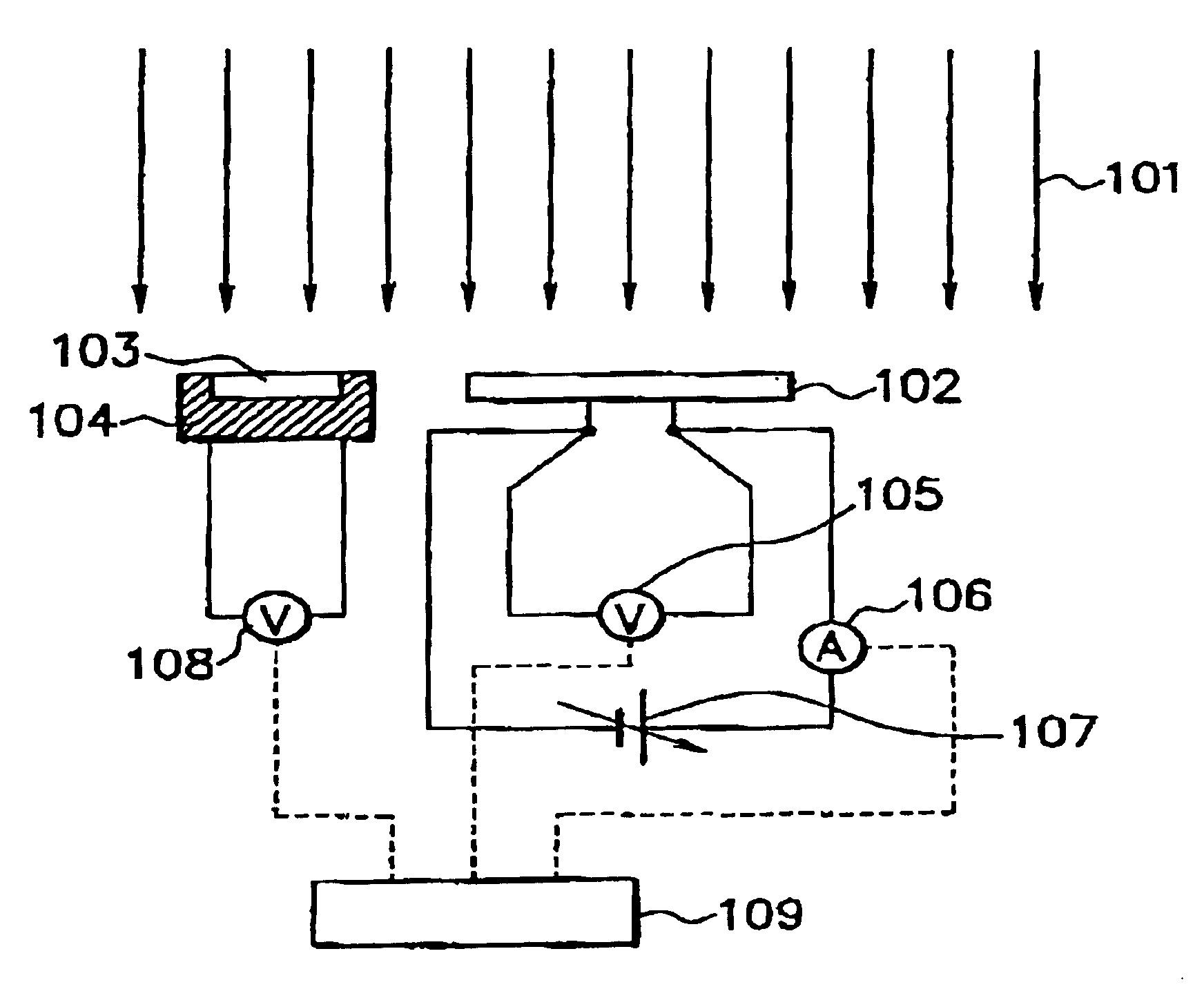
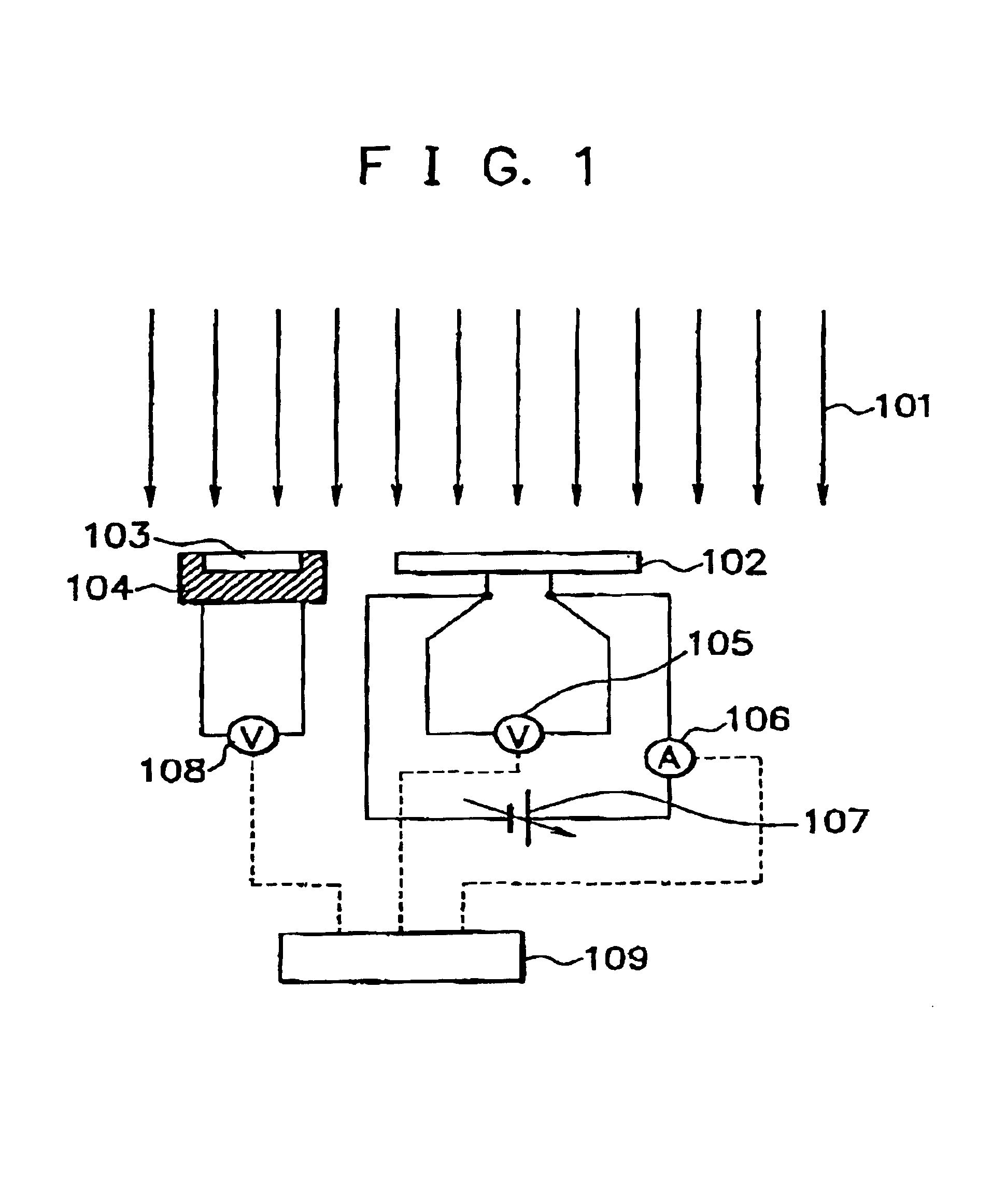
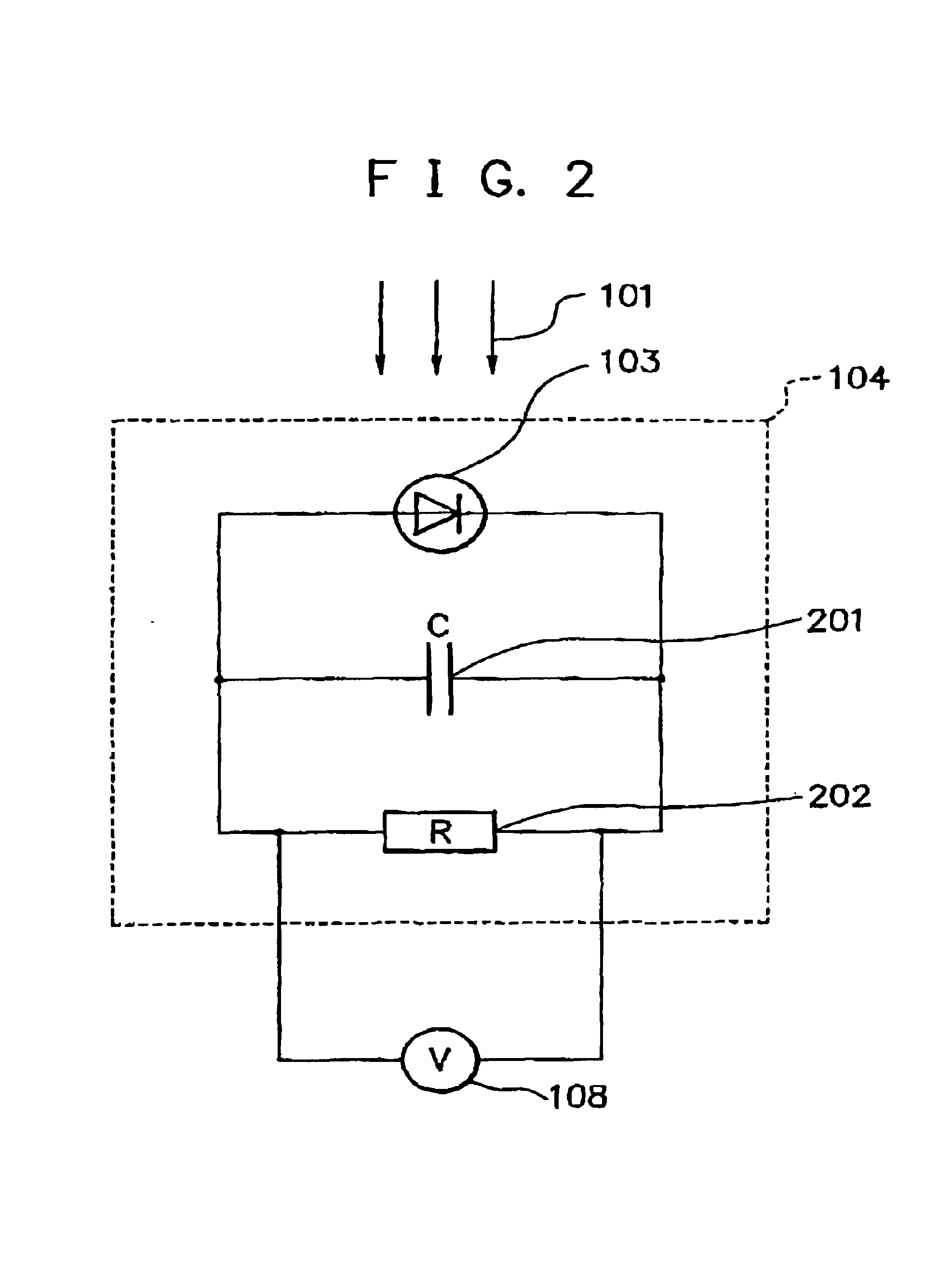
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
283 results about "Current–voltage characteristic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
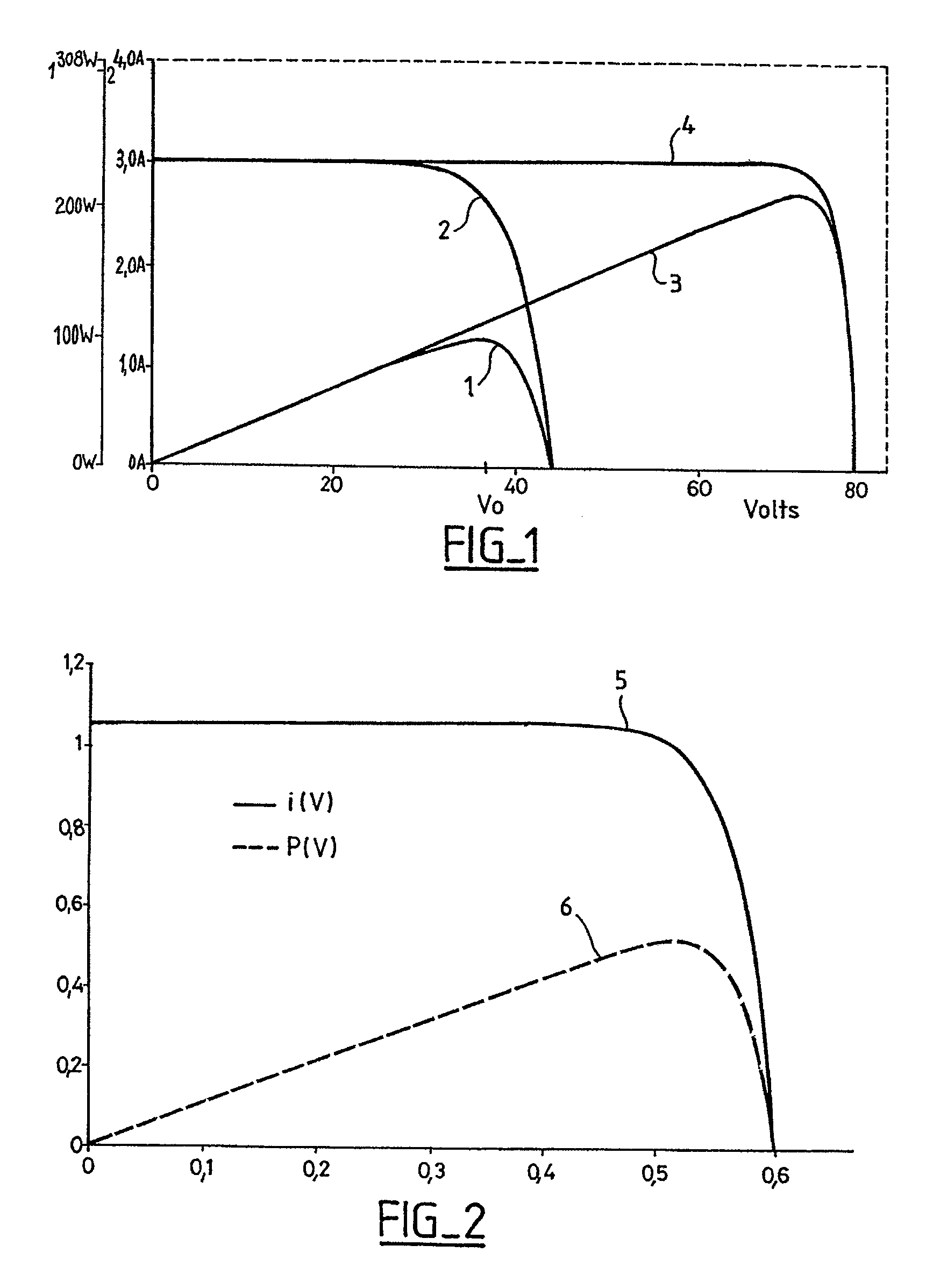
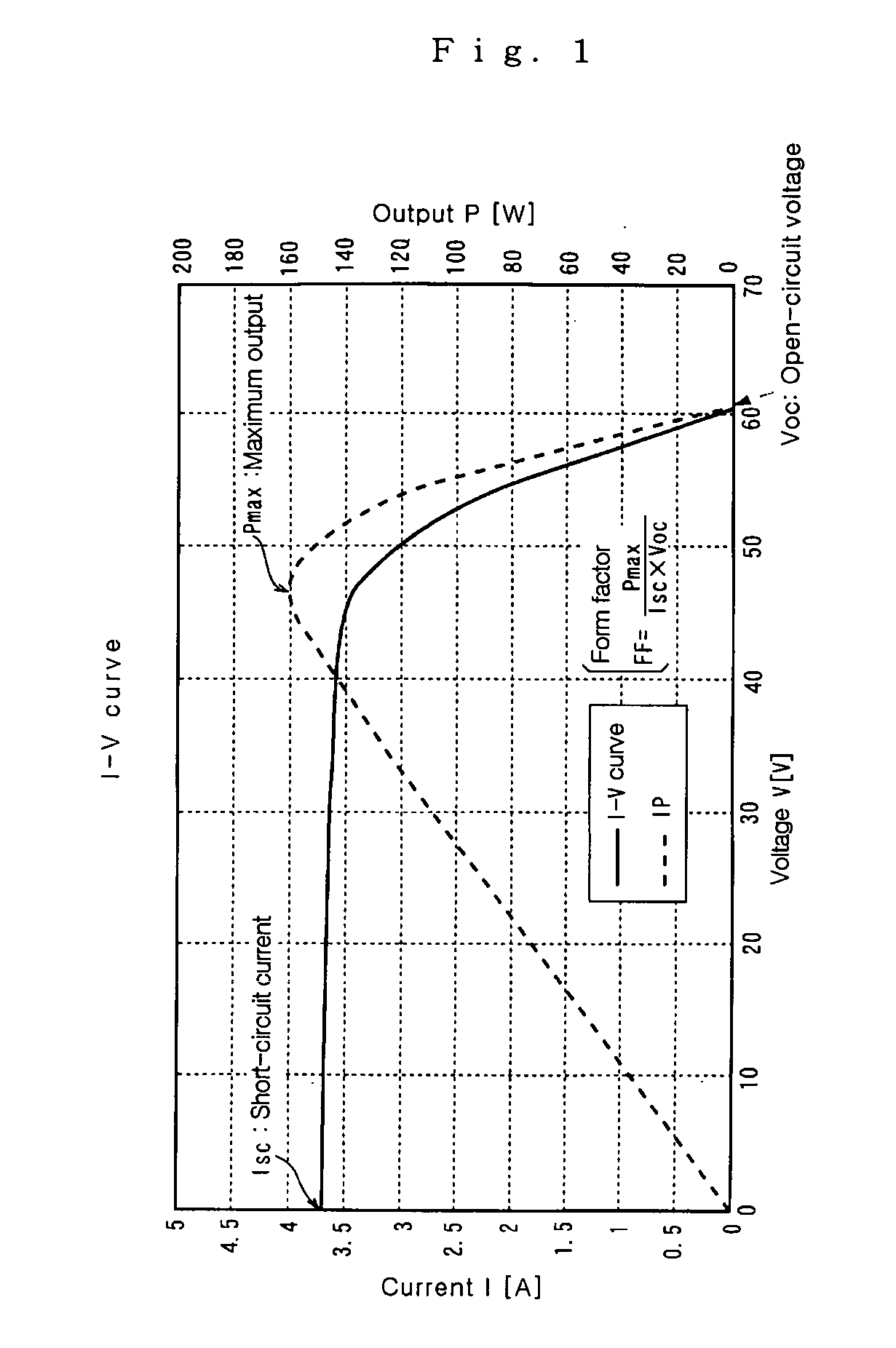
A current–voltage characteristic or I–V curve (current–voltage curve) is a relationship, typically represented as a chart or graph, between the electric current through a circuit, device, or material, and the corresponding voltage, or potential difference across it.
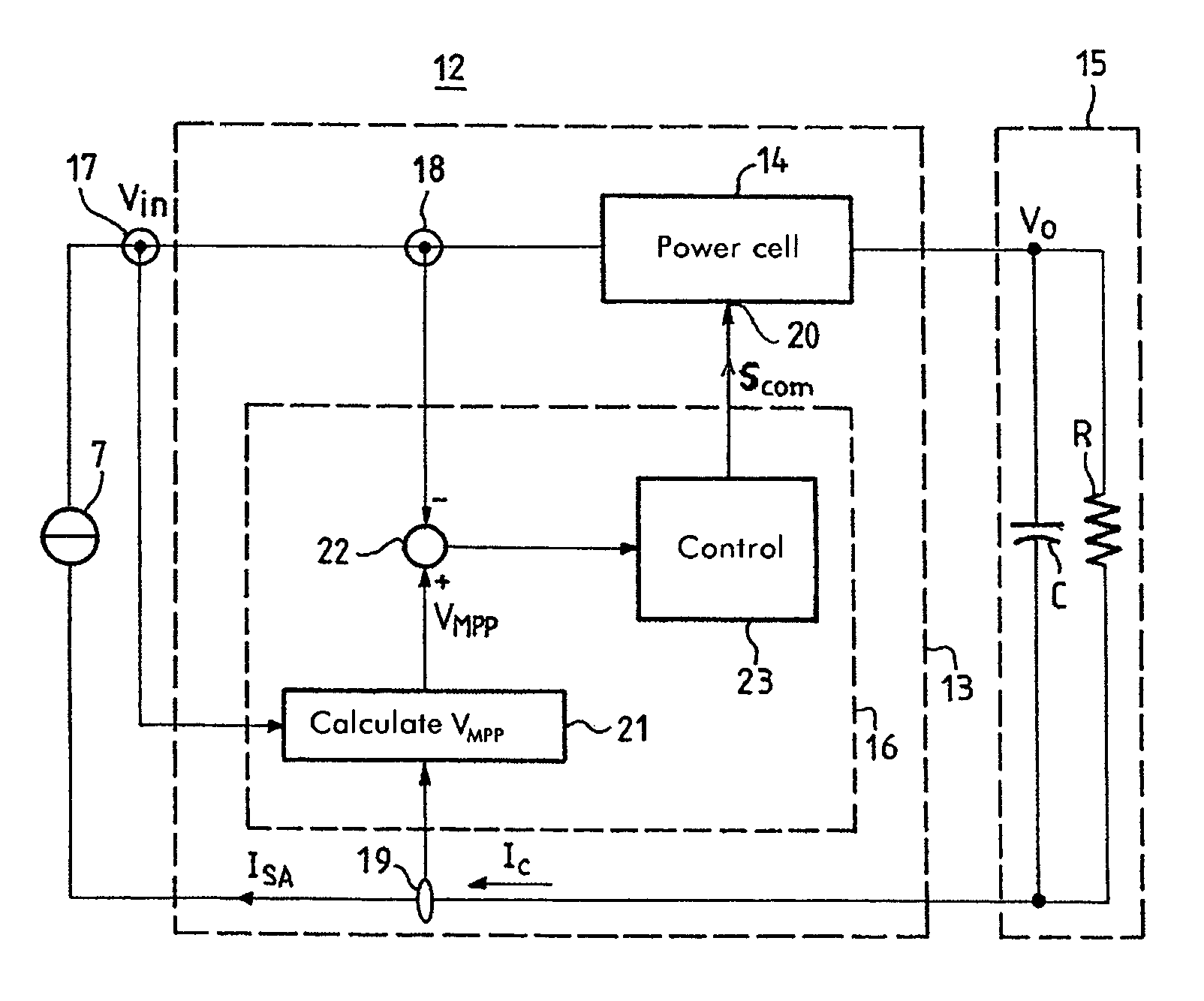
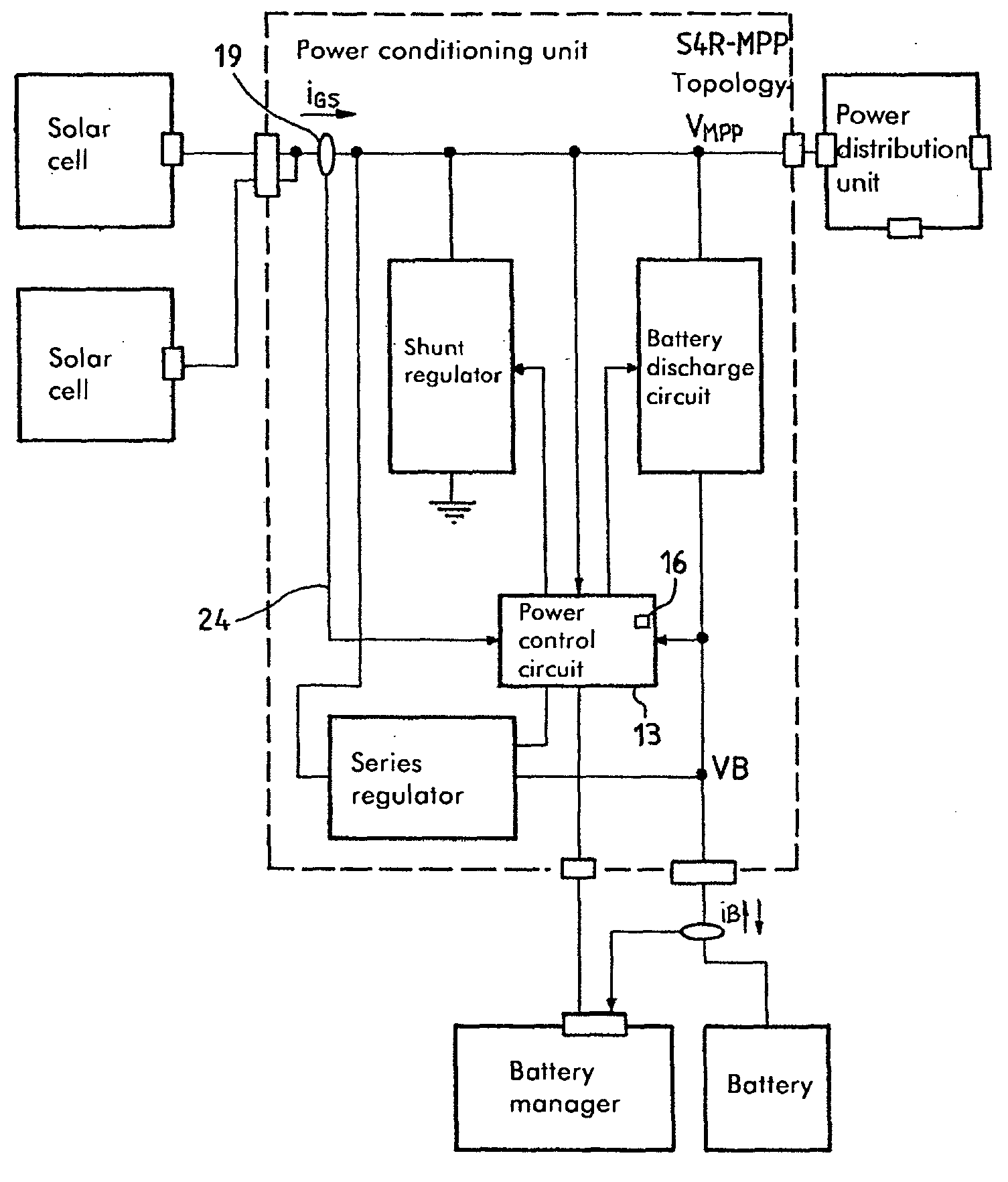
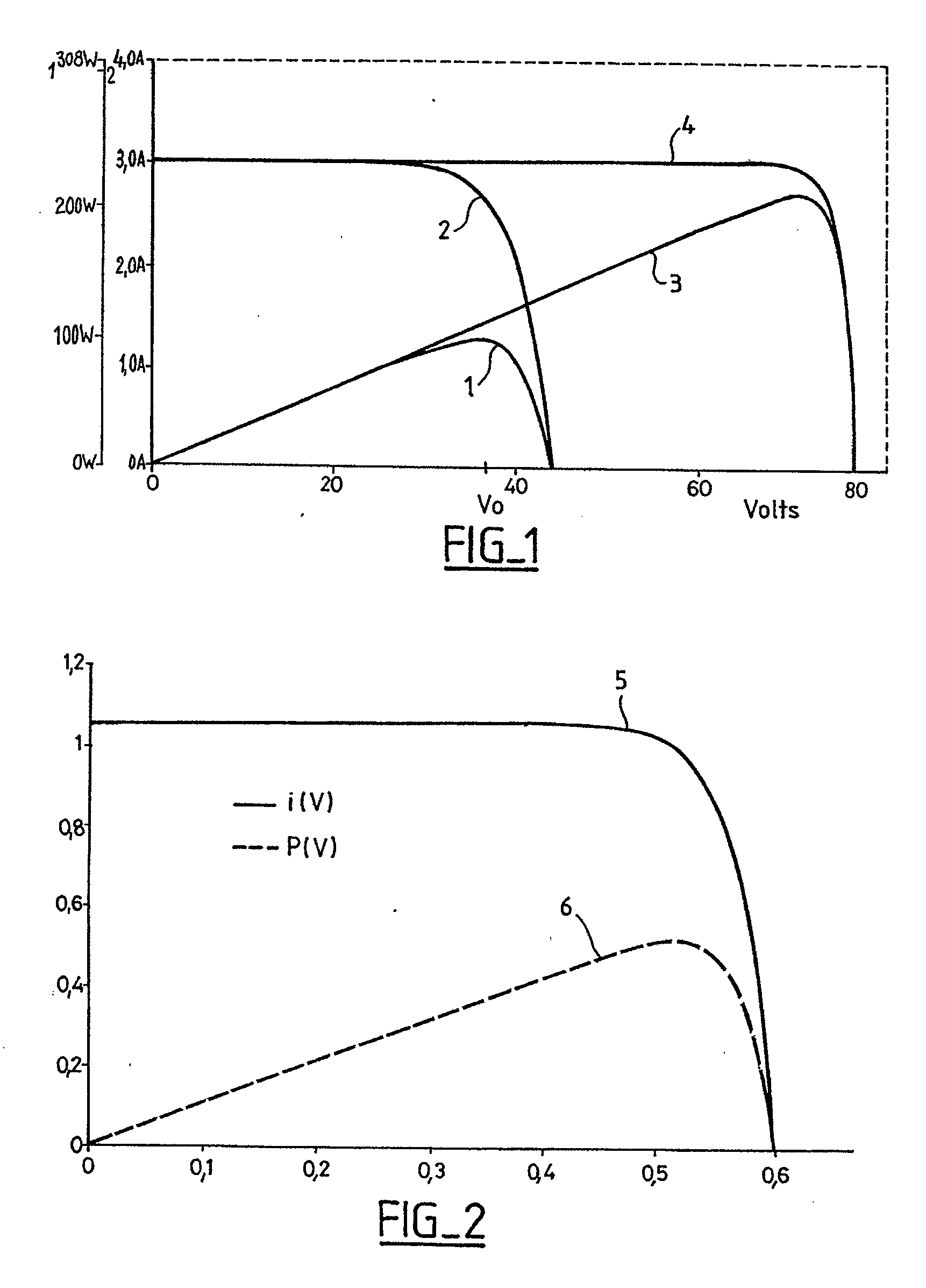
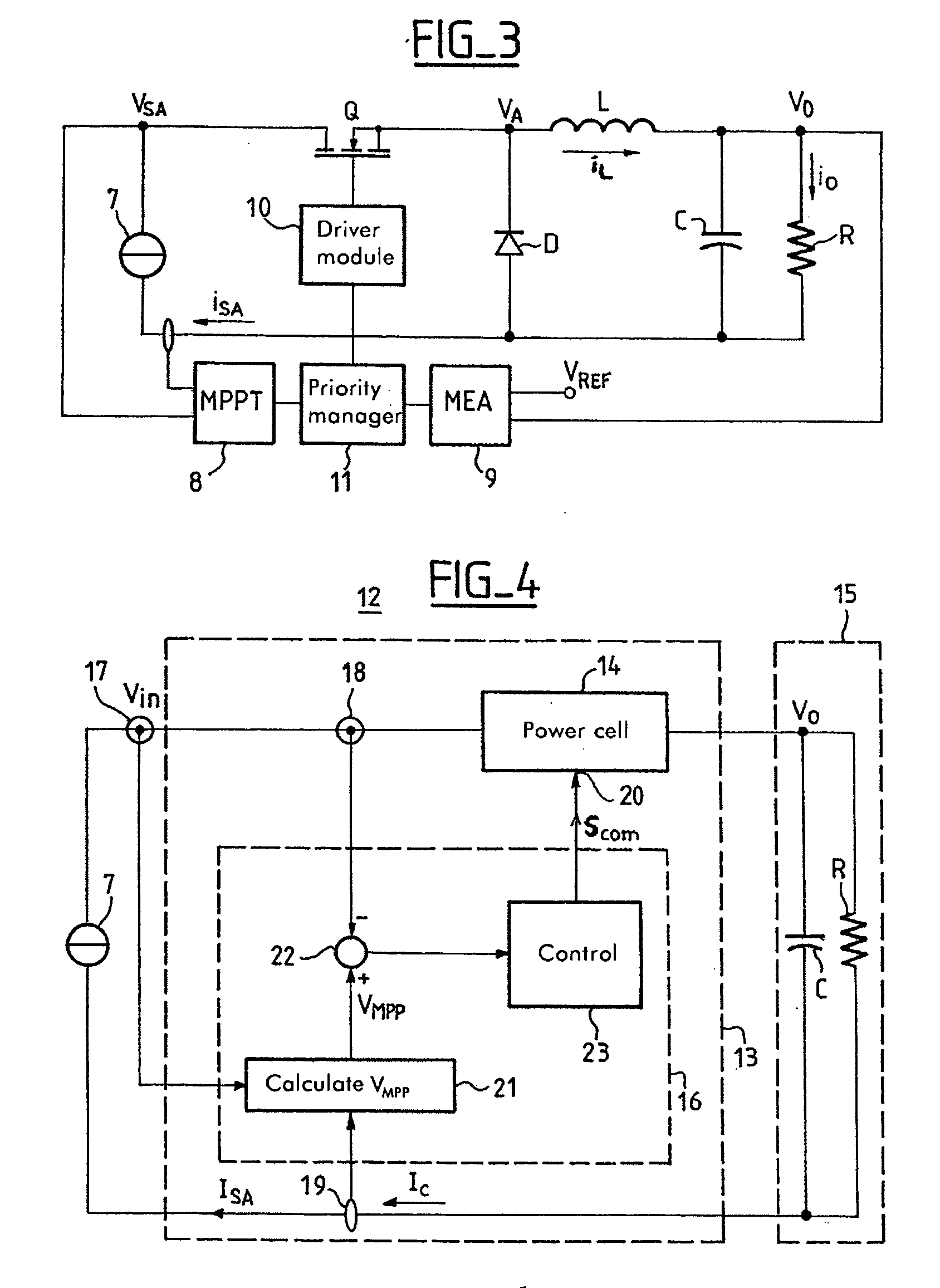
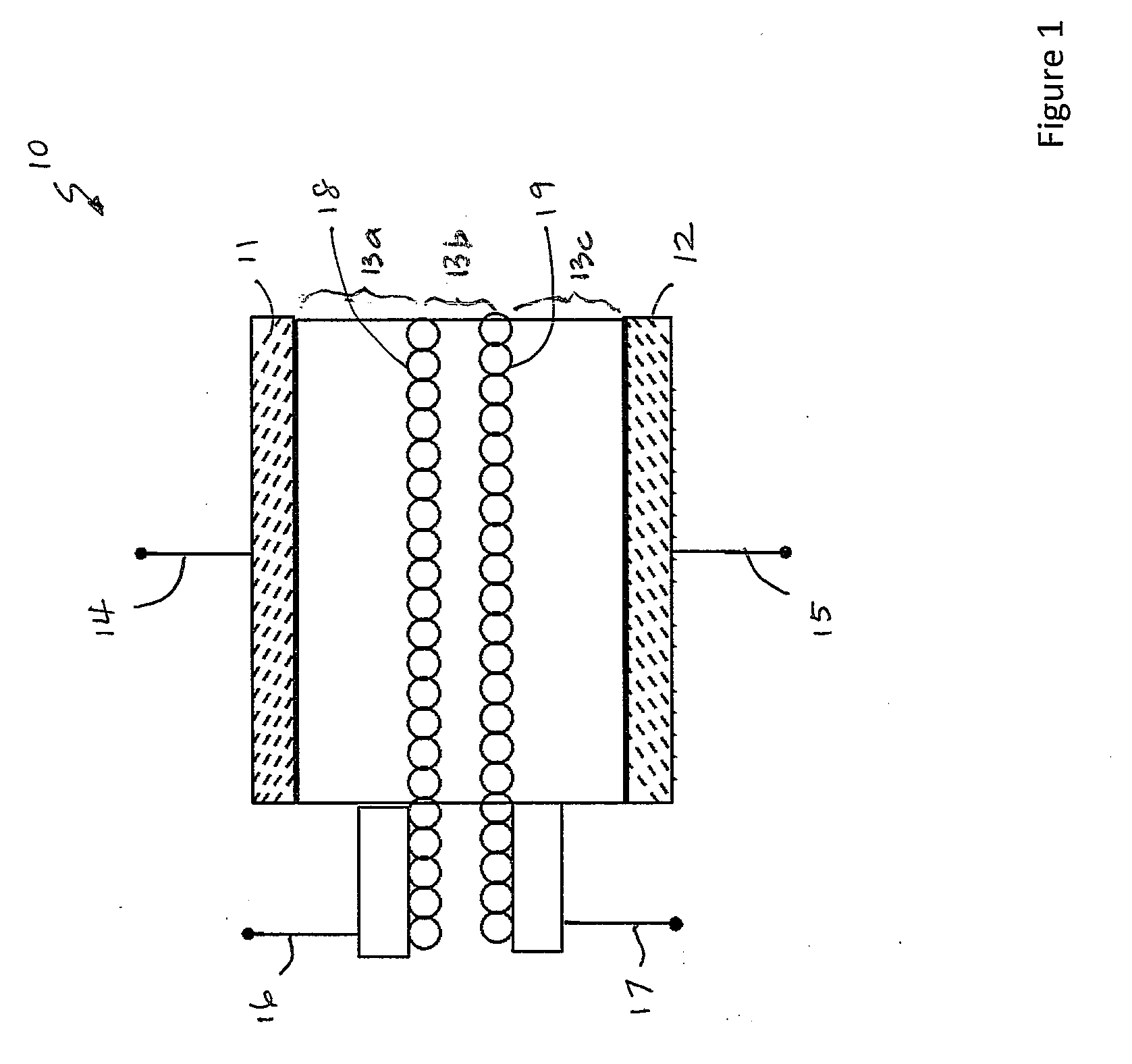
Conditioning circuit for a power supply at the maximum power point, a solar generator, and a conditioning method
InactiveUS6984970B2Batteries circuit arrangementsConversion with intermediate conversion to dcOperating pointSolar generator
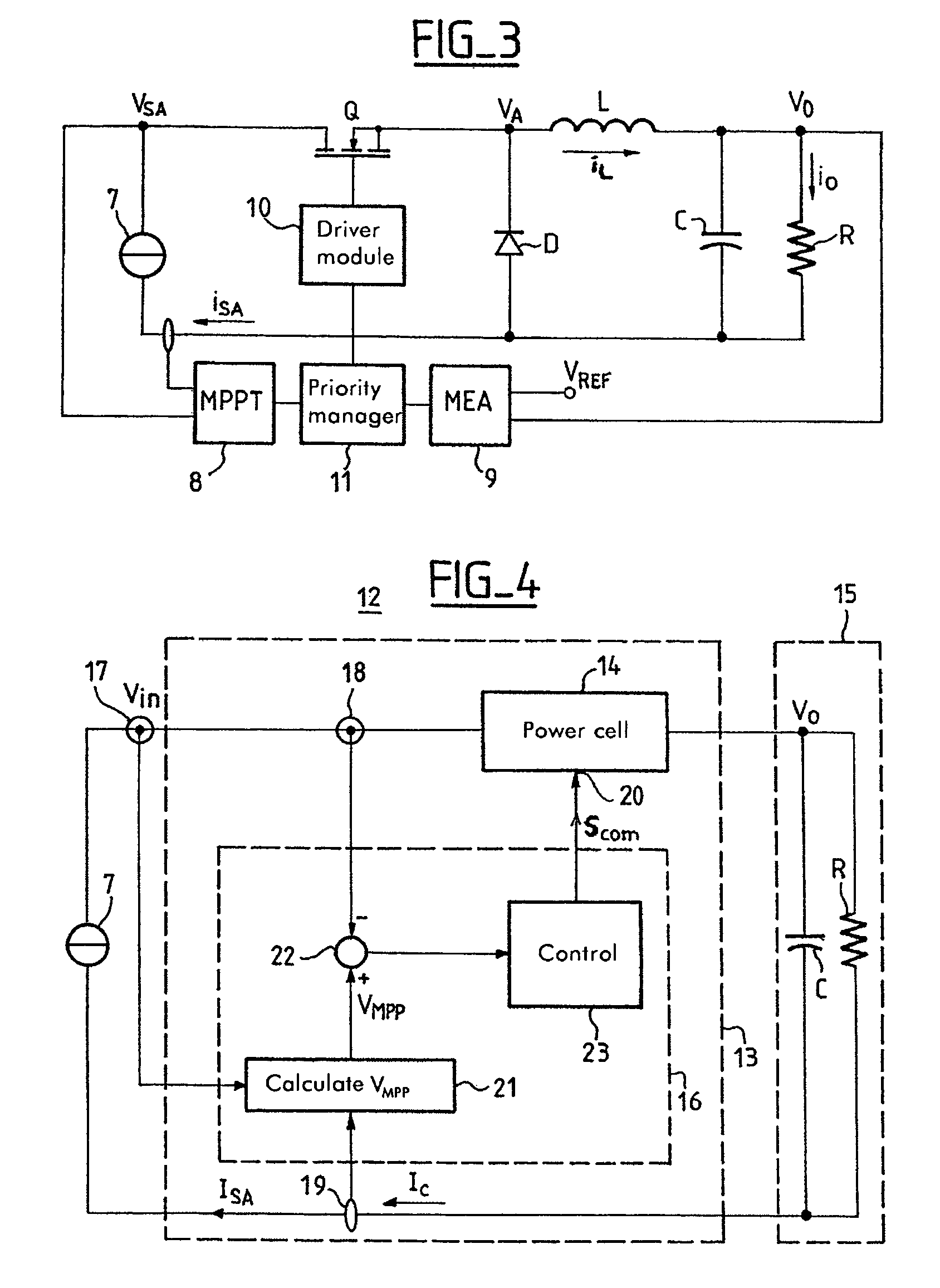
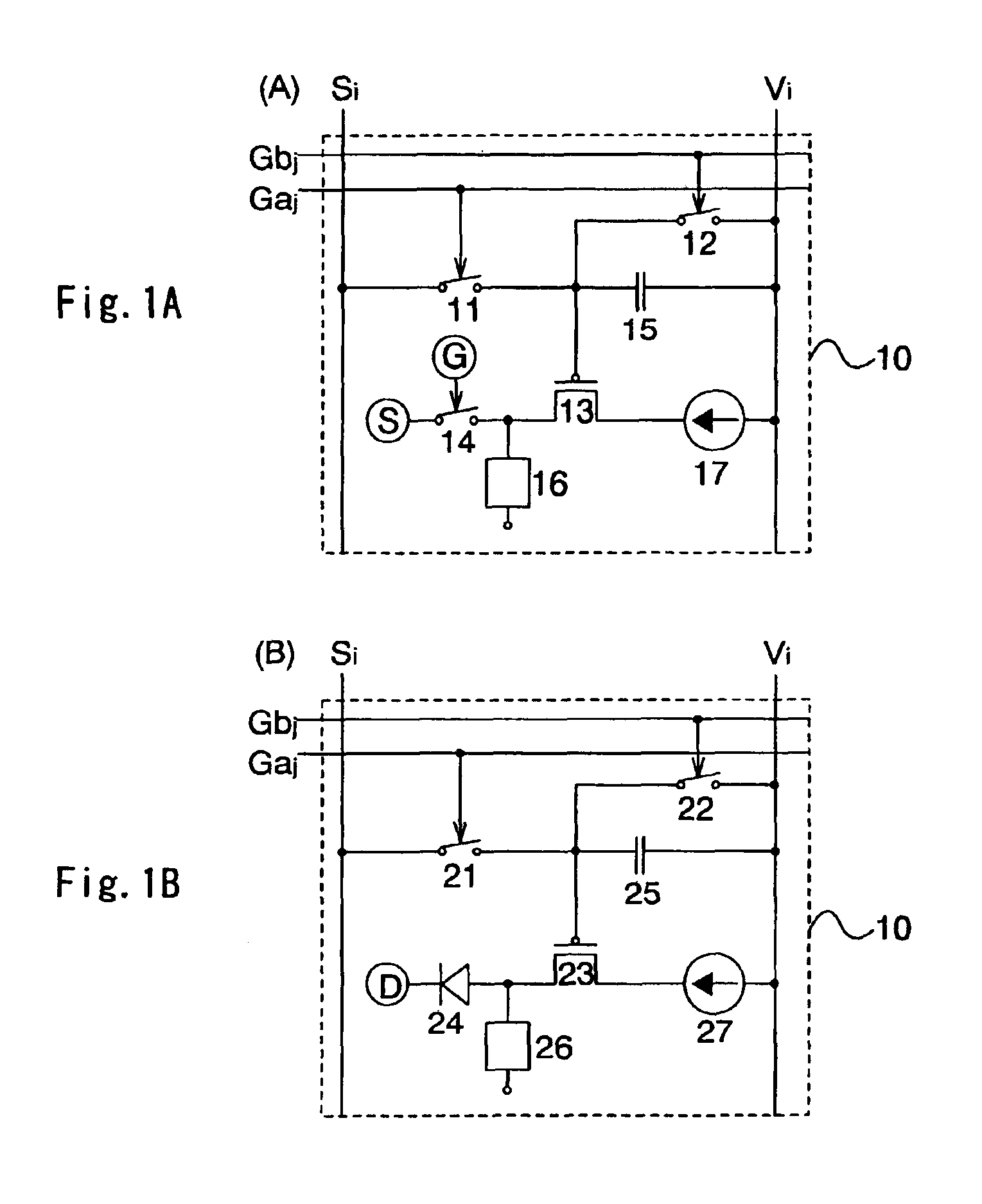
The invention relates to a conditioning circuit that measures operating points of a power supply to deduce therefrom the current-voltage characteristic thereof and to determine directly the voltage corresponding to its maximum power point, without using any kind of tracking algorithm that causes the operating point of the power unit to oscillate about the maximum power point. The maximum power point voltage VMPP is supplied to a controller which regulates a power cell by slaving it to the input voltage until the output voltage of the supply is equal to the maximum power point voltage VMPP. The invention also relates to a solar generator and an associated conditioning method. One particular application is to high-power satellites.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
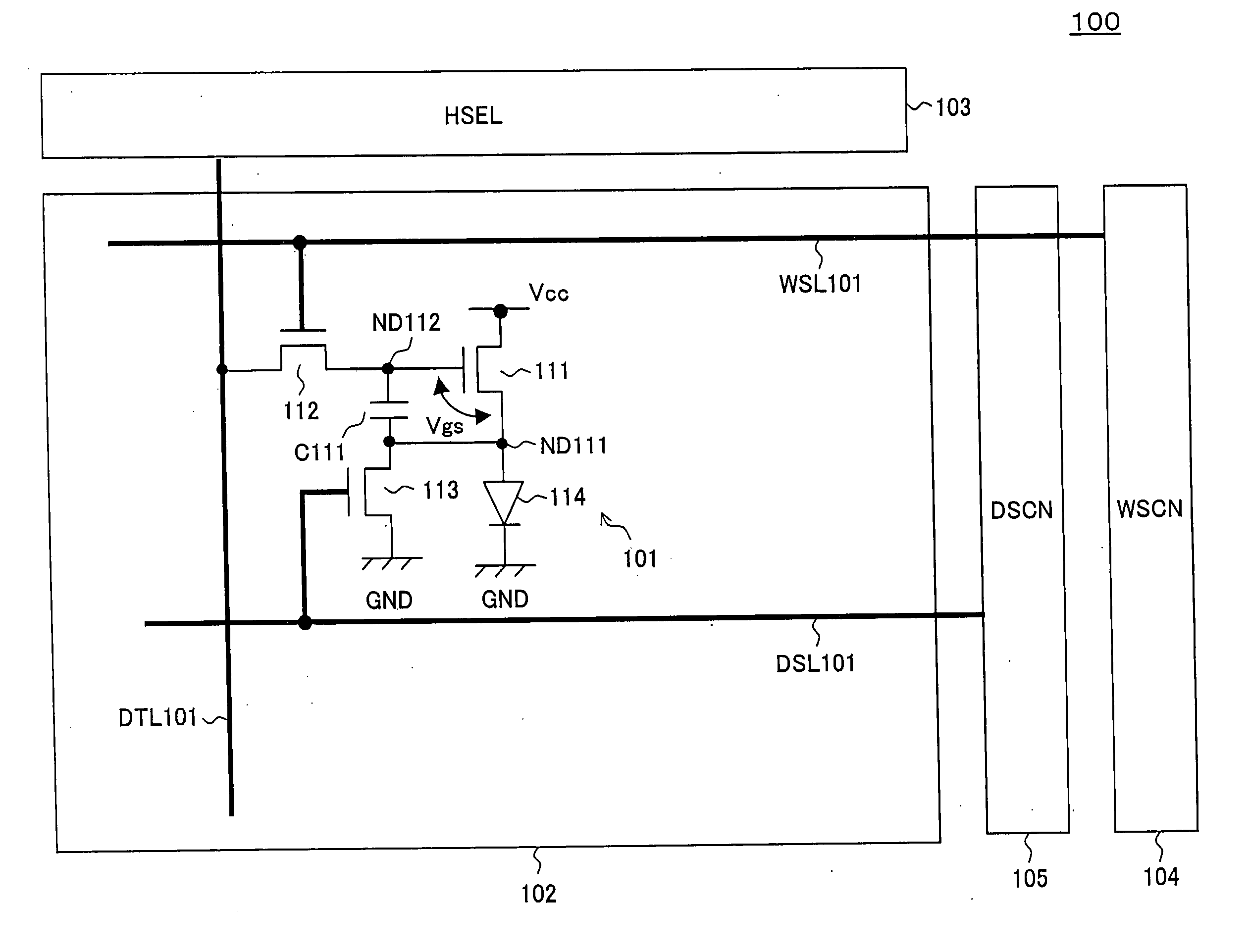
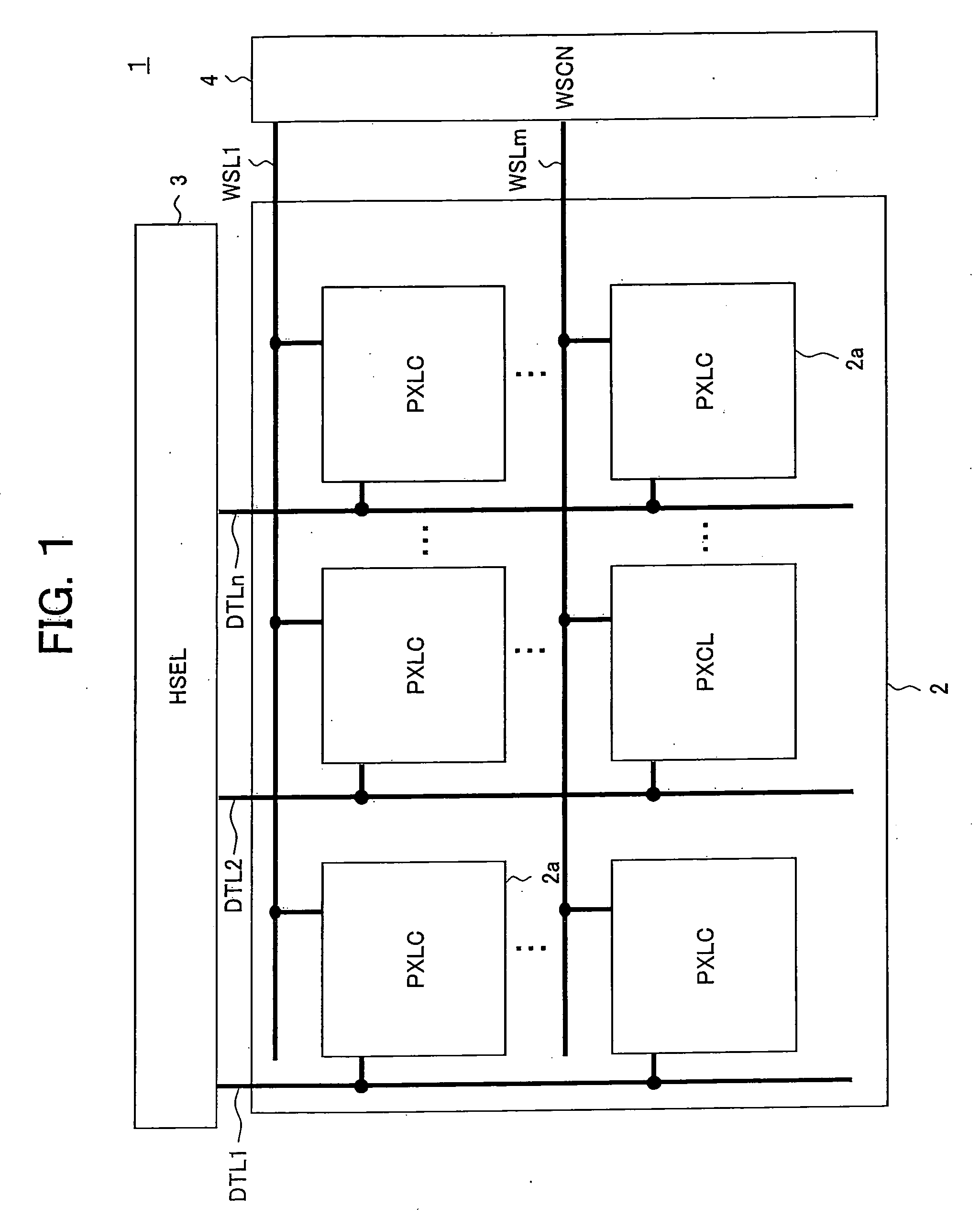
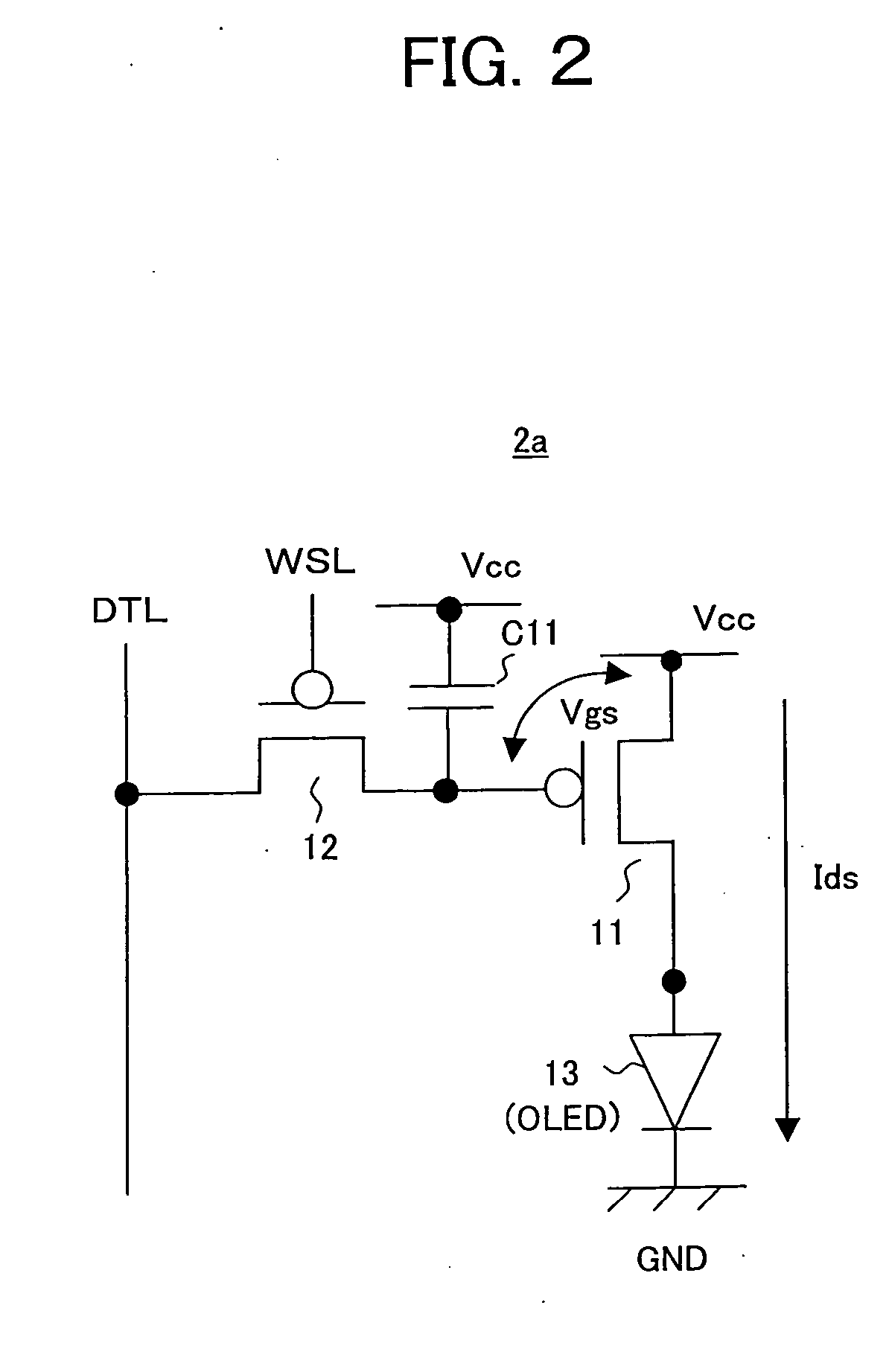
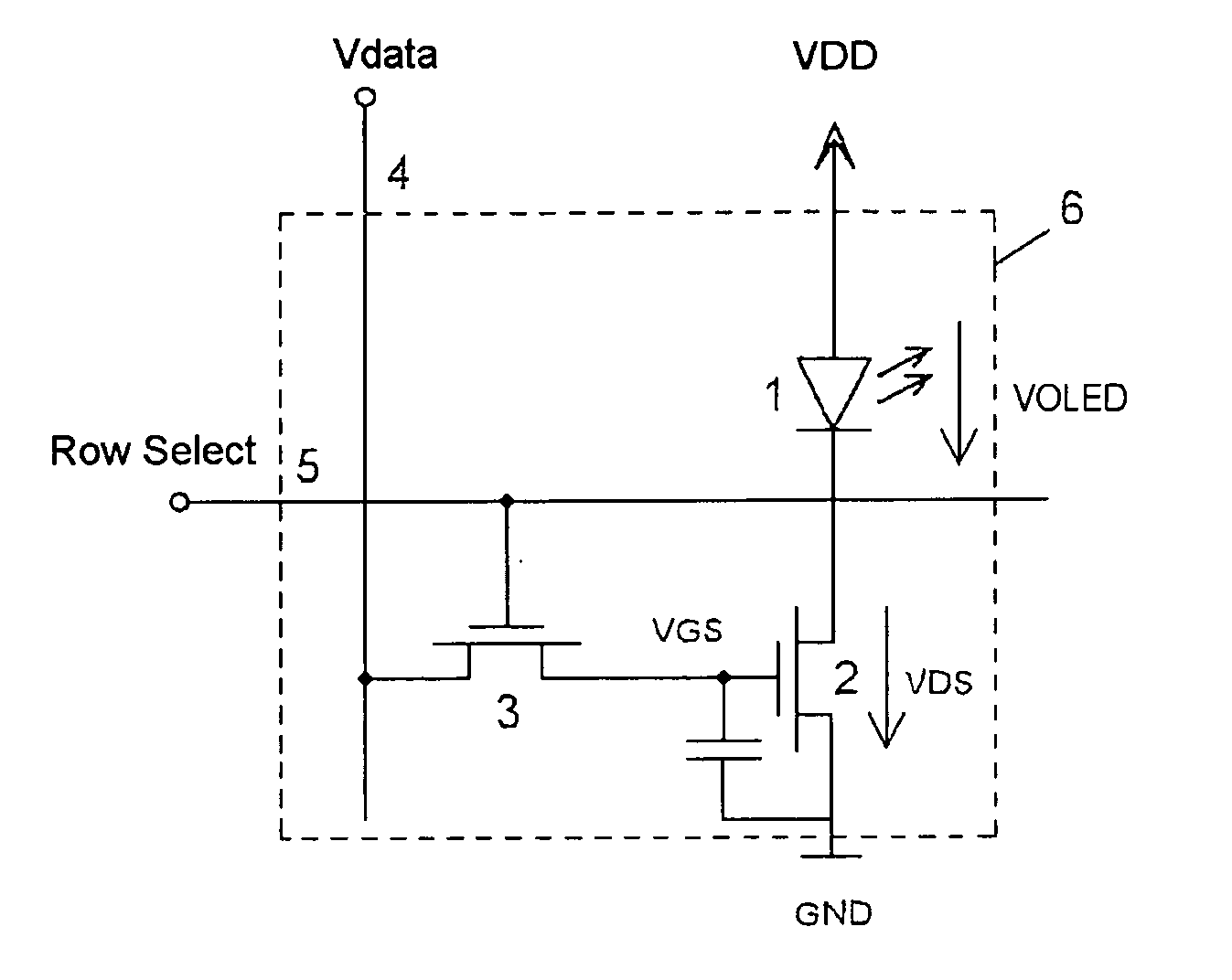
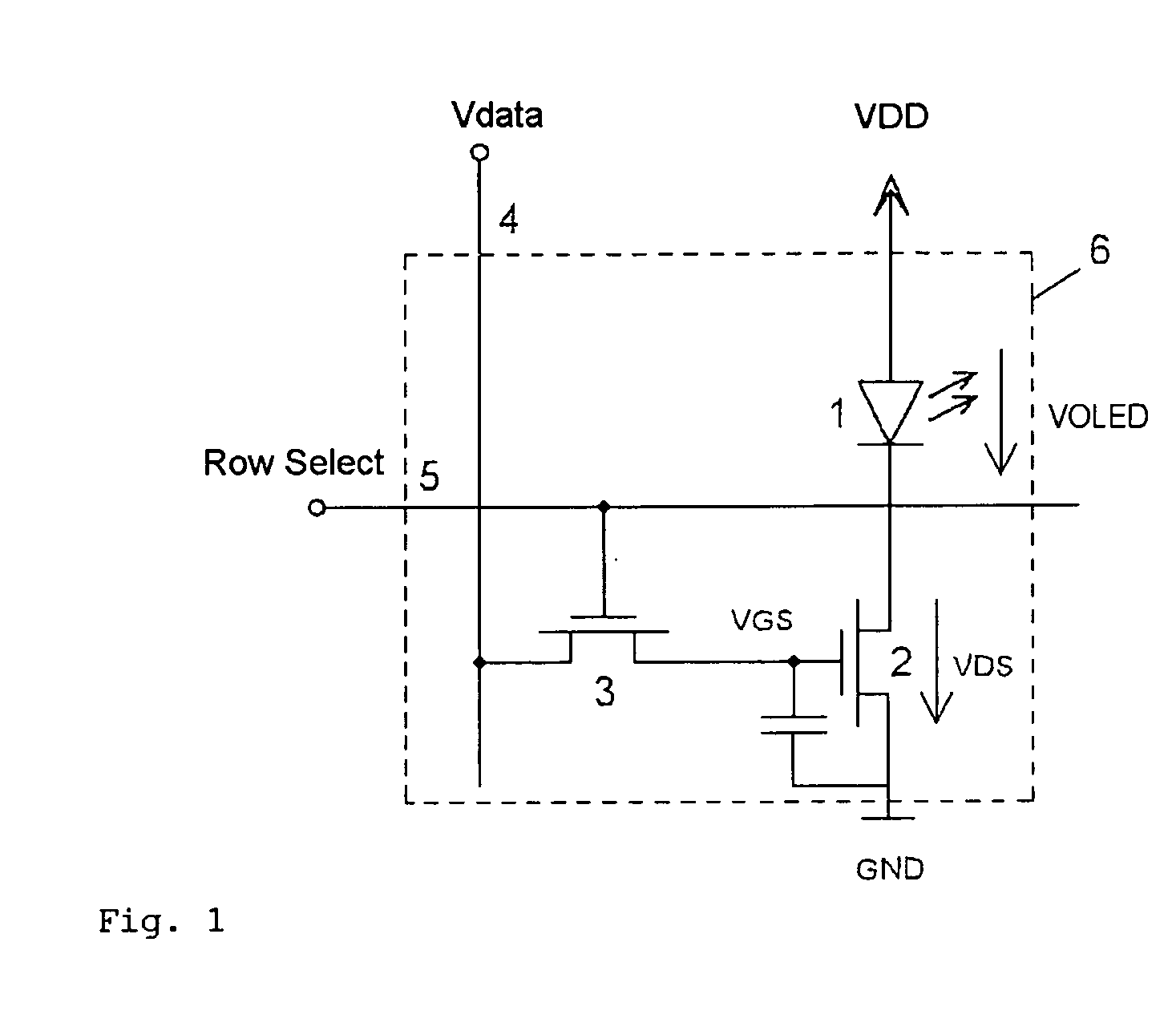
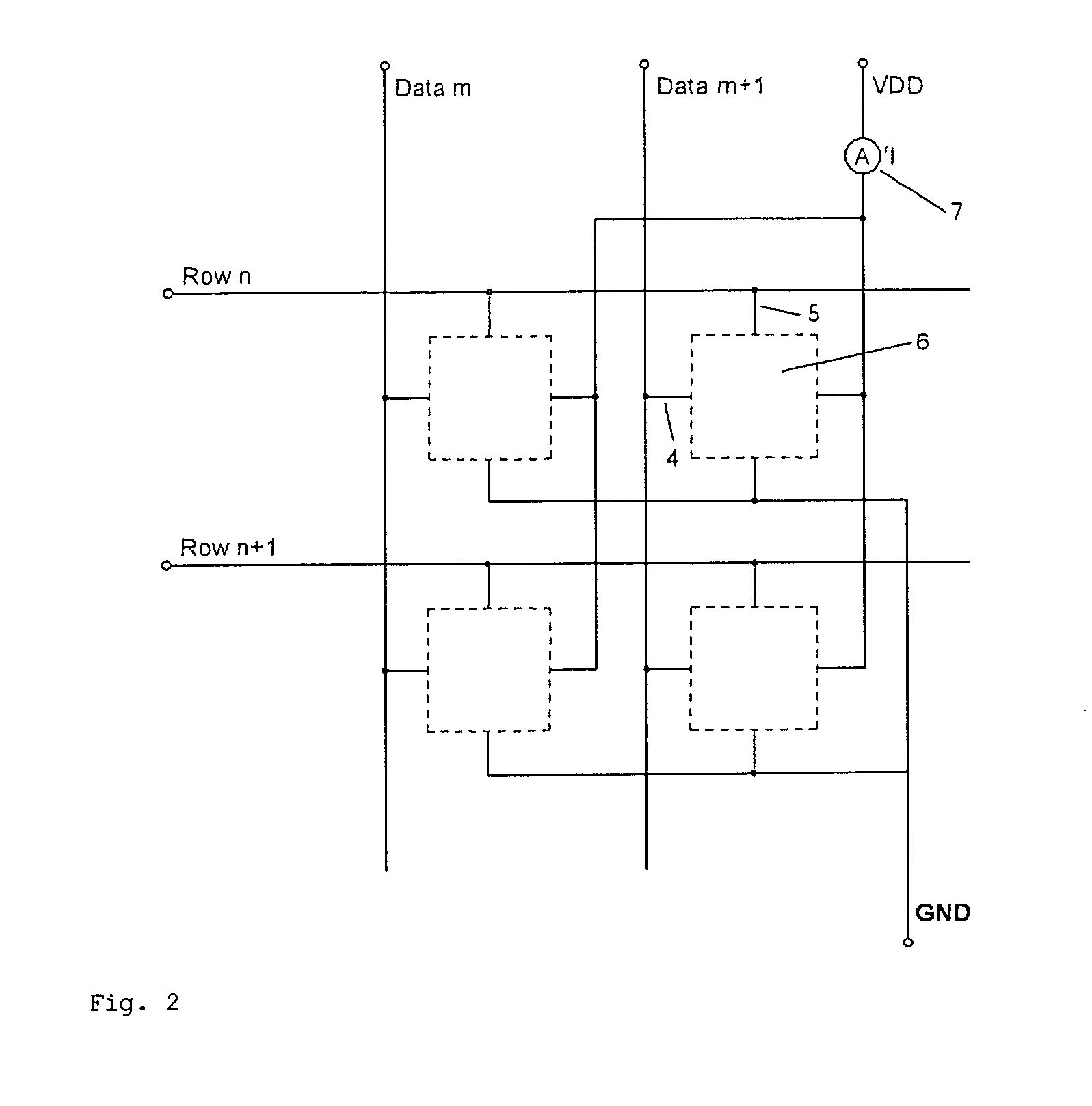
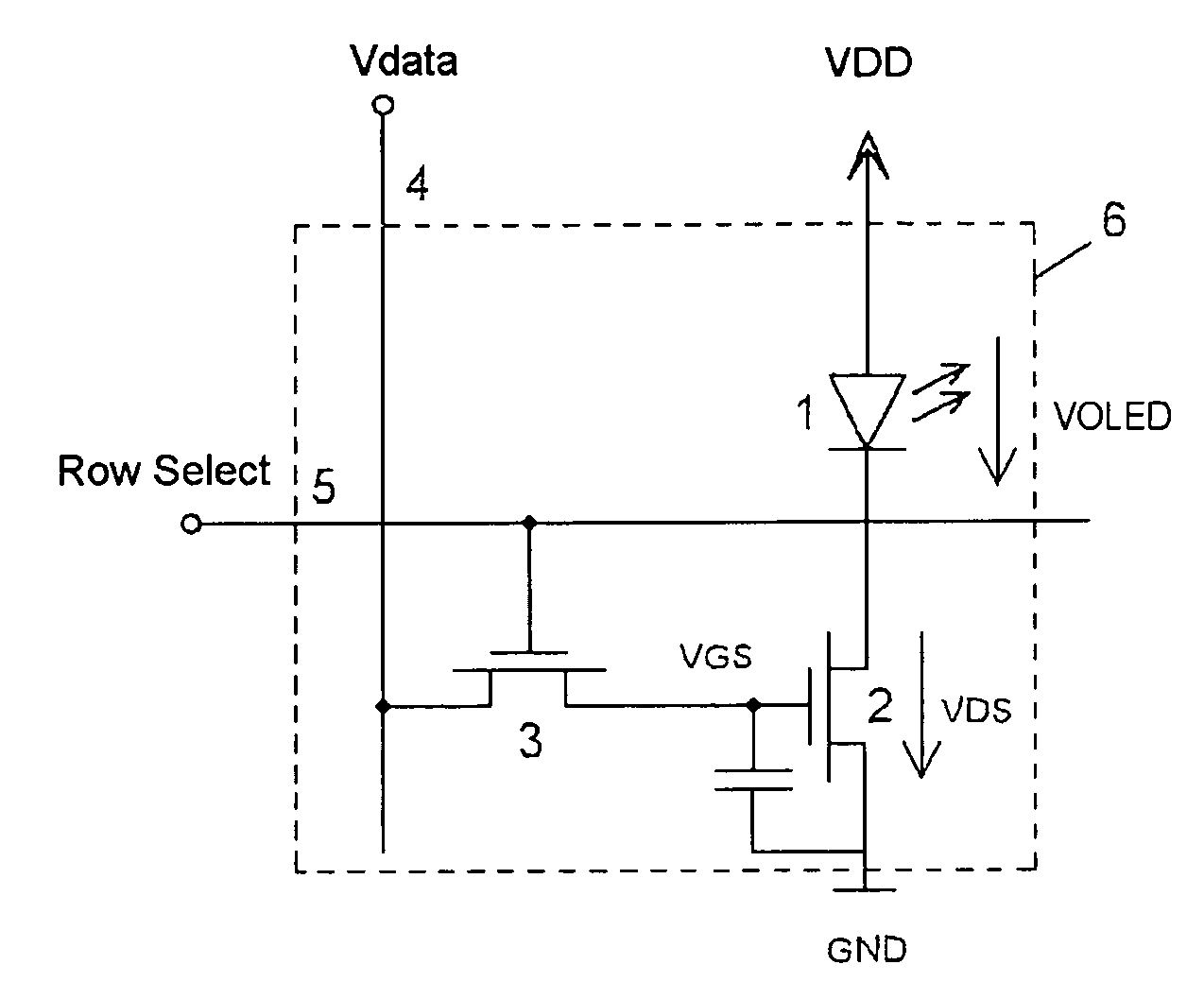
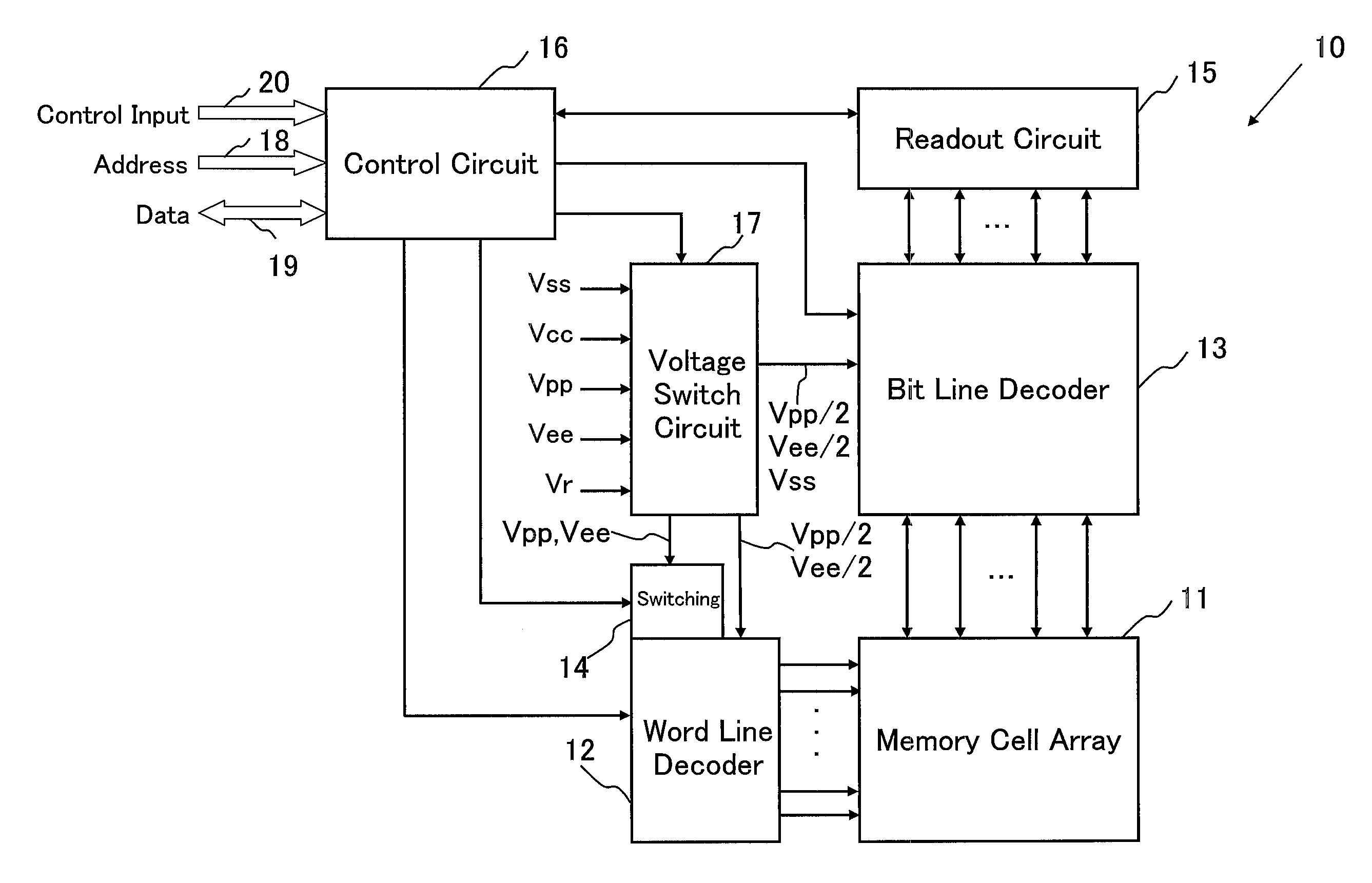
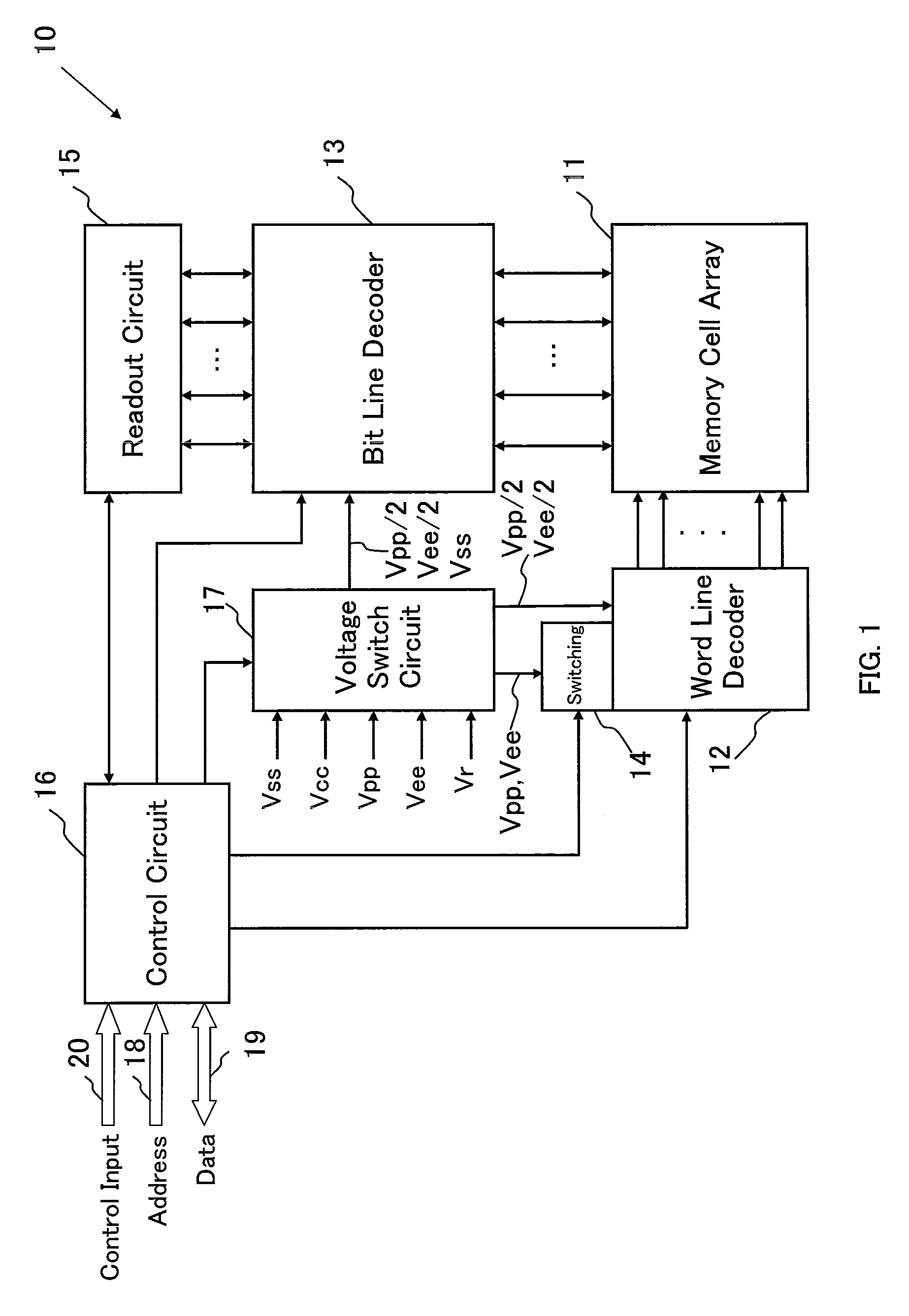
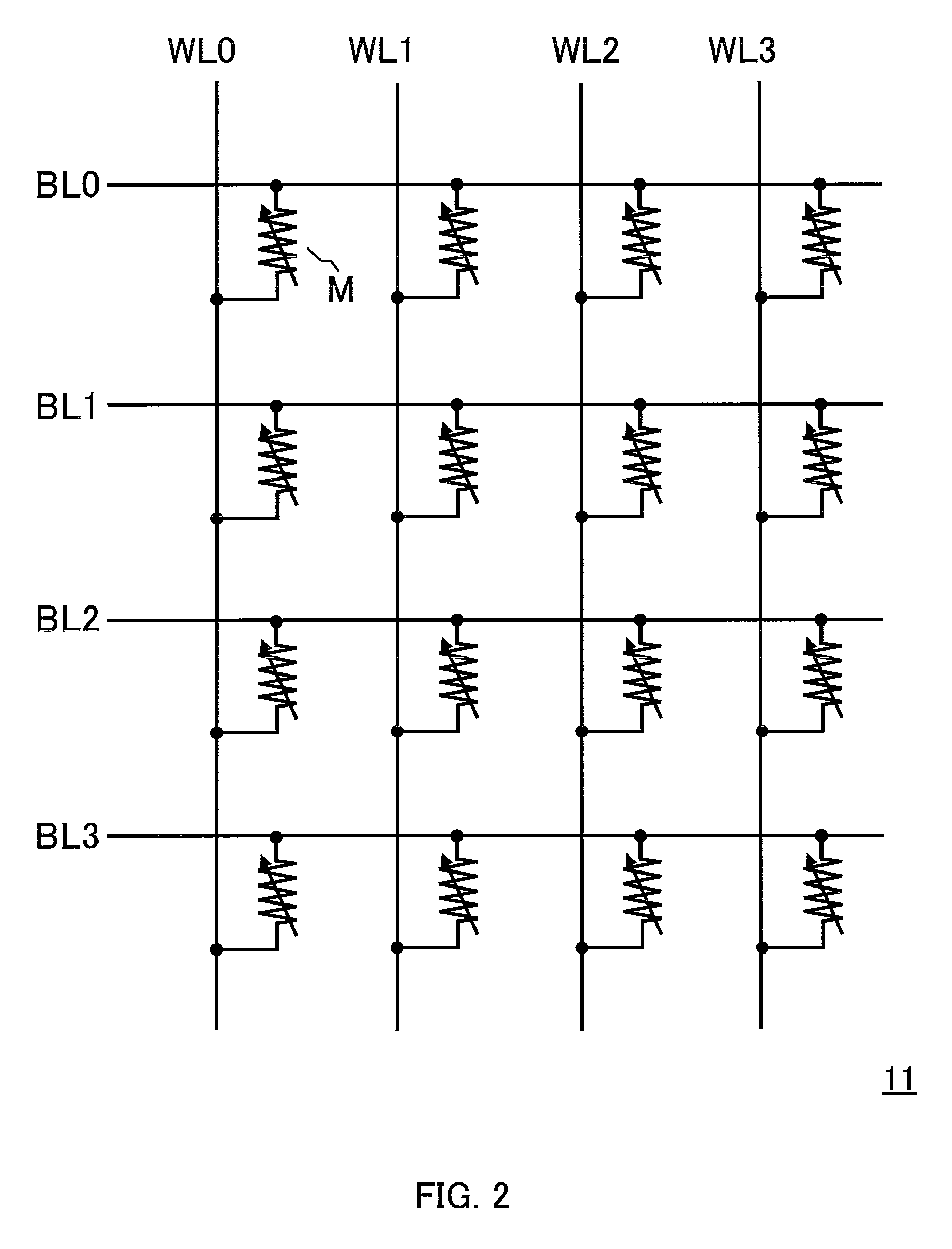
Pixel circuit, display unit, and pixel circuit drive method
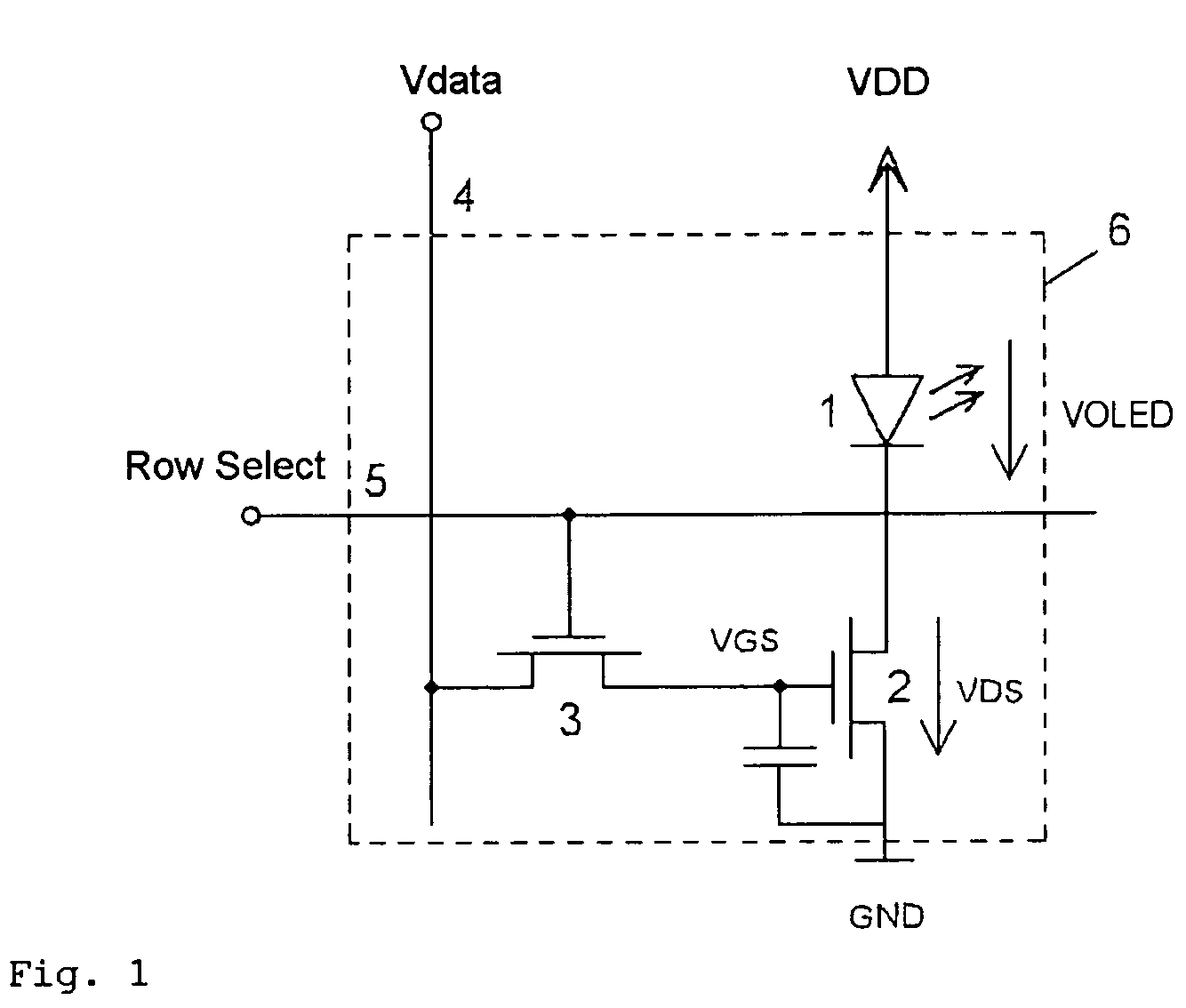
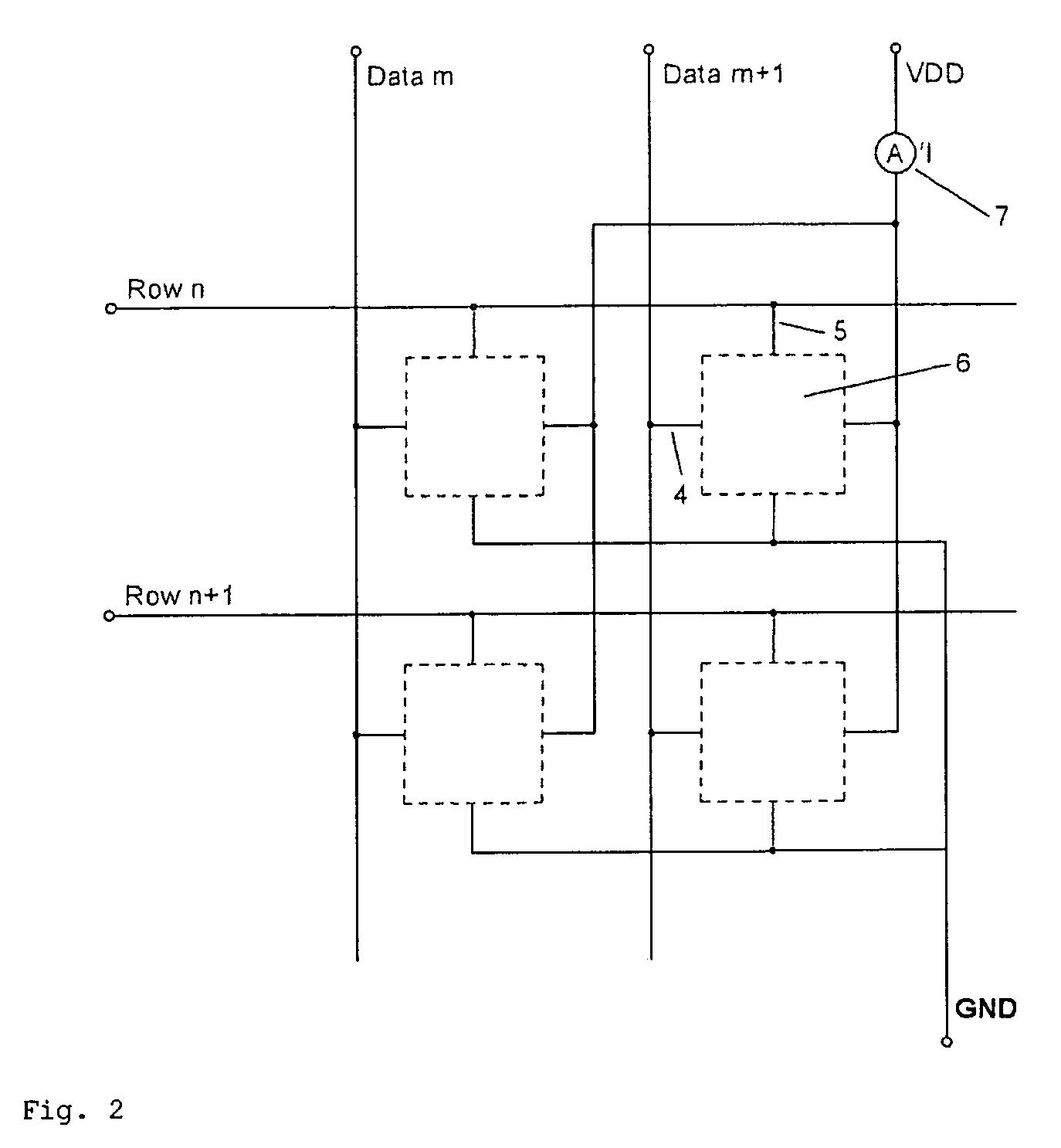
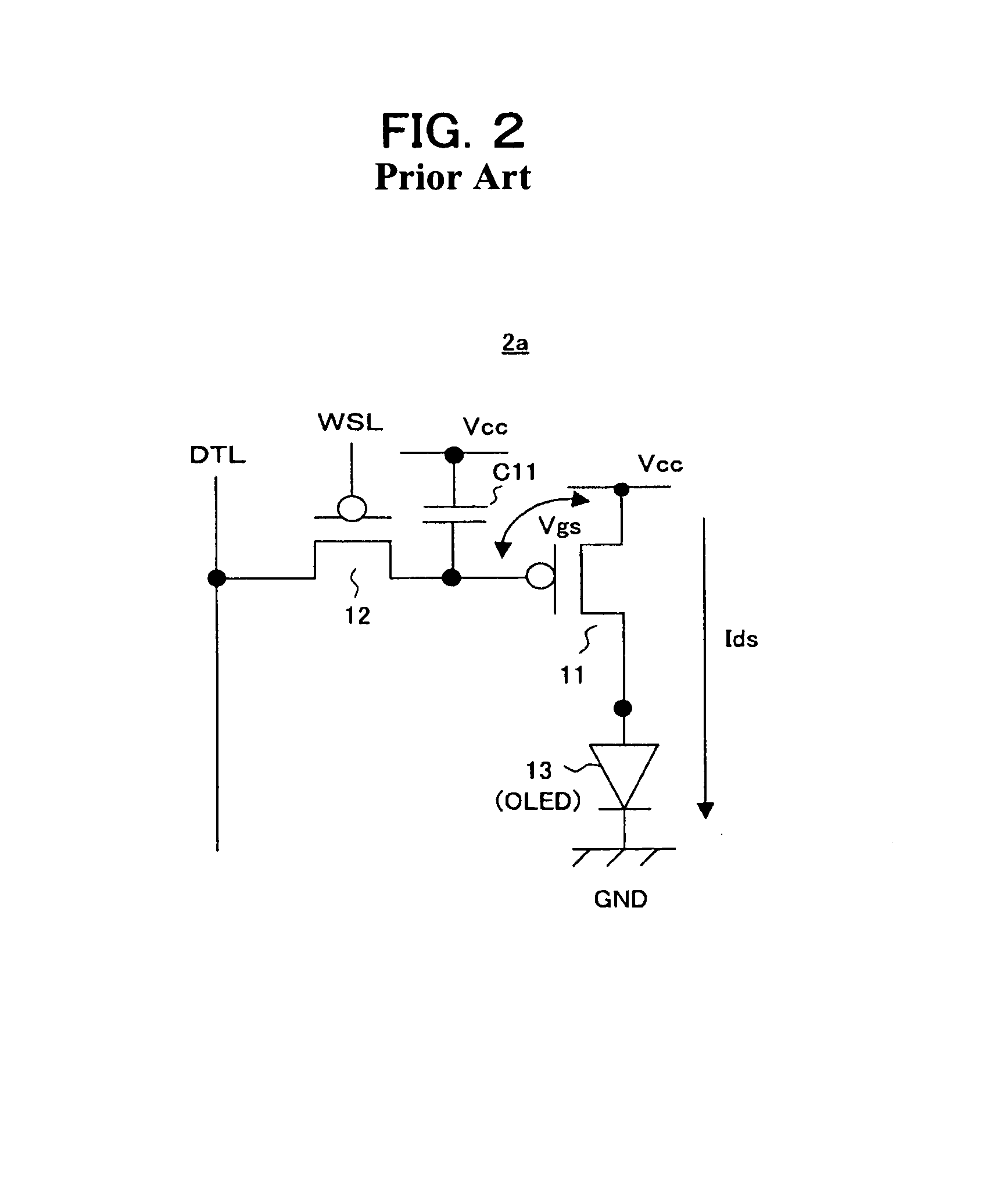
ActiveUS20070057873A1No deterioration of luminanceNo deteriorationTransistorStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceCapacitor
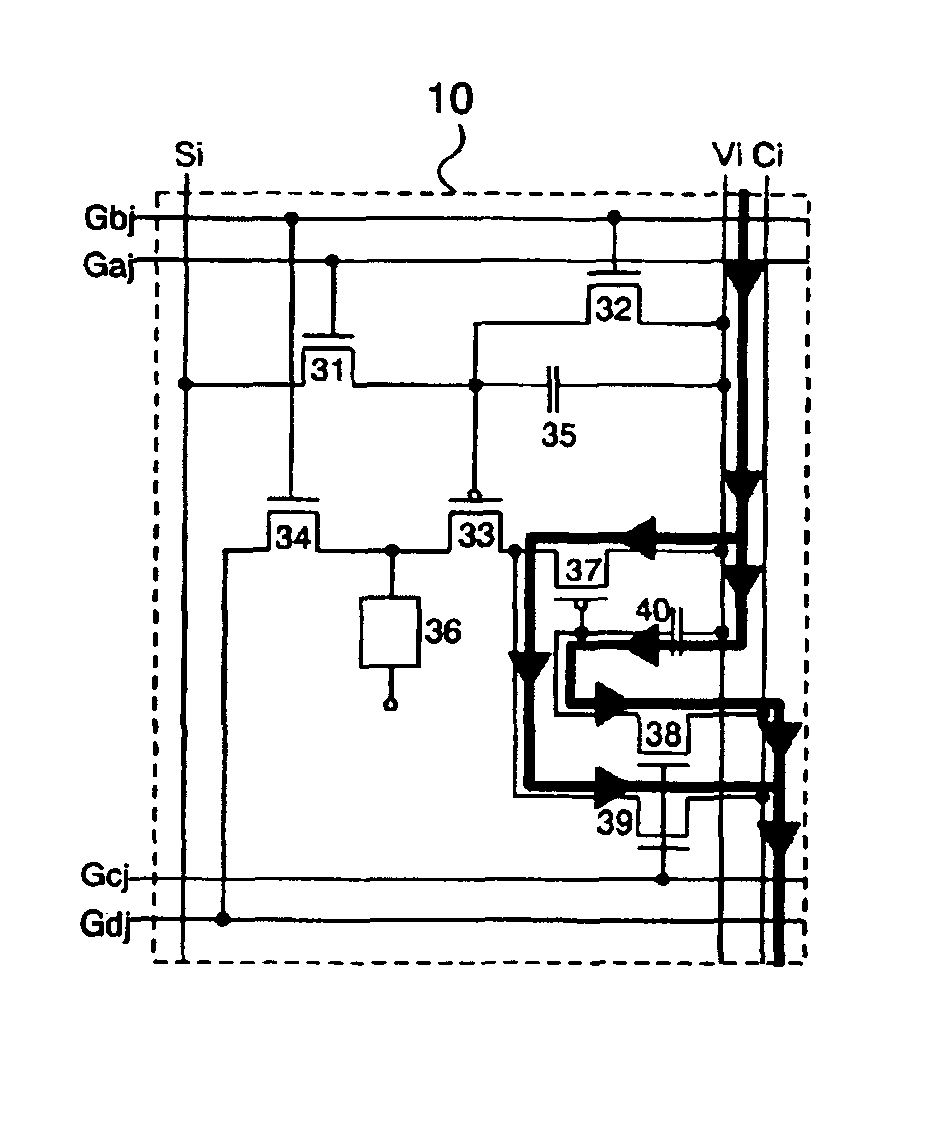
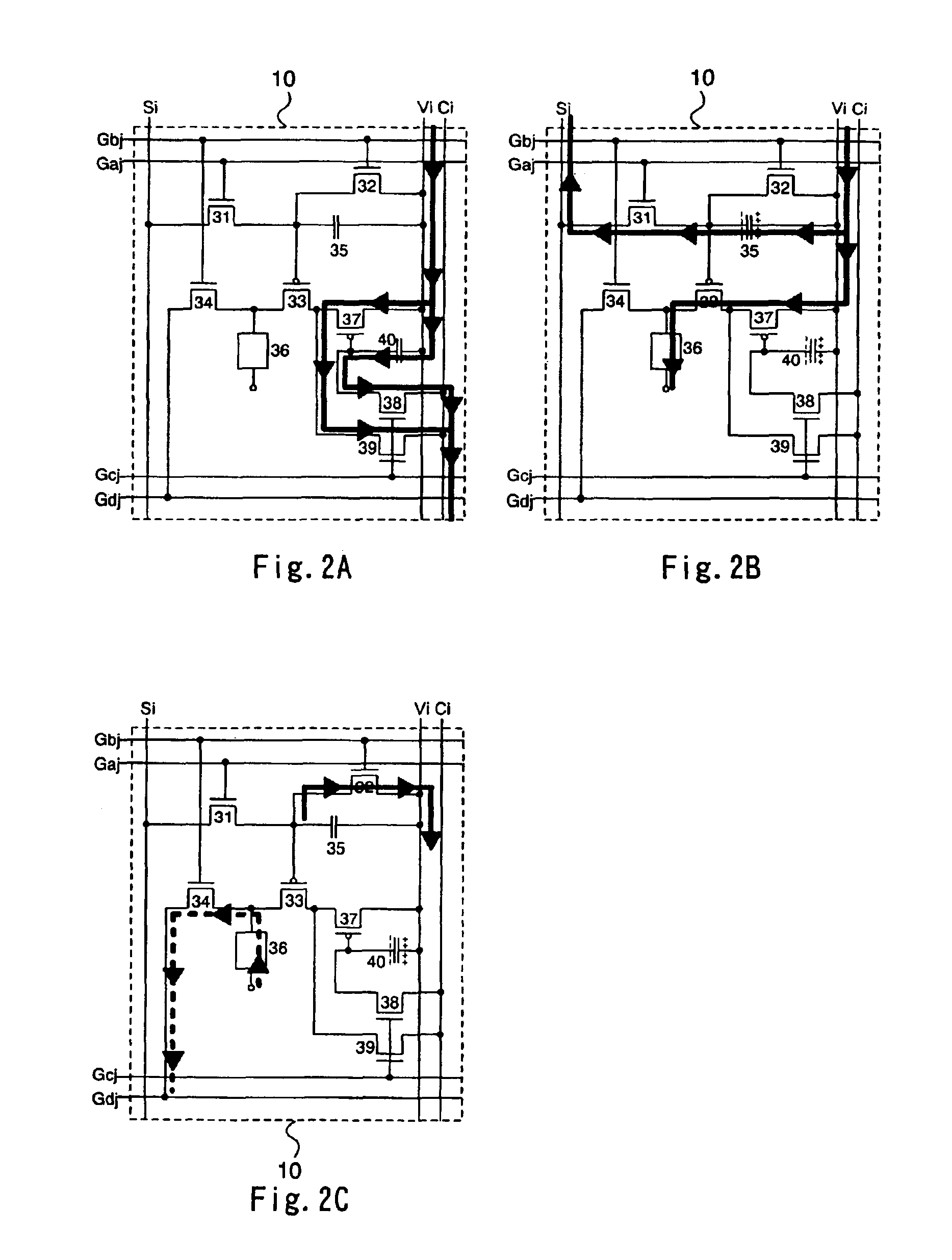
A pixel circuit, display device, and method of driving a pixel circuit enabling source-follower output with no deterioration of luminance even with a change of the current-voltage characteristic of the light emitting element along with elapse, enabling a source-follower circuit of n-channel transistors, and able to use an n-channel transistor as an EL drive transistor while using current anode-cathode electrodes, wherein a source of a TFT 111 as a drive transistor is connected to an anode of a light emitting element 114, a drain is connected to a power source potential VCC, a capacitor C111 is connected between a gate and source of the TFT 111, and a source potential of the TFT 111 is connected to a fixed potential through a TFT 113 as a switching transistor.
Owner:SONY CORP
Conditioning circuit for a power supply at the maximum power point, a solar generator, and a conditioning method
InactiveUS20050017697A1Batteries circuit arrangementsConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSolar generatorOperating point
The invention relates to a conditioning circuit that measures operating points of a power supply to deduce therefrom the current-voltage characteristic thereof and to determine directly the voltage corresponding to its maximum power point, without using any kind of tracking algorithm that causes the operating point of the power unit to oscillate about the maximum power point. The maximum power point voltage VMPP is supplied to a controller which regulates a power cell by slaving it to the input voltage until the output voltage of the supply is equal to the maximum power point voltage VMPP. The invention also relates to a solar generator and an associated conditioning method. One particular application is to high-power satellites.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method and circuit arrangement for the ageing compensation of an organic light-emitting diode and circuit arrangement
ActiveUS20060214888A1Simple wayCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingCurrent electricCurrent voltage
The invention relates to a method and a circuit arrangement for the ageing compensation of an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) which is fed from a supply voltage and is switched by means of a driver transistor operated in saturation operation, by means of a driving of the light-emitting diode. The method comprises the following steps of: storing at least one desired current-voltage value pair of a desired current-voltage characteristic curve of the light-emitting diode; transferring the driver transistor from saturation operation to linear operation during a measurement cycle; measuring a current value for the current through the light-emitting diode by means of a current measuring circuit in the measurement cycle; determining at least one present current-voltage value pair of a present current-voltage characteristic curve of the light-emitting diode by means of the measured current value; comparing the at least one present current-voltage value pair of the light-emitting diode with the desired current-voltage value pair of the light-emitting diode; and generating driving parameters for driving the light-emitting diode in a manner dependent on the result of the comparison.
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
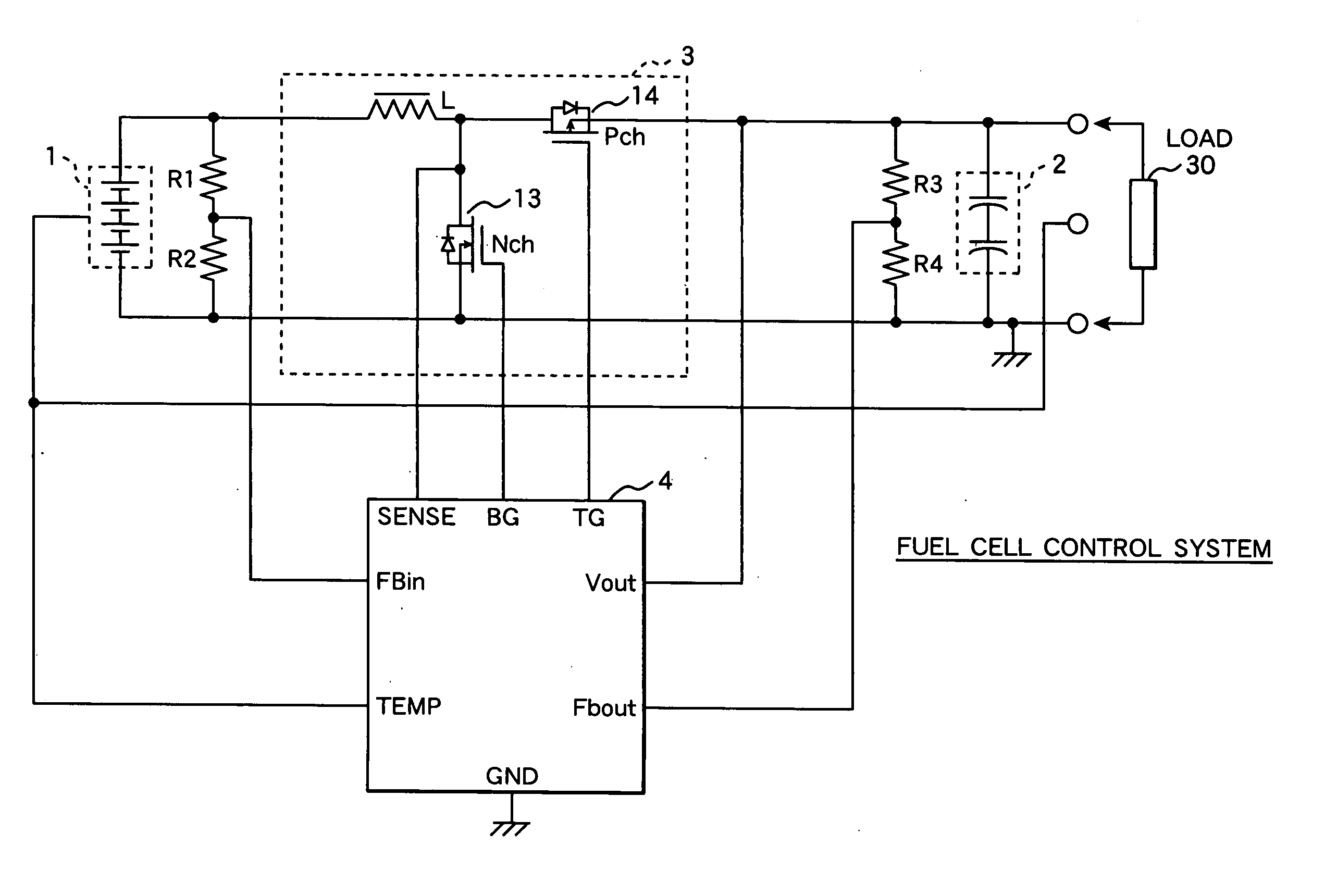
Mehotd for determining a maximum power point voltage of a fuel cell, as well as fuel cell control system and power controller used in the fuel cell control system
InactiveUS20060222916A1Reduce output powerAccurately determineMechanical power/torque controlFuel cell heat exchangePower controllerFuel cells
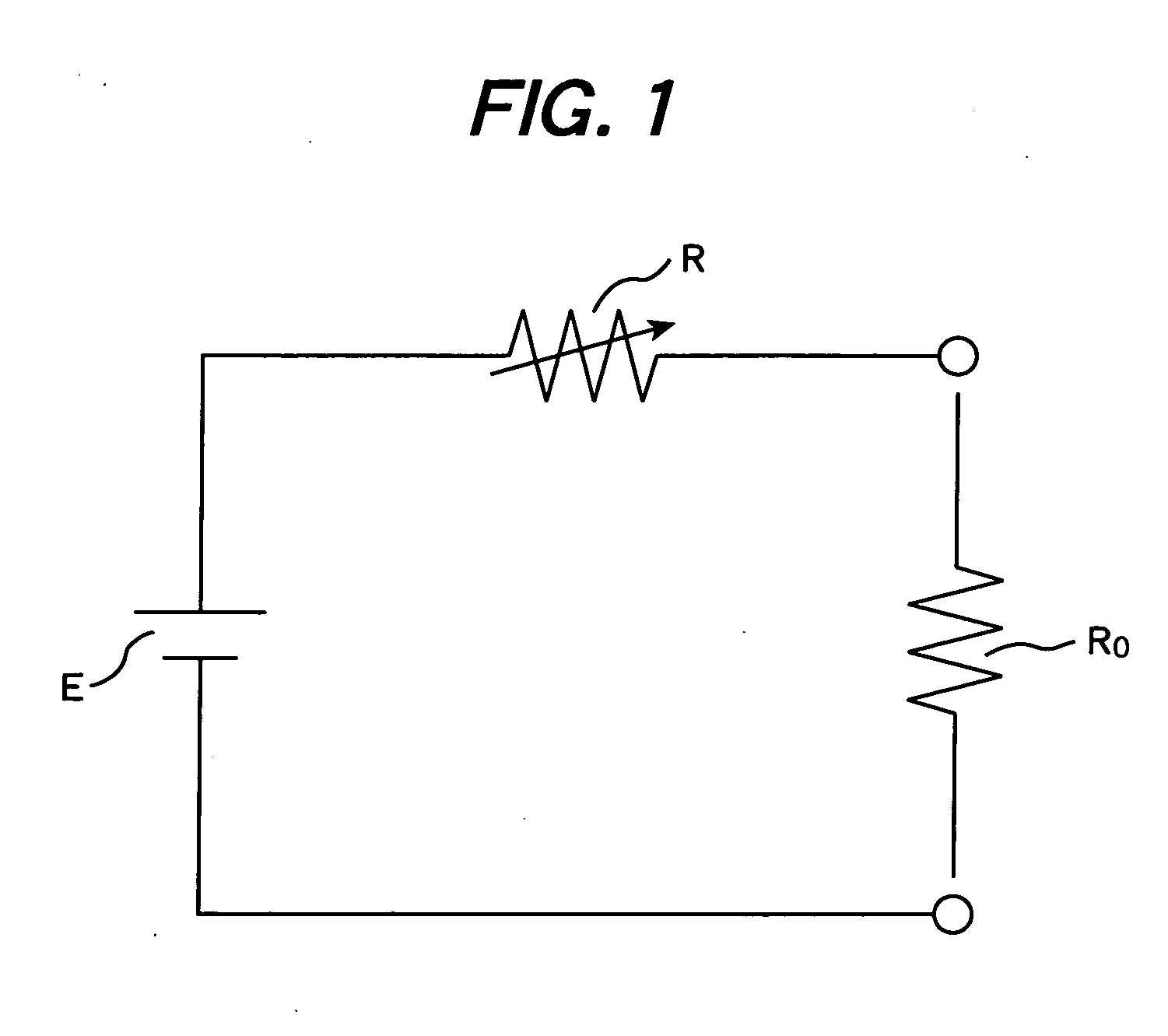
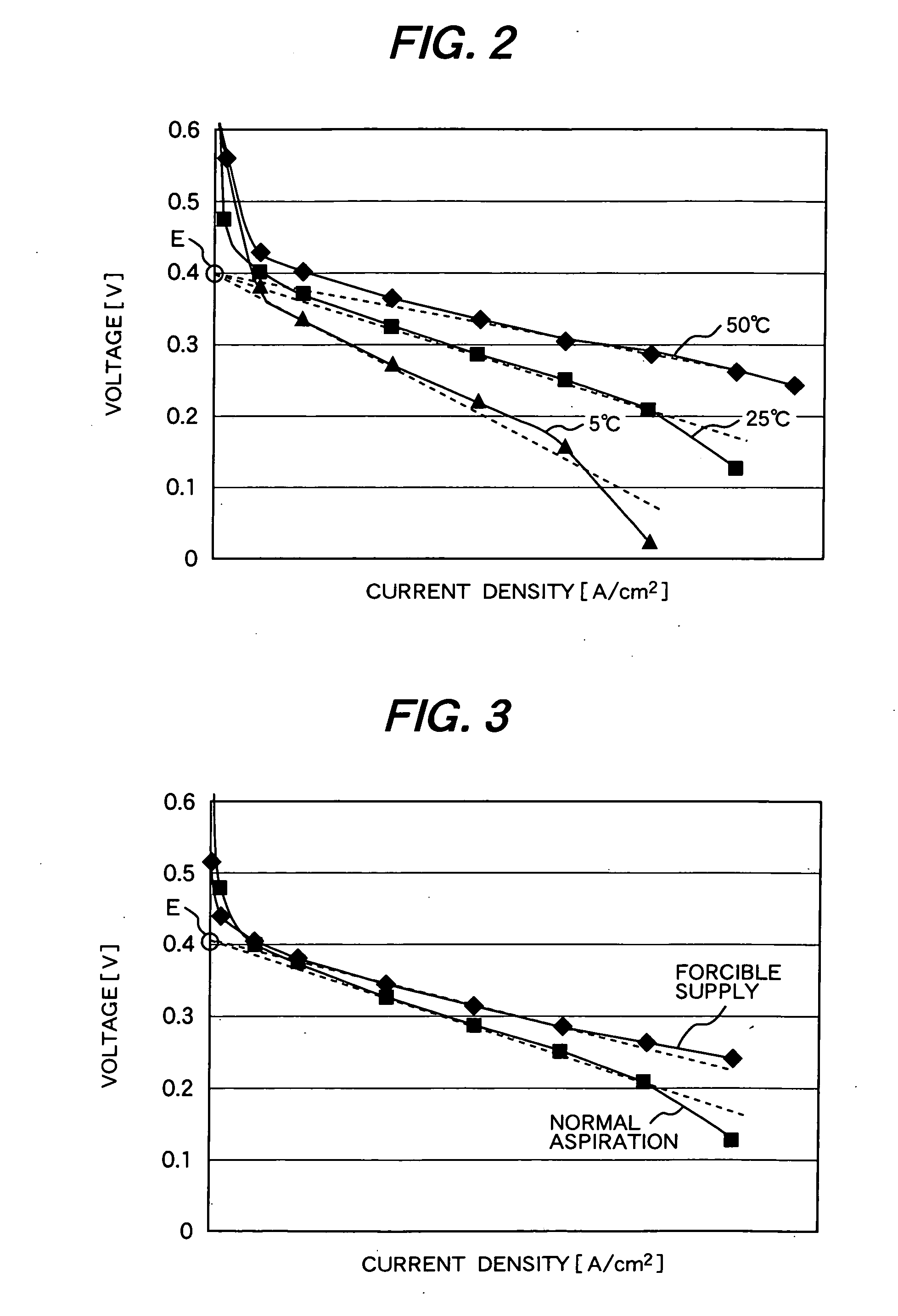
A detection voltage, which is obtained by dividing the voltage of a fuel cell 1 by resistors, is compared with a first reference voltage Vref1 by a differential amplifier. The differential voltage is input to a control section. The control section performs PWM control for the circuit section according to the difference. The first reference voltage Vref1 is set according to the dividing ratio of the resistors, based on the output voltage when the fuel cell generates power at the maximum power point. To determine the output voltage for maximum power generation, a characteristic curve representing a current-voltage characteristic is approximated by an approximating line within a range excluding an area in which the output voltage changes abruptly when the output current is nearly zero, and an extrapolated voltage is obtained on the extension line of the approximating line at an output current of zero. Fifty percent of the extrapolated voltage is then determined as the output voltage when the fuel cell generates power at the maximum power point. Thus, a fuel cell control system that identifies a highly precise output voltage for power generation at a maximum power point and controls power so that the maximum power point is not exceeded could be provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and circuit arrangement for the ageing compensation of an organic light-emitting diode and circuit arrangement
ActiveUS7656370B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingCurrent electricCurrent voltage
The invention relates to a method and a circuit arrangement for the ageing compensation of an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) which is fed from a supply voltage and is switched by means of a driver transistor operated in saturation operation, by means of a driving of the light-emitting diode. The method comprises the following steps of: storing at least one desired current-voltage value pair of a desired current-voltage characteristic curve of the light-emitting diode; transferring the driver transistor from saturation operation to linear operation during a measurement cycle; measuring a current value for the current through the light-emitting diode by means of a current measuring circuit in the measurement cycle; determining at least one present current-voltage value pair of a present current-voltage characteristic curve of the light-emitting diode by means of the measured current value; comparing the at least one present current-voltage value pair of the light-emitting diode with the desired current-voltage value pair of the light-emitting diode; and generating driving parameters for driving the light-emitting diode in a manner dependent on the result of the comparison.
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
Method for determining a maximum power point voltage of a fuel cell and use thereof
A detection voltage, which is obtained by dividing the voltage of a fuel cell 1 by resistors, is compared with a first reference voltage Vref 1 by a differential amplifier. The differential voltage is input to a control section. The control section performs PWM control for the circuit section according to the difference. The first reference voltage Vref 1 is set according to the dividing ratio of the resistors, based on the output voltage when the fuel cell generates power at the maximum power point. To determine the output voltage for maximum power generation, a characteristic curve representing a current-voltage characteristic is approximated by an approximating line within a range excluding an area in which the output voltage changes abruptly when the output current is nearly zero, and an extrapolated voltage is obtained on the extension line of the approximating line at an output current of zero. Fifty percent of the extrapolated voltage is then determined as the output voltage when the fuel cell generates power at the maximum power point. Thus, a fuel cell control system that identifies a highly precise output voltage for power generation at a maximum power point and controls power so that the maximum power point is not exceeded could be provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method of controlling rechargeable battery power and a power source apparatus
InactiveUS20060087291A1Appropriate settingAvoid excessive dischargeCharging stationsSecondary cells charging/dischargingBattery chargeMemory effect
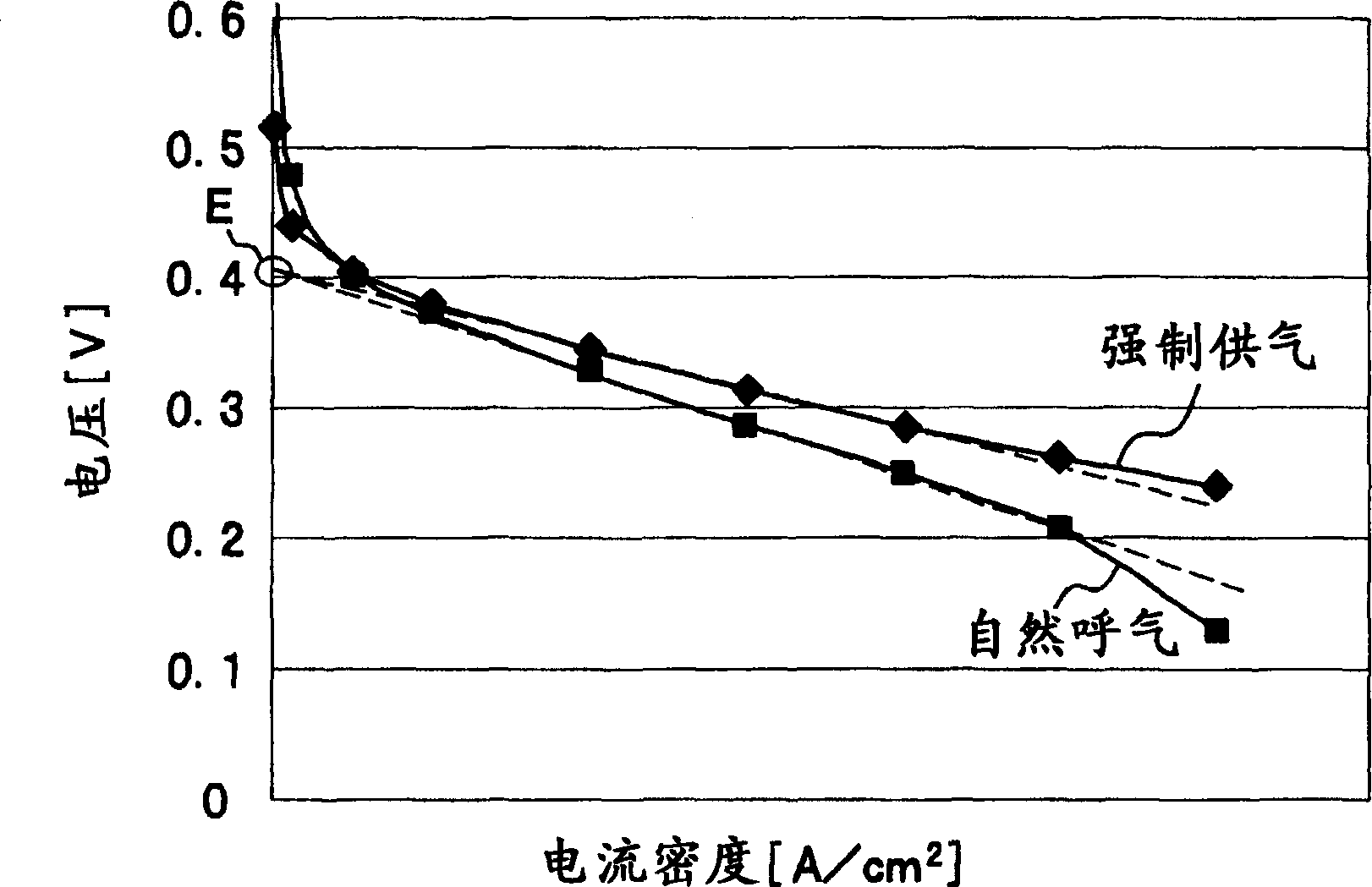
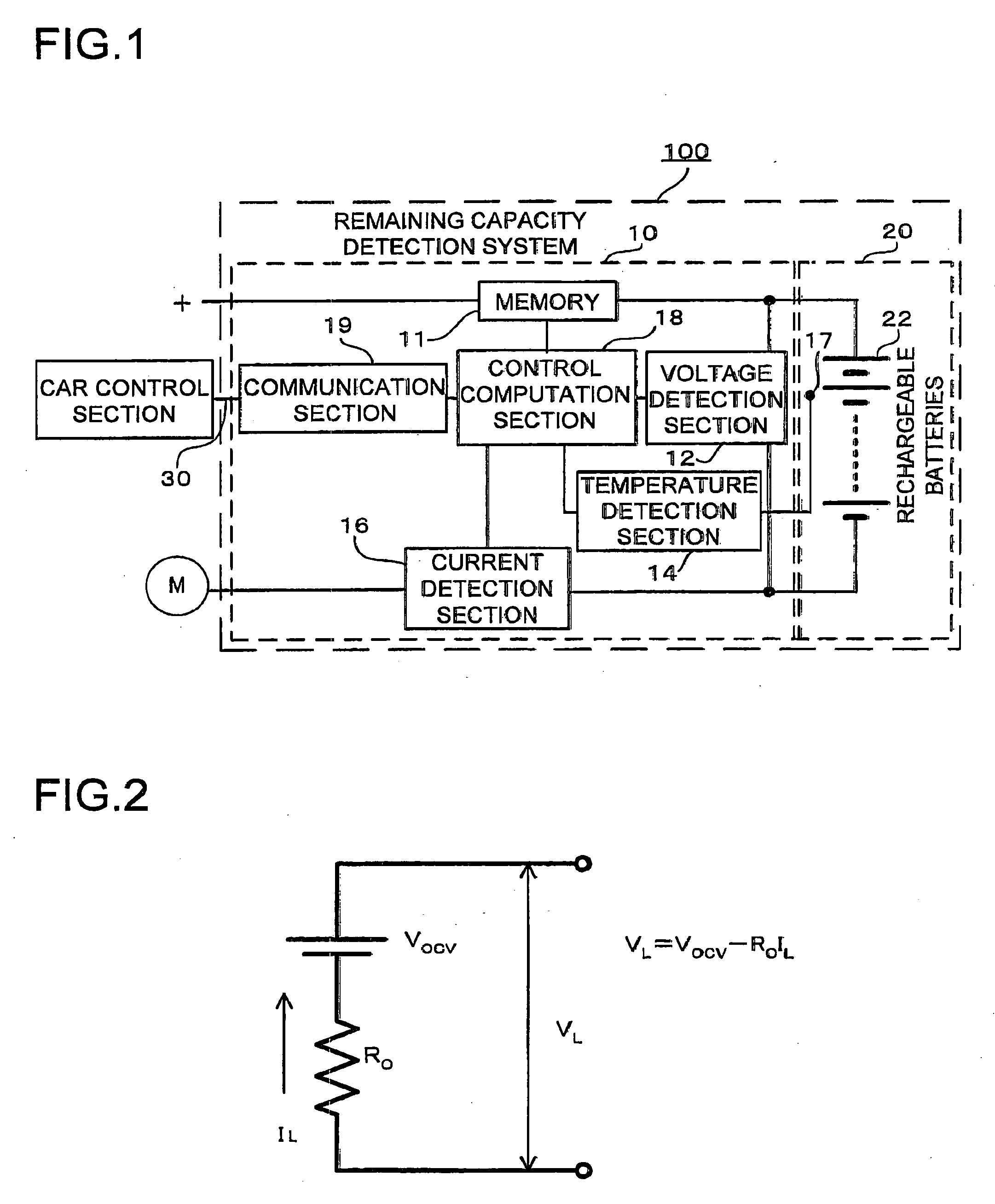
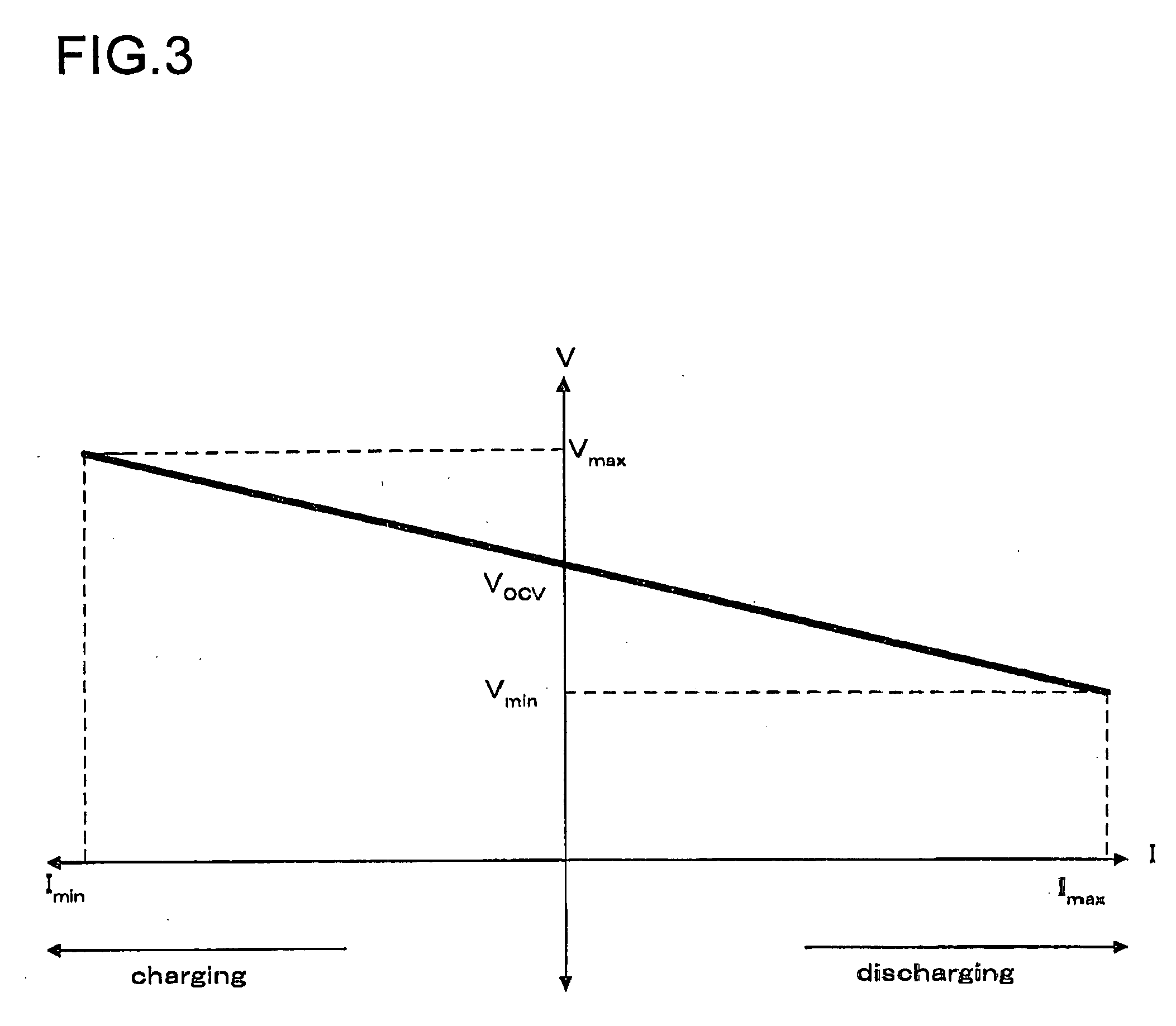
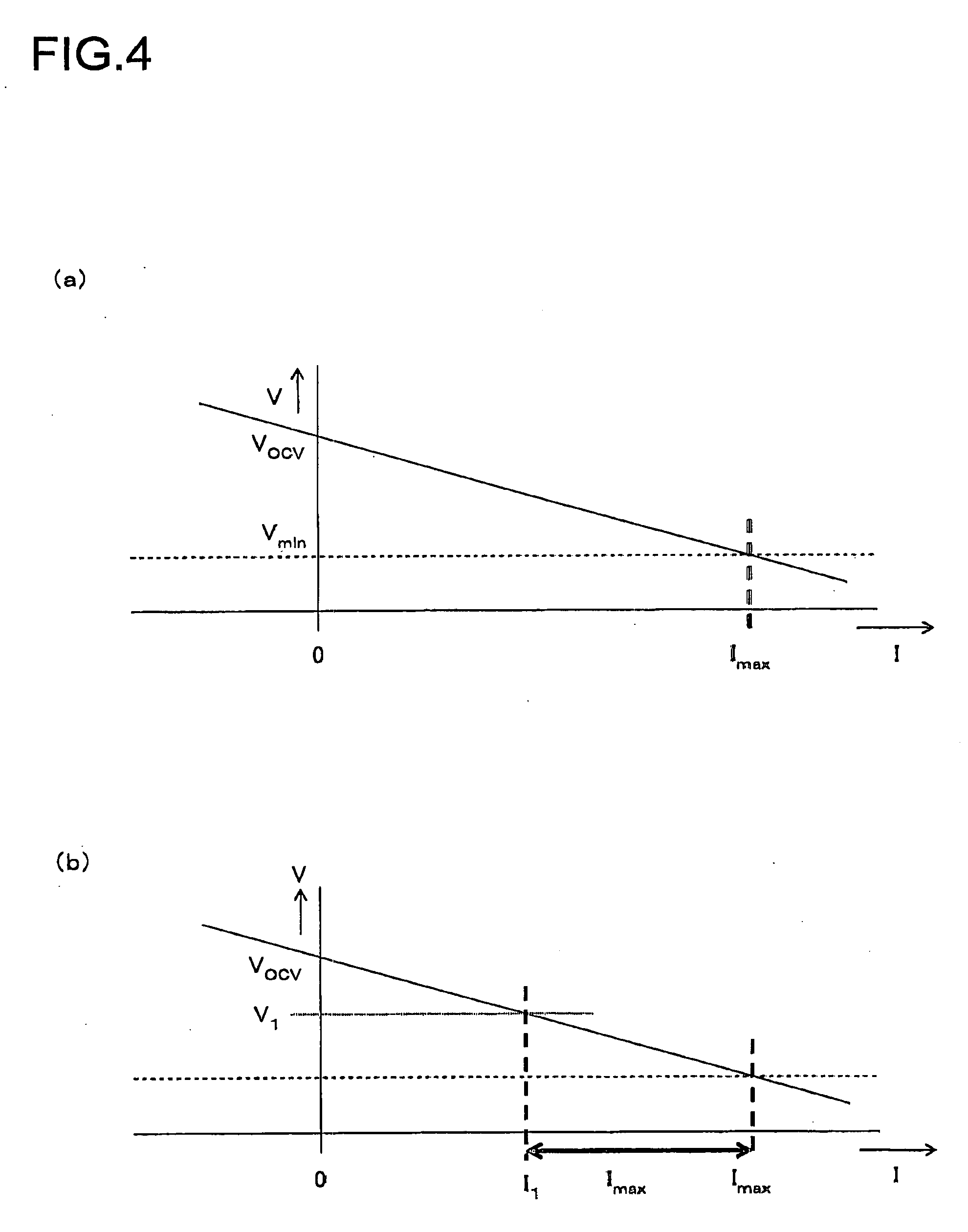
The method of controlling rechargeable battery power is a method that includes limiting the amount of usable power during rechargeable battery charging and discharging, determining a rechargeable battery current-voltage characteristic function based on rechargeable battery charging and discharging current flow and voltage, finding a limiting discharging current Imax and / or a limiting charging current Imin from a prescribed minimum voltage Vmin to prevent over-discharging and / or a prescribed maximum voltage Vmax to prevent over-charging and their intersection with the current-voltage characteristic function, and controlling current such that discharging current greater than or equal to Imax and / or charging current less than or equal to Imin does not flow through the rechargeable batteries. In this fashion, the amount of usable power can be limited considering factors such as the memory effect, and the rechargeable battery can be used to its maximum capability within the range of safe operation.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Complementary zener triggered bipolar ESD protection
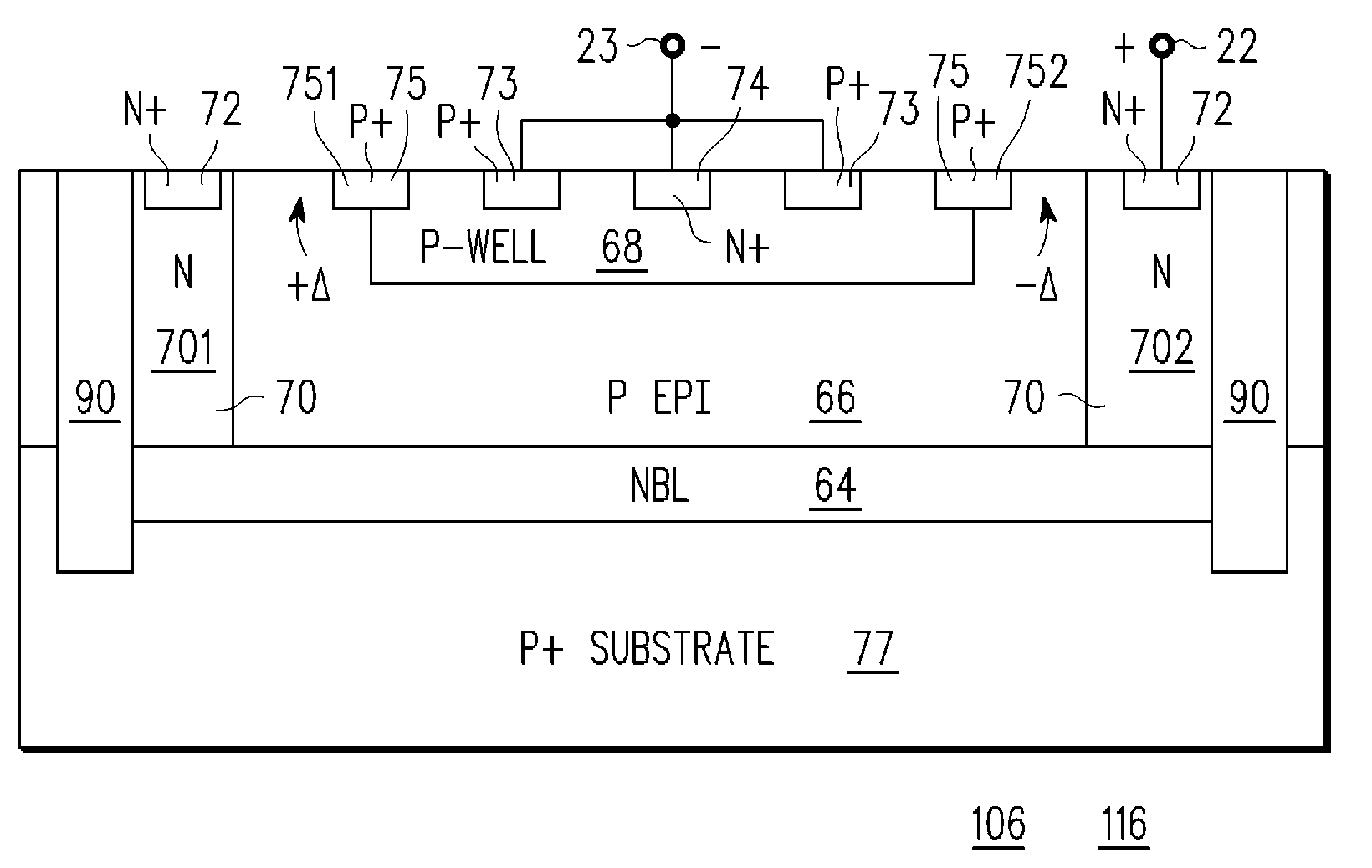
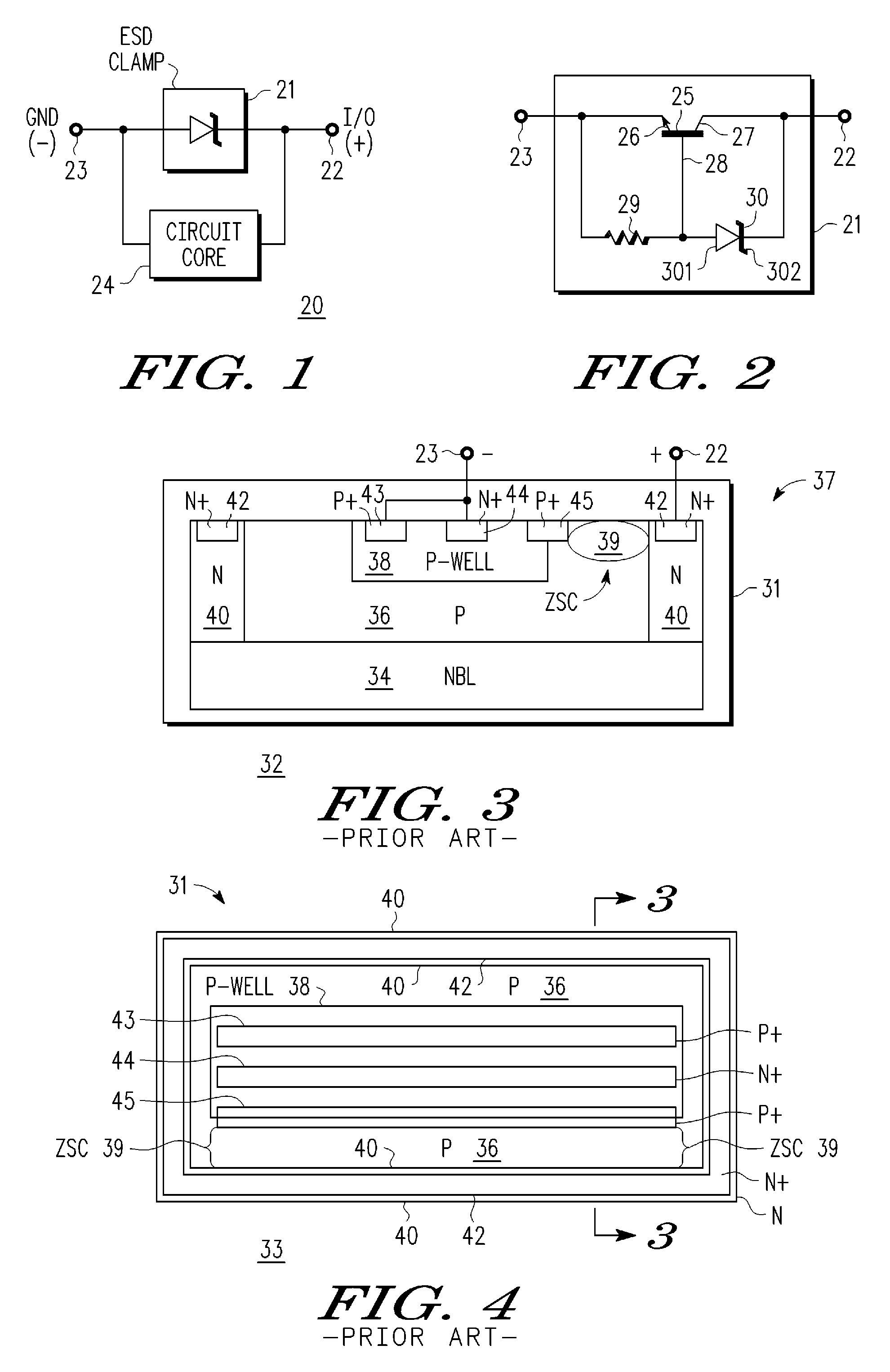
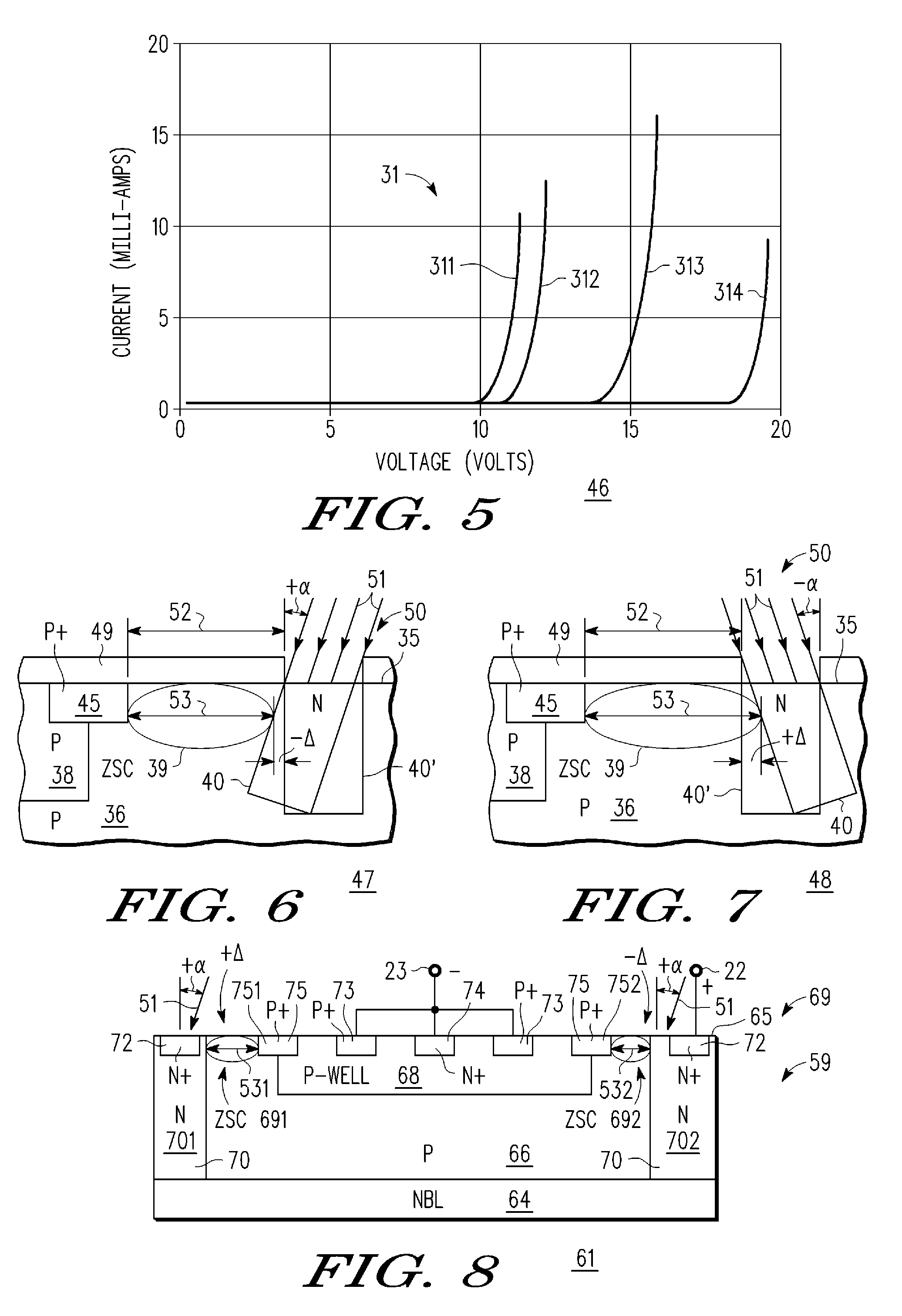
An electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection clamp (61) for I / O terminals (22, 23) of integrated circuits (ICs) (24) comprises an NPN bipolar transistor (25) coupled to an integrated Zener diode (30). Variations in the break-down current-voltage characteristics (311, 312, 313, 314) of multiple prior art ESD clamps (31) in different parts of the same IC chip is avoided by forming the anode (301) of the Zener (30) in the shape of a base-coupled P+ annular ring (75) surrounded by a spaced-apart N+ annular collector ring (70) for the cathode (302) of the Zener (30). Even though an angled implant (51, 86, 98) used to form the N+ annular collector ring (70) causes location dependent variations in the width (53) of the Zener space charge (ZSC) region (69), the improved annular shaped clamp (61) always has a portion that initiates break-down at the design voltage so that variations in the width (53) of the ZSC region (69) do not cause significant variations in the clamp's current-voltage characteristics (611, 612, 613, 614).
Owner:NXP USA INC
Light emitting device
InactiveUS20030214245A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectricitySimple Organic Compounds
The light-emitting element has a problem that reliability, heat-resisting stability and durability are low because of the deterioration in an organic compound layer. The TFT for driving the light-emitting element has a problem that variation readily occurs in its electrical characteristic due to the defects existing in grain boundaries. The present invention provides a light-emitting device by using the fact that, by applying to the light-emitting element a drive voltage having a polarity reverse to that in light emission during each constant period, the light-emitting element is improved in current-voltage characteristic. Furthermore, the present invention provides a light-emitting device made not dependent upon transistor characteristic, by controlling the amount of a current flowing through the light-emitting element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
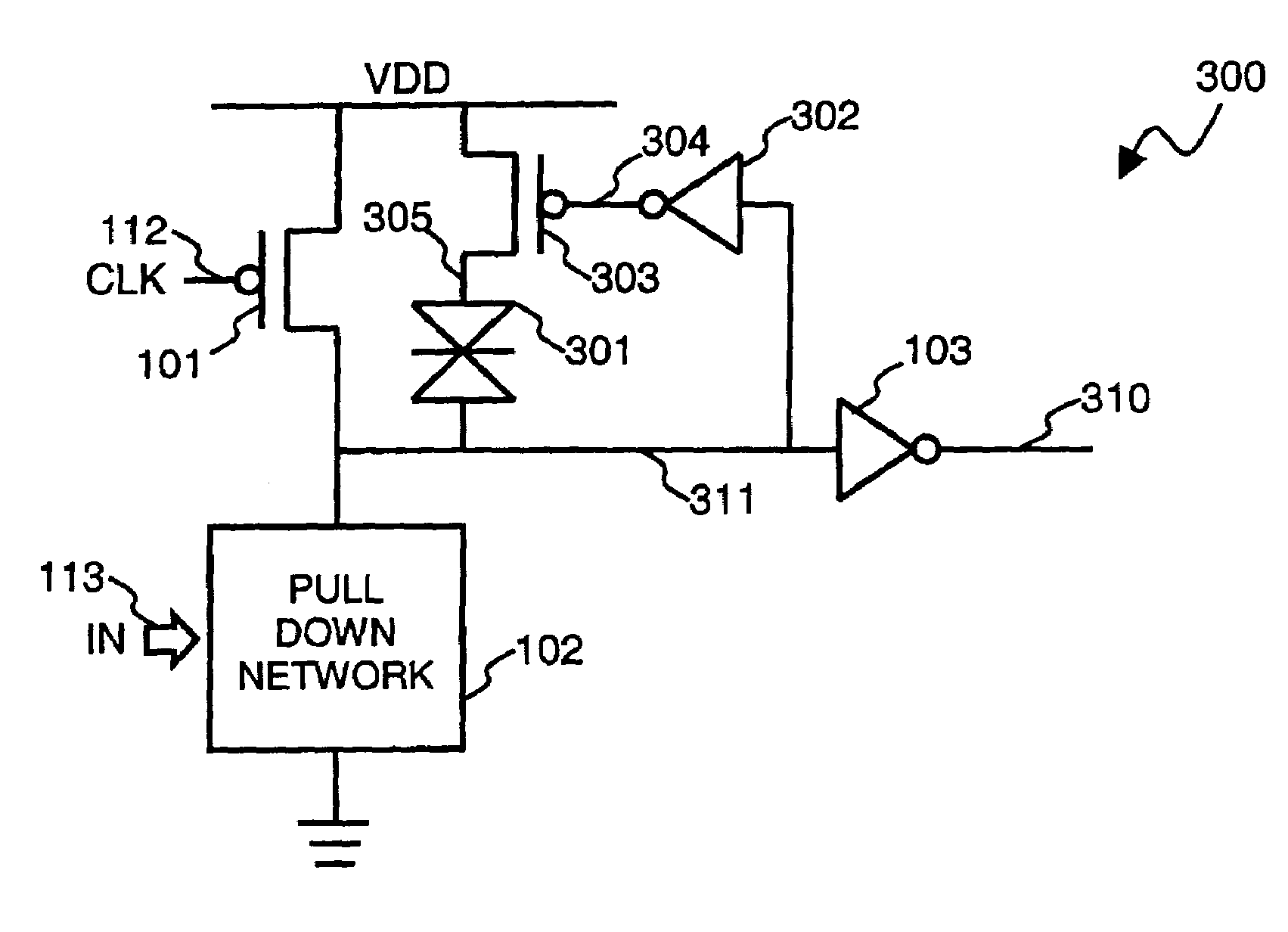
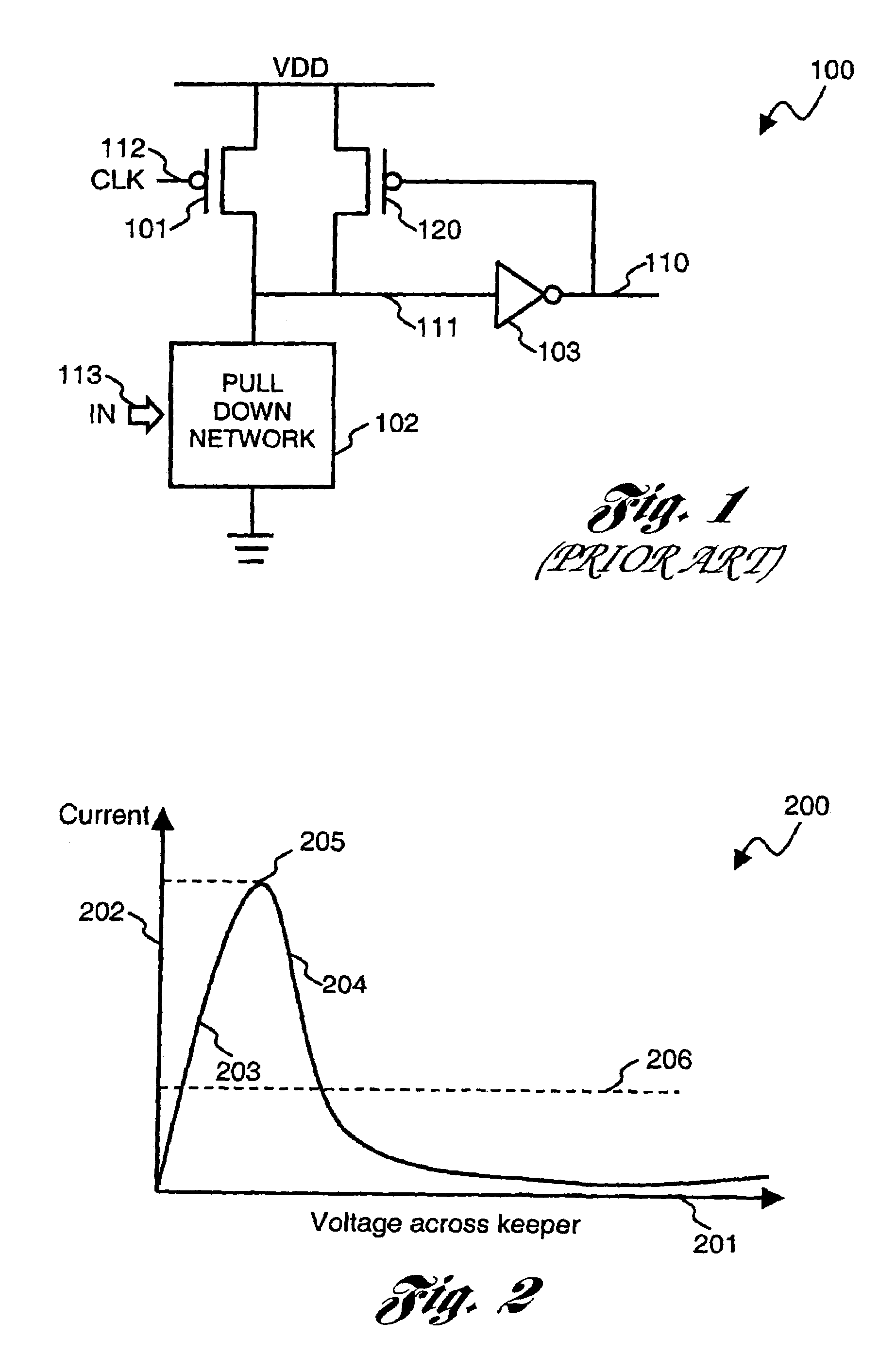
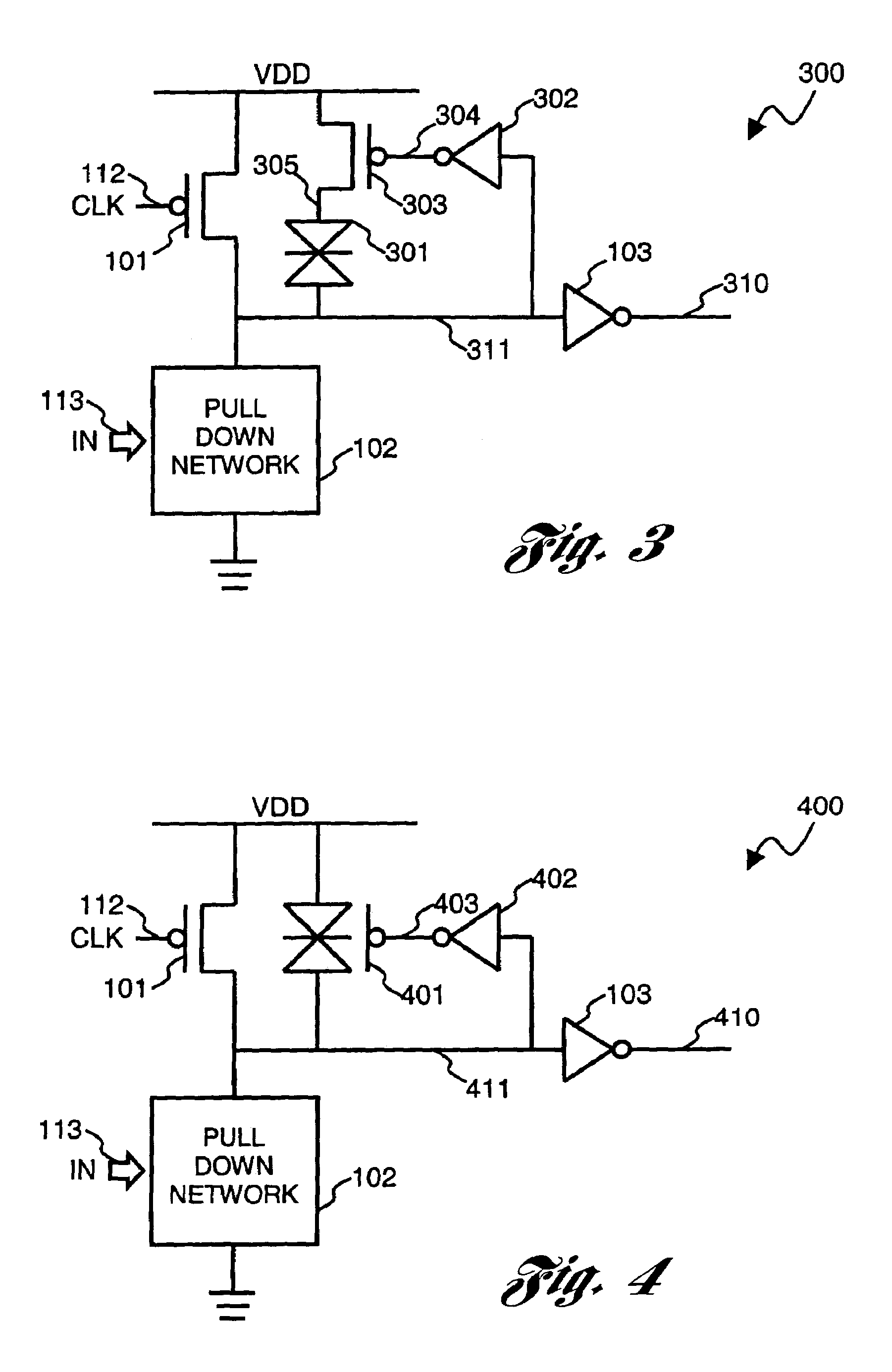
Dynamic circuits having improved noise tolerance and method for designing same
InactiveUS7088143B2Improved dynamic circuitsImprove methodLogic circuits characterised by logic functionElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A number of different dynamic circuits having improved noise tolerance and a method for designing same are provided. The circuits include a power supply node and a precharge node. Keeper circuitry is connected to the nodes and has a current-voltage characteristic that exhibits a negative differential resistance property to improve noise tolerance of the circuits.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Pixel circuit, display device, and method for driving pixel circuit
InactiveUS7714813B2No deteriorationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceCapacitor
Owner:SONY CORP
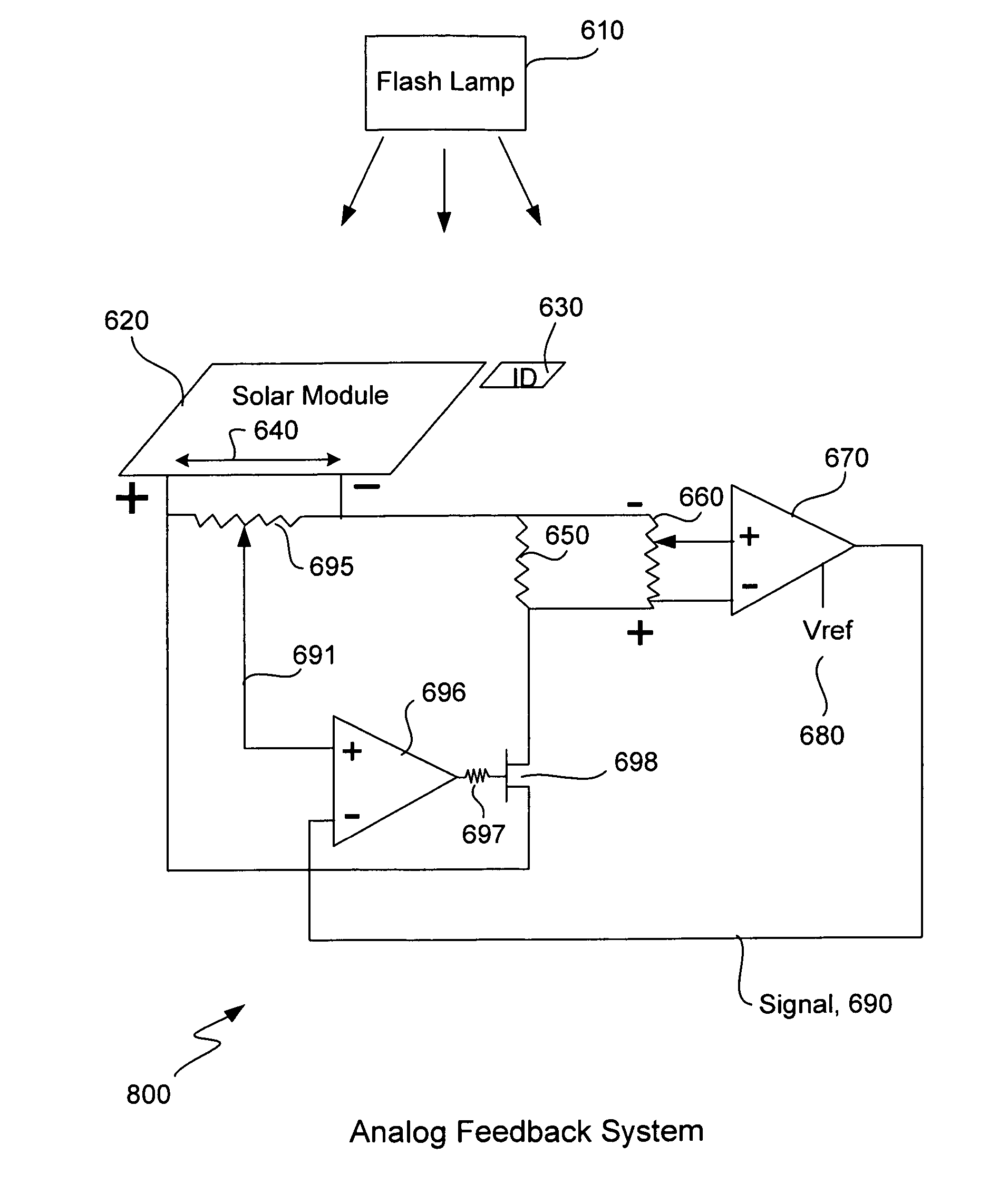
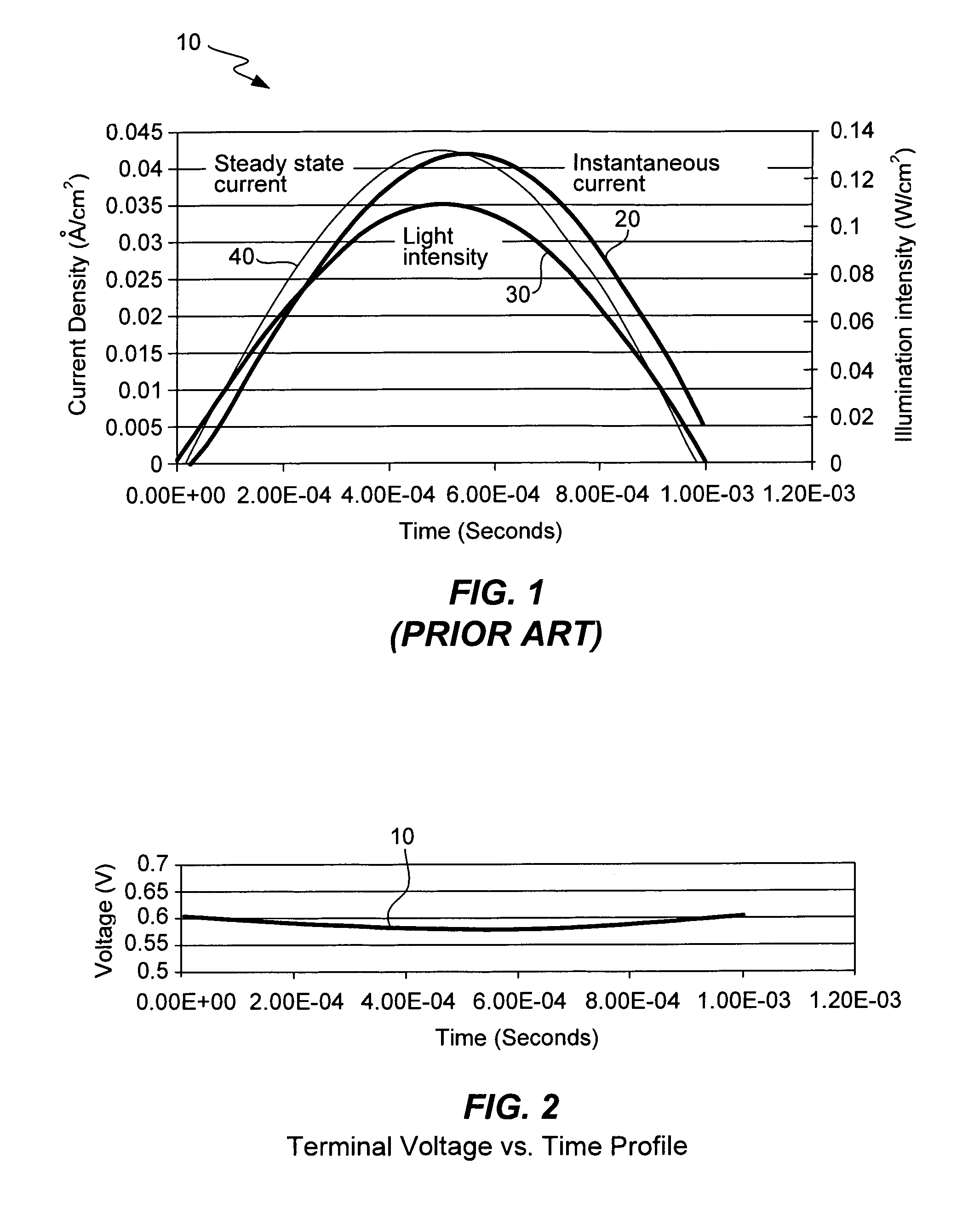
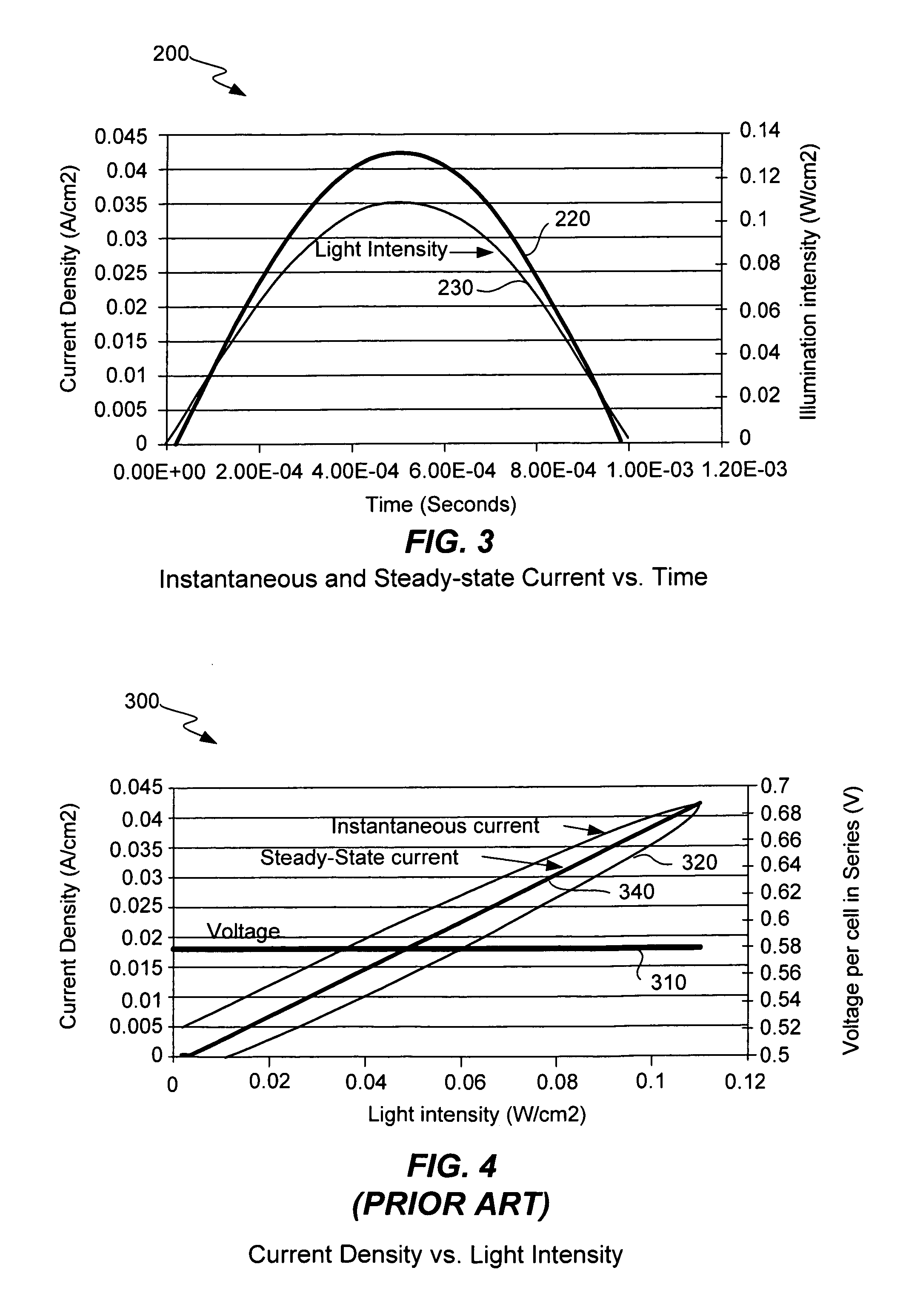
Measurement of current-voltage characteristic curves of solar cells and solar modules
ActiveUS7309850B2Accurate measurementPredictive performancePhotometry using reference valuePhotovoltaic monitoringAnalog feedbackSignal correction
A solar cell or solar module is measured during a short pulse of light in such a way that the resulting data for current and voltage at each light intensity is the same as would be measured under steady-state illumination conditions and therefore predictive of the actual performance of the solar cell or solar module in sunlight. A varying voltage is applied to the terminals of the solar cell during a light pulse so that the instantaneous current at a given voltage and light intensity during the light pulse is the same as would be measured under constant illumination at that same given intensity. A constant voltage is modified by a small signal correction that is proportional to the terminal current. Or, the small signal correction is proportional to the light intensity. An analog feedback circuit is constructed using the terminal current or light intensity for feedback in order to provide the requisite varying voltage. The varying voltage may also be supplied by digital synthesis.
Owner:SINTON CONSULTING
Organic semiconductor diode
InactiveUS7211824B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSchottky barrierP–n junction
The present invention relates to organic semiconductor diodes, in particular, to the diodes with nonlinear current-voltage characteristics, which are used for power switching, rectifying variable signals, and frequency mixing. The organic semiconductor diode with the p-n junction comprises an anode, cathode, a hole transport layer in contact with the anode, and an electron transport layer in contact with the cathode, and two transport layers being in contact with each other. Another aspect of the present invention is a Schottky barrier diode comprising anode, cathode, and an organic semiconductor layer, wherein the semiconductor layer is either hole or electron transport layer. At least one of the transport layers is characterized by a globally ordered crystalline structure with intermolecular spacing of 3.4±0.3 Å in the direction of one crystal axis. One more aspect of the present invention is a method for obtaining an organic semiconductor layer with the electron-hole type of conductivity.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Bi-layer pseudo-spin field-effect transistor
InactiveUS20100127243A1Low gate and interlayer biasesNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPeak value
A bi-layer pseudo-spin field-effect transistor (BiSFET) is disclosed. The BiSFET includes a first and second conduction layers separated by a tunnel dielectric. The BiSFET transistor also includes a first gate separated from the first conduction layer by an insulating dielectric layer, and a second gate separated from the second conduction layer by an insulating layer. These conduction layers may be composed of graphene. The voltages applied to the first and / or second gates can control the peak current and associated voltage value for current flow between top and bottom conduction channels, and interlayer current voltage characteristic exhibiting negative differential resistance. BiSFETs may be used to make a variety of logic gates. A clocked power supply scheme may be used to facilitate BiSFET-based logic.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
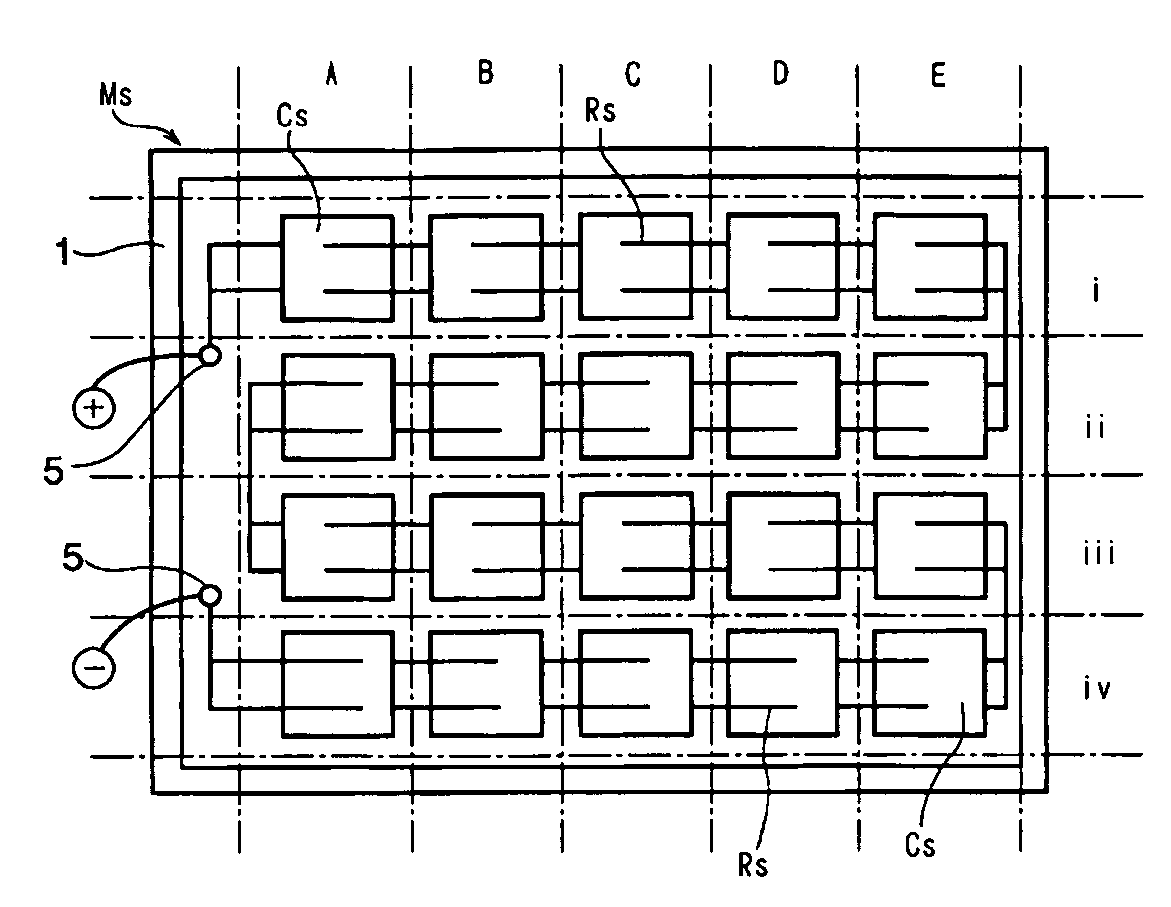
Measurement method of the current-voltage characteristics of photovoltaic devices, a solar simulator for the measurement, and a module for setting irradiance and a part for adjusting irradiance used for the solar simulator
InactiveUS20060238750A1Reduce local unevennessPhotometry using reference valuePhotovoltaic monitoringIlluminanceCurrent voltage
In a solar simulator for measuring the current-voltage characteristics of photovoltaic devices, it is to provide a measurement method using a solar simulator in which locative unevenness of irradiance on the test plane of the test plane side is drastically improved, not in a light source side, and a means for adjusting irradiance and the like. when an object is the photovoltaic devices Ms, and the current-voltage characteristics are measured by a solar simulator Ss equipped with a light source composed of a lamp and a reflector, and a part for setting the object to be measured, in which it is possible to dispose an irradiated test plane of the object to be measured opposite an illuminating surface of said light source, the whole test plane of said photovoltaic devices is divided imaginarily into a plurality of sections and a selected member for adjusting irradiance is disposed opposite the test plane of each imaginary sections so as to equalize or substantially to equalize the irradiance by the light source at every irradiated test plane of the sections, after which light from said light source is directed onto the test plane of the object to be measured.
Owner:NISSHINBO IND INC
Semiconductor device and driver control method
ActiveUS7768312B2Enhanced signalInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsElectrical resistance and conductanceP channel
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20090273964A1Guaranteed uptimeCircuit configuration becomes complexSolid-state devicesDigital storageLoad circuitHigh resistance
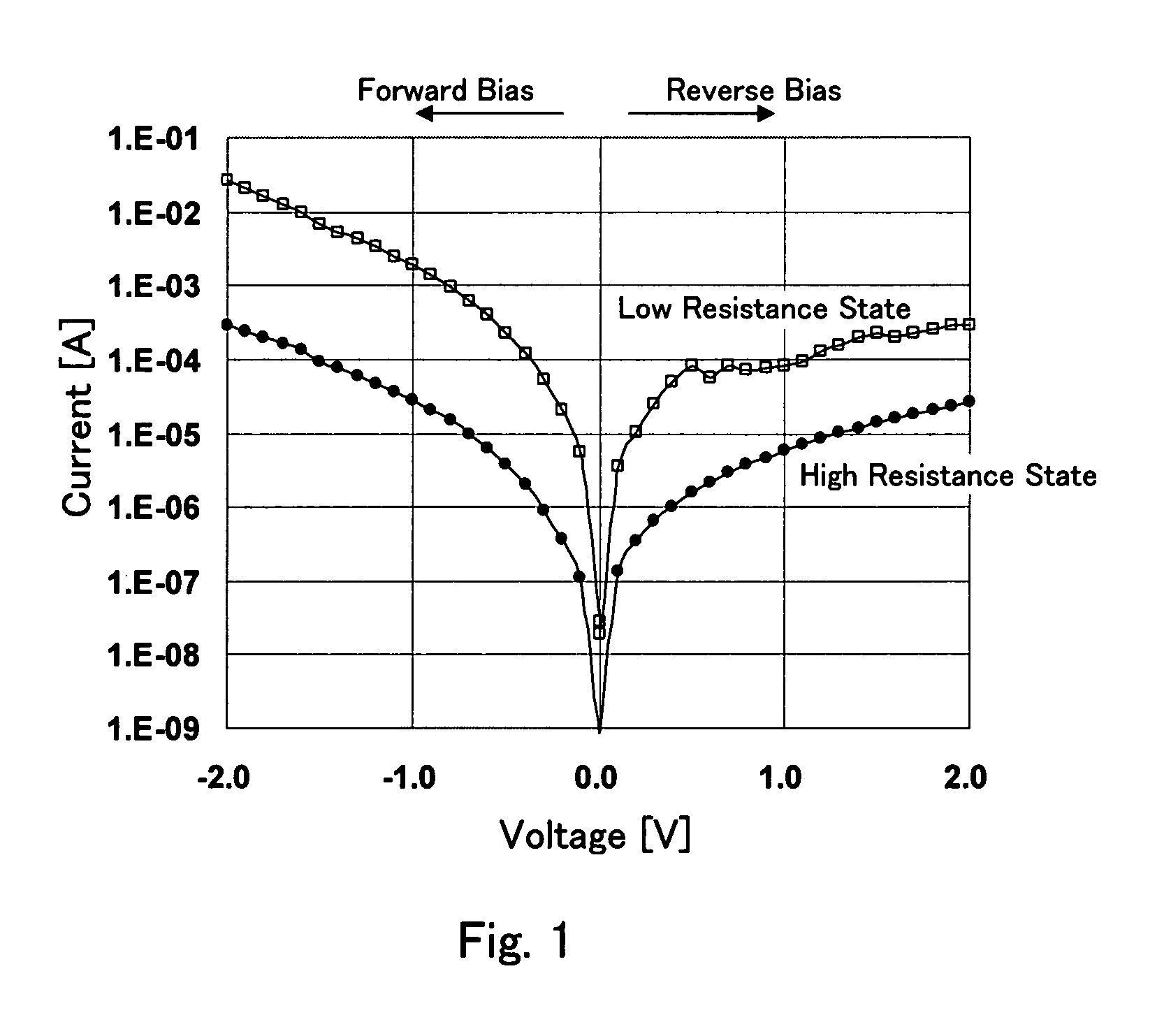
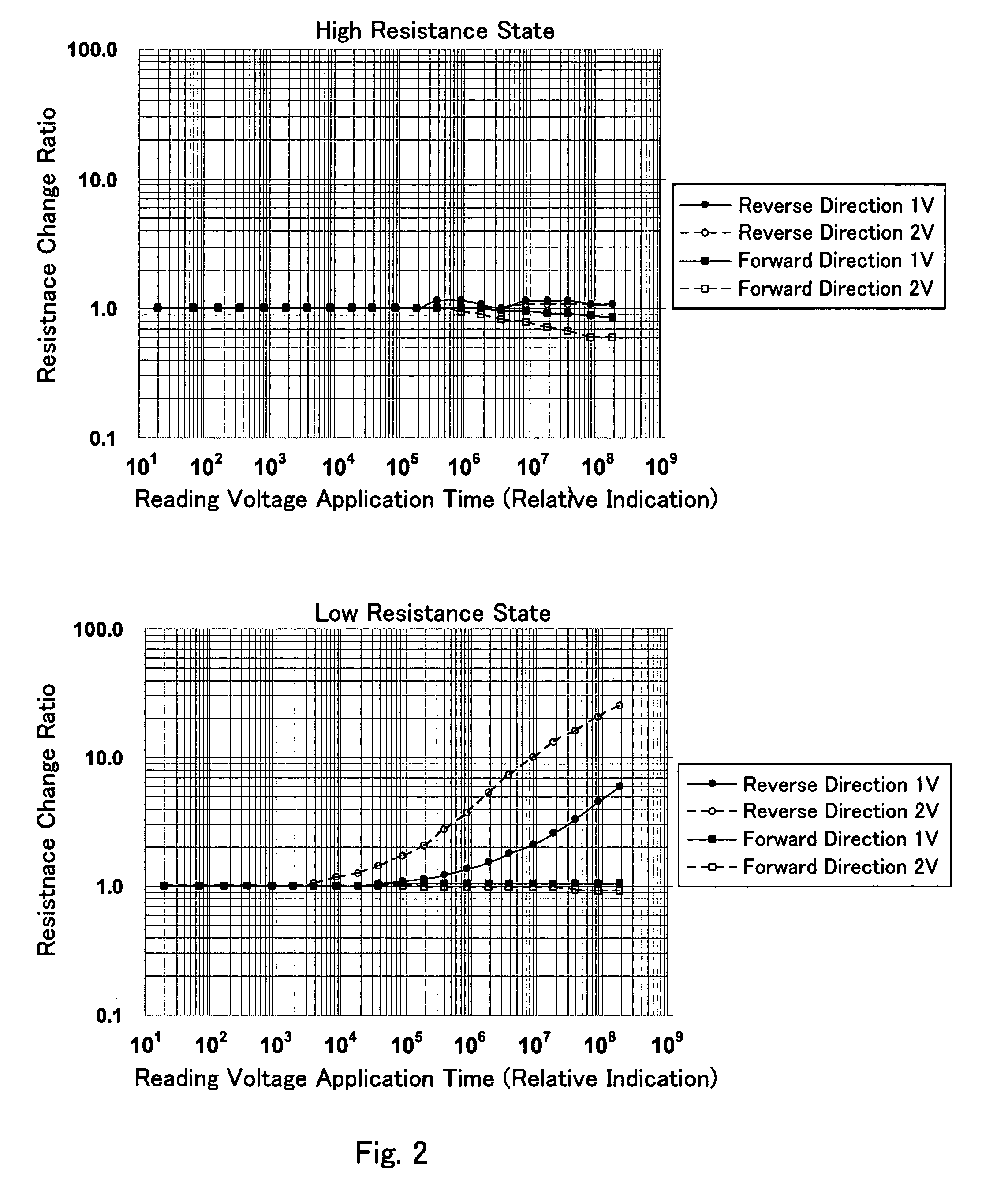
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device comprises: a two terminal structured variable resistive element, wherein resistive characteristics defined by current-voltage characteristics at both ends transit between low and high resistance states stably by applying a voltage satisfying predetermined conditions to the both ends, a transition from the low resistance state to the high resistance state occurs by applying a voltage of a first polarity whose absolute value is at or higher than a first threshold voltage, and the reverse transition occurs by applying a voltage of a second polarity whose absolute value is at or higher than a second threshold voltage; a load circuit connected to the variable resistive element in series having an adjustable load resistance; and a voltage generation circuit for applying a voltage to both ends of a serial circuit; wherein the variable resistive element can transit between the states by adjusting a resistance of the load circuit.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
Pixel circuit, display device, and method for driving pixel circuit
InactiveUS20070120795A1No deteriorationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceDisplay device
A pixel circuit, display device, and method of driving a pixel circuit enabling source-follower output with no deterioration of luminance even with a change of the current-voltage characteristic of the light emitting element along with elapse, enabling a source-follower circuit of n-channel transistors, and able to use an n-channel transistor as a drive transistor of a light emitting element while using current anode-cathode electrodes, wherein a capacitor C111 is connected between a gate and source of a TFT 111 as a drive transistor, a source side of the TFT 111 is connected to a fixed potential (for example GND) through the TFT 114, the gate and drain of the TFT 111 are connected through the TFT 113 to cancel the threshold value Vth, the threshold value Vth is charged in the capacitor C111, and the input voltage Vin is coupled with the gate of the TFT 111 from the threshold voltage Vth.
Owner:SONY CORP
Implantation for current confinement in nitride-based vertical optoelectronics
InactiveUS20030180980A1Eliminate light absorptionHigh resistivityOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsCurrent limitingOhmic contact
Ion implantation is used to increase the resistivity of semiconductor device layers for channeling the current through a low resistivity, unimplanted region such that carrier recombination takes place away from regions underneath the contacts. This eliminates absorption of light by the contact thereby providing higher light output power and better current-voltage characteristics to the semiconductor device. The incorporation of a regrown contact layer allows for an undamaged lateral conduction path, and the fabrication of ohmic contacts.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA THE OFFICE OF TECH TRANSFER
Light emitting device
InactiveUS7042162B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectricitySimple Organic Compounds
The light-emitting element has a problem that reliability, heat-resisting stability and durability are low because of the deterioration in an organic compound layer. The TFT for driving the light-emitting element has a problem that variation readily occurs in its electrical characteristic due to the defects existing in grain boundaries. The present invention provides a light-emitting device by using the fact that, by applying to the light-emitting element a drive voltage having a polarity reverse to that in light emission during each constant period, the light-emitting element is improved in current-voltage characteristic. Furthermore, the present invention provides a light-emitting device made not dependent upon transistor characteristic, by controlling the amount of a current flowing through the light-emitting element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Group-III Nitride-Based Light Emitting Device
ActiveUS20080303055A1Superior current-voltage characteristicImproved ohmic contact characteristicsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIndiumLight-emitting diode
Disclosed is a group-III nitride-based light emitting diode. The group-III nitride-based light emitting diode includes a substrate, an n-type nitride-based cladding layer formed on the substrate, a nitride-based active layer formed on the n-type nitride-based cladding layer, a p-type nitride-based cladding layer formed on the nitride-based active layer, and a p-type multi-layered ohmic contact layer formed on the p-type nitride-based cladding layer and including thermally decomposed nitride. The thermally decomposed nitride is obtained by combining nitrogen (N) with at least one metal component selected from the group consisting of nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), indium (In) and tin (Sn). An ohmic contact characteristic is enhanced at the interfacial surface of the p-type nitride-based cladding layer of the group-III nitride-based light emitting device, thereby improving the current-voltage characteristics. In addition, since the light transmittance of the transparent electrode is improved, light efficiency and brightness of the group-III nitride-based light emitting device are also improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method and apparatus for measuring photoelectric conversion device, and process and apparatus for producing photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS6946858B2Accurate measurementPhotovoltaic monitoringMaterial analysis by optical meansCurrent voltageReference device
A measuring method for measuring current-voltage characteristics of a photoelectric conversion device by irradiating light to said photoelectric conversion device and a reference device corresponding to said photoelectric conversion device at the same time while detecting an irradiance of said light using said reference device, characterized in that a light responsive time constant of a irradiance detection circuit in which said reference device is used is adjusted so that said light responsive time constant of said irradiance detection circuit comes closer to a light responsive time constant of said photoelectric conversion device. An apparatus for practicing said measuring method.
Owner:CANON KK
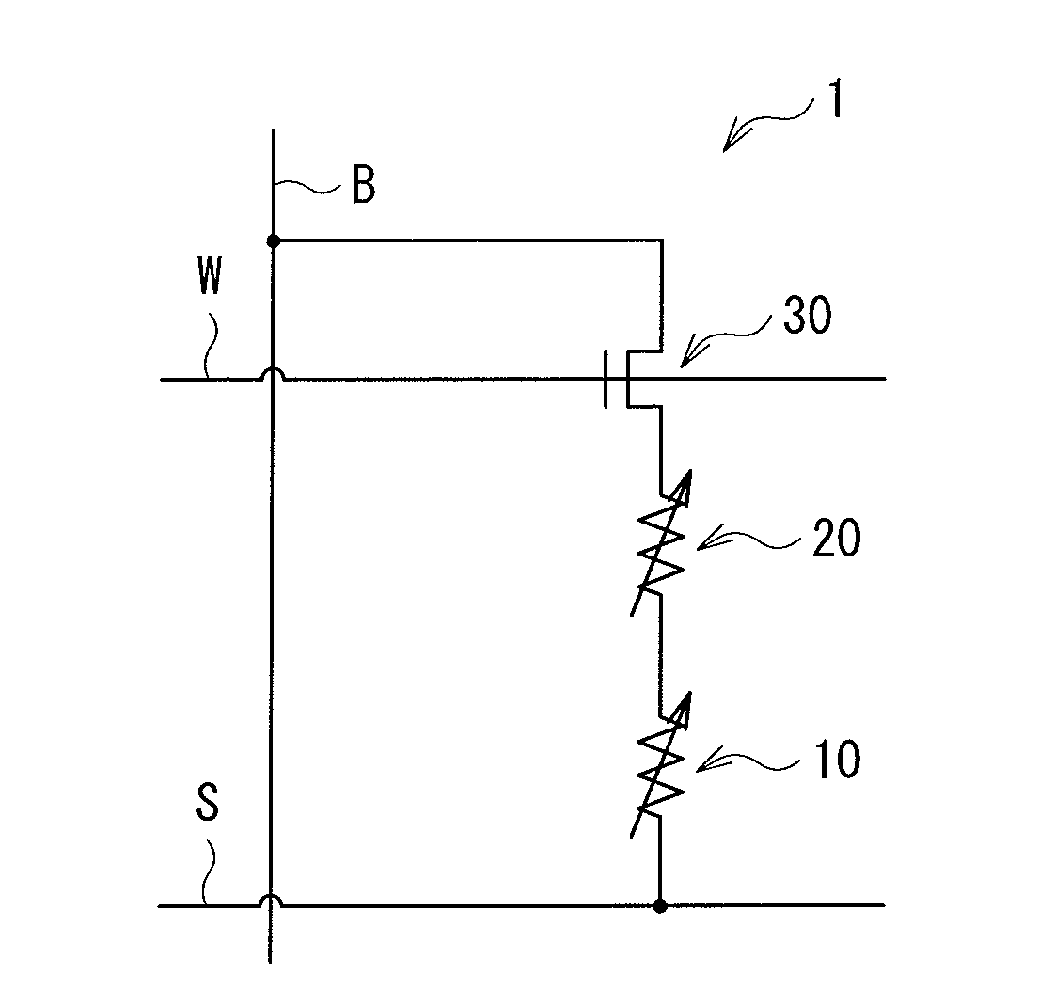
Memory cell
ActiveUS20100259967A1Stable erasing resistance independent of a repetition rateSolid-state devicesDigital storageNonlinear resistorElectrical polarity
A memory cell is provided, in which a resistance value is appropriately controlled, thereby a variable resistance element may be applied with a voltage necessary for changing the element into a high or low resistance state. A storage element 10, a nonlinear resistance element 20, and an MOS transistor 30 are electrically connected in series. The storage element 10 has a nonlinear current-voltage characteristic opposite to a nonlinear current-voltage characteristic of the MOS transistor 30, and changes into a high or low resistance state in accordance with a polarity of applied voltage. The nonlinear resistance element 20 has a nonlinear current-voltage characteristic similar to the nonlinear current-voltage characteristic of the storage element 10.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
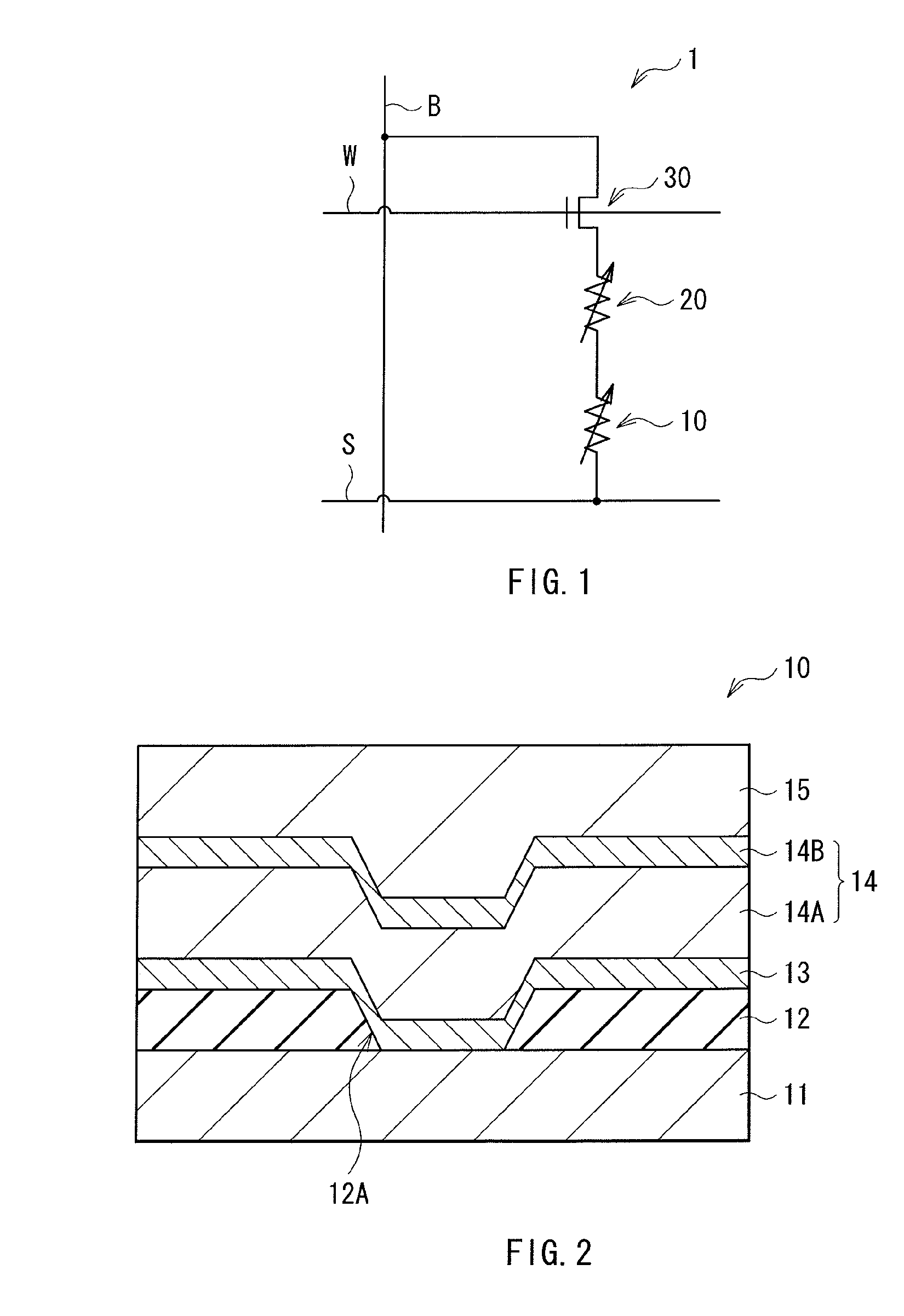
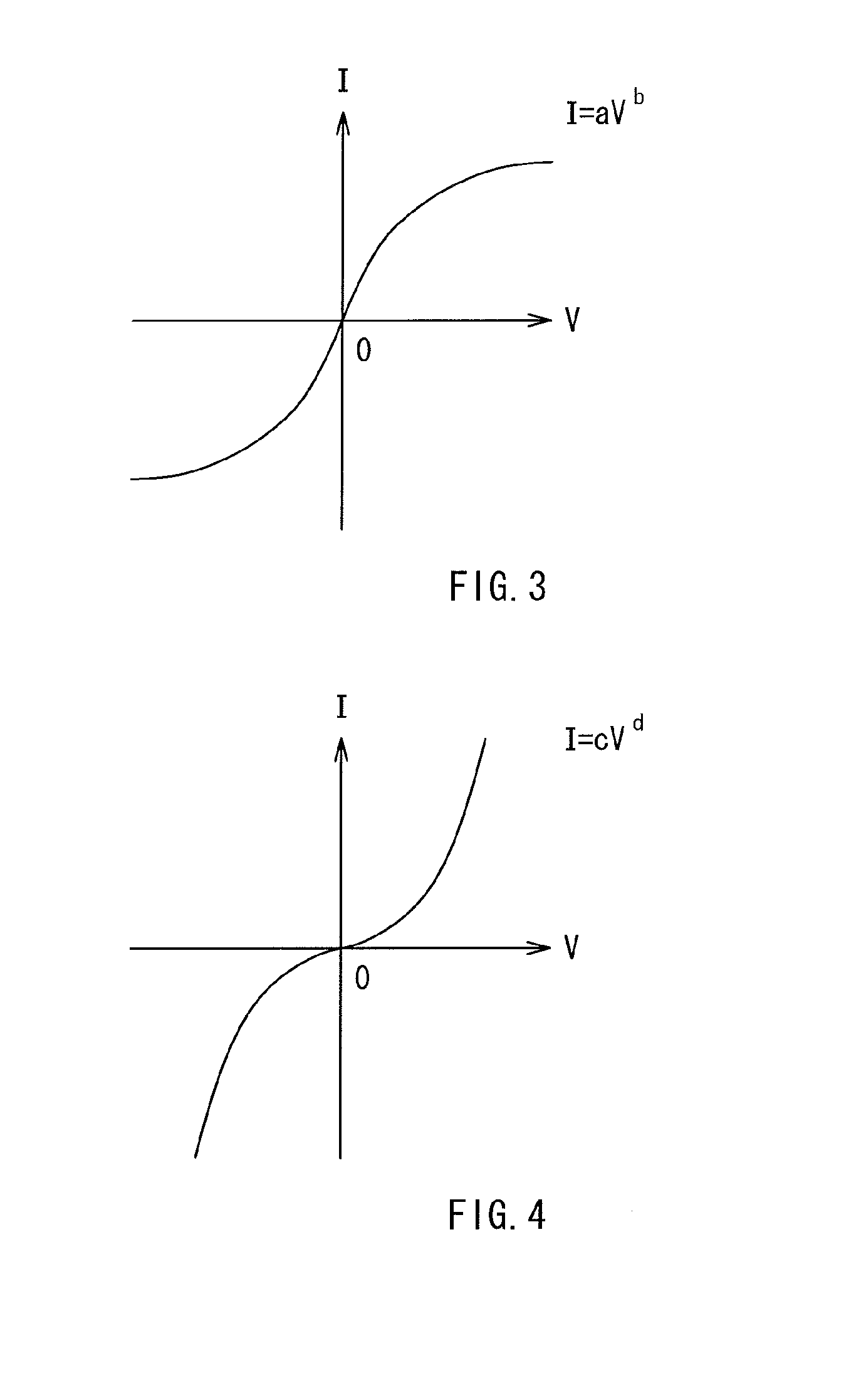
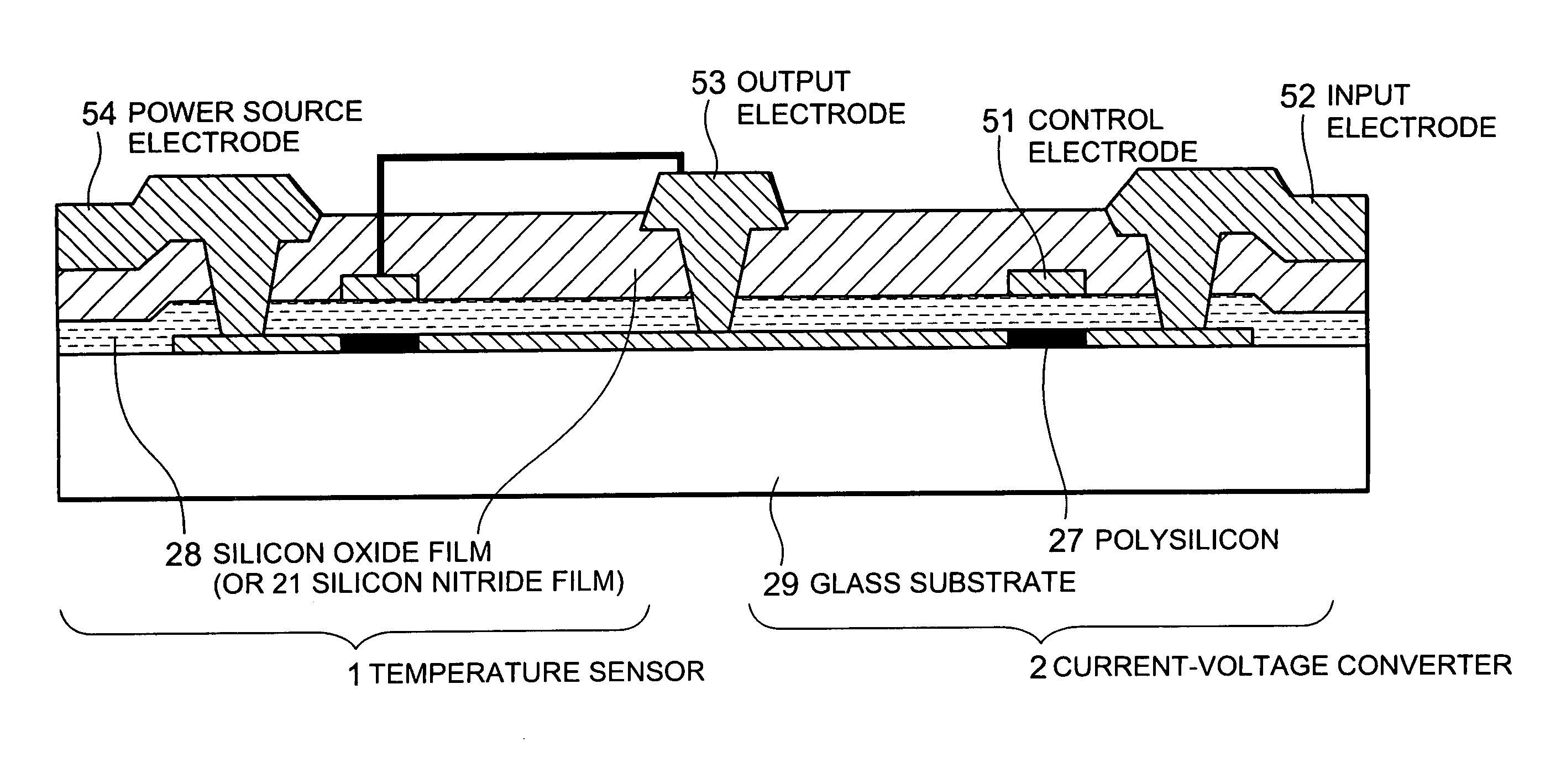
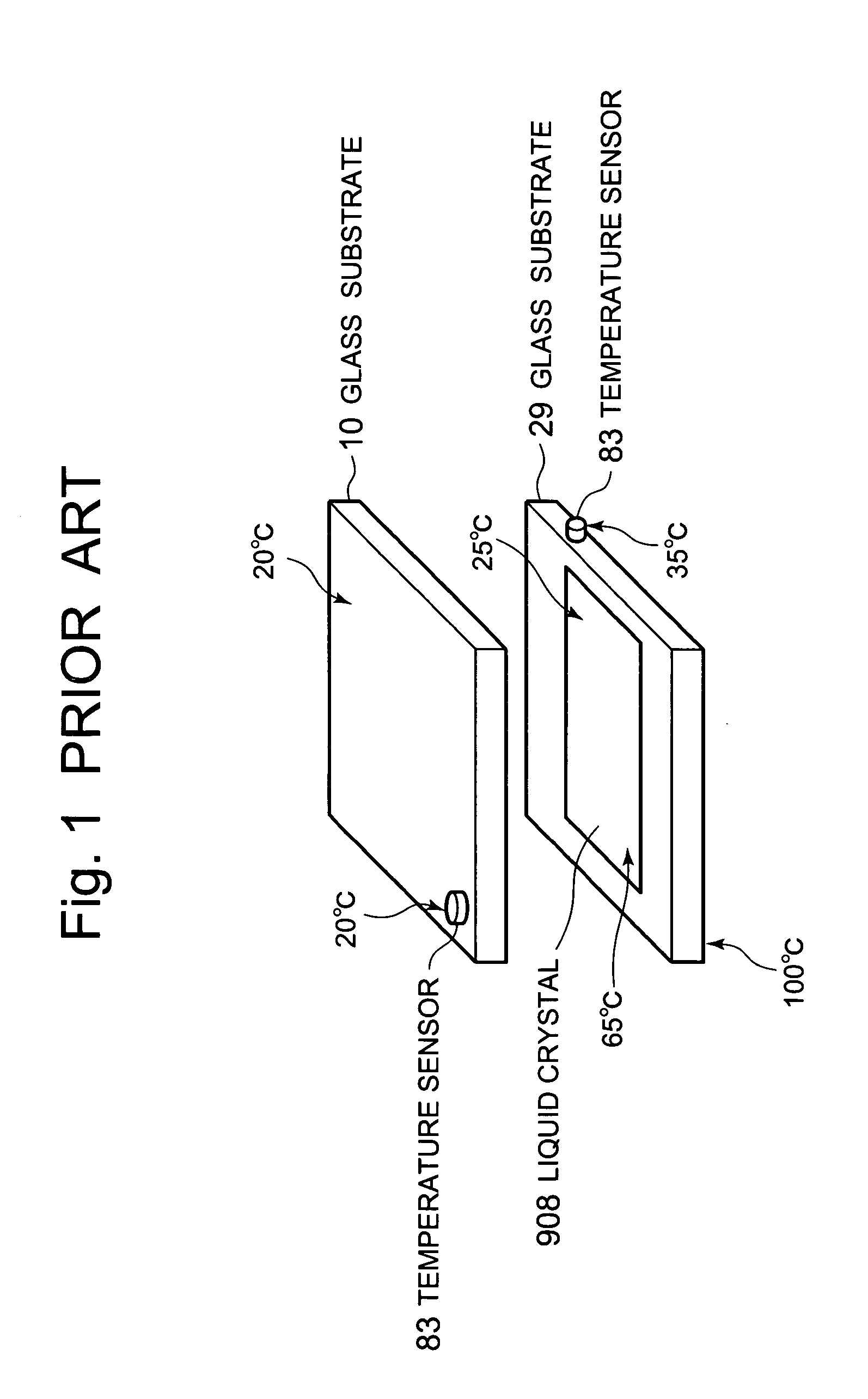
Thin-film semiconductor device, circuitry thereof, and apparatus using them
ActiveUS7728401B2Satisfactory image reproductionDifferent temperature dependenceThermometer detailsComputing operations for logarithmic/exponential functionsVoltage converterCurrent voltage
A thin-film semiconductor device comprises a temperature sensor formed of a thin-film semiconductor and sensing a temperature as current, and a current-voltage converter formed of a thin-film semiconductor and having temperature dependence in which its current-voltage characteristic is different from that of the temperature sensor. A temperature sensed by the temperature sensor is converted to a voltage by the current-voltage converter.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
Bipolar Switching Memory Cell With Built-in "On" State Rectifying Current-Voltage Characteristics
ActiveUS20120168705A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageMetal-insulator-metalElectrical resistance and conductance
A memory array is disclosed having bipolar current-voltage (IV) resistive random access memory cells with built-in “on” state rectifying IV characteristics. In one embodiment, a bipolar switching resistive random access memory cell may have a metal / solid electrolyte / semiconductor stack that forms a Schottky diode when switched to the “on” state. In another embodiment, a bipolar switching resistive random access memory cell may have a metal / solid electrolyte / tunnel barrier / electrode stack that forms a metal-insulator-metal device when switched to the “on” state. Methods of operating the memory array are also disclosed.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
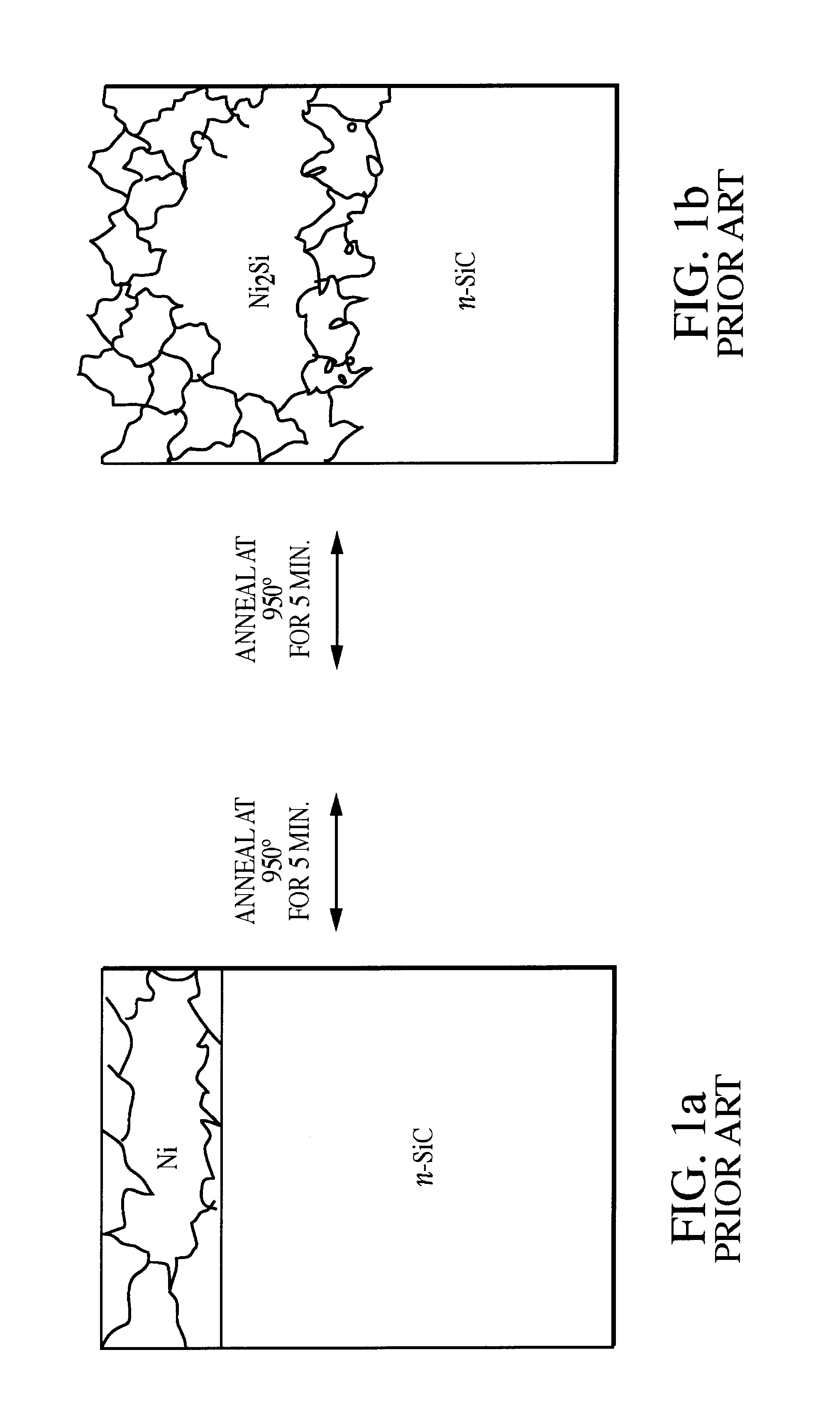
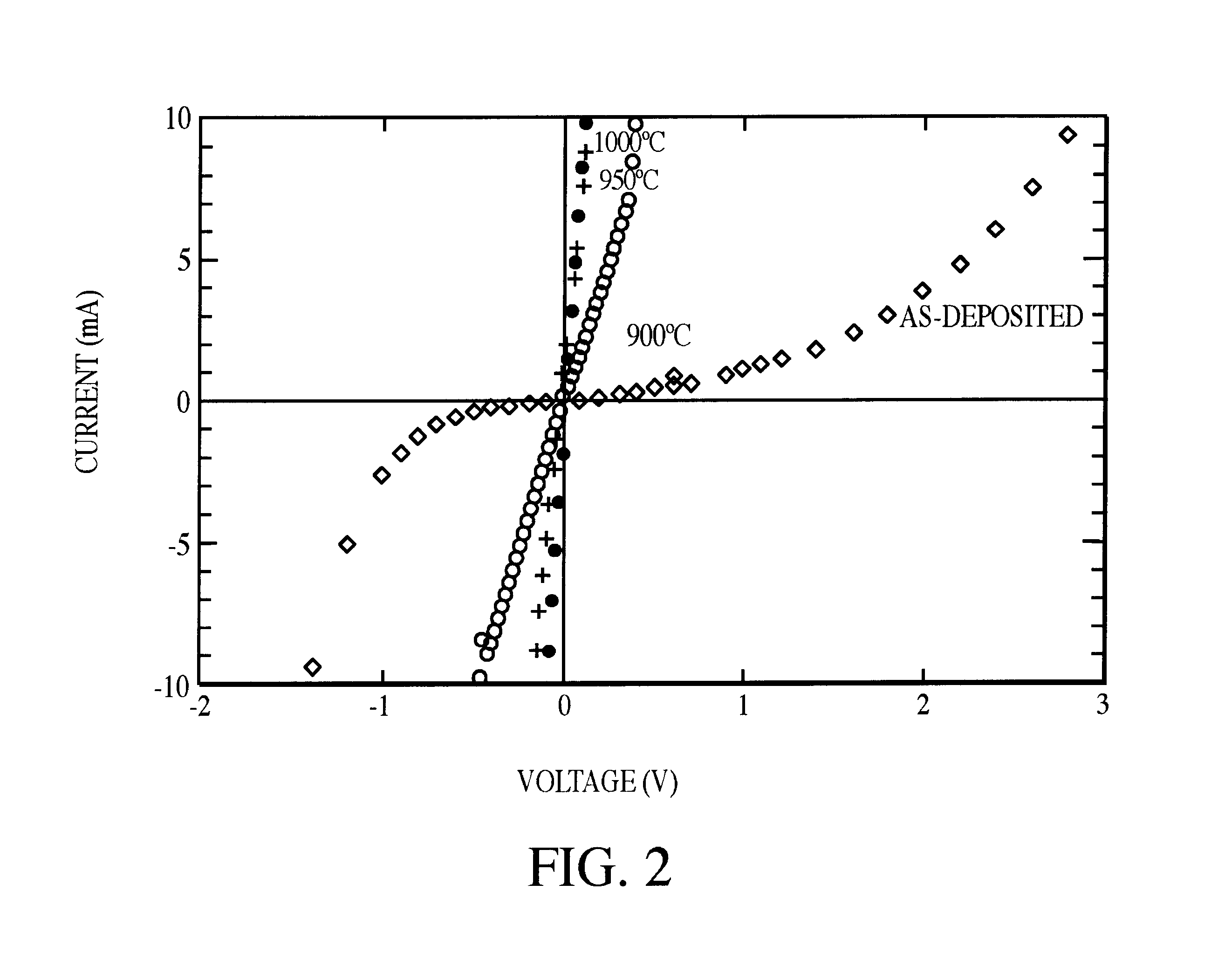
Formulation and fabrication of an improved Ni based composite Ohmic contact to n-SiC for high temperature and high power device applications
InactiveUS6759683B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetallurgyElectrical instability
A composite Pt / Ti / WSi / Ni Ohmic contact has been fabricated by a physical deposition process which uses electron beam evaporation and dc-sputter deposition. The Ni based composite Ohmic contact on n-SiC is rapid thermally annealed (RTA) at 950° C. to 1000° C. for 30s to provide excellent current-voltage characteristics, an abrupt, void free contact-SiC interface, retention of the as-deposited contact layer width, smooth surface morphology and an absence of residual carbon within the contact layer and / or at the Ohmic contact-SiC interface. The annealed produced Ni2Si interfacial phase is responsible for the superior electrical integrity of the Ohmic contact to n-SiC. The effects of contact delamination due to stress associated with interfacial voiding has been eliminated. Wire bonding failure, non-uniform current flow and SiC polytype alteration due to extreme surface roughness have also been abolished. The Ohmic contact also avoids electrical instability associated with carbon inclusions within the contact metallization and / or at the contact-SiC interface, that occur under prolonged high temperature and power device operations. Overall, this contact is reliable for high temperature and high power operations and the stresses inclusive of use under those conditions.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20080025072A1Keep reading marginAvoid changeRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsEngineering
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device comprises a memory cell including a variable resistance element changing its electric resistance by voltage application and having current-voltage characteristics in which a positive bias current flowing when a positive voltage is applied from one electrode as a reference electrode to the other electrode through an incorporated rectifier junction is larger than a negative bias current, a memory cell selection circuit for selecting the memory cell from the memory cell array, a voltage supply circuit for supplying a voltage to the memory cell so that a predetermined positive voltage corresponding to the reading operation is applied to the other electrode of the variable resistance element, in the reading operation, and a readout circuit for detecting the amount of the positive bias current and reading the information stored in the selected memory cell, in order to suppress the reading disturbance of the memory cell.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Reference voltage generating circuit using active resistance device
InactiveUS7064601B2Minimizes layout areaImprove reliabilityStatic storageElectric variable regulationLinear regionDevice form
A reference voltage generating circuit includes a current mirror circuit having first and second current paths formed between a first power source terminal and a second power source terminal in which the current mirror circuit is operated in response to a voltage level of the second current path, a reference voltage output node for providing a reference voltage and being located on the second current path, an active resistance device formed on the first current path to be operated in a linear region of a current-voltage characteristic curve of the active resistance device, and a voltage supply circuit for supplying the active resistance device with an enable voltage to control the active resistance device to be operated in the linear region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Flip-chip light emitting diode and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050121685A1Reduce contact resistivityImprove reflectivitySemiconductor devicesLight emitting deviceLight-emitting diode
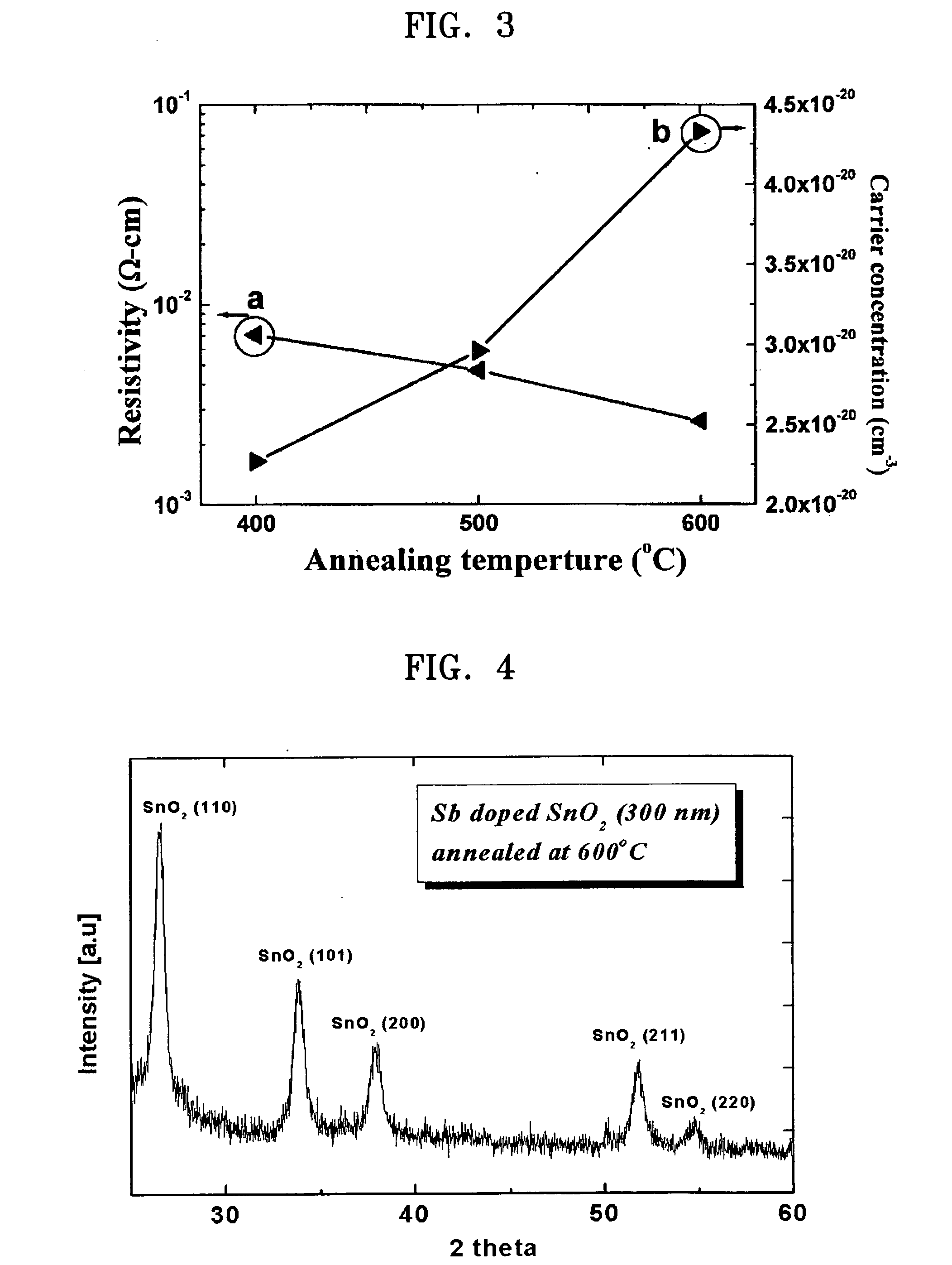
Provided are a flip-chip type light emitting device and a method of manufacturing the same. The provided flip-chip type light emitting device includes a substrate, an n-type cladding layer, an active layer, a p-type cladding layer, an ohmic contact layer formed of tin oxide to which at least one of antimony, fluorine, phosphorus, and arsenic is doped, and a reflection material formed of a reflective material. According to the provided flip-chip type light emitting device and the method of manufacturing the same, a current-voltage characteristic and durability are improved by applying a conductive oxide electrode structure having low surface resistivity and high carrier concentration.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com