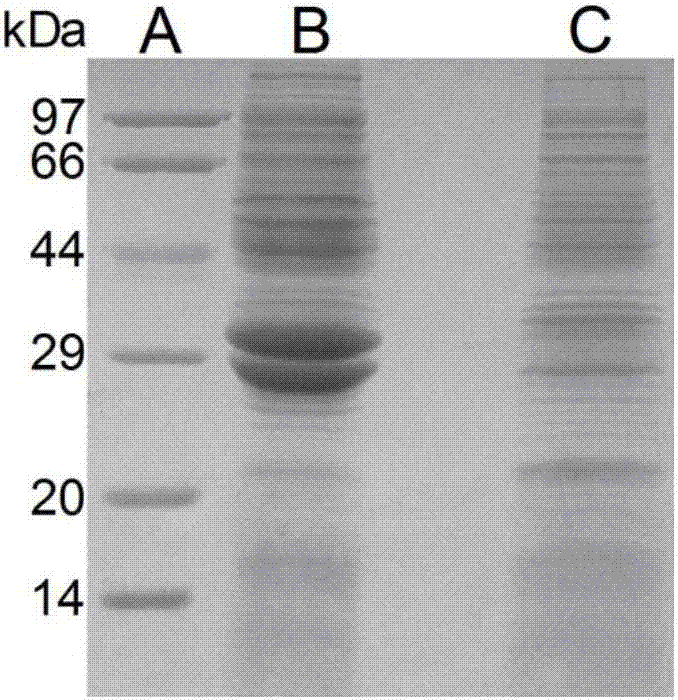
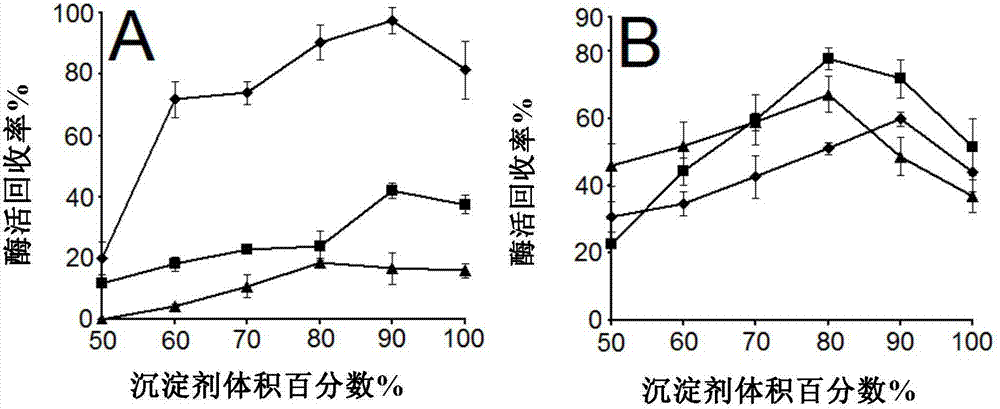
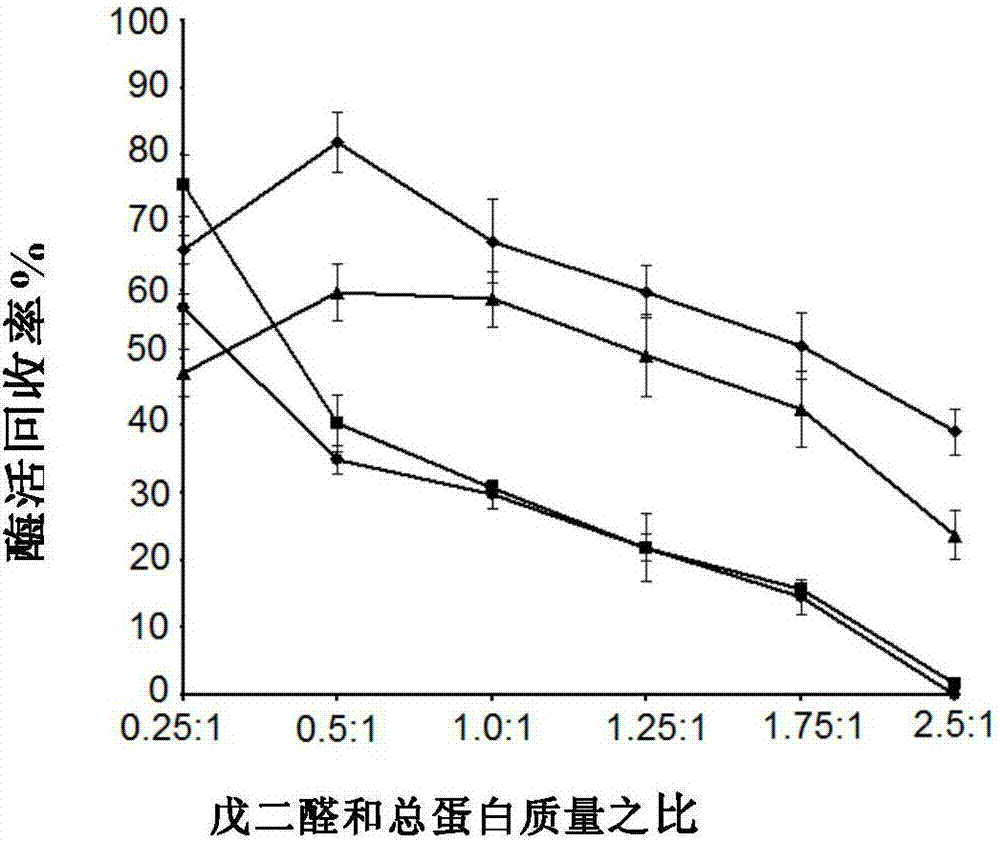
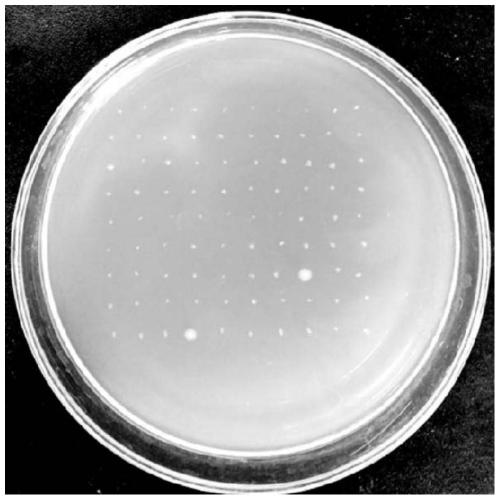
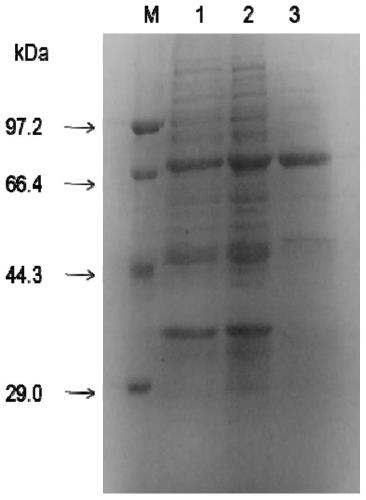
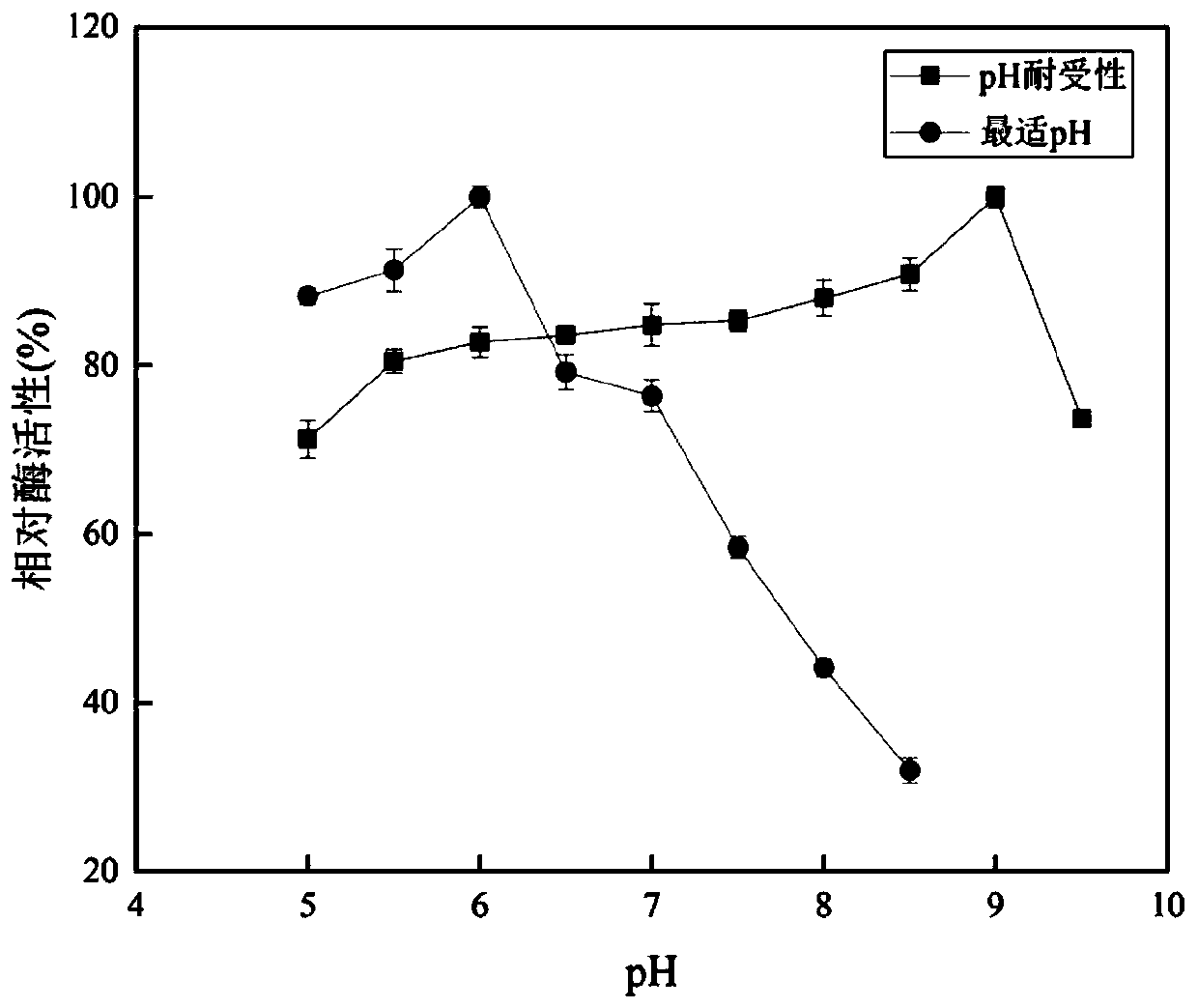
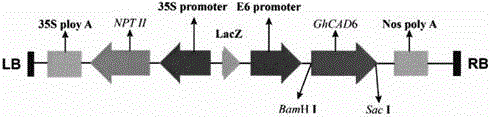
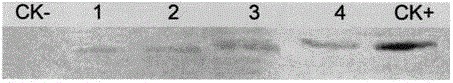
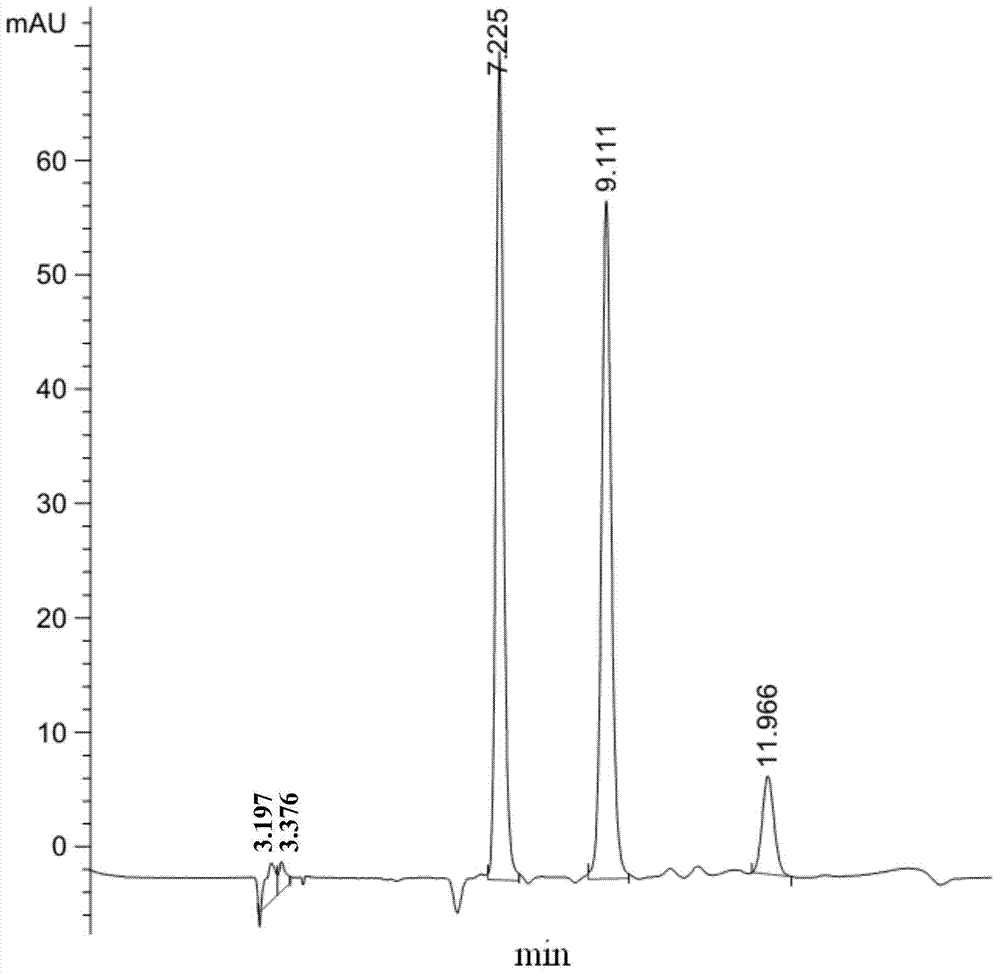
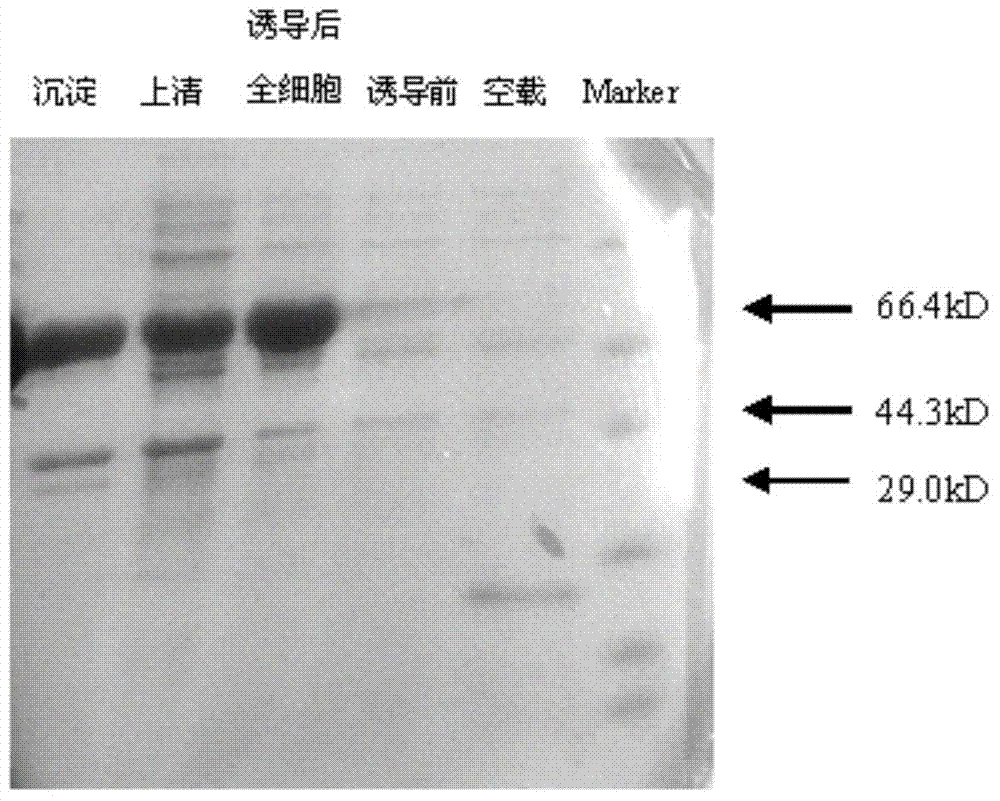
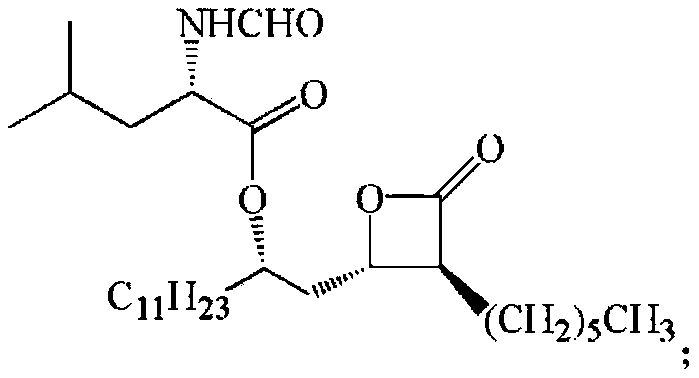
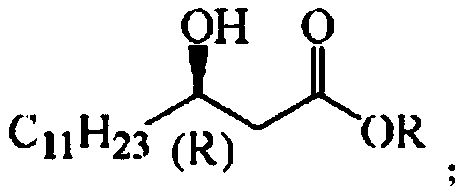
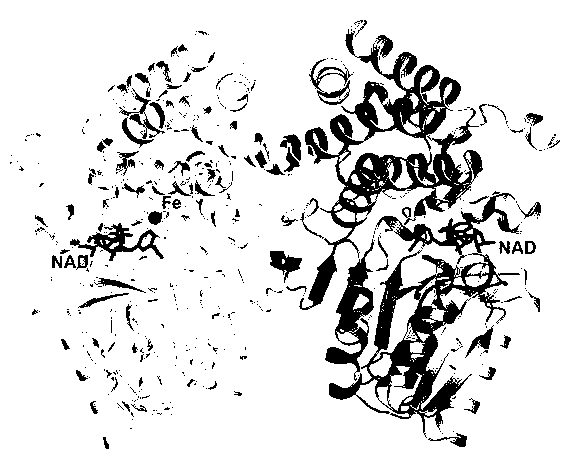Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
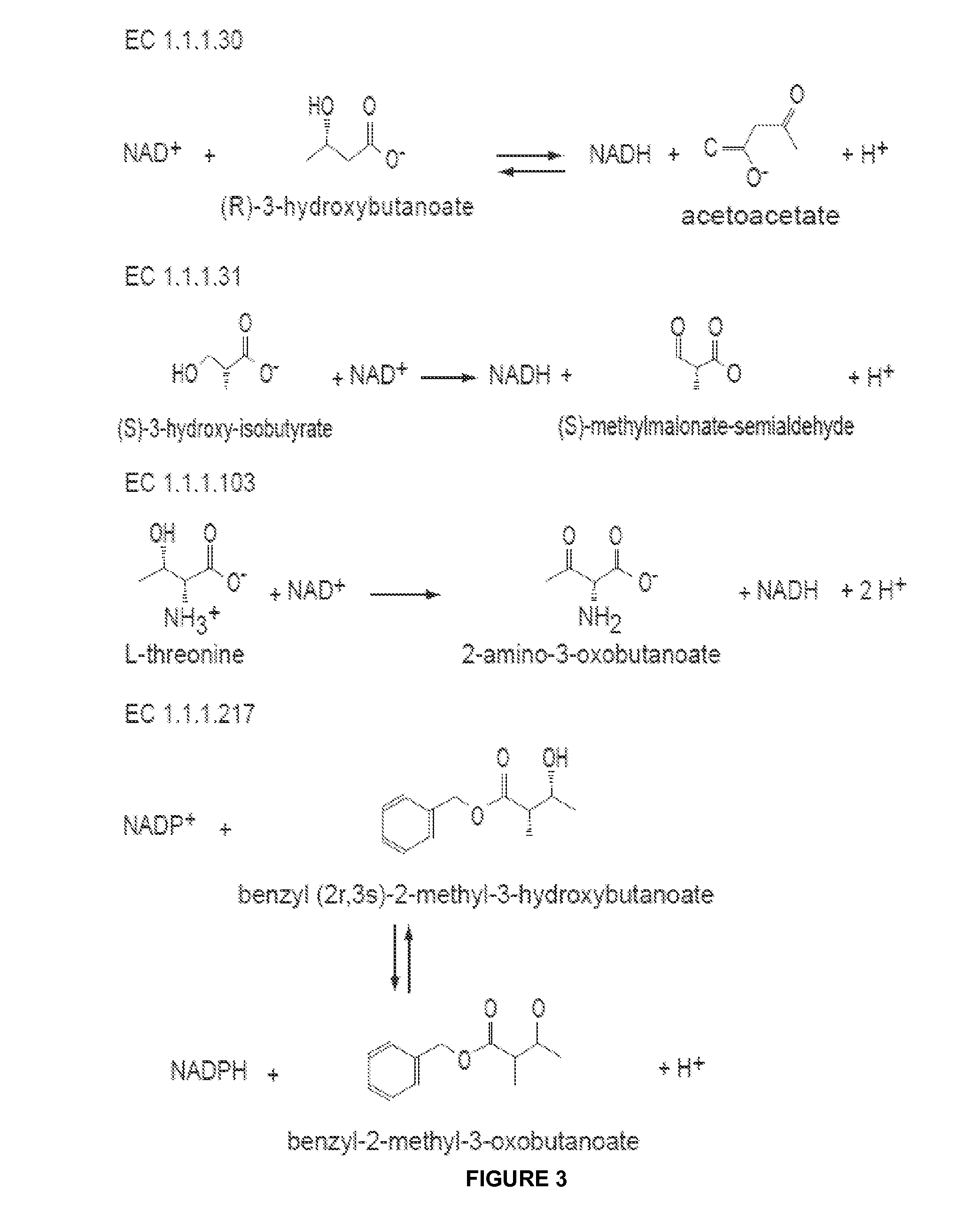
In enzymology, a cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.195) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction cinnamyl alcohol + NADP⁺ ⇌ cinnamaldehyde + NADPH + H⁺ Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are cinnamyl alcohol and NADP⁺, whereas its 3 products are cinnamaldehyde, NADPH, and H⁺. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with NAD⁺ or NADP⁺ as acceptor.
Use of mixed duplex oligonucleotides to effect localized genetic changes in plants
InactiveUS7094606B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationACC oxidaseGenetic Change
Owner:CIBUS
Method for producing an l-amino acid using a bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
InactiveUS20090203090A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaOxidoreductasesBacteroidesArginine
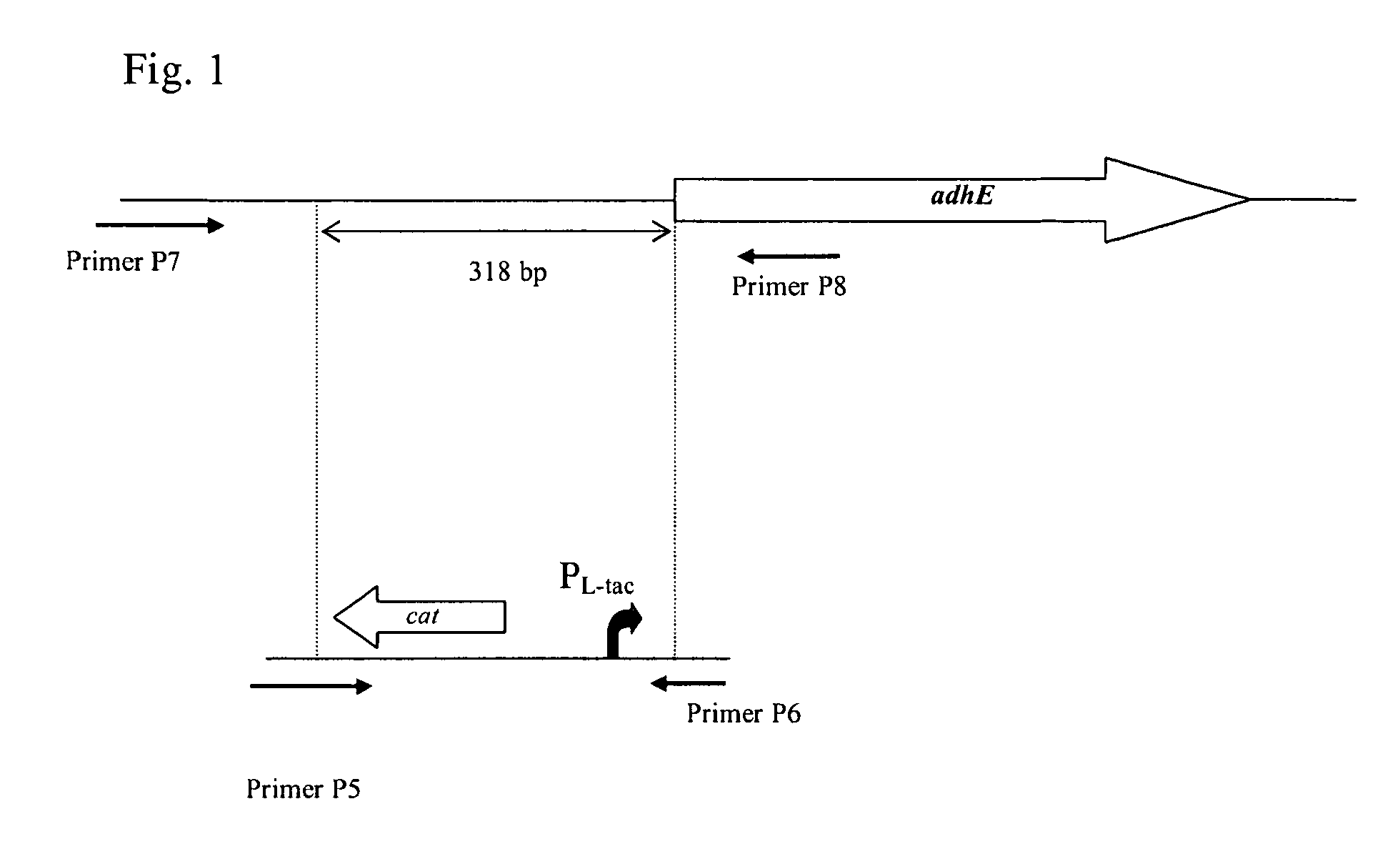
A method for producing an L-amino acid is described, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine, L-tryptophan, or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of a wild-type alcohol dehydrogenase encoded by the adhE gene or a mutant alcohol dehydrogenase which is resistant to aerobic inactivation.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Vector sgRNA CRISPR/Cas9 relevant with character of rice reddish brown glume, vector construction and application
InactiveCN108034656AThe method is efficientSave time and costMicrobiological testing/measurementHorticulture methodsAlleleExon
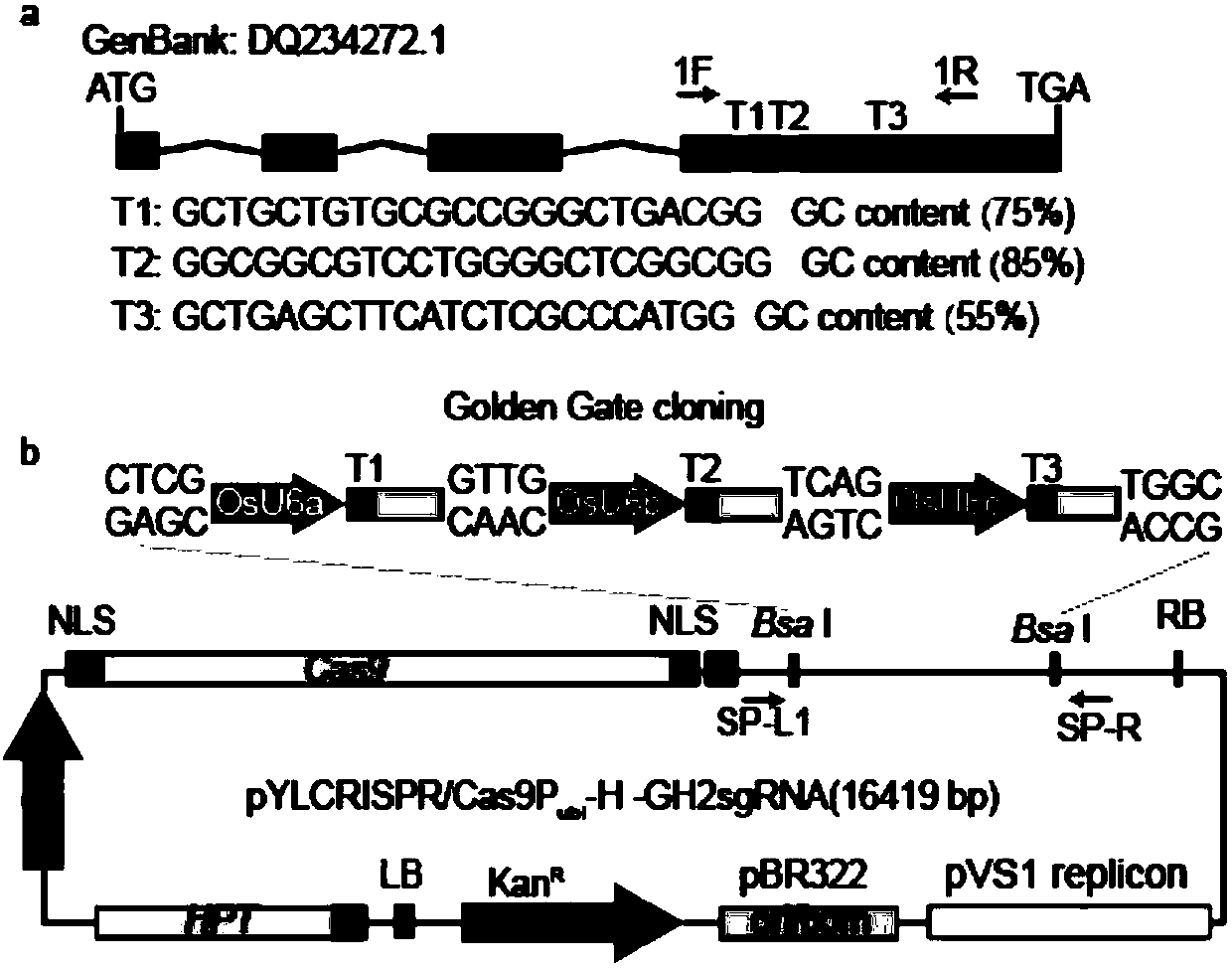
The invention discloses a vector sgRNA CRISPR / Cas9 relevant with character of rice reddish brown glume, vector construction and application, for overcoming the defect that rice with reddish brown glume can be acquired only on the condition of mutation of two alleles OsCHi. The invention provides an sgRNA segment which comprises a gRNA of which specificity is targeted to the fifth exon of cinnamylalcohol dehydrogenase(CAD) gene of rice; the sgRNA refers to T1, T2 and T3 specifically. The invention further provides a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing vector comprising the sgRNA and a construction methodof the vector. The vector can edit cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase(CAD) gene of rice. Besides, application of the segments and the vector in acquiring rice having characters of reddish brown glume andstem earing, and primer sequence for detecting CRISPR / Cas9-CAD gene reconstruction are also provided. According to the invention, conventional breeding cost can be reduced, mechanization level of hybrid rice seed production can be improved, and seeding cycle can be shortened.
Owner:SAAS BIOTECH & NUCLEAR TECH RES INST
Modified alcohol dehydrogenases for the production of fuels and chemicals
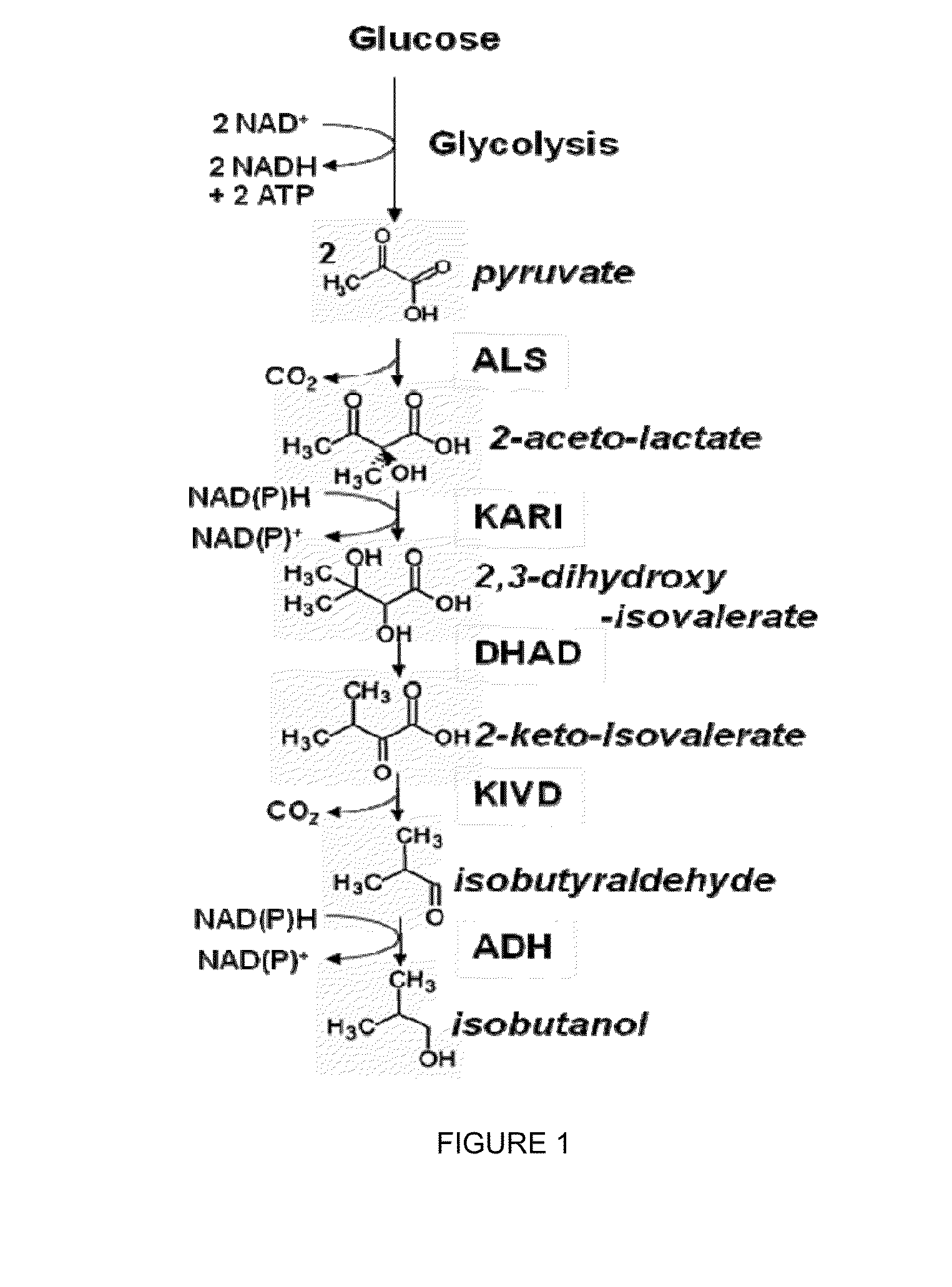
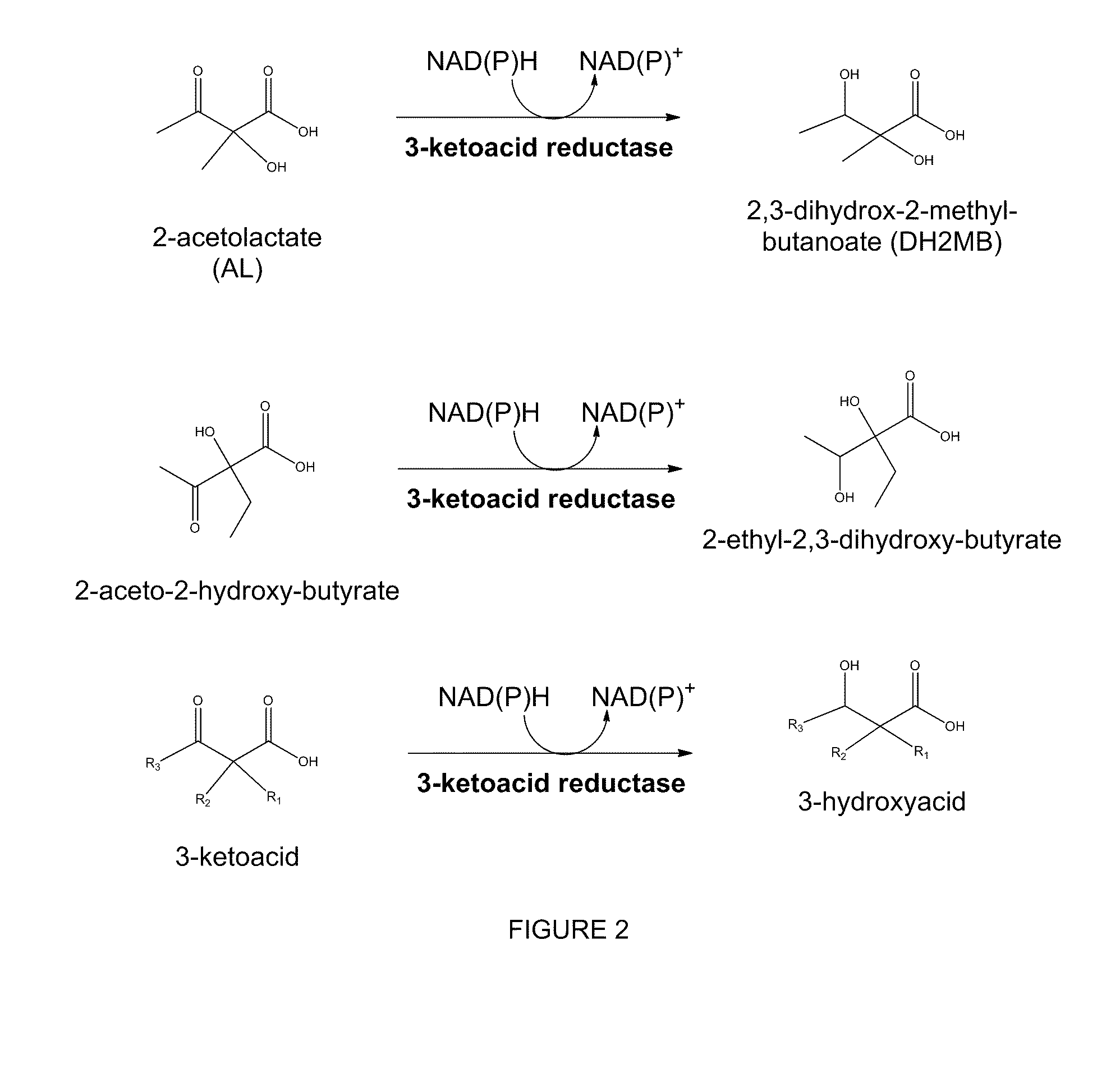
The present invention relates to recombinant microorganisms comprising biosynthetic pathways and methods of using said recombinant microorganisms to produce various beneficial metabolites. In various aspects of the invention, the recombinant microorganisms may further comprise one or more modifications resulting in the reduction or elimination of 3 keto-acid (e.g., acetolactate and 2-aceto-2-hydroxybutyrate) and / or aldehyde-derived by-products. In various embodiments described herein, the recombinant microorganisms may be microorganisms of the Saccharomyces clade, Crabtree-negative yeast microorganisms, Crabtree-positive yeast microorganisms, post-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, pre-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, and non-fermenting yeast microorganisms.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Method for simultaneously detecting gene mutations of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 and alcohol dehydrogenase 2
InactiveCN102758008ASimultaneous detection of genetic polymorphismsNo risk of contaminationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescencePolymorphism Detection
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously detecting gene mutations of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 and alcohol dehydrogenase 2. Concretely, a probe effective for detection of genetic polymorphism of the ALDH2 gene rs671 and the ADH2 gene rs1229984, a method for simultaneously detecting gene mutations and a kit for the purpose are provided. Thus the invention provides a probe for polymorphism detection, namely a probe for detection of at at least one type of genetic polymorphism of the ALDH2 gene rs671 and the ADH2 gene rs1229984, characterized in that: the probe comprises at least 1 type of fluorescently labeled oligonucleotide selected from (P1) to (P3') defined in the description.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Alcohol dehydrogenase, gene and recombinase thereof, and application of alcohol dehydrogenase in synthesis of chiral diaryl secondary alcohol
InactiveCN105936909AImprove expression levelIncrease enzyme activityOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringDiaryl ketoneGenus Kluyveromyces
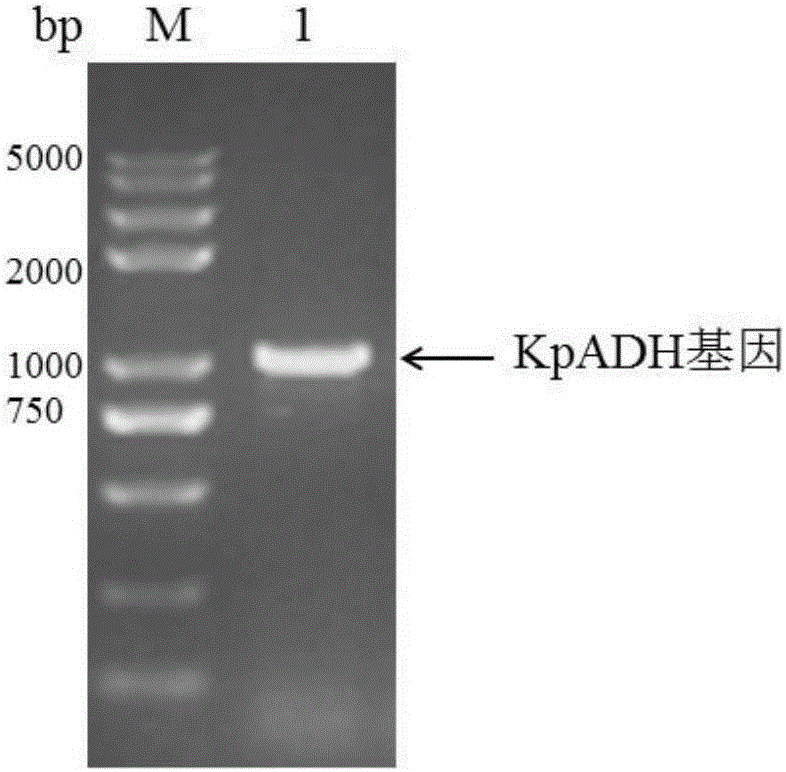
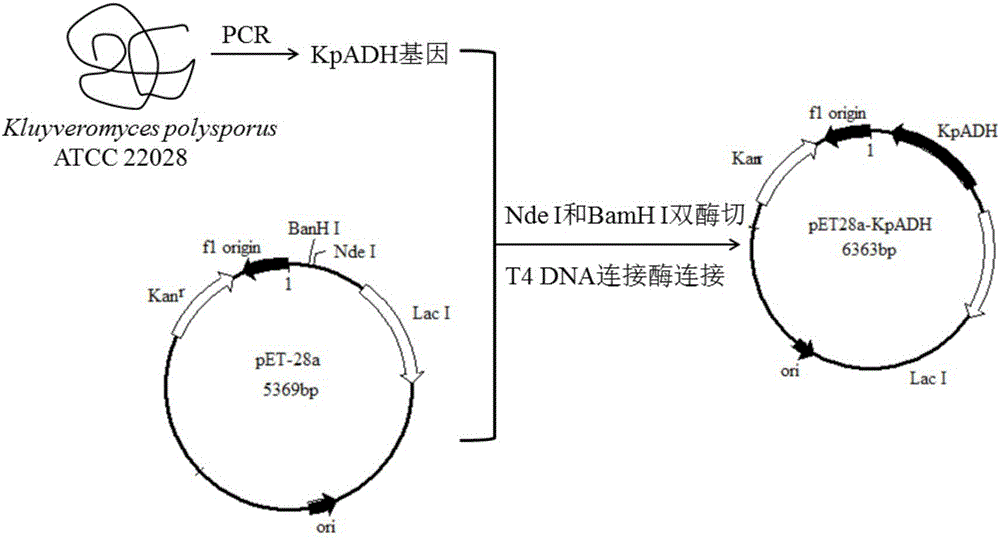
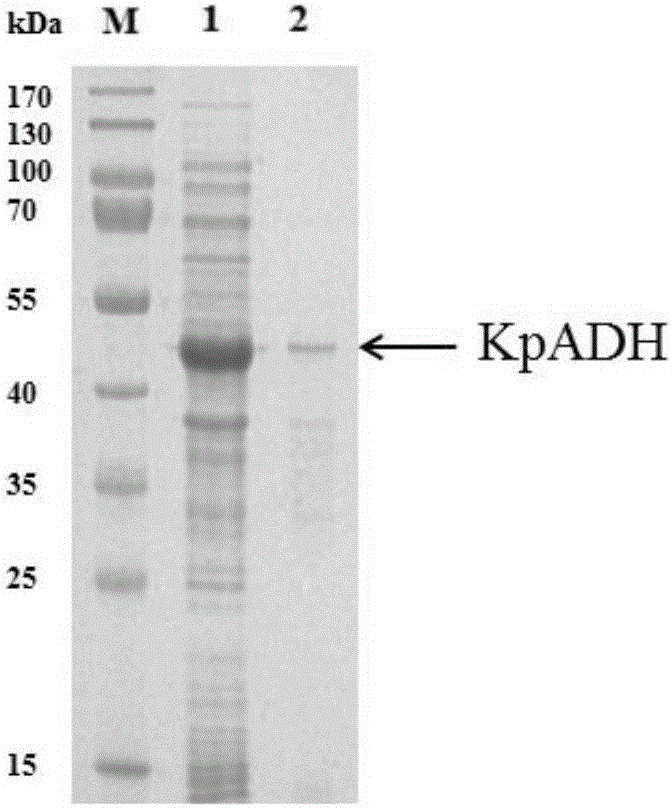
The invention discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase, a gene thereof, a recombinant expression vector and a recombinant expression transformant respectively containing the gene, a recombinase of the alcohol dehydrogenase, and an application of the alcohol dehydrogenase in asymmetric reduction synthesis of chiral diaryl secondary alcohol as a catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The alcohol dehydrogenase is from Kluyveromyces sp. CCTCCM2011385, has a carbonyl group reduction function, and also has a hydroxy group oxidation function. Extra addition of glucose dehydrogenase and other enzymes used for cofactor circulation is not needed when the alcohol dehydrogenase is used in the reduction of diaryl ketone into the chiral diaryl secondary alcohol as a biocatalyst, and the alcohol dehydrogenase has the advantages of high catalysis efficiency, mild reaction conditions, easy product recovery and low cost, so the alcohol dehydrogenase has very good application and exploitation prospect in the production of antihistamine medicines.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
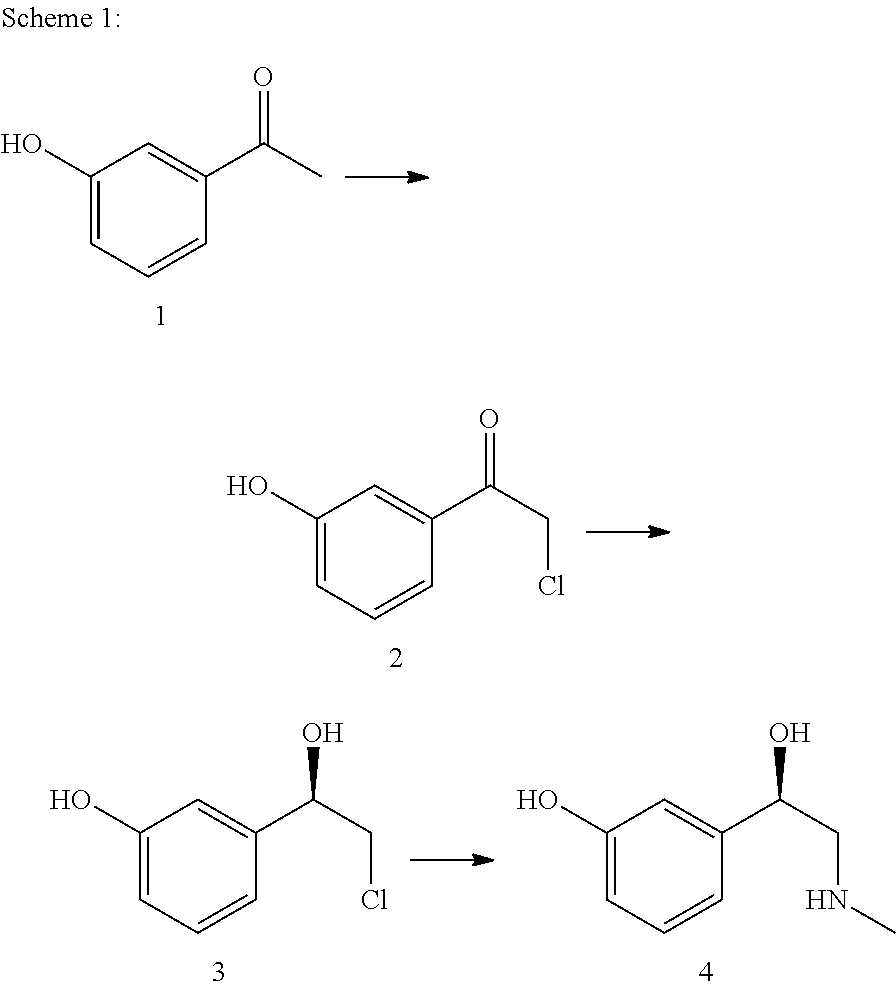
Method for producing l-phenylephrine using an alcohol dehydrogenase of aromatoleum aromaticum ebn1 (azoarcus sp. ebn1)
ActiveUS20110171700A1High stereoselectivityMoreOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationAlcoholAzoarcus sp.
The present invention relates to a multi-stage process for producing substituted, optically active alcohols, comprising an enzyme-catalyzed synthesis step, in particular a synthesis step which is catalyzed by an alcohol dehydrogenase. The inventive method is particularly suitable for producing phenylephrine, i.e. 3-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-2-methylamino-ethyl]-phenol.
Owner:BASF AG
Transgenic mice over-expressing amyloid-beta alcohol dehydrogenase (ABAD) in brain as model of alzheimer's disease and uses thereof
InactiveUS6891081B1Prevent and reduce disease progressionRelieve symptomsVectorsOther foreign material introduction processesAmyloid betaA-DNA
The present invention provides for a transgenic non-human animal whose cells contain a recombinant DNA sequence comprising a nerve tissue specific promoter operatively linked to a DNA sequence which encodes amyloid-beta peptide alcohol dehydrogenase (ABAD), and exhibits at least one phenotype from the group consisting of: overexpression of ABAD, elevated levels of basal ATP; protection from metabolic or ischemic stress.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Recombinant blue-green algae
InactiveCN101748069AAvoid toxic effectsAvoid wastingUnicellular algaeTransferasesEthanol dehydrogenaseElectron transfer
The invention discloses a recombinant blue-green algae, which is prepared by a method comprising the step of introducing genes related to butanol synthesis shown in (1) and (2) into yhe chroococcaceae blue-green algae, wherein (1) the genes related to butanol synthesis comprise encoding genes of the following enzymes: electron transfer flavoprotein A subunit, enoyl hydrase, butyryl-COA dehydrogenase and alcohol dehydrogenase; and (2) the genes related to butanol synthesis comprise encoding genes of the following enzymes: electron transfer flavoprotein B subunit, the enoyl hydrase, the butyryl-COA dehydrogenase and the alcohol dehydrogenase. The invention realizes the blue-green algae to transform inexhaustible solar energy and greenhouse gas carbon dioxide on the earth into the energy product butanol, avoids wasting grains and other organic matters in the energy regeneration process, and at the same time is beneficial for environment protection. Therefore, one of ideal methods for realizing the sustained and healthy development of clean and renewable energy sources is to utilize the recombinant blue-green algae of the invention to produce the butanol.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Alcohol dehydrogenase and uses thereof in synthesis of Duloxetine intermediate
ActiveCN105274069AHigh optical purityMild reaction conditionsBacteriaOxidoreductasesChemical synthesisDuloxetine
The invention provides an alcohol dehydrogenase with high catalytic activity, strong enantiotropic selectivity and good substrate tolerance, and provides an enzymatic synthesis method of employing the alcohol dehydrogenase to catalyze and synthesize (s)-3-substituted amido-1-(thiophenyl-2-yl)-1- propanol and furthermore Duloxetine. The invention also provides a nucleic acid sequence for encoding the alcohol dehydrogenase, a recombinant expression vector including the nucleic acid sequence, and a recombinant expression transformant, and a preparation method of the alcohol dehydrogenase, and uses of the alcohol dehydrogenase in catalyzing asymmetric reduction of carbonyl substrates. The invention has advantages that the product concentration is high, the optical purity of the product is high, the reaction condition is mild and environment-friendly, the operation is convenient and is easy to industrialize, and an extra expensive coenzyme NADP<+> / NAD<+> is not necessary.
Owner:ABIOCHEM BIOTECH CO LTD
Screening and identification method of alcohol dehydrogenase based on NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Diuncleotide) (P) (Phosphate) H (Hydrogen) fluorescence
InactiveCN102517378AShort timeImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsPhosphate
The invention provides a fast screening and identification method of alcohol dehydrogenase based on NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Diuncleotide) (P) (Phosphate) H (Hydrogen) fluorescence, which comprises the following steps of: based on the characteristic of the alcohol dehydrogenase taking NAD or NADP as coenzyme, taking a 96-pore micro-pore plate as a reaction vessel, adding a sample to be detected in a reaction system to oxidize alcohol, converting oxidized coenzyme incapable of transmitting the fluorescence into reduced coenzyme NADH or NADPH capable of transmitting the fluorescence under the excitation of a certain exciting light while the alcohol is oxidized and screening alcohol dehydrogenase producing strains through determining the change of fluorescence intensity of reaction liquid. The invention has the beneficial effects that compared with the existing alcohol dehydrogenase producing strain screening method, the fast screening and identification method has the characteristics of short time consumed, high accuracy, fewer reagent required and high throughput screening; and moreover, the reaction system is simple, the operation process is simple and convenient, and the interference factors in the reaction are less.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant spores of surface displayed silkworm alcohol dehydrogenases and preparation method of same
InactiveCN102174557AOvercome the disadvantage of instabilityHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSurface displayBiotechnology
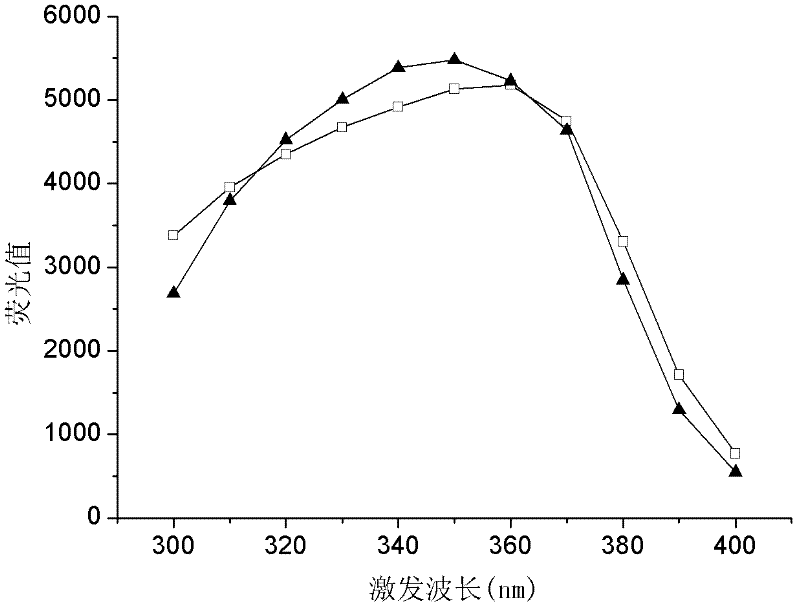
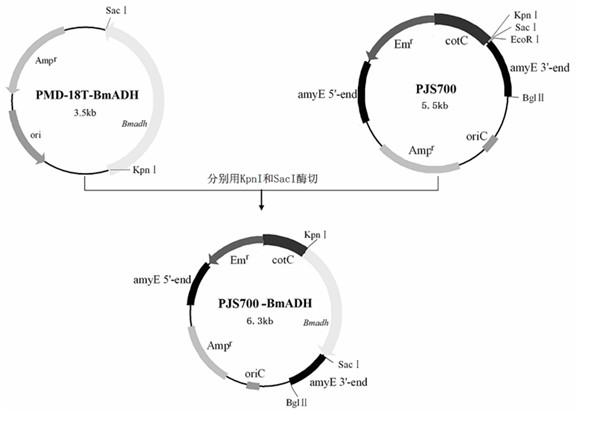
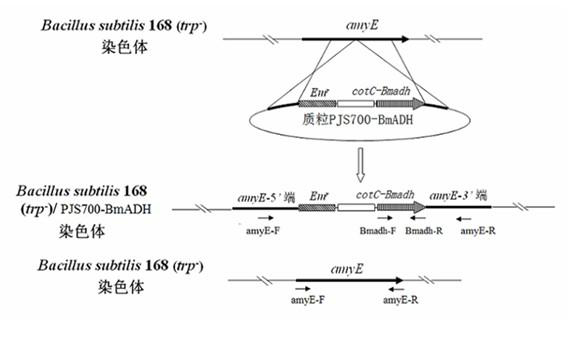
In the invention which belongs to the technical field of recombinant fusion proteins, silkworm alcohol dehydrogenases as exogenous proteins are displayed on surfaces of bacillus subtilis. Capsid protein genes cotC of spores of the bacillus subtilis, serving as molecular vectors, are recombined with silkworm alcohol dehydrogenase genes Bmadh to produce integrated recombinant plasmids which express the silkworm alcohol dehydrogenases BmADH in a fused manner so as to convert the bacillus subtilis; and exogenous genes are integrated in amylase genes amyE at special positions on a chromosome through homologous recombination, and the amylase genes are damaged, so that recombinant strains are free of the activities of the amylase genes; and therefore, recombinant bacillus subtilis strains containing fusion expressions CotC-BmaDH are successfully screened. Spores with fused proteins of silkworm alcohol dehydrogenases displayed on the surfaces are obtained through the inducible expression of the recombinant strains. In the invention, original alcohol dehydrogenases with instable temperature and pH become the fused proteins of the alcohol dehydrogenases with relatively stable activities under different environmental environments, and produced recombinant spores can be used for the direct oral administration of animals.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Use of mixed duplex oligonucleotides to effect localized genetic changes in plants
InactiveUS20030196218A1Enhanced advantageOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationACC oxidaseNucleotide
The invention concerns the use of duplex oligonucleotides about 25 to 30 base pairs to introduce site specific genetic alterations in plant cells. The oligonucleotides can be delivered by mechanical (biolistic) systems or by electrpoporation of plant protoplasts. Thereafter plants having the genetic alteration can be generated from the altered cells. In specific embodiments the invention concerns alteration in the gene that encode acid invertase, UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase, polyphenol oxidase, O-methyl transferase, cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase, ACC synthase and ACC oxidase or etr-1 or a homolog of etr-1, and plants having isolated point mutations in such genes.
Owner:CIBUS
Compositions and methods for detecting a sequence mutation in the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene associated with altered lignification in loblolly pine
InactiveUS6921643B2Precise processSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenaseLignin biosynthesis
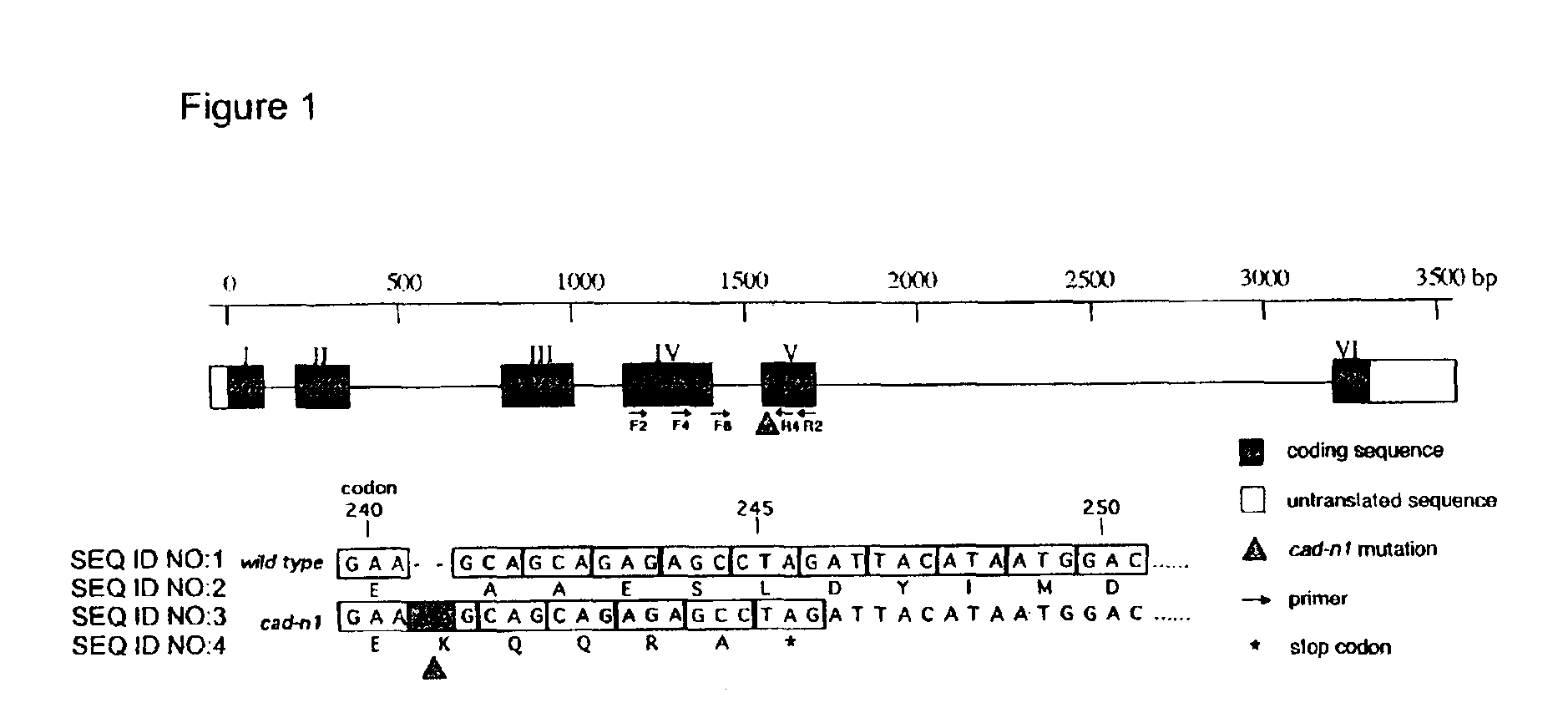
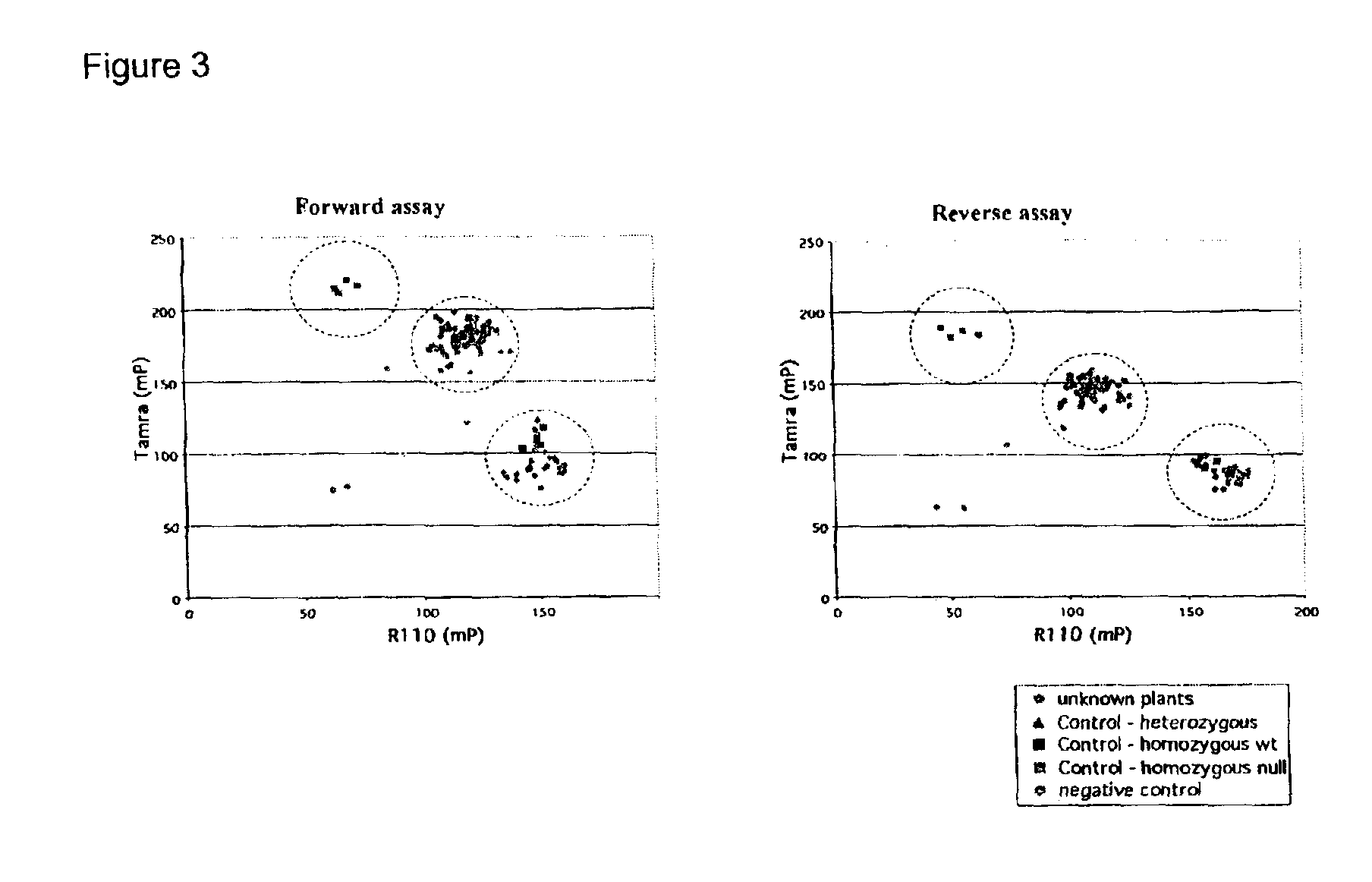
Loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) is the most important commercial tree species in the USA harvested for pulp and solid wood products. Increasing the efficiency of chemical pulping may be achieved through the manipulation of genes involved in the lignin biosynthetic pathway. A null allele of cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD) has been discovered in the loblolly pine clone 7-56 which displays altered lignin composition. During identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the cad gene, a two-base pair adenosine insertion located in exon five and unique to clone 7-56 was discovered. The sequence mutation causes a frame-shift predicted to result in premature termination of the protein. For routine detection of the mutation, a diagnostic assay was developed utilising Template-directed Dye-terminator Incorporation and Fluorescence Polarization detection (FP-TDI).
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Thermophilic alphanol alcohol dehydrogenase and crystal structure thereof
The invention relates to a crystal structure of thermophilic alphanol alcohol dehydrogenase under tail end degradation of thermophilic denitrified bacillus n-alkane. According to the crystal structure, the alcohol dehydrogenase is subjected to heterogenous expression by using escherichia coli E.coli; the pure alcohol dehydrogenase is obtained by a protein purification method; the crystal, proper for diffraction, of the alcohol dehydrogenase is obtained by a hanging-drop crystallizing method; and the crystal structure of the alcohol dehydrogenase is analyzed by an X-ray diffraction method. As the results shown, one subunit includes two structural domains, and one structural domain is separated by a crack; the N-end structural domain includes an Alpha / Beta fold similar to Rossman fold, and the structural domain also includes a binding site of NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) + coenzyme; the C-end structural domain includes an Alpha structural domain distribution similar to that of dehydro-quinate synthetase; and one iron ion is bonded to the C-end structural domain and exposed in the intermediate crack. According to the results, the spatial conformation of the alcohol dehydrogenase can be universally shown, and the theoretical guidance is provided for further searching the relationship between the structure and the function of the alcohol dehydrogenase and improving the degrading activity of the alcohol dehydrogenase.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
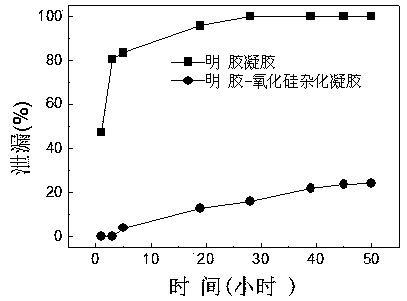
Alcohol dehydrogenase embedded gelatin-silica hybrid gel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103468669AEasy to fixReduce leak rateOn/in organic carrierOn/in inorganic carrierLow leakageSilica coating
The invention discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase embedded gelatin-silica hybrid gel and a preparation method thereof. According to invention, the grain diameter of the alcohol dehydrogenase embedded gelatin-silica hybrid gel is 3-4mm, and a silica coating is coated on a gelatin core. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing a mixed solution of gelatin and alcohol dehydrogenase; preparing a mixed solution of sodium silicate and a glutaraldehyde solution precursor; adding the mixed solution of gelatin and alcohol dehydrogenase into deionized water at a temperature of 0-4 DEG C droplet by droplet to generate alcohol dehydrogenase embedded gelatin gel particles; stirring and incubating to obtain the alcohol dehydrogenase embedded gelatin-silica hybrid gel. The preparation method has the advantages that the preparation condition is mild, the preparation process is simple and feasible, and the alcohol dehydrogenase embedded gelatin-silica hybrid gel has a strong fixing capability; compared with gelatin gel, the hybrid gel has a lower leakage rate of immobilized alcohol dehydrogenase, and lower swelling degree and better recycling stability.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
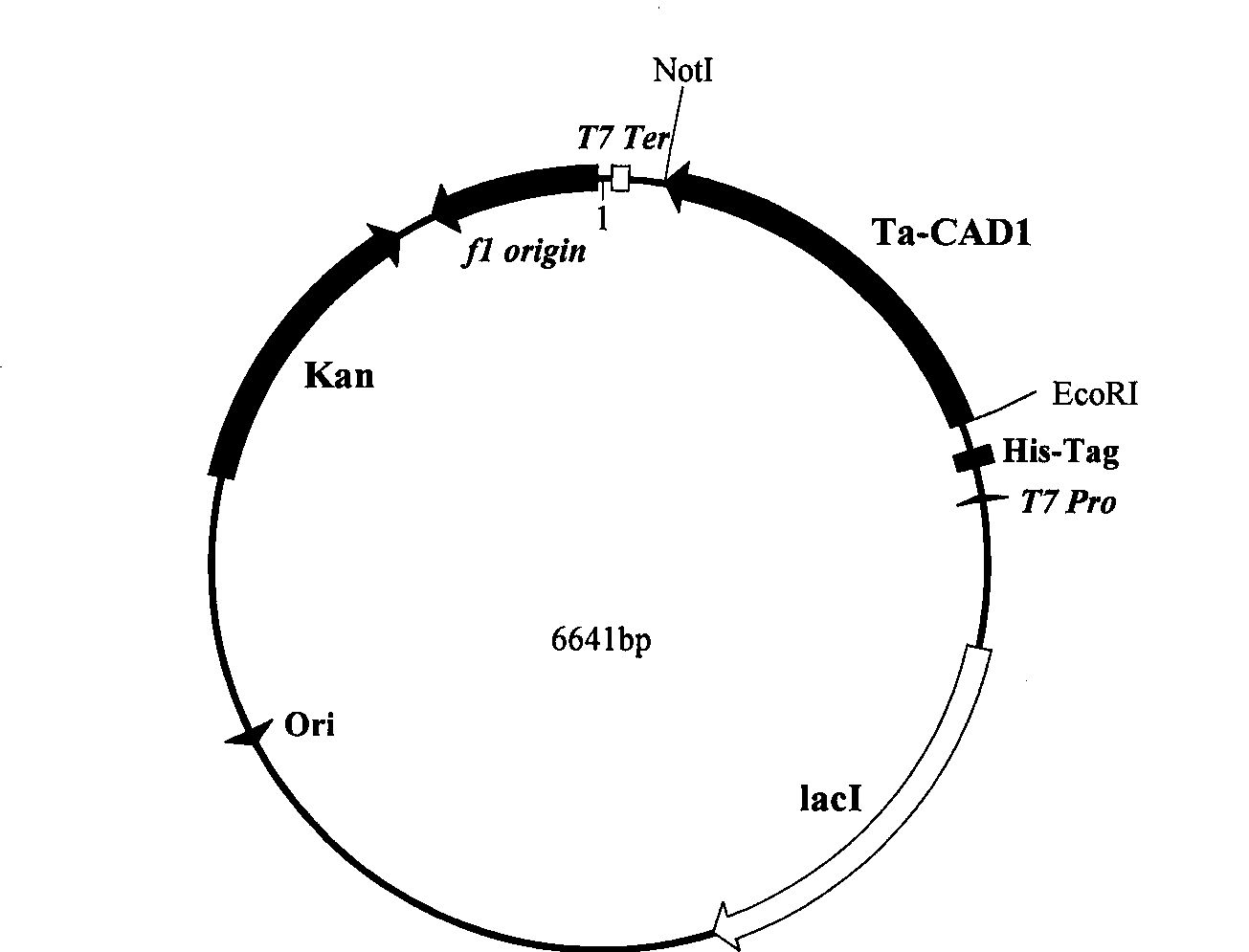
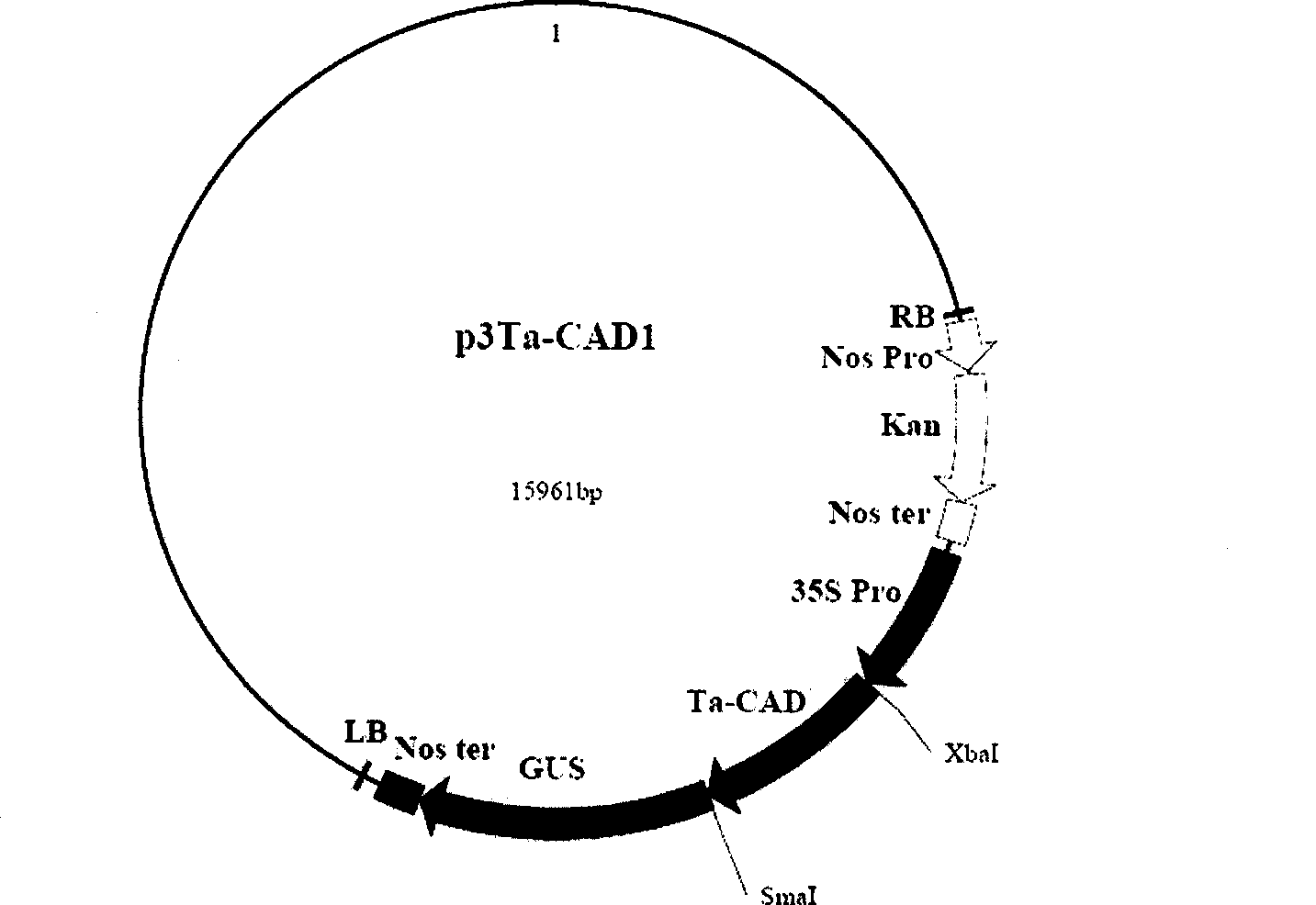
Wheat cinnamyl alcohol desaturase, encoding gene and uses thereof
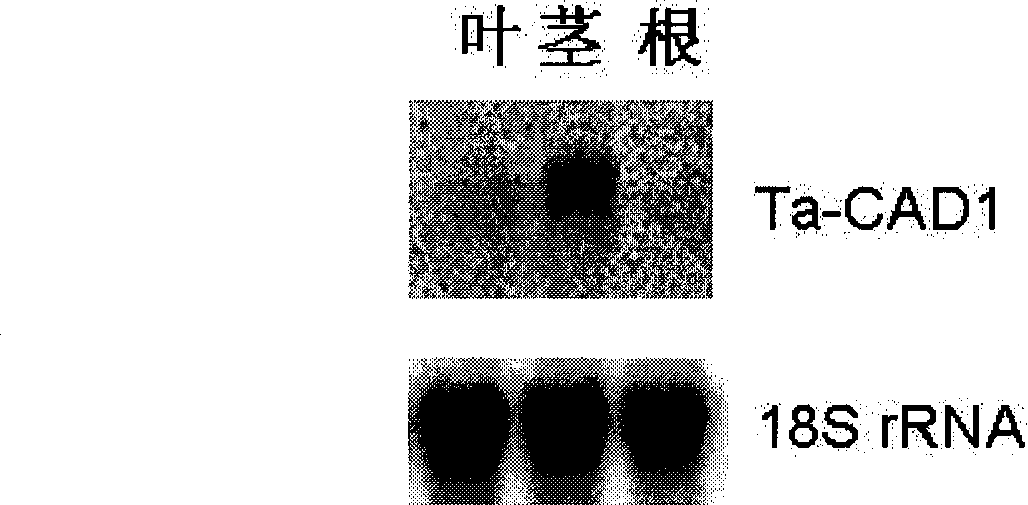
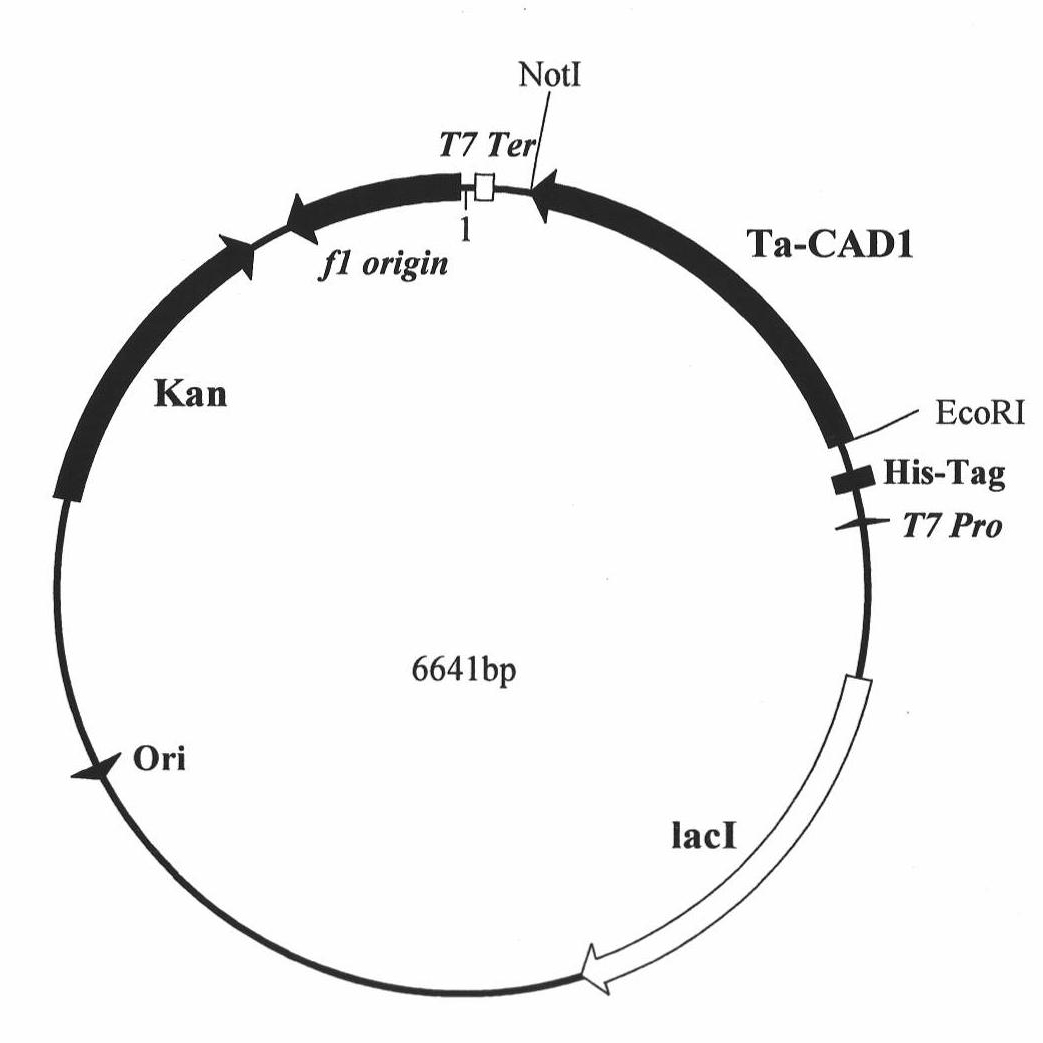
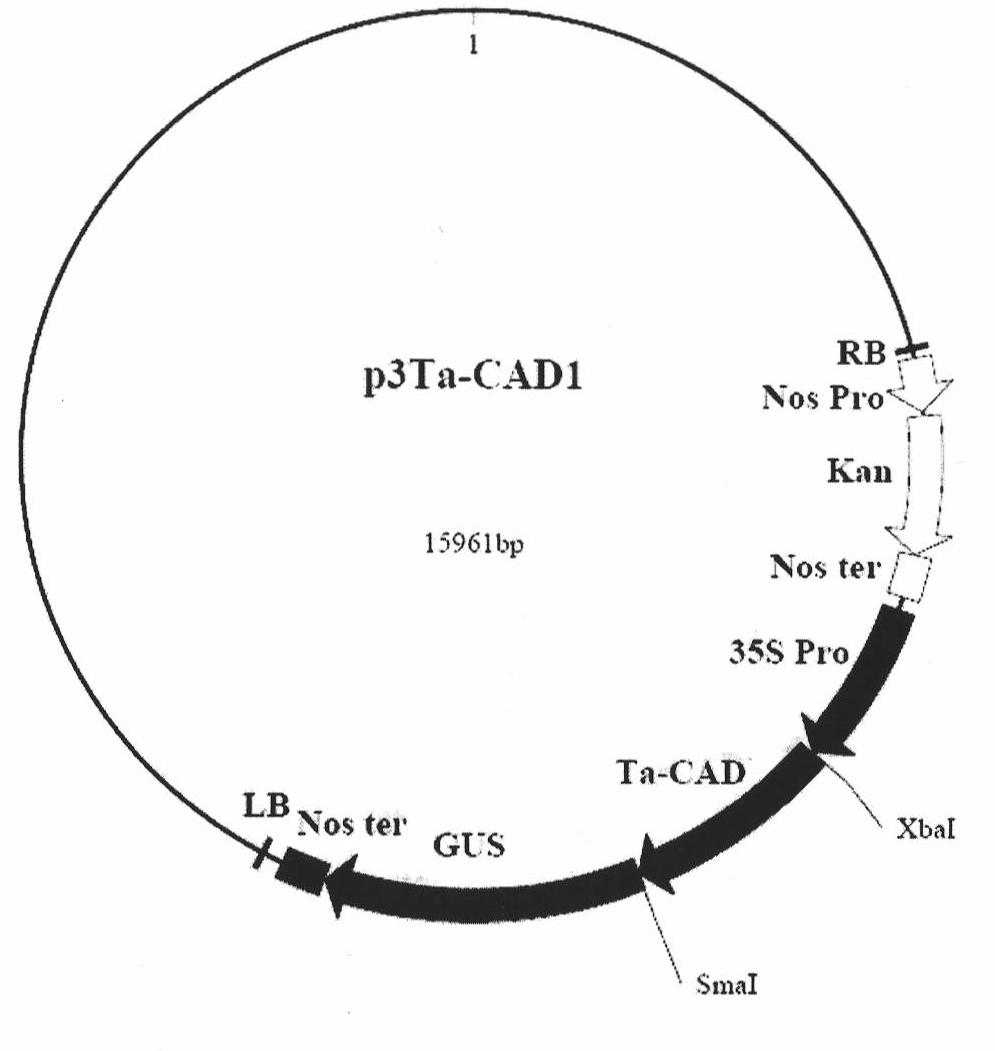
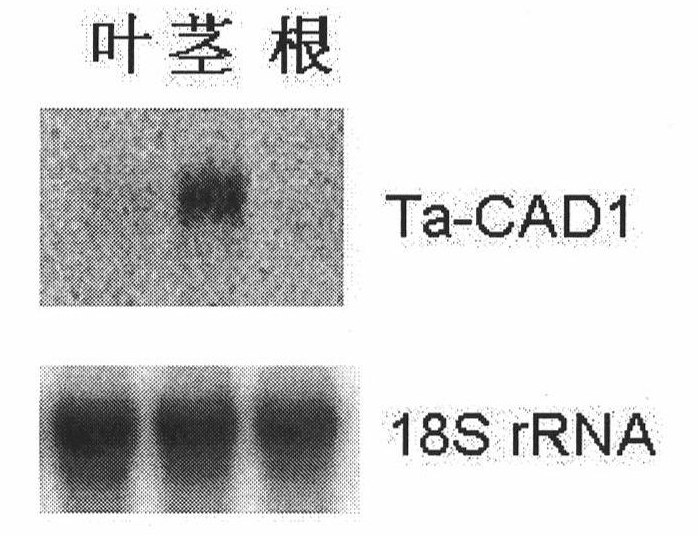
The invention discloses a cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase of wheat and an encoding gene and application thereof; the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase is the protein of the following a) or b): a) the protein composed of the amino acid sequences represented by the sequences 2 in the sequence table; b) the protein derived from a) and related to the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase function by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amine acid in the amino acid sequences represented by the sequences 2 in the sequence table. The invention further provides the encoding gene of the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase, and application of the encoding gene in culturing lodging-resistant plants. The encoding gene is introduced in the plants; and the transformed plant hosts can be wheat. The protein in the invention utilizes coniferyl aldehyde as base materials and has enzyme activities of 94.49 nmol / sec / mg, showing that the protein can control the lignin synthesis of the wheat. Northern hybridization is carried out on the Ta-CADI genes of the stems of easily-lodging and lodging-resistant wheat, which shows that the Ta-CADI genes not only control the lignin synthesis of the wheat, but also are closely related to the lodging-resistant characteristics of the stems of the wheat.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Alcohol dehydrogenase mutant, and application thereof in synthesis of bisaryl chiral alcohols
InactiveCN108504641AHigh stereoselectivityIncrease vitalityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlcoholFormate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase mutant, and an application thereof in the synthesis of bisaryl chiral alcohols, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The alcohol dehydrogenase mutant has excellent catalytic activity and stereoselectivity, and achieve efficiently catalyzed preparation of a series of chiral bisaryl alcohols with R- and S- configurations. Alcohol dehydrogenase is coupled with glucose dehydrogenase or formate dehydrogenase in order to synthesize multiple antihistamine chiral bisaryl alcohol intermediates. Compared with existing reports, the methodfor preparing the bisaryl chiral alcohols by asymmetric catalytic reduction of the alcohol dehydrogenase has the advantages of simplicity in operation, high substrate concentration, completeness in reaction, high product purity and great industrial application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Plant cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase homologs
This invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a lignin biosynthetic enzyme. The invention also relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of the lignin biosynthetic enzyme, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of the lignin biosynthetic enzyme in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Preparation method of ADH (alcohol dehydrogenase) and GDH (glucose dehydrogenase) co-crosslinked enzyme aggregates
ActiveCN107988201AImprove bioavailabilityRealize multiple reuseOxidoreductasesFermentationCinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenaseChemistry
The invention provides a preparation method of ADH (alcohol dehydrogenase) and GDH (glucose dehydrogenase) co-crosslinked enzyme aggregates. Specifically, a supernatant obtained after high-density fermentation and wall-breaking centrifugation is taken as a crude enzyme liquid, ADH and GDH in the crude enzyme liquid are subjected to glutaraldehyde cross-linking for preparation of the co-crosslinkedenzyme aggregates, and enzyme activity recovery of the co-crosslinked enzyme aggregates is increased to 82% by adding Tween 80.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
Alcohol dehydrogenase and application thereof in preparing alcohol
ActiveCN110317798AEfficient expressionGood thermal stabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliAlcohol
The invention discloses alcohol dehydrogenase. The nucleotide sequence of the alcohol dehydrogenase is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The amino acid sequence of the alcohol dehydrogenase is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The invention further discloses application of the alcohol dehydrogenase in a reaction for synthesizing alcohol with aldehyde as a substrate. The novel recombinant alcohol dehydrogenase has efficient soluble expression capability in an escherichia coli expression system, and the conversion rate of the recombinant alcohol dehydrogenase for synthesizing the alcohol in an aldehyde reducing reaction system is 90% or so.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for improving quality of cotton fibers by overexpressing GhCAD6 gene
InactiveCN105039397AHigh specific strengthIncreased fiber lengthMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationFiberAgricultural science
The invention relates to a method for improving quality of cotton fibers by overexpressing GhCAD6 gene, belonging to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a plant overexpression vector pCAMINBIA-2300-GhCAD6 from styrone dehydrogenase gene GhCAD6 in cotton fibers, transforming the vector into agrobacterium LB4404 by agrobacterium mediation, and integrating into cotton to obtain the trans-styrone dehydrogenase gene cotton plant. The field and molecular detection analysis detects that the lignin content in cotton fibers obviously increases in different development periods, the fibrocyte wall thickness obviously decreases in the cotton secondary wall rapid deposition stage, and the ripe cotton fiber surface becomes more compact and smooth. The method can maximally enhance the length of the cotton fibers by 16.935%, enhance the specific strength by 25.10% and enhance the fiber yield by 3.80%, thereby greatly improving the quality of the cotton fibers.
Owner:新疆农业科学院核技术生物技术研究所
Method for oxidizing binary primary alcohol by using alcohol dehydrogenase
The invention relates to a method for oxidizing binary primary alcohol by using alcohol dehydrogenase. The method comprises the steps of 1, providing alcohol dehydrogenase which is (a) a protein with an amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID No.1 or (b) polypeptide having at least more than 95% of homology with the amino acid sequence shown by the SEQ ID No.1 at an amino acid level; 2, in a Tris-HCl buffer solution with the pH value of 8.0-8.5, oxidizing a substrate namely binary primary alcohol into alcohol aldehyde by using alcohol dehydrogenase through an oxidation reaction in the presence of NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydrogen) oxidase NOX and NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide+). According to the method disclosed by the invention, alcohol dehydrogenase can be used as a catalyst to selectively oxidize binary primary alcohol compounds to prepare a variety of alcohol aldehyde. Compared with a chemical method for preparing alcohol aldehyde, the method disclosed by the invention is less in side reaction and has the advantages of mild reaction condition, environment friendliness, simplicity and convenience in operation, easiness in amplification and the like. A coenzyme circulating system used in the method disclosed by the invention does not generate byproducts, which is favorable for purification of a target product and subsequent operations.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
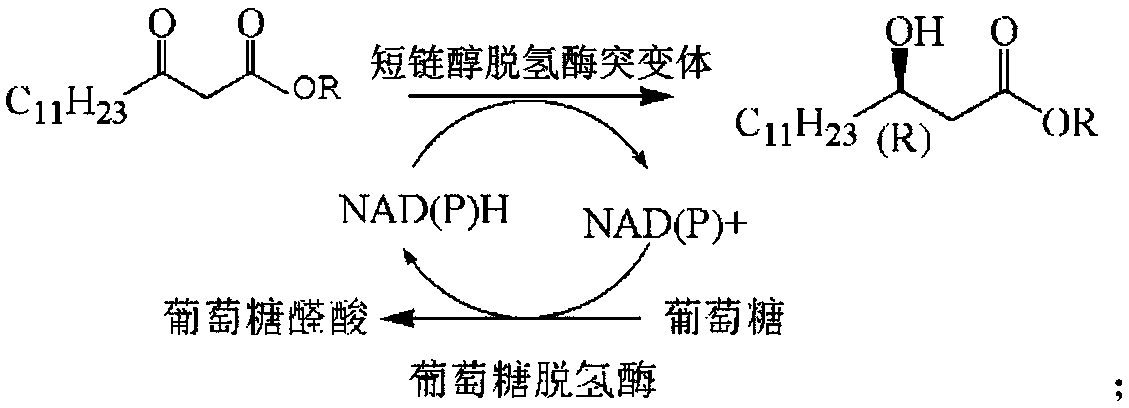
Novosphingobium short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN109097344AMild preparation conditionsThe process path is simpleOxidoreductasesFermentationEnzyme catalysisSite-directed mutagenesis
The invention relates to the technical field of dehydrogenase mutants, in particular to a novosphingobium short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase mutant and an application thereof. The novosphingobium short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase mutant adopts the amino acid sequence of novosphingobium short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase NA-ADH as a template. The short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase mutant of a marine origin is obtained by site-directed mutagenesis. The mutuant is transferred into an expression strain BL21 (DE3) to obtain thalli containing the recombinant short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase after recombination by an expression vector, and then beta-hydroxytetradecanoate is used as a substrate to prepare (R)-beta-hydroxytetradecanoate by bio-enzyme catalysis, the chiral ee value of the obtained (R)-beta-hydroxytetradecanoate can reach above 99, and the substrate conversion rate is above 95%. The preparation conditions are mild, and the process way is simple.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
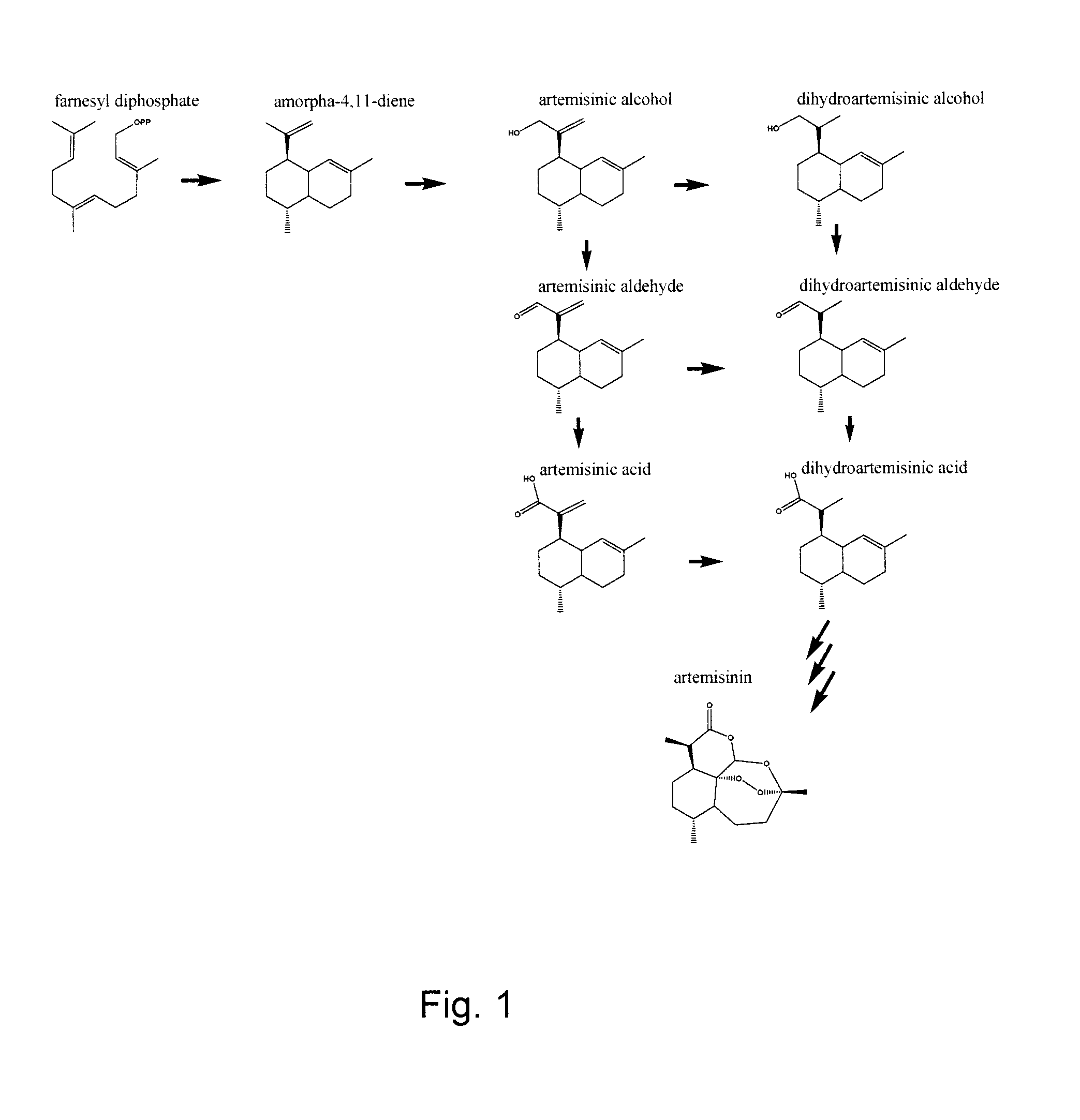
Nucleotide sequence encoding an alcohol dehydrogenase from artemisia annua and uses thereof
An isolated nucleic acid molecule cloned from Artemisia annua encodes an alcohol dehydrogenase (Adh1). Artemisia annua Adh1 enzymatically oxidizes artemisinic alcohol to artemisinic aldehyde. The nucleic acid molecule, and the enzyme encoded thereby, may be used in processes to produce artemisinic aldehyde, dihydroartemsinic aldehyde, artemisinic acid and / or dihydroartemisinic acid in a host cell. Artemisinic aldehyde, dihydroartemisinic aldehyde, artemisinic acid and / or dihydroartemisinic acid can be chemically converted to the antimalarial compound artemisinin.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Alcohol dehydrogenase for producing Atazanavir intermediate
ActiveCN109943542AMild reaction conditionsLow equipment requirementsBiofuelsOxidoreductasesWild typeSolvent
The invention discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase for producing an Atazanavir intermediate and belongs to the technical field of medical biology. The alcohol dehydrogenase shows stronger catalytic activity than a wild alcohol dehydrogenase shown as SEQ ID NO.8 and can be obtained by means of in-vitro recombination, polynucleotide mutagenesis, DNA shuffling, error-prone PCR, directional evolution methods and the like. The alcohol dehydrogenase has one or more mutations of following characteristics including T37A, D38E, P41K, D44N, V45K. The alcohol dehydrogenase has the advantages that, the reaction conditions are mild, the requirement for equipment is low, high temperature or cooling in a production process is not required, and the energy consumption is low; since enzyme catalysis has highefficiency and exclusive selectivity, no by-products are generated when a method is utilized to produce key intermediates of Atazanavir, and purification is convenient. In addition, a reaction solventmainly consists of water, the discharge amount of three wastes is small, and the alcohol dehydrogenase is environmentally friendly.
Owner:NANJING NUOYUN BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for increasing thermal stability of polymer protein and alcohol dehydrogenase with increased thermal stability
InactiveCN108690837AImprove stabilityAvoid workloadOxidoreductasesFermentationWild typeThermal stability
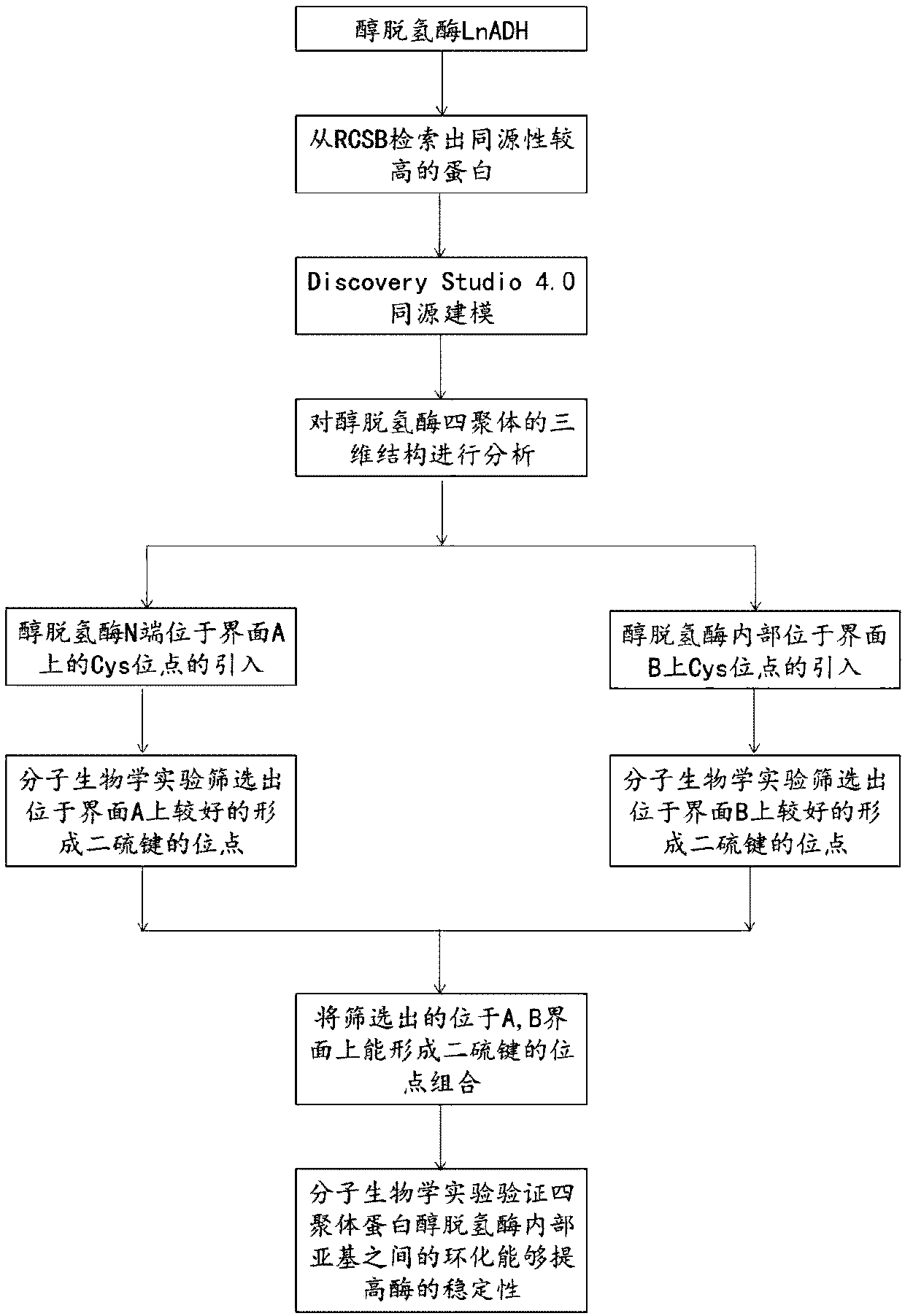
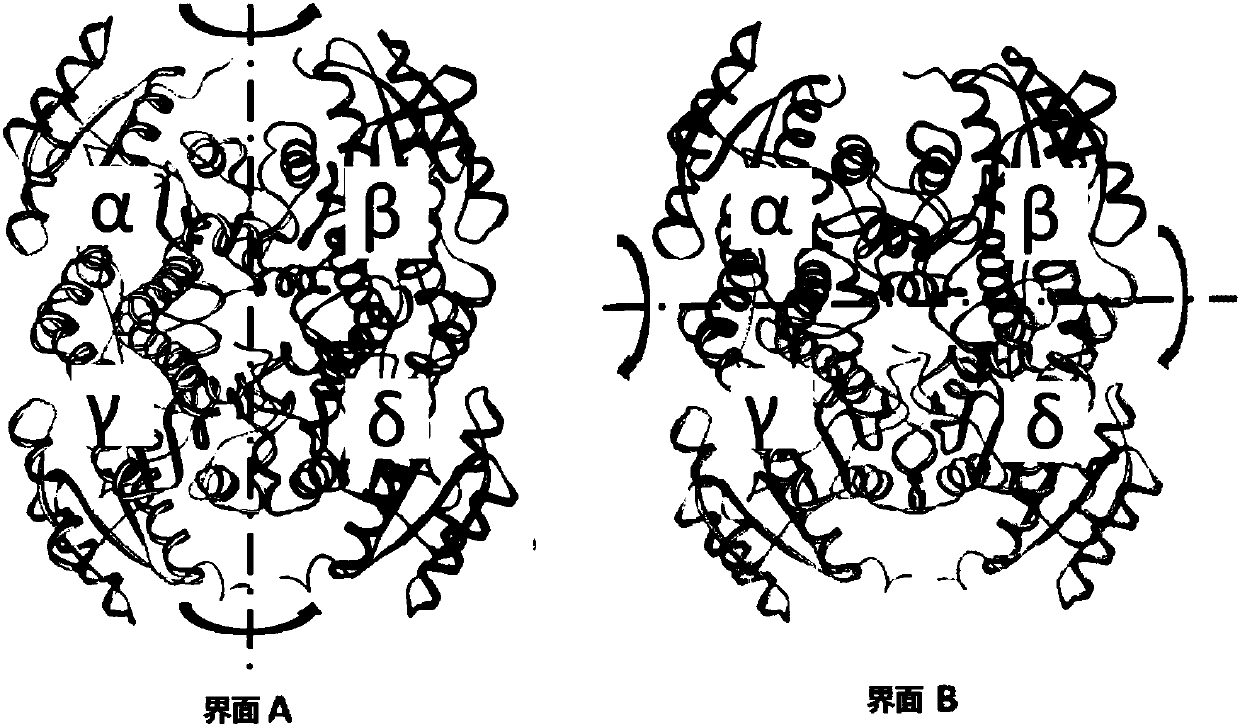
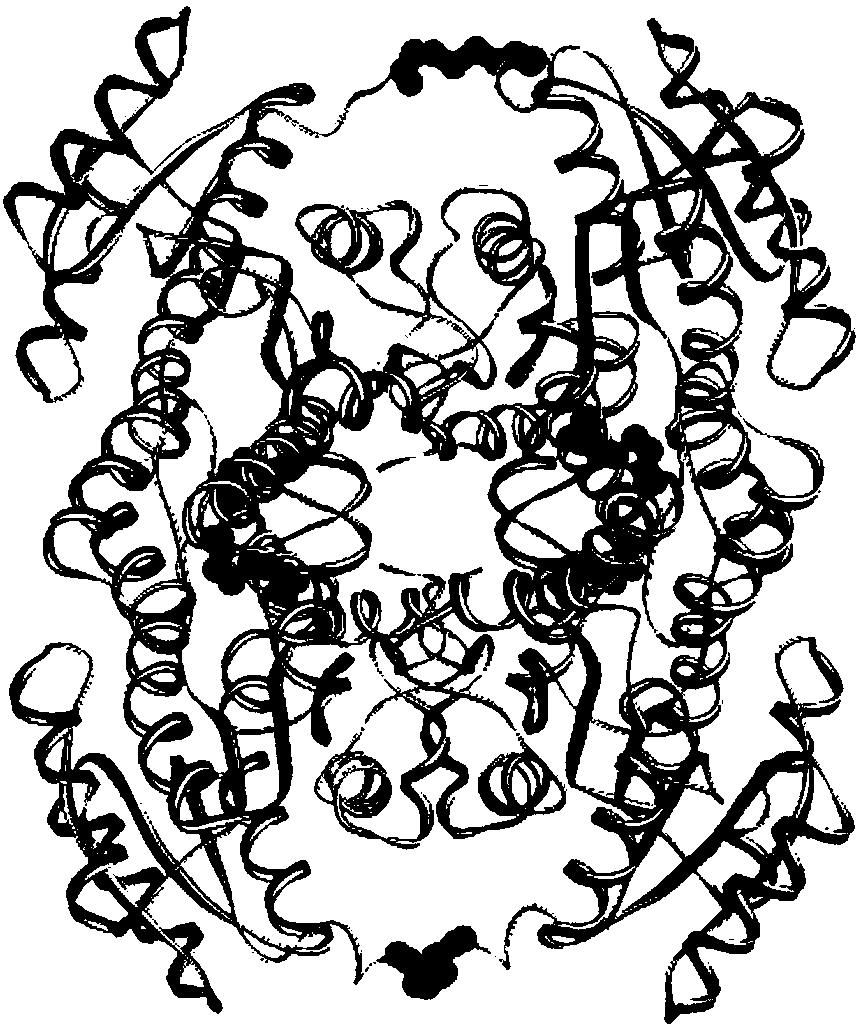
The invention discloses a method for increasing thermal stability of polymer protein and alcohol dehydrogenase with increased thermal stability, which belong to the technical field of enzyme engineering. The method for increasing the thermal stability of polymer protein is characterized in that a covalent bond mode is introduced into a contact interface of terminal N of polymer protein with adjacent N terminals (in a scope of 8 angstrom) and an internal subunit, and the subunits of polymer protein are linked to form a cyclized integral body. The sequences of alcohol dehydrogenase with increased thermal stability are respectively SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3 or SEQ ID NO.4, compared with a wild type, a T5015 value of the alcohol dehydrogenase can be respectively increased by 5.5 DEG C, 6.0 DEGC and 18 DEG C. The method avoids the problems of large screening work amount and tedious processes in the prior art, and site-specific mutagenesis has pertinency by a strategy introduced through a disulfide bond between interfaces.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Enzymic method for the enantioselective reduction of keto compounds
ActiveUS8361765B2Long stable timeHigh yieldBacteriaOxidoreductasesOrganic compoundEnantio selectivity
The invention relates to an enzymatic method for the enantioselective reduction of organic keto compounds to the corresponding chiral hydroxy compounds, an alcohol dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus minor and a method for the enantioselective production of (S)-hydroxy compounds from a racemate.
Owner:SCIENCES PO
Use of mixed duplex oligonucleotides to effect localized genetic changes in plants
InactiveUS20060288442A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationGenetic ChangePlant cell
The invention concerns the use of duplex oligonucleotides about 25 to 30 base pairs to introduce site specific genetic alterations in plant cells. The oligonucleotides can be delivered by mechanical (biolistic) systems or by electroporation of plant protoplasts. Thereafter plants having the genetic alteration can be generated form the altered cells. In specific embodiments the invention concerns the alteration in the gene that encode acid invertase, UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase, polyphenol oxidase, O-methyl transferase, cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase, ACC synthase and ACC oxidase or etr-1 or homolog of etr-1, and plants having isolated point mutations in such genes.
Owner:ARNTZEN CHARLES +3
Wheat cinnamyl alcohol desaturase, encoding gene and uses thereof
The invention discloses a cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase of wheat and an encoding gene and application thereof; the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase is the protein of the following a) or b): a) the protein composed of the amino acid sequences represented by the sequences 2 in the sequence table; b) the protein derived from a) and related to the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase function by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amine acid in the amino acid sequences represented by the sequences 2 in the sequence table. The invention further provides the encoding gene of the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase, and application of the encoding gene in culturing lodging-resistant plants. The encoding gene is introduced in the plants; and the transformed plant hosts can be wheat. The protein in the invention utilizes coniferyl aldehyde as base materials and has enzyme activities of 94.49 nmol / sec / mg, showing that the protein can control the lignin synthesis of the wheat. Northern hybridization is carried out on the Ta-CADI genes of the stems of easily-lodging and lodging-resistant wheat, which shows that the Ta-CADI genes not only control the lignin synthesis of the wheat, but also are closely related to the lodging-resistant characteristics of the stems of the wheat.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com