Preparation method of ADH (alcohol dehydrogenase) and GDH (glucose dehydrogenase) co-crosslinked enzyme aggregates
A technology of glucose dehydrogenase and alcohol dehydrogenase, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, enzymes, multi-enzyme systems, etc., can solve problems such as difficult chiral compounds and complex synthesis processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
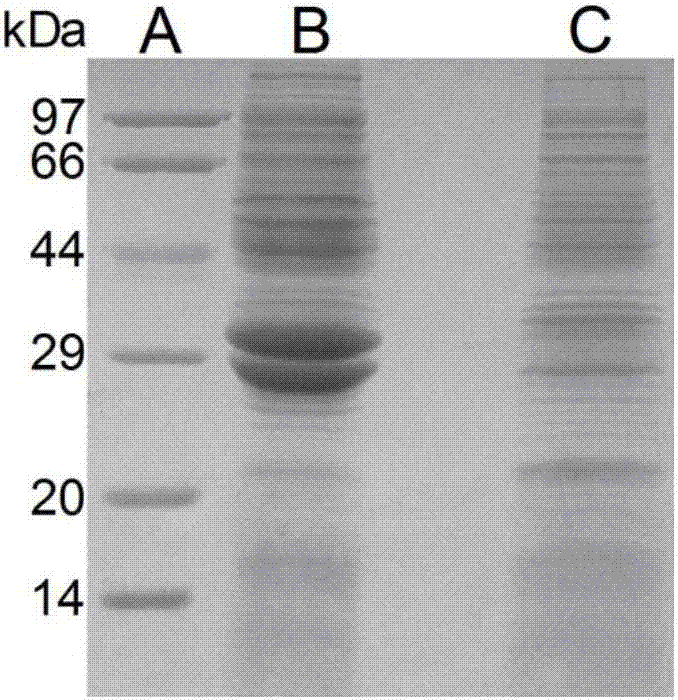
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Co-expression of alcohol dehydrogenase and glucose dehydrogenase
[0063] Use specific restriction endonucleases NdeI and XhoI (Thermo, USA) to double-enzyme digest the plasmid containing ADH and GDH. After electrophoresis, the target fragments are gel-cut and recovered. Carrier plasmid pET-28a is also double-digested with NdeI and XhoI. Enzyme digestion and gel recovery. The ADH and GDH gene fragments were respectively connected with the carrier fragments to obtain plasmids pET-28a-adh and pET-28a-gdh, both of which were resistant to ampicillin and kanamycin. The two plasmids were transformed into competent cells E.coliDH5α to obtain the co-expression strain E.coli BL21-ADH / GDH of alcohol dehydrogenase and glucose dehydrogenase. The co-expression strain was inoculated into LB medium containing ampicillin (Amp, 100 μg / ml) and kanamycin (Kan, 100 μg / ml), and cultivated overnight at 37° C. with a constant temperature shaker at 230 r / min. According to the volume ratio of...
Embodiment 2
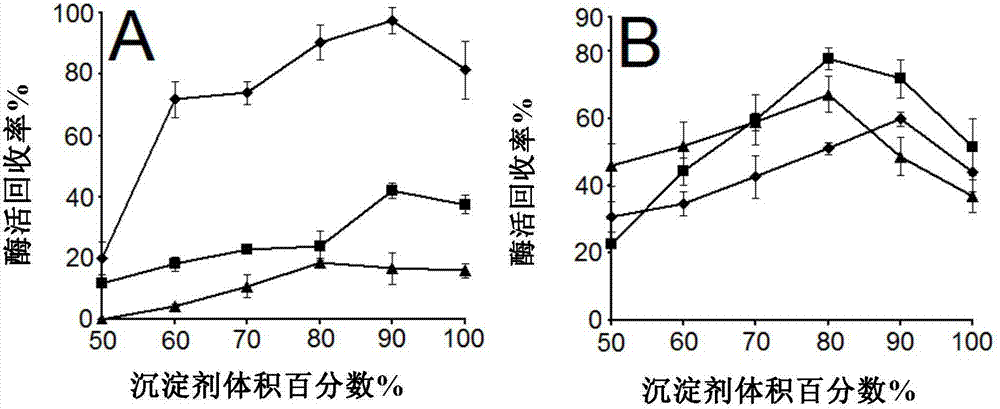
[0066] Precipitant selection
[0067] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0068] (1) In this paper, 1000 μl, 900 μl, 800 μl, 700 μl, 600 μl, and 500 μl of ethanol, acetone, and saturated ammonium sulfate solution were respectively mixed with 0 μl, 100 μl, 200 μl, 300 μl, 400 μl, and 500 μl of 0.1mol / L pH7.0 The TEA buffer solutions were mixed to prepare precipitants with volume concentrations of 100%, 90%, 80%, 70%, 60%, and 50%.
[0069] (2) Take 1ml of precipitants of different concentrations in 1.5ml EP tubes, put them in an ice-water bath for pre-cooling for 5 minutes, add 200 μl of crude enzyme solution, shake in an ice-water bath at 150r / min for 30 minutes, and then centrifuge. The above liquid is used to determine the protein content.
[0070] (3) The pellet was resuspended with 600 μl TEA buffer solution for the determination of enzyme activity. The result is as figure 2 As shown, when 90% acetone was used to precipitate the crude enzyme solution, t...
Embodiment 3
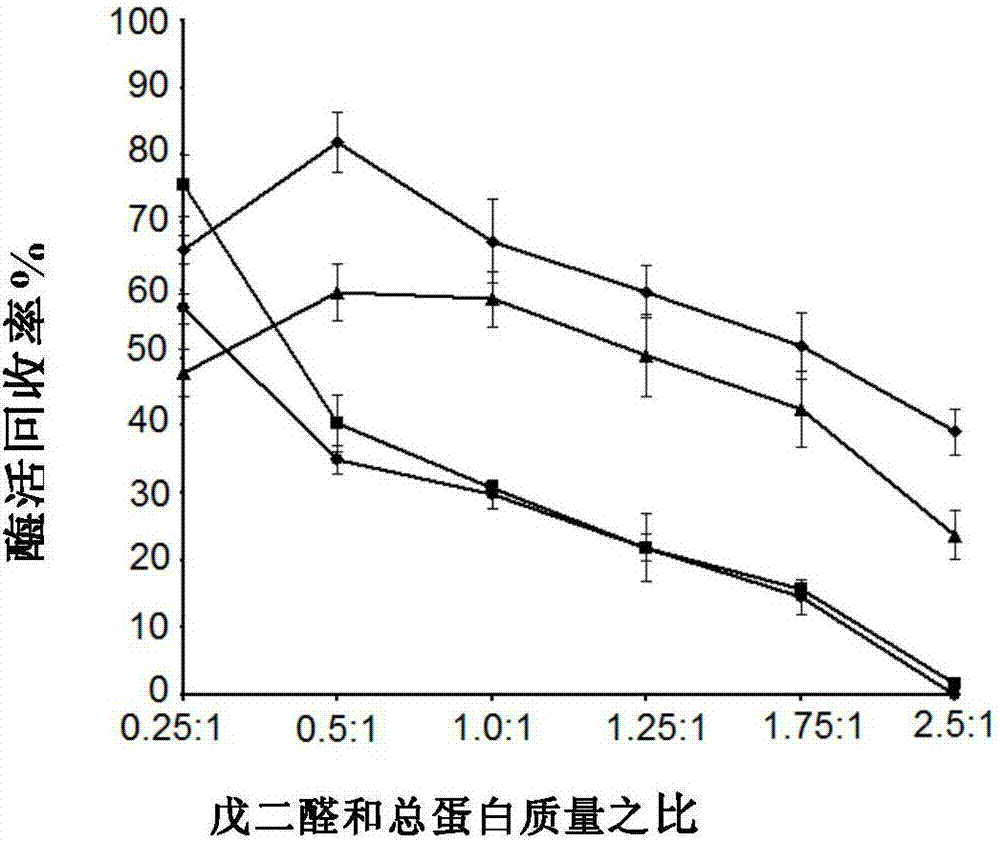
[0072] Preparation of co-crosslinked enzyme aggregates
[0073] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0074] (1) Take 18ml of acetone and 2ml of TEA buffer solution to prepare a 90% acetone solution in a beaker, seal it and put it in an ice-water bath, start stirring after precooling for 5 minutes, slowly add 4ml of crude enzyme solution dropwise, stir and precipitate for 30 minutes.
[0075] (2) 480 μl of glutaraldehyde solution with a volume fraction of 2.5% was added dropwise. At this time, the mass ratio of glutaraldehyde:total protein in the solution was 0.5, and stirred on an ice-water bath for 1.5 hours.
[0076] (3) Take 2ml of the cross-linked immobilized enzyme and centrifuge at 3000r / min, 4°C for 2min to remove the supernatant, wash it three times with an equal volume of TEA buffer solution, and resuspend the cross-linked enzyme aggregate with 1ml of TEA buffer solution for enzyme Viability assay.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com