. Benefits include increased physical properties of the aluminum-scandium alloys as well as the ability to form unique alloy structures.
Owner:LANGAN TIMOTHY +2
Preparation method of composite high-speed steel wear-resistant layer on aluminum alloy surface
InactiveCN102284786AUniform mosaicImprove wear resistanceMolten spray coatingNon-electric welding apparatusThermal sprayingHardness
The invention relates to a method for preparing a composite high-speed steel wear-resistant layer on the surface of an aluminum alloy. First, a high-speed steel coating with a thickness of 0.2 mm to 1.5 mm is thermally sprayed on the surface of an aluminum alloy, and then the thermally sprayed high-speed steel is processed by friction stir processing. The coating is evenly inlaid and fused in the aluminum alloy surface layer to form a good wear-resistant layer, and a metallurgical bond is formed between the coating and the substrate. In the invention, the thermal spraying coating is evenly inlaid and fused in the surface layer of the aluminum alloy through friction stirring processing to form a good wear-resistant layer, and a metallurgical bond is formed between the coating and the substrate. The hardness of the wear-resistant layer of the high-speed steel obtained by the invention is greater than 520HV, and the bonding strength is greater than 70MPa.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Friction Stir Fabrication
ActiveUS20100285207A1Liquid surface applicatorsPressure inorganic powder coatingNanocrystalMetal matrix composite
A low-temperature friction-based coating method termed friction stir fabrication (FSF) is disclosed, in which material is deposited onto a substrate and subsequently stirred into the substrate using friction stir processing to homogenize and refine the microstructure. This solid-state process is capable of depositing coatings, including nanocrystalline aluminum and / or metal matrix composites and the like, onto substrates such as aluminum at relatively low temperatures. A method of making rod stock for use in the FSF process is also disclosed.
Owner:MELD MFG CORP
Friction stirring and its application to drill bits, oil field and mining tools, and components in other industrial applications
InactiveUS20120273555A1Improve toughnessLong life cycleLaminationLamination apparatusFriction stir processingEquipment use
Owner:MEGASTIR TECH
Controlled speed friction stir tool probe bodies having non-linear, continuous, monotonically-decreasing curved axial profiles and integrated surface features
InactiveUS20160008918A1Welding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesFriction stir processingBiomedical engineering
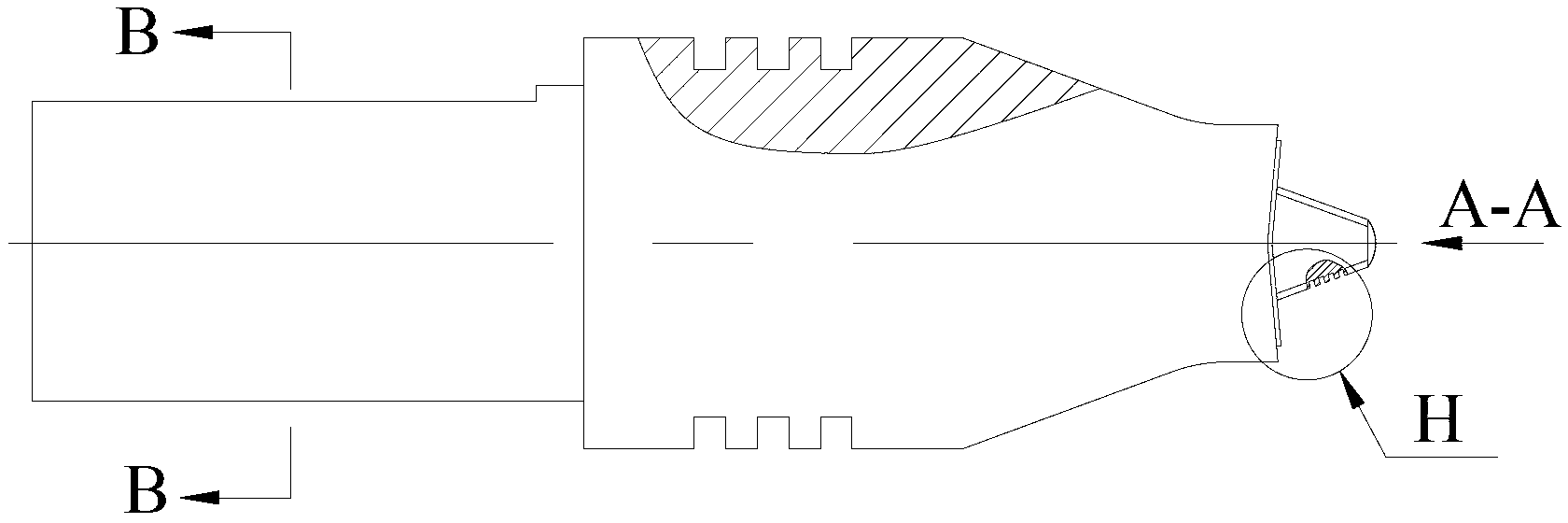
A friction stir processing tool and method for manufacturing the same are provided. The tool includes a non-consumable, interchangeable friction stir probe body. The tool includes a material flow path defined by an outer surface of a probe body, which has a non-linear, continuous, monotonically-decreasing axial profile. The probe body is adapted to engage a workpiece material to perform a friction stir process by rotating about an axis thereof thereby directing a weld material toward a distal end of the probe body along the flow path. The flow path varies in pitch as the lateral cross-sectional dimension of the probe body decreases toward the distal end thereby causing the weld material to maintain a controlled speed as it travels along the flow path. Geometric surface features such as threads, helical grooves, ridges, flutes, and / or flats, integrated with the probe body may define the flow path.
Owner:BURFORD DWIGHT A +1
Method for developing fine grained, thermally stable metallic material
InactiveUS20110076419A1Radiation applicationsPretreated surfacesAbnormal grain growthMetallic materials
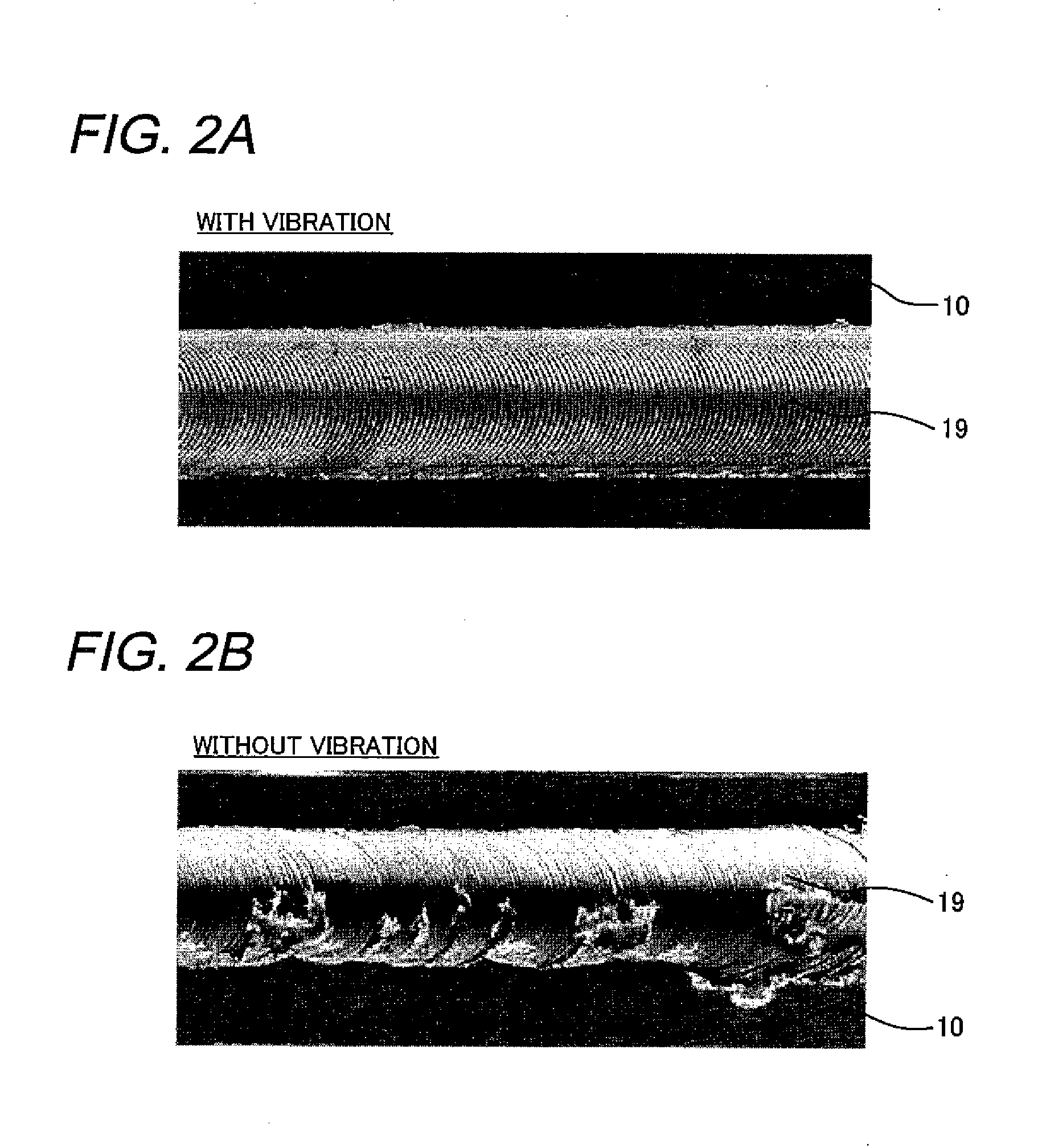
A method for developing fine grained, thermally stable metallic material in which friction stir welding or friction stir processing is performed along at least a portion of the material. Thereafter, a thin layer is removed from either side, or both sides of the material to eliminate the origin of abnormal grain growth occurring when the friction stir welded or friction stir processed material is subjected to subsequent hot forming processes. A sheet of extraneous material is optionally attached to either side, or both sides of the material prior to the friction stir welding or friction stir processing, and this extraneous material is removed after the friction stir welding or friction stir processing. A layer containing pinning particles or a sheet of extraneous material containing pinning particles is further optionally introduced on either side, or both sides of the material prior to the friction stir processing.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for preparing aluminum-based composite material plate by friction stir
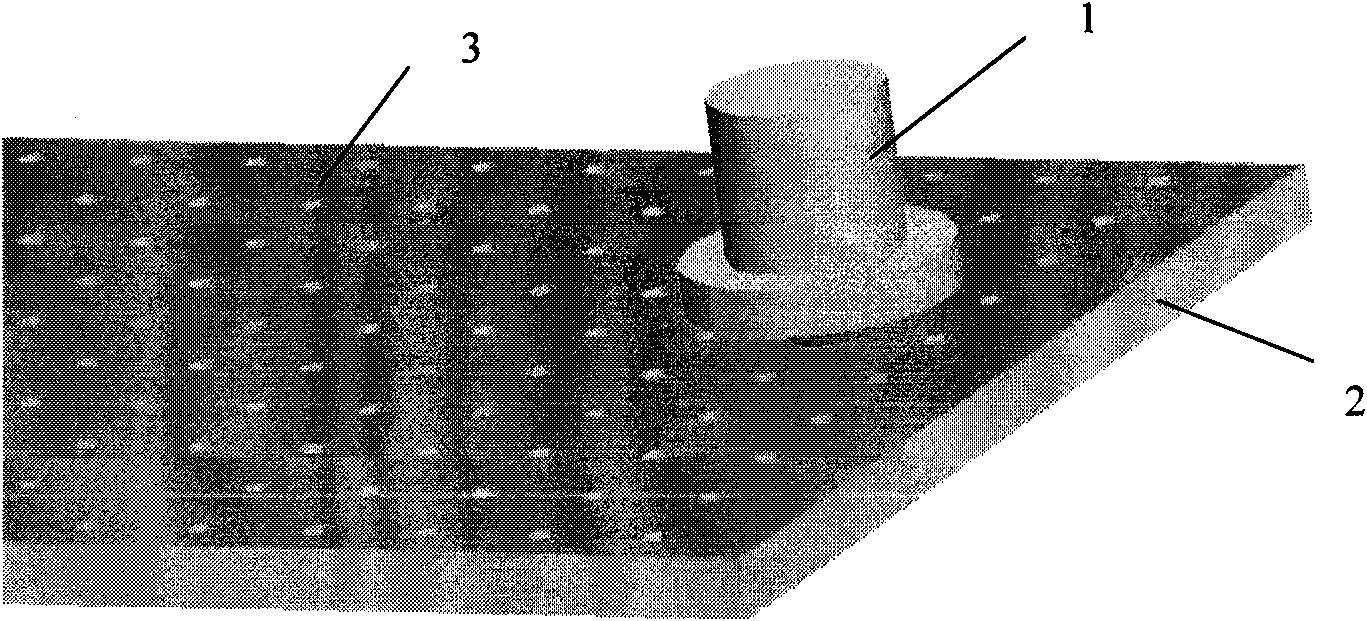
A method for preparing an aluminum-based composite material plate by friction stir comprises the following steps of: (1) forming a plurality of holes on an aluminum plate of base material, and placing reinforcing particles in the holes, thus forming an intermediate plate; (2) holding and arranging the intermediate plate between aluminum plates of surface layer, the component of which is the same with that of the aluminum plate of base material, thus forming a composite plate; (3) carrying out friction-stir processing to the composite plate by utilizing a stirring head, thus obtaining the aluminum-based composite material plate. By using the prepared Ti / Al composite plate, Ti particles are distributed uniformly in the plate and refined obviously, and particles of large size are reduced. The prepared aluminum-based composite material has high hardness which is about 2 to 3 times of matrix hardness.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Rotary holding device for gripping tool material at elevated temperatures through multiple collar assembly
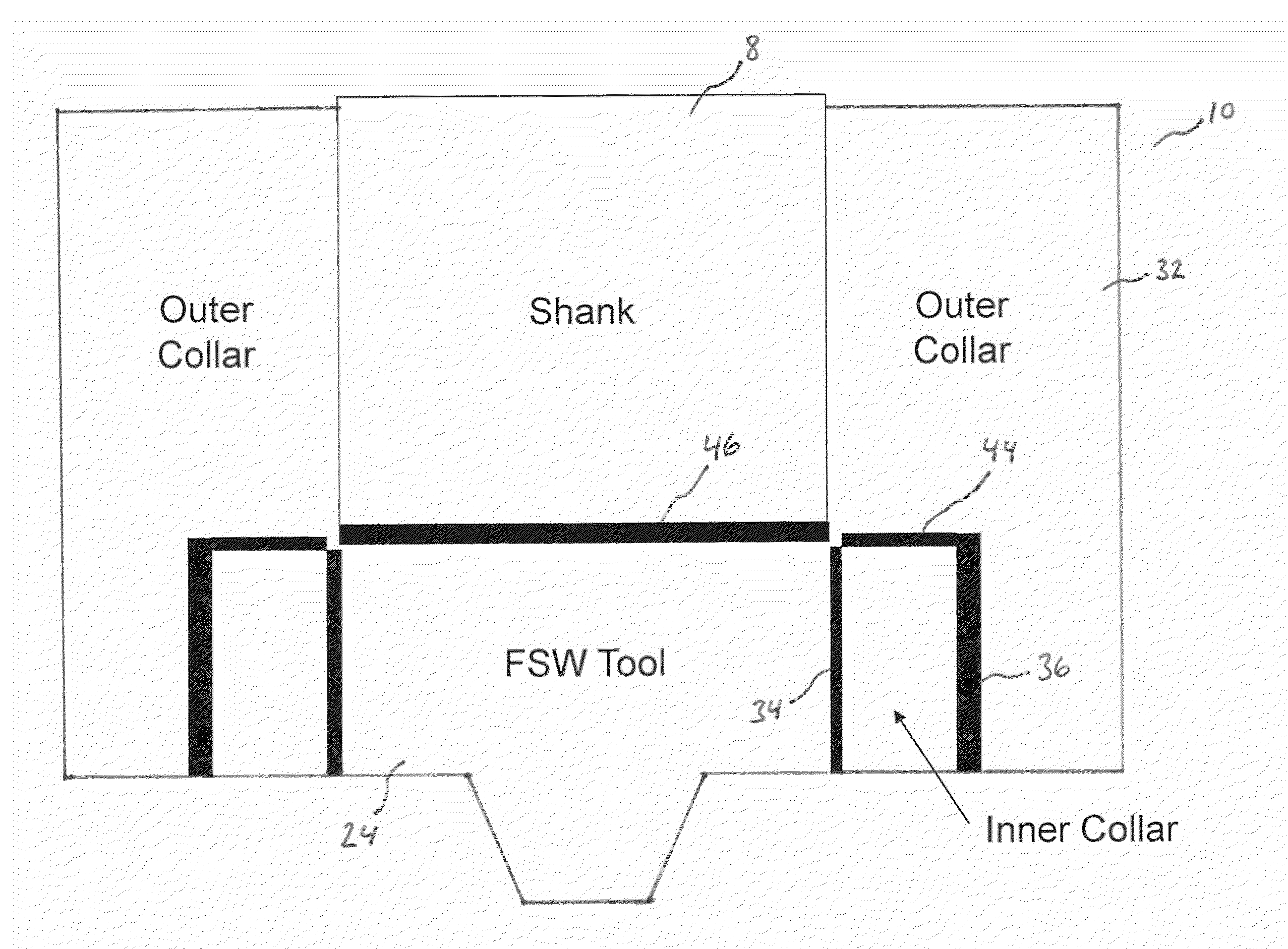
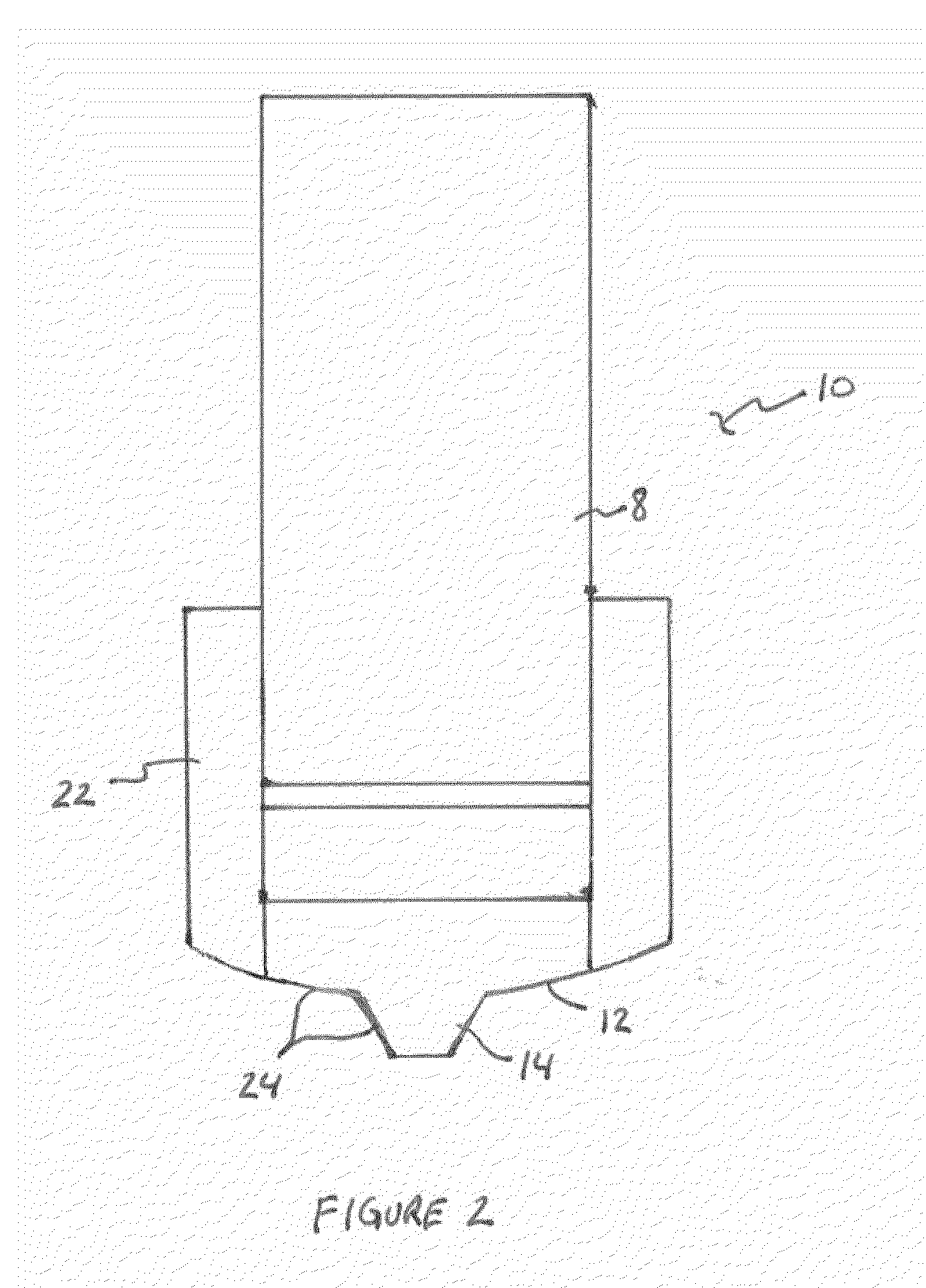
ActiveUS20100038832A1Improve stressImprove gripWelding/cutting auxillary devicesBlast furnace detailsEngineeringFriction stir processing
A tool is provided that is capable of friction stir processing, friction stir mixing, and friction stir welding of high melting temperature and low melting temperature materials, wherein the collar is now divided into at least an inner and an outer collar coupled to the shank and the FSW tip, wherein new thermal barriers enable expansion of the inner collar to be directed inward to thereby create compression on the FSW tip instead of allowing the FSW tip to become loose in the tool at elevated temperatures.
Owner:MAZAK CORP
Friction stir fabrication
ActiveUS8636194B2Liquid surface applicatorsWelding/cutting auxillary devicesNanocrystalline siliconMetal matrix composite
A low-temperature friction-based coating method termed friction stir fabrication (FSF) is disclosed, in which material is deposited onto a substrate and subsequently stirred into the substrate using friction stir processing to homogenize and refine the microstructure. This solid-state process is capable of depositing coatings, including nanocrystalline aluminum and / or metal matrix composites and the like, onto substrates such as aluminum at relatively low temperatures. A method of making rod stock for use in the FSF process is also disclosed.
Owner:MELD MFG CORP
Stir head for friction stir machining and fabrication of metal matrix composite
InactiveCN103286435AImprove liquidityEvenly distributedNon-electric welding apparatusEngineeringMetal matrix composite
The invention relates to a stir head for friction stir machining and fabrication of metal matrix composite. The stir head for friction stir machining and fabrication of the metal matrix composite is of an integrated structure which is composed of a stir pin, a shaft shoulder and a clamping body. One end of the shaft shoulder is connected with the clamping body, the center of the other end of the shaft shoulder is connected with the stir pin, the end face of the end, at which the stir pin is fixedly arranged, of the shaft shoulder is of a concave shape, a lug boss is arranged on the end face, and a spiral or circular arc groove is formed in the periphery of the stir pin on the lug boss. The shaft shoulder is provided with a lug boss structure, the quantity of fins is reduced and the quantity of extrusion outputs is increased notably by means of the outer shaft shoulder and the concave bottom surface, the mobility of plastic metal can be improved by means of a groove of an inner shaft shoulder bottom surface and the side plane of the stir pin, and thus particles are distributed in a matrix evenly.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Process for improving strength of friction stir welding (FSM) joint for discontinuously reinforced aluminum (DRA) matrix composites
ActiveCN102107327AAchieve weldingExpanded range of welding parametersNon-electric welding apparatusMechanical propertyQuenching
The invention relates to aluminum matrix composites and the field of welding, specially provides a process for improving the strength of a friction stir welding (FSM) joint for discontinuously reinforced aluminum (DRA) matrix composites, which is suitable for DRA matrix composites capable of being subjected to reinforced heat treatment. The process comprises the following steps: carrying out solution treatment on aluminum matrix composites which can be subjected to reinforced heat treatment; after the quenching operation is performed, carrying out friction stir welding on the obtained object within four hours; and carrying out natural ageing or artificial aging on the obtained weld assembly in the air according to the application demands, or carrying out reinforced heat treatment again onthe weld assembly by using a commonly-used industrial process. By using the welding process provided by the invention, the weldability of DRA matrix composites can be improved obviously, the tool wear can be reduced, and the mechanical property of a composite joint can be improved.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thick-section metal forming via friction stir processing
InactiveUS6866180B2Minimize formation of crackReduce flow stressWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesMetal formingRoom temperature
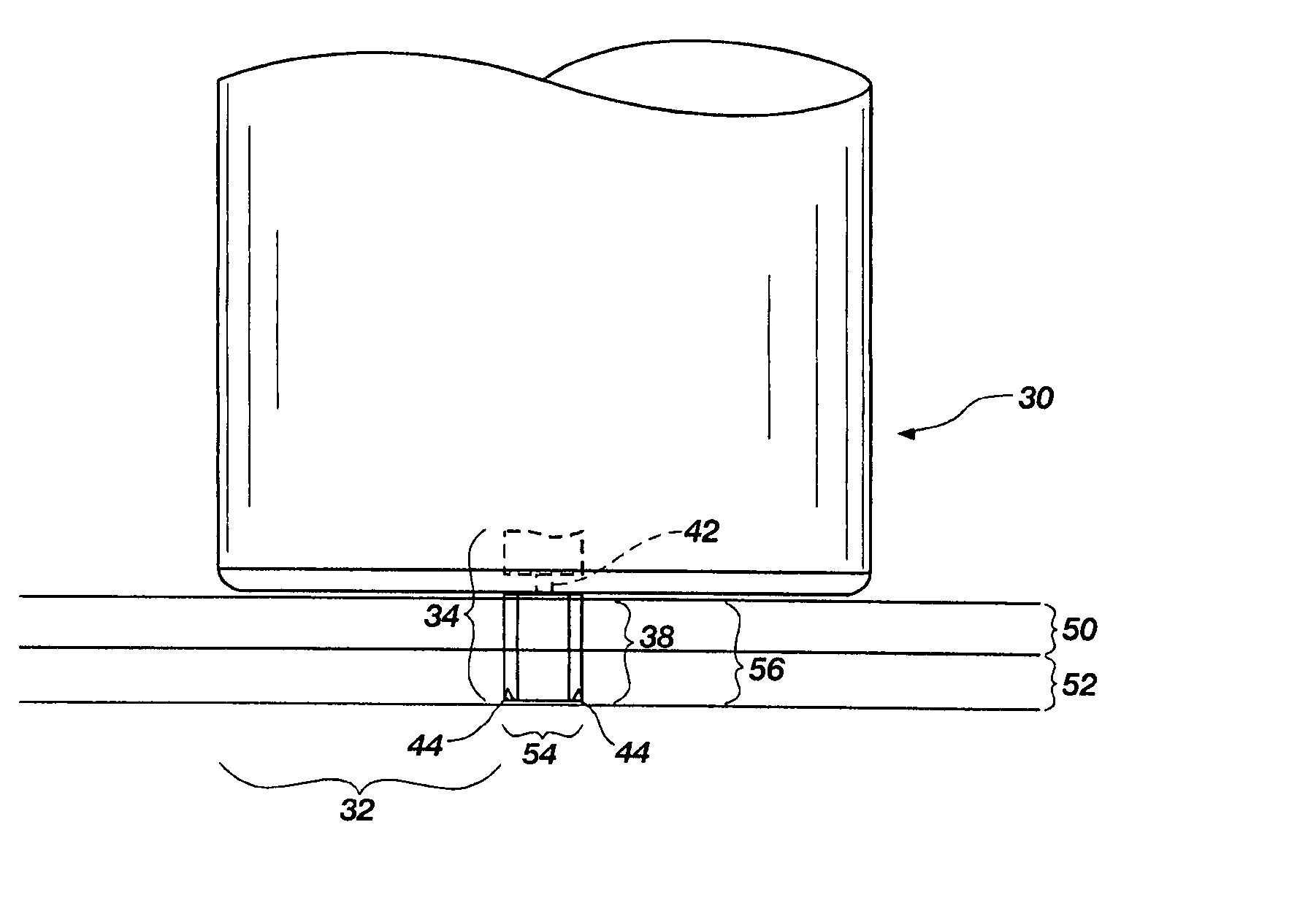
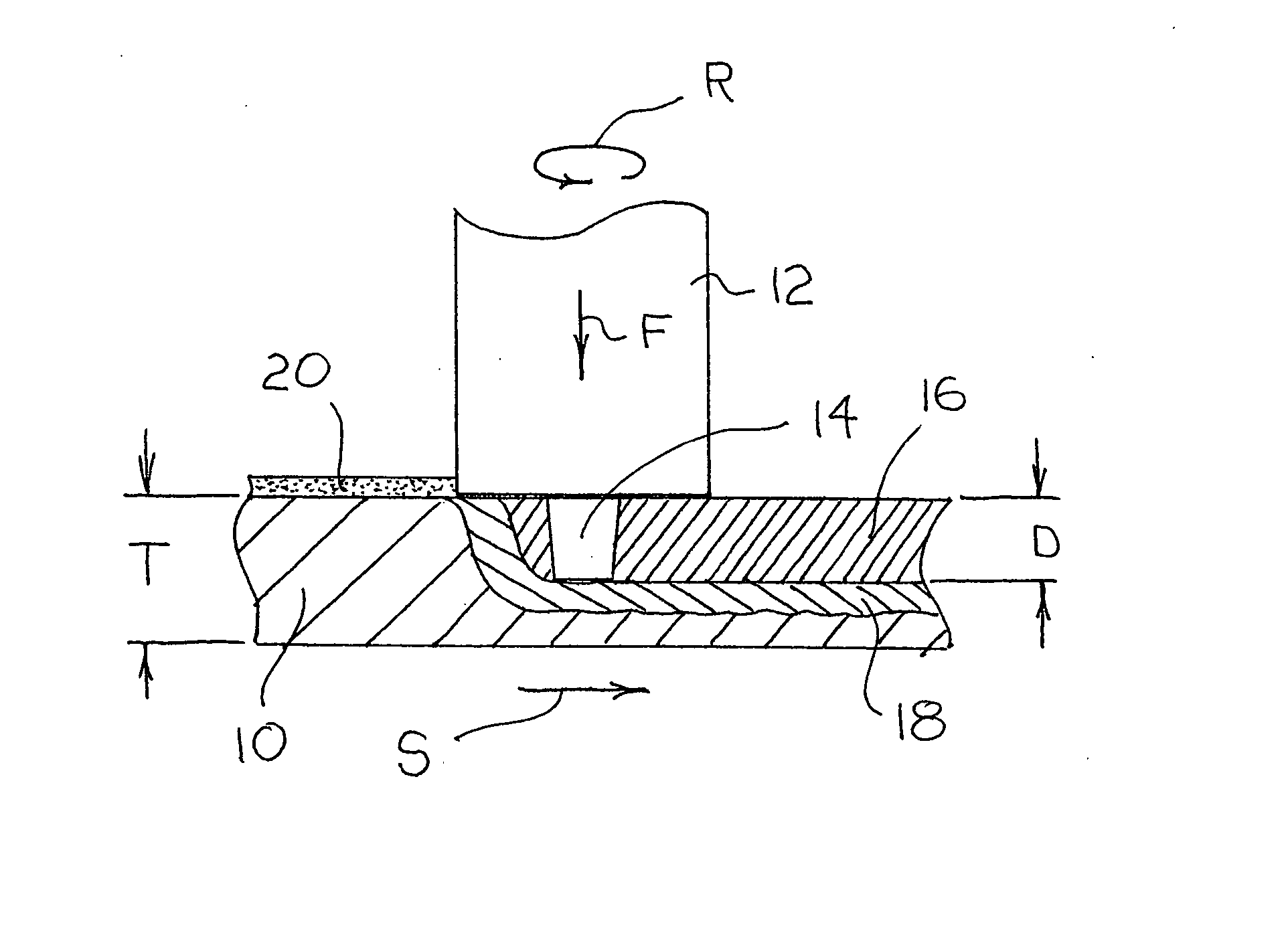
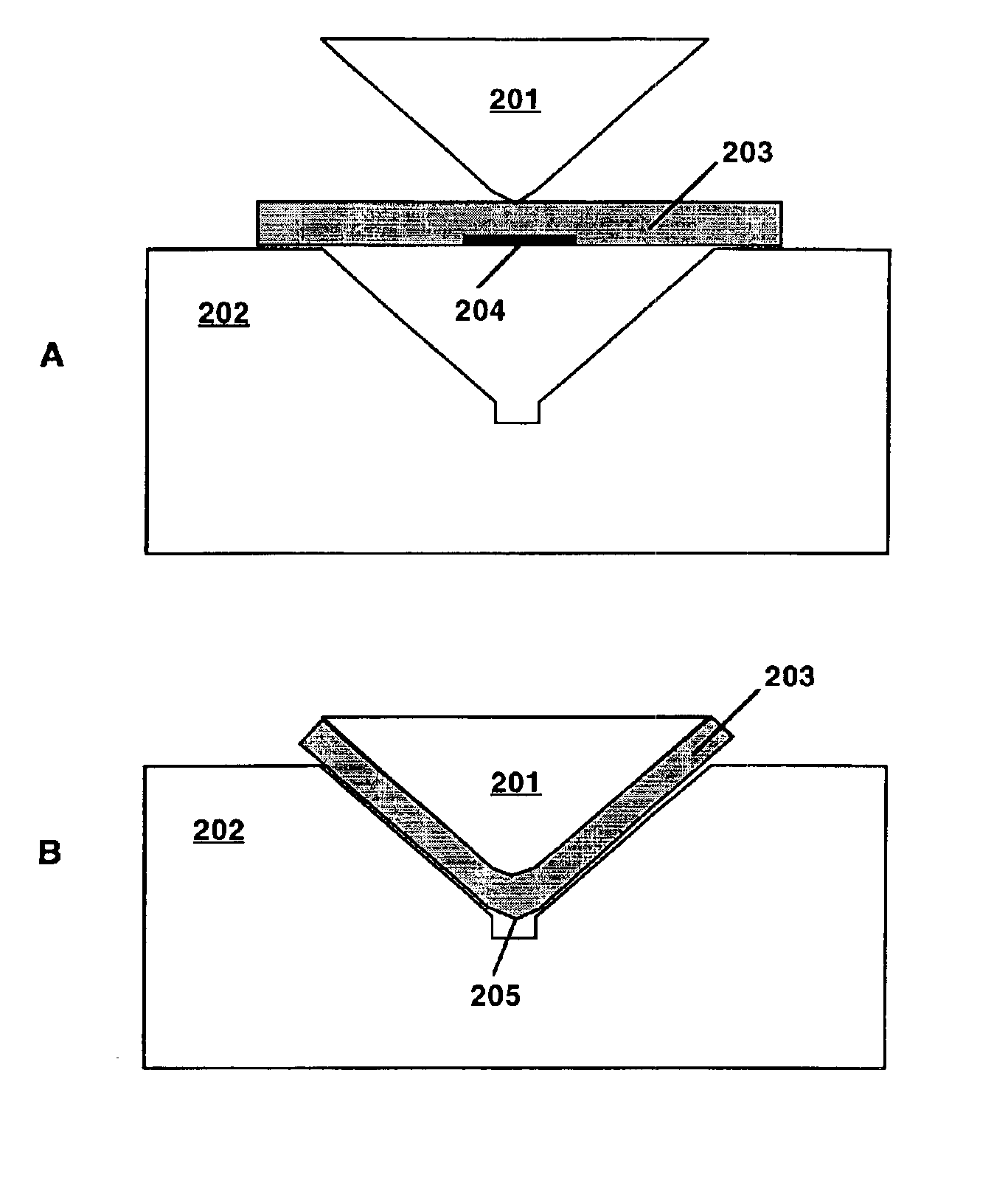
Friction stir processing (FSP) modifies the surface microstructure of metals so that thick-section metal workpieces can be bent over large angles without formation of surface cracks. A thick 2519-T8 aluminum plate (25.4 mm thick and 50.8 mm wide) was friction stir processed across the pre-tensile surface to a depth of 6.3 mm, and was then bent at room temperature over a punch with radius 38.1 mm into a v-shaped die to an 80° bend angle. Whereas unprocessed workpieces of this type exhibited surface cracking at 31° bend angle and failed at 40° bend angle, no cracking was evident for the friction stir processed workpiece up to 80° bend angle.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
In-situ interlocking of metals using additive friction stir processing
ActiveUS9511446B2Additive manufacturing apparatusVehicle componentsFilling materialsFriction stir processing
A method for joining materials using additive friction stir techniques is provided. The method joins a material to a substrate, especially where the material to be joined and the substrate are dissimilar metals. One such method comprises (a) providing a substrate with one or more grooves; (b) rotating and translating an additive friction-stir tool relative to the substrate; (c) feeding a filler material through the additive friction-stir tool; and (d) depositing the filler material into the one or more grooves of the substrate. Translation and rotation of the tool causes heating and plastic deformation of the filler material, which flows into the grooves of the substrate resulting in an interlocking bond between the substrate and filler material. In embodiments, the depositing of the filler material causes deformation of the grooves in the substrate and an interlocking configuration between the grooves of the substrate and the filler material results.
Owner:MELD MFG CORP
In-situ reaction method for preparing aluminum-base composite material
InactiveCN102717182AGood dimensional stabilitySmall sizeNon-electric welding apparatusFriction stir processingMachine tool
The invention discloses an in-situ reaction method for preparing an aluminum-base composite material. The in-situ reaction method is characterized by comprising arranging at least one groove on the surface of an aluminum material to be processed, and forming a processing area; placing the aluminum material to be processed on a friction stir processing machine tool and fixing the aluminum material by a fixture; filling and compacting packing which is about to be in in-situ reaction with a matrix to generate an enforcement in the grooves, and enabling the packing to be flush with the surface of the aluminum material; and carrying out friction stirring processing for the aluminum plate for multiple times by the aid of a stirrer with the size matching with that of the processing area to obtain the aluminum-base composite material. The aluminum-base composite material prepared by the method has the advantages that sizes of in-situ generated reinforced phases are effectively reduced, and dispersion degree of the in-situ generated reinforced phases is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Stir forming apparatus and method
ActiveUS7448528B2Improve material performanceWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesEngineeringFriction stir processing
An apparatus and method for forming a workpiece to a desired, non-planar configuration are provided. At least one friction stir forming tool, having a shoulder and a pin, is used to urge the workpiece to the desired configuration and friction stir form the workpiece. The forming tool can urge the workpiece against a contour surface of a die or a shoulder that is opposite the structural member from the tool. Thus, the forming tool plasticizes a portion of the workpiece and urges the workpiece to the desired configuration. In addition, the material properties of the workpiece can be improved by the friction stir processing.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Methods of treating hardbanded joints of pipe using friction stir processing
InactiveUS20100038408A1Improve propertiesMetal working apparatusTubular articlesMetallurgyFriction stir processing
A method for treating a wear reducing material welded to a surface of a tool used in a wellbore operation that includes friction stirring the wear reducing material into the surface of the tool is disclosed. Method for improving the properties of a wear reducing material on a tool are also disclosed.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Solid state joining using additive friction stir processing
ActiveUS9511445B2Reduce breakageReduce wearAdditive manufacturing apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesFilling materialsFriction stir processing
Owner:MELD MFG CORP
Three-body joining using friction stir processing techniques
ActiveUS20110073634A1Increase rotation speedRotational speedWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesEngineeringFriction stir processing
A friction stir tool is provided to perform friction stir riveting using a partially consumable pin, wherein the pin includes a cutting edge on a bottom surface thereof, wherein the tool is rotated at a first speed to enable cutting by the pin into a first material that is overlapping a second material, wherein after the pin has cut to a sufficient depth, the rotational speed of the tool is increased to thereby enable plasticization of the consumable pin, the first material, and the second material, wherein the tool is then rapidly decelerated until stopped, enabling diffusion bonding between the pin, the first material and the second material.
Owner:MAZAK CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com