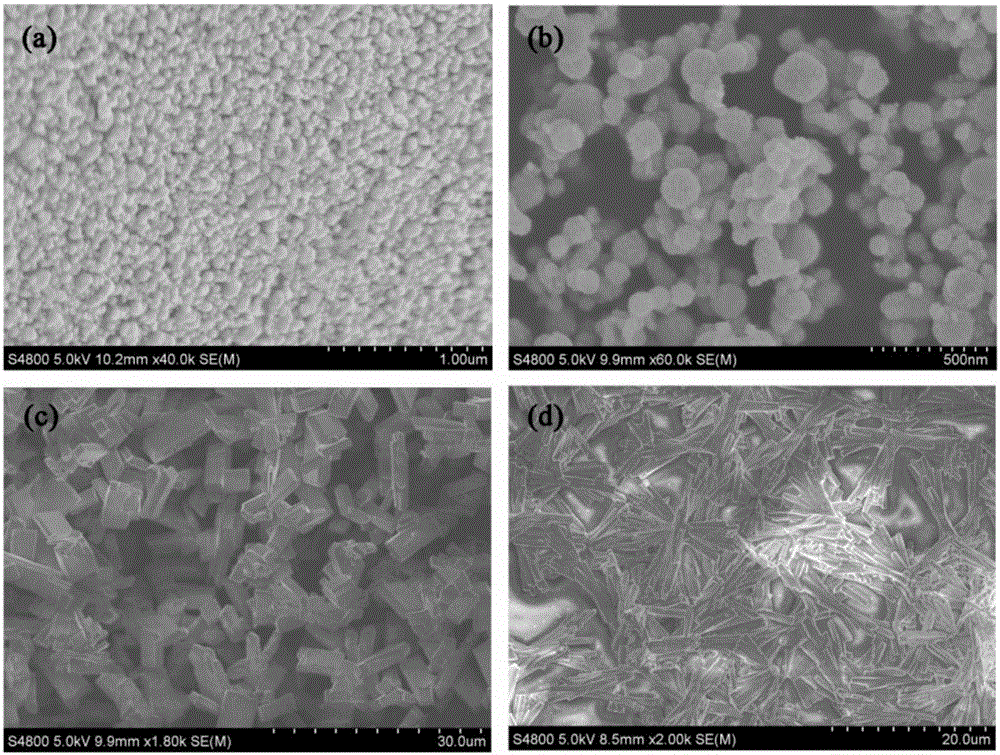
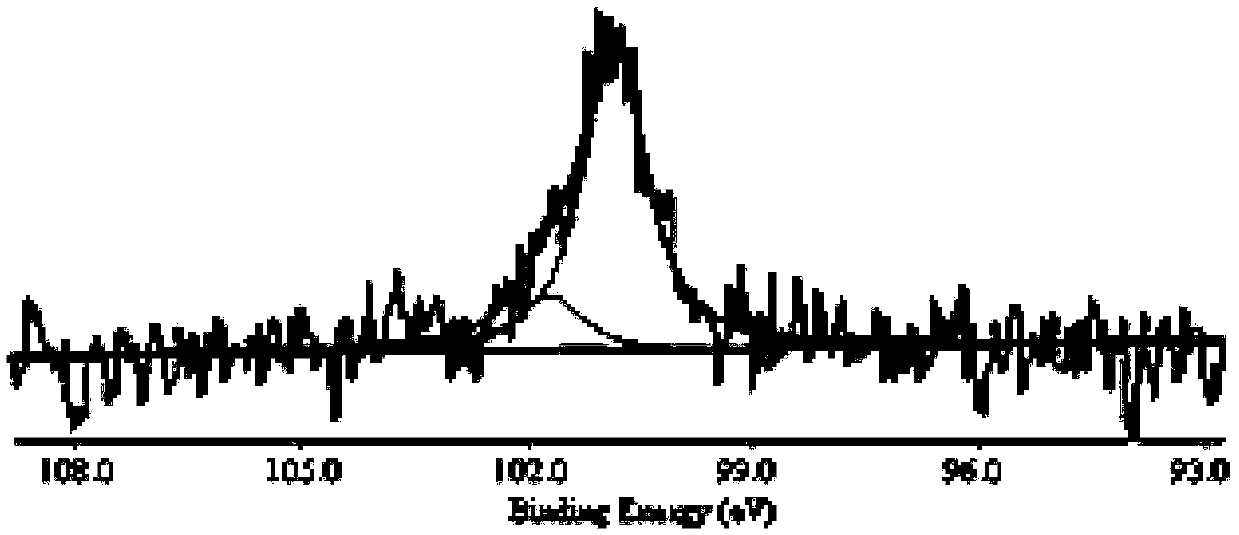
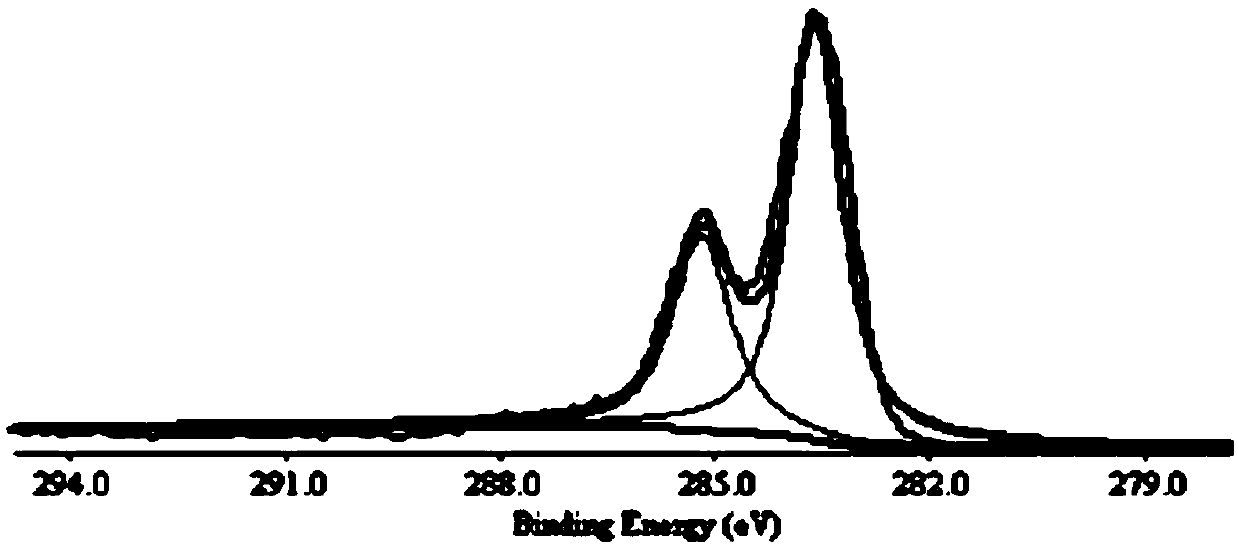
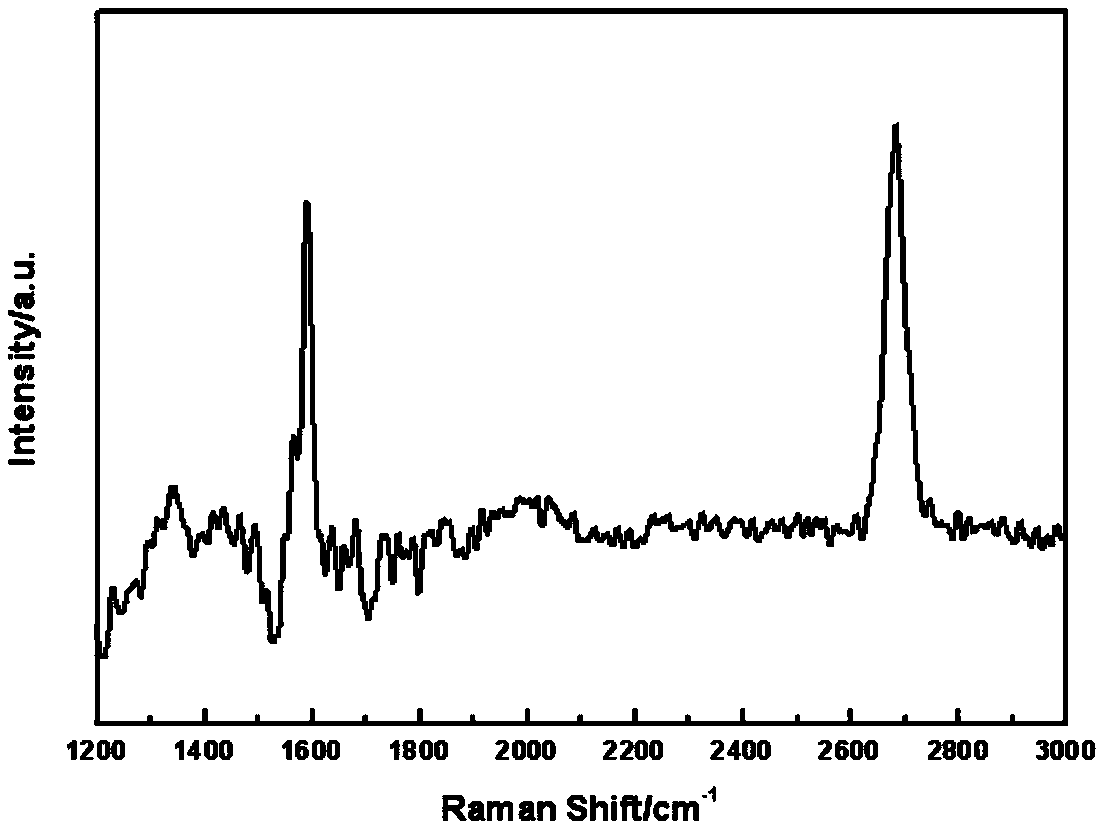
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Epitaxial graphene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
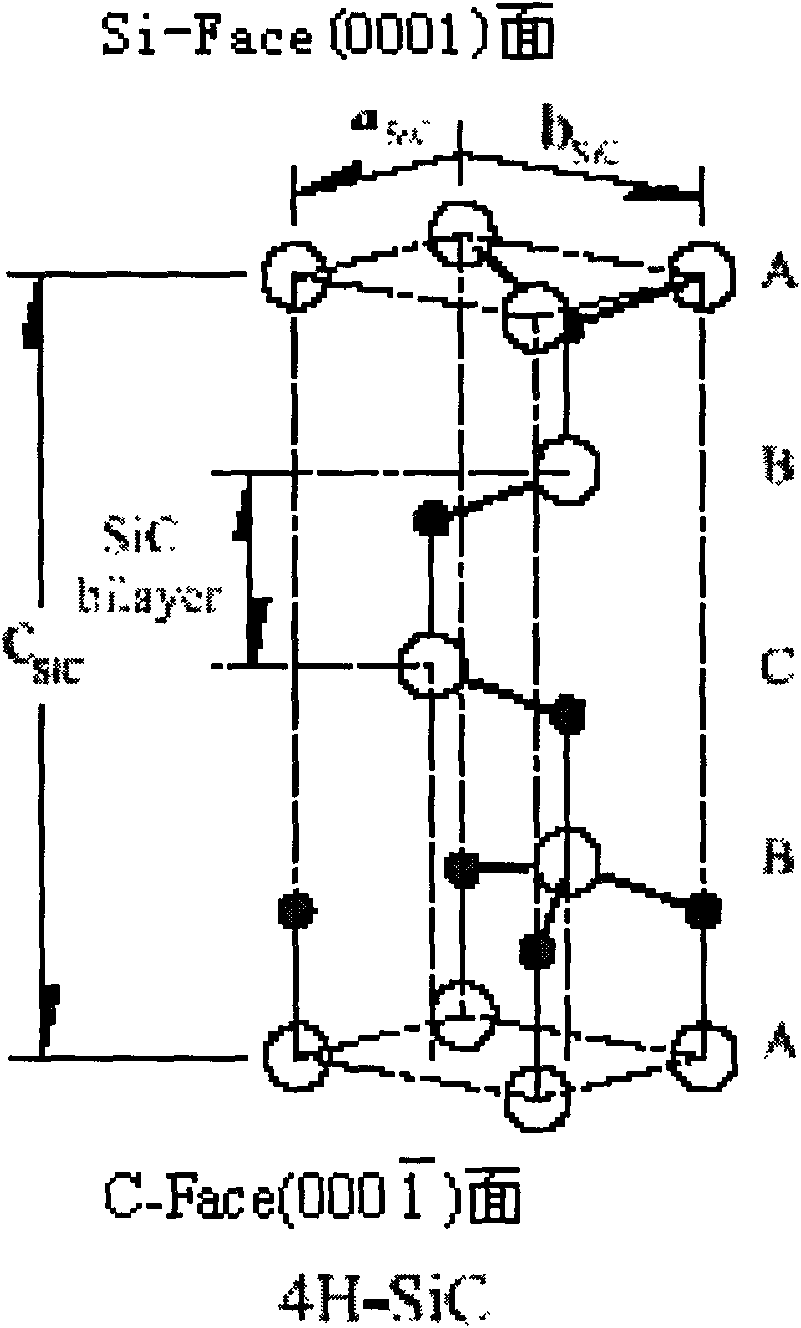
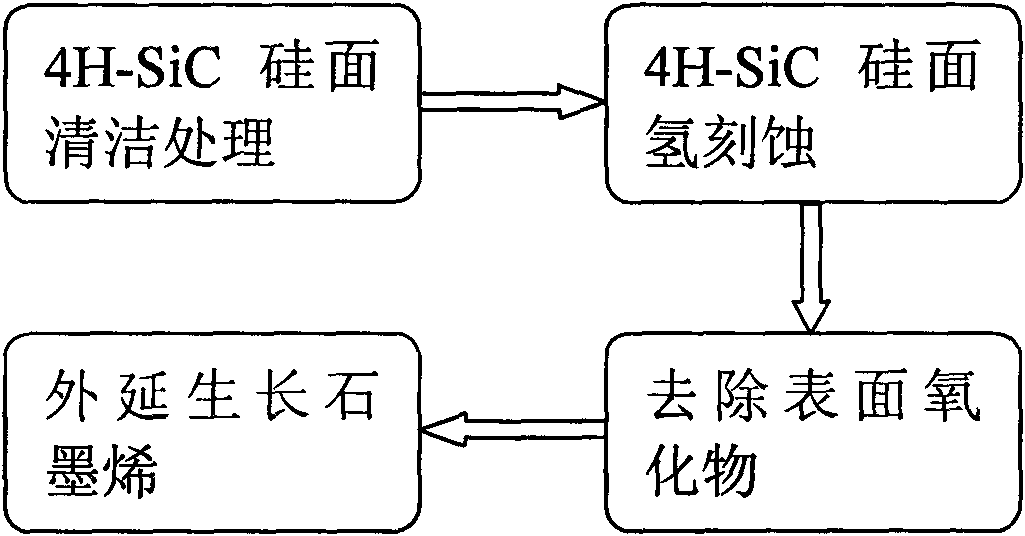
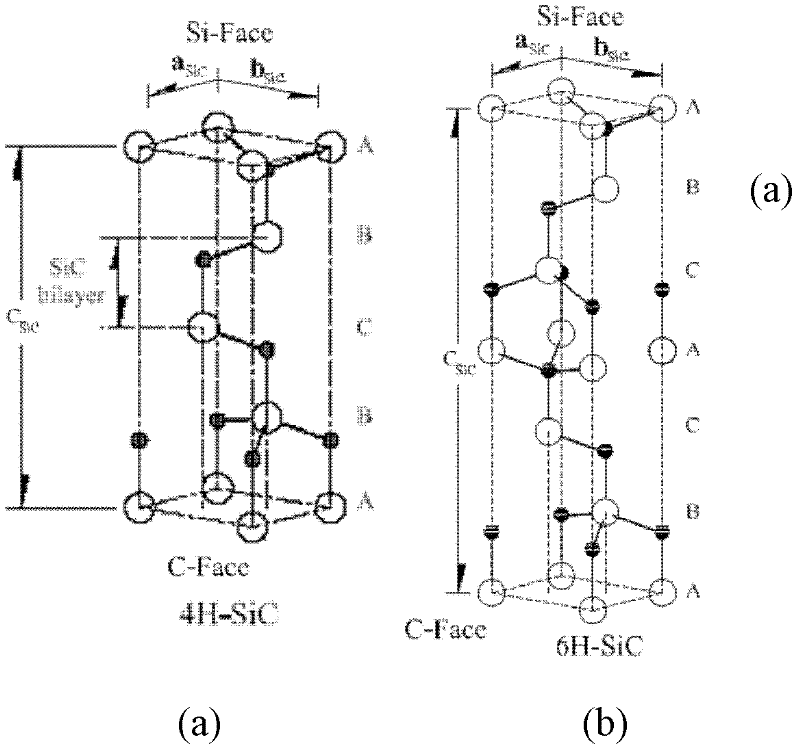
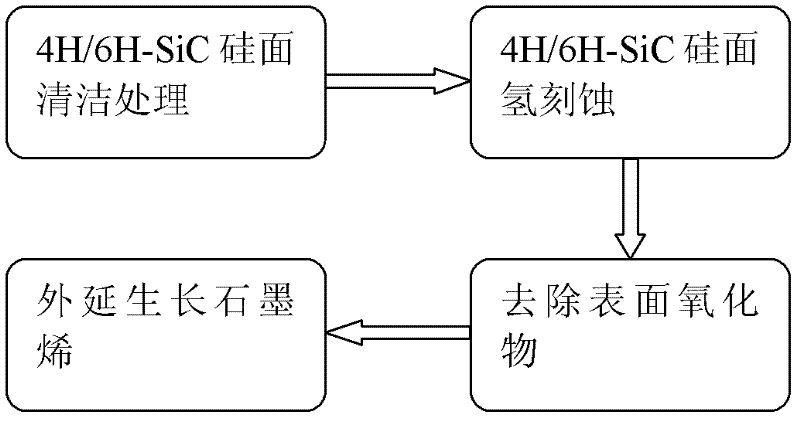
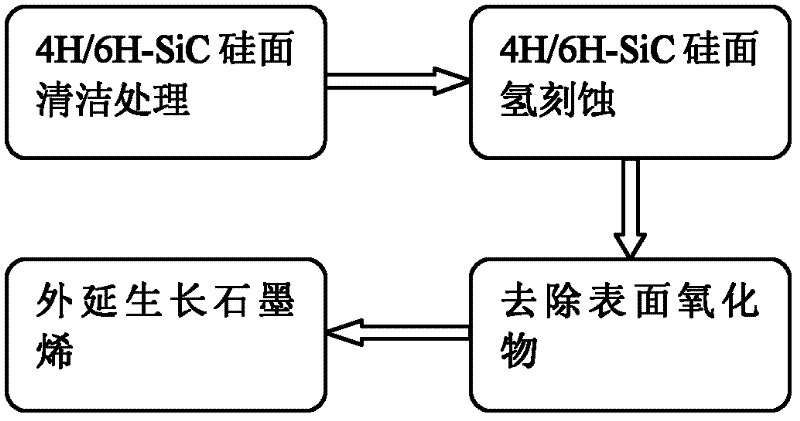
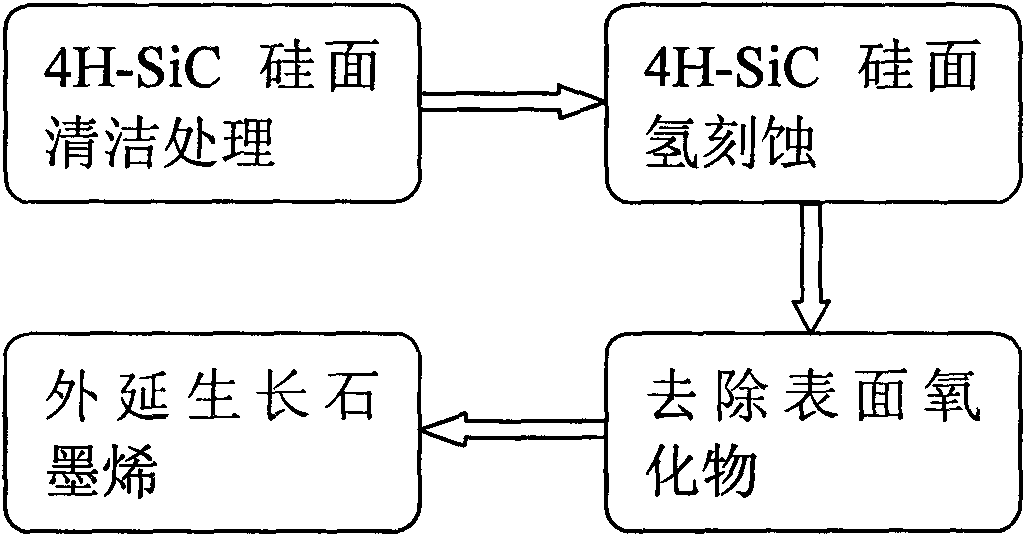
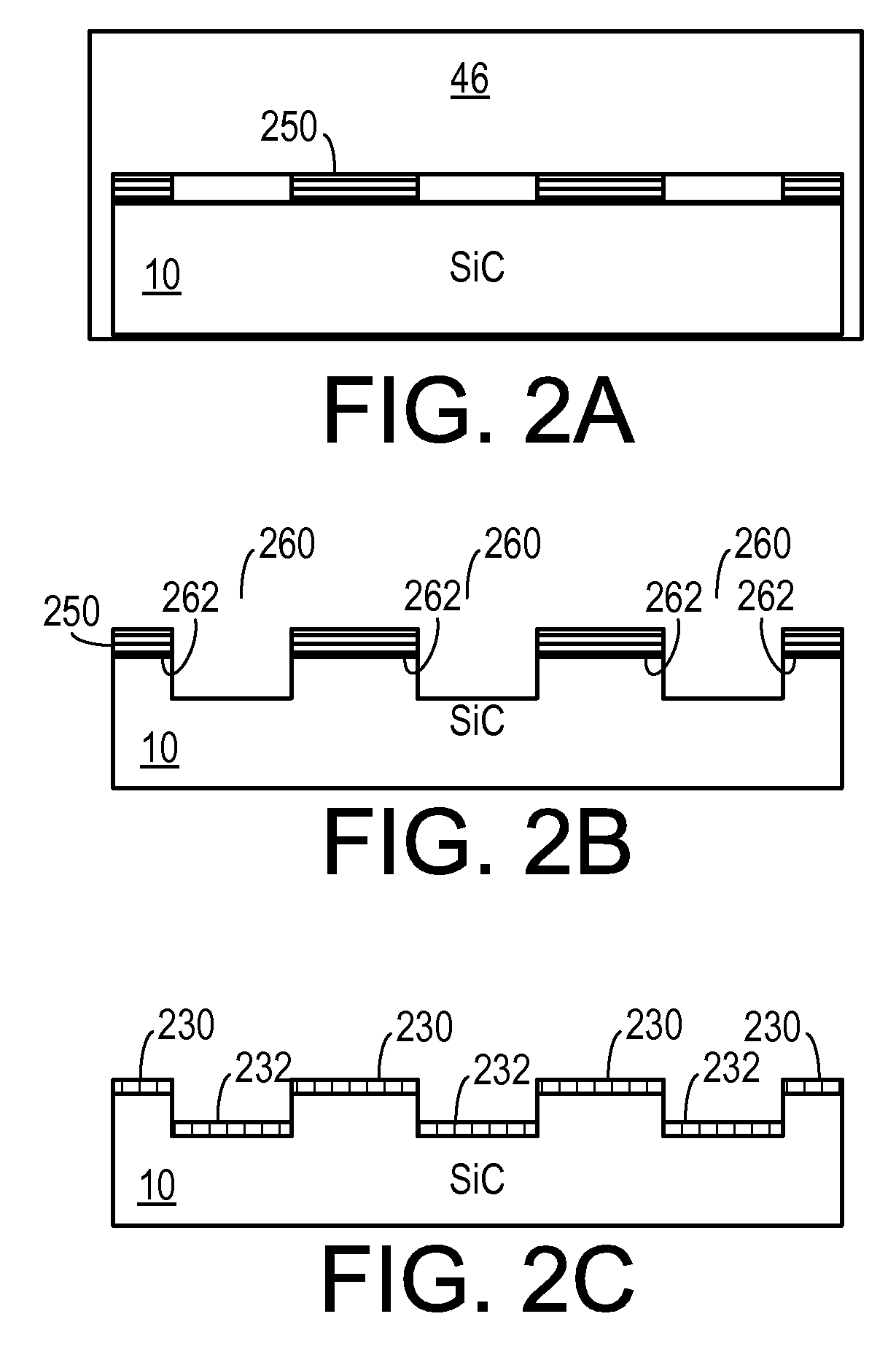
Method for graphene epitaxial growth on 4H-SiC silicon surface
InactiveCN101602503AIncrease the areaImprove uniformityPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsHydrogenSilanes
The invention discloses a method for graphene epitaxial growth on 4H-SiC silicon surface, mainly solving the problems of small graphene area and poor homogeneity during graphene epitaxial growth on the 4H-SiC silicon surface. The method is as follows: a 4H-SiC silicon surface is cleaned to remove organic remains and ionic contaminants on the surface; hydrogen and propane are led in to carry out hydrogen corrosion to the 4H-SiC silicon surface to remove surface scratches so as to form regular step-shaped stripes; silane is led in to remove oxide formed by hydrogen corrosion on the surface; under the circumstance of argon, silicon atoms are evaporated to ensure carbon atom to reconstruct and form epitaxial graphene in the form of sp by heating. The invention can be used for manufacturing epitaxial graphene materials.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
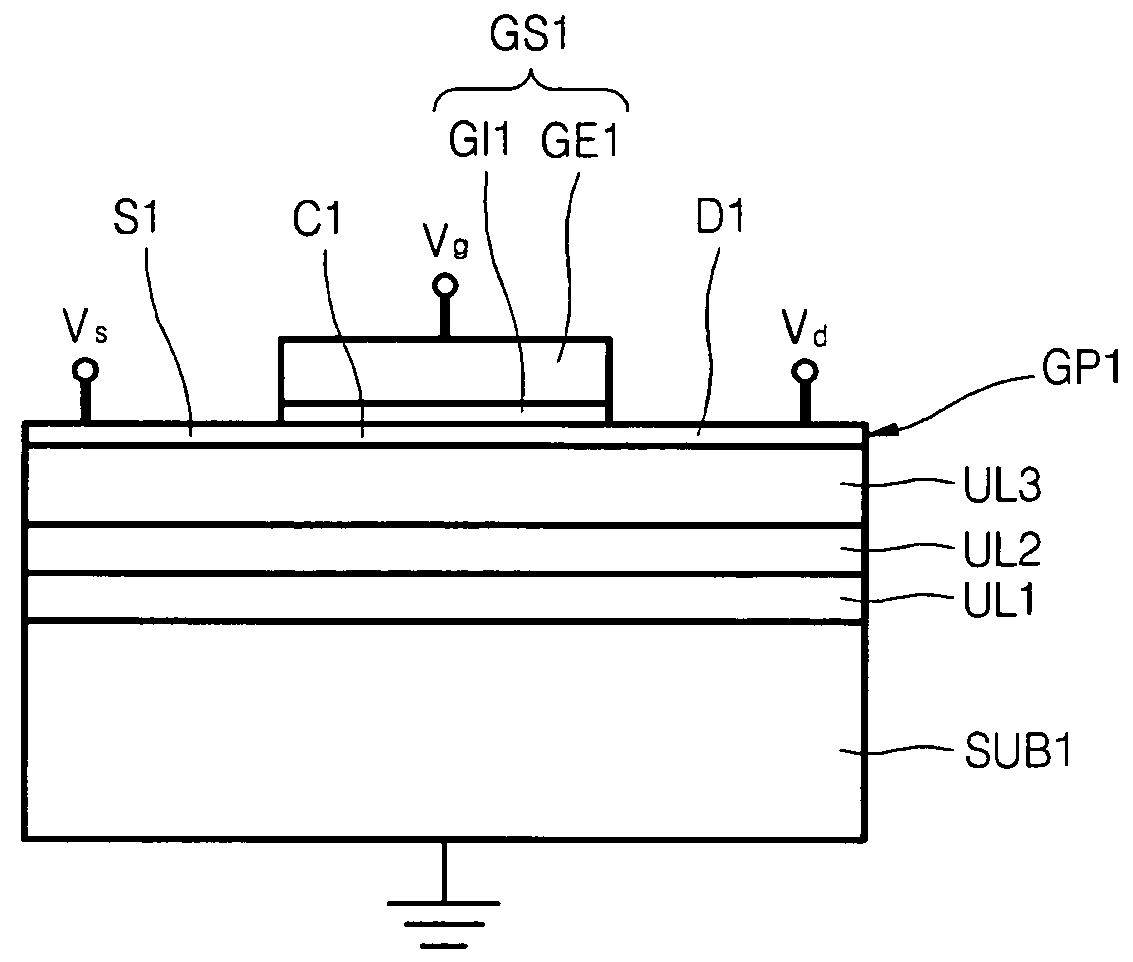
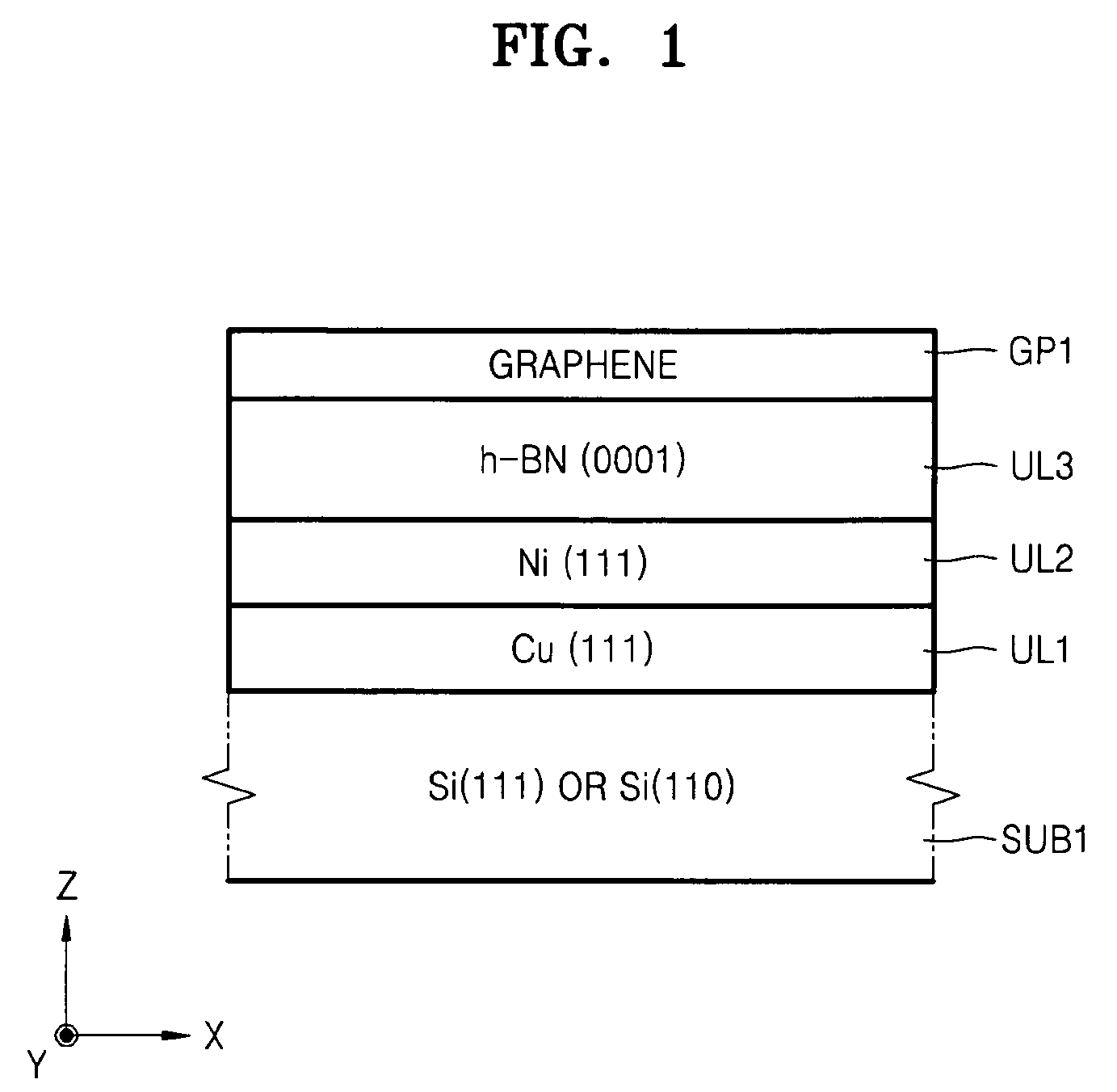
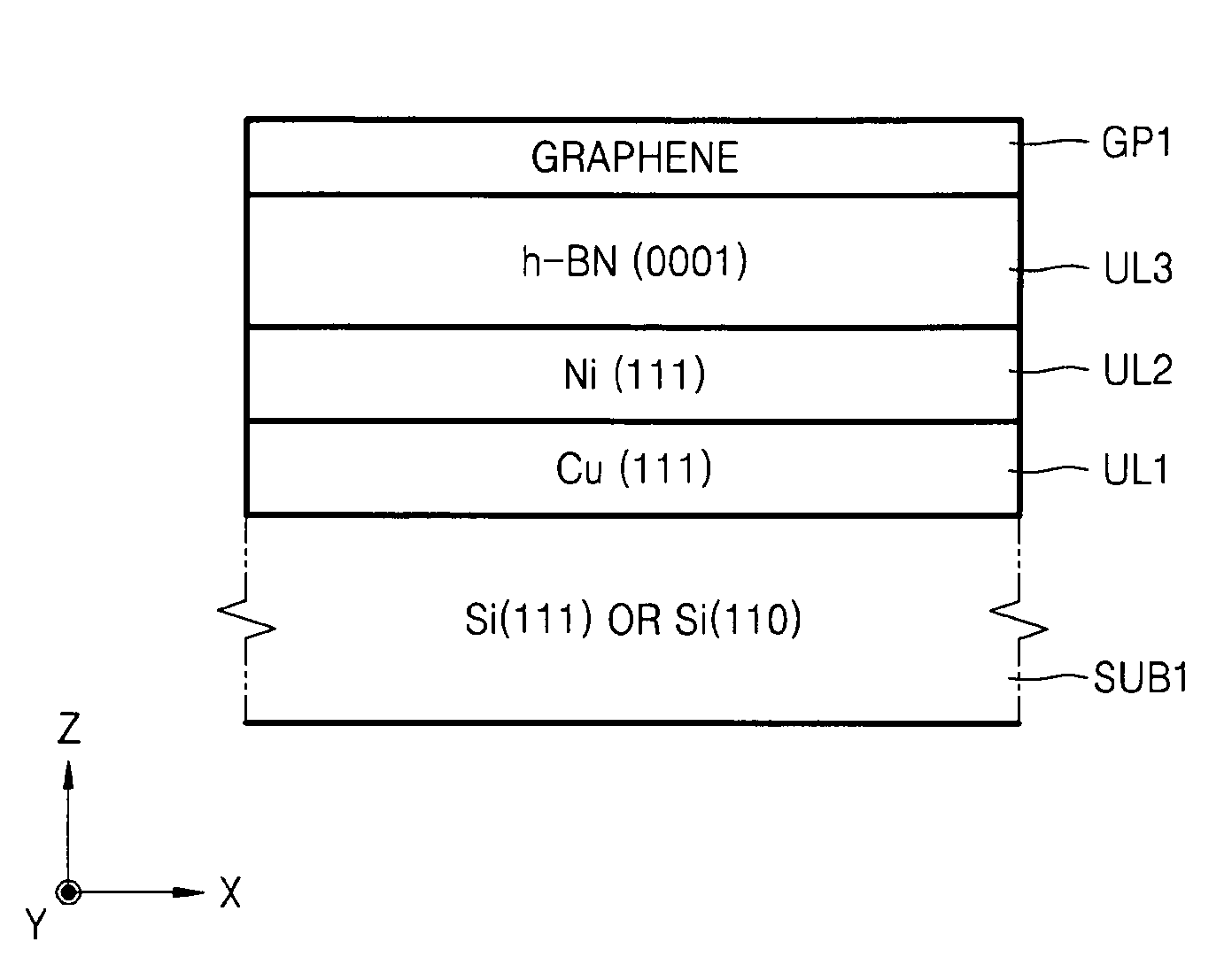
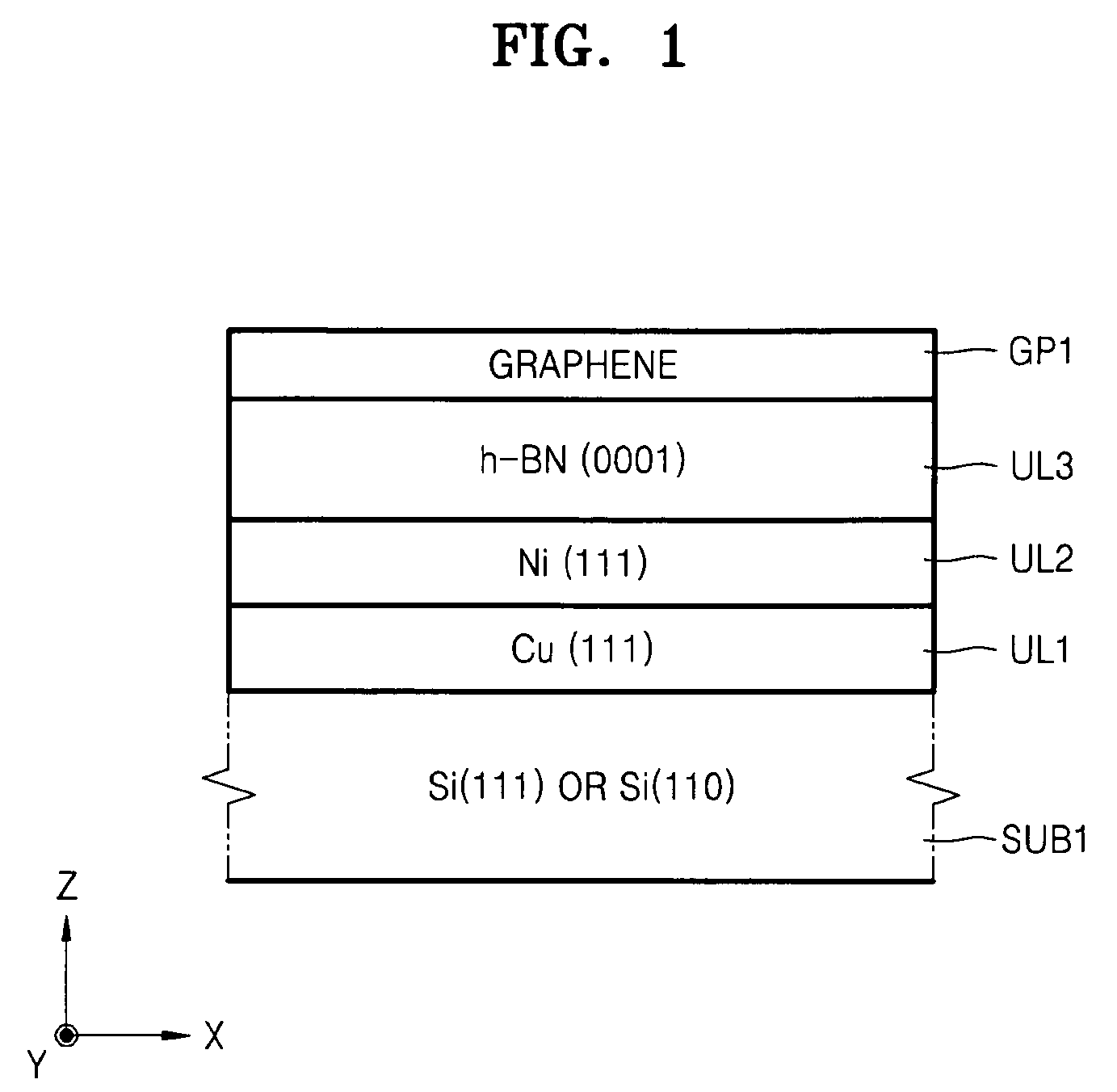
Stack structure comprising epitaxial graphene, method of forming the stack structure, and electronic device comprising the stack structure
ActiveUS20090294759A1Small widthNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsElectron
Provided are a stack structure including an epitaxial graphene, a method of forming the stack structure, and an electronic device including the stack structure. The stack structure includes: a Si substrate; an under layer formed on the Si substrate; and at least one epitaxial graphene layer formed on the under layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Graphene electrodes on a planar cubic silicon carbide (3c-sic) long term implantable neuronal prosthetic device
InactiveUS20130338744A1Increase surface areaSpecific capacitanceSpinal electrodesConductive pattern formationCapacitanceCubic silicon carbide
Graphene, can be used to make an implantable neuronal prosthetic which can be indefinitely implanted in vivo. Graphene electrodes are placed on a 3C—SiC shank and electrical insulation is provided by conformal insulating SiC. These materials are not only chemically resilient, physically durable, and have excellent electrical properties, but have demonstrated a very high degree of biocompatibility. Graphene also has a large specific capacitance in electrolytic solutions as well as a large surface area which reduces the chances for irreversible Faradaic reactions. Graphene can easily be constructed on SiC by the evaporation of Si from the surface of that material allowing for mechanically robust epitaxial graphene layers that can be fashioned into electrodes using standard lithography and etching methods.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Wafer scale epitaxial graphene transfer
Owner:ELPIS TECH INC
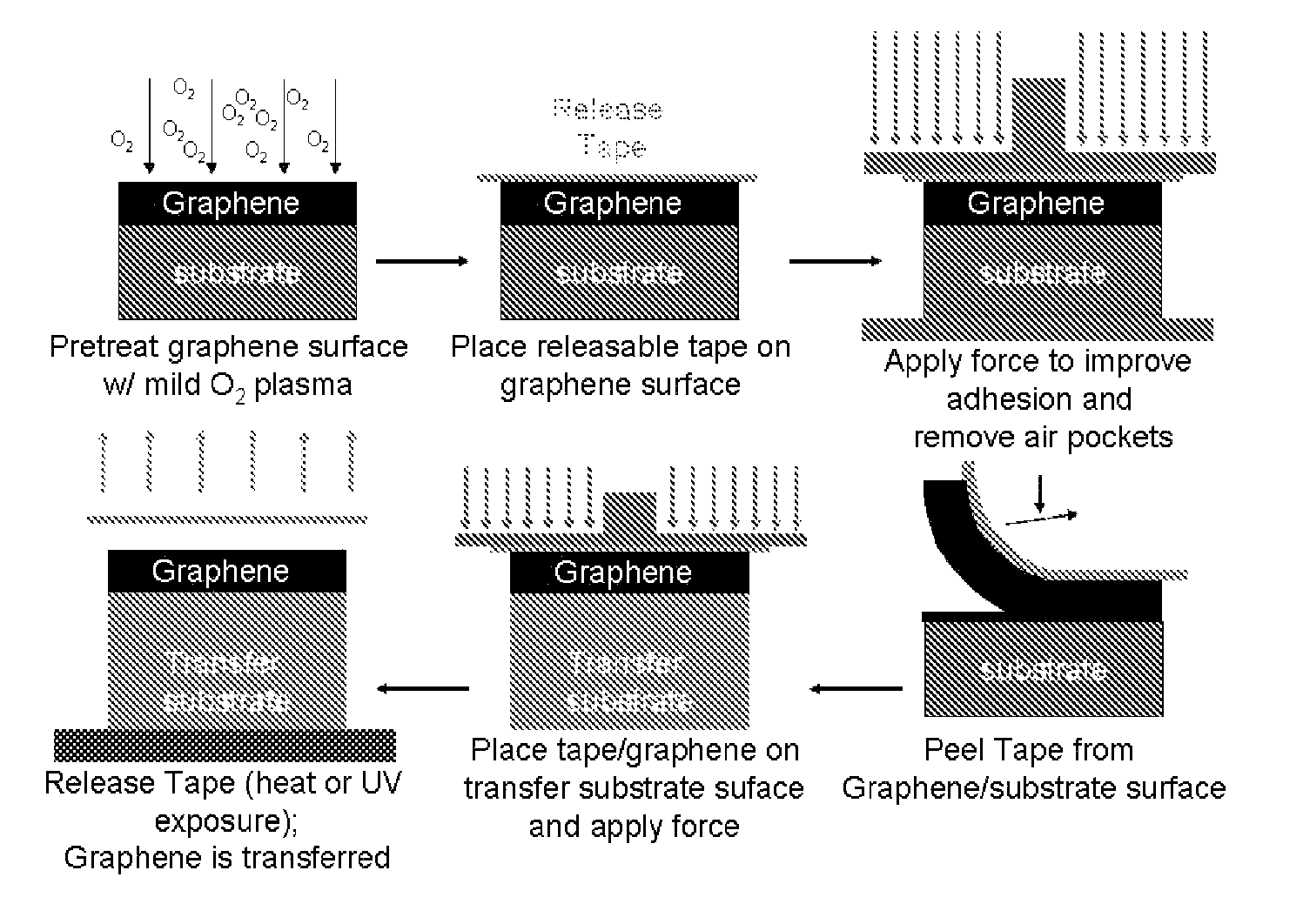
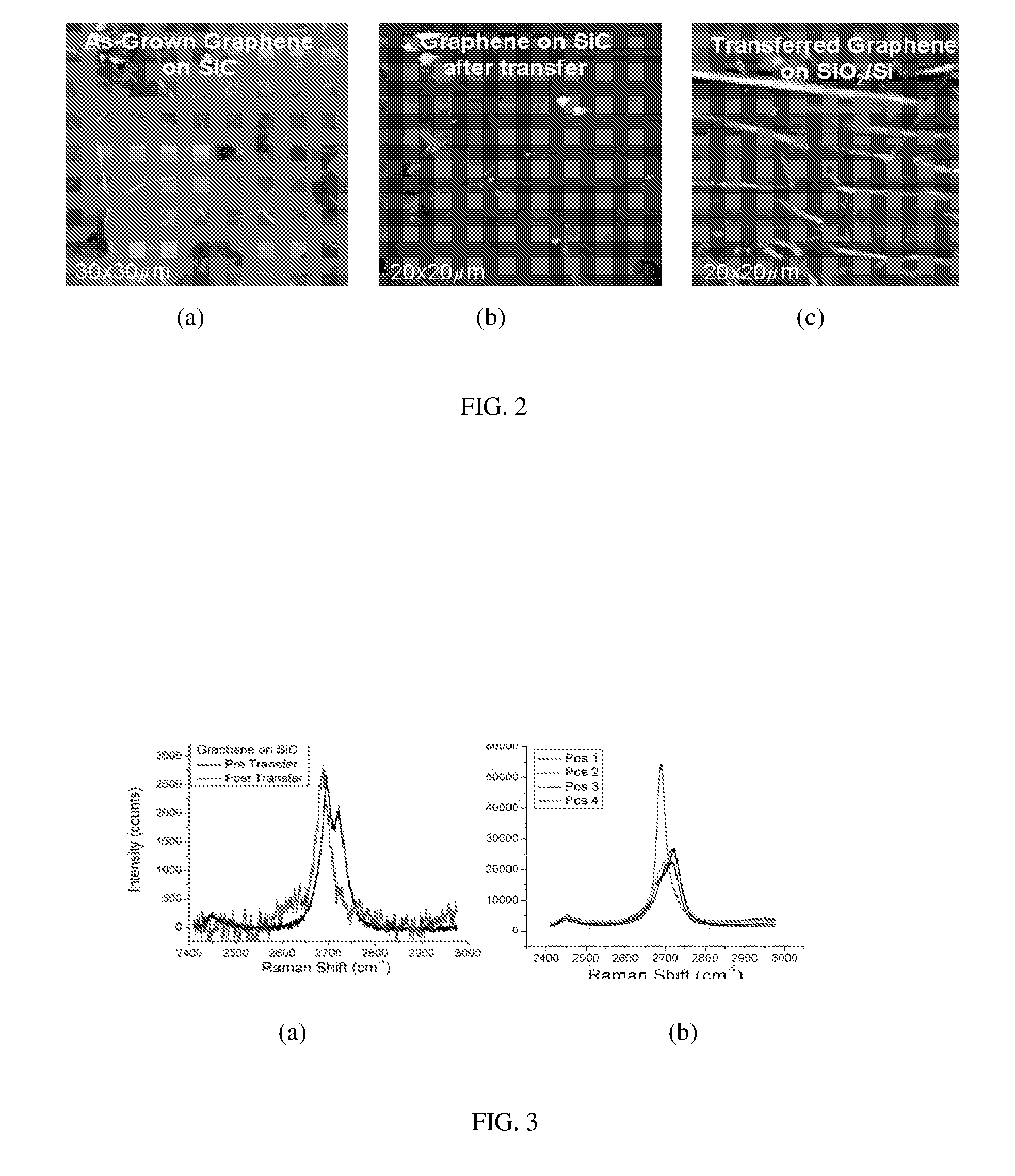
Method for the reduction of graphene film thickness and the removal and transfer of epitaxial graphene films from SiC substrates
ActiveUS8753468B2Cost efficiencyEase in device fabricationMaterial nanotechnologyLamination ancillary operationsMetal foilCvd graphene
A method for reducing graphene film thickness on a donor substrate and transferring graphene films from a donor substrate to a handle substrate includes applying a bonding material to the graphene on the donor substrate, releasing the bonding material from the donor substrate thereby leaving graphene on the bonding material, applying the bonding material with graphene onto the handle substrate, and releasing the bonding material from the handle substrate thereby leaving the graphene on the handle substrate. The donor substrate may comprise SiC, metal foil or other graphene growth substrate, and the handle substrate may comprise a semiconductor or insulator crystal, semiconductor device, epitaxial layer, flexible substrate, metal film, or organic device.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Method for extension of plumbago alkene with ultra-thin hexagonal phase silicon carbide membrane on insulated substrate
InactiveCN101492835AElectrical performance independent of substratePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesHydrogenAlkene
The invention provides a method for preparing graphene by epitaxy of an ultrathin hexagonal phase silicon carbide film on an insulating substrate. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: step one, taking the insulating substrate; step two, carrying out high-temperature etching pretreatement on the insulating substrate by hydrogen to remove surface scratch and other deficiencies so as to obtain flat surface; step three, carrying out high-temperature nitrogen treatment on the insulating substrate to activate the epitaxial surface so as to ensure that subsequent silicon carbide can be easily adhered on the surface of the substrate and maintain the same crystallographic orientation relationship with the substrate; step four, extending the hexagonal phase monocrystal silicon carbide on the insulating substrate; and step five, vaporizing silicon ions in the silicon carbide to complete preparation of the graphene on the insulating substrate.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wafer scale epitaxial graphene transfer
A method for transfer of a two-dimensional material includes forming a spreading layer of a two-dimensional material on a substrate, the spreading layer having a monolayer. A stressor layer is formed on the spreading layer, and the stressor layer is configured to apply stress to a closest monolayer of the spreading layer. The closest monolayer is exfoliated by mechanically splitting the spreading layer wherein the closest monolayer remains on the stressor layer.
Owner:ELPIS TECH INC
Graphene electrodes on a planar cubic silicon carbide (3C-SiC) long term implantable neuronal prosthetic device
InactiveUS8751015B2Increase surface areaIncrease capacitanceSpinal electrodesConductive pattern formationCapacitanceElectricity
Graphene, can be used to make an implantable neuronal prosthetic which can be indefinitely implanted in vivo. Graphene electrodes are placed on a 3C—SiC shank and electrical insulation is provided by conformal insulating SiC. These materials are not only chemically resilient, physically durable, and have excellent electrical properties, but have demonstrated a very high degree of biocompatibility. Graphene also has a large specific capacitance in electrolytic solutions as well as a large surface area which reduces the chances for irreversible Faradaic reactions. Graphene can easily be constructed on SiC by the evaporation of Si from the surface of that material allowing for mechanically robust epitaxial graphene layers that can be fashioned into electrodes using standard lithography and etching methods.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
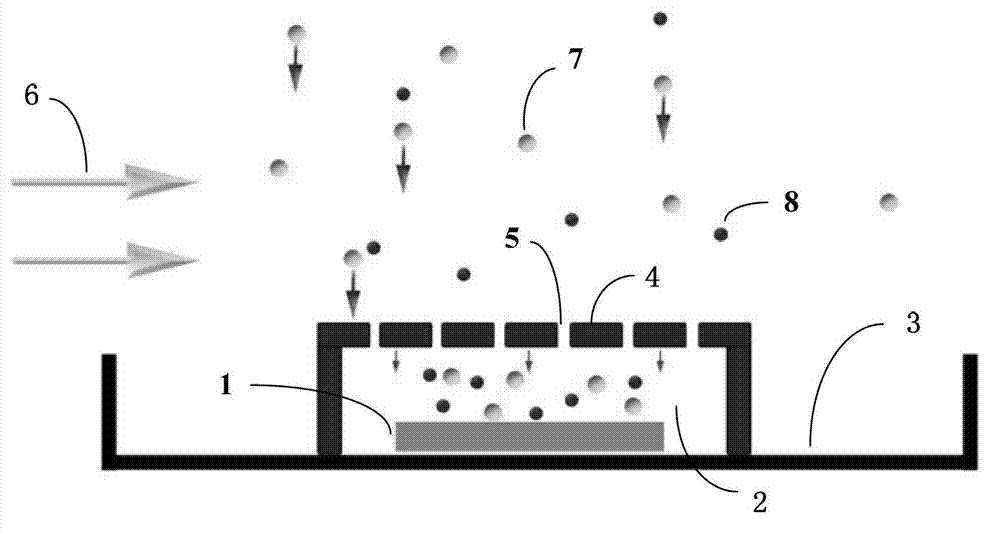
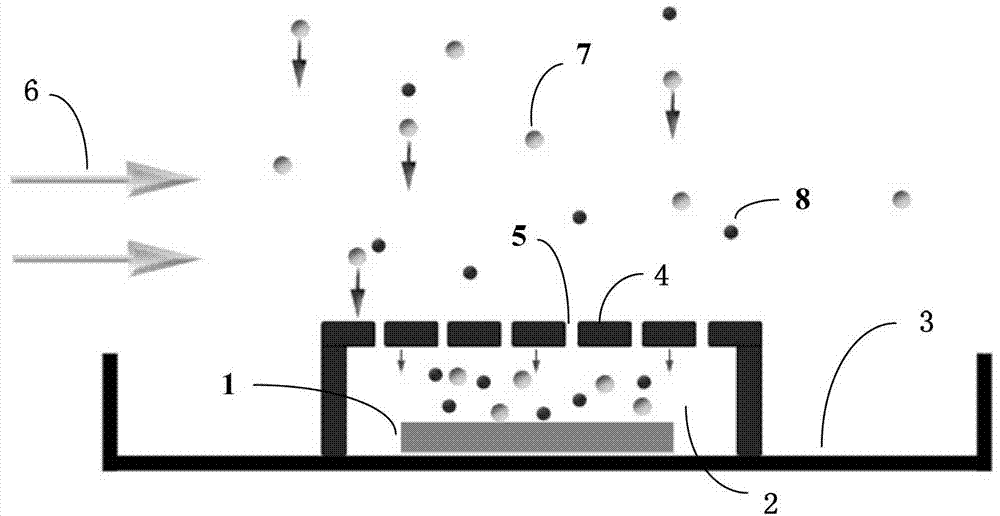
Method for preparing epitaxial graphene by thermal cracking silicon carbide
The invention relates to a method for preparing epitaxial graphene by thermal cracking silicon carbide, and belongs to the technical field of materials. According to the method improved based on method for preparing epitaxial graphene by argon assistant thermal cracking silicon carbide, in the process for preparing epitaxial graphene by argon assistant thermal cracking silicon carbide, a graphite cover (4) with a plurality air holes (5) covers a silicon carbide substrate (1) in an electric induction heating graphite boat, so that the disturbance of air flow and temperature is reduced, and graphene with a greater domain area can be obtained. Due to air holes (5), on the one hand, sublimation of Si is not affected, and on the other hand, the sublimating speed of Si is appropriately controlled to appropriately reduce the growing speed of graphene so as to better control growth thickness of graphene. The air holes (5) are consistent in aperture and uniformly distributed. The uniformity and the electronic mobility of graphene prepared are greatly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
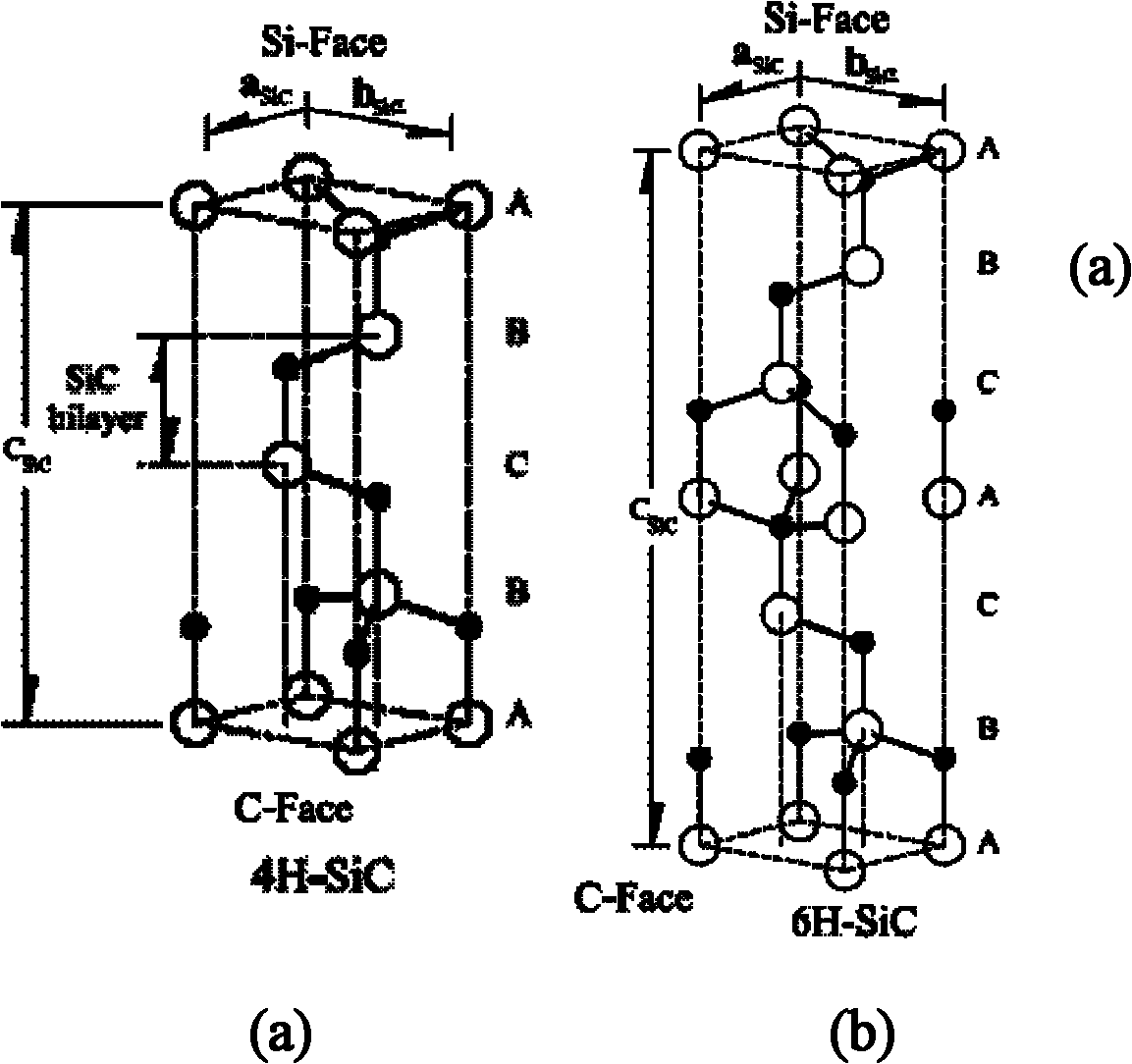
Method for epitaxial growth of wafer-level graphene on 4H/6H-SiC (0001) surface
InactiveCN102433586AEasy to cleanIncrease the areaPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesHydrogenSilanes
The invention discloses a method for epitaxial growth of wafer-level graphene on a 4H / 6H-SiC (0001) surface. The method mainly solves the problem that based on the prior art, during epitaxial growth of graphene on a 4H / 6H-SiC surface, a graphene area is small and graphene uniformity is low. The method comprises the following steps of 1, cleaning a 4H / 6H-SiC (0001) surface to remove organic residues and ionic pollutants on the 4H / 6H-SiC (0001) surface, 2, feeding hydrogen, and carrying out hydrogen etching of the cleaned 4H / 6H-SiC (0001) surface to remove surface scratches so that regular bench-shaped stripes are formed, 3, feeding silane to remove oxides which are formed on the 4H / 6H-SiC (0001) surface by the hydrogen etching, and 4, heating in a low-argon pressure environment to evaporate silicon atoms so that carbon atoms are rearranged on the 4H / 6H-SiC (0001) surface by a sp2 method to form epitaxial graphene. Graphene obtained by the method has a large area and good uniformity and can be utilized for preparation of a wafer-level epitaxial graphene material.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
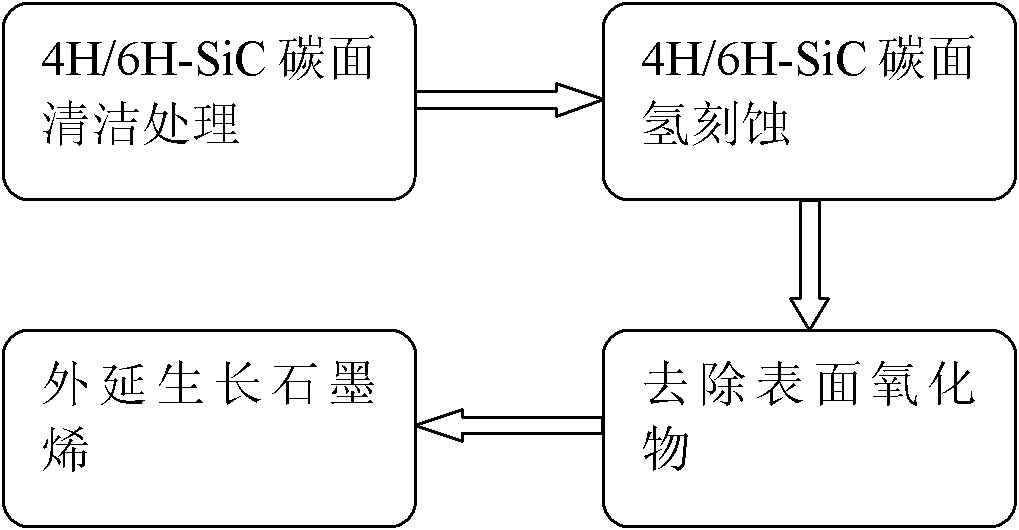
Method for realizing epitaxial growth of wafer level graphene on 4H/6H-SiC carbon surfaces
The invention discloses a method for realizing epitaxial growth of wafer level graphene on 4H / 6H-SiC carbon surfaces, which aims to realize that when epitaxial growth of wafer level graphene is realized by an existing method, the area of produced graphene is too small and uniformity of the graphene is low. The method includes steps of cleaning and treating the 4H / 6H-SiC carbon surfaces to remove organic residues and ion pollutant on the surfaces, filling hydrogen to realize hydrogen etching for the 4H / 6H-SiC carbon surfaces to remove scratches of the surfaces, and forming regular step-shaped strips; feeding silane to remove oxide caused by hydrogen etching on the surfaces; feeding argon flow to realize sublimation of silicon atoms under the condition of pressure of 2mbar by the aid of heating, and realizing reconstitution of surfaces of substrate in a sp2 mode by the aid of carbon atoms to form epitaxial graphene. The graphene prepared by the aid of the process method has larger area and fine uniformity, and the method can be applied to preparing wafer level epitaxial graphene materials.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Stack structure comprising epitaxial graphene, method of forming the stack structure, and electronic device comprising the stack structure
ActiveUS8159037B2NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsEpitaxial graphene
Provided are a stack structure including an epitaxial graphene, a method of forming the stack structure, and an electronic device including the stack structure. The stack structure includes: a Si substrate; an under layer formed on the Si substrate; and at least one epitaxial graphene layer formed on the under layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for preparing silicon intercalated monolayer graphene
InactiveUS20110086756A1Quality improvementSufficient energyMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesMonolayer grapheneCvd graphene
A method of preparing the electronic material called silicon intercalated epitaxial monolayer graphene comprises the steps of growing large scale high-quality graphene on metal surface, depositing silicon on the prepared epitaxial graphene and annealing to high temperature to intercalate the silicon to the interface of graphene and metal surface. Depending on the quantity of the silicon deposited on the graphene surface, the numbers of the silicon layers on the interface can be controlled and adjusted.
Owner:GAO HONG JUN +8
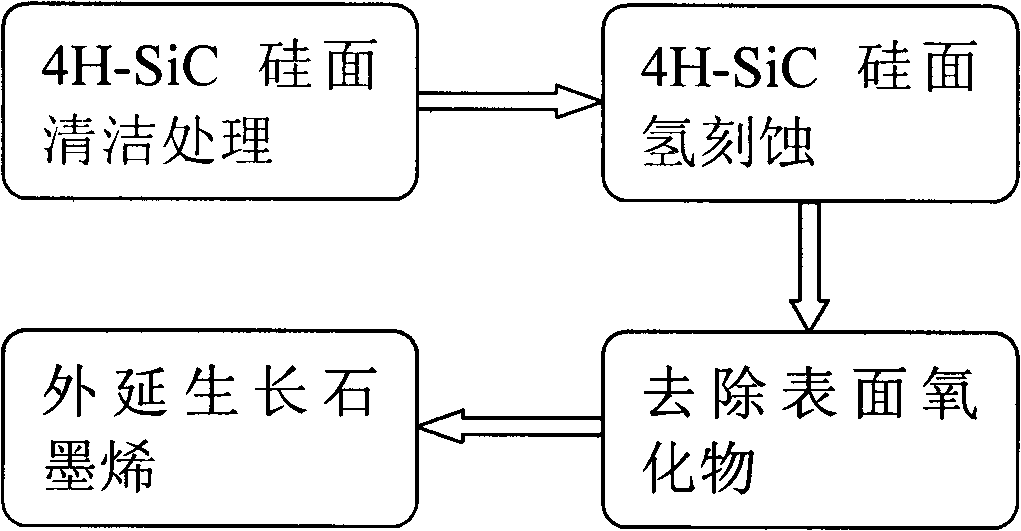
Method for graphene epitaxial growth on 4H-SiC silicon surface
InactiveCN101602503BIncrease the areaImprove uniformityPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsHydrogenSilanes
The invention discloses a method for graphene epitaxial growth on 4H-SiC silicon surface, mainly solving the problems of small graphene area and poor homogeneity during graphene epitaxial growth on the 4H-SiC silicon surface. The method is as follows: a 4H-SiC silicon surface is cleaned to remove organic remains and ionic contaminants on the surface; hydrogen and propane are led in to carry out hydrogen corrosion to the 4H-SiC silicon surface to remove surface scratches so as to form regular step-shaped stripes; silane is led in to remove oxide formed by hydrogen corrosion on the surface; under the circumstance of argon, silicon atoms are evaporated to ensure carbon atom to reconstruct and form epitaxial graphene in the form of sp<2> by heating. The invention can be used for manufacturing epitaxial graphene materials.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Incorporation of functionalizing molecules in nanopatterned epitaxial graphene electronics
In a method of making graphite devices, a thin-film graphitic layer disposed against a preselected face of a substrate is created on the preselected face of the substrate. A preselected pattern is generated on the thin-film graphitic layer. At least one functionalizing molecule is attached to a portion of the graphitic layer. The molecule is capable of interacting with π bands in the graphitic layer.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Epitaxial graphene with thickness modulation
InactiveUS20160009560A1Easy to controlIncreasing the thicknessFrom gel stateMaterial nanotechnologyOptical transparencyCvd graphene
The present invention relates to a novel graphene sheet with modulated thickness comprising electrically conductive areas of an array of ridges constituting a grid structure on graphene surface wherein the ridging areas are integrally formed with the graphene sheet and are themselves made of graphene. The invention further relates to a method for producing the thickness modulated graphene material of above type by way of a special capping technique where the capping structure having an array of protrusions is involved so that the said capping would transfer its physical structure to the graphene surface to form areas with improved electrically conductivity and optical transparency.
Owner:SABANCI UNIVERSITY
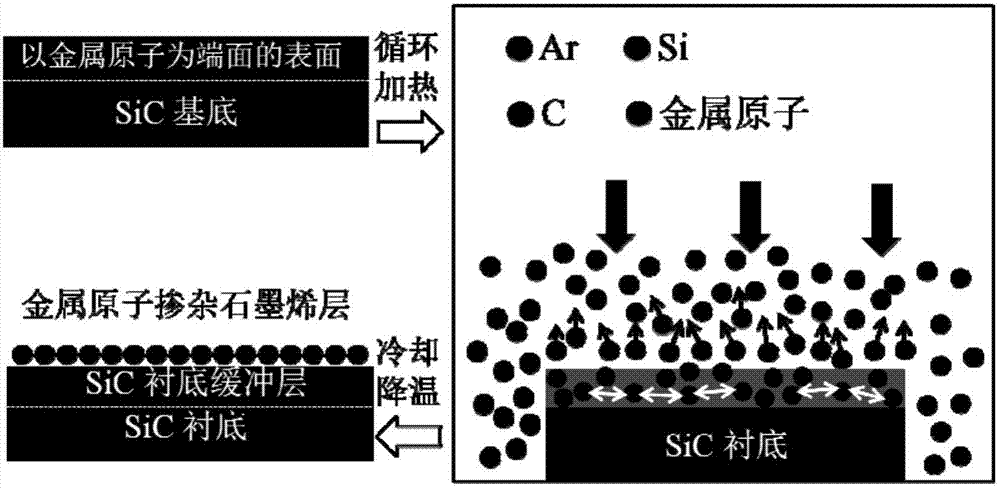
Preparation method of metal atom-doped large-area regular epitaxial graphene
ActiveCN107316804AAvoid damageSimplified growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGrapheneOperabilityCvd graphene
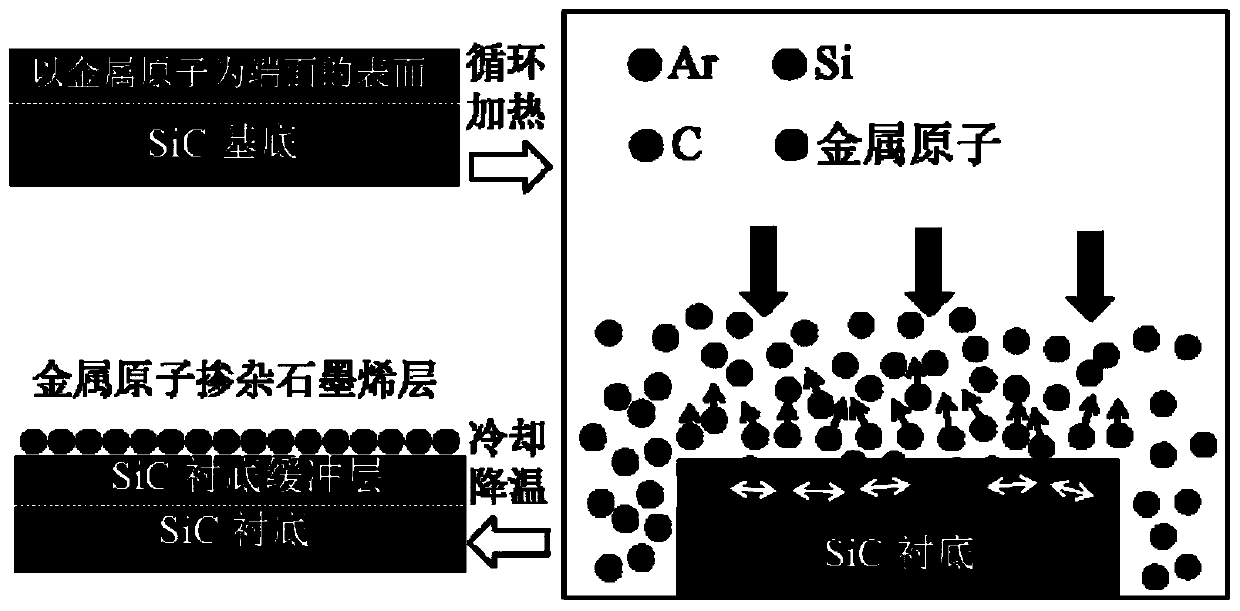
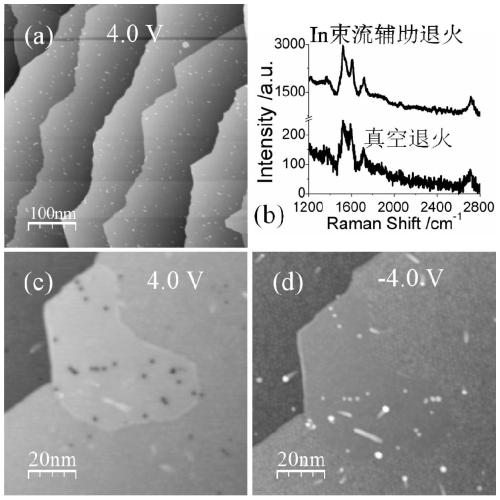
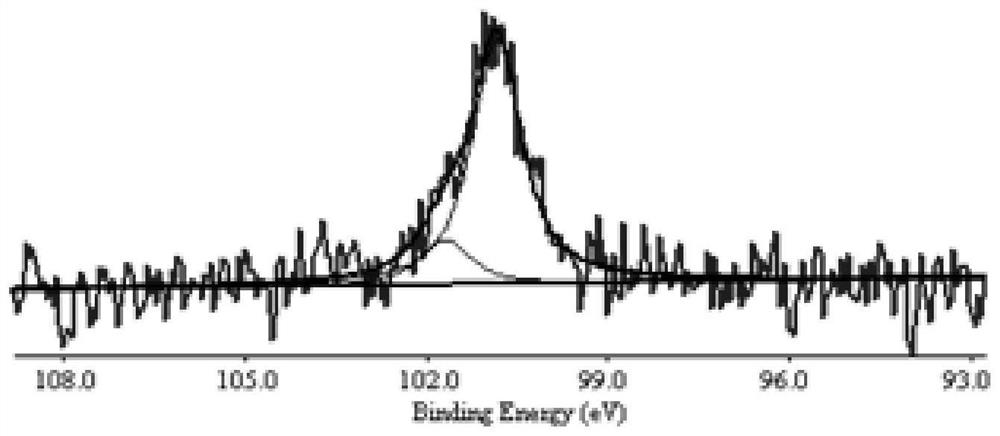
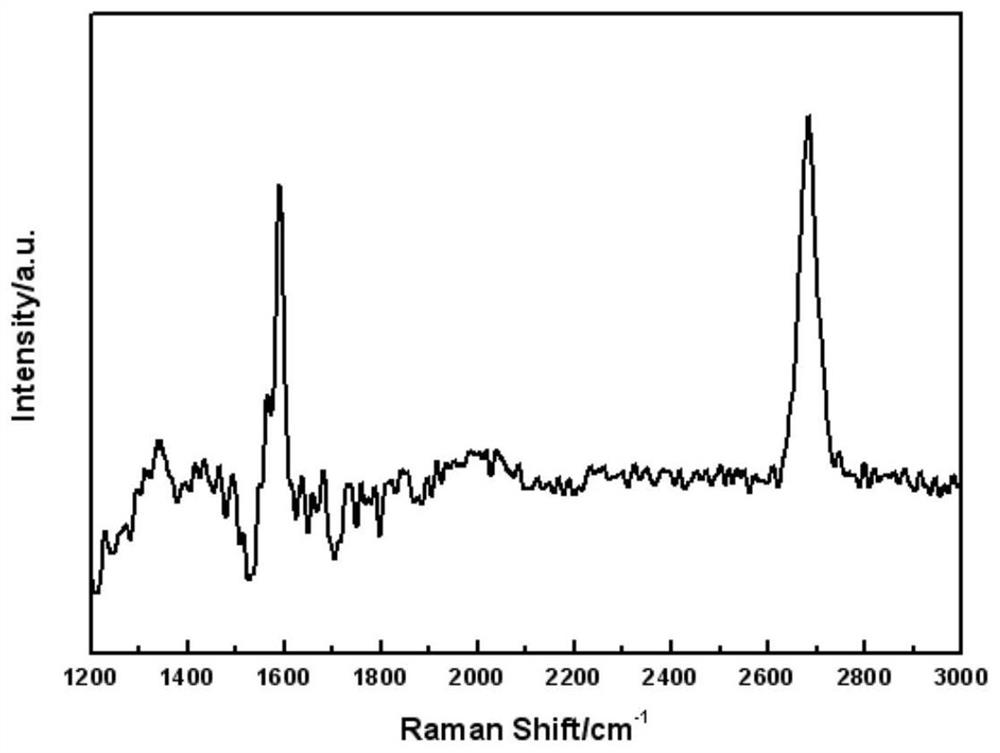
The invention discloses a preparation method of metal atom-doped large-area regular epitaxial graphene, and applied to the technical field of microelectronics. Metal atoms are introduced to a SiC pyrolysis process and Ar atmosphere is adopted for protection in an auxiliary manner, so that the large-area regular epitaxial graphene can be prepared, external metal atoms also can be guided to be directly participated in a graphene lamination layer growth process, thereby promoting atom intercalation or hybridization between metal atoms and C atoms to realize doping of metal atoms, and avoiding damage to the overall structure of graphene caused by ion implantation; pretreatment of metal atom beams is the important premise of realizing doping, and by virtue of the Ar atmosphere environment, generate of surface holes can be suppressed, so that regular and uniform surface appearance of the epitaxial graphene sample is ensured; and the preparation method is simple in technical idea, high in operability, is a stable and effective metal atom doping method, and capable of providing significant guidance and reference to optimization preparation and performance improvement of epitaxial graphene.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for regulating electronic band gap in SiC-based epitaxial graphene
InactiveCN105088350ATunable electronic bandgapOvercoming controllabilityAfter-treatment detailsLattice defectsFold change
The invention discloses a method for regulating an electronic band gap in SiC-based epitaxial graphene. The method comprises the following steps of (a) calculating the damage distribution as well as electronic and nuclear energy loss distribution of irradiation ions in SiC crystals through SRIM software, and calculating an energy band structure of defected graphene; (b) irradiating an SiC-based epitaxial graphene sample by using an ion beam to form epitaxial graphene with the defected structure; (c) respectively observing metallographic structures of irradiated and non-irradiated graphene by using a metallographic microscope, and observing the surface folding changes of the irradiated and non-irradiated graphene by using a scanning electron microscope; (d) calculating the lattice defect amount of the graphene sample under different irradiation conditions through the formula as shown in the specification; and (e) testing the band gap in the epitaxial graphene by virtue of an infrared spectrum to achieve the aim of regulating the band gap. A controllable defected structure is generated in the graphene by using an ion irradiation method, furthermore, the electronic band gap in the graphene is regulated, and therefore, the defects of poor controllability and repeatability in the traditional process are overcome.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
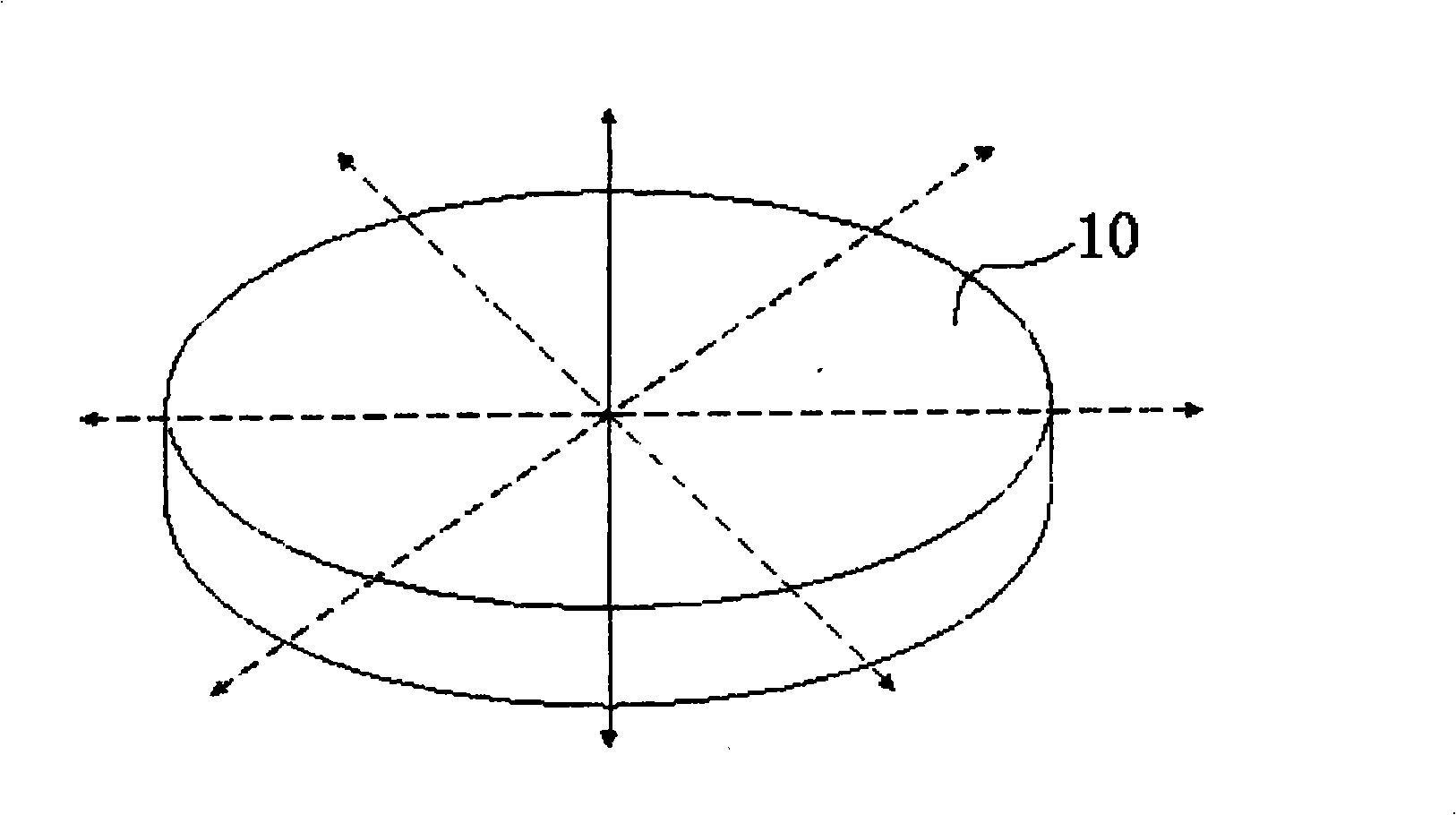
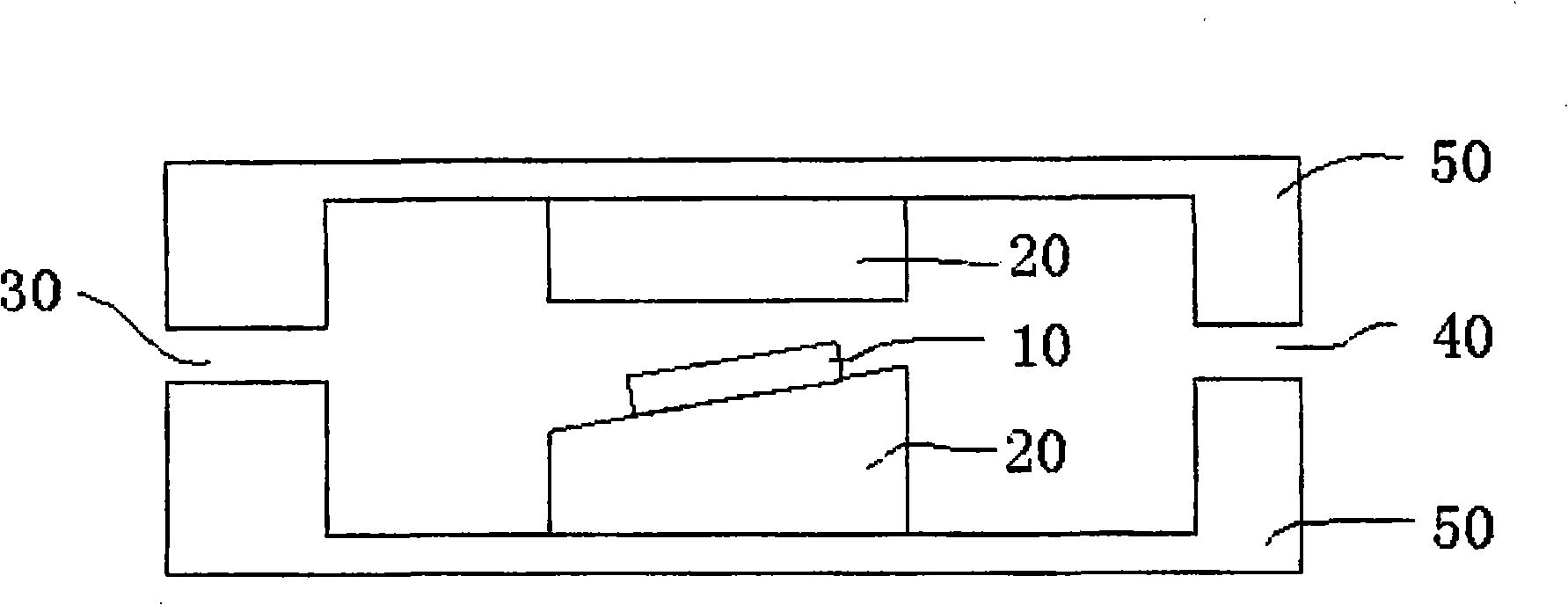
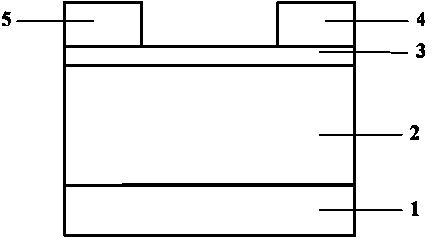
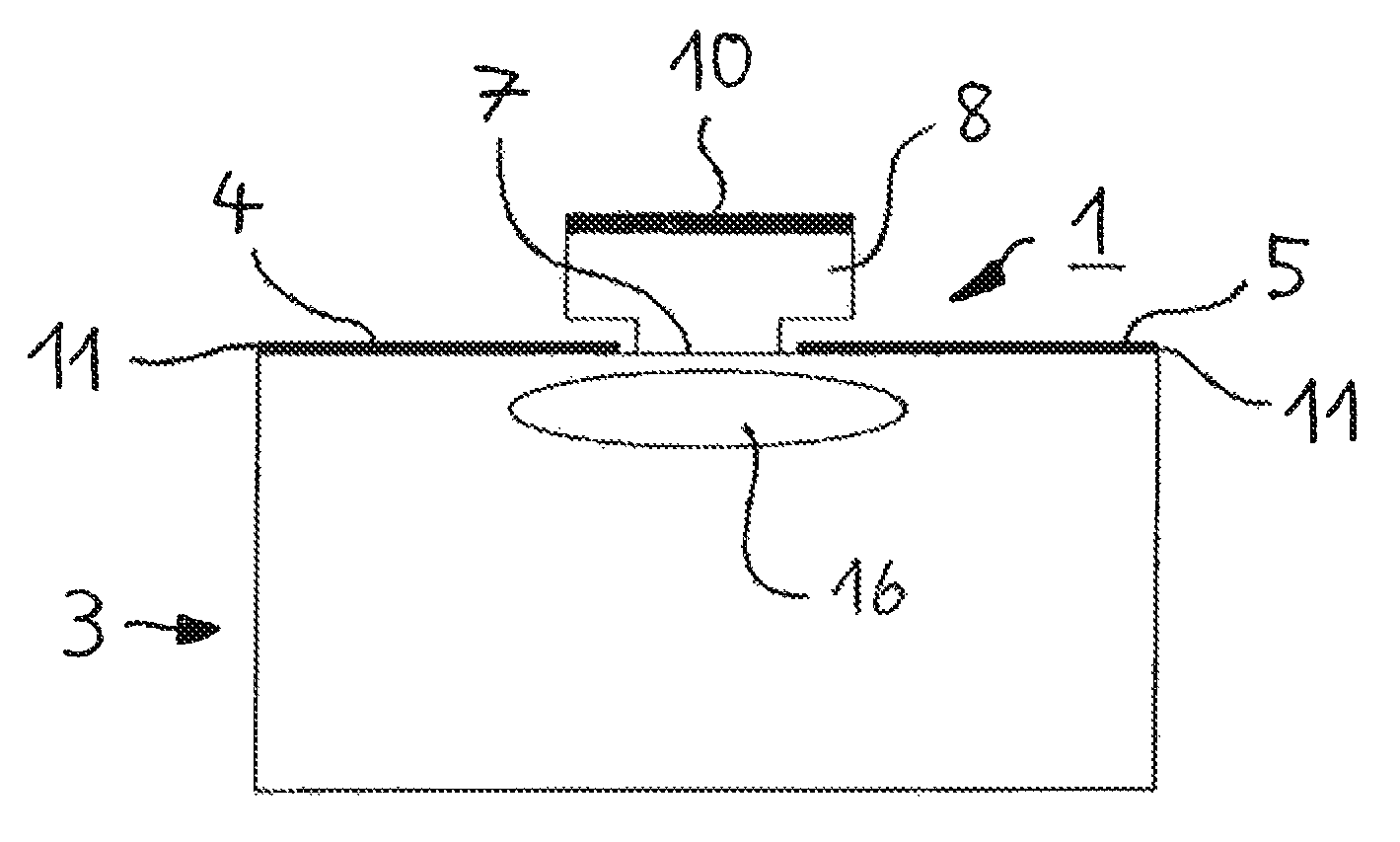
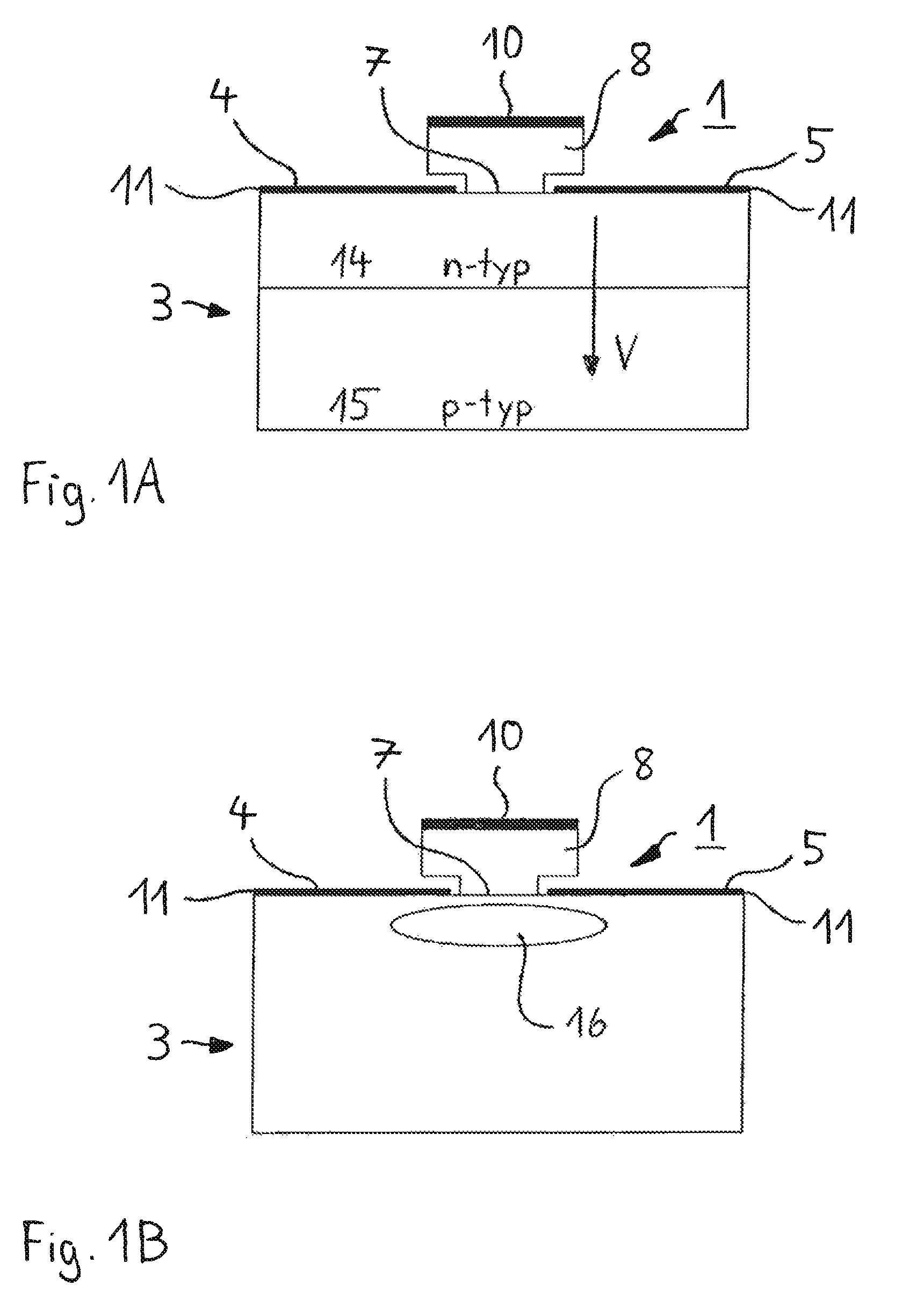
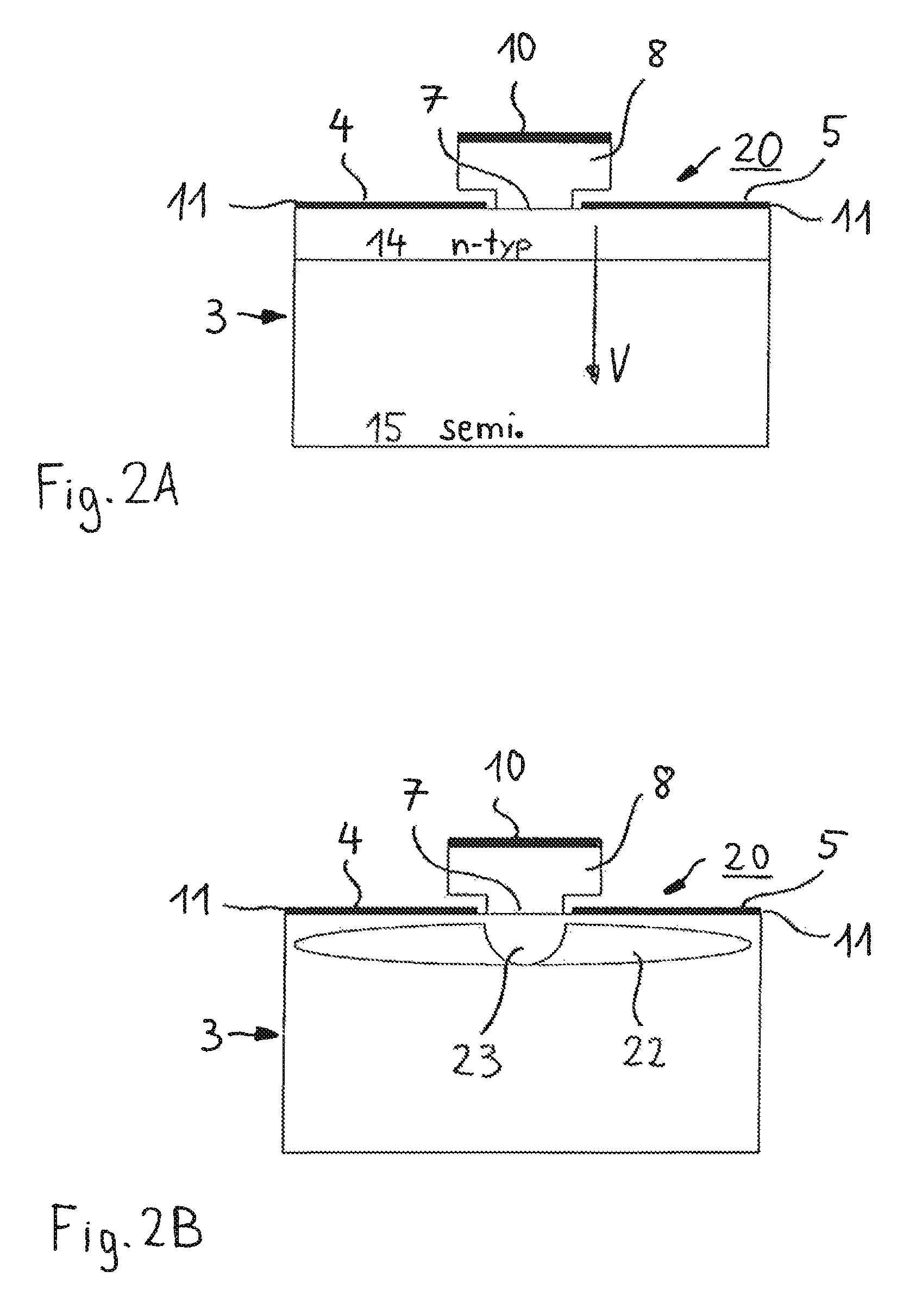
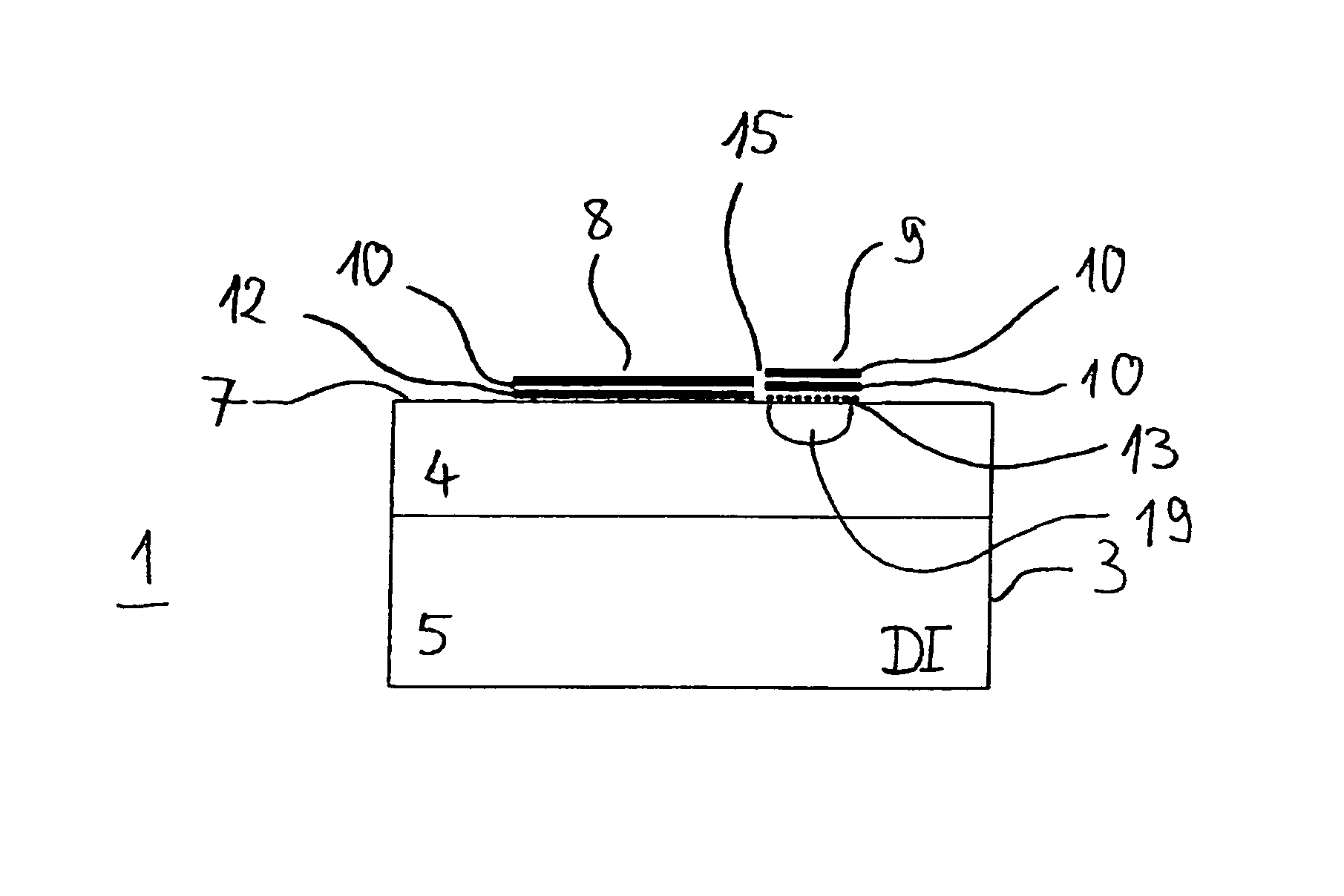
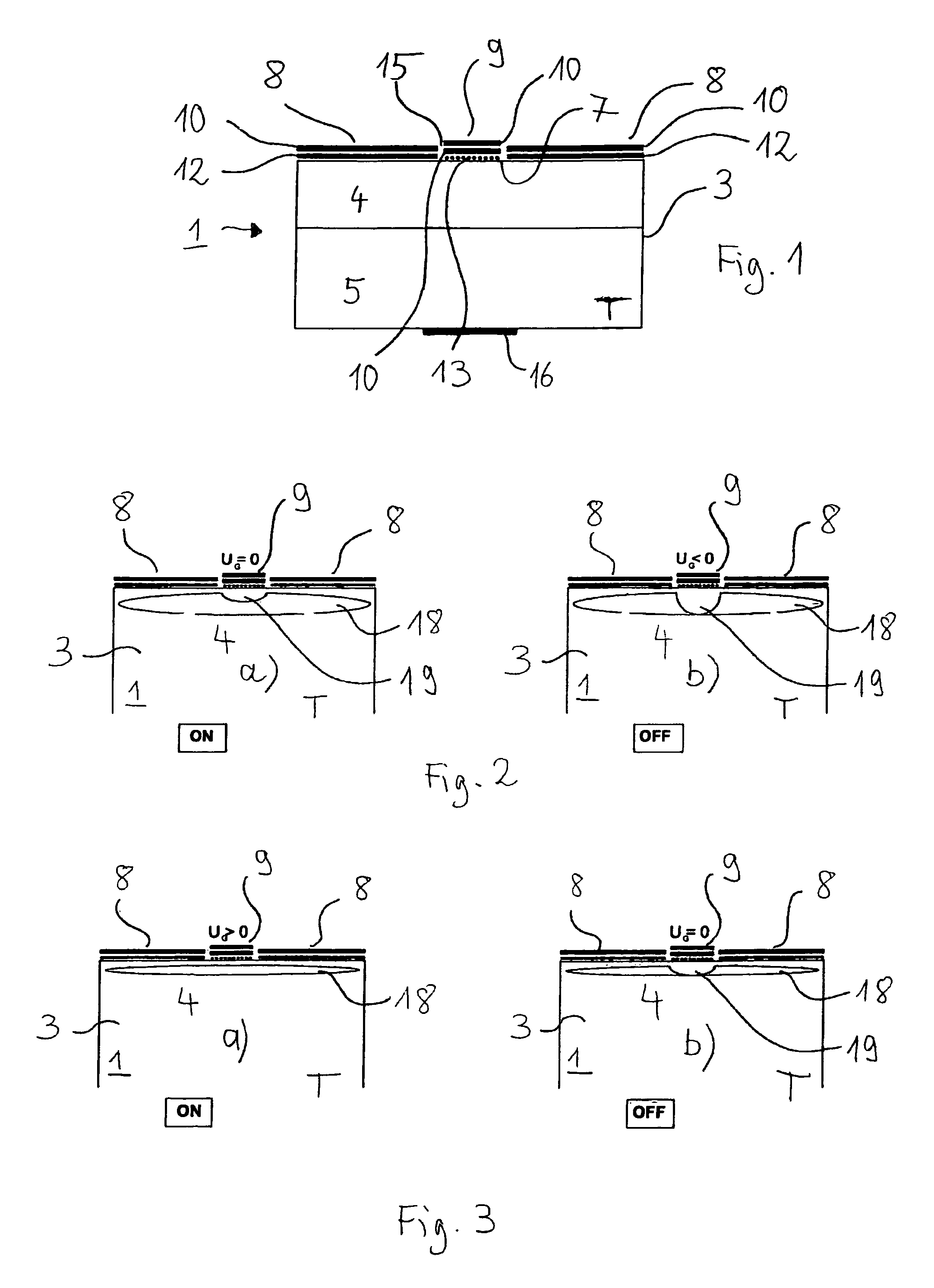
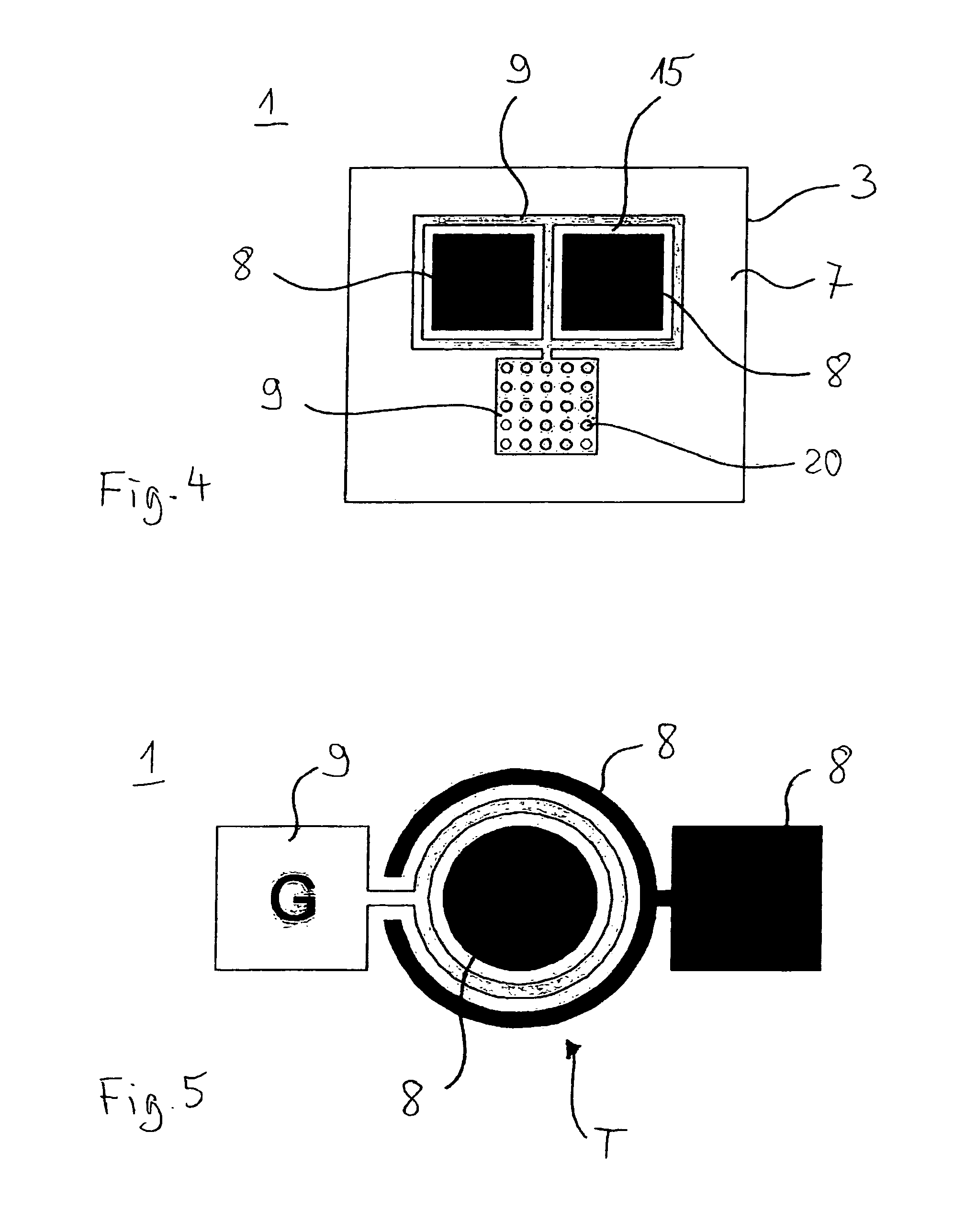
Semiconductor component
A semiconductor component (1, 20, 30) comprising a semiconductor substrate (3) composed of silicon carbide and comprising separate electrodes (4, 5) applied thereto, said electrodes each comprising at least one monolayer of epitaxial graphene (11) on silicon carbide, in such a way that a current channel is formed between the electrodes (4, 5) through the semiconductor substrate (3).
Owner:FRIEDRICH ALEXANDER UNIV ERLANGEN NURNBERG
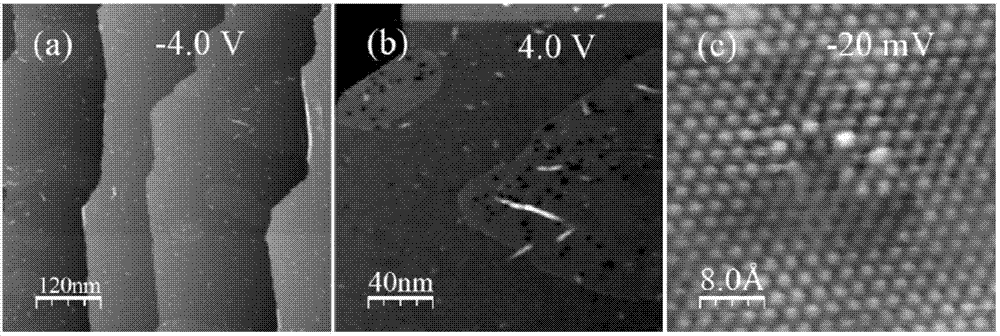
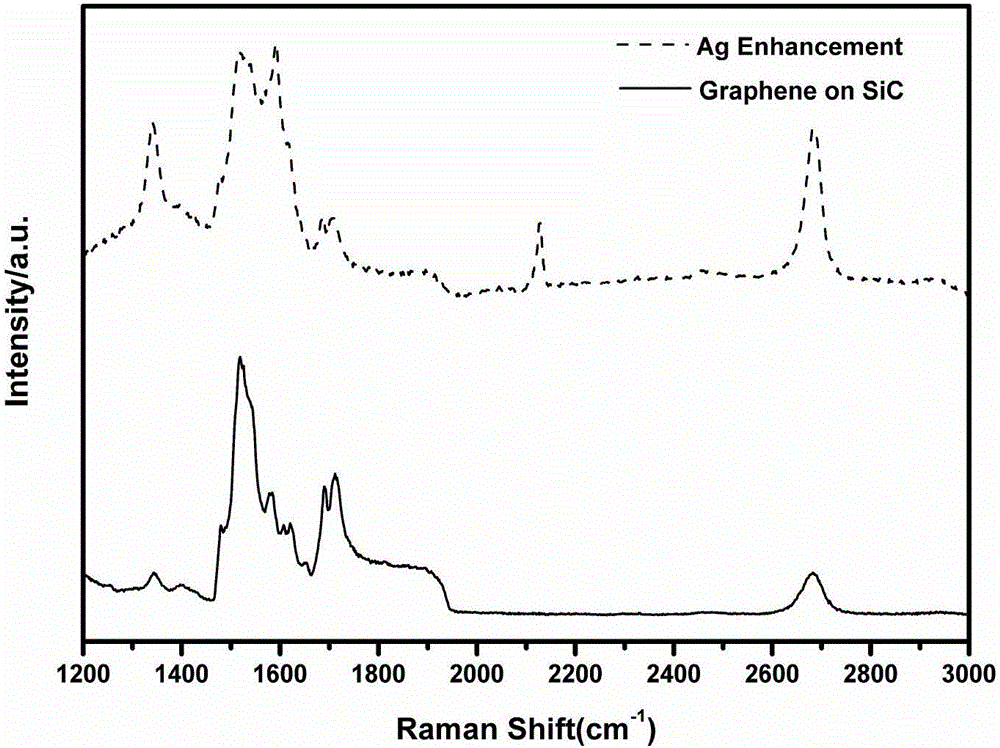
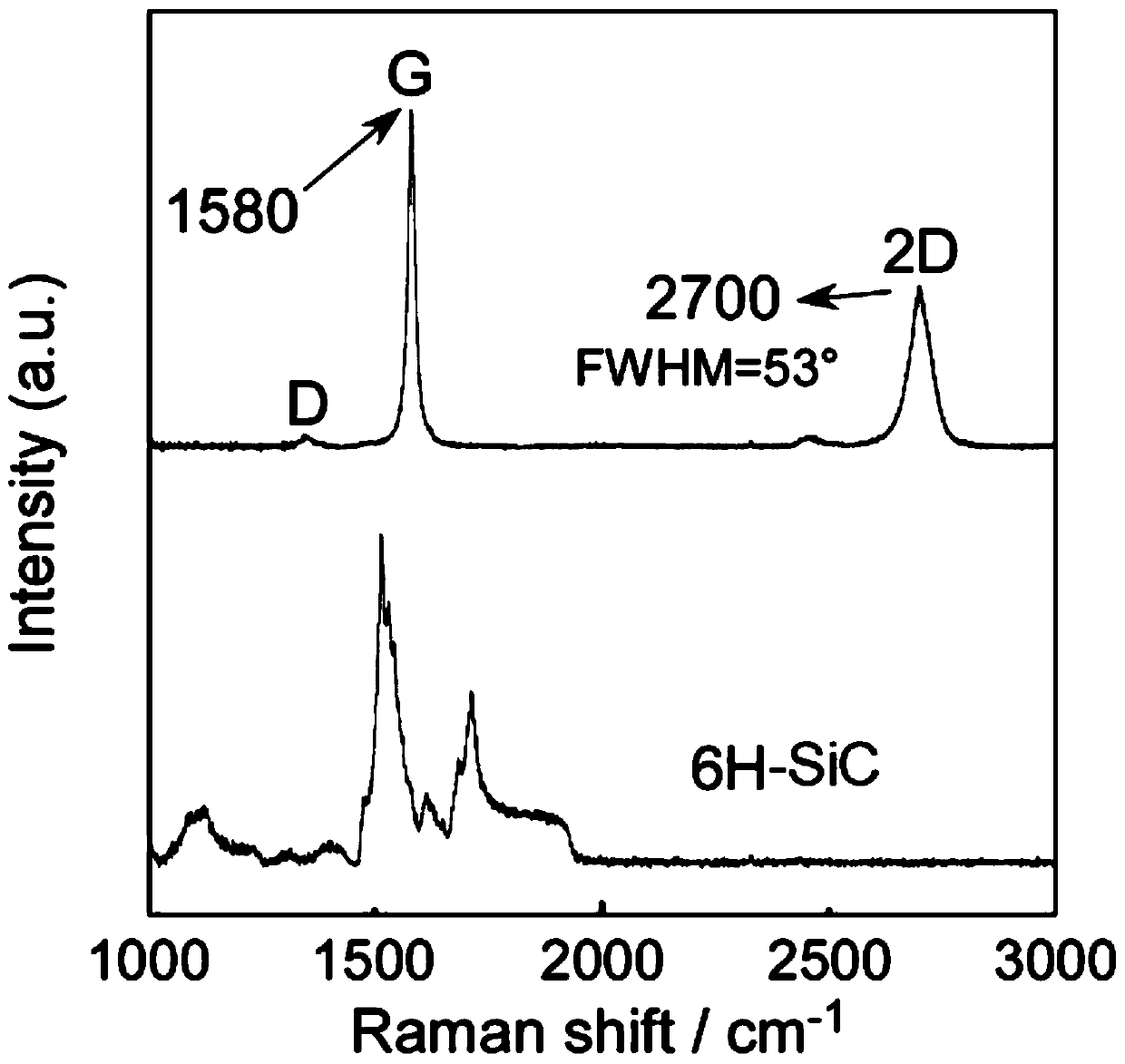
Method for characterization of graphene epitaxially grown on SiC based on Ag-particle Raman enhancement effect
The invention relates to a method for characterization of graphene epitaxially grown on SiC based on Ag-particle Raman enhancement effect. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly spraying Ag particles onto a quasi-freestanding graphene wafer at first, and then carrying out testing by using microscopic Raman spectroscopy so as to learn about the situation of bonding of a Si-H bond. According to the invention, the intercalation degree of hydrogen atoms can be directly determined by directly characterizing the Si-H bond in virtue of the Ag-particle Raman enhancement effect; influence of experimental conditions on hydrogen intercalation effect is visually fed back by analyzing the proportion of the Si-H bond in a testing area; and during visual characterization of the Si-H bond, the characteristic G peak, 2D peak and defect D peak of graphene are enhanced to certain extents, which greatly helps further accurate analysis of the structure and the properties like defects of graphene.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for preparing graphene and graphene device by epitaxy of pretreated SiC substrate
ActiveCN110556283AQuality improvementInhibition of nucleation densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenHydrogen etching
The invention relates to a method for preparing graphene and a graphene device by epitaxy of a pretreated SiC substrate. The method comprises the following steps: performing hydrogen etching on the SiC substrate and then performing oxidation treatment on the SiC substrate after hydrogen etching at a temperature of 800-1300 DEG C for the treatment time of 15-120min; and then rising the temperatureto 1450-1700 DEG C in an inert atmosphere on the pretreated SiC substrate for graphene growth. The SiC surface is passivated through oxidation pretreatment so that nucleation density of the graphene epitaxially grown on the SiC substrate is reduced, the graphene material with larger size and better performance is obtained, and the SiC epitaxial graphene wafer is subjected to deposition, photolithography, doping and integration procedures accordingly so as to prepare the corresponding graphene device.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for manufacturing epitaxy graphene back gate transistor with nitrogen-doped SiC substrate
ActiveCN103943510AEasy to operateAvoid secondary pollutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh electronCvd graphene
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing an epitaxy graphene back gate transistor with a nitrogen-doped SiC substrate. The method includes the steps of carrying out doping on the smooth and even SiC substrate through nitrogen ions generated through a semiconductor ion implantation machine, implanting the nitrogen ions with parameters ranging from 30 kev to 150 kev into the upper half portion of the SiC substrate to serve as a dielectric layer, implanting the nitrogen ions with parameters ranging from 500 kev to 1000 kev into the lower half portion of the SiC substrate to serve as a grid electrode, growing graphene on the SiC substrate with the implanted nitrogen ions in an epitaxy mode, and forming a graphene groove layer. According to the method, the transistor is manufactured directly through the SiC substrate, the grid electrode and the dielectric layer do not need to be deposited, operation is simple, and secondary pollution in the manufacturing process is avoided; the epitaxy-grown graphene is good in electrical property and has the high electron mobility.
Owner:江苏卓远半导体有限公司
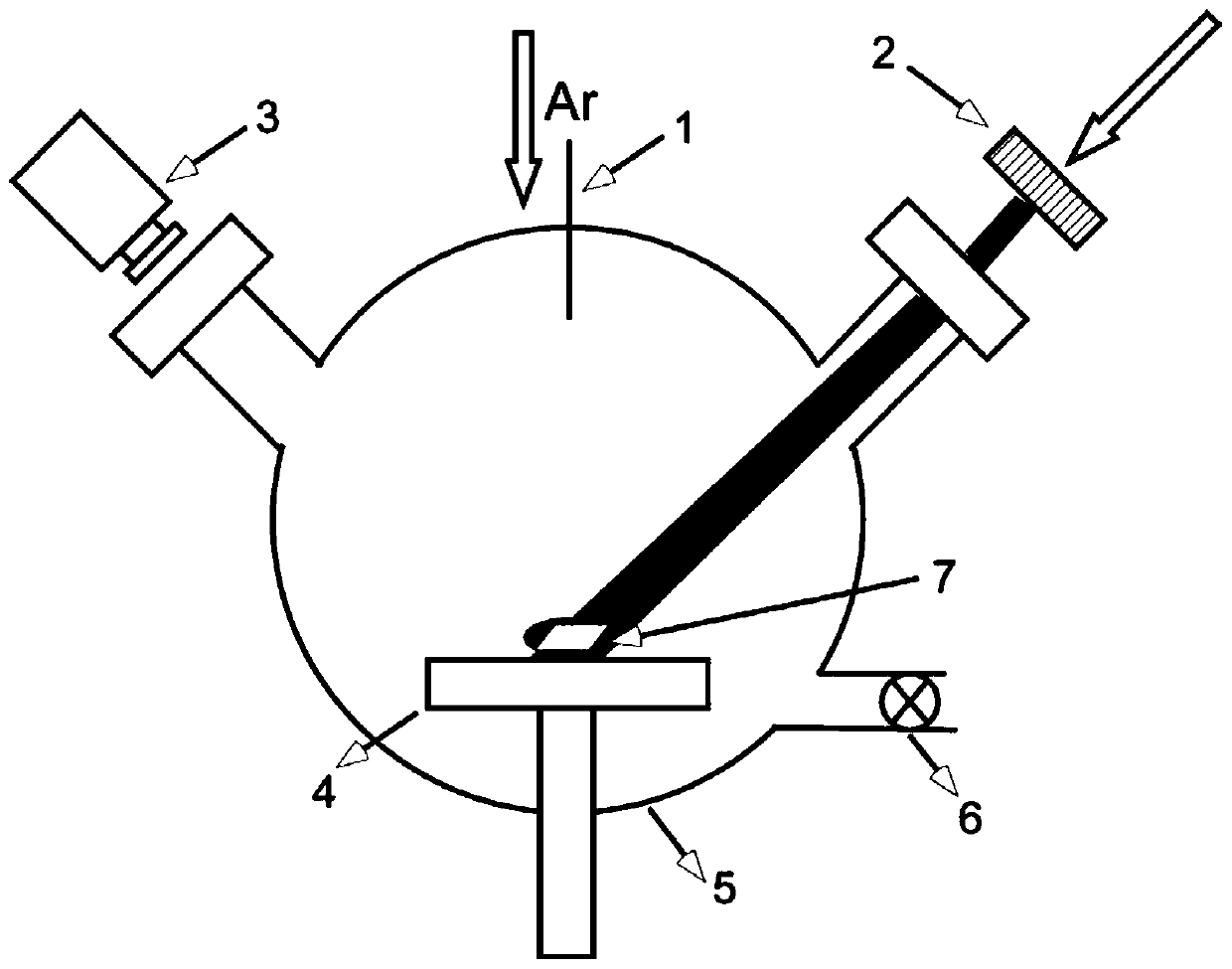
Method for preparing epitaxial graphene through laser heating
ActiveCN111017914AReduce square resistanceThe number of layers is controllableGraphenePhysical chemistryGraphite
The invention provides a method for preparing epitaxial graphene by laser heating. The method comprises the following steps: 1) putting a SiC substrate into a deposition cavity of a laser chemical vapor deposition device, and introducing high-purity Ar gas into the cavity to regulate the gas pressure in the cavity to 1000-10000 Pa; (2) starting laser to irradiate the SiC substrate to heat the surface of the substrate to 1500-2000 DEG C at a rate of 400-600 DEG C / s, and continuously irradiating for 1-5 min; and 3) adjusting the laser power to reduce the temperature of the surface of the substrate to 600 DEG C at a rate of 100-200 DEG C / s, and naturally cooling to room temperature to obtain the epitaxial graphene on the surface of the SiC substrate. The method can rapidly prepare the epitaxial graphene with a large growth area, and the prepared epitaxial graphene has the characteristics of high conductivity, controllable layer number and high crystal quality.
Owner:气相科技(武汉)有限公司
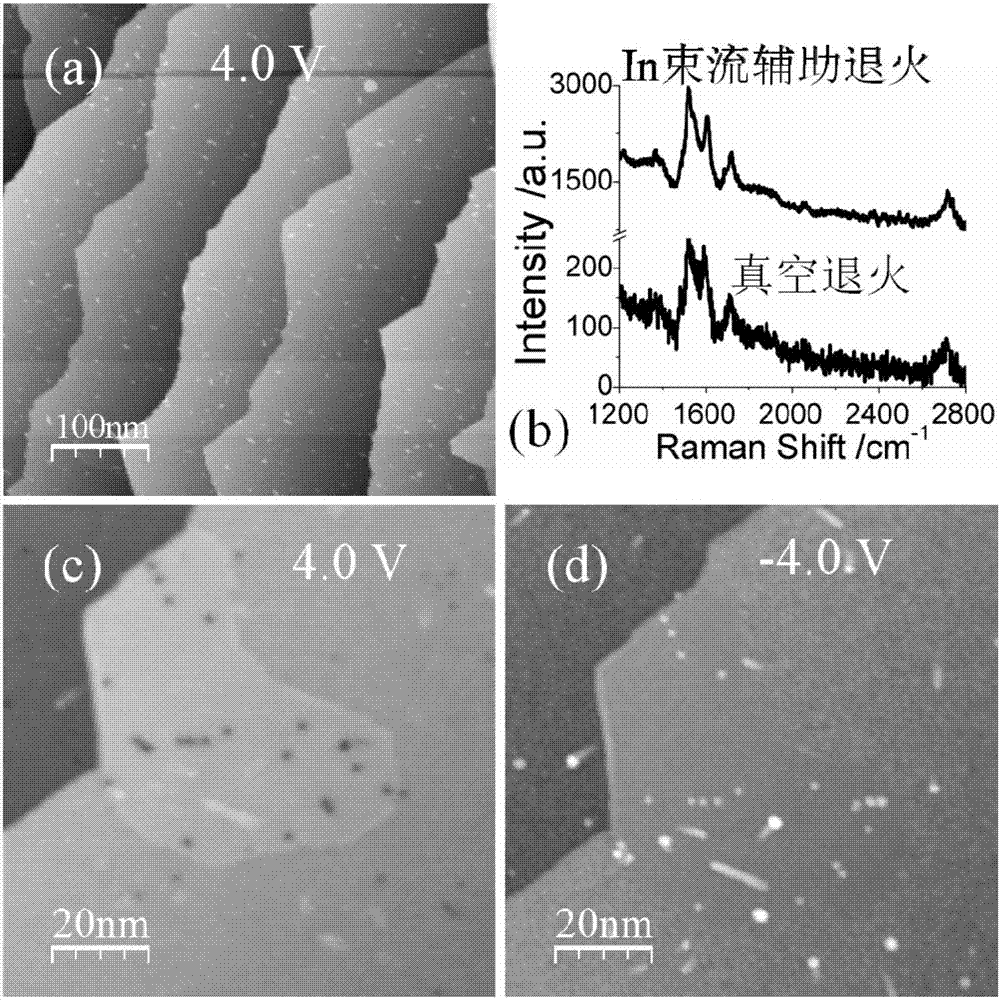
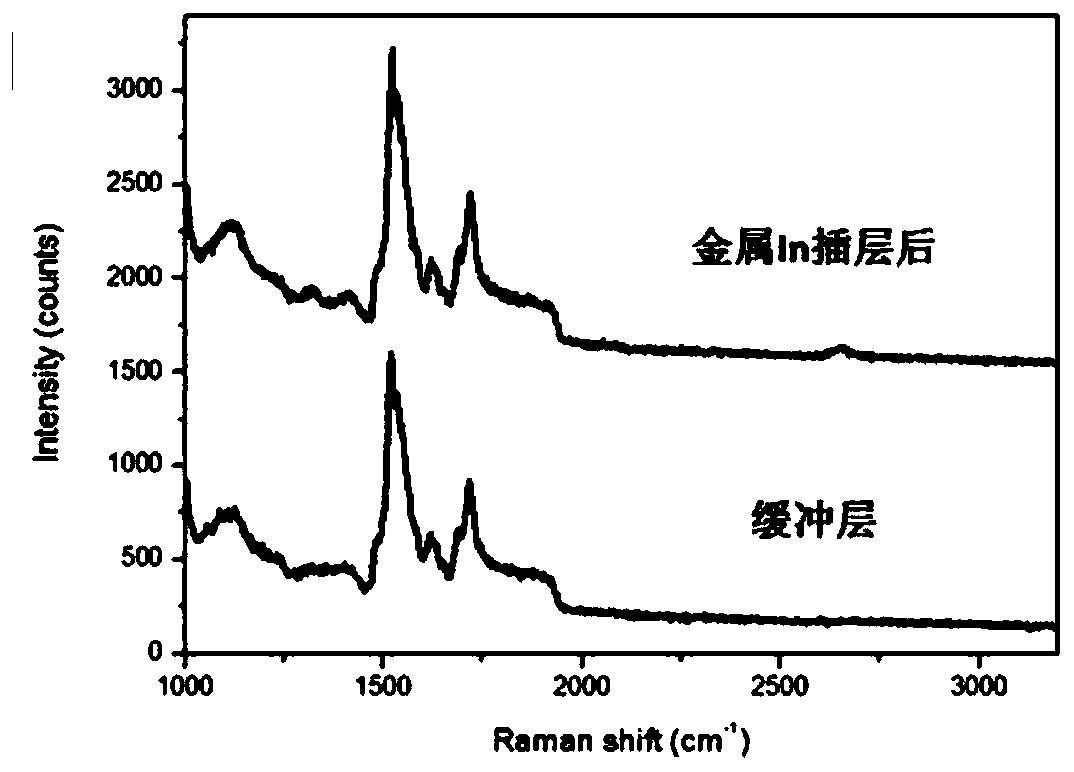
Method for preparing single-layer large-area graphene by utilizing metal intercalation
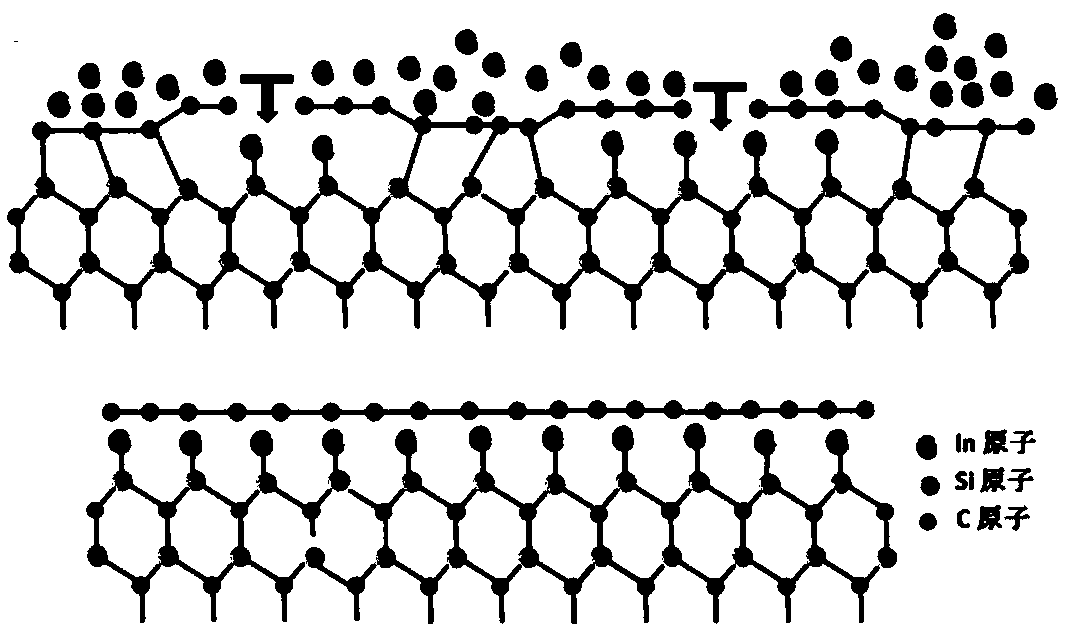
ActiveCN110697696ALow preparation temperatureLittle temperature dependenceSingle layer grapheneGraphiteSingle layer graphene
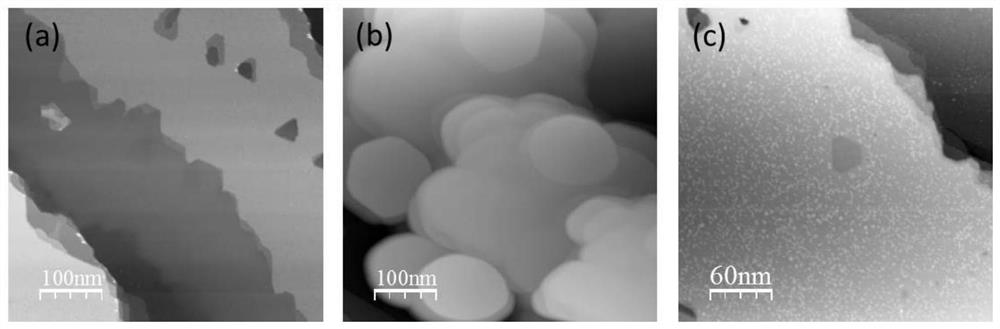
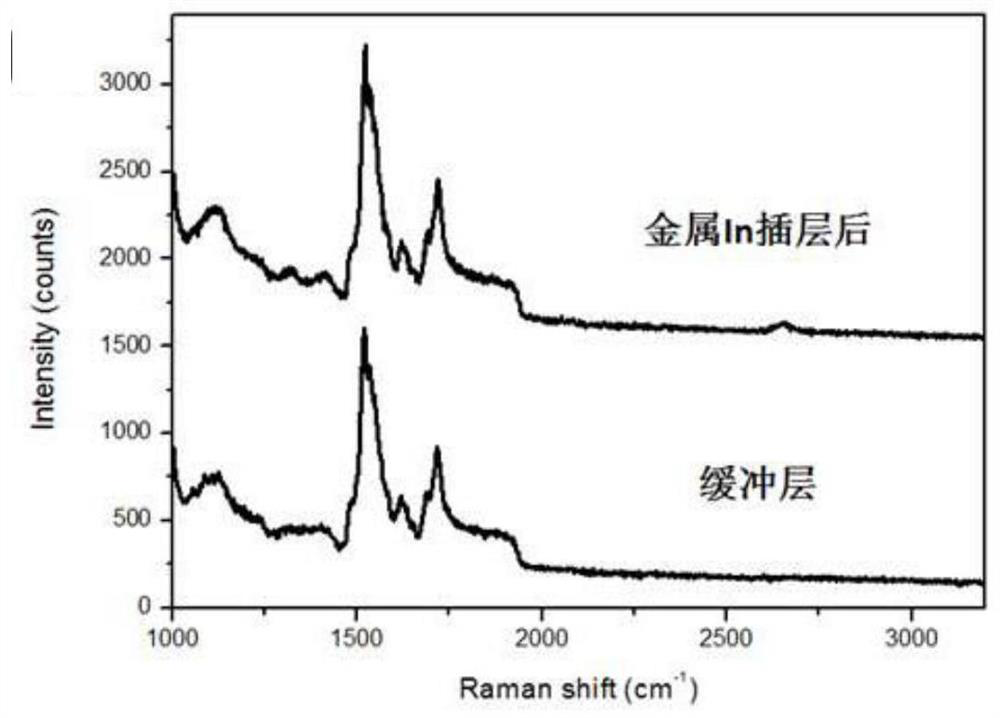
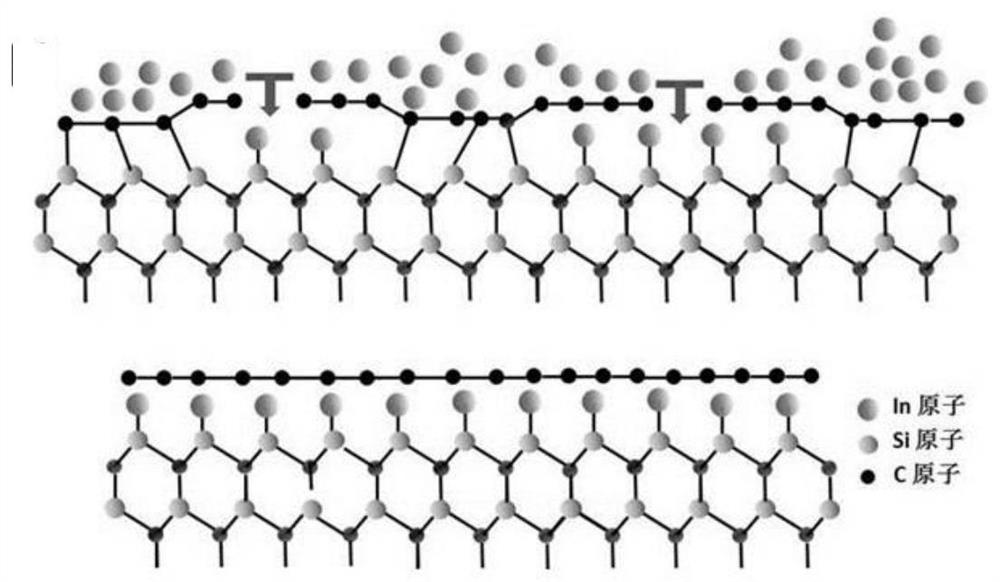
The invention discloses a preparation technology of large-area single-layer graphene. In atom intercalation is carried out on a buffer layer by using an intercalation technology; for a surface only having the buffer layer originally, In atoms are intercalated between the buffer layer and a SiC substrate and enable the buffer layer to be converted into graphene; so on one hand, the large-area single-layer graphene is prepared, and on the other hand, the preparation temperature of the graphene is reduced. For the surface where the original buffer layer and the single-layer epitaxial graphene coexist, the In atoms are intercalated between the buffer layer and the SiC substrate, the buffer layer becomes graphene and is perfectly connected with the original epitaxial graphene, and the large-area single-layer graphene is formed. Besides, the graphene formed by intercalation is weak in interaction with the substrate and is in a separated state, so ionization effect is achieved. By using the technology, the large-area graphene can be prepared, and the layer thickness of the graphene can be controlled; so important guidance and reference values are provided for the application of graphene in the fields of related microelectronics, superconductivity, strain engineering and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Semiconductor component
A semiconductor component (1, 20, 30) comprising a semiconductor substrate (3) composed of silicon carbide and comprising separate electrodes (4, 5) applied thereto, said electrodes each comprising at least one monolayer of epitaxial graphene (11) on silicon carbide, in such a way that a current channel is formed between the electrodes (4, 5) through the semiconductor substrate (3).
Owner:FRIEDRICH ALEXANDER UNIV ERLANGEN NUERNBERG
Electronic device
An electronic device (1) includes a semiconductor substrate (3) having a front surface (7), a first electrode (8) and a second electrode (9) disposed on the front surface (7) of the substrate (3), wherein the first electrode (8) and the second electrode (9) each have at least one epitaxial graphene monolayer (10). The at least one epitaxial graphene monolayer (10) of the first electrode (8) forms an ohmic contact with the substrate (3) and the at least one epitaxial graphene monolayer (10) of the second electrode (9) forms a Schottky barrier with the substrate (3).
Owner:FRIEDRICH ALEXANDER UNIV ERLANGEN NURNBERG
Method for preparing epitaxial graphene by thermal cracking silicon carbide
The invention relates to a method for preparing epitaxial graphene by thermal cracking silicon carbide, and belongs to the technical field of materials. According to the method improved based on method for preparing epitaxial graphene by argon assistant thermal cracking silicon carbide, in the process for preparing epitaxial graphene by argon assistant thermal cracking silicon carbide, a graphite cover (4) with a plurality air holes (5) covers a silicon carbide substrate (1) in an electric induction heating graphite boat, so that the disturbance of air flow and temperature is reduced, and graphene with a greater domain area can be obtained. Due to air holes (5), on the one hand, sublimation of Si is not affected, and on the other hand, the sublimating speed of Si is appropriately controlled to appropriately reduce the growing speed of graphene so as to better control growth thickness of graphene. The air holes (5) are consistent in aperture and uniformly distributed. The uniformity and the electronic mobility of graphene prepared are greatly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A method for preparing large-area regular epitaxial graphene doped with metal atoms
ActiveCN107316804BAvoid damageSimple processGrapheneSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOperabilityCvd graphene
The invention discloses a preparation method of metal atom-doped large-area regular epitaxial graphene, and applied to the technical field of microelectronics. Metal atoms are introduced to a SiC pyrolysis process and Ar atmosphere is adopted for protection in an auxiliary manner, so that the large-area regular epitaxial graphene can be prepared, external metal atoms also can be guided to be directly participated in a graphene lamination layer growth process, thereby promoting atom intercalation or hybridization between metal atoms and C atoms to realize doping of metal atoms, and avoiding damage to the overall structure of graphene caused by ion implantation; pretreatment of metal atom beams is the important premise of realizing doping, and by virtue of the Ar atmosphere environment, generate of surface holes can be suppressed, so that regular and uniform surface appearance of the epitaxial graphene sample is ensured; and the preparation method is simple in technical idea, high in operability, is a stable and effective metal atom doping method, and capable of providing significant guidance and reference to optimization preparation and performance improvement of epitaxial graphene.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
A method for preparing graphene and graphene devices by epitaxy on a pretreated sic substrate
ActiveCN110556283BQuality improvementInhibition of nucleation densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingHydrogen etching
The invention relates to a method for epitaxially preparing graphene and graphene devices by pretreating SiC substrates. It includes the steps of: performing hydrogen etching on the SiC substrate, and then performing oxidation treatment on the SiC substrate after hydrogen etching, at a temperature of 800-1300° C., and a treatment time of 15-120 minutes; The temperature of the substrate is raised to 1450-1700°C for graphene growth. The present invention passivates the surface of SiC through oxidation pretreatment, reduces the nucleation density of SiC substrate epitaxial growth graphene, thereby obtains the graphene material with larger size and better performance, and on this basis SiC epitaxial graphene The wafer undergoes deposition, photolithography, doping and integration procedures to prepare corresponding graphene devices.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
A method for large-area monolayer graphene preparation using metal intercalation
ActiveCN110697696BLow preparation temperatureLittle temperature dependenceSingle layer grapheneGraphiteSingle layer graphene
The invention discloses a large-area single-layer graphene preparation technology. The buffer layer is intercalated with In atoms by using the intercalation technology. Originally, only the surface of the buffer layer is used, and the In atoms are inserted between the buffer layer and the SiC substrate to make the buffer layer Converting to graphene, on the one hand, a single layer of large-area graphene is prepared, and on the other hand, the preparation temperature of graphene is reduced. On the surface where the original buffer layer and single-layer epitaxial graphene coexist, In atoms are inserted between the buffer layer and the SiC substrate, the buffer layer becomes graphene and is perfectly connected with the original epitaxial graphene, forming a large-area single-layer graphene . In addition, the intercalation-formed graphene has a weak interaction with the substrate, and it is separated graphene, which achieves the effect of ionization. This technology can not only prepare large-area graphene, but also control the layer thickness of graphene, which provides important guidance and reference value for applications in related fields such as microelectronics, superconductivity, and strain engineering.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com