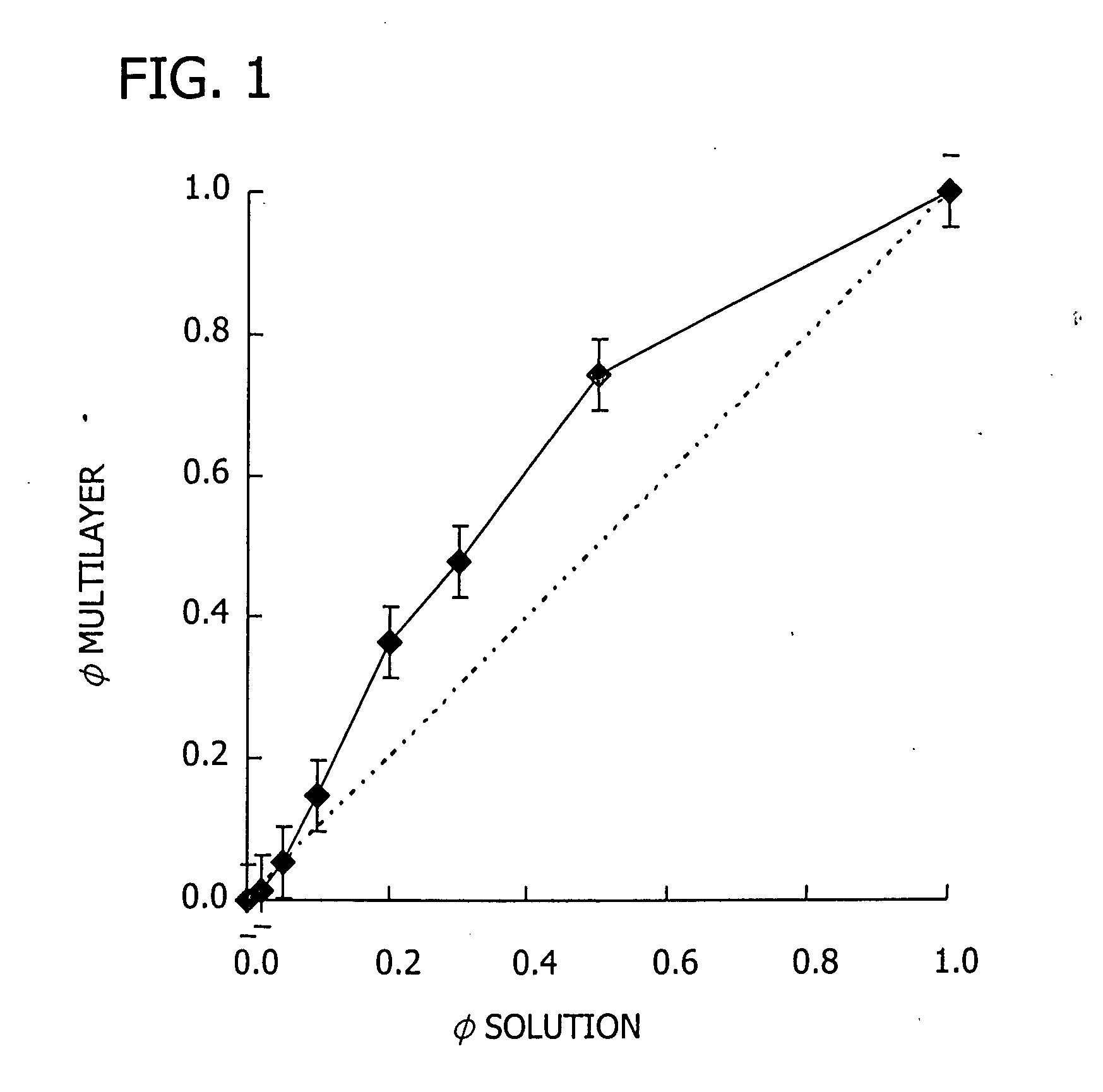
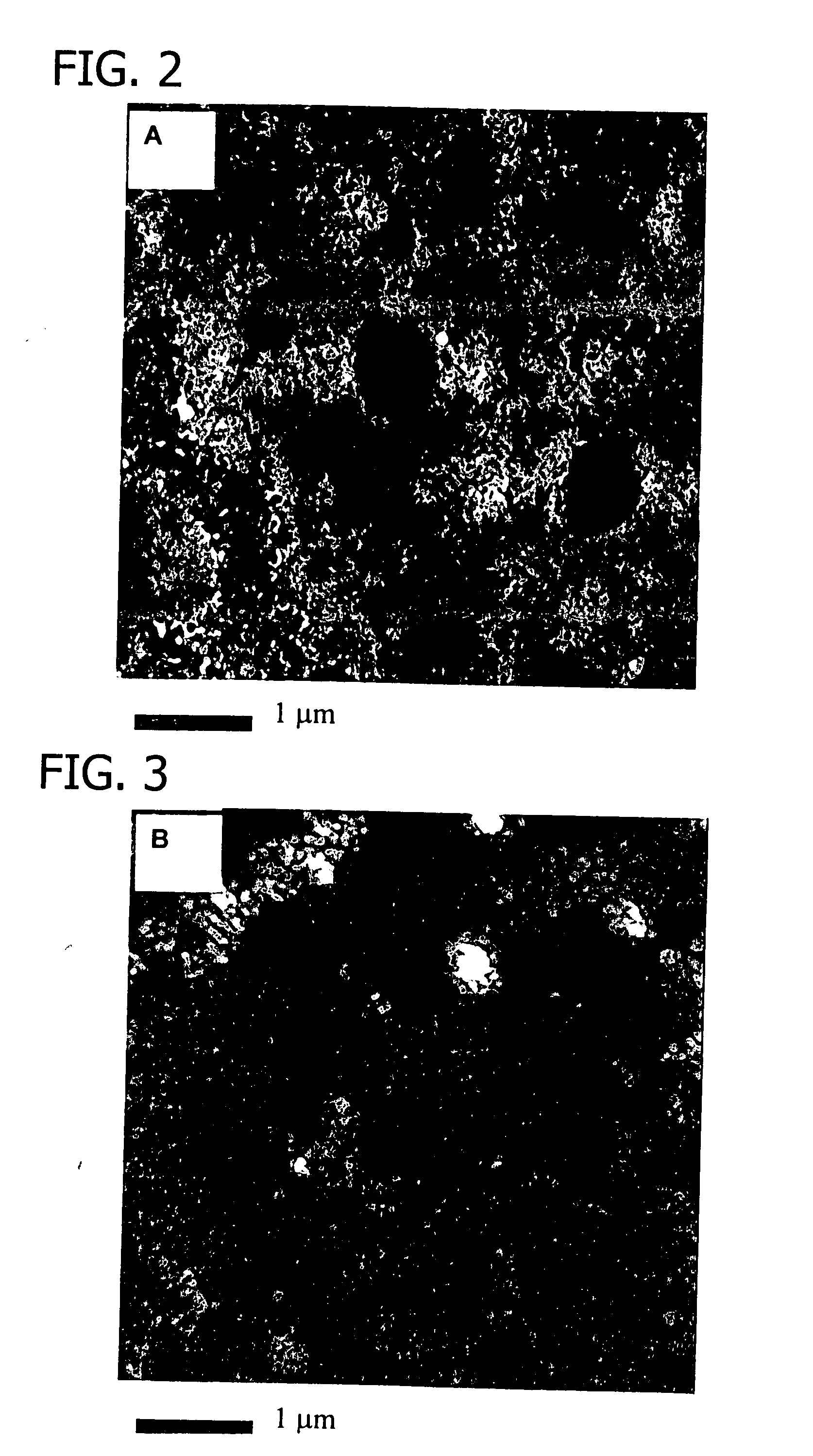
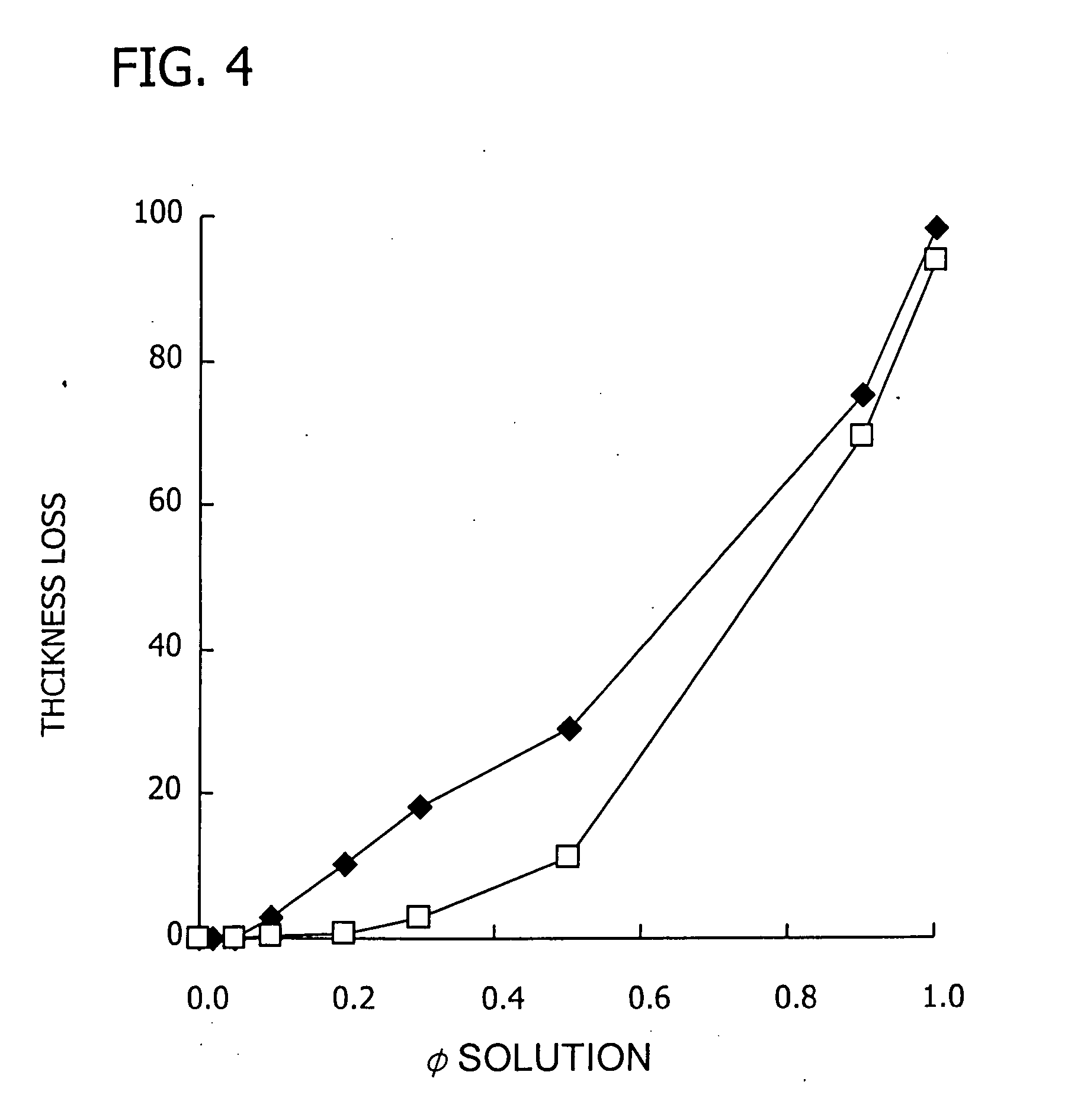
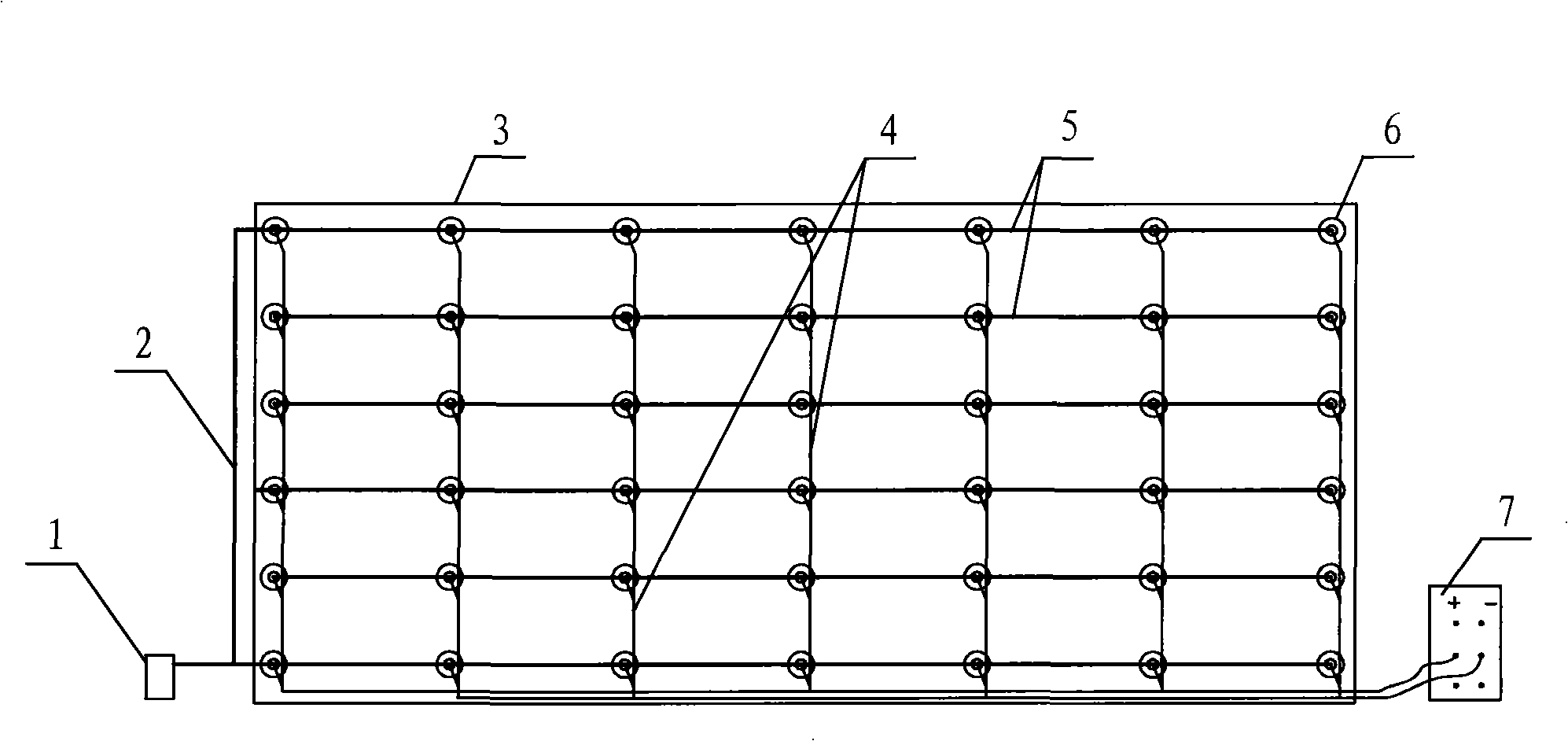
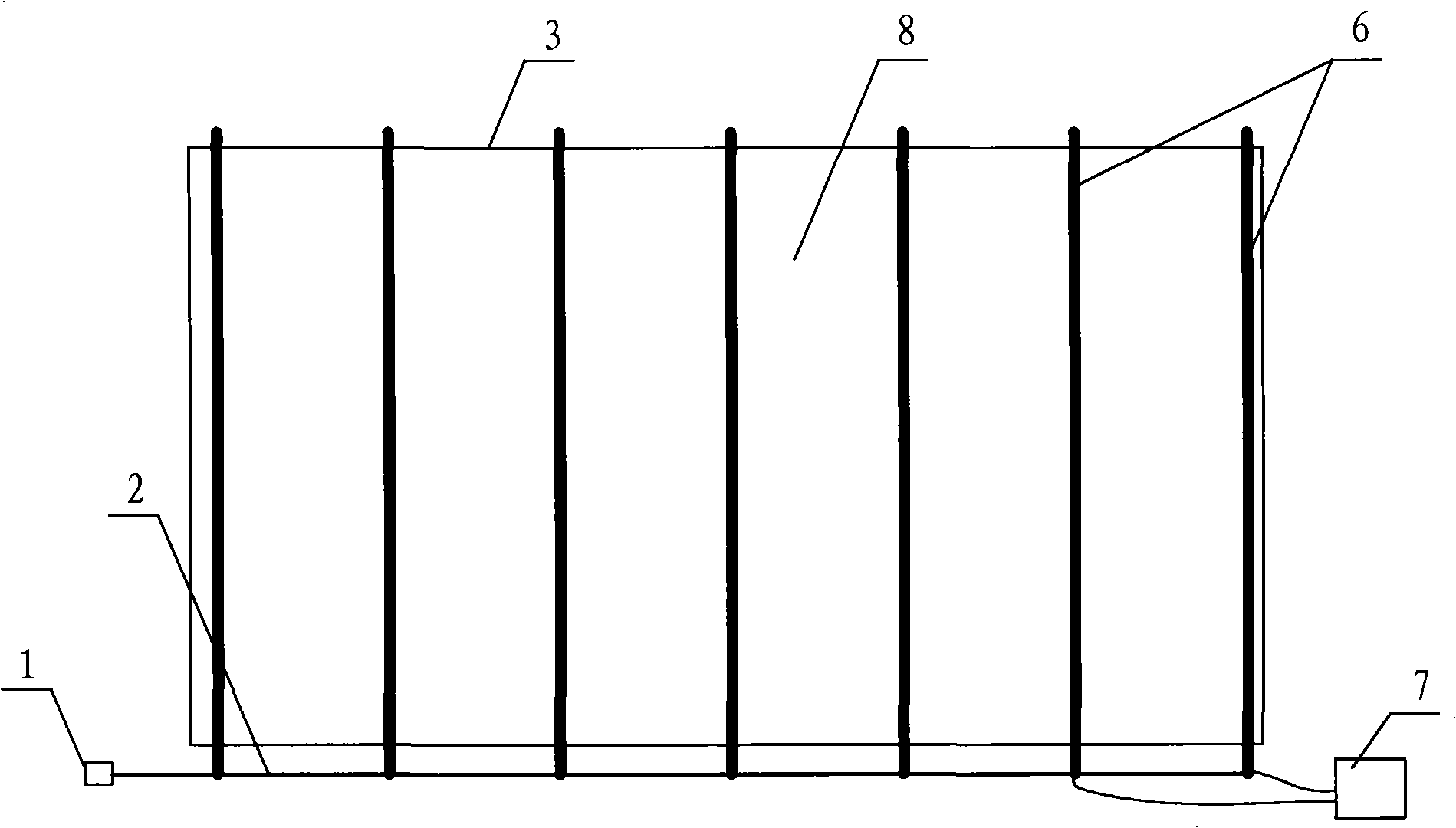
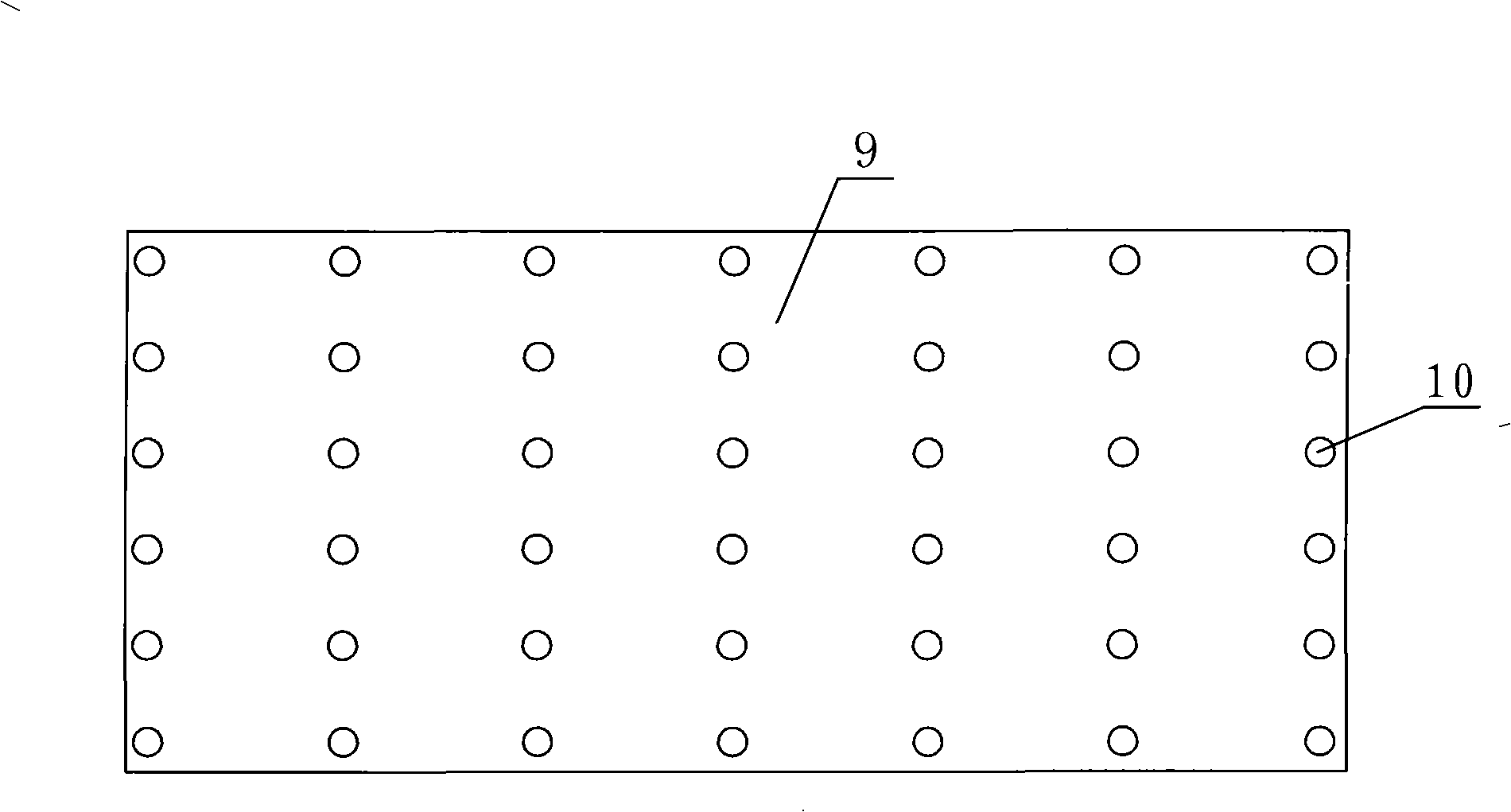
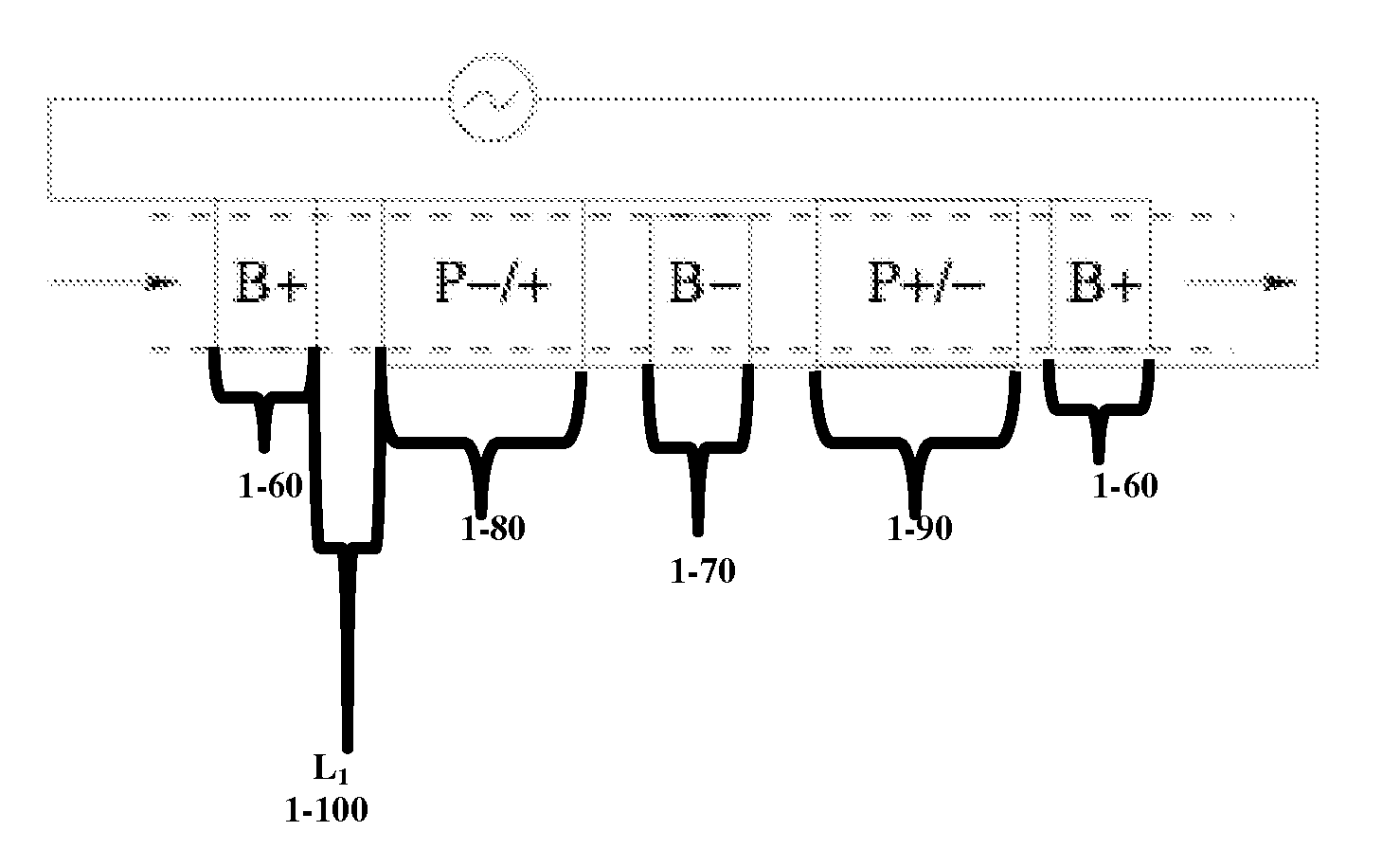
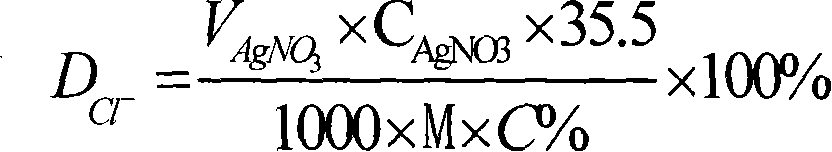Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
247 results about "Electro-osmosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electroosmotic flow (or electro-osmotic flow, often abbreviated EOF; synonymous with electroosmosis or electroendosmosis) is the motion of liquid induced by an applied potential across a porous material, capillary tube, membrane, microchannel, or any other fluid conduit. Because electroosmotic velocities are independent of conduit size, as long as the electrical double layer is much smaller than the characteristic length scale of the channel, electroosmotic flow will have little effect. Electroosmotic flow is most significant when in small channels. Electroosmotic flow is an essential component in chemical separation techniques, notably capillary electrophoresis. Electroosmotic flow can occur in natural unfiltered water, as well as buffered solutions.
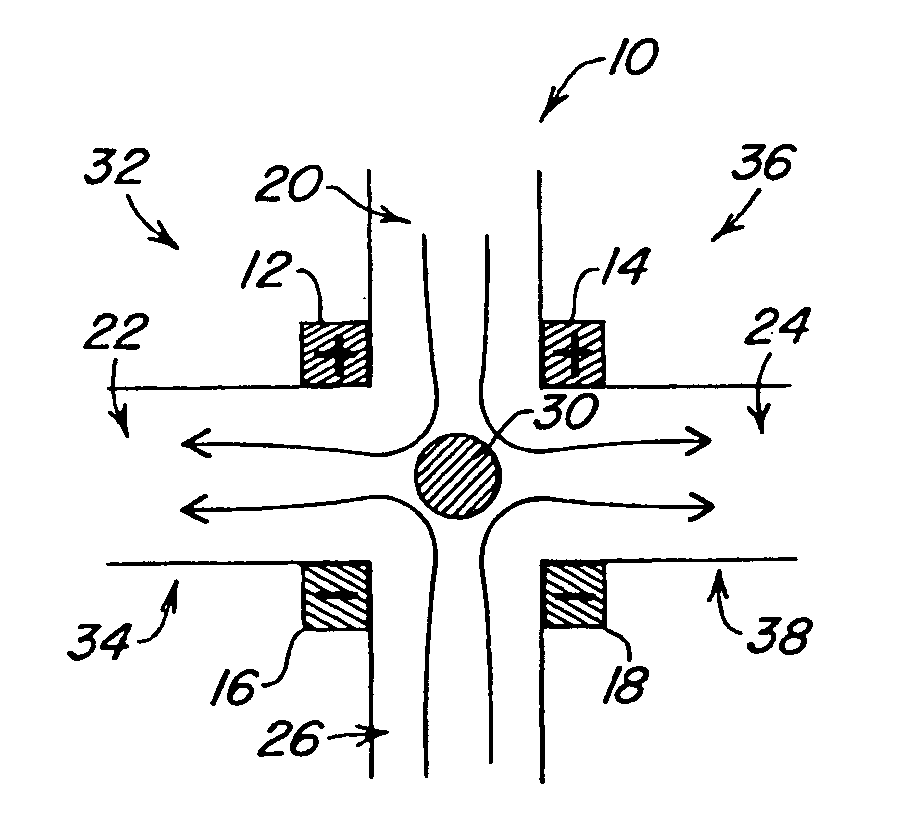
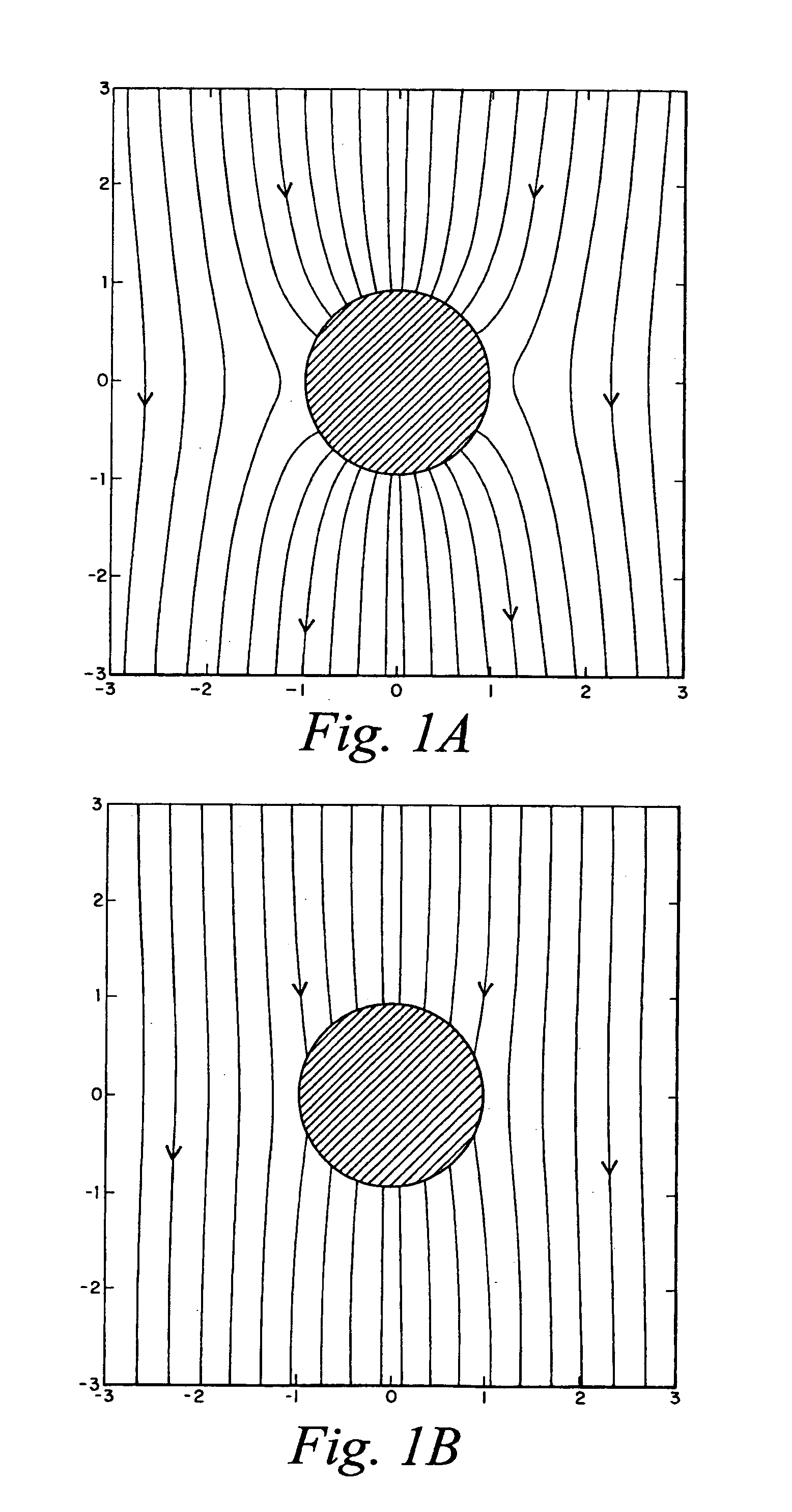
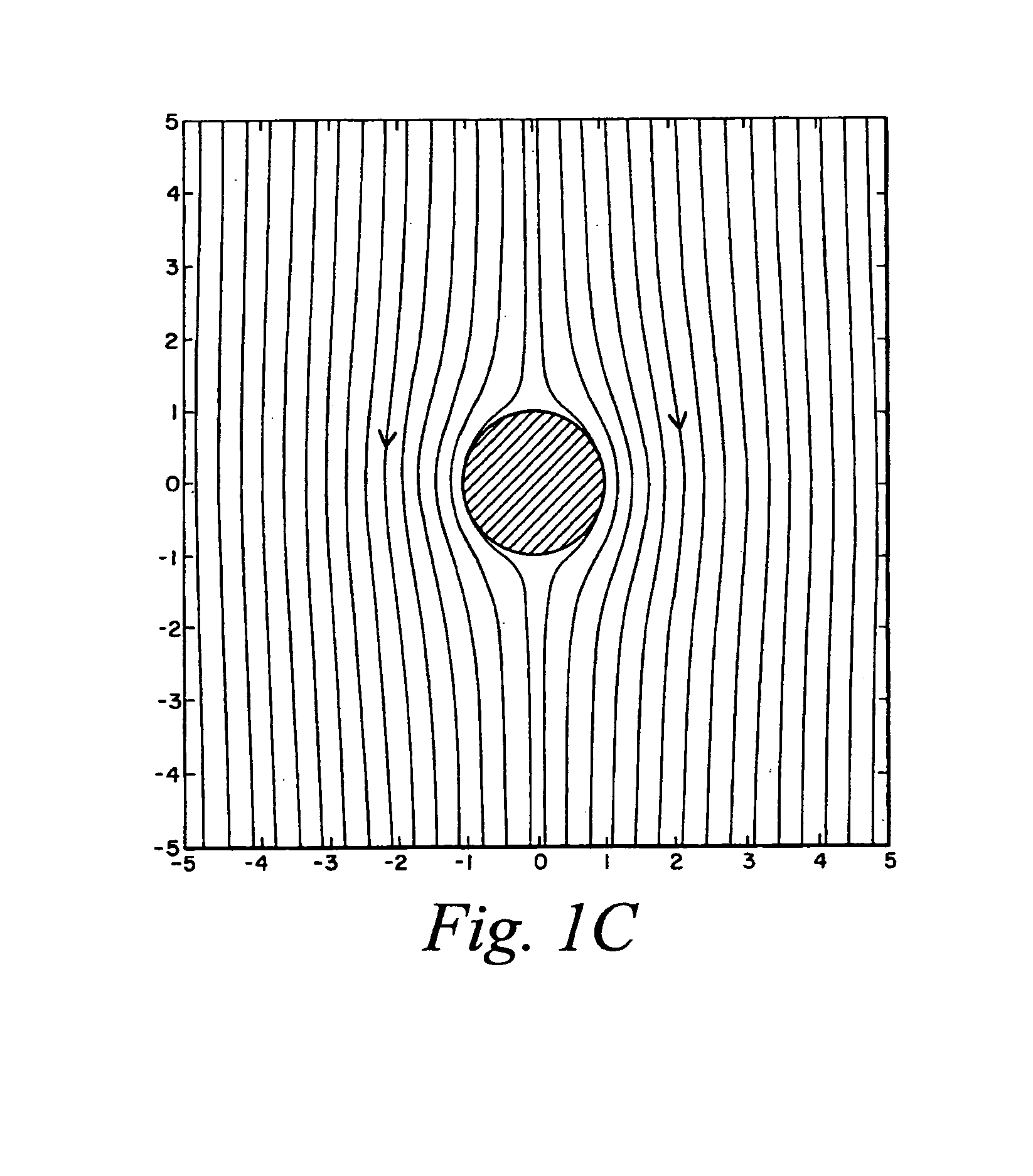
Microfluidic pumps and mixers driven by induced-charge electro-osmosis
InactiveUS7081189B2Sludge treatmentElectrostatic separatorsElectrical conductorCondensed matter physics
A microfluidic device includes one or more microchannels providing a passageway for transmitting an electrolyte fluid. A field source provides a defined field in the one or more microchannels, wherein at least one conductor element that is placed in at least one specific location in the device. Interactions between the defined field and the at least one conductor element produce electro-osmotic flows so that the electrolyte fluid is driven across the one or more microchannels.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
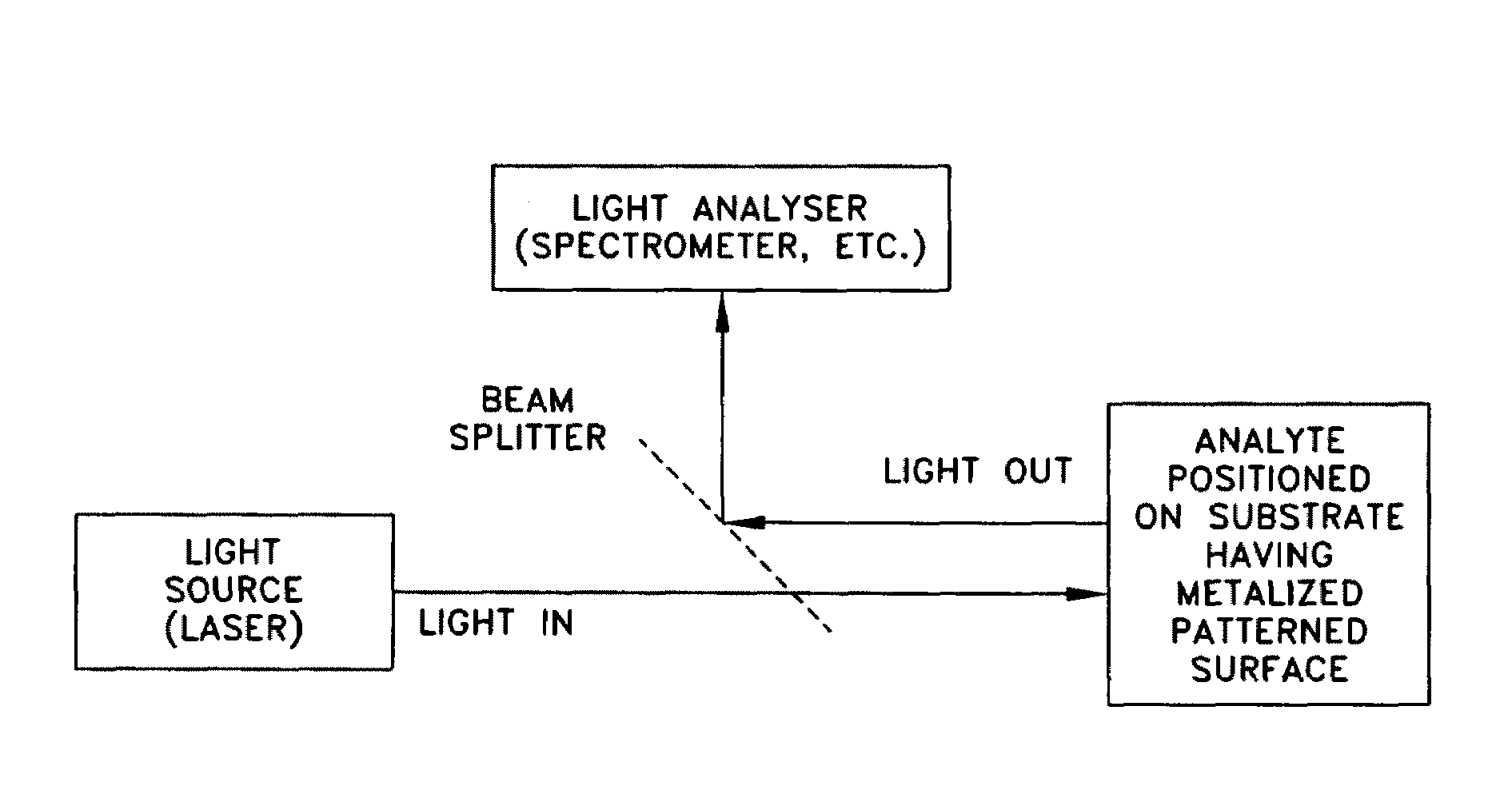
Applications of laser-processed substrate for molecular diagnostics
Owner:EBSTEIN STEVEN M
Applications of laser-processed substrate for molecular diagnostics
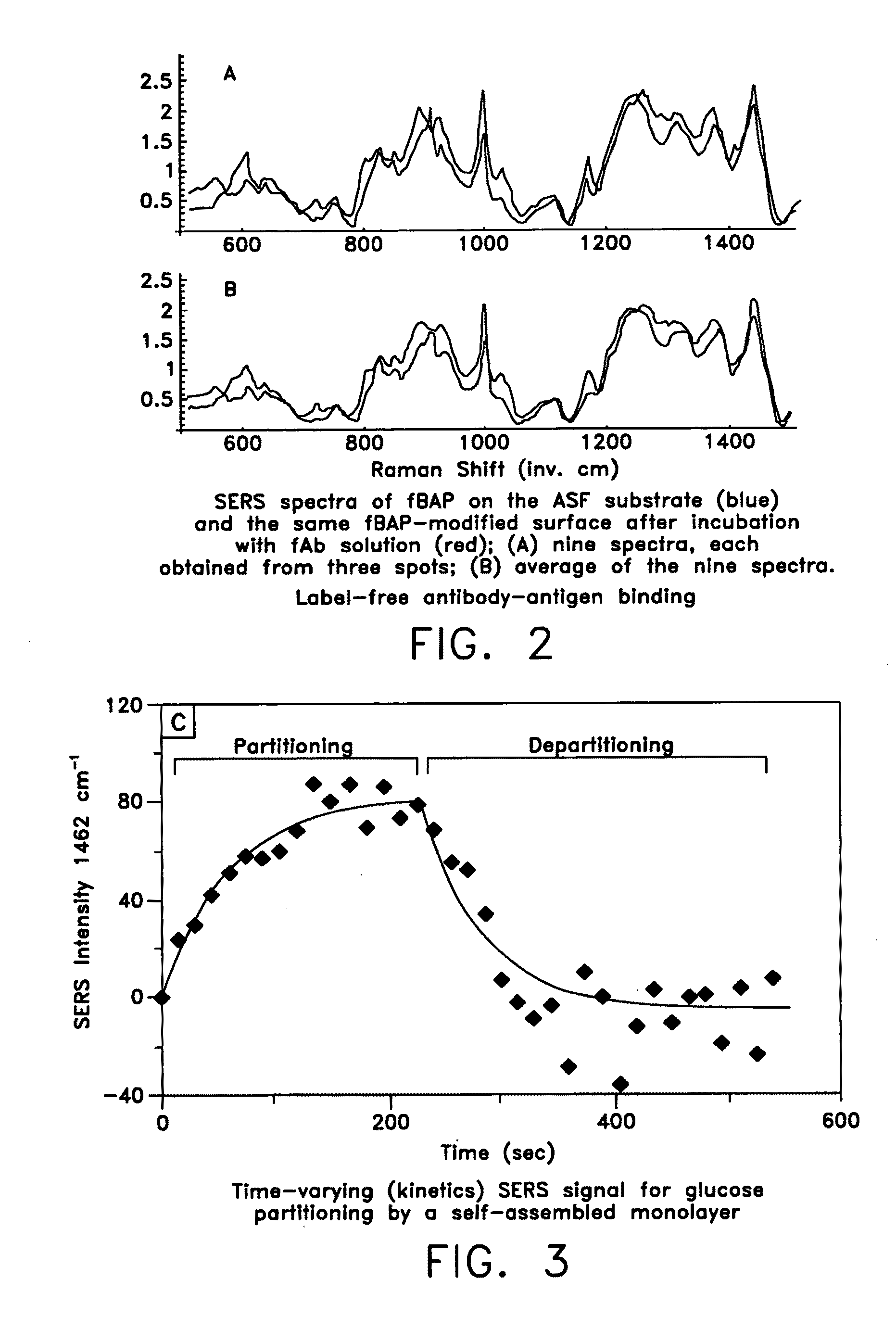
ActiveUS20070115469A1Facilitate SERS analysisMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometryChemical reactionPhotonics
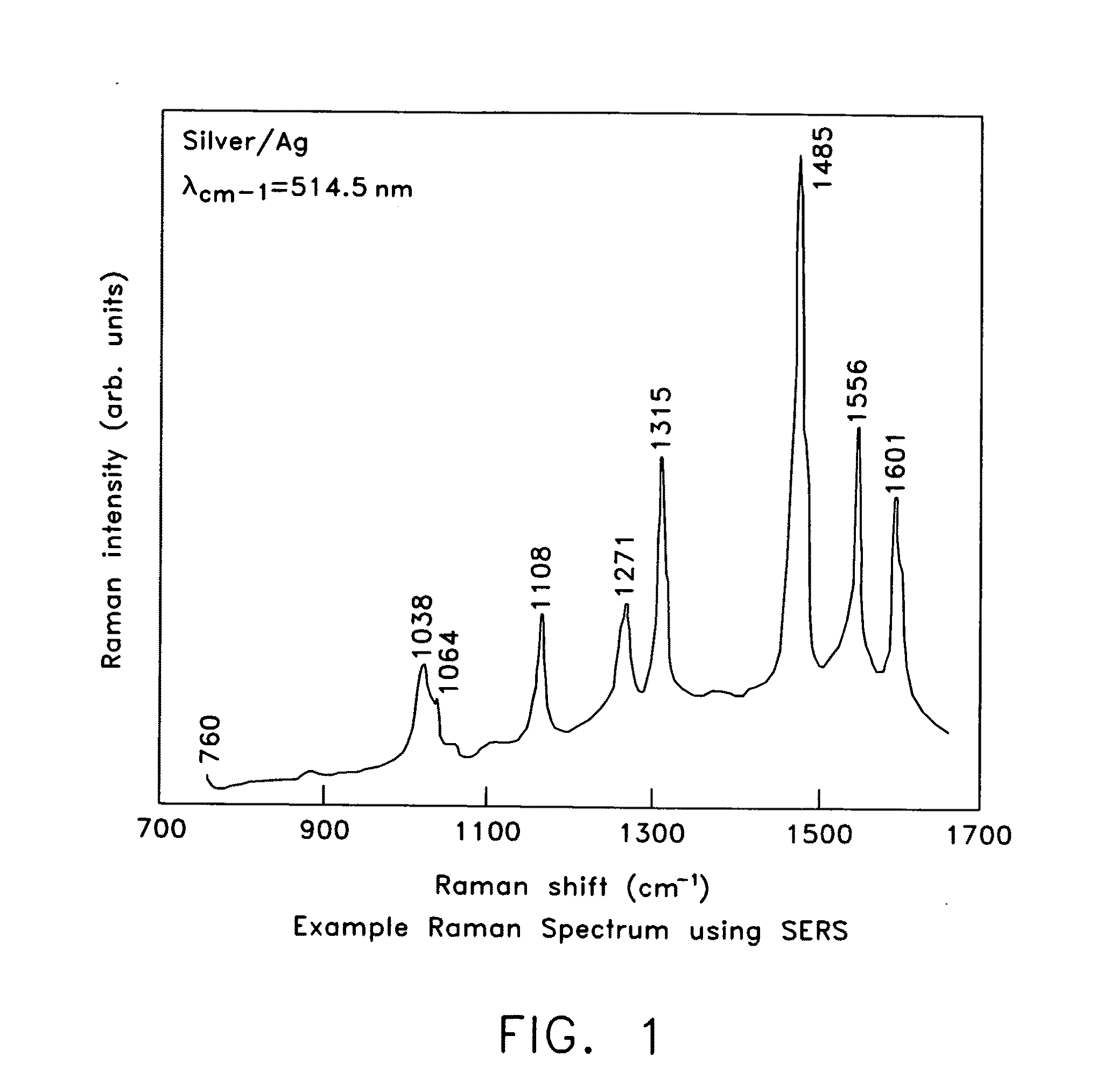
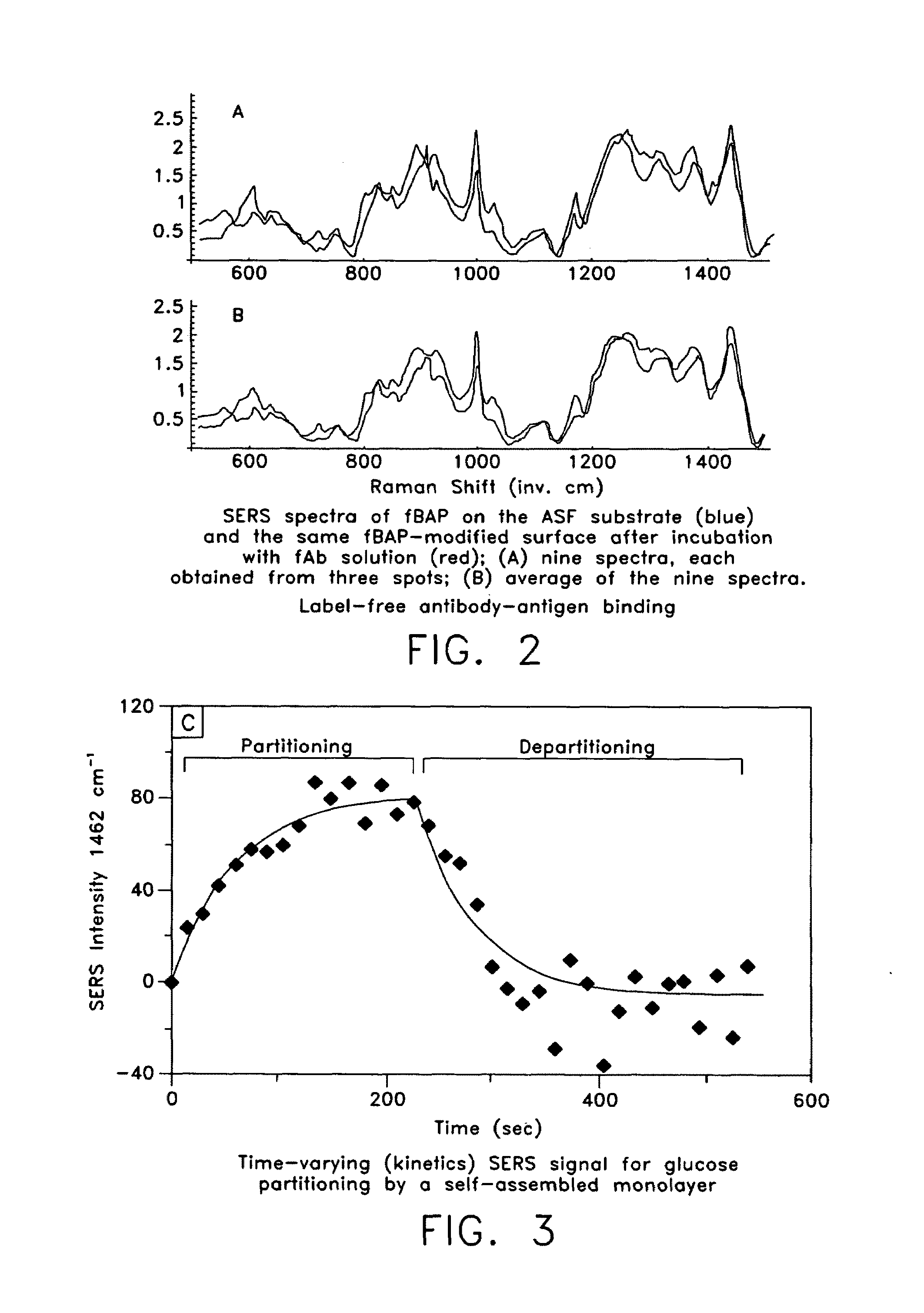
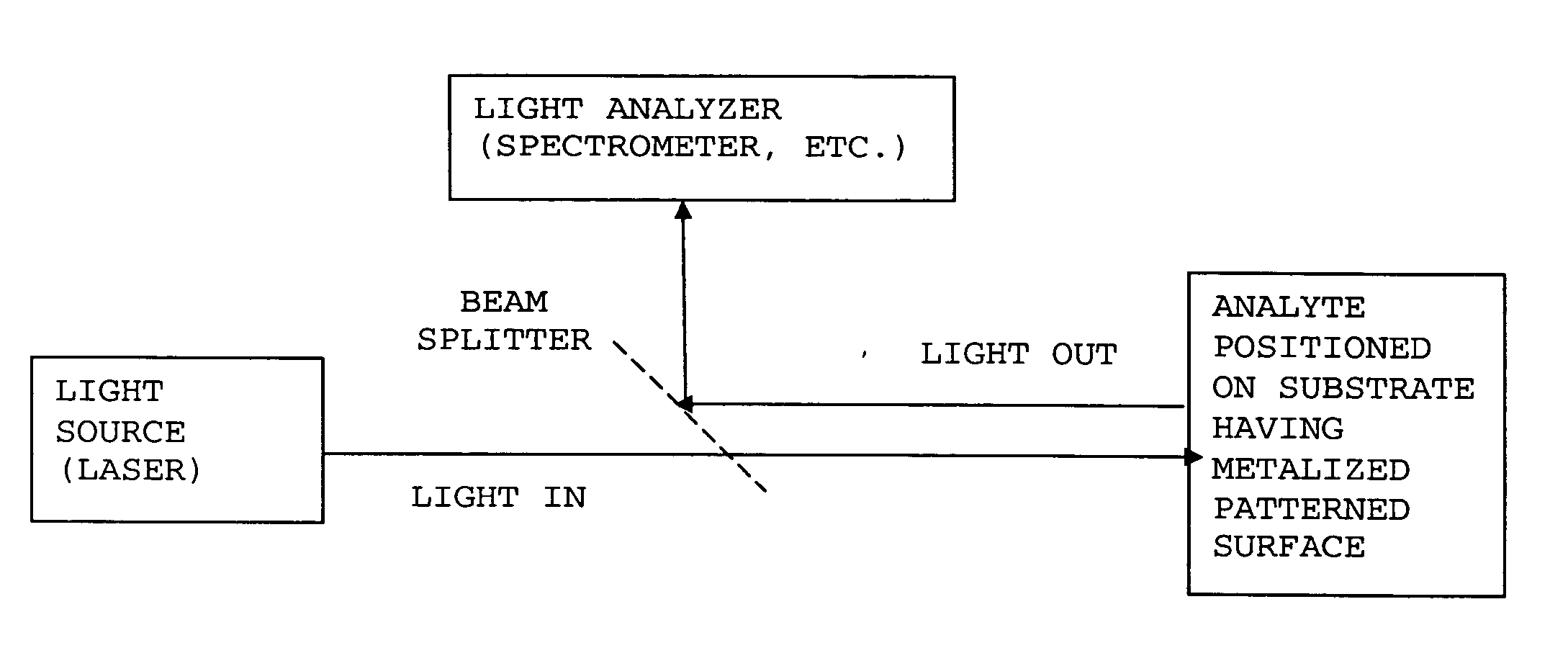
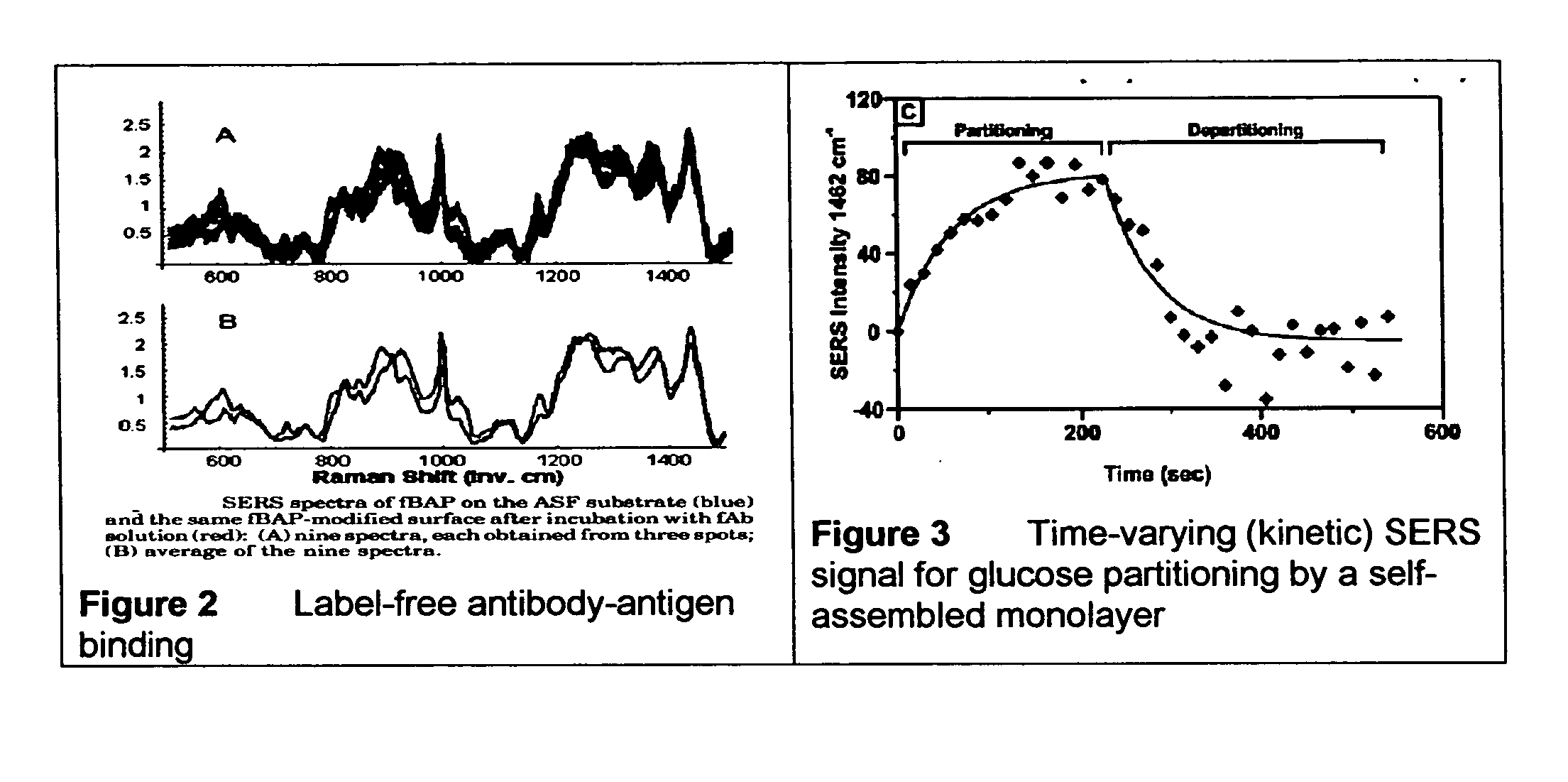
Surface enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) and related modalities offer greatly enhanced sensitivity and selectivity for detection of molecular species through the excitation of plasmon modes and their coupling to molecular vibrational modes. One of the chief obstacles to widespread application is the availability of suitable nanostructured materials that exhibit strong enhancement of Raman scattering, are inexpensive to fabricate, and are reproducible. I describe nanostructured surfaces for SERS and other photonic sensing that use semiconductor and metal surfaces fabricated using femtosecond laser processing. A noble metal film (e.g., silver or gold) is evaporated onto the resulting nanostructured surfaces for use as a substrate for SERS. These surfaces are inexpensive to produce and can have their statistical properties precisely tailored by varying the laser processing. Surfaces can be readily micropatterned and both stochastic and self-organized structures can be fabricated. This material has application to a variety of genomic, proteomic, and biosensing applications including label free applications including binding detection. Using this material, monolithic or arrayed substrates can be designed. Substrates for cell culture and microlabs incorporating microfluidics and electrochemical processing can be fabricated as well. Laser processing can be used to form channels in the substrate or a material sandwiched onto it in order to introduce reagents and drive chemical reactions. The substrate can be fabricated so application of an electric potential enables separation of materials by electrophoresis or electro-osmosis.
Owner:EBSTEIN STEVEN M
Electroosmotic flow for end labelled free solution electrophoresis
InactiveUS20070215472A1Easy to separateIncreased hydrodynamic frictionSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityElectrophoresis
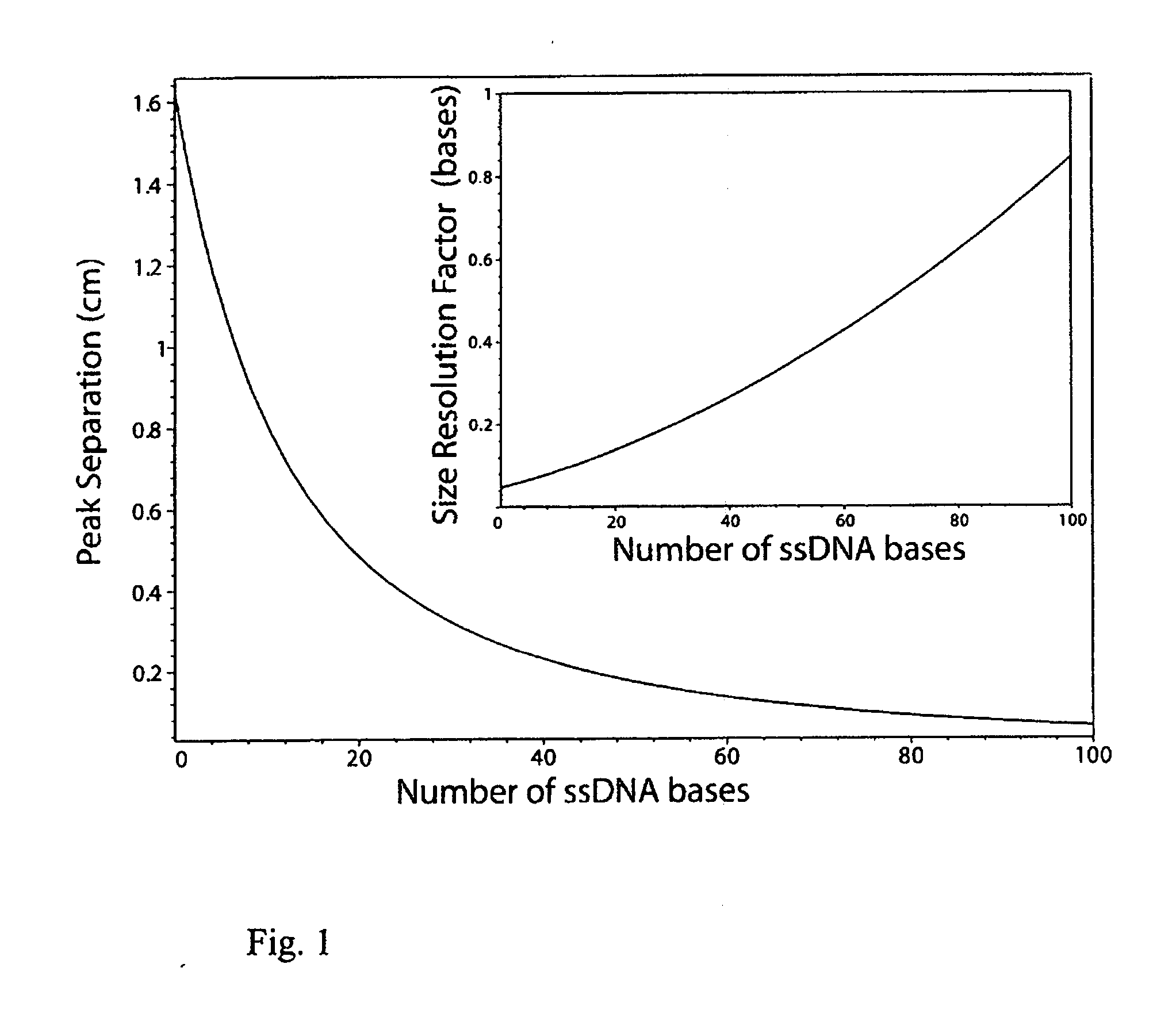
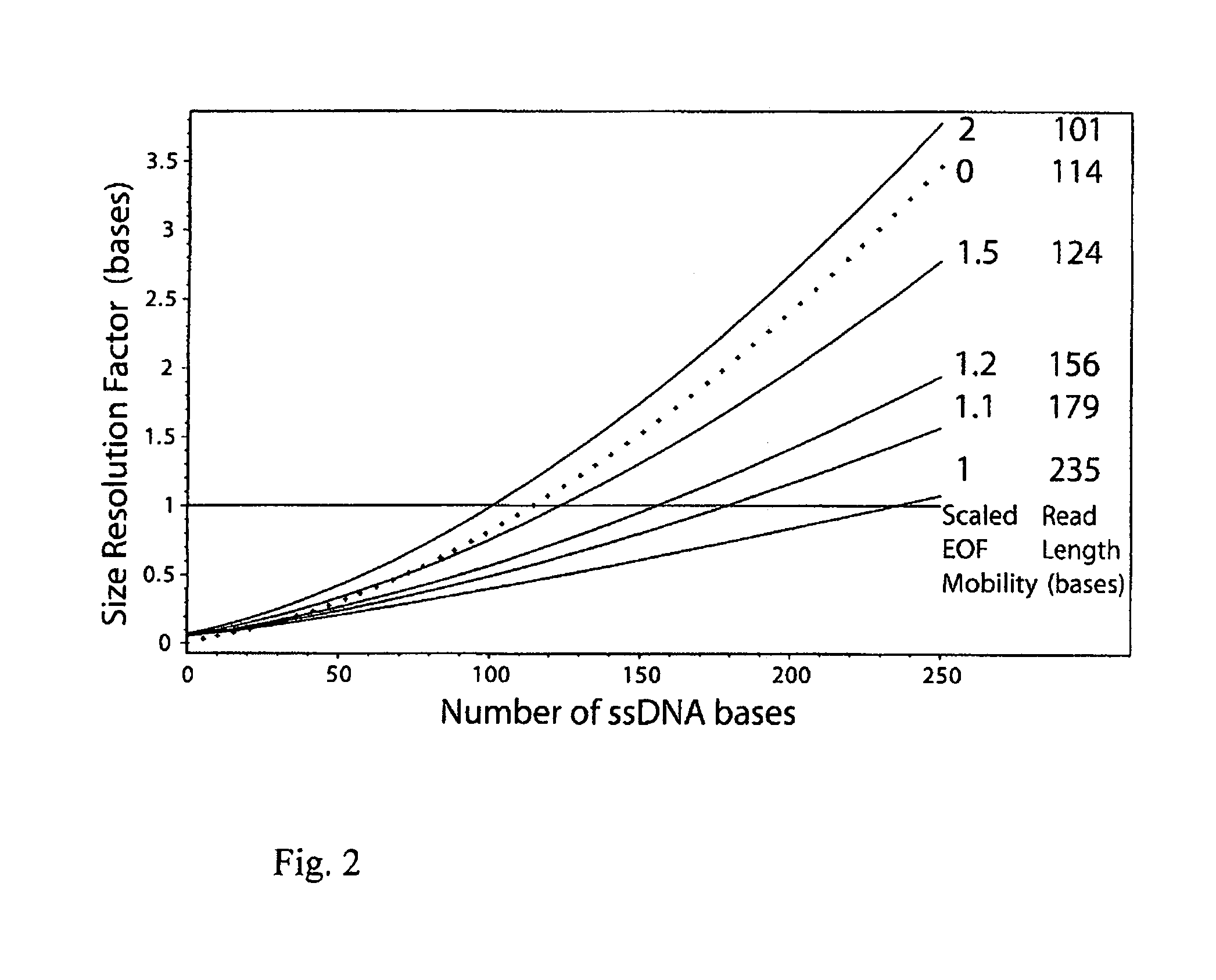
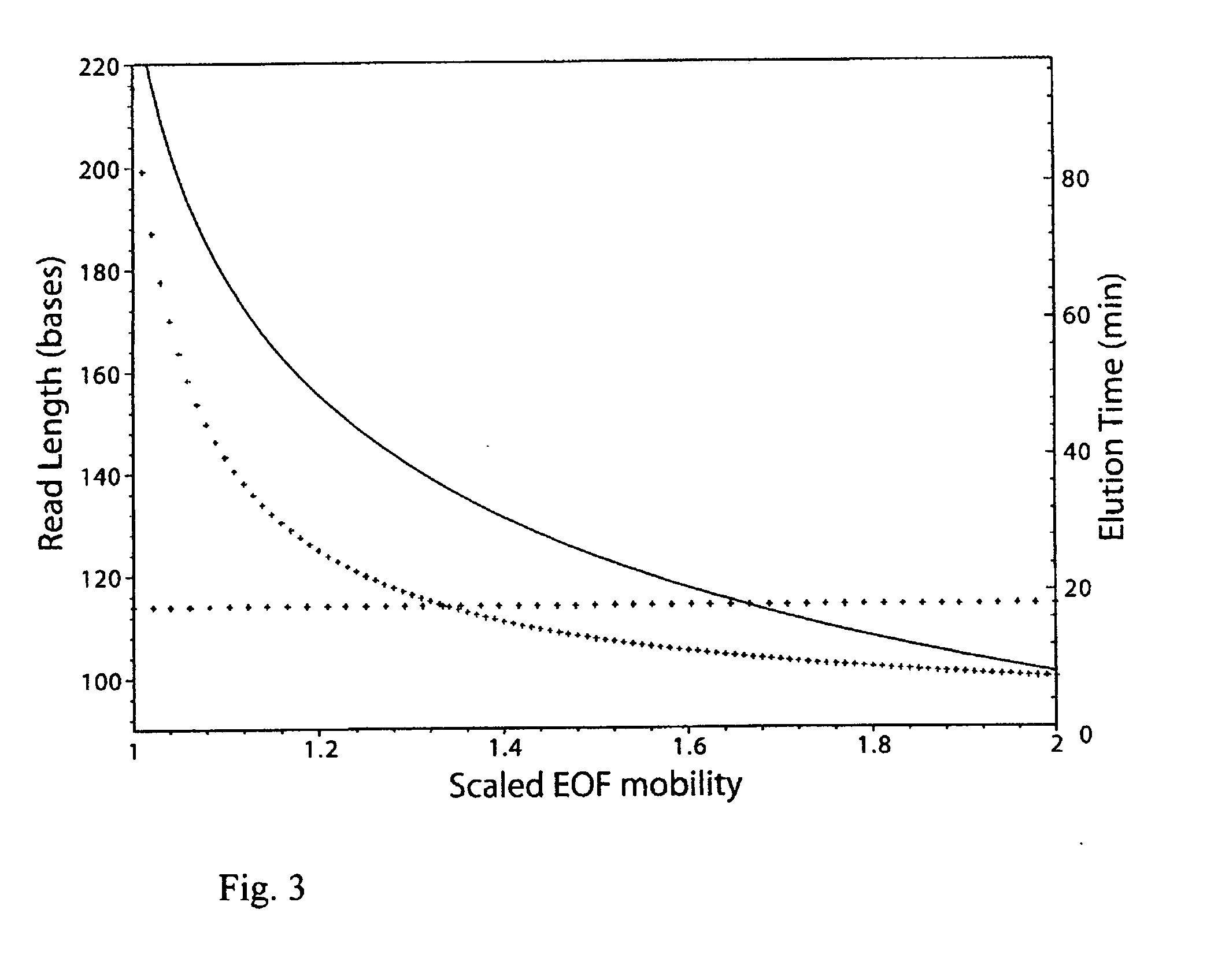
End Labelled Free Solution Electrophoresis (ELFSE) provides a means of separating polymer molecules such as ssDNA according to their size, via free solution electrophoresis, thus eliminating the need for polymer separation via gels or polymer matrices. Here, significant improvements in ELFSE are disclosed via concurrent exposure of the polymer molecules to an electroosmotic flow. When the methods are applied to DNA sequencing by ELFSE, significant improvements in read length are observed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
Remoulding soft clay sample preparation device and method based on vacuum combined electron-osmosis effect
The invention discloses a remoulding soft clay sample preparation device and a remoulding soft clay sample preparation method based on a vacuum combined electron-osmosis effect. Nonwoven geotextile, a gravel layer, a sand mat layer and an electron-osmosis cathode are sequentially paved on an osmosis drainage base; the upper and lower ends of a latex film are respectively turned outward and sleeved on a sample loading solidification cylinder and are fixed with the osmosis drainage base by a bolt through a flange; a water vapor separation cylinder is provided with an electric contact vacuum member and is connected with the osmosis drainage base and a vacuum pump respectively through an air pipe; slurry is poured into the designated height of the sample loading solidification cylinder, and an electro-osmosis anode is put in; and the electro-osmosis anode and the electro-osmosis cathode are respectively connected with a programmable direct-current power supply by wires. Under the combined effect of vacuum negative pressure and electro-osmosis, the drainage solidification speed of a soil body is increased, and the solidification stress level in a soil body sample preparation process can be adjusted. According to the device and the method disclosed by the invention, the size of a sample tank is reduced, and meanwhile, the number of sample preparation each time is increased by preparing multiple groups of soil samples; the device has a simple structure and is convenient for operation and sample taking; and the sample preparation period is short, and secondary cutting, disturbance and waste of soil samples are effectively avoided.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Microfluidic pumps and mixers driven by induced-charge electro-osmosis
This invention provides devices and apparatuses comprising the same, for the mixing and pumping of relatively small volumes of fluid. Such devices utilize nonlinear electrokinetics as a primary mechanism for driving fluid flow. Methods of cellular analysis and high-throughput, multi-step product formation using, devices of this invention are described.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method of composite electroosmosis, vacuum precipitation and vacuum preload reinforcement foundation and device thereof
ActiveCN101182709AGuaranteed closureExpand the scope of reinforcementSoil preservationEngineeringPermeability coefficient
The invention discloses a method for strengthening the foundation with composite electroosmosis, vacuum dewatering and vacuum preloading, and aims to provide a method for foundation treatment, especially for various types of soil with a permeability coefficient of <10-5cm / s in a large area. Methods of strengthening soft soil foundations. The device used in the method of the present invention adopts a composite pipe and a redundant film with openings or a mesh cap eye film or a mesh cap eye vacuum film with a connector. The method of the invention is a method for reinforcing the foundation that combines electroosmosis, vacuum dewatering and vacuum preloading, and can be implemented in parallel. It has the advantages of balanced treatment, simple and convenient construction, short project time, and high cost performance.
Owner:广西华业建筑工程有限公司
Laser-processed substrate for molecular diagnostics
ActiveUS20090279085A1Facilitate SERS analysisMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometryChemical reactionPhotonics
Surface enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) and related modalities offer greatly enhanced sensitivity and selectivity for detection of molecular species through the excitation of plasmon modes and their coupling to molecular vibrational modes. One of the chief obstacles to widespread application is the availability of suitable nanostructured materials that exhibit strong enhancement of Raman scattering, are inexpensive to fabricate, and are reproducible. I describe nanostructured surfaces for SERS and other photonic sensing that use semiconductor and metal surfaces fabricated using femtosecond laser processing. A noble metal film (e.g., silver or gold) is evaporated onto the resulting nanostructured surfaces for use as a substrate for SERS. These surfaces are inexpensive to produce and can have their statistical properties precisely tailored by varying the laser processing. Surfaces can be readily micropatterned and both stochastic and self-organized structures can be fabricated. This material has application to a variety of genomic, proteomic, and biosensing applications including label free applications including binding detection. Using this material, monolithic or arrayed substrates can be designed. Substrates for cell culture and microlabs incorporating microfluidics and electrochemical processing can be fabricated as well. Laser processing can be used to form channels in the substrate or a material sandwiched onto it in order to introduce reagents and drive chemical reactions. The substrate can be fabricated so application of an electric potential enables separation of materials by electrophoresis or electro-osmosis.
Owner:EBSTEIN STEVEN M
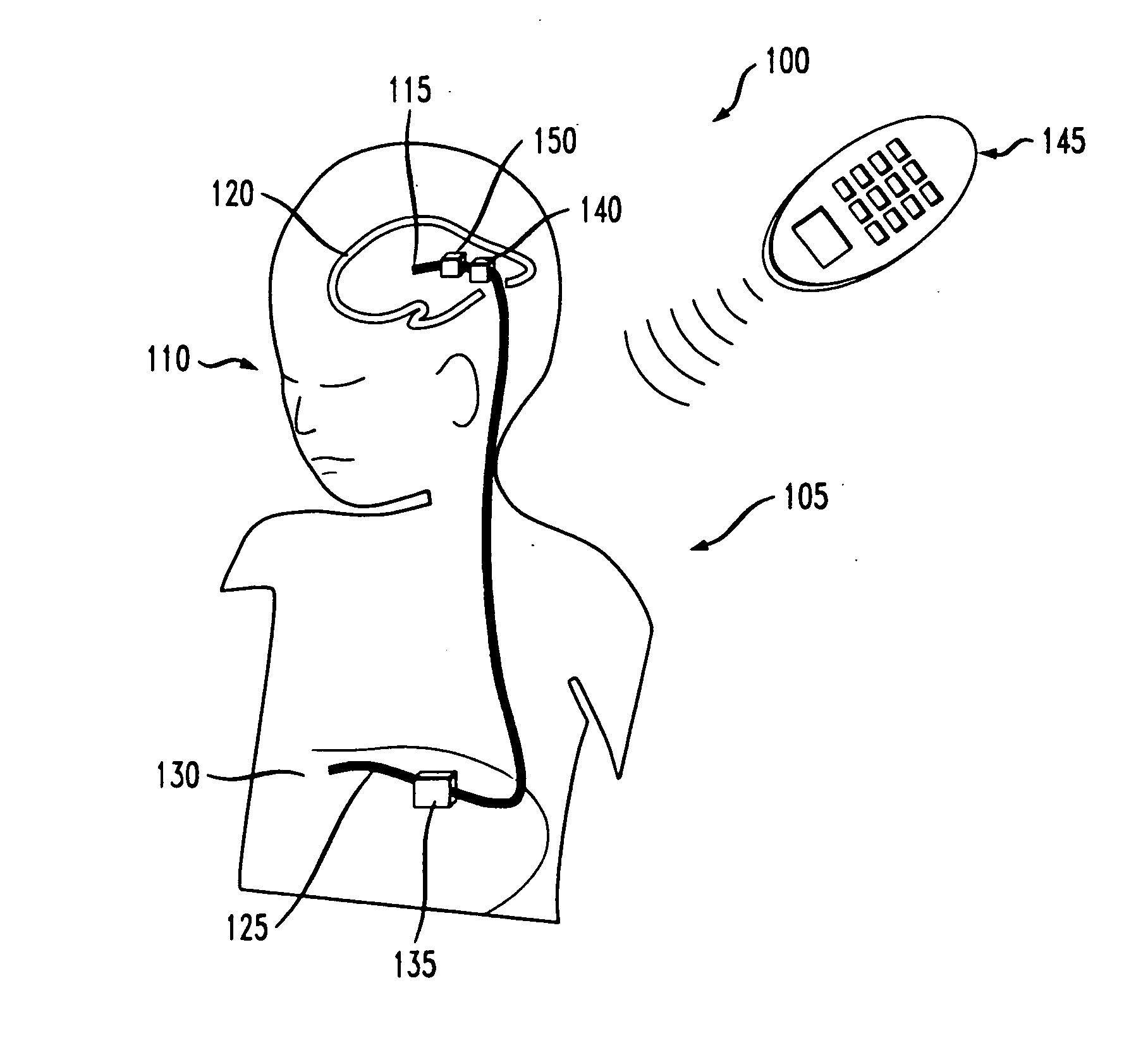
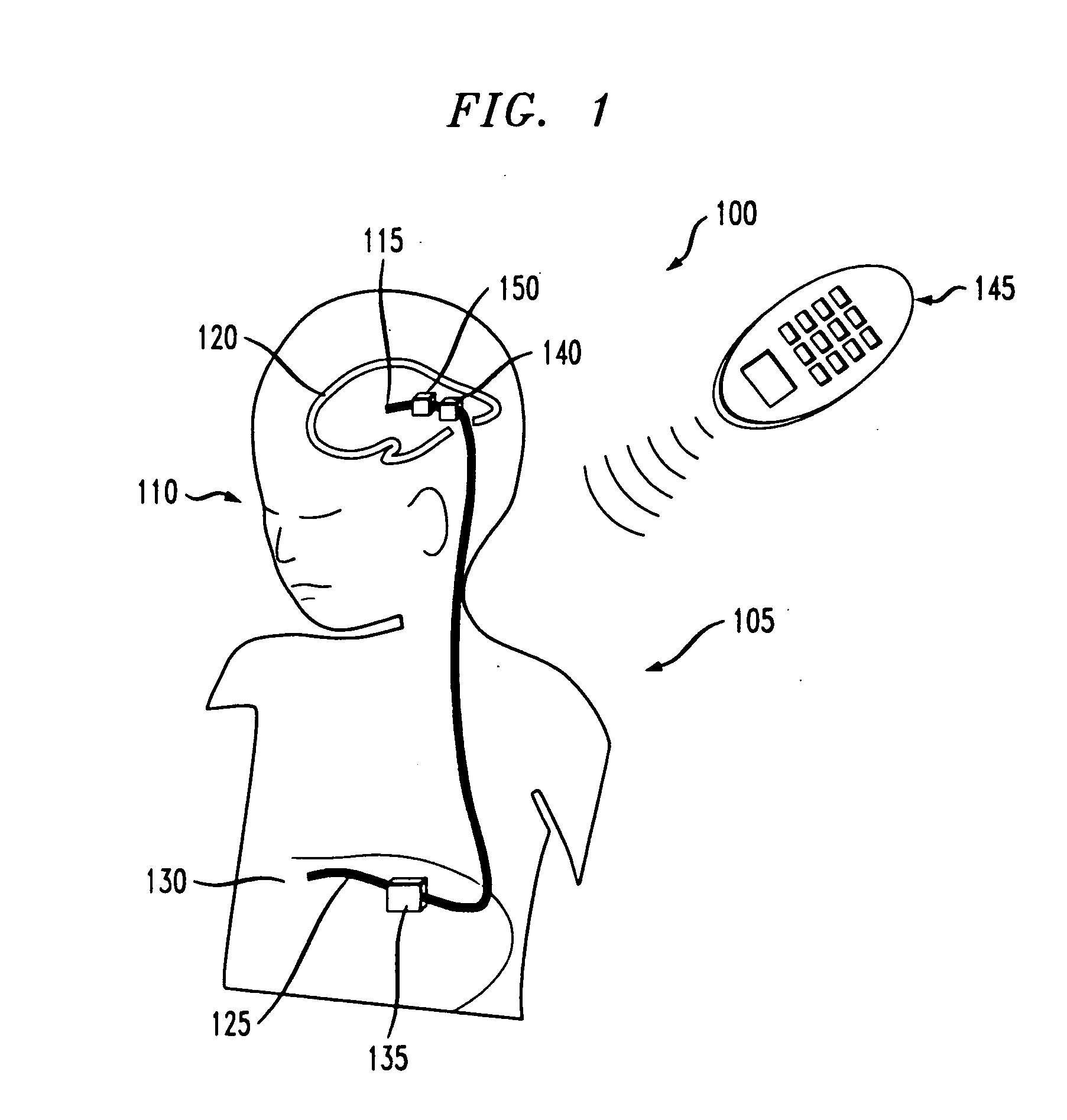
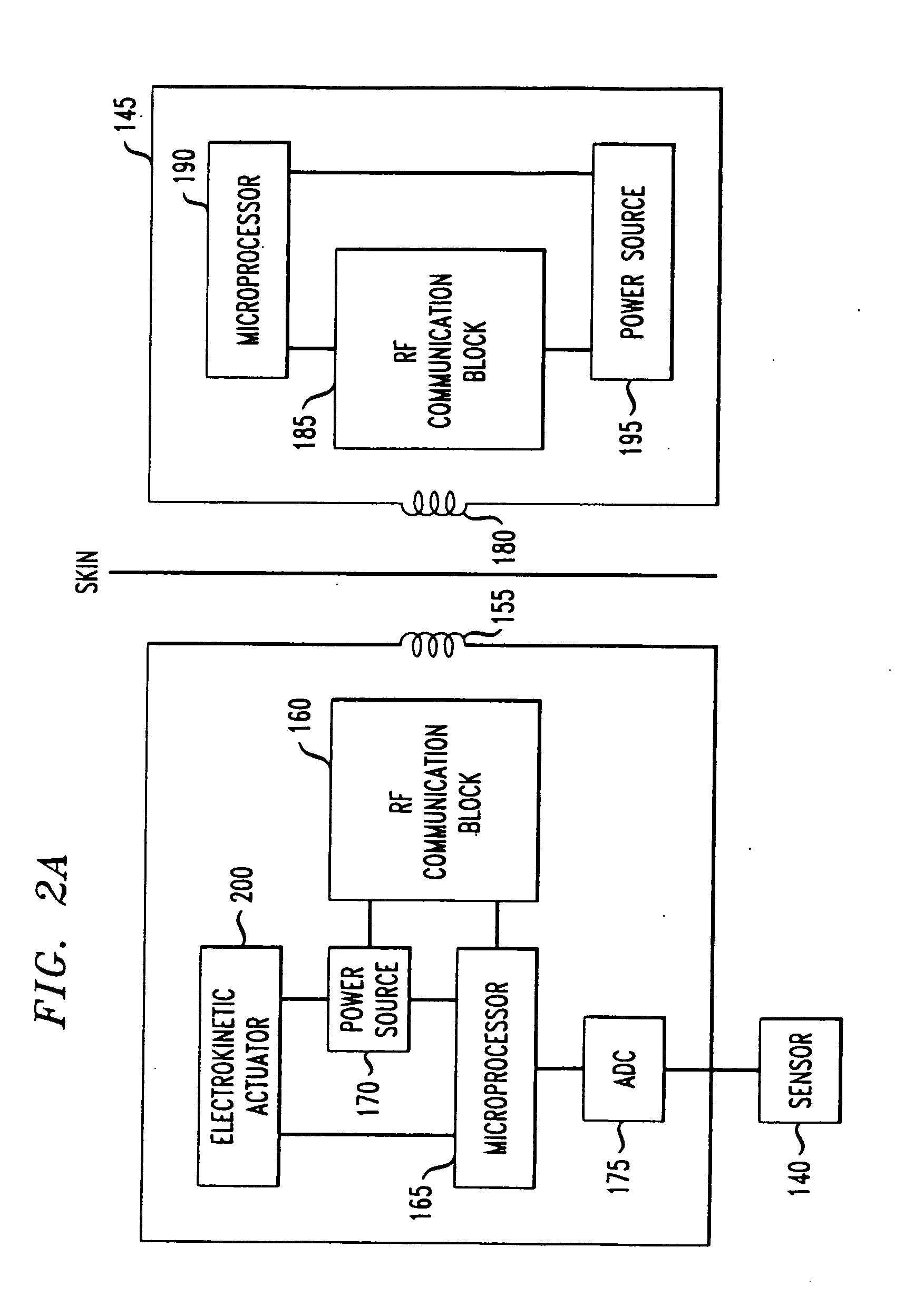
Electrokinetic actuator to titrate fluid flow
An electrokinetic actuator for fluid flow titration including two chambers separated from one another by a porous dielectric disposed therebetween. A plurality of electrodes are disposed about a perimeter of the first and second chambers. Polar electrolyte disposed within the actuator is able to pass through the porous dielectric between the first and second chambers upon the application of an electric field or electric potential to the plural electrodes. A mechanical valve actuation mechanism connected to the second chamber allows for fine titration of fluid flow using electro-osmosis, including full-flow and / or complete cut-off. The polar electrolyte is isolated to prohibit intermixing with a fluid being titrated (such as cerebrospinal fluid).
Owner:CODMAN NEURO SCI
Variable charge films for controlling microfluidic flow
ActiveUS20060065529A1Separation efficiency can be improvedEasy to separateSludge treatmentWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCharged polymersMaterials science
A microfluidic device for carrying a liquid, the device comprising a microfluidic channel having an interior wall and a polyelectrolyte film on the interior wall whereby liquid carried by the channel contacts the polyelectrolyte film, the polyelectrolyte film having a thickness of about 1 to about 1000 nanometers and comprising an interpenetrating network of a predominantly positively charged polymer and a predominantly negatively charged polymer, the predominantly positively charged polymer, the predominantly negatively charged polymer or both containing (i) a pH insensitive positively or negatively charged repeat unit having a pKa greater than 9 or less than 3, and (ii) a pH sensitive repeat unit, the pH sensitive repeat unit having a pKa of 3 to 9, whereby the pH of liquid in the microfluidic channel may be used to control the velocity or direction of electroosmotic flow of the liquid within said microfluidic channel.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Flow device
Liquid flow devices, particularly microfluidic devices, containing solid porous materials. Flow in the devices can be pressure-driven flow and / or electroosmotic flow. The porous materials are preferably pre-shaped, for example divided from a sheet of porous material, so that they can be assembled with liquid-impermeable barrier materials around them. The devices can for example be prepared by lamination. A wide variety of devices, including mixing devices, is disclosed. A mixing device is illustrated in FIG. 23.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI PTE LTD
Method for preparing fresh-water ice by utilizing seawater and brackish water
ActiveCN103086529AApplicable to the needs of fishing and preservationSuitable for industrial productionGeneral water supply conservationLighting and heating apparatusFiltration membraneDihydrogen oxide
The invention relates to a method for preparing fresh-water ice by utilizing sweater and brackish water. The existing ice marker only has a pure ice making function and does not have a desalting function. The method comprises the following steps of: performing primary filtration, secondary filtration, tertiary filtration and quaternary filtration on the seawater or the brackish water sequentially through a multi-medium filter, a security filter, a micro-filtration membrane and an ultra-filtration membrane, so as to obtain the quaternary filtered fluid; desalting the quaternary filtered fluid by virtue of a separating method of membrane distillation, forward osmosis or electro-osmosis to obtain desalted water with the purity greater than and equal to 99.9%; and obtaining the fresh-water ice through air-cooling or water-cooling condensing of the desalted water. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the fresh-water ice can be automatically prepared by utilizing the seawater or the brackish water; when the inlet water is the seawater or the brackish water with salinity higher than 2%, the fresh-water ice can be prepared through multi-medium filtration, security filtration, micro filtration, ultra-filtration and salt-water separating systems as well as an ice making system, so that the method is especially applicable to the needs of catching and fresh-keeping of ocean fishing vessels.
Owner:NINGBO WANJIE WATER TECH
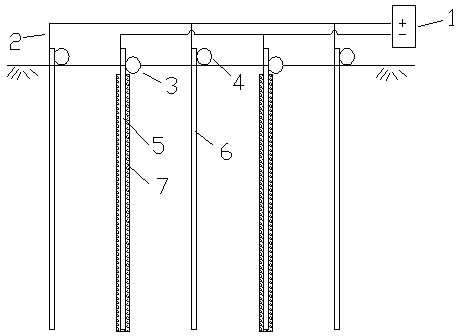
In-situ treatment method for electrically repairing heavy metal contaminated soil based on plastic electrode
InactiveCN104368596AEfficient removalEasy to operateContaminated soil reclamationWater dischargeElectrokinetic remediation
The invention relates to an in-situ treatment method for electrically repairing heavy metal contaminated soil based on a plastic electrode. The in-situ treatment method is characterized by comprising the following steps: step I, determining the treatment depth of contaminated soil by performing soil experiment; step II, leveling ground; step III, performing water irrigation and pre-soaking on soil with the water content of less than 30%; step IV, distributing an anode plastic electrode (6) and a cathode plastic electrode (5); step V, distributing a water discharge pipe (3) and a water filling pipe (4); step VI, respectively connecting the cathode plastic electrode (5) and the anode plastic electrode (6) by using conducting wires (2), and gathering the cathode plastic electrode (5) and the anode plastic electrode (6) to be connected to positive and negative electrodes of a direct current power supply (1); and step VII, powering on the direct current power supply (1), and starting electro-osmosis treatment. The in-situ treatment method for electrically repairing the heavy metal contaminated soil based on the plastic electrode, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages that the in-situ treatment method can be used for rapidly reducing the heavy metal content of a soil body, and is relatively high in environmental protection performance.
Owner:江阴市华宏盈飞电渗科技有限公司
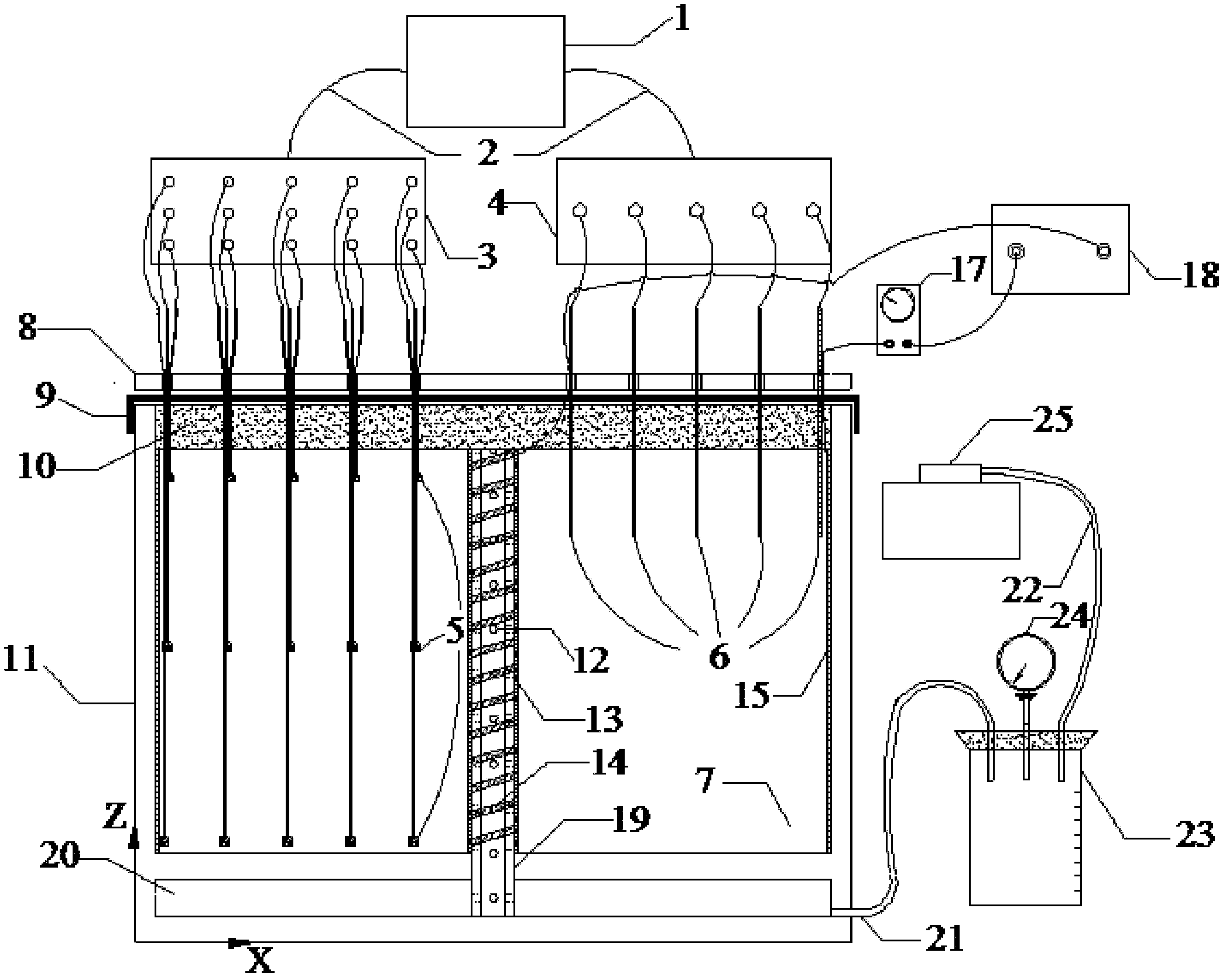
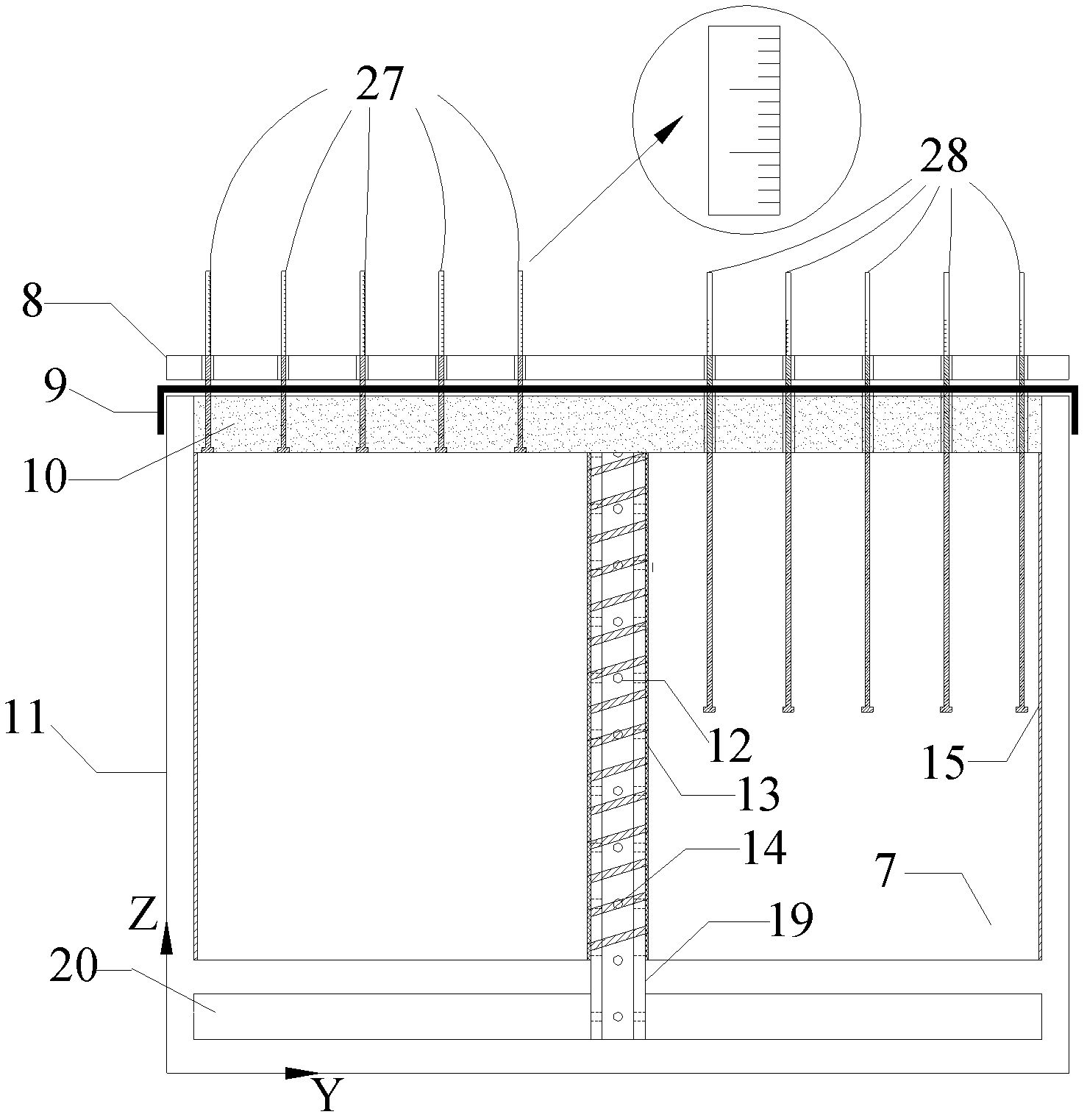
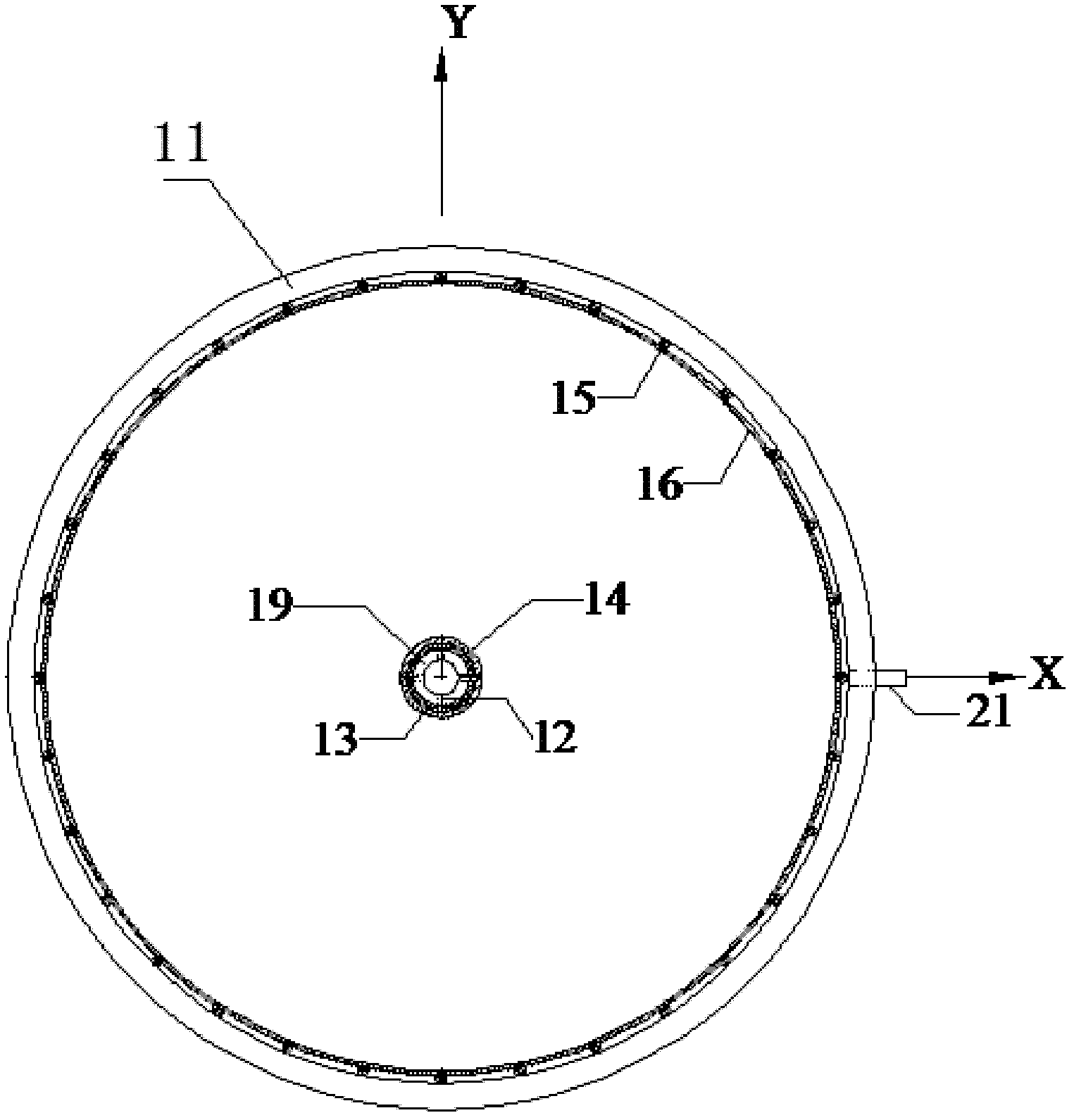
Indoor vacuum electro-osmosis combined solidification tester
ActiveCN102565139AHigh degree of automationReliable dataMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEarth material testingVacuum pumpMaterials science
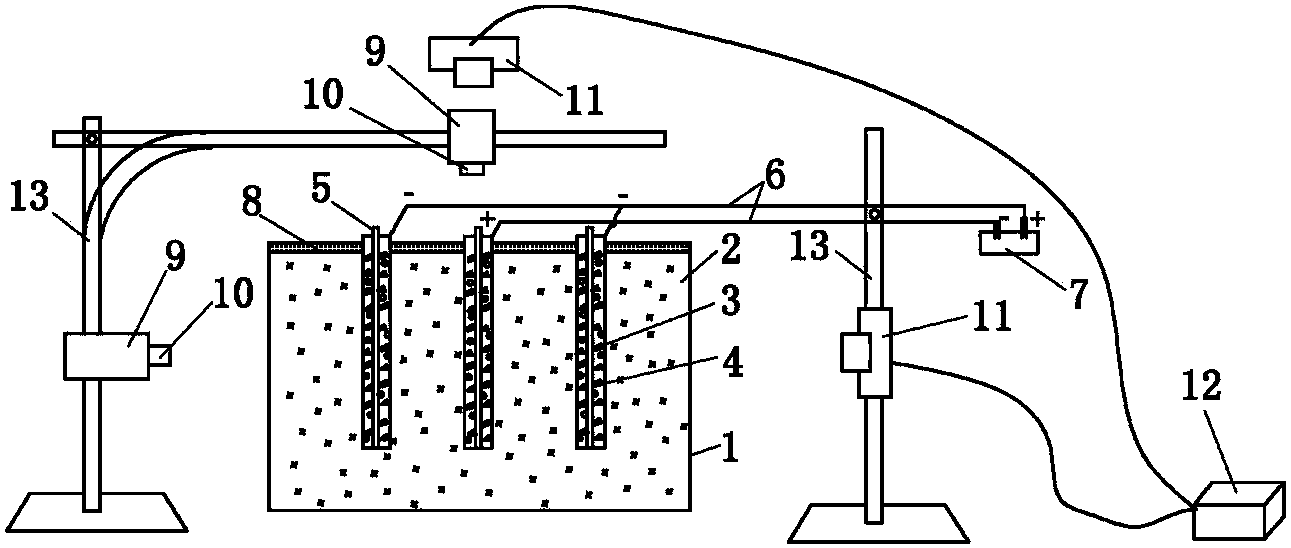
The invention relates to an indoor vacuum electro-osmosis combined solidification tester. An anode iron wire is arranged around a main cylinder and is connected with electrode collars. The soil sample layer and the water storage layer of the main cylinder are communicated through a vertical drain pipe. The vertical drain pipe is covered by a layer of geotextile. A cathode iron wire is wound outside the geotextile. The cathode iron wire, the anode iron wire, an ampere meter and a power supply are serially connected to form a loop. Four rows of guide holes are centrosymmetrically arranged on a top plate at the upper part of the main cylinder. Hole pressure sensors, level sensors, surface settlement marks and layered settlement marks respectively penetrate through the four rows of guide holes. The sensors are connected with a computer through acquisition instruments. A water storage layer at the lower layer of the main cylinder is communicated with a gas-water separation device. The upper part of the gas-water separation device is communicated with a vacuum meter and a vacuum pump. The indoor vacuum electro-osmosis combined solidification tester can be used for conducting indoor exploration tests to different soil body samples through a vacuum electro-osmosis combined effect or a single effect, can monitor the real-time change situation of various parameters in soil samples in the process and can quantitatively analyze the solidification result.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
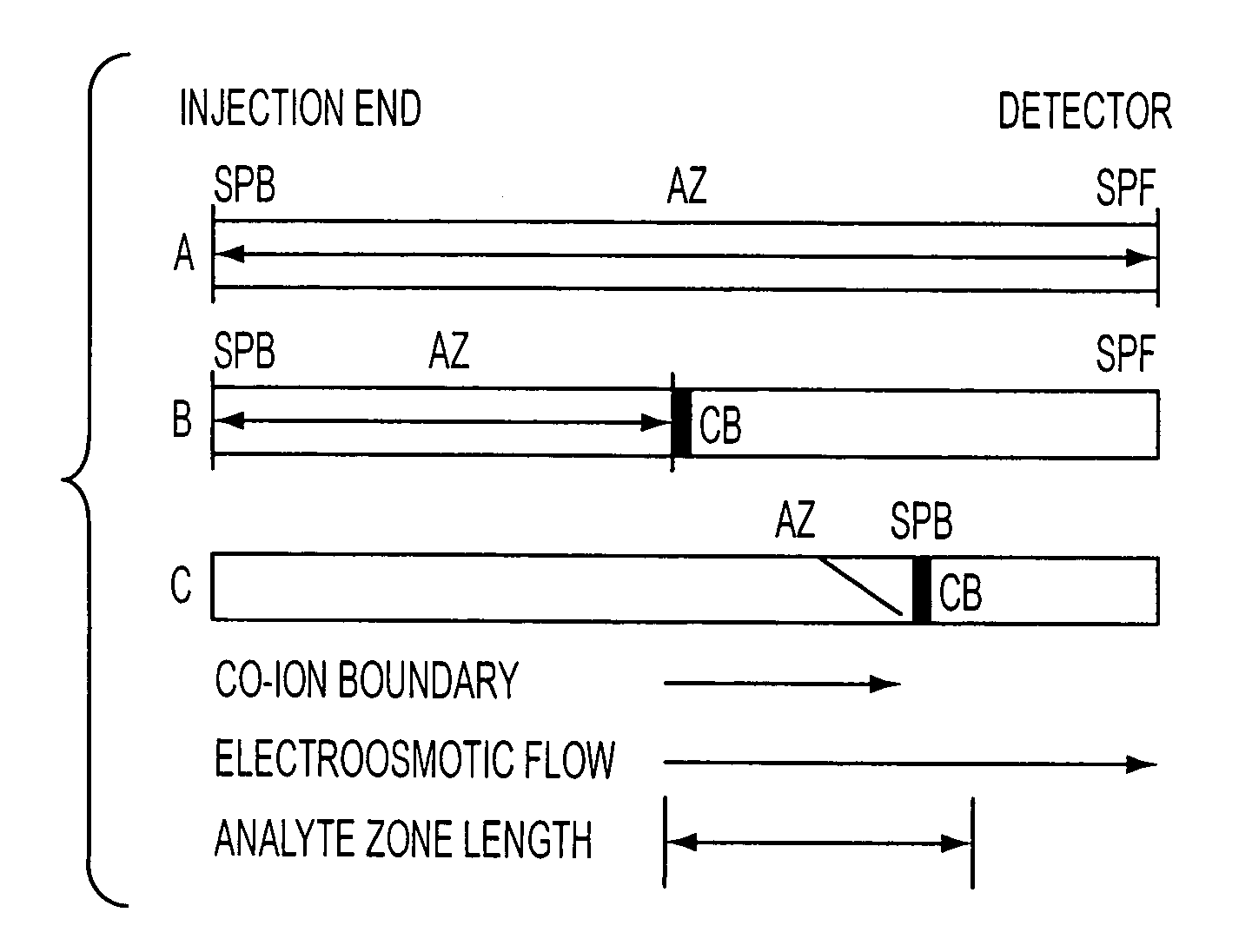
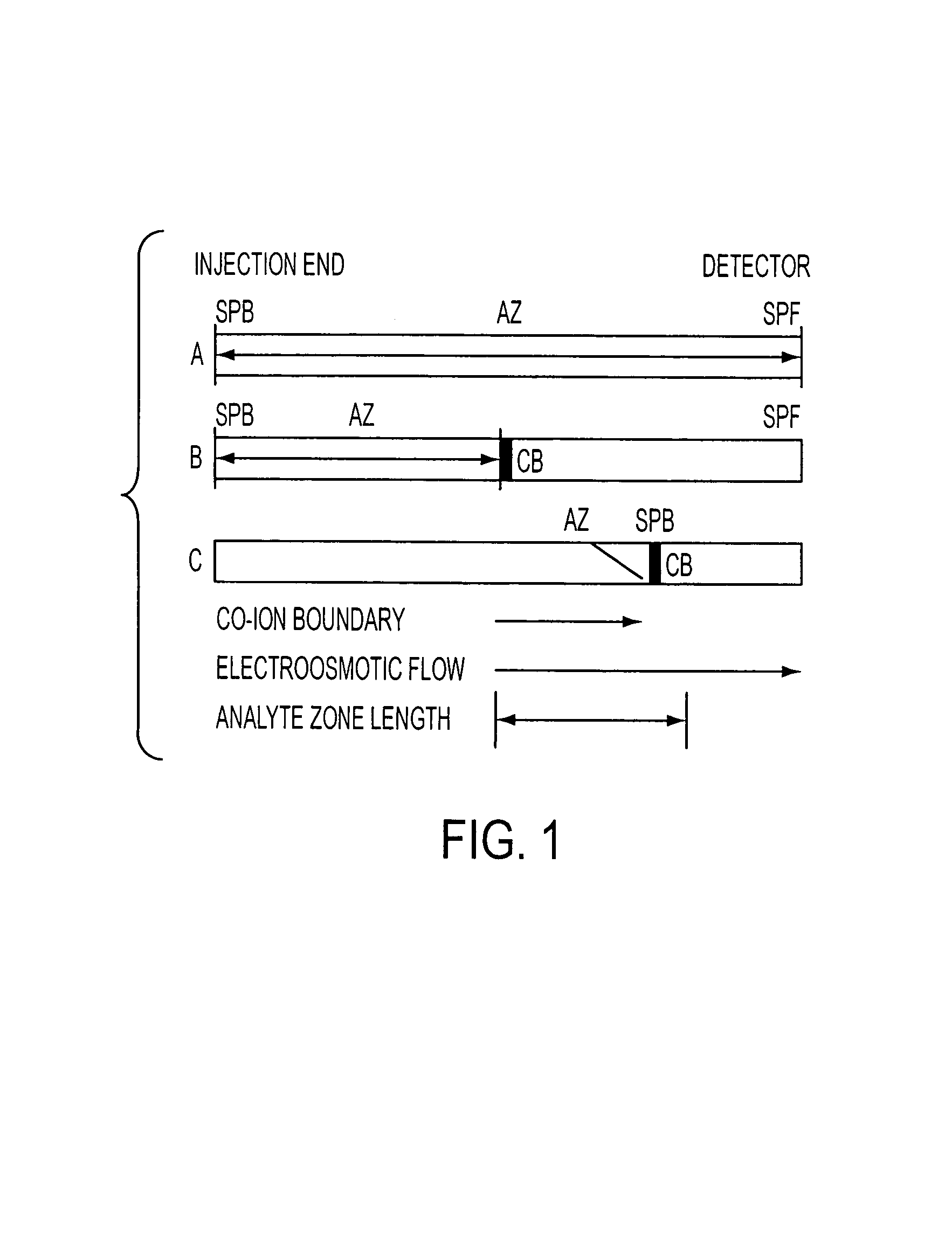
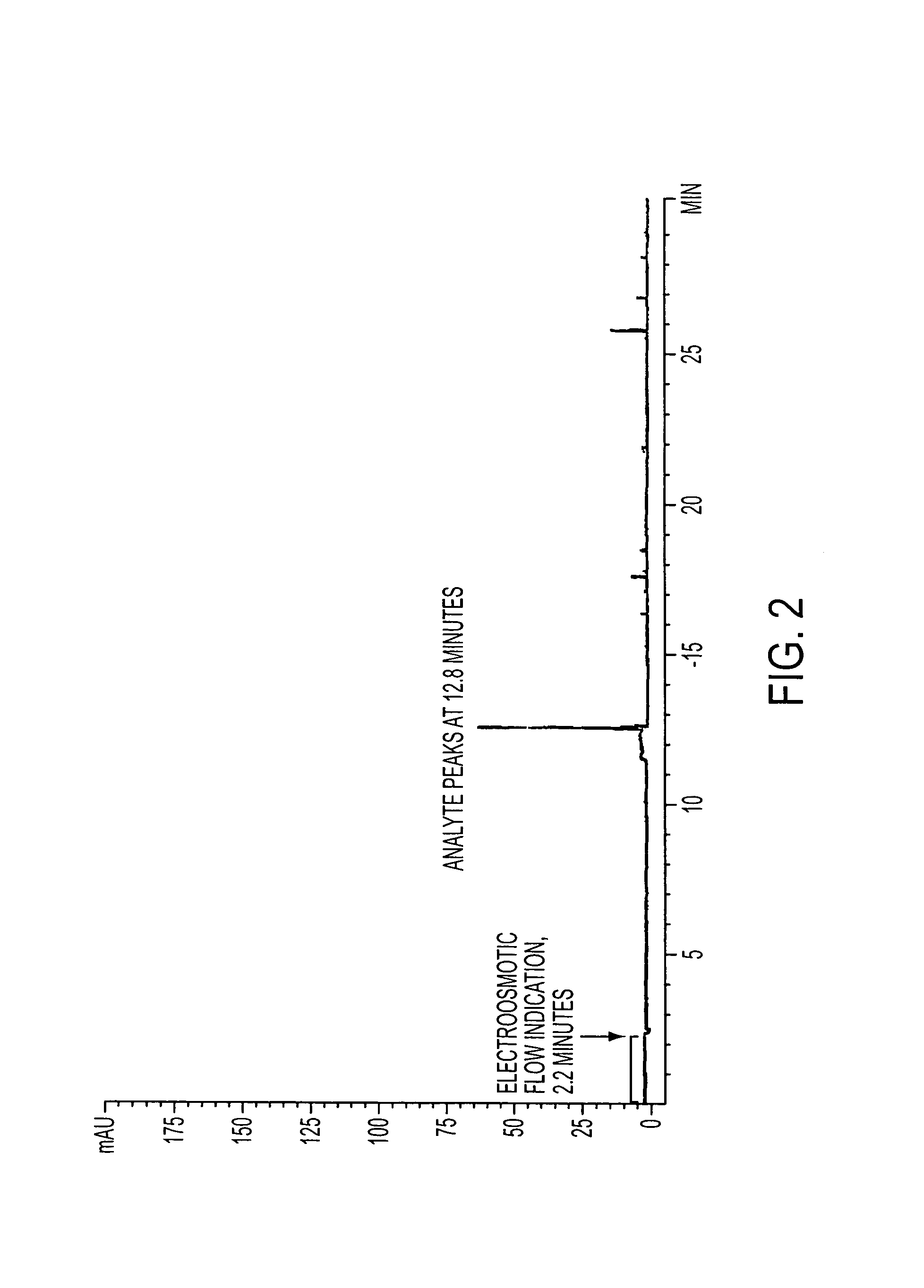
Method for orthogonal analyte stacking/injection systems in electrophoresis
InactiveUS7223325B2High resolutionFaster and high injectionSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary volumePresent method
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
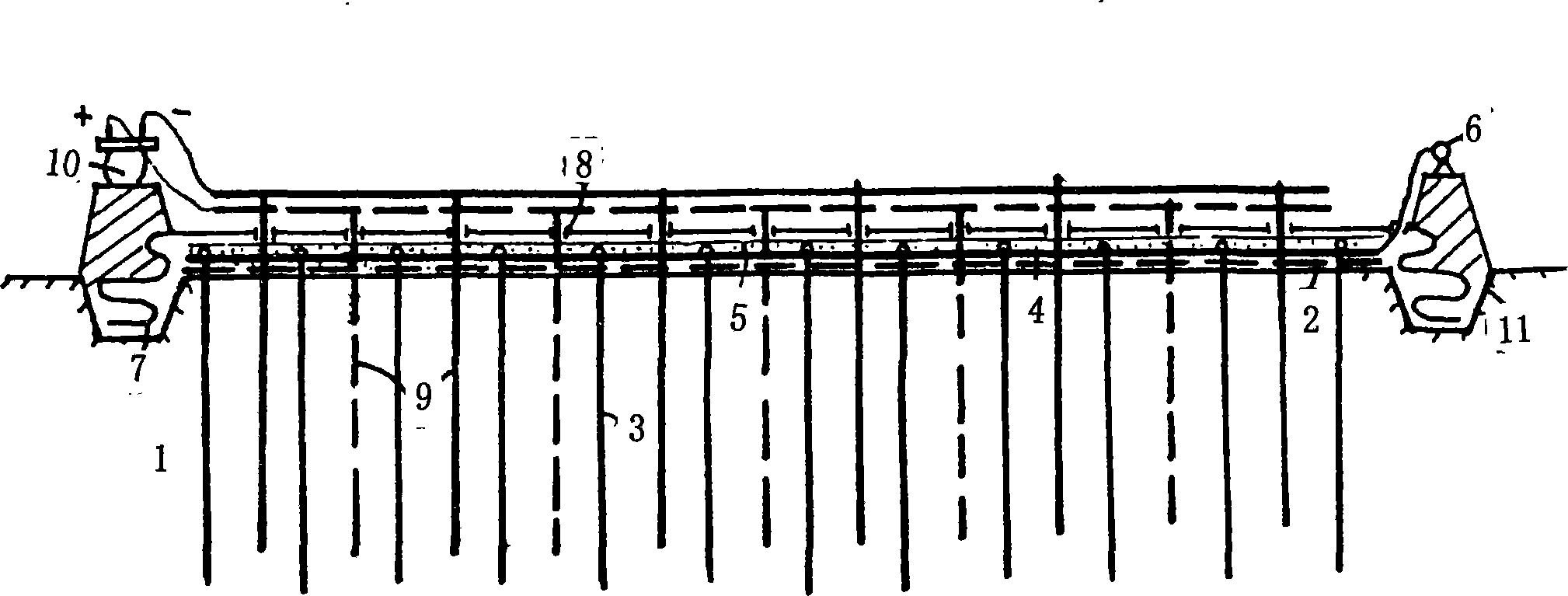
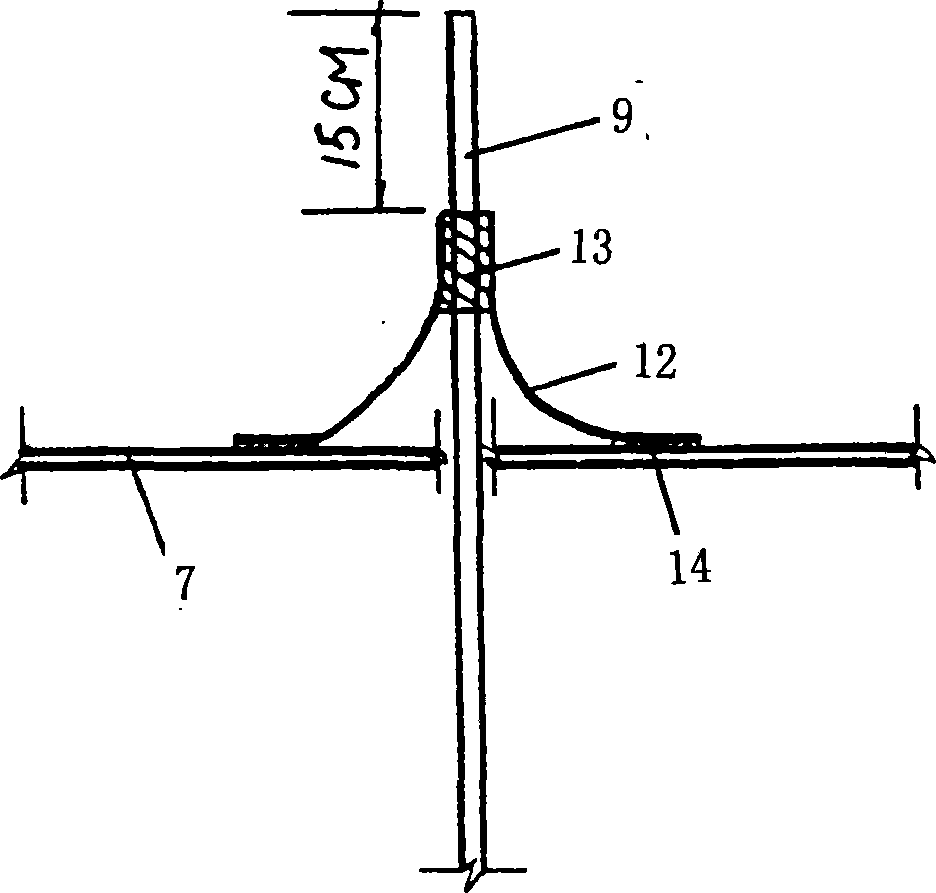
Soft groundsill fastening method based on vacuum electroosmosis composite preloading method
InactiveCN101245592AConsolidation Index ImprovementGood value for moneySoil preservationVacuum pumpingSoil science
The invention relates to a reinforcing method of a soft soil ground based on a vacuum electro-osmotic compound preloading method, and aims at solving the problems that the effective vacuum-pumping time is short, the construction period is long and the intensity of the soft soil in a site is low after reinforced when using the existing vacuum preloading method to process the superfine soil particles into the soft soil ground of a main body; the method comprises the following steps: (1) the vacuum preloading method is adopted to reinforce the soft soil of the site once; (2) a secondary reinforcement is done for the soft soil of the site by adopting a vacuum preloading combined electro-osmosis method; (3) vibrating rolling and leveling of the site are carried out finally; the reinforcing method has the advantages of high consolidation index, good cost performance and short construction period.
Owner:张志铁
Microfluidic pumps and mixers driven by induced-charge electro-osmosis
This invention provides devices and apparatuses comprising the same, for the mixing and pumping of relatively small volumes of fluid. Such devices utilize nonlinear electrokinetics as a primary mechanism for driving fluid flow. Methods of cellular analysis and high-throughput, multi-step product formation using, devices of this invention are described.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Process and apparatus for treating sludge by the combined action of electro-osmosis and pressure
InactiveUS20050016870A1Easy to dehydrateReduce distanceCellsPolycrystalline material growthSludgeEngineering
The present invention relates to a process for treating sludge by the combined action of electro-osmosis and pressure. This process comprises providing a cell for treating the sludge, the cell comprising at least two electrodes including at least one cathode and at least one anode. At least one of the electrodes is movable, and at least one of the electrodes is perforated so as to drain effluents. Then, the sludge is introduced into the cell between the at least two electrodes, each of the electrodes defining a surface adapted to constantly contact the sludge. Then, the sludge is submitted to an electric current by applying a voltage to the electrodes, and applying a pressure to the sludge. by means of the at least one movable electrode so as to permit a constant contact between the surfaces and the sludge. An apparatus for carrying out such a process is also disclosed.
Owner:GL&V CANADA INC
Electro-osmosis consolidation shearing device
InactiveCN103278402AAvoid disturbing influenceStable and continuous loadingWater resource protectionMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesStability parameterSoft clay
The invention discloses an electro-osmosis consolidation shearing device. The electro-osmosis consolidation shearing device comprises a frame, a vertical loading system, a horizontal shearing loading system and an electric insulation experiment box, wherein the frame comprises a bottom frame and a portal frame; the bottom frame is fixedly connected with the portal frame; the vertical loading system is fixedly connected to the upper wall of the portal frame, and comprises a shaft pressure air cylinder, a shaft pressure displacement electronic sensor and a shaft force sensor; the electric insulation experiment box comprises electrode tubes, an upper shearing box and a lower shearing box; during an electro-osmosis experiment, soil is placed in the upper shearing box and the lower shearing box, and the electrode tubes are inserted into the soil. The electro-osmosis consolidation shearing device is high in experiment efficiency, small in occupation area, convenient to operate, compact in structure, accurate and reliable in determination result, and applicable to an indoor or field experiment for the electro-osmosis test on soft clay and mucky soil in eastern coastal regions and the Pearl River Delta region, and serves for solving the related engineering problems of foundation deformation and stability parameter determination in geotechnical engineering problems of foundation treatment, coastal reclamation, port revetment and the like.
Owner:GUANGXI COMM PLANNING SURVEYING & DESIGNING INST +2
Grouting and chemical electro osmosis combined discrete material pile model testing device and testing method
InactiveCN103940853ASimple and fast operationIncrease awarenessMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEarth material testingModel testingEngineering
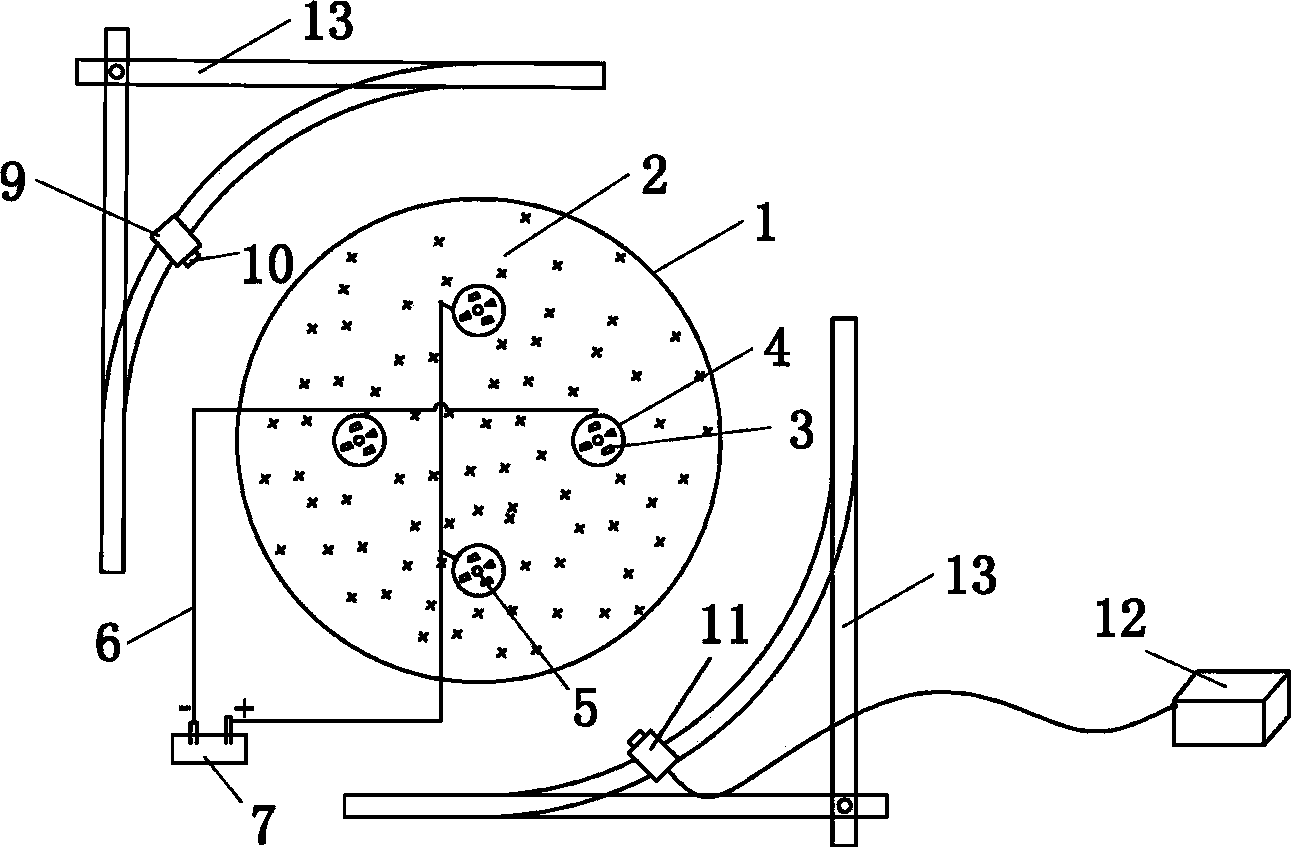
The invention discloses a grouting and chemical electro osmosis combined discrete material pile model testing device and testing method. The testing device is characterized by comprising a transparent model tank, wherein a transparent pressure plate is arranged at the upper part of the transparent model tank, a discrete material pile is arranged in the transparent model tank, an electric geogrid is pre-buried in the outer side of the discrete material pile, the top part of the electric geogrid is connected with the positive electrode and the negative electrode of a direct current power supply by lead wires respectively, a grouting pipe is pre-buried at the center position inside a pile body, the discrete material pile is simulated by water-soluble transparent soil and soil at the periphery of the pile is simulated by oil-soluble transparent soil, one side and the upper part of the outside of the transparent model tank are provided with a laser source arranged on a moving mechanism, a digital camera arranged on the moving mechanism and used for observing the space of the transparent model tank is arranged on the front view surface and the top view surface of the outside of the transparent model tank, and the digital camera is connected with a processing device by a data line. The testing device is simple and convenient to operate and has strong repeatability, and the prepared transparent soil is similar to the natural soil body in property; the testing method can be used for chemical electro osmosis, formation of the grouting pile body, and visual observation and measurement of grout seepage in the soil at the periphery of the pile.
Owner:HUNAN CITY UNIV
Deep strengthening method of vacuum electroosmosis dewatering and low-energy dynamic compaction
InactiveCN101016739AShorten the consolidation timeReduced chance of "rubbery soil"Soil preservationEngineeringPrecipitation
The invention discloses a deep densification method for a vacuum electro osmosis precipitation and a lower energy dynamic consolidation and its construction procedures comprises (1) a vacuum well point precipitation, (2) the vacuum electro osmosis precipitation, (3) the lower energy dynamic consolidation, (4) a vibration rolling and a leveling field, characterized in that a field drainage system should be first constructed before the vacuum well point precipitation proceeded. The method of constructing the field drainage system is that the middle coarse sand bedding is spread on the field, and the bedding which is thicker than 40 centimeters is consisted of a horizontal drainage with a drainage drain, while a plastic drain-board is inserted in the sand bedding and keeps distance of 0.8-1.4 meters between adjacent boards, and the length of the plastic drain-board is equal with a fastening depth, thereby constructing a vertical drainage system, and then a clay layer is spread and compacted on the bedding. An intact drainage system consists of the middle coarse sand bedding and the plastic drain-board in the invention, therefore deep and shallow soft soil is all strengthened, and the power of the lower energy dynamic consolidation is increased thereby expanding the effect depth of the lower energy dynamic consolidation and realizing the deep soft soil fastened.
Owner:张志铁 +1
Resin filling type ion chromatography electrolysis self-regeneration suppressor
ActiveCN102735792AEliminate or mitigate performance impactReduce distortionComponent separationFiberIon chromatography
The invention relates to a resin filling type ion chromatography electrolysis self-regeneration suppressor which is capable of analyzing materials by utilizing electrolysis, electro-osmosis and iron exchange and is used for eliminating countra-ion in a solution and lowering background conductance of a leacheate. The middle layer of the resin filling type ion chromatography electrolysis self-regeneration suppressor provided by the invention is fiber adding and hardening silicon sheet or bulk four-fluorine belt materials. In the vertical direction of a splint, two splint electrolysis chamber flow guide slots are staggered, and the liquid enters into the suppressor from one side, so that the technical problems that the middle layer of the existing resin filling type ion chromatography electrolysis self-regeneration suppressor has strict requirements to the filling materials are solved, the internal chambers are reduced, and base lines and peak shapes are influenced, so that the liquid among layers is easy to leak, and redundant filling materials are extruded so as to cause the sealing difficulty.
Owner:QINGDAO SHENGHAN CHROMATOGRAPH TECH CO LTD
Method for treating deep soft soil foundation by combining chemical electro-osmosis method and vacuum preloading method
InactiveCN102094414AHigh strengthAccelerate the rate of consolidationSoil preservationChemical solutionChemical reaction
The invention discloses a method for treating a deep soft soil foundation by combining a chemical electro-osmosis method and a vacuum preloading method. In the method, vertical porous drain pipes and metal electrodes are inserted and chemical solution is injected into the soft soil foundation, horizontal drain boards and seal geomembranes are laid on the top of a soil layer, direct current is supplied, vacuumization is carried out, and under the action of direct-current electric field force, water with positive charge and cation solution flow to a cathode and anion solution with negative charge flows to an anode to form electro-osmosis and chemical reaction; meanwhile, under the action of internal and external pressure difference formed through vacuumization, water is quickly discharged from the drain pipe in which the cathode is positioned; and the solidification and compactness of the foundation soil are accelerated and the soil strength of the soil is improved. Compared with the common vacuum preloading method, the method has the advantages that: the soft soil treatment depth is increased, the deep layer of the soil of which the vacuum degree is difficult to reduced can be reached, and under the action of the direct-current electric field force, the solidification rate of the soil is improved and the construction period is shortened. Through the method, the construction process is simple, the operability is high, the construction period is short, the quality control and detection are facilitated, and the soil strength is improved obviously.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Tank type electroosmosis sludge soil reproducing method and device thereof
ActiveCN101311133AHave diversityFlexible operationSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningContaminated soil reclamationSludgeEngineering
The invention relates to a tank type electro-osmosis method for reconstructing soil with silt; the method adopts a tank as a silt treatment carrier for electro-osmosis dewatering, and then a vacuum drainage device or / and a vacuum preloading device or / and a static load device or / and a forced ramming device can be additionally arranged according to requirements for improving dewatering efficiency; the assignment of the electrodes of an electro-osmosis device can be in a horizontal way or a vertical way, which is flexible and diversified; the method of the invention has large treatment capacity and can simplify equipment and lower cost to the utmost extent, and high voltage and strong electric current can be applied during electro-osmosis to shorten treatment time and enhance dewatering efficiency.
Owner:陈江涛
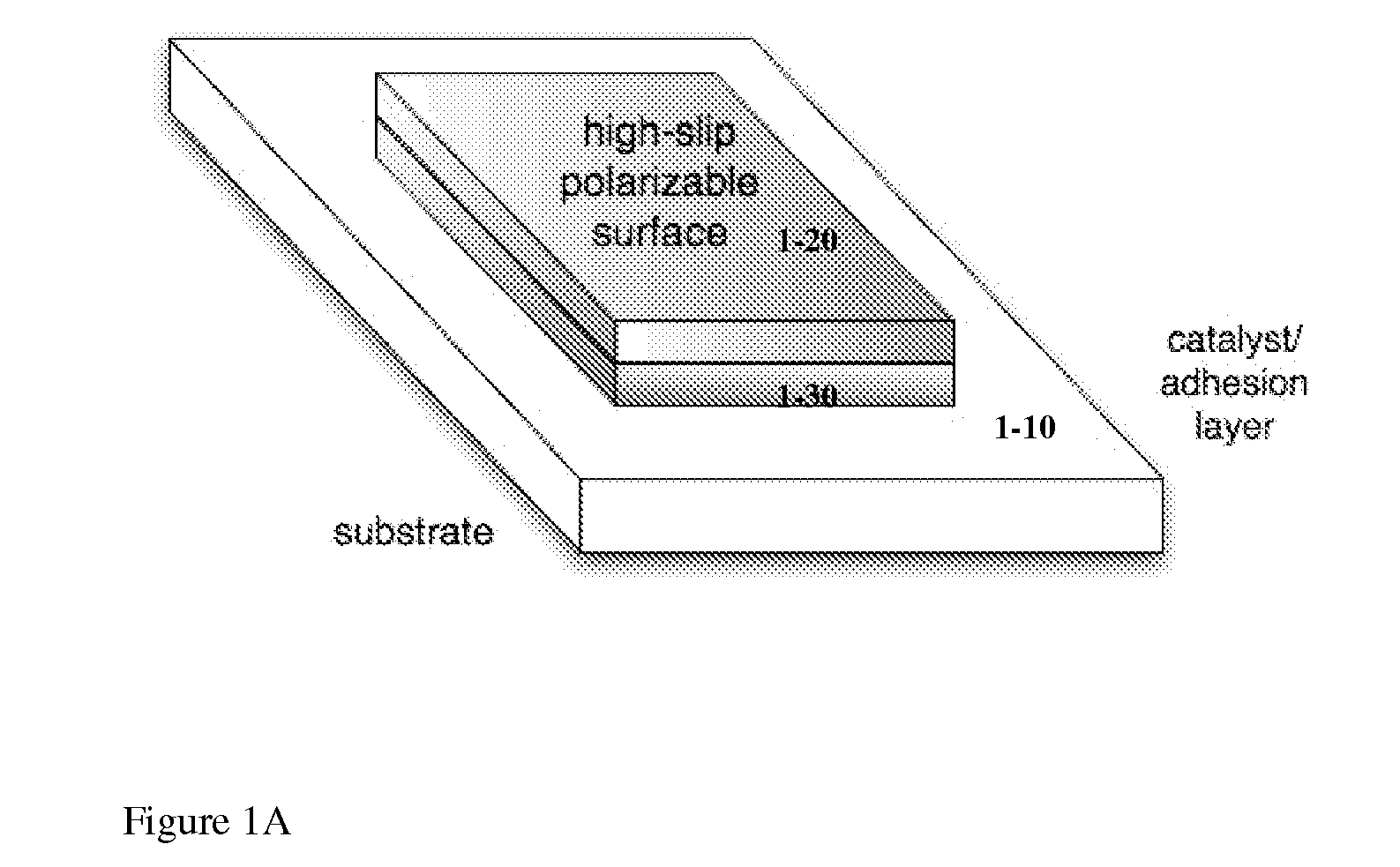
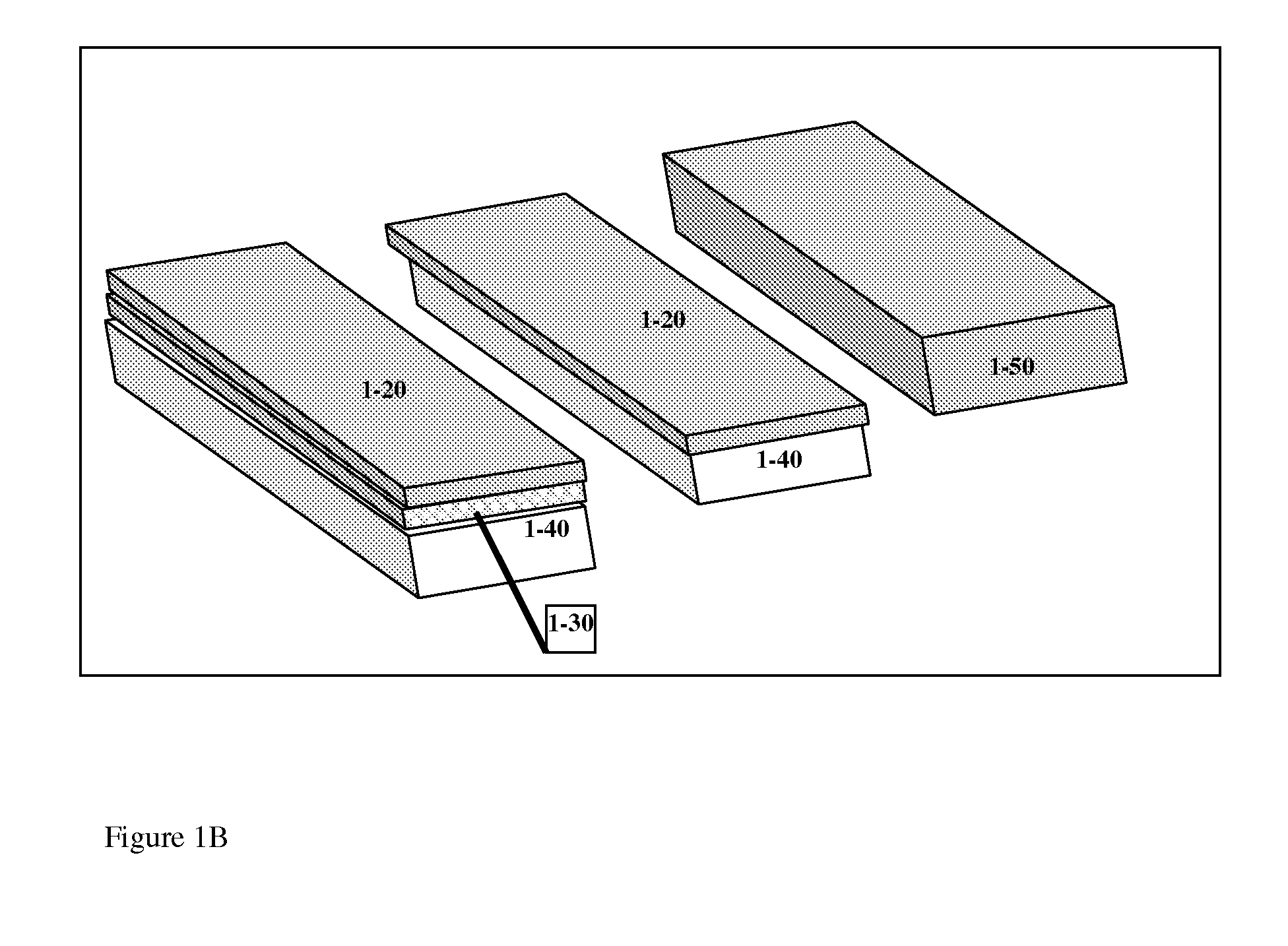
Induced-charge electrokinetics with high-slip polarizable surfaces
InactiveUS20100264032A1Rapid electroosmotic flowEnhanced electrophoretic mobilitySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementInduced-charge electrokineticsNanoparticle
This invention provides devices and apparatuses comprising the same, for fast pumping and mixing of relatively small volumes of electrolytes and ionic fluids and materials suspended thereby. Such devices utilize nonlinear induced-charge electro-osmosis as a primary mechanism for driving fluid flow. Such devices comprise a polarizable surface, which is incorporated in the electrodes or pumping elements of the devices as well as a material, which promotes hydrodynamic slip at a region proximal thereto, when the device is subjected to non-linear electro-osmotic flow. Examples of such materials are provided. This invention also provides nanoparticles and microparticles incorporating such materials to enhance nonlinear induced-charge electrophoretic motion. Methods of use of the devices and particles of this invention are described.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for rapidly measuring reinforcing steel tarnishing criticality chlorine ion concentration
InactiveCN101226167AReduce critical concentration determination timeWon't happenMaterial electrochemical variablesAutomatic controlSteel bar
The invention discloses a method for quickly measuring steel bar corrosion critical chloride ion density, belonging to steel corrosion detection technique. The method comprises arranging prepared a concrete sample with a non-immersion reference electrode and an immersion working electrode into an electro-osmosis tank, adding 3-20V direct-current voltages at two sides of the concrete sample, detecting the current of the macro battery composed of the immersion working electrode and the non-immersion reference electrode, if the macro battery current reaches the value of corrosion germination, stopping the electro-osmosis test, or else, continuing and repeating the processes as adding voltage, stopping powering and macro battery current detection until the macro battery current reaches the value of corrosion germination, stopping the electro-osmosis test. And after the electro-osmosis test, the invention uses potential titration to test chloride ion density in concrete. The inventive method can significantly reduce critical chloride ion density test time and realize automatic test control via detecting macro battery current.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
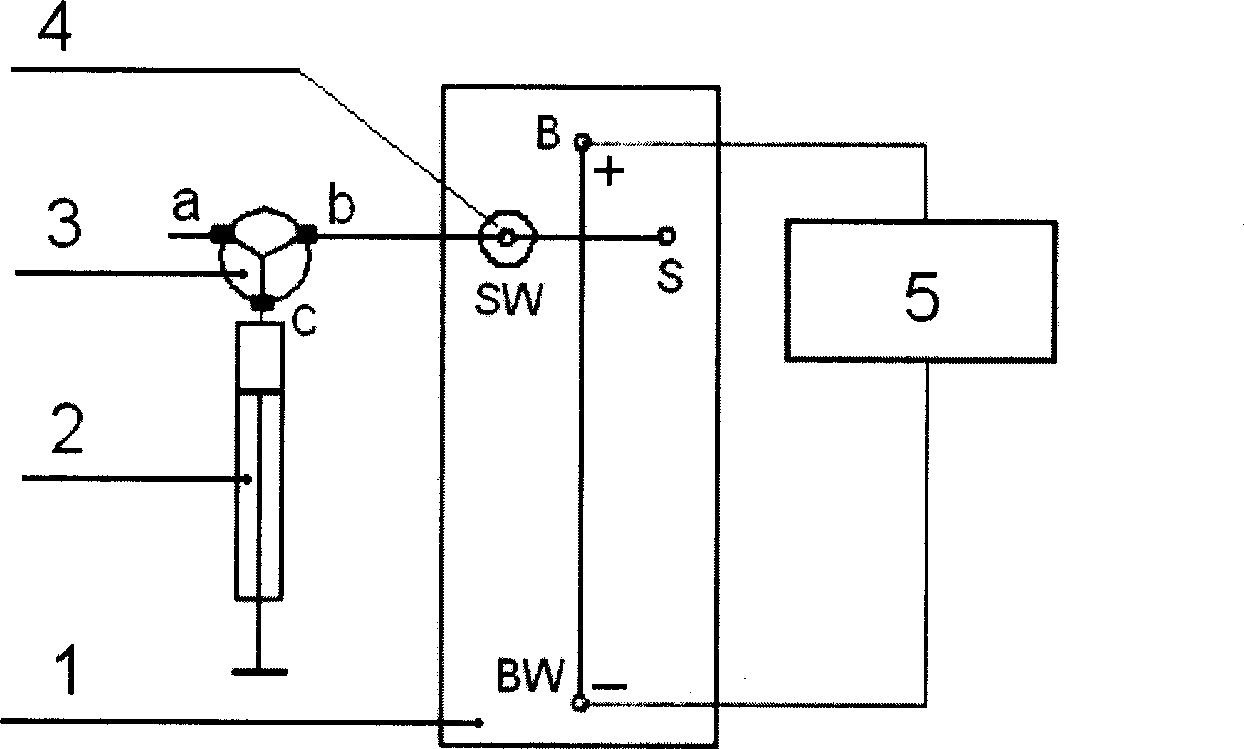
Micro flow control chip capillary electrophoresis negative pressure sampling method
InactiveCN1737562AAvoid discriminatory effectsAvoid dependenceSemi-permeable membranesFixed microstructural devicesElectricityCapillary electrophoresis
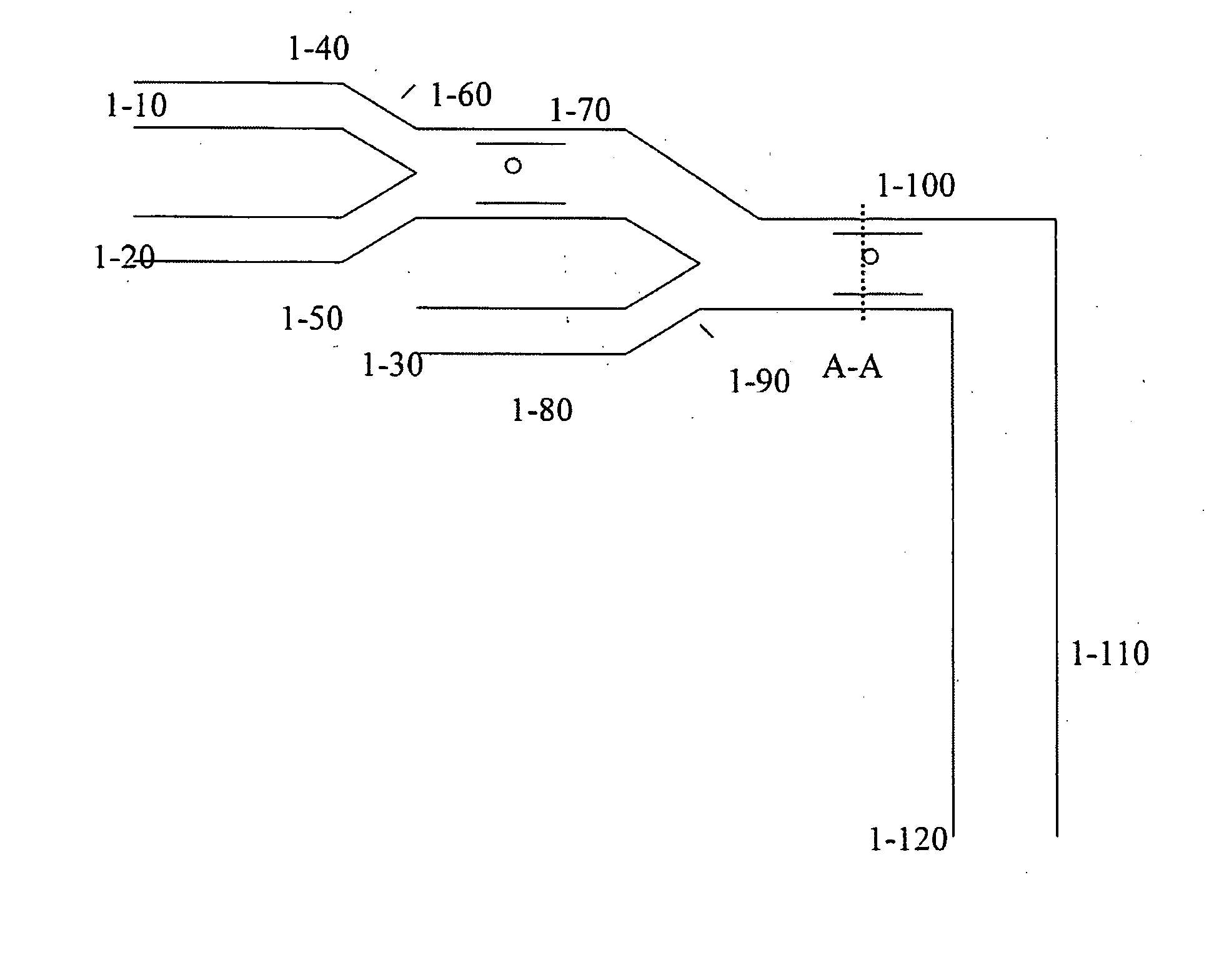
This invention relates to one electrophoresis sample in and isolation method of micro flow control capillary, which is characterized by the following: using micro flow control chip network structure; adopting column plug pump and taking sample from waste pool air through three-way valve and interface to form negative pressure; the micro flow chip and other sample solution and buffer liquid flowing downward and forming stable sample plug in the crossing place of sample in channel and isolation channel and connecting the valve with air through three-way valve.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
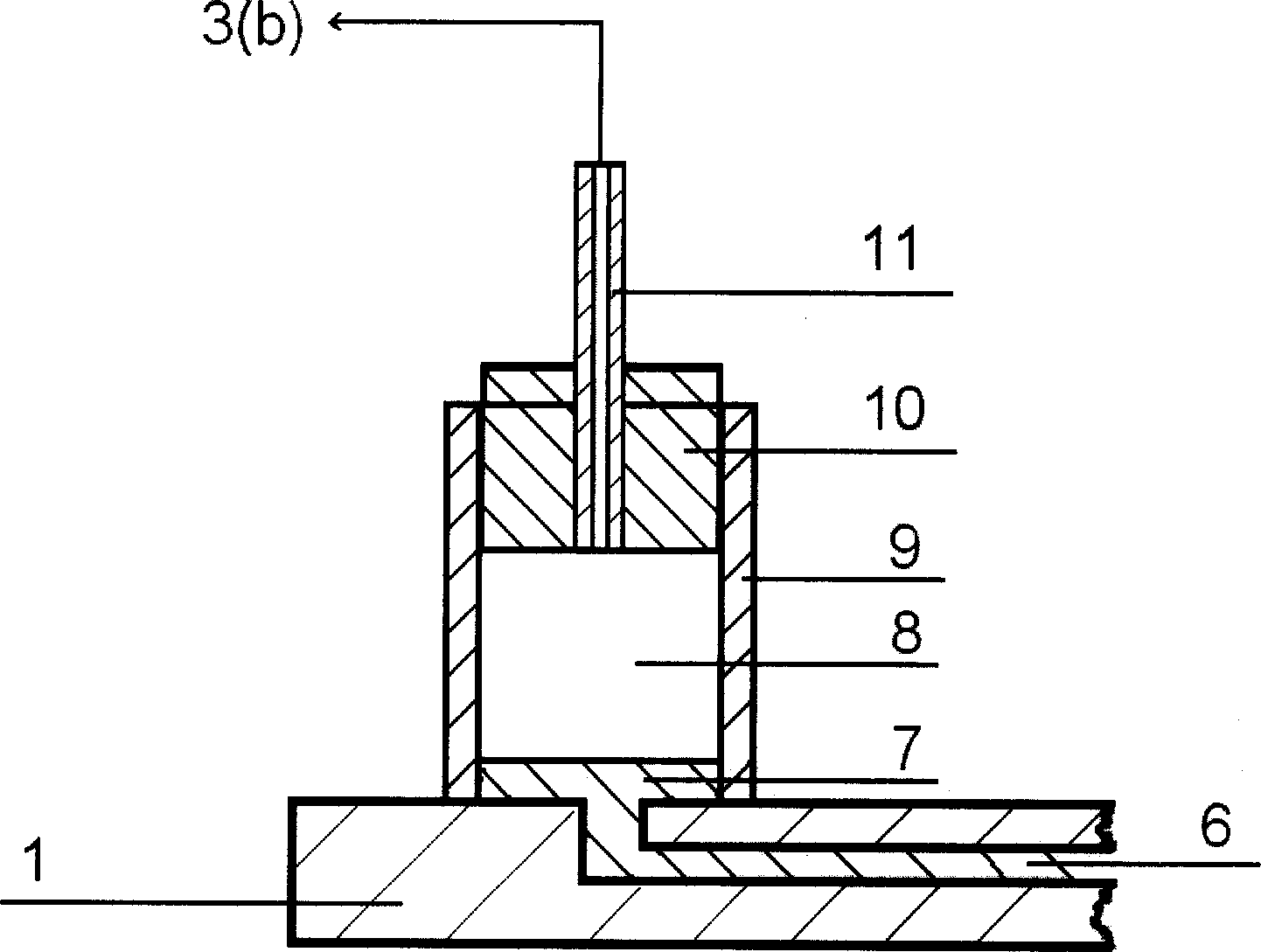
Method for stabilizing foundation based on electro-osmosis technique and bucket foundation negative pressure technique
InactiveCN101824819AAdd depthImprove reinforcement effectSoil preservationSuction forceWater discharge
The invention discloses a method for stabilizing a foundation based on a bucket foundation electro-osmosis technique and a negative pressure technique. The method comprises the following steps of; 1) reserving holes on a cover plate on the bucket top of a bucket foundation, vertically and fixedly connecting a water discharge pipe under the cover plate of the bucket top and reserving sieve pores on the pipe wall, and laying geotextile under the cover plate of the bucket top; 2) arranging an electro-osmosis anode on the inner wall of the bucket foundation and an electro-osmosis cathode on the water discharge pipe and connecting the anode and the cathode with an electro-osmosis water discharge power supply respectively; 3) sucking the bucket foundation by using the reserved holes to form a negative pressure and sinking the bucket foundation under the negative pressure in place; and 4) drawing water and / or air out of the bucket foundation by negative pressure equipment through the water discharge pipe, and stabilizing the foundation under the negative pressure according to the pre-pressing value of the foundation soil. The method has the advantages that: the foundation soil is over-consolidated through the foundation per se by using the electro-osmosis technique and the suction force applied by the negative pressure equipment so as to effectively increase the depth and the width of the foundation stabilization and improve the bearing capacity and the stability of the bucket foundation; and the method also has the advantages of simple equipment, simple and convenient construction, short construction period, obvious economic benefit and low comprehensive construction cost.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
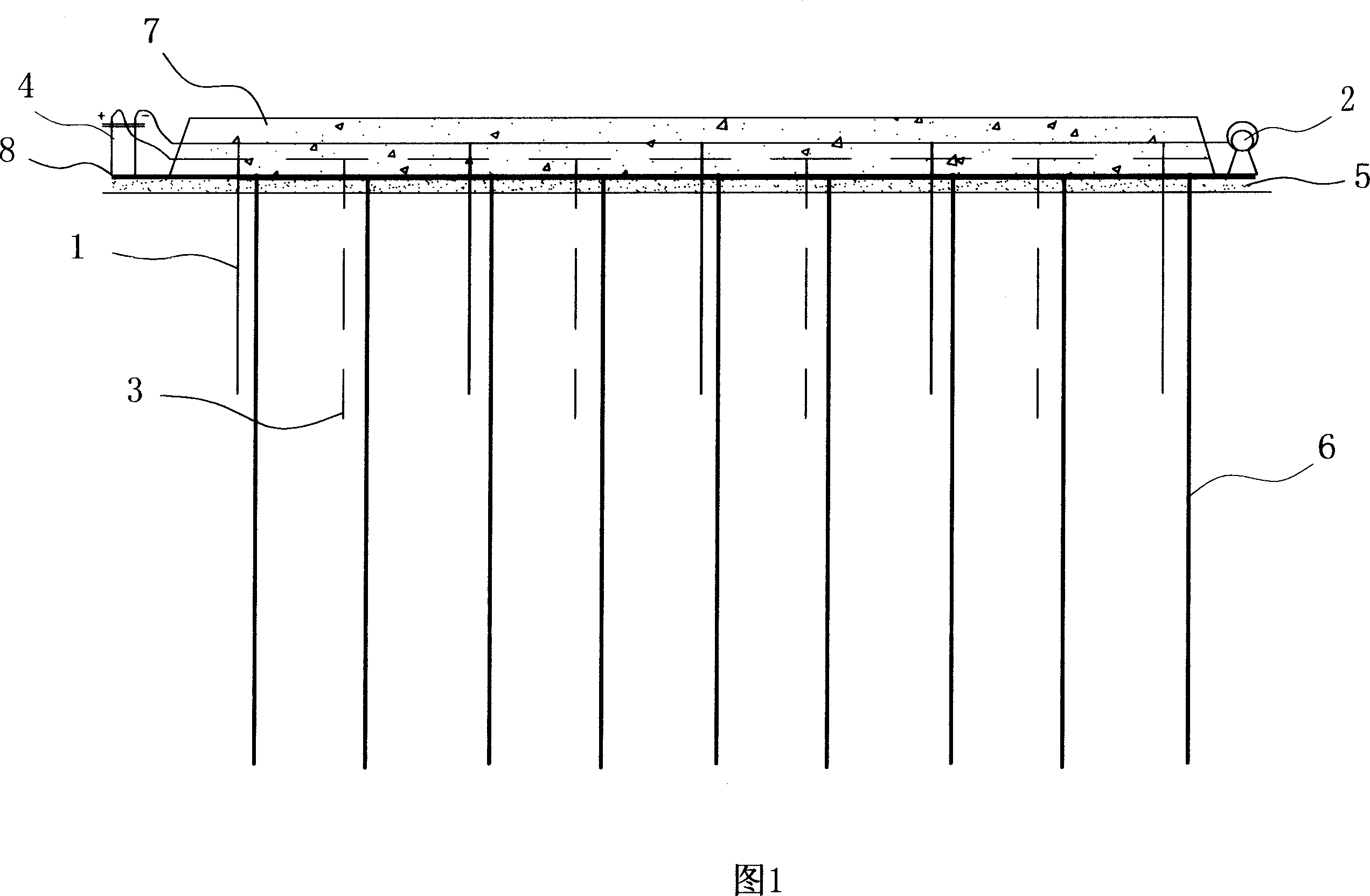
Device and method for preparative electrophoresis
InactiveUS20050072675A1Avoid flowReduce conductivitySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisMicrofiltration membrane
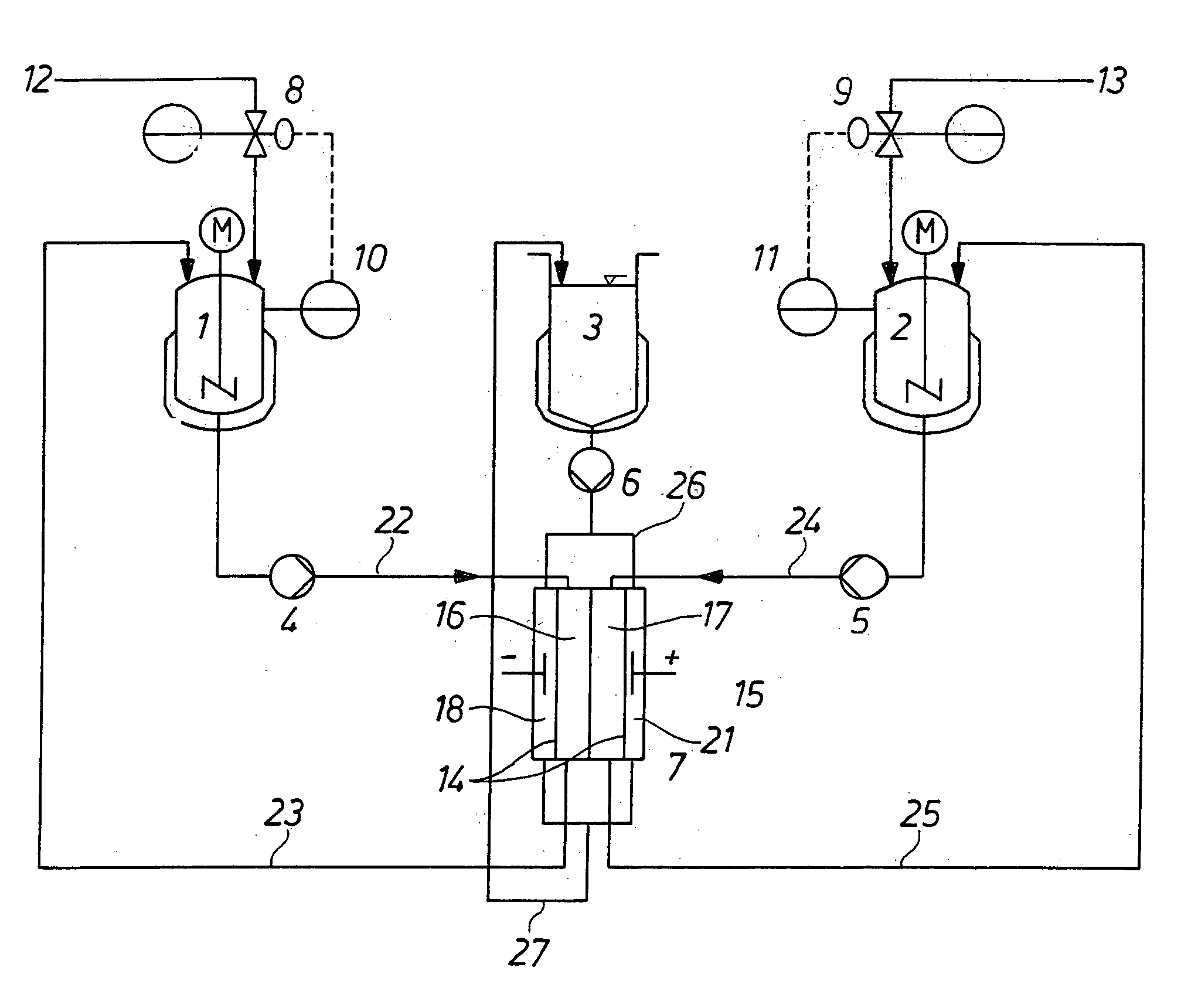
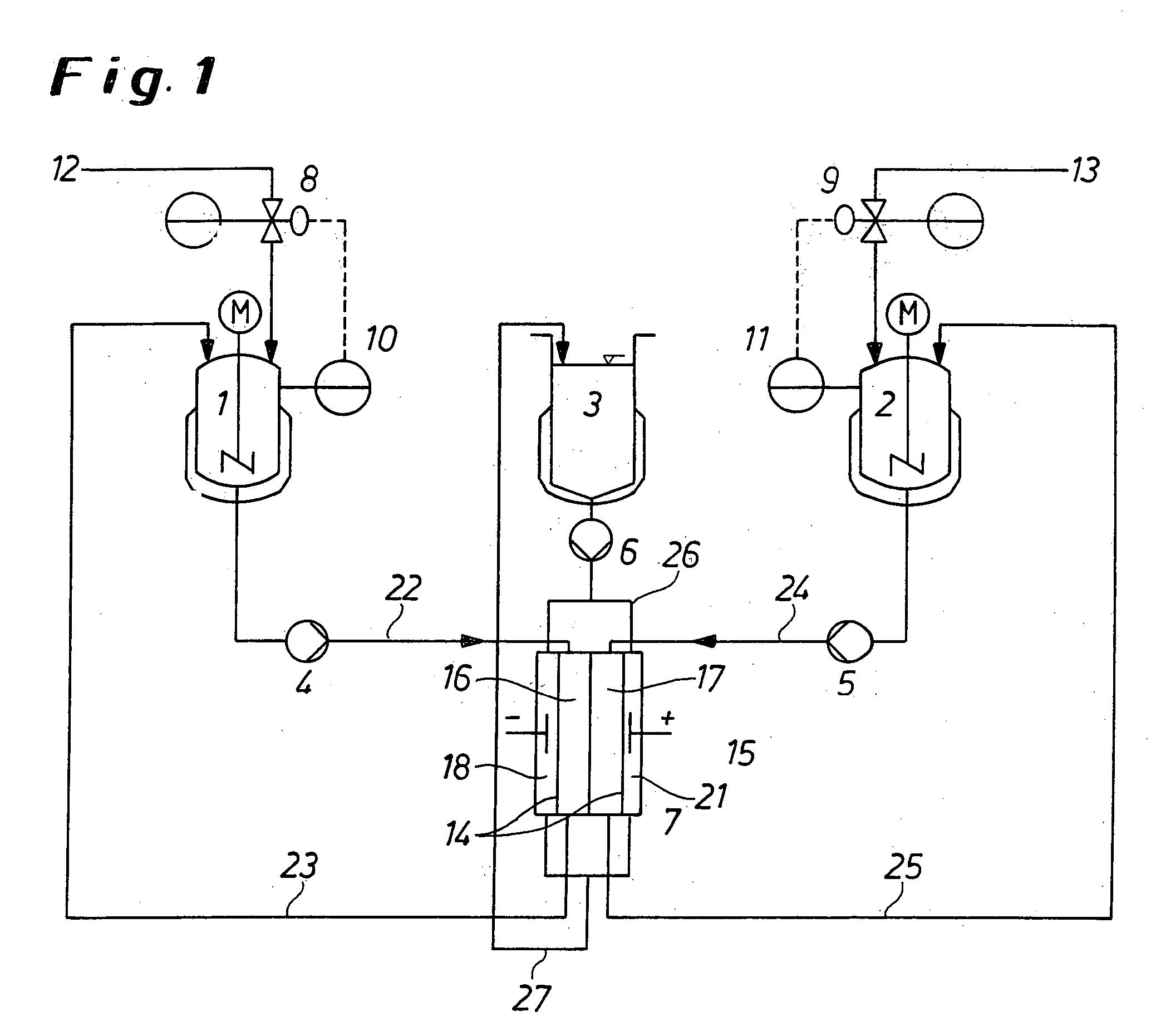
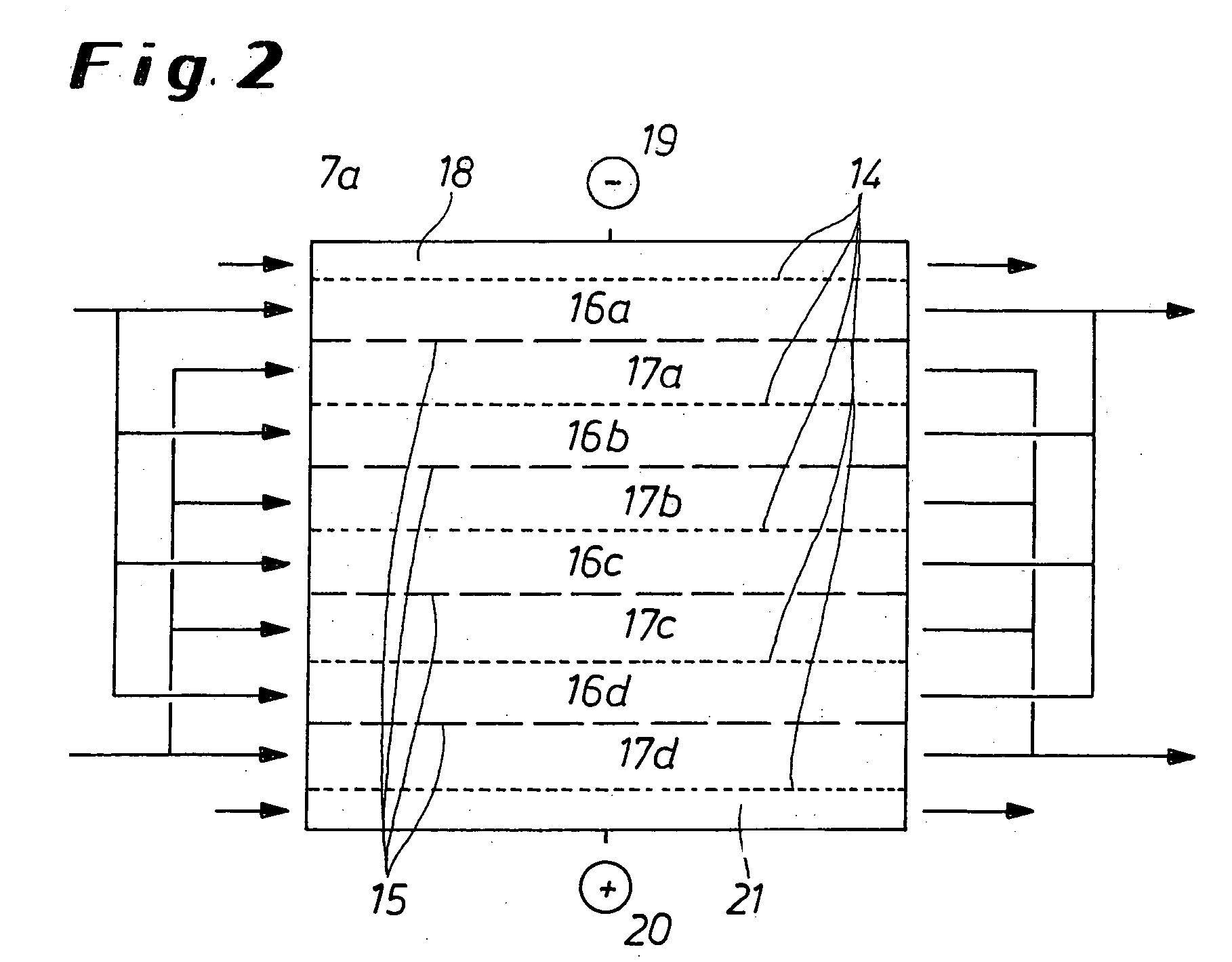
Method and appliance for carrying out membrane electrophoresis using microfiltration or ultrafiltration membranes, wherein the electroosmotic flow which develops in the membrane pores is reduced or offset by pressure superposition. The appliance for the membrane electrophoresis comprises at least an at least quadrupartite separation chamber (7), having at least one diluate space (16) and one concentrate space (17) and also a cathode space (18) and an anode space (21) having electrodes as anode (19) and cathode (20), with the individual spaces (16, 17, 18, 21) being separated from each other by ultrafiltration or microfiltration membranes (14, 15); feed lines (22) and discharge lines (23) for the diluate, feed lines (24) and discharge lines (25) for the concentrate, optionally feed lines (26) and discharge-lines (27) for the electrode rinsing solution, and also a device (8; 10) or (9; 11) for pressure regulation by means of which a pressure difference, in particular of at least 3 kPa, can be generated between the diluate space (16) and the concentrate space (17).
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Cell capturing chip based on inductive charge electro-osmosis induced by rotating electric field
InactiveCN106399091AReduce conductivityEasy to operateBiomass after-treatmentIndividual particle analysisMain channelDielectrophoresis
The invention discloses a cell capturing chip based on inductive charge electro-osmosis induced by a rotating electric field, and relates to a micro-fluidic chip based on inductive charge electro-osmosis induced by the rotating electric field. The invention aims to solve the problem that a dielectrophoresis capturing method is not suitable for capturing small cell and joule heat is easily generated in capturing the cell. A PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) cover plate is fixed on a glass substrate, and two PDMS channels perpendicular to each other are arranged on the PDMS cover plate; both ends of two PDMS channels are respectively provided with a main channel inlet, a main channel outlet, a secondary channel inlet and a secondary channel outlet; a suspension electrode array is placed at an intersection of the PDMS; an inner end part of a first exciting electrode, an inner end part of a second exciting electrode, an inner end part of a third exciting electrode and an inner end part of a fourth exciting electrode are respectively located at four different directions of the suspension electrode array. The invention has the beneficial effects that the cell capturing chip is small in captured cell size, high in capturing efficiency, and is not easy to generate joule heat. The cell capturing chip based on the vortex of the flow field is applicable to capture cells with different sizes.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com