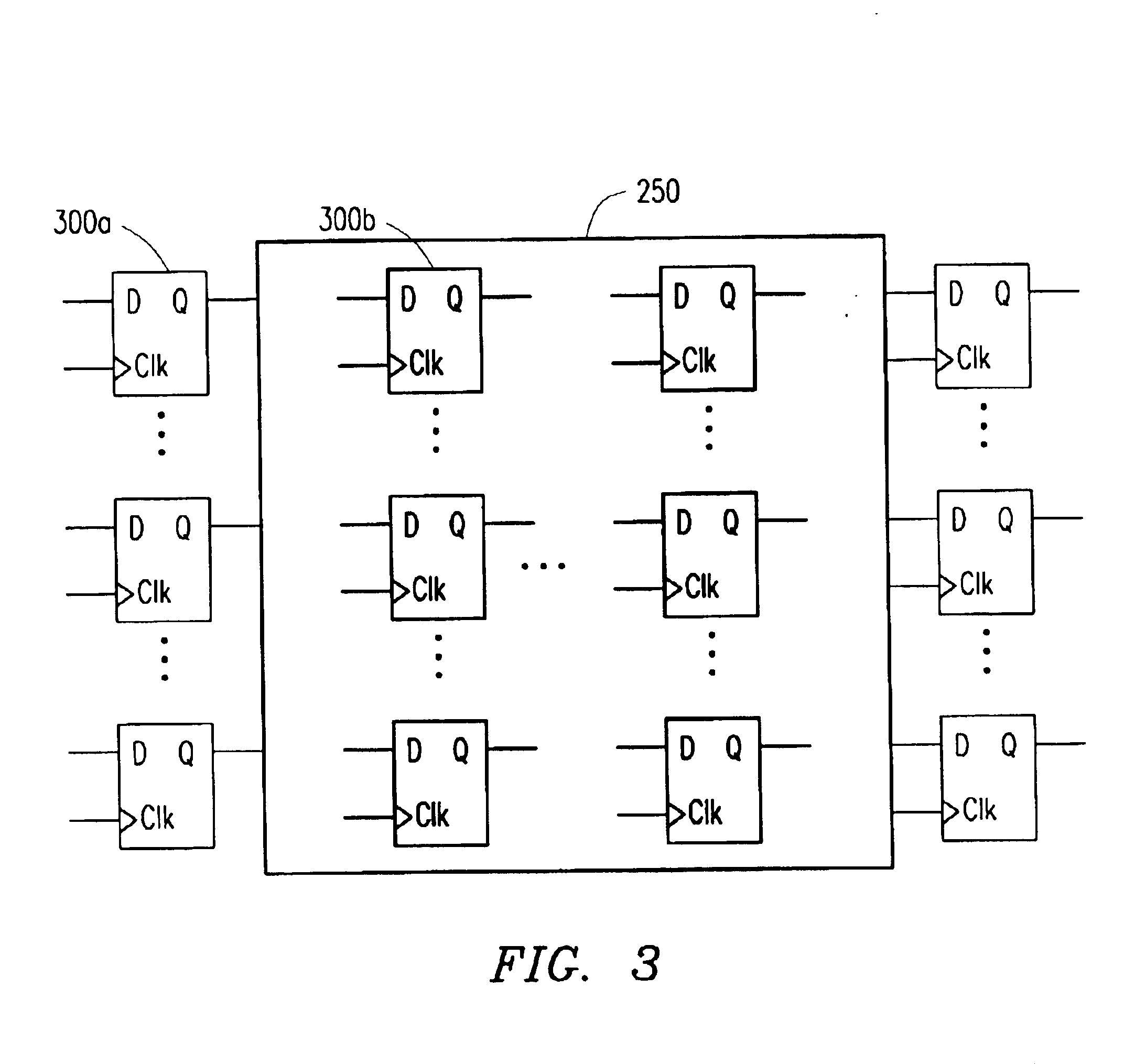
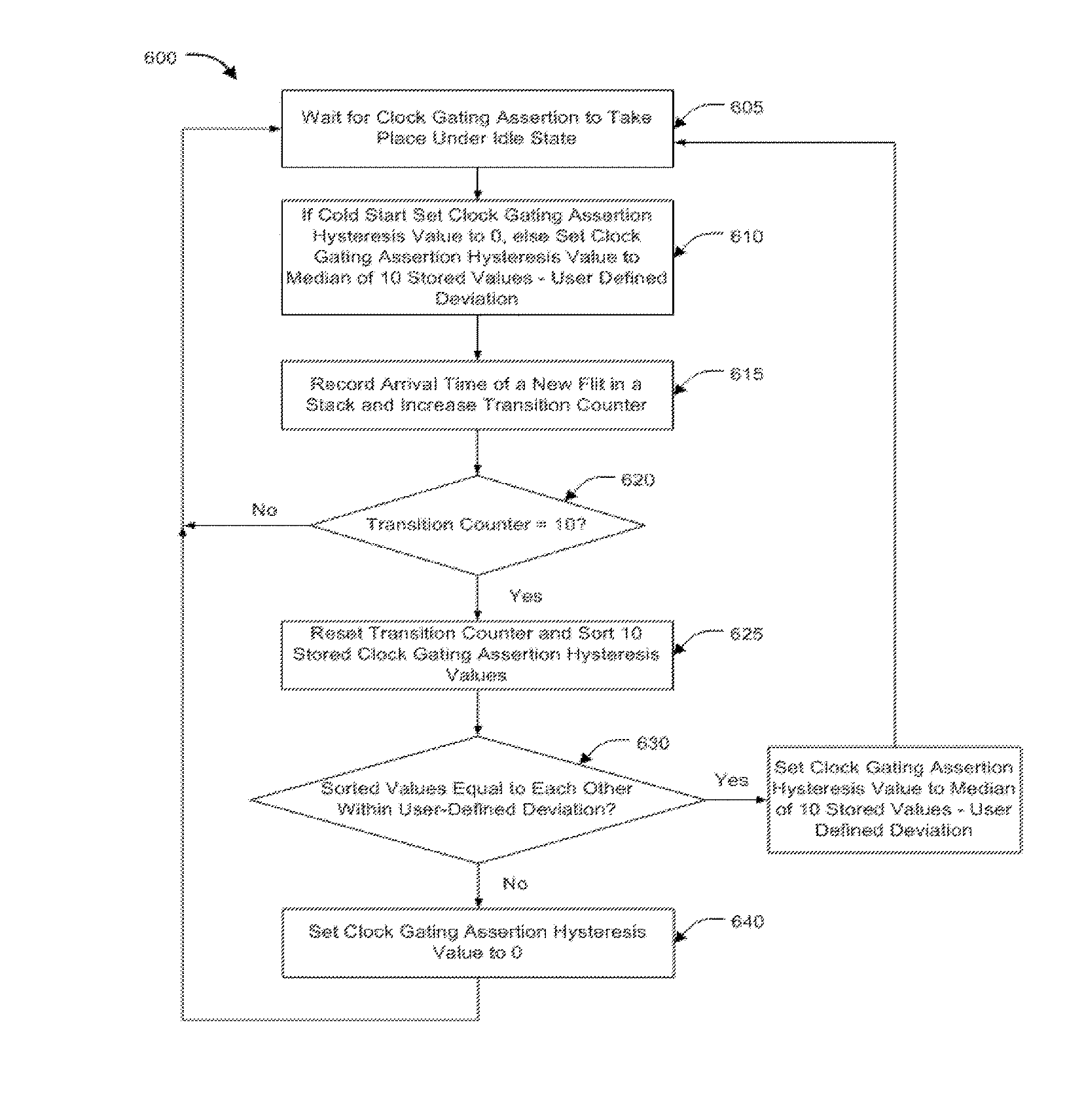
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
605 results about "Clock gating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
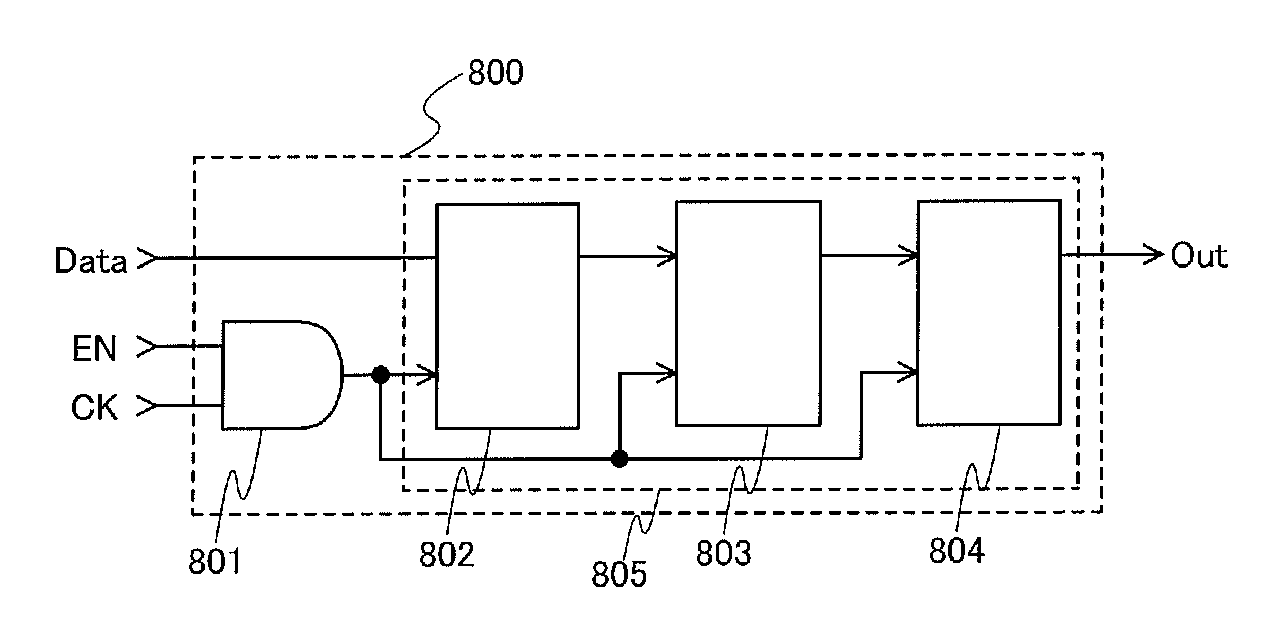
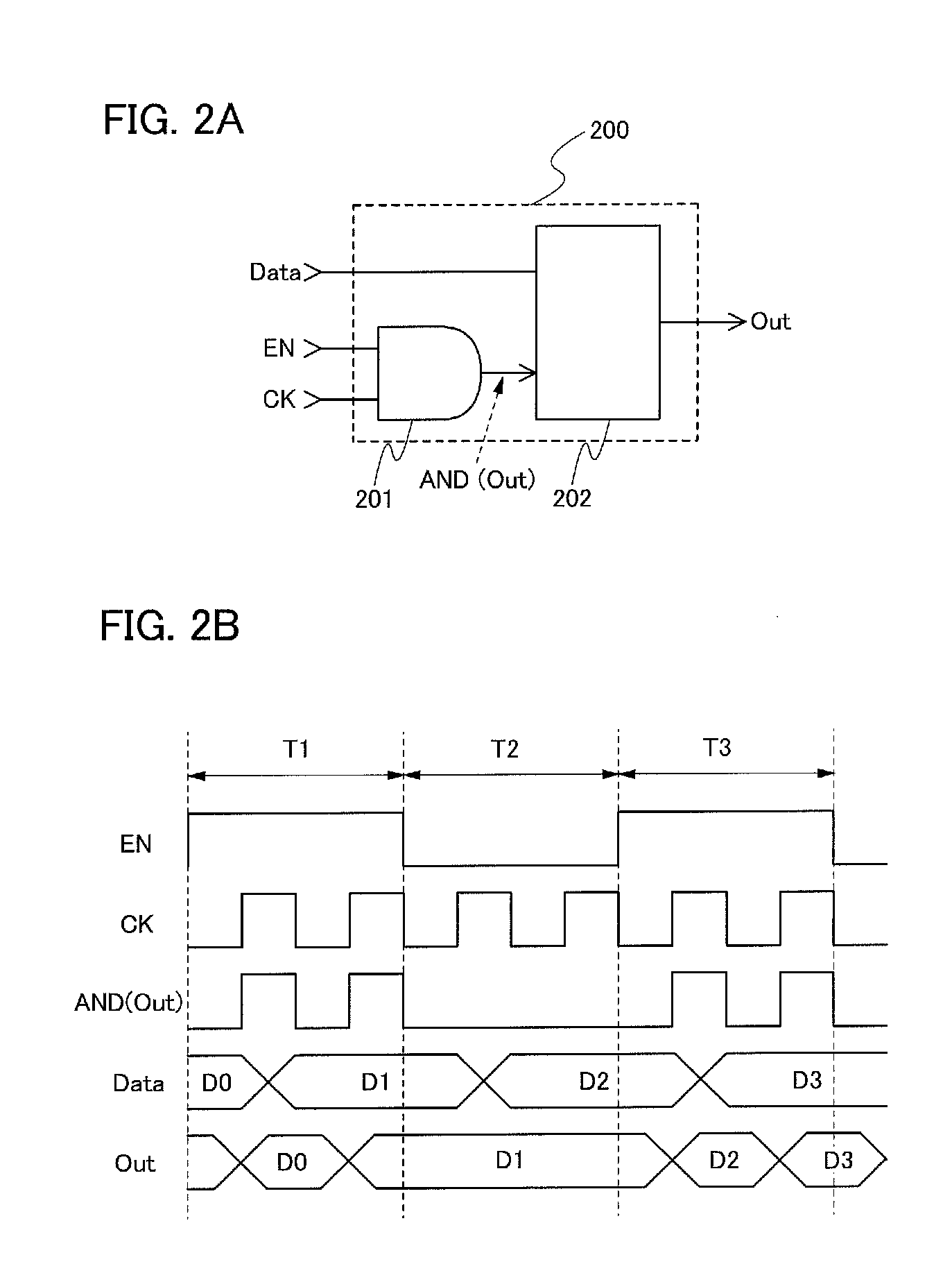
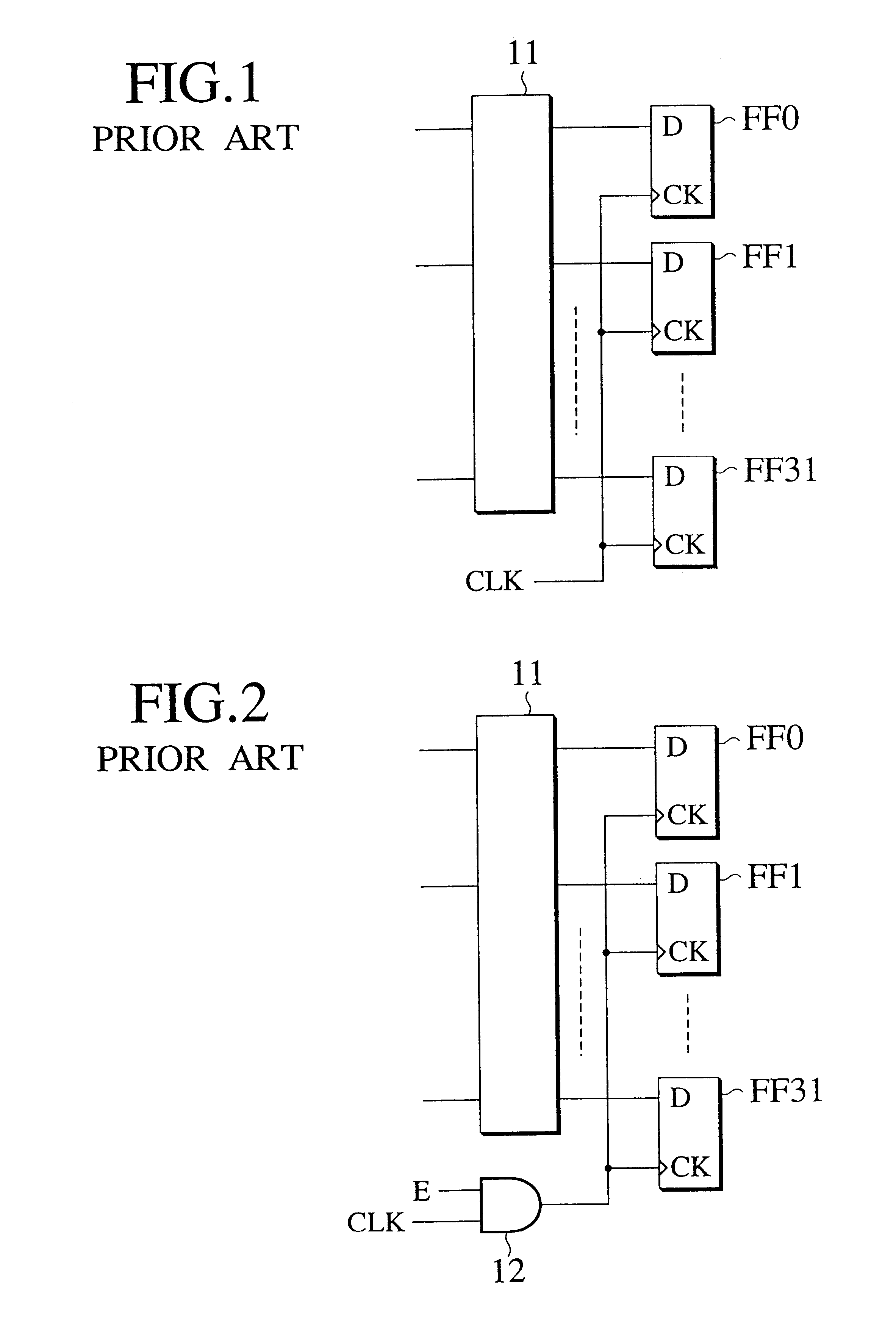
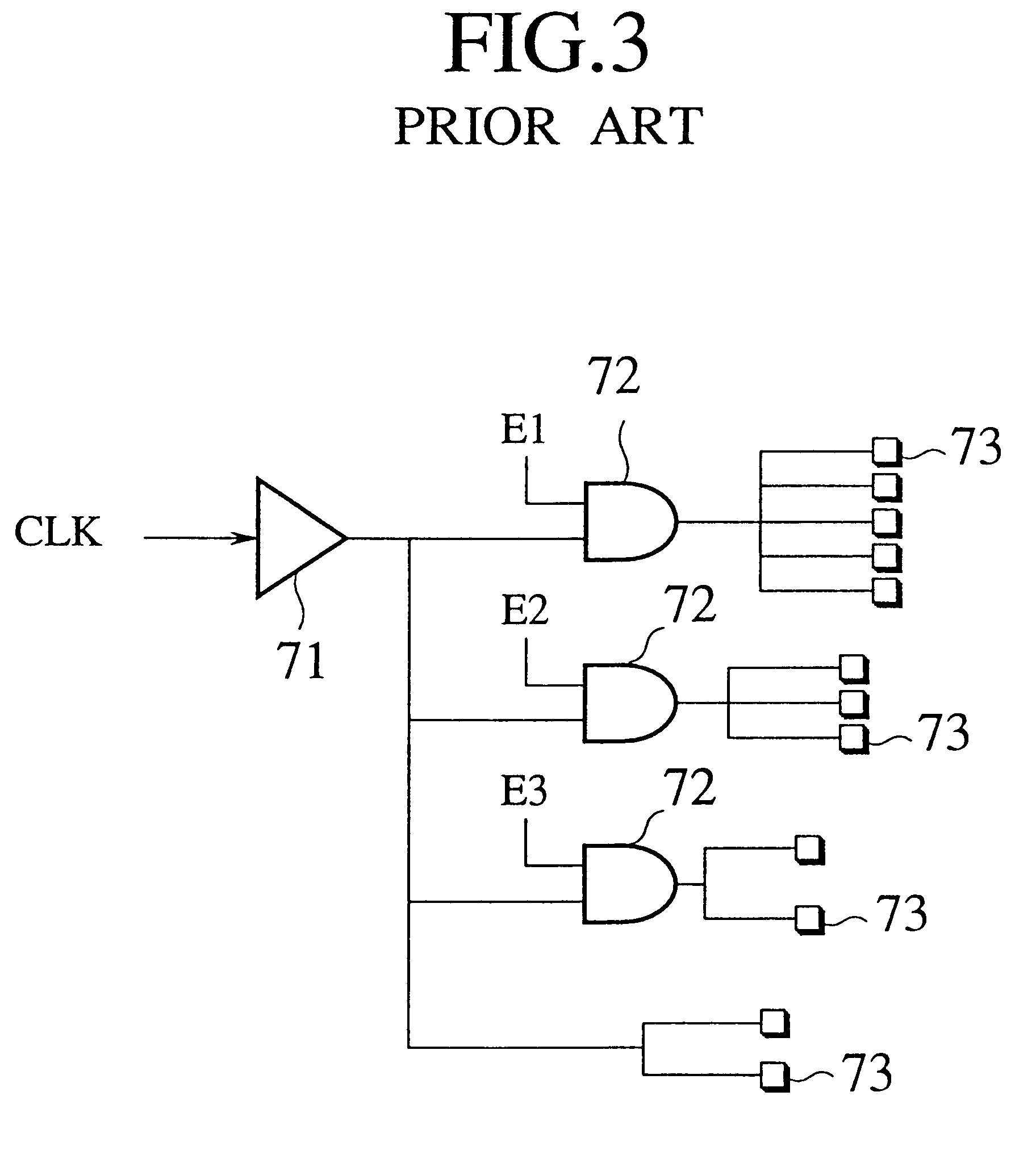
Clock gating is a popular technique used in many synchronous circuits for reducing dynamic power dissipation. Clock gating saves power by adding more logic to a circuit to prune the clock tree. Pruning the clock disables portions of the circuitry so that the flip-flops in them do not have to switch states. Switching states consumes power. When not being switched, the switching power consumption goes to zero, and only leakage currents are incurred.
Logic circuit and semiconductor device
ActiveUS8207756B2Reduce dynamic power consumptionLeakage of highTransistorPower reduction by control/clock signalHydrogen concentrationPower semiconductor device
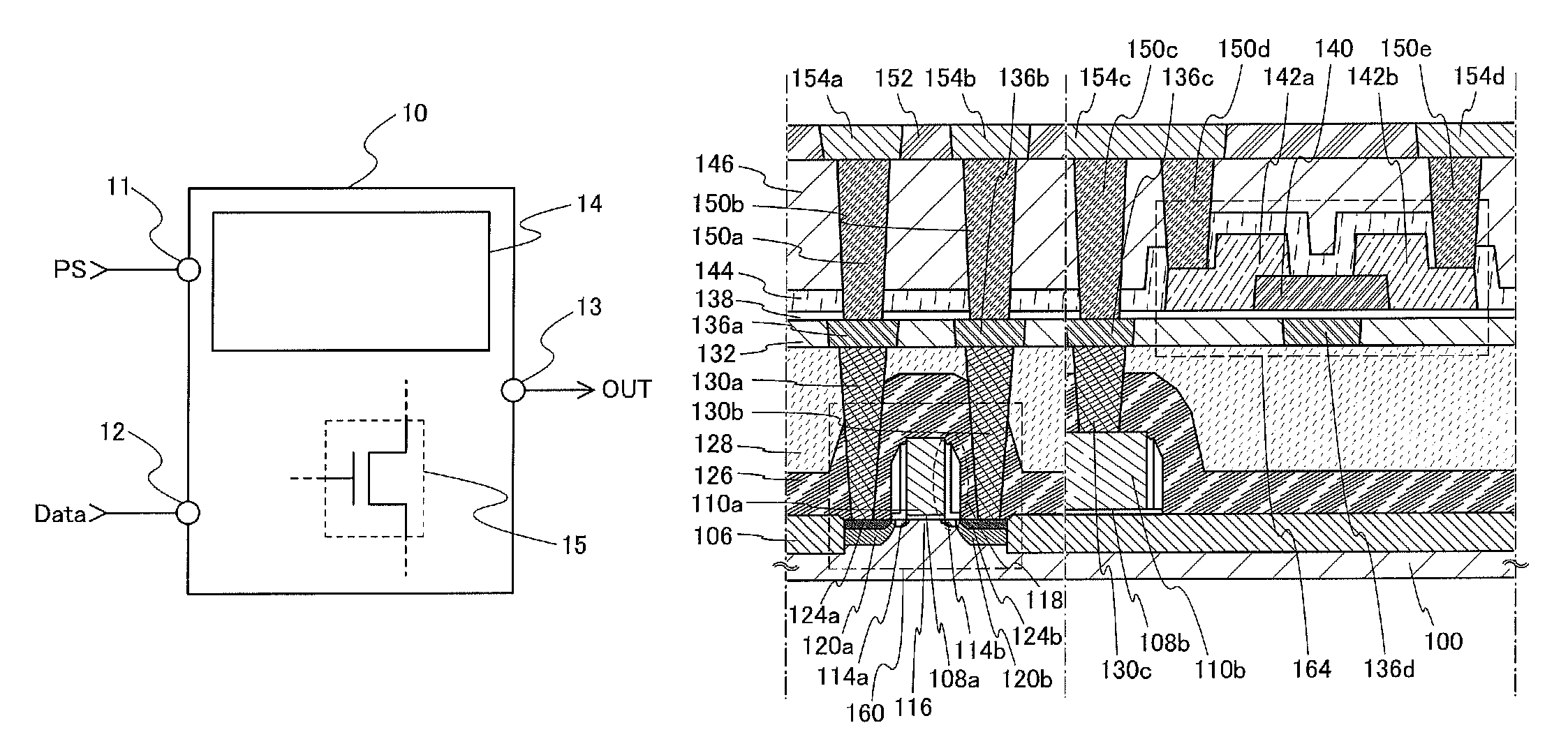
In a logic circuit where clock gating is performed, the standby power is reduced or malfunction is suppressed. The logic circuit includes a transistor which is in an off state where a potential difference exists between a source terminal and a drain terminal over a period during which a clock signal is not supplied. A channel formation region of the transistor is formed using an oxide semiconductor in which the hydrogen concentration is reduced. Specifically, the hydrogen concentration of the oxide semiconductor is 5×1019 (atoms / cm3) or lower. Thus, leakage current of the transistor can be reduced. As a result, in the logic circuit, reduction in standby power and suppression of malfunction can be achieved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Function based dynamic power control
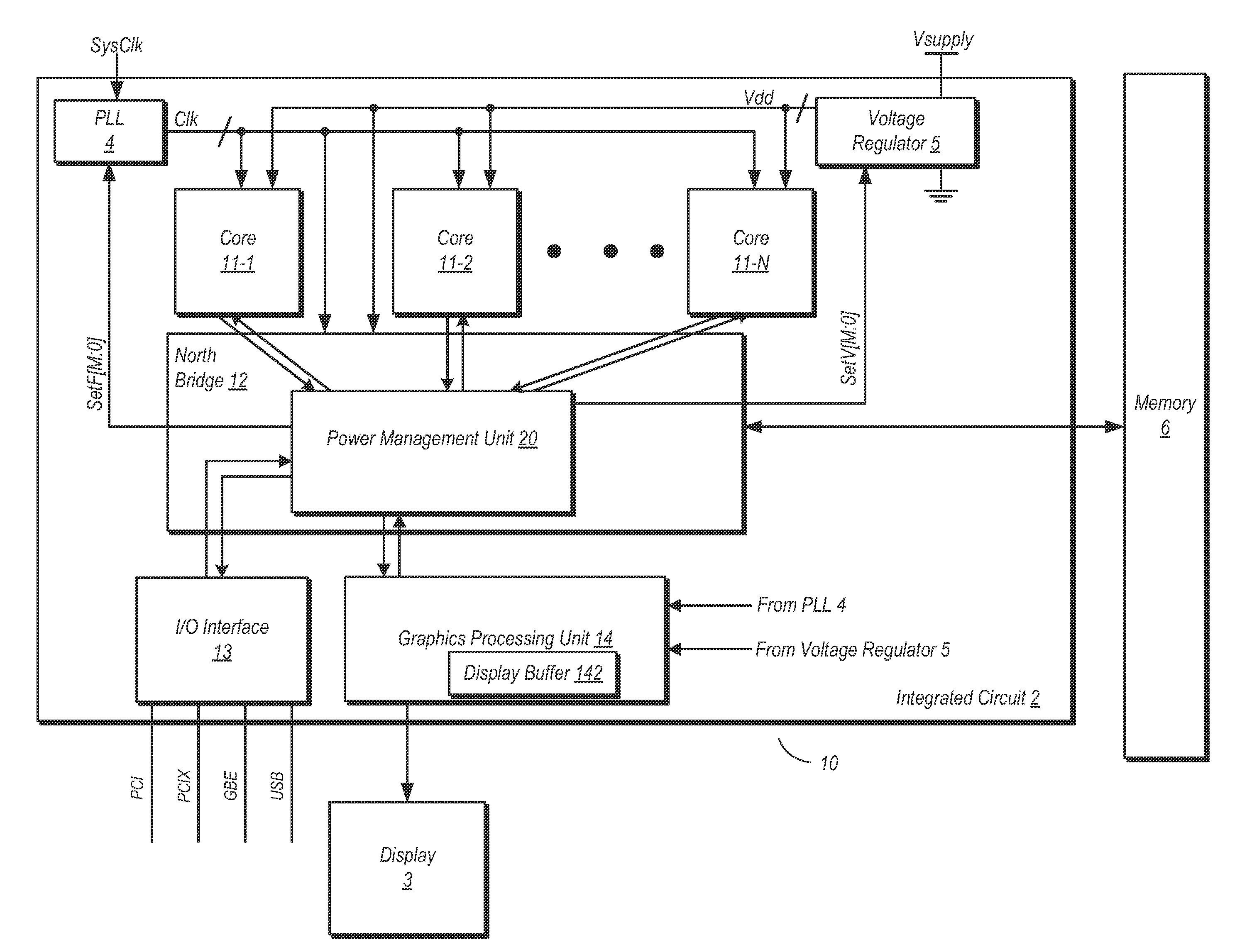
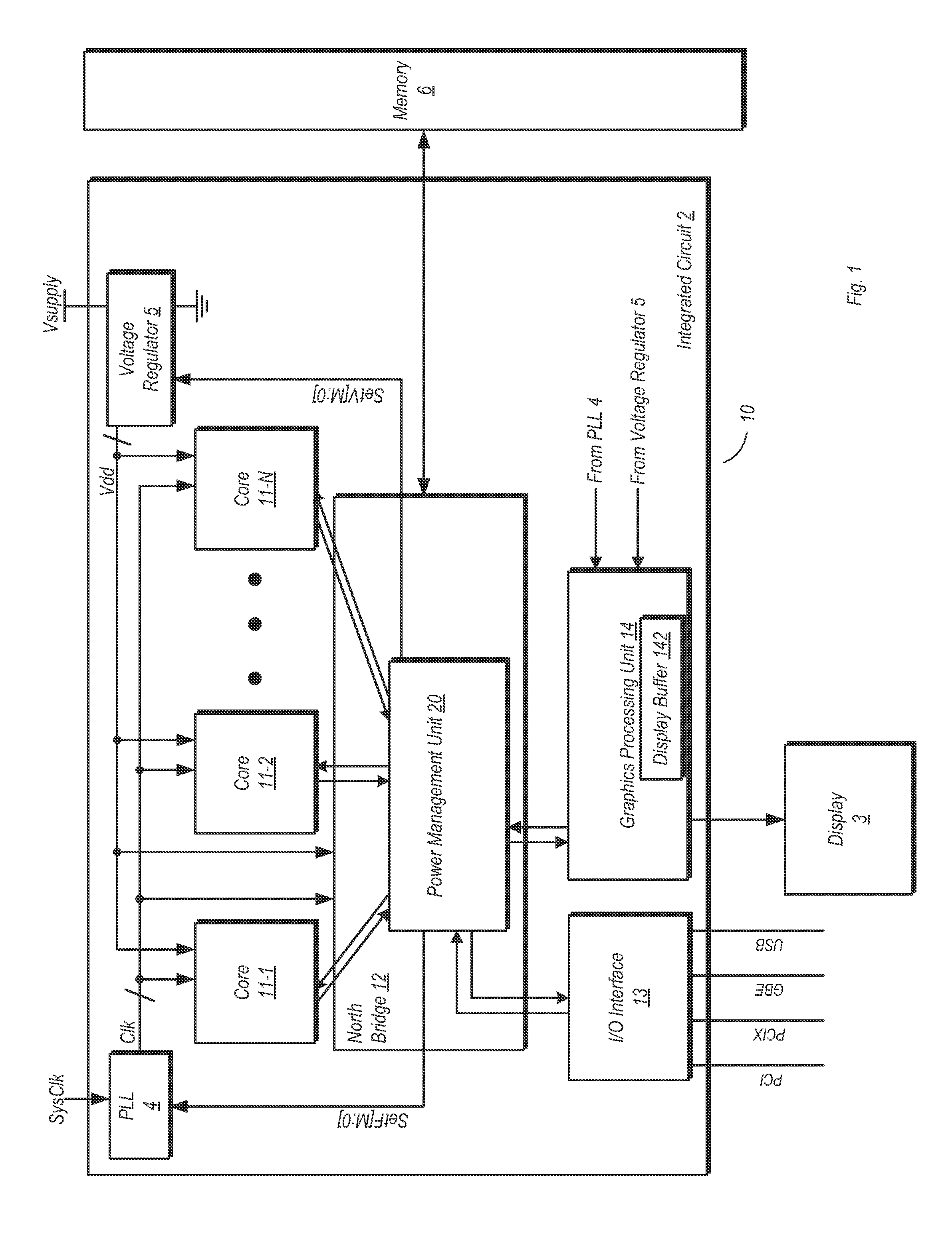
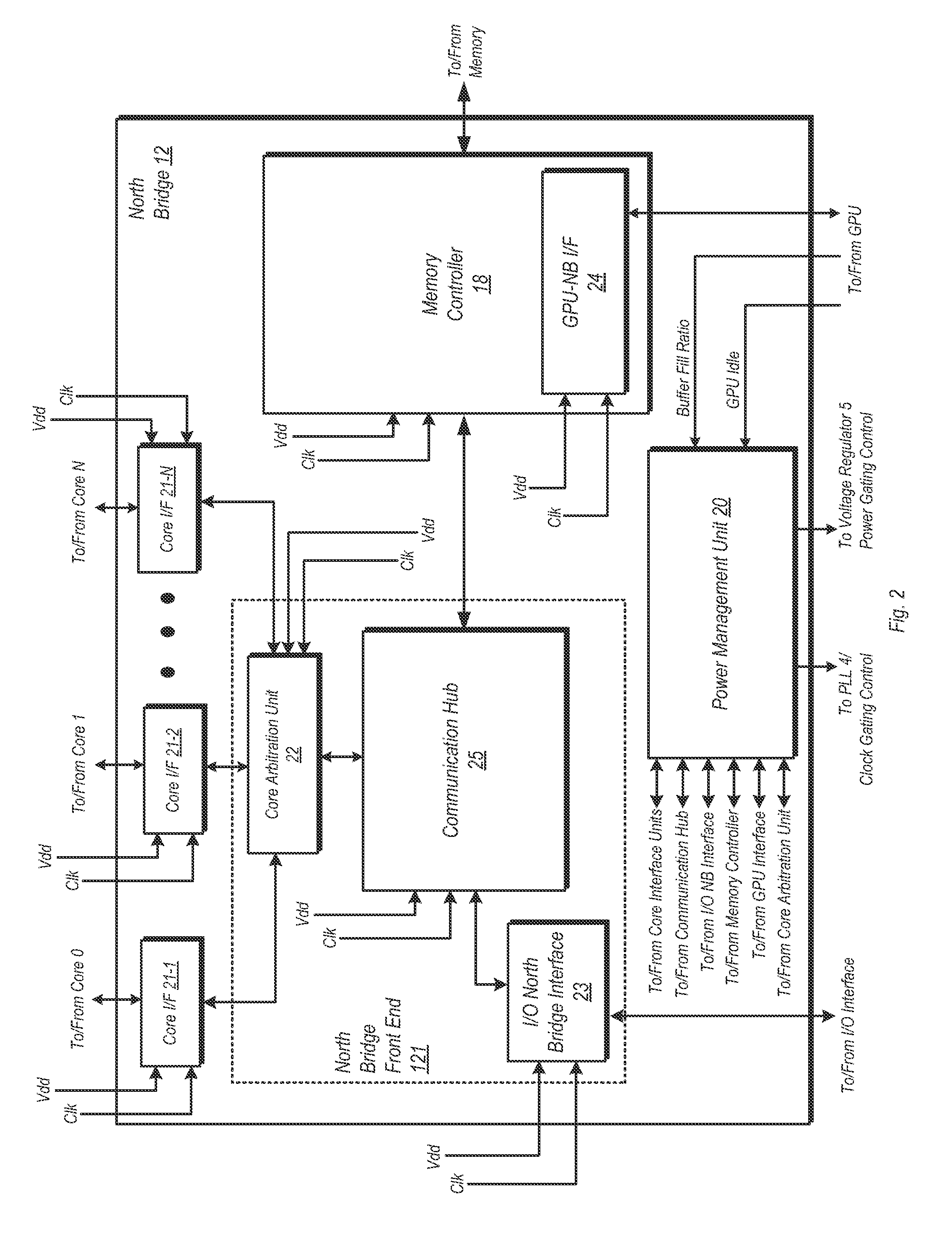
ActiveUS20120102344A1Energy efficient ICTGenerating/distributing signalsPower Management UnitMemory controller
A system and method for dynamic function based power control is disclosed. In one embodiment, a system includes a bridge unit having a memory controller and a communication hub coupled to the memory controller. The system further includes a power management unit, wherein the power management unit is configured to clock-gate the communication hub responsive to determining that each of a plurality of processor cores are in an idle state and that an I / O interface unit has been idle for an amount of time exceeding a first threshold. The power management unit is further configured to clock-gate the memory controller responsive to clock-gating the communication hub and determining that a memory coupled to the memory controller is in a first low power state. The power management unit may also perform power-gating of functional units subsequent to clock-gating the same.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Programmable output interface for lower level open system interconnection architecture
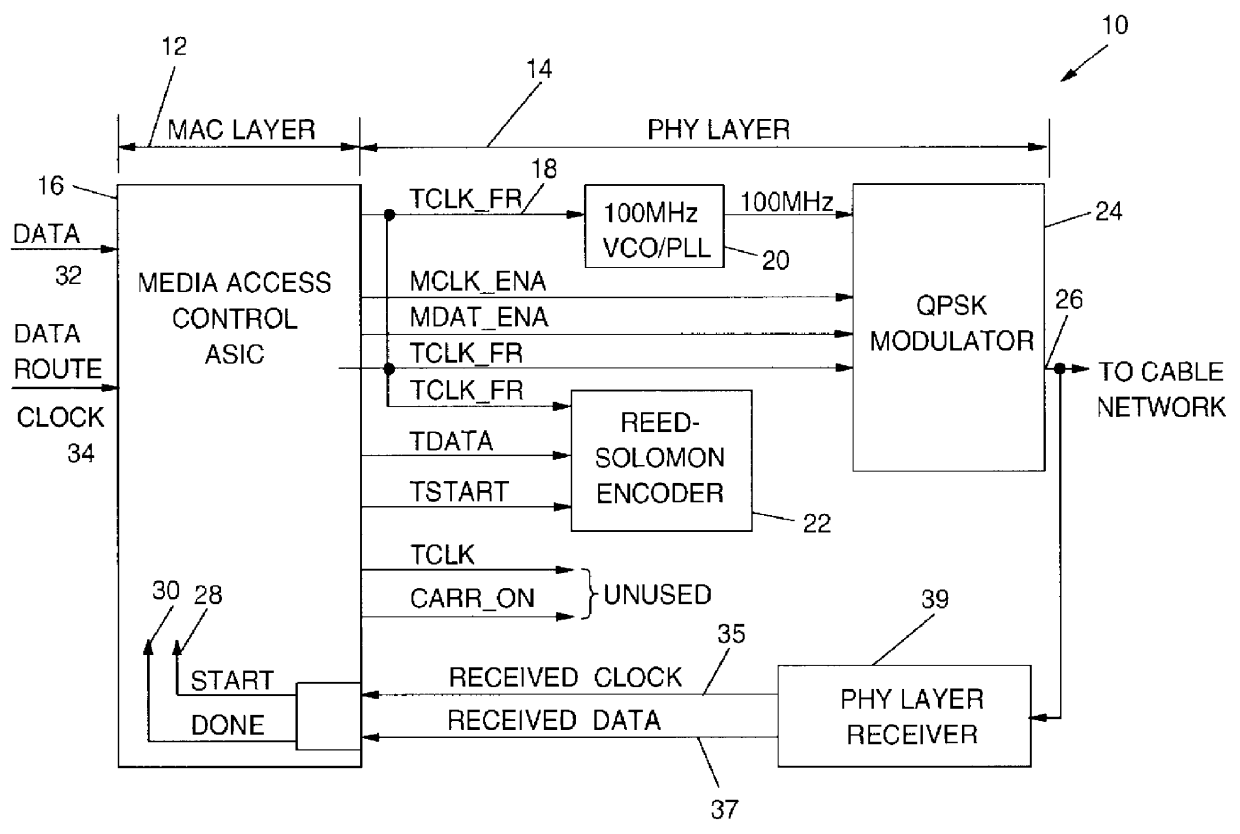
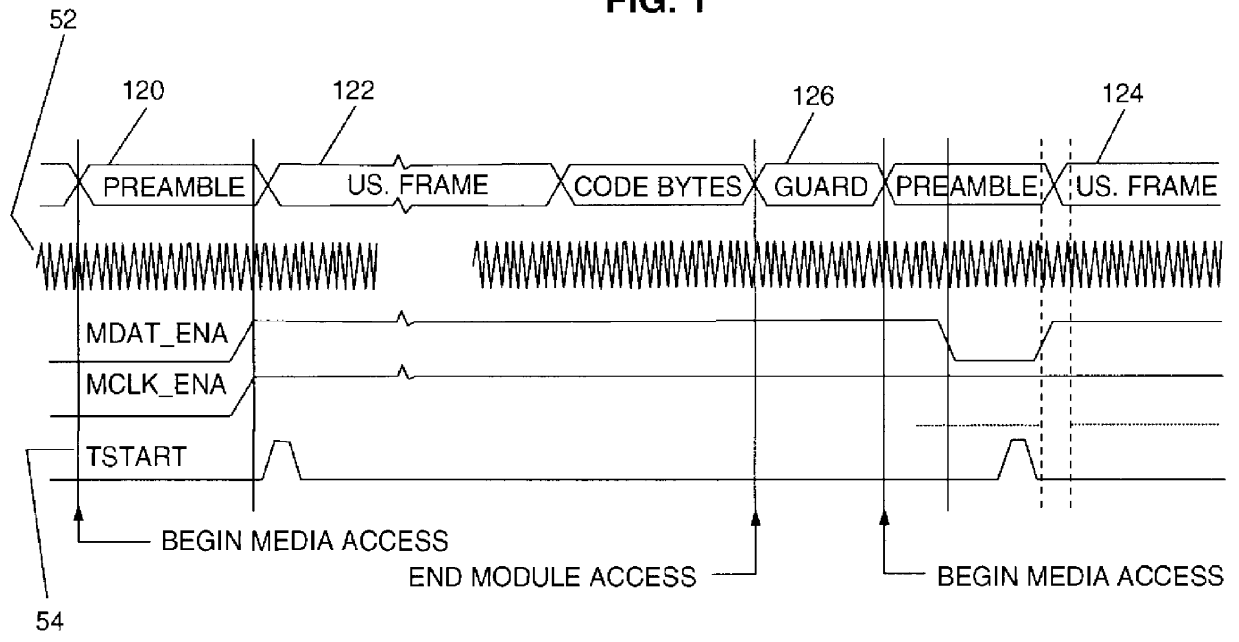
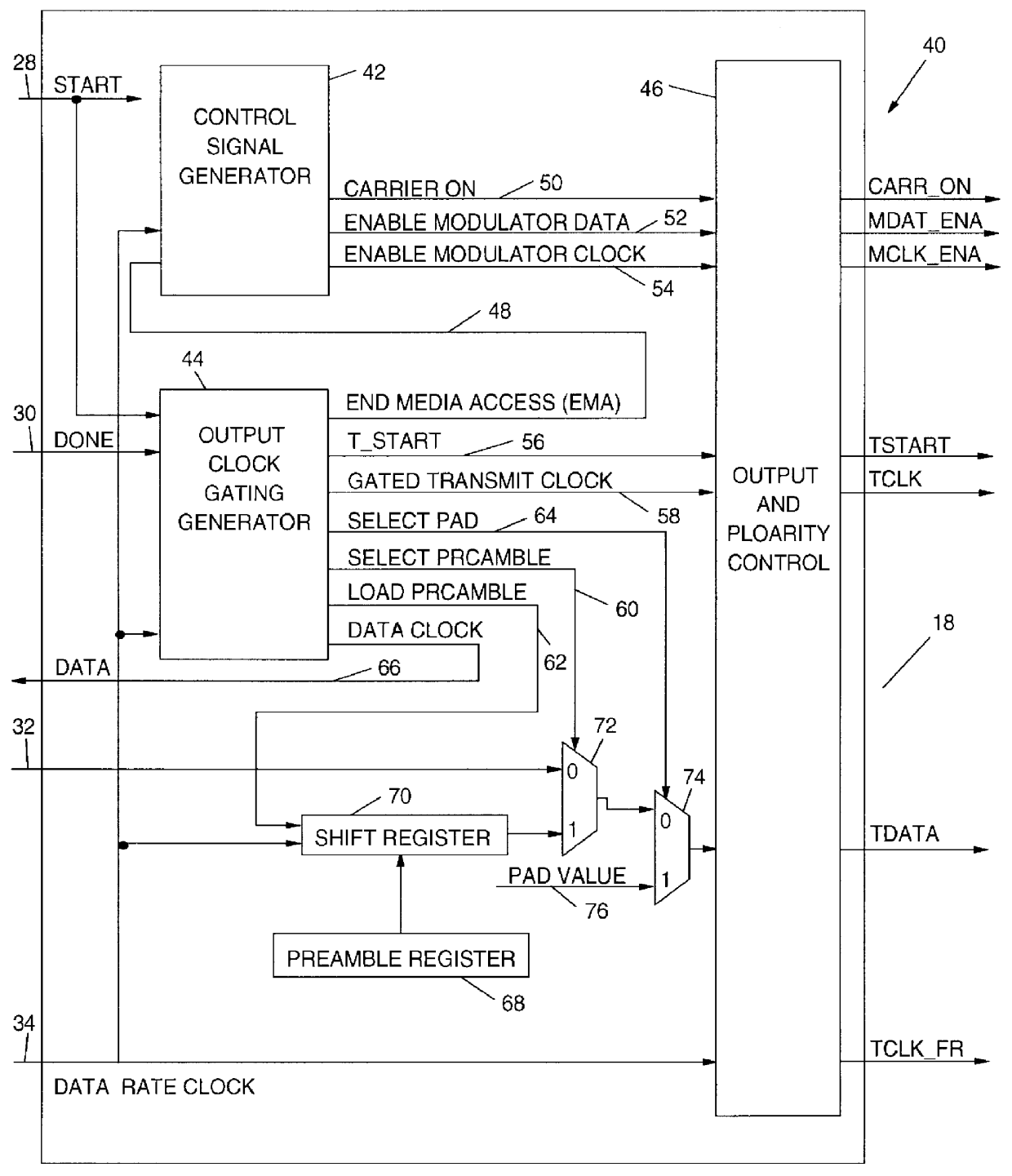
InactiveUS6049837ABroadband local area networksMultiple digital computer combinationsControl signalData rate
A programmable output interface in an Open System Interconnection (OSI) enables a Media Access (MAC) Layer to access a variety of Physical (PHY) Layer implementations without redesign of the interface. The programmable interface includes a control signal generator; an output clock gating generator, and an output polarity control device coupled to the PHY layer. The interface receives media access Start; media access Done signals; a Data Rate clock signal and a data signal. The control signal generator provides control signals for the physical layer components via the polarity control device. The active signal polarity and the relative timing of the control signals are controlled by programmable registers. The output clock gating generator provides clock signals to the physical layer components via the polarity control in response to the Start; Done and Data Rate signals. The output generator clock includes programmable interval registers for the various frame intervals including a User Pause Interval (UPI); Preamble Interval (PI); User Send Interval (USI), etc. The polarity control provides the correct signal polarity for each control, clock, and data signal.
Owner:IBM CORP
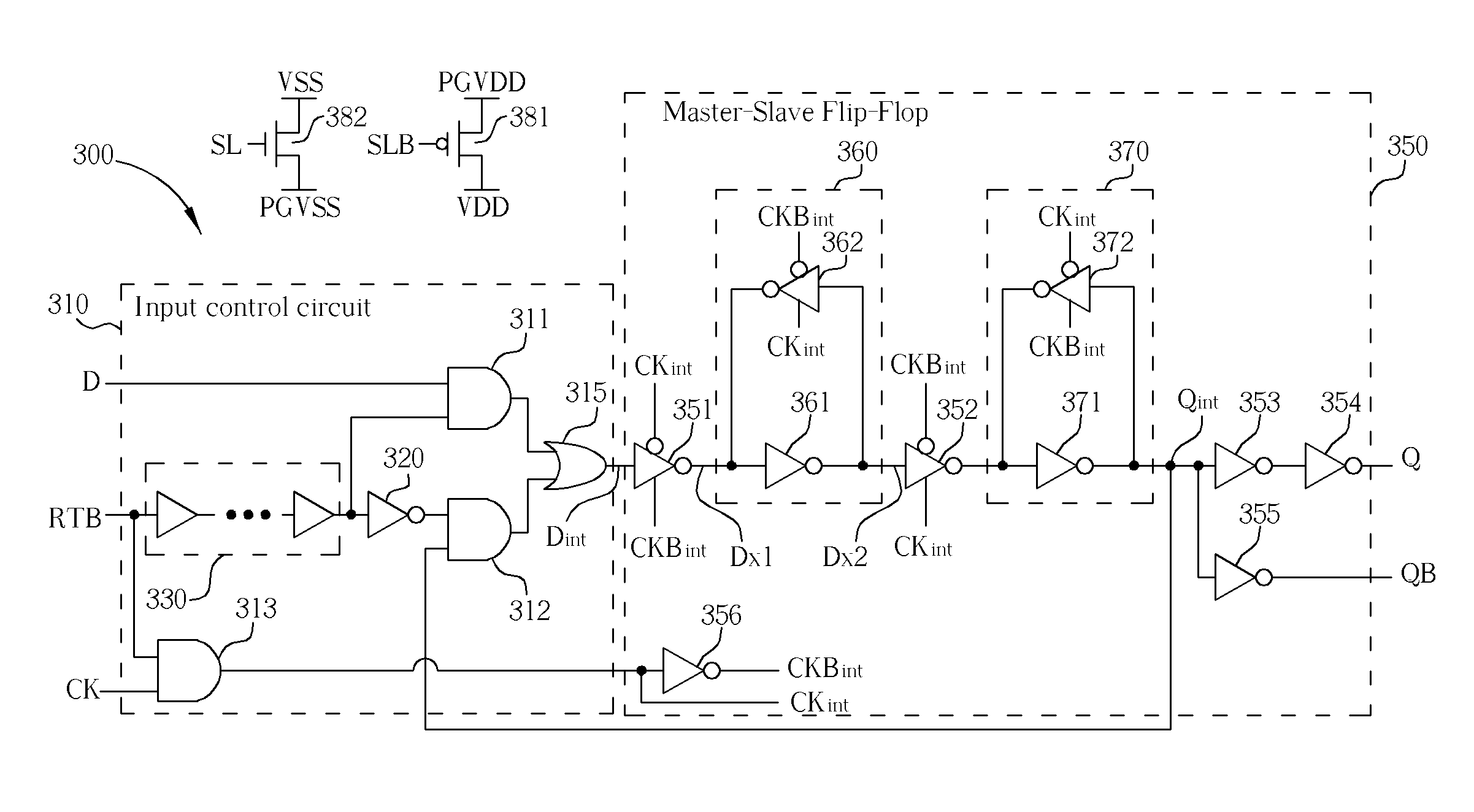
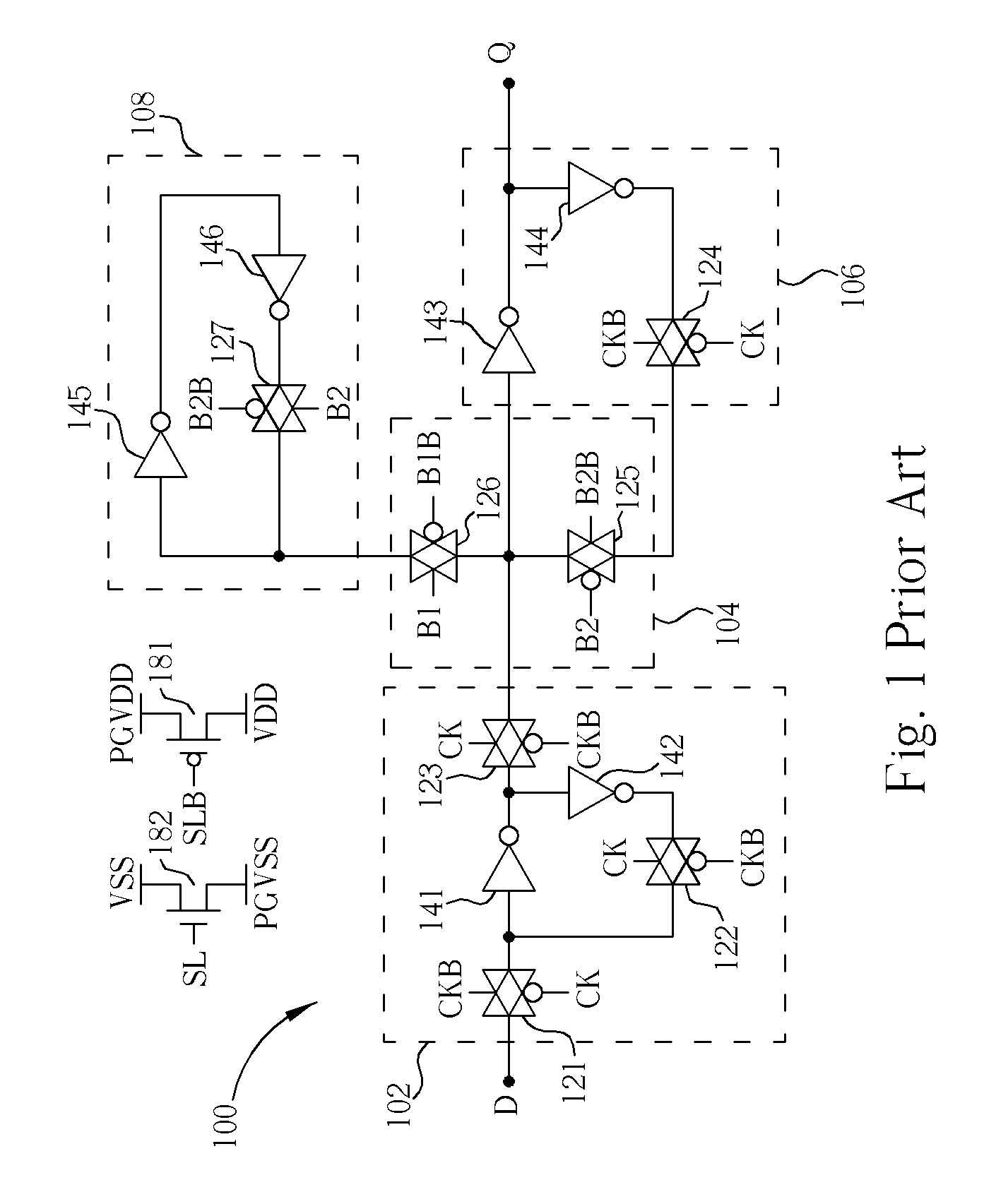
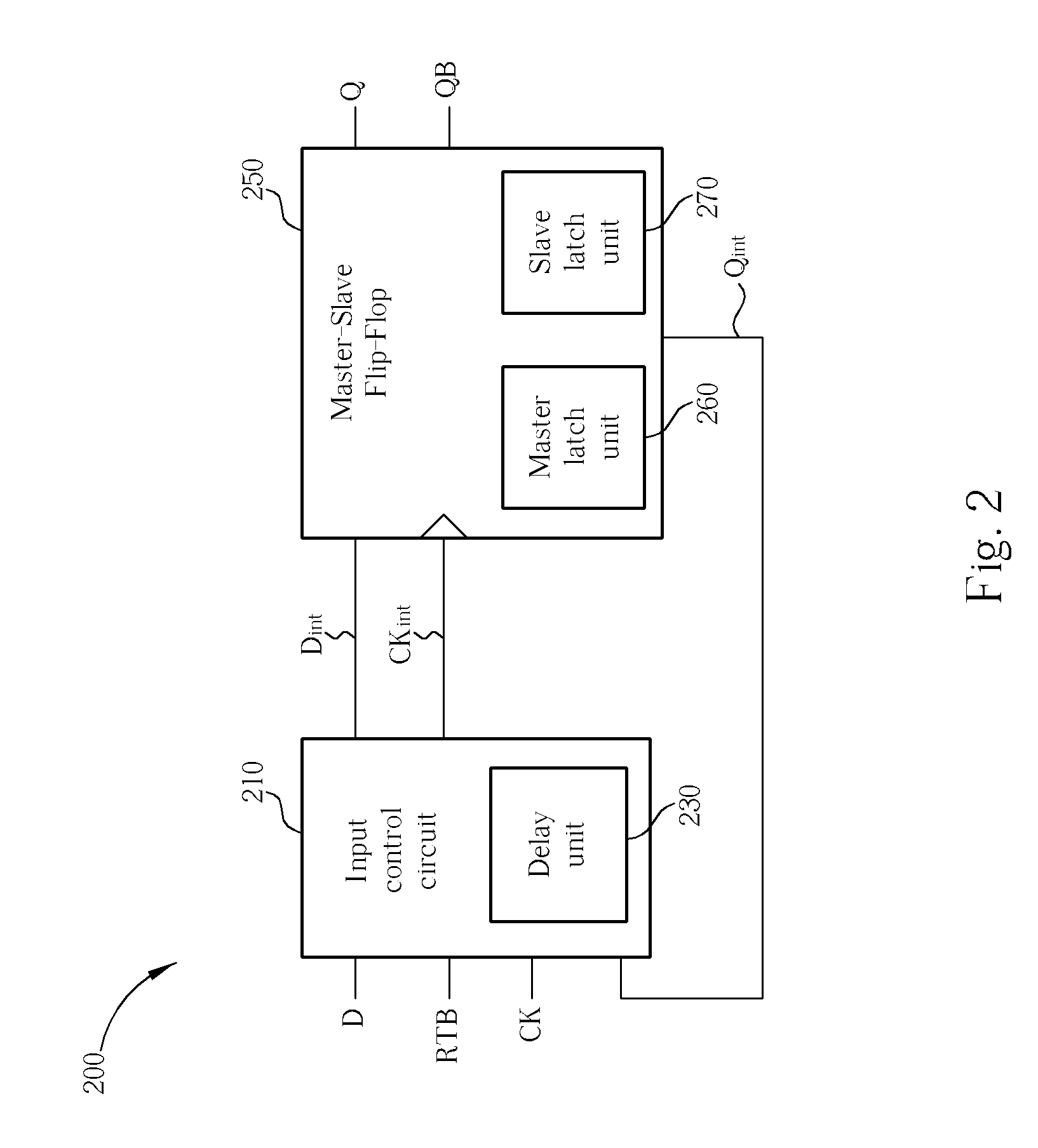
Data retention cell and data retention method based on clock-gating and feedback mechanism
ActiveUS7391250B1Logic circuits characterised by logic functionDigital storageInput controlData signal
For retaining an output data signal of a data retention cell in a power-saving mode, a slave latch unit of the data retention cell is powered with a real power for preserving the output data signal. The output data signal is furnished backward to an input control circuit of the data retention cell. The data signal furnished to a master latch unit of the data retention cell is controlled to switch between an input data signal and the output data signal by the input control circuit in response to a retention signal. The switching of the data signal for refreshing the master latch unit is delayed by a delay unit of the input control circuit, which functions to make sure that the data-preserving process is properly operated on any transition from the power-saving mode to a power-active mode.
Owner:MARLIN SEMICON LTD
Logic circuit and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110102018A1Reduce hydrogen concentrationTotal current dropTransistorPower reduction by control/clock signalHydrogen concentrationPower semiconductor device
In a logic circuit where clock gating is performed, the standby power is reduced or malfunction is suppressed. The logic circuit includes a transistor which is in an off state where a potential difference exists between a source terminal and a drain terminal over a period during which a clock signal is not supplied. A channel formation region of the transistor is formed using an oxide semiconductor in which the hydrogen concentration is reduced. Specifically, the hydrogen concentration of the oxide semiconductor is 5x1019 (atoms / cm3) or lower. Thus, leakage current of the transistor can be reduced. As a result, in the logic circuit, reduction in standby power and suppression of malfunction can be achieved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Low-power clock gating circuit
InactiveUS7576582B2Reduce power consumptionElectric pulse generatorMulti-threshold CMOSDrain current
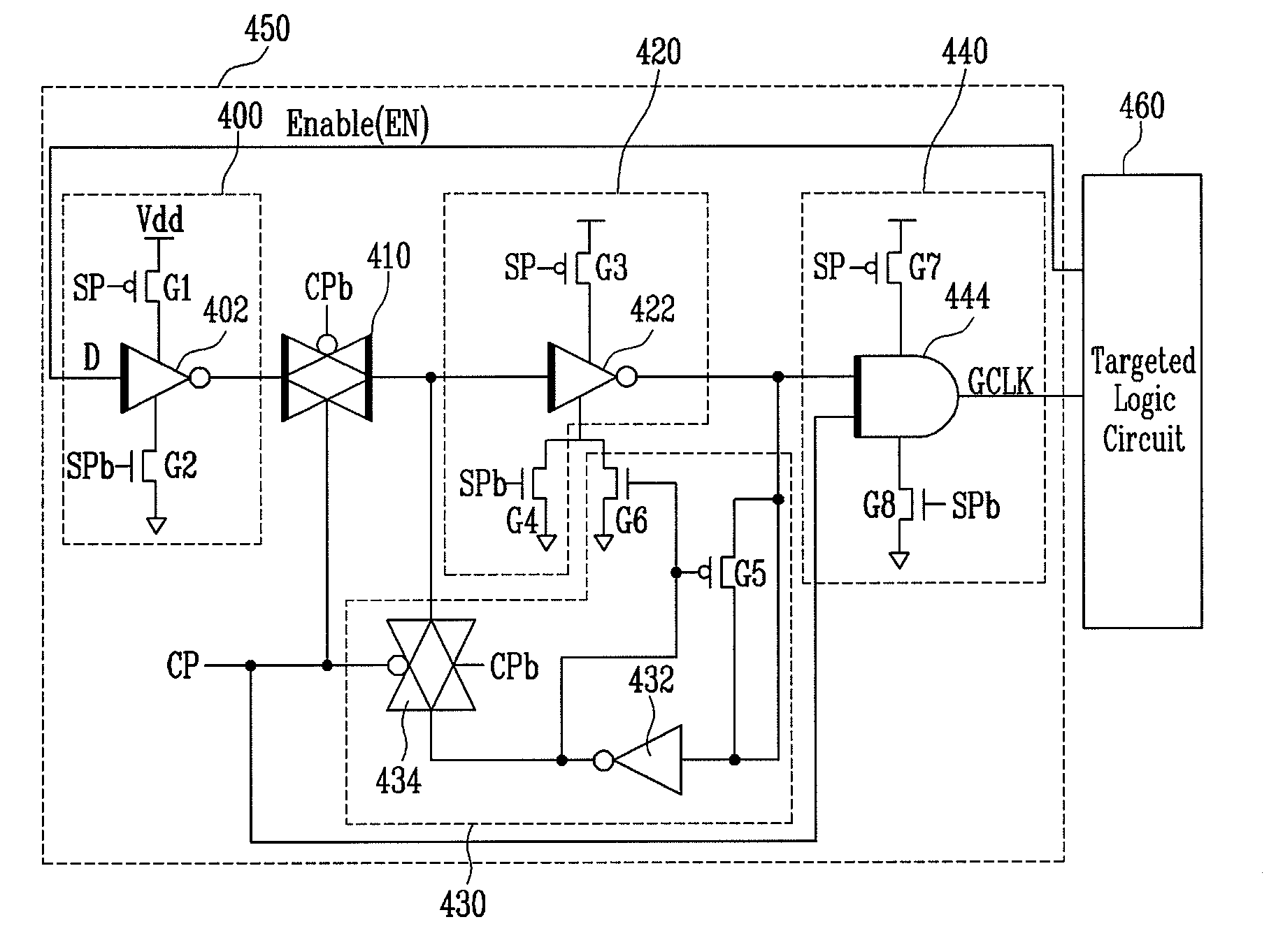
Provided is a low-power clock gating circuit using a Multi-Threshold CMOS (MTCMOS) technique. The low-power clock gating circuit includes a latch circuit of an input stage and an AND gate circuit of an output stage, in which power consumption caused by leakage current in the clock gating circuit is reduced in a sleep mode, and supply of a clock to a unused device of a targeted logic circuit is prevented by the control of a clock enable signal in an active mode, thereby reducing power consumption. The low-power clock gating circuit using an MTCMOS technique uses devices having a low threshold voltage and devices having a high threshold voltage, which makes it possible to implement a high-speed, low-power circuit, unlike a conventional clock gating circuit using a single threshold voltage.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
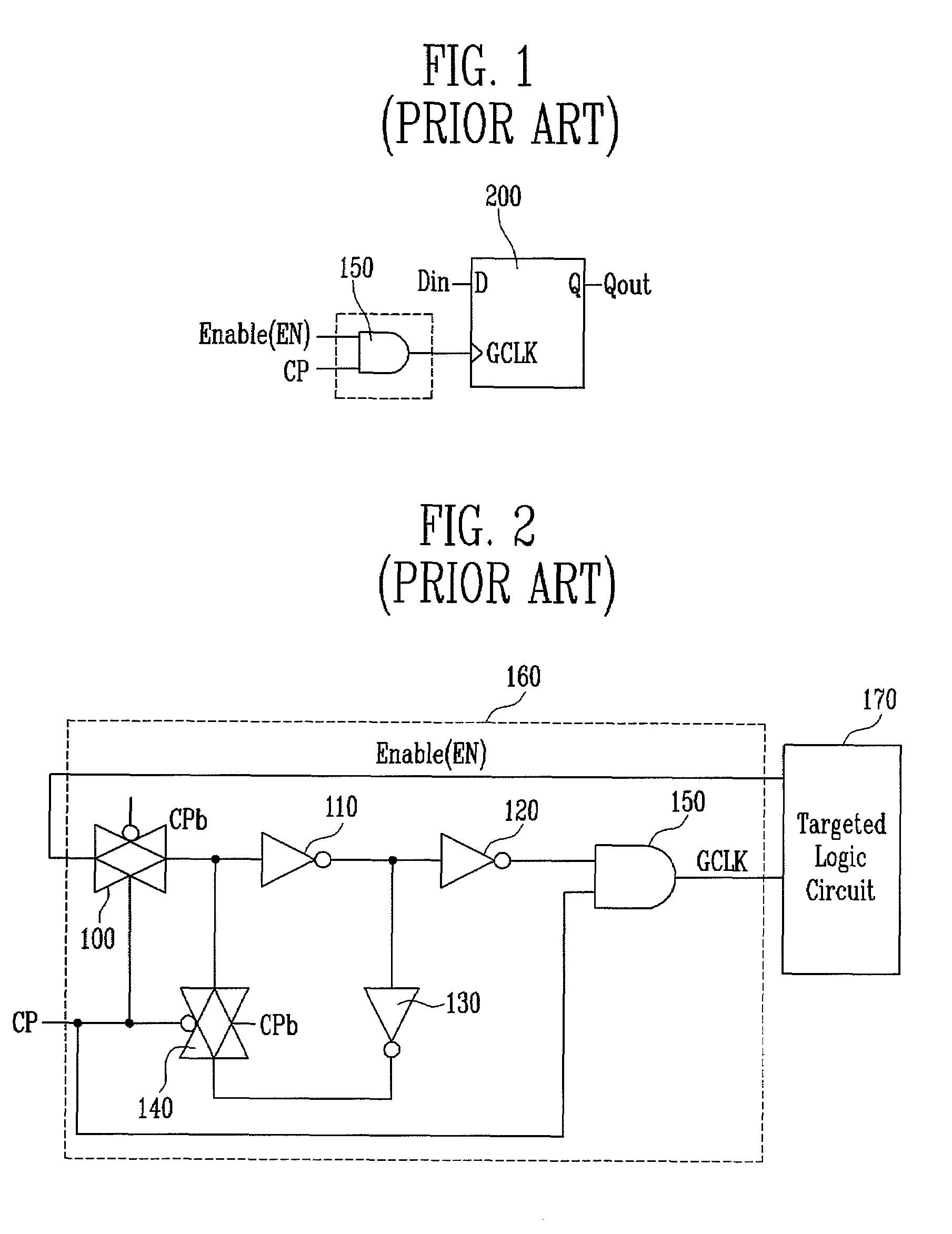
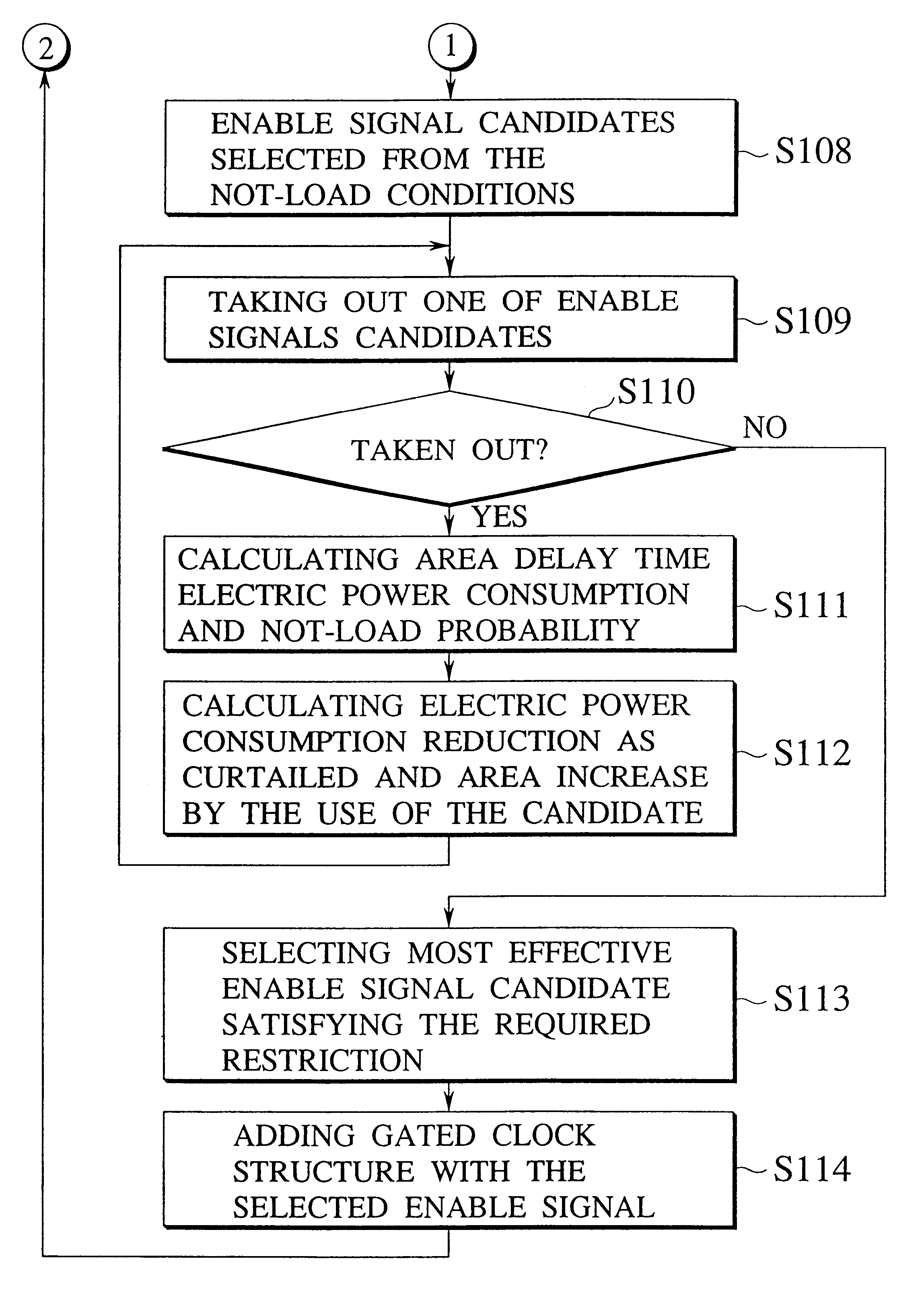
Method and apparatus for clock gated logic circuits to reduce electric power consumption
InactiveUS6272667B1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer Aided DesignDelayed time
A computer aided design technique for clock gated logic circuits effective to reduce the electric power consumption is disclosed. The computer aided design for clock gated logic circuits is conducted by extracting, by the use of information about a clock gated logic circuit under the design, a halt condition under which a clocked circuit driven by a clock signal can halt with no clock signal supplied, generating enable signal candidates, from said halt condition, which can be used as enable signals in the clock gated logic circuit, analyzing the clock gated logic circuit in order to obtain information about a delay time of signal transmission and electric power consumption reduction if respective one of enable signal candidates is used as an enable signal of a clock gating circuit inserted in the clock gated logic circuit under the design, storing enable signal candidate information including the result of the analysis conducted by said analysis step in a information store means, selecting an appropriate one of the enable signal candidates which satisfy given restrictions regarding a delay time of signal transmission in the clock gated logic circuit under the design, by the use of said enable signal candidate information; and adding the clock gating circuit activated with the enable signal as selected by said enable signal selection step to the clock gated logic circuit under the design.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Current-stabilizing switch power source with voltage ripple detection circuit
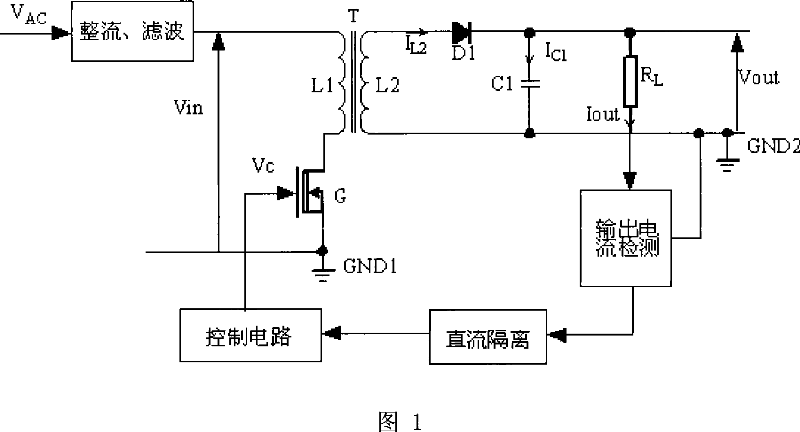
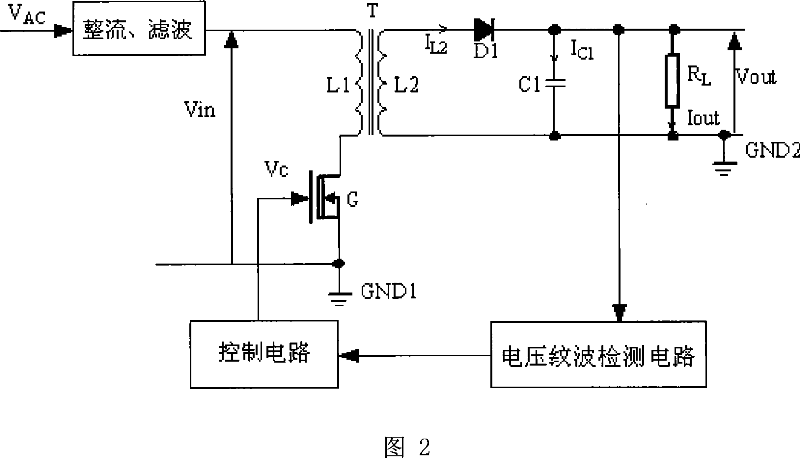
InactiveCN101039077AEliminate DC Power DissipationImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationControl circuitElectron
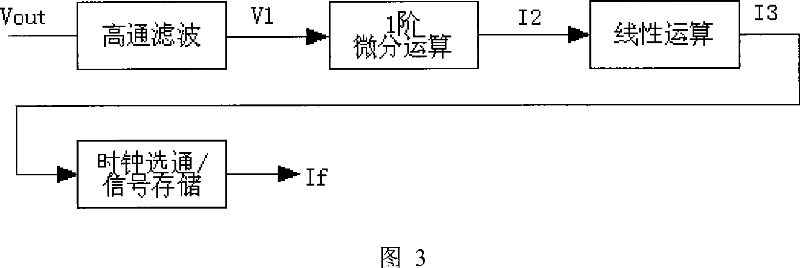
The invention provides a current regulation power supply relating to electric technique field. The power supply output current dc amount is detected by a voltage ripple detecting circuit and fed back to a control circuit to control the turn-on and turn-off of the power switch tube thus to realize regulated output. The voltage ripple detecting circuit of the current regulation switch power supply provided by this invention comprises a high pass filtering module, a second order differentiation operation module, a linear operation module, and a clock gating / signal memory module which are connected in series sequentially. The voltage ripple of the current regulation switch power supply output voltage is firstly extrated and then performed by second order differentiation, linear operation and memory extension to 'resume' the dc output voltage of the current regulation switch power supply which is finally fed back to PWM, PFM or PSM control ciucuit so as to realize regulated output via adjusting the turn-on and turn-off of the power switch tube by the control circuit. The present invention has higher power efficiency and lower circuit cost as well as smaller power supply volume compared with prior current regulation switch power supply.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
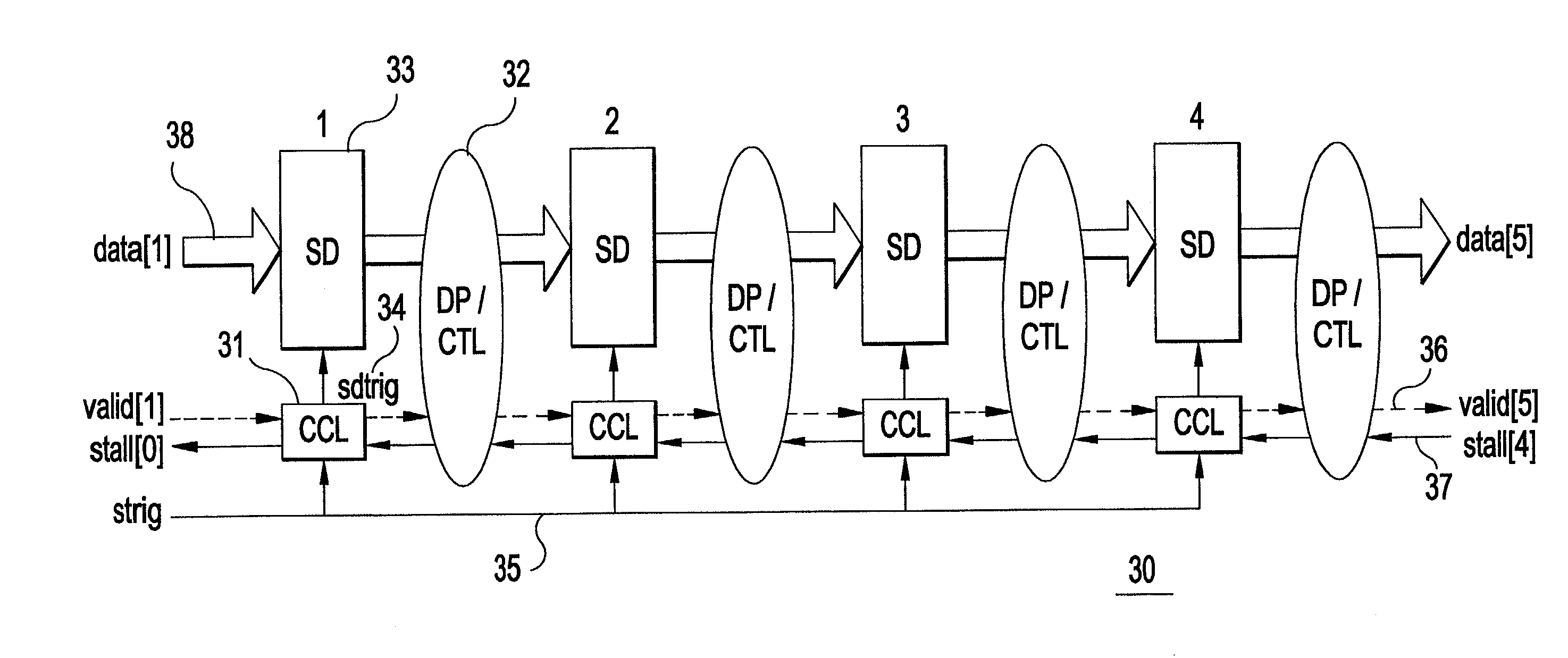
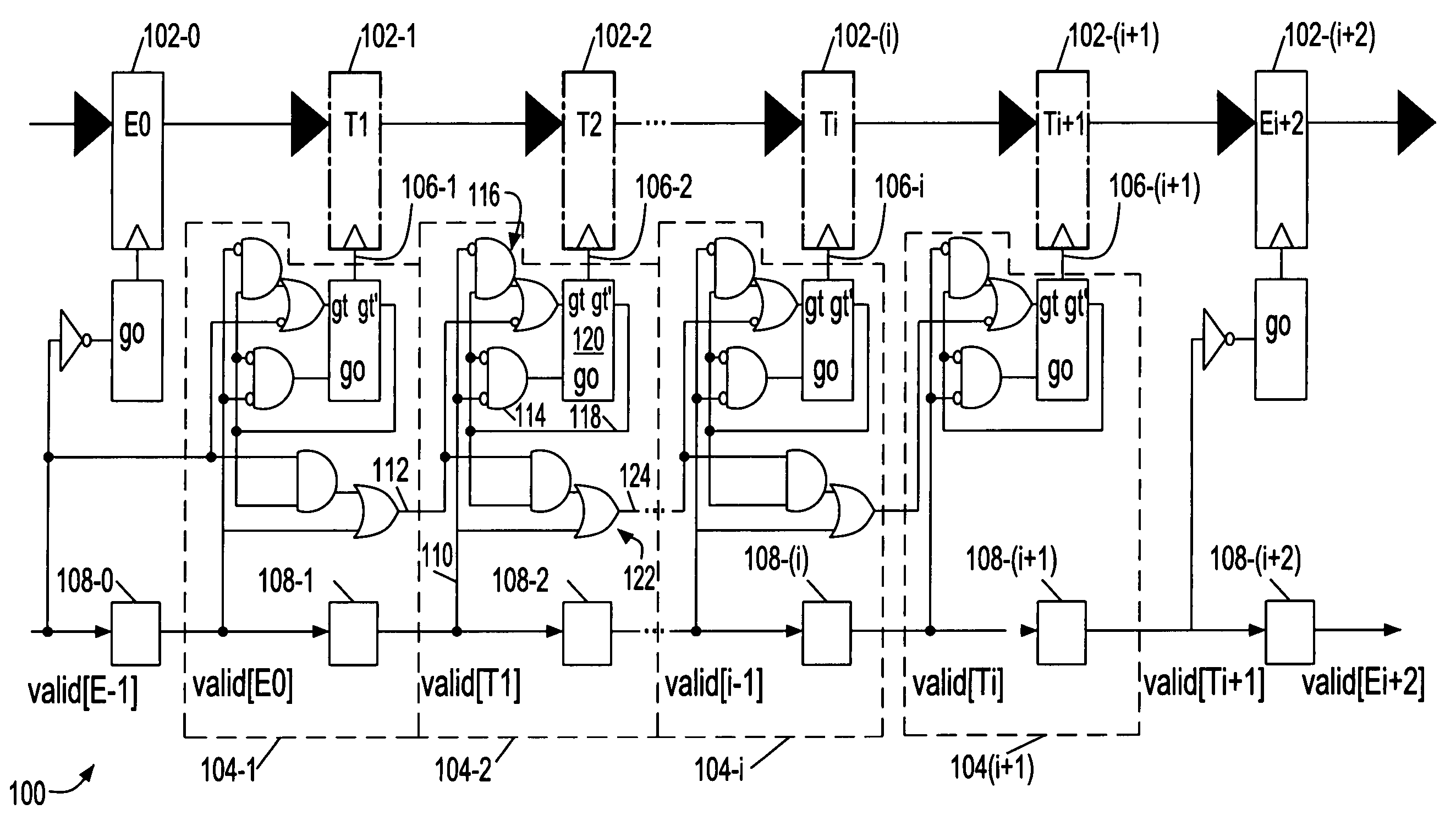
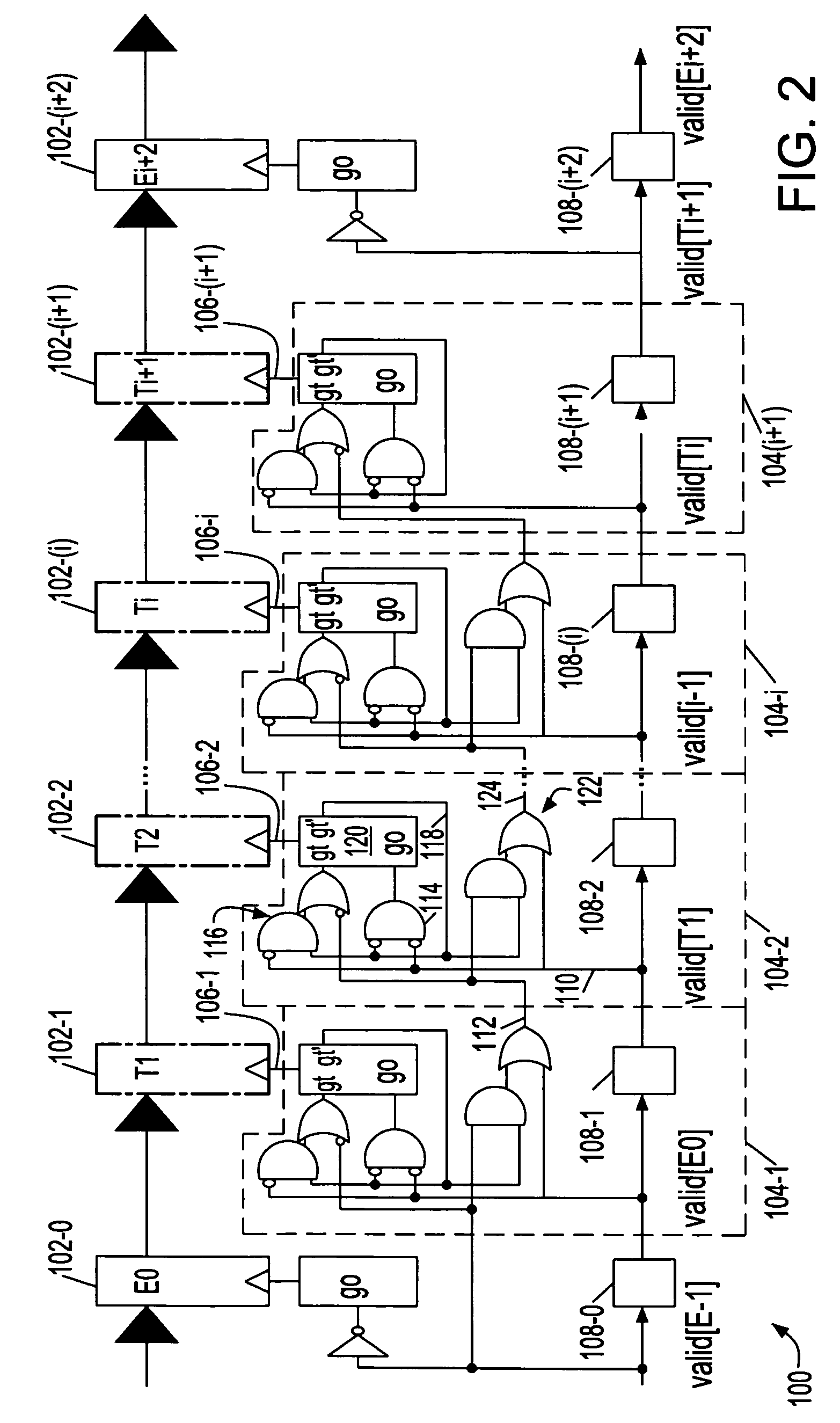
Interlocked synchronous pipeline clock gating
ActiveUS7065665B2Increase flexibilityReduce effortEnergy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsEvent triggerComputer science
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method For Optimized Automatic Clock Gating
ActiveUS20080301594A1Reduce Switching Power ConsumptionConsumes less powerCAD circuit designMulti-objective optimisationComputer architectureCombinational logic
A method of optimizing clock-gated circuitry in an integrated circuit (IC) design is provided. A plurality of signals which feed into enable inputs of a plurality of clock gates is determined, where the clock gates gate a plurality of sequential elements in the IC design. Combinational logic which is shared among the plurality of signals is identified. The clock-gated circuitry is transformed into multiple levels of clock-gating circuitry based on the shared combinational logic.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
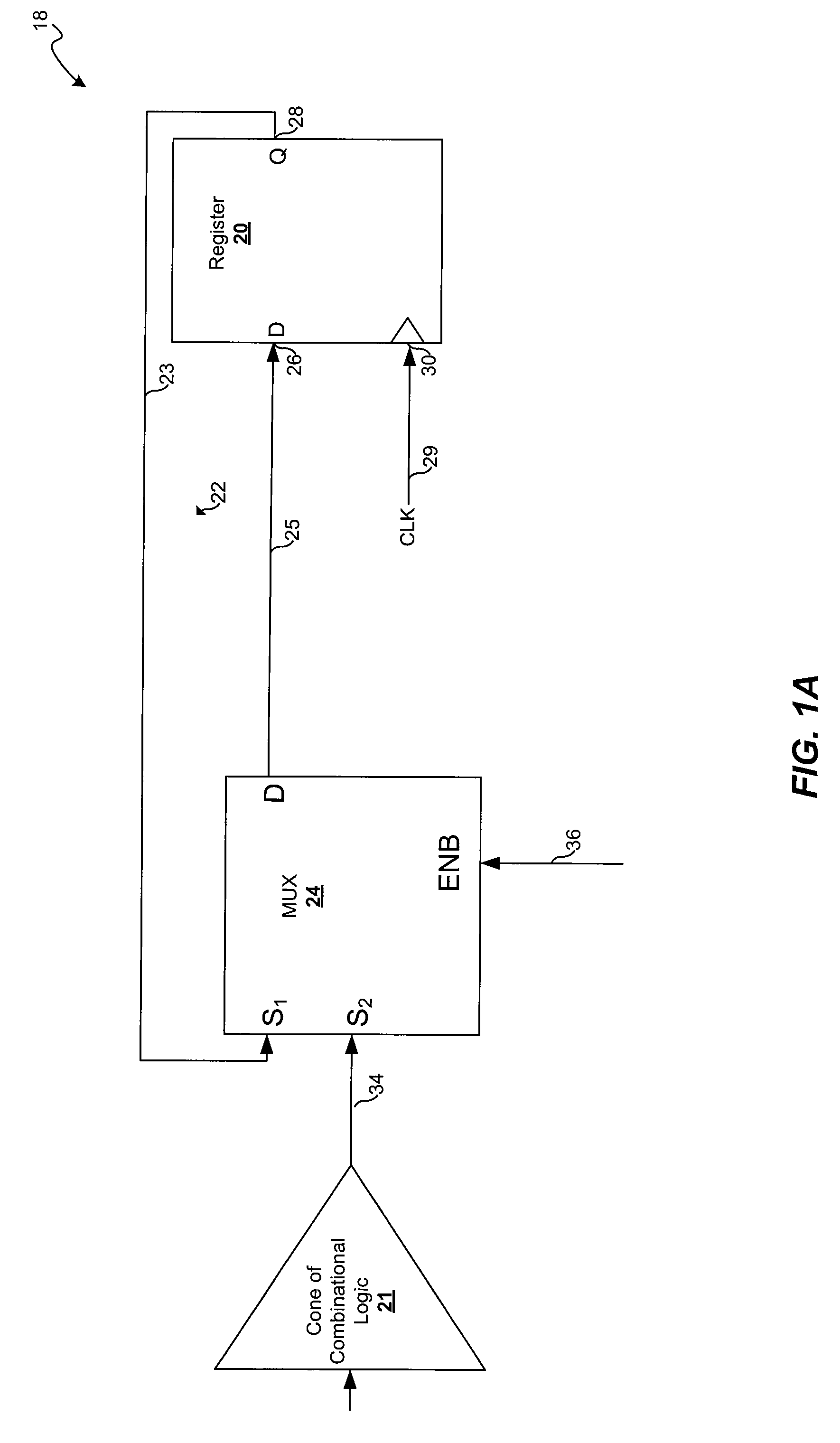
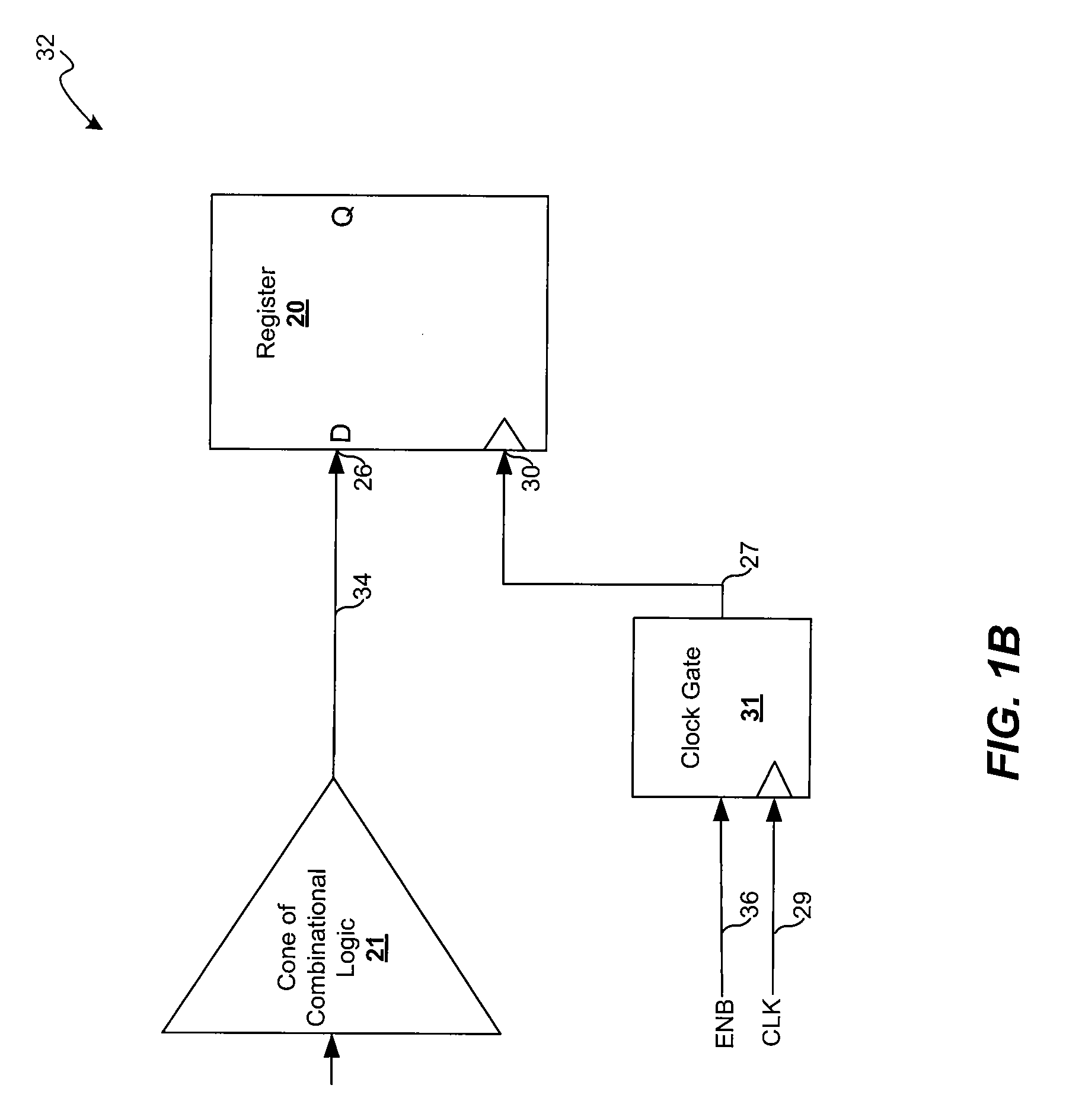
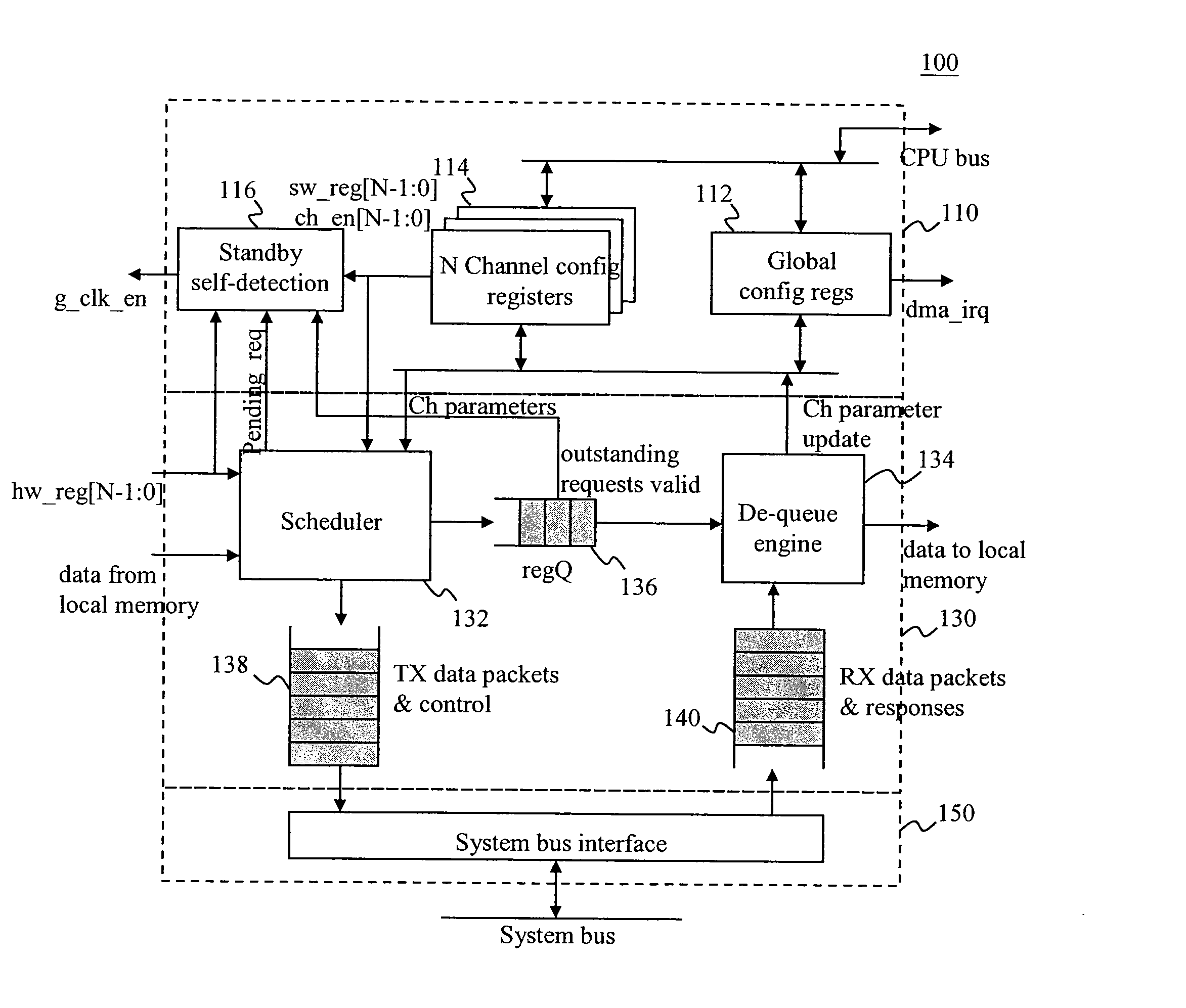
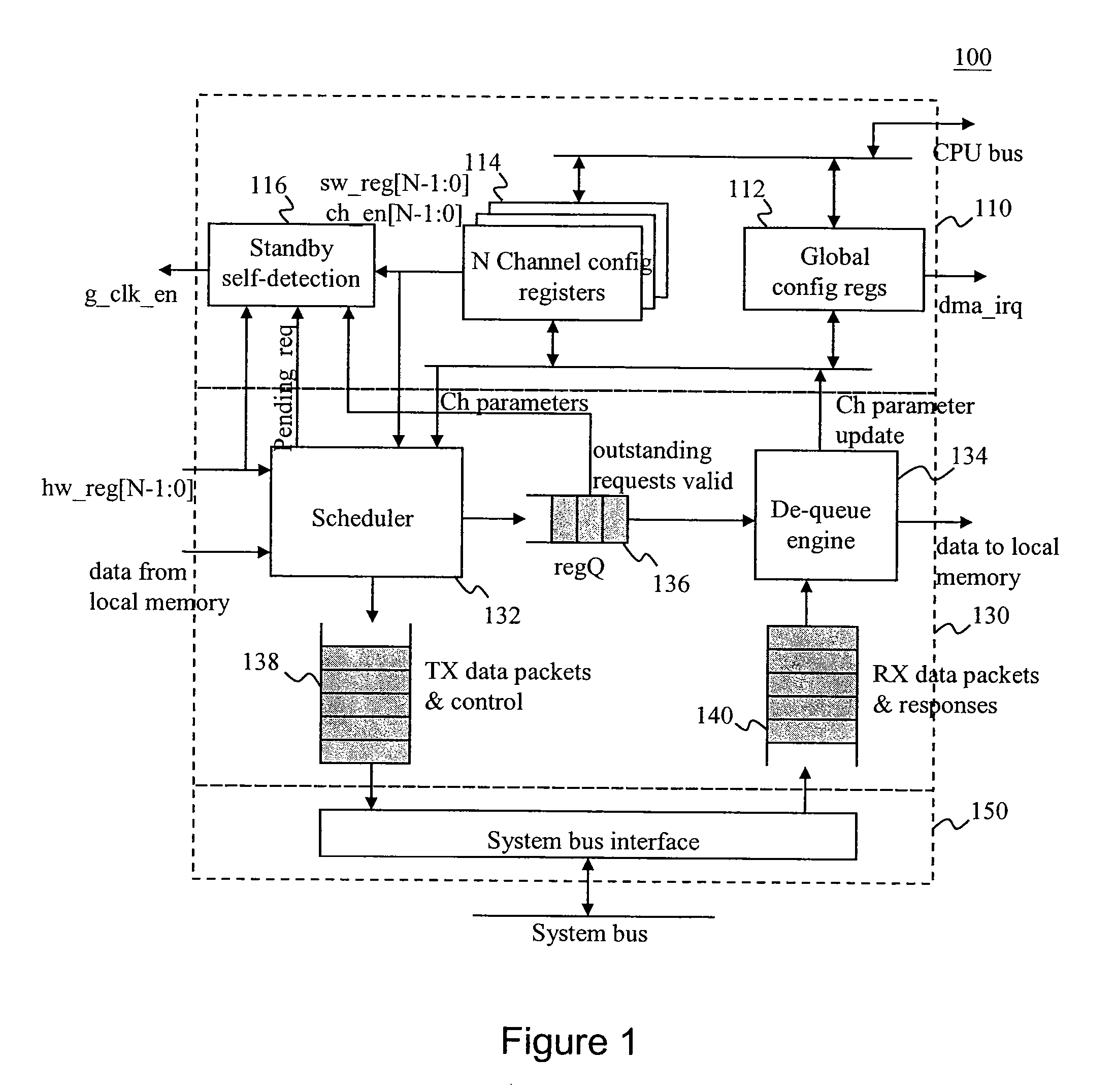
DMA Controller With Self-Detection For Global Clock-Gating Control
InactiveUS20070162648A1Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTEnergy efficient computingCell schedulingClock tree
A standby self-detection mechanism in a DMA controller which reduces the power consumption by dynamically controlling the on / off states of at least one clock tree driven by global clock-gating circuitry is disclosed. The DMA controller comprises a standby self-detection unit, a scheduler, at least one set of channel configuration registers associated with at least one DMA channel, and an internal request queue which holds already scheduled DMA requests that are presently outstanding in the DMA controller. The standby self-detection unit drives a signal to a global clock-gating circuitry to selectively turn on or off at least one of the clock trees to the DMA controller, depending on whether the DMA controller is presently performing a DMA transfer.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
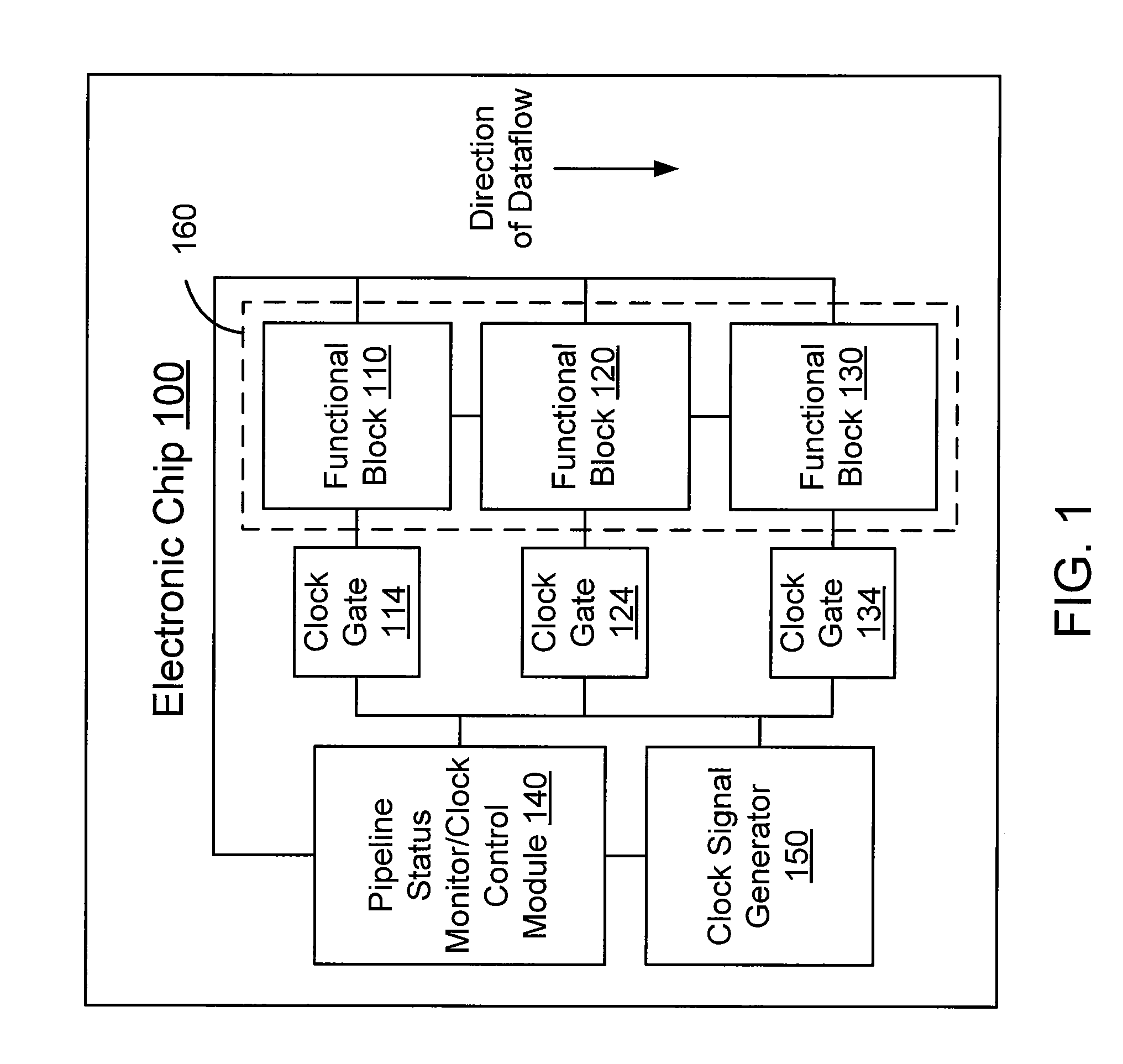
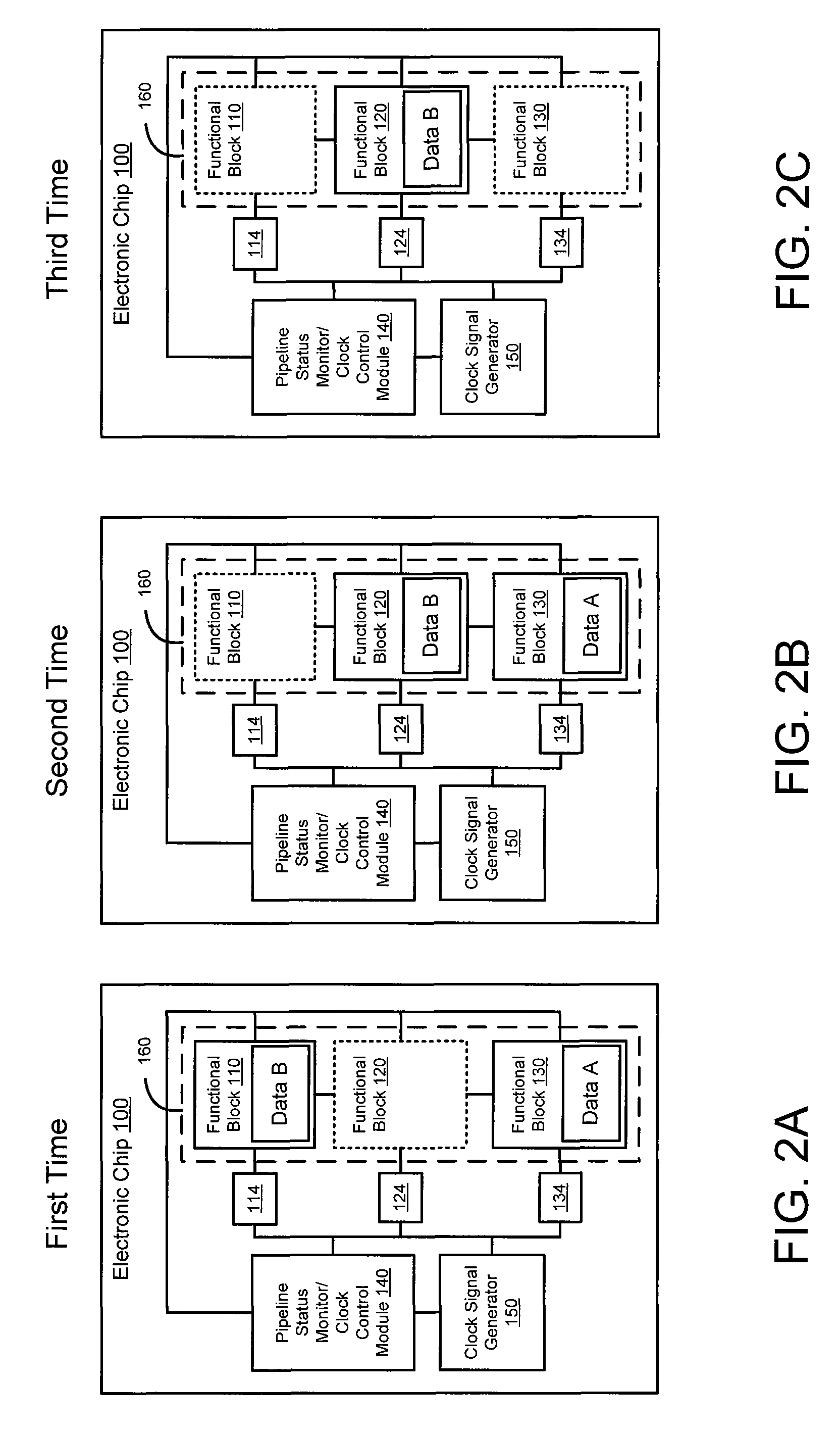
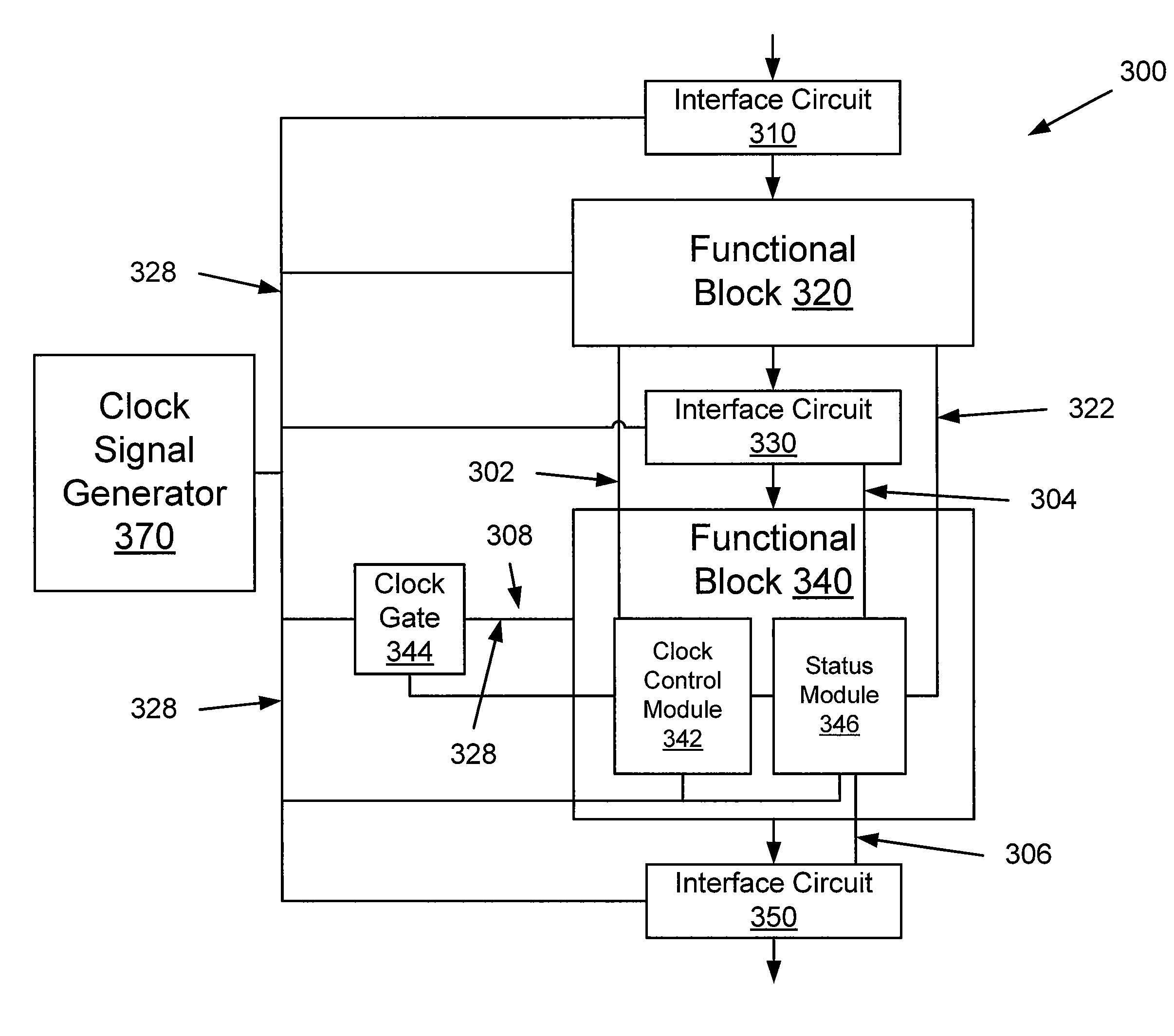
Functional block level clock-gating within a graphics processor
An embodiment of the invention includes receiving an indicator of a flow of data associated with a graphics processing stage within a graphics pipeline of a graphics processor. A clock signal to a portion of the graphics processing stage is modified based on a status of the flow of data. The clock signal is received from a clock signal generator within the graphics processor.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
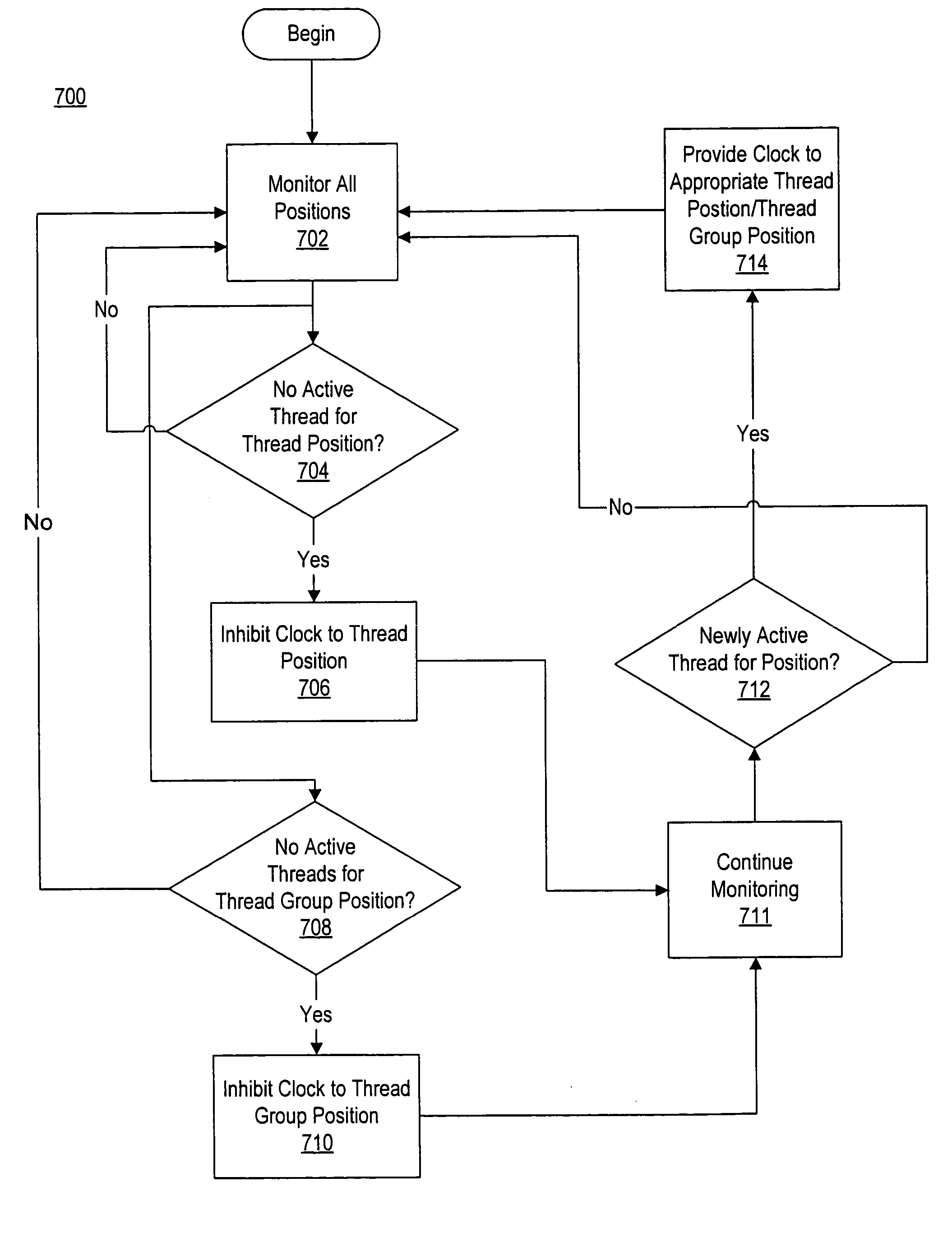
Thread-based clock enabling in a multi-threaded processor
ActiveUS20060005051A1Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementProcessing InstructionControl power
A method and apparatus for controlling power consumption in a multi-threaded processor. In one embodiment, the processor includes at least one logic unit for processing instructions. The logic unit includes a plurality of positions, wherein each of the plurality of positions corresponds to at least one instruction thread. Clock signals may be provided to the logic unit via a clock gating unit. The clock gating unit is configured to inhibit a clock signal from being provided to a corresponding one of the thread positions when no instruction thread is active for that position. The inhibiting of the clock signal for an inactive thread position may reduce power consumption by the processor.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
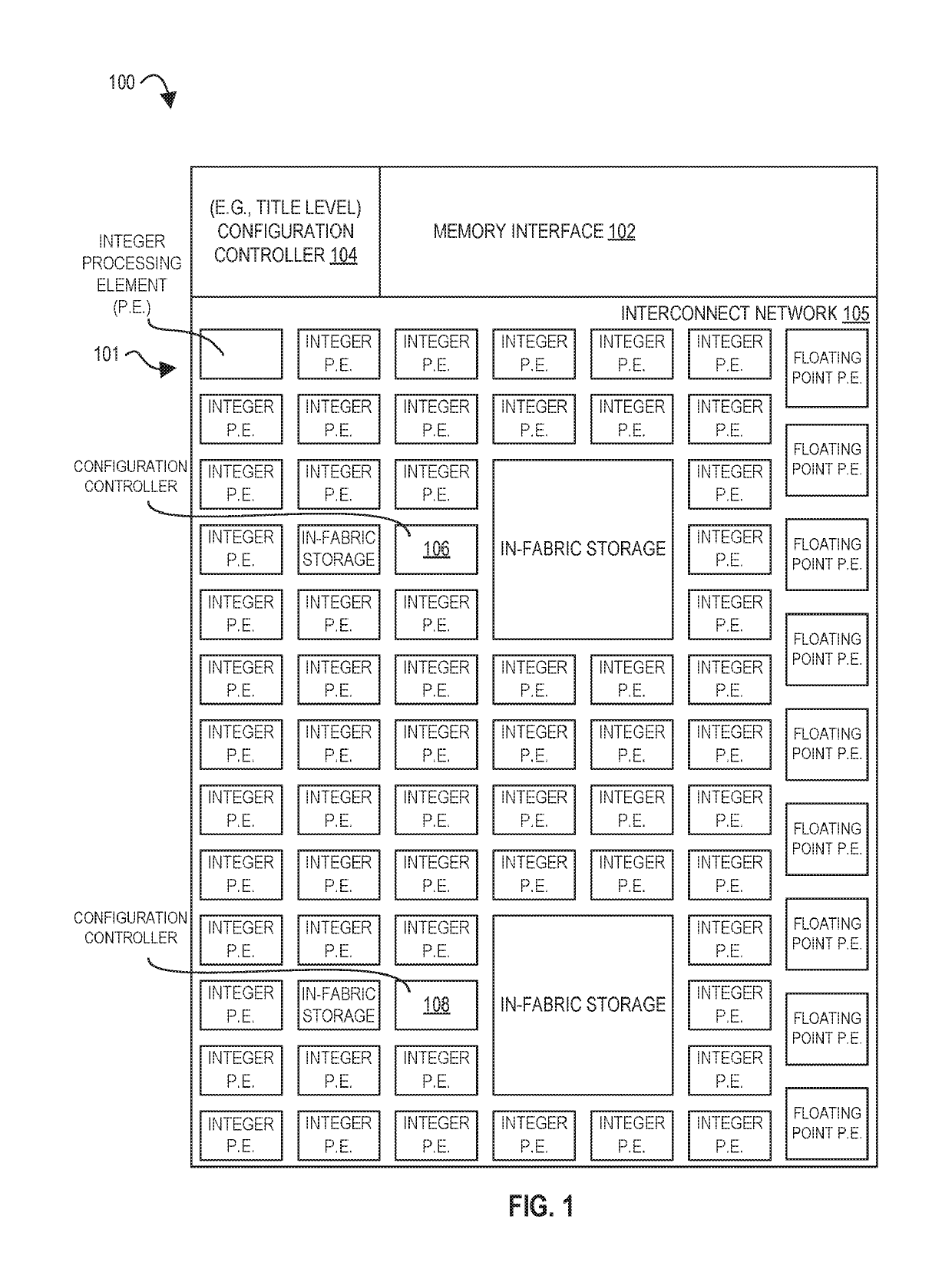
Processors and methods for configurable clock gating in a spatial array
InactiveUS20190101952A1Easy to adaptImprove performanceDataflow computersSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsSignal onParallel computing
Methods and apparatuses relating to configurable clock gating in spatial arrays are described. In one embodiment, a processor includes processing elements; an interconnect network between the processing elements; and a configuration controller, coupled to a first processing element and a second processing element of the plurality of processing elements and the first processing element having an output coupled to an input of the second processing element, to configure the second processing element to clock gate at least one clocked component of the second processing element, and configure the first processing element to send a reenable signal on the interconnect network to the second processing element to reenable the at least one clocked component of the second processing element when data is to be sent from the first processing element to the second processing element.
Owner:INTEL CORP
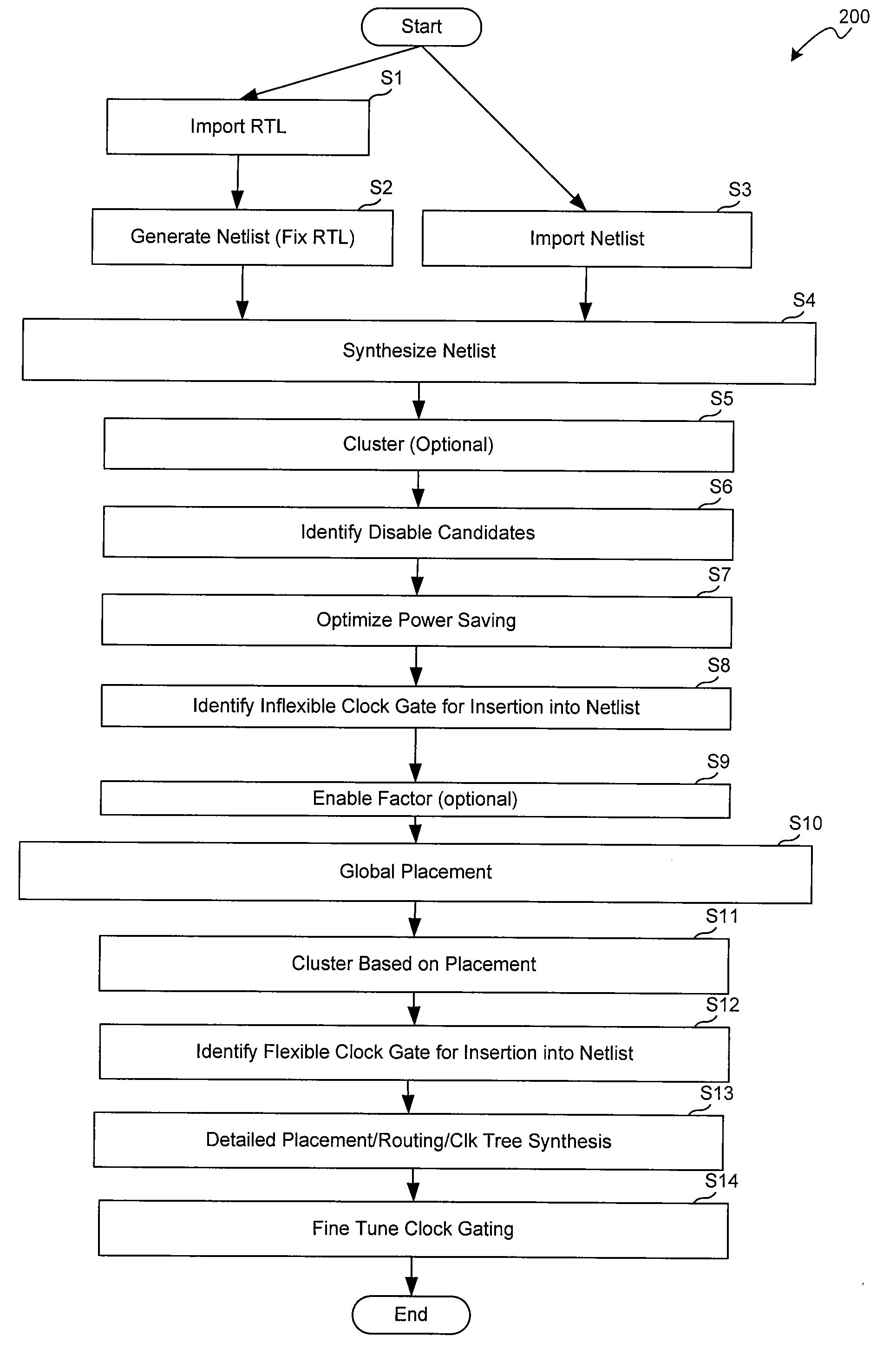
Identification and implementation of clock gating in the design of integrated circuits
ActiveUS7076748B2Improve efficiencyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProcessor registerClock gating
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
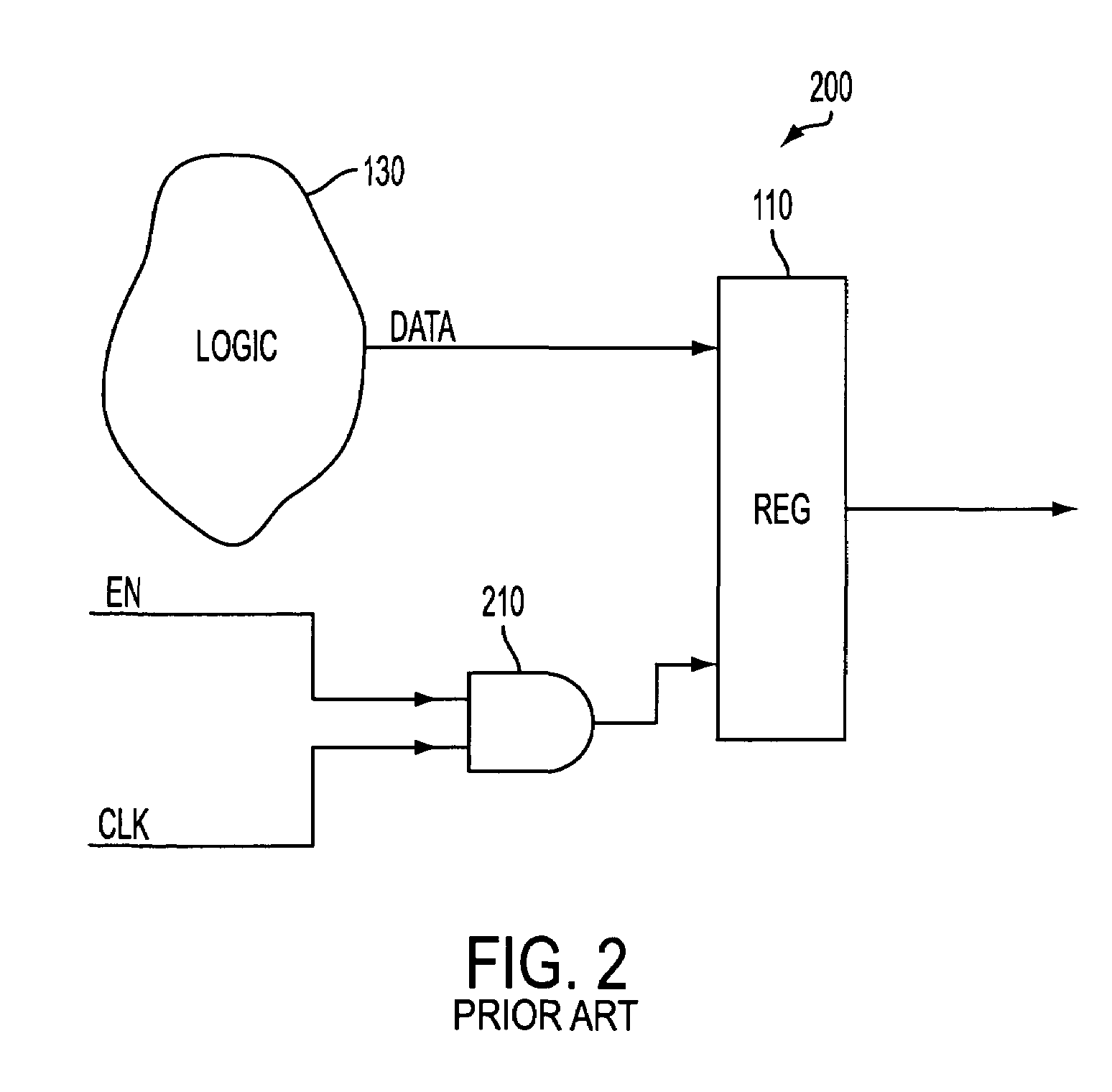
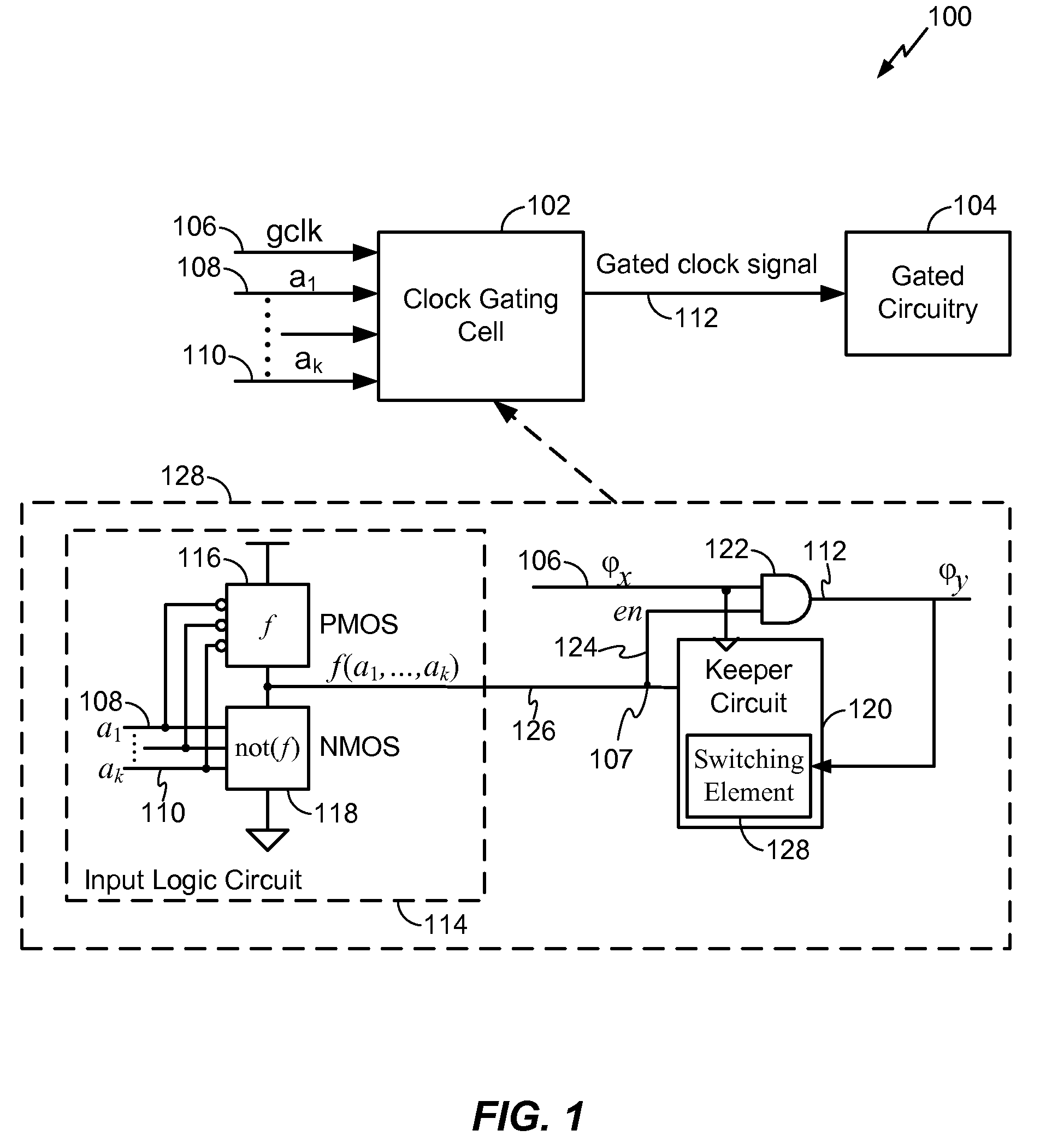
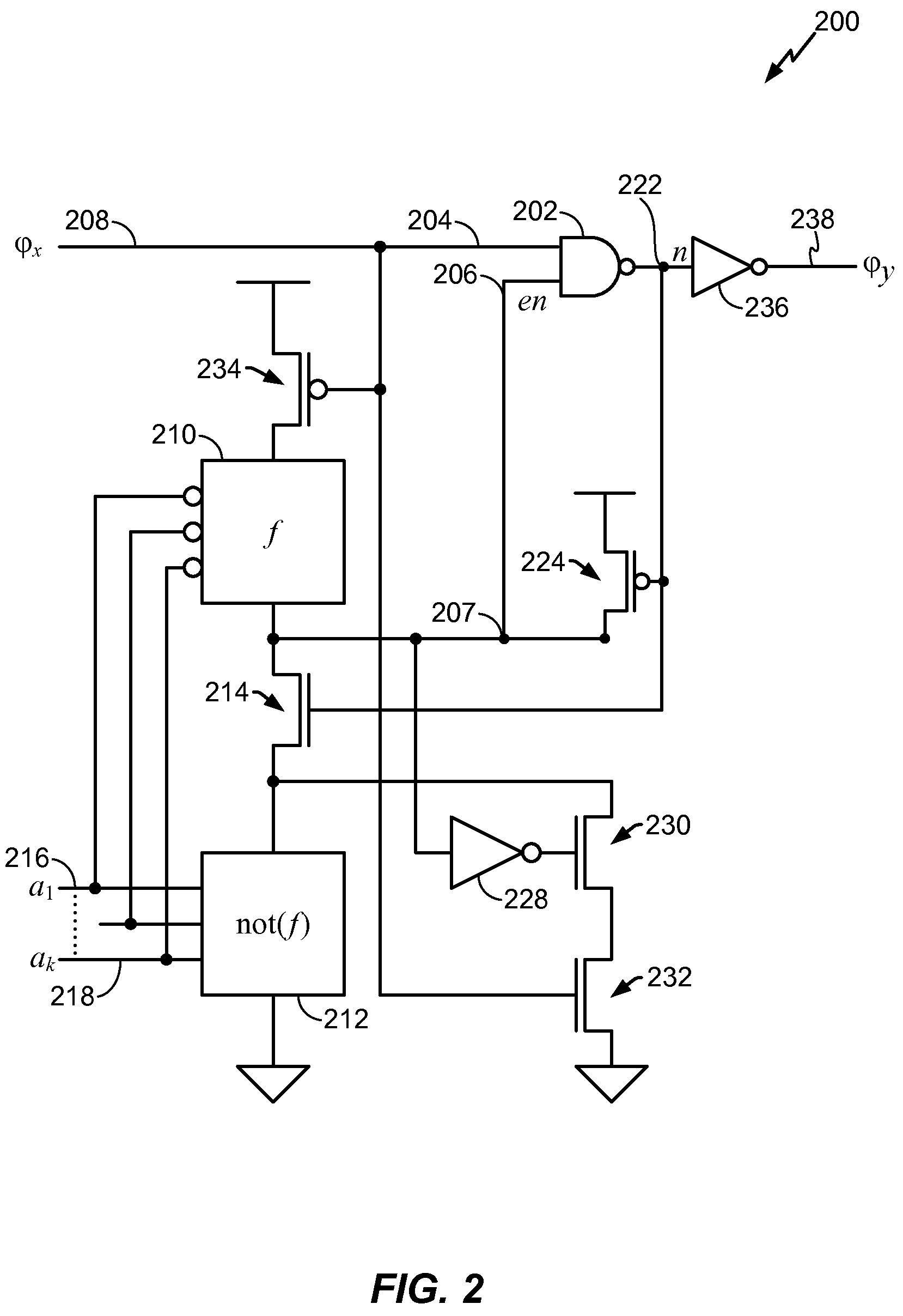
Clock gating system and method
ActiveUS7902878B2Reduce in quantityReduce areaPower reduction by control/clock signalGenerating/distributing signalsEngineeringLogic circuitry
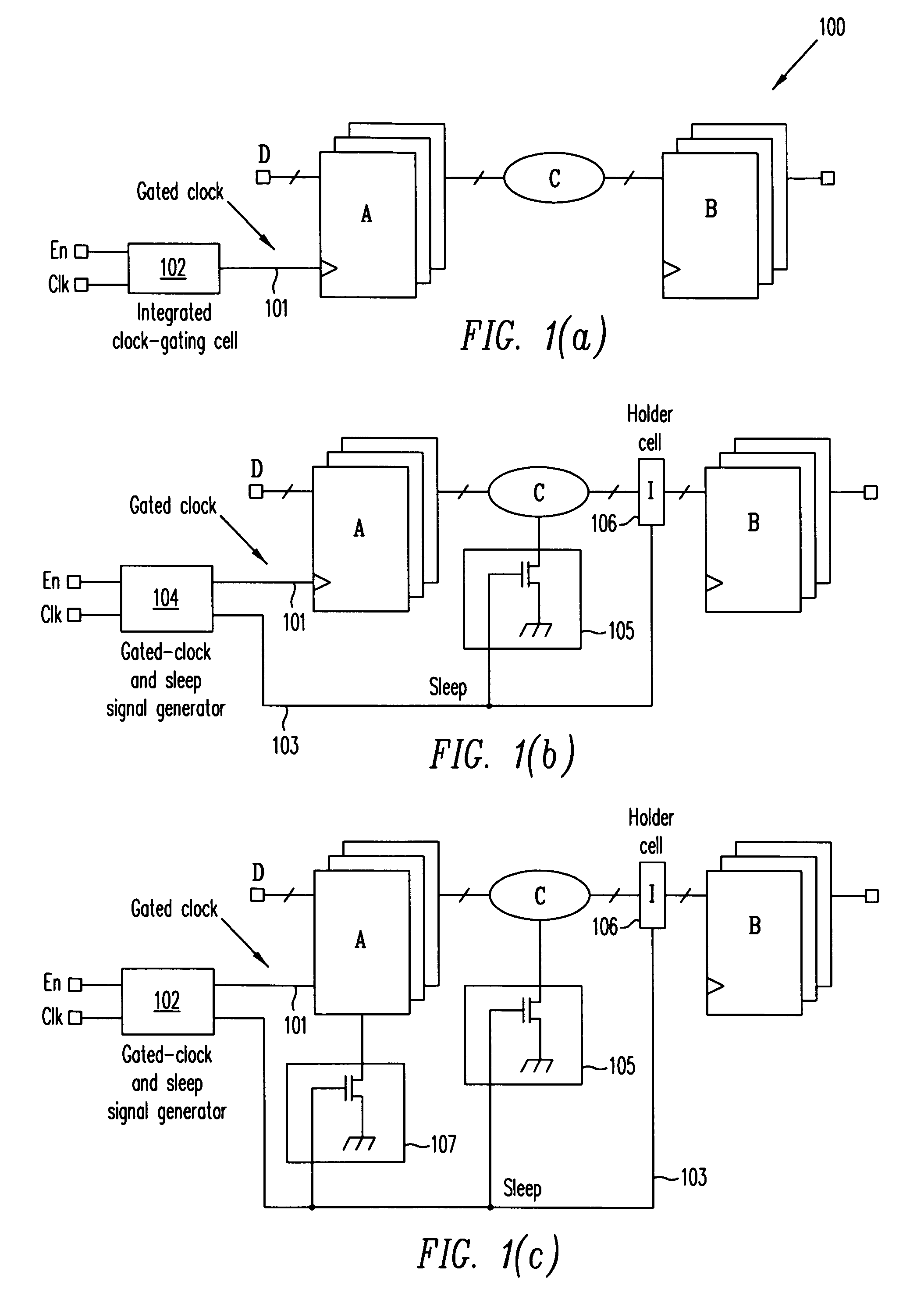
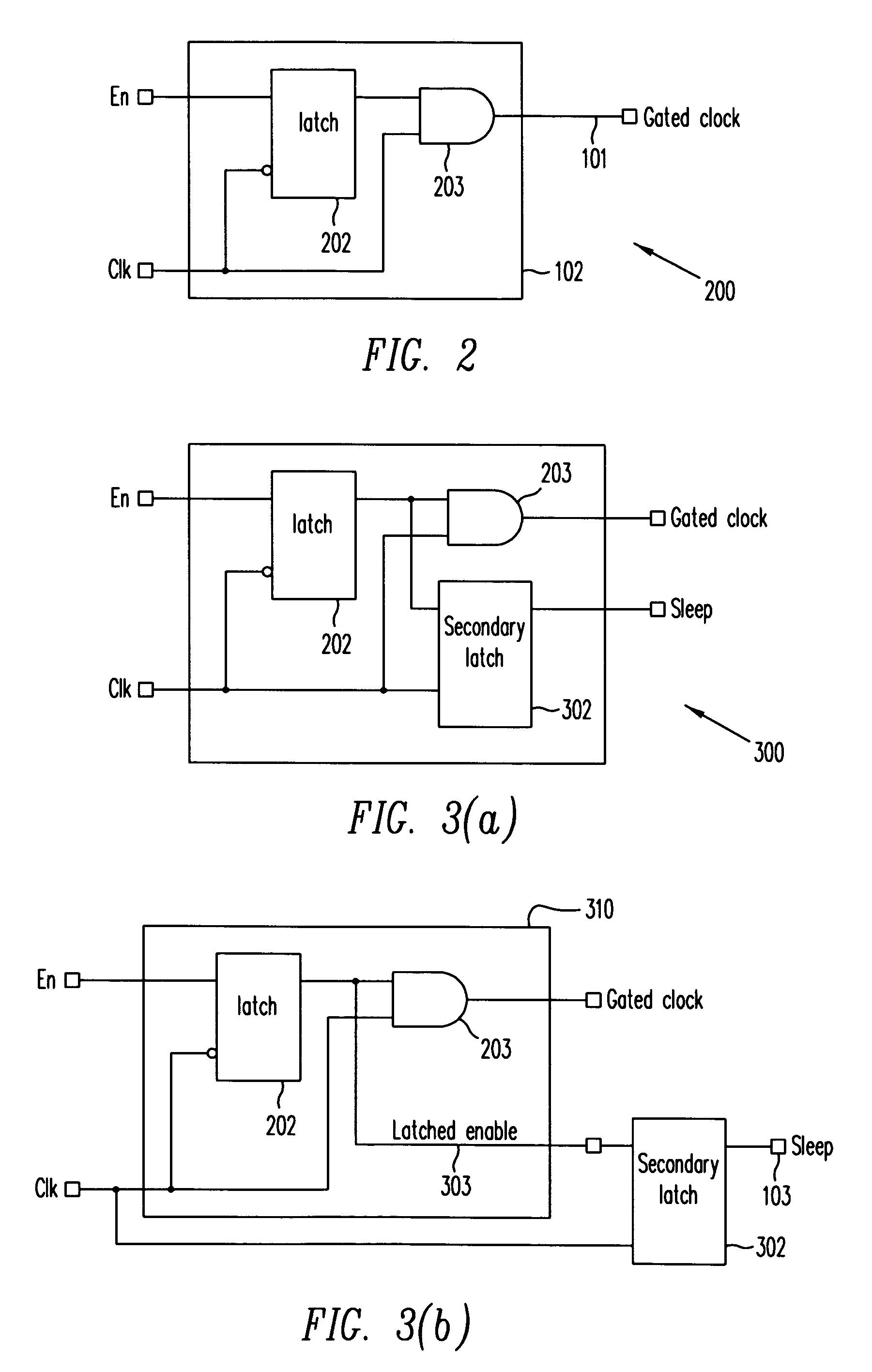
A clock gating system and method is disclosed. In a particular embodiment, the system includes an input logic circuit having at least one input to receive at least one input signal and having an output at an internal enable node. A keeper circuit includes at least one switching element that is responsive to a gated clock signal and is coupled to the internal enable node to selectively hold a logical voltage level at the internal enable node. The system further includes a gating element responsive to an input clock signal and to the logical voltage level at the internal enable node to generate the gated clock signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
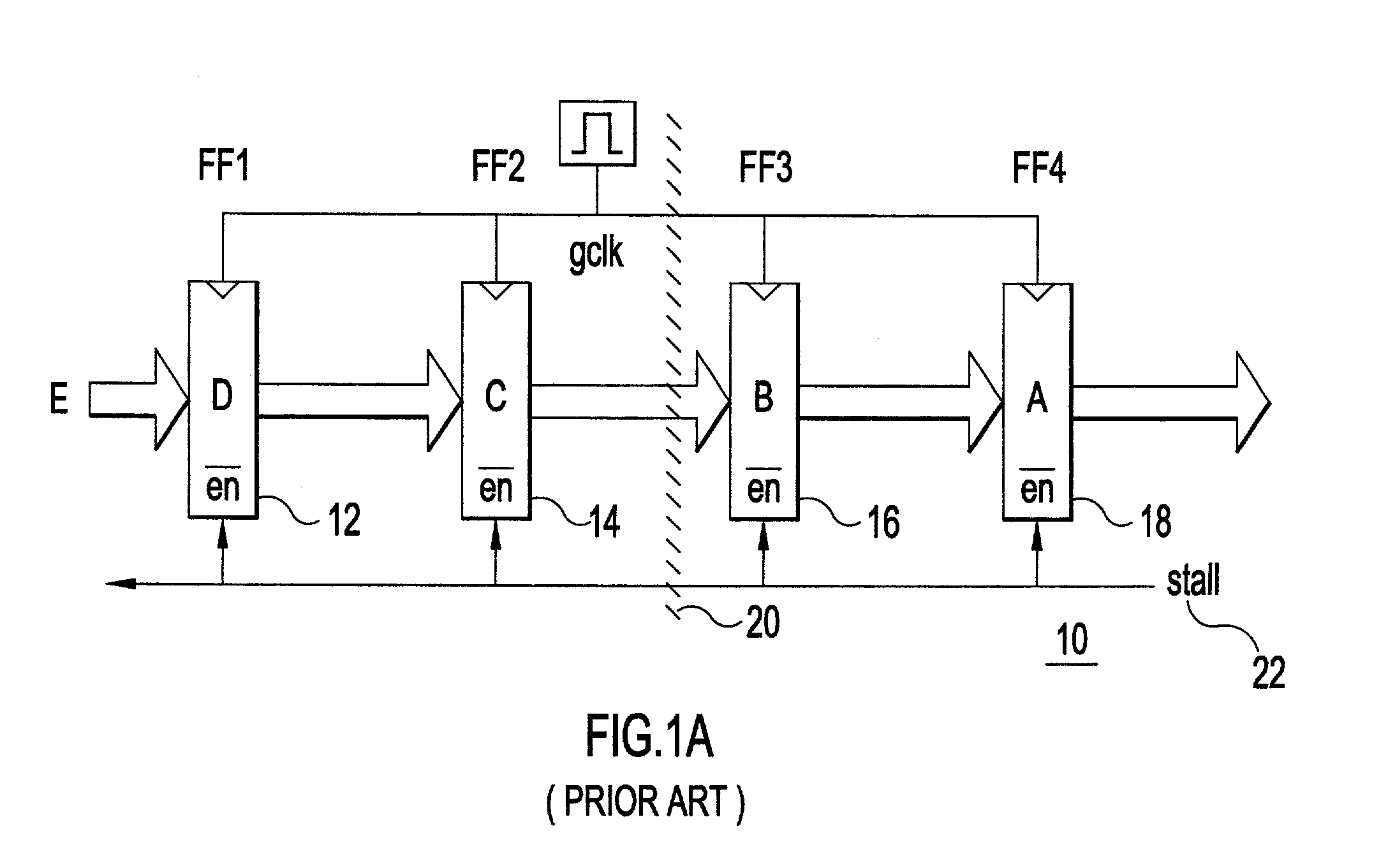
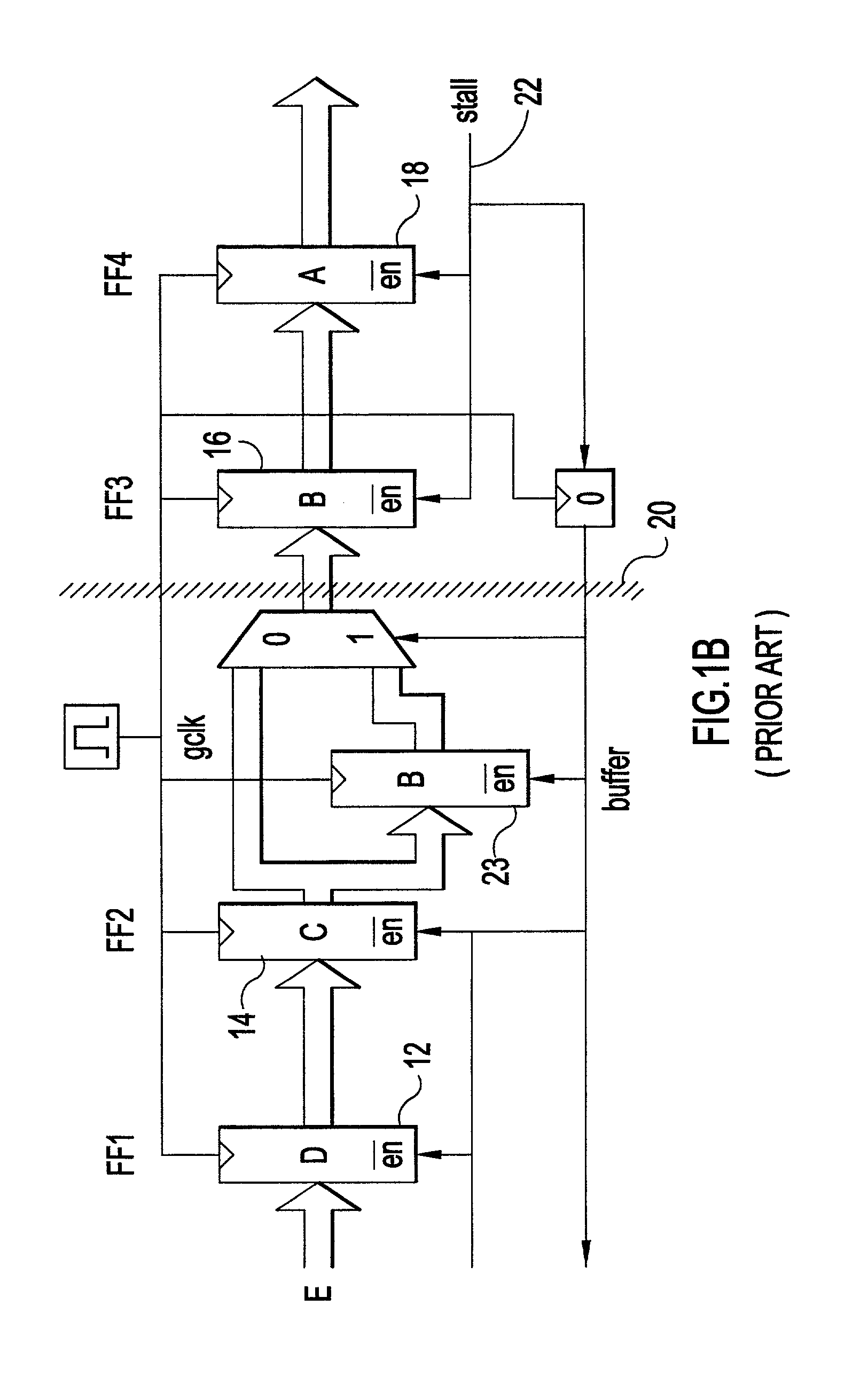
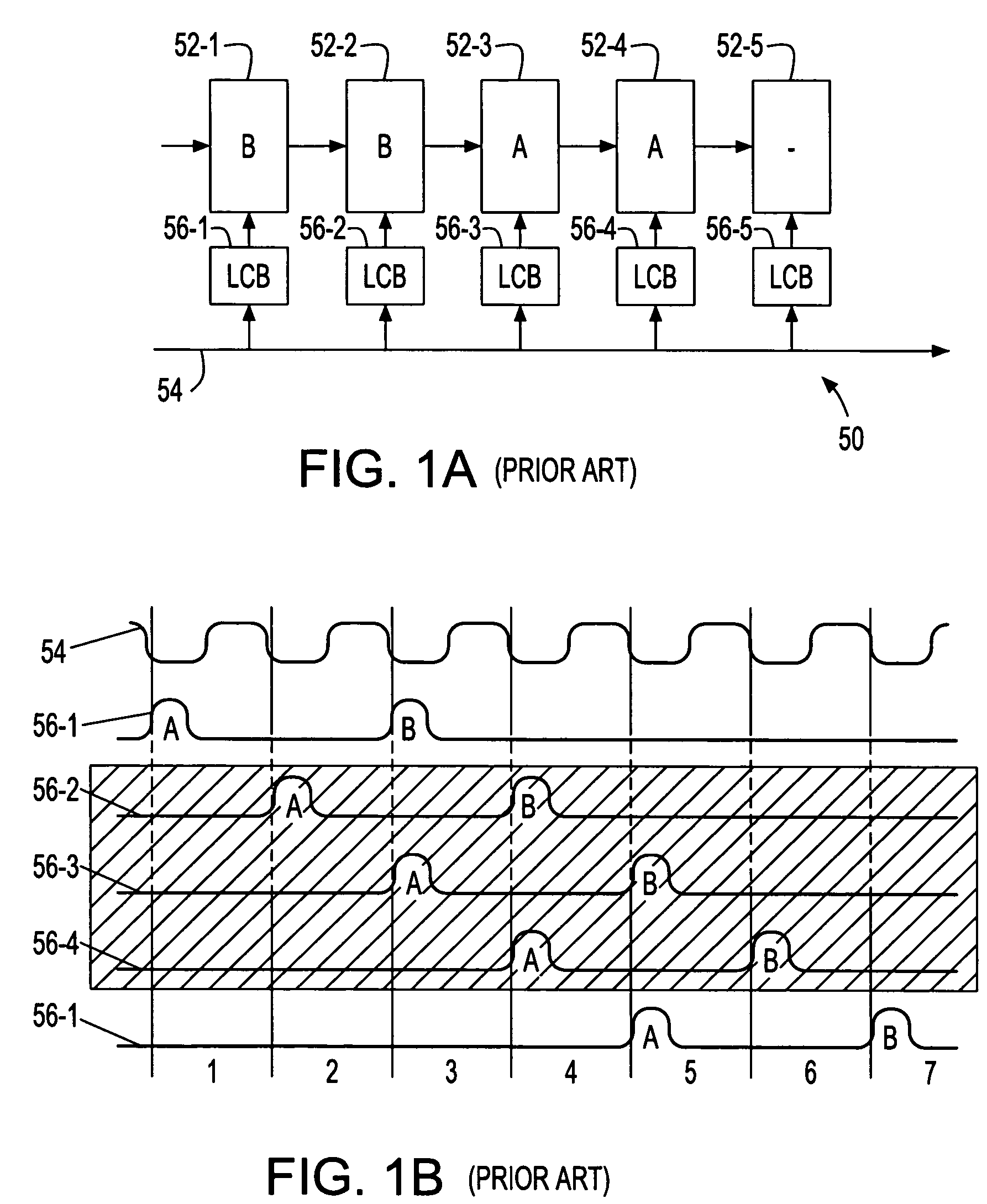
Synchronous pipeline with normally transparent pipeline stages
ActiveUS7076682B2Increase flexibilityReducing pipeline operating frequencyVolume/mass flow measurementDigital computer detailsEngineeringIntermediate stage
A synchronous pipeline segment and an integrated circuit (IC) including the segment. The segment includes an input stage, an output stage and at least one intermediate stage. A place holder latch associated with each stage indicates whether valid stage data is in the stage. A local clock buffer provides a local clock gating a corresponding stage. The input and output stages are normally opaque and intermediate stages are normally transparent. Data items pass locally asynchronously between the input and output stages and are separated by opaque gated intermediate stages.
Owner:IBM CORP
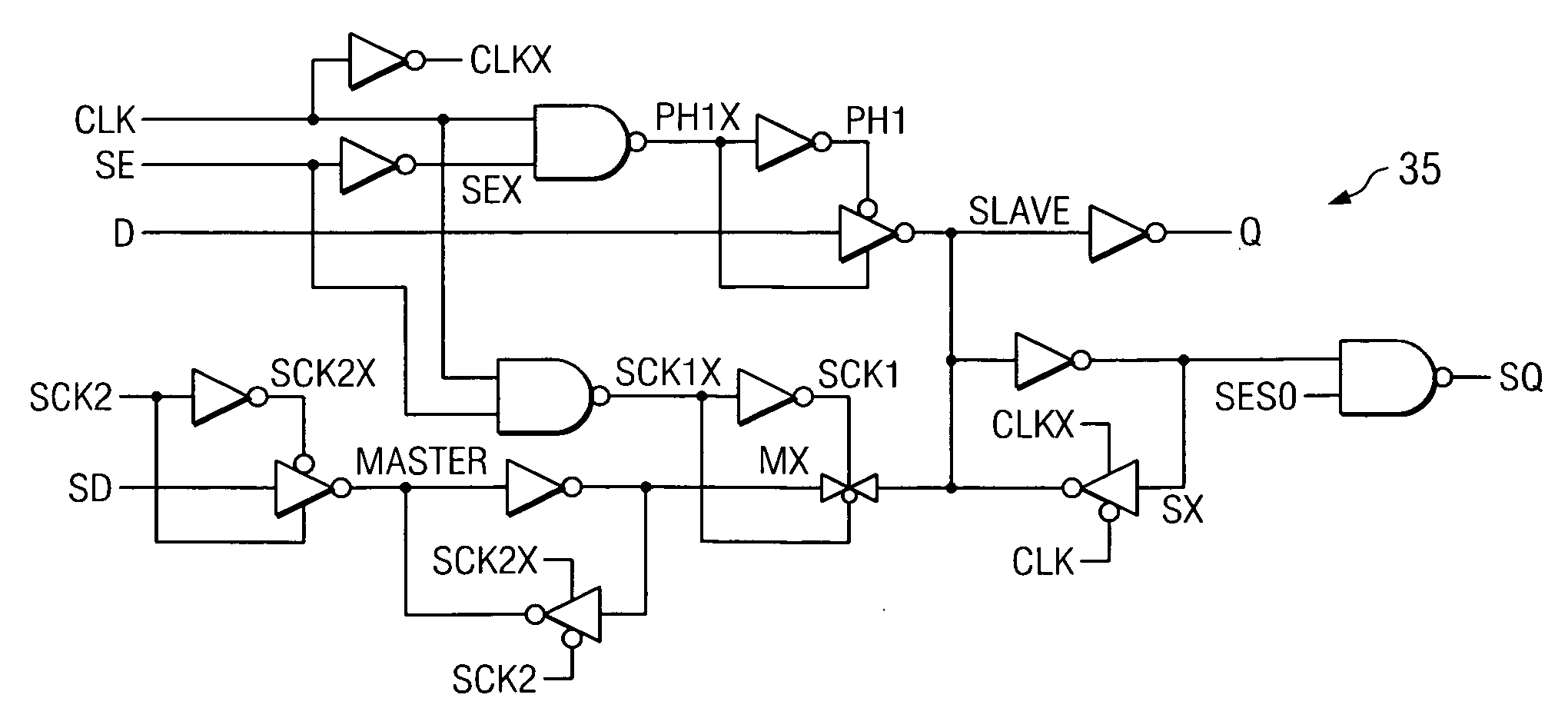
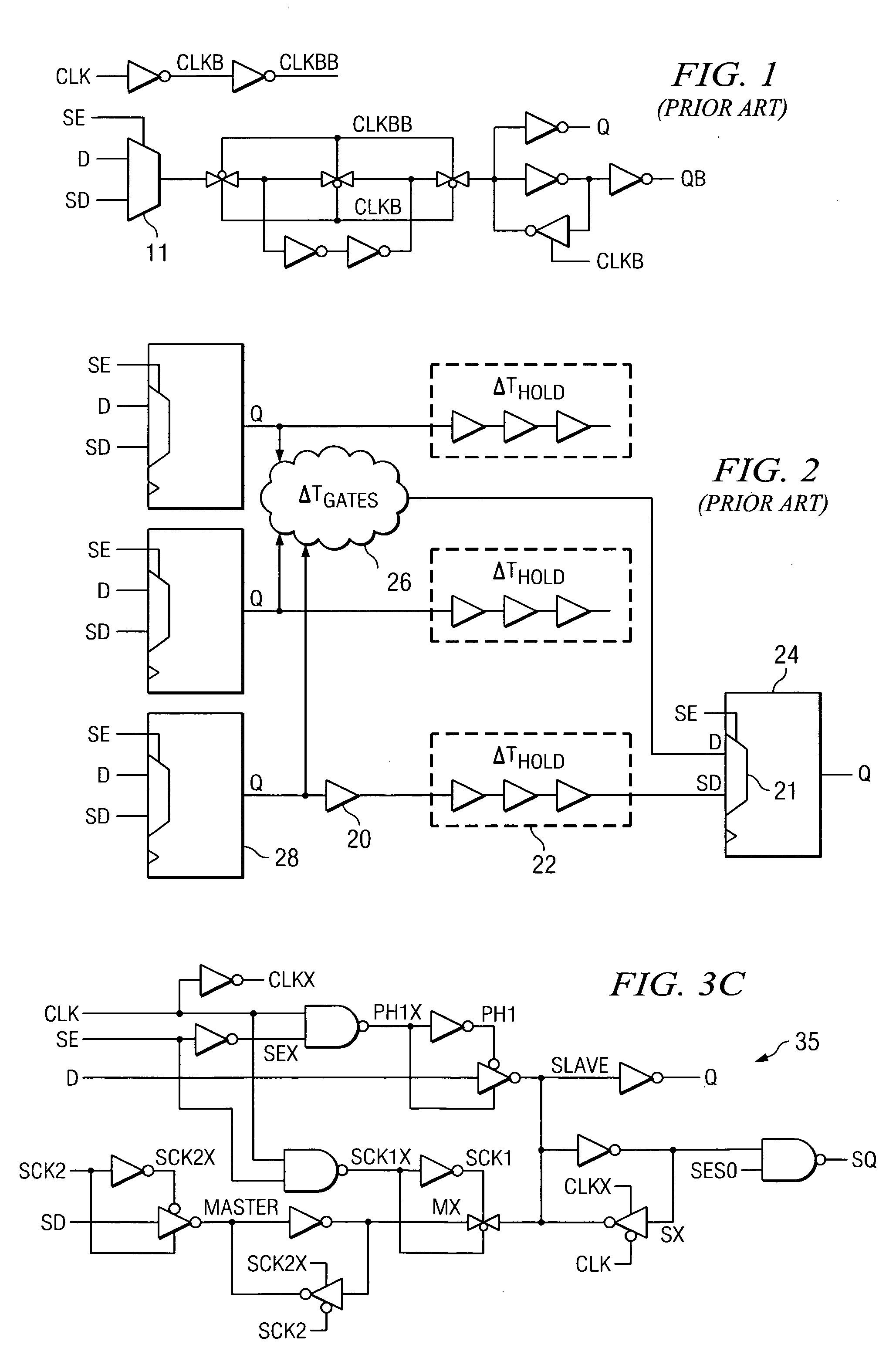
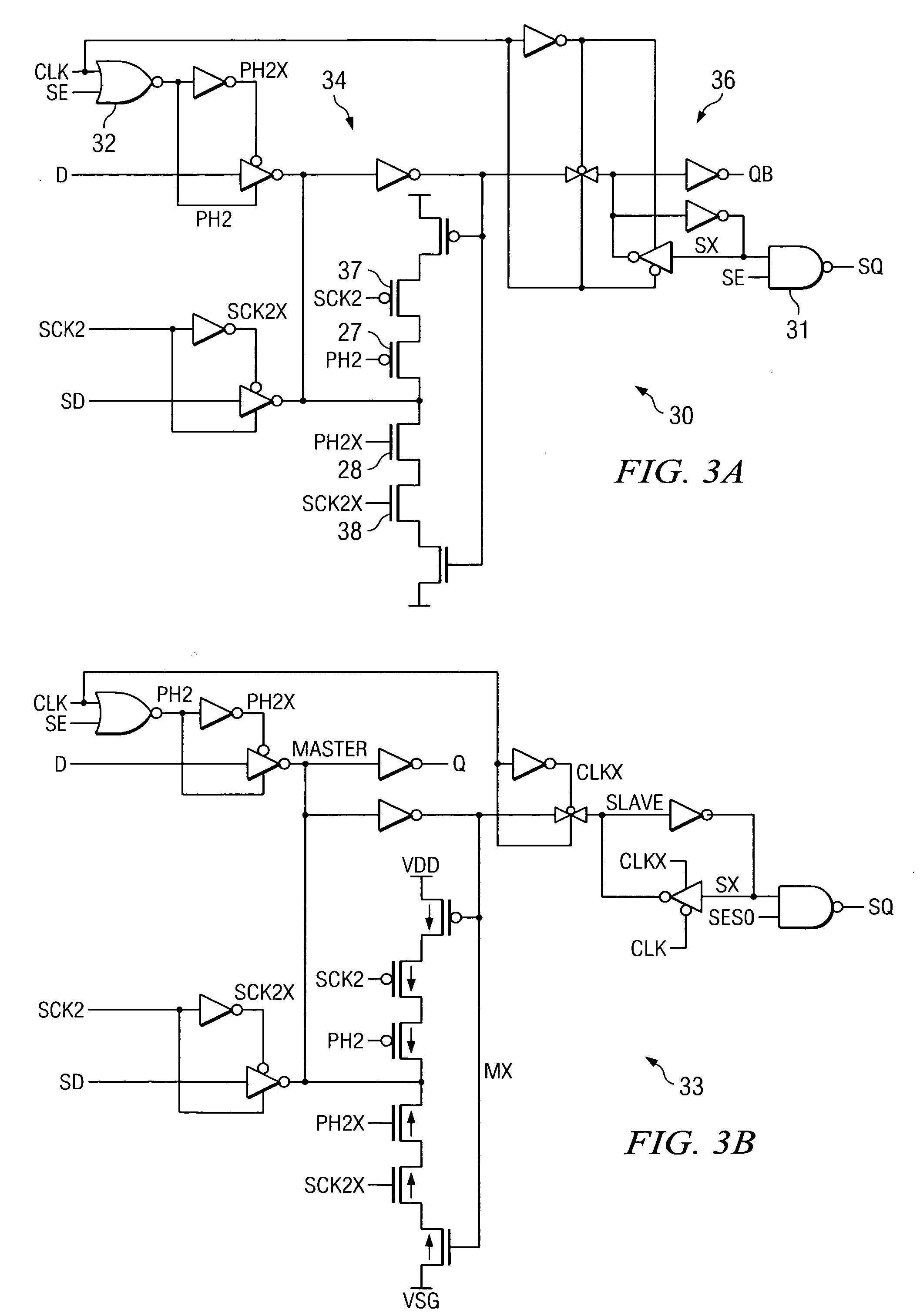
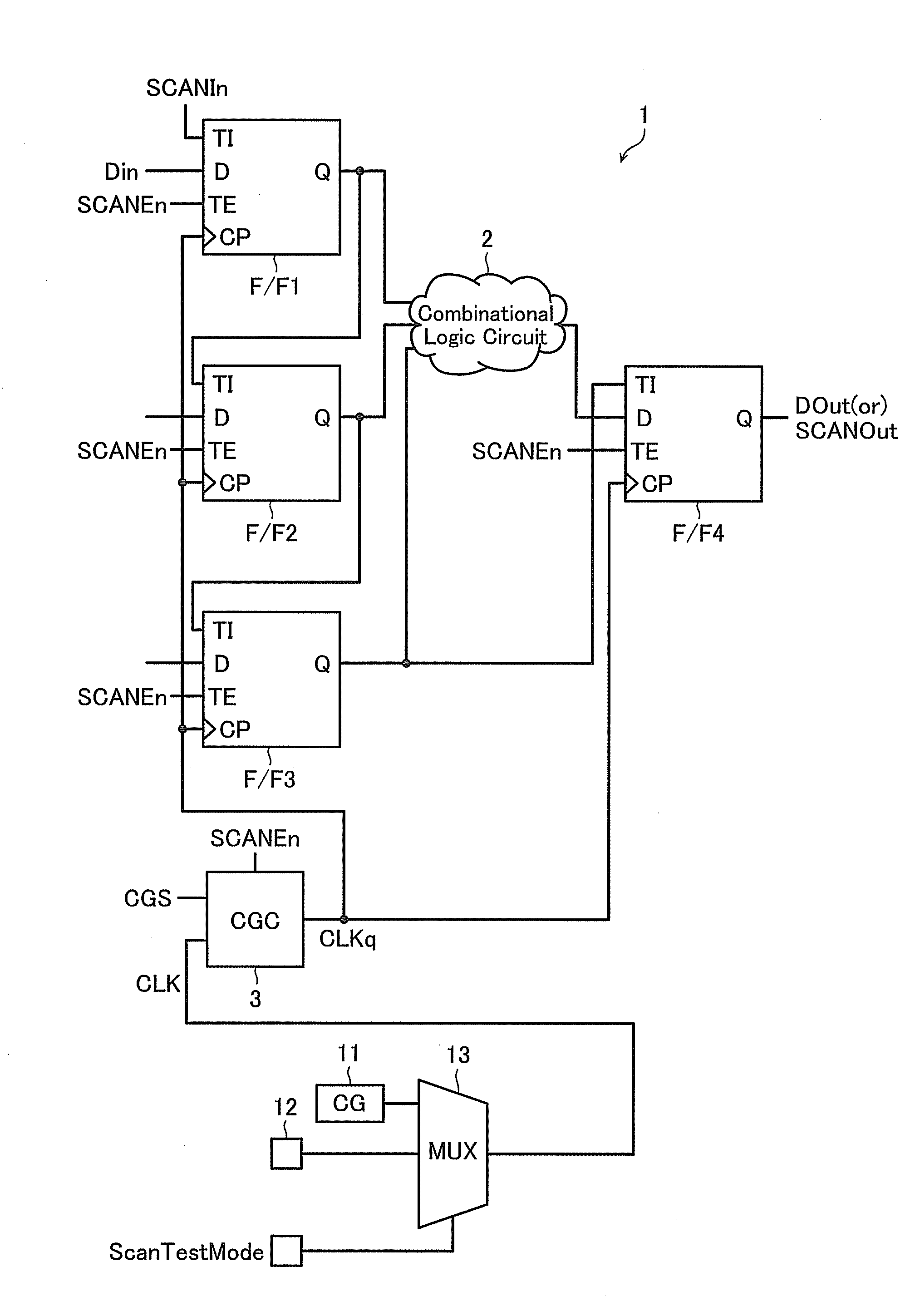
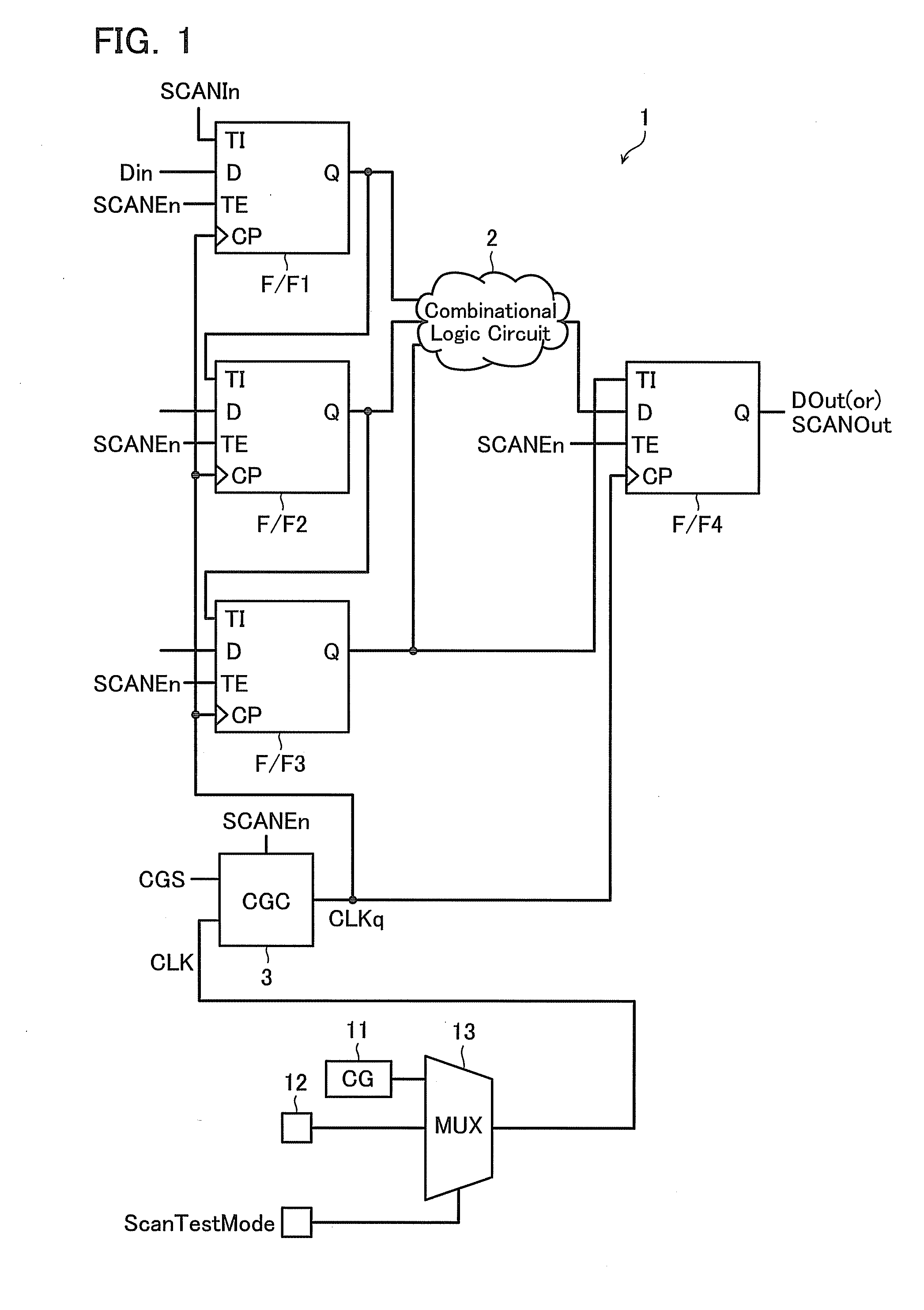
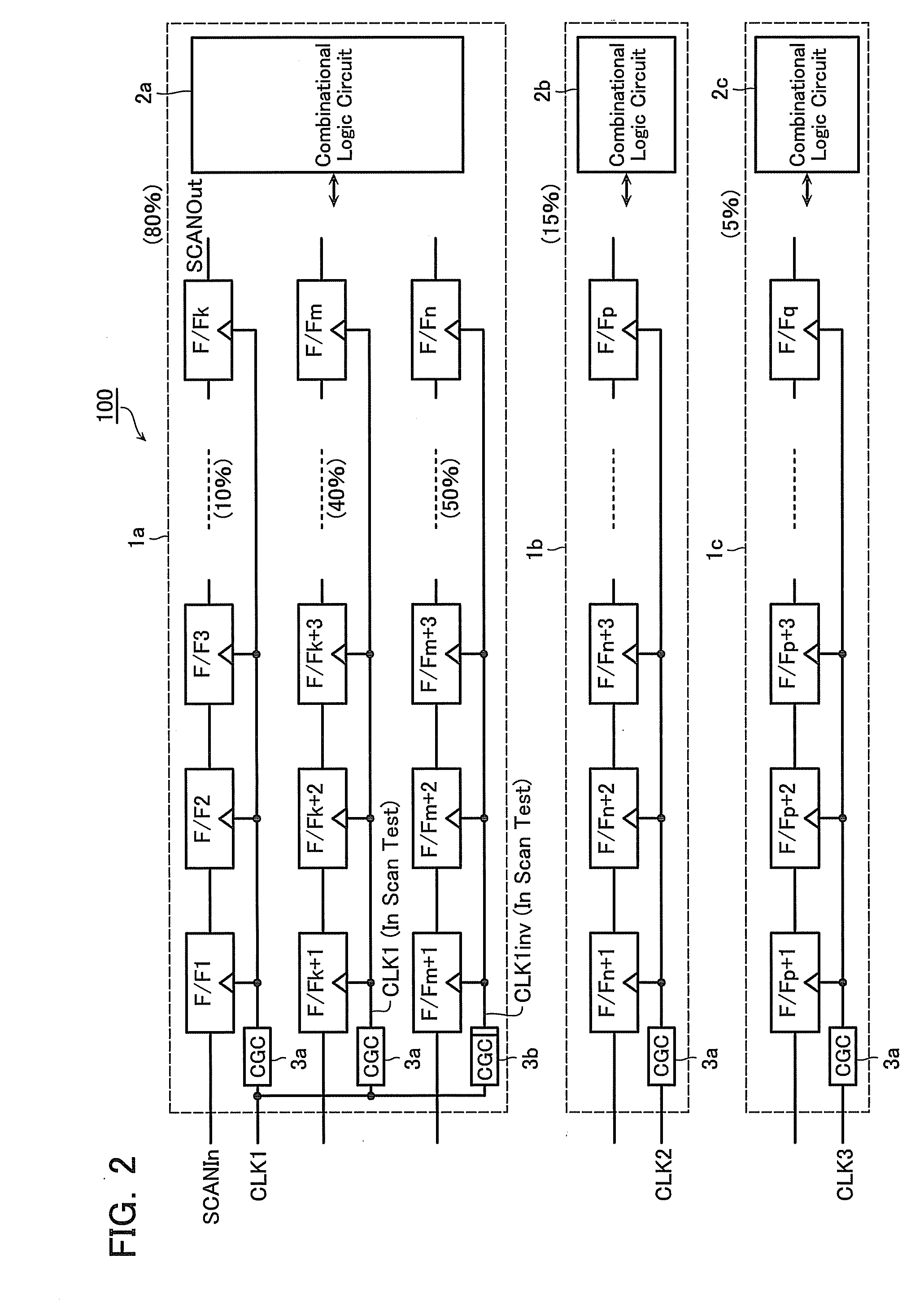
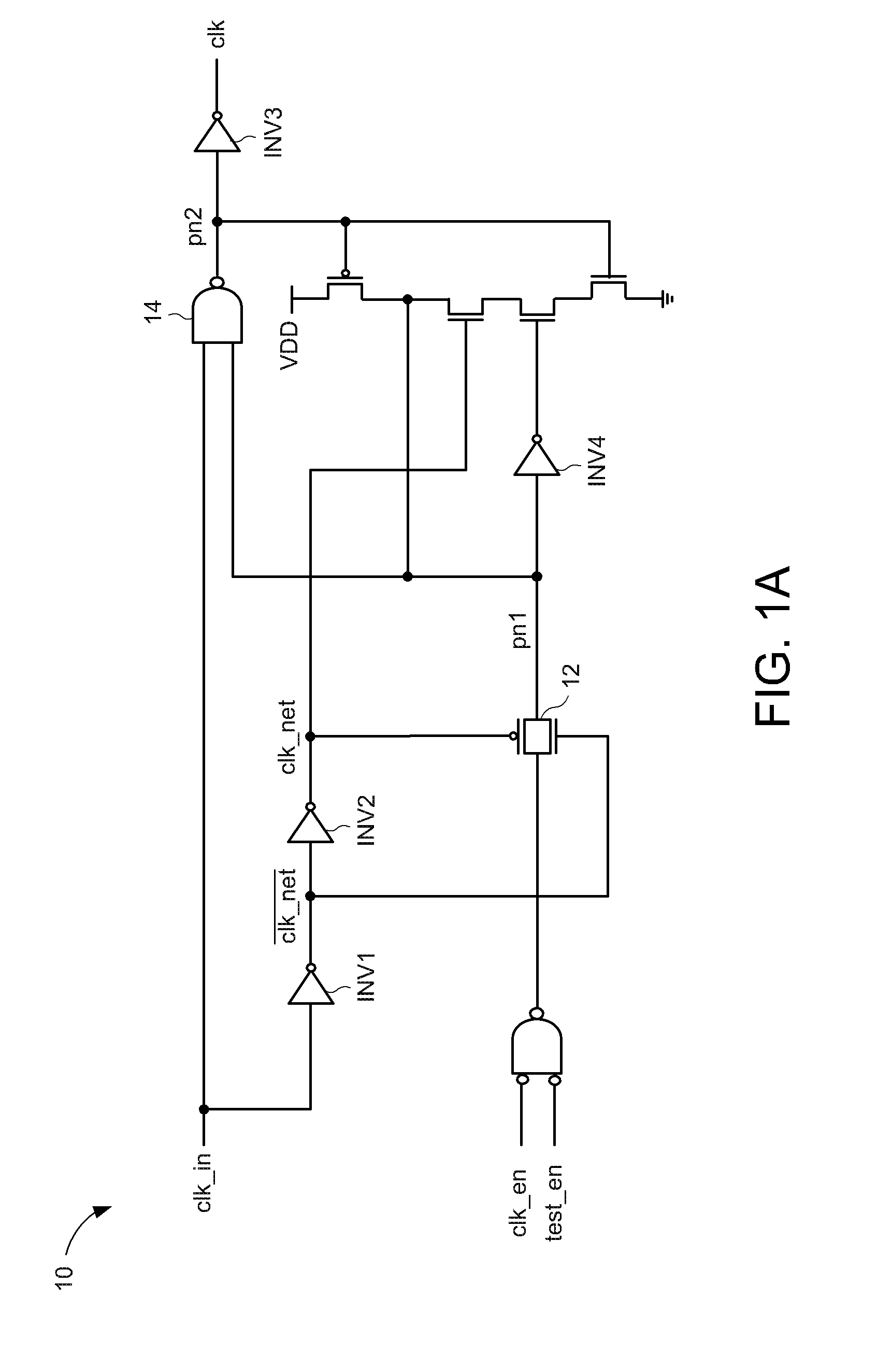
Digital design component with scan clock generation
A master and a slave stage of a flip-flop are each separately clocked with non-overlapping clock signals during scan mode to eliminate a data input scan mode multiplexer. Separate, non-overlapping clocking permits the elimination of hold violations in scan mode for scan mode flip flop chains, permitting the elimination of delay buffers in the scan mode data paths. Resulting application circuits have reduced circuit area, power consumption and noise generation. A clock generator for scan mode clocking is provided to obtain the separate, non-overlapping scan mode clocks. Scan mode clocks may be generated with a toggle flip flop, a pulse generator or a clock gating circuit.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and device for clock gate controlling
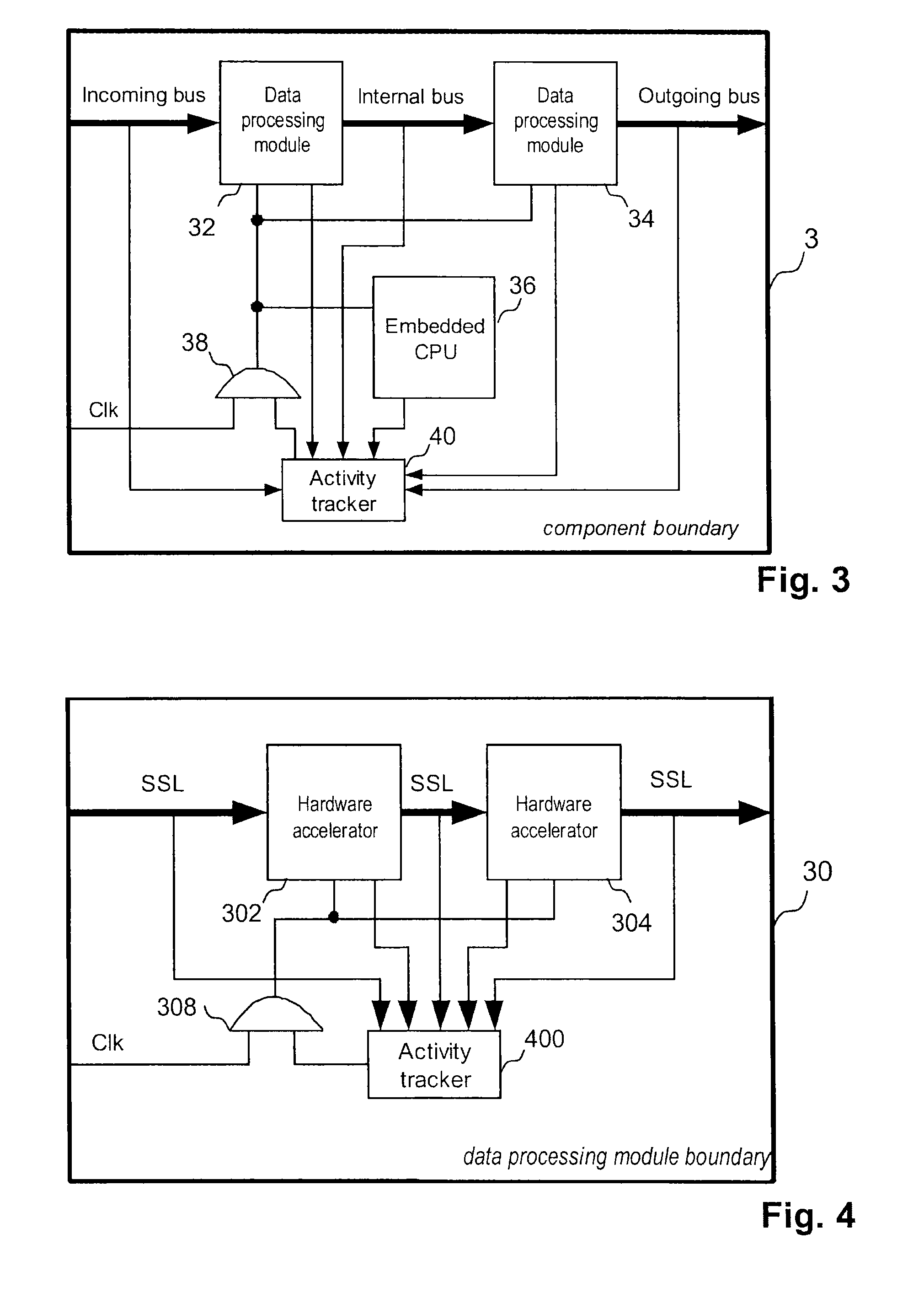
InactiveUS20110202788A1Increase coverageReduced activityEnergy efficient ICTGenerating/distributing signalsStreaming dataData transmission
A method and an activity tracking device for controlling clock gating of a data processing block is provided. The processing block is one of a plurality of data processing blocks of a circuitry system interconnected by a streaming data bus. The activity tracking device receives a busy indication from processing units and streaming data bus segments of the data processing block to keep track of the data transfer and processing activity therein, and has an output connected to a clock gate at the root of the local clock distribution network of the data processing block to gate off the clock of the data processing block when an idle condition is detected, and to recover the clock when a wake-up condition is detected. This provides a low complexity way of automatic clock gating in SoC designs, and generally a way to reduce power consumption of electronic devices.
Owner:INTEL CORP
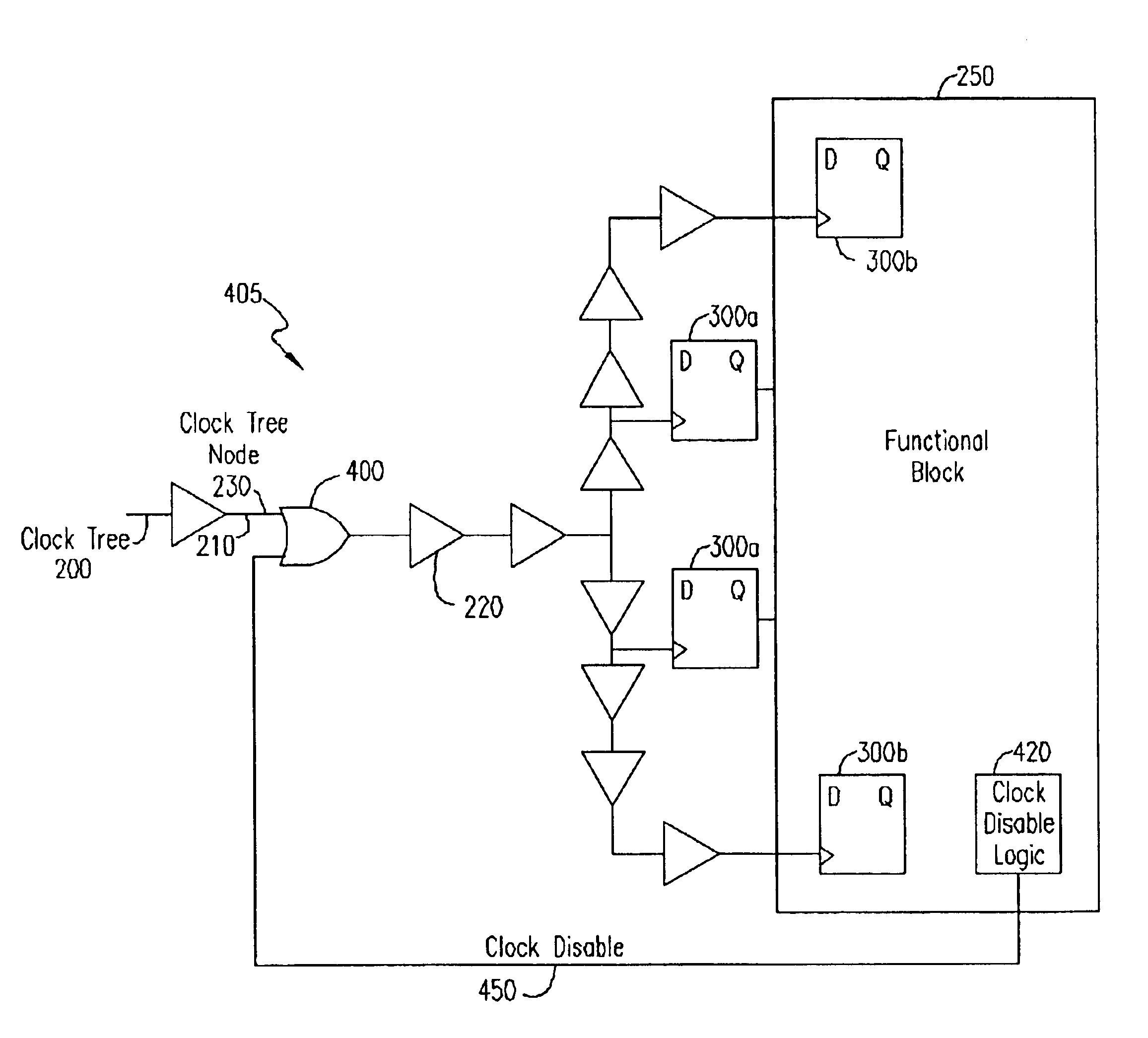
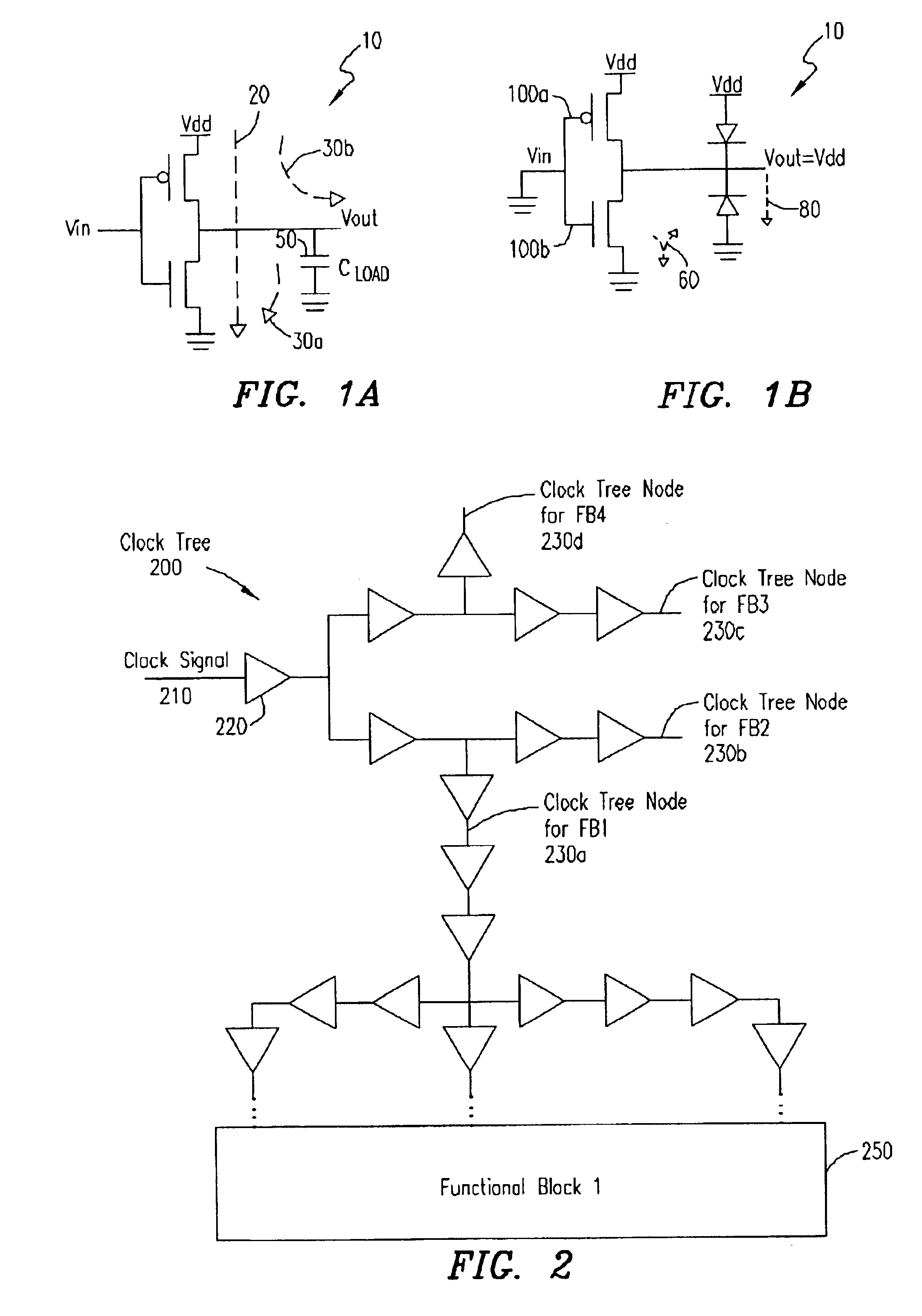
Method and apparatus for clock gating clock trees to reduce power dissipation
ActiveUS6822481B1Reduce power consumptionAvoid switchingEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingClock treeLogic gate
A clock gating circuit reduces the power dissipation in a digital circuit including at least one functional block by gating the clock signal at an input to a clock tree feeding the functional block. The clock gating circuit includes a logic gate that receives a clock signal and a clock disable signal generated by the functional block, and gates the clock signal at the input to the clock tree feeding the functional block. Further, a global signal generator is provided to transmit a global signal to each of the functional blocks to prevent the generation of clock disable signals, when necessary, such as during testing of chips.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
Clock gating for system-on-chip elements
ActiveUS9571341B1Save powerReducing latency penaltySubstation remote connection/disconnectionPower supply for data processingComputer hardwareNetworks on chip
An aspect of the present disclosure provides a hardware element in a Network on Chip (NoC), wherein the hardware element includes a clock gating circuit configures one or more neighboring hardware elements to activate before receiving new incoming data and to sleep after a defined number of cycles, wherein the defined number of cycles can be counted from a cycle having non-receipt of incoming data and / or having a clearance of all data within an input queue of a source hardware element.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
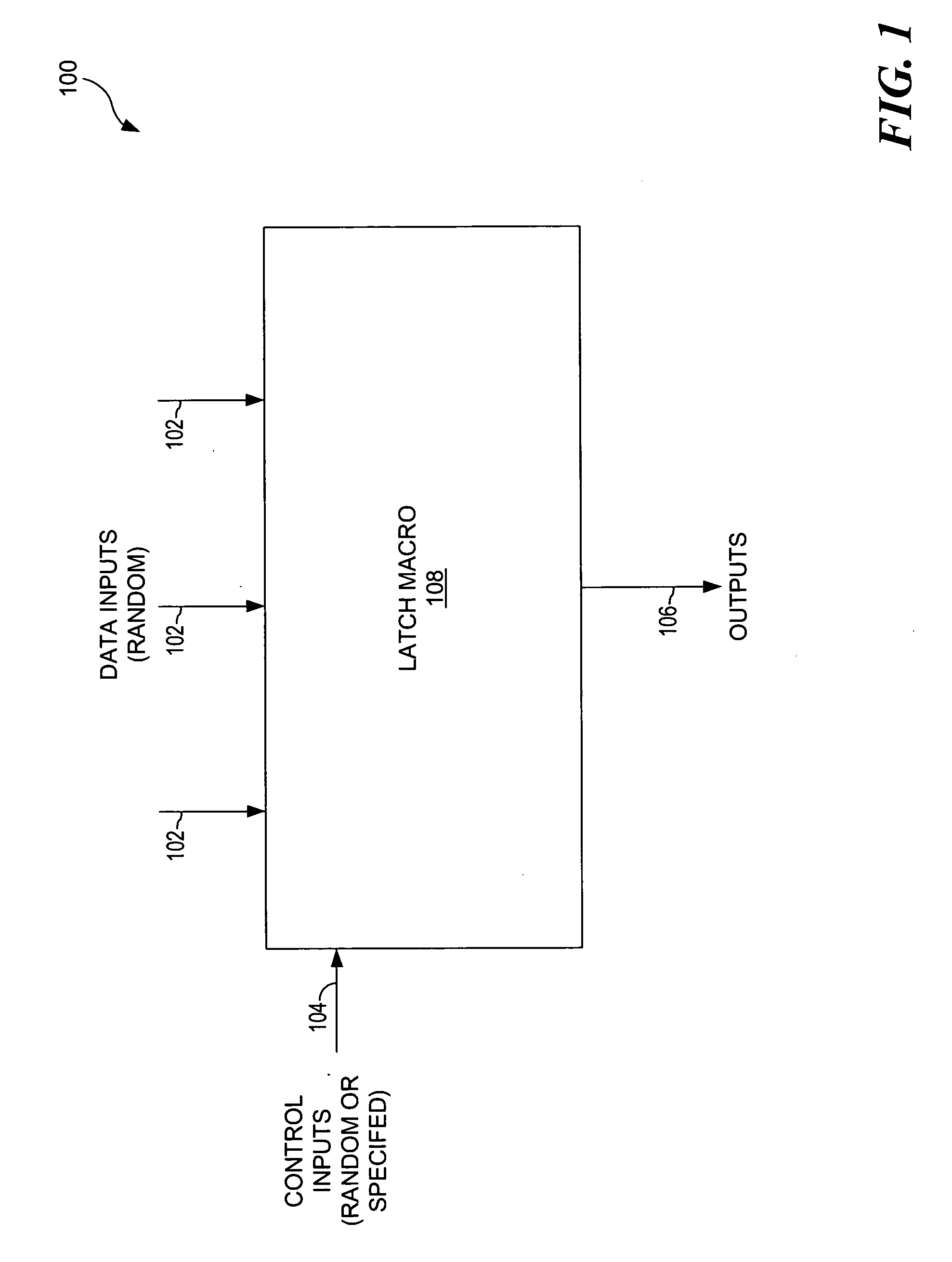
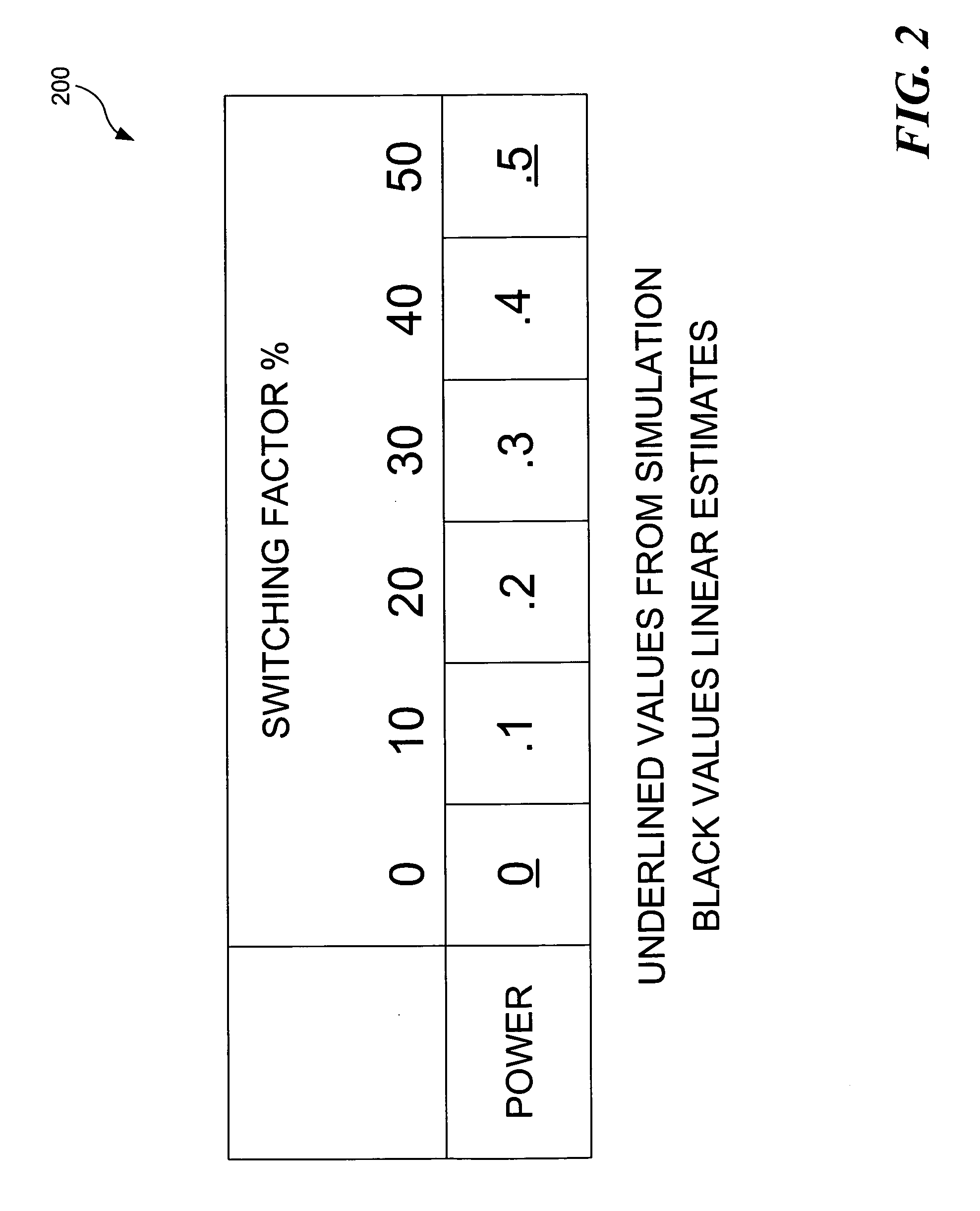
Method and apparatus to generate circuit energy models with multiple clock gating inputs
InactiveUS20060168456A1Energy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementBiological activationClock gating
A method, a computer program, and an apparatus are provided for generating circuit energy models for a macro using multiple clock gating inputs. Circuit energy models are used to estimate system power consumption. The present invention enables circuit energy models to be created for macros that contain multiple clock gating inputs. Energy tables are created based upon the macro's input switching factor and the clock activation percentage. The clock activation percentage is produced by turning on and off the multiple clock gating inputs during the simulations. These energy tables are generated from a minimum number of power simulations. By using clock activation percentage as a parameter accurate power estimations are produced.
Owner:IBM CORP
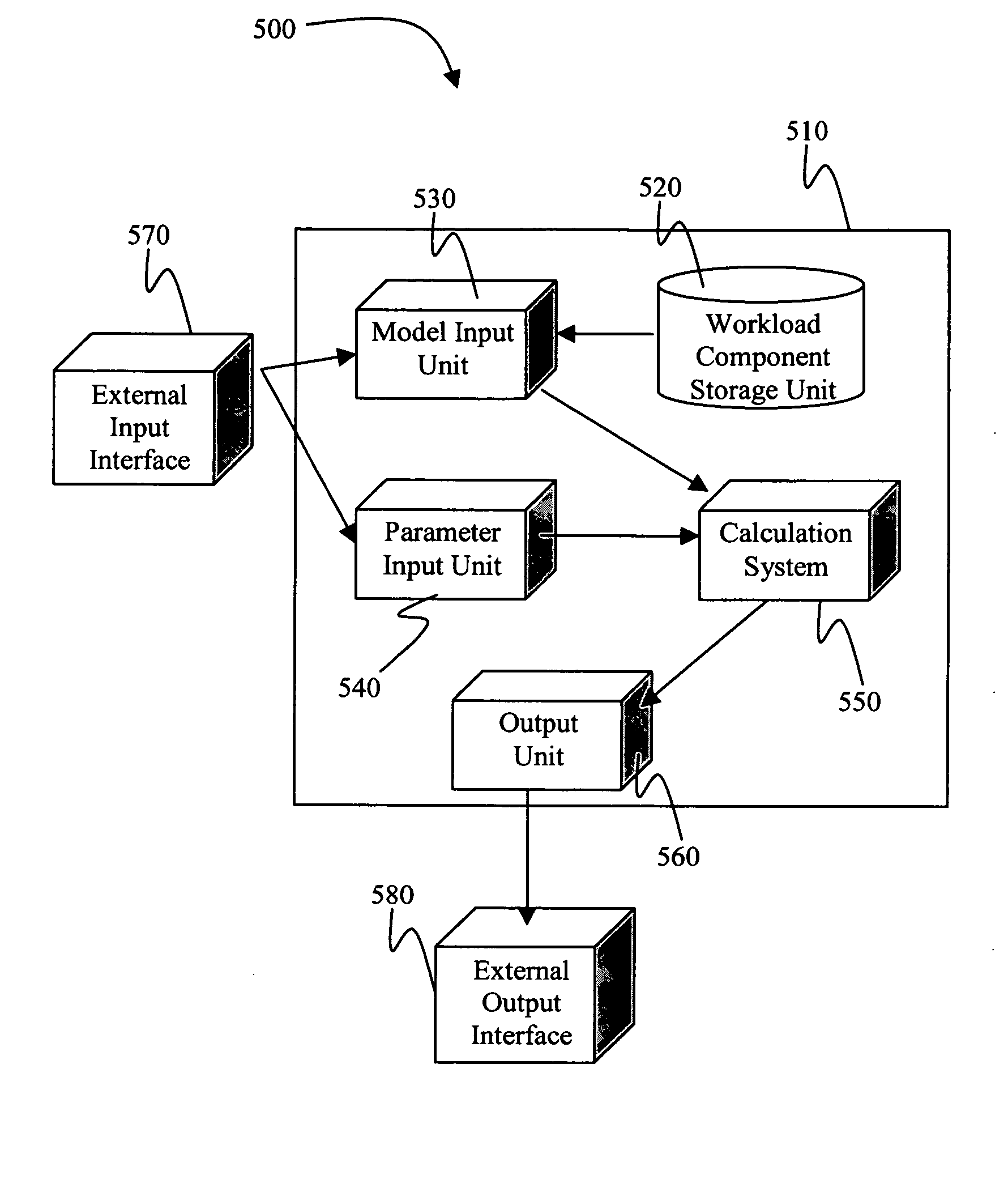
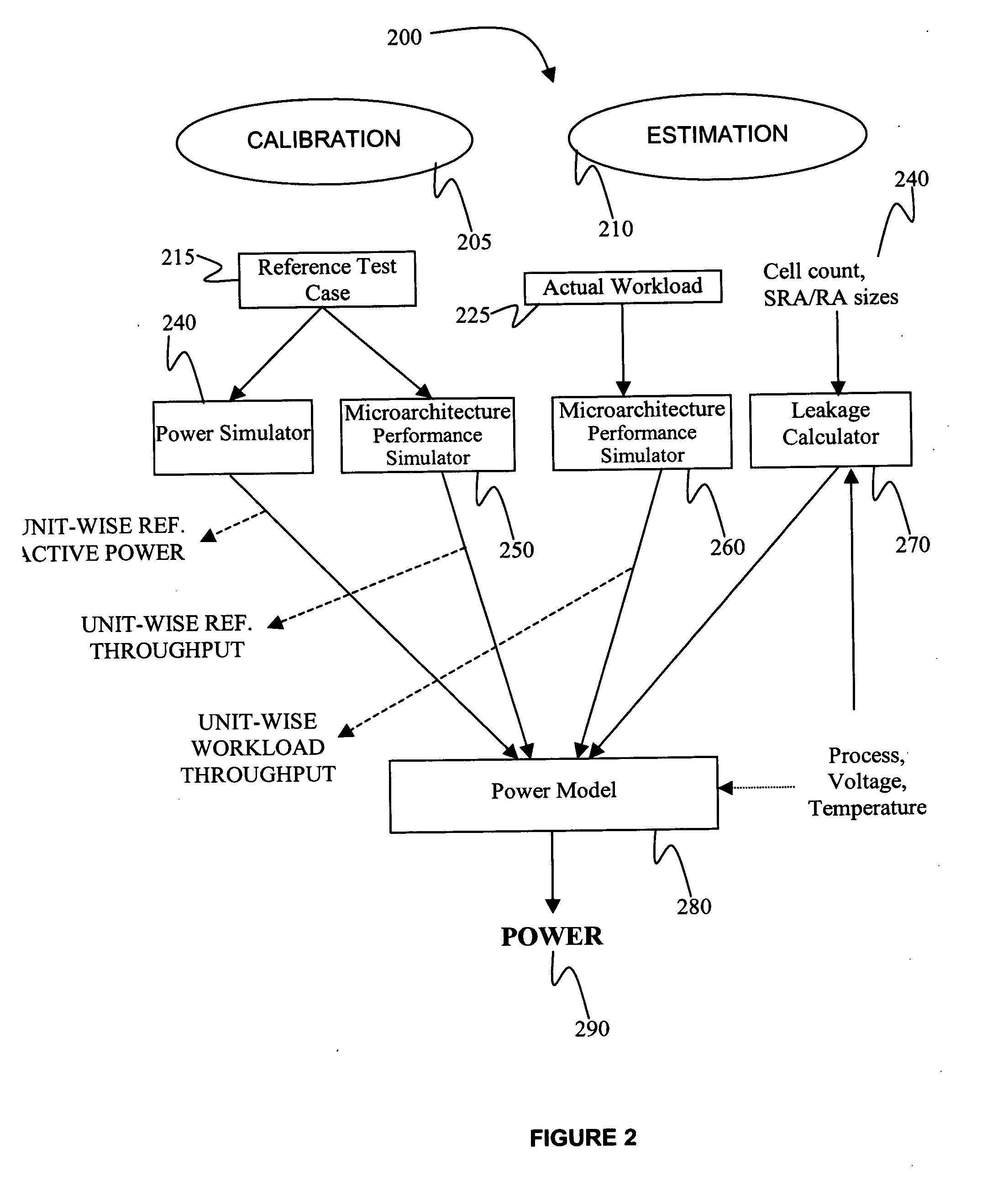
Architectural level throughput based power modeling methodology and apparatus for pervasively clock-gated processor cores
InactiveUS20060080625A1Improve performanceAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsCAD circuit designPower analysisReference test
A method, system, and apparatus for estimating the power dissipated by a processor core processing a workload, where the method includes analyzing a reference test case to generate a reference workload characteristic. Analyzing an actual workload to generate an actual workload characteristic. Performing a power analysis for the reference test case to establish a reference power dissipation value. Estimating an actual workload power dissipation value responsive to the actual and reference workload characteristics and the reference power dissipation value
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
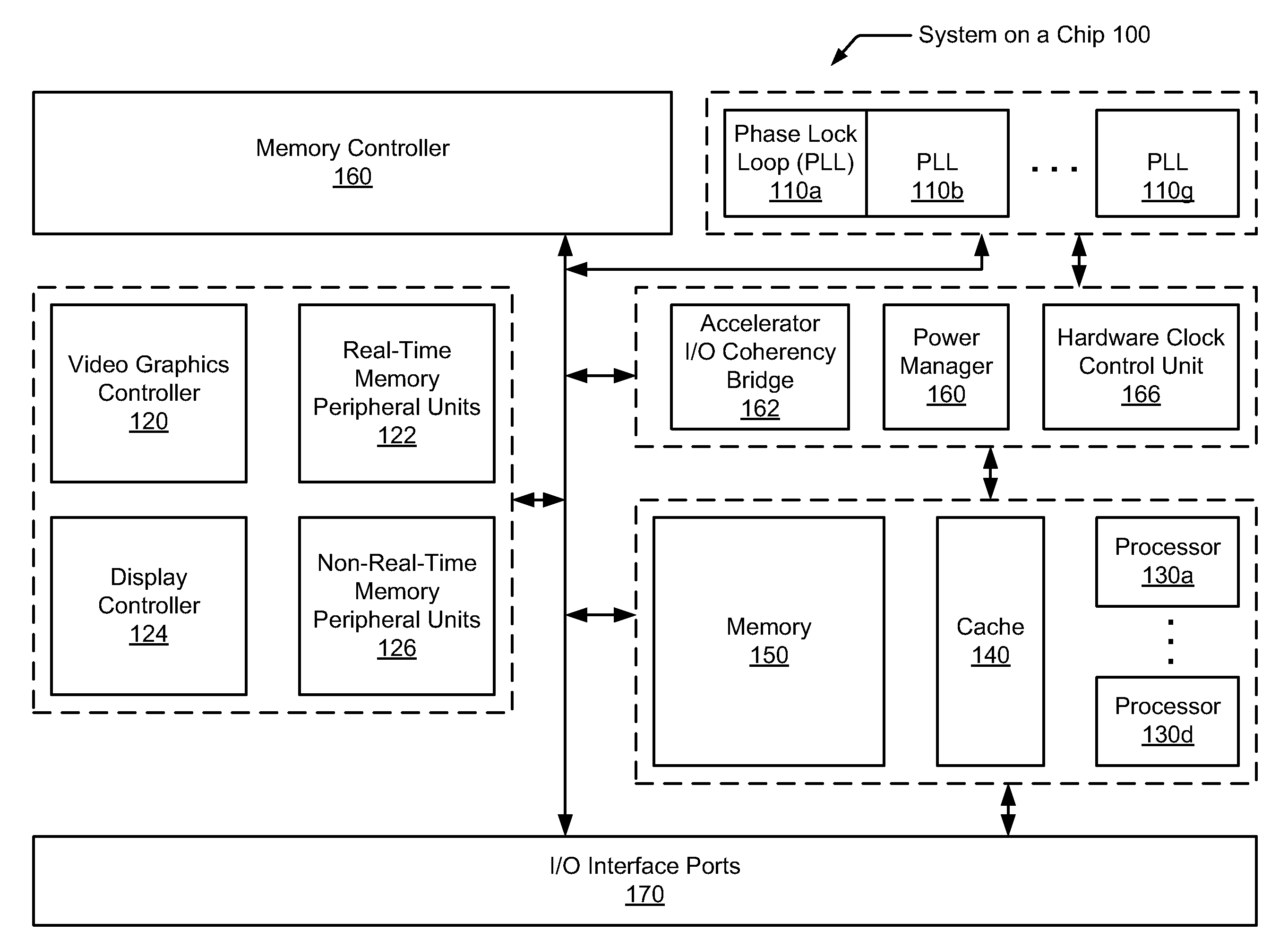
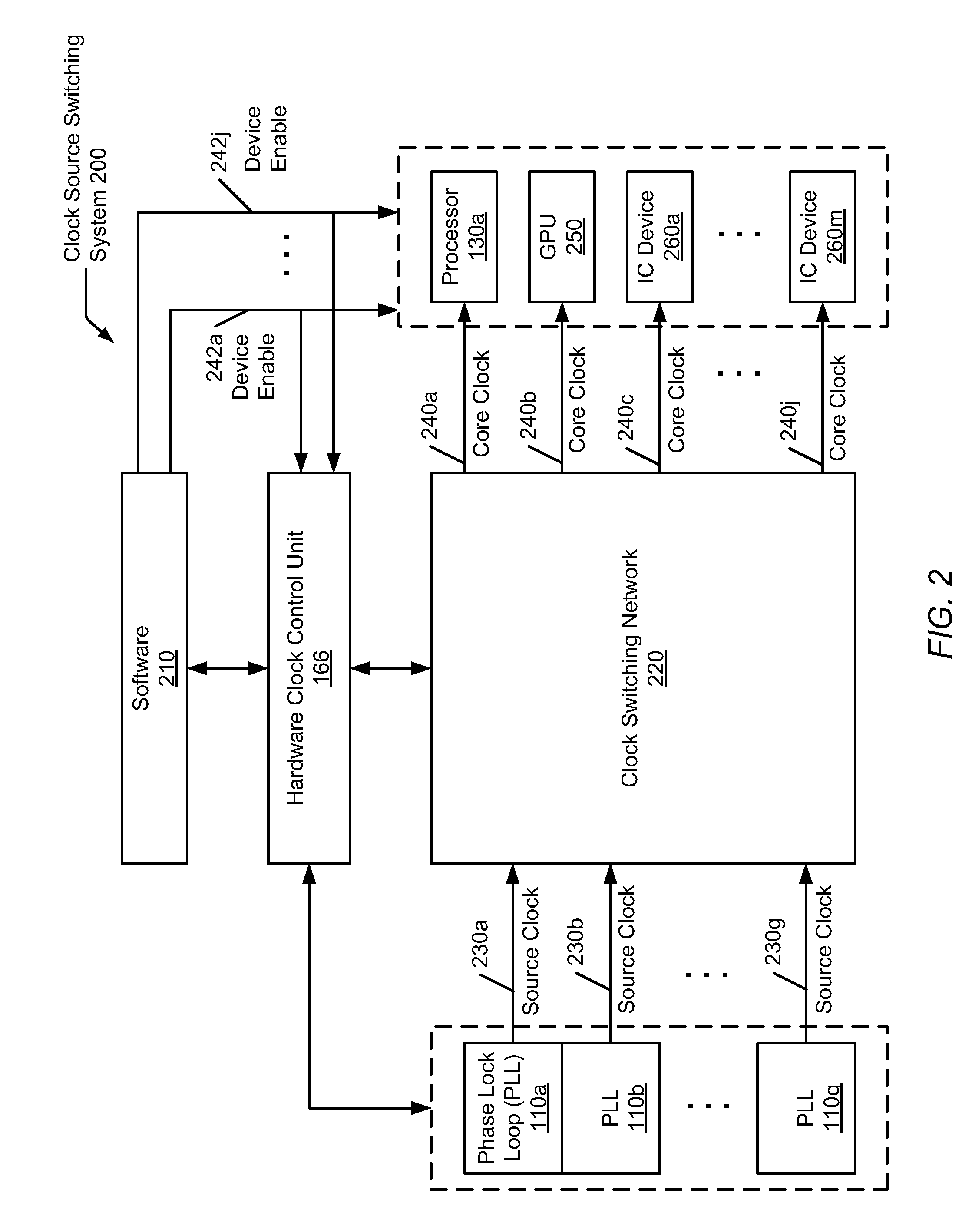
Hardware-based automatic clock gating
A system and method for automatically updating with hardware clock tree settings on a system-on-a-chip (SOC). A SOC includes a hardware clock control unit (HCCU) coupled to a software interface and a clock tree. The SOC also includes multiple integrated circuit (IC) devices, wherein each IC device receives one or more associated core clocks provided by one or more phase lock loops (PLLs) via the clock tree. The HCCU receives a software-initiated request specifying a given IC device is to be enabled. The HCCU identifies one or more core clocks used by the given IC device. For each one of the identified core clocks, the HCCU configures associated circuitry within the clock tree to generate an identified core clock. The HCCU may also traverse the clock tree and disable clock generating gates found not to drive any other enabled gates or IC devices.
Owner:APPLE INC
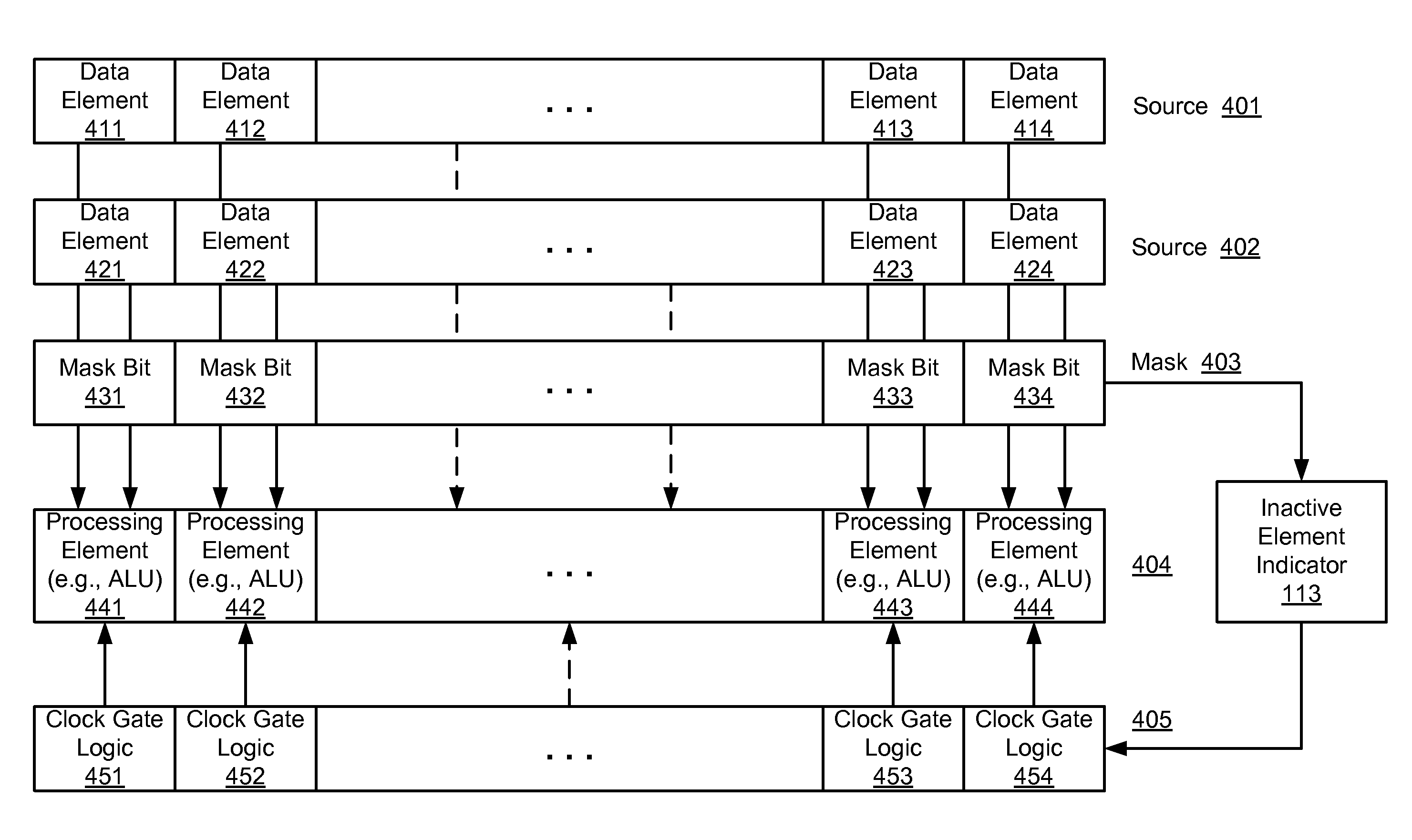
Vector mask driven clock gating for power efficiency of a processor
ActiveUS20150220345A1Energy efficient ICTProgram control using stored programsScheduling instructionsPower Management Unit
A processor includes an instruction schedule and dispatch (schedule / dispatch) unit to receive a single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instruction to perform an operation on multiple data elements stored in a storage location indicated by a first source operand. The instruction schedule / dispatch unit is to determine a first of the data elements that will not be operated to generate a result written to a destination operand based on a second source operand. The processor further includes multiple processing elements coupled to the instruction schedule / dispatch unit to process the data elements of the SIMD instruction in a vector manner, and a power management unit coupled to the instruction schedule / dispatch unit to reduce power consumption of a first of the processing elements configured to process the first data element.
Owner:INTEL CORP
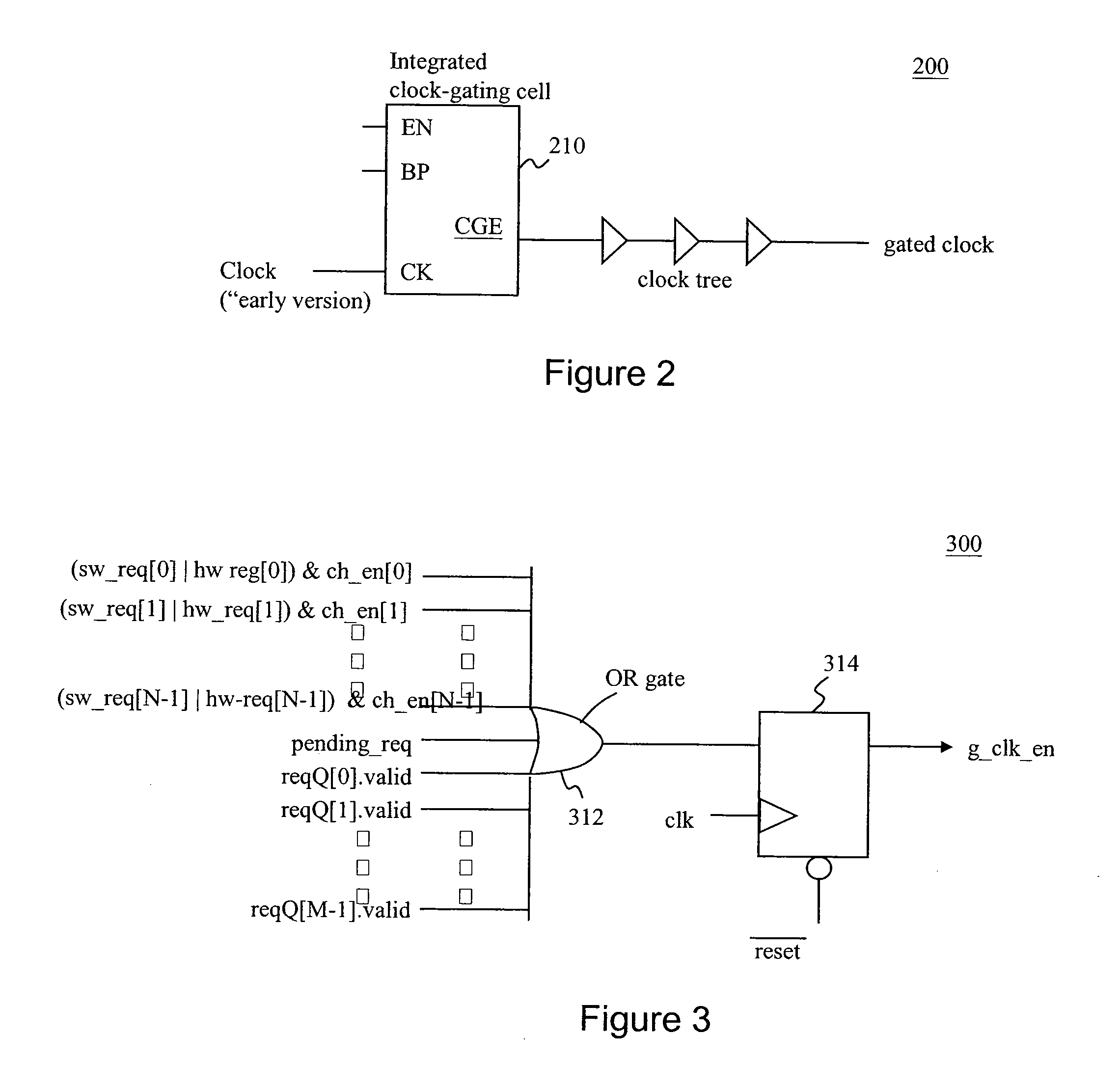
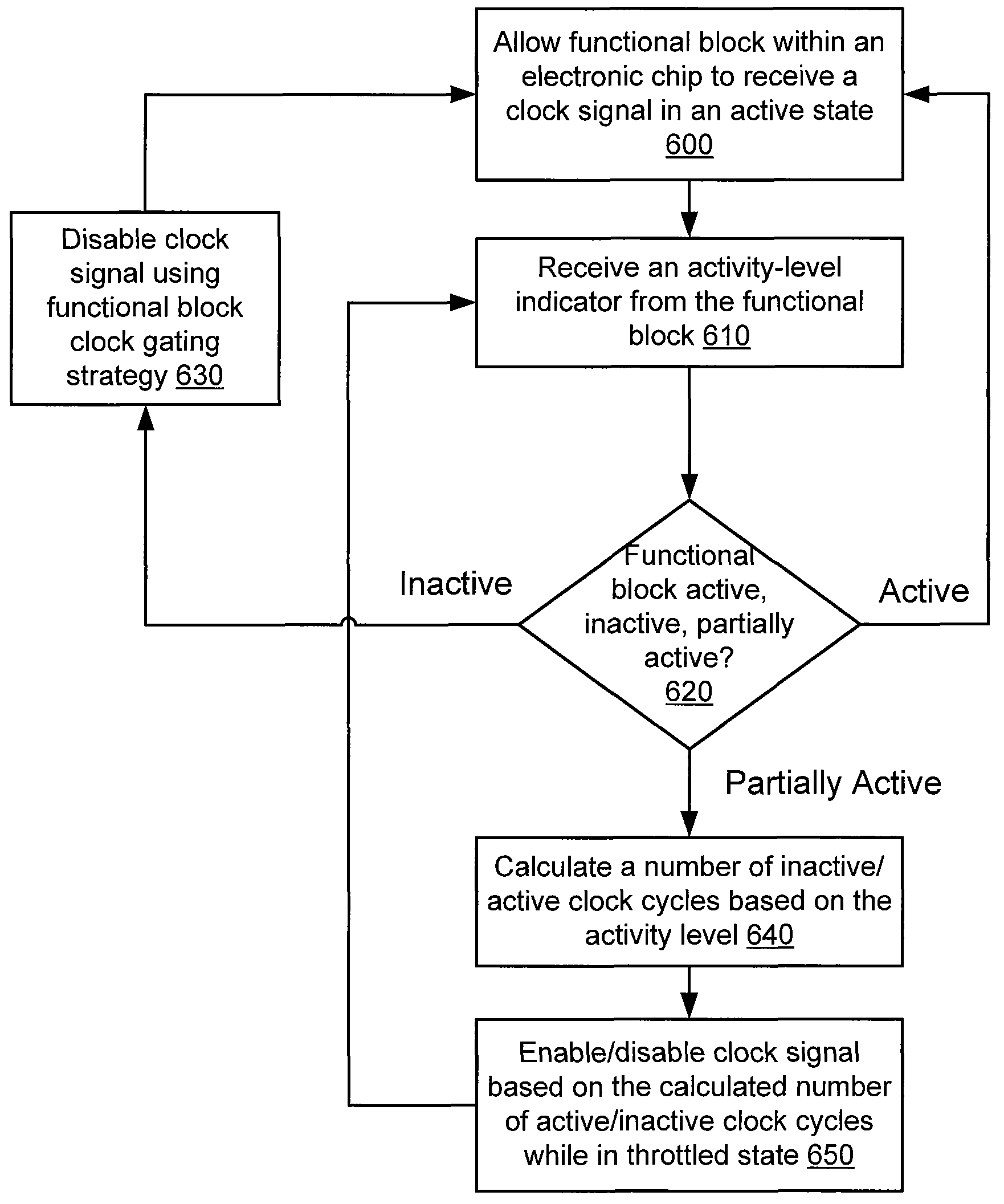
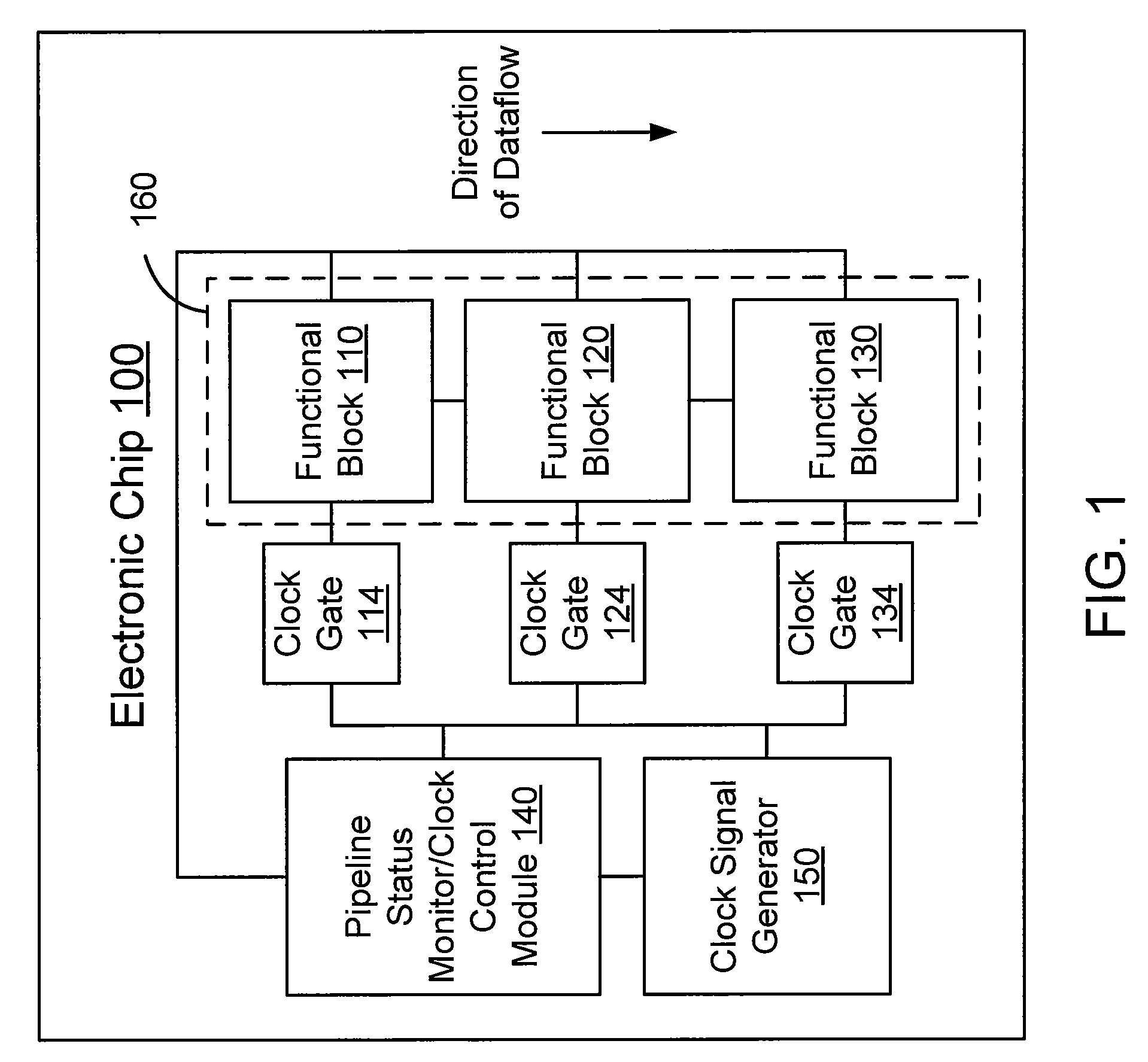
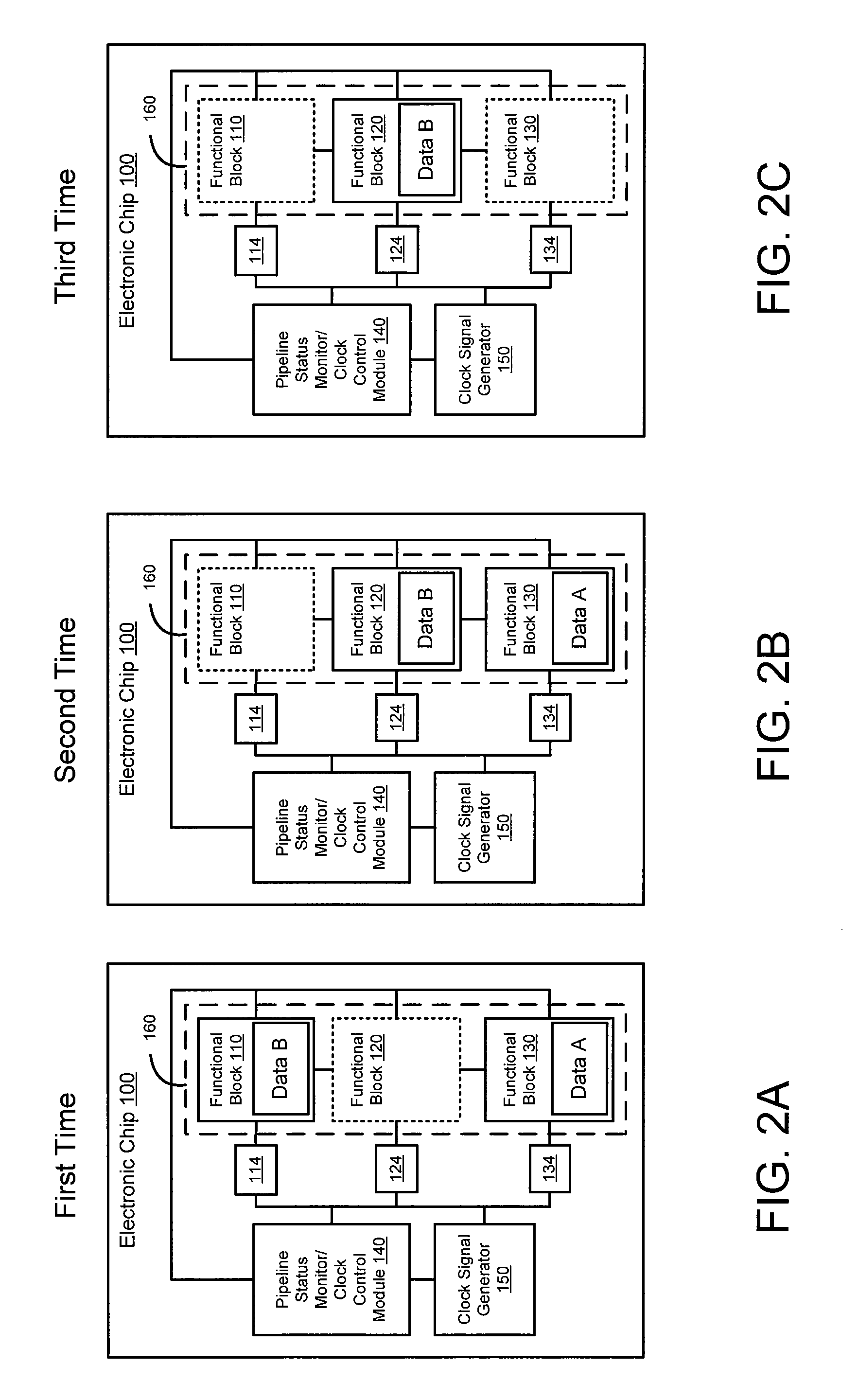
Automatic functional block level clock-gating
An embodiment of the invention includes receiving an indicator of an activity-level of a functional block within an electronic chip. The functional block is included in a processing pipeline having a plurality of functional blocks. Each functional block from the plurality is configured to receive a clock signal from a clock signal generator. A status of the functional block is determined based on the activity-level. The clock signal to at least a portion of the functional block is disabled when the status is an inactive status.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit and design automation system
A scan chain circuit causes a plurality of flip-flops to function as shift registers during execution of a scan test and can execute a scan shift that serially transfers test pattern data for the scan test. A clock gating circuit controls output of a pulse of a clock signal supplied to the scan chain circuit in accordance with a clock gating signal, whereas disables the clock gating signal based on a logic of a scan enable signal authorizing the scan shift. A first clock gating circuit included in the clock gating circuit disables the clock gating signal during the scan shift based on the logic of the scan enable signal and also inverts the clock signal and outputs a result of inverting.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
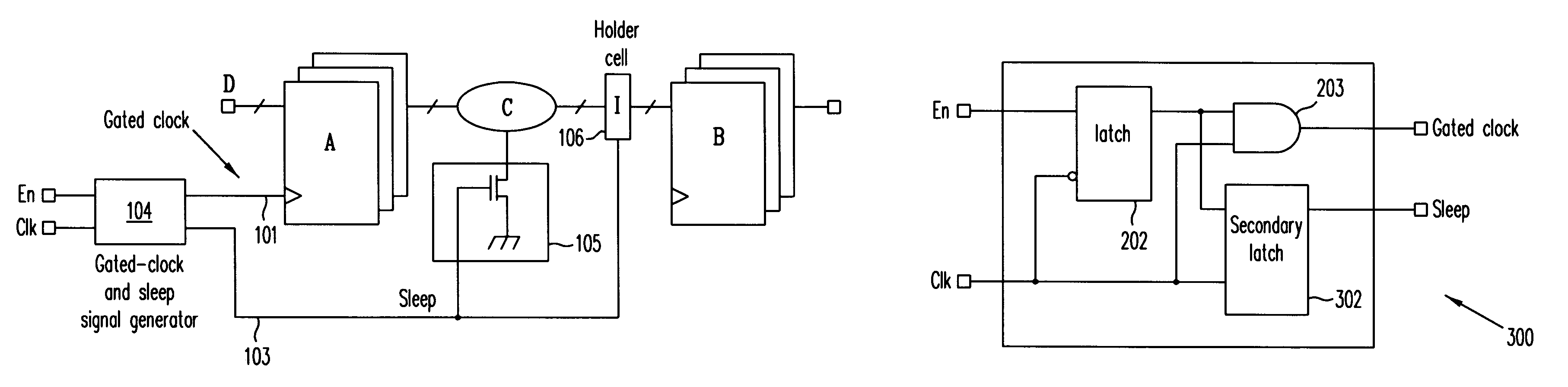
Automatic extension of clock gating technique to fine-grained power gating
A method extends a clock-gating technique to provide a sleep signal for controlling switch circuits that reduce active leakage power. Using this extension of the clock-gating technique, fine-grained power-gating is achieved. The method automatically identifies, at an RTL or a gate level, the logic circuits that can be power-gated. The method of the present invention derives a sleep signal for fine-grained power-gating that may be applicable to both time-critical and non-time-critical designs.
Owner:ANSYS
Single event radiation effect resistant reinforced latch circuit
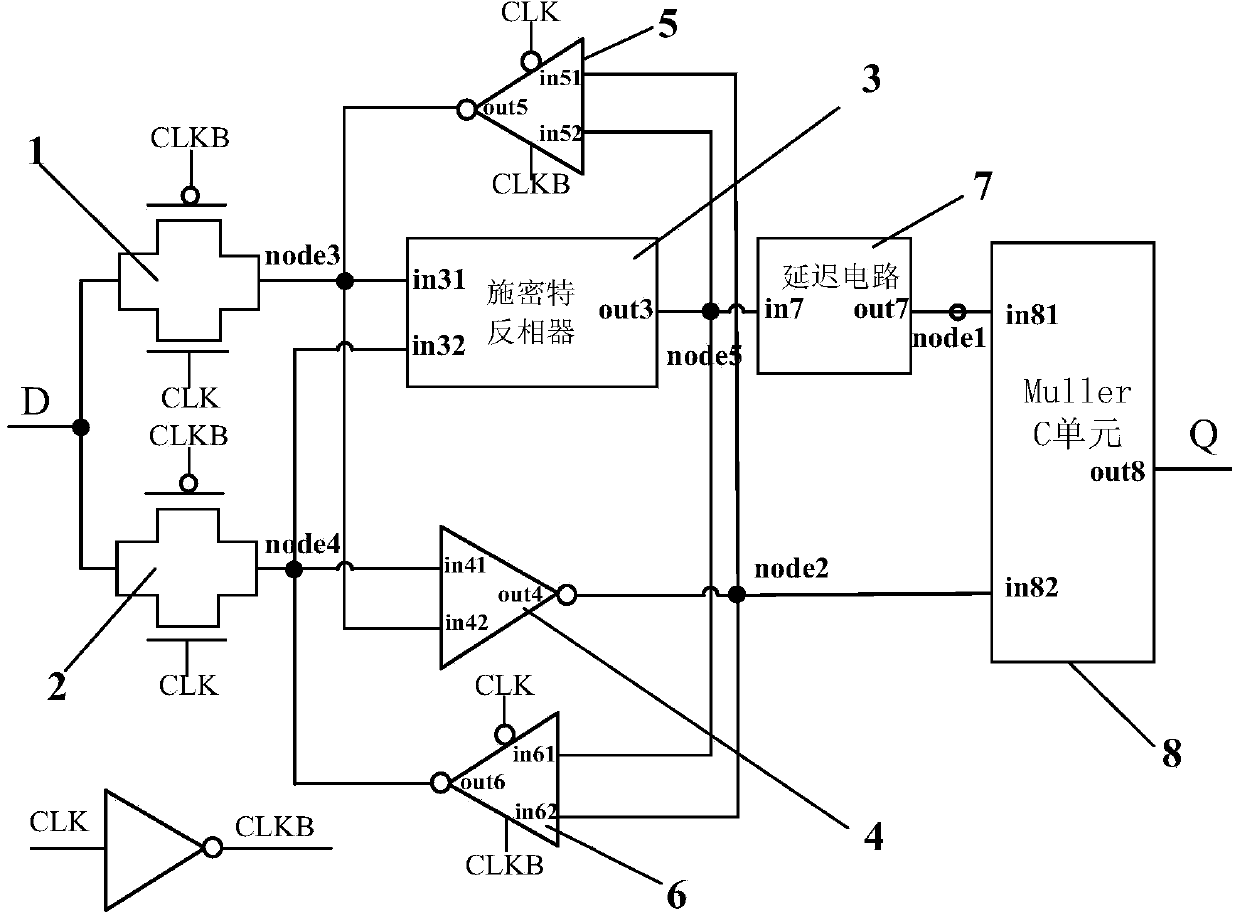
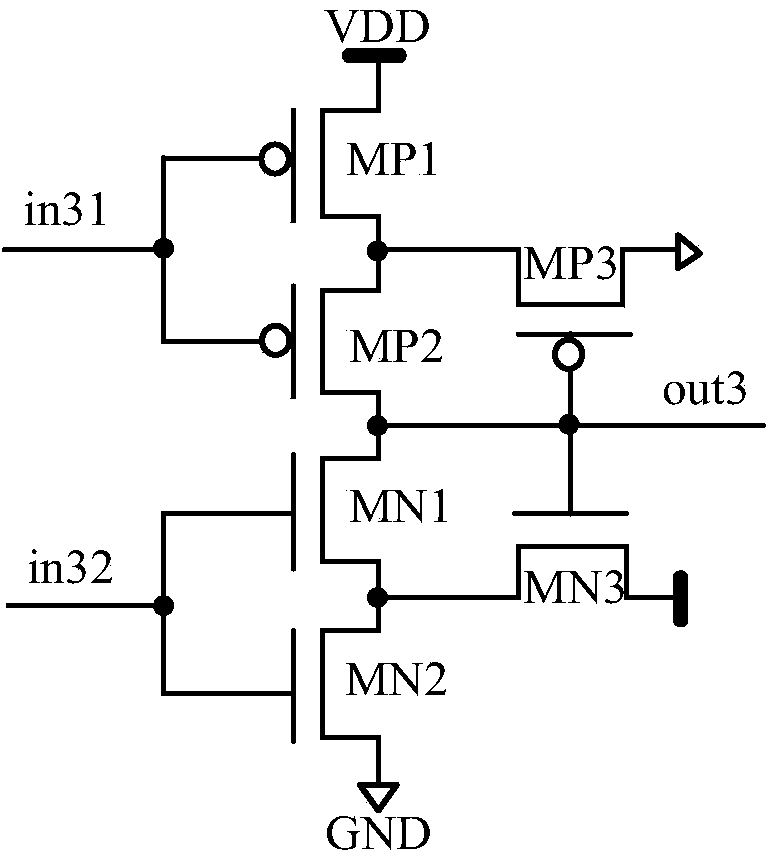
InactiveCN104202037AFully hardenedReduce power consumptionElectric pulse generatorLogic circuitsHysteresisTransmission gate
The invention discloses a single event radiation effect resistant reinforced latch circuit. The single event radiation effect resistant reinforced latch circuit comprises a first transmission gate unit, a second transmission gate unit, a Schmitt inverter, a conventional input separation inverter, a first input separation clock-controlled inverter, a second input separation clock-controlled inverter, a delay circuit and a MullerC unit circuit. When the single event radiation effect resistant reinforced latch circuit operates under a transparent mode, a hysteresis effect of the Schmitt inverter and a delay difference of a latch interior unit are effectively used and SET pulses from a combinational logic unit are shielded through the MullerC unit; when the single event radiation effect resistant reinforced latch circuit operates under a latch mode, any interior node generating SEU due to the irradiation effect can be recovered through states of other nodes through a DIC unit structure having a self-recovery capability and correct output of the latch is guaranteed; accordingly the single event radiation effect resistant reinforced latch circuit has the advantages of effectively eliminating the radiation effect influences and being applicable to a clock gating circuit and small in power consumption and area costs.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Clock gating circuit for reducing dynamic power
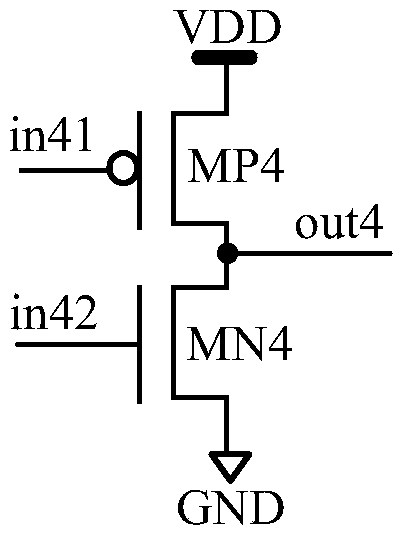
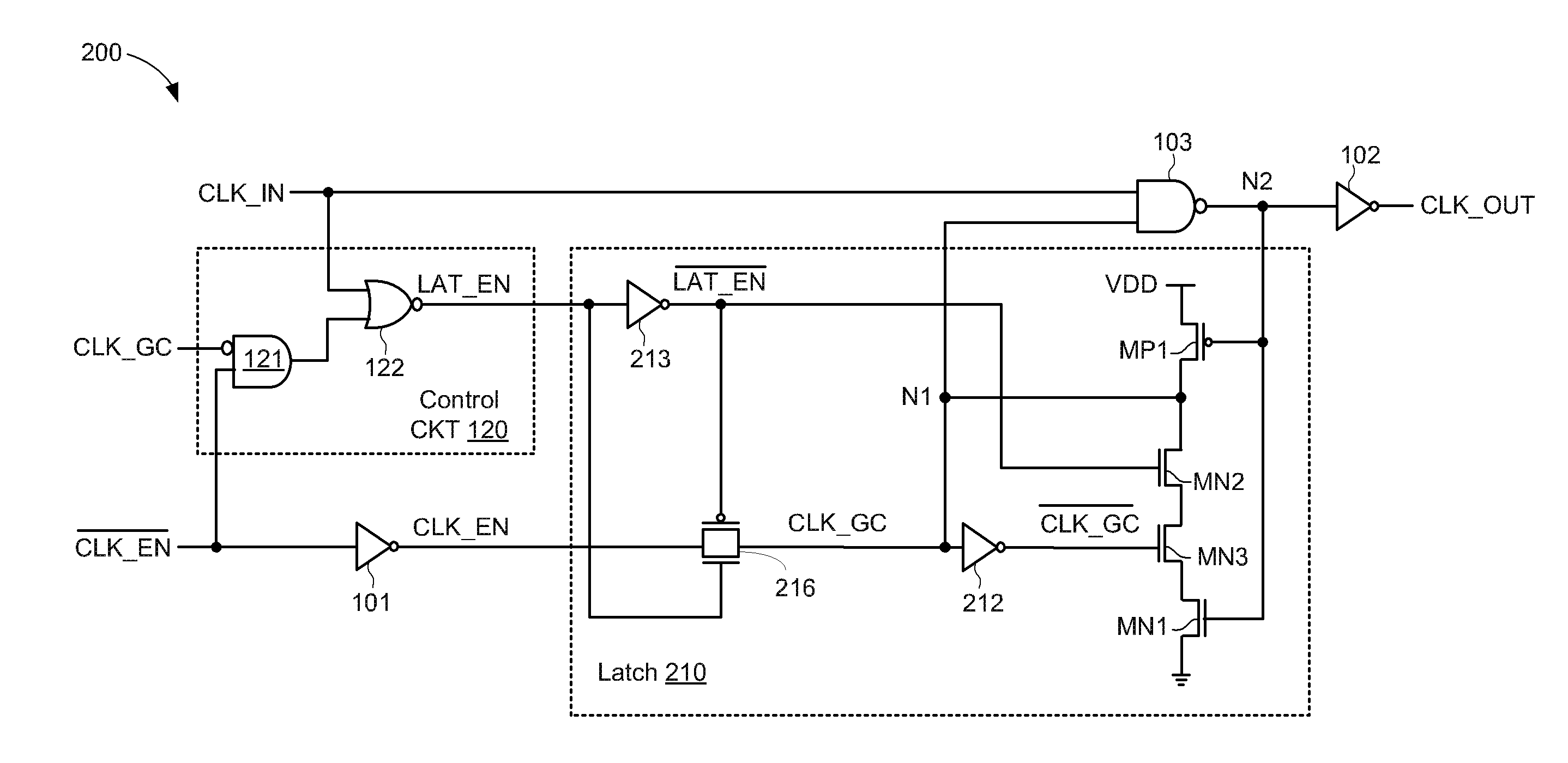
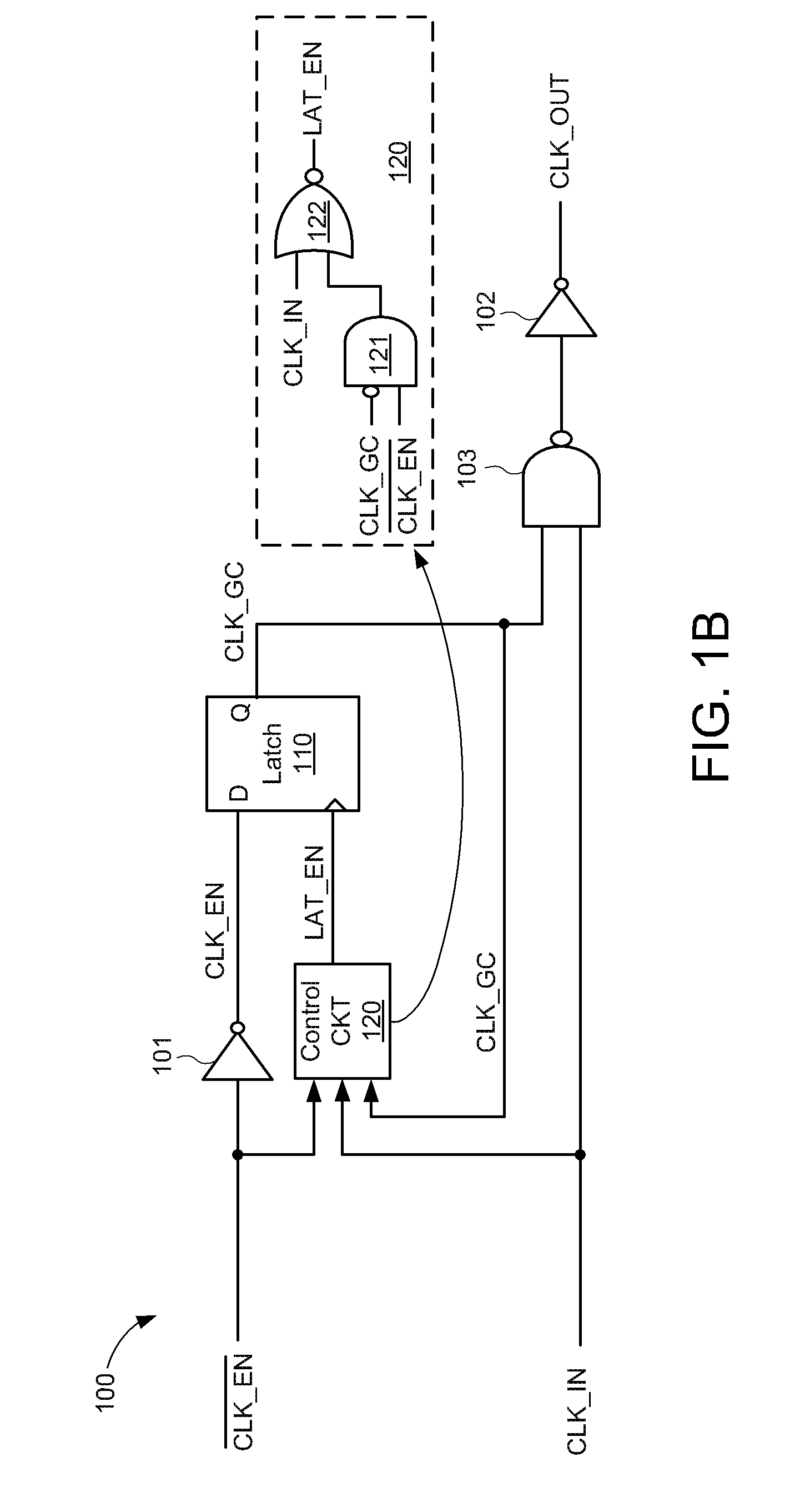
ActiveUS20150200669A1Power reduction by control/clock signalElectric pulse generatorData terminalControl signal
A clock-gating circuit is disclosed that may reduce unnecessary power consumption associated with clock distribution networks. For some embodiments, the clock-gating circuit includes a latch control circuit, a storage latch, and a logic gate. The control circuit has inputs to receive an input clock signal, a clock enable signal, and a clock gating control signal, and has an output terminal to generate a latch enable signal. The latch has a data terminal responsive to the clock enable signal, a latch enable terminal responsive to the latch enable signal, and an output to generate the clock gating control signal. The logic gate has inputs to receive the input clock signal and the clock gating control signal, and has an output terminal to generate an output clock signal. The clock-gating circuit may reduce power consumption during an enabled state by maintaining the latch enable signal at a constant logic state, thereby reducing dynamic power consumption by preventing internal logic gates from dynamically switching logic states while the input clock signal is gated.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com