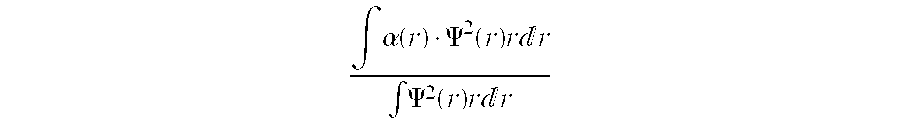Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Dispersion-shifted fiber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
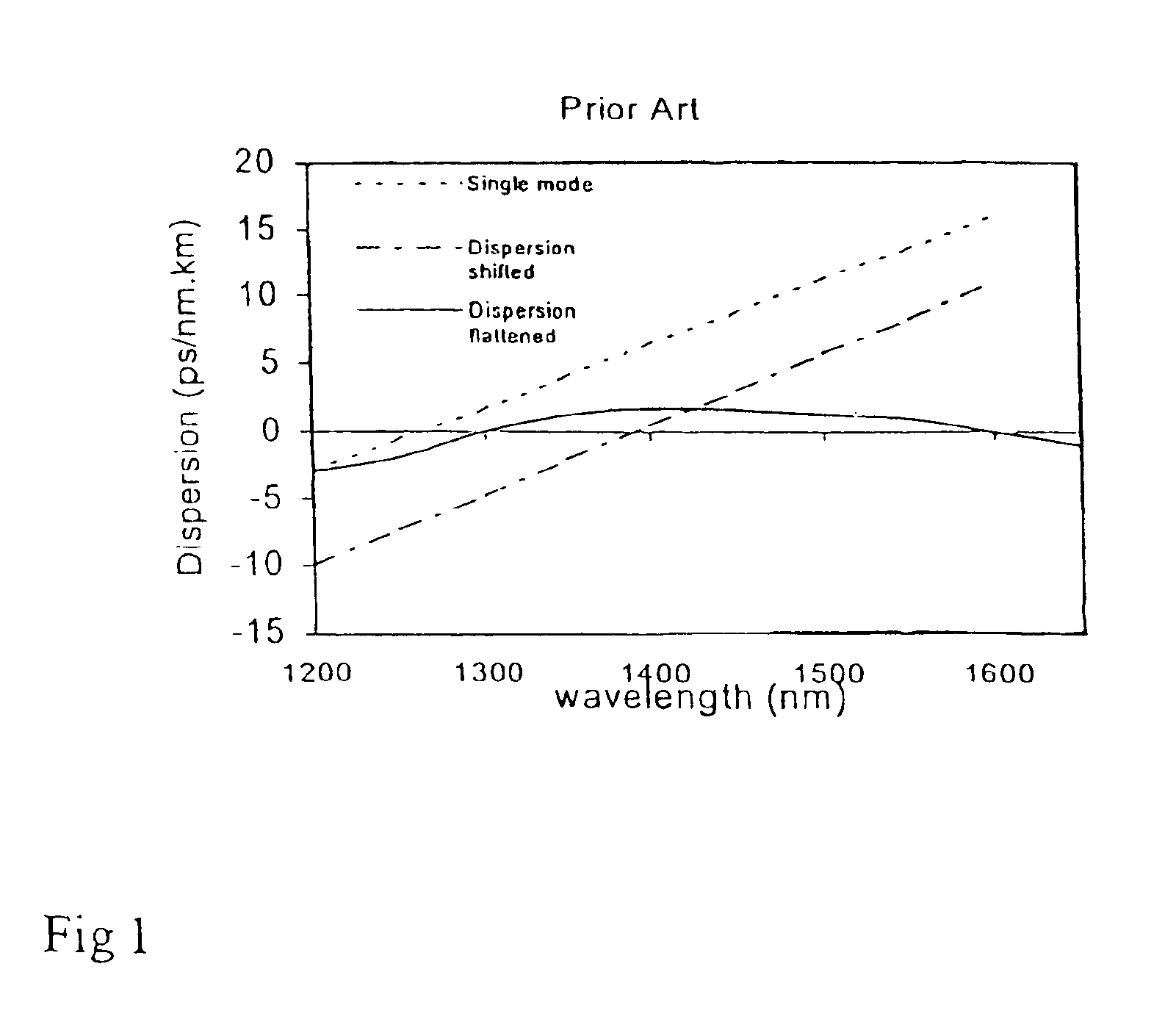
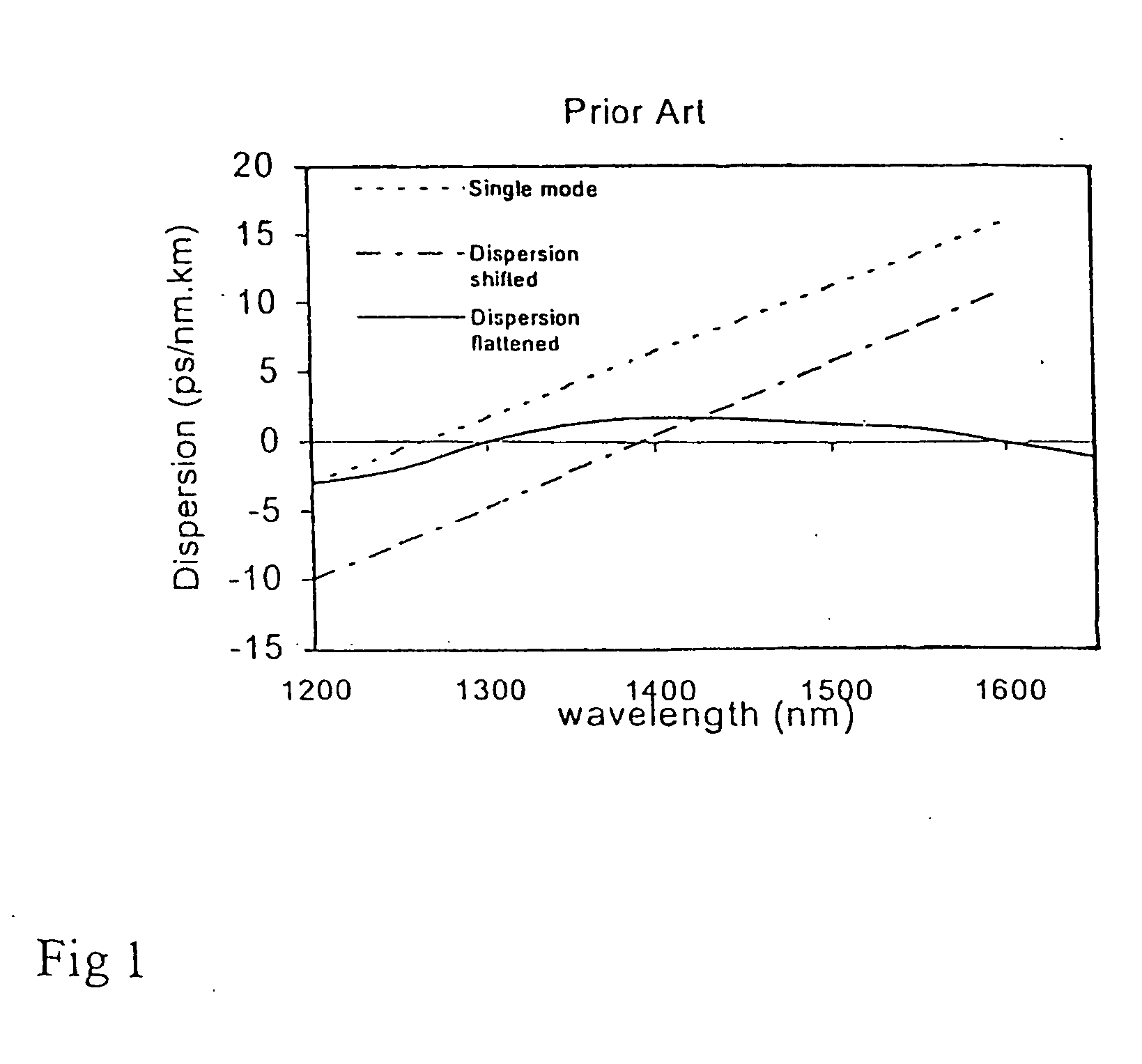
Dispersion-shifted fiber (DSF) is a type of optical fiber made to optimize both low dispersion and low attenuation. Dispersion Shifted Fiber is a type of single-mode optical fiber with a core-clad index profile tailored to shift the zero-dispersion wavelength from the natural 1300 nm in silica-glass fibers to the minimum-loss window at 1550 nm. The group velocity or intramodal dispersion which dominates in single-mode fibers includes both material and waveguide dispersion. Waveguide dispersion can be made more negative by changing the index profile and thus be used to offset the fixed material dispersion, shifting or flattening the overall intramodal dispersion. This is advantageous because it allows a communication system to possess both low dispersion and low attenuation. However, when used in wavelength division multiplexing systems, dispersion-shifted fibers can suffer from four-wave mixing which causes intermodulation of the independent signals. As a result, nonzero dispersion shifted fiber is often used.
Dispersion-Shifted Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20090252469A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
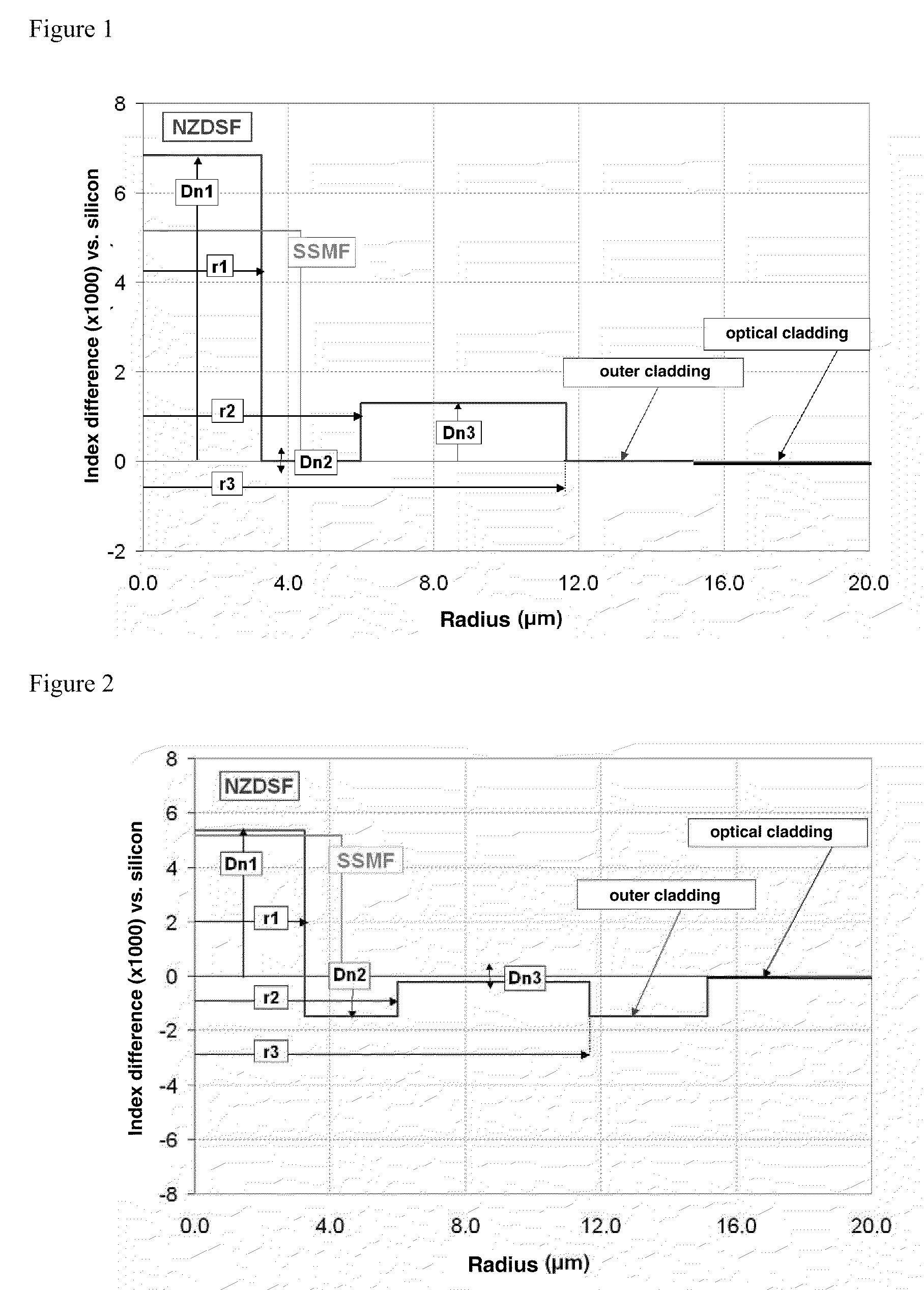
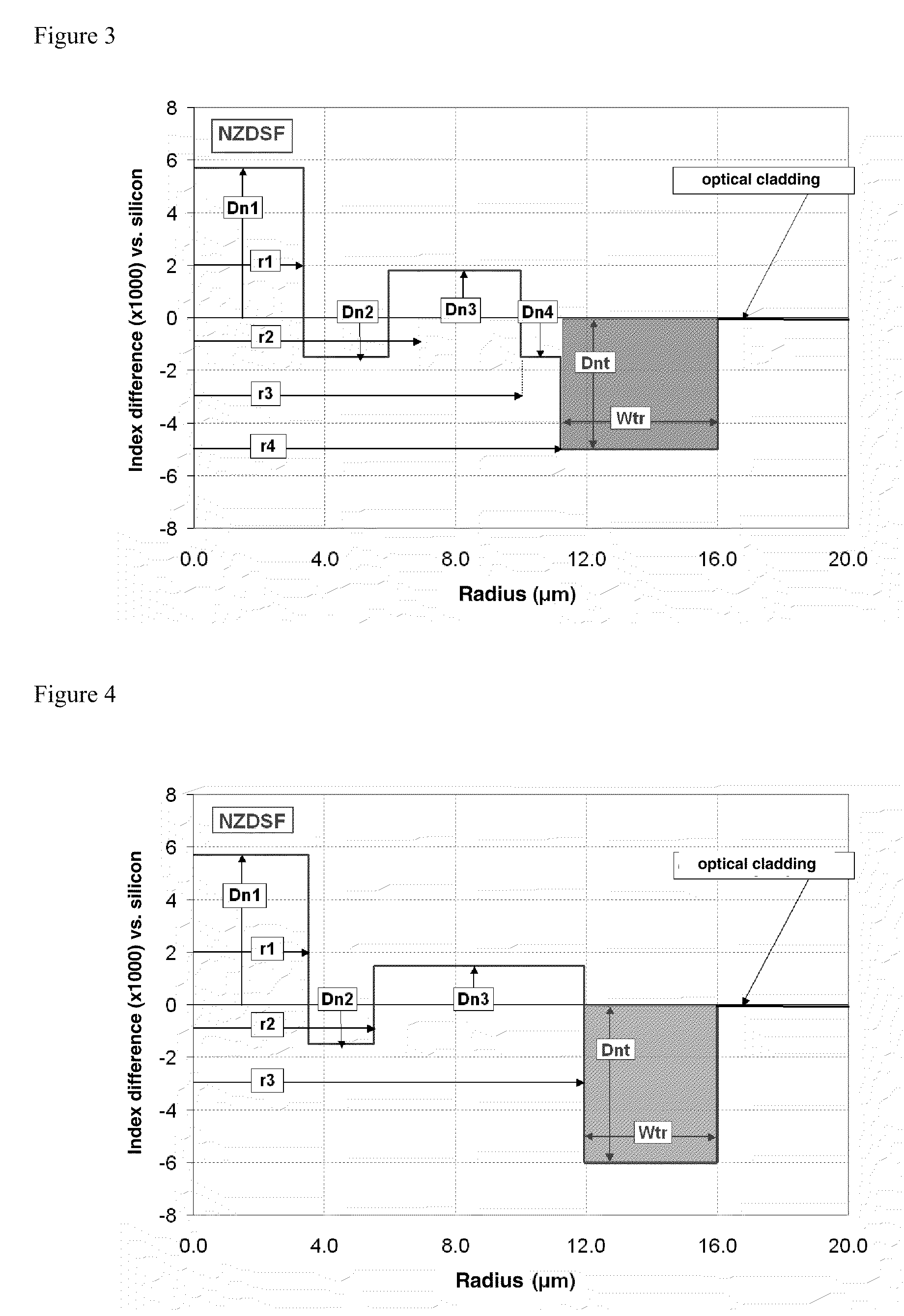
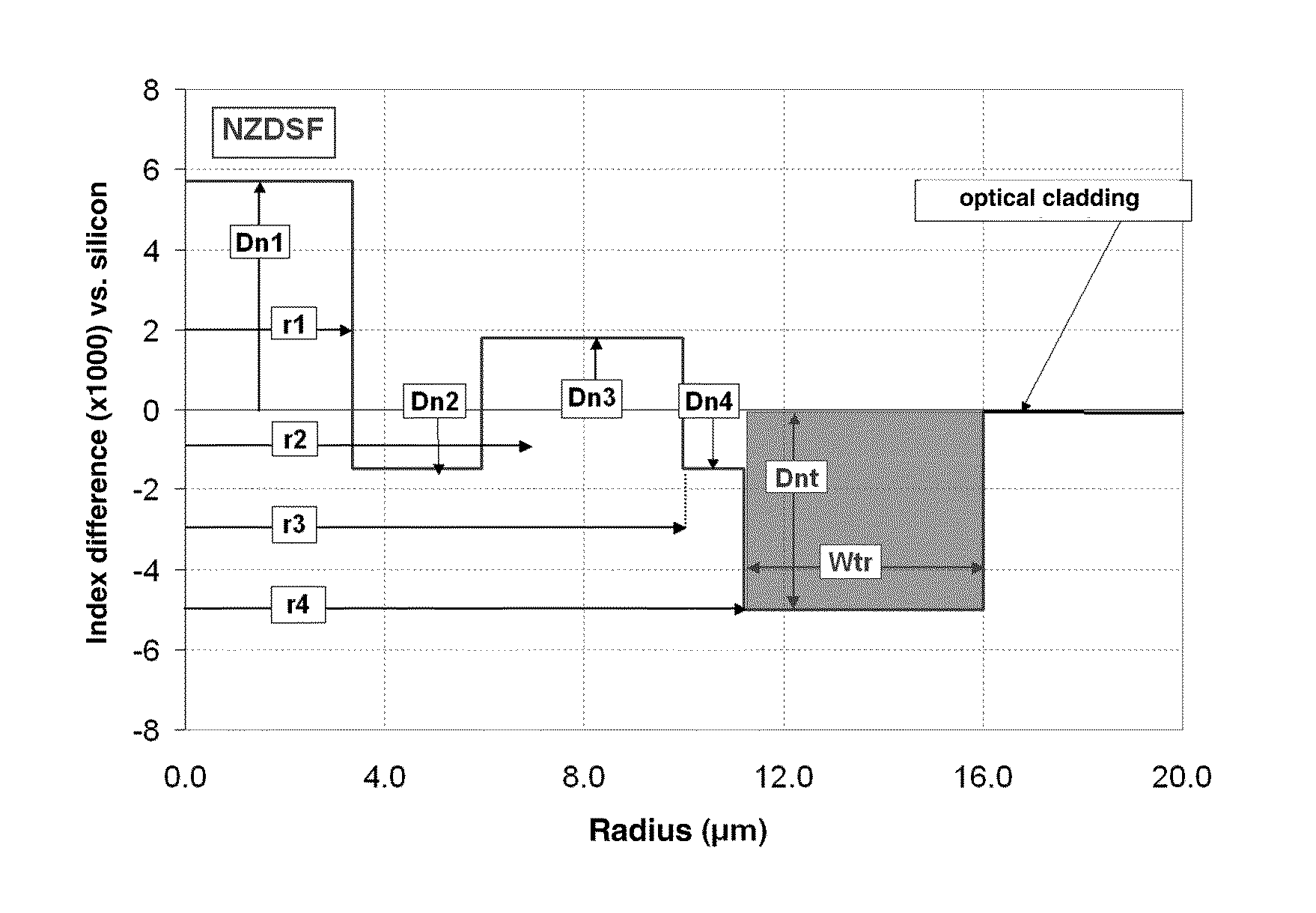
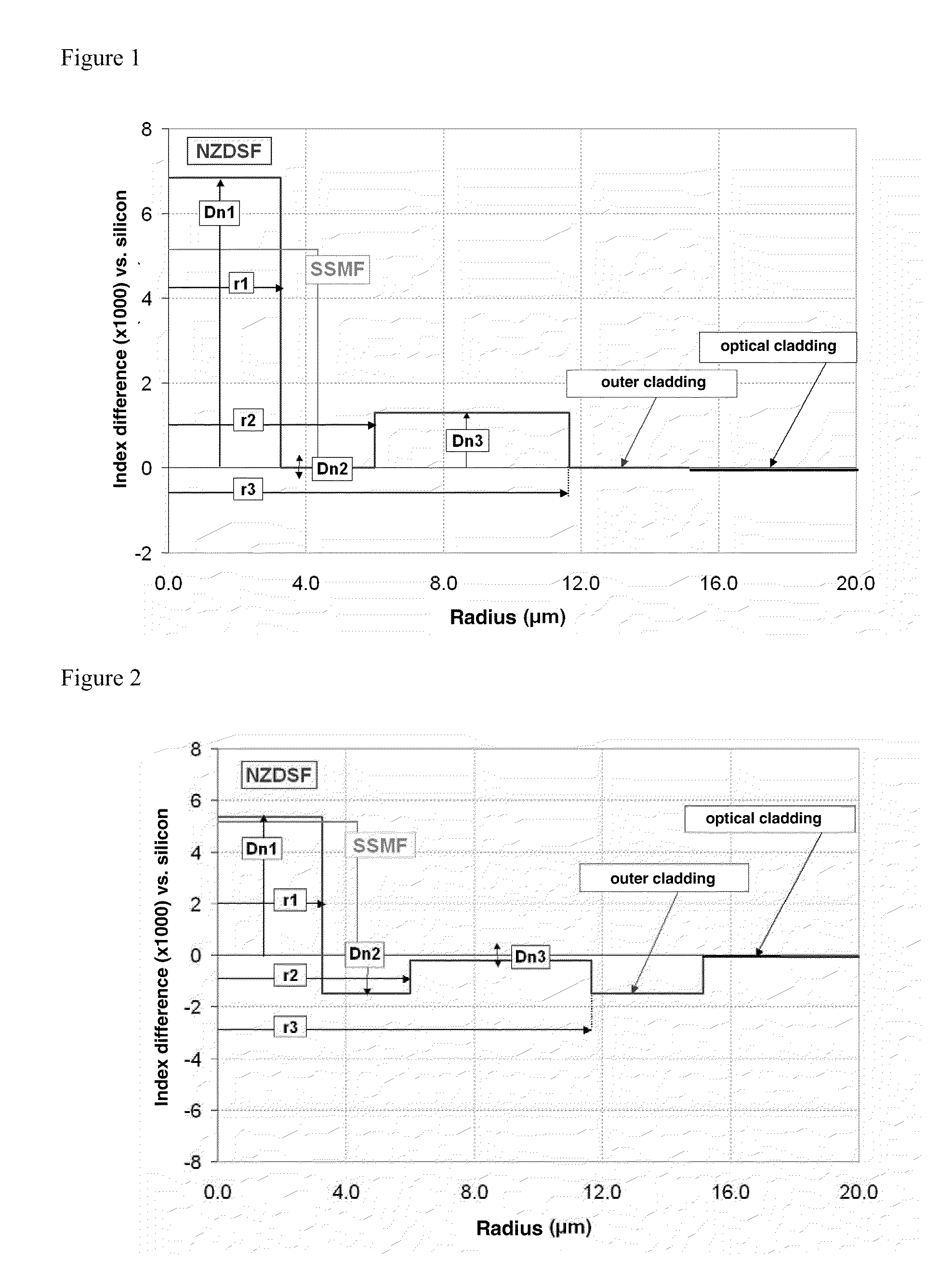
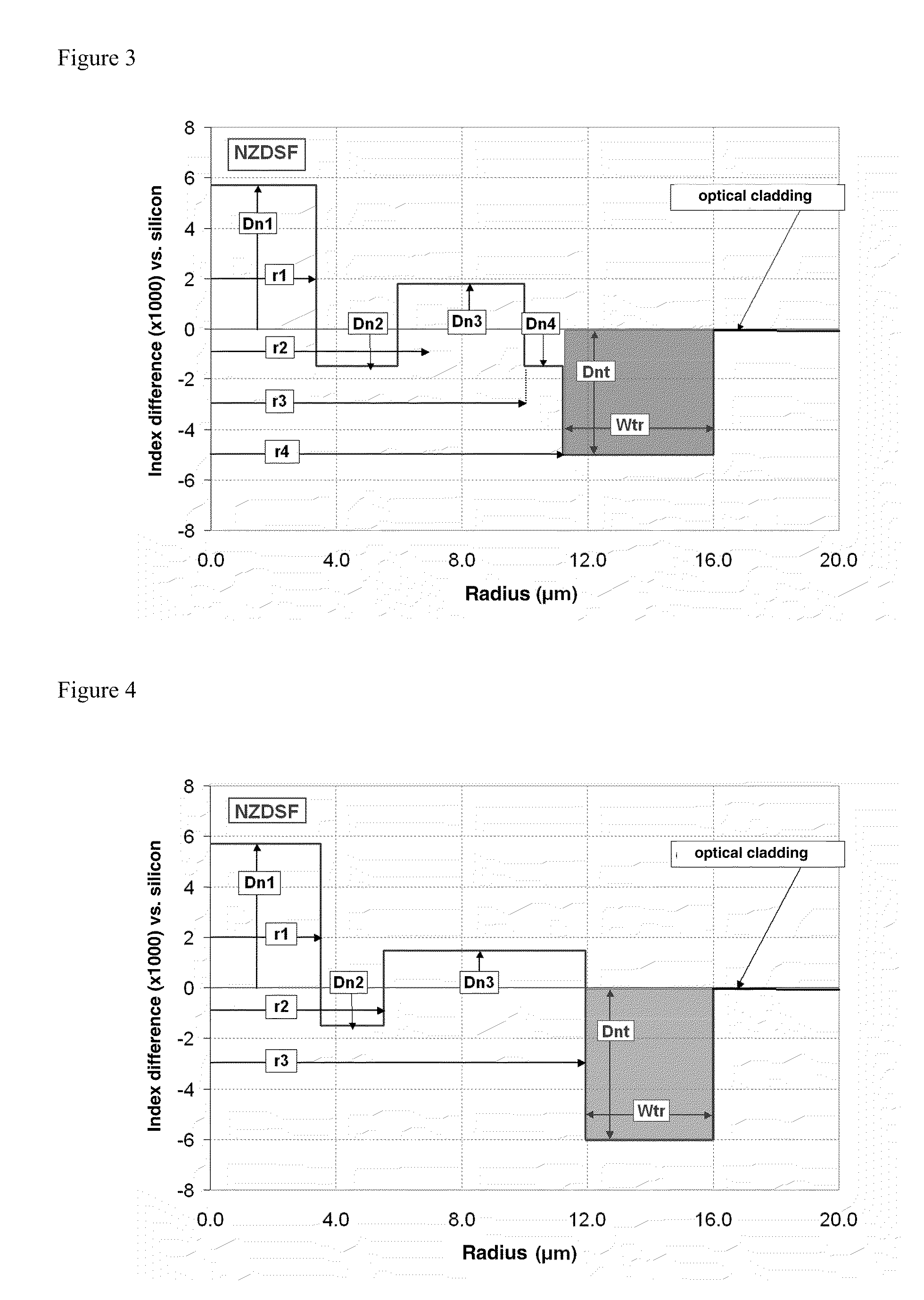
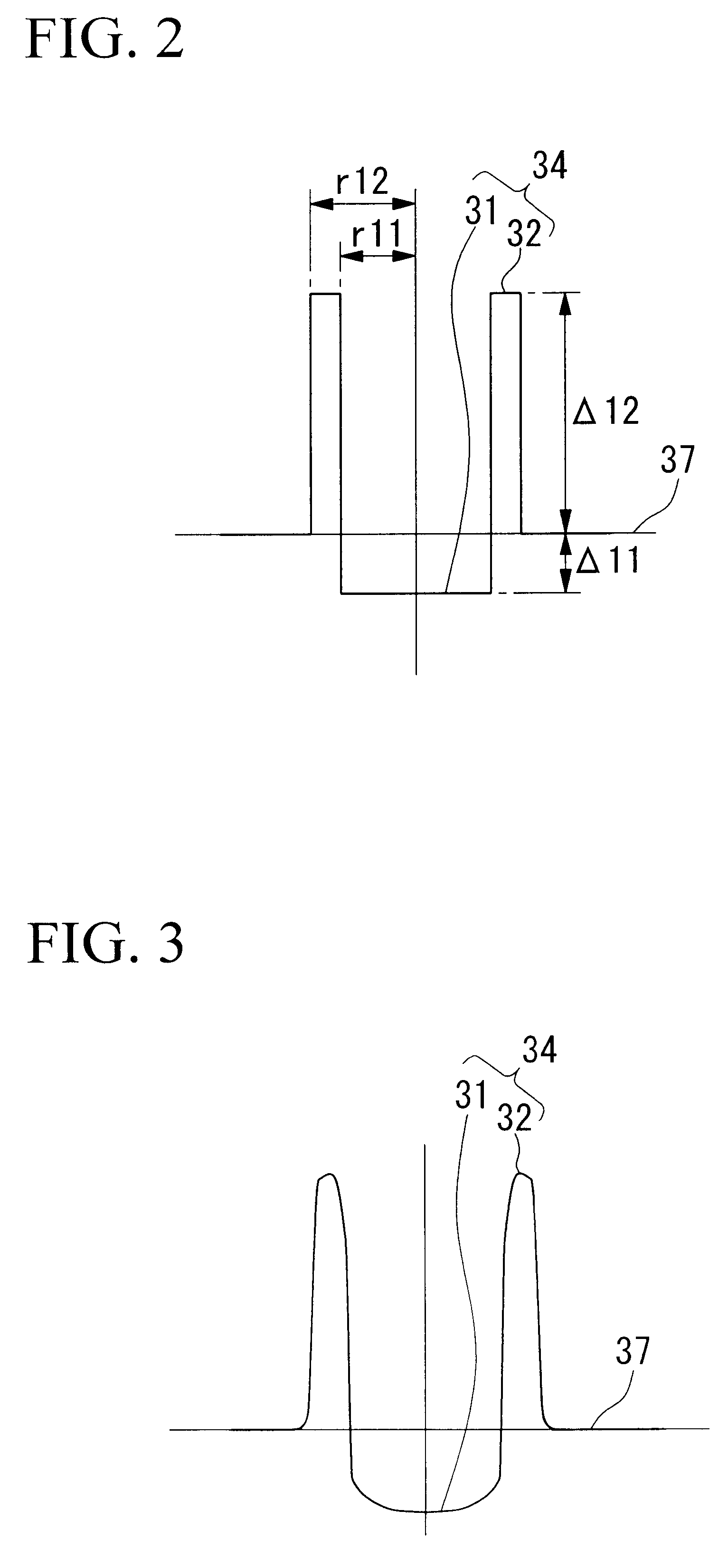
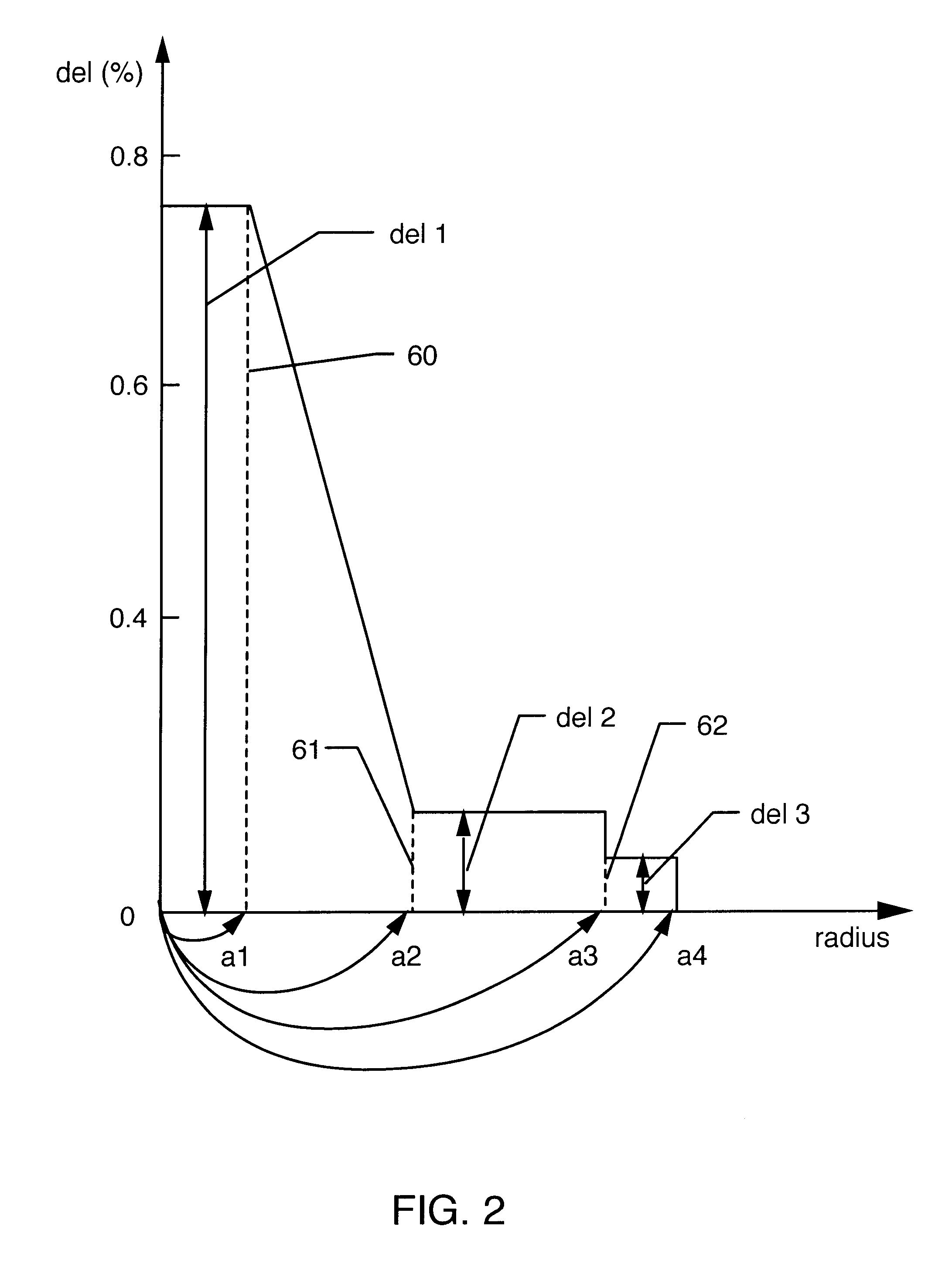
A dispersion-shifted optical fiber (NZDSF) includes a central core (r1, Dn1), an inner cladding having at least three zones with a first intermediate cladding zone (r2, Dn2), a second ring zone (r3, Dn3) and a third buried trench zone (Wtr, Dnt). The buried trench zone has an index difference (Dnt) with the optical cladding between −5·10−3 and −15·10−3 and has a width (Wtr) between 2.5 μm and 5.5 μm. The present optical fiber, at a wavelength of 1550 nm, has reduced Rayleigh scattering losses of less than 0.164 dB / km, with limited bending losses.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Broadband tunable single-passband microwave photon filter generating system
InactiveCN103955028AHigh out-of-band rejection ratioHigh Q valueCoupling light guidesContinuous lightOptical coupler
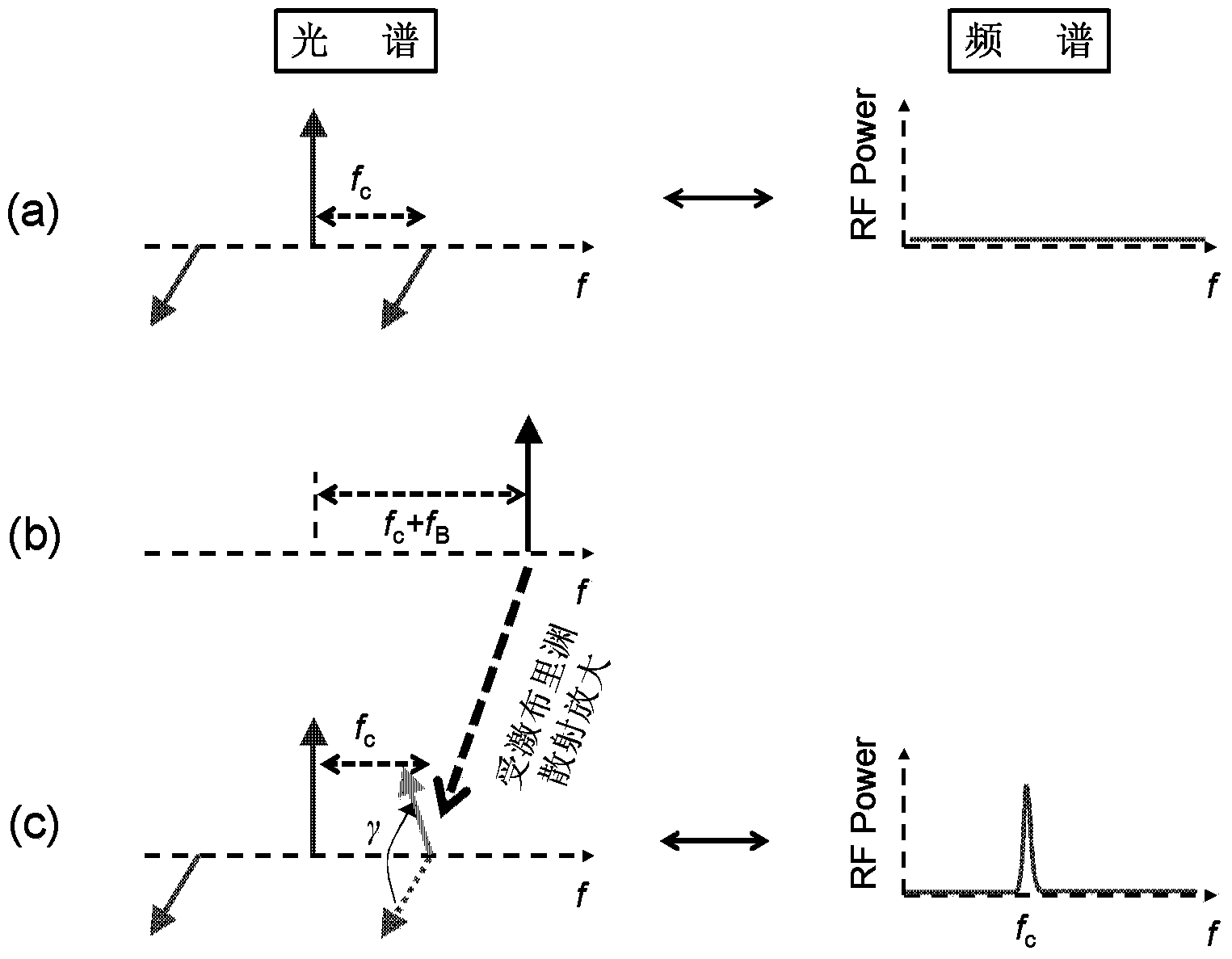
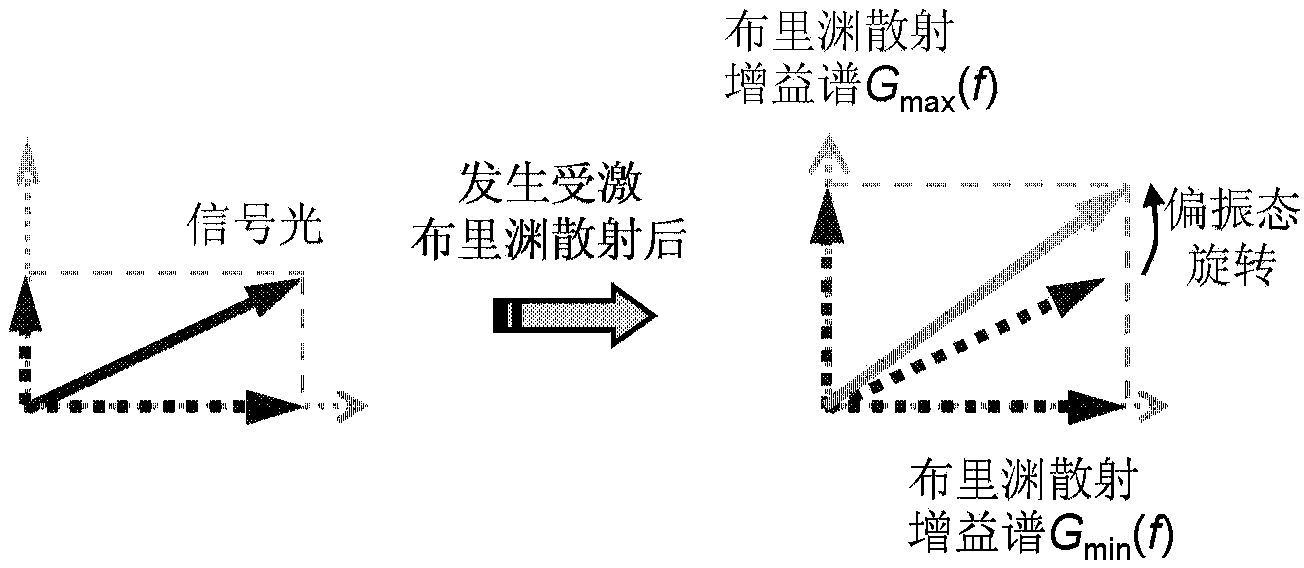
The invention discloses a broadband tunable single-passband microwave photon filter generating system. The system comprises a laser, an optical coupler, a polarization modulator, a dispersion displacement optical fiber, a photoelectric detector, a vector network analyzer, a strength modulator and an optical fiber; the laser is used for providing continuous light signals; the optical coupler is used for dividing the continuous light signals into the first path of light signals and the second path of light signals; the polarization modulator is used for modulating the polarization state of the first path of light signals; the dispersion displacement light fiber is used for performing stimulated Brillouin scattering on the detection light signals under the induction effect of pump light signals; the photoelectric detector is used for receiving the detection light signals which are processed in a stimulated Brillouin scattering mode and output by the dispersion displacement optical fiber and generating microwave signals; the vector network analyzer is used for receiving microwave signals output by the photoelectric detector, performing measurement frequency response on the microwave signals, and outputting the microwave signals to the a first polarization modulator at the same time; the strength modulator is used for modulating the polarization state of the first path of light signals and outputting the first path of light signals which are modulated; the optical fiber is used for filtering the first path of light signals which are modulated, and the first path of light signals serve as the pump light signals.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dispersion-compensating optical fiber, and, optical transmission line and dispersion-compensating module respectively including the same
InactiveUS6477306B2Improve scalabilityAvoid it happening againOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingLength waveDispersion compensation
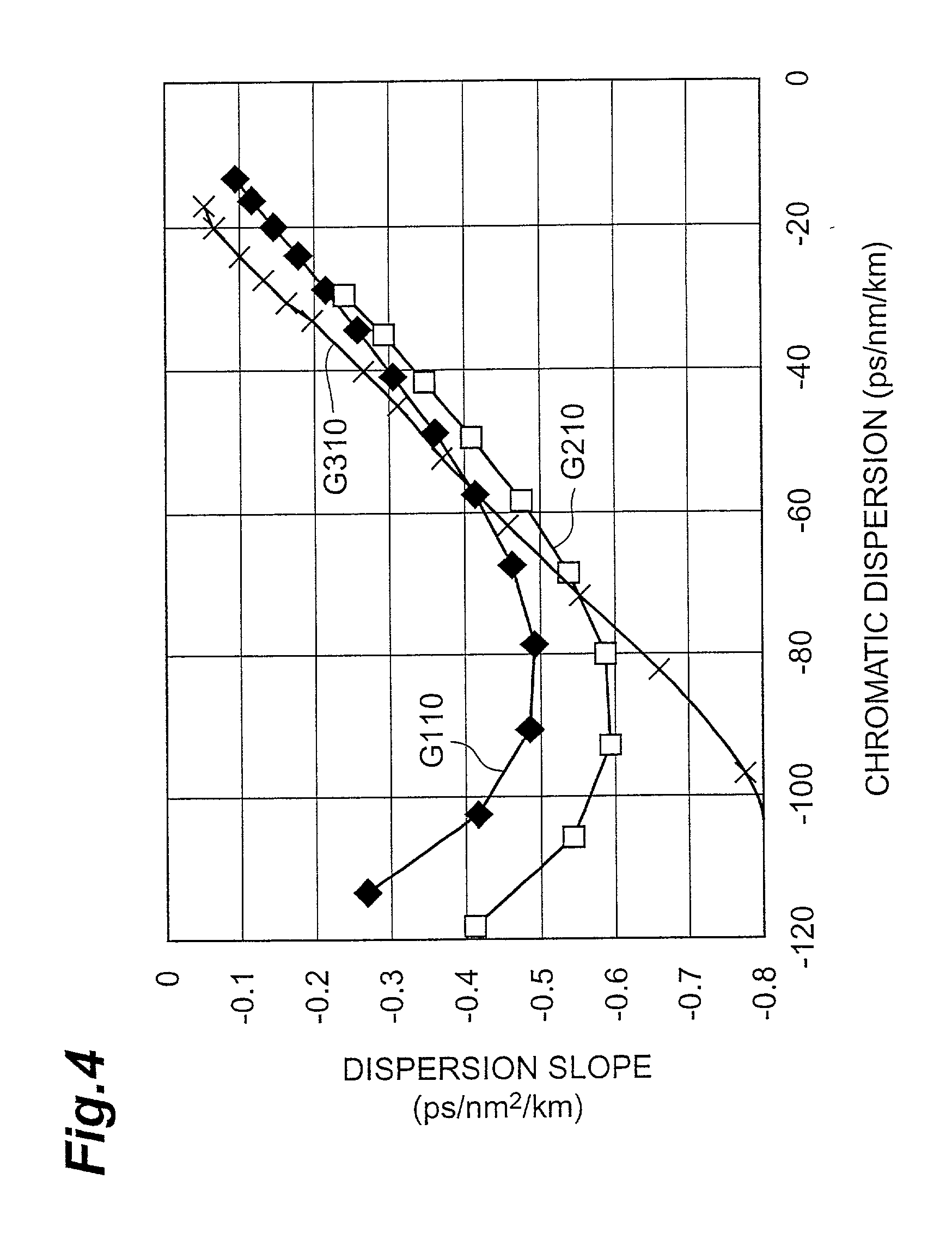
The invention is directed to a dispersion-compensating optical fiber which can compensate for the chromatic dispersion and dispersion slope of a non-zero dispersion-shifted optical fiber by a short length. The dispersion-shifted optical fiber constitutes an optical transmission line together with a dispersion-compensating optical fiber fusion-spliced thereto. The dispersion-compensating optical fiber has, at a wavelength of 1550 nm, a chromatic dispersion DDCF of -40 ps / nm / km or less and a ratio (DDCF / SDCF) of dispersion slope SDCF to the chromatic dispersion DDCF of 0.005 / nm or more.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Dispersion shifted fiber having low dispersion slope
InactiveUS6879764B2Improve the level ofMinimize non-linearitiesOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesFiberRefractive index
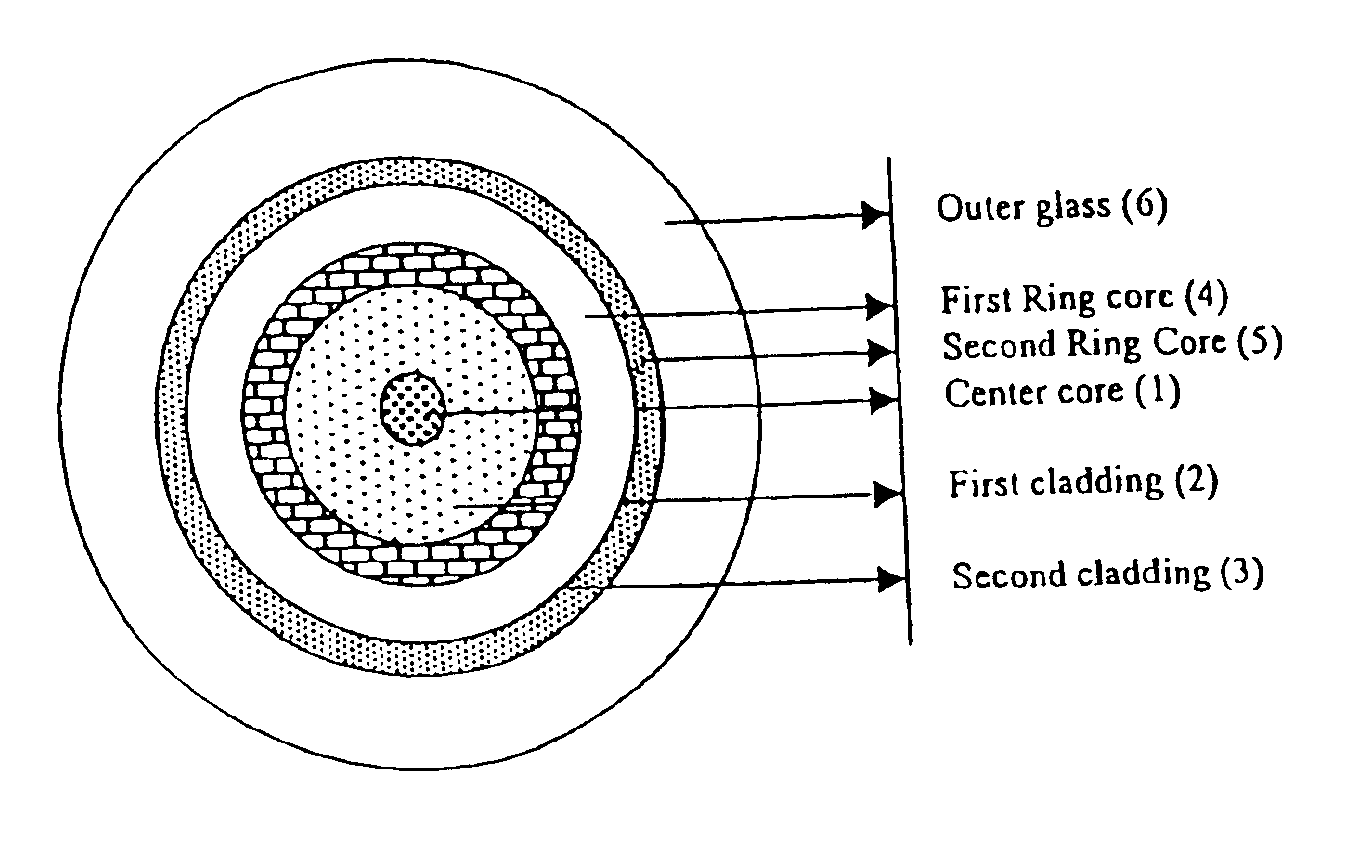
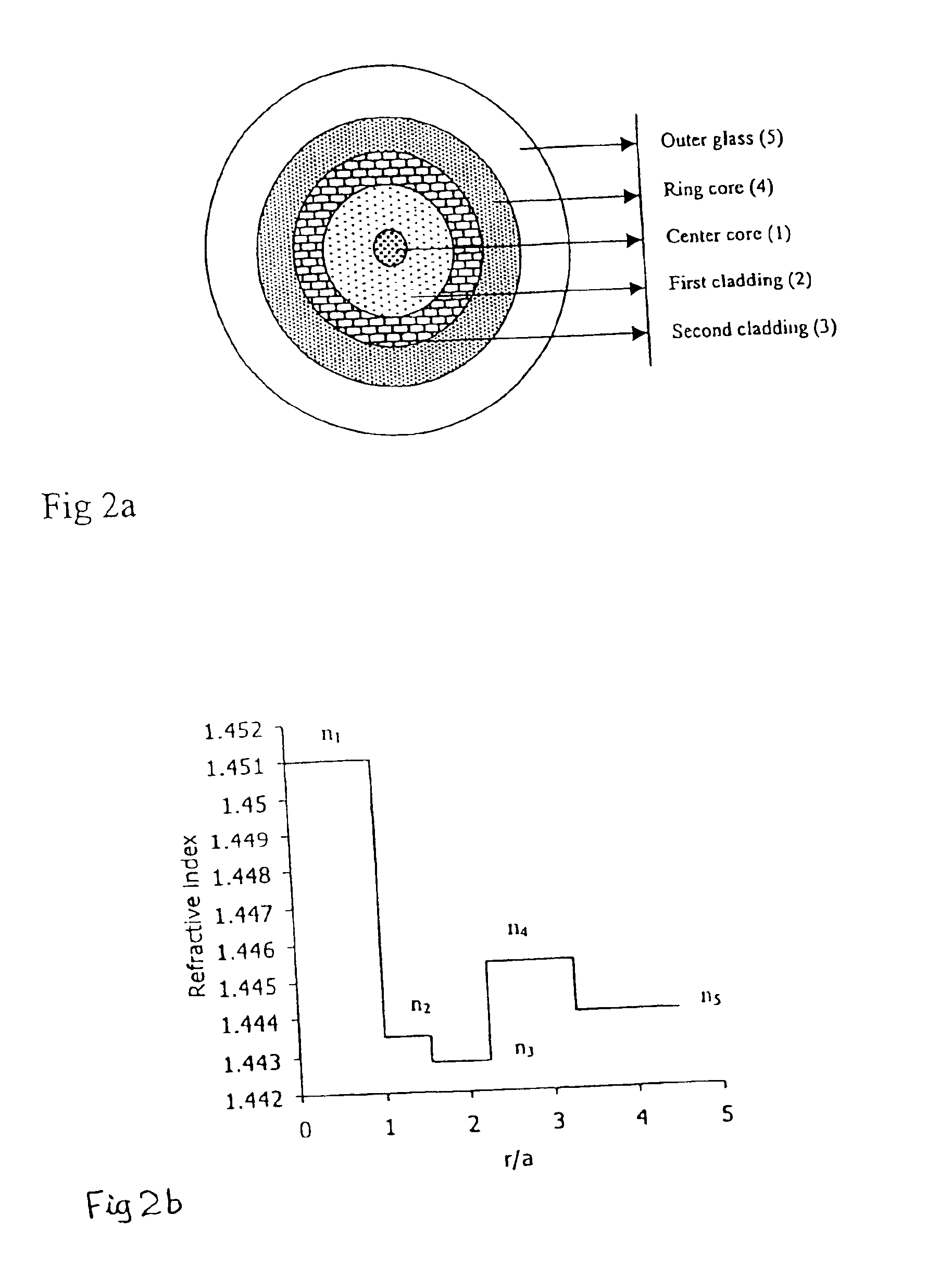
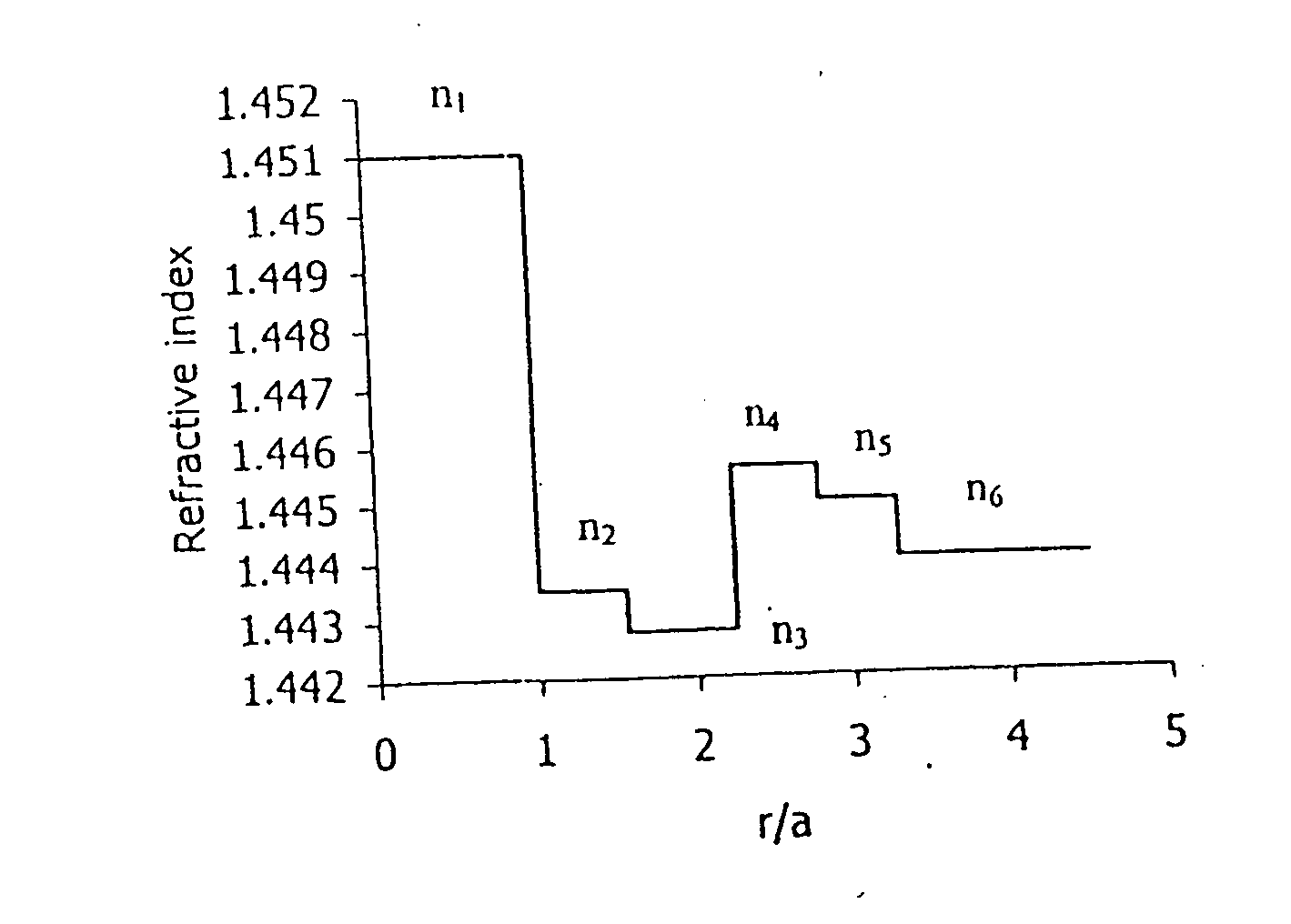
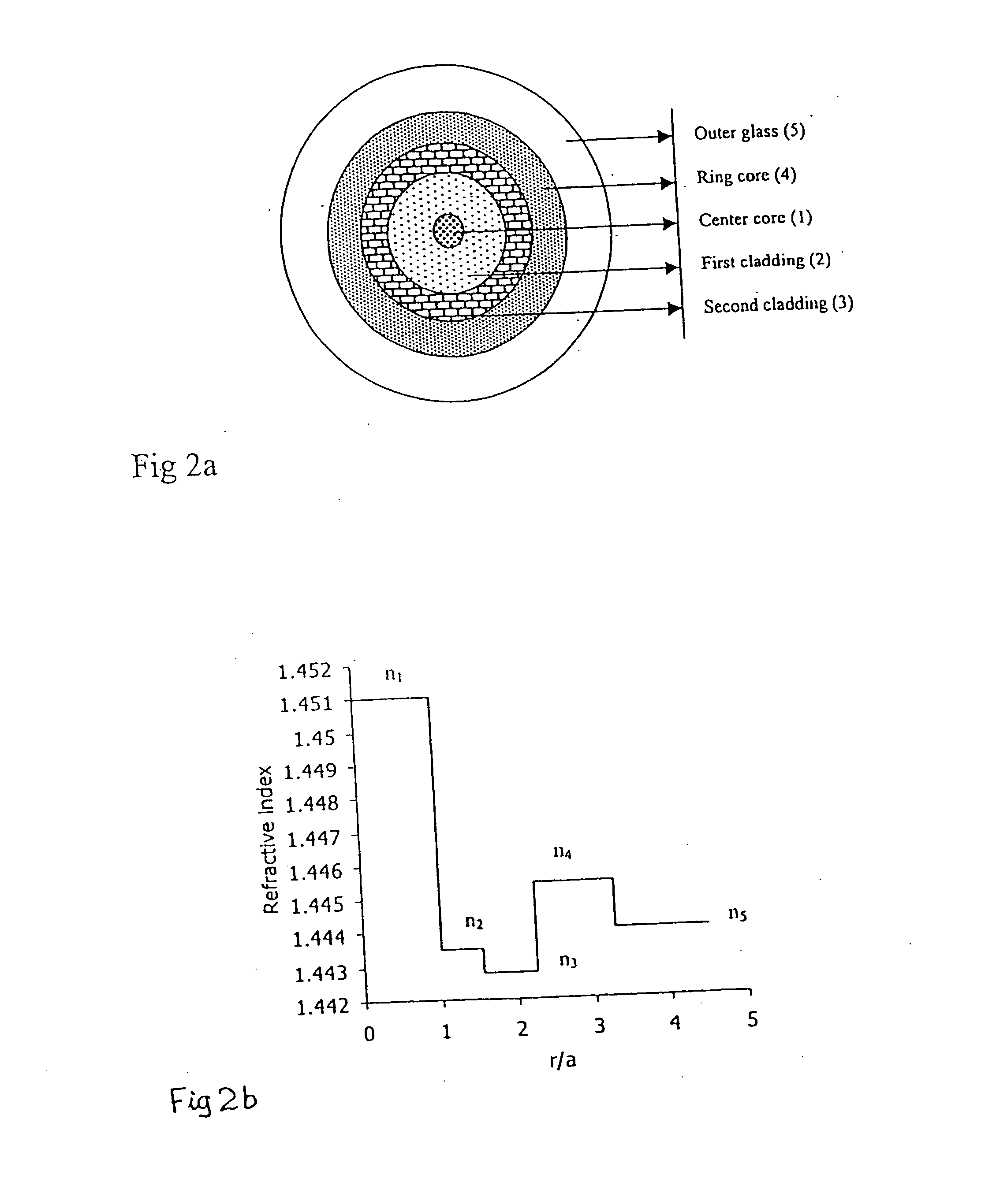
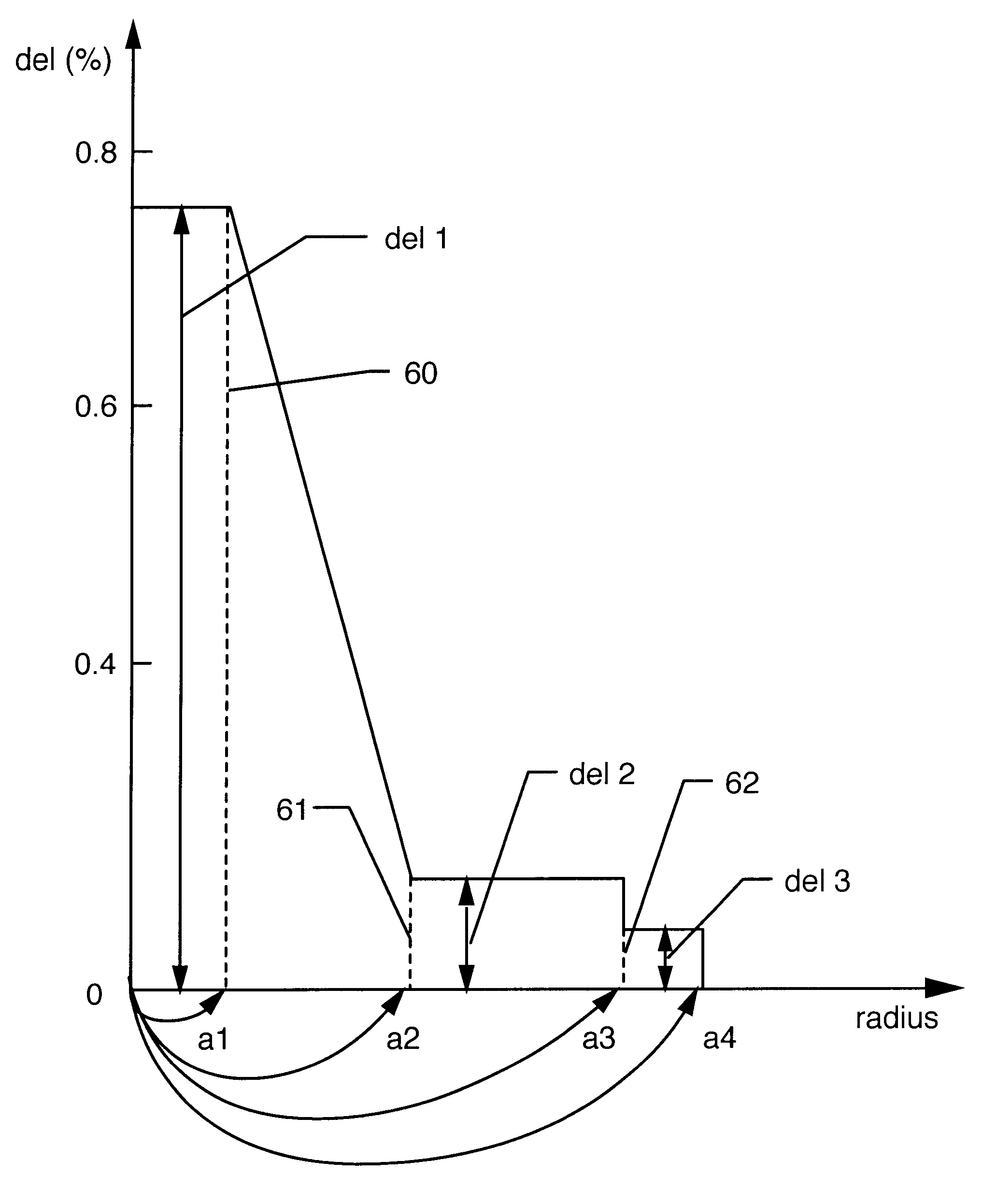
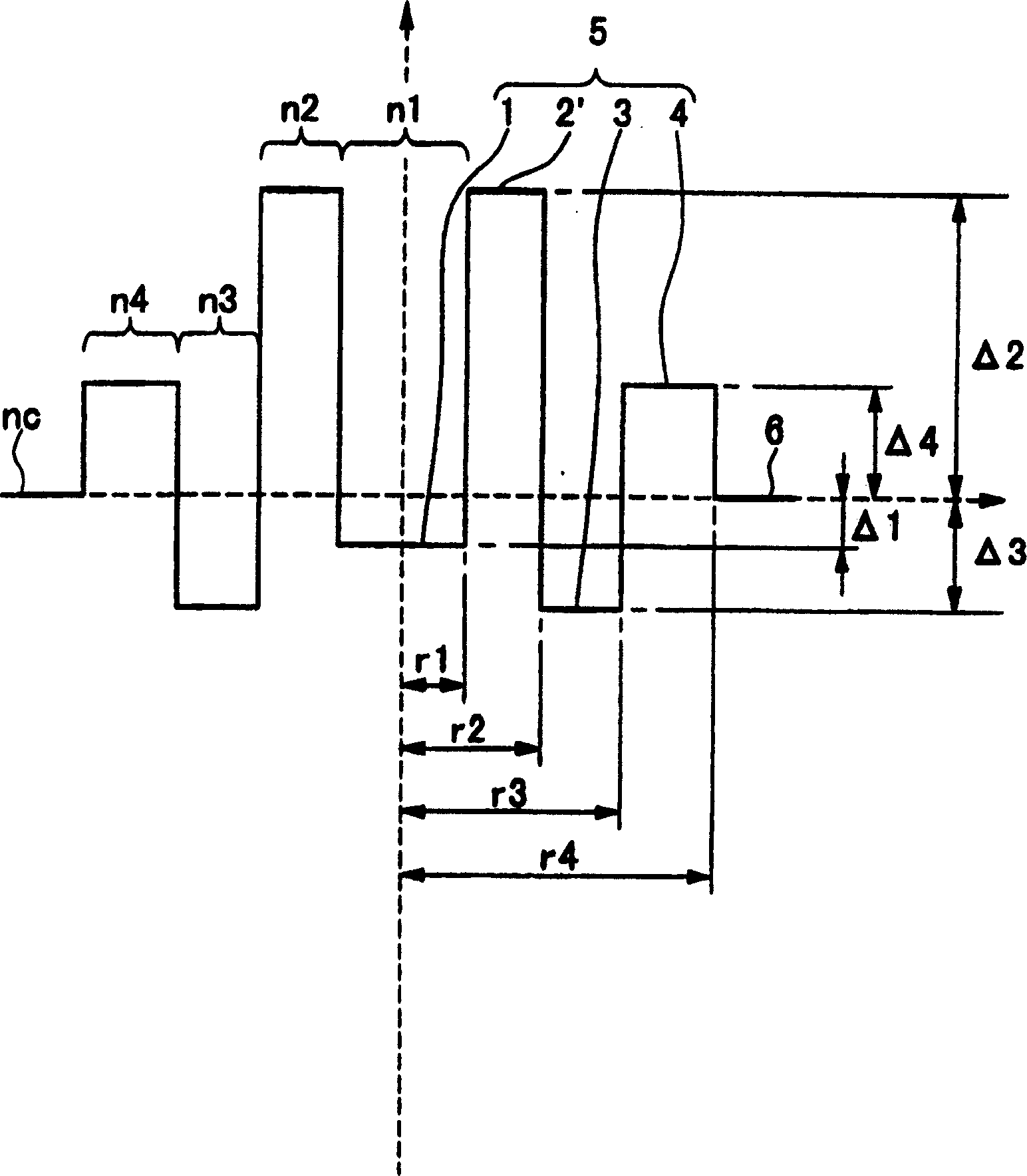
Dispersion shifted fiber having low dispersion slope comprising a center core, two claddings, a ring core and the outer glass region, wherein the first cladding is provided onto the outer periphery of the center core, the second cladding is provided onto outer periphery of the first cladding and the ring core is provided onto outer periphery of the second cladding, and the outer glass region surrounds the ring core, and the center core and the ring core have higher refractive indices, and the claddings have lower refractive indices than the outer glass region, and the refractive indices are constrained by the equation n1>n4>n5>n2>n3. In accordance with preferred embodiment the fiber comprises of a center core, two claddings, two ring cores, and an outer glass region, wherein the first cladding is provided onto the outer periphery of the center core, the second cladding 3 is provided onto the outer periphery of the first cladding, the first ring core is provided onto the outer periphery of the second cladding, the second ring core 5 is provided onto the outer periphery of the first ring core and the outer glass region surrounds the second ring core, and the refractive indices are constrained by the equation n1>n4>n5>n6>n2>n3.
Owner:STERLITE TECHNOLOGIES
Wavelength conversion apparatus
A wavelength converter which employs an optical fiber and has high converter efficiency. The polarization planes of a signal light and an exciting light outputted from a laser diode (LD) (103) are respectively controlled by polarization controllers (PC's) (101 and 104) and the phases of the lights are respectively modulated by phase modulators (PM's) (102 and 105) in accordance with modulation signals outputted form an oscillator (110). Then, the output lights form the PM's (102 and 105) are multiplexed by a coupler (106). After the multiplexed signal light and exciting light are amplified by an optical amplifier (EDFA) (107), they are imputed to a dispersion shift fiber (DSP) (108). After wavelength transformation (four light waves mixing (FWM) is practiced in the DSP, and FWM light is outputted through a band-pass filter (BPF) (109).
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Dispersion-shifted optical fiber
ActiveUS8055111B2Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
A dispersion-shifted optical fiber (NZDSF) includes a central core (r1, Dn1), an inner cladding having at least three zones with a first intermediate cladding zone (r2, Dn2), a second ring zone (r3, Dn3) and a third buried trench zone (Wtr, Dnt). The buried trench zone has an index difference (Dnt) with the optical cladding between −5·10−3 and −15·10−3 and has a width (Wtr) between 2.5 μm and 5.5 μm. The present optical fiber, at a wavelength of 1550 nm, has reduced Rayleigh scattering losses of less than 0.164 dB / km, with limited bending losses.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Dispersion shifted optical fiber
InactiveUS6546177B1Improve featuresReduction in dispersion slopeGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingEngineeringLength wave
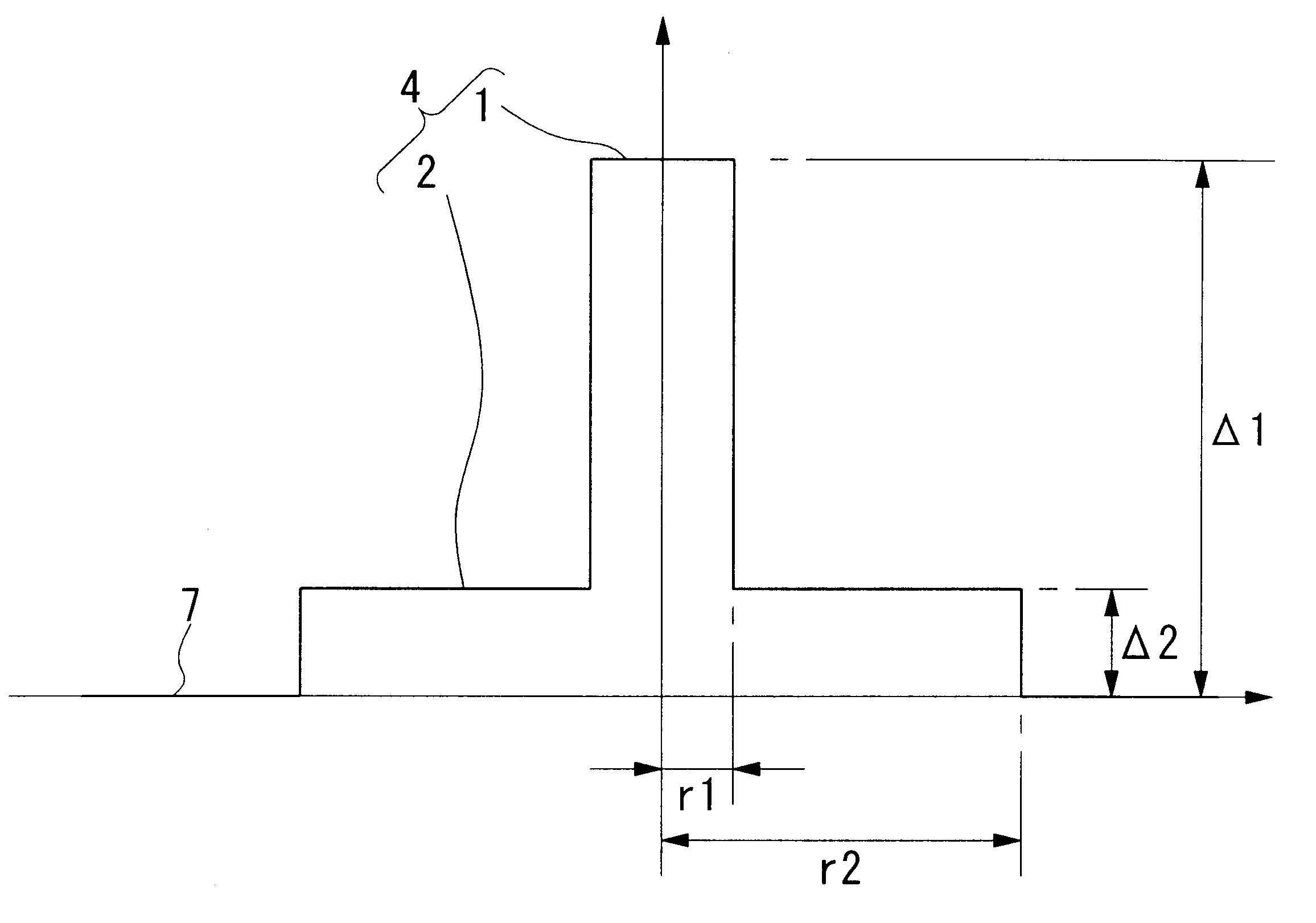
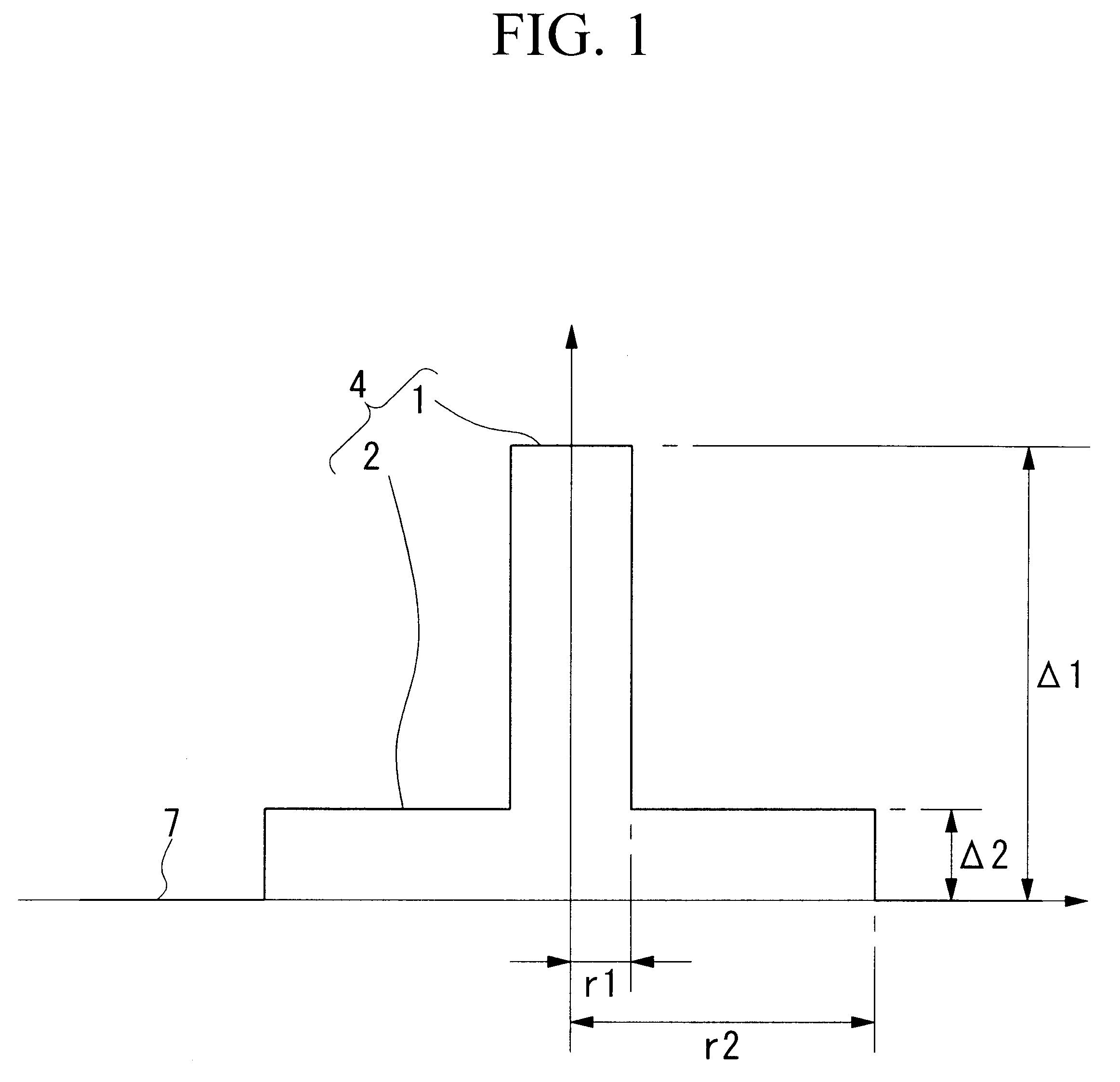
In the present invention, by forming a dispersion shifted optical fiber that has a refractive index profile comprising: a central core portion 1; a step core portion 2 provided at an outer periphery of the central core portion 1 and having a refractive index lower than that of the central core portion 1; and cladding 7 provided at an outer periphery of the step core portion 2 and having a refractive index lower than that of the step core portion 2, and which dispersion shifted optical fiber has, in a used wavelength band that is selected from between 1490 and 1625 nm, chromatic dispersion values of 7 to 15 ps / km / nm, an Aeff of 60 to 150 mum2, a dispersion slope of 0.09 ps / km / nm2 or less, a bending loss of 100 dB / m or less, and a cutoff wavelength that provides essentially single mode transmission, it is possible to reduce the cost of the system and to achieve n improvement in the transmission characteristics.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
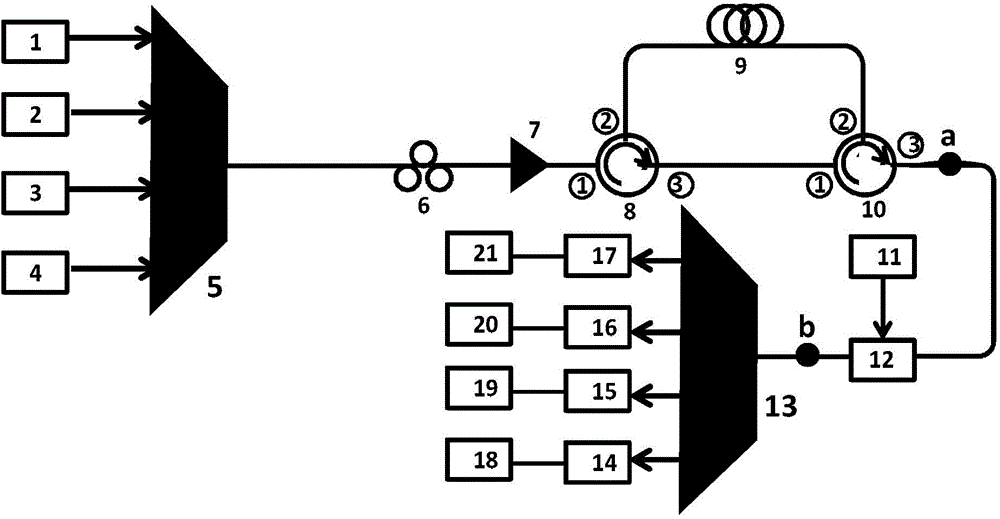
Multi-frequency high-precision microwave photon frequency measuring scheme based on stimulated brillouin effect
ActiveCN104614585ARealize frequency instantaneous detectionLow costFrequency measurement arrangementElectricityMicrowave
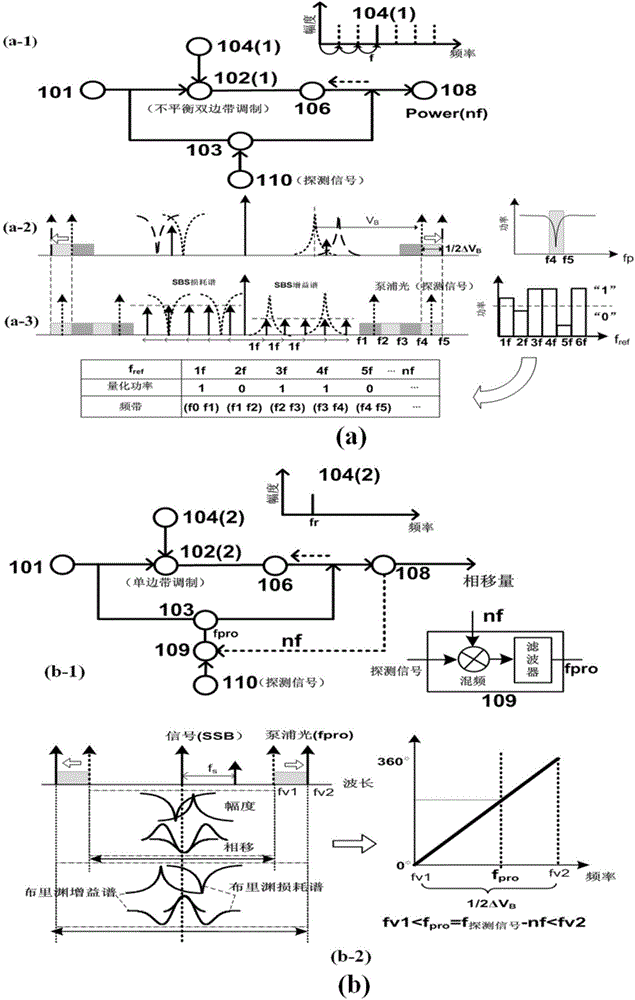
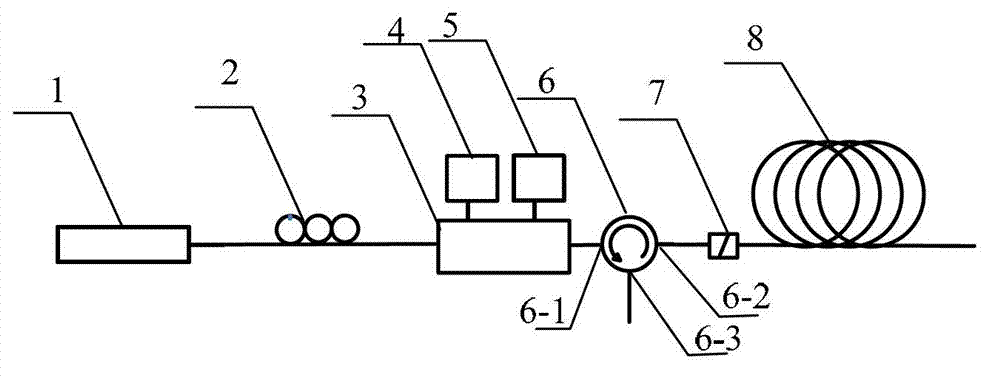
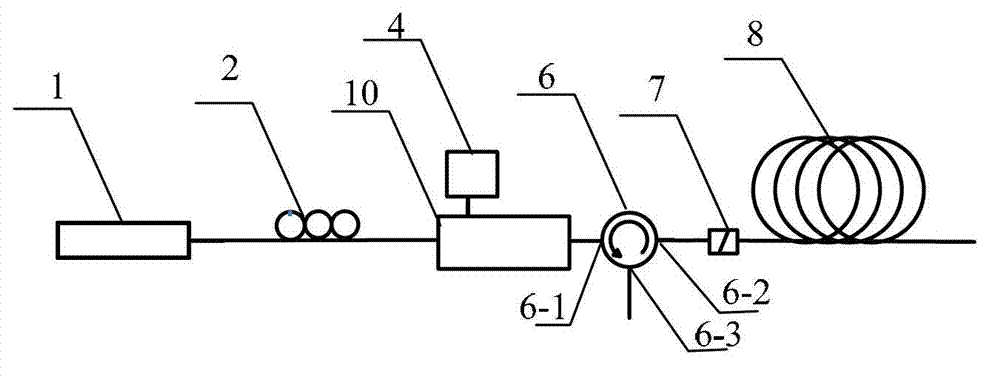
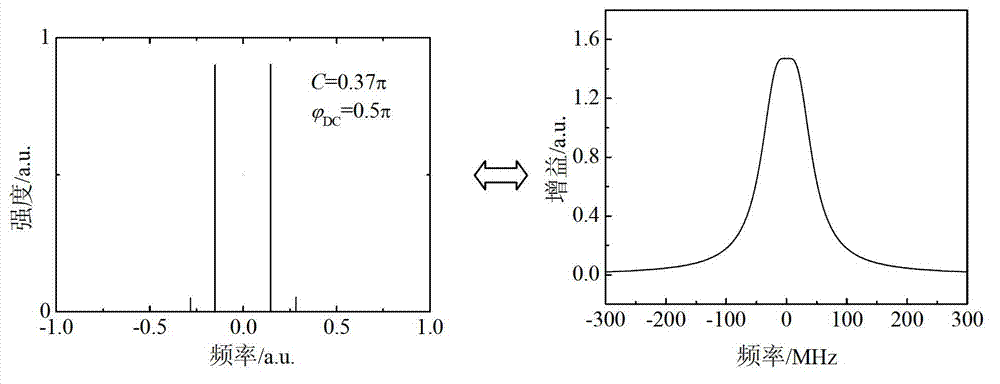
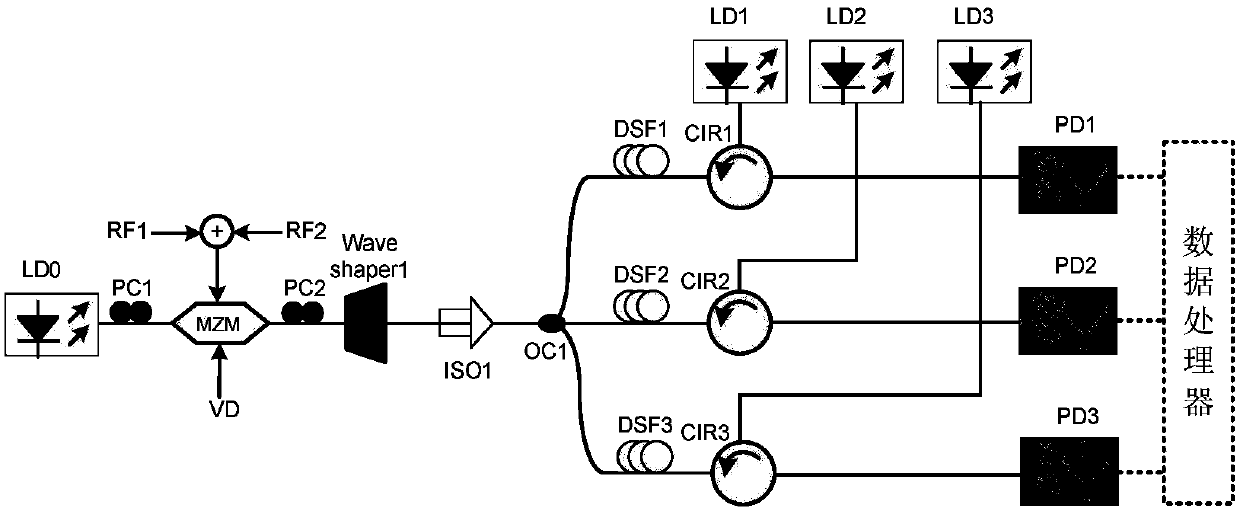
The invention discloses a multi-frequency high-precision microwave photon frequency measuring scheme based on stimulated brillouin effect. The multi-frequency high-precision microwave photon frequency measuring scheme comprises a single-wavelength laser device (101), a dual-drive mach-zehnder modulator (102), a mach-zehnder modulator (103), a optical isolator (105), a dispersion-shift optical fiber (106), an optical circulator (107), a photoelectric detector (108), an electric processing unit (109), a reference microwave source (104). Compared with other microwave photo frequency measuring schemes, double mapping relationship which are dynamic frequency-power mapping and frequency-phase mapping in the brillouin effect are respectively utilized, the multi-frequency instant measuring and the single-frequency error measuring are combined, so that the multi-frequency high-precision microwave photo frequency measuring is realized. The multi-frequency high-precision microwave photon frequency measuring scheme can be applied to the electronic countermeasure and the microwave detecting field.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Dispersion-compensating optical fiber, and, optical transmission line and dispersion-compensating module respectively including the same
InactiveUS20010033724A1Improve scalabilityAvoid it happening againOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingLength waveDispersion compensation
The invention is directed to a dispersion-compensating optical fiber which can compensate for the chromatic dispersion and dispersion slope of a non-zero dispersion-shifted optical fiber by a short length. The dispersion-shifted optical fiber constitutes an optical transmission line together with a dispersion-compensating optical fiber fusion-spliced thereto. The dispersion-compensating optical fiber has, at a wavelength of 1550 nm, a chromatic dispersion DDCF of -40 ps / nm / km or less and a ratio (DDCF / SDCF) of dispersion slope SDCF to the chromatic dispersion DDCF of 0.005 / nm or more.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
SBS broadband tunable optical fiber delay system
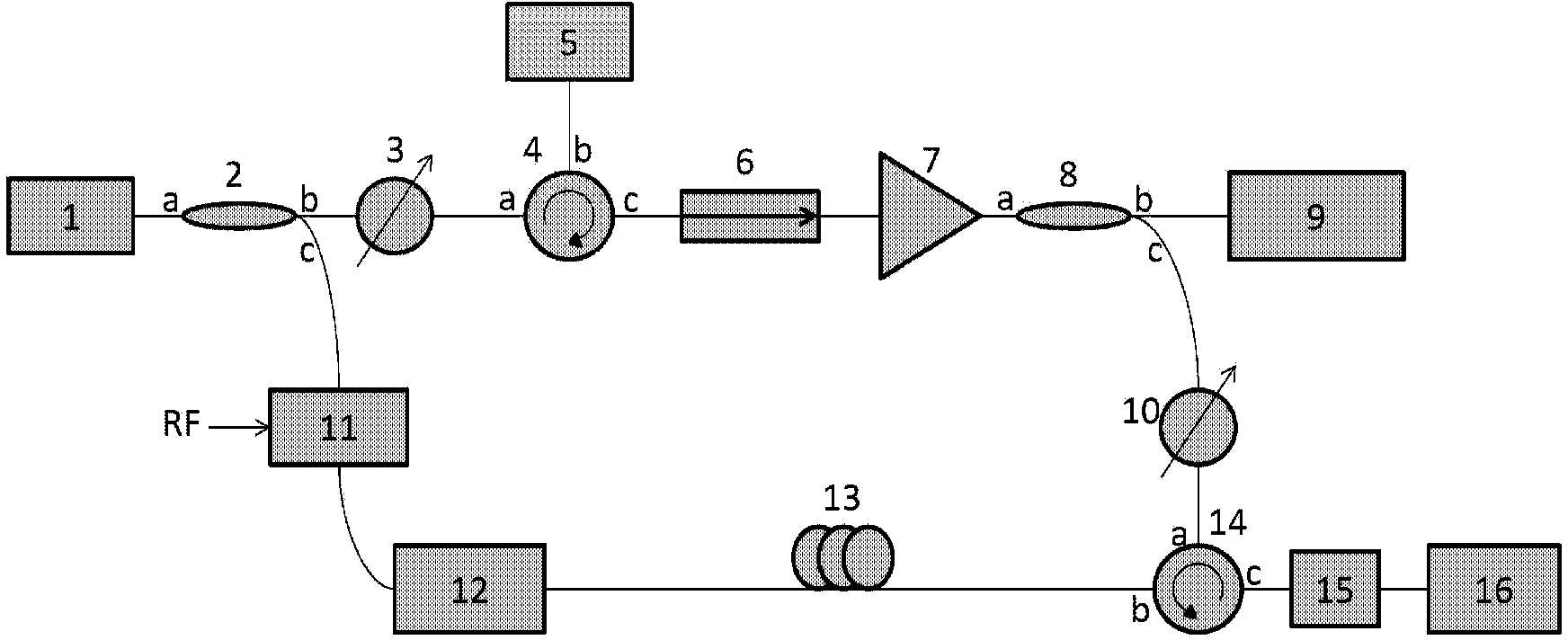
The invention discloses a broadband tunable optical fiber delay system of stimulated brillouin scattering. The SBS broadband tunable optical fiber delay system comprises a main laser, a first optical coupler, a first tunable optical attenuator, a first optical circulator, a slave laser, an optical amplifier, a second tunable optical attenuator, a second optical circulator, a Mach-Zehnder modulator, an optical fiber Bragg grating and a diffusion shifted fiber, wherein the first optical coupler is used for dividing the laser into first bean of laser and a second beam of laser; the first tunable optical attenuator is used for adjusting the laser power of the first beam of laser; the first optical circulator is used for injecting the first beam of laser into the slave laser; the slave laser is excited by the first beam of laser to produce nonlinear spectral light; the optical amplifier is used for amplifying the power of the pump light; the second optical circulator is used for injecting the pumping light into the diffusion shifted fiber; the Mach-Zehnder modulator, is used for modulating a microwave signal for the second beam of laser; the optical fiber Bragg grating is used for carrying out the phase position modulation for optical signal carrier; the diffusion shifted fiber is delayed under the effect of the stimulated brillouin scattering of the pump light in the propagation process of the diffusion shifted fiber.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microwave photon up-conversion device and method based on photoelectric oscillator
ActiveCN108199776AHigh spectral purityRadio-over-fibreElectromagnetic repeatersErbium dopingFrequency shift
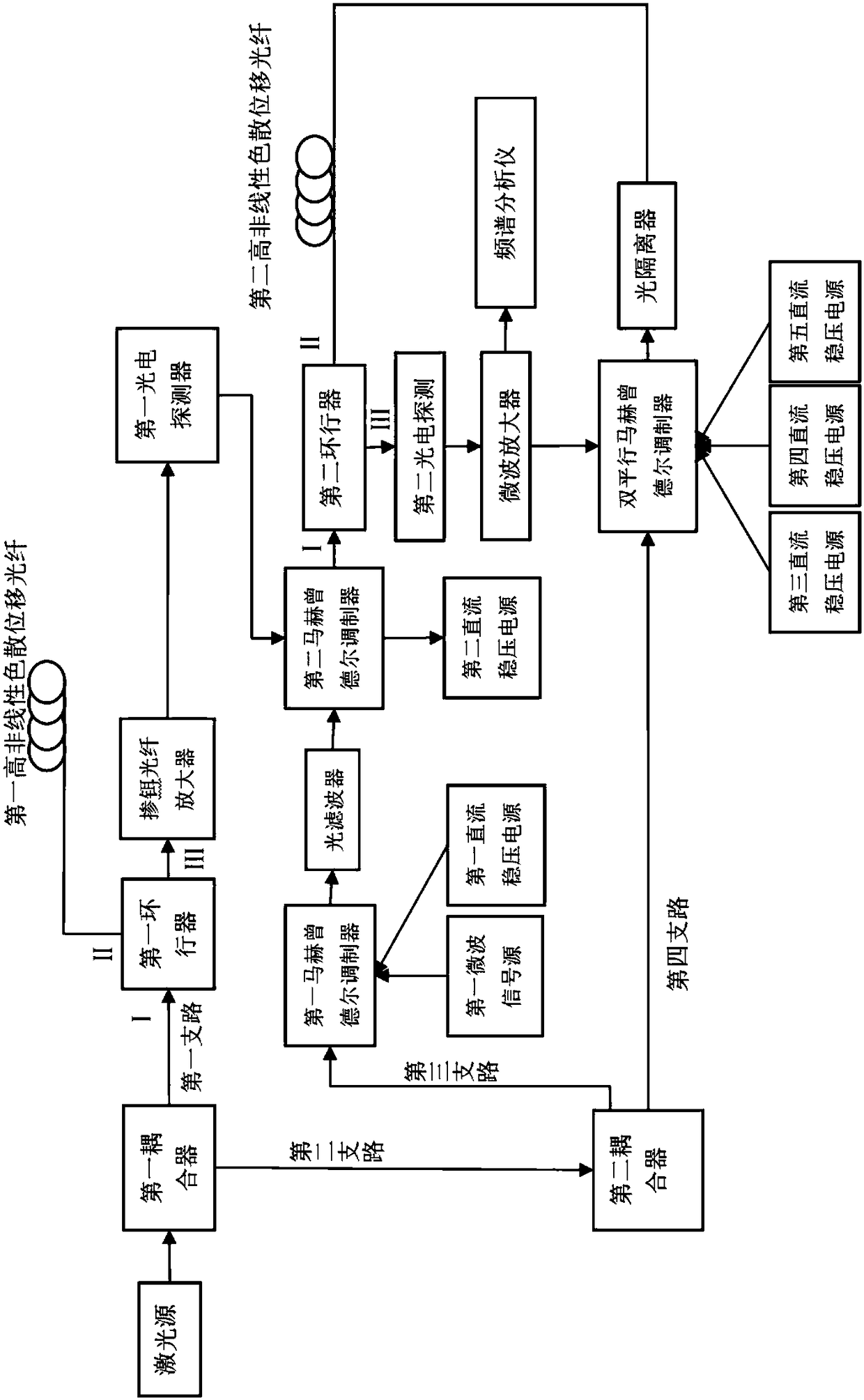
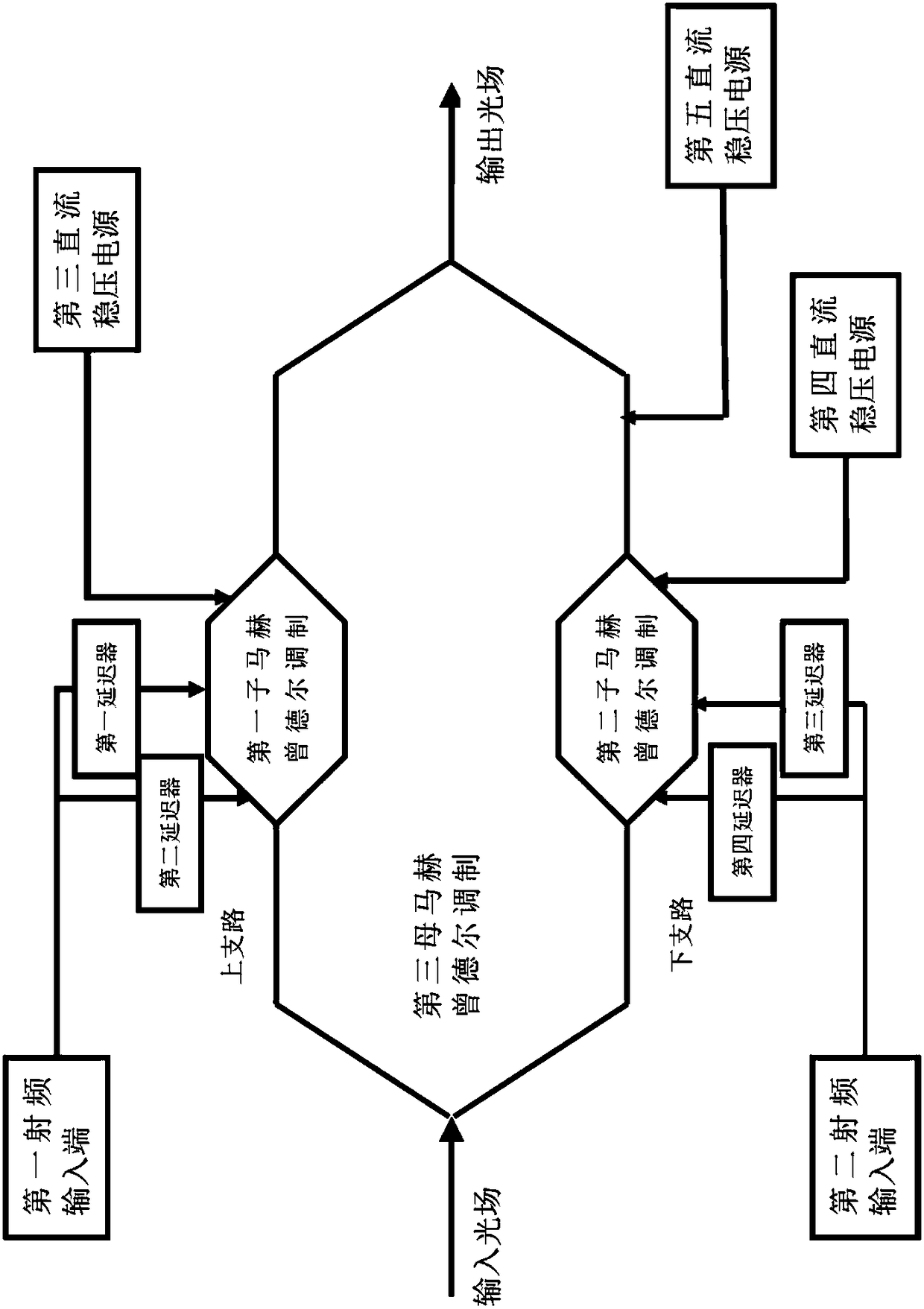
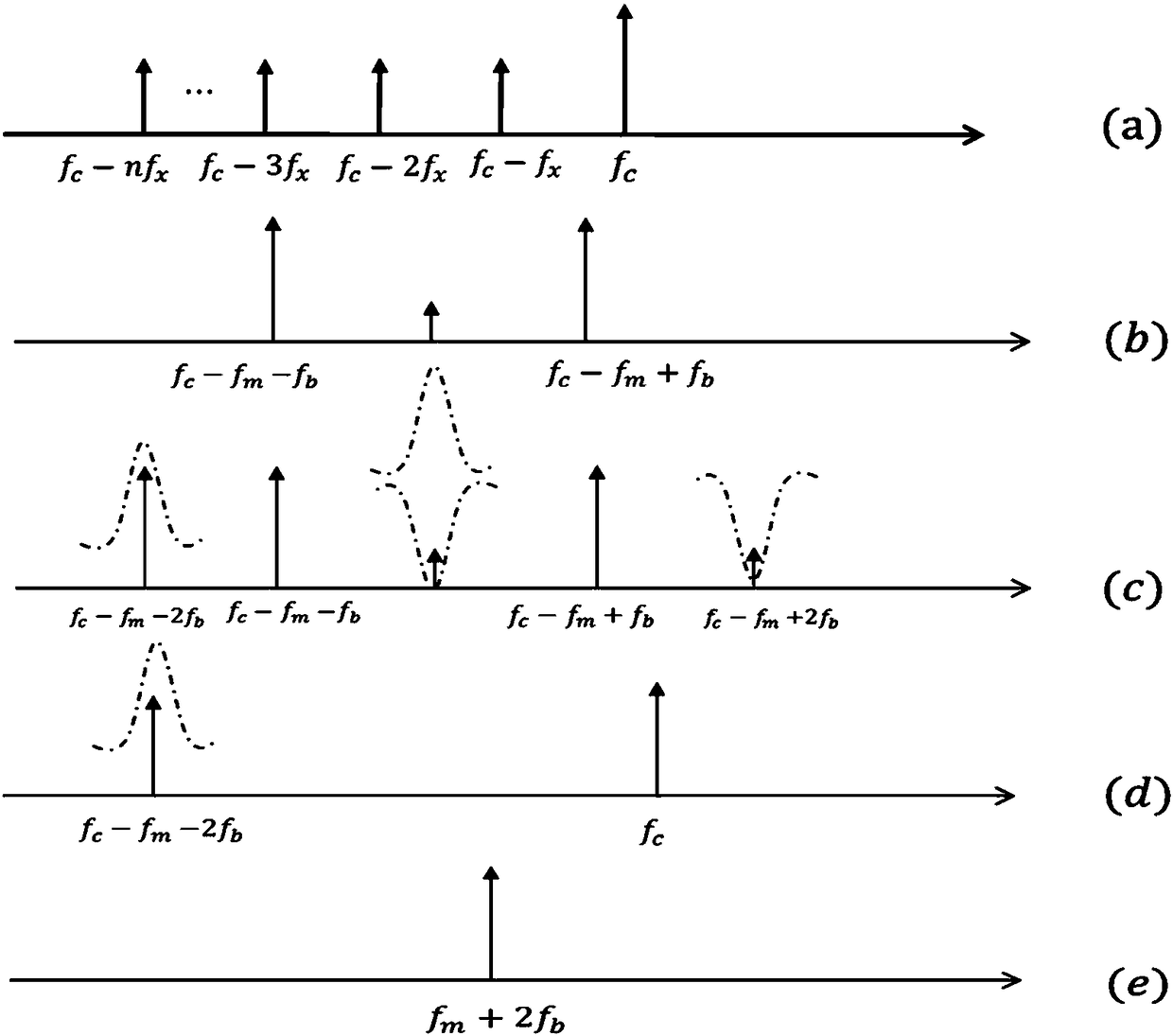
The invention discloses a microwave photon up-conversion device and method based on a photoelectric oscillator and belongs to the technical field of microwave photonics. The device is composed of a laser source, a first coupler, a first circulator, a first high nonlinearity dispersion displacement optical fiber, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, a first photoelectric detector, a second coupler, a first Mach-Zehnder modulator, a first microwave signal source, a first direct current voltage-stabilized power supply, an optical filter, a second Mach-Zehnder modulator, a second direct current voltage-stabilized power supply, a second circular, a second high nonlinearity dispersion displacement optical fiber, a second photoelectric detector, a microwave amplifier, a double-parallel Mach-Zehnder modulator, a third direct current voltage-stabilized power supply, a fourth direct current voltage-stabilized power supply, a fifth direct current voltage-stabilized power supply, an optical isolator and a spectrum analyzer. A Brillouin frequency shift value f of the high nonlinearity optical fiber is 9.2GHz, and a signal with frequency of f<m> can be up converted to f<m>+18.4GHz, so alow quality and low frequency intermediate signal is converted into a high quality and high frequency signal.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Double-pump Fourier domain mode-locked fiber optical parametric oscillator
InactiveCN102749785AAchieve laser outputFlexible tuning range controlNon-linear opticsOptical tomographyGrating
The invention relates to a fiber optical parametric oscillator for achieving Fourier domain mode-locked laser output. Seed light output by two semiconductor lasers is modulated by phase and amplified by a high power optical amplifier to serve as pump light, the pump light is output from the pump output end of a wavelength division multiplexer and enters high nonlinear fiber through a polarization controller, and a part of the pump light is transferred into signal light in the high nonlinear fiber due to fiber nonlinear effect. After the signal light passes through a second optical isolator, dispersion-shifted fiber and a tunable filter, most energy is fed back to the high nonlinear fiber from a high power shunt ratio output end of an optical coupler with 9:1 power shunt ratio through the wavelength division multiplexer so as to form resonance laser output. When modulation frequency of the tunable filter is equal to fundamental frequency of a laser resonant cavity, the Fourier domain mode-locked laser output can be obtained. The fiber optical parametric oscillator achieves the Fourier domain mode-locked laser output, has significant application value in the fields of optical tomography, fiber bragg grating sensing and the like, and has the advantages of being high in wavelength scanning frequency, flexible in laser output spectrum tuning range control and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Compact coherent high brightness light source for the mid-IR and far IR
ActiveUS8861555B2Increase spectral bandwidthImprove fluencyLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreMode locked fiber laserMetrology
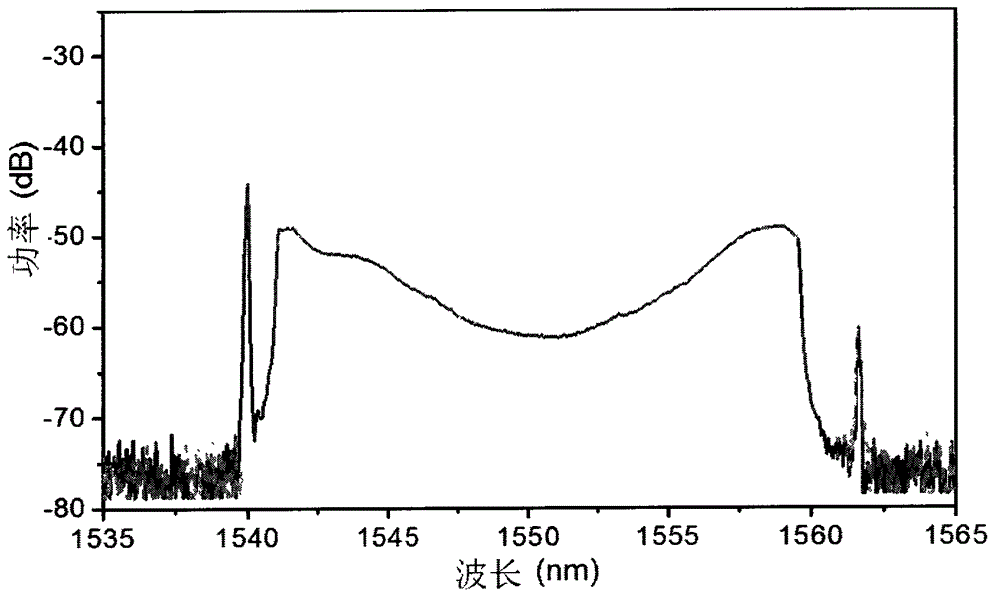
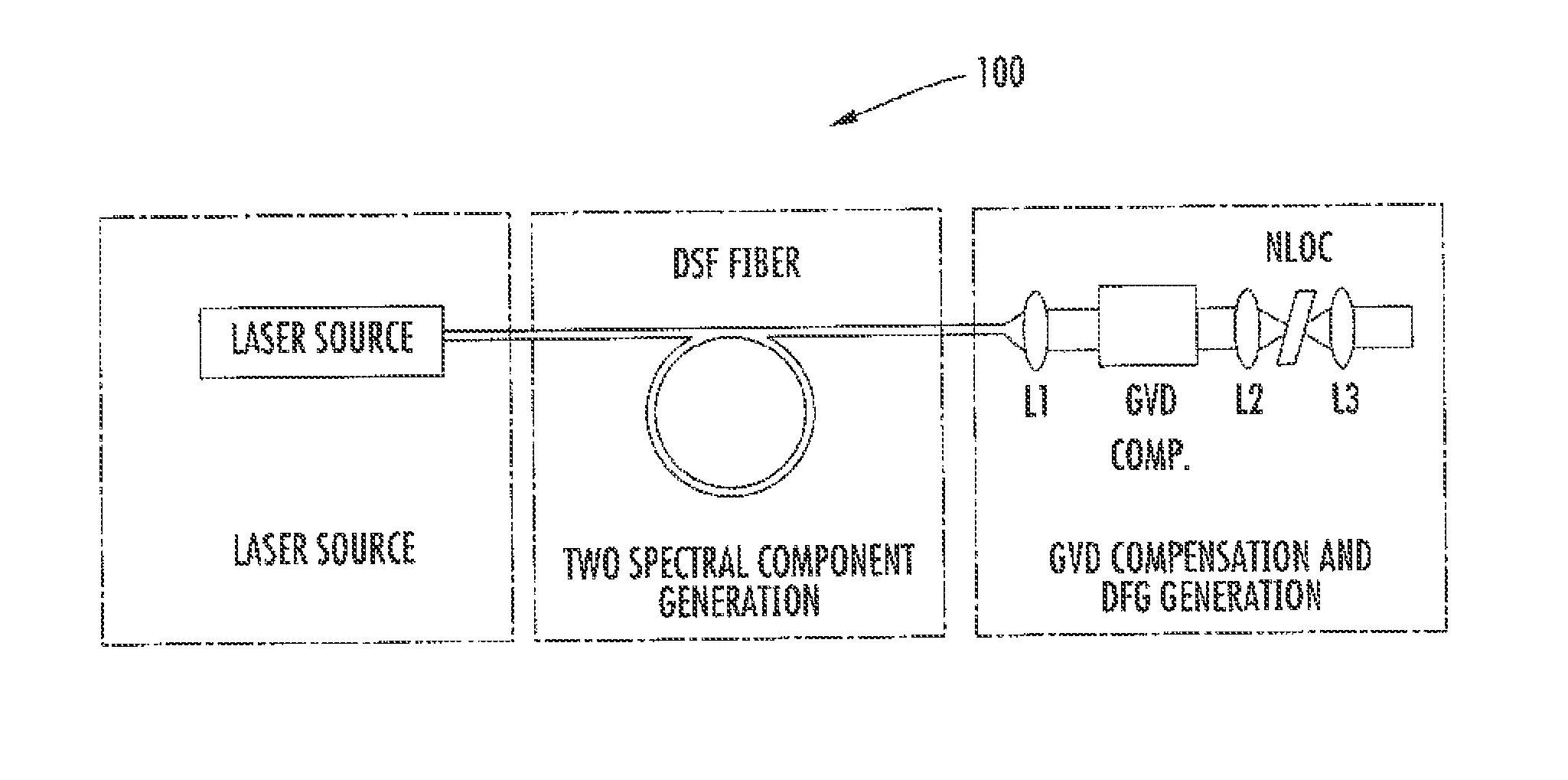
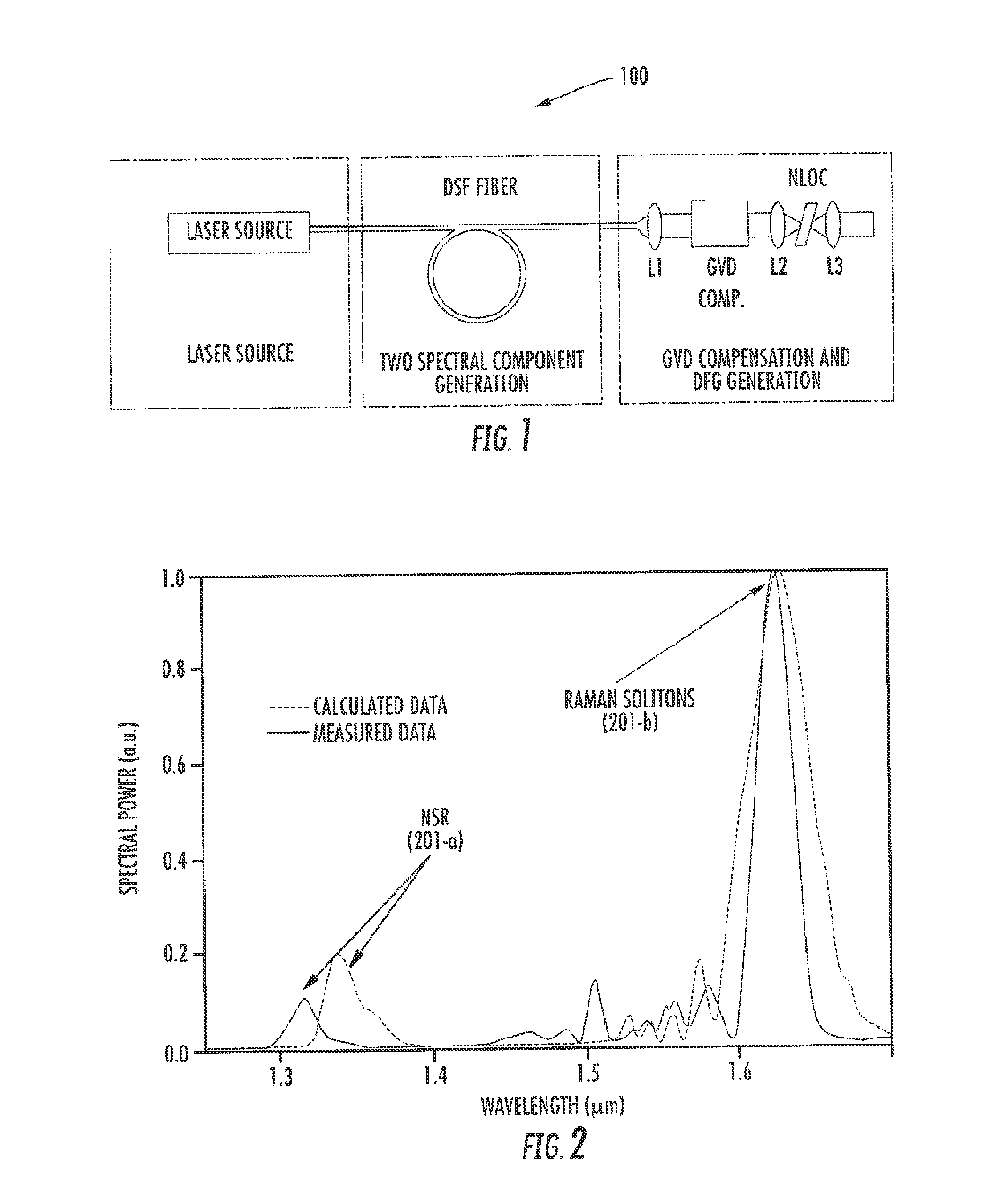
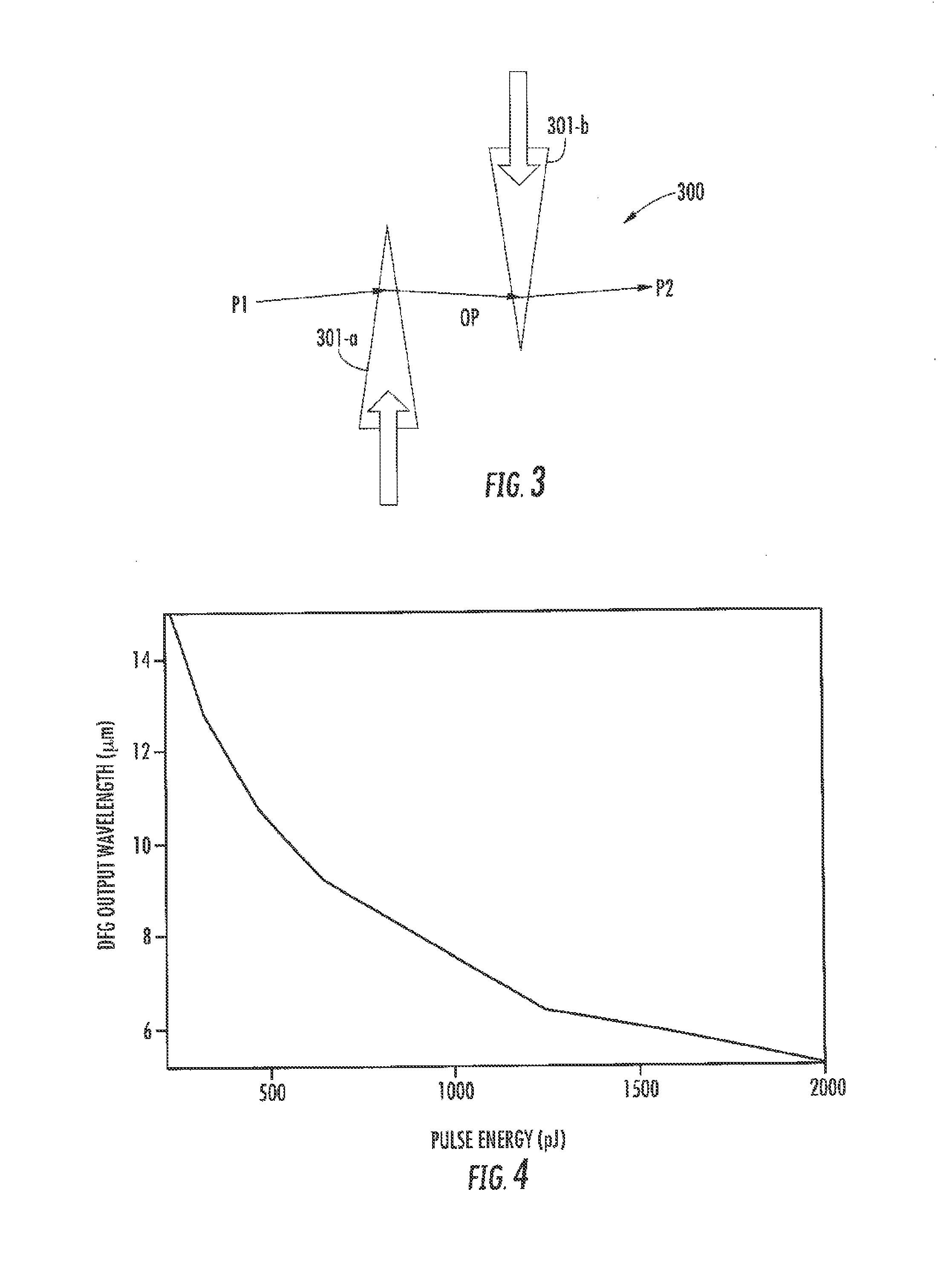
Compact laser systems are disclosed which include ultrafast laser sources in combination with nonlinear crystals or waveguides. In some implementations fiber based mid-IR sources producing very short pulses and / or mid-IR sources based on a mode locked fiber lasers are utilized. A difference frequency generator receives outputs from the ultrafast sources, and generates an output including a difference frequency. The output power from the difference frequency generator can further be enhanced via the implementation of large core dispersion shifted fibers. Exemplary applications of the compact, high brightness mid-IR light sources include medical applications, spectroscopy, ranging, sensing and metrology.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
High-sensitivity optical vector network analyzer based on stimulated Brillouin scattering
ActiveCN104165756ASimple structureHigh sensitivityTesting optical propertiesPhase responseCarrier signal
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity optical vector network analyzer based on stimulated Brillouin scattering. The high-sensitivity optical vector network analyzer based on the stimulated Brillouin scattering comprises a narrow-linewidth laser device, an optical coupler, a polarization controller, a strength modulator, an optical isolator, a filter, a chromatic dispersion displacement optical fiber, a circulator, a photoelectric detector, a vector network analyzer body, a microwave signal source and an optical amplifier. According to the high-sensitivity optical vector network analyzer based on the stimulated Brillouin scattering, carrier waves of an optical signal obtained after optical filtering are attenuated through stimulated Brillouin scattering, test errors caused by high-order edges are eliminated through two testing amplitude and phase responses of a photon passive device, and thus the testing precision of the optical vector network analyzer is improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
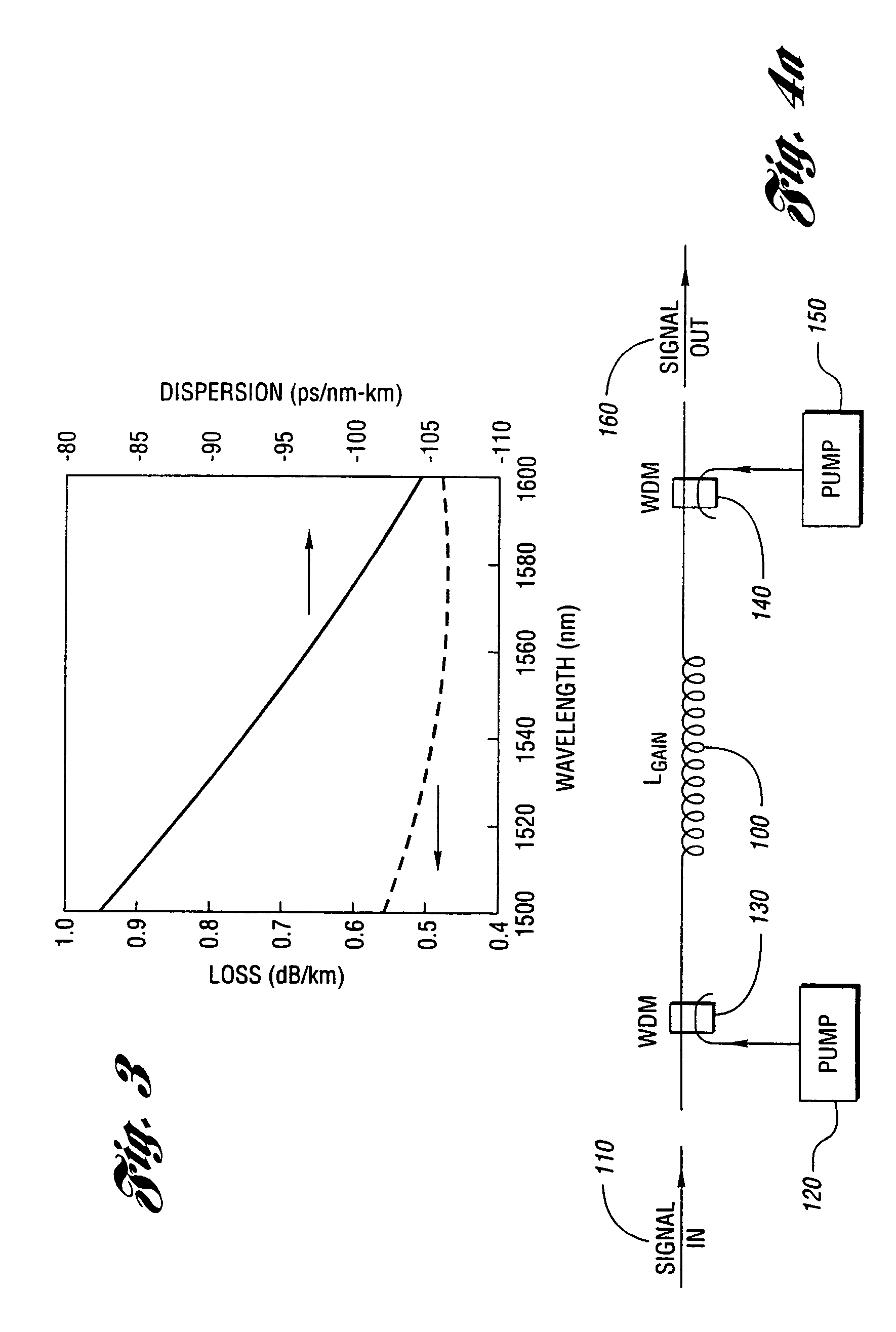
Fiber-optic compensation for dispersion, gain tilt, and band pump nonlinearity
InactiveUS6985283B1Simple system implementationCost-effectiveLaser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesErbium dopingInstability
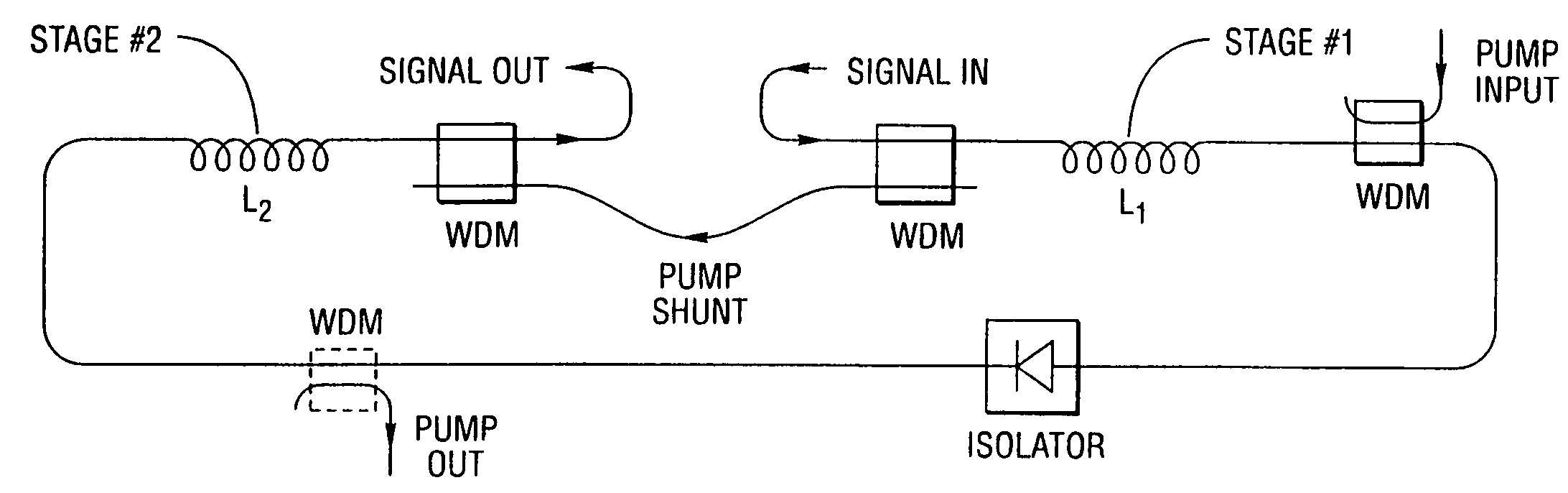
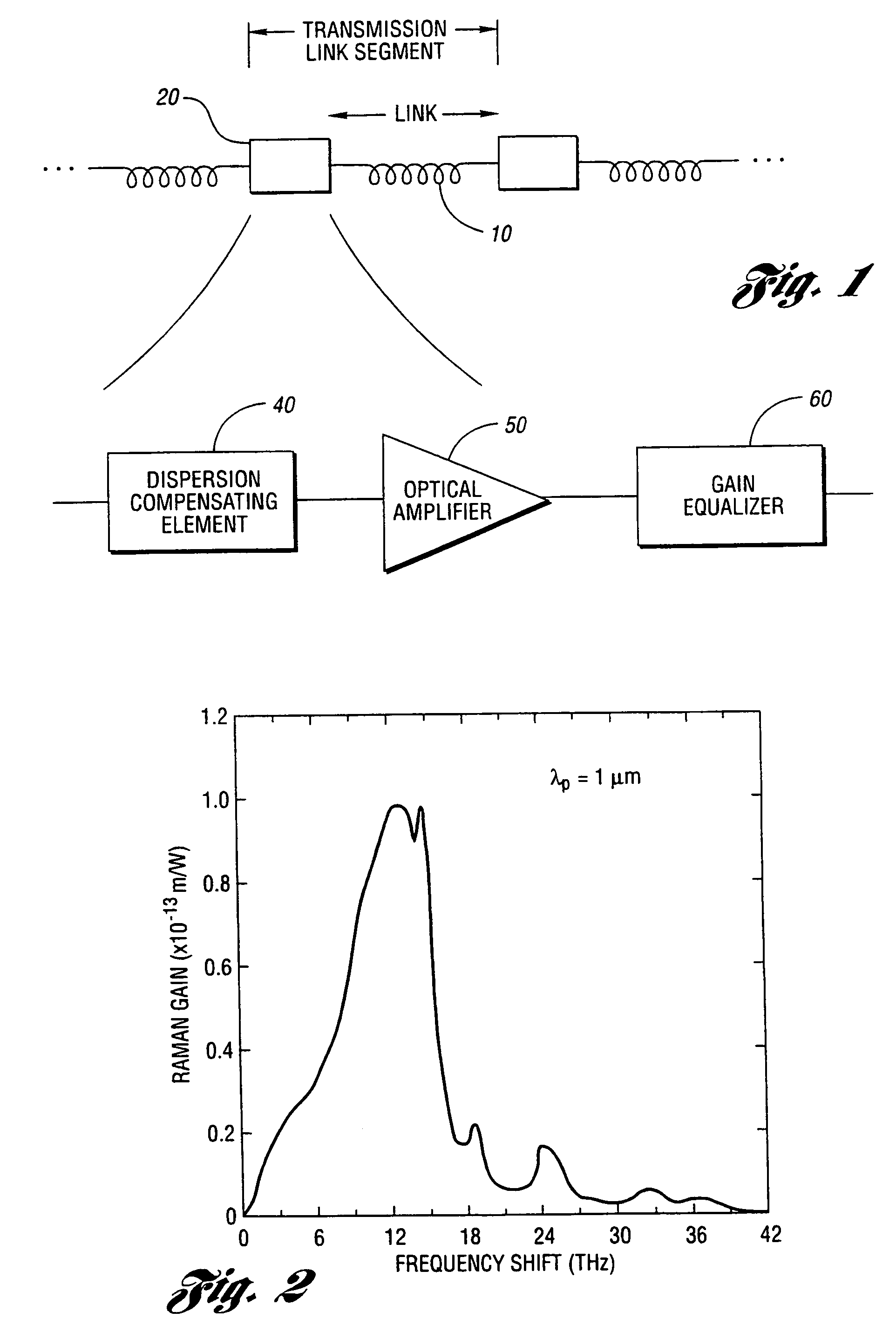
An apparatus and method are described for combining optical amplification and dispersion compensation in a Raman amplifier. A Dispersion-Managing Raman Amplifier (DMRA) combines Raman amplification with dispersion compensation by selecting the length and dispersion of the gain fiber to balance the dispersion of the link. This gain fiber is also single-mode at the signal and pump wavelengths. The pumping level is adjusted to balance the losses from the gain fiber and transmission link, while the pumping configuration is selected to remain within the 3 dB loss length for the pumping light. When the amplifier is split into two segments, the two segments may be joined by an isolator, a gain equalization element, and / or an optical add / drop multiplexer. For WDM transmission systems based on dispersion-shifted fiber (DSF), operation in the “violet band” between 1430–1530 nm is based on Raman amplification. By using a DMRA, a dispersion and nonlinearity managed system can be implemented. In particular, 4WM does not phase match in such a system, and modulation instability is absent in the transmission link. Furthermore, gain equalization can be added to the DMRA by cascading one or two Mach-Zehnder frequency filters. The invention also includes a method for symmetrically adding channels below and above the C-band, the gain tilt within the C-band can be minimized. Therefore, a roughly equal number of channels should be placed in the short-wavelength S-band and the long-wavelength L-band to minimize the Raman energy exchange in the C-band. Also, whereas C- and L-bands can be amplified using erbium-doped fiber amplifiers, the S-band can use either discrete or distributed Raman amplifiers. To minimize the interaction between pumps for different bands, alternate band pumps can be spatially dispersed and / or cross-polarized. The distributed Raman amplification can be achieved by pumping the transmission line with discrete laser diodes or by a Raman oscillator.
Owner:NEPTUNE SUBSEA IP LTD +1
Dispersion shifted fiber having low dispersion slope
InactiveUS20040197063A1Improve the level ofMinimize non-linearitiesOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexEngineering
Dispersion shifted fiber having low dispersion a slope comprising a centre core, two claddings, a ring core and the outer glass region, wherein the first cladding is provided onto the outer periphery of the centre core, the second cladding is provided onto outer periphery of the first cladding and the ring core is provided onto outer periphery of the second cladding, and the outer glass region surrounds the ring core, and the centre core and the ring core have higher refractive indices, and the claddings have lower refractive indices than the outer glass region, and the refractive indices are constrained by the equation n1>n4>n5>n2>n3. In accordance with preferred embodiment the fibre comprises of a centre core, two claddings, two ring cores, and an outer glass region, wherein the first cladding is provided onto the outer periphery of the centre core, the second cladding 3 is provided onto the outer periphery of the first cladding, the first ring core is provided onto the outer periphery of the second cladding, the second ring core 5 is provided onto the outer periphery of the first ring core and the outer glass region surrounds the second ring core, and the refractive indices are constrained by the equation n1>n4>n5>n2>n3.
Owner:STERLITE TECHNOLOGIES
Method and device for obtaining flattop Brillouin gain spectra based on pumping modulation in liquid core optical fibers
InactiveCN102820613AWide working wavelength rangeFlexible operationLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialOptical fiber couplerLight spectrum
A method and a device for obtaining flattop Brillouin gain spectra based on pumping modulation in liquid core optical fibers solve the problem in the existing method and device that flattop gain spectra cannot be obtained when adopted dispersion displacement optical fibers or standard single mode optical fibers are over long and equal amplitude pumping wires are fewer and intrinsic Brillouin gain spectra cannot be changed. The method comprises modulating lasers output by a laser to obtain multiple spectral line pumping light, inputting the multiple spectral line pumping light in the liquid core optical fibers, and obtaining the flattop Brillouin gain spectra, namely spectra of backward Brillouin scattering light in the liquid core optical fibers. The device is composed of the laser, a polarization controller, a strength modulator, a signal generator, a direct current DC stabilized power supply, an optical fiber circulator, an optical fiber coupler and the liquid core optical fibers, and another device is composed of a signal generator, an optical fiber circulator, an optical fiber coupler, the liquid core optical fibers and a phase modulator. The method and the device are applicable to obtaining of the flattop Brillouin gain spectra.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Spot size converter and optical apparatus
InactiveCN104570235ASmall sizeLow loss couplingCoupling light guidesDispersion-shifted fiberSingle-mode optical fiber
A spot size converter includes a first silicon waveguide core that includes a width-fixed region having a fixed width and a width-tapered region continuing to the width-fixed region and having a width reducing toward a terminal portion, and a second waveguide core continuing to the first silicon waveguide core and covering at least the width-tapered region. The first silicon waveguide core has a thickness-wise step in the width-fixed region.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Multiple wavelength ultra continuous light sources
InactiveCN1540906AShorten the lengthStable wavelength and frequencyLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsContinuous lightFiber coupler
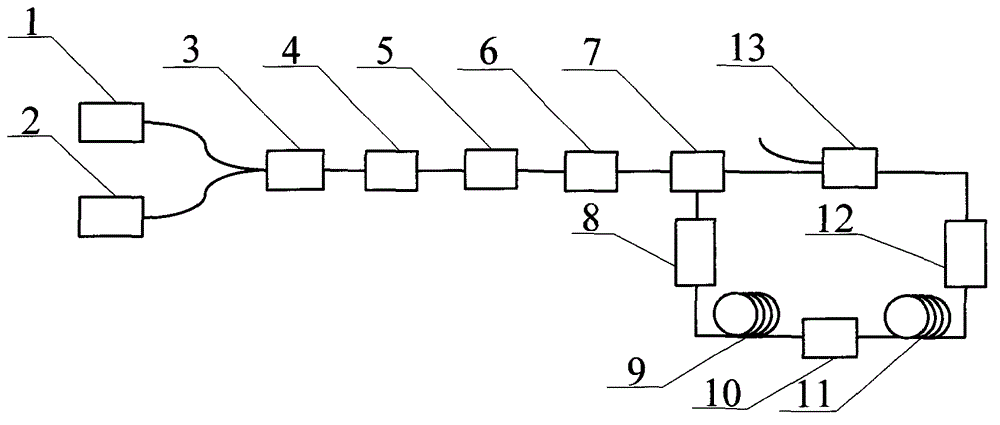
The multiple wavelength ultra continuous light source of dense wavelength division multiplexing belongs to optical communication area. Two fiber-coupler forms loop type cavity. Continuous light output from semiconductor laser through connection of 50:50 fiber coupler is input to phase modulator. Connection sequence is as following: from radio frequency microwave source to phase modulator, dispersed fiber, powerful erbium doping amplifier, dispersion displacement optical fiber, 90:10 fiber coupler. 90% output port is connected to another input port of 50:50 fiber couplers. 10% port is connected to one end of erbium doping fiber amplifier, and another end of the erbium doping fiber amplifier is input to demultiplexer. The invention through modulation generates stable shorter light wavelength with lower injected optical power.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Device and method for simultaneously measuring frequencies of multiple microwave signals
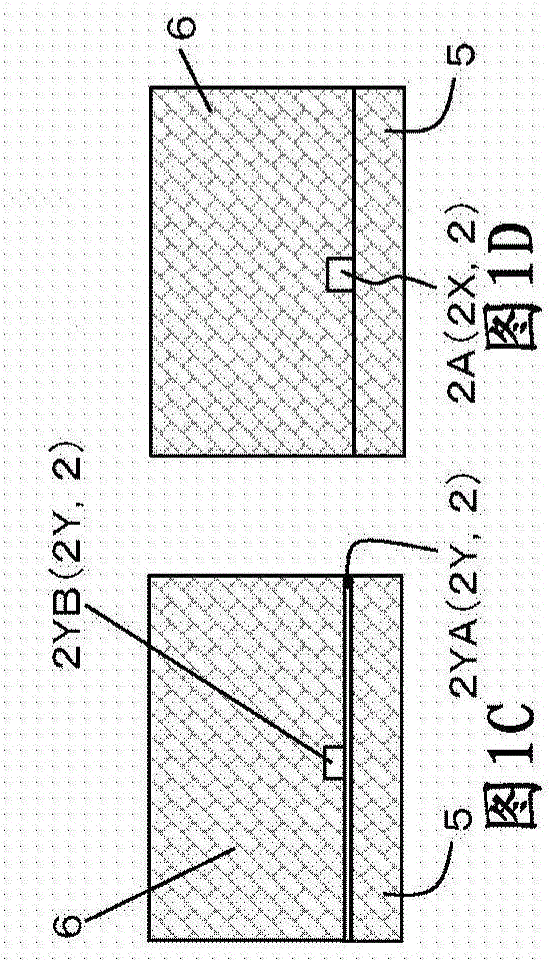
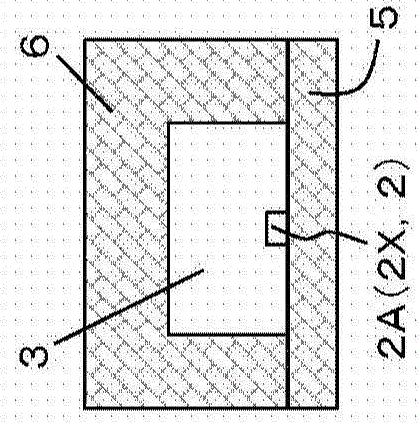
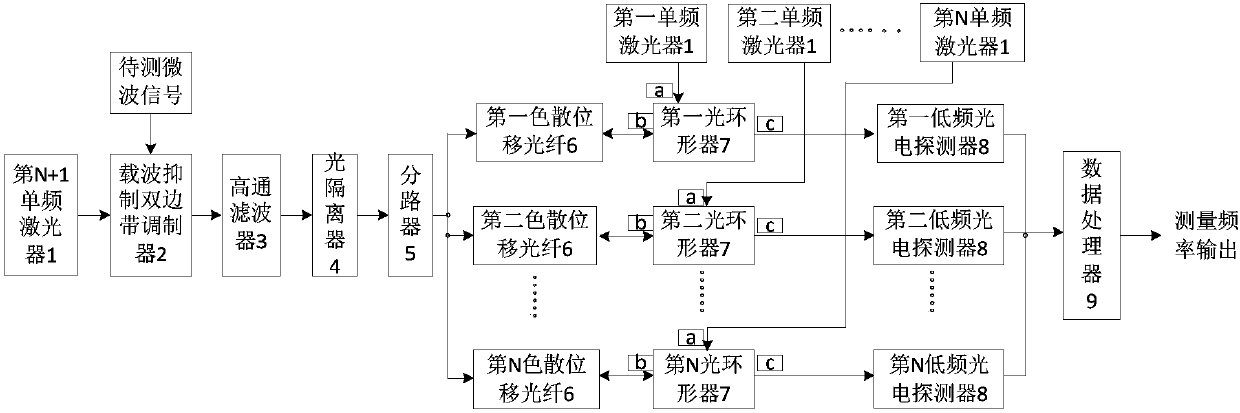
ActiveCN107765086AWide measurement frequency rangeImprove measurement resolutionFrequency to amplitude conversionICT adaptationImage resolutionEngineering
The invention discloses a device and a method for simultaneously measuring the frequencies of multiple microwave signals. An upper side-band optical signal including the frequency of a to-be-measuredmicrowave signal is obtained through a modulator and a filter and sent to dispersion shifted fibers. When the frequency difference of laser signals input to the two ends of any dispersion shifted fiber is Brillouin frequency shift, part of energy of a laser signal output by a corresponding single-frequency laser is transferred to the upper side-band optical signal. A data processor measures the output current of a low-frequency photoelectric detector under the condition that the to-be-measured microwave signal is not added and the output current of the low-frequency photoelectric detector under the condition that the to-be-measured microwave signal is added, and compares the currents. If the output current of the low-frequency photoelectric detector under the condition that the to-be-measured microwave signal is added is larger, the to-be-measured microwave signal contains a microwave signal of a corresponding frequency. If the output current of the low-frequency photoelectric detectorunder the condition that the to-be-measured microwave signal is added is unchanged or smaller, the to-be-measured microwave signal does not contain a microwave signal of a corresponding frequency. Multiple microwave frequencies can be instantaneously measured. Moreover, the measurement frequency range is wide, and the measurement resolution is as high as 0.1GHz.
Owner:MINNAN NORMAL UNIV
Optical fiber tape of low polarization mode dispersion characteristic and method for measuring dynamic viscoelasticity of the optical fiber tape
InactiveUS7209614B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFibre mechanical structuresDwdm transmissionDynamic viscoelasticity
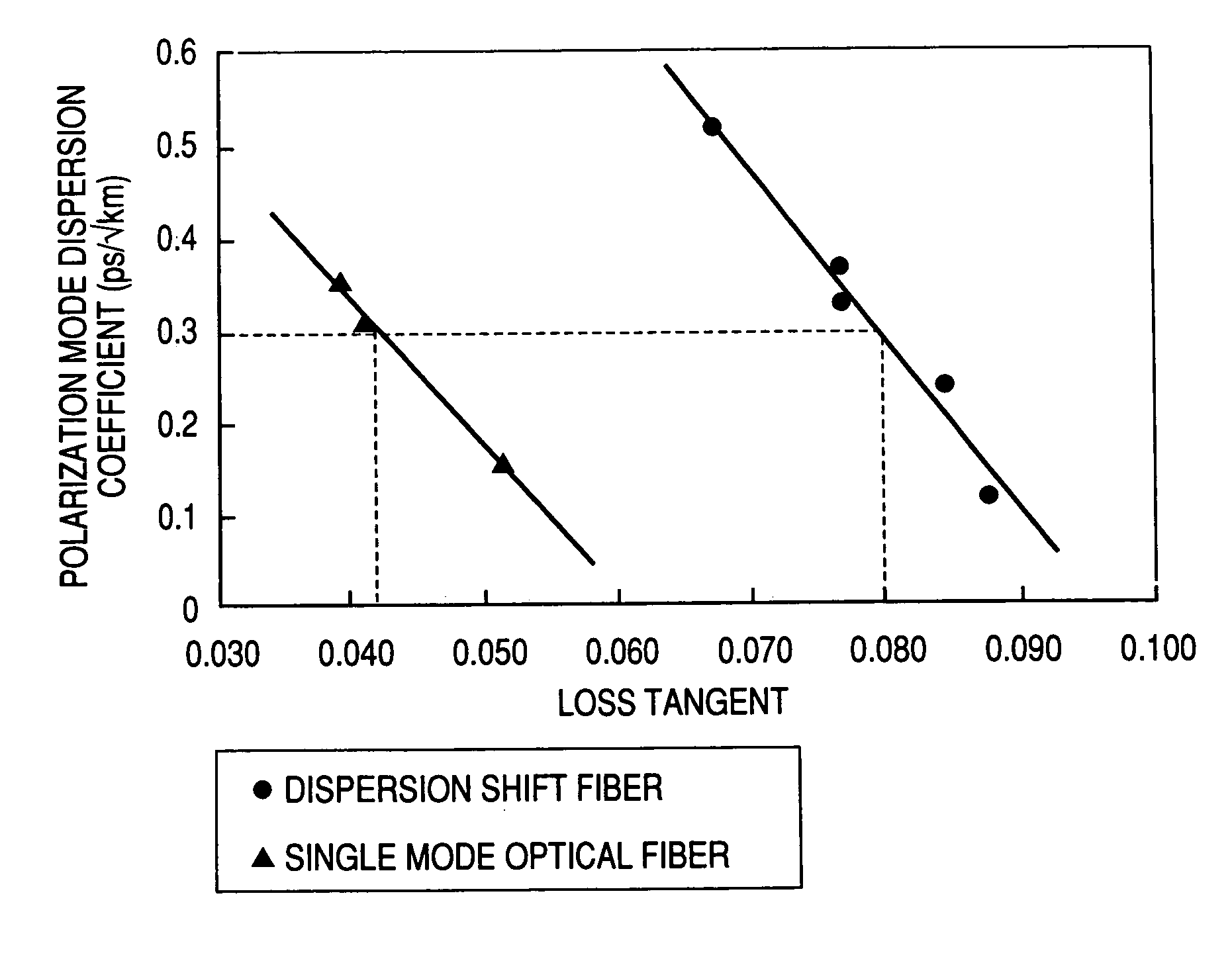
An optical fiber tape having low polarization mode dispersion characteristics and applied to a dense wavelength multiplex (DWDM) transmission system of a transmission rate from several Gb / s to several tens of Gb / S. We have found out that the polarization mode dispersion of an optical fiber tape relates to the loss tangent (tan δ) determined when the dynamic viscoelasticity is measured, and that particularly, if the loss tangent of when a dispersion shift fiber is used is made 0.080 or more and the loss tangent of when a single mode optical fiber is used is made 0.042 or more, the polarization mode coefficient of dispersion (PMD) is reduced to 0.3 ps / √km preferable to realize a DWDM transmission system.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
High-dispersion fibers for high-speed transmission
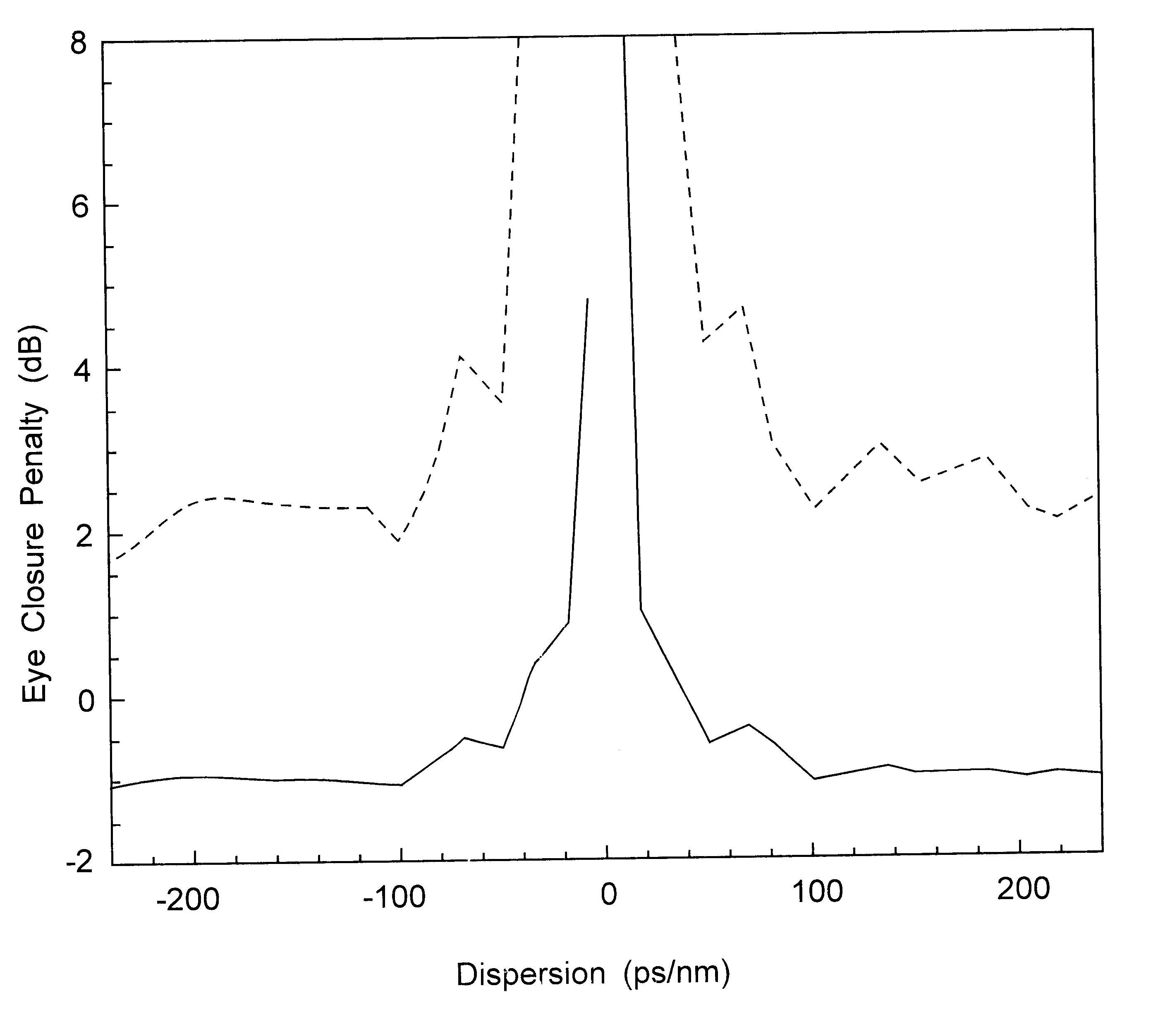
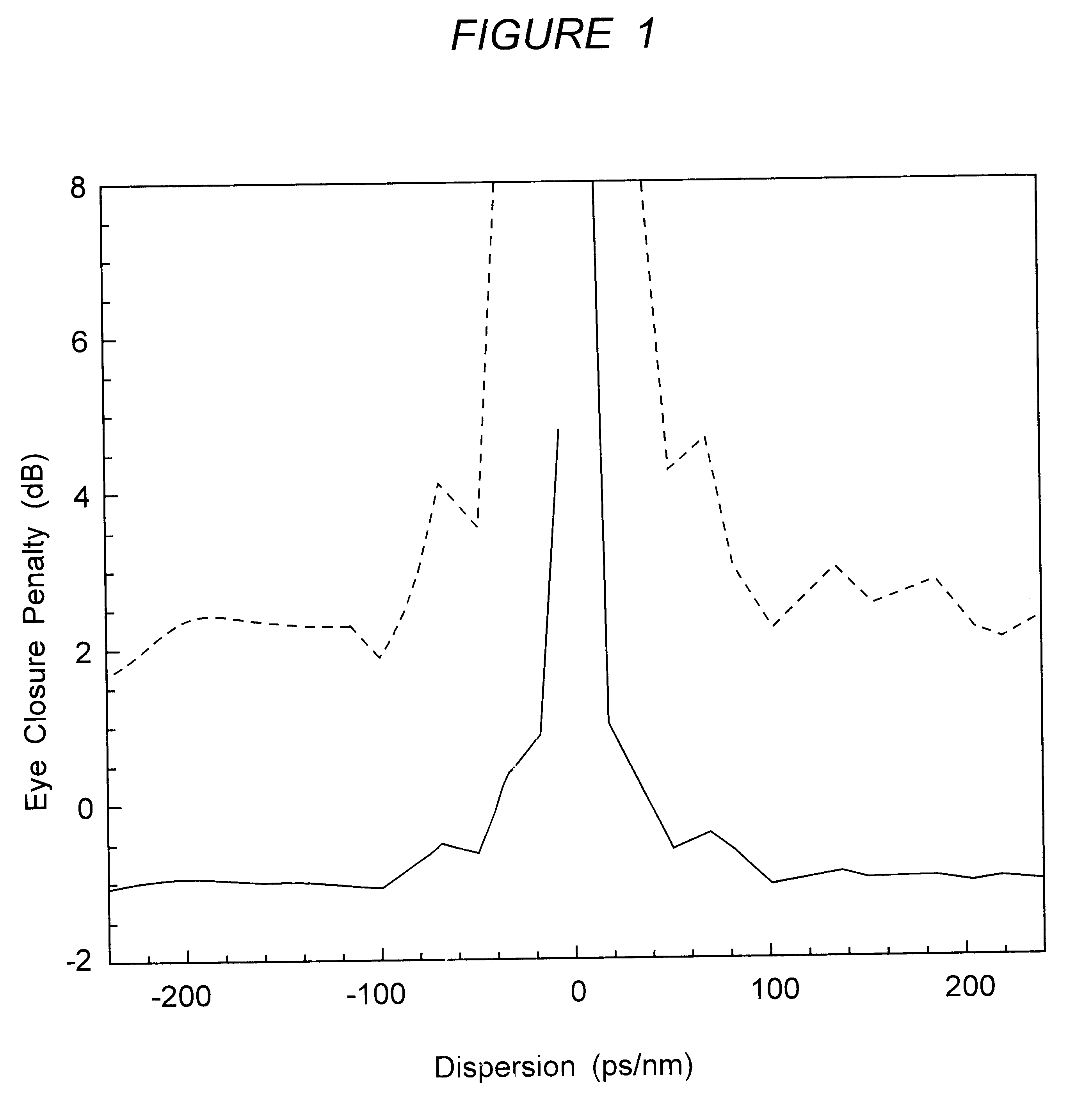
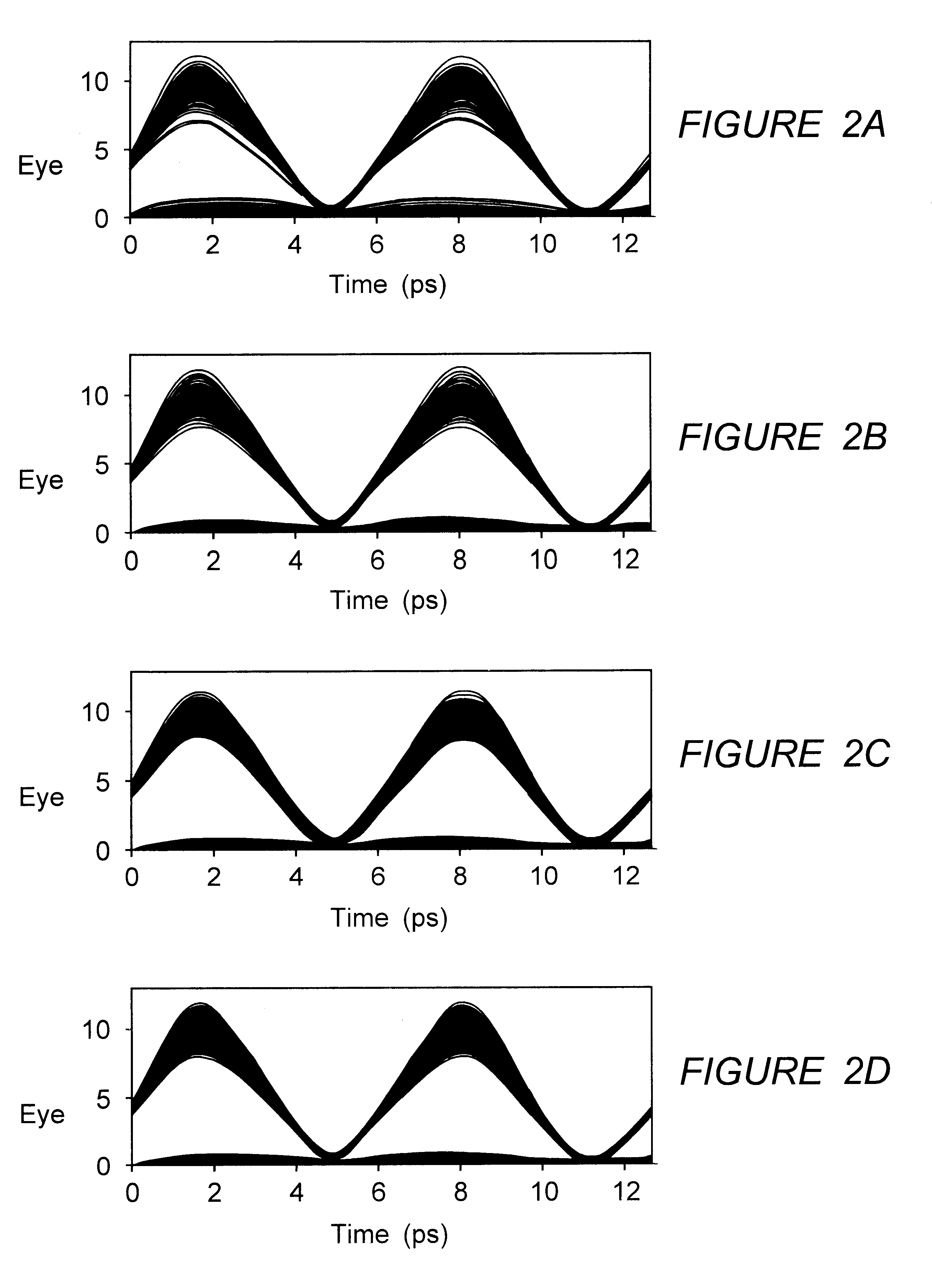
The specification describes an optical transmission system for high speed, high capacity digital pulse transmission, i.e. at least 10 Gb / s at a duty cycle of at least 10%, which uses transmission fiber with a dispersion value greater than 20 ps / (nm-km) or more negative than -5 ps / (nm-km). The system operates in the pseudo-linear transmission mode (PLTM). In the PLTM it was discovered that pulse distortion decreases, i.e. eye closure penalty actually decreases, as the dispersion value increases. System performance actually improves by increasing the value of absolute dispersion of the transmission fiber.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
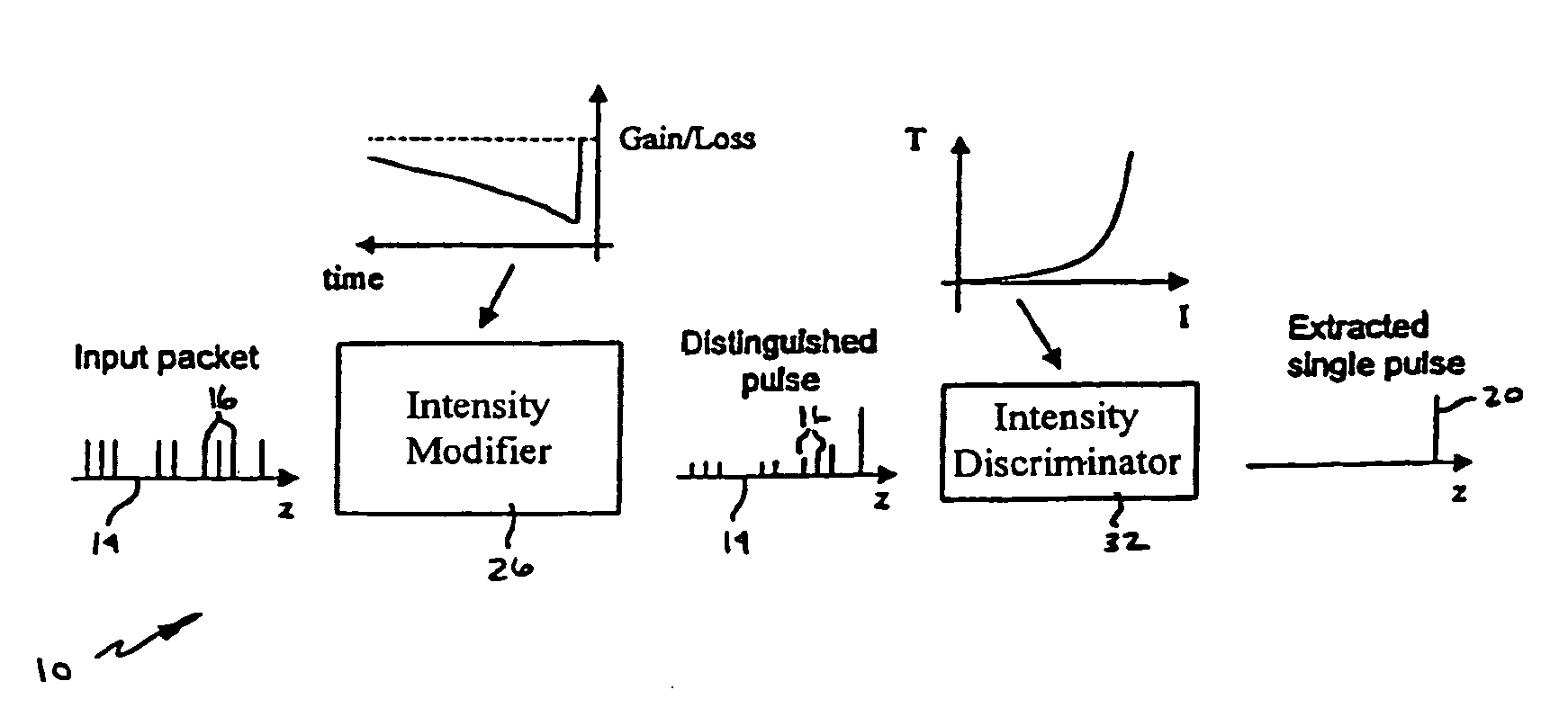
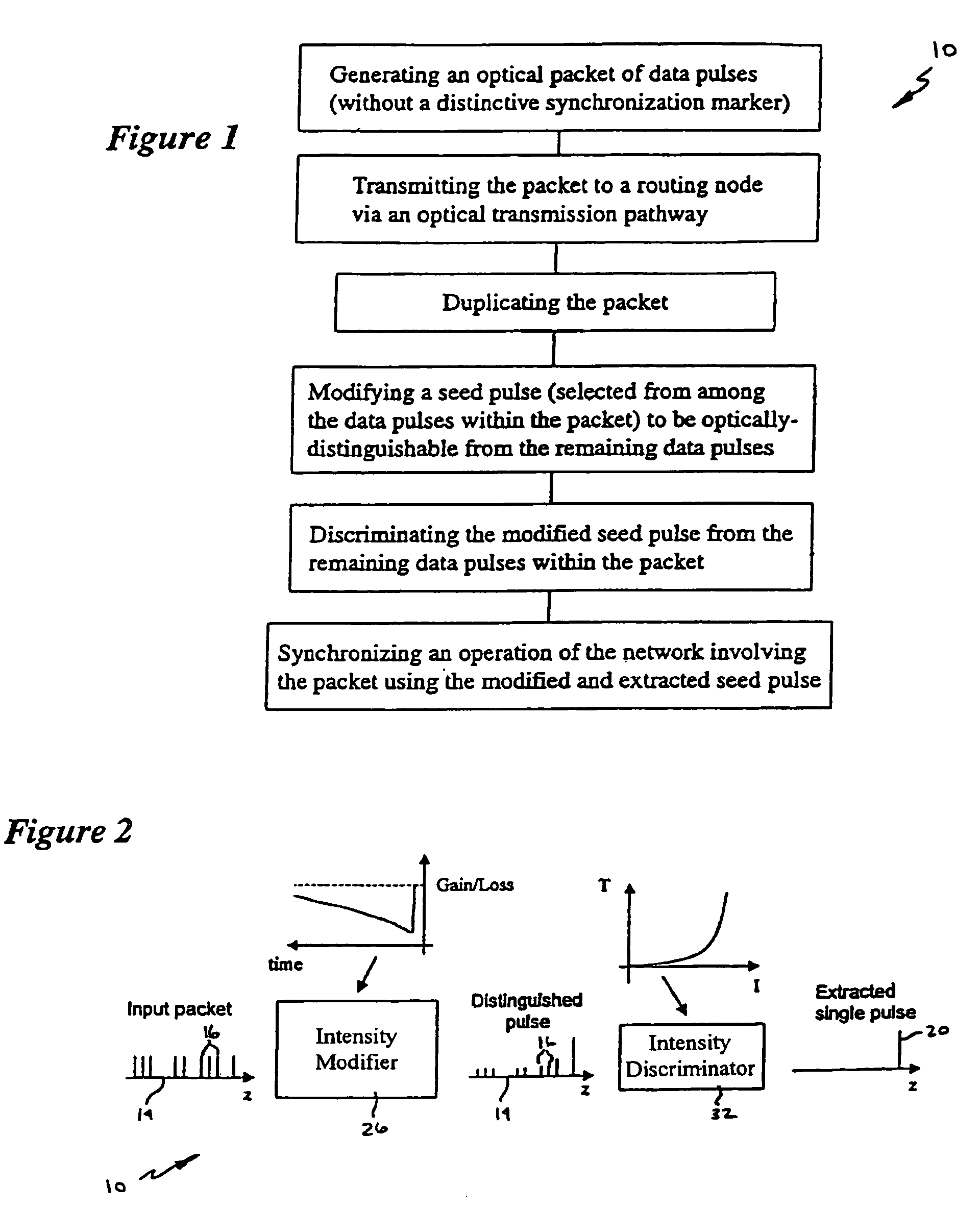
Self-synchronization of an optical packet network using seed pulses extracted from within the packets
InactiveUS7099593B1Same characteristicsCladded optical fibreTime-division optical multiplex systemsDiscriminatorBandpass filtering
Owner:UNIV OF MICHIGAN THE
Micro-cantilever beam fiber grating micro-displacement sensor based on quantum enhancement
PendingCN110260800AAchieve ultra-high sensitivity measurementAvoid stressUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyGratingSpectrum analyzer
The invention discloses a micro-cantilever beam fiber grating micro-displacement sensor based on quantum enhancement. The micro-cantilever beam fiber grating micro-displacement sensor comprises a laser, a 2*1 coupler, a filter, an erbium-doped fiber amplifier, a filter, a fiber polarization controller, a fiber polarization beam splitter, a dispersion displacement fiber, a coarse wavelength division multiplexer, a fiber isolator, a fiber Bragg grating, a micro-cantilever beam, a balance detector and a spectrum analyzer. According to the invention, quantum entangled double light beams generated after four-wave frequency mixing are used, the quantum entangled double light beams have high quantum correlation, the intensity difference quantum noise of each mode is reduced, the detection light and the reference light quantum correlation noise are subtracted to generate a noise substrate lower than the shot noise limit, so that signals annihilated under the quantum noise can be detected, and thus, ultra-high sensitivity measurement of micro-displacement breaking through the quantum noise limit is achieved. The micro-cantilever beam fiber grating micro-displacement sensor has the advantages of high sensitivity, safety, reliability and the high practical value.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Swept wavelength broadband Raman pump source
ActiveUS6967767B2High repetition rateLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionFiberLinear dispersion
A swept wavelength source for broad bandwidth Raman pump applications includes a source of ultrashort (e.g., picosecond) optical pulses. The pulse train output from the source is then applied as an input to a linear dispersive element (such as a section of negative dispersion-shifting fiber) which functions to “stretch” the ultrashort pulses, causing the pulses to become separated in time, with a continuous shift in the wavelength through the length of the pulse.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Dispersion shifted optical fiber having triple clad
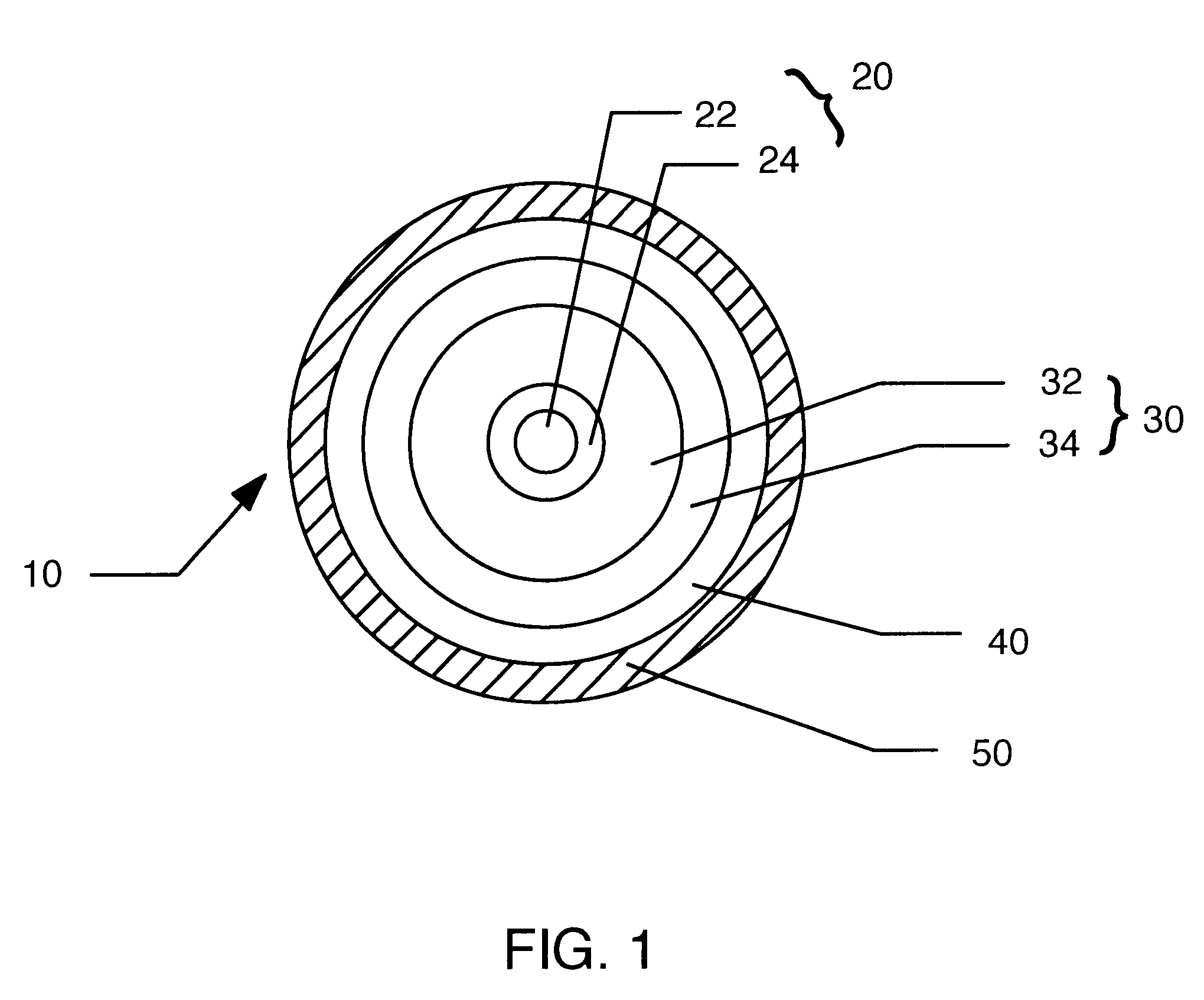
InactiveUS6516125B1Increase the effective areaDecreased bending lossOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingLength waveSilicon dioxide
The present invention is related to a dispersion-shifted optical fiber for use in a wavelength division multiplexing system, which comprises a core, an inner clad, and a silica clad, wherein the optical fiber has a relatively low dispersion at a wavelength of 1550 nm, an effective area of 60 mum2 and small bending loss. The core consists of a first and a second core, wherein the core has a refractive index distribution. The inner clad consists of a first inner clad having a refractive index smaller than that of the second core and a second inner clad having a refractive index smaller than that of the second inner clad. A silica clad surrounds the inner clad and has a refractive index smaller than that of the second inner clad.
Owner:LG CABLE LTD (KR)
System and method for generating multi-wavelength laser source using highly nonlinear fiber
A number of embodiments provide multi-Wavelength Laser Source (MWLS) designs based on Super Continuum (SC) generation using Highly Non-Linear optical Fiber (HNLF). Advantageously, in some embodiments this technology only needs a single wavelength locking mechanism to tune and lock the whole set of channels to the ITU grid. Furthermore, in some embodiments, this laser system is able to provide wavelength channels in all the S, C and L bands. In this design, the optical signal provided by an initial seed laser source goes through a wavelength channel multiplier stage based on HNLF and is expanded in the frequency domain to cover a wider wavelength range. The wavelength channel multiplier consists of a number of optical fibers including various combinations of HNLF, single mode fiber and dispersion shifted fibers.
Owner:PELETON PHOTONIC SYST
Optical transmission system
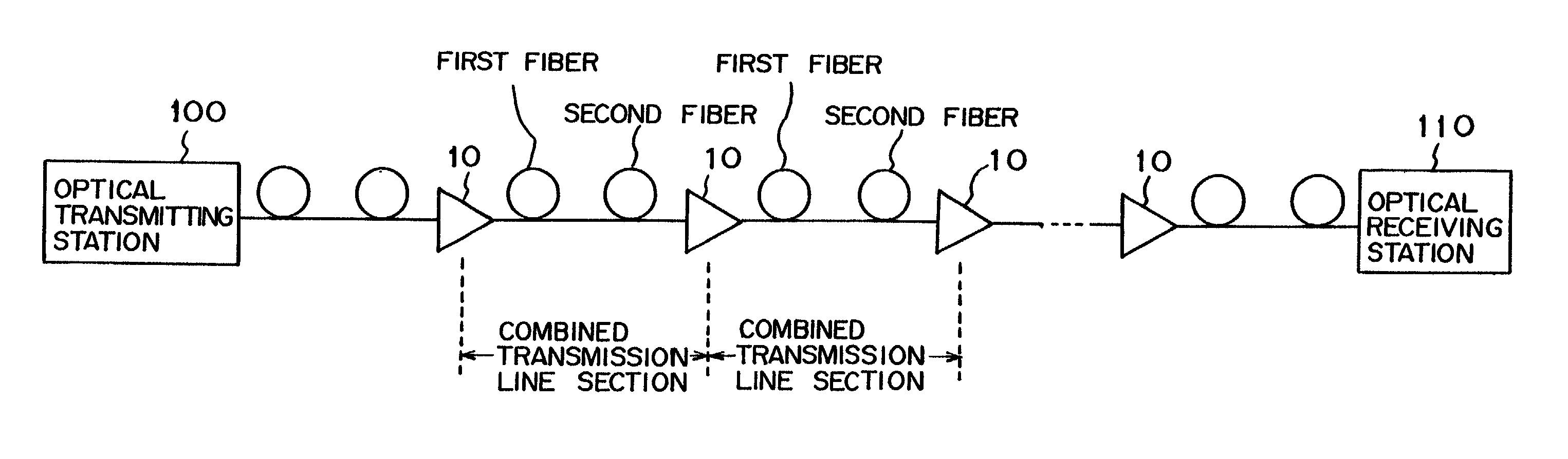
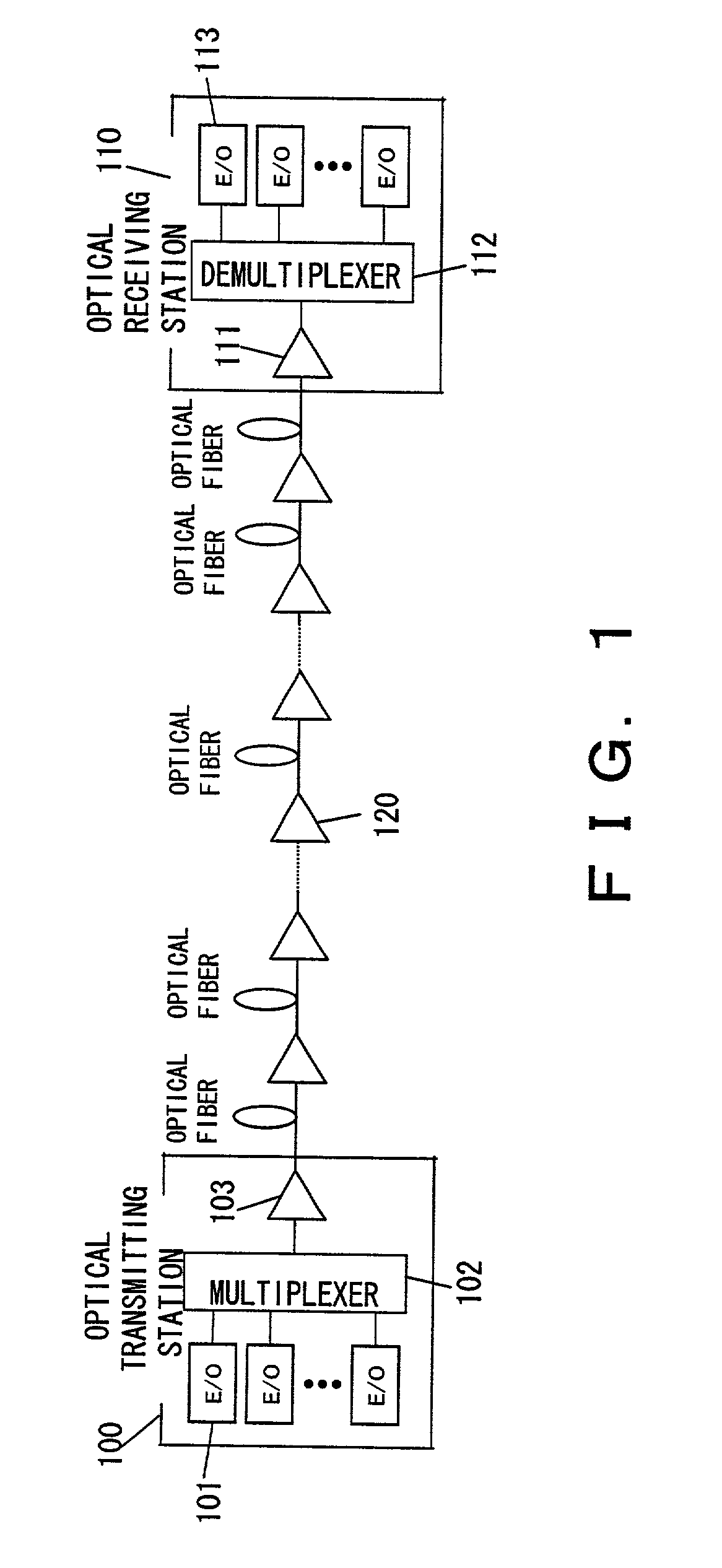
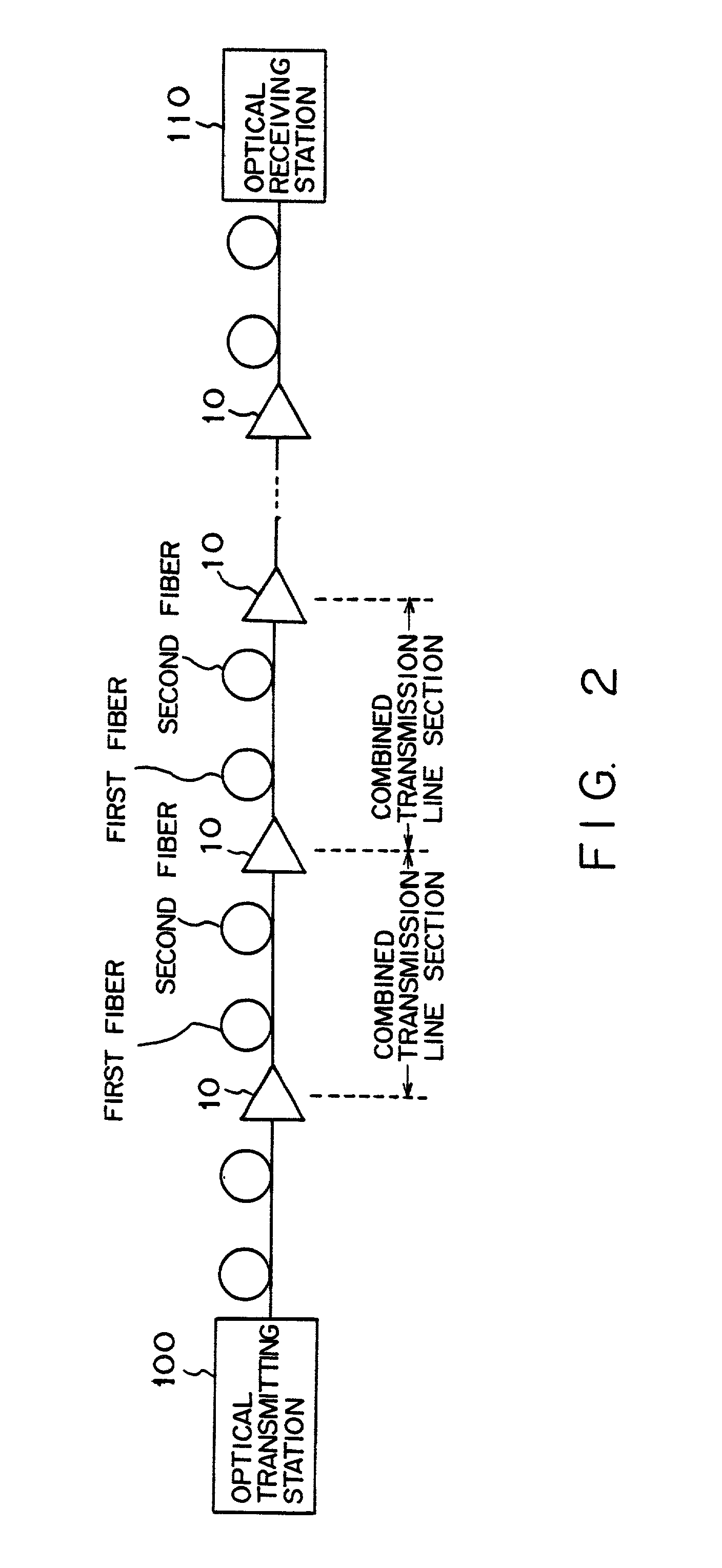
InactiveUS7209654B2Little degradationSmall mode field diametersLaser using scattering effectsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberOptical data transmission
A plurality of optical repeaters are provided on a transmission line between an optical transmitting station and an optical receiving station. A combined transmission line section is provided between optical repeaters. The combined transmission line section is composed of the first optical fiber, which is a positive-dispersion fiber, and the second optical fiber, which is a negative-dispersion fiber. Signal light is inputted to the first optical fiber in each combined transmission line section. Each optical repeater inputs pump light to the second optical fiber.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical sampling system based on quantum dot mode-locked laser devices
ActiveCN104155721ASimple structureAchieve integrationOptical light guidesPolarization controllerPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses an optical sampling system based on quantum dot mode-locked laser devices. The system comprises the multiple quantum dot mode-locked layer devices, a wavelength division multiplexer, a polarization controller, an optical amplifier, a first circulator, a dispersion displacement optical fiber, a second circulator, a random waveform generator, a sampling device, a wave resolving multiplexer, a plurality of photoelectric detectors and a plurality of electric signal processing modules. Optical sampling is achieved based on the quantum dot mode-locked laser devices, the wavelength-division multiplexing technology and a Brillouin balancer, the system structure is simple, the wideband and all-optical sampling can be achieved, and the sampling precision is higher under the situation that the sampling rate is high.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dispersion shift optical fiber
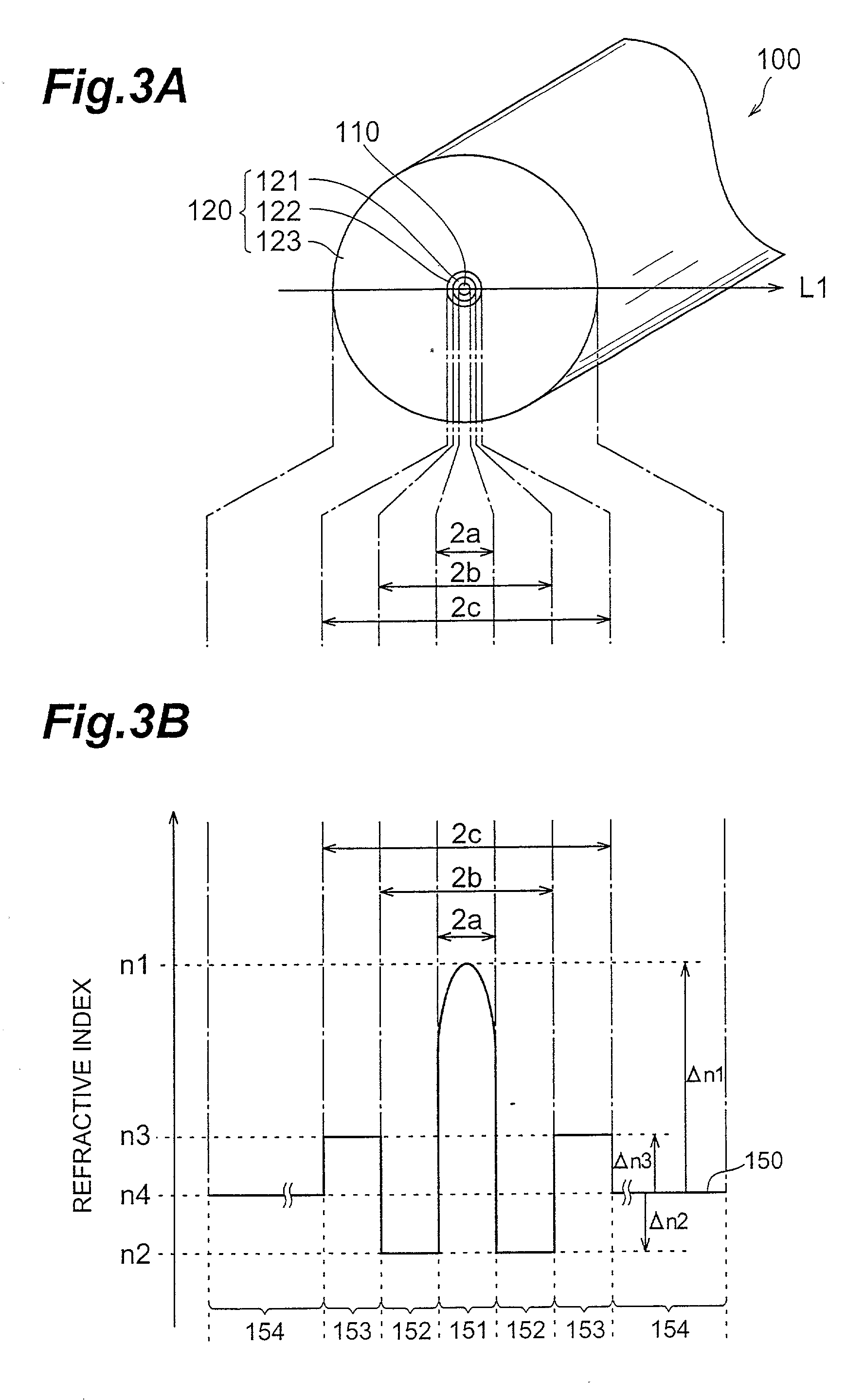
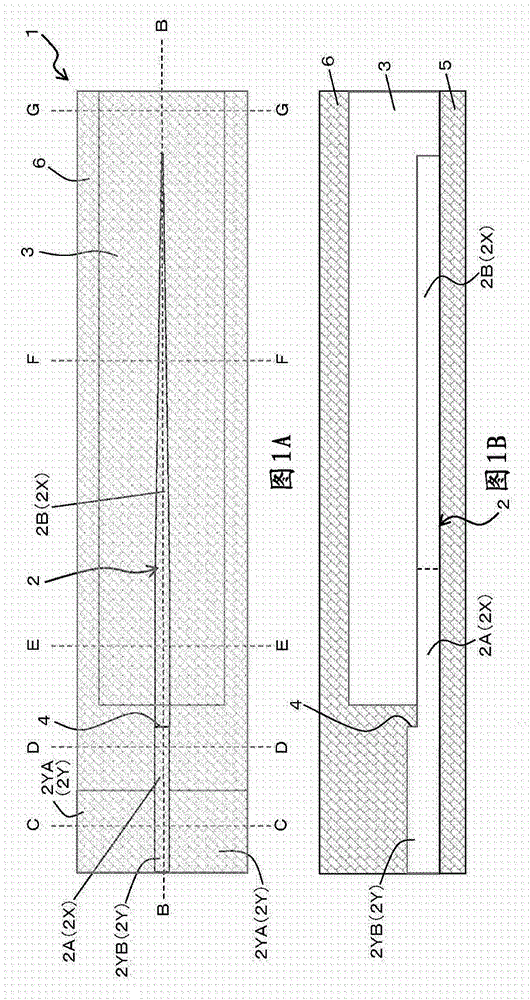
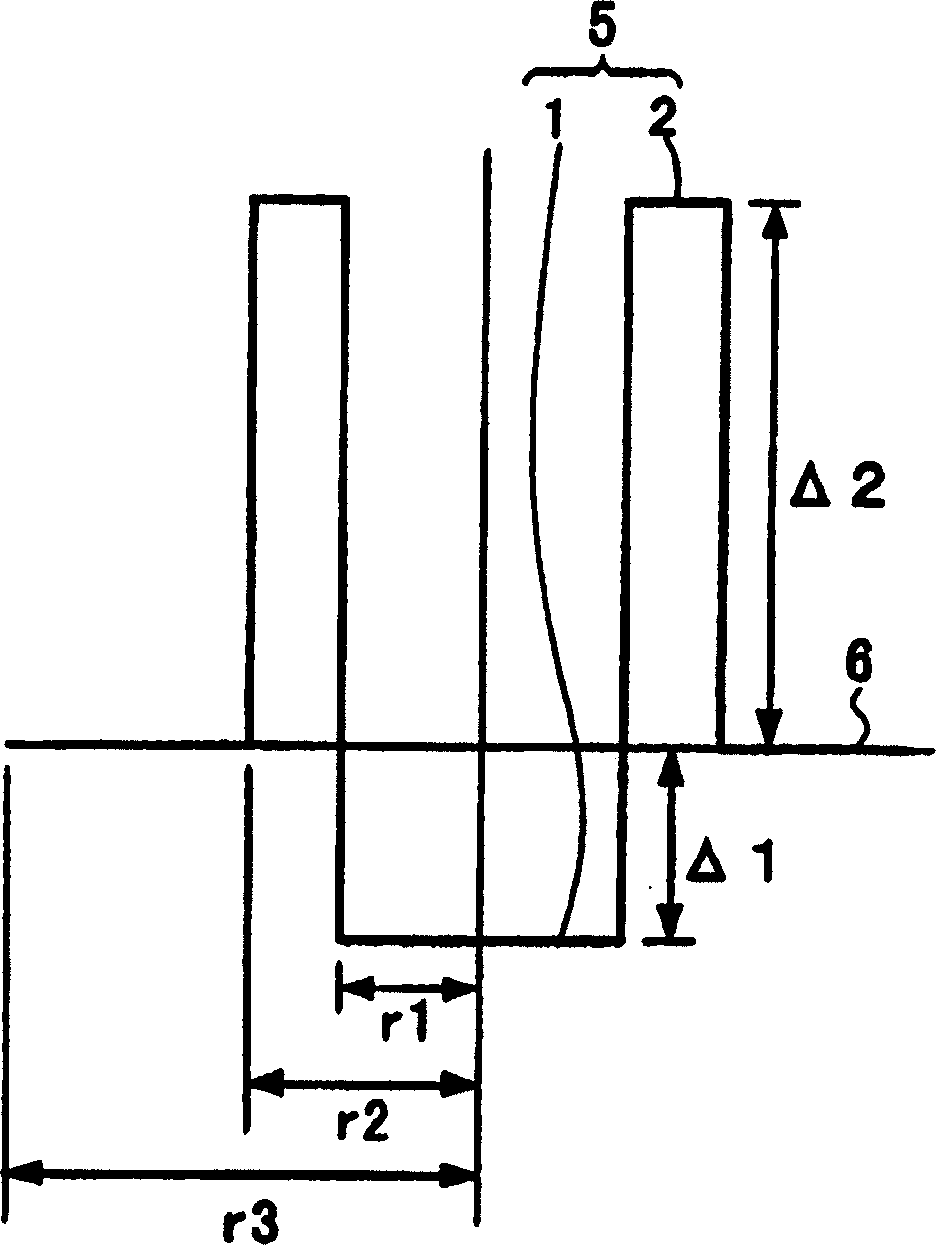
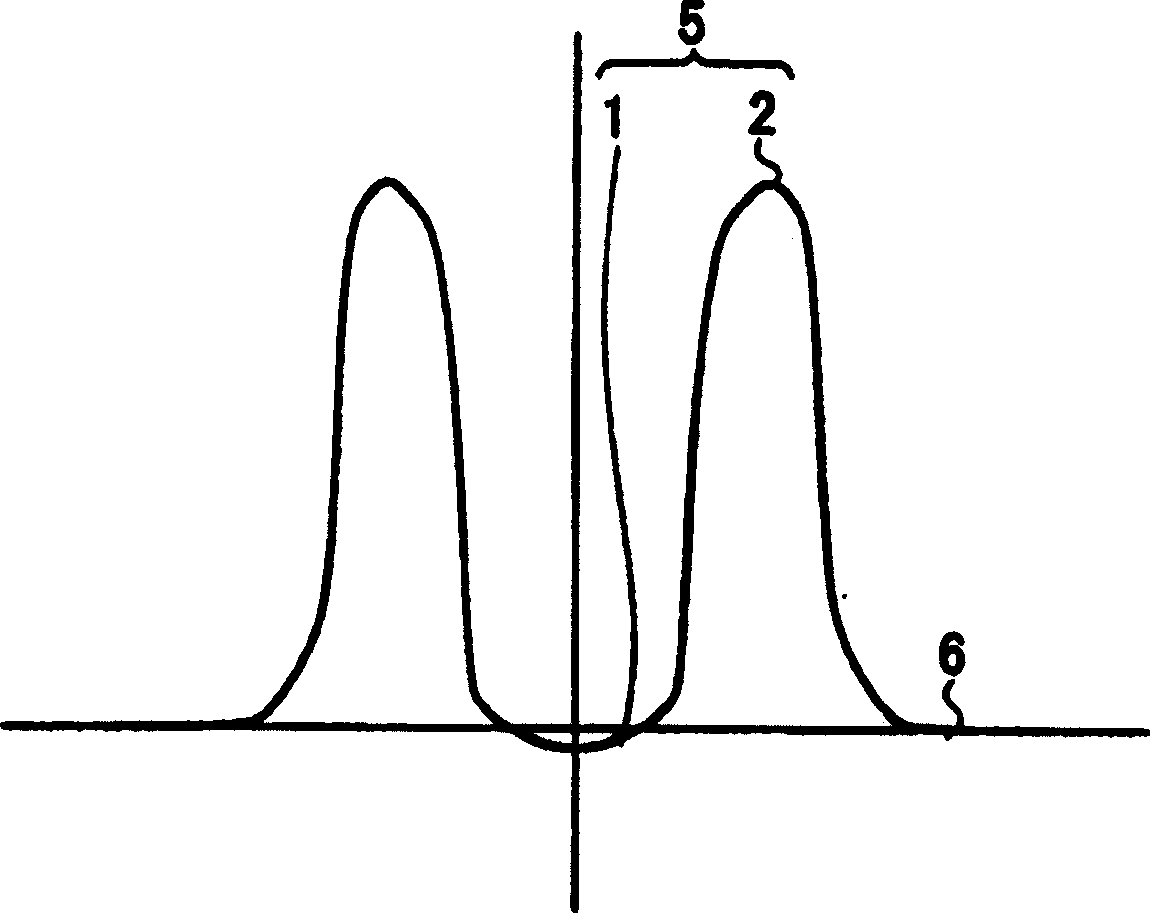
The present invention provides a dispersion-shifted optical fiber, which is formed by a core and a cladding provided on its outer periphery, the core includes a central core; a peripheral core, the peripheral core is arranged on the outer periphery of the central core, and its refractive higher than that of the central core, the cladding has a refractive index profile whose refractive index is smaller than that of the peripheral core, and by properly setting the structural parameters, it is substantially a single mode, and the bending loss is below 100dB / m condition, in addition, the effective core cross-sectional area can be sufficiently increased, and the dispersion slope can be reduced.
Owner:FUJIKURA LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com