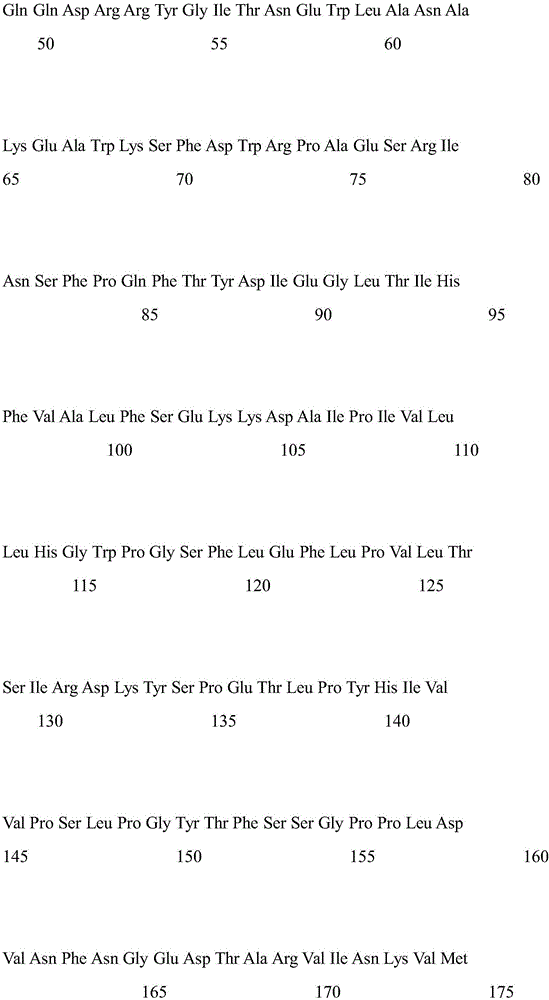
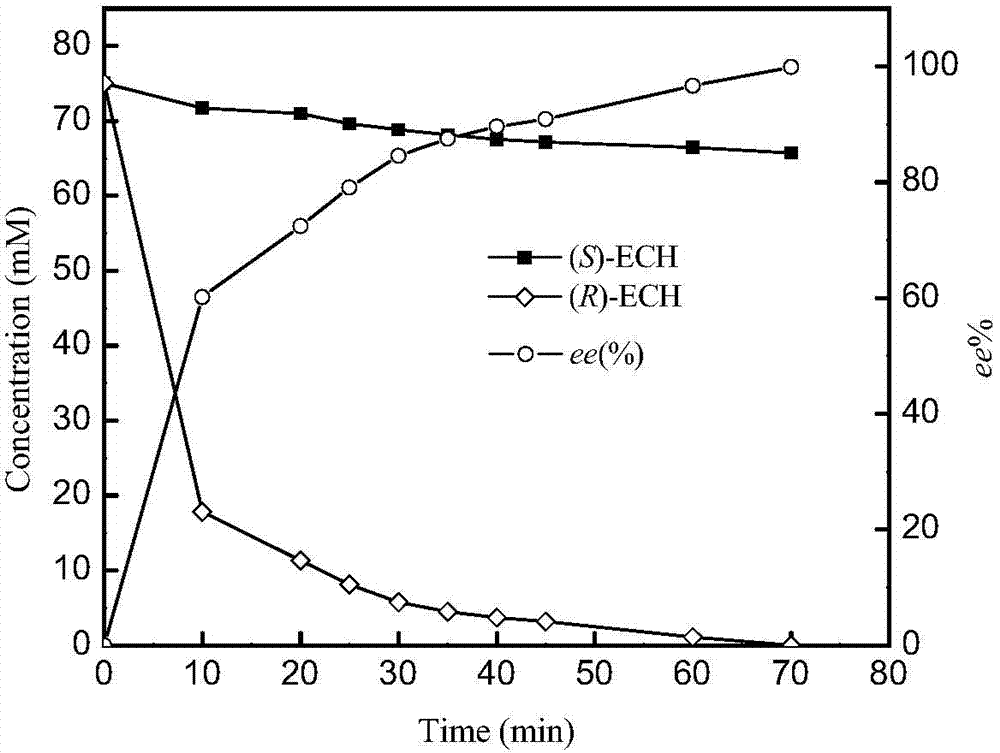
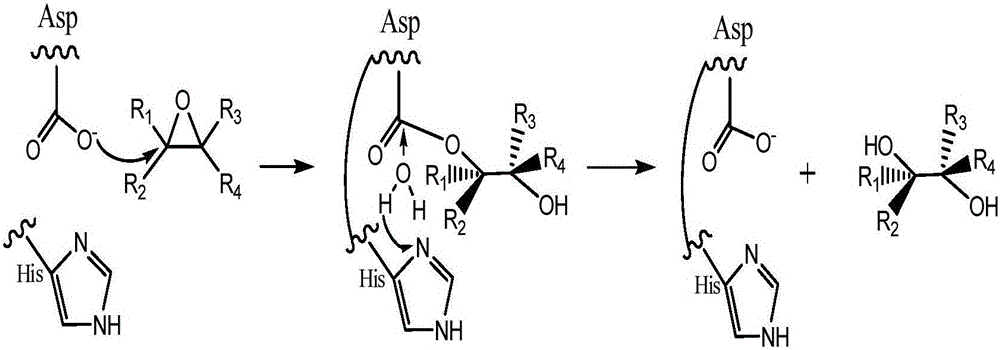
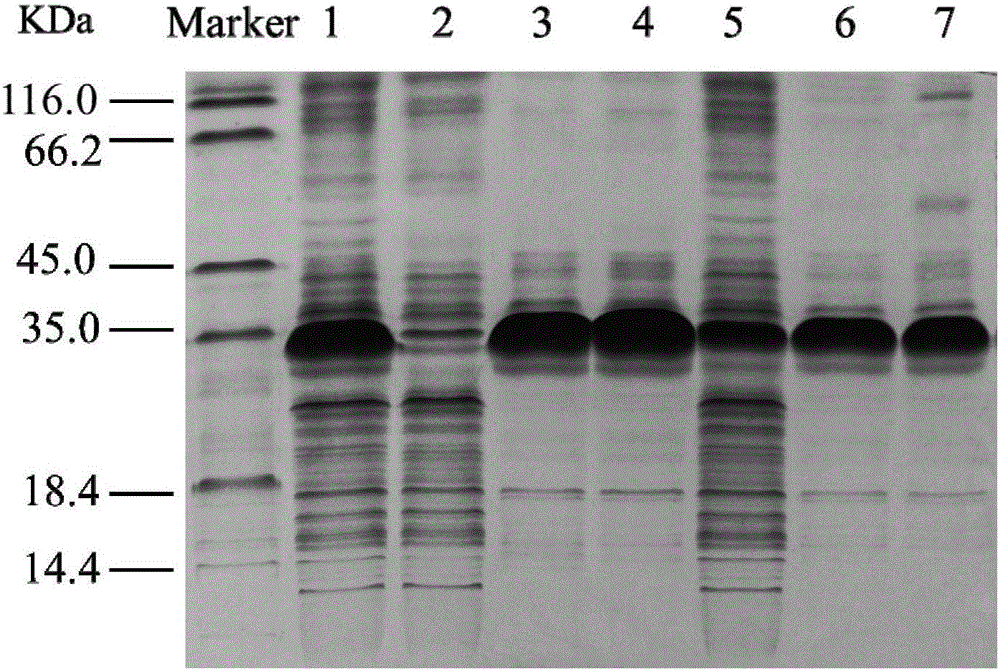
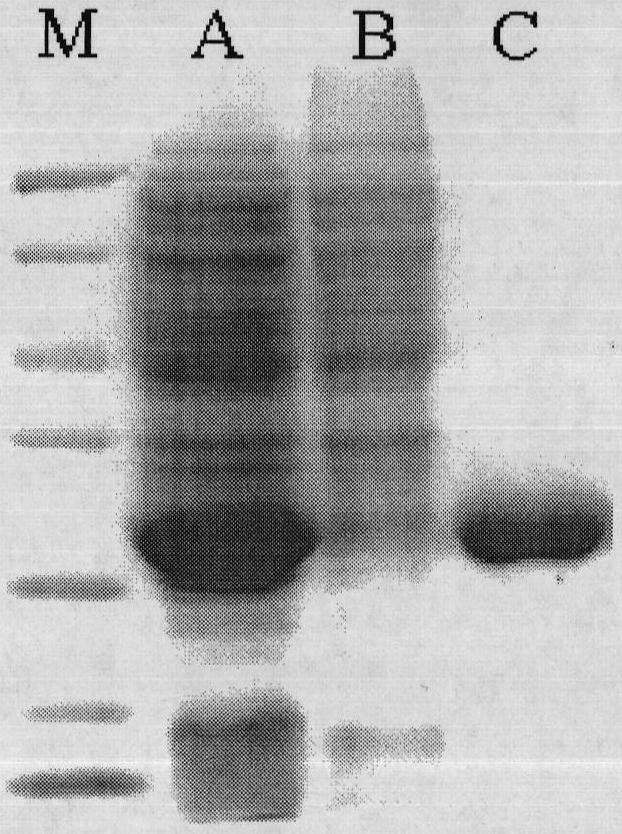
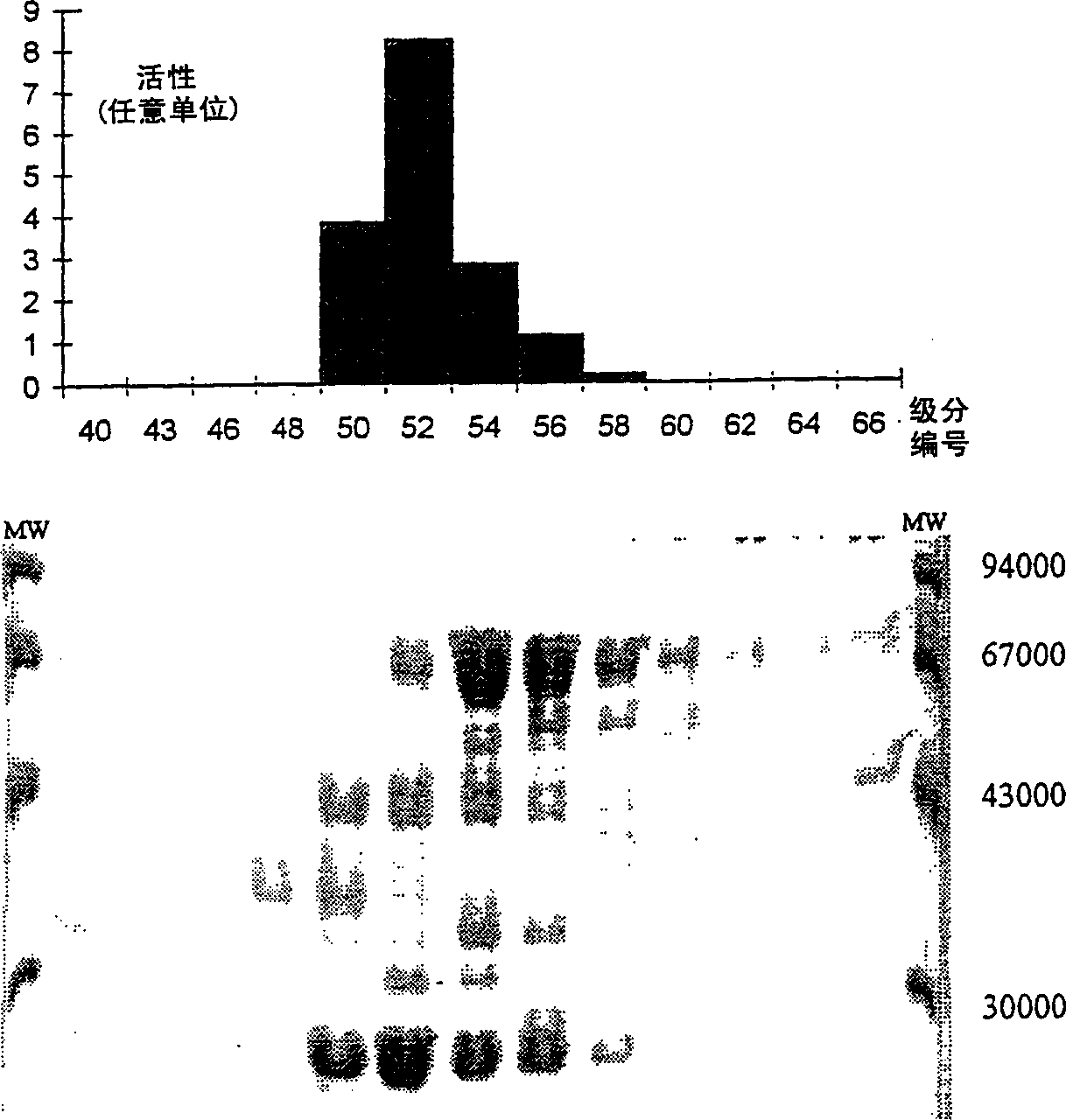
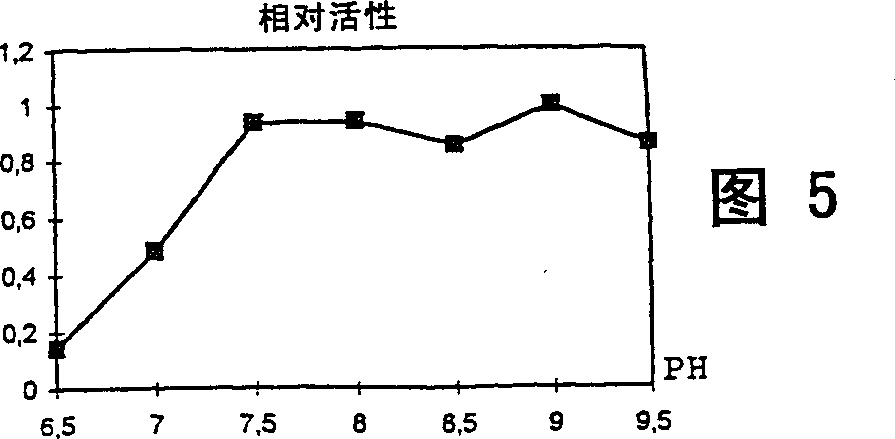
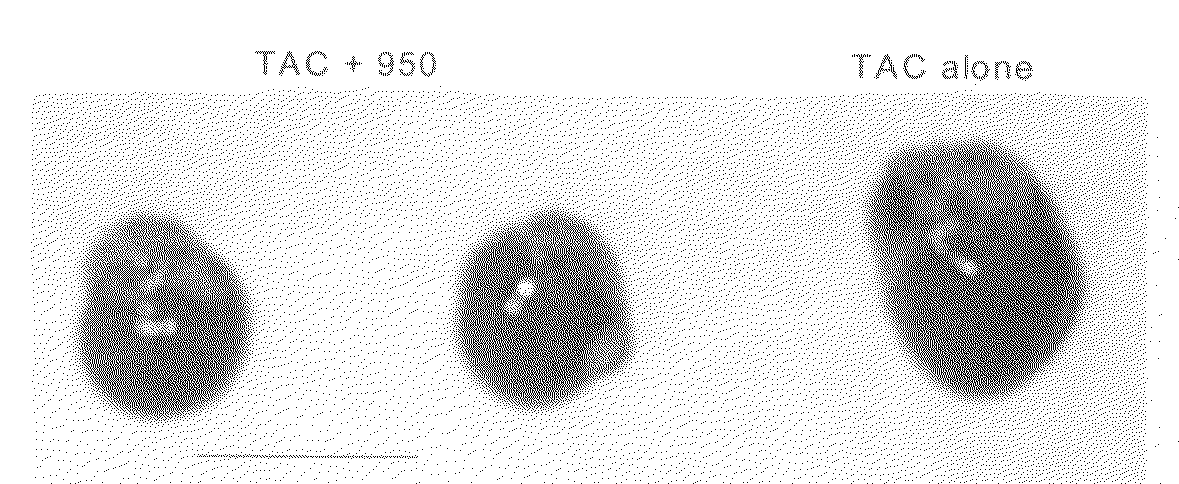
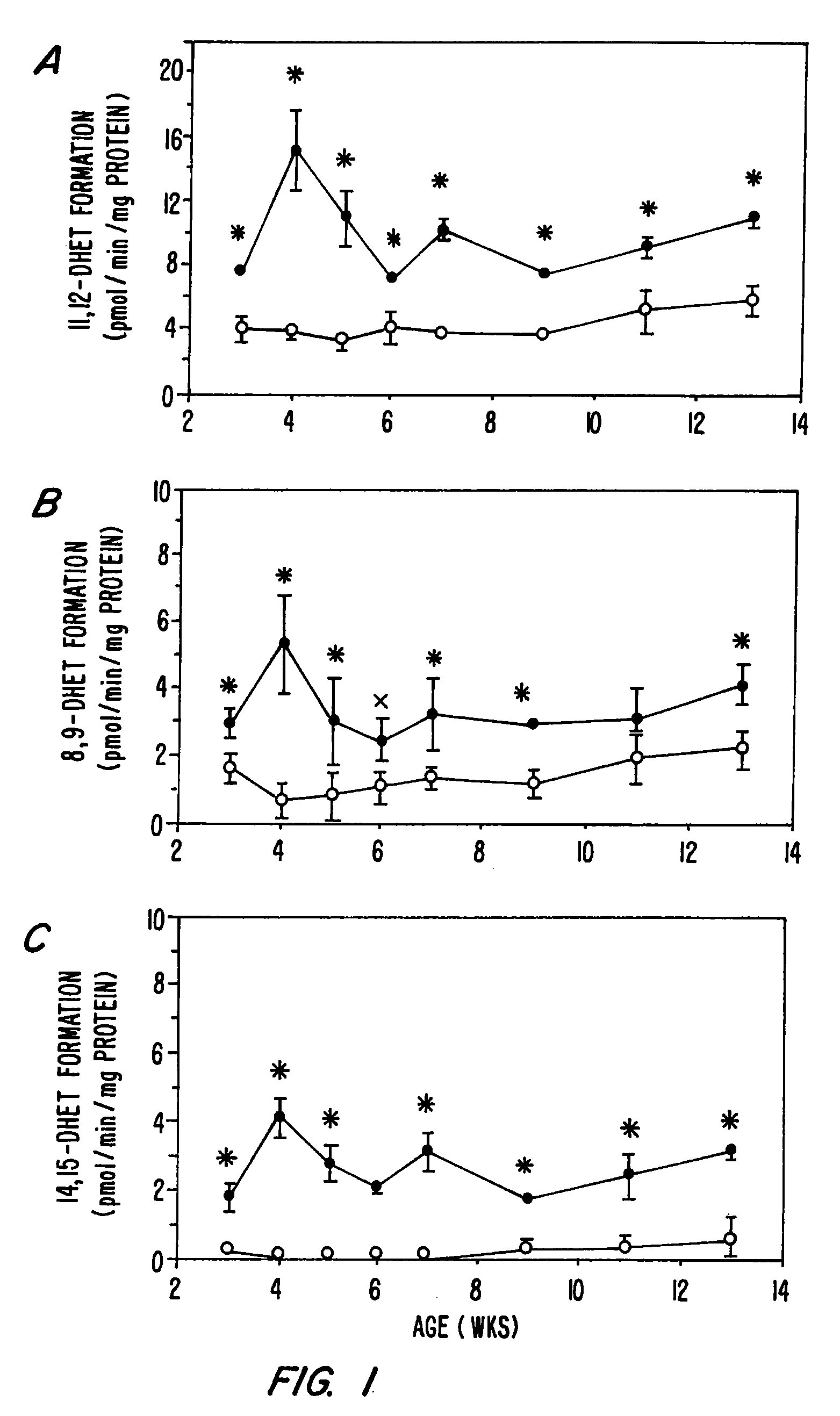
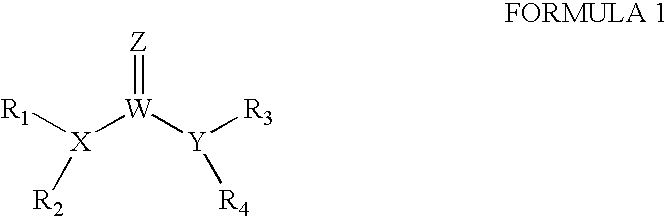Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
105 results about "Epoxide hydrolase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
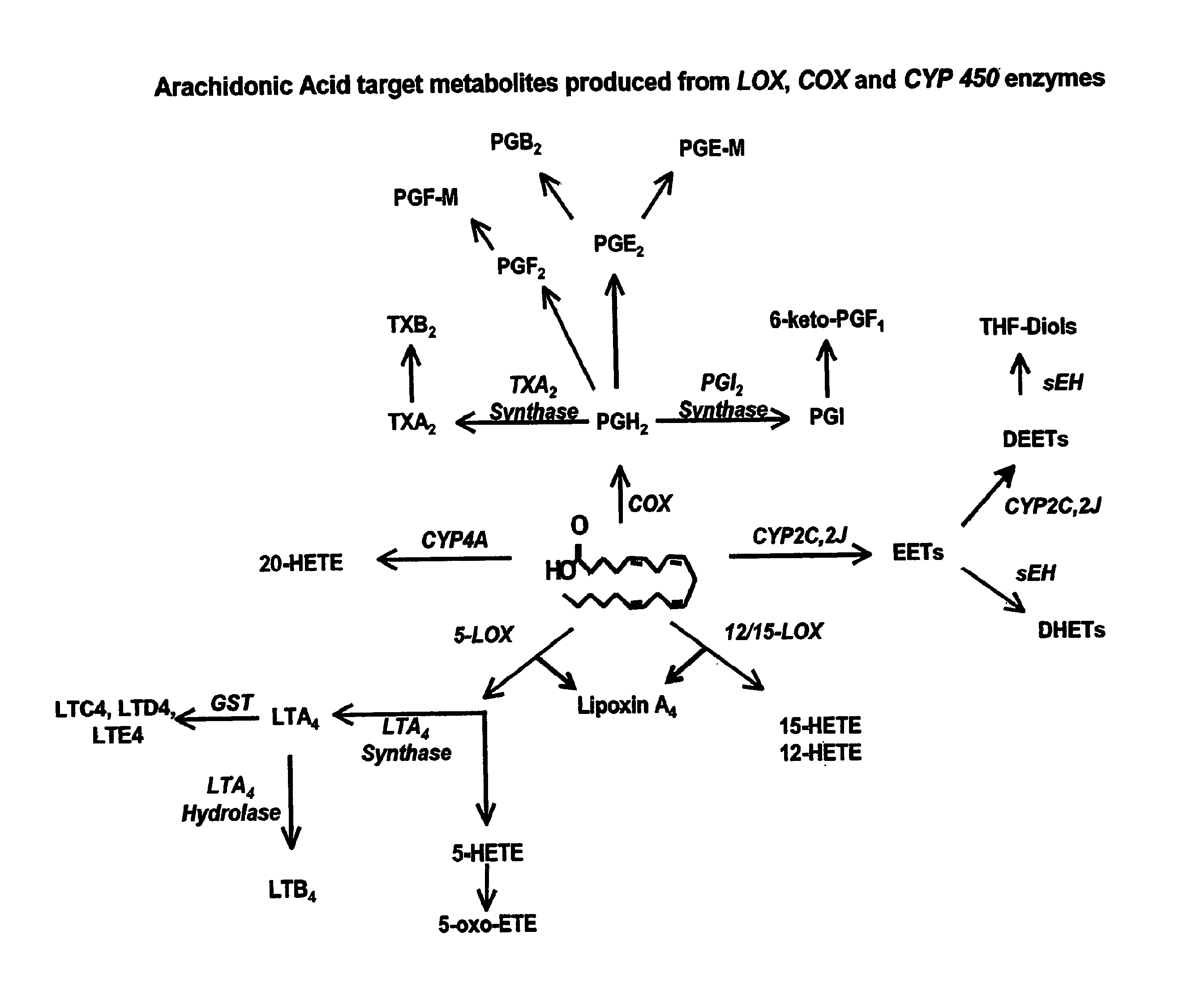
Epoxide hydrolases (EH's), also known as epoxide hydratases, are enzymes that metabolize compounds that contain an epoxide residue; they convert this residue to two hydroxyl residues through a dihydroxylation reaction to form diol products. Several enzymes possess EH activity. Microsomal epoxide hydrolase (epoxide hydrolase 1, EH1, or mEH), soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH, epoxide hydrolase 2, EH2, or cytoplasmic epoxide hydrolase), and the more recently discovered but not as yet well defined functionally, epoxide hydrolase 3 (EH3) and epoxide hydrolase 4 (EH4) are structurally closely related isozymes. Other enzymes with epoxide hydrolase activity include leukotriene A4 hydrolase, Cholesterol-5,6-oxide hydrolase, MEST (gene) (Peg1/MEST), and Hepoxilin-epoxide hydrolase. The hydrolases are distinguished from each other by their substrate preferences and, directly related to this, their functions.
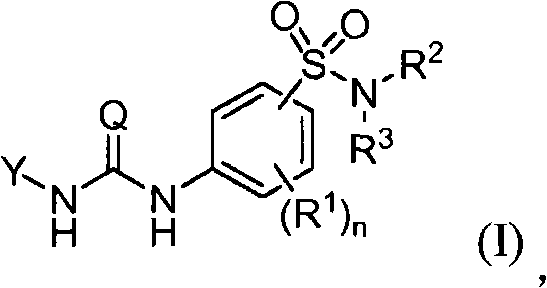
Inhibitors of epoxide hydrolases for the treatment of hypertension
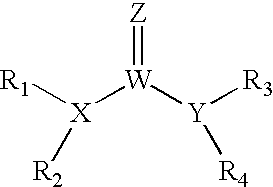
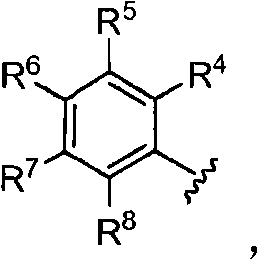
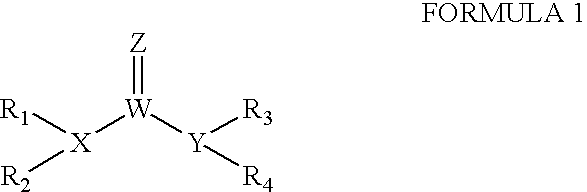
The invention provides compounds that inhibit epoxide hydrolase in therapeutic applications for treating hypertension. A preferred class of compounds for practicing the invention have the structure shown by Formula Iwherein Z is oxygen or sulfur, W is carbon phosphorous or sulfur, X and Y is each independently nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur, and X can further be carbon, at least one of R1-R4 is hydrogen, R2 is hydrogen when X is nitrogen but is not present when X is sulfur or oxygen, R4 is hydrogen when Y is nitrogen but is not present when Y is sulfur or oxygen, R1 and R3 is each independently C1-C20 substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, acyl, or heterocyclic.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE +2
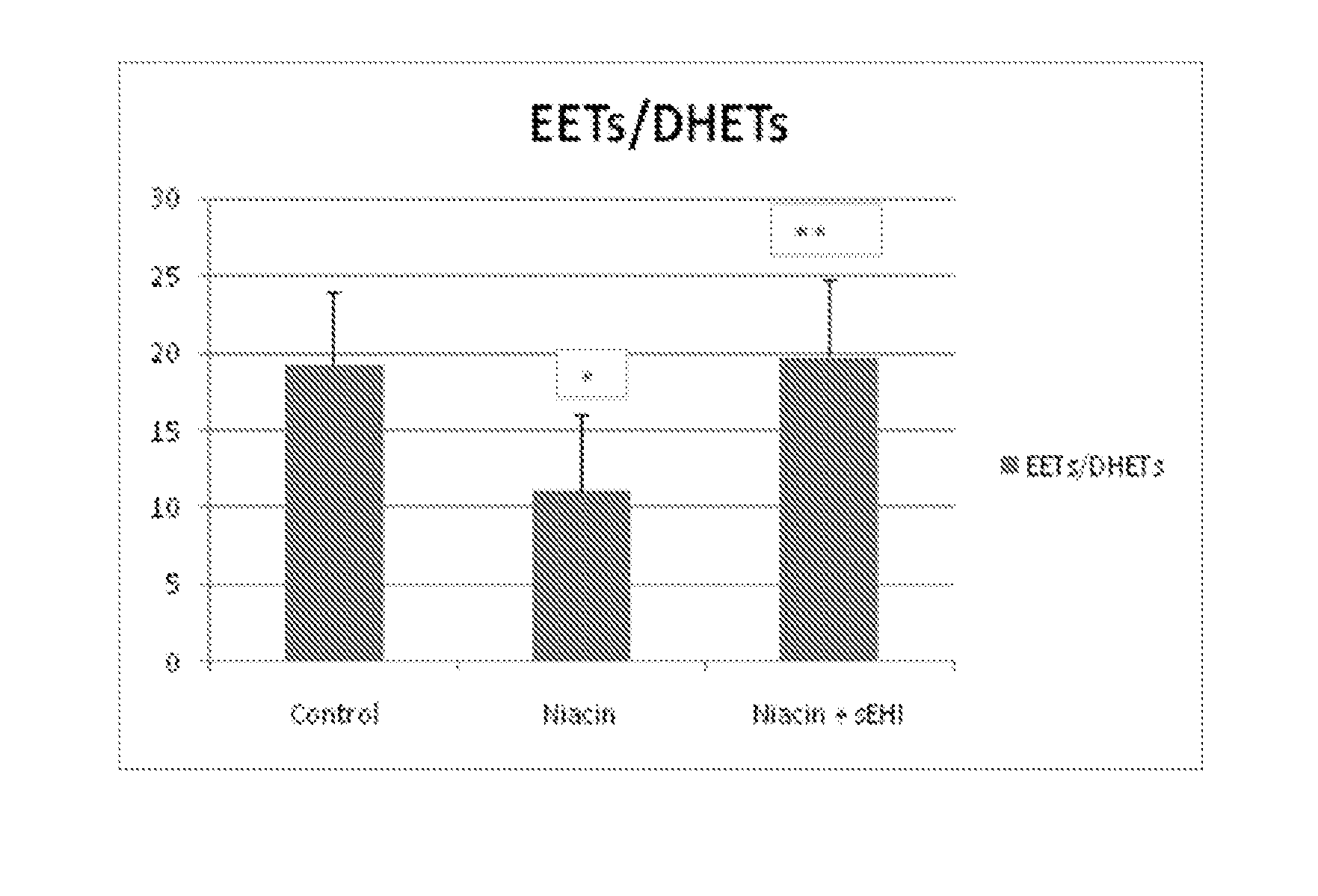
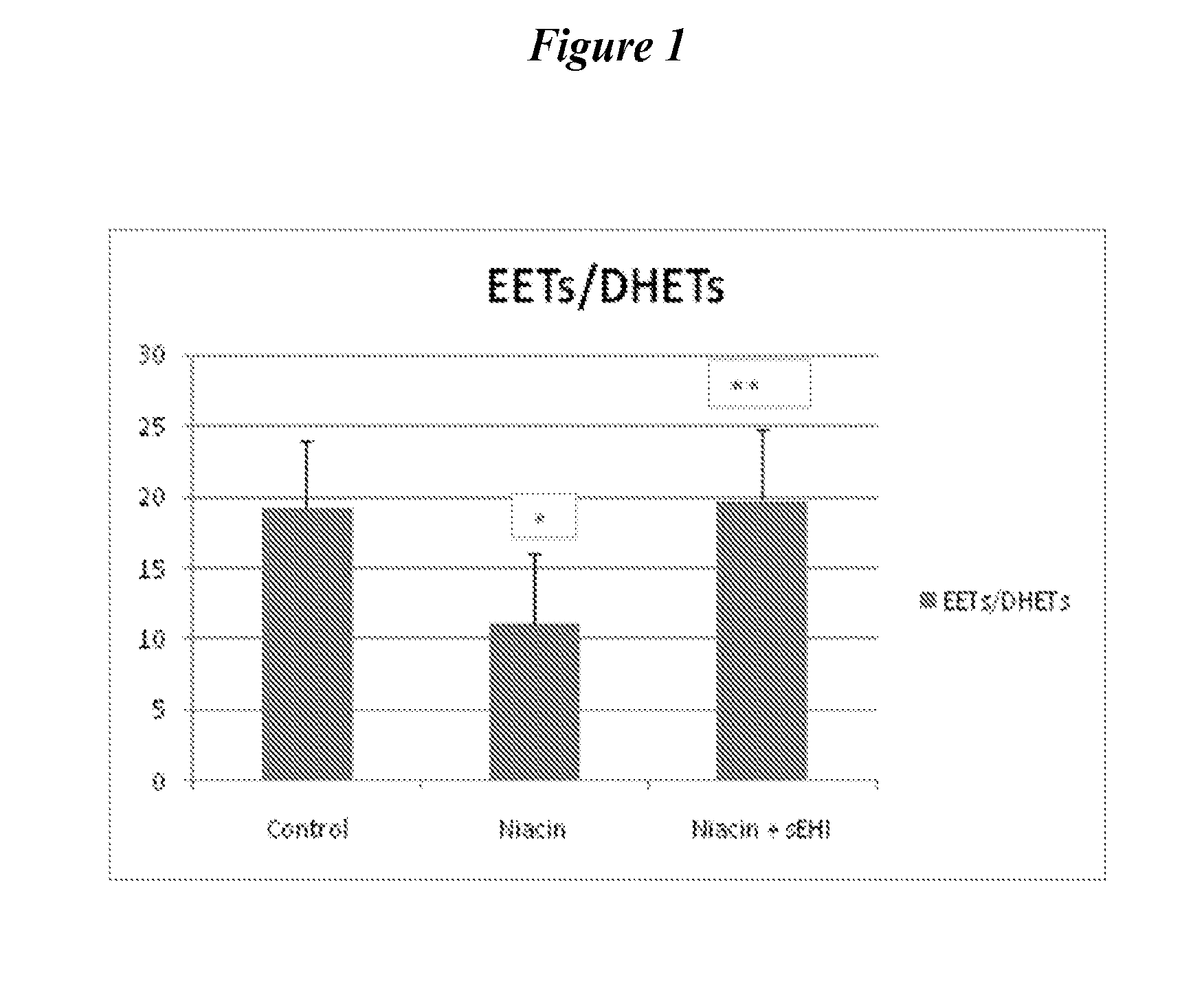
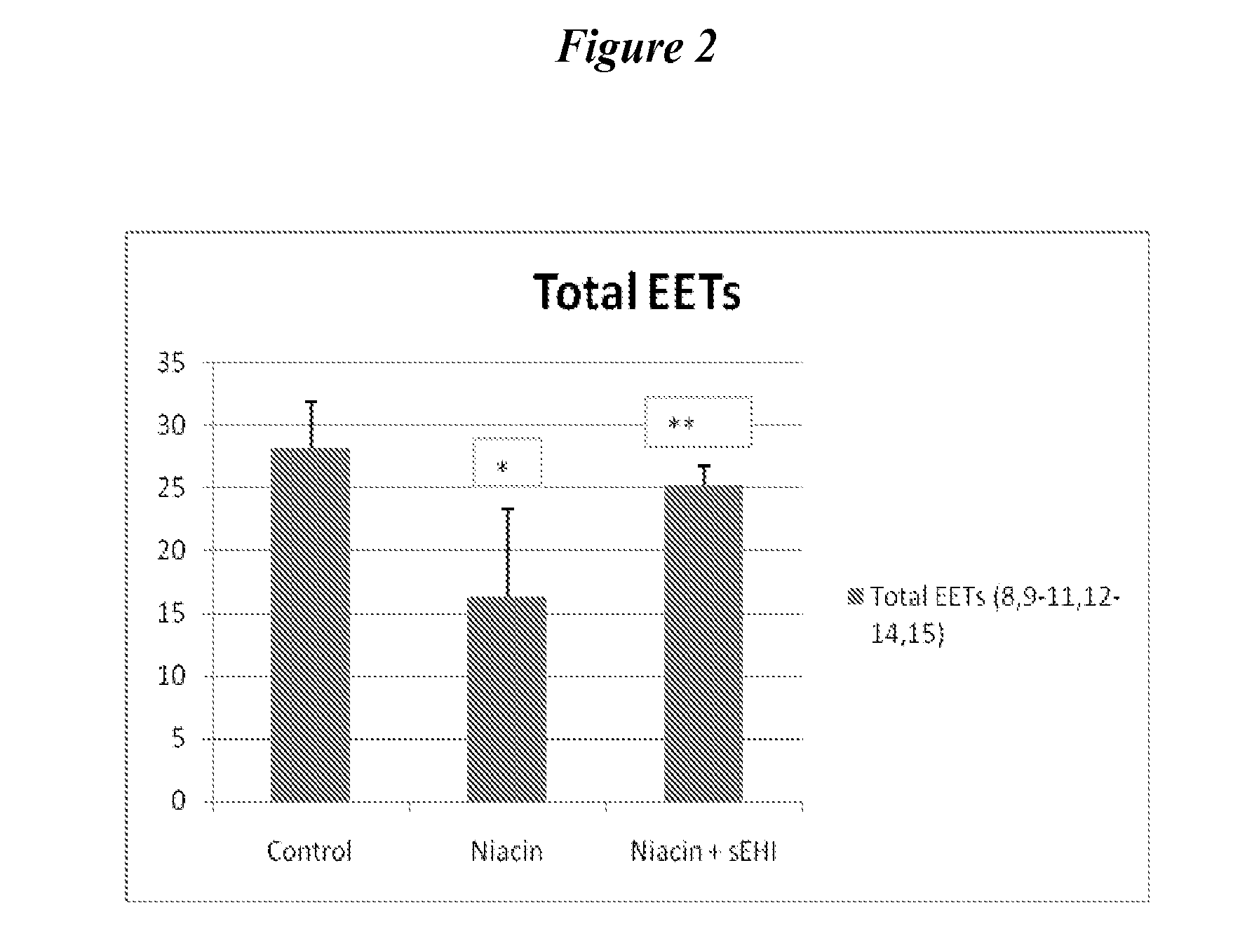
Inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase to inhibit or prevent niacin-induced flushing
InactiveUS20120046251A1Prevent and reduce and block substantial flushingPrevent, reduce or block substantial flushingSalicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideCutaneous vasodilationSide effect
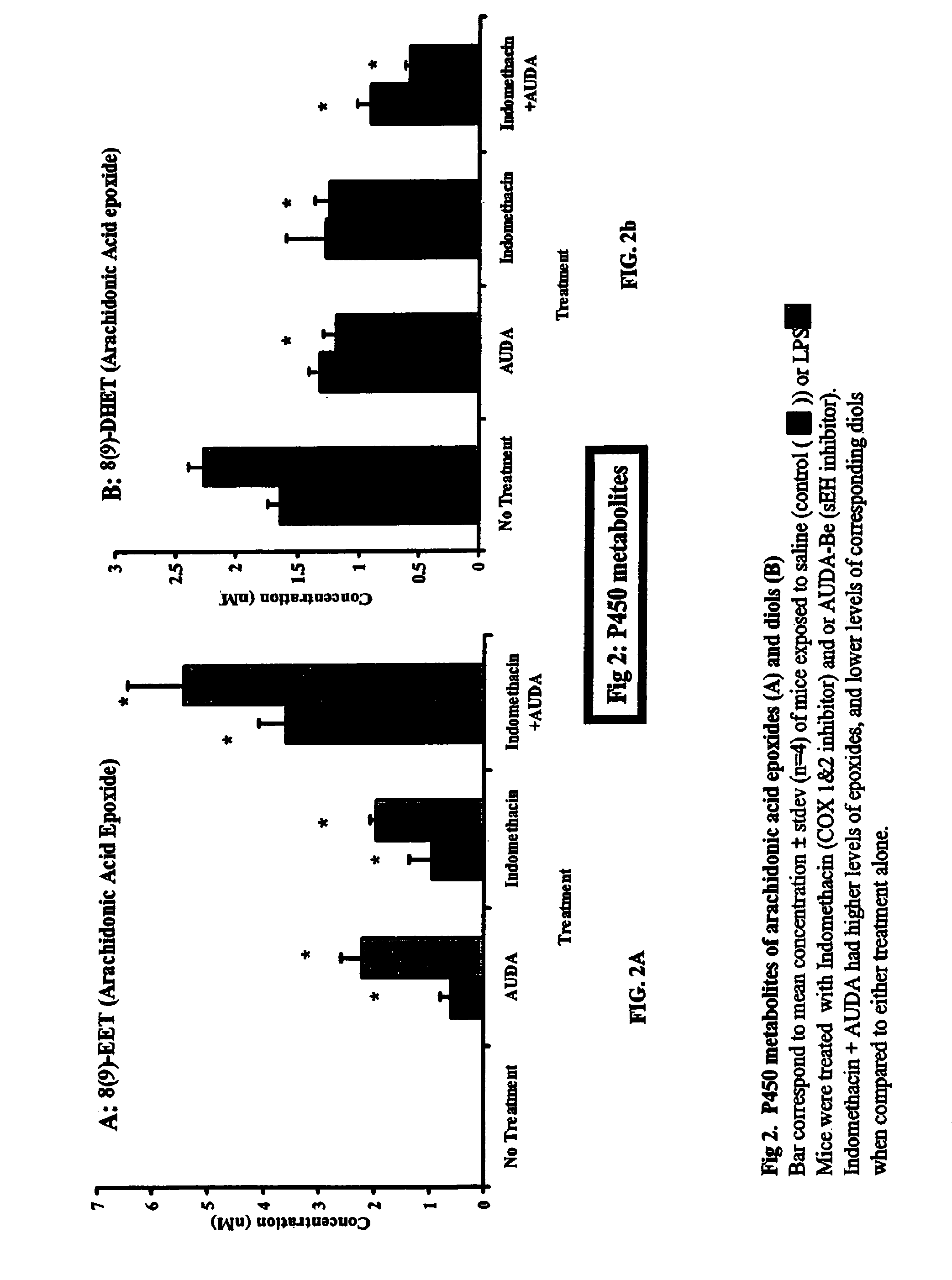
The invention discloses methods of using cis-epoxyeicosantrienoic acids (“EETs”), inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase (“sEH”), or a combination of an EET and an inhibitor of sEH, to reduce or prevent niacin-induced cutaneous vasodilation (“flushing”) in subjects suffering from this undesirable side effect of receiving therapeutic amounts of niacin.
Owner:SCHAEFER SAUL
Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors
Disclosed are sulfonamide compounds of formula (I), wherein R-R, Y and m are as defined in the claims, and compositions that inhibit soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH), methods for preparing the compounds and compositions, and methods for treating patients with such compounds and compositions. The compounds, compositions, and methods are useful for treating a variety of sEH-mediated diseases, including hypertensive, cardiovascular, inflammatory, pulmonary, and diabetes-related diseases.
Owner:ARETE THERAPEUTICS INC
Inhibitors of epoxide hydrolases for the treatment of hypertension
The invention provides compounds that inhibit epoxide hydrolase in therapeutic applications for treating hypertension. A preferred class of compounds for practicing the invention have the structure shown by Formula 1 wherein Z is oxygen or sulfur, W is carbon phosphorous or sulfur, X and Y is each independently nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur, and X can further be carbon, at least one of R1-R4 is hydrogen, R2 is hydrogen when X is nitrogen but is not present when X is sulfur or oxygen, R4 is hydrogen when Y is nitrogen but is not present when Y is sulfur or oxygen, R1 and R3 is each independently C1-C20 substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, acyl, or heterocyclic.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Use of cis-Epoxyeicosantrienoic acids and inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase to reduce pulmonary infiltration by neutrophils
InactiveUS20050222252A1Slowing and inhibiting progressionInhibit progressPowder deliveryBiocideHydrolase inhibitorDepressant
It has now been discovered that inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase (“sEH”) are useful in reducing the severity of or inhibiting the progression of obstructive pulmonary diseases, restrictive airway diseases, and asthma. Administering a cis-epoxyeicosantrienoic acid (“EET”) in addition to the inhibitor is at least additive, and may be synergistic, in reducing or inhibiting these conditions and diseases, as measured by reduced numbers of neutrophils present in the lung. The inhibitor of sEH may be a nucleic acid, such as a small interfering RNA.
Owner:CALIFORNIA UNIV OF TH RGT
Kidney bean epoxide hydrolase mutant with improved catalytic activity and enantio-convergent property
ActiveCN106119220AImproved EnantionormalityEnhanced enantiouniform catalytic propertiesBacteriaHydrolasesSite-directed mutagenesisMutant
The invention discloses a kidney bean epoxide hydrolase mutant with improved catalytic activity and enantioconvergent property, belonging to the fields of genetic engineering and protein expression. A strain of epoxide hydrolase mutant PvEH1 <L105I / M160A / M175I> with improved catalytic activity and enantio-convergent property can be obtained by reforming the molecular structure of epoxide hydrolase (EH) by means of a site-directed mutation biotechnology on the basis of EH with certain enantio-convergent catalysis characteristic. The mutant has the advantages of high enantio-selectivity and high catalytic activity, thus having greater application potential and also laying a theoretical foundation for the study of the EH.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
High-enantiomer selectivity epoxide hydrolase and gene coded thereby
The invention belongs to the field biotechnology and discloses use of an RT-PCR method in cloning an epoxide hydrolase gene (PchEHA) from a BKM-F1767 strain (Phanerochaete chrysosporium BKM-F1767) of fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium and a nucleotide sequence and an amino acid sequence of a coding region of the PchEHA. Cloned plasmid pTEHA containing the gene, a recombinant expression plasmid pET28EHA containing the gene and a genetic engineering strain Escherichia coli E.coli BL21(DE3) / PeT28EHA containing the PchEHA gene are provided to prepared the recombinant epoxide hydrolase. The epoxide hydrolase of the invention has catalytic activity for various epoxides and shows enantiomer selectivity of different degrees, particularly high enantiomer selectivity for epoxyethylbenzene. The recombinant epoxide hydrolase of the invention can be used in the fields of the kinetic resolution of a chiral epoxide racemic mixture, the asymmetric catalysis of epoxides, and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
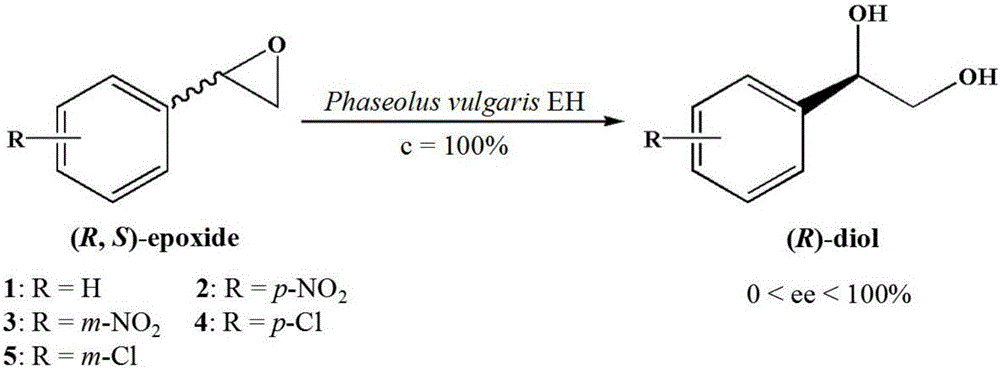
Epoxide hydrolase sourced from Phaseolus vulgaris and application thereof
The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase sourced from Phaseolus vulgaris and an application thereof and belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase gene (pveh2) sourced from a leguminous plant, Phaseolus vulgaris, as well as a corresponding amino sequence. The invention provides a recombinant plasmid pET28a(+)-pveh2 and a genetic engineering bacteria E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a(+)-pveh2, which comprise the gene. A recombinant epoxide hydrolase is prepared through expression by the bacterial strain. The invention provides a method of biocatalysis through fermentation with an enzyme produced by the recombinant bacterial strain constructed in the invention, thus producing enantiomerically pure R-type styrene oxide (ee > 99%); in addition, final yield can reach 49.3%, which is approximate to a theoretical value, 50%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
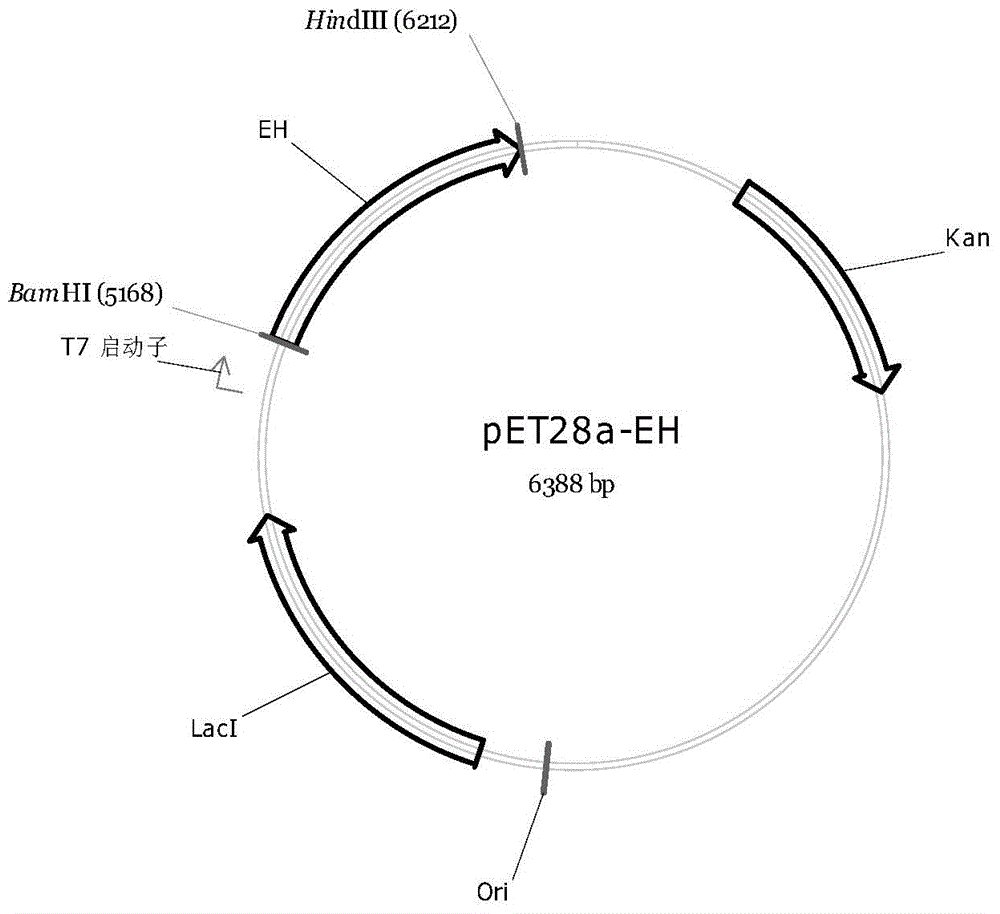
Epoxide hydrolase enzyme gene and encoding enzymeand and carrier and engineering bacteria and application
The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase enzyme gene, encoding enzymeand, carrier, and recombination gene engineering bacteria which are derived from solid mycete ZJB120203, and application in preparation of recombination epoxide hydrolase. The epoxide hydrolase enzyme gene can be connected with expression carrier and obtain expression recombinant plasmid Pet28a-EH obtaining the epoxide hydrolase enzyme gene, and the expression recombinant plasmid Pet28a-EH converses into escherichia coli BL21 and recombinant escherichia coli is obtained. The recombinant escherichia coli contains recombinant epoxide hydrolase enzyme gene. The recombinant escherichia coli can be used for enzyme resource, and racemic epichlorohydrin and racemic phenyl ethylene oxide are used for substrate, then the bioconversion reaction is carried out and S-epichlorohydrin and R-phenyl ethylene oxide which are with high optical purity are prepared.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Alleviating neuropathic pain with EETs and sEH inhibitors
The invention discloses methods of using cis-epoxyeicosantrienoic acids (“EETs”), inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase (“sEH”), or a combination of an EET and an inhibitor of sEH, to alleviate neuropathic pain in subjects suffering from such pain.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Alleviating neuropathic pain with eets and seh inhibitors
ActiveUS20100267807A1Treating and reducing and alleviating and inhibiting and preventing neuropathic painBiocideNervous disorderEpoxide hydrolaseDepressant
The invention discloses methods of using cis-epoxyeicosantrienoic acids (“EETs”), inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase (“sEH”), or a combination of an EET and an inhibitor of sEH, to alleviate neuropathic pain in subjects suffering from such pain.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Inhibitors of epoxide hydrolases for the treatment of inflammation
The invention provides compounds that inhibit epoxide hydrolase in therapeutic applications for treating hypertension. A preferred class of compounds for practicing the invention have the structure shown by Formula 1 wherein Z is oxygen or sulfur, W is carbon phosphorous or sulfur, X and Y is each independently nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur, and X can further be carbon, at least one of R1-R4 is hydrogen, R2 is hydrogen when X is nitrogen but is not present when X is sulfur or oxygen, R4 is hydrogen when Y is nitrogen but is not present when Y is sulfur or oxygen, R1 and R3 is each independently C1-C20 substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, acyl, or heterocyclic.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
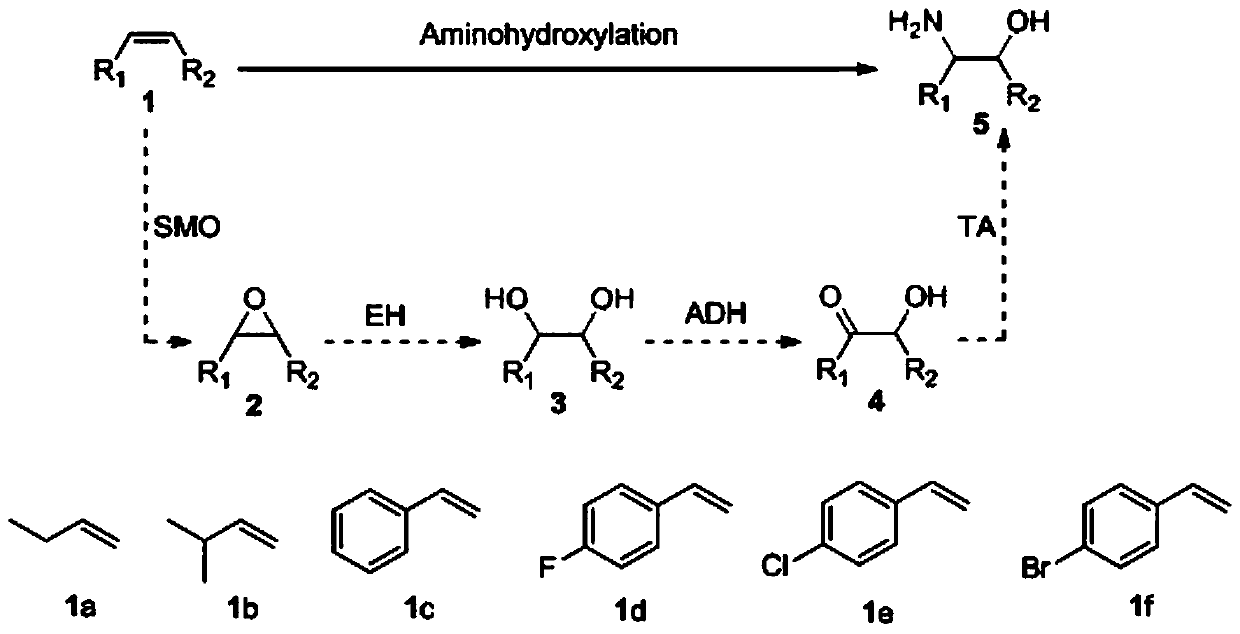
Method for preparing chiral beta-amino alcohol by asymmetric amine hydrogxylation of olefin through cascade biocatalysis
InactiveCN110172484AAvoid lostAchieve recyclingMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliEpoxide metabolism
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and provides a method for preparing chiral beta-amino alcohol by asymmetric amine hydroxylation of an olefin compound through cascade biocatalysis. Olefin monooxygenase, epoxide hydrolase, alcohol dehydrogenase and transaminase are taken as biocatalysts; olefin is used as a substrate and a reaction is performed in a phosphate buffer solutionto synthesize the chiral beta-amino alcohol. The conversion rate reaches up to 99% and the ee value is 97-99%. The olefin monooxygenase / alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) / (R)-(+)-1 phenylethylamine (R-MBA)in a cascade biocatalytic system drives the reaction to be carried out towards a direction beneficial for product generation, and a cofactor NAD<+> is regenerated. The whole-cell cascade biocatalysisis realized through using engineering recombinant escherichia coli cells, and the chiral beta-amino alcohol is obtained. The method is used for converting the cheap olefin compound into various different chiral beta-amino alcohols; the catalytic efficiency is high, reaction conditions are mild, a reaction process is simple, the energy consumption is low, and the method is in line with the principle of green chemistry.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Aspergillus usamii epoxide hydrolase mutants with improved enantioselectivity
The invention discloses aspergillus usamii epoxide hydrolase mutants with improved enantioselectivity, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering and biological catalysis. Aspergillus usamii epoxide hydrolases (AuEH2) are subjected to molecular modification on the basis of rational designs and are combined with site-saturation mutagenesis methods for genes, so that the multiple epoxide hydrolase mutants with the improved enantioselectivity can be obtained. The aspergillus usamii epoxide hydrolase mutants have the advantages that racemic styrene oxide (rac-SO) can be catalyzed by the six mutants AuEH2A250I, AuEH2A250M, AuEH2A250Y, AuEH2A250S, AuEH2A250L and AuEH2A250V with the improved enantioselectivity, and the enantiomeric ratios (E values) of the six mutants can be increased and respectively reach 48, 27.2, 23.9, 21.8, 20.0 and 19.4 from the original 16 as compared with wild type mutants.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Epoxide hydrolase mutant, engineering bacteria and application of epoxide hydrolase mutant
The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase mutant, an engineering bacteria and application of the epoxide hydrolase mutant. The epoxide hydrolase mutant is obtained by carrying out single-point mutation or multi-point mutation on amino acid in the 182rd position, the 207th position and / or the 240th position of an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.13. Compared with the wild type epoxide hydrolase, the epoxide hydrolase mutant provided by the invention has higher catalytic activity and stereoselectivity; and the epoxide hydrolase mutant is particularly applied to preparing (S)-epoxy chloropropane by splitting racemic epichlorohydrin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
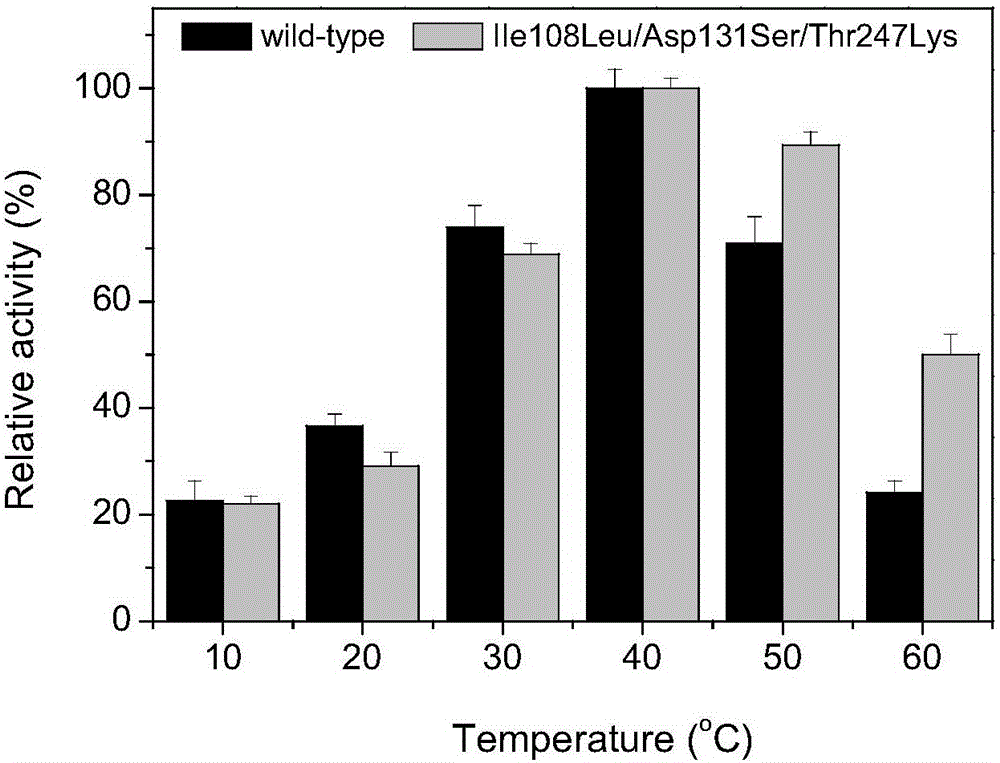
Epoxide hydrolase mutant and application thereof
InactiveCN105734028AImprove selectivity E valueIncrease enzyme activityHydrolasesFermentationDouble mutationHalf-life
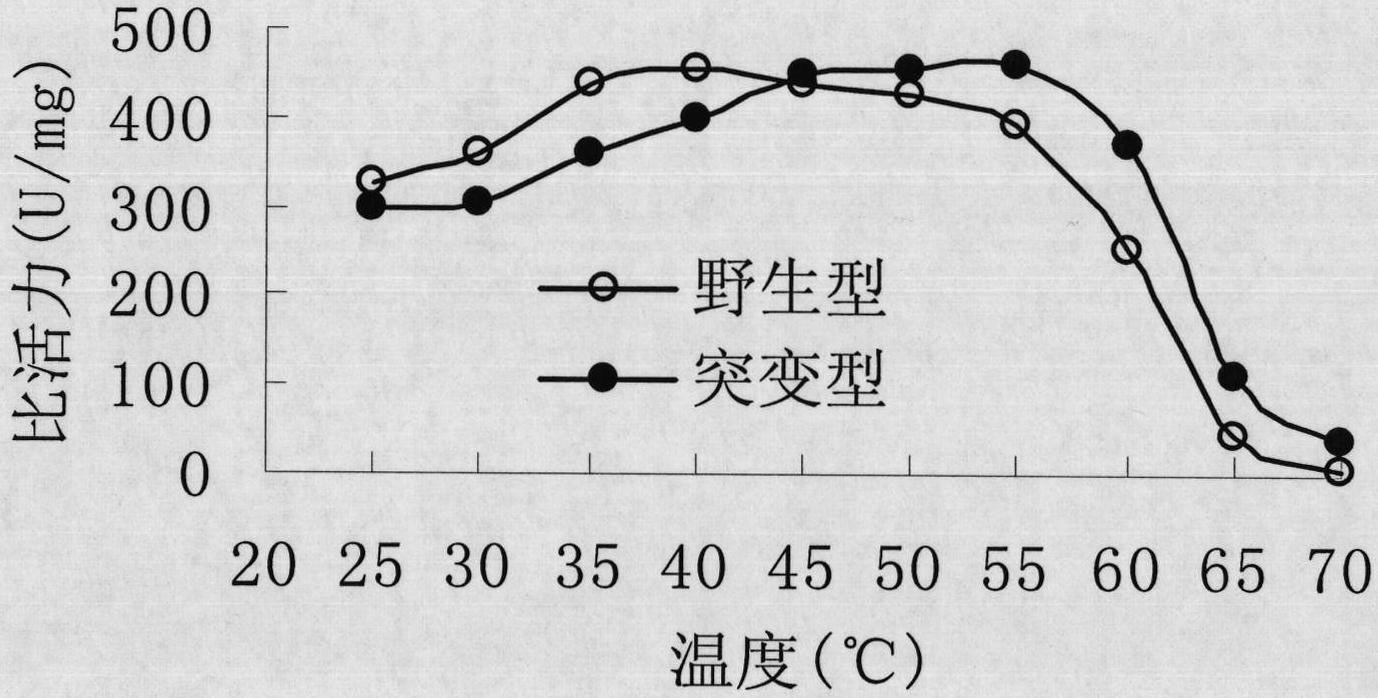
The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase mutant and its application. The mutant is the 108th isoleucine or the 131st aspartic acid or the 247th aspartic acid in the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2. Threonine is obtained by carrying out single mutation, double mutation or triple mutation; compared with the unmutated epoxide hydrolase mutant, the enzymatic activity, stereoselectivity and stability of the epoxide hydrolase mutant according to the present invention Significantly improved; Among them, the specific enzyme activity of the mutant was improved by 5.4 times compared with the original enzyme, reaching 315.2U / mg, the half-life was improved by 12.8 times, the enantioselective E value was improved by 2.1 times, and the epoxide hydrolase mutant was In the two-phase system, 800mM racemic epichlorohydrin can be catalytically resolved, and the yield of R-epichlorohydrin reaches more than 90% of the theoretical yield, and the enantioselectivity is greater than 99%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
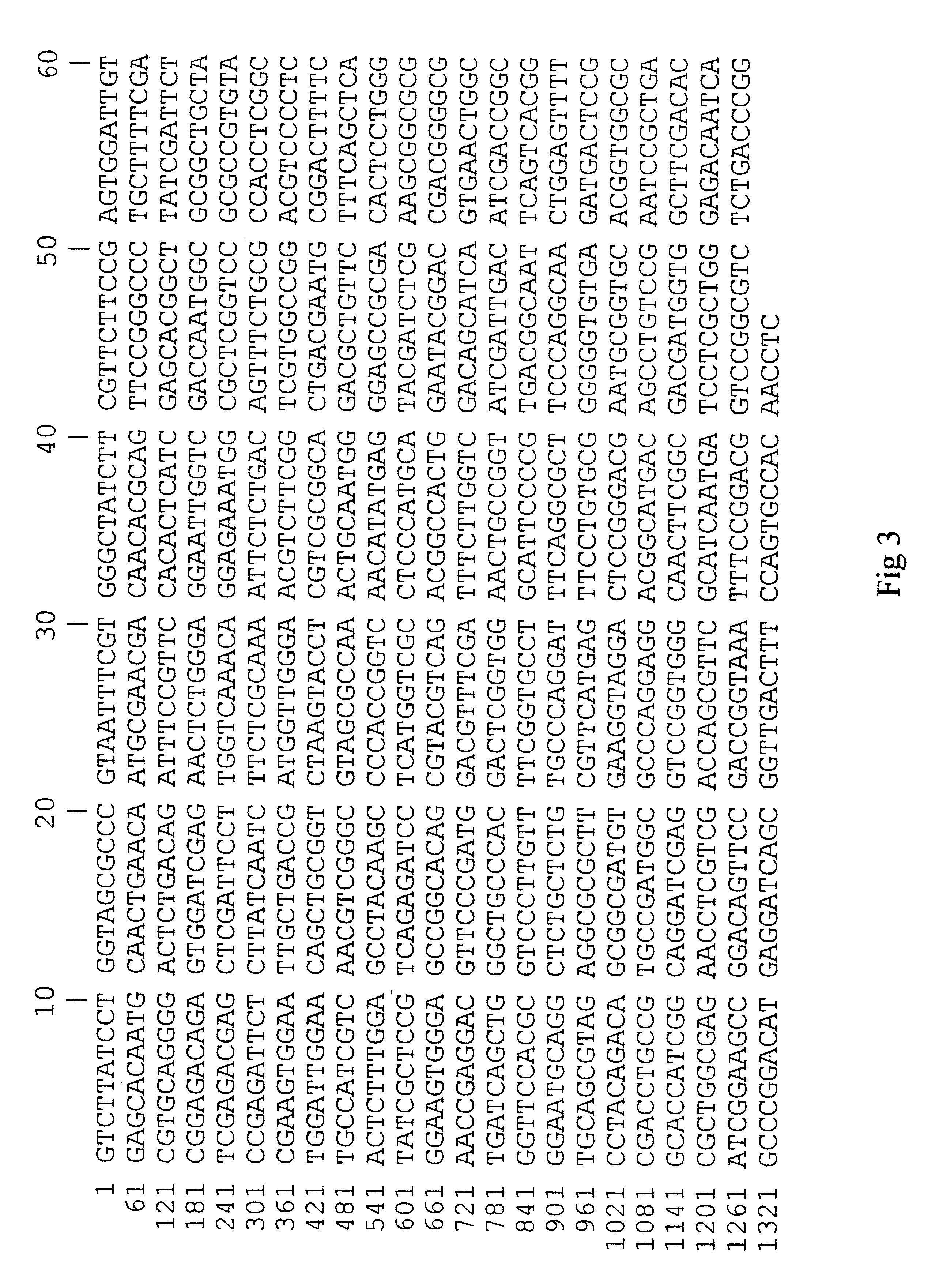
Epoxide hydrolase
The present invention is related to an isolated and purified nucleotide sequence from microbial origin, encoding an epoxide hydrolase, the vector comprising said nucleotide sequence, the recombinant host cell transformed by said nucleotide sequence and the epoxide hydrolase amino acid sequence encoded by said nucleotide sequence and / or expressed by said recombinant host cell.
Owner:PURATOS NAAMLOOZE VENNOOTSCHAP
Epoxide hydrolase and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101942471AImprove temperature stabilityMaintain high enzyme activityFungiBacteriaNucleotideTyrosine
The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase and a preparation method thereof. The amino acid of the 163rd site of the main body amino acid sequence of the epoxide hydrolase is phenylalanine, the main body amino acid sequence of the epoxide hydrolase is SEQ ID No: 10, and the epoxide hydrolase is coded by DNA molecules (expressed as SEQ ID No: 9) of the main body amino acid sequence. The preparation method for the epoxide hydrolase comprises that: tyrosine of the 163rd site of the main body amino acid sequence of the wild epoxide hydrolase is substituted by using the phenylalanine, the main body amino acid sequence of the wild epoxide hydrolase is SEQ ID No: 4, and the wild epoxide hydrolase is coded by DNA molecules (expressed as SEQ ID No: 3) of the main body amino acid sequence. Compared with the wild epoxide hydrolase, the epoxide hydrolase has high temperature stability and maintains high enzyme activity, can be used for hydrolyzing cis-epoxysuccinic acid or L (+)-tartaric acid or salt thereof, and prolongs the service life of a biocatalyst in the industrialized production.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIOKING BIOCHEM ENG
Treating neuropathic pain with seh inhibitors
Provided are methods for treating, reducing, alleviating, and / or inhibiting neuropathic pain by orally, intravenously or intrathecally administering an effective amount of an inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase ("sEH"), to a patient in need thereof. The neuropathic pain treated is selected from the group consisting of post-herpetic neuralgia, trigeminal neuralgia, focal peripheral nerve injury, and anesthesia dolorosa, central pain due to stroke or mass lesion, spinal cord injury, or multiple sclerosis, and peripheral neuropathy due to diabetes, HIV, or chemotherapy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Epoxide hydrolase
The present invention is related to an isolated and purified nucleotide sequence from microbial origin, encoding an epoxide hydrolase, the vector comprising said nucleotide sequence, the recombinant host cell transformed by said nucleotide sequence and the epoxide hydrolase amino acid sequence encoded by said nucleotide sequence and / or expressed by said recombinant host cell.
Owner:普瑞图斯股份有限公司
Use of cis-epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase to reduce cardiomyopathy
The invention provides methods for inhibiting cardiomyopathy and for inhibiting cardiac arrhythmia, by administering to an individual in need thereof a cis-epoxyeicosantrienoic acid, an inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH), or both. In some embodiments, the method comprises administering to the individual a nucleic acid encoding an inhibitor of sEH. Cardiomyopathies treatable by the methods of the invention include cardiac hypertrophy and dilated cardiomyopathy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Inhibitors of epoxide hydrolases for the treatment of inflammation
The invention provides compounds that inhibit epoxide hydrolase in therapeutic applications for treating hypertension. A preferred class of compounds for practicing the invention have the structure shown by Formula 1wherein Z is oxygen or sulfur, W is carbon phosphorous or sulfur, X and Y is each independently nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur, and X can further be carbon, at least one of R1-R4 is hydrogen, R2 is hydrogen when X is nitrogen but is not present when X is sulfur or oxygen, R4 is hydrogen when Y is nitrogen but is not present when Y is sulfur or oxygen, R1 and R3 is each independently C1-C20 substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, acyl, or heterocyclic.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Treating Neuropathic Pain with Seh Inhibitors
ActiveUS20150065540A1Reducing and alleviating and inhibiting neuropathic painBiocideOrganic chemistryRisk strokeEpoxide metabolism
Provided are methods for treating, reducing, alleviating, and / or inhibiting neuropathic pain by orally, intravenously or intrathecally administering an effective amount of an inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase (“sEH”), to a patient in need thereof. The neuropathic pain treated is selected from the group consisting of post-herpetic neuralgia, trigeminal neuralgia, focal peripheral nerve injury, and anesthesia dolorosa, central pain due to stroke or mass lesion, spinal cord injury, or multiple sclerosis, and peripheral neuropathy due to diabetes, HIV, or chemotherapy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
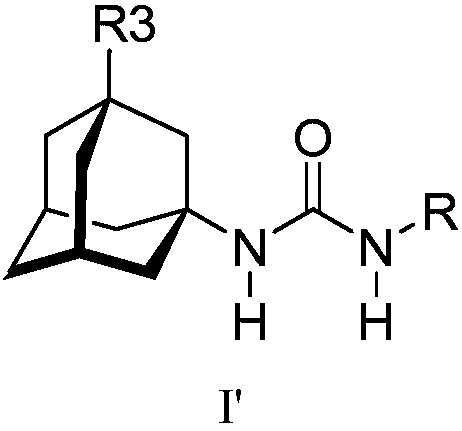
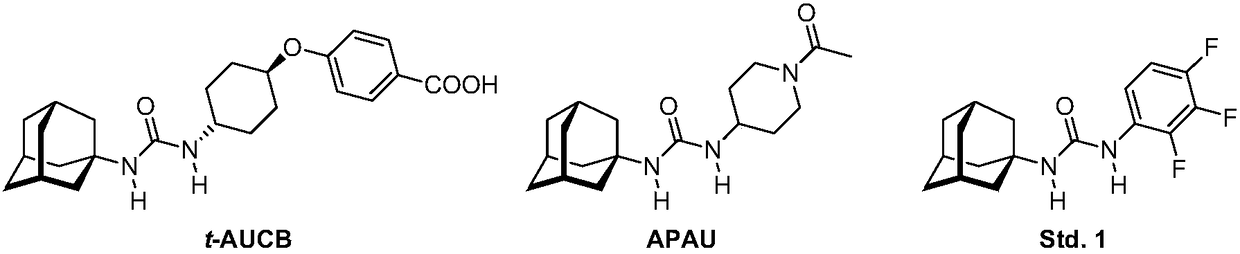
Analogs of adamantylureas as soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors
N-(2-oxaadamantan-1-yl)ureas of formula I, where R3 is H, C1-C3 alkyl, cyclohexyl or phenyl; R is -[CH2]n -Y; n is 0-15; in -[CH2]n - 0-n / 3 of the methylene groups are optionally replaced by non adjacent oxygen atoms; and Y is a 3- or 4-substituted phenyl, a 3- or 4-substituted cyclohexyl, a N-substituted piperidin-4-yl, a N-substituted piperidin-3-yl, a di- or tri-fluorosubstituted phenyl, 4-chloro-3-trifluoromethylphenyl, 3-chloro-4-trifluoromethylphenyl, 4-fluoro-3-trifluoromethylphenyl, or 3-fluoro-4-trifluoromethylphenyl; have epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitory activities similar to thoseof their N-(adamantan-1-yl)urea analogs. Thus, compounds I are useful as API for the treatment of sEH mediated diseases. Besides, in general, compounds (I) have higher water solubilities and lower melting points, what make them more promising from the point of view of pharmacokinetics and formulation.
Owner:UNIV DE BARCELONA
Epoxide hydrolase as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention relates to an epoxide hydrolase having amino acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention relates to an encoding gene for the epoxide hydrolase which has amino acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also relates to an application of the epoxide hydrolase, by the epoxide hydrolase, chiral aromatic epoxide is prepared by adopting racemic aromatic epoxide as a substrate. The epoxide hydrolase provided by the invention can be in a form of wet thallus or lyophilized thallus of the whole cell and can also be in a form of crude enzyme liquid or pure enzyme, by adopting racemic aromatic epoxide as the substrate, the enantiomerically pure chiral aromatic epoxide is prepared (ee is greater than 99%).
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Use of inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase to synergize activity of cox and 5-lox inhibitors
The invention relates to methods, compositions, and uses of those compositions for making medicaments, for potentiating the beneficial effects of inhibitors of COX-1, COX-2, and 5-LOX, and reducing adverse effects, by also administering inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase (“sEH”), with or without also administering one or more cis-epoxyeicosantrienoic acids. The invention further relates to the use of inhibitors of sEH as analgesics and to methods and compositions of epoxides of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, optionally with an inhibitor of sEH, to reduce pain or inflammation or both.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Use of cis-epoxyeicosantrienoic acids and inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase to reduce pulmonary infiltration by neutrophils
It has now been discovered that inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase (“sEH”) are useful in reducing the severity of or inhibiting the progression of obstructive pulmonary diseases, restrictive airway diseases, and asthma. Administering a cis-epoxyeicosantrienoic acid (“EET”) in addition to the inhibitor is at least additive, and may be synergistic, in reducing or inhibiting these conditions and diseases, as measured by reduced numbers of neutrophils present in the lung. The inhibitor of sEH may be a nucleic acid, such as a small interfering RNA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Epoxy hydrolase, gene thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN102242085AHigh catalytic efficiencyDeepen understandingBacteriaHydrolasesEpoxyBacillus megaterium
The invention discloses a novel epoxy hydrolase, a gene of the epoxy hydrolase, a recombination expressor and a recombination expression transformant containing the gene, a method for preparing a recombinase by using the recombination expression transformant, and an application of the recombined epoxy hydrolase in catalyzing racemic epoxide enantioselective hydrolysis for producing chiral epoxideand diol. The recombined epoxy hydrolase provided by the invention is originated from bacillus megaterium. The epoxy hydrolase can be used for synthesizing various optically active epoxides and vicinal diols. The epoxy hydrolase has advantages of high catalysis efficiency, high enantioselectivity, and mild reaction condition. The epoxy hydrolase is environment-friendly. Compared with wild bacterium whole cells, the epoxy hydrolase provided by the invention contributes to a better catalysis effect and a better applicability of substrates. The epoxy hydrolase has a good prospect to be applied in industrial productions.
Owner:SUZHOU BAIFUAN ENZYME TECH
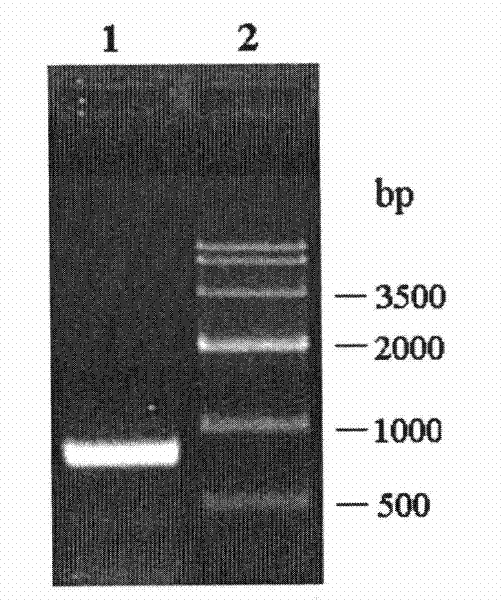
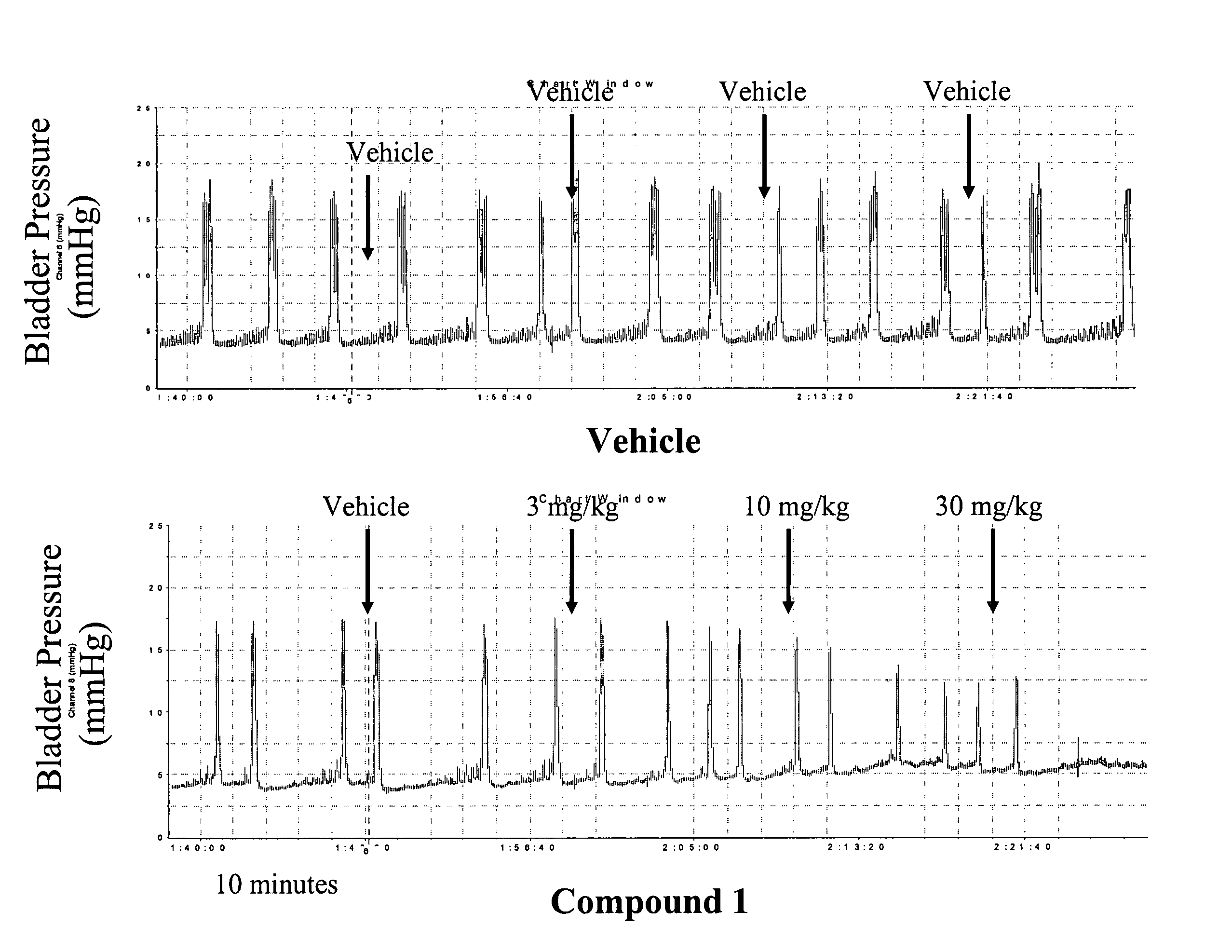
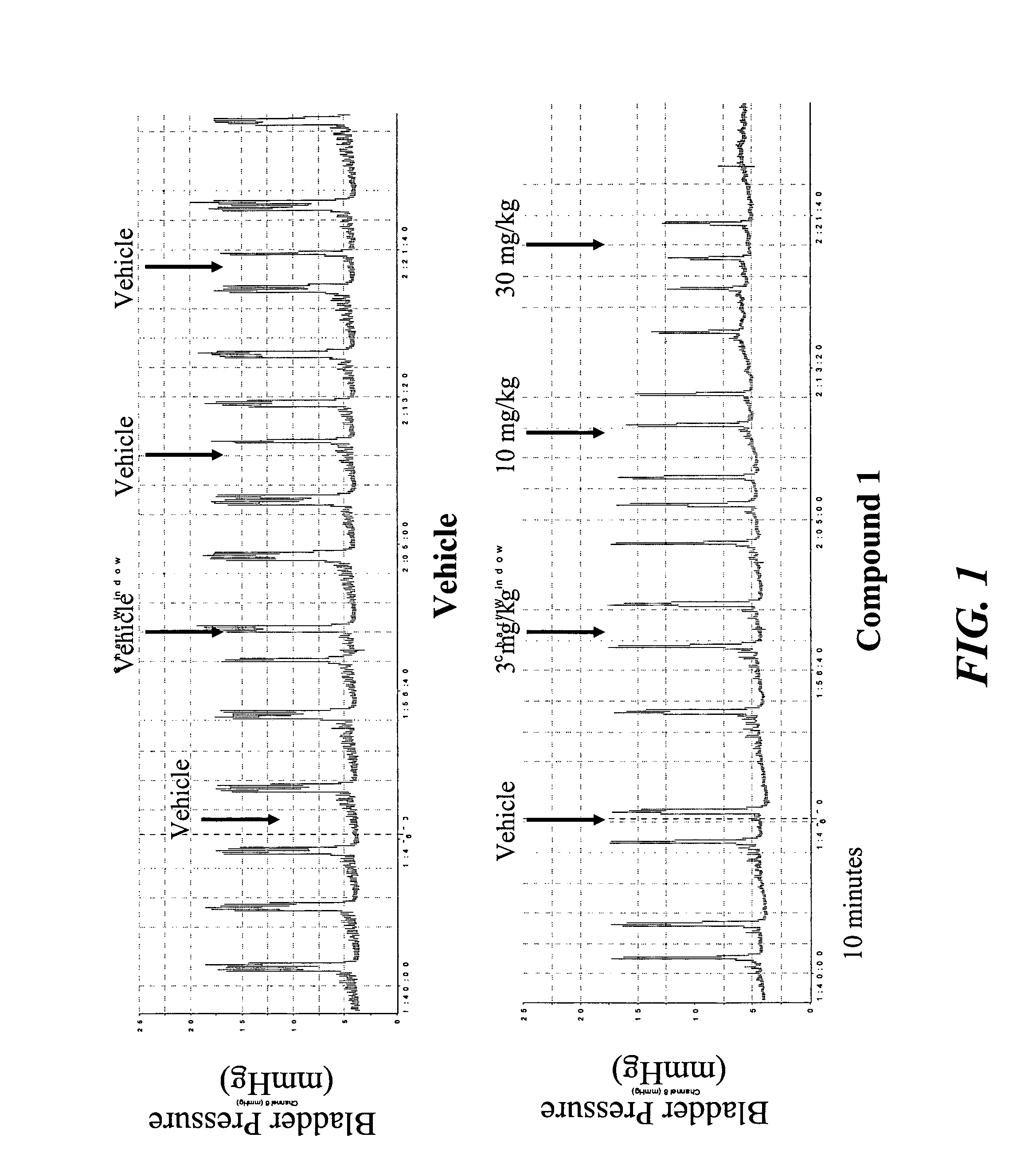
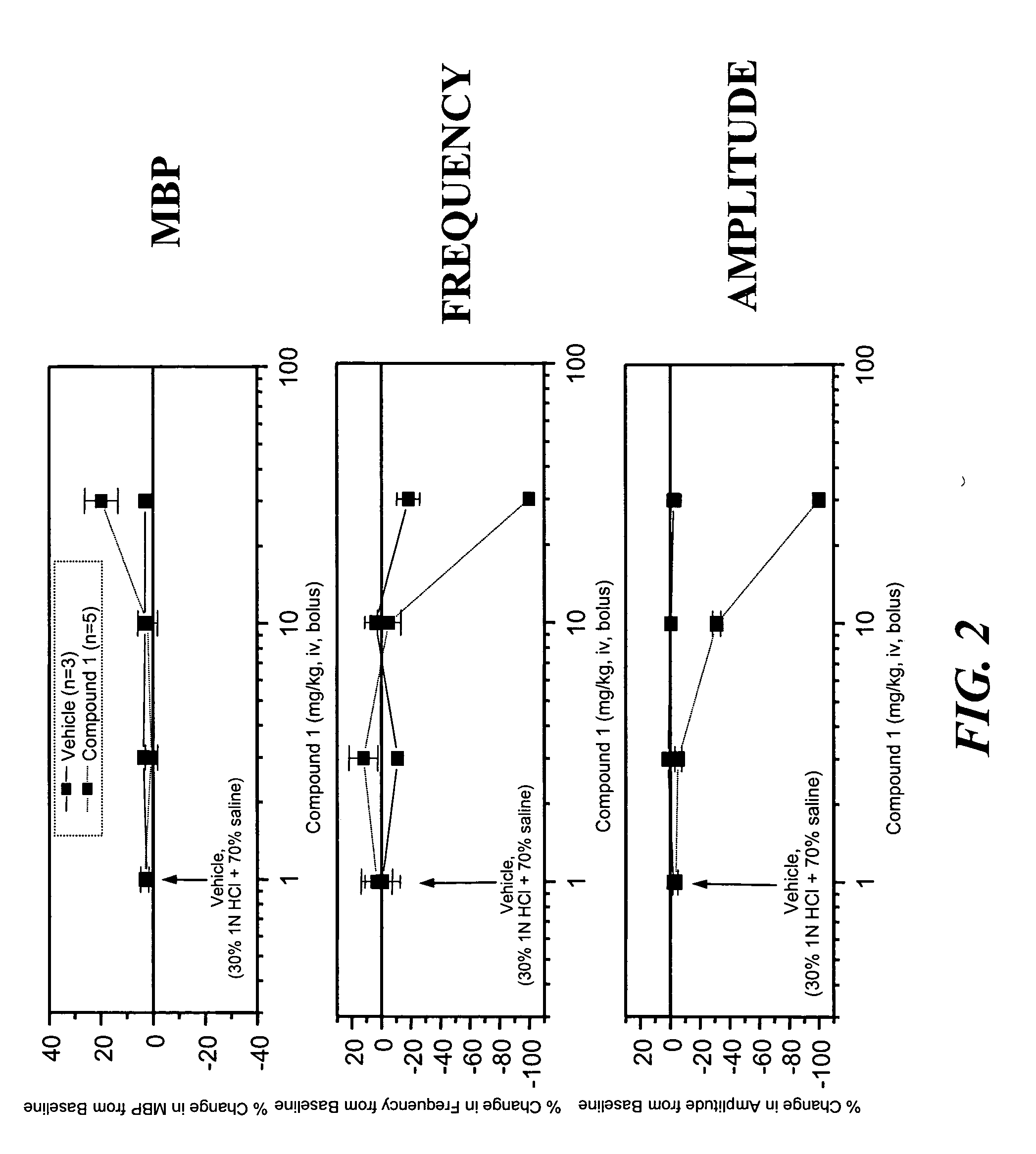
Methods of treating genitourinary disorders using inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
Methods of treating avian hypertension
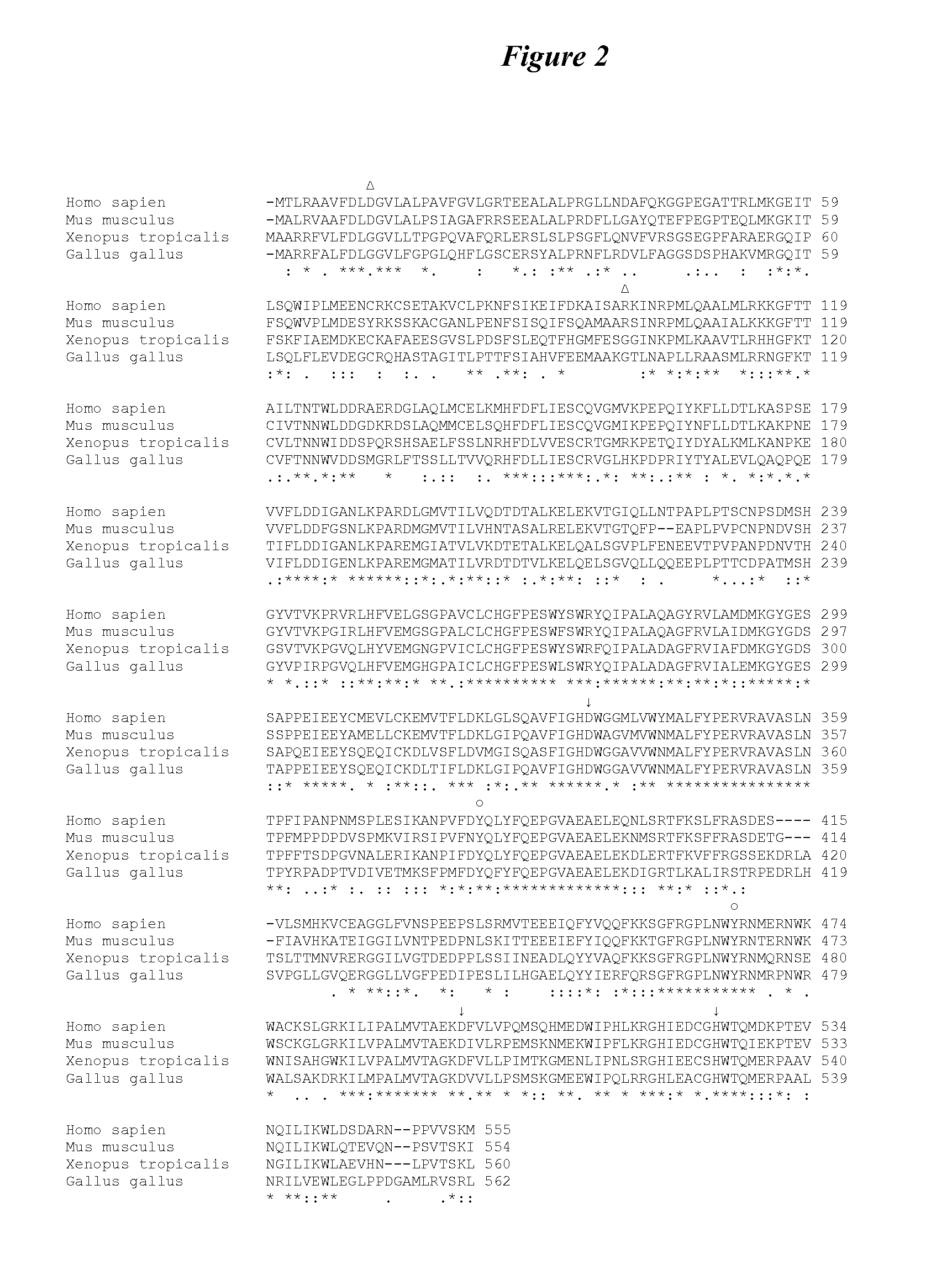
The present invention provides methods of treating avian pulmonary hypertension syndrome by administering to an avian subject a therapeutically effective amount of an inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase (“sEHI”), alone or co-administered in combination with a cis-epoxyeicosantrienoic acid (“EET”). The invention also provides nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of an avian soluble epoxide hydrolase.
Owner:TEXAS A&M +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com