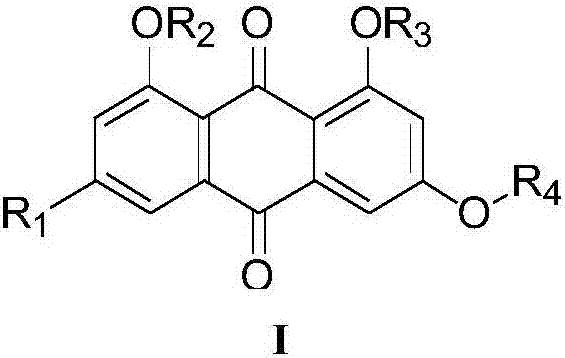
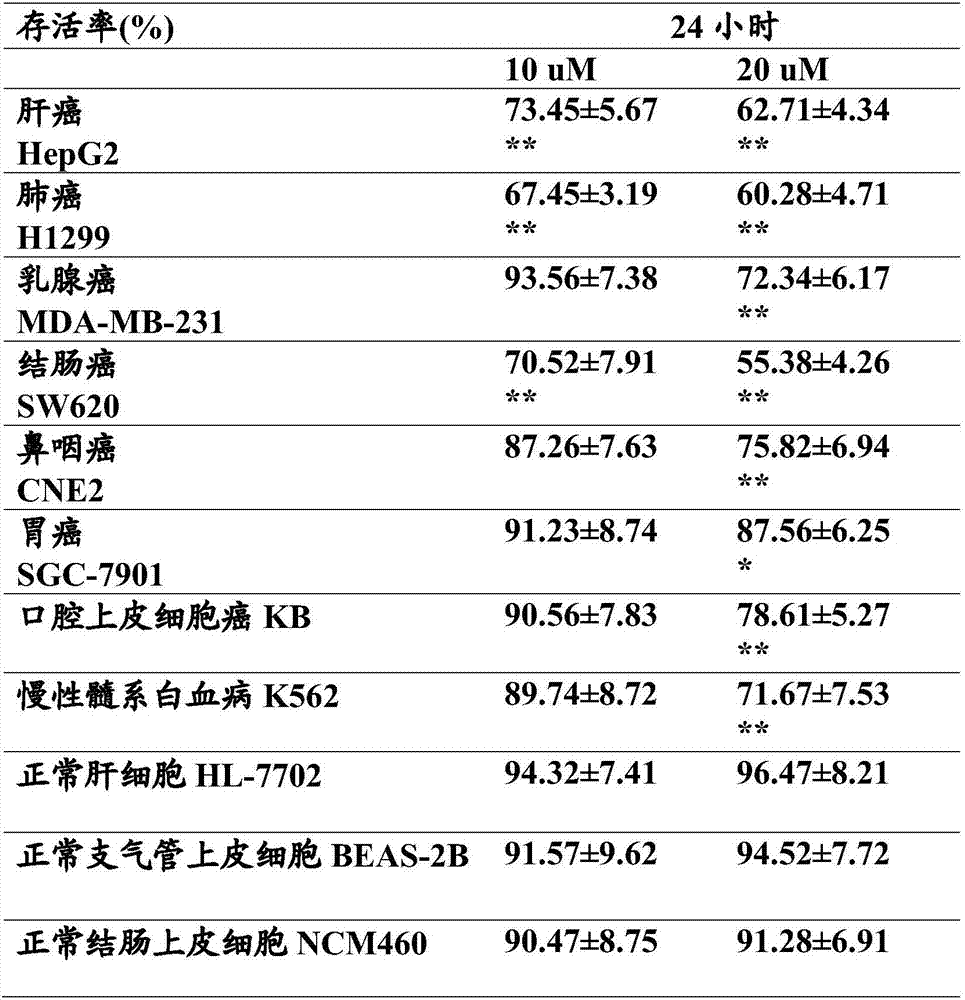
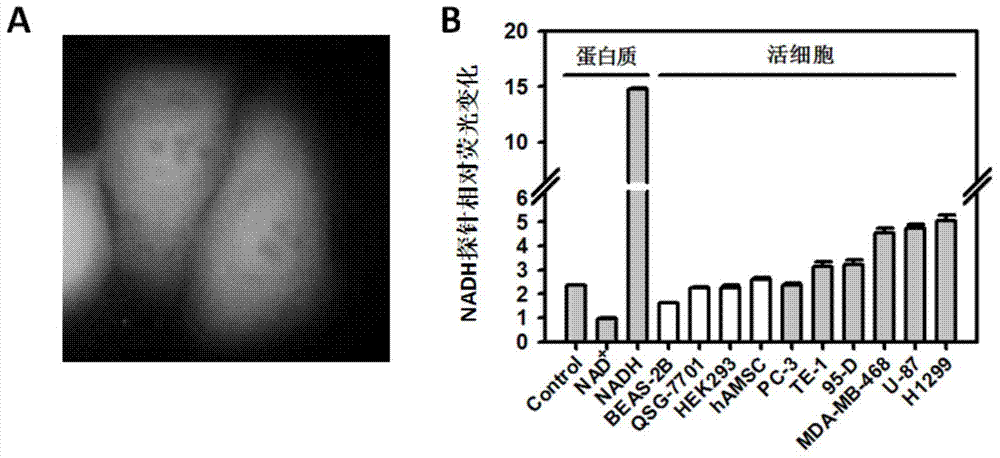
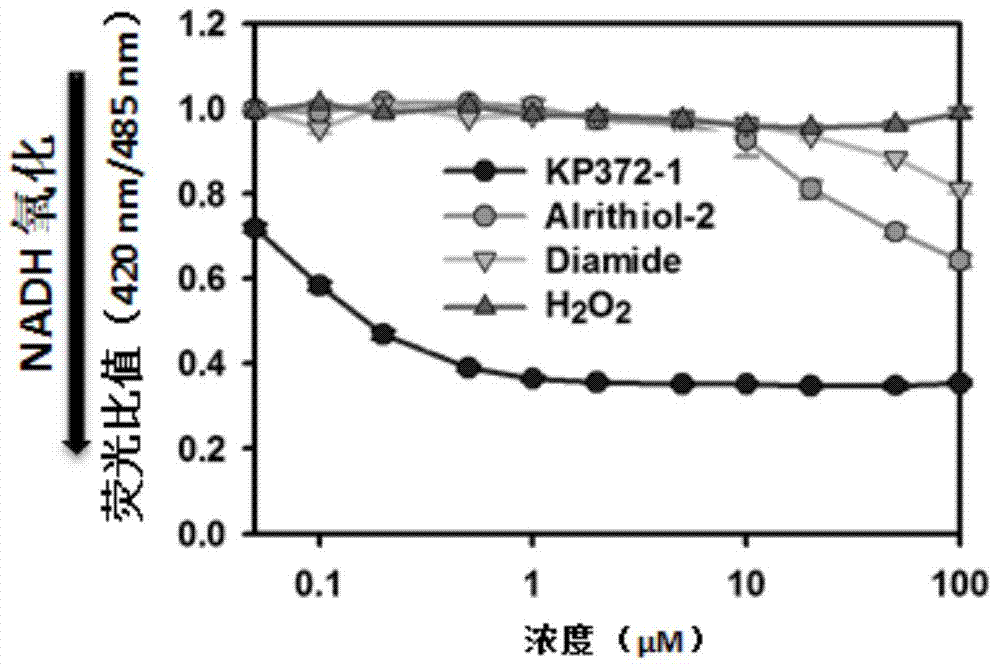
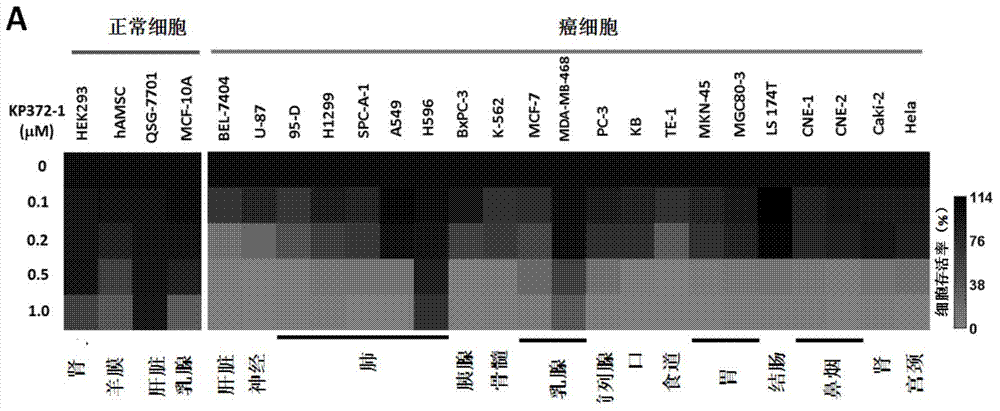
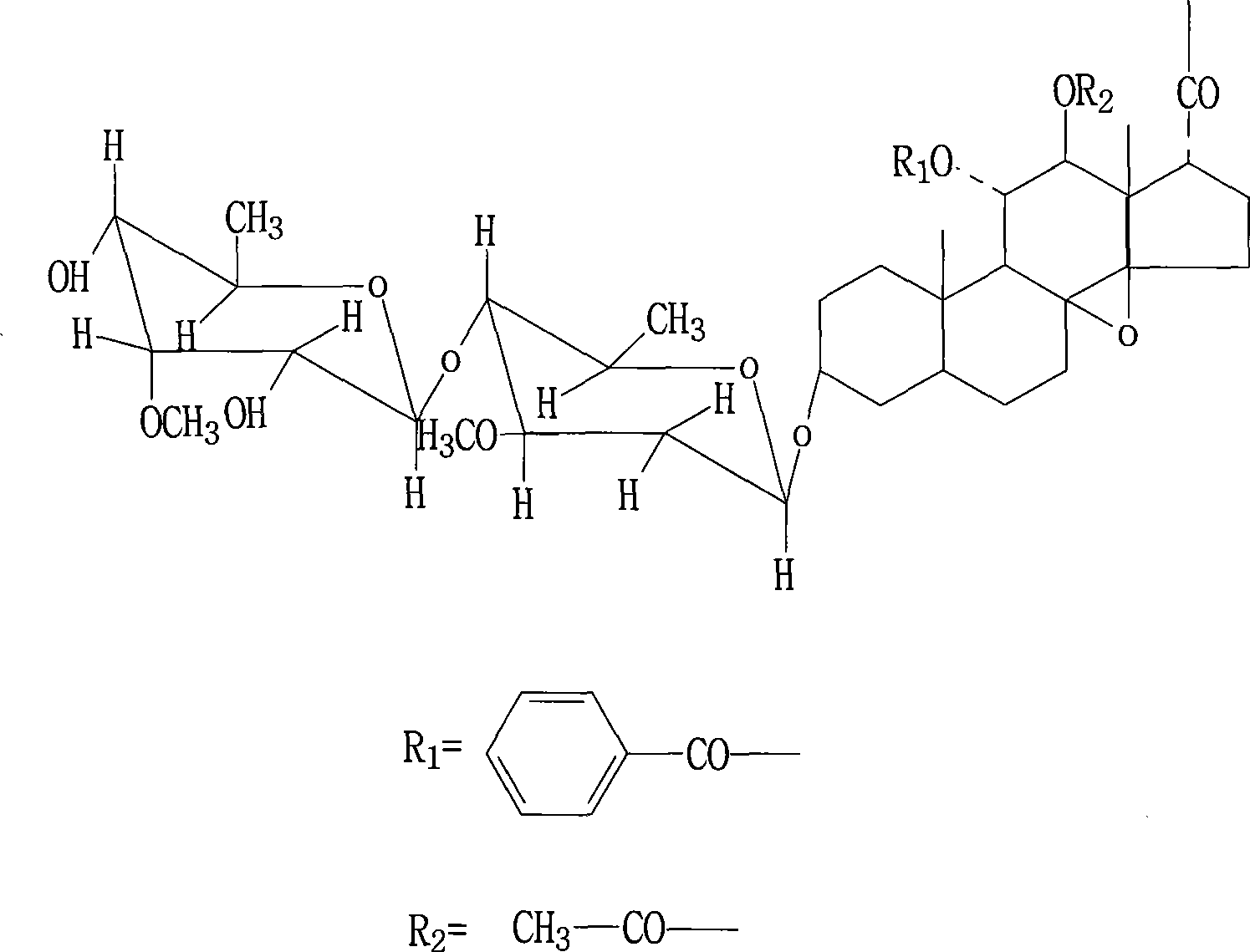
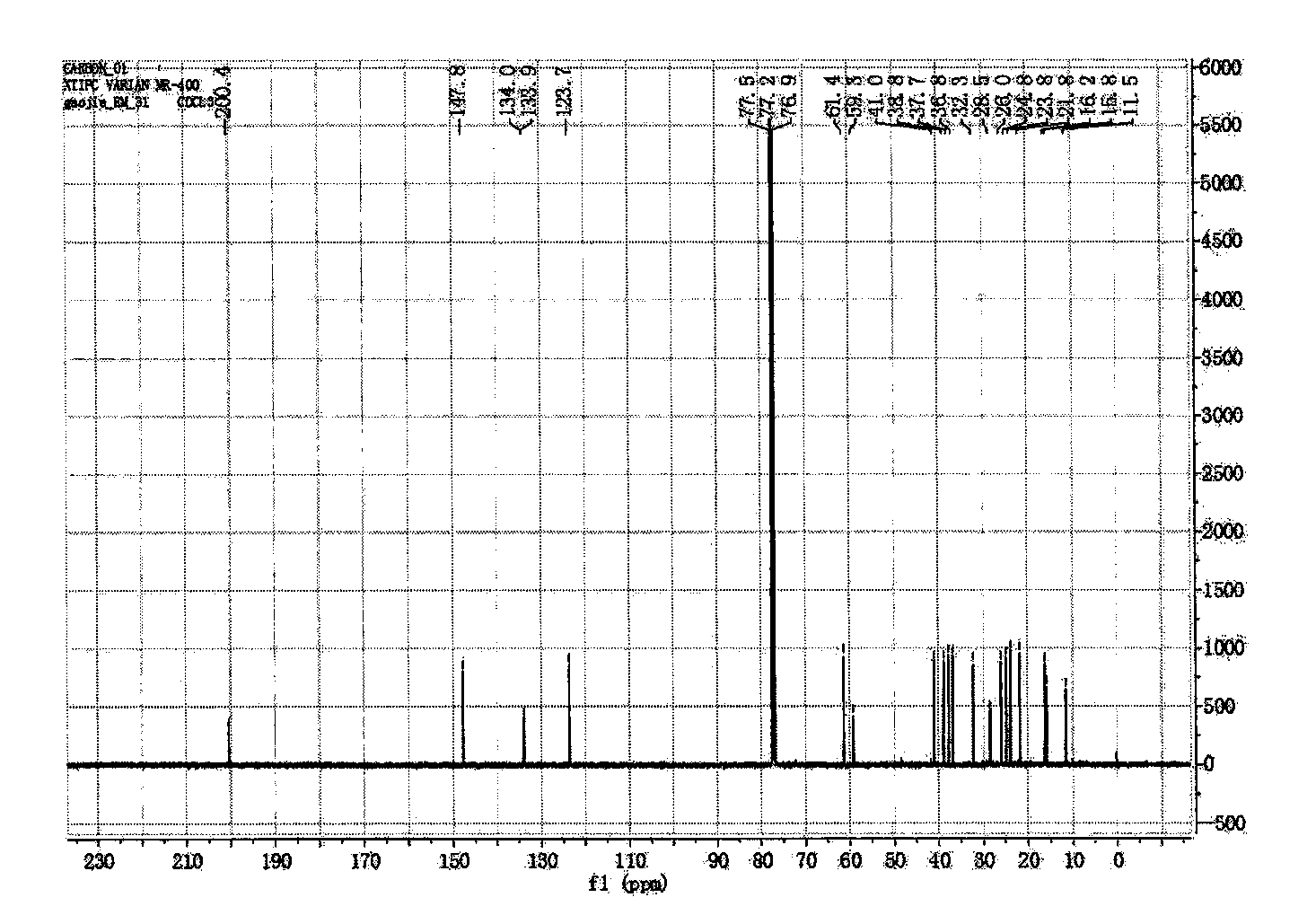
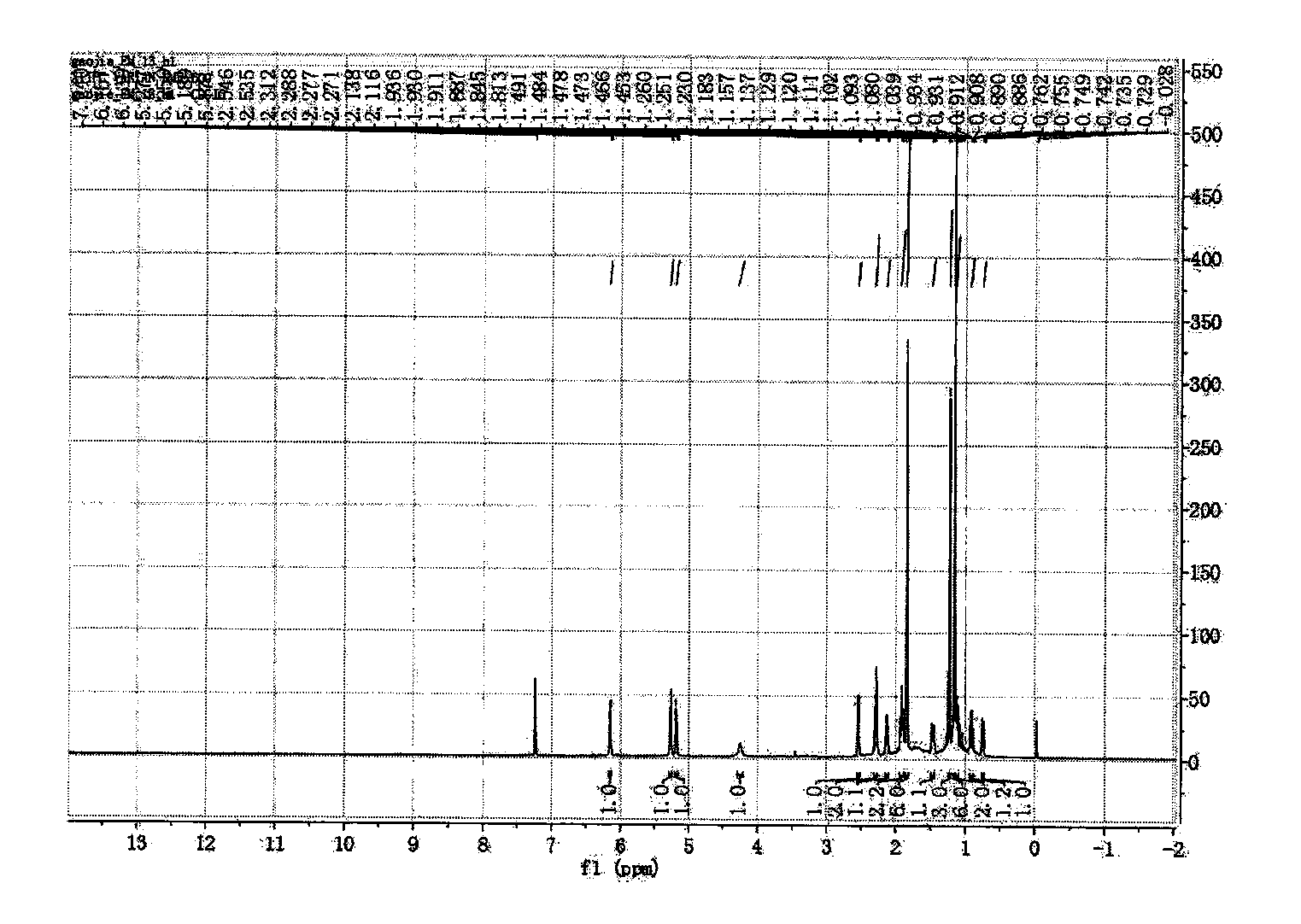
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
60 results about "Epidermoid carcinoma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Epidermoid carcinoma: A type of lung cancer in which the cells are flat and look like fish scales. Also called squamous cell carcinoma.
Application of zedoary root cyclic diolefine in preparing medicament for treating tumour disease and disease caused by virus
The invention relates to a new application of furanodiene in pharmacy field, in particular to the application of the furanodiene in the preparation of medicines for treating the various malignant tumor diseases such as oophoroma, cervical carcinoma, gastric cancer, liver cancer, leucocythemia, lung cancer, oral carcinoma (epidermoid carcinoma), rectal adenocarcinoma, mammary cancer, malignant melanoma, colonic adenocarcinoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, carcinoma of prostate, etc. The invention also relates to the application of the furanodiene in the preparation of drugs for treating the diseases caused by herpesvirus, influenza virus and hepatitis B virus.
Owner:HONGGUAN BIO PHARMA CO LTD
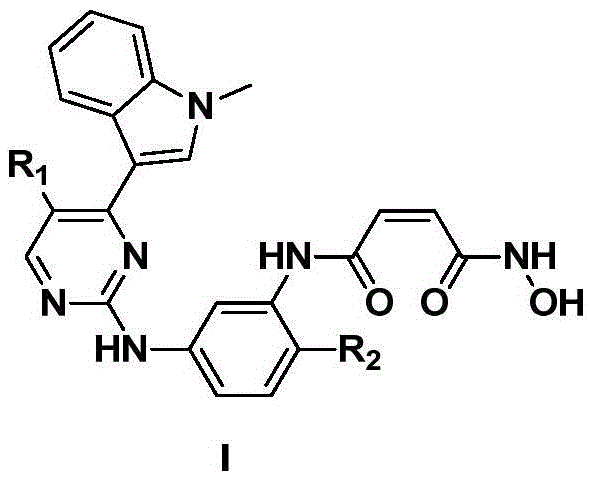
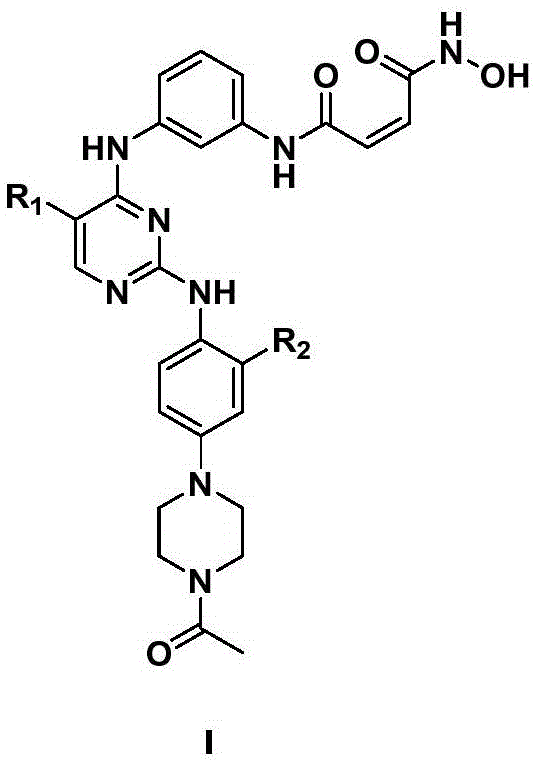
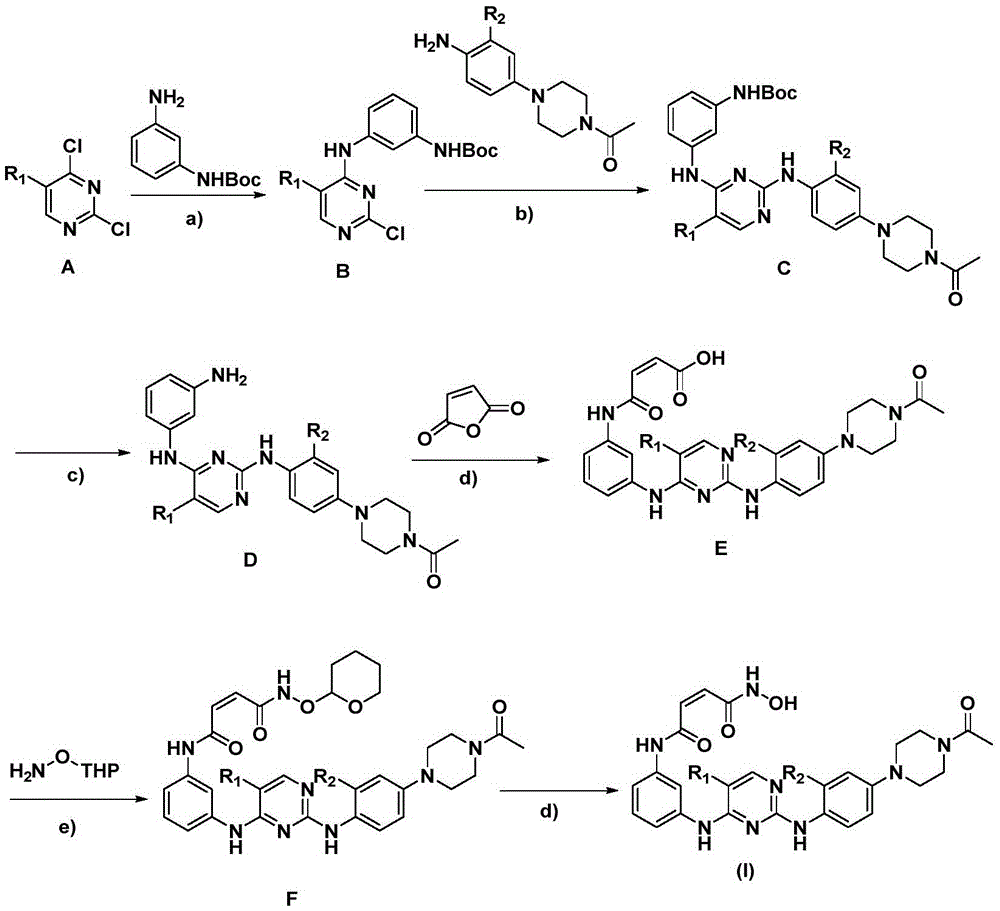
2-arylamine pyrimidine derivatives containing hydroxamic acid fragments and preparation and application
InactiveCN105646454AStrong growth inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsCarcinoma cell lineHydroxamic acid
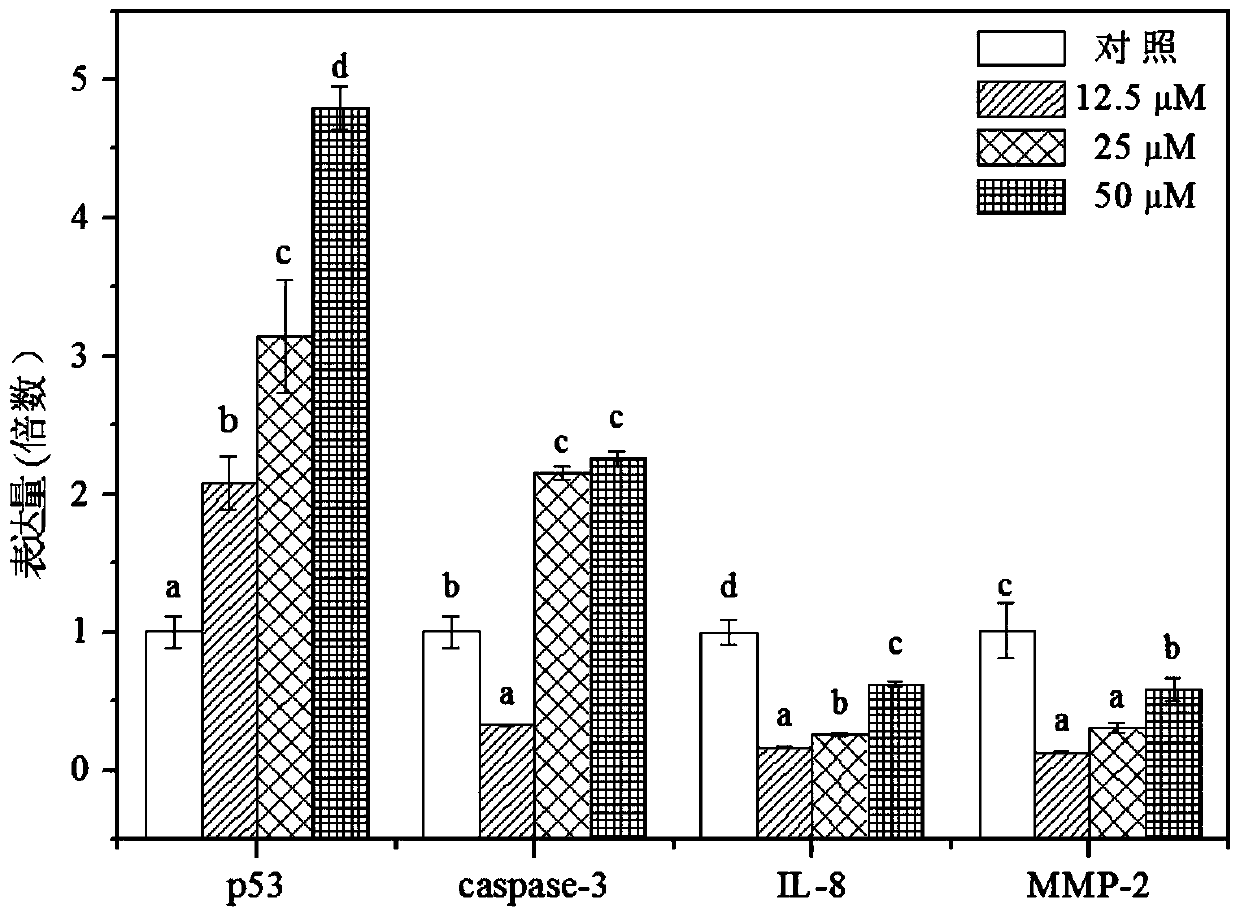
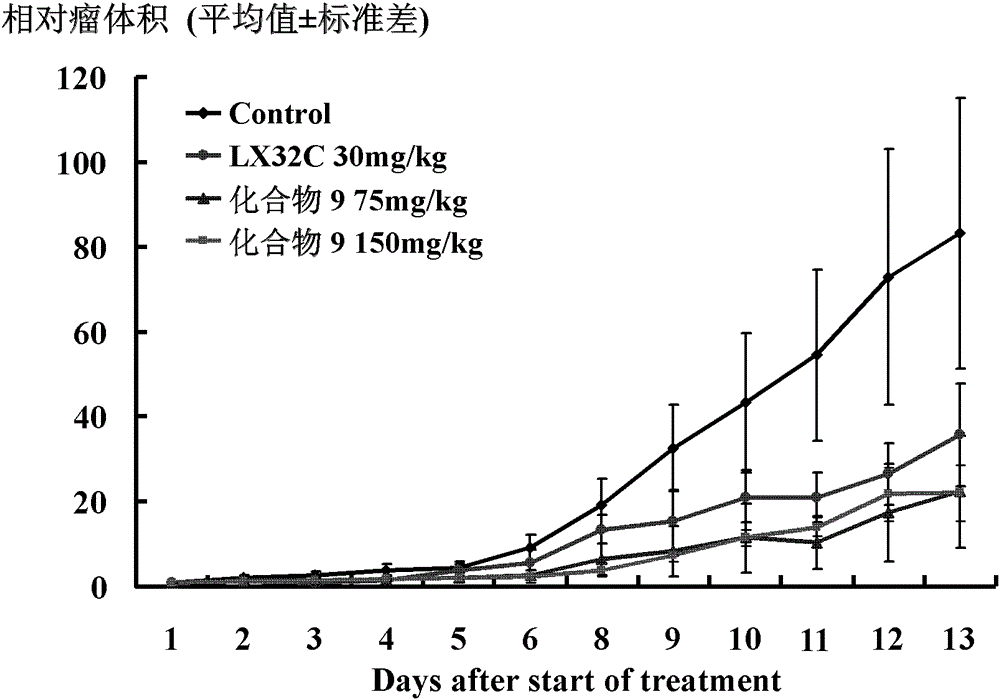
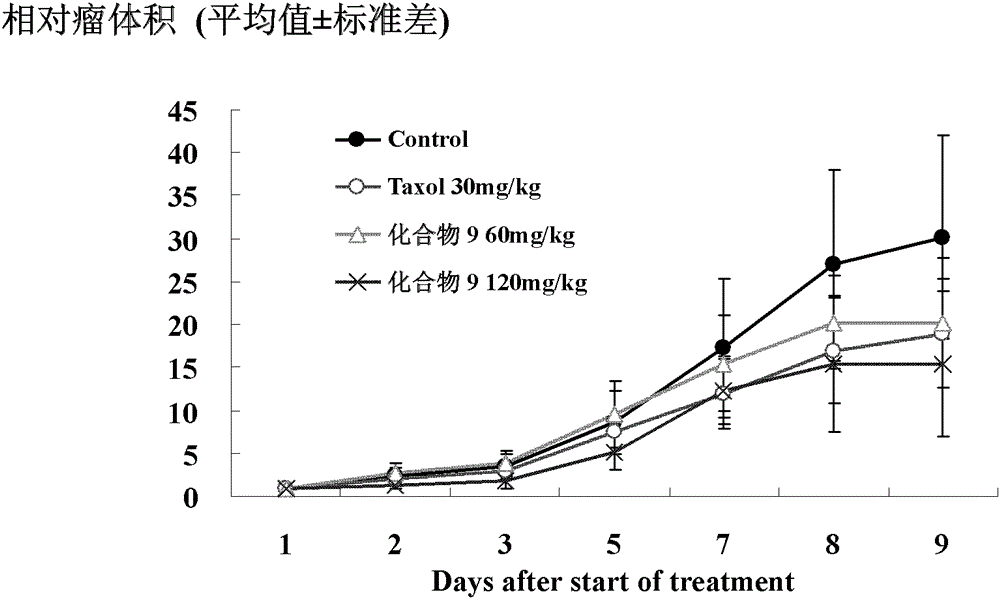
The invention provides 2-arylamine pyrimidine derivatives containing hydroxamic acid fragments shown in the formulas I and II. 2-arylamine pyrimidine containing carboxyl fragments is mainly used as a parent nucleus and is subjected to single-step condensation and related modification with hydroxylamine protected by THP to obtain a target compound. An experiment proves that the derivatives has the remarkable anti-proliferative effect on tumor cells (an overexpression EGFR human epidermal carcinoma cell line A431 and a human pulmonary carcinoma cell line H1975 resisting Gefitinib) related to EGFR tyrosine kinase activity on the cellular level, and tumor cells (a human cervical carcinoma cell line Hela, a human hepatoma cell line HepG2, a human promyelocytic acute leukemia cell line HL60, a human oral epidermoid carcinoma cell line KB, a human colon cancer cell line SW620) related to the HDAC histone acetylase activity, and the corresponding medicine for resisting cancer cells can be prepared. The general structural formula is shown in the description.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Passive targeting of cytotoxic agents
InactiveUS20070190060A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsProstate cancer cellAnticarcinogen
The present invention provides methods of treating cancer cells comprising administering to a patient in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a non-specific antibody conjugated to a cytotoxin, wherein the cancer cells do not express an antigen to which the non-specific antibody binds. In one embodiment, the non-specific antibody is an anti-CD33 antibody (e.g., hp67.6), an anti-CD22 antibody (e.g., g5 / 44), or an anti-CD20 antibody (e.g., rituximab). In another embodiment, the non-specific antibody does not bind a human antigen. The cancer cells treated can be, e.g., gastric, colon, non-small cell lung (NSCLC), breast, epidermoid, or prostate carcinoma cells. In one embodiment, the cytotoxin is calicheamicin. Calicheamicin can be conjugated to the non-specific antibody using a 4-(4′-acetylphenoxy)butanoic acid (AcBut) or (3-Acetylphenyl)acetic acid (AcPAc) linker. In another embodiment, the antibody to the non-specific antigen conjugated to a cytotoxin is administered in combination with a bioactive agent, e.g., an anti-cancer agent.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Derivatives of amyris alcohols and eudesmol for treating cold sores and herpes
InactiveUS20100120907A1Alleviate and eliminate soreImprove lipophilicityBiocideOrganic chemistryAmyrisDisease
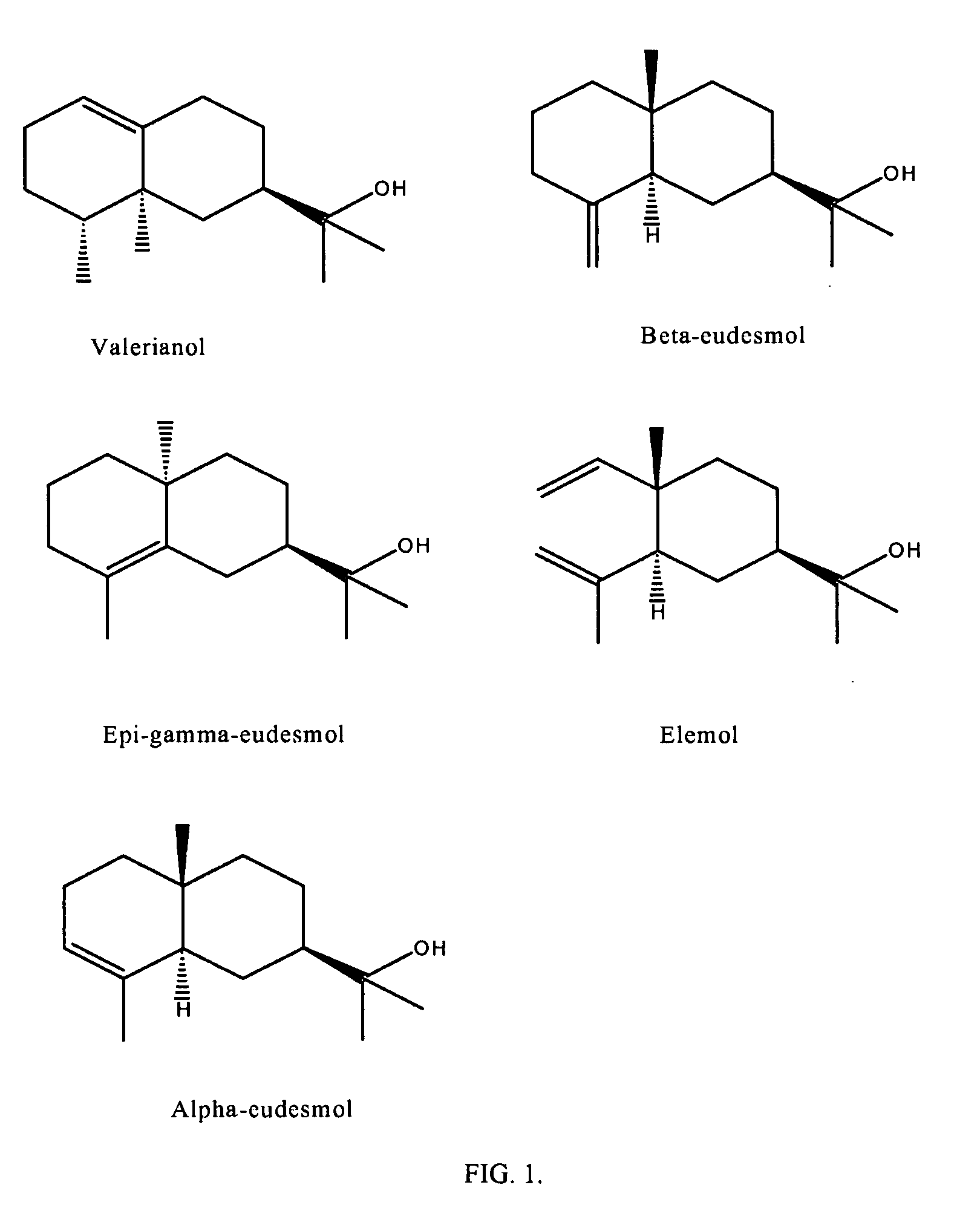
Provided are topical formulations comprising an Amyris alcohol and / or ester derivatives of Amyris alcohol which may be used for the treatment of diseases including herpes virus infection (e.g., HSV-1, HSV-2), epidermoid carcinoma, cold sores, and human papillomavirus. Amyris alcohols contemplated for use with the present invention include valerianol, beta-eudesmol, epi-gamma-eudesmol, elemol, alpha-eudesmol, and ester derivatives thereof.
Owner:TRINITY LAB INC
Secalonic acid I derived from penicillium oxalicum and application of secalonic acid I for preparing medicine for preventing human oral epidermoid carcinoma
ActiveCN107298669AAntiproliferative activityOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesSecalonic acidCuticle
The invention relates to secalonic acid I derived from penicillium oxalicum and application of the secalonic acid I for preparing a medicine for preventing human oral epidermoid carcinoma. The compound has a function of inhibiting human oral epidermoid carcinoma cell proliferation. The structural formula of the secalonic acid I is as shown in the specification. Through fermentation culture of Penicillium oxalicum IBPT-6, a fermented substance is prepared, and the compound is separated and purified from the fermented substance. Tests show that the compound has relatively high anti-tumor activity upon human oral epidermoid carcinoma cells KB. The compound can be used for preventing human oral epidermoid carcinoma cell proliferation inhibition medicines or anti-tumor medicines for studying human oral epidermoid carcinoma.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Secalonic acid H derived from penicillium oxalicum and application of secalonic acid H for preparing medicine for preventing human oral epidermoid carcinoma
The invention relates to secalonic acid H derived from penicillium oxalicum and application of the secalonic acid H for preparing a medicine for preventing human oral epidermoid carcinoma. The compound has a function of inhibiting human oral epidermoid carcinoma cell proliferation. The structural formula of the secalonic acid I is as shown in the specification. Through fermentation culture of Penicillium oxalicum IBPT-6, a fermented substance is prepared, and the compound is separated and purified from the fermented substance. Tests show that the compound has relatively high anti-tumor activity upon human oral epidermoid carcinoma cells KB. The compound can be used for preventing human oral epidermoid carcinoma cell proliferation inhibition medicines or anti-tumor medicines for studying human oral epidermoid carcinoma.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
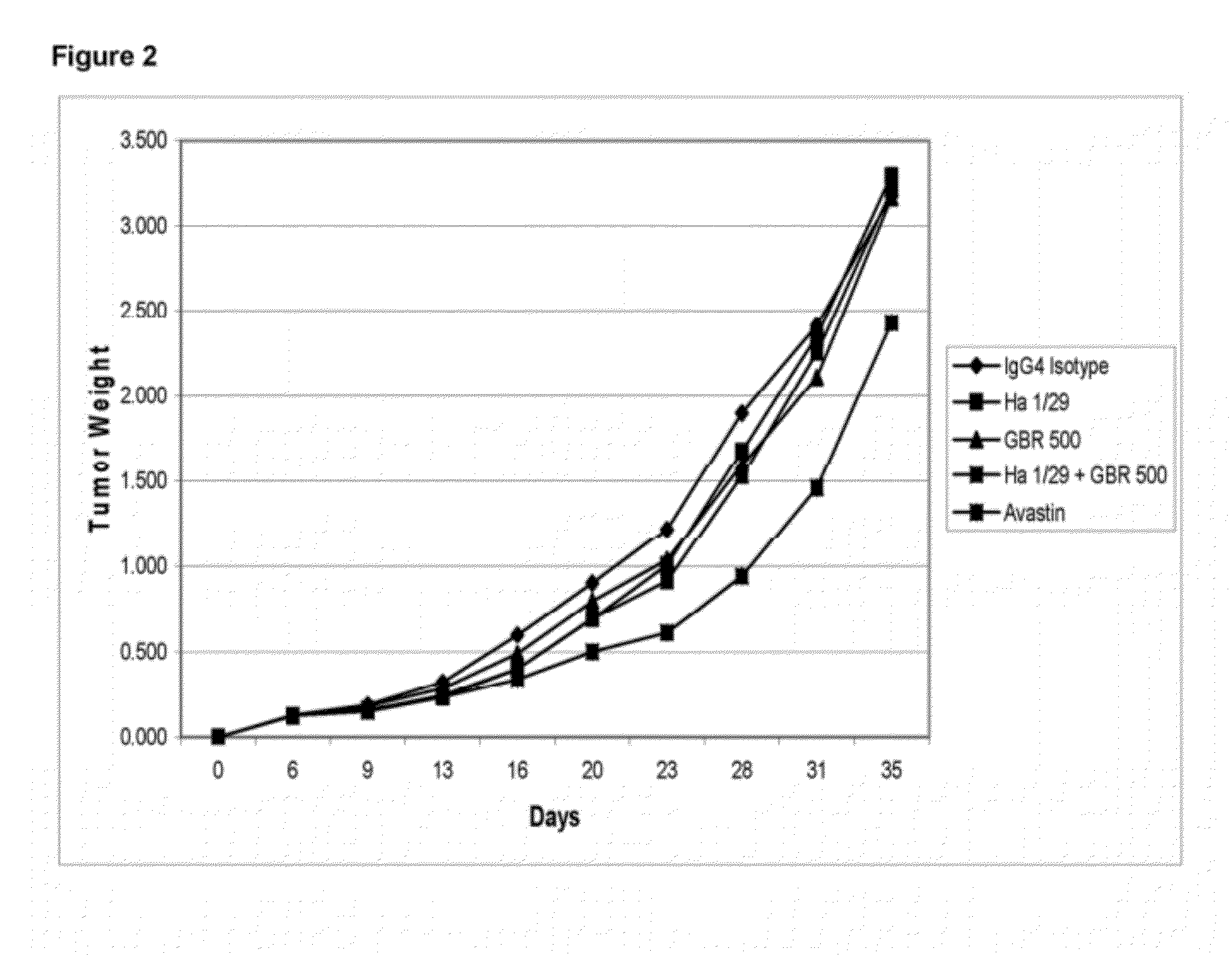
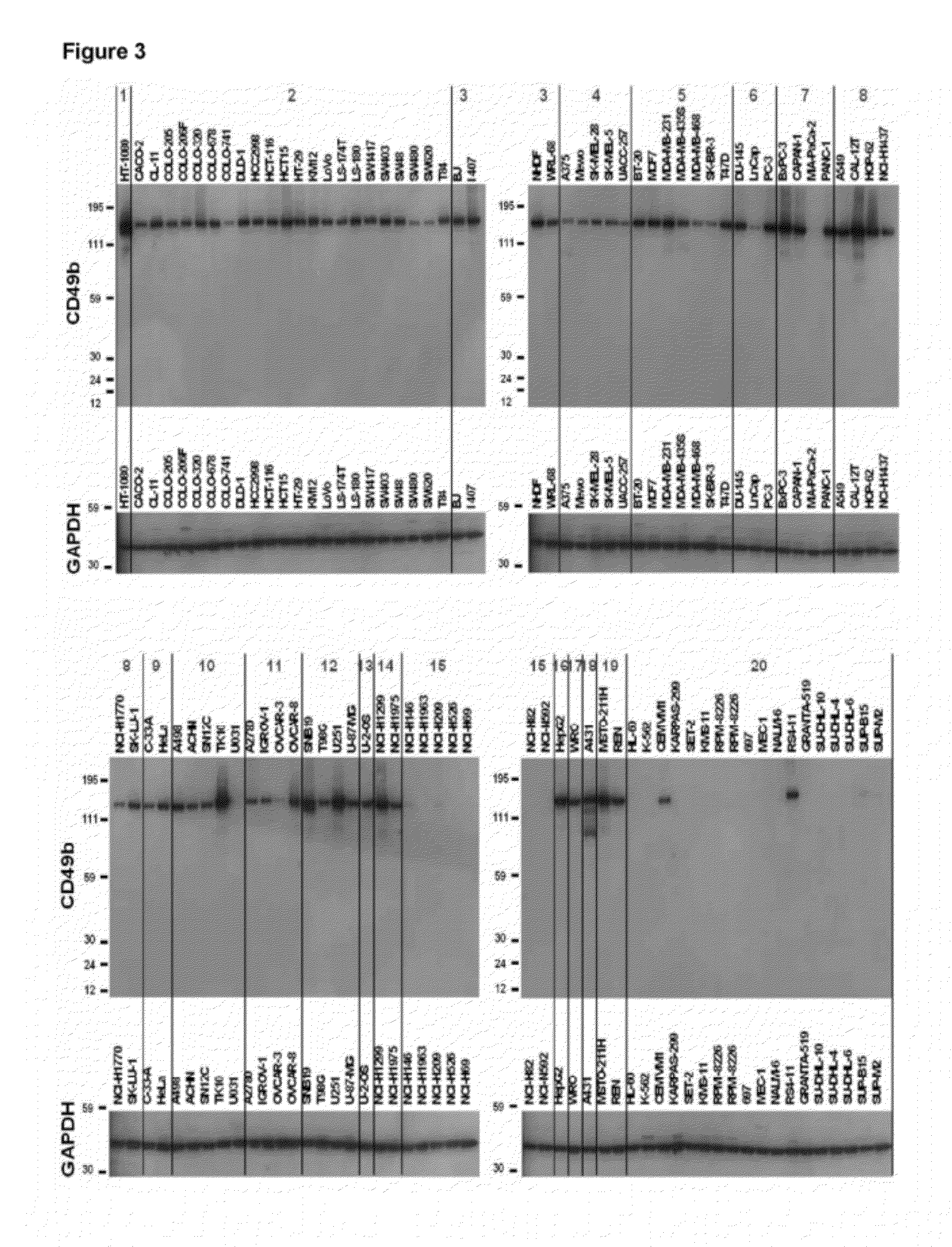
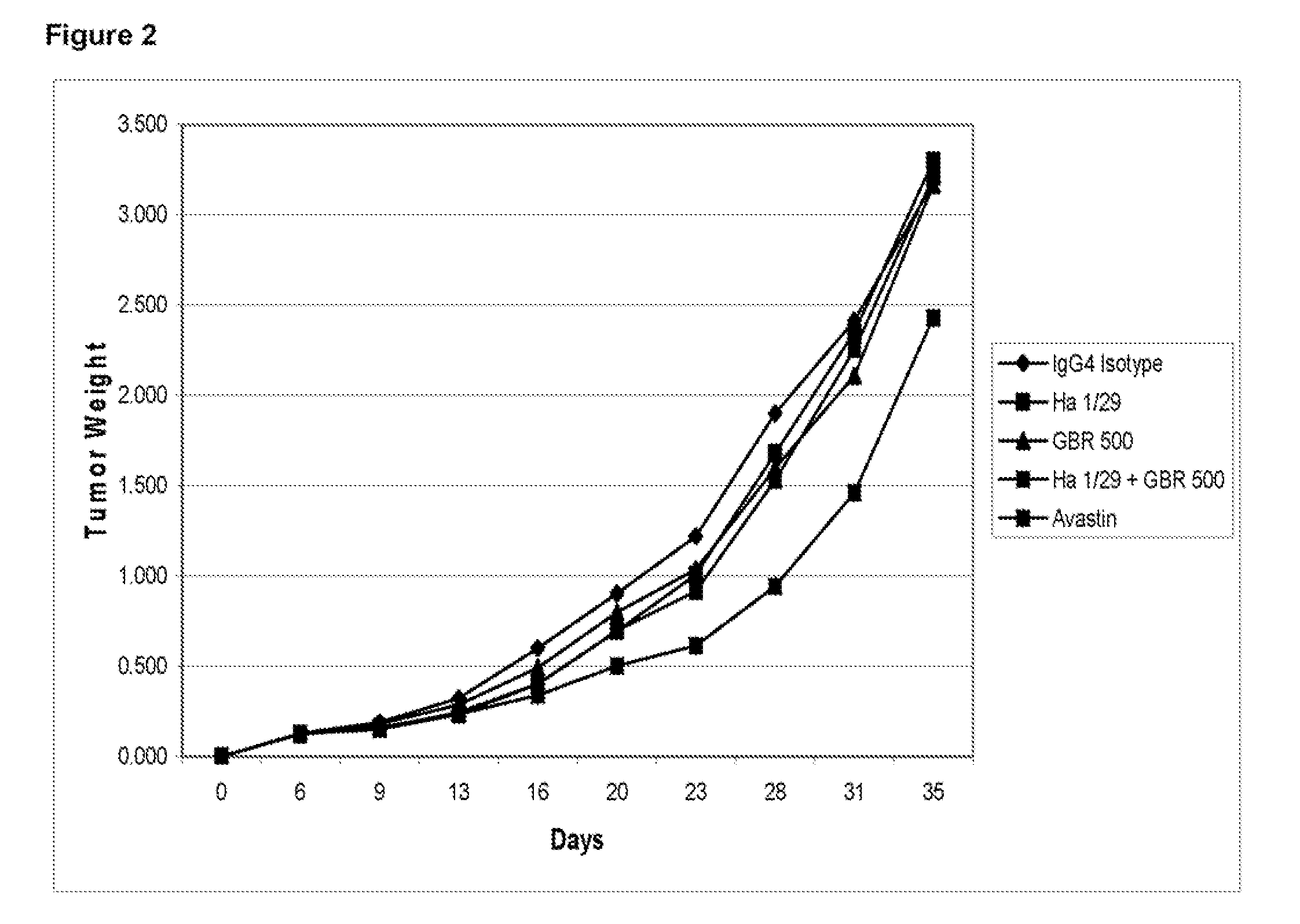
Treatment with anti-alpha2 integrin antibodies
The invention relates to treatment of cancer. More specifically the invention relates to methods of treating cancer selected from the group consisting of squamous cell cancer, lung cancer including small-cell lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, adenocarcinoma of the lung, and squamous carcinoma of the lung, cancer of the peritoneum, hepatocellular cancer, gastric or stomach cancer including gastrointestinal cancer, pancreatic cancer, glioblastoma, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, liver cancer, bladder cancer, hepatoma, breast cancer, colon cancer, colorectal cancer, endometrial or uterine carcinoma, salivary gland carcinoma, kidney or renal cancer, liver cancer, prostate cancer, vulval cancer, thyroid cancer, hepatic carcinoma and various types of head and neck cancer, as well as B-cell lymphoma including low grade / follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL); small lymphocytic (SL) NHL; intermediate grade / follicular NHL; intermediate grade diffuse NHL; high grade immunoblastic NHL; high grade lymphoblastic NHL; high grade small non-cleaved cell NHL; bulky disease NHL; mantle cell lymphoma; AIDS-related lymphoma; and Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia; chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL); Hairy cell leukemia; chronic myeloblastic leukemia; and post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD), as well as abnormal vascular proliferation associated with phakomatoses, edema such as that associated with brain tumors, Meigs' syndrome, melanoma, mesothelioma, multiple myeloma, fibrosarcoma, osteosarcoma and epidermoid carcinoma, by administering antibodies directed to α2β1 integrin.
Owner:ICHNOS SCI SA
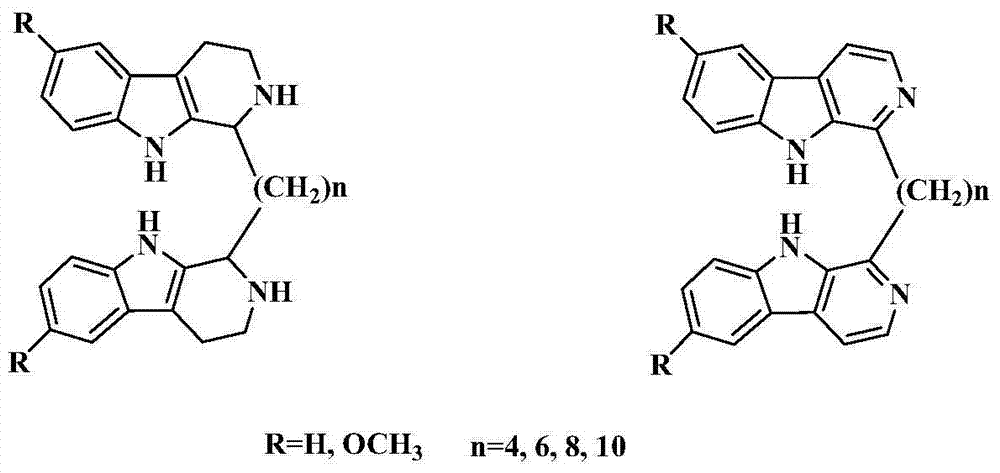
3-position bis-beta-carboline alkali compound, and preparation method, pharmaceutical composition and application thereof
The invention discloses a bis-beta-carboline alkali compound, and a preparation method, a pharmaceutical composition and application thereof. Specifically, the bis-beta-carboline alkali compound and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof are shown in the general formula I. The bis-beta-carboline alkali compound is prepared by condensation of beta-carboline intermediates and dihaloalkane hydrocarbons. The invention further discloses a pharmaceutical composition and application of the bis-beta-carboline alkali compound in preparing anti-tumor drugs. The pharmaceutical composition comprises an effective dose of bis-beta-carboline alkali compound shown in the formula I and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and the tumor comprises melanoma, gastric cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, kidney cancer, liver cancer, oral epidermoid carcinoma, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer and colon cancer.
Owner:XINJIANG HUASHIDAN PHARMA RES
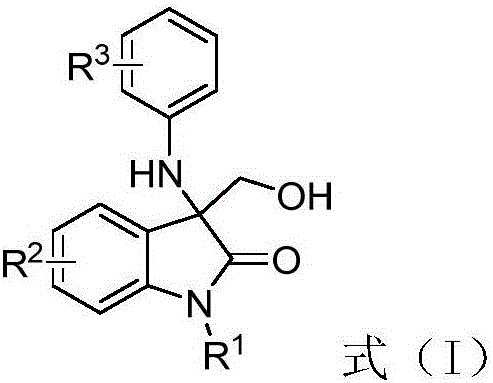
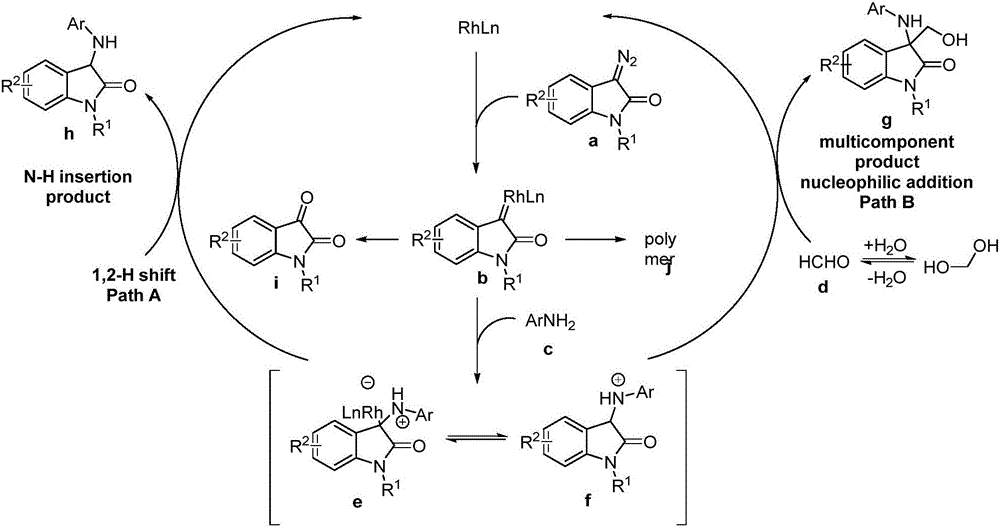
3-amino-3-hydroxymethyloxindole derivative as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106631976APrevent proliferationThe preparation method is simple and easy to obtainOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsHepatocellular carcinomaEpidermoid carcinoma
The invention discloses a 3-amino-3-hydroxymethyloxindole derivative shown as a formula (I) and a preparation method thereof. The 3-amino-3-hydroxymethyloxindole derivative is obtained by taking 3-diazooxindole, aniline and formaldehyde as raw materials, taking rhodium acetate as a catalyst and taking an organic solvent as a solvent through a one-step reaction. The preparation method disclosed by the invention can be used for constructing a compound with a plurality of functional groups in one step, and has the characteristics of high flexibility, high selectivity, efficient atom economy, high yield and simplicity and safety in operation and the like. The invention further discloses an inhibition effect of the 3-amino-3-hydroxymethyloxindole derivative shown as the formula (I) on proliferation of five types of tumor cells including human osteosarcoma cells (SJSA-1), human colorectal cancer cells (HCT-116), hepatocellular carcinoma cells (BEL7402), human oral epidermoid carcinoma cells (KB) and human T-cell leukemia cells (Jurkat).
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Folate-modified cholesterol-bearing pullulan as a drug carrier
InactiveUS20070042970A1Enhances complex formationClear effectBiocideSugar derivativesPullulanCholesterol
Folate modified cholesterol-bearing pullulan (FA-CHP) was synthesized by the reaction of folic acid γ-2-aminoethylamide and 4-nitorophenyl chloroformate-activated cholesterol-bearing pullulan, wherein folate and pullulan are connected through a NH—CH2—CH2—NH group. Approximately 0.5-1 folates are connected per about 100 glycoside units of pullulan. Then, several combinations of FA-CHP, cholesterol-bearing pullulan (CHP) and doxorubicin (DOX) mixture were tested for cancer selective cytotoxicity. A mixture of FA-CHP, CHP and DOX of 1:4:0.02 (weight ratio) gave sharp and selective damage to cells of a human epidermoid cancer KB known as expressing a high level of folate receptor. The same mixture inhibited the growth of HuH7 cells, which is a human hepatocellular carcinoma and is unknown as a folate receptor.
Owner:CHEM SOFT R&D
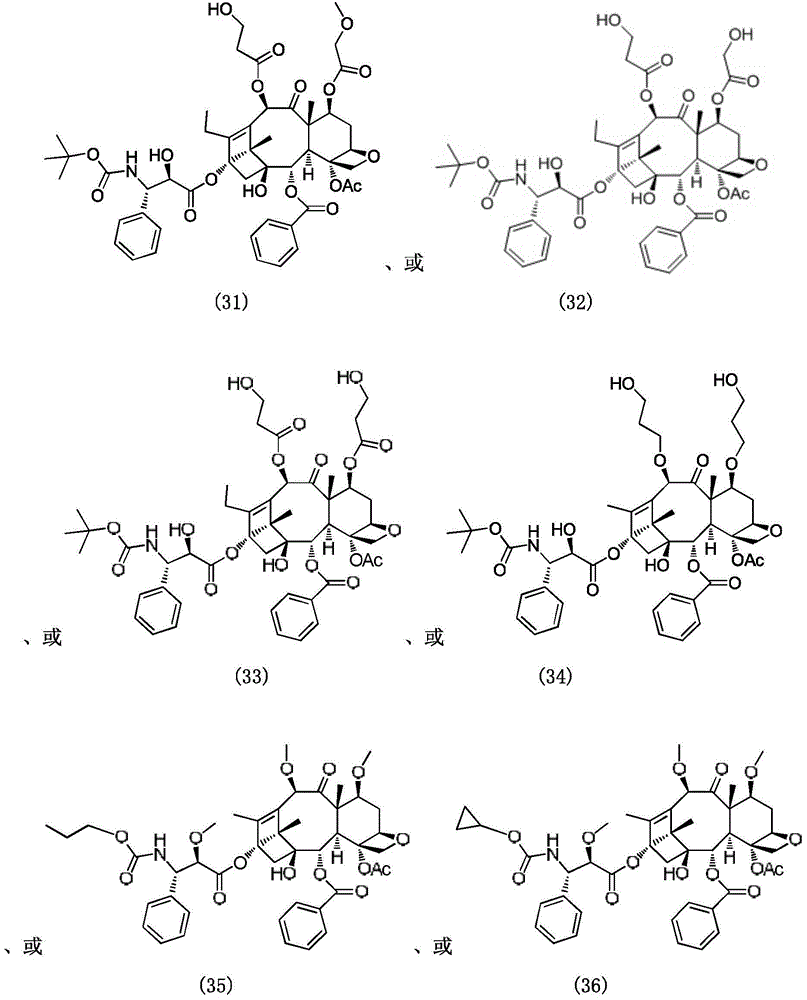
Paclitaxel derivatives and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104086514AGood anticancer effectHigh anticancer activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryFibroblastic TumorSolubility
The invention provides paclitaxel derivatives with a general structural formula (I) as described in the invention. The invention further provides application of the paclitaxel derivatives in preparation of drugs used for preventing or treating fibrosarcoma, liver cancer, lung cancer, leukemia, epidermoid carcinoma, breast cancer, prostatic cancer, lymphoma, stomach cancer, myeloma and pancreatic cancer. The derivatives synthesized in the invention have better water-solubility compared with paclitaxel and are superior to paclitaxel in the aspect of a plurality of anticancer effects.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Application of nobiletin
ActiveCN105030559ALow effective doseLittle potential side effectsOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsMedicineEpidermoid carcinoma
The invention discloses application of nobiletin, and particularly discloses application of nobiletin in preparation of health products or medicines for preventing and / or treating oral cancer. Through the anti-proliferation effects of monomeric compounds, namely hesperetin, naringenin and nobiletin, in rutaceae citrus fruits and peels on human oral epidermoid carcinoma cells, the experiments show that the hesperetin, naringenin and nobiletin have an obvious effect on inhibiting proliferation of human oral epidermoid carcinoma cells, and the effect of the nobiletin on inhibiting oral cancer cells is most obvious, so that the nobiletin can be used for preparing health products and medicines with effects on preventing and treating oral cancer and is suitable for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
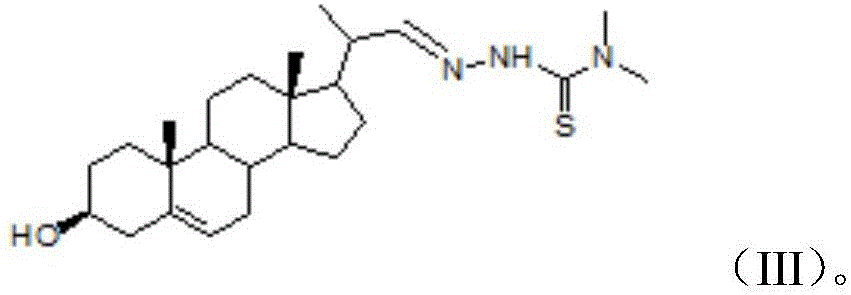
22-nor-stigmasta thiosemicarbazone compound and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN105859821AGood inhibitory effectNon-cytotoxicSteroidsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellCytotoxicity
The invention discloses a 22-nor-stigmasta thiosemicarbazone compound and a preparing method and application thereof. The structural formula of the 22-nor-stigmasta thiosemicarbazone compound is shown in the description. In vitro cancer cell growth and proliferation activity inhibition tests show that the prepared 22-nor-stigmasta thiosemicarbazone compound has a remarkable inhibition effect on various tumor cell strains such as human nipple thyroid gland cancer cells, human oral cavity epidermoid carcinoma cells and cervical cancer. Meanwhile, the 22-nor-stigmasta thiosemicarbazone compound is free of cytotoxicity on human kidney epithelial cells (HEK293T) and can be used for preparing medicine for treating cancer.
Owner:南宁师范大学
22-abeo-stigmasterol benzimidazole compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105820206AEnhanced inhibitory effectNon-cytotoxicOrganic active ingredientsSteroidsCancer cellCytotoxicity
The invention discloses a 22-abeo-stigmasterol benzimidazole compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the 22-abeo-stigmasterol benzimidazole compound is shown in the specification; experiments for in-vitro inhibition of growth and proliferation activities of cancer cells show that the 22-abeo-stigmasterol benzimidazole compound prepared by the preparation method has remarkable inhibition effect to multiple tumor cell strains such as human papillary thyroid cancer cells, human oral epidermoid carcinoma cells, cancer cell strains of cervical cancer and the like. Meanwhile, the 22-abeo-stigmasterol benzimidazole compound has no cytotoxicity to human kidney epithelial cells (HEK293T) and can be applied to the preparation of drugs for treating cancers.
Owner:张项春
Application of physcion and derivative thereof in preparation of antitumor drugs
InactiveCN107213144AInhibition is effectiveNo side effectsOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectEpidermoid carcinoma
The invention belongs to the field of medicines and particularly relates to an application of physcion and a derivative thereof in preparation of antitumor drugs. The activity of a liver cancer cell, a lung cancer cell, a breast cancer cell, a colon cancer cell, a nasopharynx cancer cell, a gastric cancer cell, a human oral epidermoid carcinoma cell and a chronic myelogenous leukemia cell can be effectively inhibited by employing a pharmaceutical composition containing the physcion and the derivative thereof as active components, and especially the pharmaceutical composition has a more significant inhibition effect on the liver cancer cell, the lung cancer cell and the colon cancer cell. The physcion and the derivative thereof have an anti-tumor effect of inhibiting transplantation tumor growth for tumor-bearing nude mice with a liver cancer, a lung cancer and a colon cancer. Furthermore, the physcion and the derivative thereof have no toxic and side effect on a normal body. A foundation is laid for development of high-efficiency and low-toxicity novel broad-spectrum anti-tumor drugs of the physcion and the derivative thereof.
Owner:潘小平
Application of indeno triazine compounds as substrate of quinone oxidoreductase depending on NAD (P) H
InactiveCN103520165AAnti-cancerRadiosensitizationAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsCancer cellReactive oxygen radicals
The invention discloses application of indeno triazine compounds as a substrate of quinone oxidoreductase depending on NAD (P) H. The indeno triazine compounds are catalyzed through the quinone oxidoreductase depending on the NAD (P) H to generate an oxidation reduction cycle reaction, a large number of reactive oxide free radicals are generated, strong oxidative stress is induced, and the obvious lethal effect on lung cancer, liver cancer, cervical cancer, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, nasopharynx cancer, kidney clear cell carcinoma, oral epidermoid carcinoma, chronic myelogenous leukemia, intestinal cancer, brain cancer, gastric cancer, esophagus cancer and other cancer cells expressed by the quinone oxidoreductase depending on the NAD (P) H is achieved. The indeno triazine compounds used as the substrate of the quinone oxidoreductase depending on the NAD (P) H can also be used as sensitizers for treating the cancer with radiotherapy, and have the obvious anticancer synergistic effect. In addition, the indeno triazine compounds used as the substrate of the quinone oxidoreductase depending on the NAD (P) H have antibacterial and antifungal activity.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Use of marsdenia tenacissima new glycoside B in preparing medicine for treating tumor disease and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an application of a compound marsdenia tenacissima glycoside B which is extracted and separated from natural plant marsdenia tenacissima in the preparation of a drug for remedying tumour diseases including various malignant tumour diseases, such as ovary cancer, stomach cancer, liver cancer, leucocythemia, lung cancer, oral epidermoid carcinoma, rectal adenocarcinoma, breast cancer, malignant melanocarcinoma, colon adenocarcinoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, prostate cancer, etc. The invention also relates to a preparation technology of the marsdenia tenacissima glycoside B. After using water extraction and alcohol sedimentation, the invention uses an innovative chloroform extraction and aether sedimentation technology by chloroform extraction and also creatively adding aether, thereby reducing the content of impurity in extract obviously, and the marsdenia tenacissima glycoside B with high purity can be obtained just by silica gel column separation at a time. The method has high yield and simple operation, does not require a preparation type precision instrument of high performance liquid phase and other similar instruments and is closer to the requirement of the industrialized production.
Owner:HANGZHOU MINSHENG PHARM CO LTD
Macrocyclic diterpenoid compounds separated from euphorbia macrorrhiza C.A.Mey and application
ActiveCN104387344AOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsEpidermoid carcinomaDrug resistance
The invention relates to macrocyclic diterpenoid compounds separated from euphorbia macrorrhiza C.A.Mey and application. The macrocyclic diterpenoid compounds separated from euphorbia macrorrhiza C.A.Mey respectively belong to five different diterpenoid scaffold types. The macrocyclic diterpenoid compounds are subjected to in-vitro cytotoxic activity determination and anti-drug-resistance activity determination. Experiment results show that the macrocyclic diterpenoid compounds separated from euphorbia macrorrhiza C.A.Mey have cytotoxic activity on human oral-cavity epidermoid carcinoma KB cell and human oral-cavity epidermoid carcinoma drug-resistant strain KBv200 to different degrees, have certain anti-drug-resistance activity, and is applicable to antitumor medicines.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Detection of MECT1-MAML2 fusion products
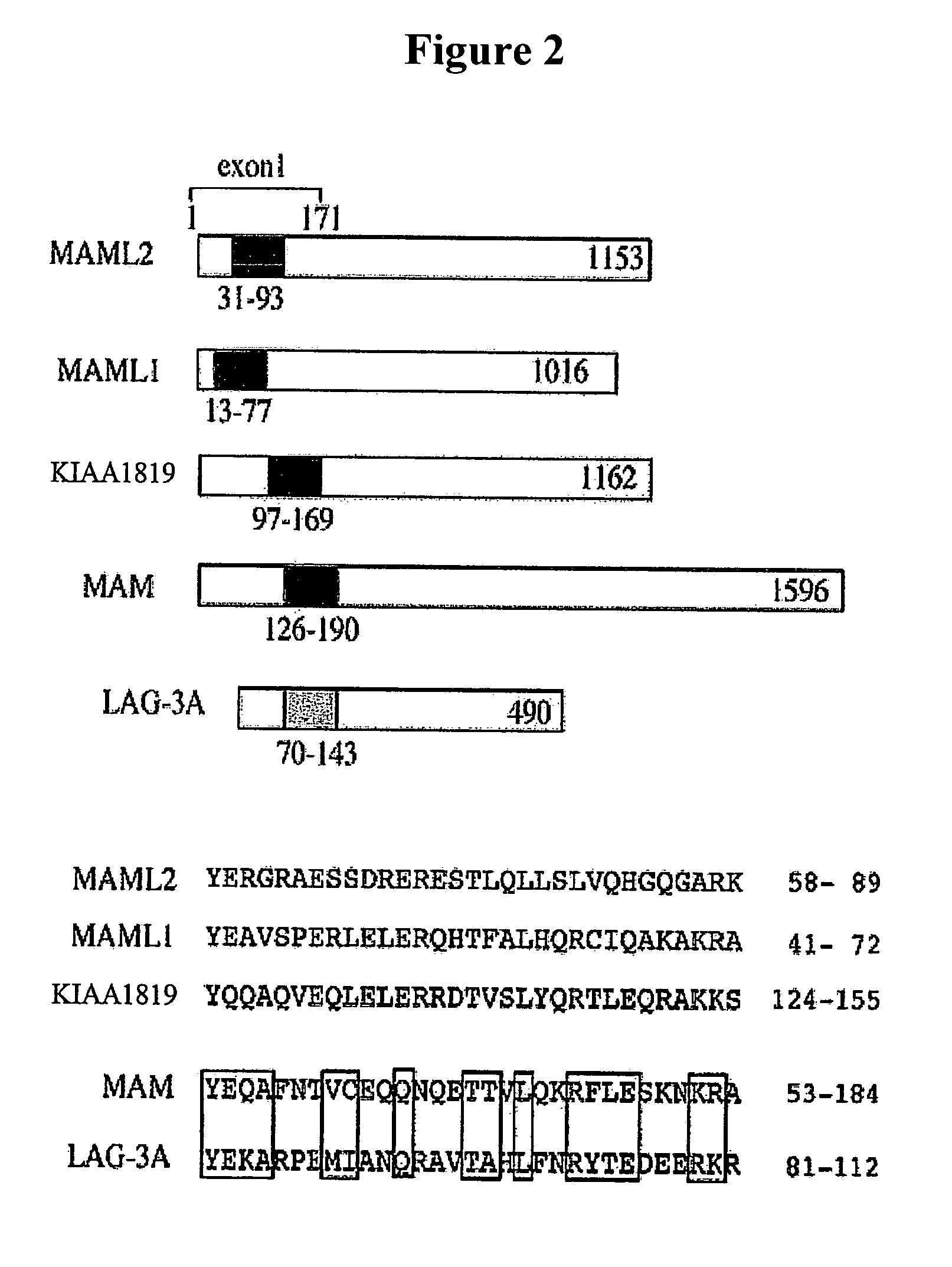
InactiveUS7214488B2Optimize treatment planImprovement of pre- and/or post-operative managementMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationParotid Mucoepidermoid CarcinomaEpidermoid carcinoma
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, including cancers involving the NOTCH pathway. In particular, the present invention provides methods and compositions for the diagnosis of mucoepidermoid carcinoma, the most common malignant salivary gland tumor. The present invention further provides methods and compositions for the diagnosis of other tumors associated with the t(11;19)(q14–21;12–13) translocation.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Human ron-related gene variant associated with cancers
ActiveUS20080085510A1TransferasesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsURINARY BLADDER CARCINOMACervix
The invention relates to the nucleic acid and polypeptide sequences of three novel human Ron-related gene variants (Ron-V1, Ron-V2, and Ron-V3). The invention also provides a process for producing the polypeptides of the variants, as well as uses for the nucleic acid, polypeptide and antibodies to same in diagnosing human breast carcinoma, breast adenocarcinoma, cervix epidermoid carcinoma, cervix epitheloid carcinoma, colon adenocarcinoma, urinary bladder carcinoma, prostate carcinoma, esophagus epidermoid carcinoma and esophagus carcinoma.
Owner:VISGENEER
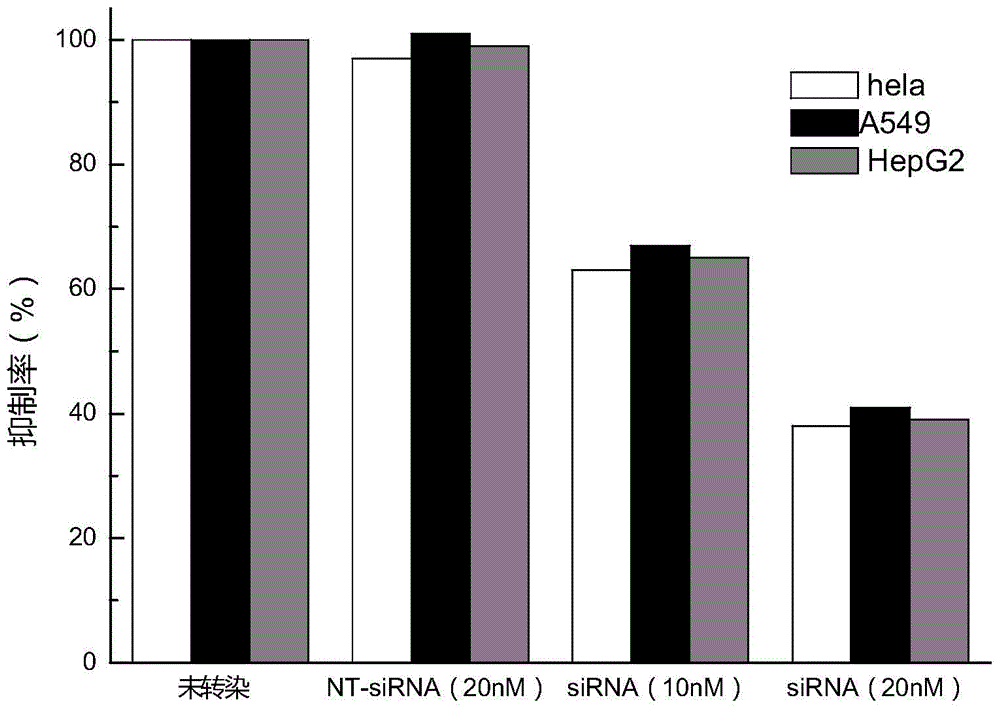
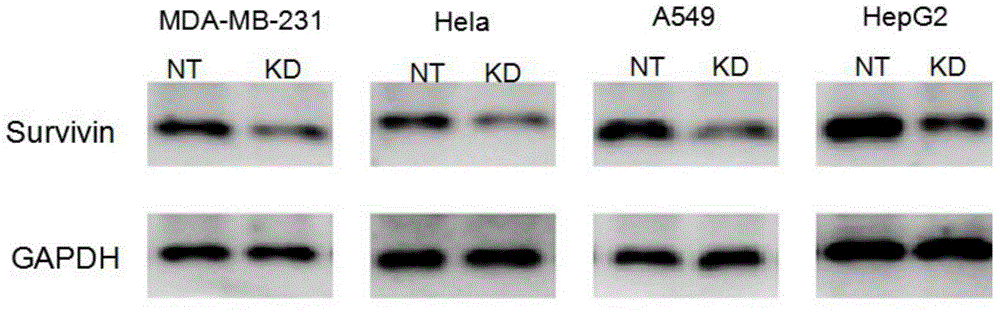
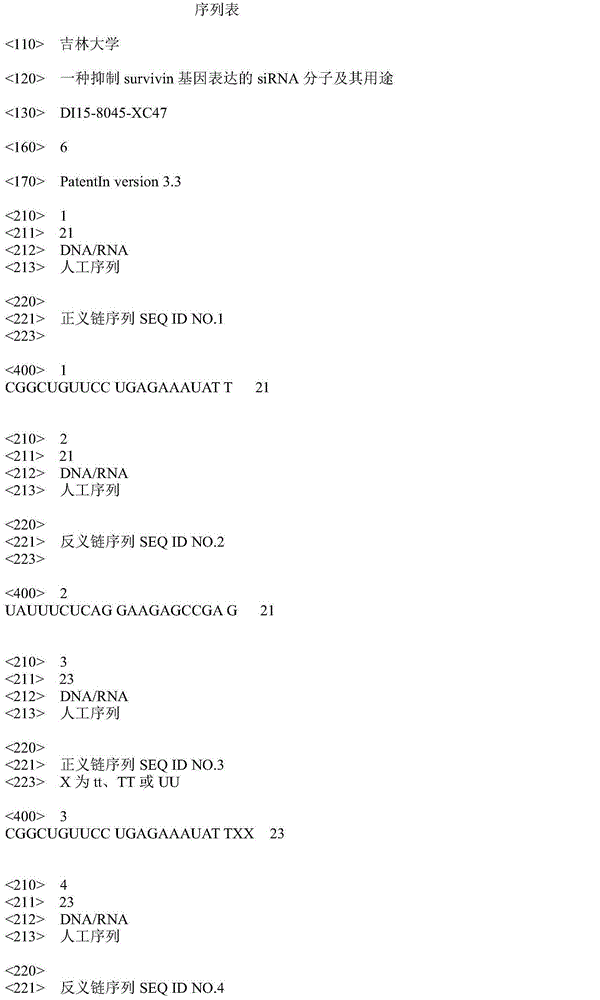
siRNA molecule for inhibiting survivin gene expression and application of siRNA molecule
InactiveCN105002183AKeep aliveOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTherapeutic intentEpidermoid carcinoma
The invention discloses a siRNA sequence for inhibiting survivin gene expression. The siRNA sequence has the broad spectrum siRNA anti-tumor effect, and the excellent inhibiting effect on breast cancer, lung cancer, intestinal cancer, liver cancer, leukemia, stomach cancer, cervical cancer, human oral epidermoid carcinoma and the like in vitro, particularly on breast cancer, lung cancer and cervical cancer cells. When the siRNA double-strand sequence enters an organism through a certain manner, the expression of disease related protein can be efficiently and specifically inhibited, so that related disease genes are silent, the target gene expression can be effectively knocked out, and the treating purpose can be achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
American cockroaches effective parts for anti-tumor prepared by macroporous adsorption resin and use
ActiveCN101214262BAnthropod material medical ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCancer cellCytotoxicity
The present invention relates to a periplaneta americana extract effective part with cytotoxic activity, a preparation method and a medical purpose thereof. The periplaneta americana extract effective part of the present invention is refined from fresh or dry blattidae periplaneta americana body which is extracted by alcohol water, processed for macroporous resin column chromatography and is eluted by alcohol solvent. The periplaneta americana extract effective part obtained by the present invention has obvious cytotoxicity and internal anticancer efficacy towards oral epidermoid carcinoma (KB) cell, poorly differentiated gastric abenocarcinoma tumour (BGC-823) cell, human chronic myelogonium leukaemia cancer (K562) cell and human myelogonium leukaemia cancer cell (HL-60) and can be used for preparing for a drug and a health care product for remedying the tumours.
Owner:KUNMING SINOWAY NATURAL PHARMA
7 site-connected bis(beta-carboline alkaloid) compound and its preparation method, pharmaceutical composition and use
The invention discloses a 7 site-connected bis(beta-carboline alkaloid) compound and its preparation method, pharmaceutical composition and use. The bis(beta-carboline alkaloid) compound and its medicinal salt are shown in the general formula I. The bis(beta-carboline alkaloid) compound is prepared by condensation of a beta-carboline intermediate and dihalogenated alkane. The invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition. The pharmaceutical composition comprises an effective dose of the bis(beta-carboline alkaloid) compound shown in the formula I and pharmaceutically acceptable carriers. The invention relates to a use of the bis(beta-carboline alkaloid) compound in preparation of drugs for resisting cancers such as melanoma, stomach cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, kidney cancer, liver cancer, human oral epidermoid carcinoma, cervical carcinoma, ovarian cancer, pancreas cancer, prostate cancer and colorectal carcinoma.
Owner:XINJIANG HUASHIDAN PHARMA RES
Treatment with Anti-alpha2 integrin antibodies
ActiveUS20100158904A1Inhibit bindingAvoid stickingNervous disorderMuscular disorderUterine carcinomaLymphoid Tumor
The invention relates to treatment of cancer. More specifically the invention relates to methods of treating cancer selected from the group consisting of squamous cell cancer, lung cancer including small-cell lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, adenocarcinoma of the lung, and squamous carcinoma of the lung, cancer of the peritoneum, hepatocellular cancer, gastric or stomach cancer including gastrointestinal cancer, pancreatic cancer, glioblastoma, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, liver cancer, bladder cancer, hepatoma, breast cancer, colon cancer, colorectal cancer, endometrial or uterine carcinoma, salivary gland carcinoma, kidney or renal cancer, liver cancer, prostate cancer, vulval cancer, thyroid cancer, hepatic carcinoma and various types of head and neck cancer, as well as B-cell lymphoma including low grade / follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL); small lymphocytic (SL) NHL; intermediate grade / follicular NHL; intermediate grade diffuse NHL; high grade immunoblastic NHL; high grade lymphoblastic NHL; high grade small non-cleaved cell NHL; bulky disease NHL; mantle cell lymphoma; AIDS-related lymphoma; and Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia; chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL); Hairy cell leukemia; chronic myeloblastic leukemia; and post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD), as well as abnormal vascular proliferation associated with phakomatoses, edema such as that associated with brain tumors, Meigs' syndrome, melanoma, mesothelioma, multiple myeloma, fibrosarcoma, osteosarcoma and epidermoid carcinoma, by administering antibodies directed to α2β1 integrin.
Owner:ICHNOS SCI SA
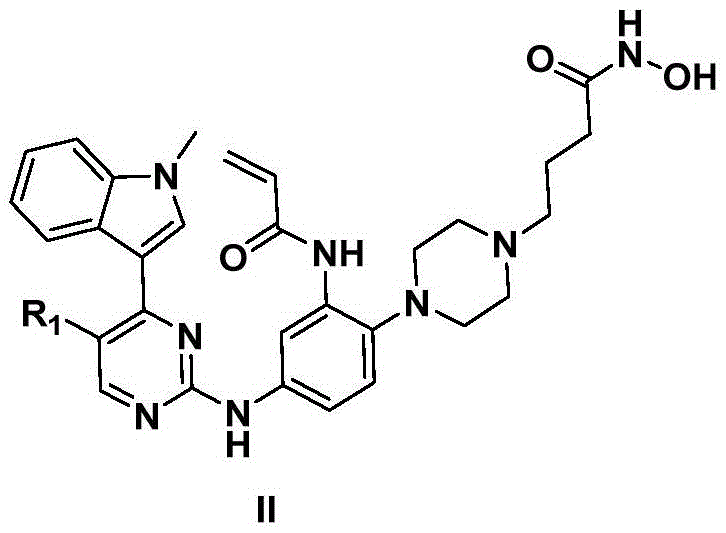
2,4-diarylamine pyrimidine derivatives containing hydroxamic acid fragments and preparation and application
InactiveCN105646371AStrong growth inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCarcinoma cell lineHydroxamic acid
The invention provides 2,4-diarylamine pyrimidine derivatives containing hydroxamic acid fragments shown in formulas I and II. 2,4-diarylamine pyrimidine containing carboxyl fragments is mainly used as a parent nucleus and is subjected to single-step condensation and related modification with hydroxylamine protected by THP to obtain a target compound. An experiment proves that the remarkable anti-proliferative effect is achieved for tumor cells (a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line H1975 and an overexpression EGFR human epidermal carcinoma cell line A431) related to EGFR tyrosine kinase activity on the cellular level, and a human cervical carcinoma cell line Hela, a human oral epidermoid carcinoma cell line KB, a human promyelocytic acute leukemia cell line HL60, a human hepatoma cell line HepG2, a human colon cancer cell line SW620 and other tumor cells related to the HDAC histone acetylase activity, and the corresponding medicine for resisting cancer cells can be prepared. The general structural formula is shown in the description.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Application of Nobiletin
ActiveCN105030559BStrong proliferative activityIncrease proliferative activityCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsEpidermoid carcinomaCancer cell proliferation
The invention discloses the application of nobiletin, in particular the application in the preparation of health products or medicines for preventing and / or treating oral cancer. The antiproliferative effects of nobiletin, naringenin and nobiletin on the human oral epidermoid cancer cell through the monomeric compounds nobiletin, naringenin and nobiletin in the citrus fruits of Rutaceae showed that nobietin, naringenin and nobiletin had the effect on human oral epidermoid cancer cells. The proliferation of cancer cells is obviously inhibited, and nobiletin has the most obvious effect of inhibiting the proliferation of oral cancer cells. It can be used to prepare health care products and medicines that can prevent and treat oral cancer, and is suitable for large-scale promotion.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Simplified structure of three asprosin, its preparation method, its pharmaceutical composition and use
ActiveCN102795975BStrong inhibitory activityEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationMelanomaProstate cancer
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
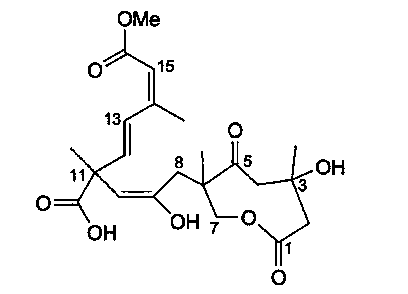
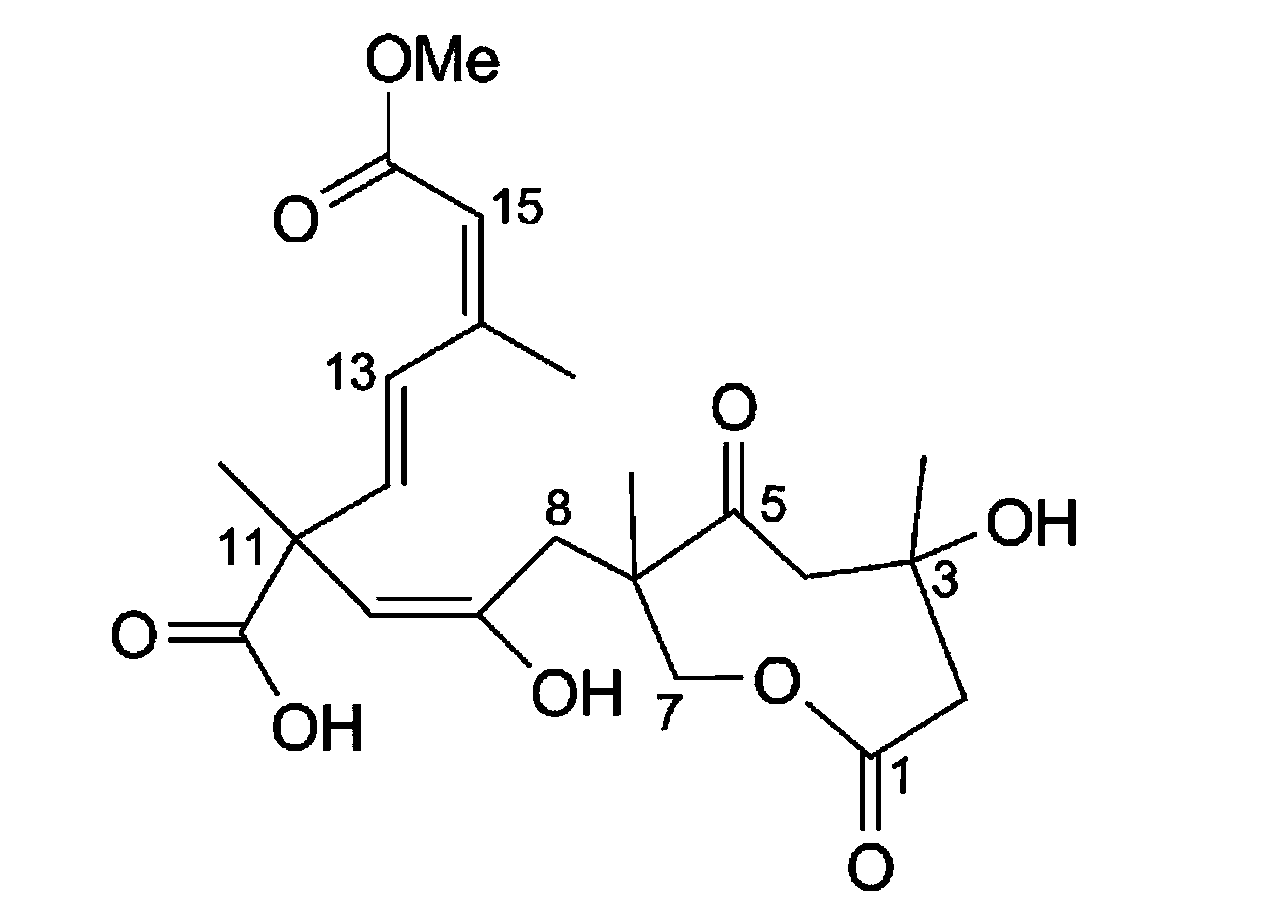
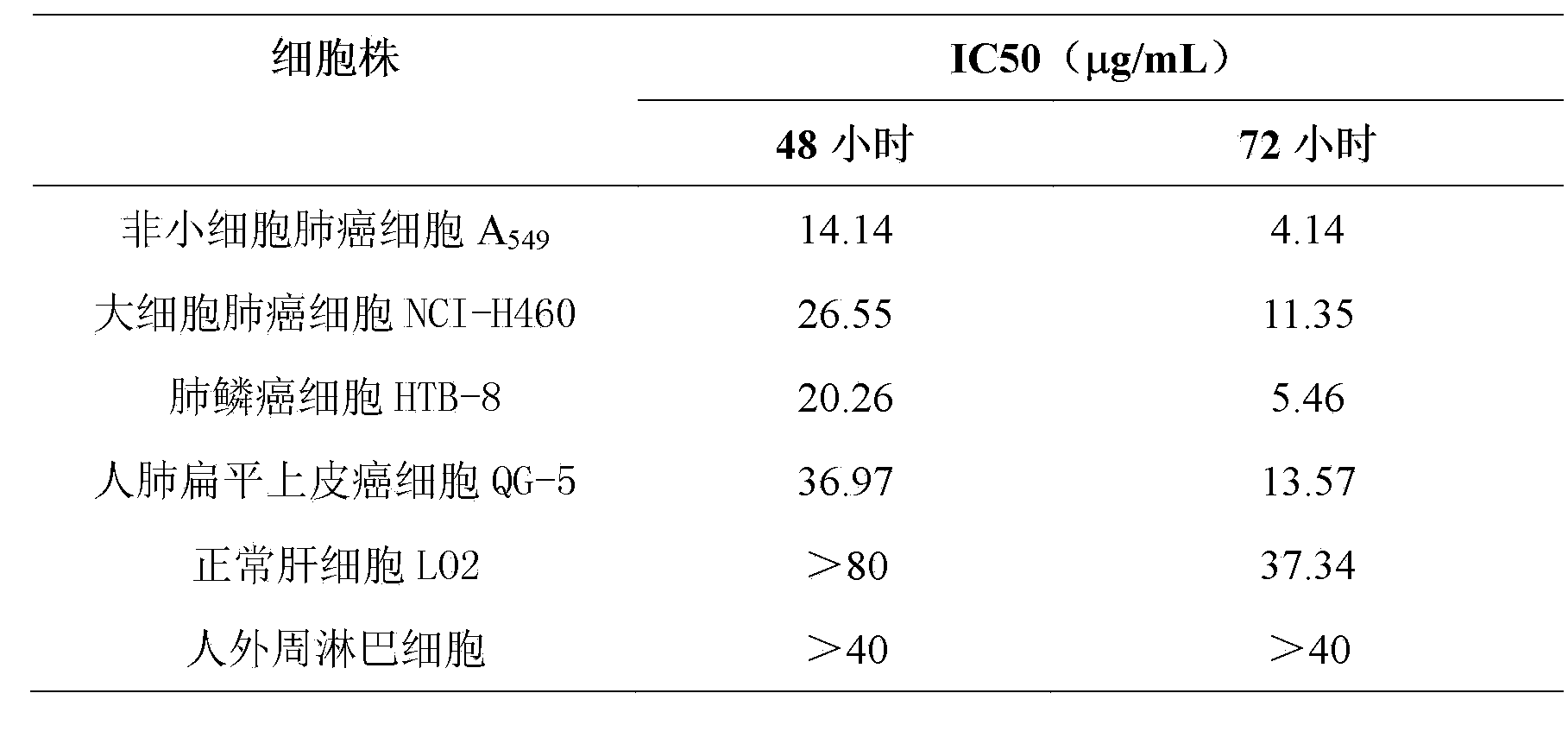
Application of Sarcaboside B in preparation of medicines for treating lung cancer
InactiveCN103356542AOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsPeripheral blood mononuclear cellEpidermoid carcinoma
The invention discloses an application of Sarcaboside B in preparation of medicines for treating lung cancer. The Sarcaboside B has good anti-lung cancer activity and can be used for the preparation of anti-lung cancer medicines, belonging to the technical field of new applications of medicines. The Sarcaboside B can be used for obviously inhibiting non-small cell lung cancer cells A549 cultured in vitro, giant cell lung cancer cells NCI-H460, lung squamous carcinoma cells HTB-8 and human lung epidermoid carcinoma cells QG-5 and has a little inhibiting effect on human normal hepatic cells LO2 and peripheral blood mononuclear cells and obvious selectivity. The application of the Sarcaboside B in preparation of the medicines for treating lung cancer is disclosed by the invention for the first time. As the skeleton type of the Sarcaboside B belongs to a brand-new skeleton type, the Sarcaboside B has unexpected strong inhibitory activity on lung cancer cells.
Owner:丁圣雨
Application of a thiourea molecule in the preparation of antitumor drugs
ActiveCN105582002BNon-cytotoxicExert anti-tumor effectAmide active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCarbon numberThiourea
Owner:杭州墨丘利生物医药科技有限公司
Application of egfr inhibitors in the preparation of drugs for the treatment of muc1 positive tumors
ActiveCN106924739BPrevent proliferationEasy to controlAntineoplastic agentsNitrile/isonitrile active ingredientsCancer cellEpidermoid carcinoma
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com