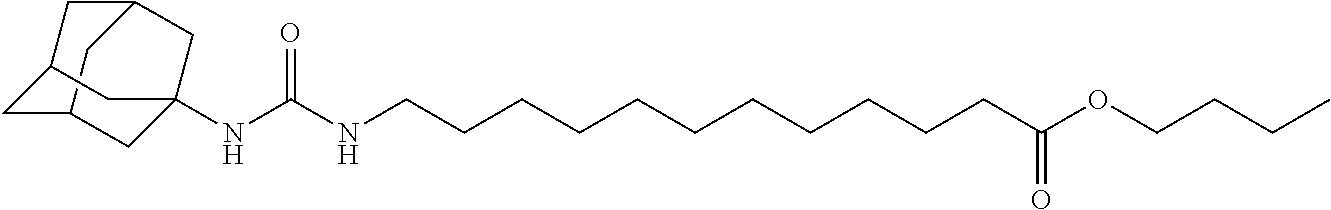
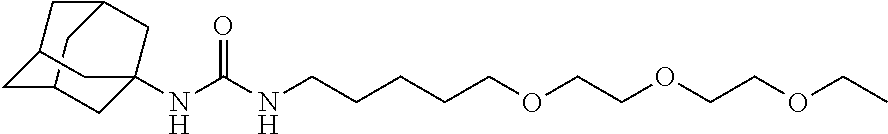
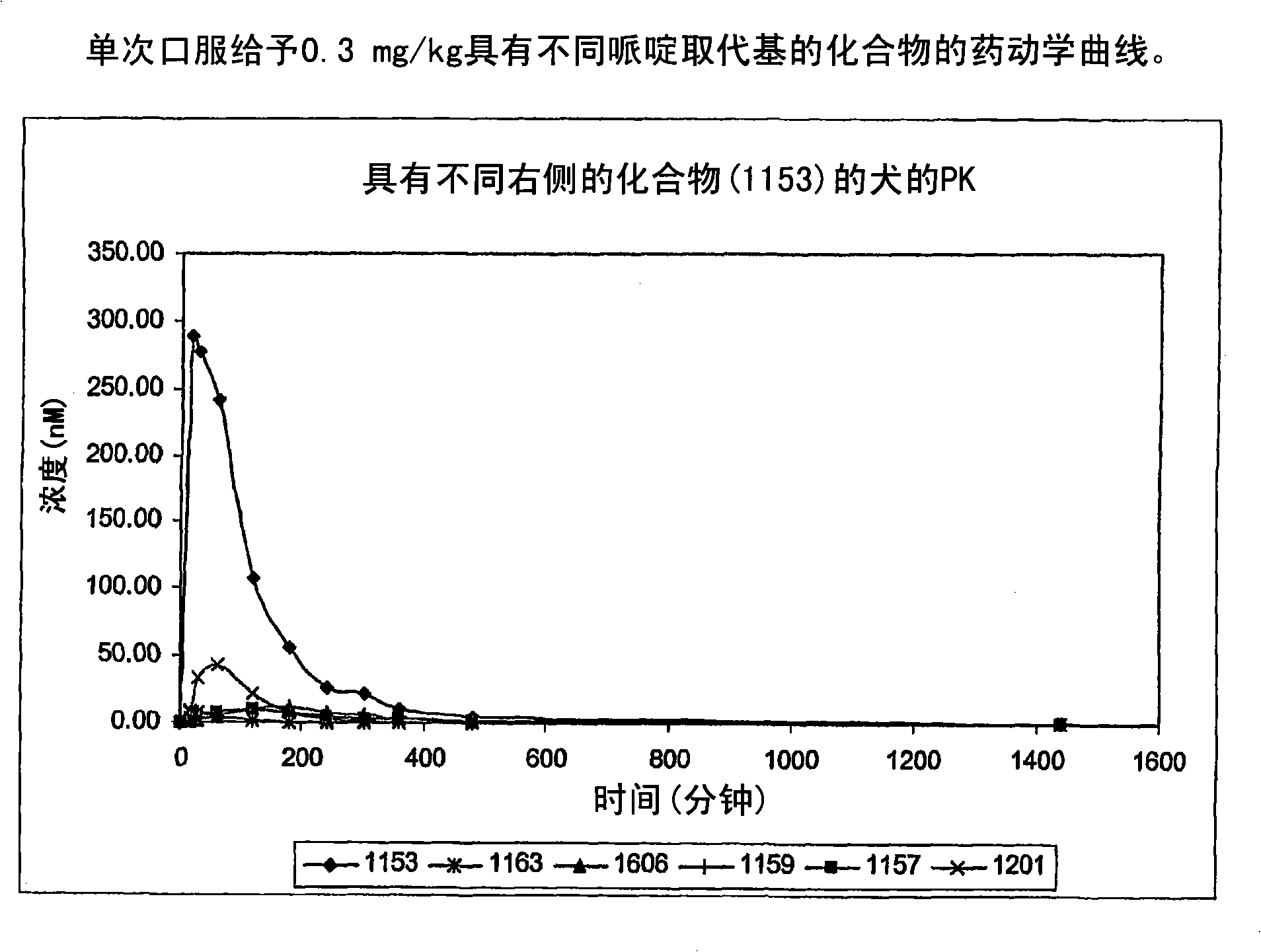
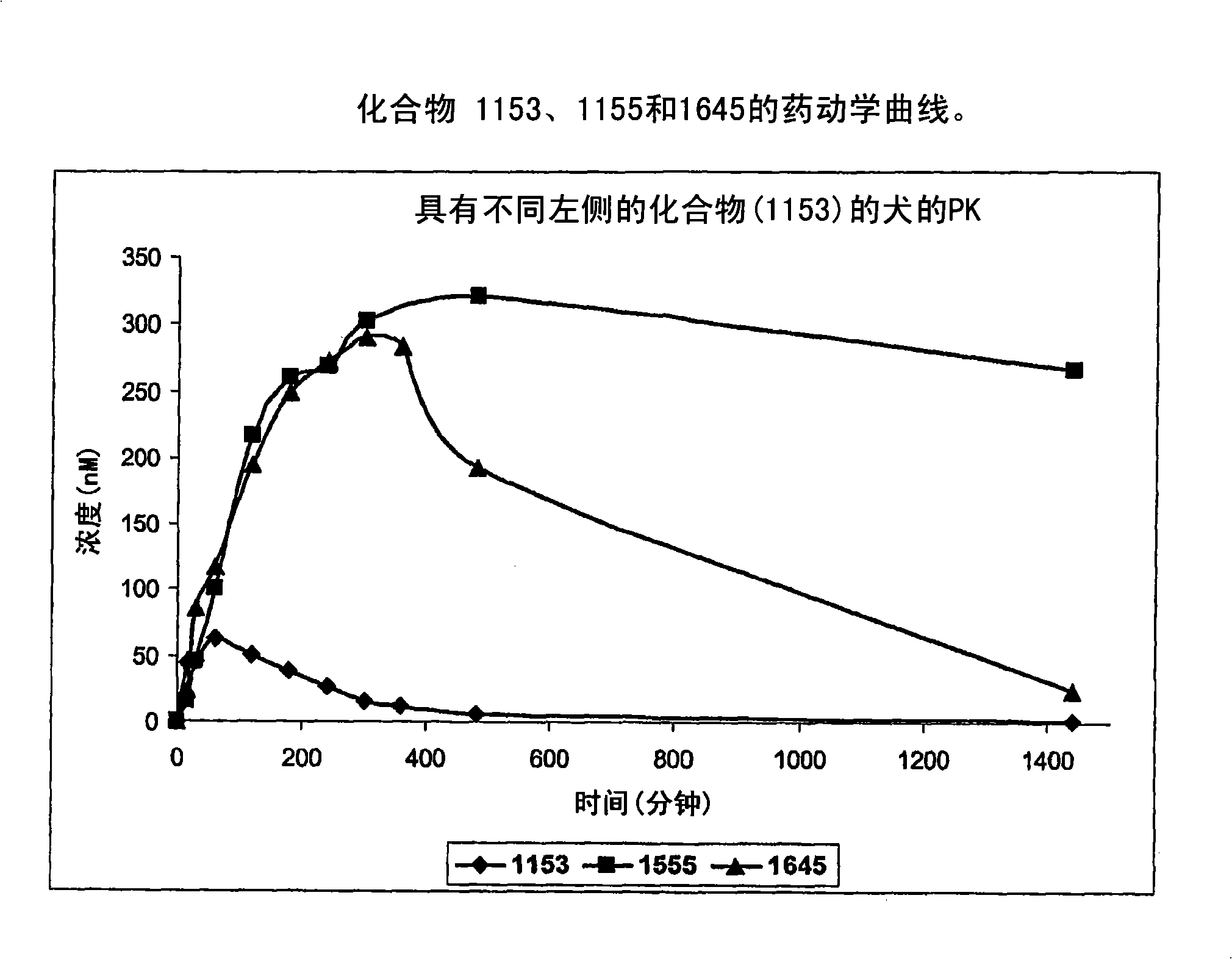
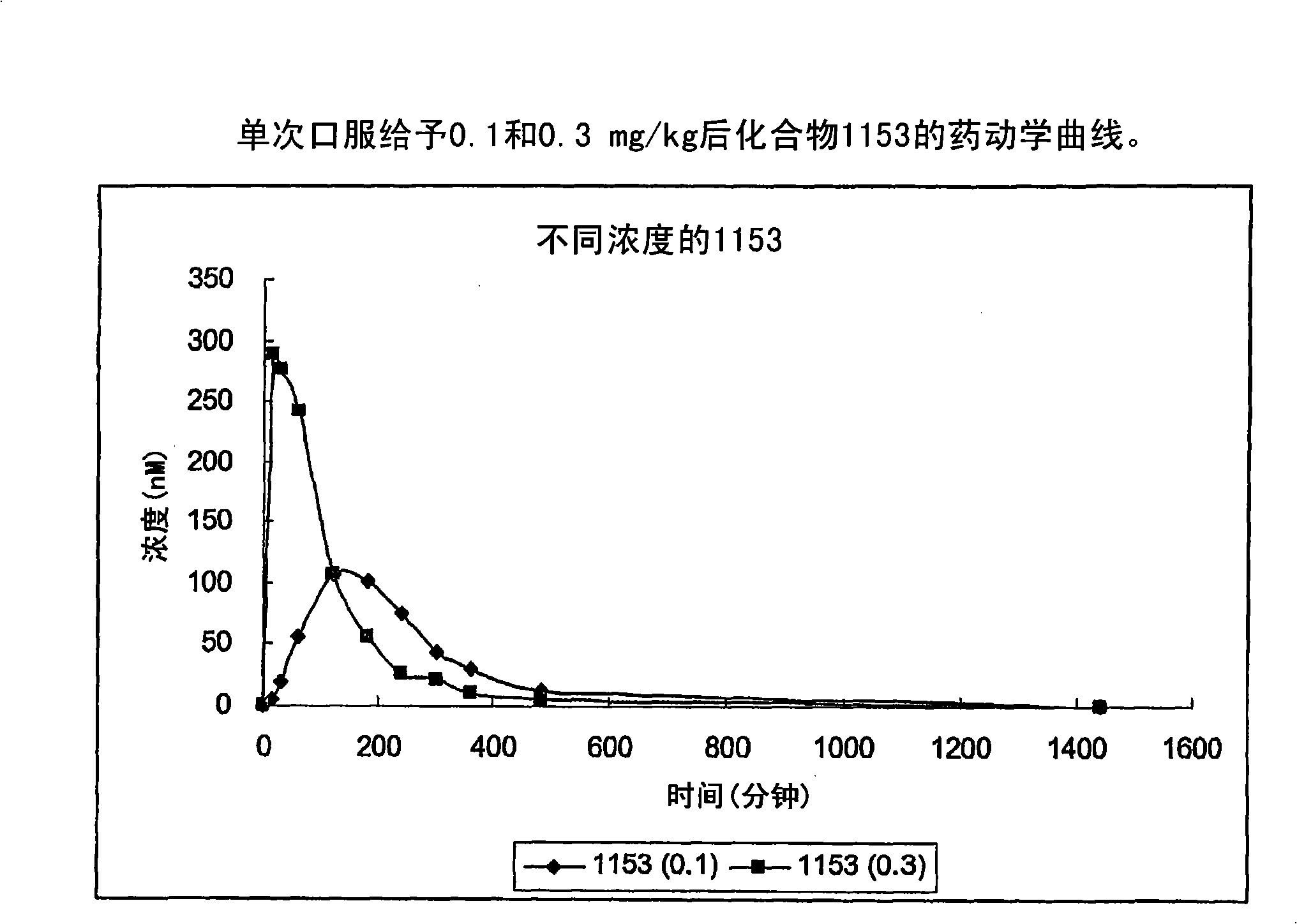
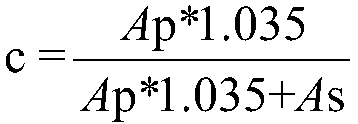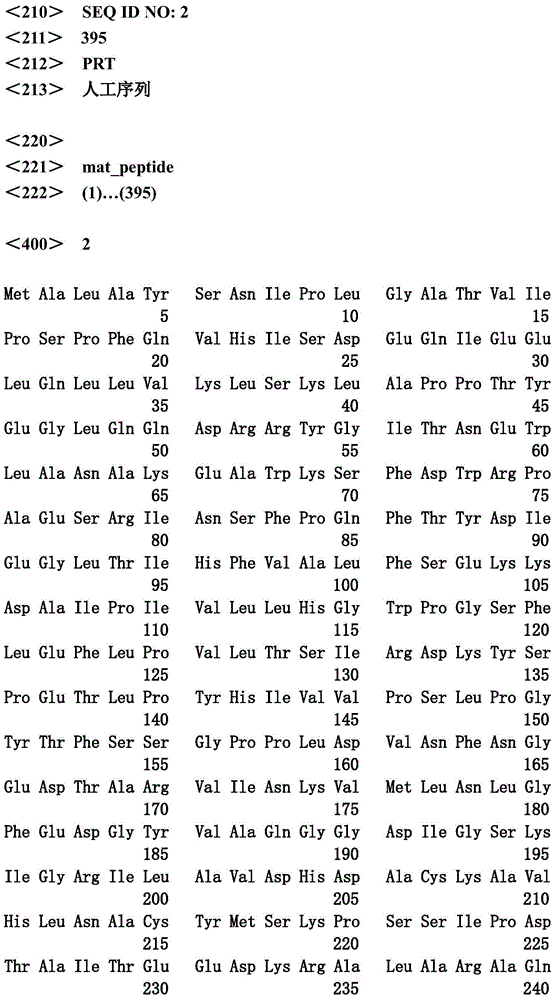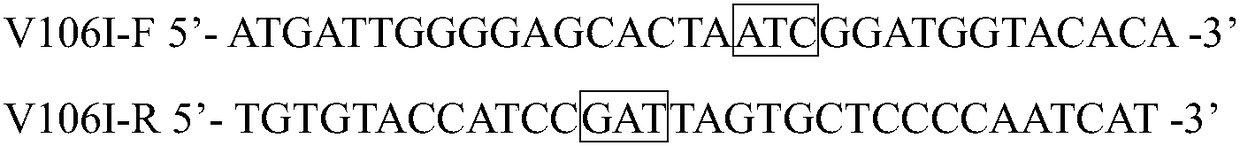Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Epoxide Hydrolases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
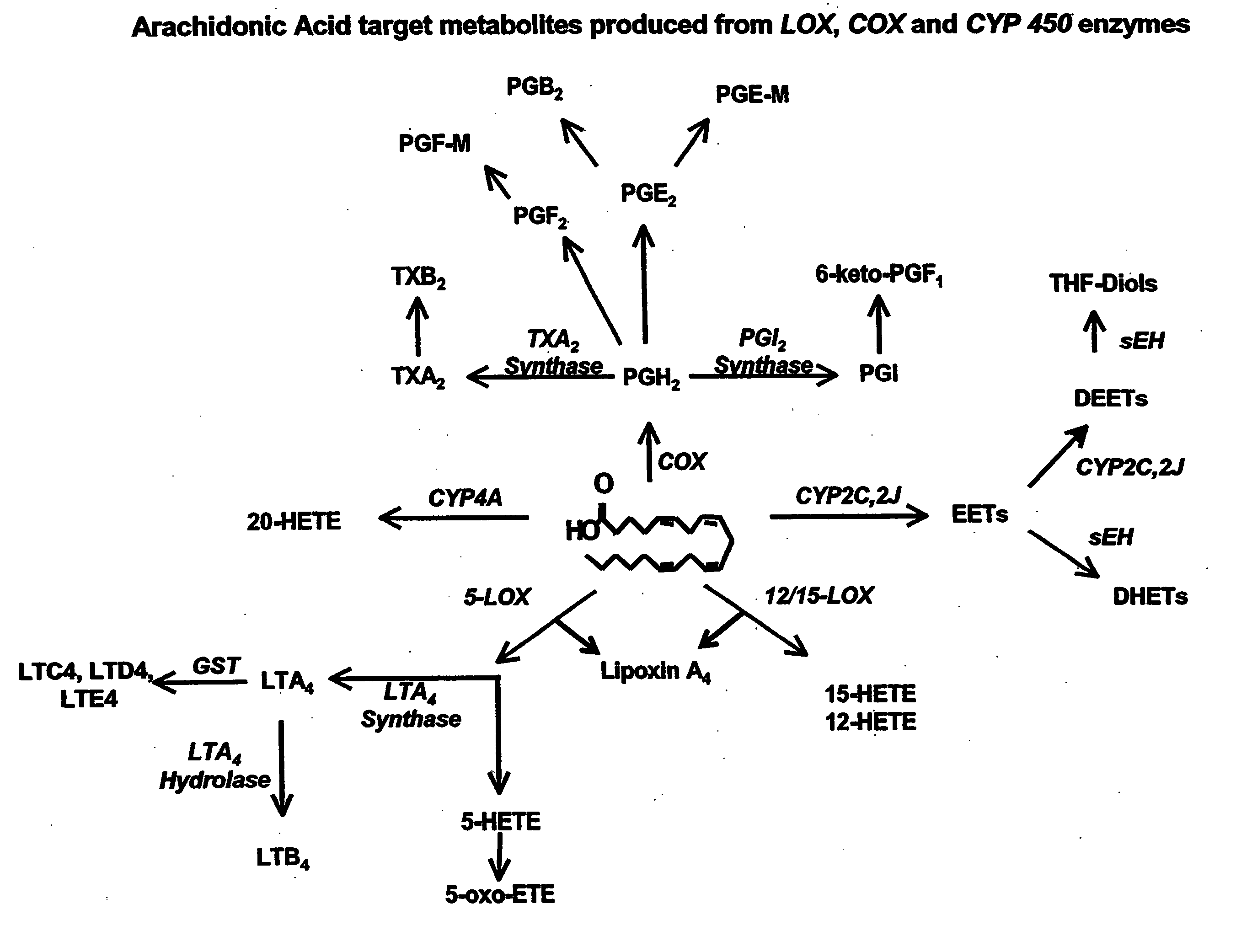
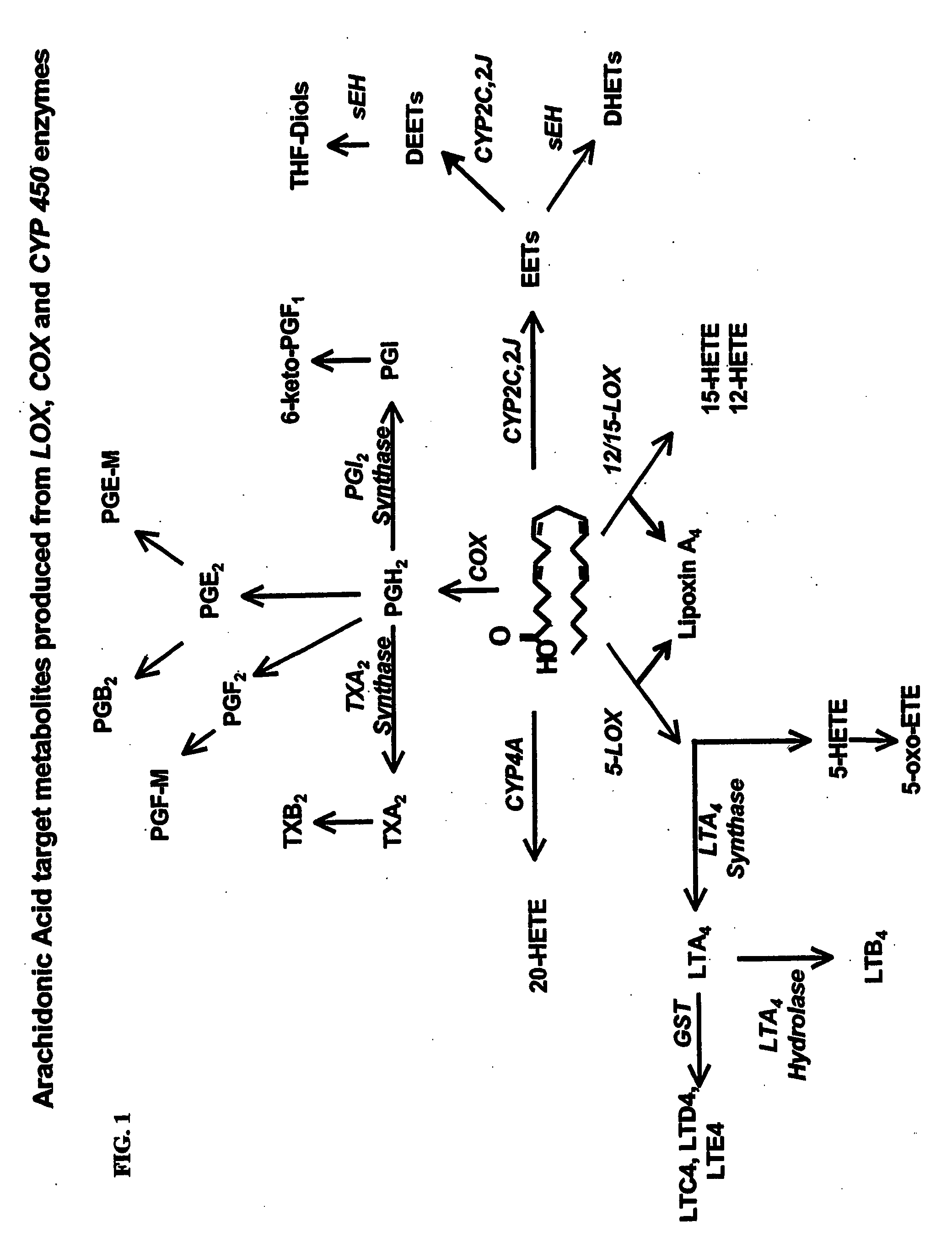
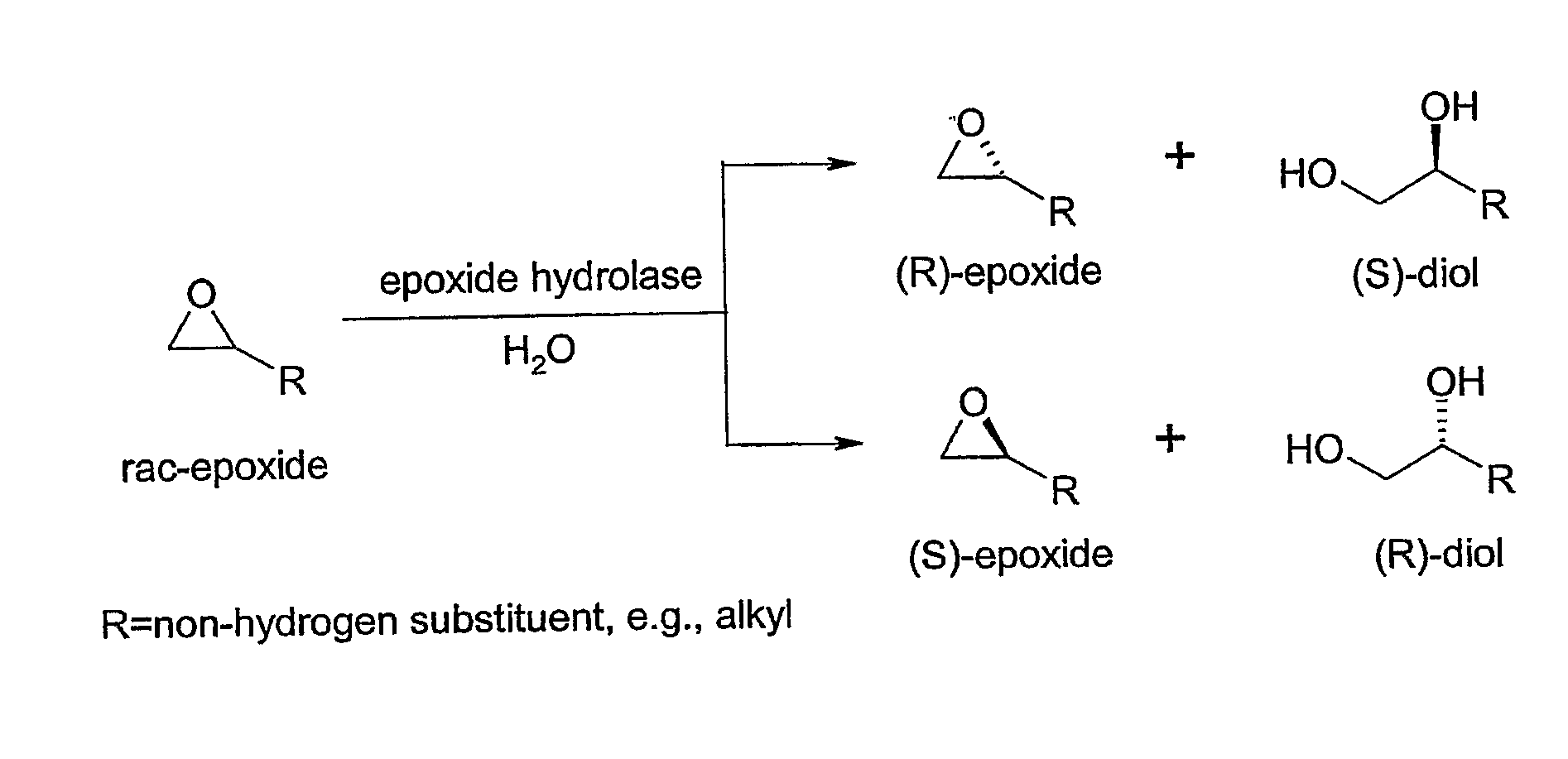
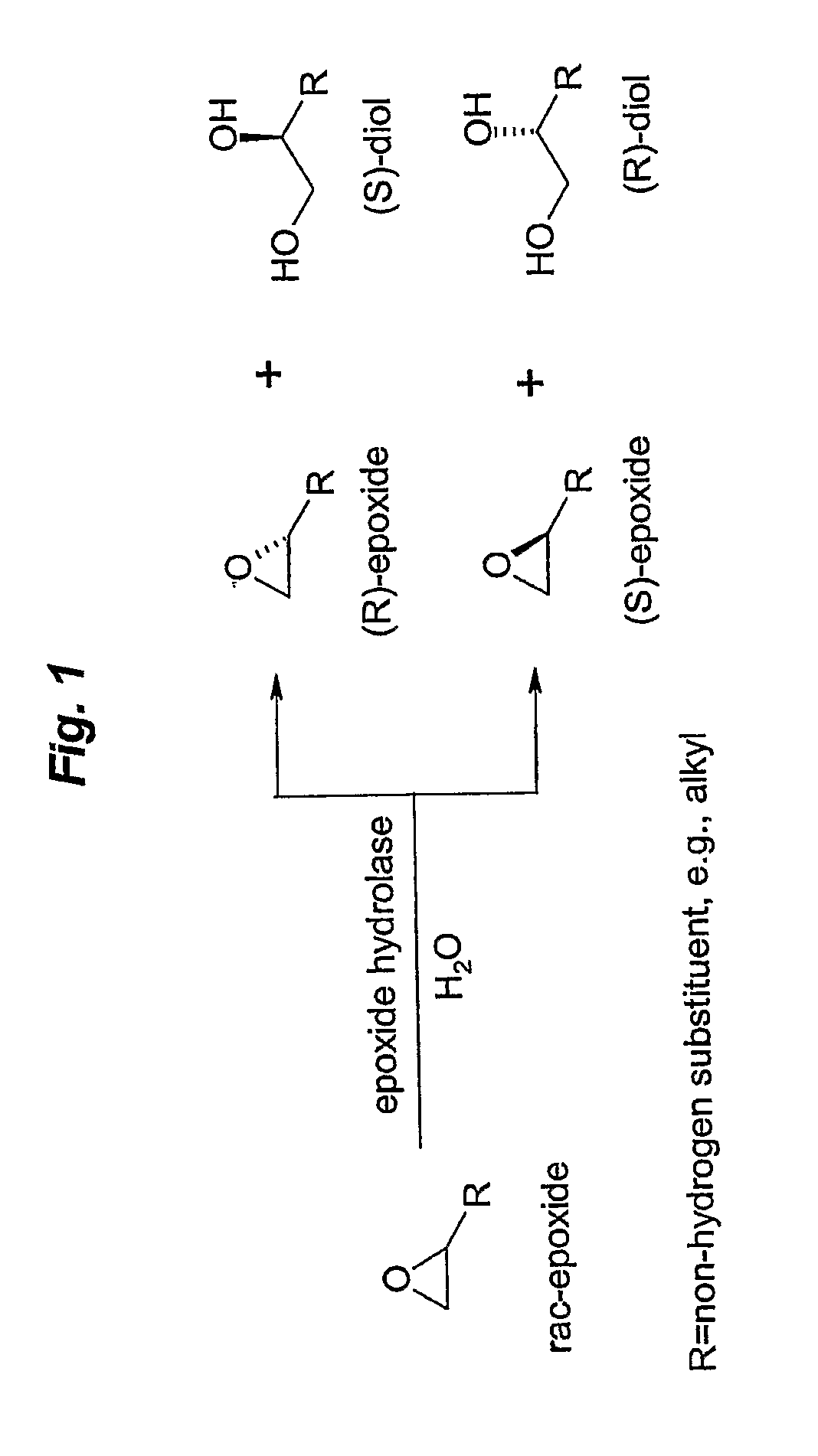
Enzymes that catalyze reversibly the formation of an epoxide or arene oxide from a glycol or aromatic diol, respectively.
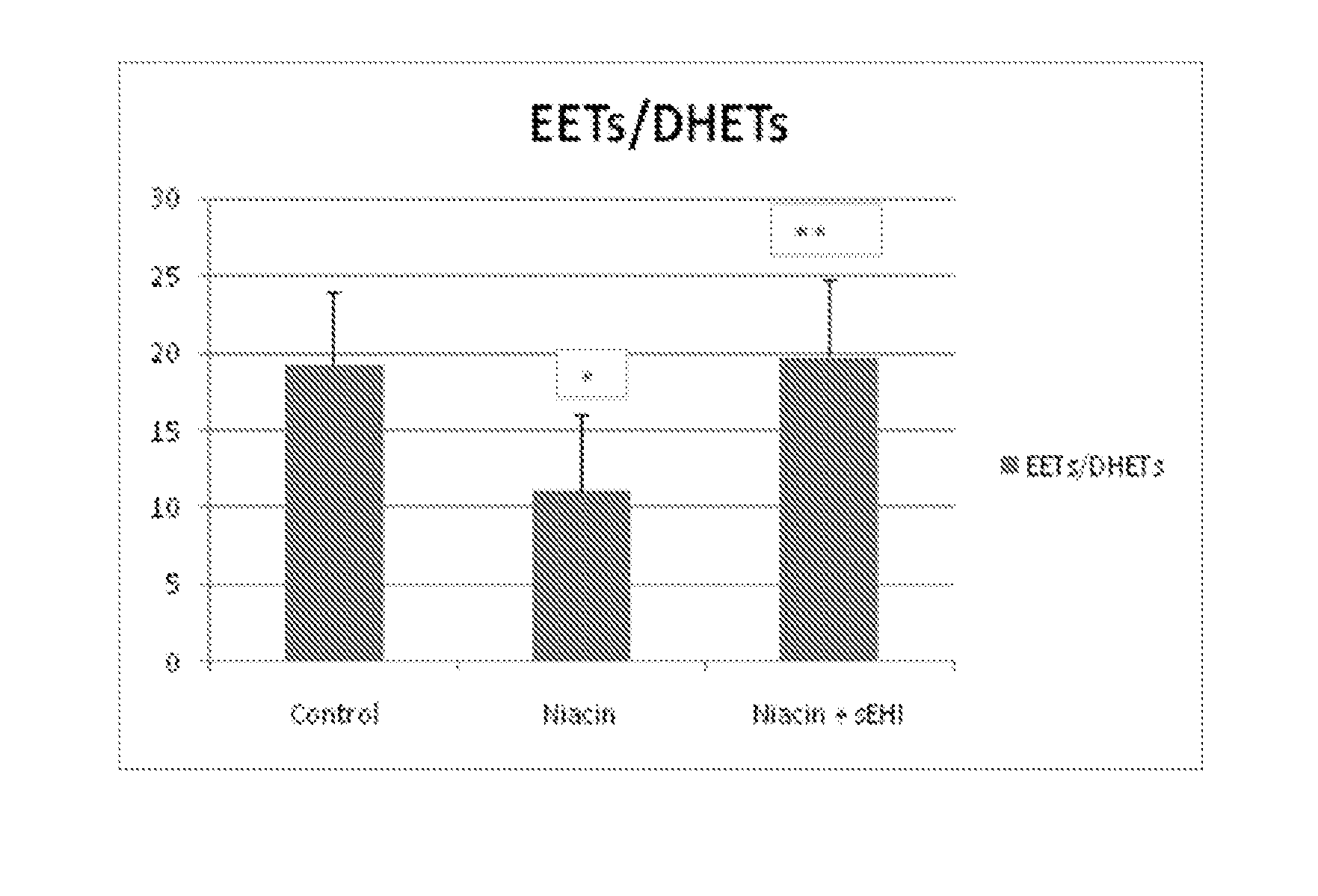
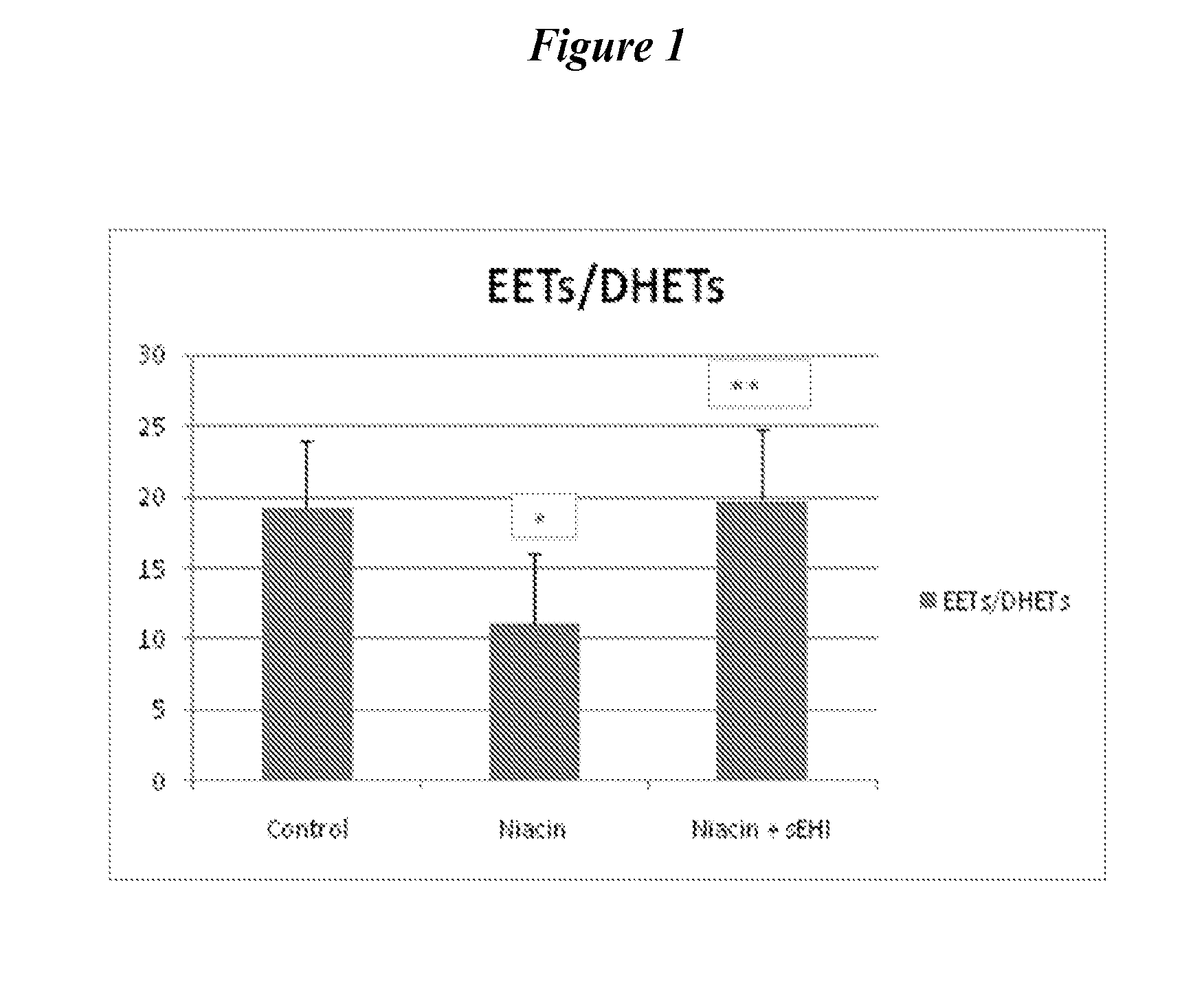
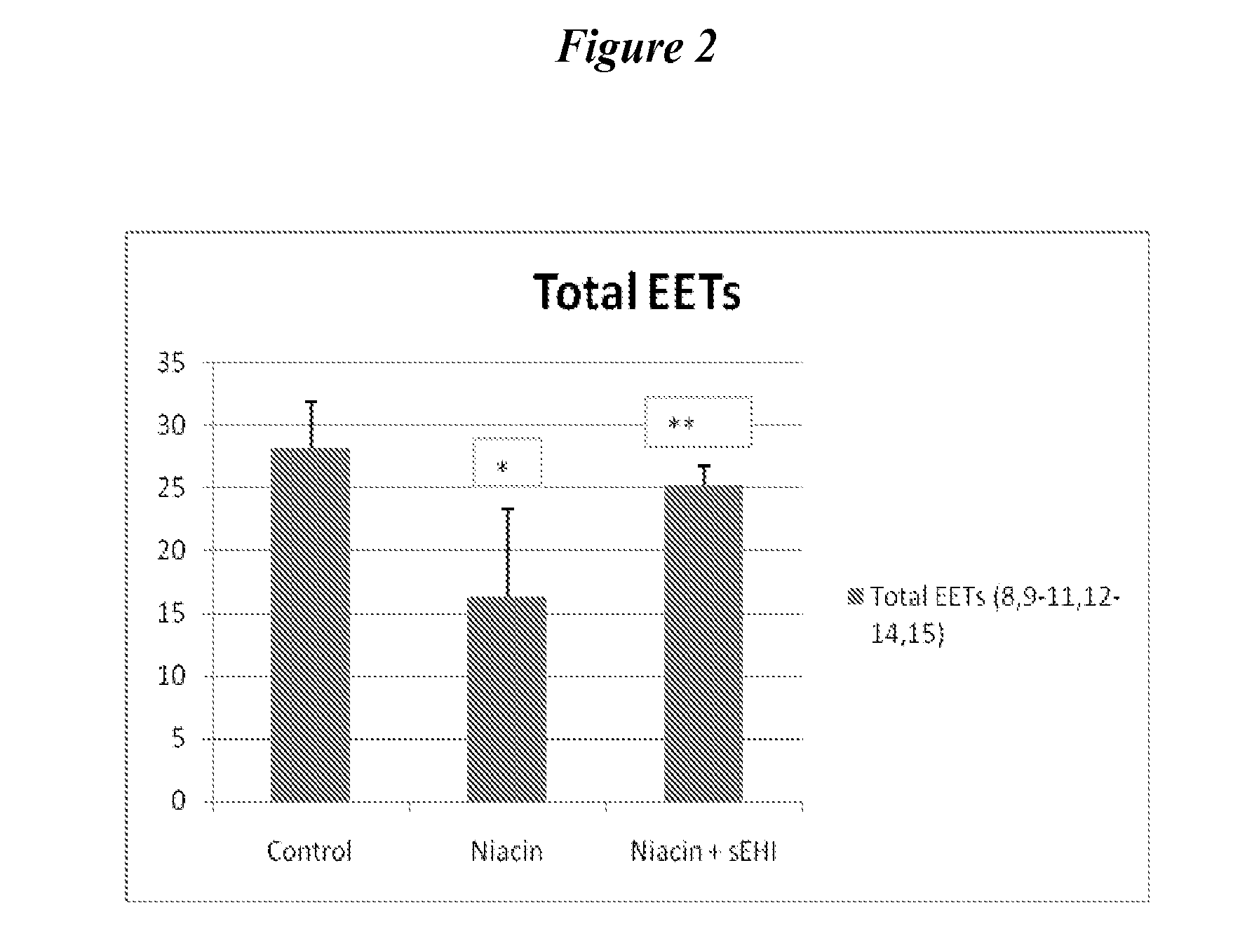
Inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase to inhibit or prevent niacin-induced flushing
InactiveUS20120046251A1Prevent and reduce and block substantial flushingPrevent, reduce or block substantial flushingSalicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideCutaneous vasodilationSide effect
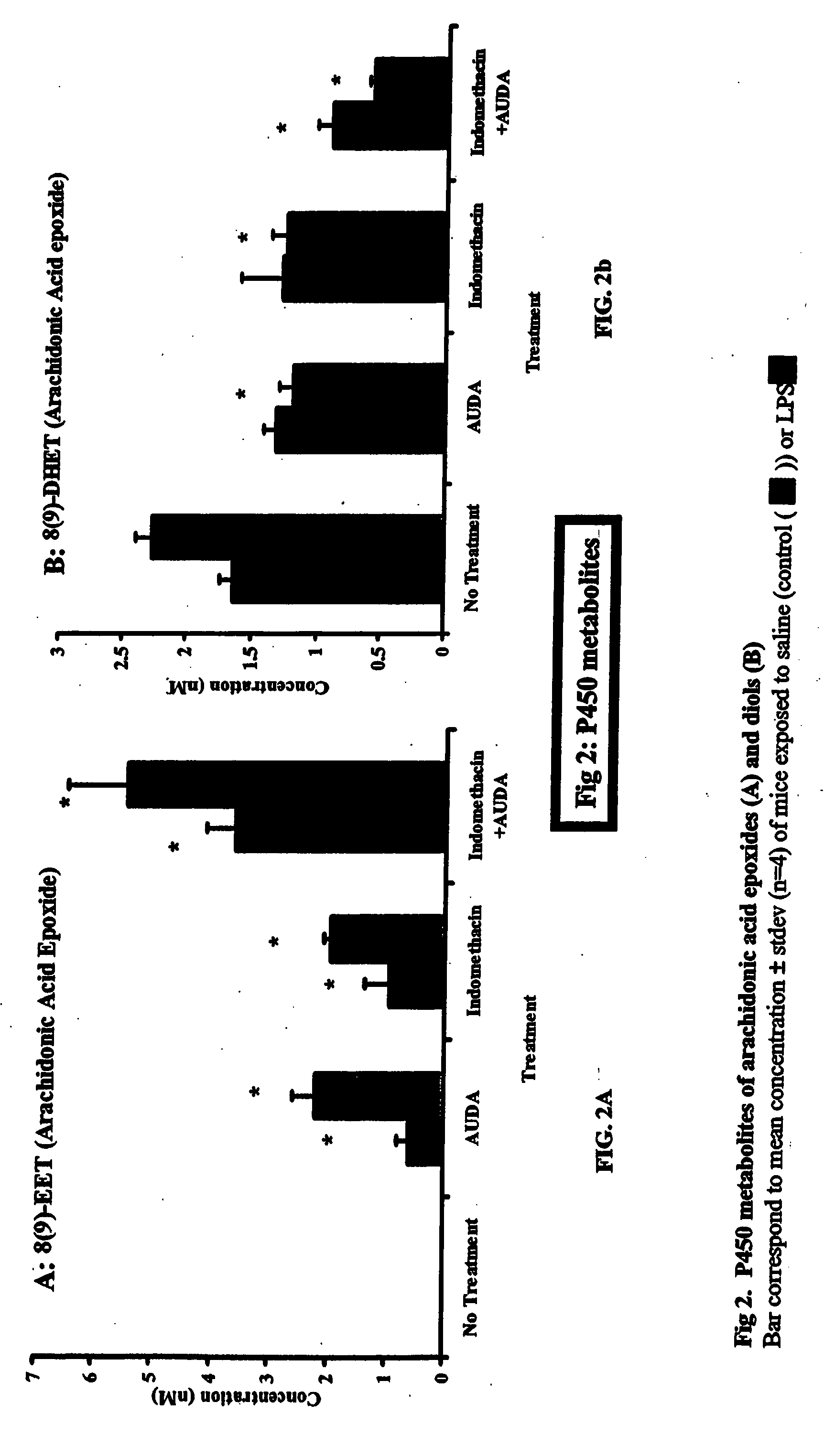
The invention discloses methods of using cis-epoxyeicosantrienoic acids (“EETs”), inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase (“sEH”), or a combination of an EET and an inhibitor of sEH, to reduce or prevent niacin-induced cutaneous vasodilation (“flushing”) in subjects suffering from this undesirable side effect of receiving therapeutic amounts of niacin.
Owner:SCHAEFER SAUL
Use of inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase to synergize activity of COX and 5-LOX inhibitors
ActiveUS20060178347A1Improve effectGood effectBiocideNervous disorderEpoxide hydrolaseAnalgesic agents
The invention relates to methods, compositions, and uses of those compositions for making medicaments, for potentiating the beneficial effects of inhibitors of COX-1, COX-2, and 5-LOX, and reducing adverse effects, by also administering inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase (“sEH”), with or without also administering one or more cis-epoxyeicosantrienoic acids. The invention further relates to the use of inhibitors of sEH as analgesics and to methods and compositions of epoxides of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, optionally with an inhibitor of sEH, to reduce pain or inflammation or both.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Kidney bean epoxide hydrolase mutant with improved catalytic activity and enantio-convergent property
ActiveCN106119220AImproved EnantionormalityEnhanced enantiouniform catalytic propertiesBacteriaHydrolasesSite-directed mutagenesisMutant
The invention discloses a kidney bean epoxide hydrolase mutant with improved catalytic activity and enantioconvergent property, belonging to the fields of genetic engineering and protein expression. A strain of epoxide hydrolase mutant PvEH1 <L105I / M160A / M175I> with improved catalytic activity and enantio-convergent property can be obtained by reforming the molecular structure of epoxide hydrolase (EH) by means of a site-directed mutation biotechnology on the basis of EH with certain enantio-convergent catalysis characteristic. The mutant has the advantages of high enantio-selectivity and high catalytic activity, thus having greater application potential and also laying a theoretical foundation for the study of the EH.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
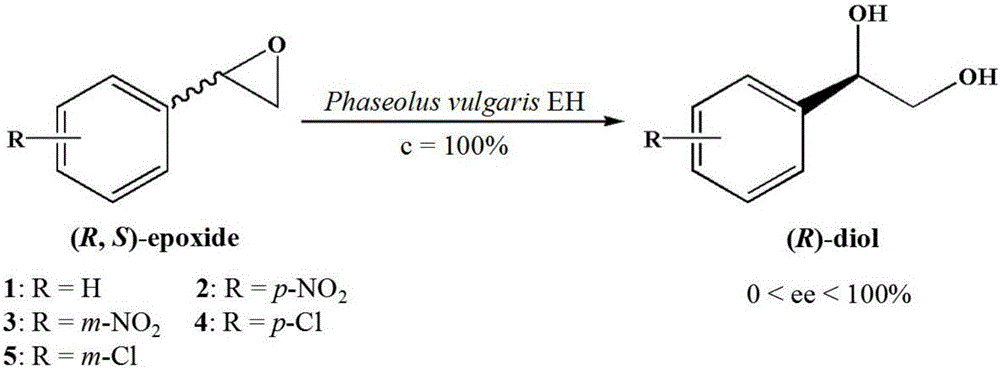
Epoxide hydrolase sourced from Phaseolus vulgaris and application thereof
The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase sourced from Phaseolus vulgaris and an application thereof and belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase gene (pveh2) sourced from a leguminous plant, Phaseolus vulgaris, as well as a corresponding amino sequence. The invention provides a recombinant plasmid pET28a(+)-pveh2 and a genetic engineering bacteria E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a(+)-pveh2, which comprise the gene. A recombinant epoxide hydrolase is prepared through expression by the bacterial strain. The invention provides a method of biocatalysis through fermentation with an enzyme produced by the recombinant bacterial strain constructed in the invention, thus producing enantiomerically pure R-type styrene oxide (ee > 99%); in addition, final yield can reach 49.3%, which is approximate to a theoretical value, 50%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Reducing Nephropathy with Inhibitors of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase and Epoxyeicosanoids
The invention provides uses and methods for reducing nephropathy in persons with diabetes mellitus (particularly Type 2 diabetes), in persons with metabolic syndrome, in persons with triglyceride levels over 215 mg / dL, and in persons with a cholesterol level over 200 mg / dL, by administering an inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase (“sEH”). Optionally, a cis-epoxyeicosantrienoic acid (“EET”) can be administered with the sEH inhibitor. The invention further provides for using EETs in conjunction with one or more sEH inhibitors to reduce hypertension, and for compositions of EETs coated with a material insoluble in an acid of pH 3 but soluble in a solution with a pH of 7.4 or higher.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Epoxide hydrolase mutant as well as gene and application of epoxide hydrolase mutant
InactiveCN103013945AHigh catalytic activityHigh enantioselectivityBacteriaHydrolasesWild typeEpoxide metabolism
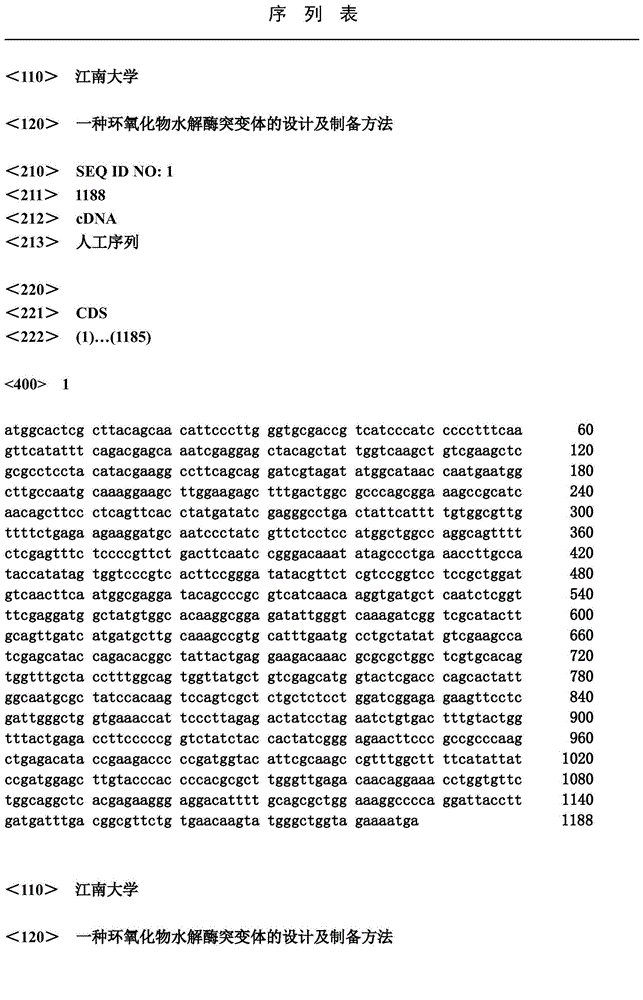
The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase mutant as well as a gene and an application of the epoxide hydrolase mutant. The epoxide hydrolase mutant is protein which is obtained by substituting one amino acid at one site or multiple sites of the 123th, 128th, 144th 145th, 168th, 219th and 221st amino acid of the protein with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No: 1 in a sequence table and deriving from the protein with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No: 1 and has epoxide hydrolase activity. Compared with wild type epoxide hydrolase, the epoxide hydrolase mutant provided by the invention can greatly improve hydrolytic activity and enantioselectivity of the racemization epoxide, and is particularly suitable for splitting and catalyzing the racemization naphthyl glycidyl ether to prepare (S)- naphthyl glycidyl ether and further synthesize racemic medicament (S)-propranolol. The hydrolase mutant has good industrial application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Aspergillus usamii epoxide hydrolase mutants with improved enantioselectivity
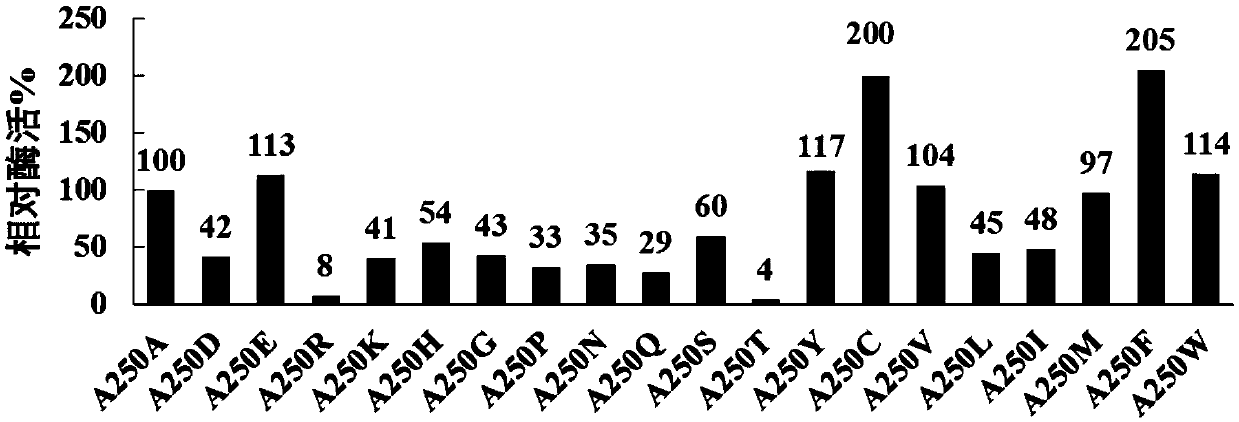
The invention discloses aspergillus usamii epoxide hydrolase mutants with improved enantioselectivity, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering and biological catalysis. Aspergillus usamii epoxide hydrolases (AuEH2) are subjected to molecular modification on the basis of rational designs and are combined with site-saturation mutagenesis methods for genes, so that the multiple epoxide hydrolase mutants with the improved enantioselectivity can be obtained. The aspergillus usamii epoxide hydrolase mutants have the advantages that racemic styrene oxide (rac-SO) can be catalyzed by the six mutants AuEH2A250I, AuEH2A250M, AuEH2A250Y, AuEH2A250S, AuEH2A250L and AuEH2A250V with the improved enantioselectivity, and the enantiomeric ratios (E values) of the six mutants can be increased and respectively reach 48, 27.2, 23.9, 21.8, 20.0 and 19.4 from the original 16 as compared with wild type mutants.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Reducing nephropathy with inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase and epoxyeicosanoids
The invention provides uses and methods for reducing nephropathy in persons with diabetes mellitus (particularly Type 2 diabetes), in persons with metabolic syndrome, in persons with triglyceride levels over 215 mg / dL, and in persons with a cholesterol level over 200 mg / dL, by administering an inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase (“sEH”). Optionally, a cis-epoxyeicosantrienoic acid (“EET”) can be administered with the sEH inhibitor. The invention further provides for using EETs in conjunction with one or more sEH inhibitors to reduce hypertension, and for compositions of EETs coated with a material insoluble in an acid of pH 3 but soluble in a solution with a pH of 7.4 or higher.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
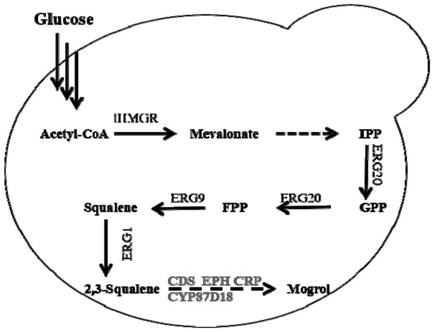
Synthesis method of terpenoid and glycosylation products thereof in synthesis route of mogrol
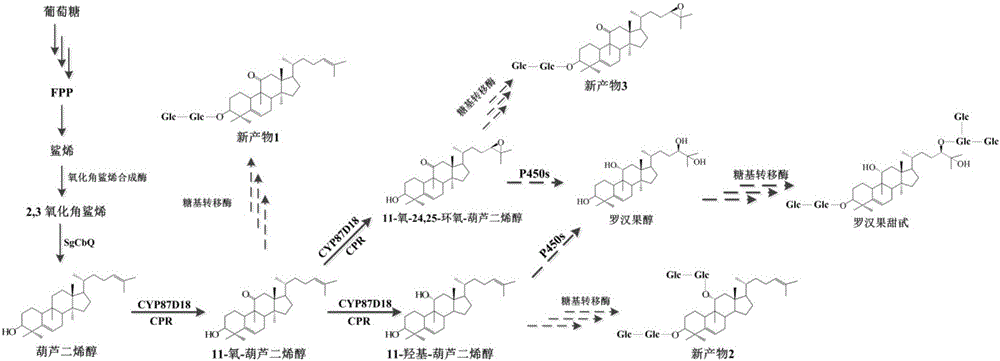
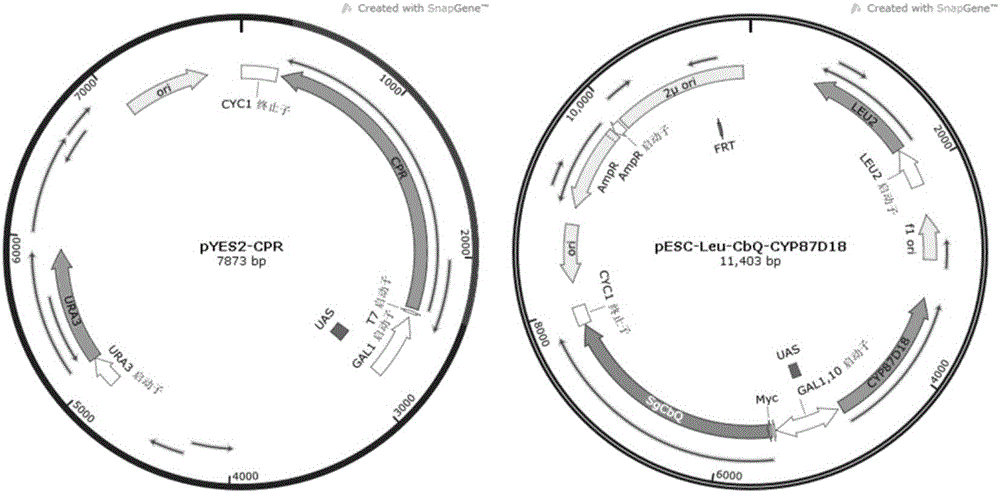
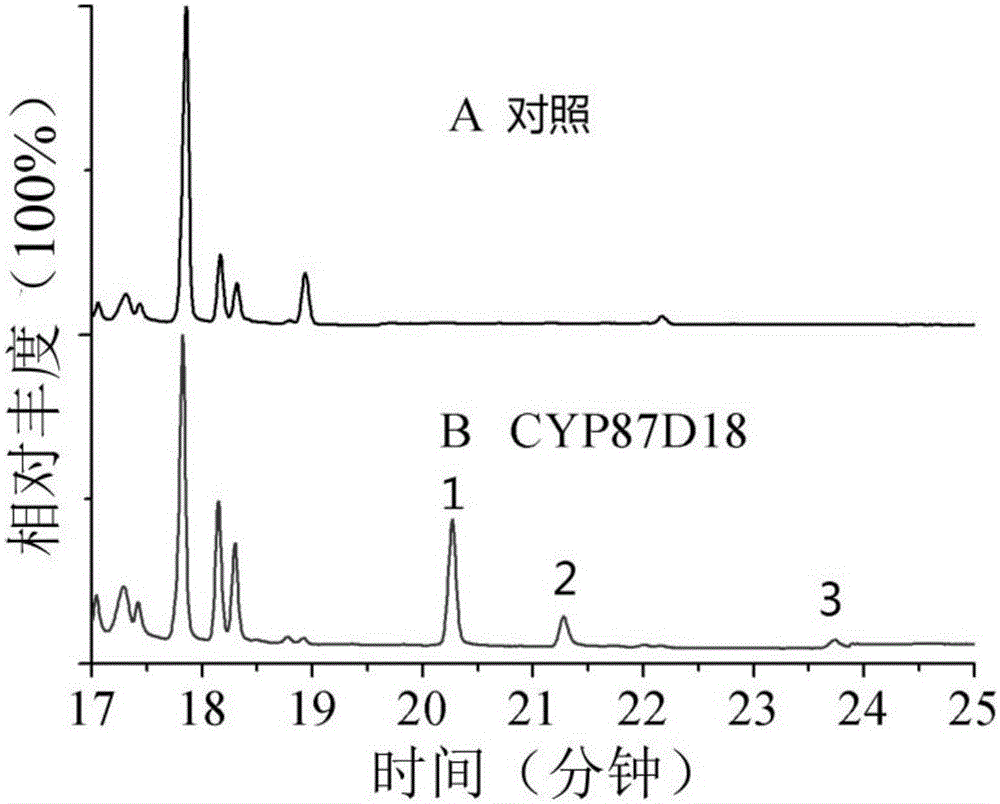
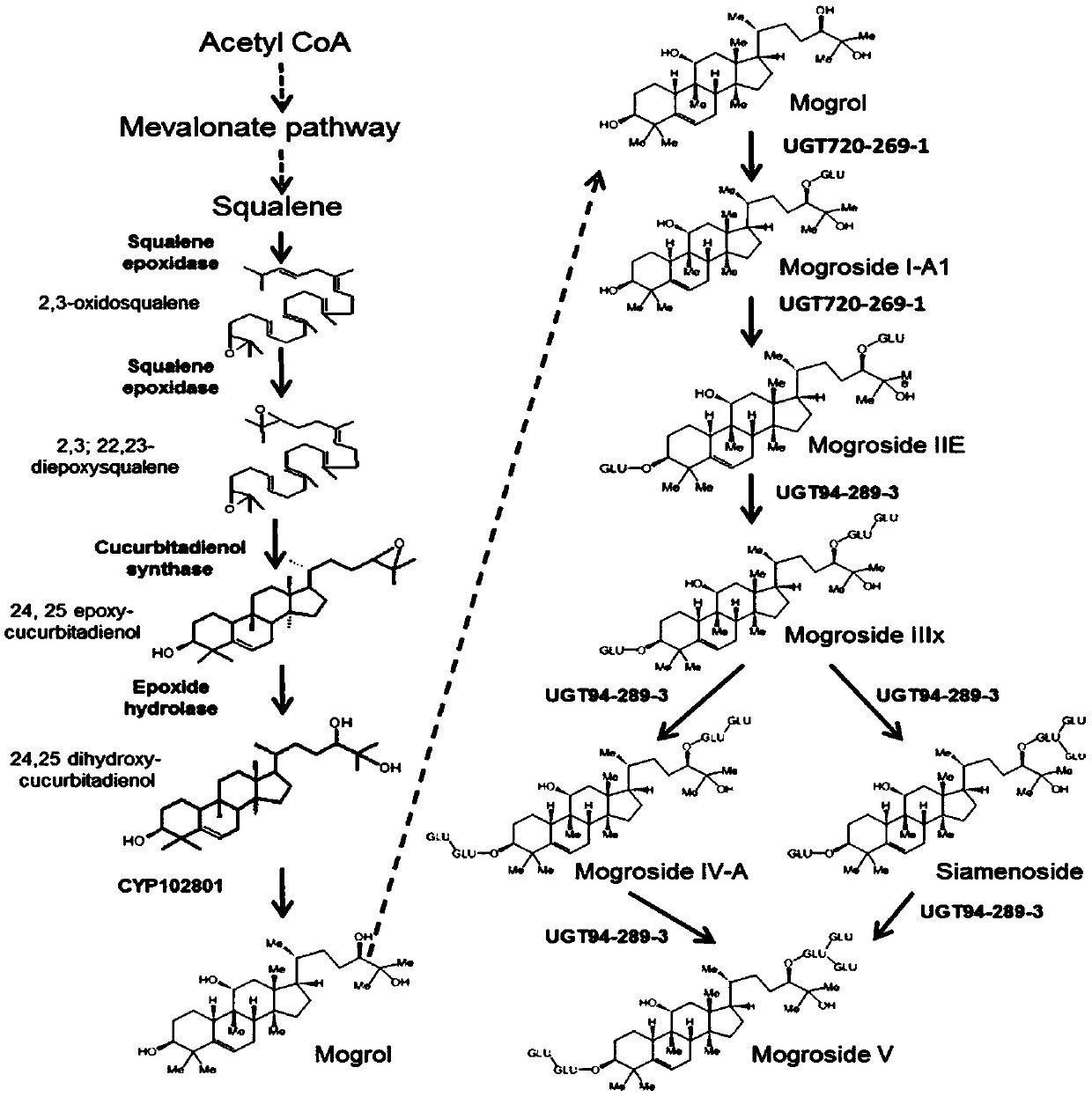
The invention discloses a microbial fermentation method for synthesizing triterpene compounds, namely a distillers yeast recombination strain SY2 containing cucurbitane dienol synthetase SgCbQ, P450 CYP87D18 and cytochrome reductase CPR, in the metabolism route of mogrol, which takes dextrose as a substrate to synthesize three new products including 11-oxygen-cucurbitane dienol, 11-hydroxy-cucurbitane dienol and 11-oxygen-24, 25-epoxy-cucurbitane dienol. The invention further discloses a metabolism route for synthesizing mogrol through cucurbitane dienol, namely the cucurbitane dienol is catalyzed through P450 CYP87D18 and synthesized into 11-oxygen-cucurbitane dienol, 11-oxygen-cucurbitane dienol is catalyzed through enzyme and synthesized into 11-hydroxy-cucurbitane dienol and 11-oxygen-24, 25-epoxy-cucurbitane dienol, and 11-hydroxy-cucurbitane dienol and 11-oxygen-24, 25-epoxy-cucurbitane dienol can be synthesized into the mogrol through other P450 or epoxide hydrolase. The invention further discloses a novel thought for obtaining more glycosylation products by catalyzing new products through glycosyl transferase. The method has significance for determining the synthesis route of mogrol and synthesizing relevant intermediate metabolites and glycosylation products through the microbial fermentation method.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Production Of Enantiopure alpha-Hydroxy Carboxylic Acids From Alkenes By Cascade Biocatalysis
The invention provides compositions comprising an alkene epoxidase and a selective epoxide hydrolase, such as a recombinant microorganism comprising a first heterologous nucleic acid encoding an alkene epoxidase and a second heterologous nucleic acid encoding a selective epoxide hydrolase. Exemplary alkene epoxidases include StyAB, while exemplary selective epoxide hydrolases include epoxide hydrolases from Sphingomonas, Solanum tuberosum, or Aspergillus. The invention also provides non-toxic methods of making enantiomerically pure vicinal diols or enantiomerically pure alpha-hydroxy carboxylic acids using these compositions and microorganisms.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Microbial kinetic resolution of ethyl-3,4-epoxybutyrate
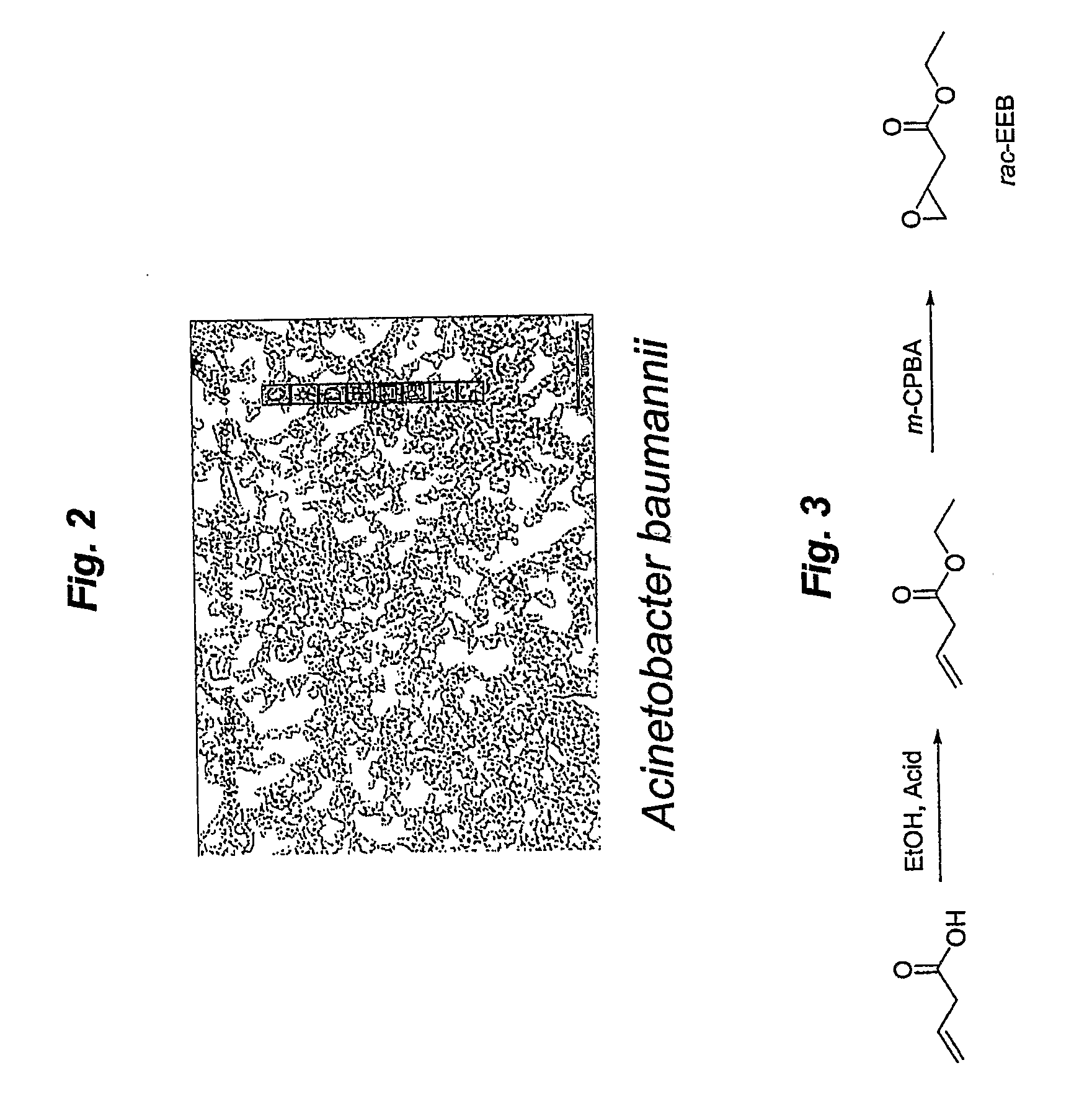
Two novel microorganisms, Acinetobacter baumanni ATCC PTA-8303 and Cryptoeoecus albiduz ATCC PTA 8302 having epoxide hydrolase activity are described. The epoxide hydrolases from these microorganisms can be used to selectively hydrolyze (via epoxide opening) one enantiomer of ethyl-3,4-epoxybutyrate in a racemic mixture by a kinetic resolution process to result in the accumulation of the other enantiomer. Methods of preparing the microorganisms and their use in a kinetic resolution process of racemic ethyl-3,4-epoxybutyrate are also disclosed.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
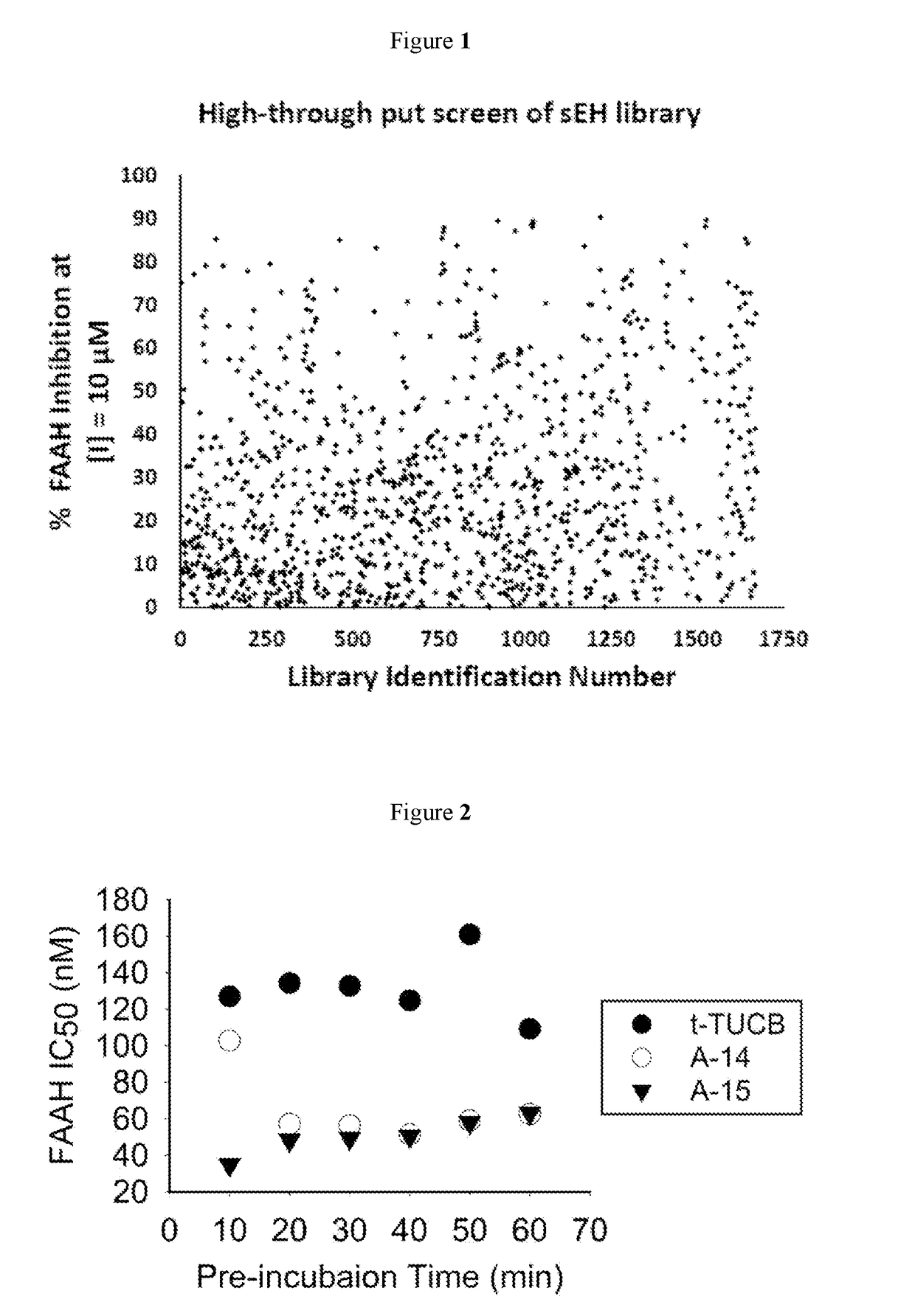
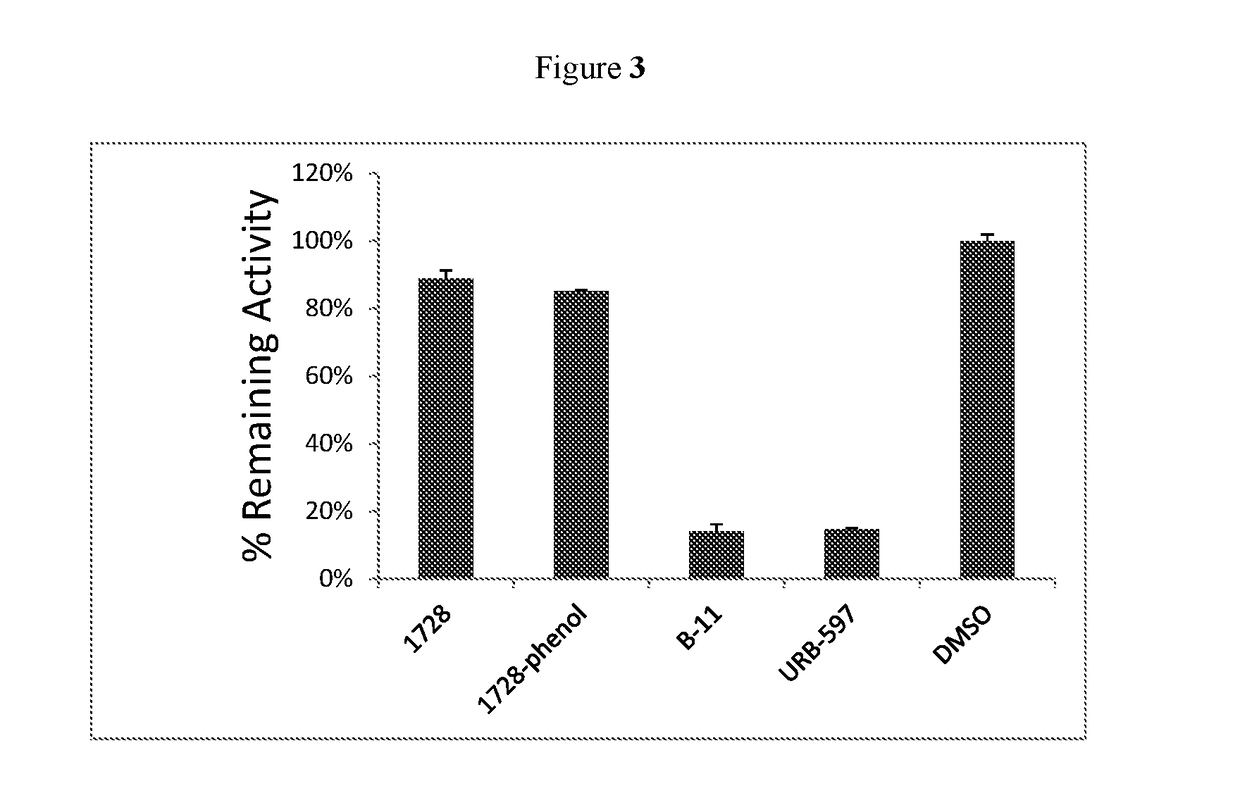
Inhibitors for soluble epoxide hydrolase (SEH) and fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH)
The present invention provides compounds that are dual inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase and fatty acid amide hydrolase. The present invention also provides methods of using the compounds to inhibit soluble epoxide hydrolase and fatty acid amide hydrolase, and to treat cancer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
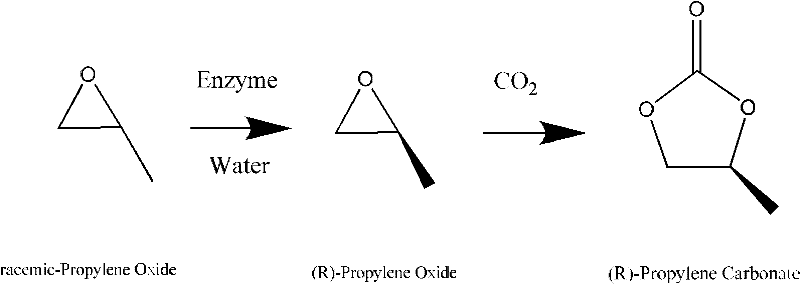
Preparation method of (R)-propene carbonate
InactiveCN102391239AWide variety of sourcesReduce riskOrganic chemistryOrganic solventEpoxide metabolism
The invention relates to a preparation method of (R)-propene carbonate, which comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing propylene oxide and epoxide hydrolase ECU1040 with water, carrying out reaction for 10-40 hours at the temperature of 0-5 DEG C, then, stopping the reaction, and distilling (R)-propylene oxide at normal atmosphere; and (2) mixing the obtained (R)-propylene oxide with an organic solvent, adding quinine and organic amine, leading in carbon dioxide gas at the temperature of 10-30 DEG C while stirring until the carbon dioxide gas is not absorbed, carrying out reaction for a total reaction time of 15-30 hours, and then obtaining the (R)-propene carbonate. The preparation method is simple and practical, the sources of the raw materials are wide, the reaction is carried out at the normal pressure, the risk is low, the equipment investment is small, the yield is high, the optical purity of the product reaches over 99% e.e, and thus, the preparation method has an excellentindustrial prospect.
Owner:上海科利生物医药有限公司
Epoxide hydrolase from rhodosporidium paludigenum and application of epoxide hydrolase
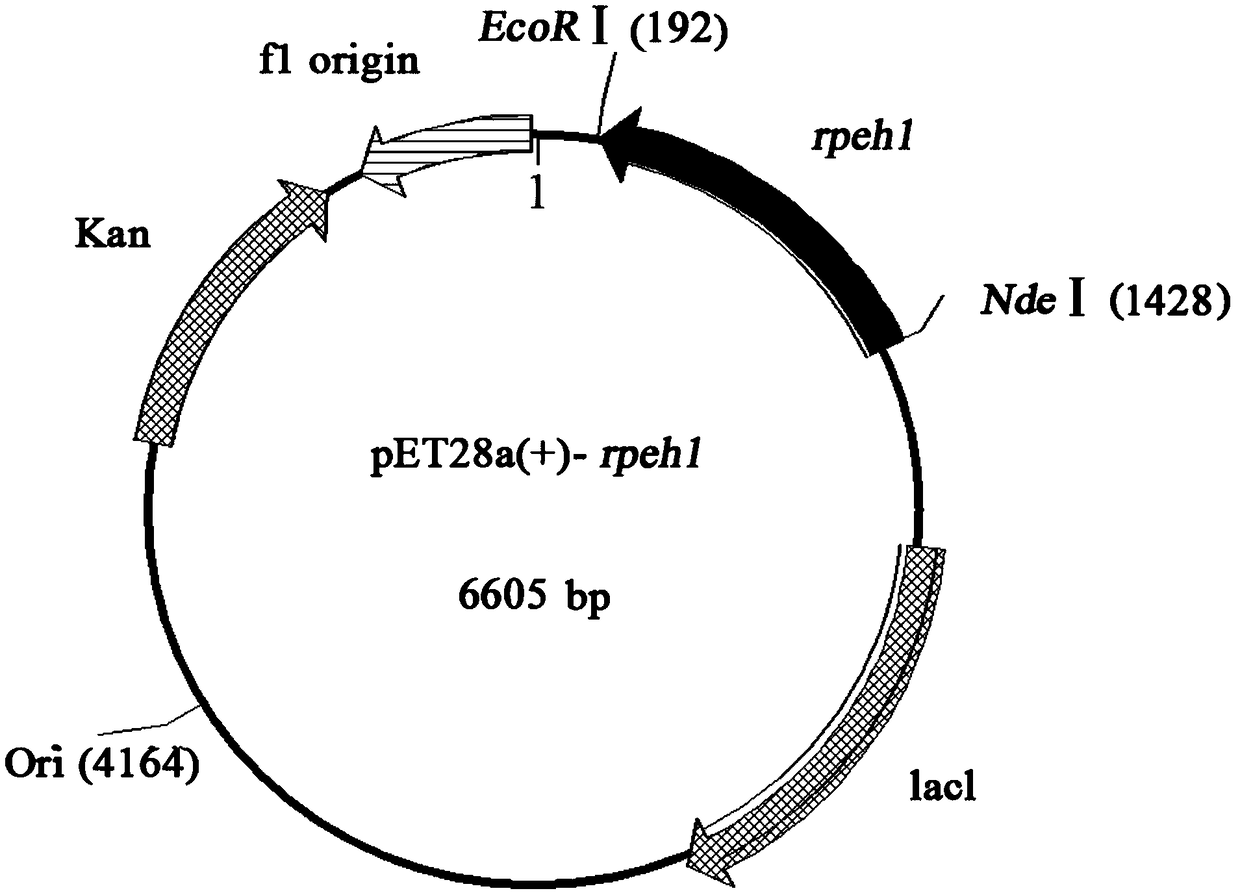
ActiveCN109355271AHigh catalytic activityImprove catalytic selectivityHydrolasesGenetic engineeringEpoxide hydrolase 3Phenyl glycol
The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase from rhodosporidium paludigenum and application of the epoxide hydrolase, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The epoxide hydrolase and the application have the advantages that epoxide hydrolase genes (rpeh1) from the rhodosporidium paludigenum R. paludigenum and corresponding amino acid sequences are provided; recombinant plasmids pET28a(+)-rpe1 with the genes and genetically engineered bacteria E. coli BL21 (DE3) / pET28a(+)-rpeh1 are constructed, and recombinant epoxide hydrolases are prepared by the aid of bacterial strains; biologicalcatalysis can be carried out by the constructed genetically engineered bacteria, and accordingly the ee of enantiomerically pure R-type phenyl glycol obtained by means of preparation is higher than 73%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for degrading 1,2,3-TCP (trichloropropane) by engineered strain bacillus subtilis
The invention discloses a method for degrading 1,2,3-TCP (trichloropropane) by engineered strain bacillus subtilis. According to the method, firstly, alkyl halide dehalogenase genes, halogenohydrin dehalogenase genes and epoxide hydrolase genes which can degrade 1,2,3-TCP and intermediate products of the 1,2,3-TCP are synthesized; the gene sequence and the codase amino acid sequence are respectively shown as SEQ ID NO.1 to 6; then, the bacillus subtilis integrating carrier containing the gene is built; the carrier converts the bacillus subtilis; by a gene ectopic integration and resistance gene knock-out method, the gene is integrated into the bacillus subtilis genome; the engineered strain bacillus subtilis capable of secreting and expressing alkyl halide dehalogenase, halogenohydrin dehalogenase and epoxide hydrolase is obtained. The engineered strain bacillus subtilis has a good degradation effect on TCP and TCP intermediate products; the complete TCP degradation can be realized; the characteristics of high degradation efficiency, high TCP tolerance, stable inheritance and the like are realized; the application prospects are good.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Magnetic cellulose-dimethyl imidazole zinc salt and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN105622985AEasy to recycleEasy to reuseOxidoreductasesOn/in organic carrierCelluloseZinc nitrate
The invention belongs to the technical field of new function materials, and particularly relates to magnetic cellulose-dimethyl imidazole zinc salt and a preparing method and application thereof. Cellulose is dissolved in NaOH-Urea aqueous solution, nanometer Fe3O4 is added while stirring, water is added for regeneration, and product separation and washing are conducted to obtain magnetic cellulose; the magnetic cellulose and zinc nitrate solution are mixed and stirred for 5-30 min, then 2-methylimidazole solution is added for reaction lasting 0.5-24 h while stirring, and the obtained solid is subjected to magnetic separation, washing and drying to obtain the magnetic cellulose-dimethyl imidazole zinc salt. The product can be used as a carrier for enzyme immobilization, can immobilize a series of enzymes including lipase, papain, mung bean epoxide hydrolase and peroxidase, and has the potential to be a carrier of protein drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Pathogen from rice, chemically inducible promoter and their use
The present invention provides one kind of DNA sequence segment, which is obtained from rice, can be infected by rice blast and induced by salicylic acid and jasmonic acid, and may be used as pathological and chemical inducing promoter. The DNA sequence segment is the transcriptional control area is rice hydroperoxl fatty acid hydroxylated epoxide hydrolase gene and features that it has the nucleotide sequence of the promoter from site-1 to site-2789 shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The functional analog obtained via inserting, replacing and / or deleting one or several nucleotide sequences into the nucleotide sequence may be used to reach the aim of the present invention. The present invention may be used as pathological and chemical inducing promoter, molecular mark probe, rice re-separating control sequence or relevant control sequence for other transgenic plant and in breeding disease resisting plant.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Engineering strain for expressing epoxide hydrolase of kidney beans, and application of engineering strain
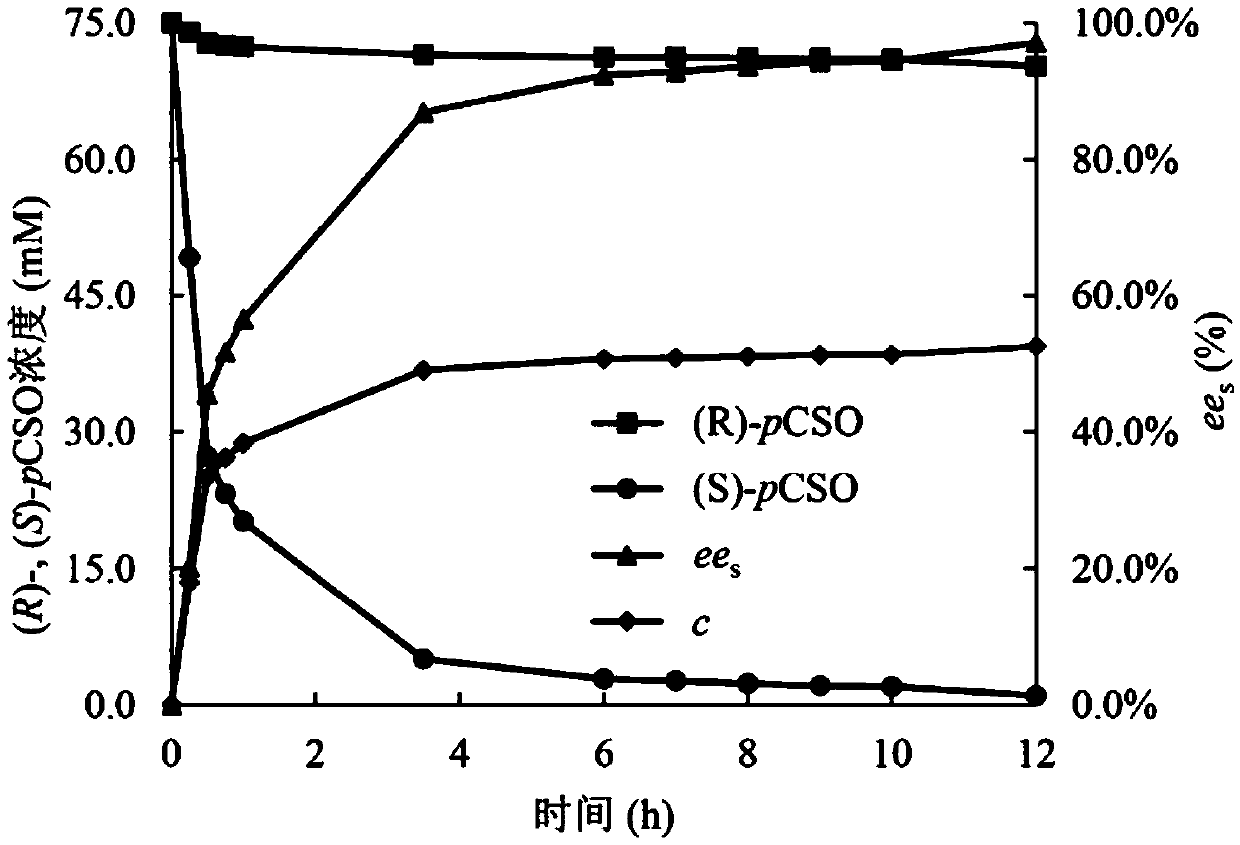
The invention discloses an engineering strain for expressing epoxide hydrolase of kidney beans, and application of the engineering strain, belonging to the field of biological engineering technology. The invention provides the epoxide hydrolase and recombinant escherichia coli for expressing the epoxide hydrolase. The epoxide hydrolase provided by the invention can catalyze racemic p-chloro-epoxyethylbenzene (rac-pCSO) to generate (R)-p-chloro-phenyl ethylene glycol (pCPED); when the conversion rate reaches 99.7%, an enantiomer excess value of the product is 85.1%eep. Compared with other plant-derived epoxide hydrolases, the epoxide hydrolase provided by the invention increases the value by 10 times.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
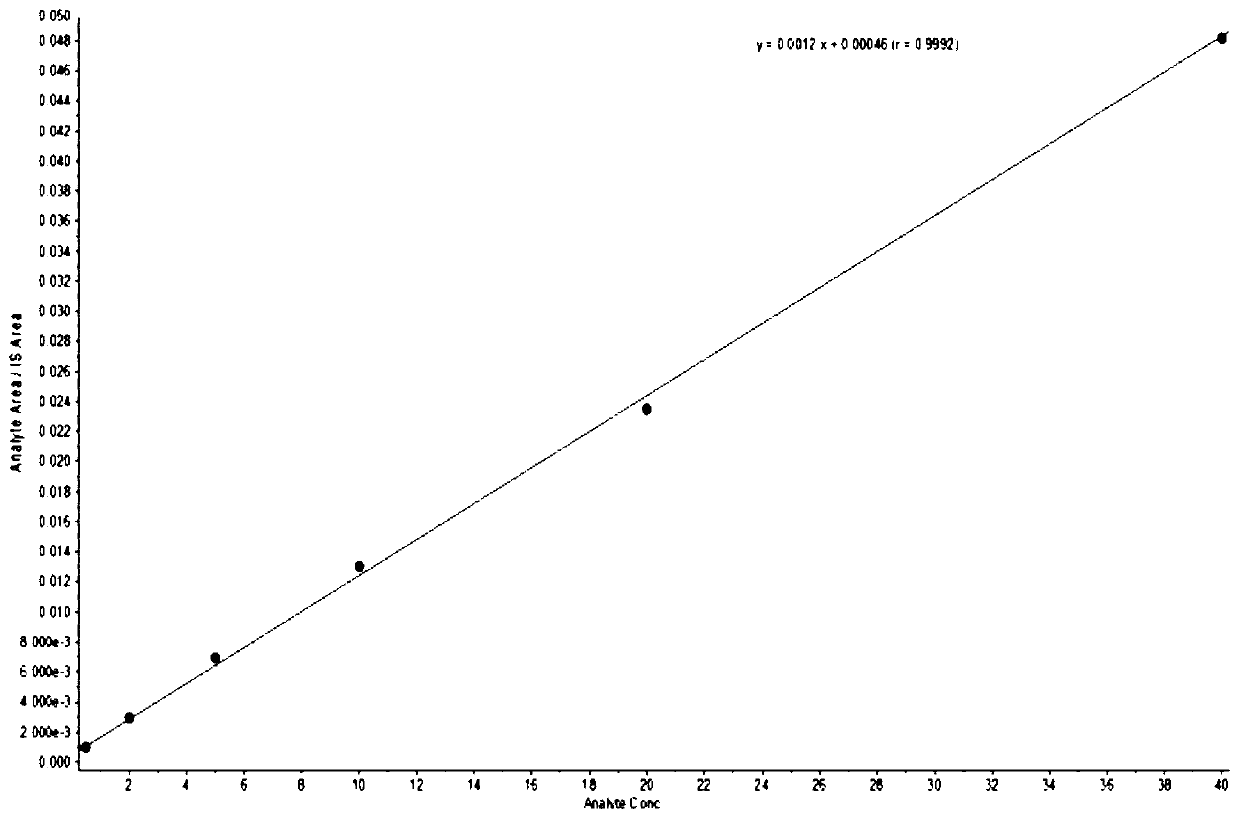
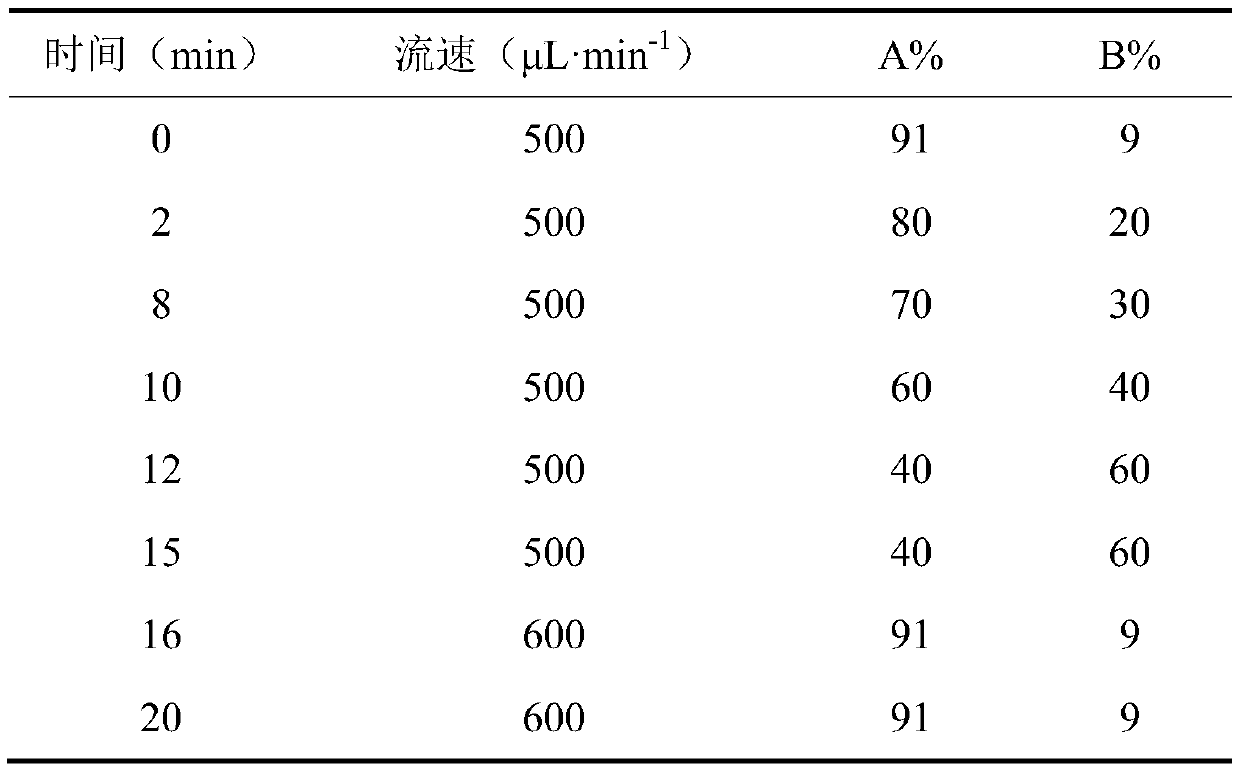
Method for detecting soluble epoxide hydrolase by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
The invention discloses a method for detecting soluble epoxide hydrolase by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. The method comprises the following steps: (1) screening a specific polypeptide of the soluble epoxide hydrolase from tissues, and showing the amino acid sequence of the specific polypeptide as SEQ ID NO.1; taking specific polypeptide as a standard substance, carrying out detecting by utilizing a mass spectrum isotope internal standard quantitative method and a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method, and establishing a standard curve by taking the concentration of the standard substance as an abscissa and the ratio of a quantitative daughter ion peak area to an isotope internal standard peak area as an ordinate; and (2) determining the concentration of the specific polypeptide in a sample by the liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method, and then carrying out converting and calculating to obtain the concentration of the soluble epoxide hydrolase in the sample. According to the present invention, a peptide fragment with characteristics of stable enzymolysis and high enzymolysis efficiency is selected from the representative characteristic peptide fragmentwith stable property as the quantitative peptide fragment, such that advantages of accuracy, precision, sensitivity and the like are realized, and the sEH in the rat tissue can be effectively, accurately and quantitatively analyzed.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL OF TCM
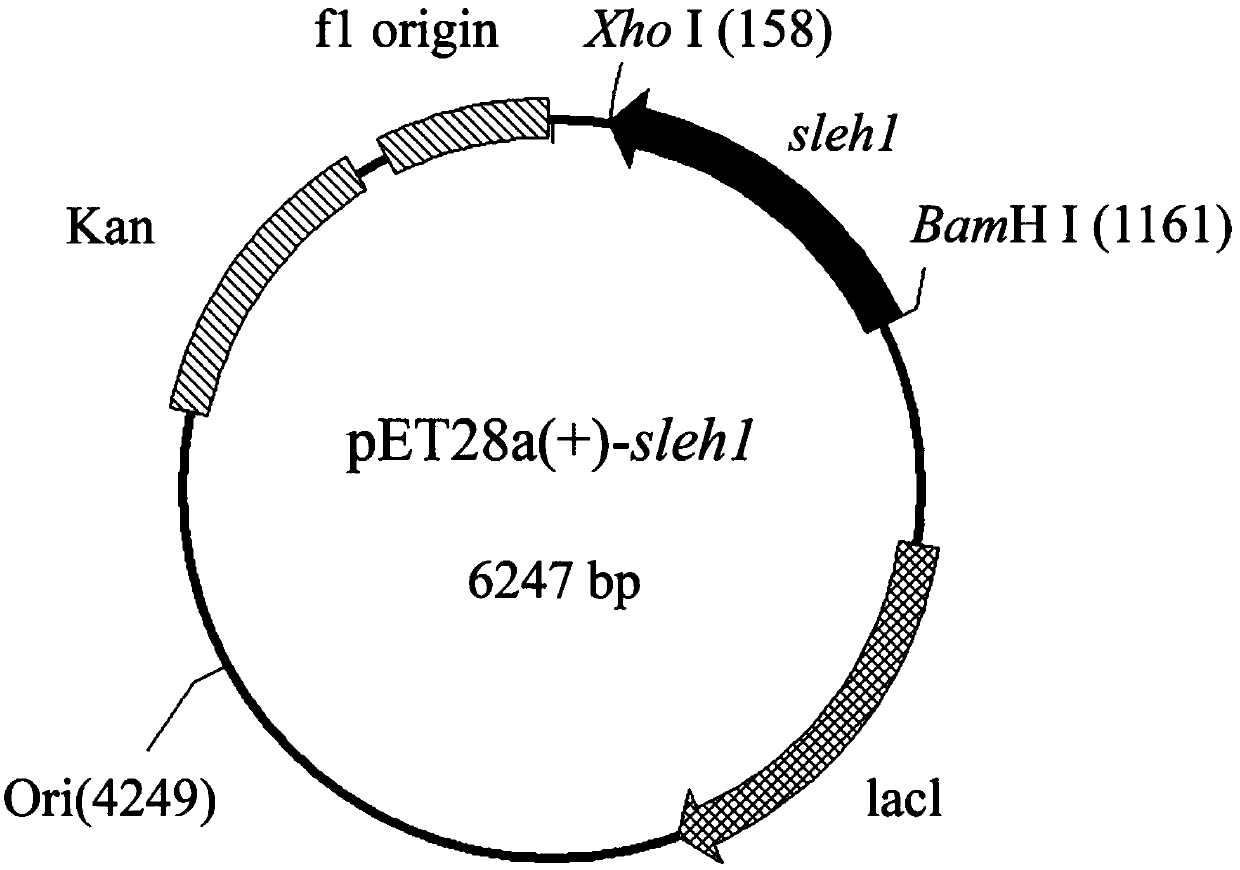
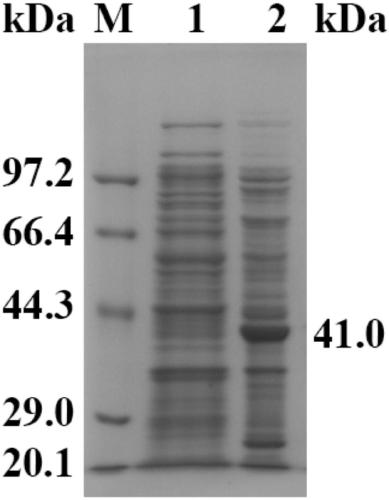
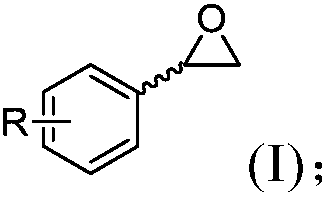
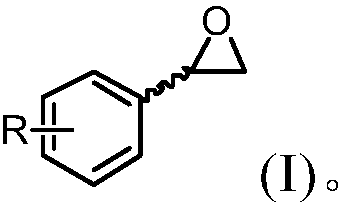
Method for preparing (R)-(4-chlorophenyl)oxirane from recombinant escherichia coli
InactiveCN109652354AStrong enantioselectivityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for preparing (R)-(4-chlorophenyl)oxirane from recombinant escherichia coli, and belongs to the technical field of biology. According to the method, tomato-derived epoxide hydrolase is expressed in escherichia coli, and a genetically engineered bacterium E.coli / sleh1 is constructed, and expression of the strain is used for preparing recombinant epoxide hydrolase. The invention provides a method for biological catalysis by using enzyme produced by fermenting the recombinant strain constructed in the method. (R)-(4-chlorophenyl)oxirane (ee is larger than 98%) ofenantiopure is prepared by catalyzing 150 mM racemized (4-chlorophenyl)oxirane; besides, the final yield reaches 47.5% and is close to the theoretical value of 50%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Epoxide hydrolase mutant and application thereof in enantiomeric normalizing hydrolysis of epoxides
The invention relates to an epoxide hydrolase mutant and an application thereof in enantiomeric normalizing hydrolysis of epoxides and discloses a series of epoxide hydrolase mutants, which have veryhigh catalytic activity and stereo-selectivity. The invention also discloses the application of the epoxide hydrolase mutant. By using the epoxide hydrolase mutant for catalyzing an enantiomeric normalizing hydrolysis reaction of a racemized styrene oxide and a derivative thereof, enantiomeric normalizing degree is high, reaction conditions are gentle, the process is environment-friendly, and theproduct has high optical purity. The obtained mutation site has universality about other epoxide hydrolases, so that the epoxide hydrolase mutant has extensive application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Design and preparation method of epoxide hydrolase mutant
ActiveCN104531630AHigh enantioselectivityHigh catalytic efficiencyHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyEpoxide metabolism
The invention provides design and construction of AuEH2G218S and AuEH2S247Y mutant enzymes with high enantio-selectivity. The mutation sites are finally determined by sequence homology analysis, homologous modeling, molecular docking and dynamic simulation. Mutant genes obtained by a megaprimer RPC technology are named Aueh2G218S and Aueh2S247Y. The invention further discloses a method for construction and efficient expression of mutant engineering bacteria; and the prepared mutant enzymes have the characteristics of high enantio-selectivity and catalytic activity, and have relatively large industrial production potential.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Kidney bean epoxide hydrolase mutant with improved catalytic activity
The invention discloses a kidney bean epoxide hydrolase mutant with improved catalytic activity and belongs to the fields of gene engineering and protein expression. The mutant mutates valine at the 106th site into isoleucine on the basis of amino acid shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The catalytic activity of mutant enzyme PvEH1V106I obtained by shaking flask induction for 10h, disclosed by the invention, is 234.75U / g, which is 1.49 times that of wild type enzyme (157.15U / g).
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Engineering strain for biosynthesizing mogrol by taking glucose as substrate, construction and application thereof
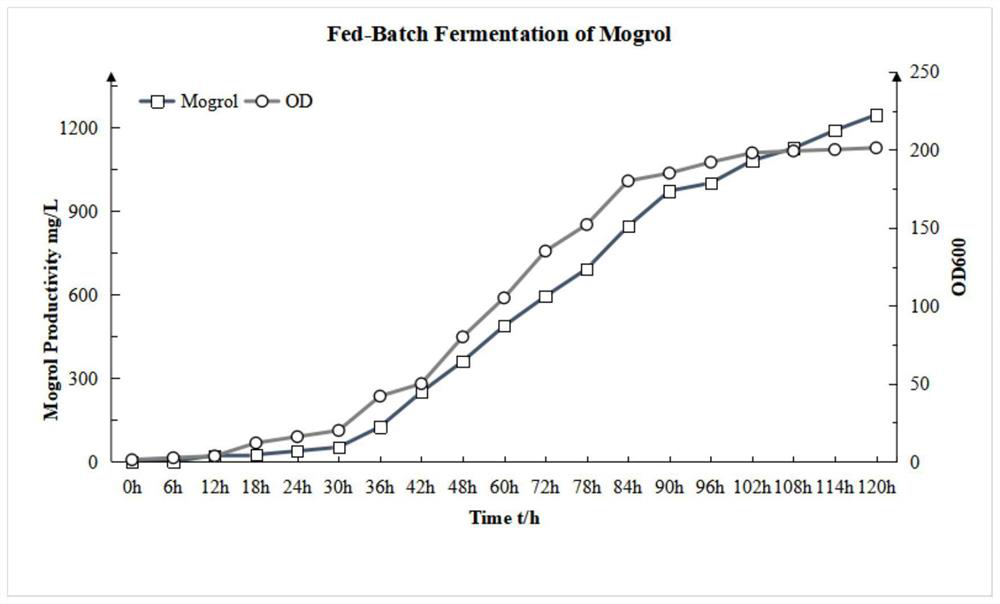
The invention discloses an engineering strain for biosynthesizing mogrol by taking glucose as a substrate as well as construction and application of the engineering strain, and belongs to the technical field of biology. A chassis yeast engineering bacterium is constructed by enhancing squalene oxidation module expression, improving an MVA metabolic pathway and knocking out a lanosterol competition pathway, heterologous protein cucurbitadienol synthase, epoxide hydrolase and cell P450 enzyme are expressed on the basis of the chassis bacterium, and the yeast engineering bacterium for biosynthesis of mogrol is constructed. According to the method, mogrol can be synthesized from the beginning, the environment is not polluted, the yield is high, the cost is low, and a basis is provided for industrial production of mogrol.The finally produced mogrol reaches 1.2 g / L, which is the highest level reported at present.
Owner:河北维达康生物科技有限公司
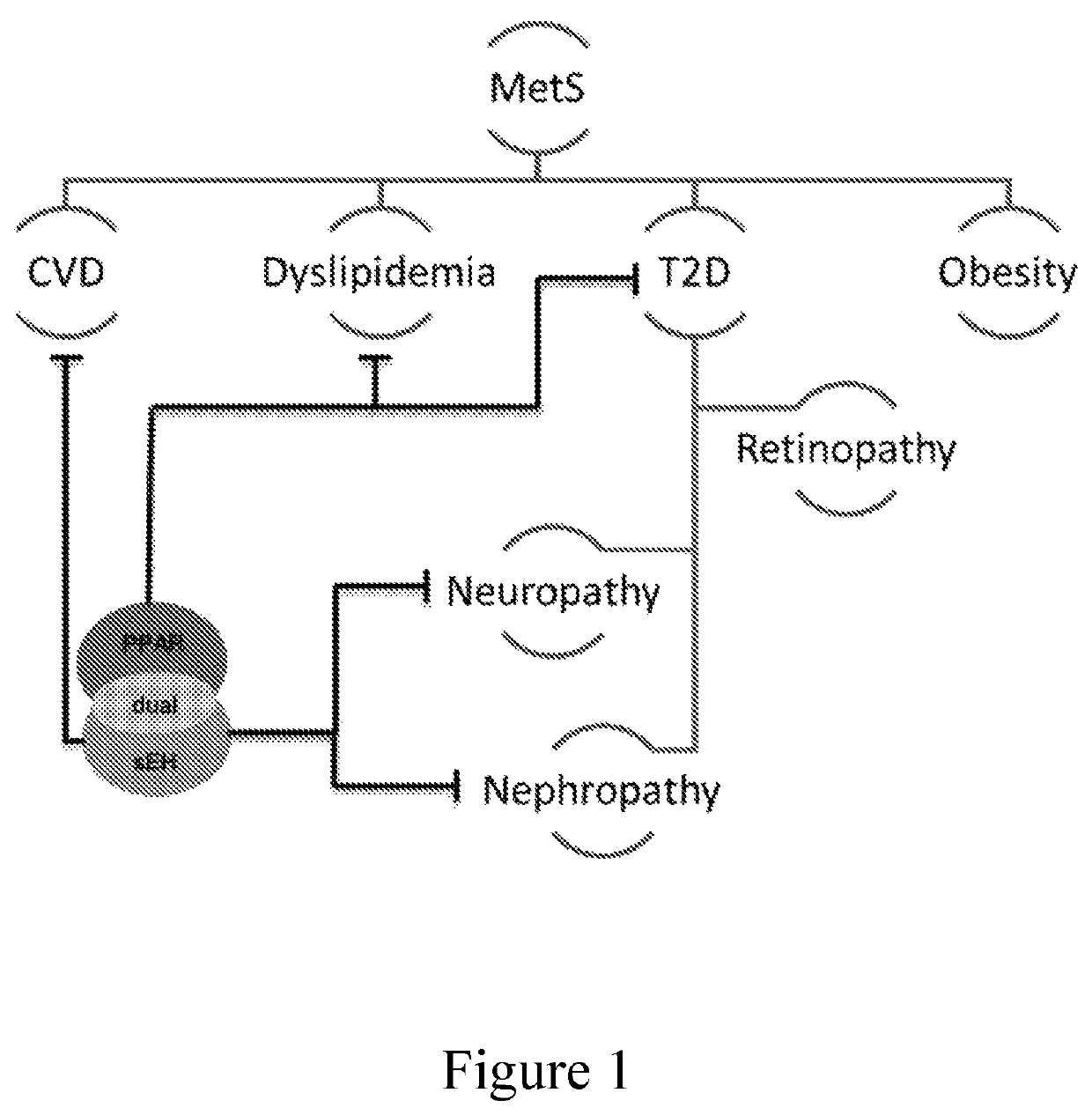
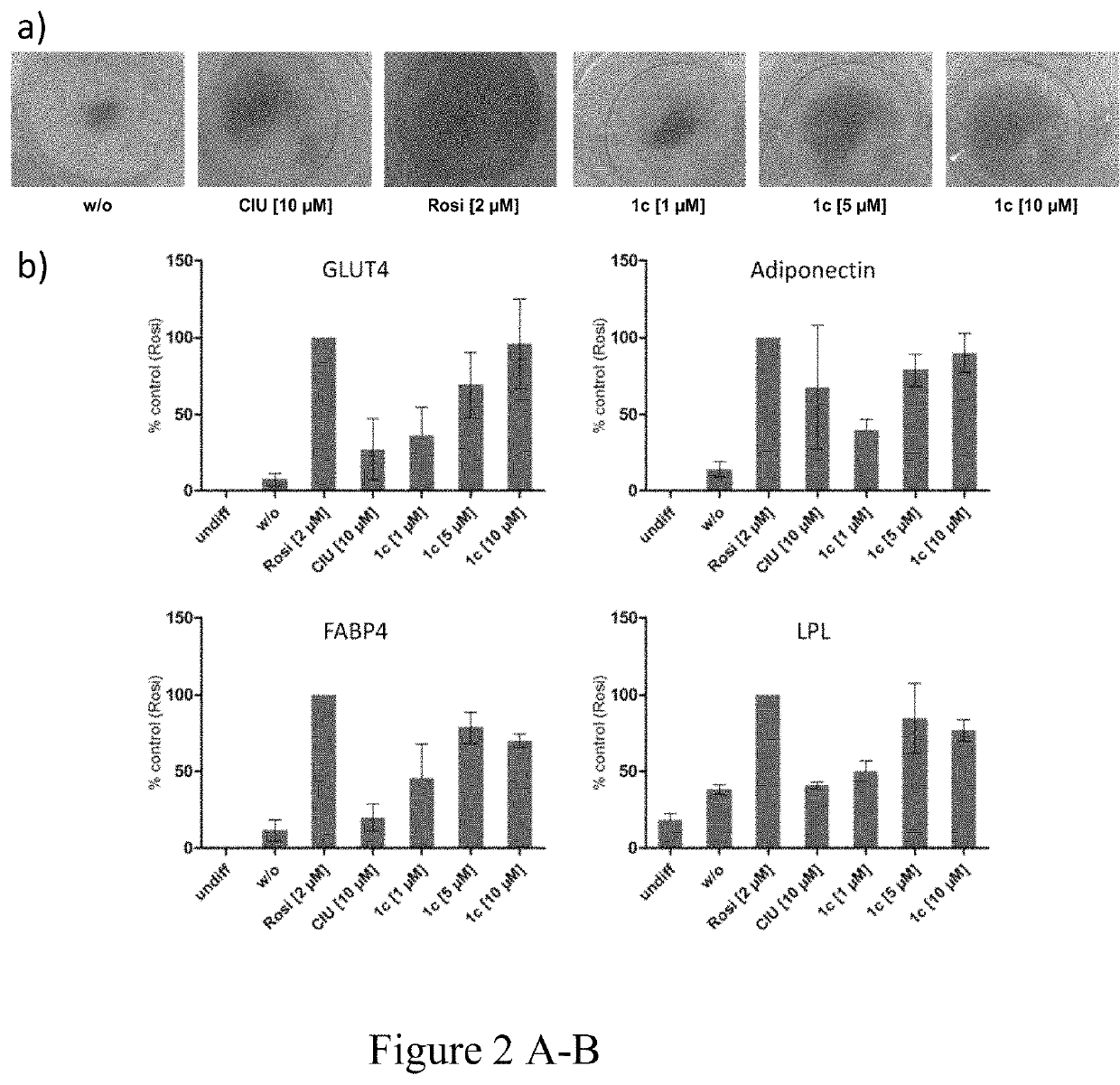
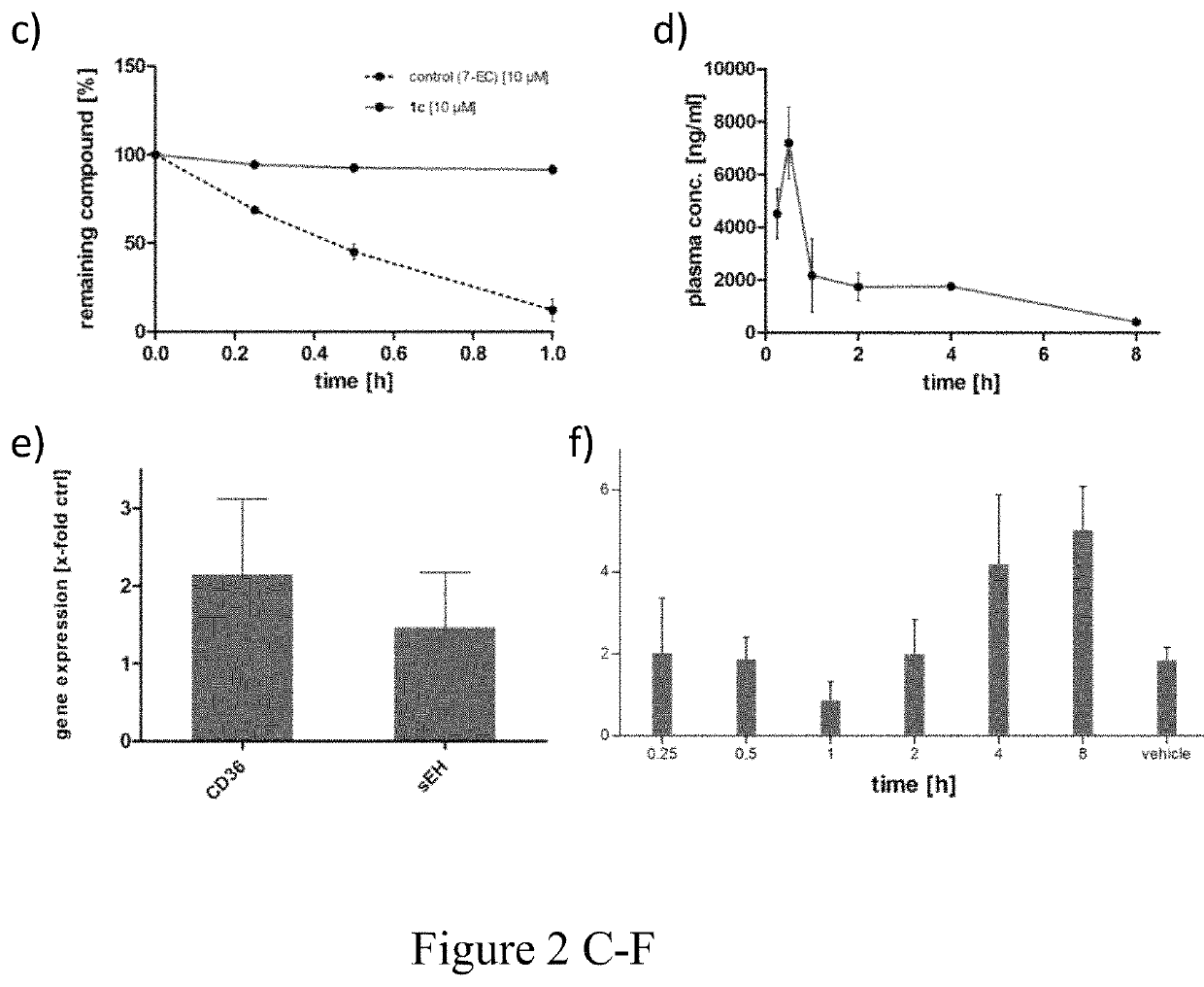
Diabetes and metabolic syndrome treatment with a novel dual modulator of soluble epoxide hydrolase and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors
N-benzylbenzamides that act as dual soluble soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) / peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) modulators and are useful as medications in the treatment of Metabolic Syndrome (MetS) cluster diseases, including diabetes. Methods of making and using the same are further provided.
Owner:THE MEDICAL COLLEGE OF WISCONSIN INC +1
Application of related gene for improving content of mogroside
The invention discloses a mogroside synthesis regulation gene Sgesph7 and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. According to the mogroside synthesis regulation gene Sgesph7 and the application thereof, by means of whole genome sequencing of Siraitia grosvenorii(Swingle)C.Jeffrey and the analysis of the RNA-seq sequence of different tissue, secondary metabolic pathways associated with the tissue specificity and characters are utilized, and therefore the Siraitia grosvenorii(Swingle)C.Jeffrey epoxide hydrolases Sgeph7 gene with Siraitia grosvenorii(Swingle)C.Jeffrey fruits specifically expressed; and the content of the mogroside in the Siraitia grosvenorii(Swingle)C.Jeffrey fruits can be regulated and controlled by adjusting the expression of the gene, and the geneis used for obtaining a new variety or new strain of the Siraitia grosvenorii(Swingle)C.Jeffrey with the high mogroside content and has important theoretical and practical significance in research ofthe taste mechanism of fruits of cucurbitaceae plants and the breeding work of the taste of the fruits of the cucurbitaceae plants.
Owner:怀化兴科创生物技术有限公司
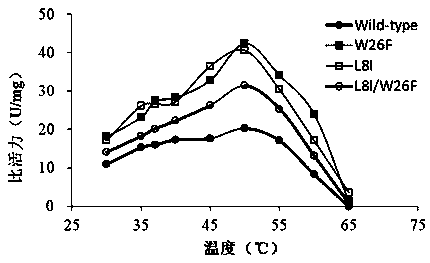
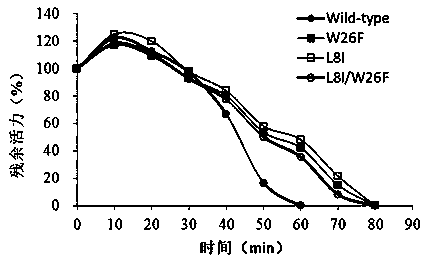
Epoxide hydrolase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111269901AImprove activity stabilityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaHydrolasesTryptophanEngineered genetic
An epoxide hydrolase mutant and application thereof belong to the technical field of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The epoxide hydrolase mutant is obtained by carrying out single-site mutation or multi-site mutation on the 8th site and / or the 26th site of an amino acid sequence of wild-type epoxide hydrolase shown as SEQ ID No.4, wherein the single-site mutation is to mutate leucine atthe 8th site into isoleucine or mutate tryptophan at the 26th site into phenylalanine. According to the epoxide hydrolase mutant obtained by the invention, the activity and the thermal stability of the enzyme are greatly improved. Some genetically engineered bacteria expressing the mutant epoxide hydrolase are obtained through a genetic engineering technology, and the genetically engineered bacteria are used for producing D (-)-tartaric acid, so that the activity of cells is greatly improved, the service life of the cells is greatly prolonged, and the requirements of current industrial application are met.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Piperidinyl, indolyl, pirinidyl, morpholinyl and benzimidazolyl urea derivatives as inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase for the treatment of hypertension, inflammations and other diseases
InactiveCN101405264AOrganic chemistryMetabolism disorderRESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME ADULTUrea derivatives
Compounds of the formula (I); wherein R<1> is a member selected from the group consisting of C1-C8alkyl, arylC0-C8alkyl, C3-C12cycloalkyl and heterocyclyl, Y<1> is selected from the group consisting of a bond, C(R<5>)2, NR<5> and O; Y<2> is selected from the group consisting of a bond, NR<5> and O; each R<2>, R<3> and R<5> is independently selected from the group consisting of H, alkyl and COR<6>; A is heterocyclyl, optionally substituted with from 1 to 2 R<7> substituents; L is selected from the group consisting of a direct bond, C1-C12alkylene, C1-C12heteroalkylene, C3-C6cycloalkylene, arylene, heteroarylene, -CO-, -SOin- and -Se-; R<4> is selected from the group consisting of H, C1C8alkyl, C2-C6alkenyl, C2-C6alkynyl, C1,-C8heteroalkyl, arylC0-C8alkyl, C3C,12cycloalkyl and heterocyclyl, are claimed. The compounds are inhibitors of the soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) and useful for the treatment of hypertension, inflammation, adult respiratory distress syndrome; diabetic complications; end stage renal disease; Raynaud syndrome and arthritis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Aspergillus usamii epoxide hydrolase mutants with improved enantioselectivity
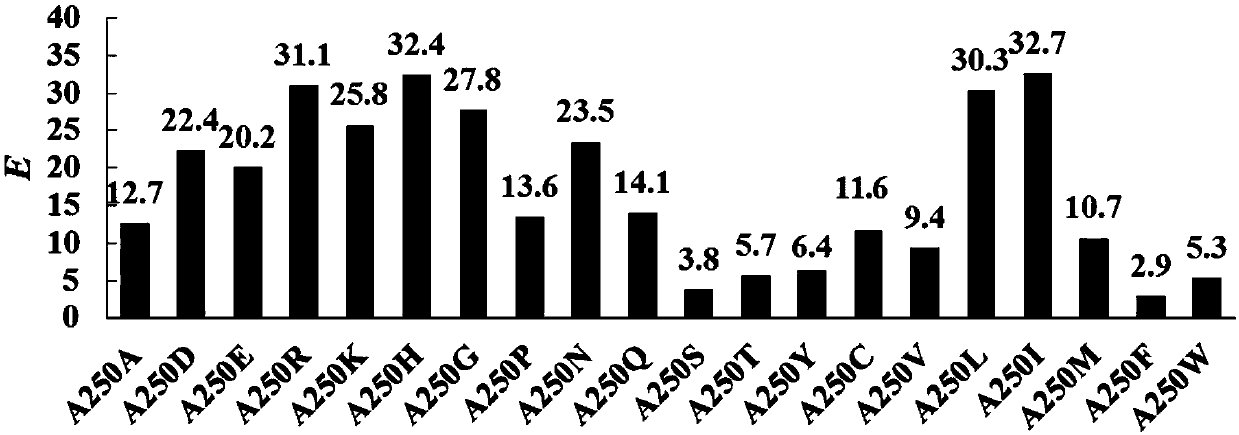
The invention discloses Aspergillus usamii epoxide hydrolase mutants with improved enantioselectivity, and belongs to the technical fields of enzyme engineering and biocatalysis. Based on rational design, molecular transformation of the Aspergillus usamii epoxide hydrolase (AuEH2) is carried out; and combined with a site-directed saturation mutation method, a plurality of epoxide hydrolase mutantswith enhanced enantioselectivity are obtained. Enantiomeric ratios (E value) of the 9 enantioselectivity-enhanced mutants catalyzing rac-pMPGE are increases to 32.4, 31.1, 27.8, 25.8, 23.5, 22.4, 20.2, 14.1, and 13.6 correspondingly compared to an E value of 12.7 of a wild type.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Soluble epoxide hydrolase as a target for ocular neovascularization
InactiveUS20180228764A1Potent antiangiogenic activitySuppressed CNV vascular volumeOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseOcular neovascularization
Methods of using compounds that inhibit soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) for the treatment of ocular diseases, and in particular, of wet age-related macular degeneration (AMD), are disclosed herein.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com