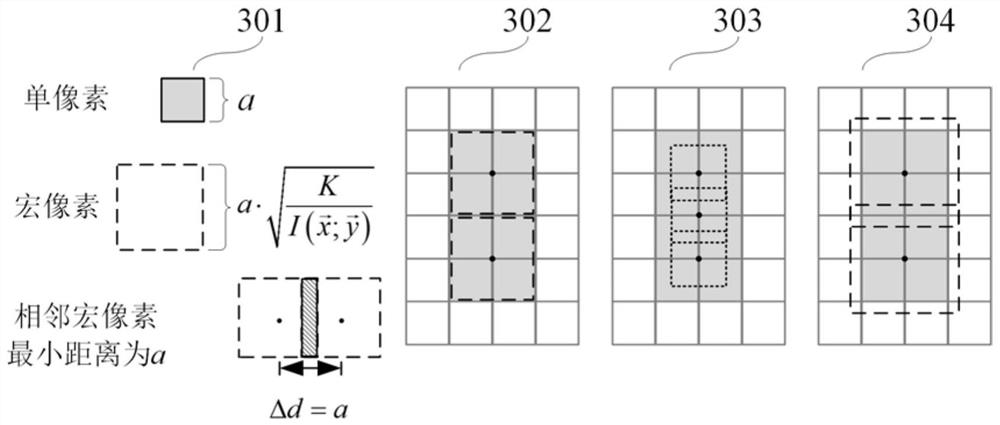
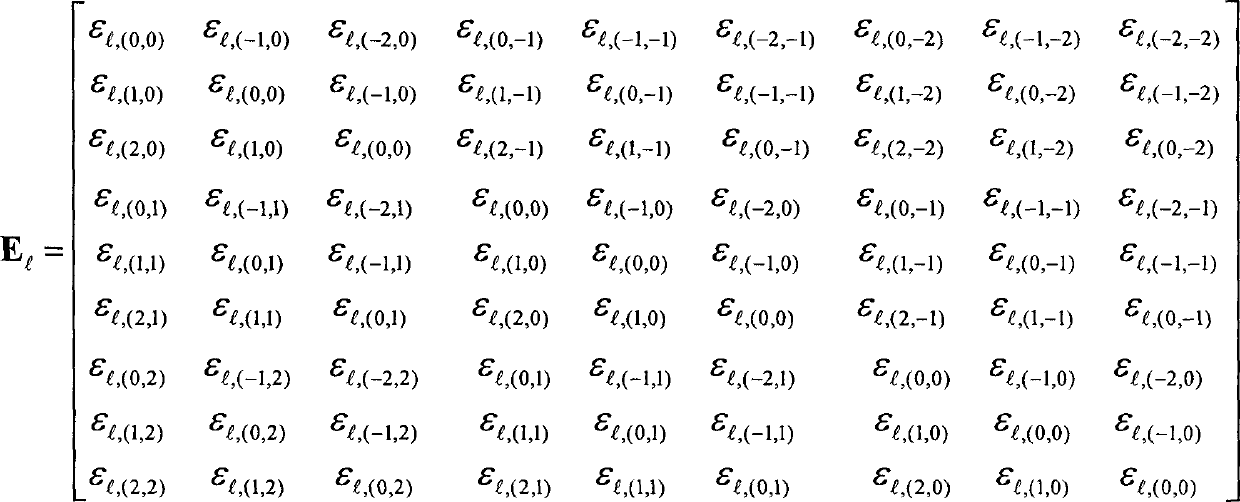Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Computational lithography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
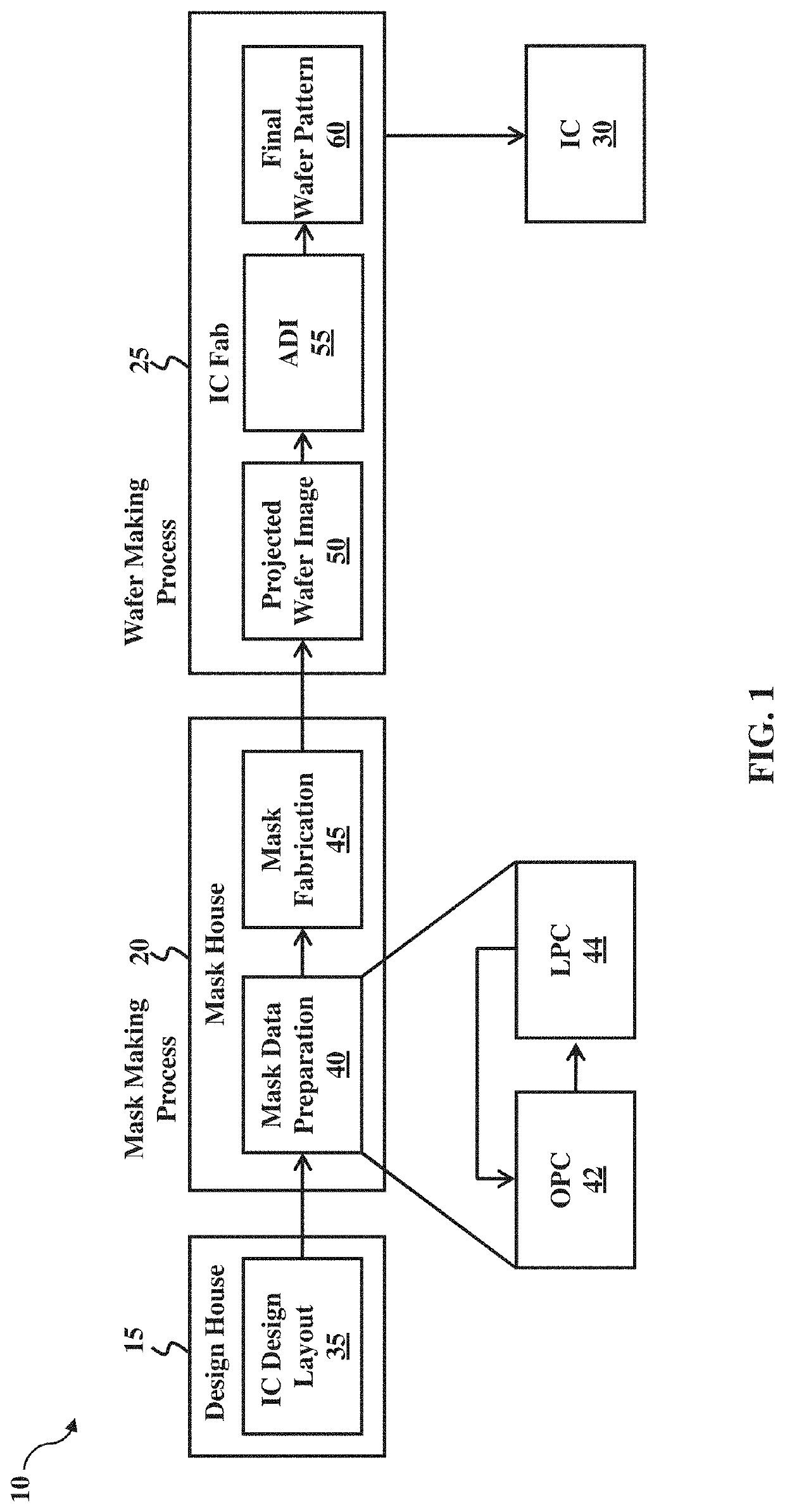
Computational lithography (also known as computational scaling) is the set of mathematical and algorithmic approaches designed to improve the resolution attainable through photolithography. Computational lithography has come to the forefront of photolithography in 2008 as the semiconductor industry grappled with the challenges associated with the transition to 22 nanometer CMOS process technology and beyond.
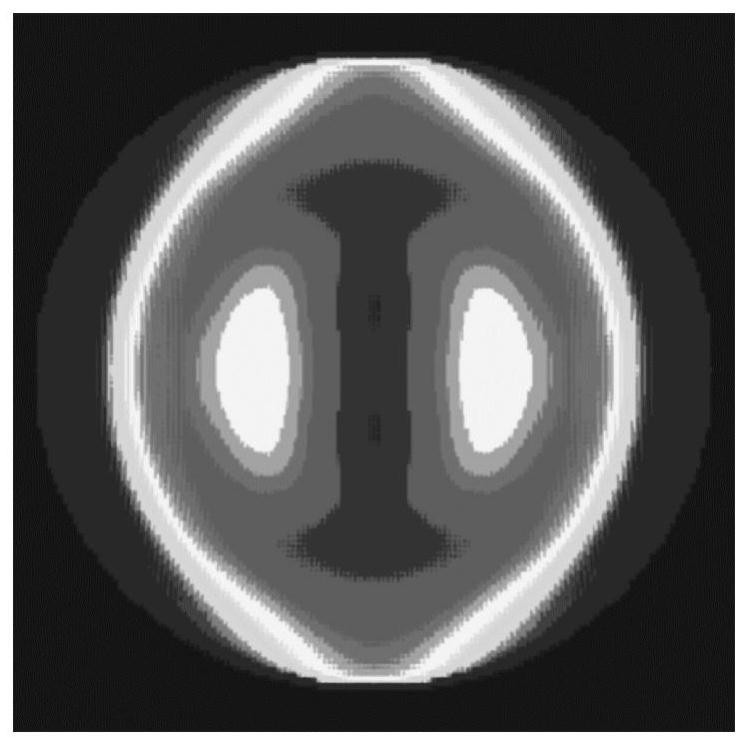
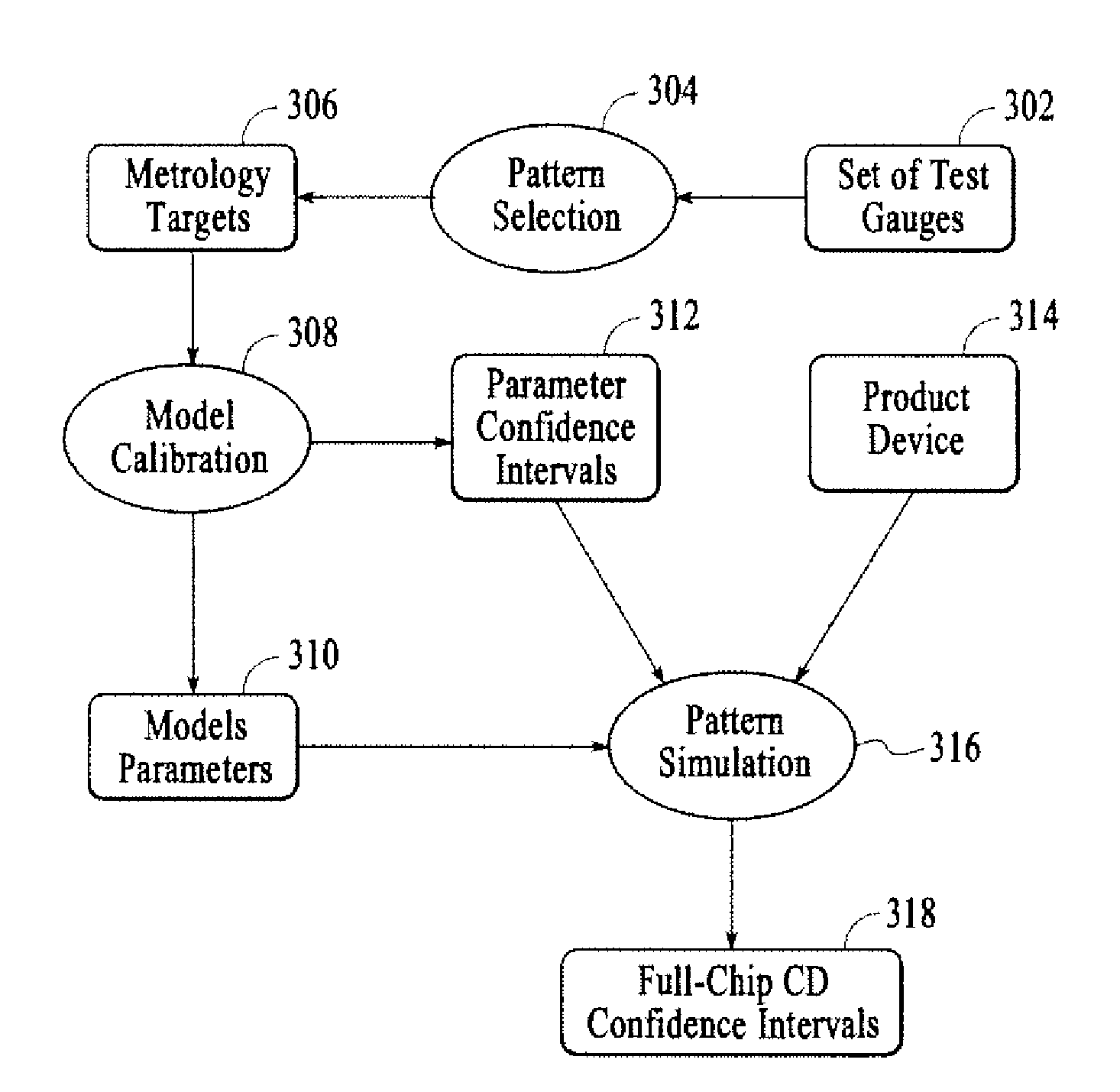
Pattern selection for lithographic model calibration
InactiveUS20100122225A1Detecting faulty computer hardwarePhotomechanical apparatusAlgorithmModel parameters
The present invention relates generally to methods and apparatuses for test pattern selection for computational lithography model calibration. According to some aspects, the pattern selection algorithms of the present invention can be applied to any existing pool of candidate test patterns. According to some aspects, the present invention automatically selects those test patterns that are most effective in determining the optimal model parameter values from an existing pool of candidate test patterns, as opposed to designing optimal patterns. According to additional aspects, the selected set of test patterns according to the invention is able to excite all the known physics and chemistry in the model formulation, making sure that the wafer data for the test patterns can drive the model calibration to the optimal parameter values that realize the upper bound of prediction accuracy imposed by the model formulation.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
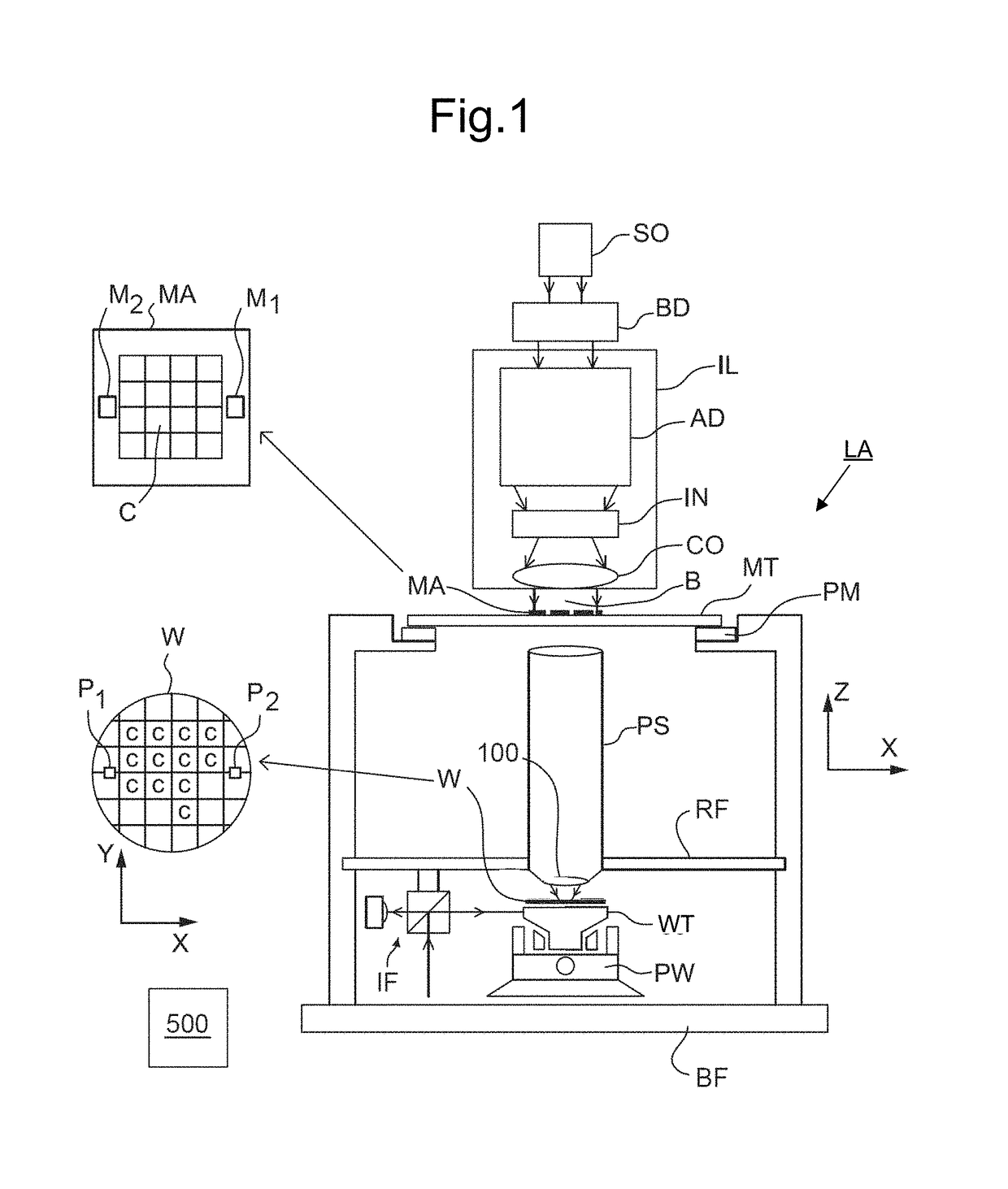
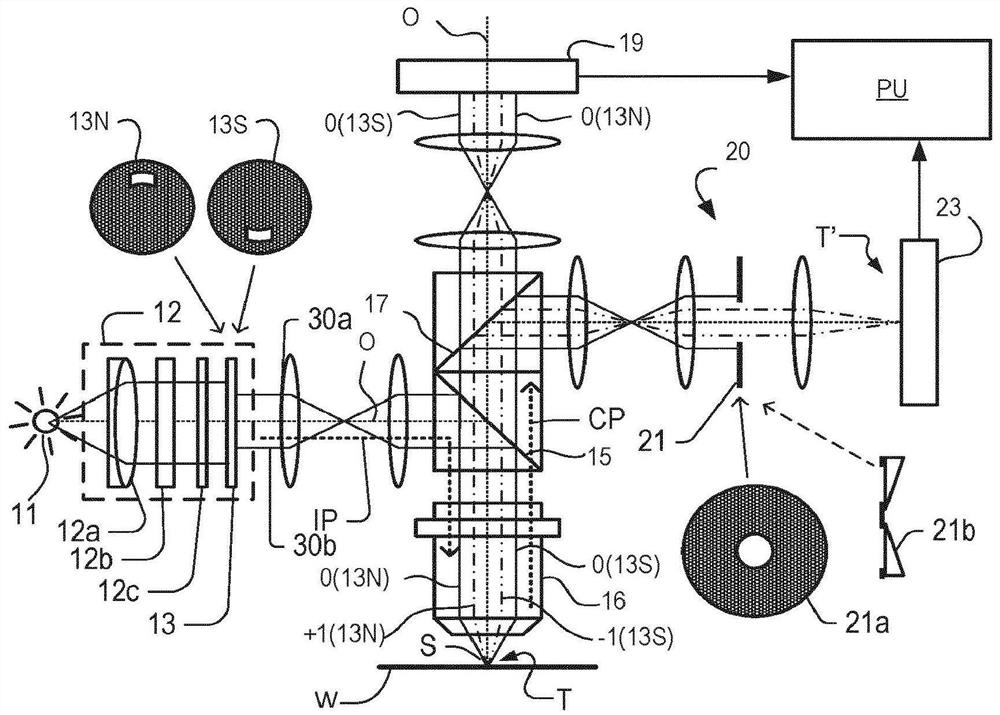
Method of Measuring a Target, Substrate, Metrology Apparatus, and Lithographic Apparatus
ActiveUS20180024054A1Scattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMetrologyDiffraction order
Disclosed is a method of measuring a target, an associated substrate, a metrology apparatus and a lithographic apparatus. In one arrangement the target comprises a layered structure. The layered structure has a first target structure in a first layer and a second target structure in a second layer. The method comprises illuminating the target with measurement radiation. Scattered radiation formed by interference between plural predetermined diffraction orders is detected. The predetermined diffraction orders are generated by diffraction of the measurement radiation from the first target structure and are subsequently diffracted from the second target structure. A characteristic of the lithographic process is calculated using the detected scattered radiation formed by the interference between the predetermined diffraction orders.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
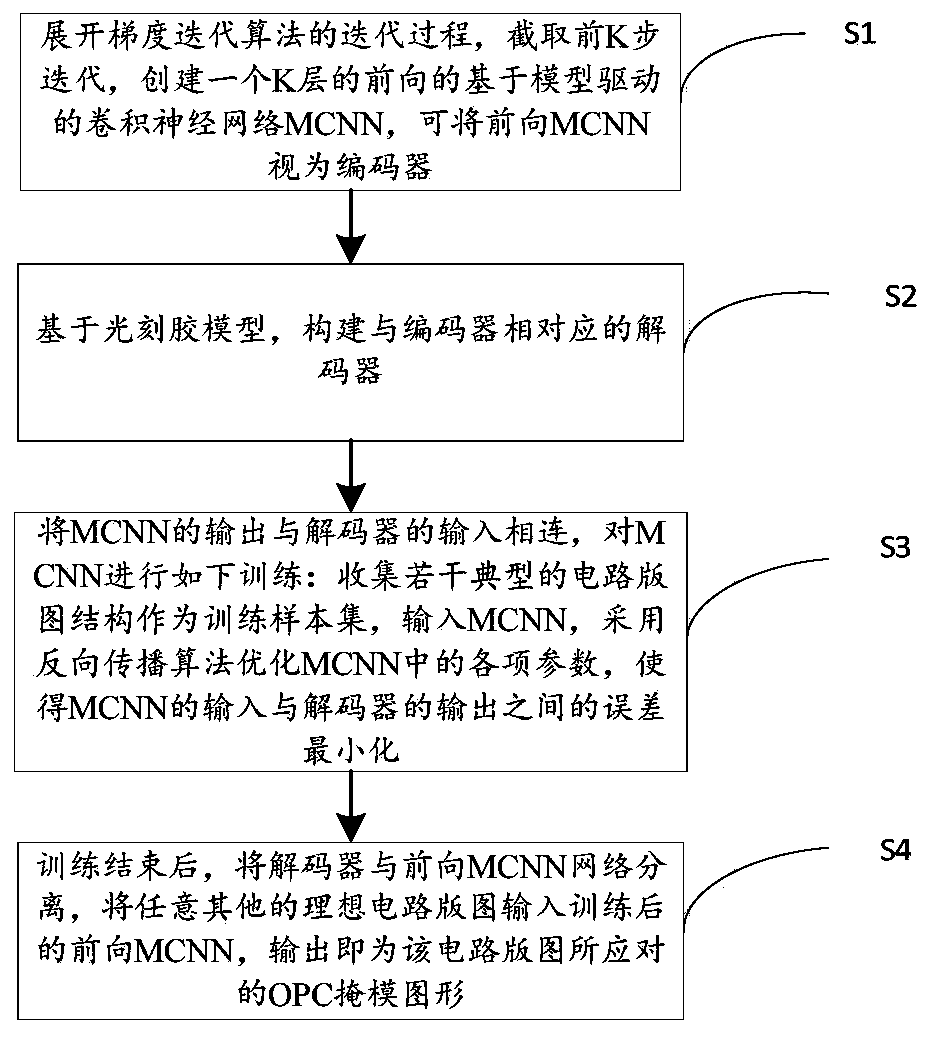
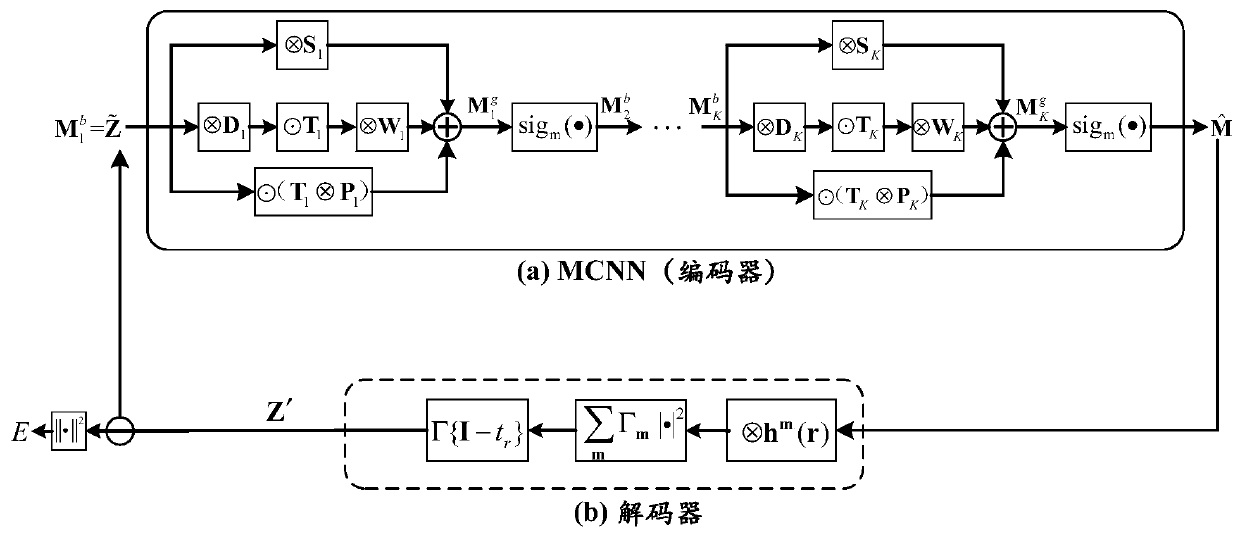
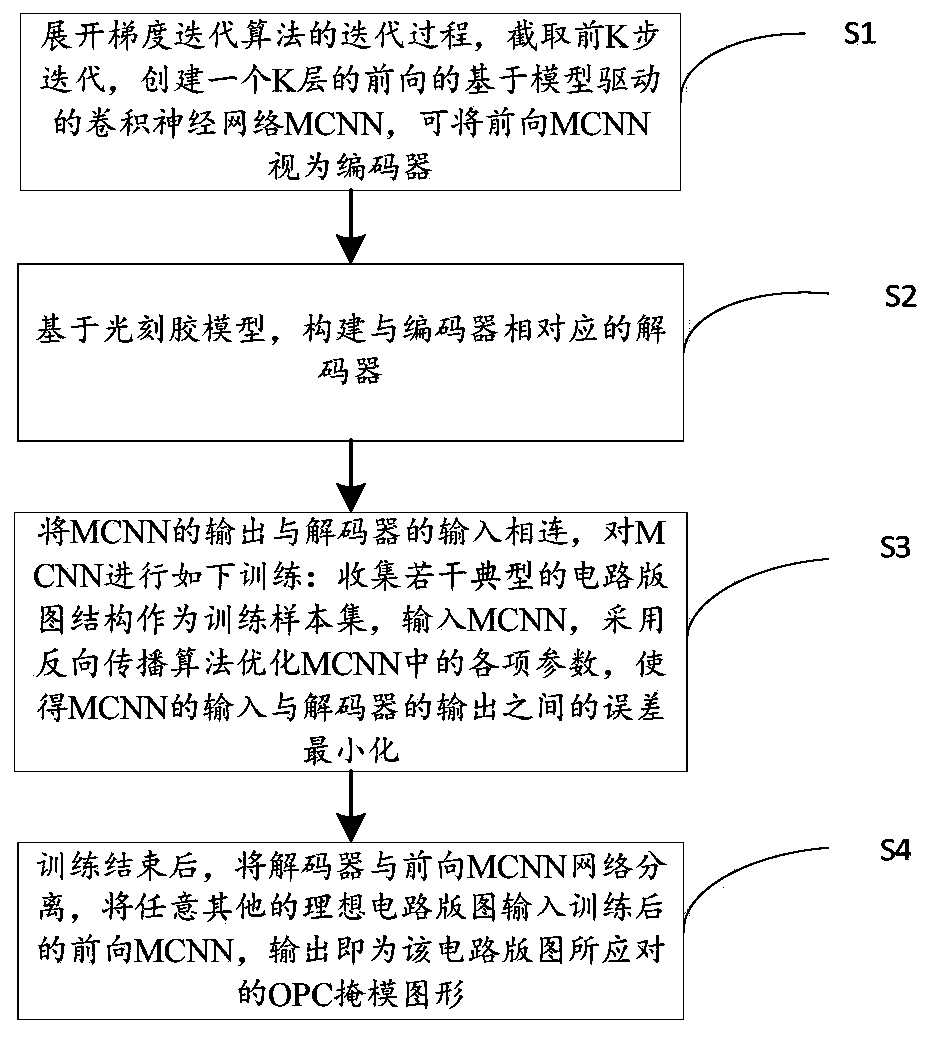
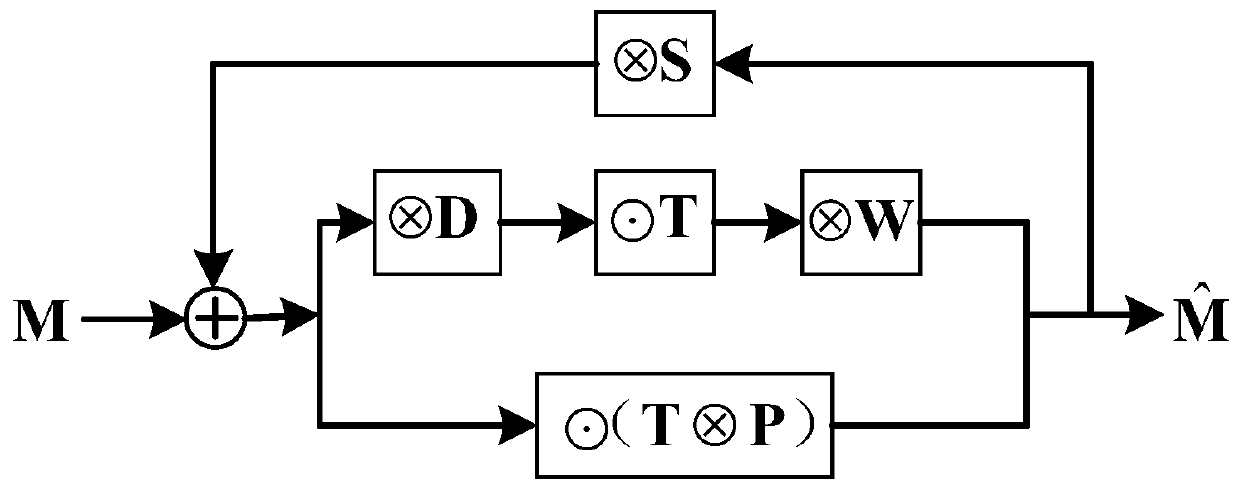
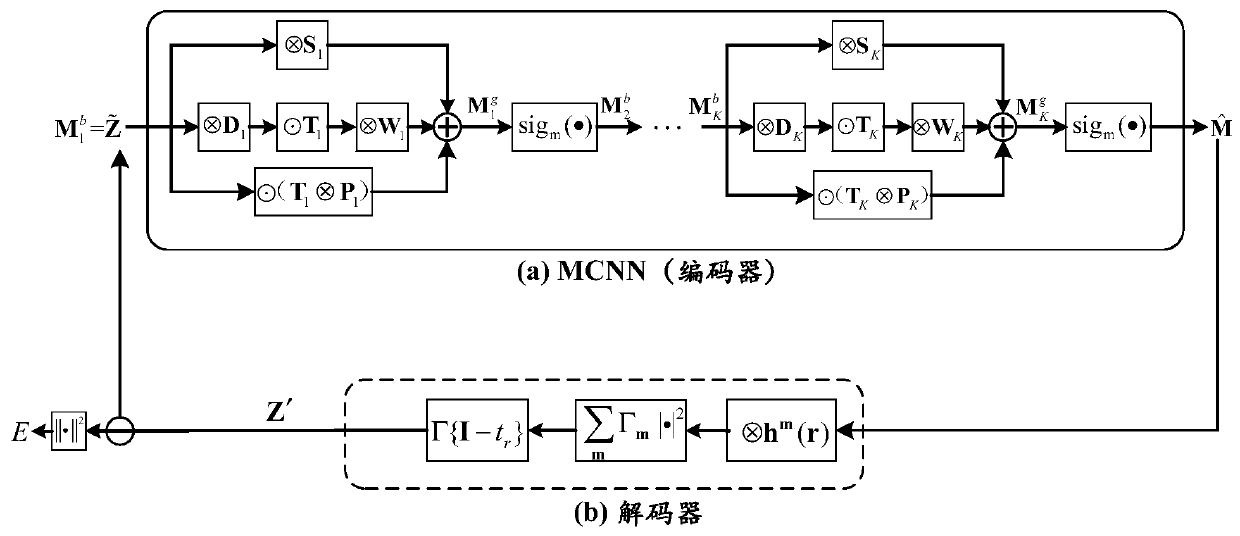
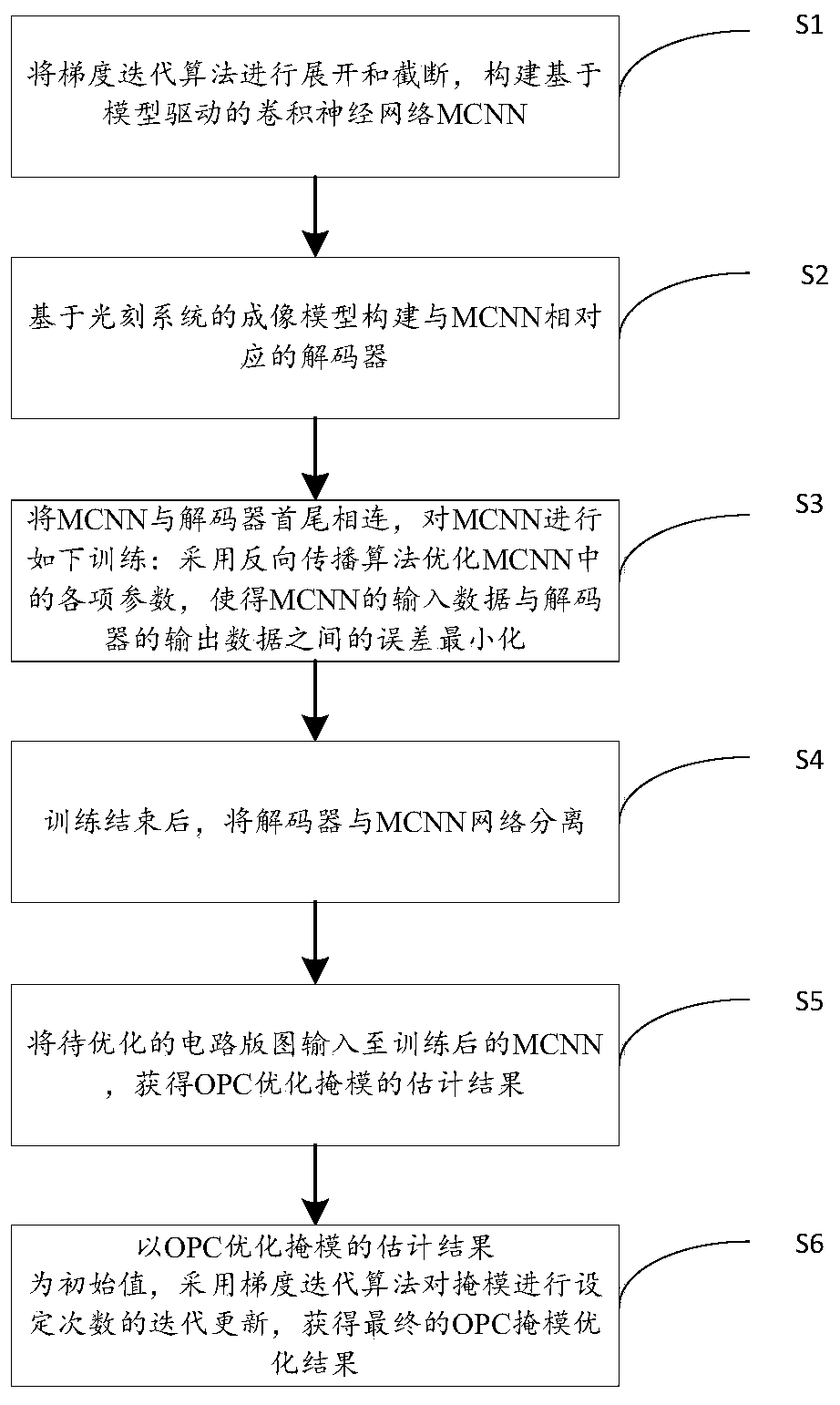
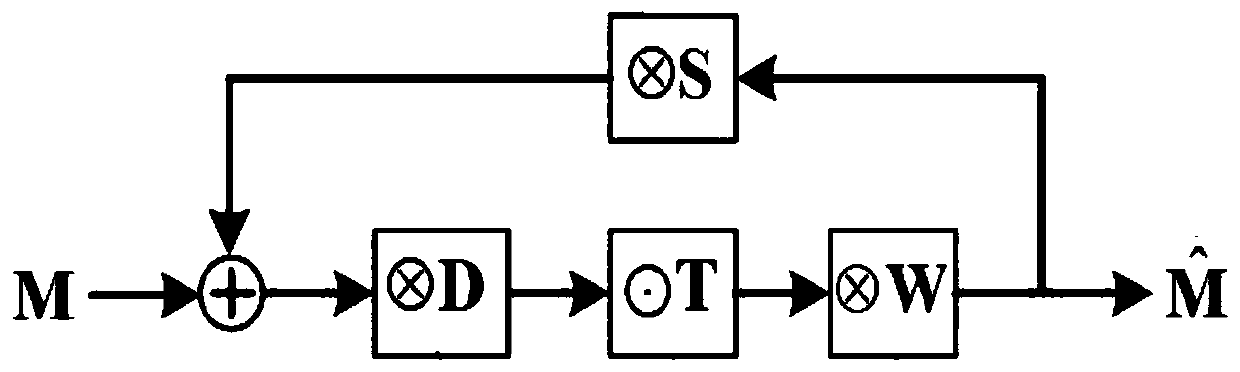
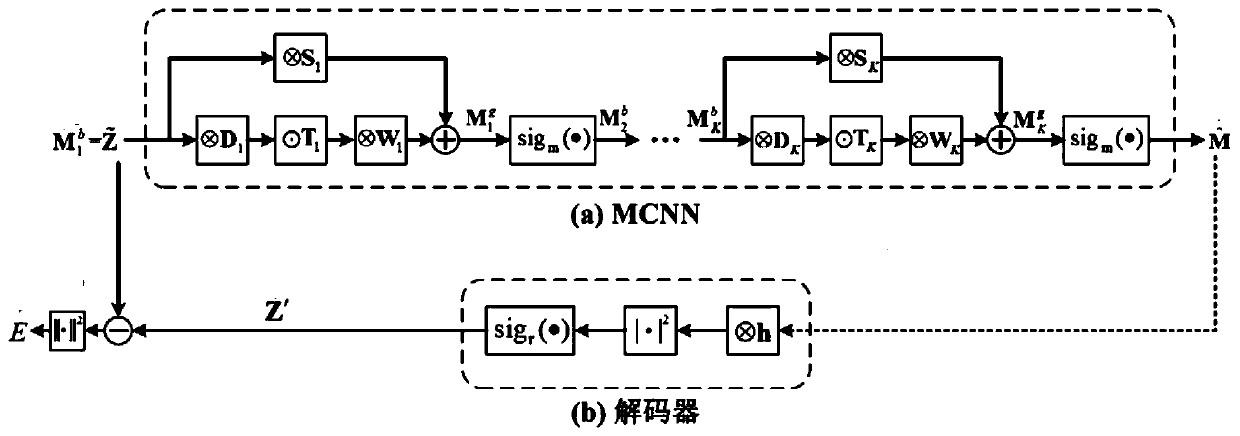
Computational lithography method for model-driven convolution neural network
ActiveCN108535952AImprove image qualityReduce computational complexityPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLithographic artistAlgorithm
The invention discloses a computational lithography method for a model-driven convolution neural network (MCNN), and the method can improve the computation speed and convergence performance of OPC (optical proximity correction) method. The technical scheme includes: expanding and truncating the gradient iterative algorithm, and constructing a model-driven convolution neural network (MCNN); based on an imaging model of a lithography system, constructing a decoder corresponding to the MCNN; bringing the MCNN and the decoder to end-to-end connection, and subjecting the MCNN to the following training: optimizing the parameters of the MCNN by back propagation algorithm to minimize the error between the input data of MCNN and the decoder; separating the decoder from the MCNN at the end of the training; inputting a to-be-optimized circuit layout into the trained MCNN so as to obtain an estimated result of an OPC mask; taking the estimated result of OPC mask as the initial value, and carryingout iterative updating on the set number of times of the mask by gradient iterative algorithm, thus obtaining the final OPC mask optimization result.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Measuring method of photolithographic process window
ActiveCN106325005AThe value range is accuratePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusNumerical rangeProcess window
The invention discloses a measuring method of a photolithographic process window, comprising the following steps: providing a wafer with a plurality of structures to be measured in array distribution formed by photoetching a focus value and exposing energy matrixes; acquiring a line imaging chart of the structures to be measured through an electron beam microscope; analyzing the line imaging chart by a multi-pixel threshold method, acquiring a marginal distribution curve of the lines in one-dimension direction, computing the line roughness according to the marginal distribution curve, and drawing a relation curve between pixel value and line roughness; taking the marginal pixel value corresponding to the continually varying minimal line roughness as a line marginal position reference, and computing a line reference width according to the line marginal position reference; and carrying out data analysis on the line reference width and minimal line roughness of all the structures to be measured, and computing the numerical range of the photolithographic process window. The measuring method improves the accuracy in measuring the photolithographic process window.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Deep learning method for computational lithography
ActiveCN110187609AReduce computational complexityImprove the efficiency of OPC optimizationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusAlgorithmUltraviolet
The invention discloses a deep learning method for computational lithography, which can improve the optimization speed and convergence performance of a traditional OPC (Optical Proximity Correction) method and can be used for deep ultraviolet DUV lithography and extreme ultraviolet EUV (Extreme Ultraviolet) lithography. The method comprises the steps of: developing a gradient iterative algorithm,intercepting a plurality of steps, combining a photoetching system imaging model and a photoresist model to create a forward MCNN (Model-driven Convolution Neural Network), namely an encoder; creatinga decoder corresponding to the encoder, connecting the output of the MCNN with the input of the decoder, taking a certain distance between the input of the MCNN and the output of the decoder as a cost function to train MCNN parameters; inputting training set samples into the MCNN, and optimizing the parameters in the MCNN to minimize the errors between the input of the MCNN and the output of thedecoder; and after the training is completed, separating the MCNN from the decoder, and adopting the MCNN to obtain OPC mask patterns corresponding to other circuit layouts.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Computational lithography modeling method and device
ActiveCN110262191AHigh precisionGuaranteed accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusGraphicsIntegrated circuit manufacturing
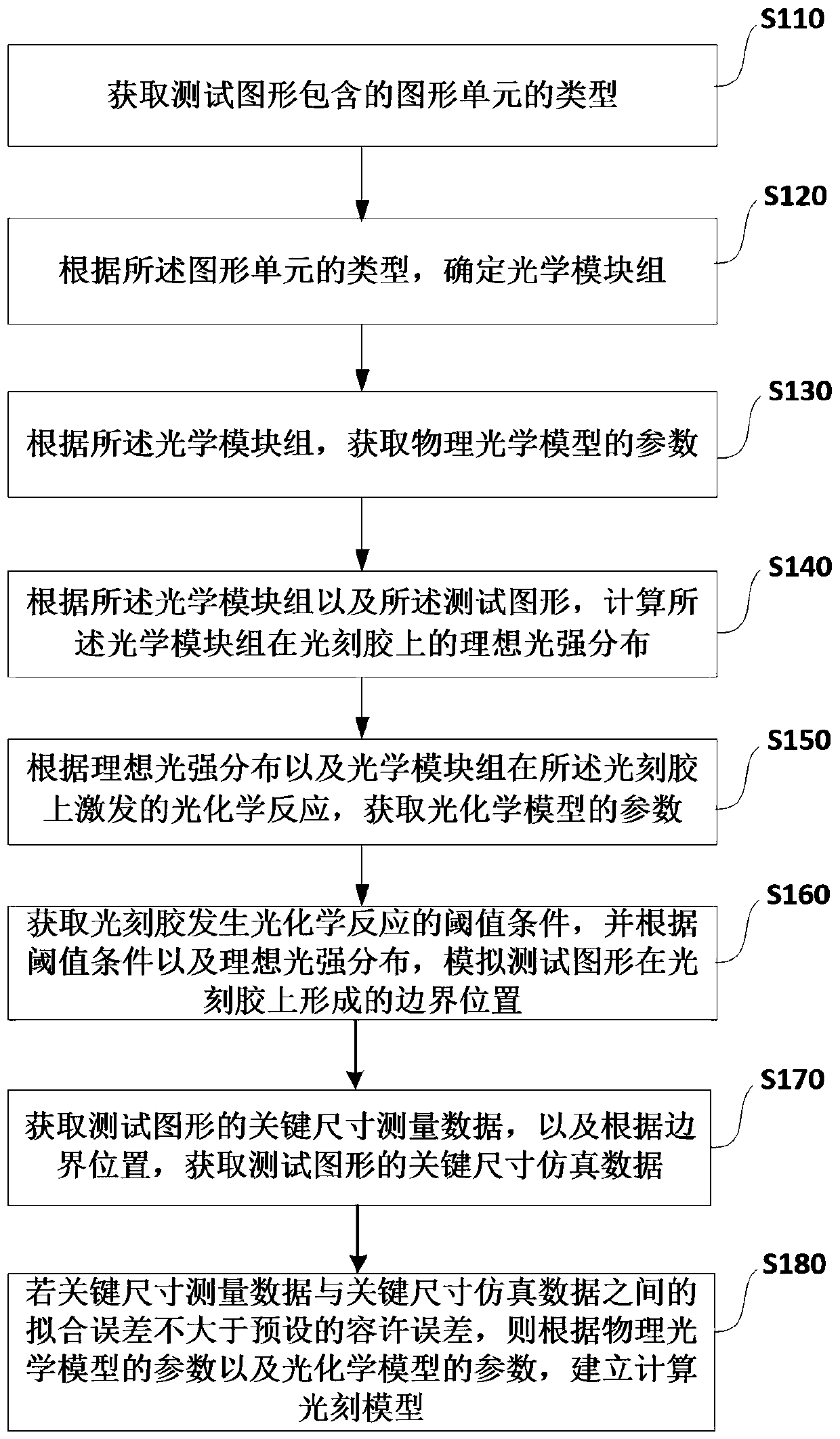
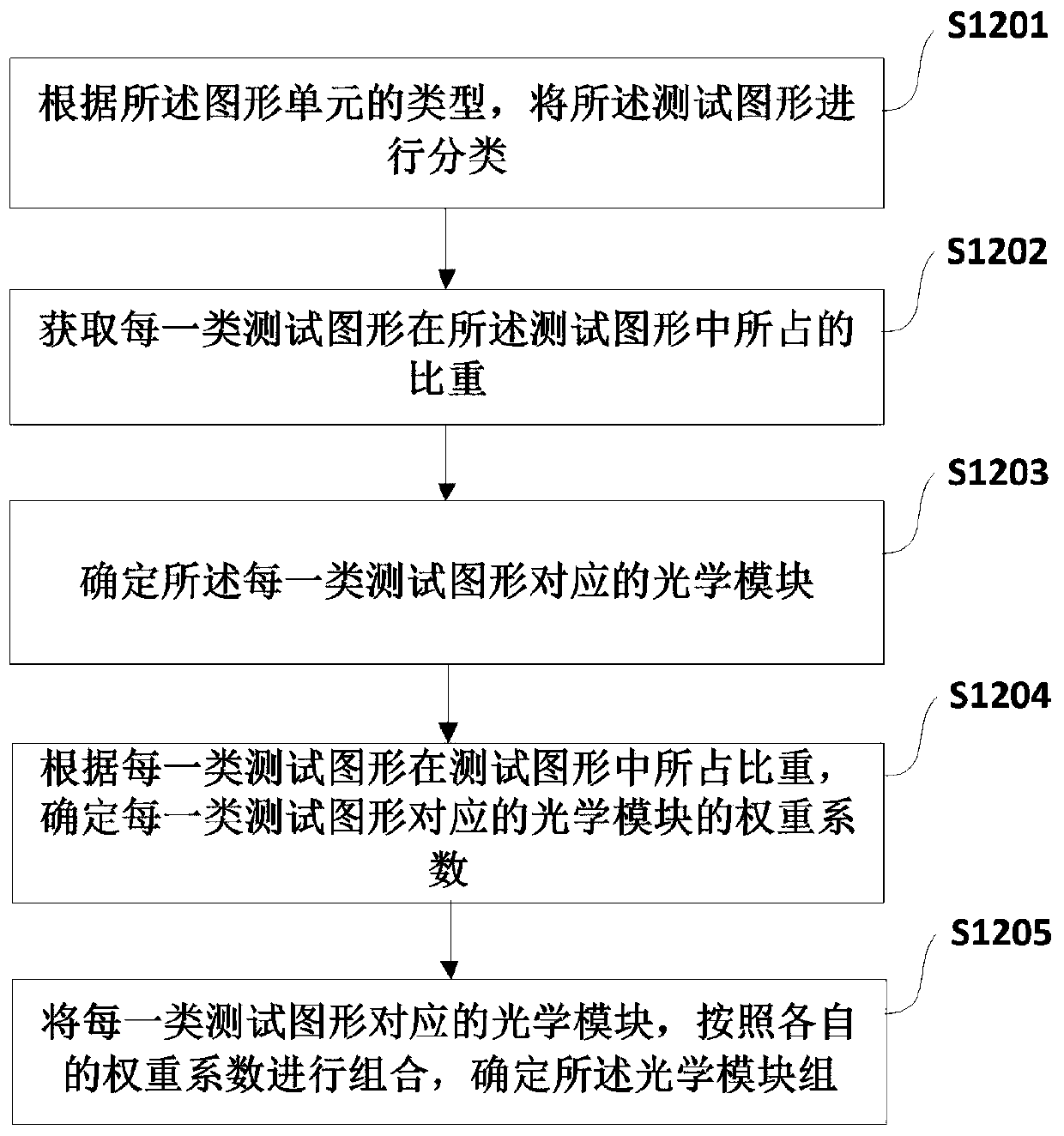
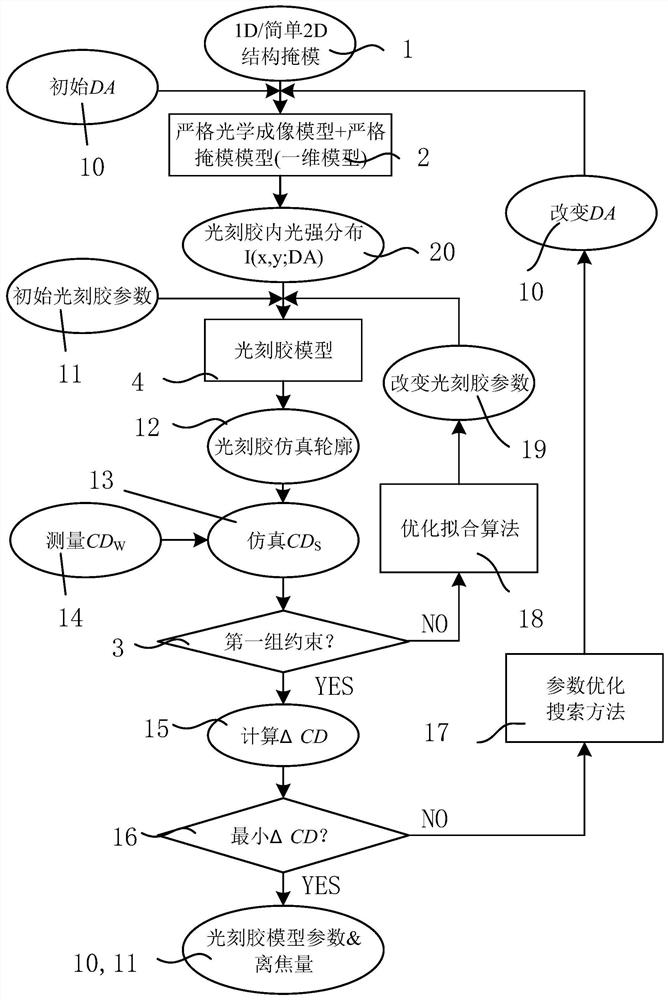
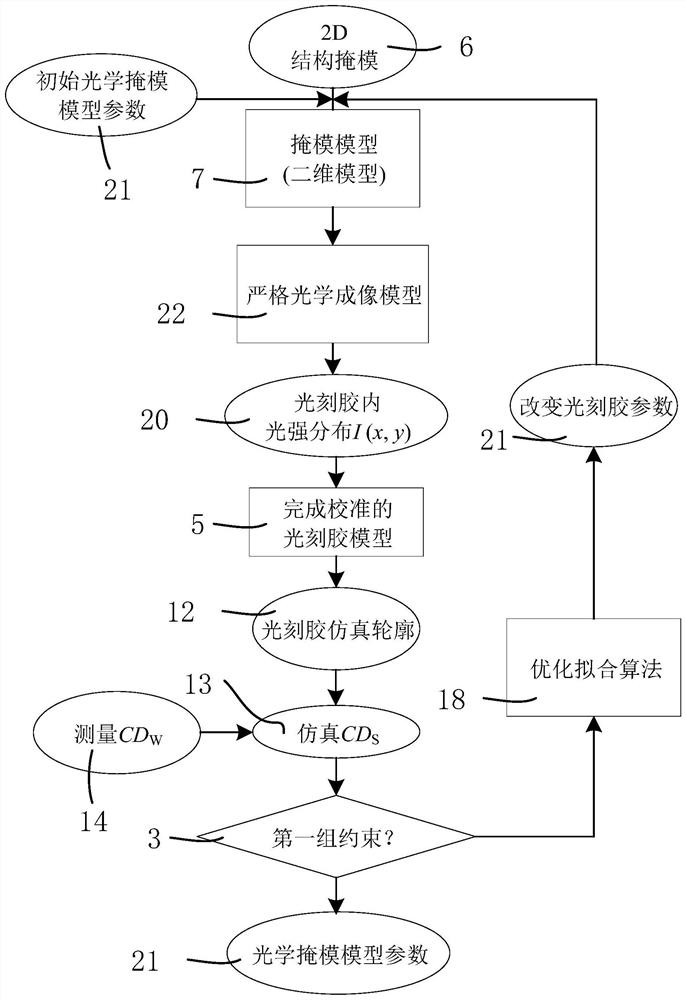
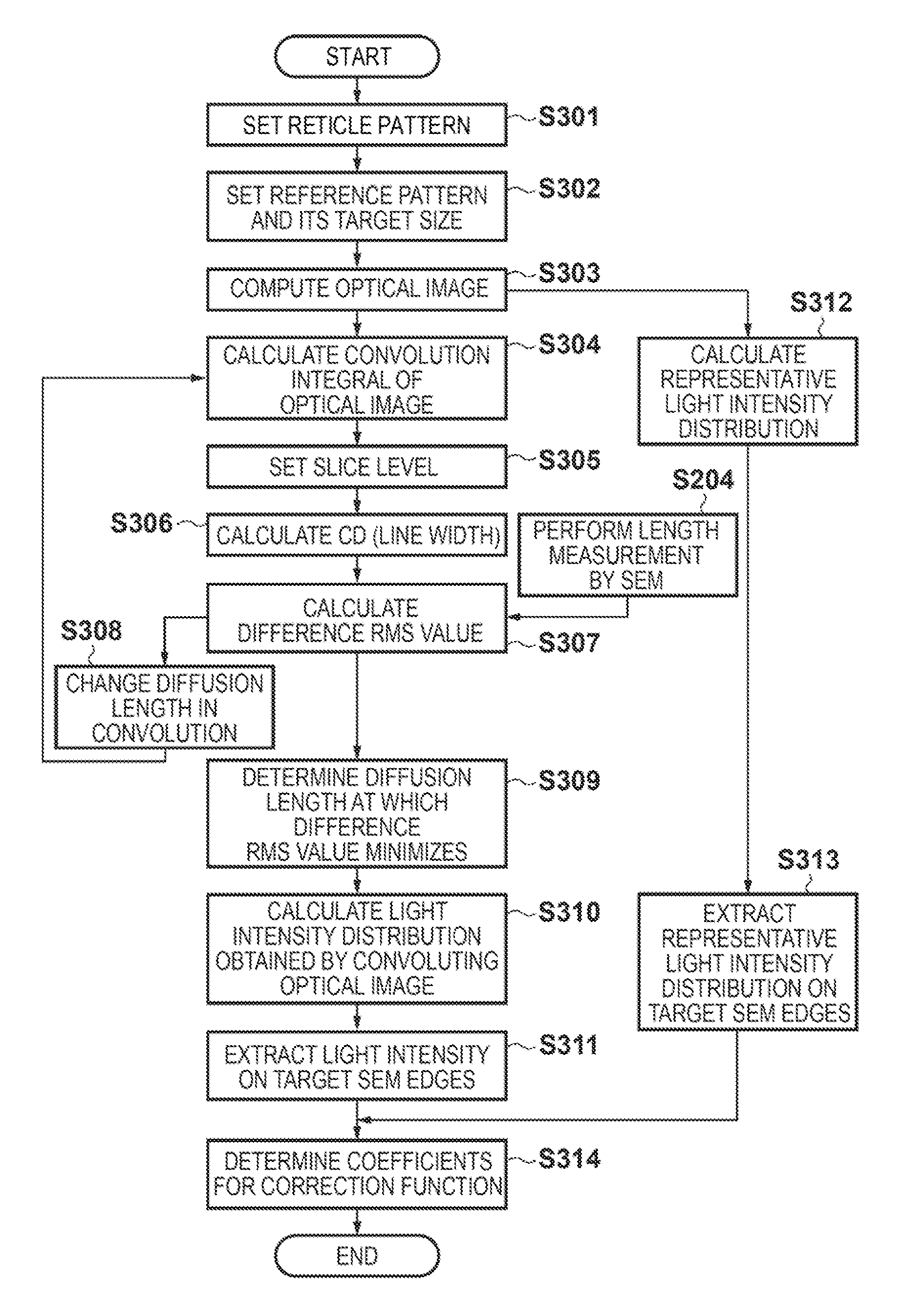
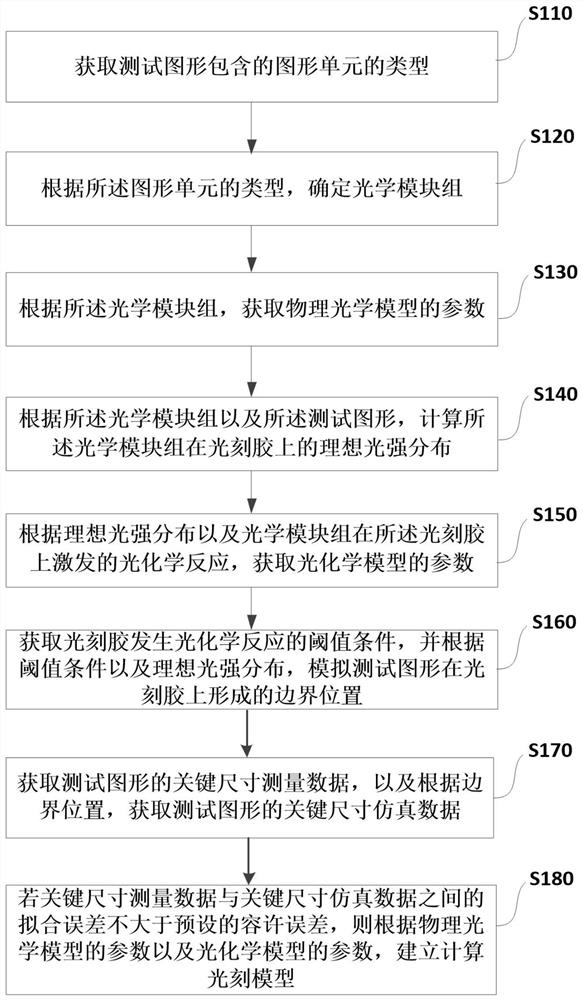
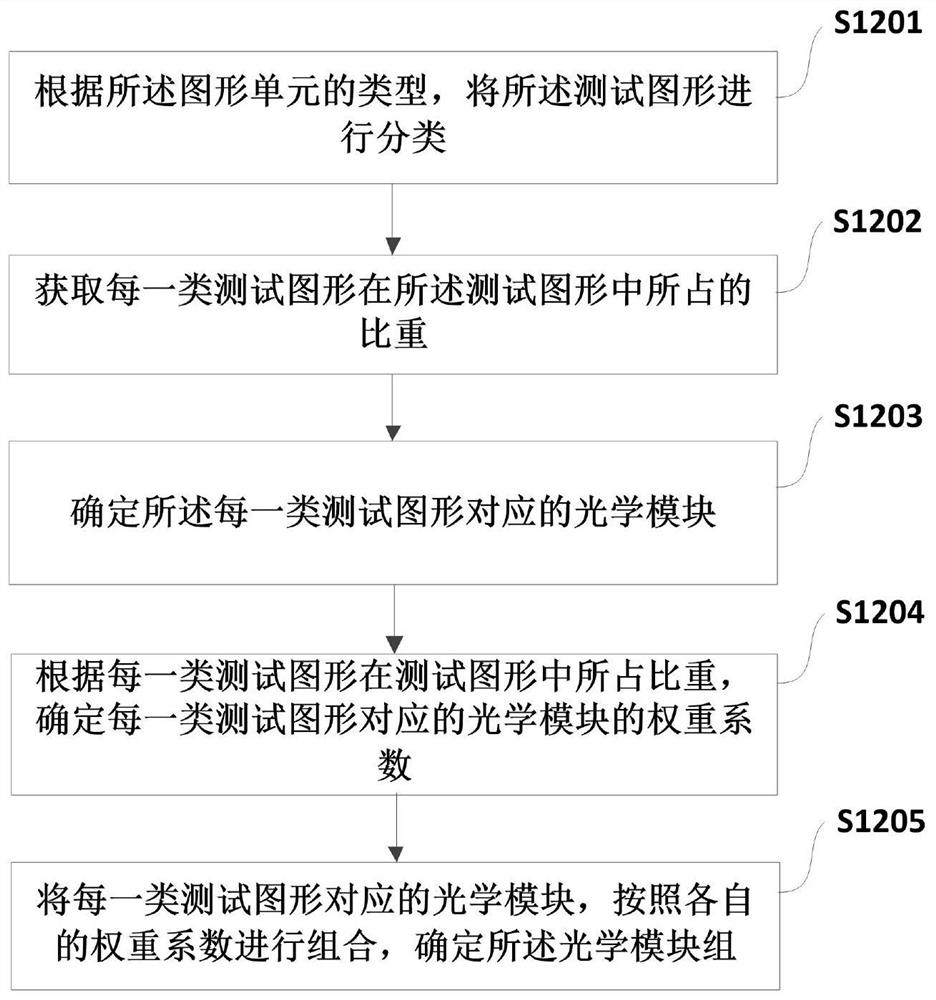
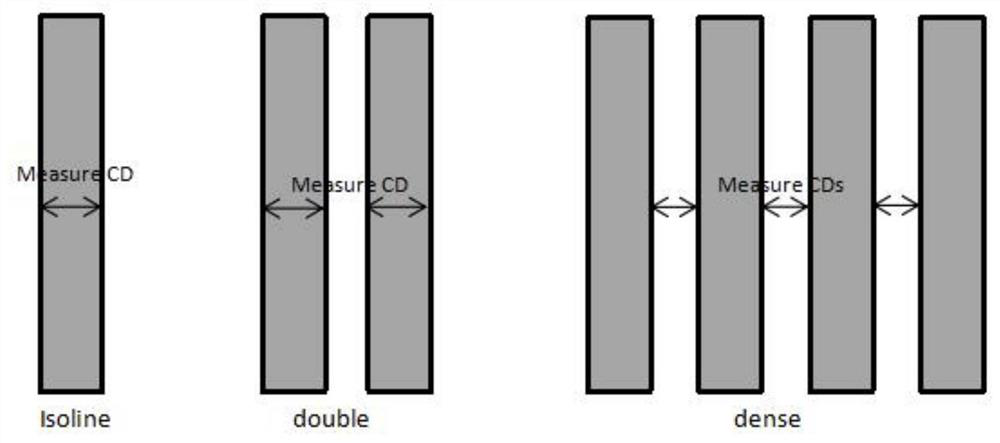
The application relates to the technical field of integrated circuit manufacturing and discloses a computational lithography modeling method and device. The method comprises the steps of determining an optical module group by acquiring the type of a graphic unit included in a test pattern, and then acquiring the parameters of a physical optical model according to the optical module group; calculating the ideal light intensity distribution of the optical module group on the photoresist, and acquiring the parameters of a photochemical model according to the ideal light intensity distribution and a photochemical reaction excited by the optical module group on the photoresist; then simulating a boundary position formed by the test pattern on the photoresist, acquiring the key dimension simulation data of the test pattern, and establishing a computational lithography model if a fitting error between the key dimension measurement data and the key dimension simulation data is not greater than a preset allowable tolerance. The computational lithography modeling method disclosed in the application improves the precision of a lithography model by establishing different optical modules to simulate different graphic units.
Owner:MOYAN COMPUTATIONAL SCI NANJING PTE LTD
Informatics calculation photoetching method
ActiveCN112083631AImprove convergence accuracyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusInformation transmissionAlgorithm
The invention provides an informatics calculation photoetching method, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, establishing a calculation photoetching channel model according to an information theory, then solving optimal mask distribution, optimal photoetching system parameters and process parameters under the information theory, and finally, improving the convergence precision of a calculation photoetching algorithm by adopting the information theory. Therefore, the essence of the method is that a channel model is used for depicting a photoetching system, a photoetching imaging process is abstracted into a channel transmission process, a mask pattern and photoetching imaging are regarded as input and output signals of a channel, and photoetching system parameters, photoetching process parameters and the like are regarded as channel parameters influencing photoetching layout information transmission; the calculation photoetching is adopted to optimize the mask, which is equivalent to the encoding process of the signal; that is to say, an informatics model for calculating photoetching is established, a photoetching pattern information transmission mechanism and rule are researched through adoption of a mathematical method, the theoretical limit for calculating photoetching imaging precision can be obtained, and the convergence precision of a calculation photoetching algorithm is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Integrated neural network for computational lithography
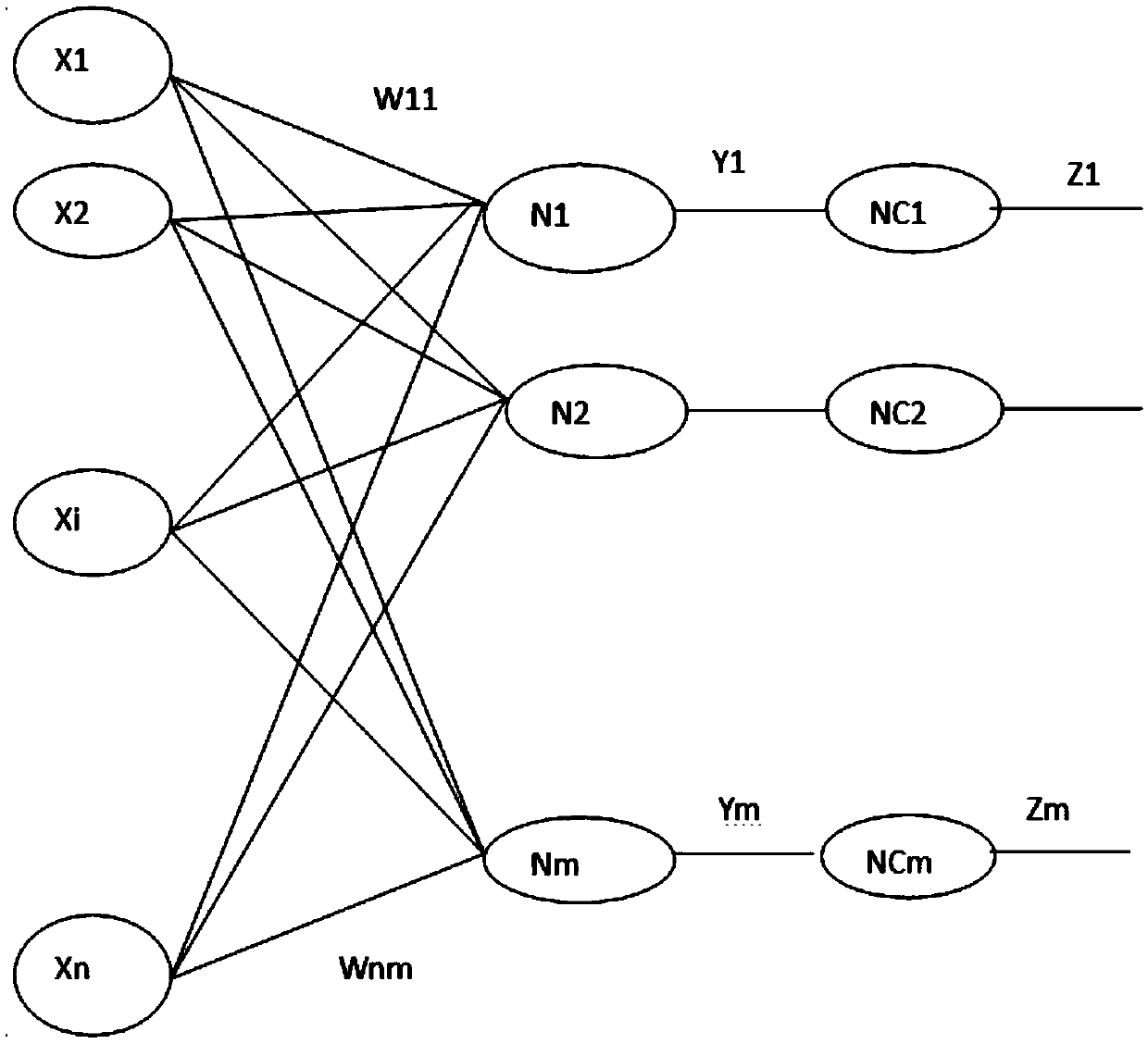
ActiveCN108665060AImprove efficiencyEasy and fast learning processPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusFeature vectorAlgorithm
Disclosed is an integrated neural network for computational lithography. The integrated neural network comprises a conjugate neural network and a feedforward neural network, and an output end of the conjugate neural network is connected with an input end of the feedforward neural network; the conjugate neural network is used for extracting a feature vector of the computational lithography and inputting the extracted feature vector to the feedforward neural network, wherein according to a method for using the conjugate neural network to extract the feature vector of the computational lithography, Yj is equal to sigmaiWijXi, and Zj is equal to the product of Yj and Yj*; Zj is the extracted feature vector, Wij is a parameter of the conjugate neural network, Xi is the adjacent environment of an i point on a photomask, and Yj* is the conjugation of Yj. According to the integrated neural network for the computational lithography, the conjugate convolutional neural network structure for extracting the feature vector and the feedforward neural network are combined to form the integrated neural network, and the integrated neural network can be used for various types of computational lithography learning.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT
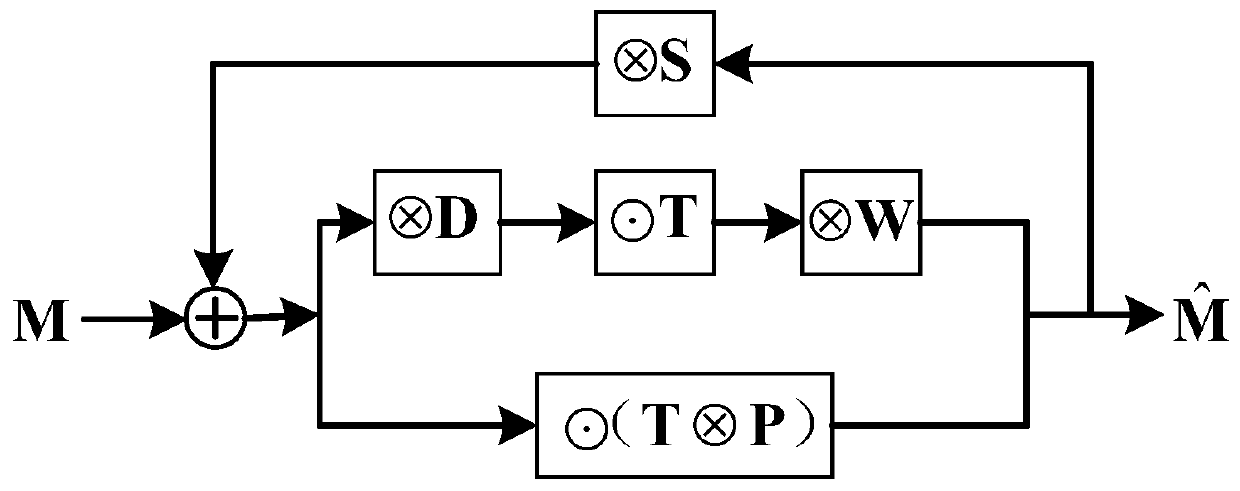
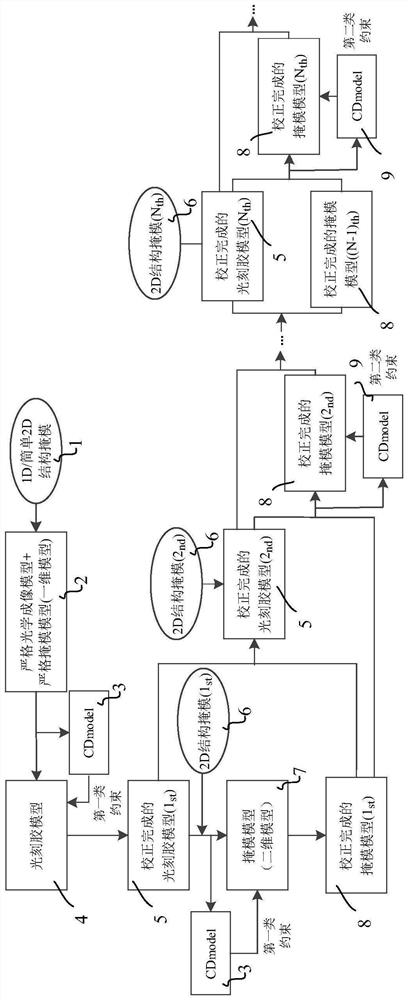
Separated strict modeling and calibration method for mask model and photoresist model
PendingCN114326287ARealize decoupled calibrationAvoid strict solutionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusEngineeringComputational physics
The invention belongs to the technical field related to computational lithography in the semiconductor industry, and particularly discloses a separate strict modeling and calibration method for a mask model and a photoresist model. According to the method, a new thought of step-by-step mask model and photoresist model parameter decoupling calibration is adopted, the strictness of an optical imaging model and a mask model is emphasized and utilized, the complex and time-consuming strict solution of the near field of the thick mask with the complex two-dimensional structure is avoided, and the near field of the thick mask with the complex two-dimensional structure is strictly solved only from the strict solution of the near field of the mask with the one-dimensional or simple two-dimensional structure. Therefore, separate strict calibration and calibration of the photoresist model and the mask model suitable for a complex two-dimensional structure can be completed. Besides, on the basis of the calibration result of the separated mask model and the photoresist model, a joint iterative calibration method of the photoresist model and the mask model is provided, and the obtained calibration result can enable the model to better conform to the actual physical condition.
Owner:武汉宇微光学软件有限公司
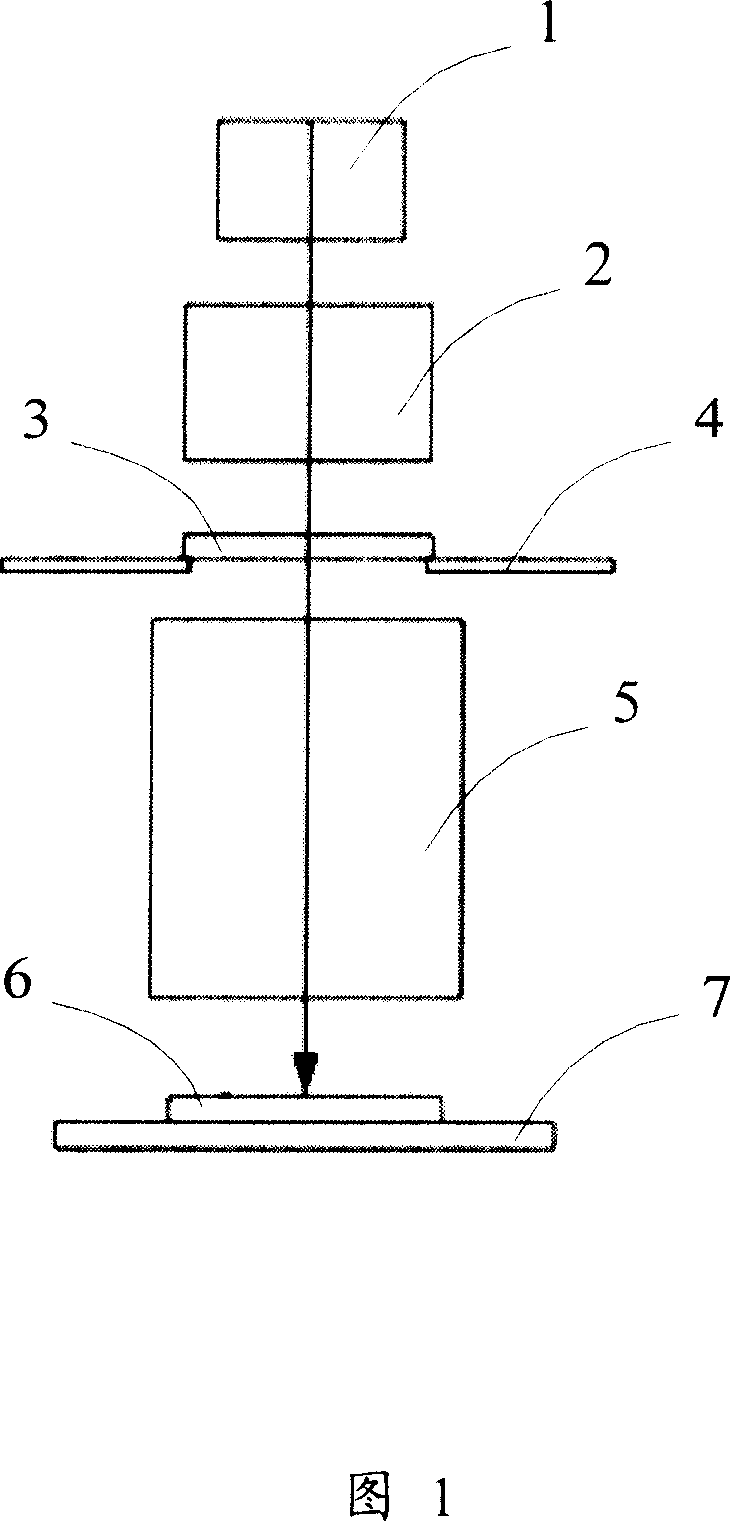
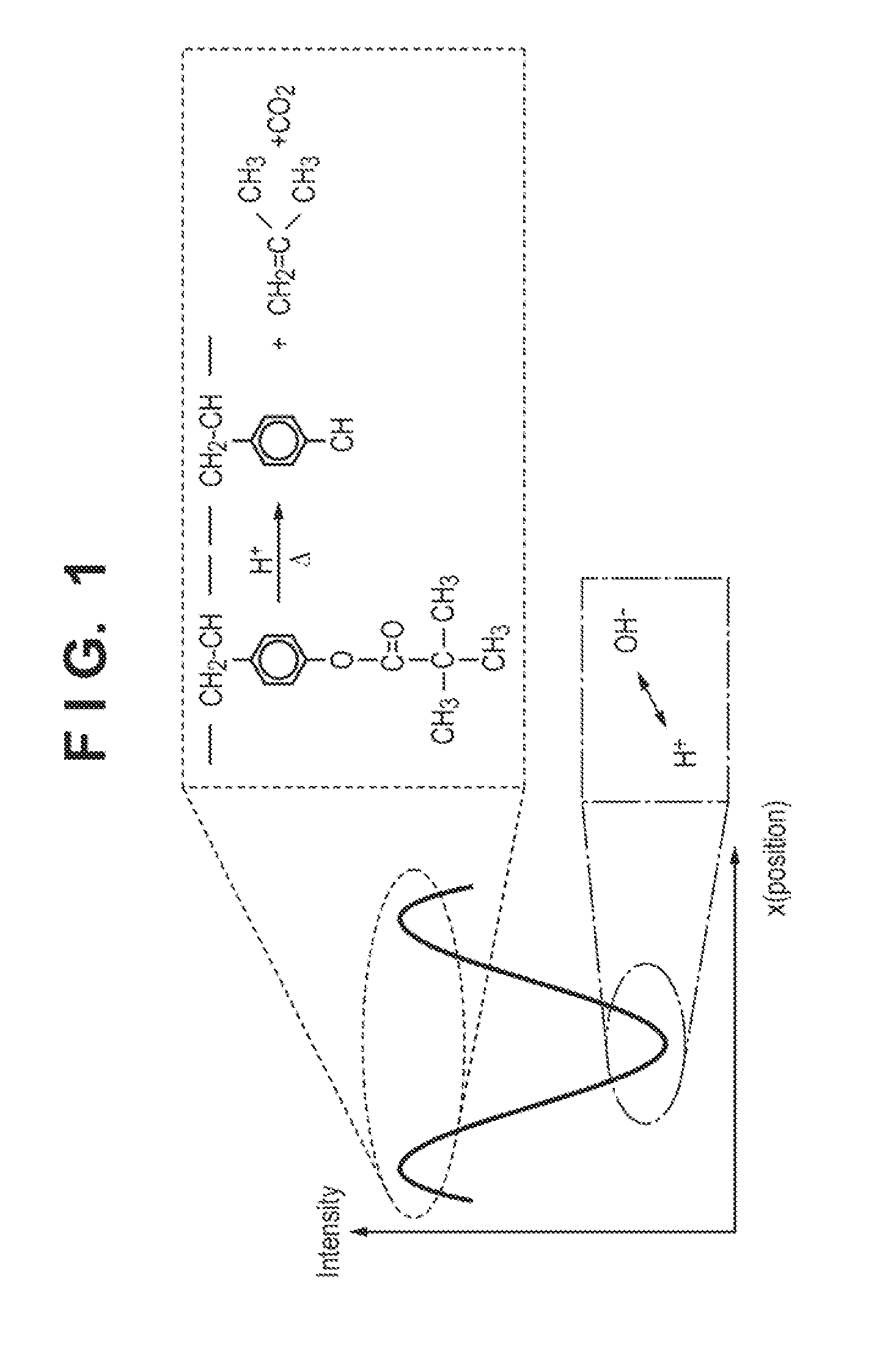
Moving phase grating mark and method for utilizing same in detecting image forming quality of photoetching machine
ActiveCN1928721AEasy to detectImprove detection accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusFine linePhase grating
The provided shift phase grating mark included close line mark forms on mask of photo-etching machine and also includes small-width fine line mark. The corresponding detection method for image quality of photo-etching machine comprises: exposing the grating mark on the substrate, detecting the imaging position offset of grating mark exposed on mask; calculating the vertical imaging quality parameter. Compared with prior art, this invention simplifies detection process, and fit to take a complete parameter detection for vertical imaging quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
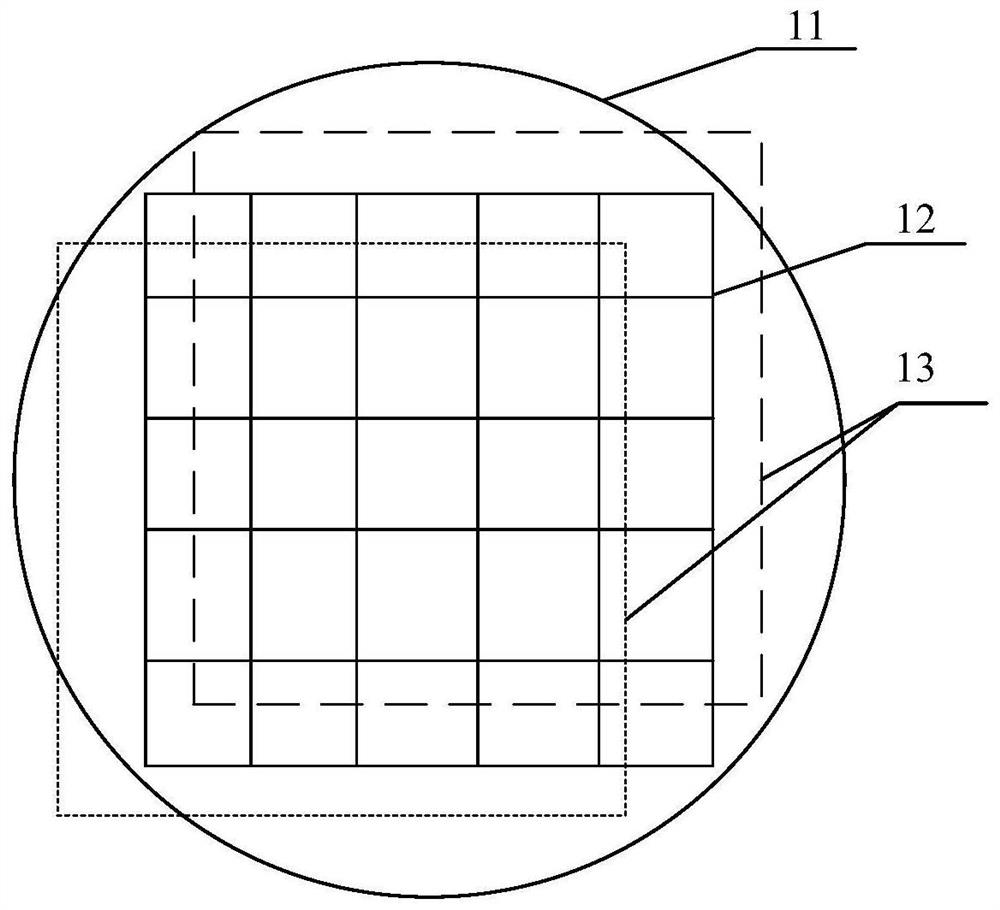
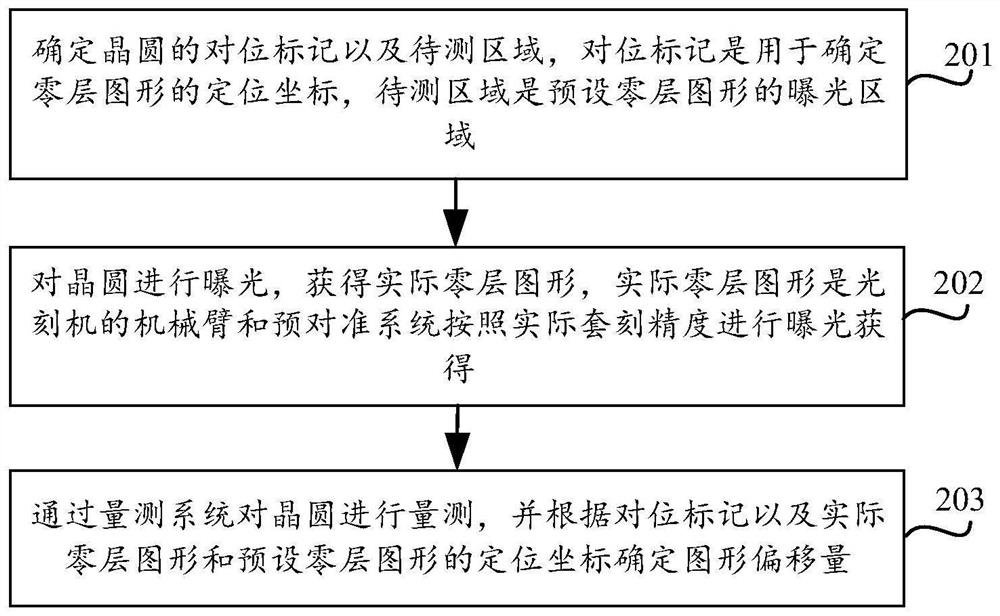
Method and device for reducing wafer overlay deviation
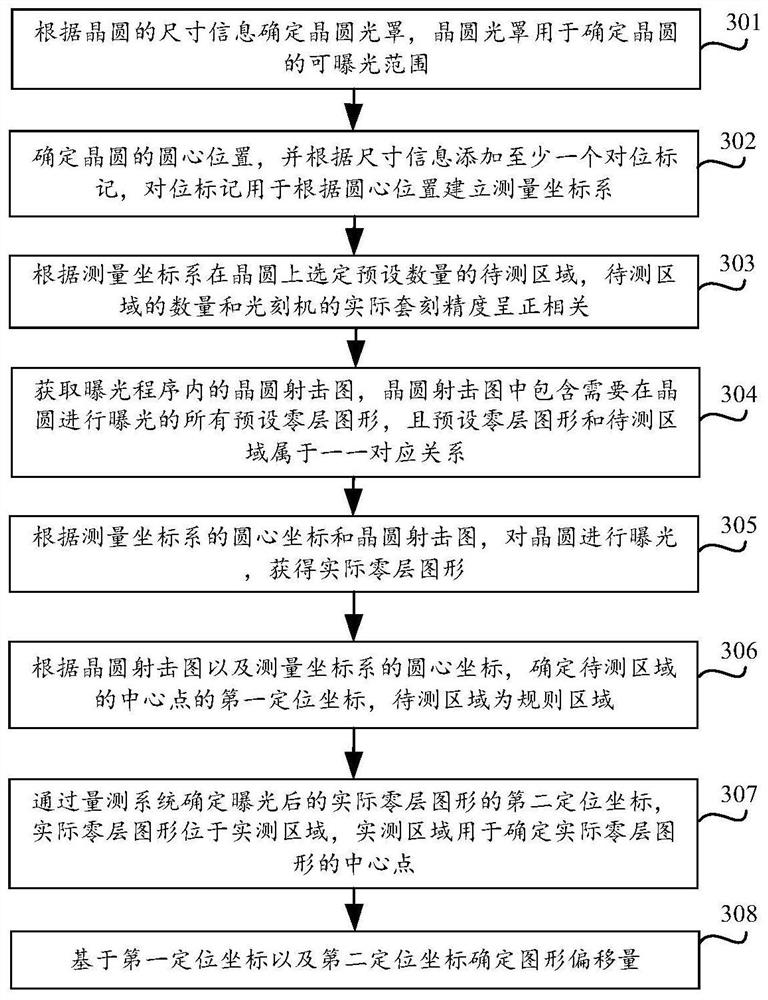
PendingCN114200790AReduced actual overlay deviationReduced overlay deviationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusWaferExposure
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and device for reducing wafer overlay deviation, and the method comprises the steps: determining an alignment mark of a wafer and a to-be-detected region, the alignment mark being used for determining a positioning coordinate of a zero-layer pattern, and the to-be-detected region being an exposure region of a preset zero-layer pattern; exposing the wafer to obtain an actual zero-layer pattern; the wafer is measured through the measuring system, the pattern offset is determined according to the alignment mark and the positioning coordinates of the actual zero-layer pattern and the preset zero-layer pattern, and the pattern offset is used for calculating the alignment precision of the photoetching machine, so that when it is determined that the actual alignment precision of the photoetching machine is smaller than the alignment precision threshold value, response is made in time. According to the technical scheme, the alignment mark is arranged and the coordinate system is measured, so that the actual alignment precision of the photoetching machine can be determined according to the positioning coordinate of the zero-layer pattern, the wafer alignment deviation caused by the transmission deviation of the mechanical arm is corrected in time, and the resource waste is avoided.
Owner:SOI MICRO CO LTD +1
Method of measuring a target, and metrology apparatus
ActiveUS10606178B2Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusDiffraction orderOptical axis
Disclosed is a method of measuring a target, and a metrology apparatus. In one arrangement the target comprises a layered structure. The layered structure has a first target structure in a first layer and a second target structure in a second layer. The method comprises illuminating the target with measurement radiation using an illumination profile in the illumination pupil (u) that is offset from an imaginary line (IL) in the illumination pupil passing through the optical axis, to allow propagation to a detection region of the detection pupil of an allowed order (v2, v4) of a predetermined diffraction order while limiting propagation to the detection region of an equal and opposite order (v1′, v3′) of that predetermined diffraction order. Scattered radiation of plural double-diffracted allowed diffraction orders (w2, w4) is detected. A characteristic of the lithographic process is calculated using the detected scattered radiation of the predetermined diffraction orders.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Extreme ultraviolet lithography light source mask optimization method
PendingCN112394615AHigh accuracy of imaging simulationImprove image qualityPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusImaging qualityEngineering
An extreme ultraviolet lithography light source mask optimization method comprises the following steps: representing a light source and a mask pattern by adopting pixels, calculating a photoresist image through a thick mask imaging model corrected by point pulse, and taking a pattern error between the photoresist pattern and a target pattern as an evaluation function to obtain a mask pattern; andoptimizing light source distribution and mask patterns by adopting a particle swarm optimization (SLPSO) algorithm based on a social learning mechanism. According to the method, the evaluation function is established by using the extreme ultraviolet lithography thick mask imaging model, so the imaging calculation precision in the optimization process is improved. In addition, the optimization efficiency and the optimization capability are effectively improved by using the SLPSO algorithm, and the imaging quality is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
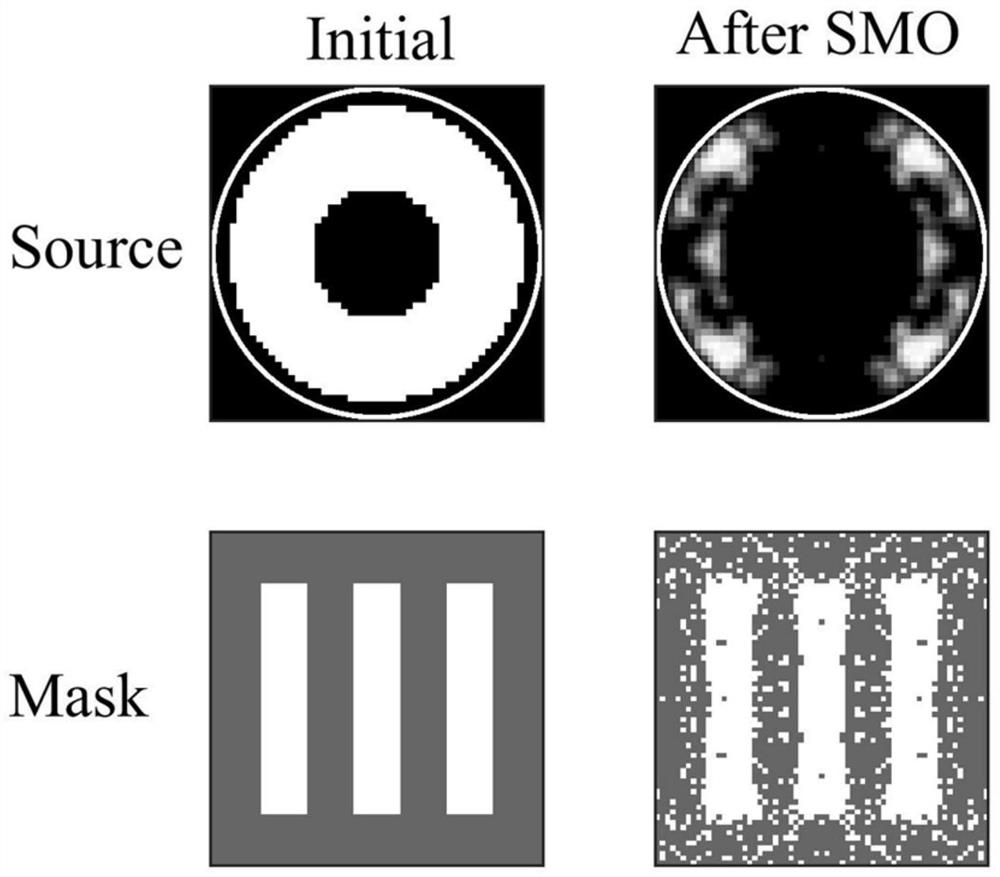
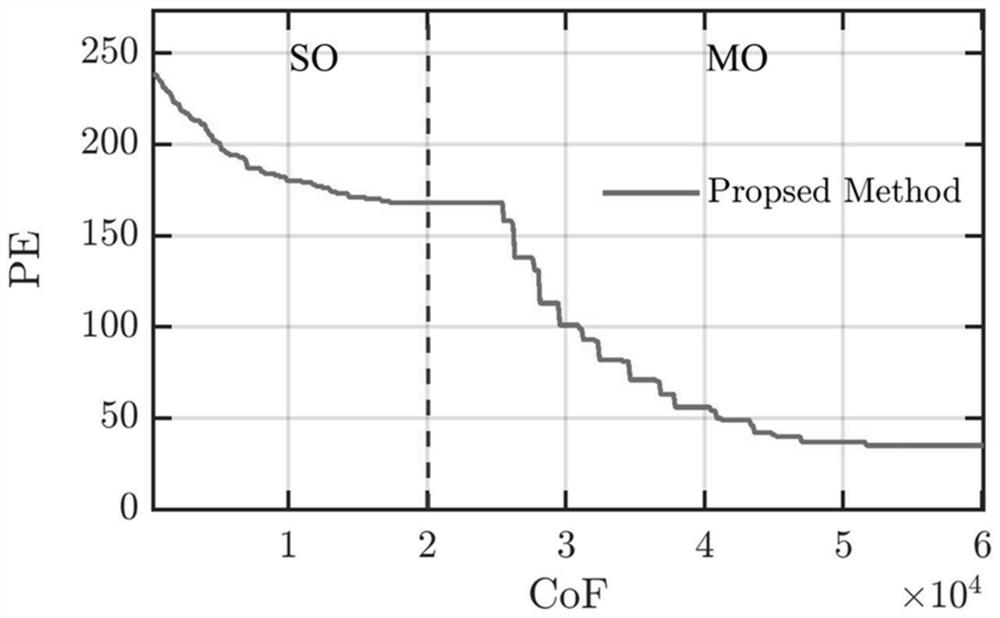
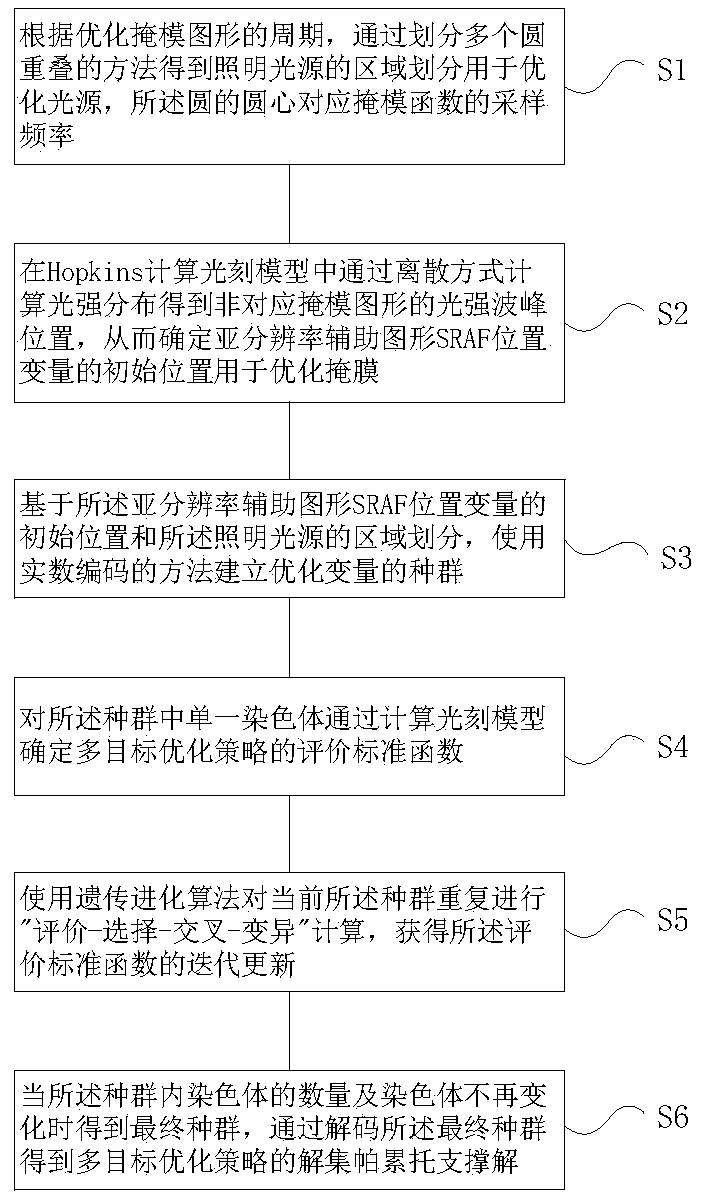
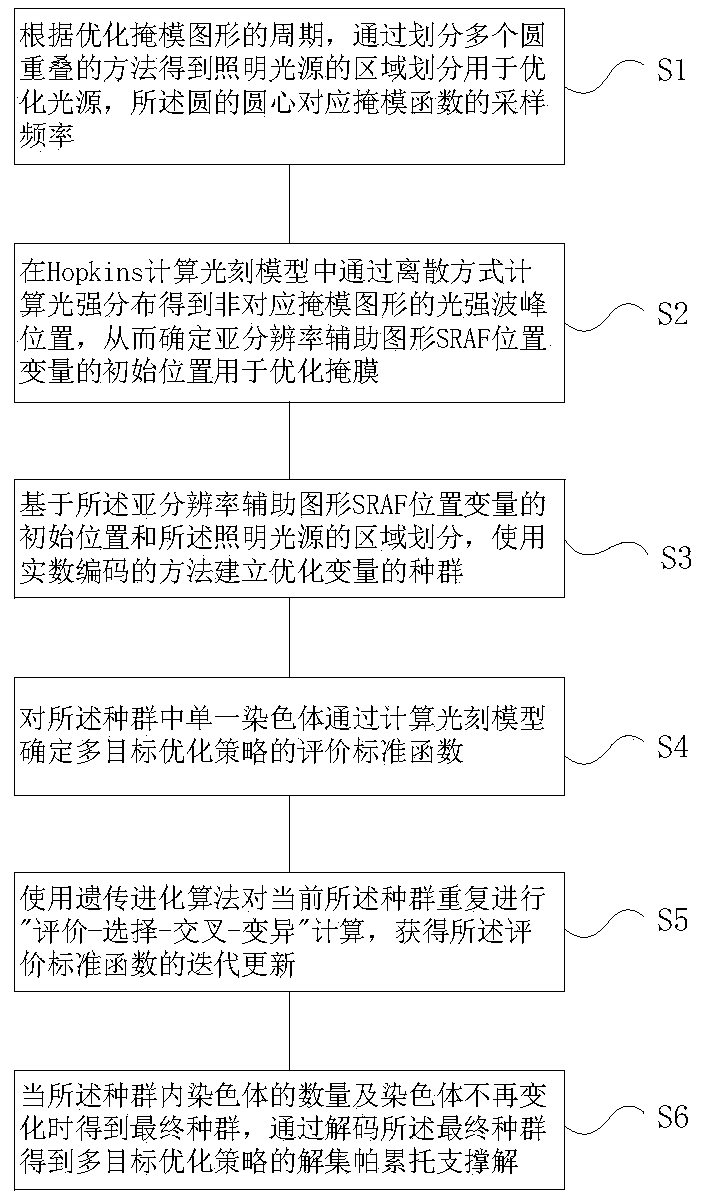
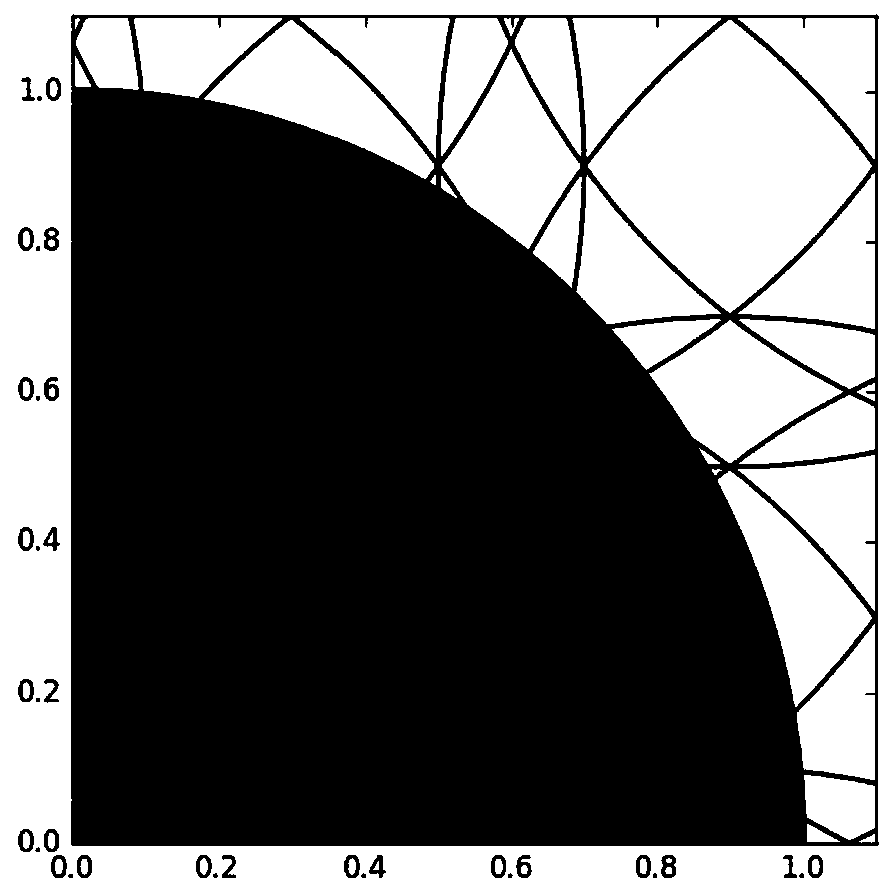
Photolithographic process resolution enhancing method and device based on multi-target optimization
ActiveCN110597023AImprove work efficiencyHigh-resolutionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusAlgorithmStandard function
The invention relates to the technical field of the photolithographic process for semiconductor production and particularly relates to a photolithographic process resolution enhancing method and device based on multi-target optimization. The method comprises steps of obtaining regional division of an illumination light source through a method of dividing a plurality of circles to be overlapped foroptimizing the light source; determining an initial position of a sub-resolution auxiliary graph SRAF position variable for optimizing a mask; establishing a population of optimization variables by using a real number encoding method; determining an evaluation standard function of a multi-target optimization strategy for a single chromosome in the population by calculating a photolithographic model; repeatedly carrying out evaluation-selection-crossover-variation calculation of the current population by using the genetic evolution algorithm to obtain iterative update of the evaluation standard function; decoding a final population to obtain a solution set Pareto support solution of the multi-target optimization strategy.
Owner:MOYAN COMPUTATIONAL SCI NANJING PTE LTD
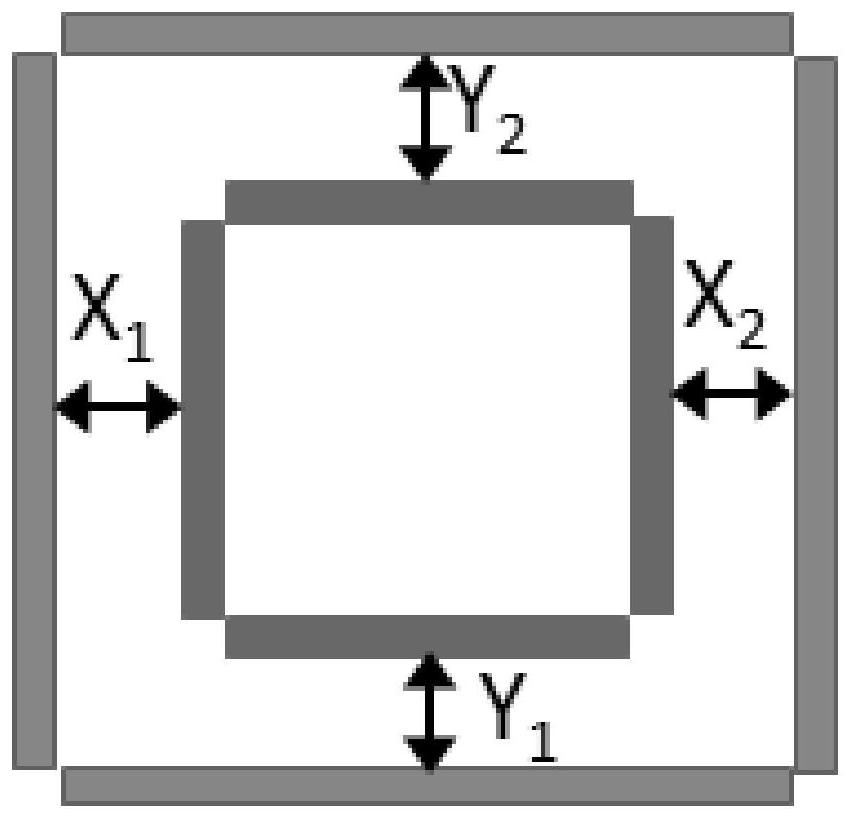
Computing method for diffraction field of double-absorbing-layer alternating phase shift contact hole mask
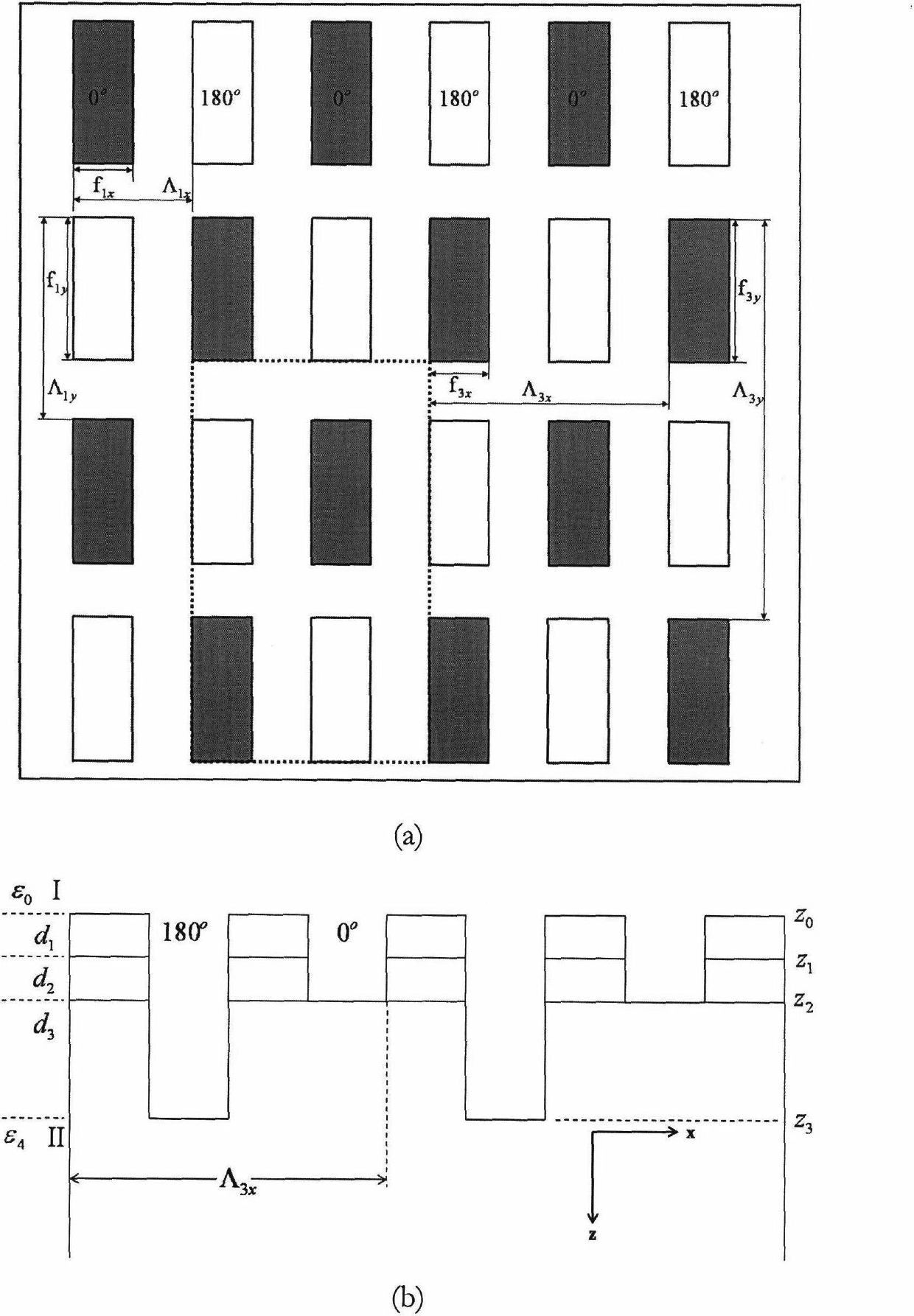
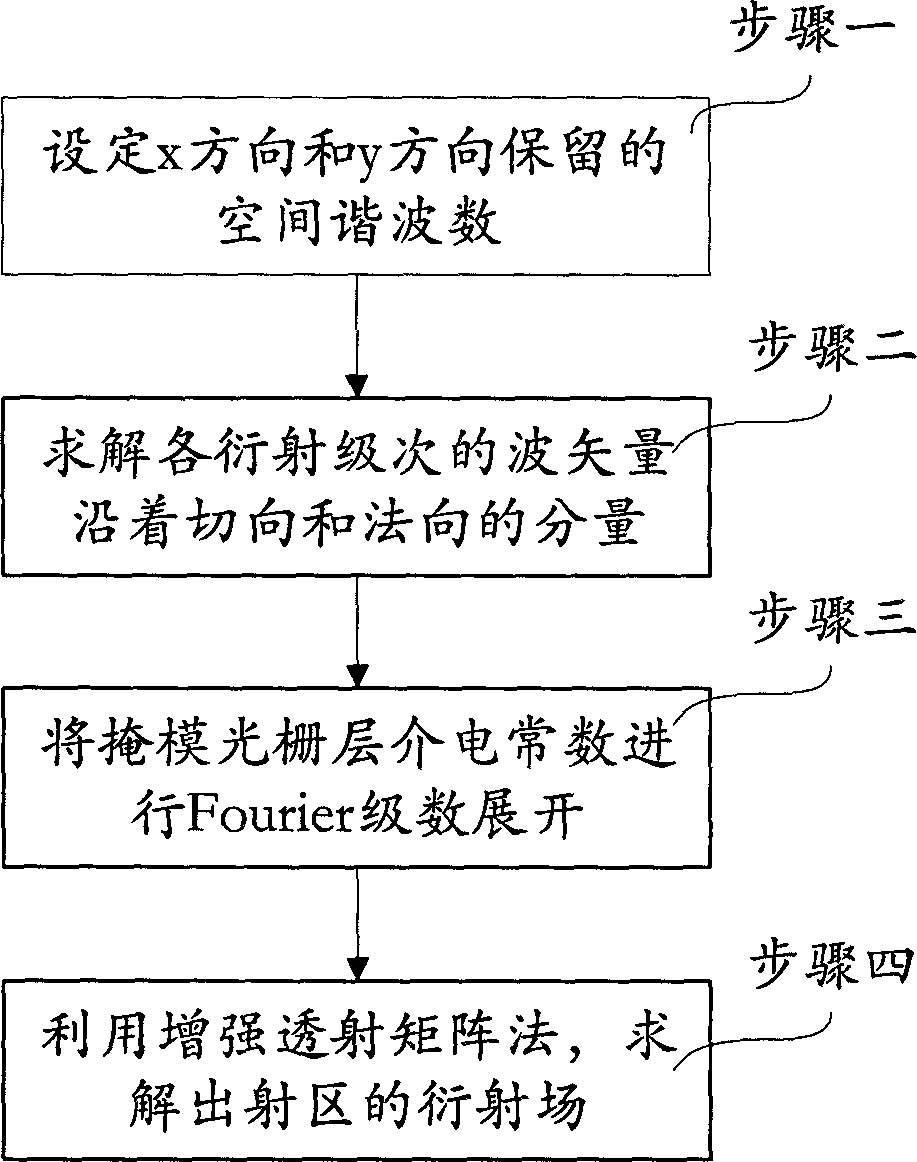
The invention provides a computing method for a diffraction field of a double-absorbing-layer alternating phase shift contact hole mask. According to the method, diffraction of the double-absorbing-layer alternating phase shift contact hole mask in photo-etching can be quickly computed. The computing method specifically comprises the following steps of: 1, setting harmonic number reserved in the x direction and setting harmonic number reserved in the y direction; 2, solving components of wave vector of each diffraction order in the tangential direction and the normal direction according to a Floquet condition; 3, performing Fourier series expansion on dielectric constant of a two-dimensional grating on each layer and a reciprocal of the dielectric constant; and 4, solving the diffraction field of an emission region by using an enhanced transmission matrix method. In two orthogonal directions, the Fourier series expansion is performed by selecting the minimum common multiple of cycles of three grating layers in the corresponding orthogonal direction, so that the diffraction of a plurality of layers of two-dimensional mask gratings with different cycles in the two orthogonal directions can be analyzed, and meanwhile, the diffraction field of the double-absorbing-layer alternating phase shift contact hole mask can be quickly solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
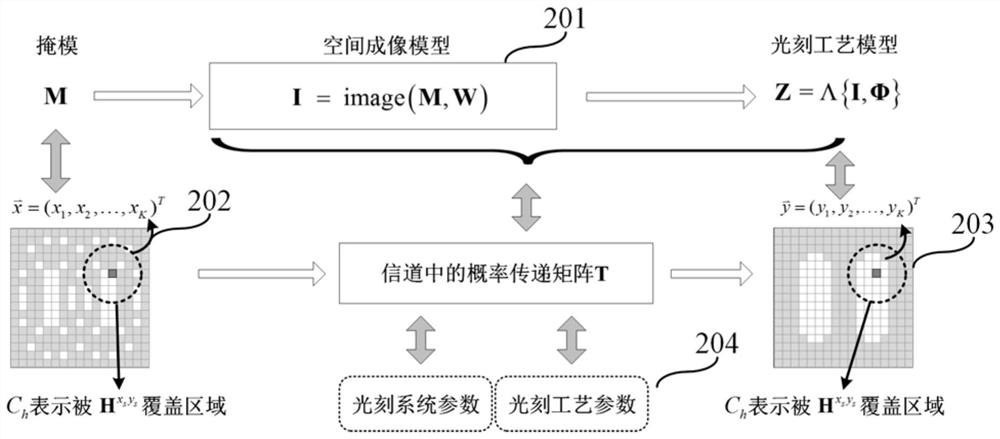
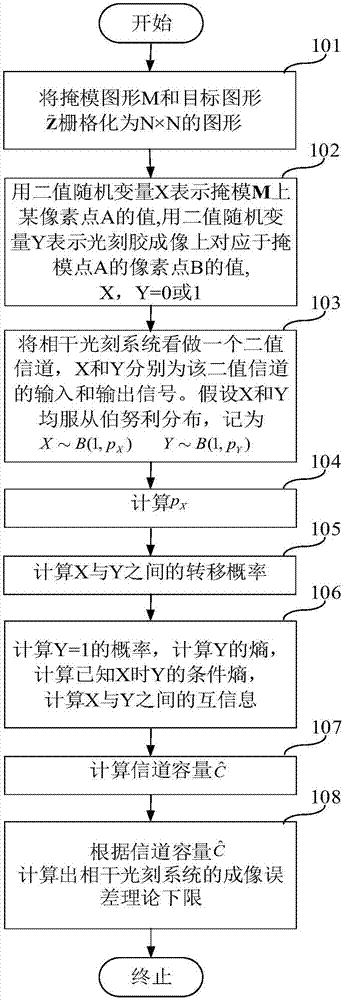
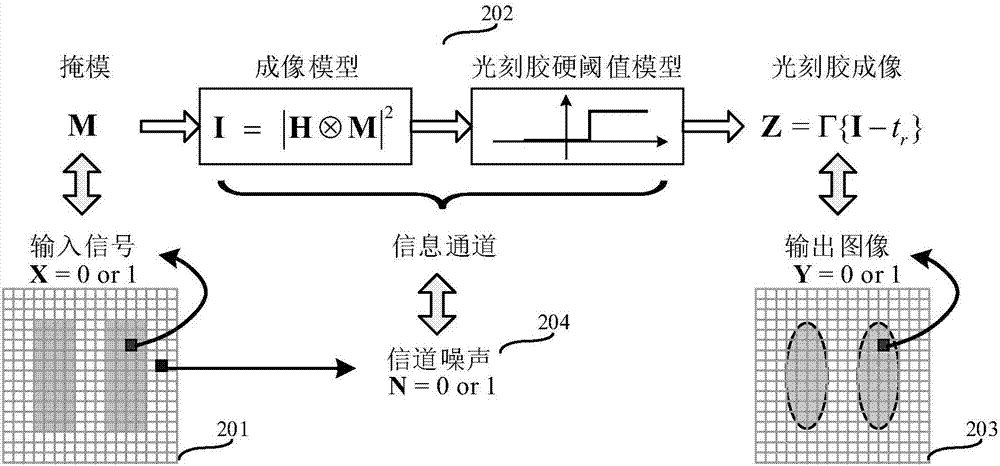
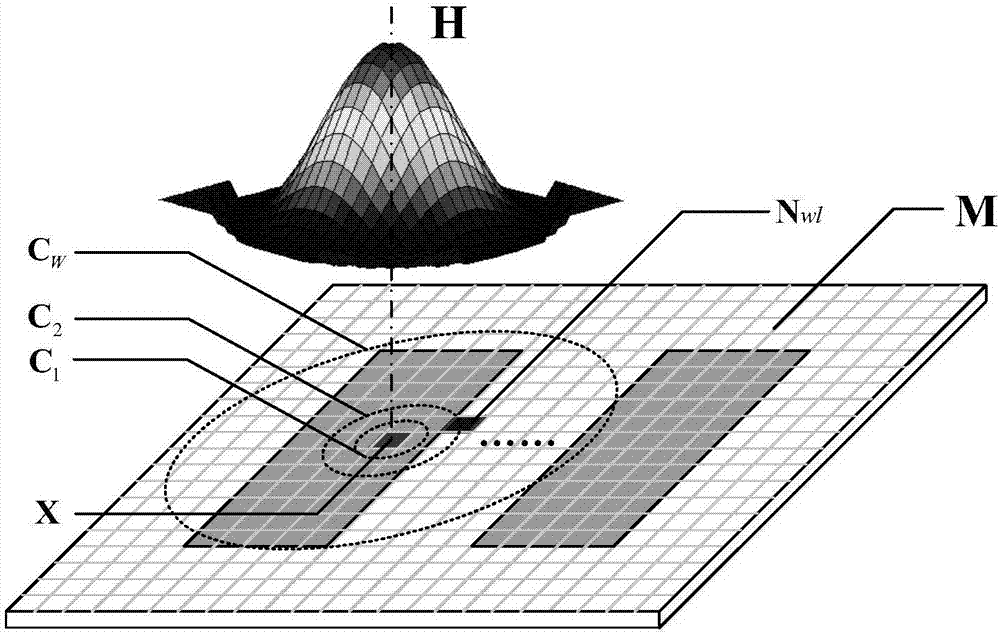
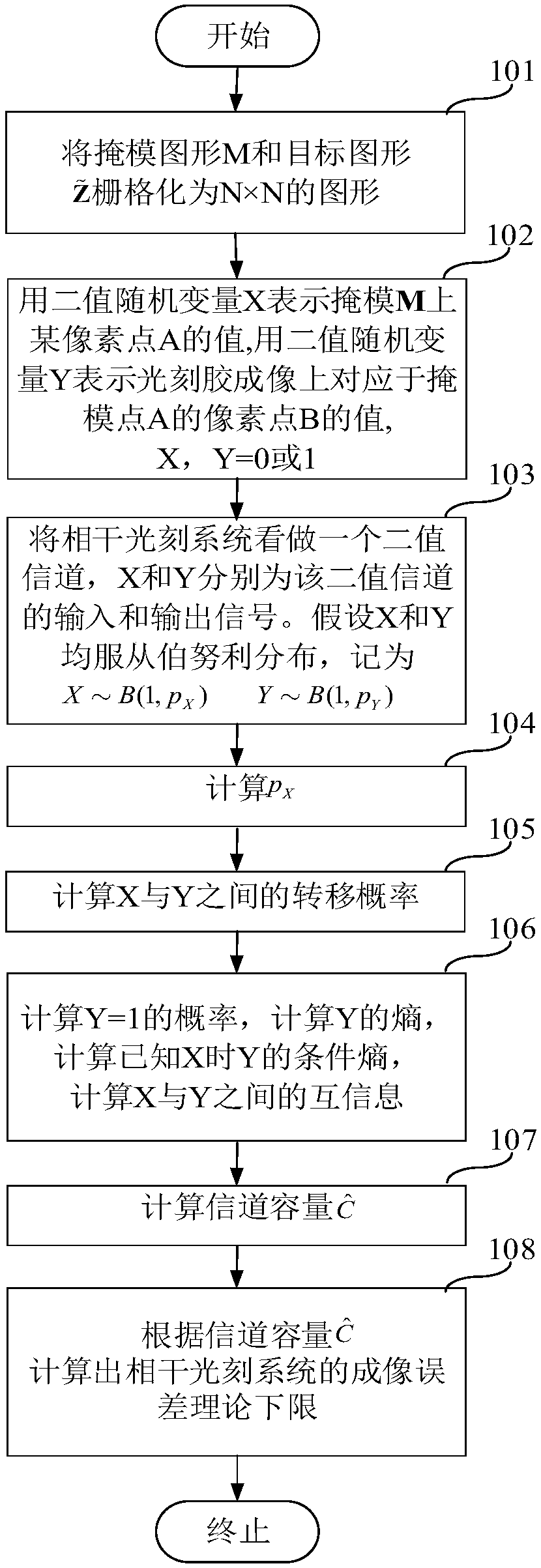
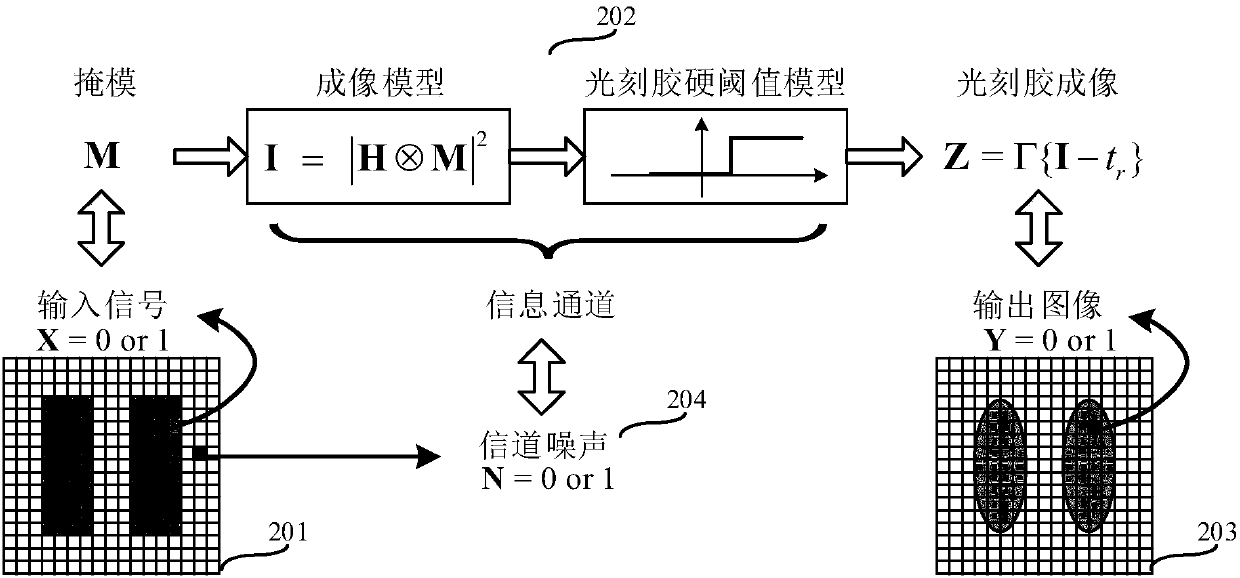
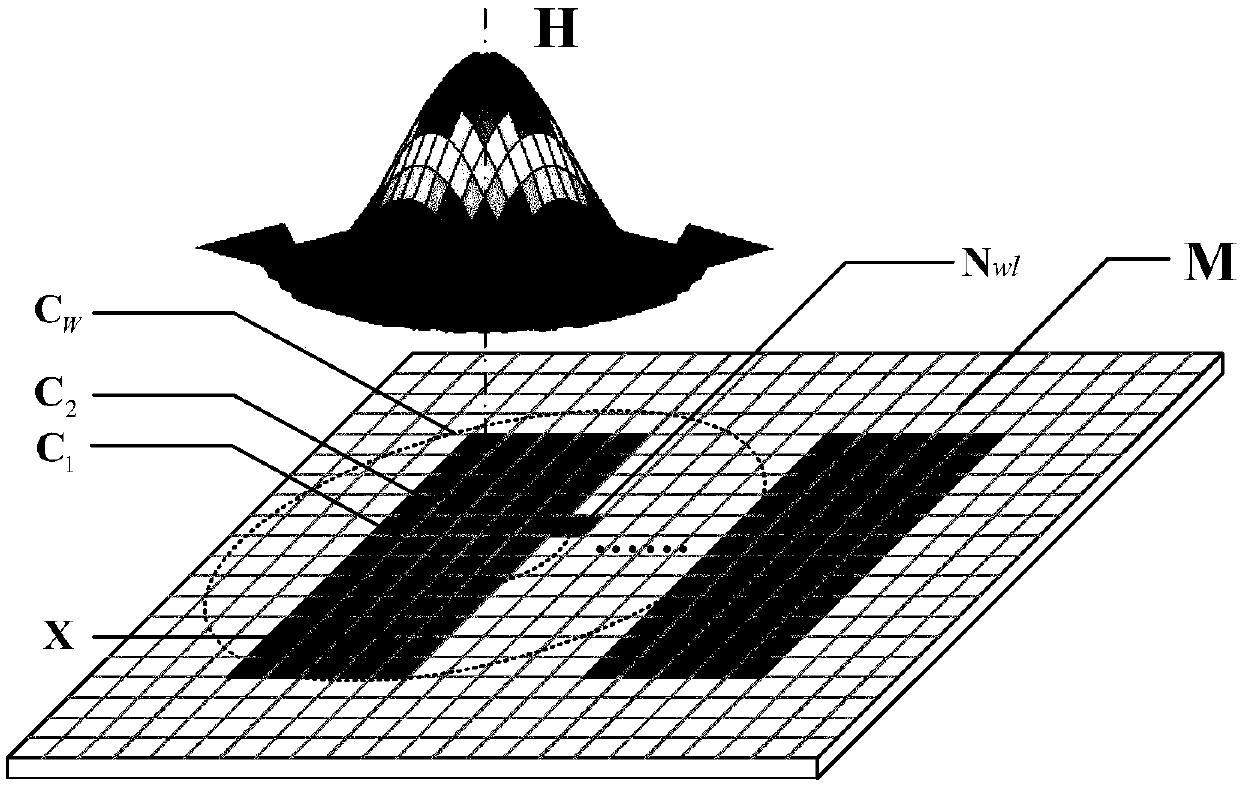
Method for calculating channel capacity and imaging error lower limit of coherent imaging photoetching system
ActiveCN107037695APhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGraphicsLower limit
The invention relates to a method for calculating channel capacity and imaging error lower limit of a coherent imaging photoetching system. The method comprises the steps of rasterizing a mask pattern M; expressing a value of a pixel point A on a mask image M with a binary random variable X, and expressing a value of a pixel point B, corresponding to the pixel point A, on a photoresist image Z with a binary random variable Y; viewing the coherent photoetching system as a binary channel, wherein the X and the Y are respectively an input signal and an output signal of the binary channel; calculating probability pX when the X is equal to 1; calculating transfer probability pij between the X and the Y; calculating probability pY when the Y is equal to 1, and further calculating mutual information I (X; Y) between the X and the Y; taking the maximum value C-bar of the mutual information as the channel capacity; and calculating an image error theoretical lower limit of the coherent photoetching system according to the channel capacity C-bar. By the method, a theoretical basis and a simulation basis can be provided for deeper understanding of an image information transmission mechanism and development of an advanced calculation photoetching technology in the photoetching system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Resist pattern calculation method and calculation program storage medium
ActiveUS9448495B2Improve calculation accuracyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusResistComputer science
Owner:CANON KK
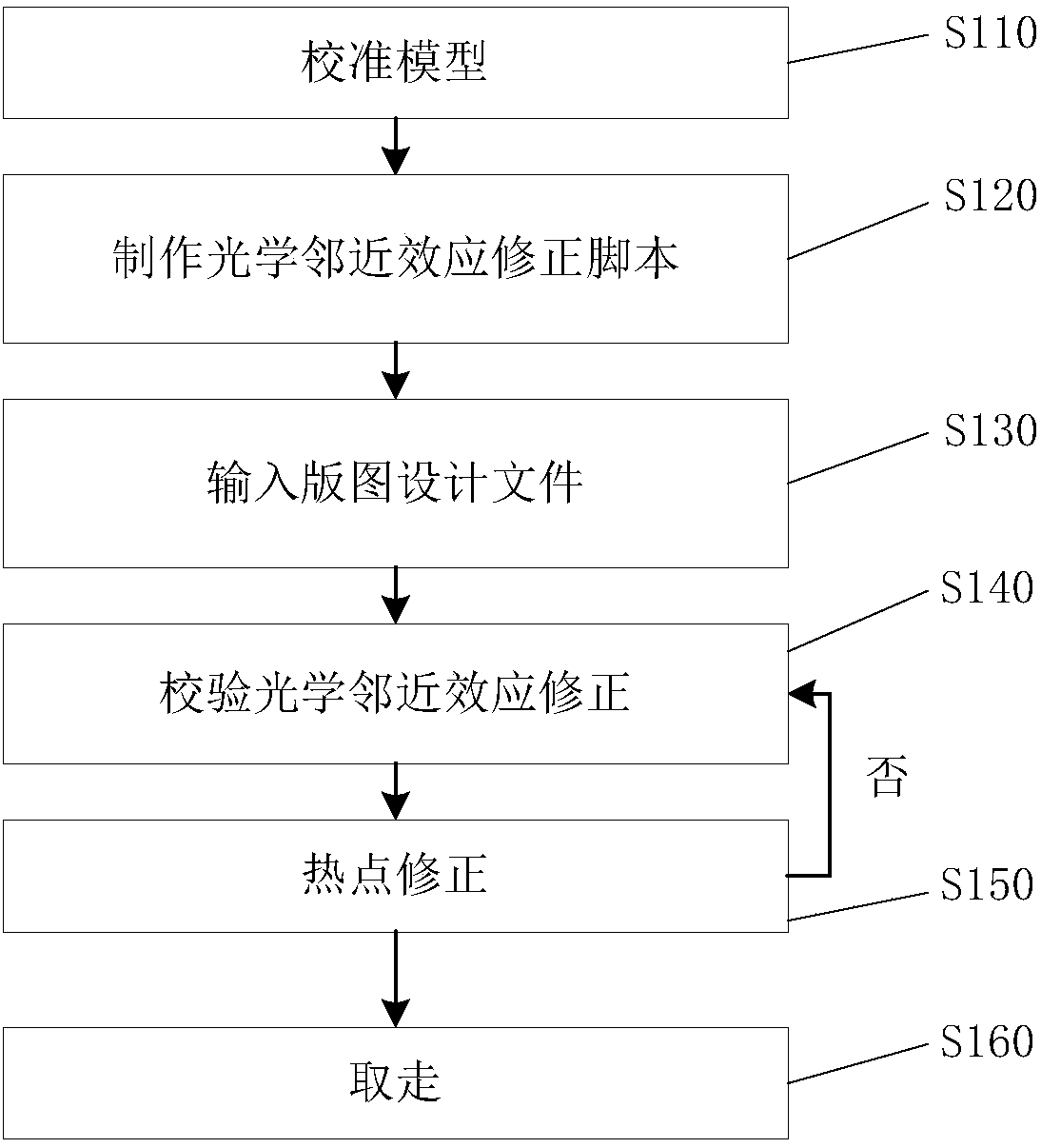
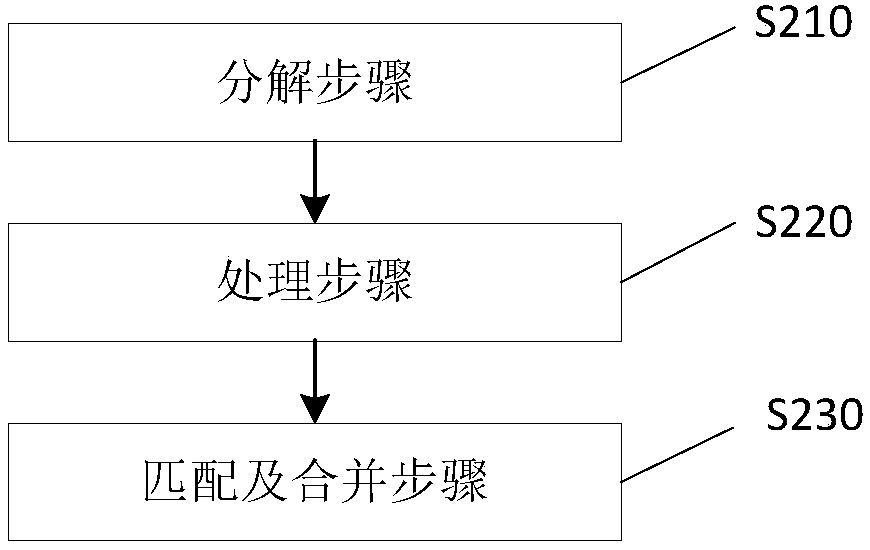
Computational lithography method and system for optical proximity effect correction
ActiveCN109932864AOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputer architectureOptical proximity correction
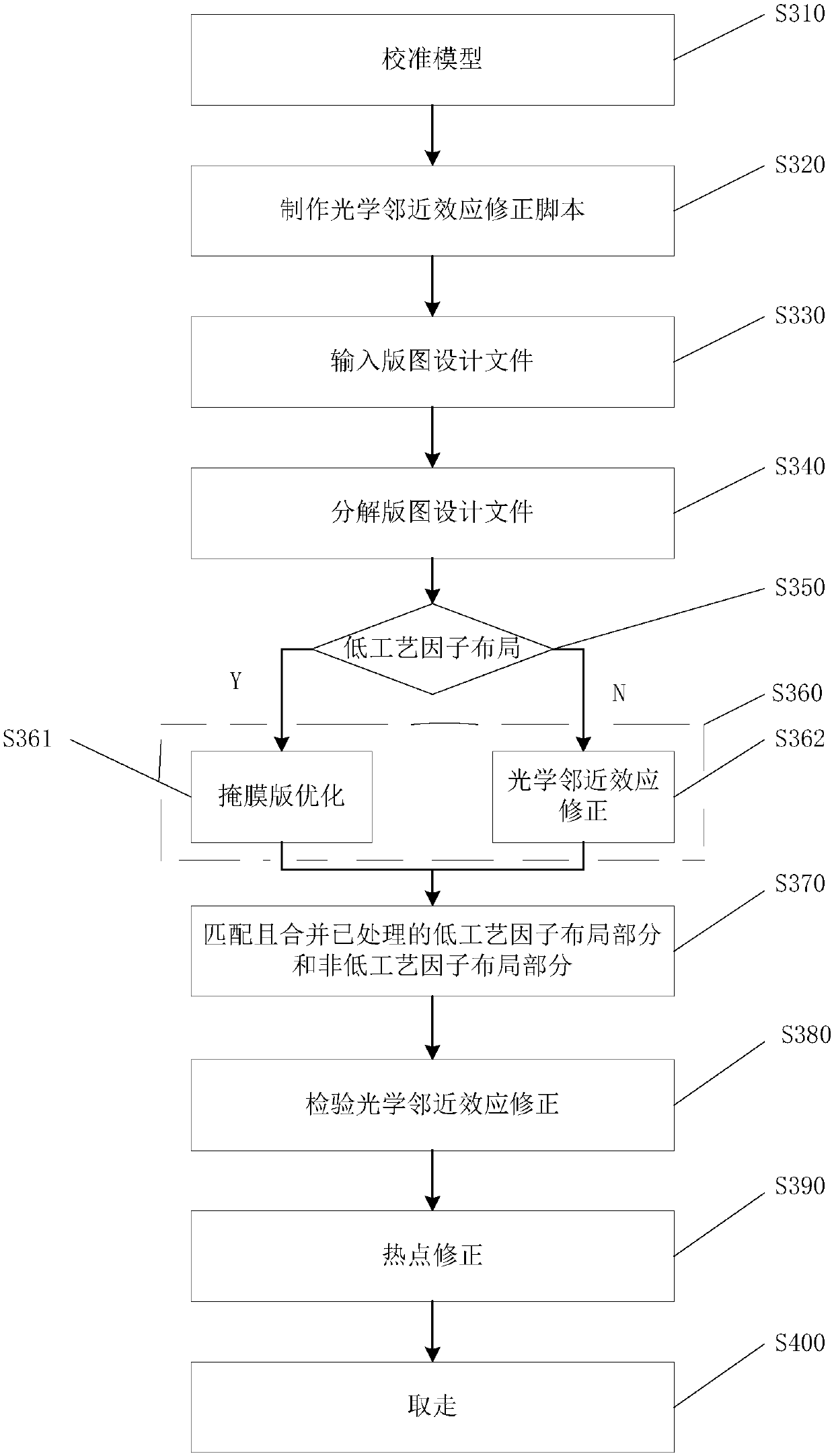
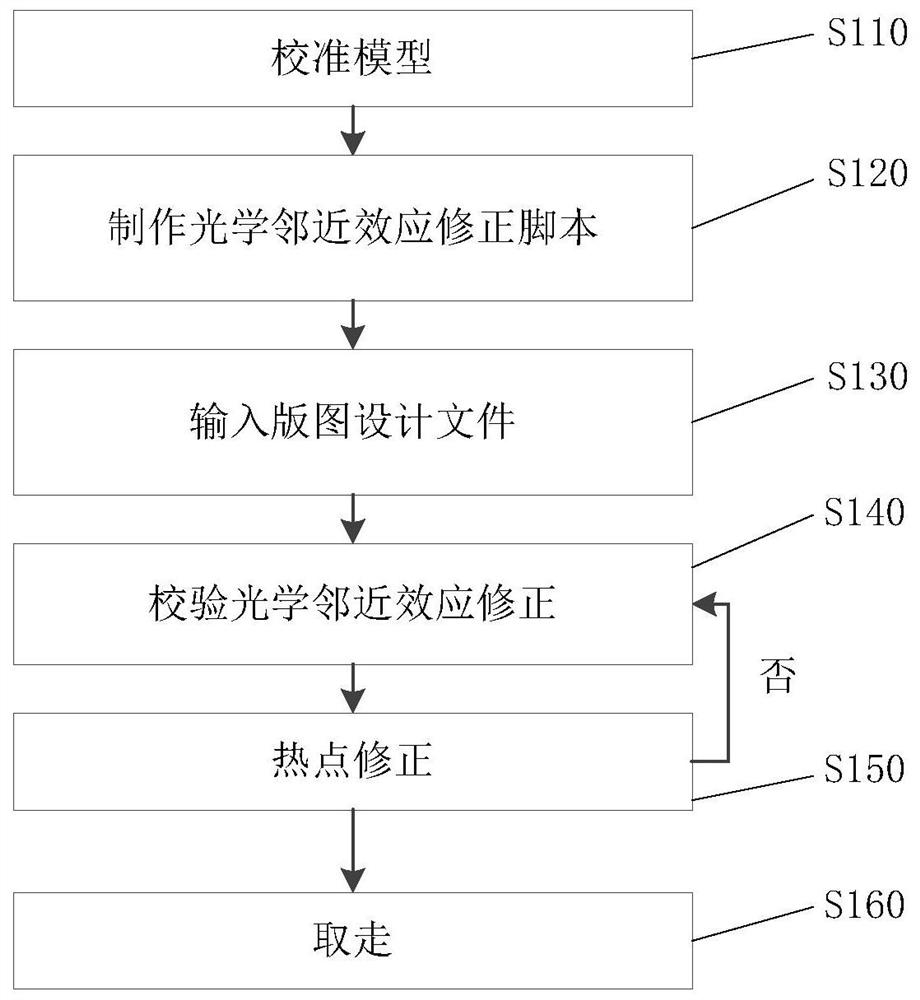
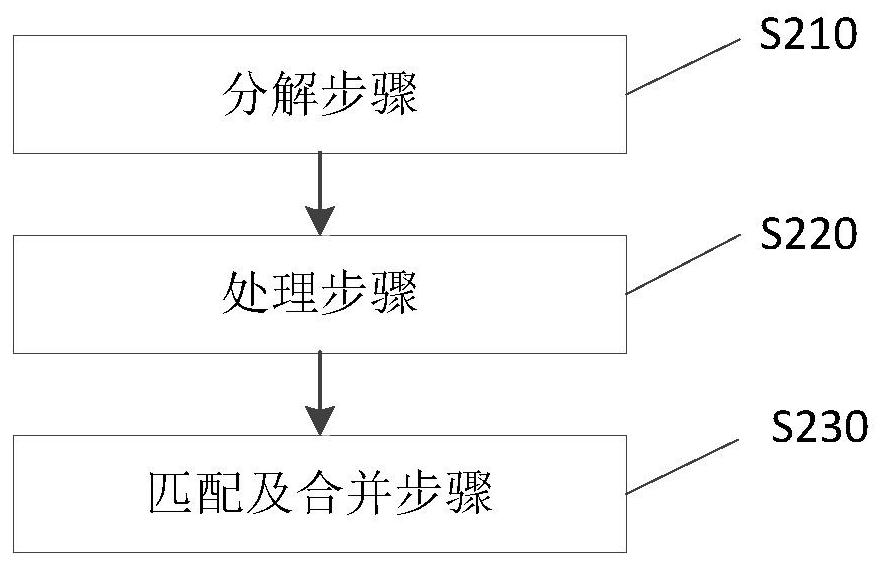
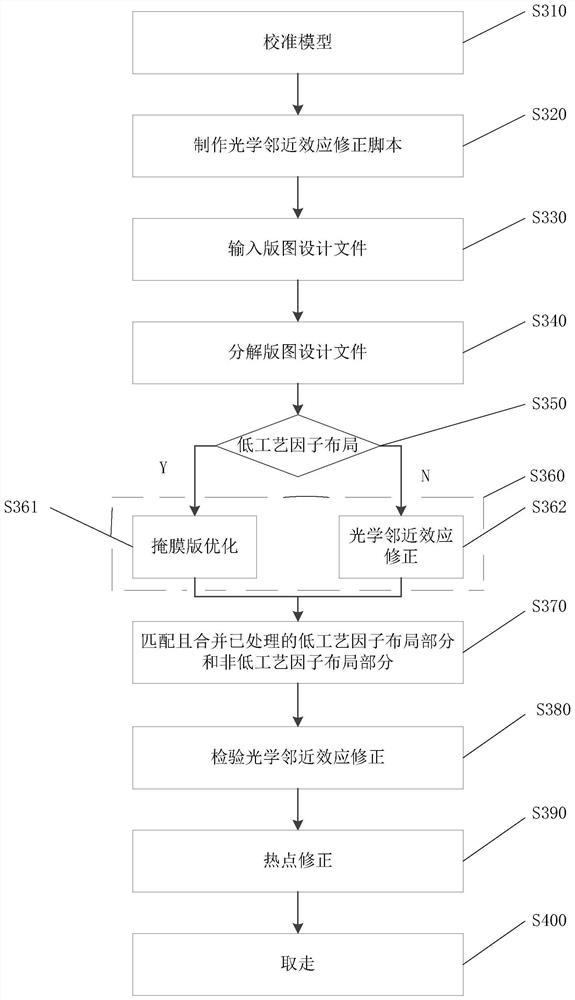
The invention provides a computational lithography method for optical proximity effect correction. The computational lithography method comprises the following steps: an input layout design document is decomposed into a first layout part and a second layout part according to the value of the process factor, wherein the process factor of the first layout part is lower than a preset threshold, and the process factor of the second layout part is higher than a preset threshold; the first layout part and the second layout part are processed separately; and the processed first layout part and the processed second layout part are matched and combined. Because the first layout part and the second layout part are processed separately, the processing quality is improved, there is no need to iteratively execute the optical proximity correction inspection step and the hot spot correction step, and the output speed of layout design documents is improved. The invention also provides a computationallithography system for optical proximity effect correction.
Owner:CHANGXIN MEMORY TECH INC
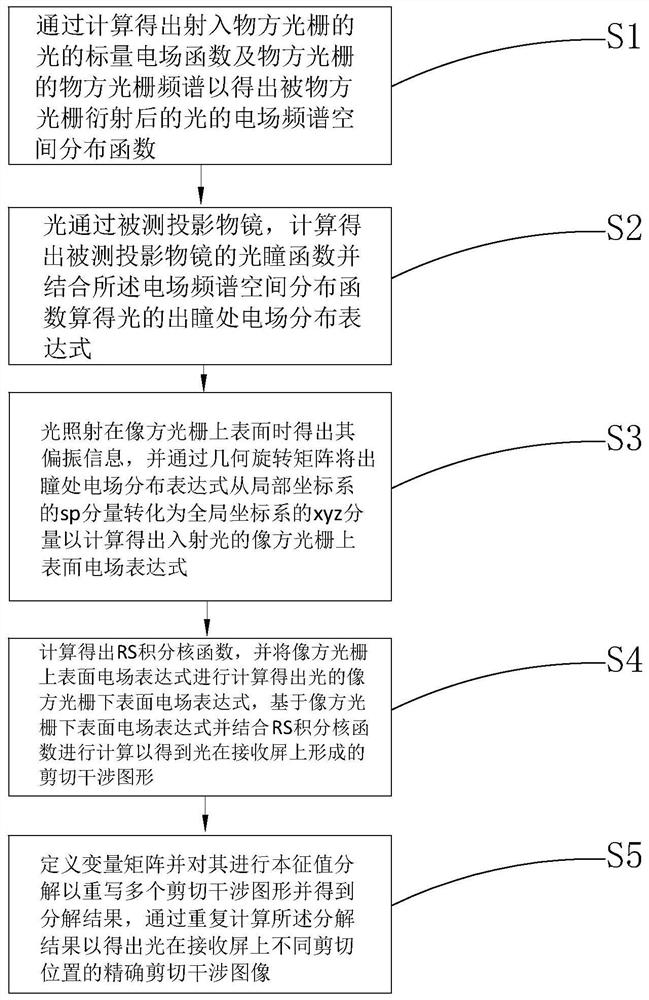
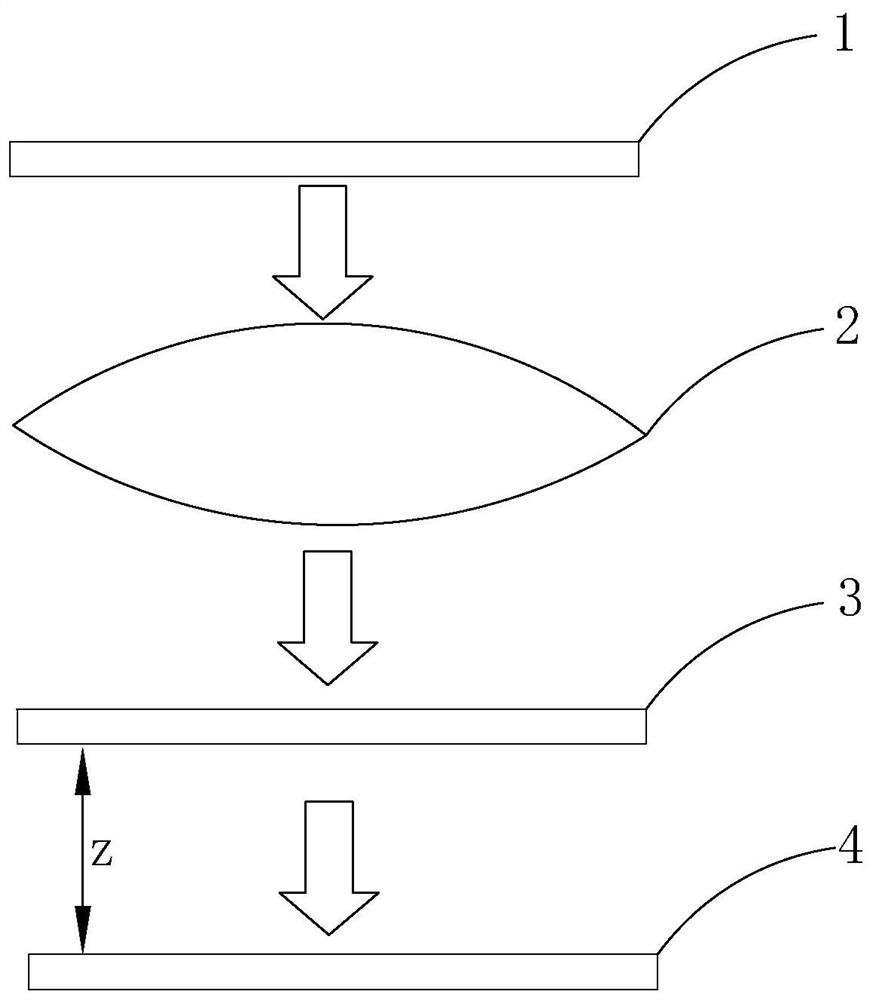
Method of calculating Ronchi shear interference image in photoetching projection objective
ActiveCN112114501AAvoid the problem that it is difficult to obtain the shear interference image accuratelyEasy to calculateOptical measurementsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusGratingMicroscope objective
The invention provides a method for calculating a Ronchi shear interference image in a photoetching projection objective. According to the method, a strict photoetching vector model is used for calculation in the process of transmitting light emitted by a light source from an object-side grating to an image-side grating, and the method can be suitable for object-side and image-side gratings in anyshape. And strict Rayleigh-Sommerfeld diffraction integration is adopted for calculation in the process of light from the image space optical grating to the receiving screen. According to the methodfor calculating the Ronchi shear interference image in the photoetching projection objective, calculation is carried out by adopting a strict photoetching vector model and Rayleigh-Sommerfeld diffraction integration, so that near fields or far fields of an object space grating and an image space grating do not need to be considered, and paraxial approximation and other factors do not need to be considered for a receiving screen; the problem that a shearing interference image is difficult to obtain accurately due to large limitation of a traditional test method is solved.
Owner:DONGFANG JINGYUAN ELECTRON LTD
Method and structure for measuring photoetching overlay error before and after epitaxy
ActiveCN113109997AAccurate calculationEliminate the defects of bloated blurSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEtchingVernier scale
The invention provides a method and structure for measuring photoetching overlay errors before and after epitaxy, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the etching on the surface of a first substrate, and forming a vernier main scale original mark; carrying out epitaxy on the first substrate surface to form a second substrate surface, setting a vernier main ruler scale mark according to the existing morphology of the vernier main ruler scale original mark, and setting the original point of the vernier main ruler scale mark; carrying out photoetching on the surface of the second substrate to form vernier scale marks; and detecting the actual alignment point of the vernier main scale scale mark and the vernier scale scale mark, and calculating the photoetching overlay error according to the actual alignment point and the vernier scale precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI SILIGHT TECH
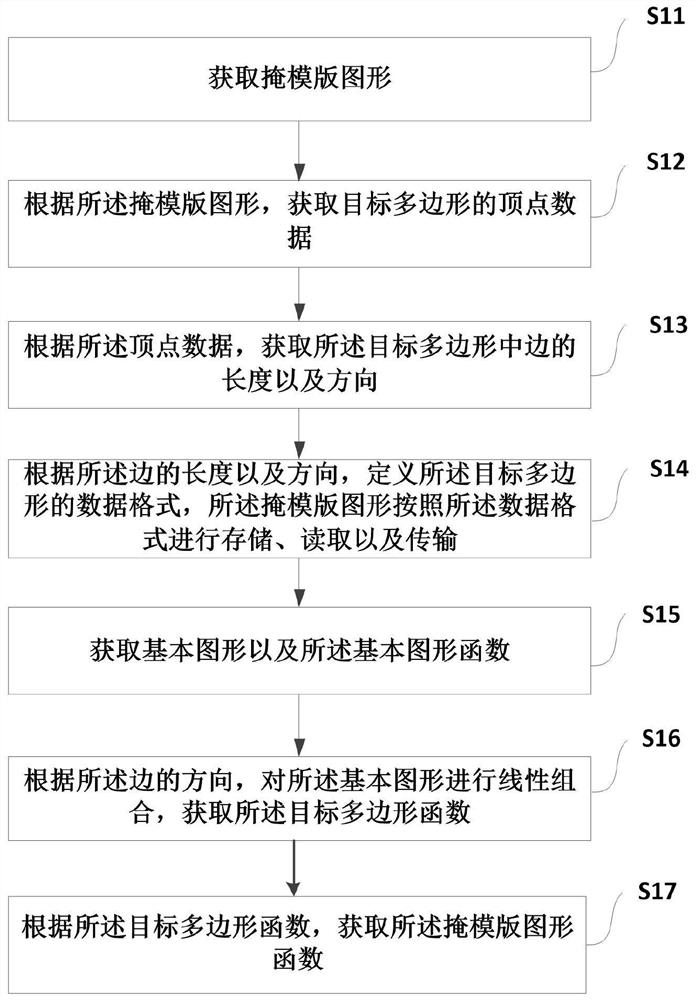
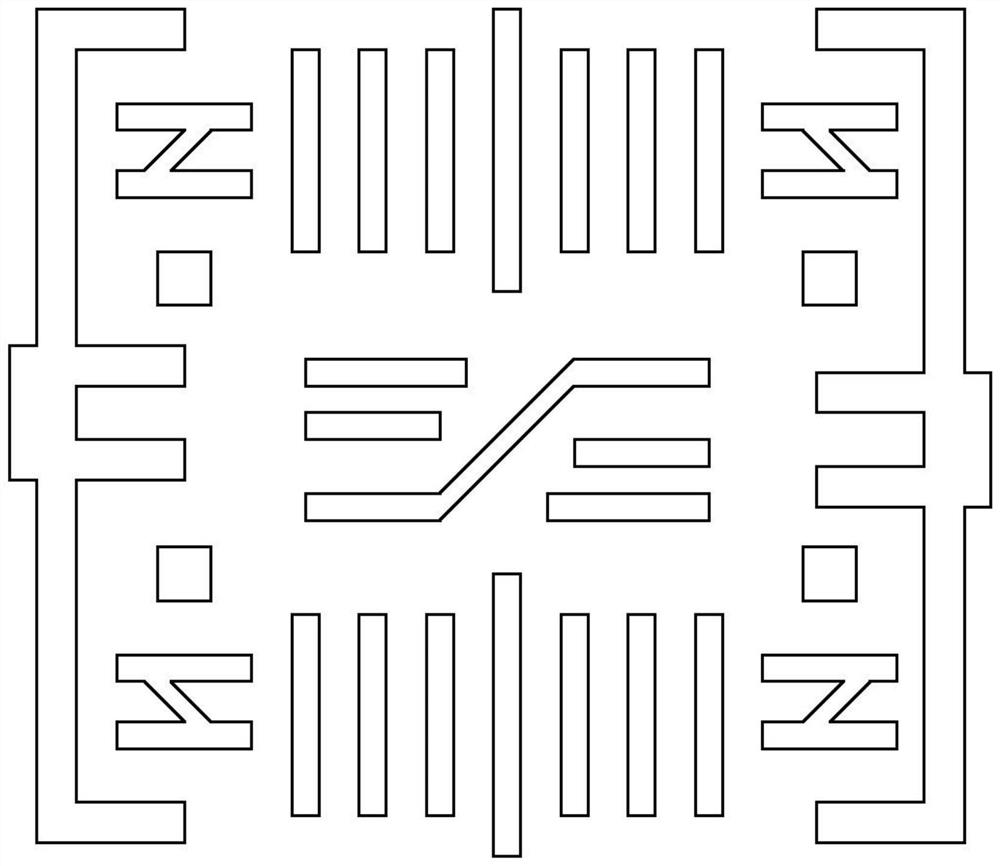
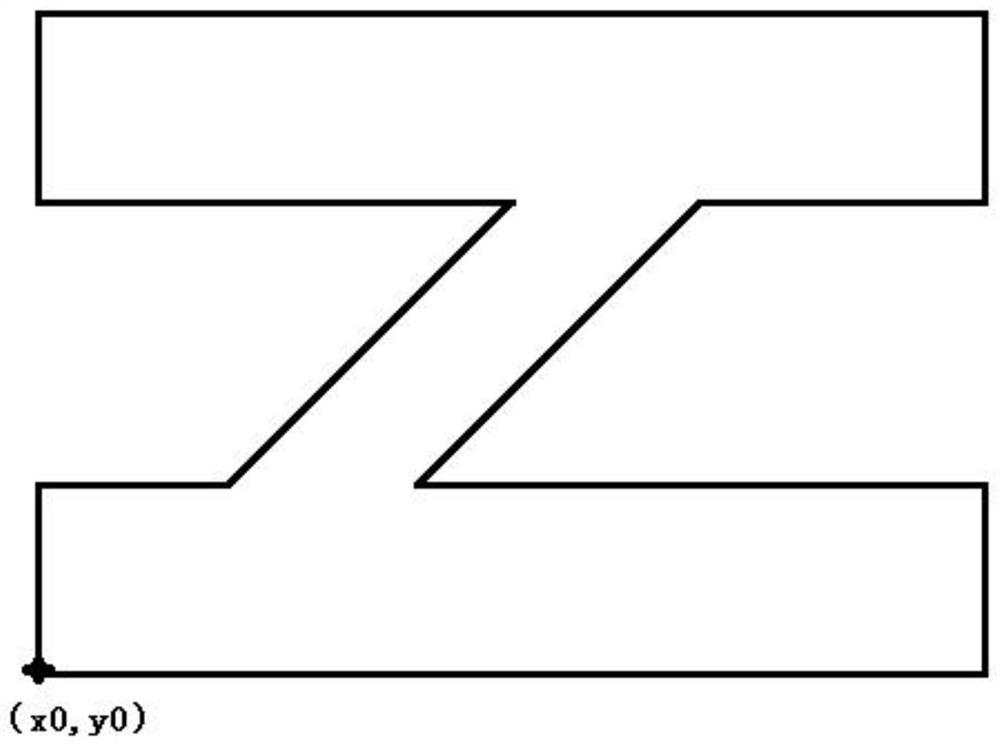
Method and device for processing reticle in computational lithography
ActiveCN109656106BImprove efficiencySave storage spacePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGraphicsAlgorithm
Owner:MOYAN COMPUTATIONAL SCI NANJING PTE LTD
A computational lithography modeling method and device
ActiveCN110262191BHigh precisionGuaranteed accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusGraphicsIntegrated circuit manufacturing
This application relates to the technical field of integrated circuit manufacturing, and discloses a computational lithography modeling method and device. In this method, the optical module group is determined by obtaining the type of the graphic unit contained in the test pattern, and then according to the optical module group, the obtained Parameters of the physical optics model. Calculate the ideal light intensity distribution of the optical module group on the photoresist, and obtain the parameters of the photochemical model according to the ideal light intensity distribution and the photochemical reaction excited by the optical module group on the photoresist. Then simulate the boundary position of the test pattern formed on the photoresist, and obtain the critical dimension simulation data of the test pattern, if the fitting error between the critical dimension measurement data and the critical dimension simulation data is not greater than the preset allowable error, a computational lithography model is established. The computational lithography modeling method disclosed in the present application effectively improves the accuracy of the computational lithography model by establishing different optical modules to simulate different graphics units.
Owner:MOYAN COMPUTATIONAL SCI NANJING PTE LTD
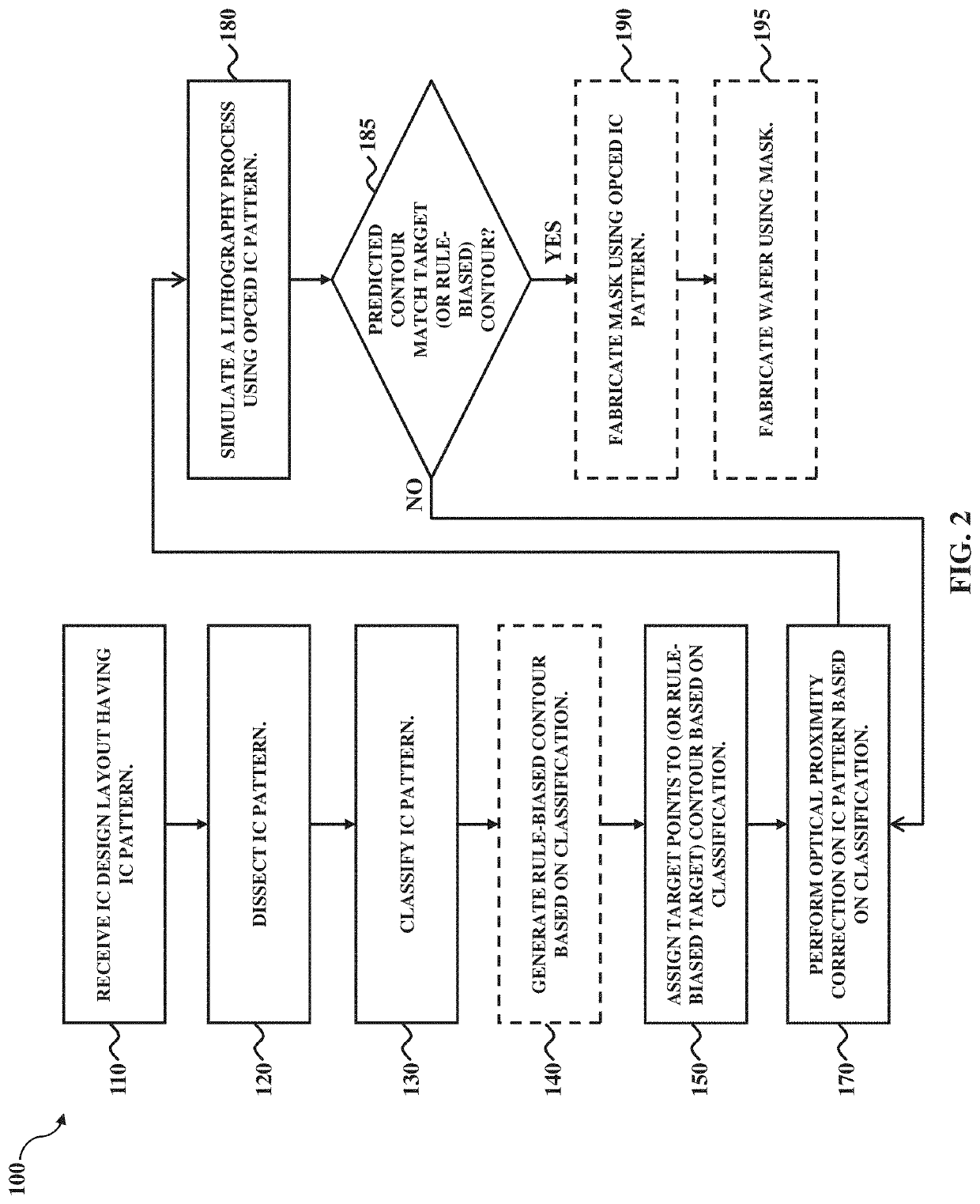
Optical proximity correction methodology using pattern classification for target placement
Optical proximity correction (OPC) based computational lithography techniques are disclosed herein for enhancing lithography printability. An exemplary mask optimization method includes receiving an integrated circuit (IC) design layout having an IC pattern; generating target points for a contour corresponding with the IC pattern based on a target placement model, wherein the target placement model is selected based on a classification of the IC pattern; and performing an OPC on the IC pattern using the target points, thereby generating a modified IC design layout. The method can further include fabricating a mask based on the modified IC design layout. The OPC can select an OPC model based on the classification of the IC pattern. The OPC model can weight the target placement model.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
A method and device for enhancing the resolution of photolithography process based on multi-objective optimization
ActiveCN110597023BImprove work efficiencyHigh-resolutionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLithography processAlgorithm
The invention relates to the technical field of the photolithographic process for semiconductor production and particularly relates to a photolithographic process resolution enhancing method and device based on multi-target optimization. The method comprises steps of obtaining regional division of an illumination light source through a method of dividing a plurality of circles to be overlapped foroptimizing the light source; determining an initial position of a sub-resolution auxiliary graph SRAF position variable for optimizing a mask; establishing a population of optimization variables by using a real number encoding method; determining an evaluation standard function of a multi-target optimization strategy for a single chromosome in the population by calculating a photolithographic model; repeatedly carrying out evaluation-selection-crossover-variation calculation of the current population by using the genetic evolution algorithm to obtain iterative update of the evaluation standard function; decoding a final population to obtain a solution set Pareto support solution of the multi-target optimization strategy.
Owner:MOYAN COMPUTATIONAL SCI NANJING PTE LTD
Computational Lithography Method and System for Optical Proximity Correction
The present invention provides a computational lithography method for optical proximity effect correction. The computational lithography method decomposes the input layout design file into a first layout part and a second layout part according to the value of the process factor, wherein the process factor of the first layout part is lower than a preset threshold, and the second layout part is The process factor of the layout part is greater than the preset threshold; then the first layout part and the second layout part are processed respectively; then, the processed first layout part and the second layout part are matched and merged layout section. Since the first layout part and the second layout part are processed separately, the processing quality is improved, so it is no longer necessary to iteratively perform the step of correcting the optical proximity effect and the step of correcting the hot spot, thereby improving the output speed of the layout design file. The present invention also provides a computational lithography system for optical proximity effect correction.
Owner:CHANGXIN MEMORY TECH INC
A Method for Calculating Channel Capacity and Imaging Error Lower Limit of Coherent Imaging Lithography System
ActiveCN107037695BPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLower limitInformation transmission
The invention relates to a method for calculating channel capacity and imaging error lower limit of a coherent imaging photoetching system. The method comprises the steps of rasterizing a mask pattern M; expressing a value of a pixel point A on a mask image M with a binary random variable X, and expressing a value of a pixel point B, corresponding to the pixel point A, on a photoresist image Z with a binary random variable Y; viewing the coherent photoetching system as a binary channel, wherein the X and the Y are respectively an input signal and an output signal of the binary channel; calculating probability pX when the X is equal to 1; calculating transfer probability pij between the X and the Y; calculating probability pY when the Y is equal to 1, and further calculating mutual information I (X; Y) between the X and the Y; taking the maximum value C-bar of the mutual information as the channel capacity; and calculating an image error theoretical lower limit of the coherent photoetching system according to the channel capacity C-bar. By the method, a theoretical basis and a simulation basis can be provided for deeper understanding of an image information transmission mechanism and development of an advanced calculation photoetching technology in the photoetching system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
A Deep Learning Approach to Computational Lithography
ActiveCN110187609BReduce computational complexityImprove the efficiency of OPC optimizationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusAlgorithmUltraviolet
The invention discloses a deep learning method for computational lithography, which can improve the optimization speed and convergence performance of the traditional OPC method, and can be used for both deep ultraviolet DUV lithography and extreme ultraviolet EUV lithography. Firstly, the gradient iterative algorithm is expanded and its first steps are intercepted, combined with the imaging model of the lithography system and the photoresist model, a forward model-driven convolutional neural network MCNN, namely the encoder, is created. Create a decoder corresponding to the encoder, connect the output of the MCNN to the input of the decoder, use a certain distance between the input of the MCNN and the output of the decoder as a cost function, and train the parameters of the MCNN. The training set samples are input into MCNN, and the parameters in MCNN are optimized to minimize the error between the input of MCNN and the output of the decoder. After the training is completed, the MCNN is separated from the decoder, and the OPC mask graphics corresponding to other circuit layouts can be obtained by using the MCNN.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Methods and patterning devices and apparatuses for measuring focus performance of a lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method
PendingCN113260926APhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusEngineeringMaterials science
Disclosed is a method for selecting a structure for focus monitoring. The method comprises: simulating a Bossung response with focus of a focus dependent parameter, for one or more different structures; and selecting a structure for focus monitoring in a manufacturing process based on the results of said simulating step. The simulating step may be performed using a computational lithography simulation.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
A Computational Lithography Method Based on Model-Driven Convolutional Neural Networks
ActiveCN108535952BImprove image qualityReduce computational complexityPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a computational lithography method for a model-driven convolution neural network (MCNN), and the method can improve the computation speed and convergence performance of OPC (optical proximity correction) method. The technical scheme includes: expanding and truncating the gradient iterative algorithm, and constructing a model-driven convolution neural network (MCNN); based on an imaging model of a lithography system, constructing a decoder corresponding to the MCNN; bringing the MCNN and the decoder to end-to-end connection, and subjecting the MCNN to the following training: optimizing the parameters of the MCNN by back propagation algorithm to minimize the error between the input data of MCNN and the decoder; separating the decoder from the MCNN at the end of the training; inputting a to-be-optimized circuit layout into the trained MCNN so as to obtain an estimated result of an OPC mask; taking the estimated result of OPC mask as the initial value, and carryingout iterative updating on the set number of times of the mask by gradient iterative algorithm, thus obtaining the final OPC mask optimization result.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
A Neural Network-Based Correction Method for Electron Beam Proximity Effect
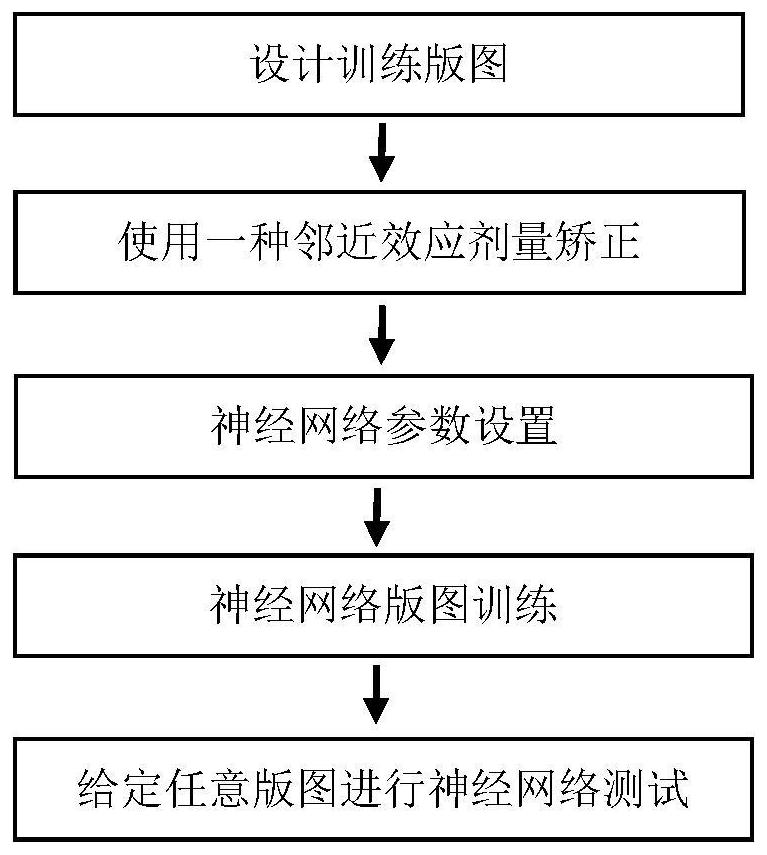
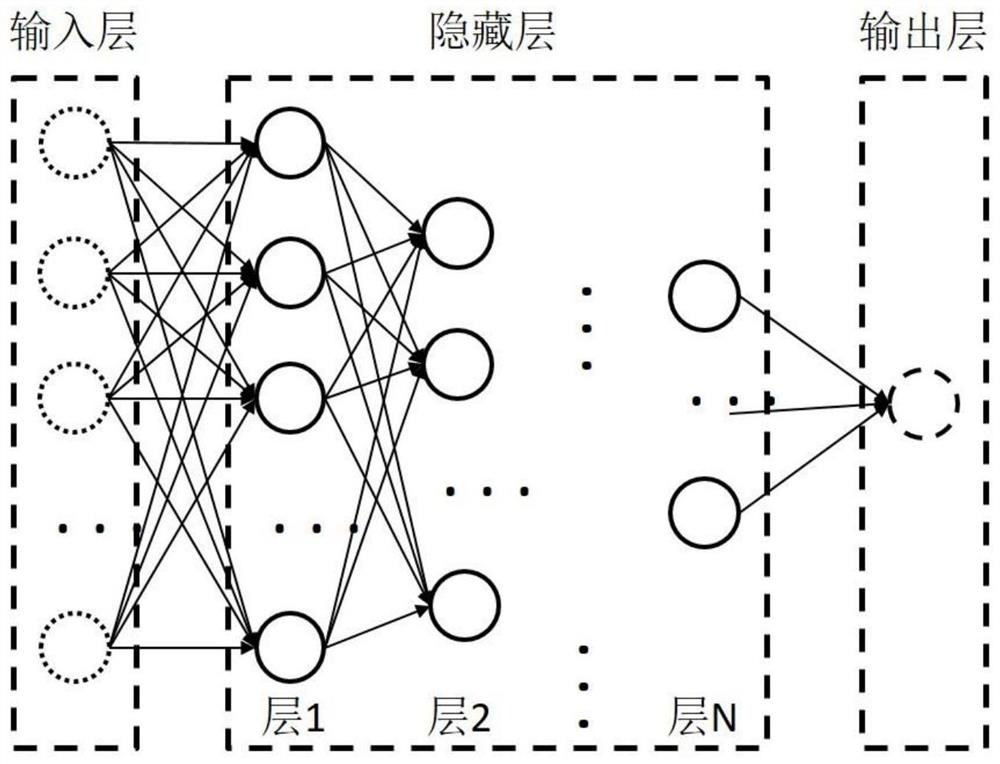
ActiveCN111538213BHigh precisionImprove efficiencyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusAlgorithmSimulation
The invention belongs to the field of computational lithography, and discloses a method for correcting the proximity effect of an electron beam based on a neural network. The present invention first corrects the dose of the designed training layout through any kind of proximity effect dose correction method, then adjusts the neural network parameters, and performs neural network training on the training layout according to the prescribed input method to obtain an adaptive neural network. Network, and finally predict the correction dose of any exposure layout according to the specified input method. The invention realizes the correction of the proximity effect of the electron beam based on the neural network, and solves the correction calculation of the proximity effect of the electron beam exposure. On the basis of ensuring high-precision correction, the calculation efficiency of the correction is greatly improved, and it has high calculation accuracy and high calculation efficiency. Efficiency and other characteristics.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com