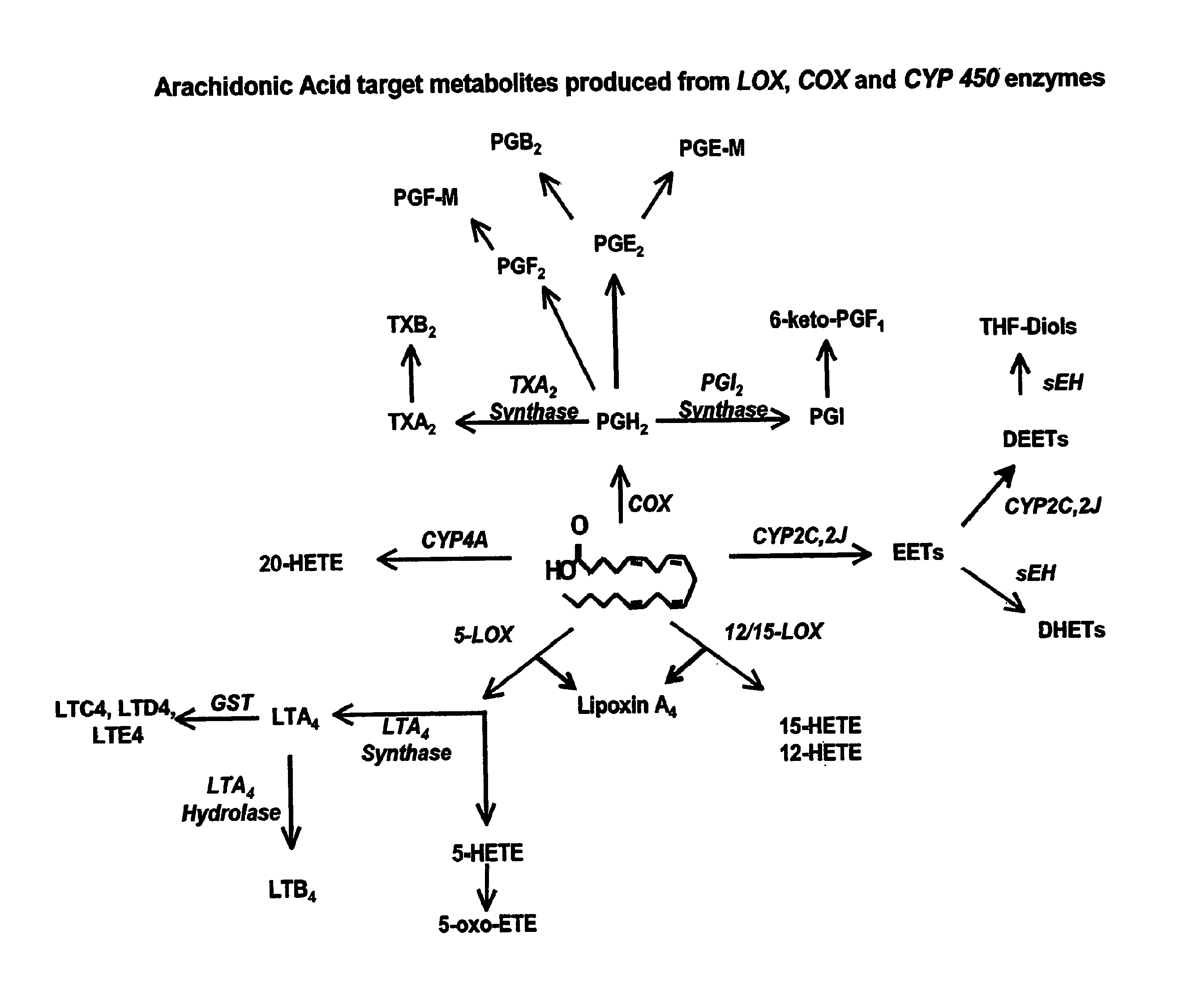
Use of inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase to synergize activity of cox and 5-lox inhibitors
a technology of soluble epoxide hydrolase and inhibitor, which is applied in the direction of biocide, elcosanoid active ingredients, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of apoptosis or cell death, and achieve the effect of increasing the
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
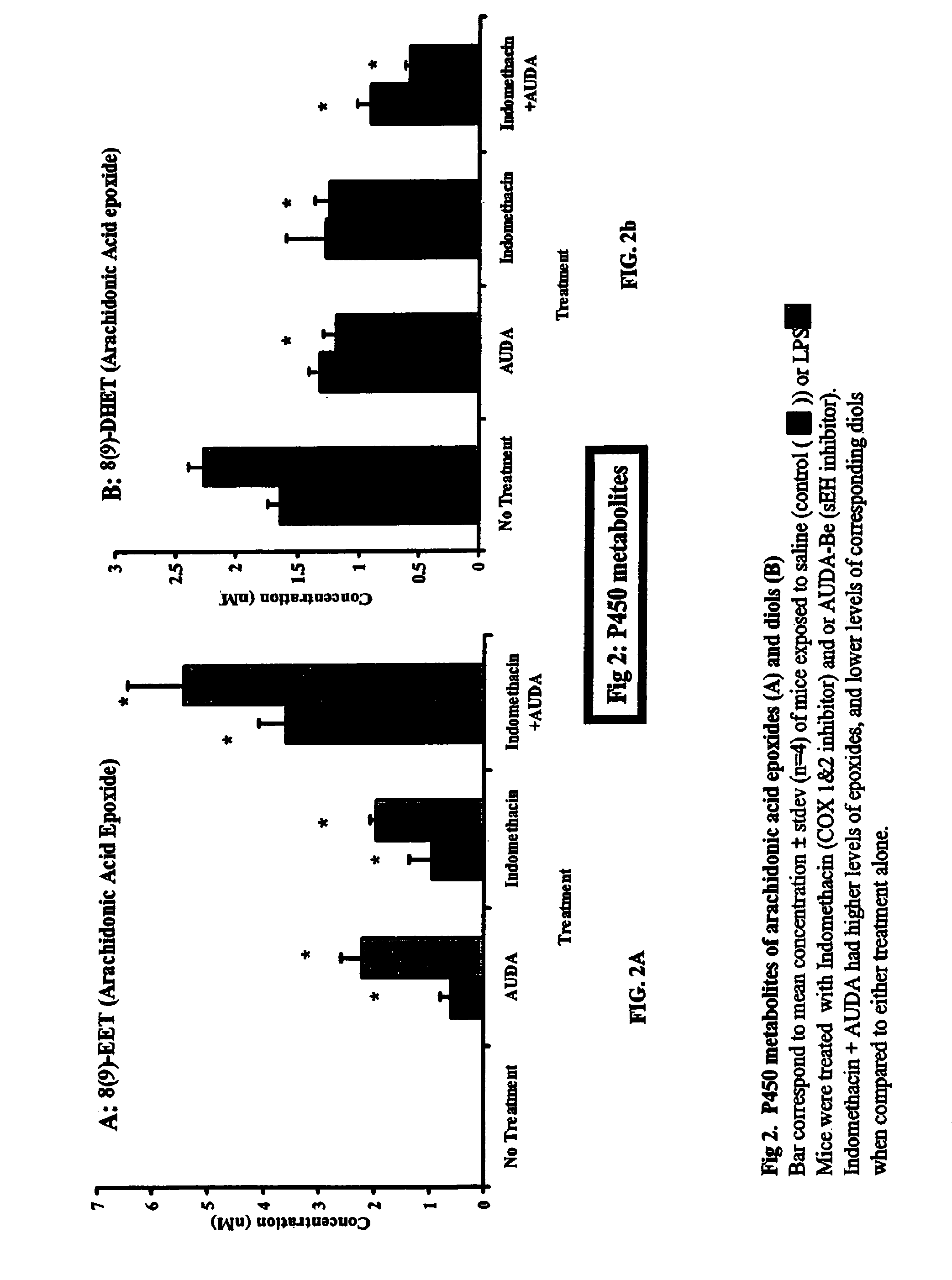
[0132]This Example sets forth the materials and methods used in the studies whose results are set forth in FIGS. 2a and 2b.
Animal Experiments
[0133]Male, 7- to 8-week-old C57BL / 6 mice (Charles River, Wilmington, Mass.) weighing between 22 and 28 g were used in the inflammation experiments. The mice were acclimated for 5 days prior to experimentation. They were housed in groups of four per cage, in a controlled environment in American Association for Laboratory Animal Care-accredited facilities and were fed mouse chow ad libitum.
[0134]The mice were administered lipopolysaccharide (“LPS”) to induce inflammatory responses. Saline was used as a carrier for the LPS. The sEH inhibitor used in the studies was 12-(3-adamantane-1-yl-ureido)-dodecanoic acid butyl ester (AUDA-BE). Because AUDA-nBE takes some time to reach physiologically effective levels in the body, mice to which AUDA-BE was to be administered were given the AUDA-BE prior to exposure to LPS.
[0135]The mice were divided into gr...
example 2
[0145]This Example discusses the results of the studies conducted using the materials and methods discussed in the previous Example.
[0146]FIGS. 2A and 2B show the levels of 8,9 EET and 8,9 DHET, respectively, in mice injected with sterile saline alone or with sterile saline and lipopolysaccharide (“LPS”). As described in Example 1, groups of mice were treated with the COX-1 and -2 inhibitor indomethacin, or with AUDA butyl ester (AUBA-BE), or with both indomethacin and AUDA-BE.
[0147]Referring to FIG. 2A, as shown on the far left of the Figure, mice that were not treated with either AUDA-BE or indomethacin showed no detectable levels of 8,9 EET. The results for the three groups of mice represented in the rest of the figure show two bars, one black and one gray. The black bar in each group represents the concentration of 8,9 EET seen in mice that received the treatment (AUDA-BE, indomethacin, or both, as stated on the axis), but which were not also exposed to the inflammatory agent LP...
example 3
[0149]This Example sets forth materials and methods for tail flick and hind paw withdrawal studies showing response to pain stimuli.
[0150]Briefly, mice are kept under 12:12 h light: dark cycle and water and food is supplied ad libitum. Mice are trained for three days to the experimental chambers in 30 min sessions each time. The next day baseline readings are taken. Vehicle control (oleic oil) is then injected sc in the next day and measurements are taken. Two days later, animals are injected through the sc route with test compounds dissolved in the oil vehicle and their responses are recorded after 90 minutes.
[0151]Tail flick and hind paw withdrawal latency tests are conducted according to D'Amour and Smith, J Pharmacol Exp Ther 72:74-9 (1941), and Woolfe and McDonald, J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 80:300-7 (1944). In tail flick assays, mice are placed in restrainers and left undisturbed for 30 minutes. Readings are then taken by placing the posterior end of the tail onto a tail flick appa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| residence times | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| v/v | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com