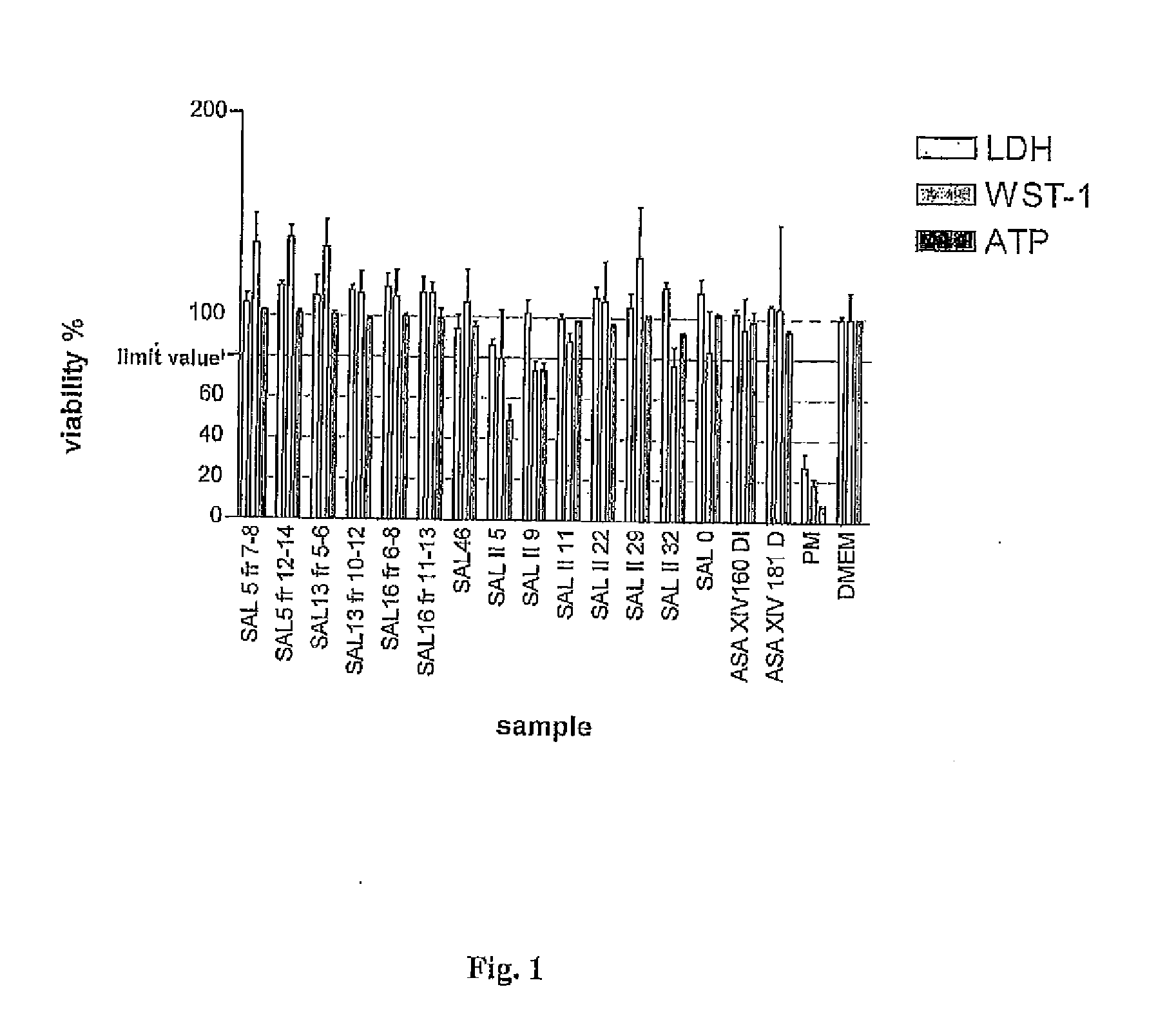
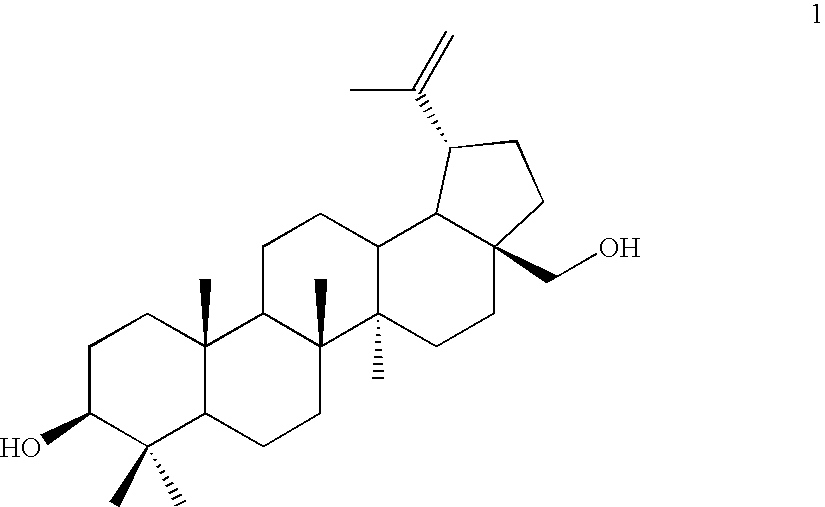
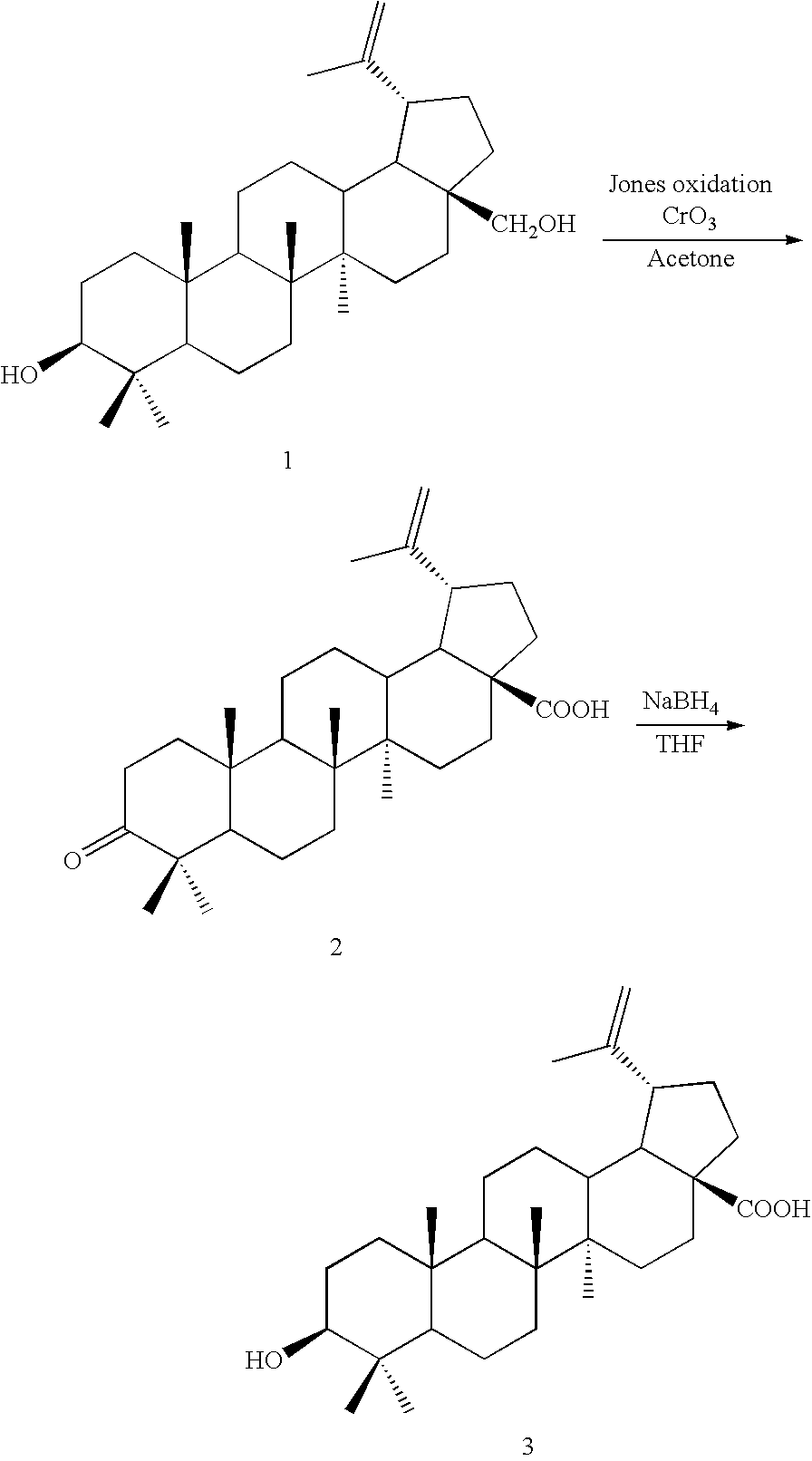
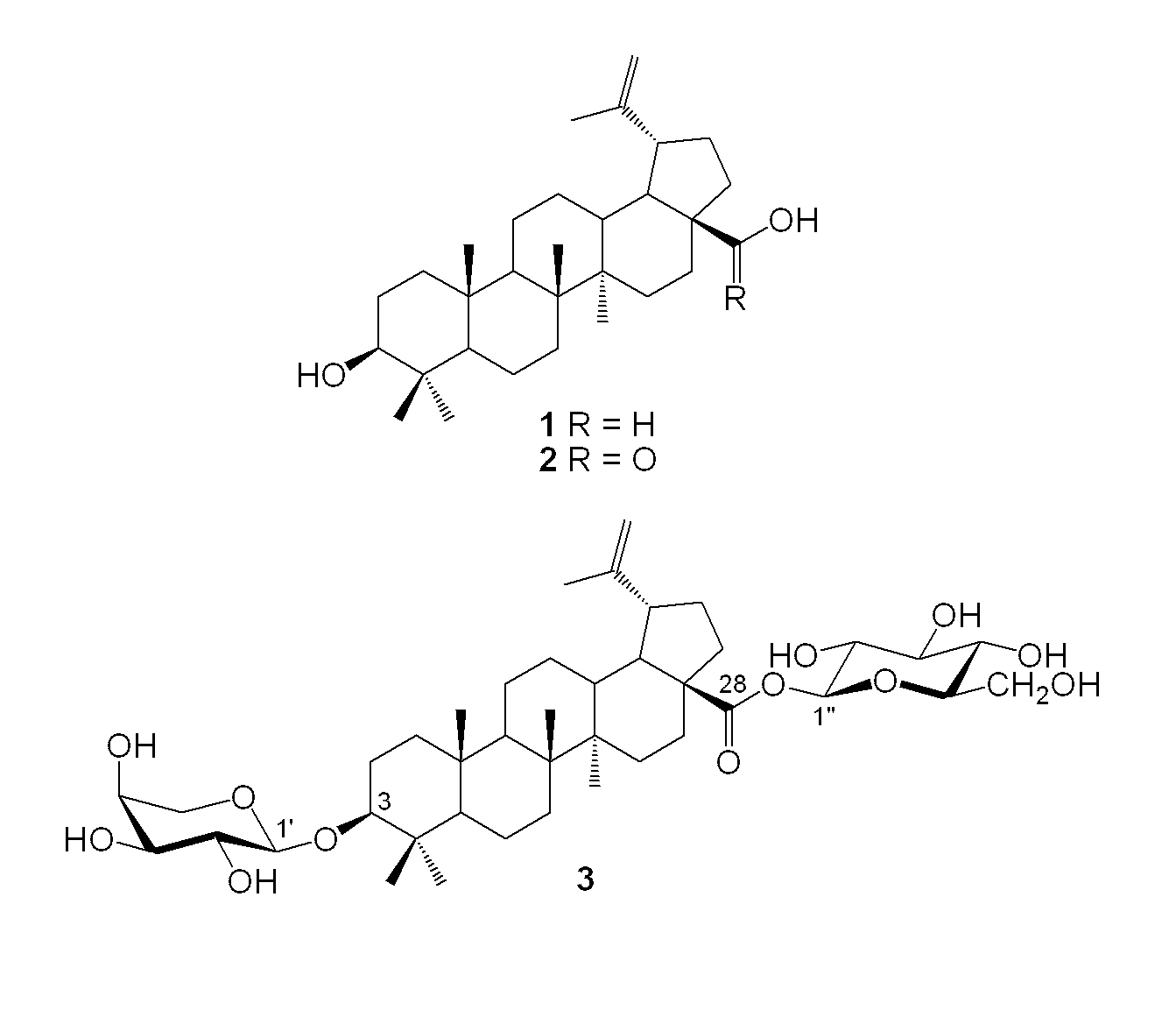
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
99 results about "Betulin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
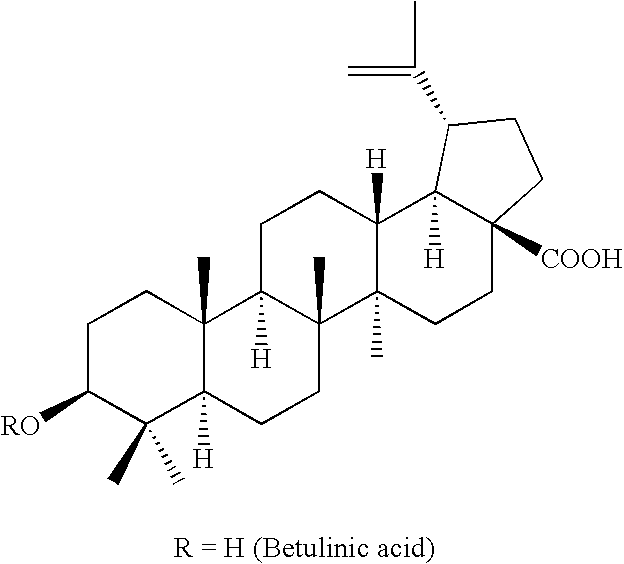
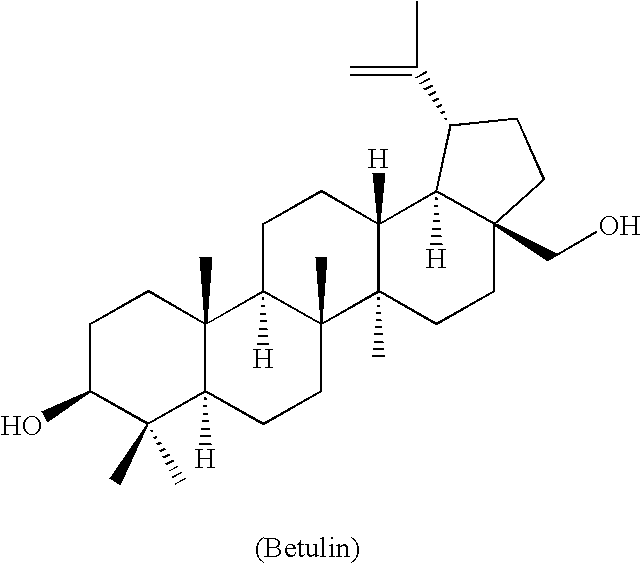
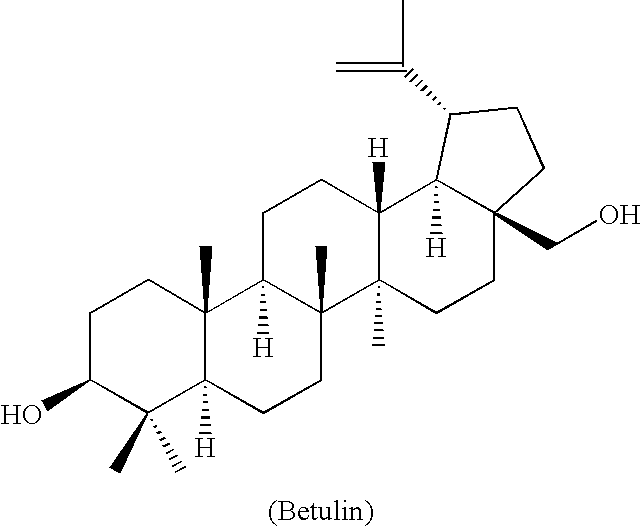
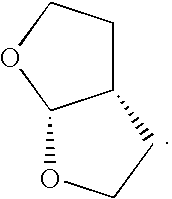
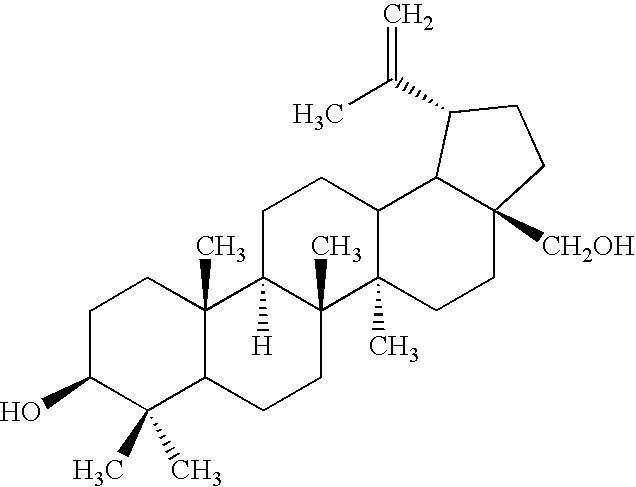
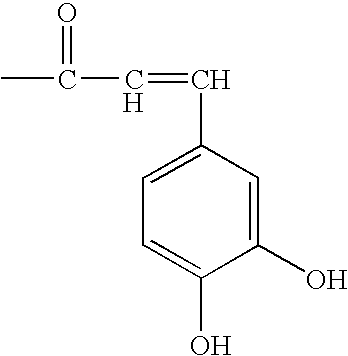
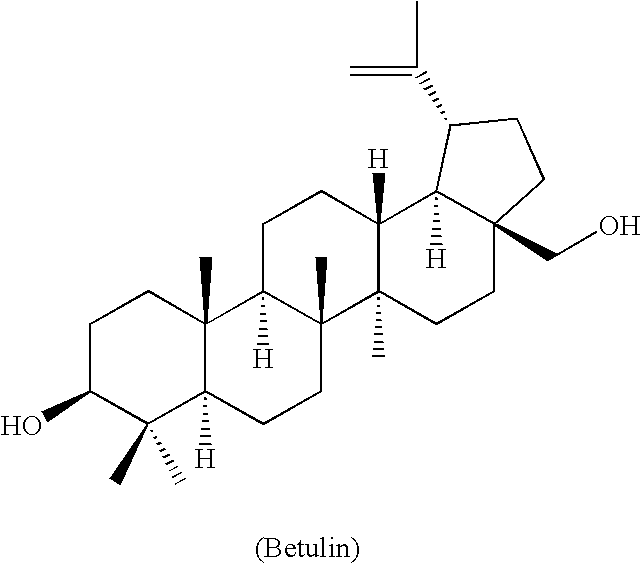
Betulin is an abundant, naturally occurring triterpene. It is commonly isolated from the bark of birch trees. It forms up to 30% of the dry weight of silver birch bark. It is also found in birch sap. Inonotus obliquus and red alder also contain betulin.
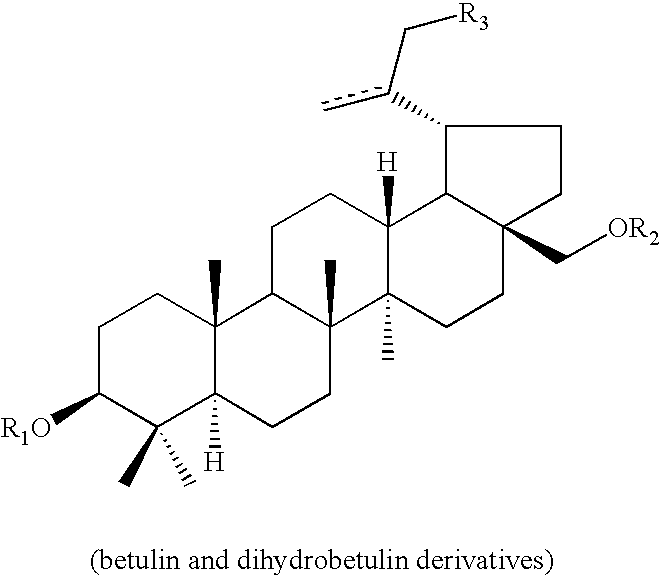
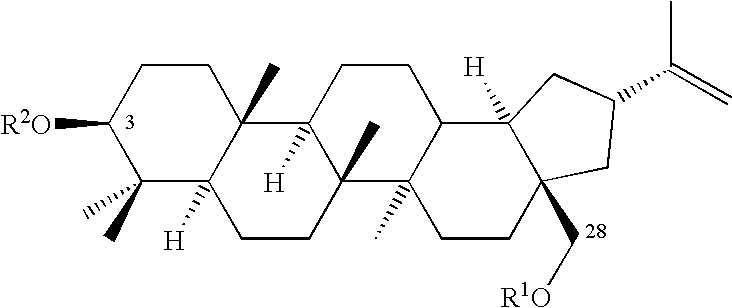
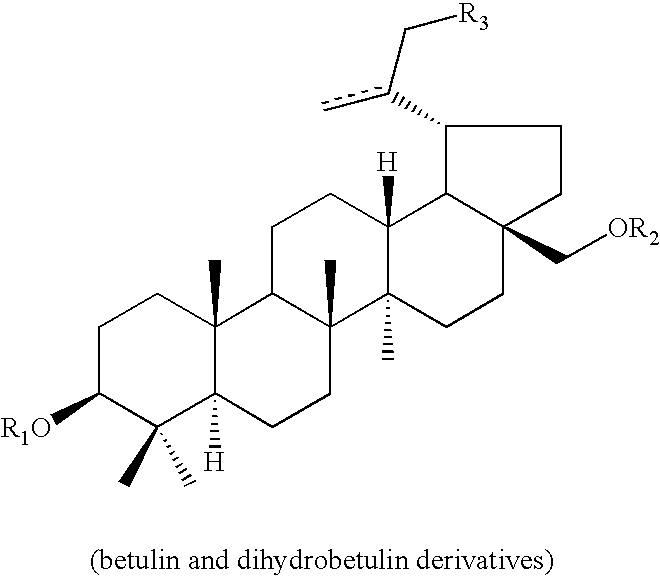
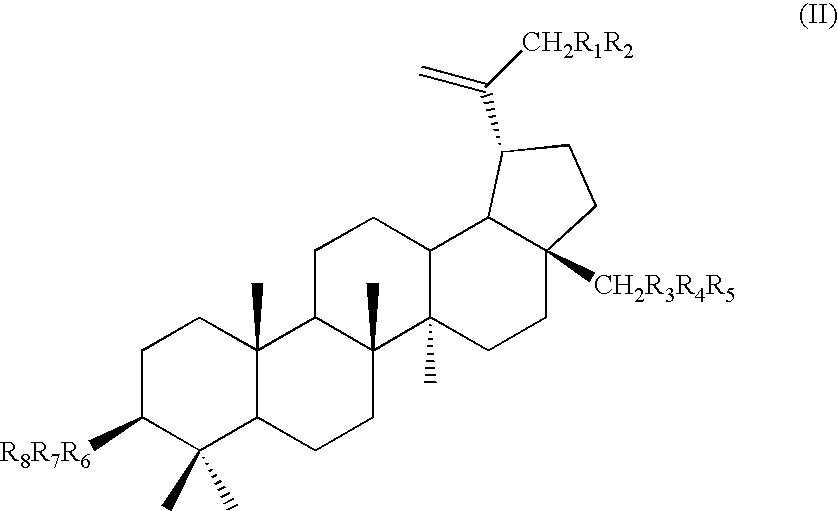
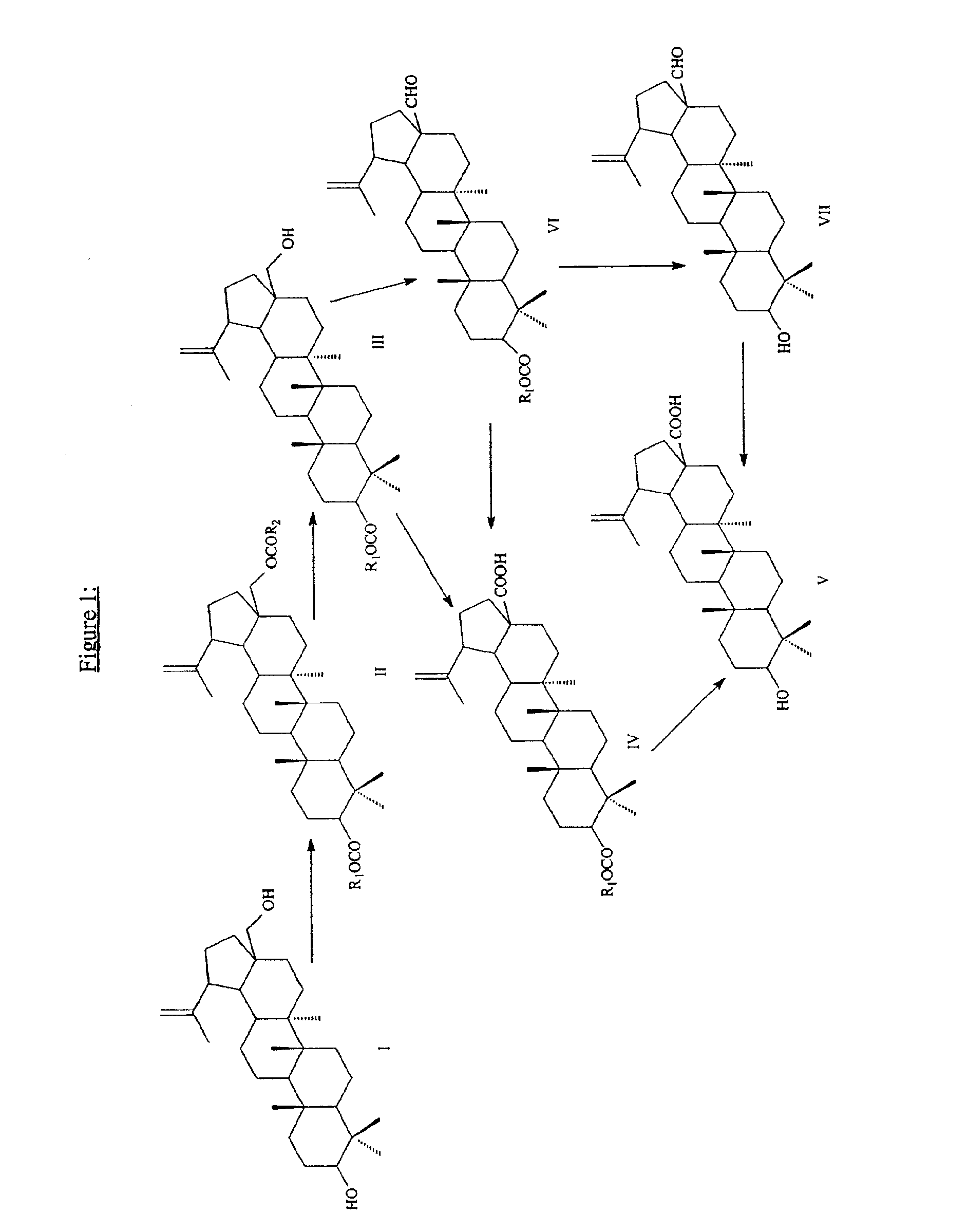
Monoacylated betulin and dihydrobetulin derivatives, preparation thereof and use thereof
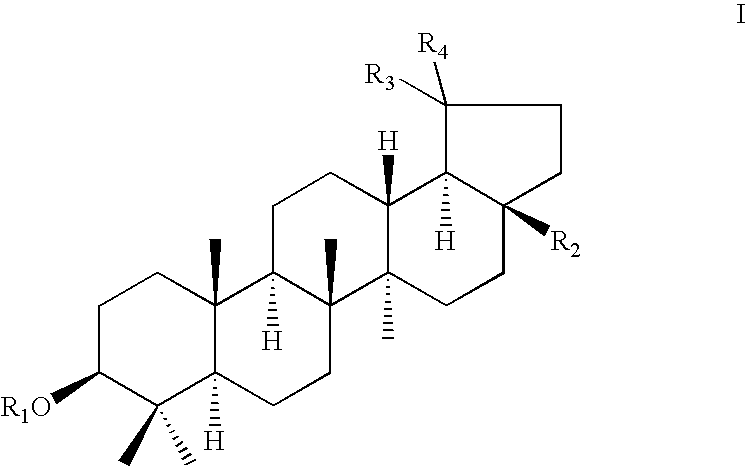
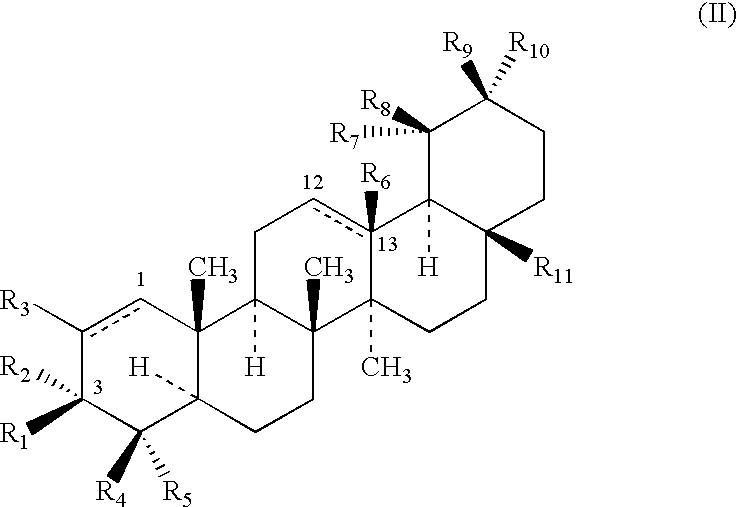
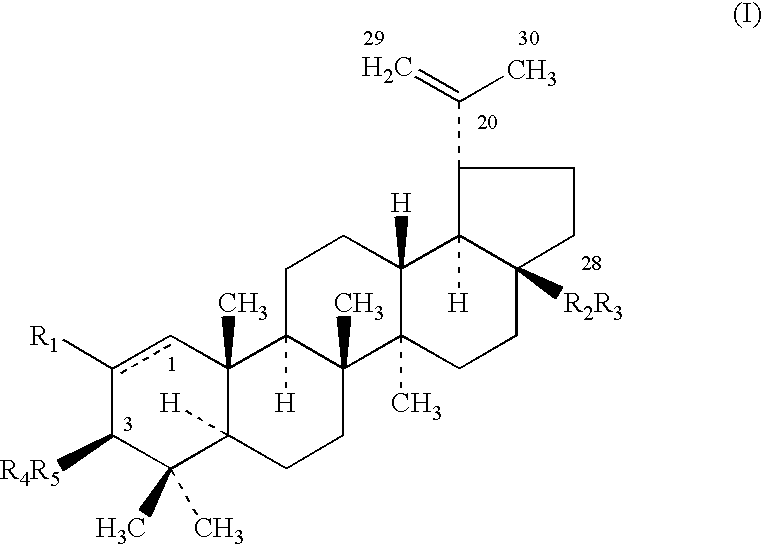
Betulin and dihydrobetulin acyl derivatives according to the present invention have been found to have potent anti-HIV activity. The compounds of the present invention have Formula I as described herein, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof; wherein R1 is a C2-C20 substituted or unsubstituted carboxyacyl or ester thereof; R2 is hydrogen, halogen, hydroxyl or —OR3, R3 is C2-C20 substituted or unsubstituted carboxyacyl; and R4 is hydrogen or C(C6H5)3; wherein the dashed line represents an optional double bond between C20 and C29.
Owner:MYREXIS INC +2
Anti-fungal formulation of triterpene and essential oil
InactiveUS20050014730A1Less-expensive to manufactureEasy to synthesizeOrganic active ingredientsBiocideTriterpeneAnti fungal
The present invention provides for pharmaceutical compositions that includes a triterpene (e.g., betulin) and an essential oil (Vicks® Vapor Rub). The present invention also provides for a cosmetic formulation that includes a triterpene (e.g., betulin) and an essential oil (Vicks® Vapor Rub). The present invention also provides a method of treating a fungal infection that includes administering (e.g., topically applying) an effective amount of the pharmaceutical composition to the tissue afflicted with the fungal infection, or the tissue at risk of being afflicted with the fungal infection.
Owner:NATURNORTH TECH +1
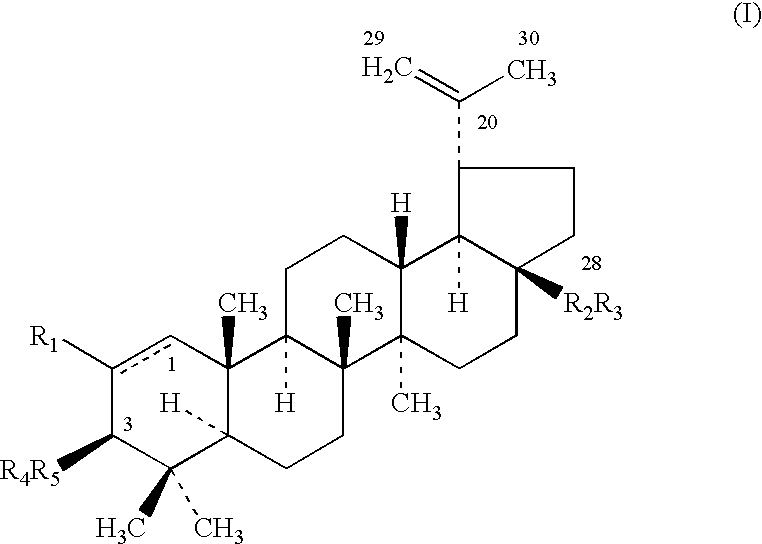
Novel betulin derivatives, preparation thereof and use thereof
The present invention relates to novel synthetic derivatives of betulin and the use of such derivatives as pharmaceuticals. The present invention is directed to novel compounds of Formula I: or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug thereof.
Owner:MYREXIS INC
Hair and skin protecting compositions based on esters or ethers of betulin
Personal care compositions and formulations, which include conventional concentrations of known hair and skin altering components and a cosmetically acceptable amount of oil-soluble betulin and allo-betulin esters or ethers derived from betulin or allo-betulin in effective amounts are disclosed.
Owner:GLINSKI JAN
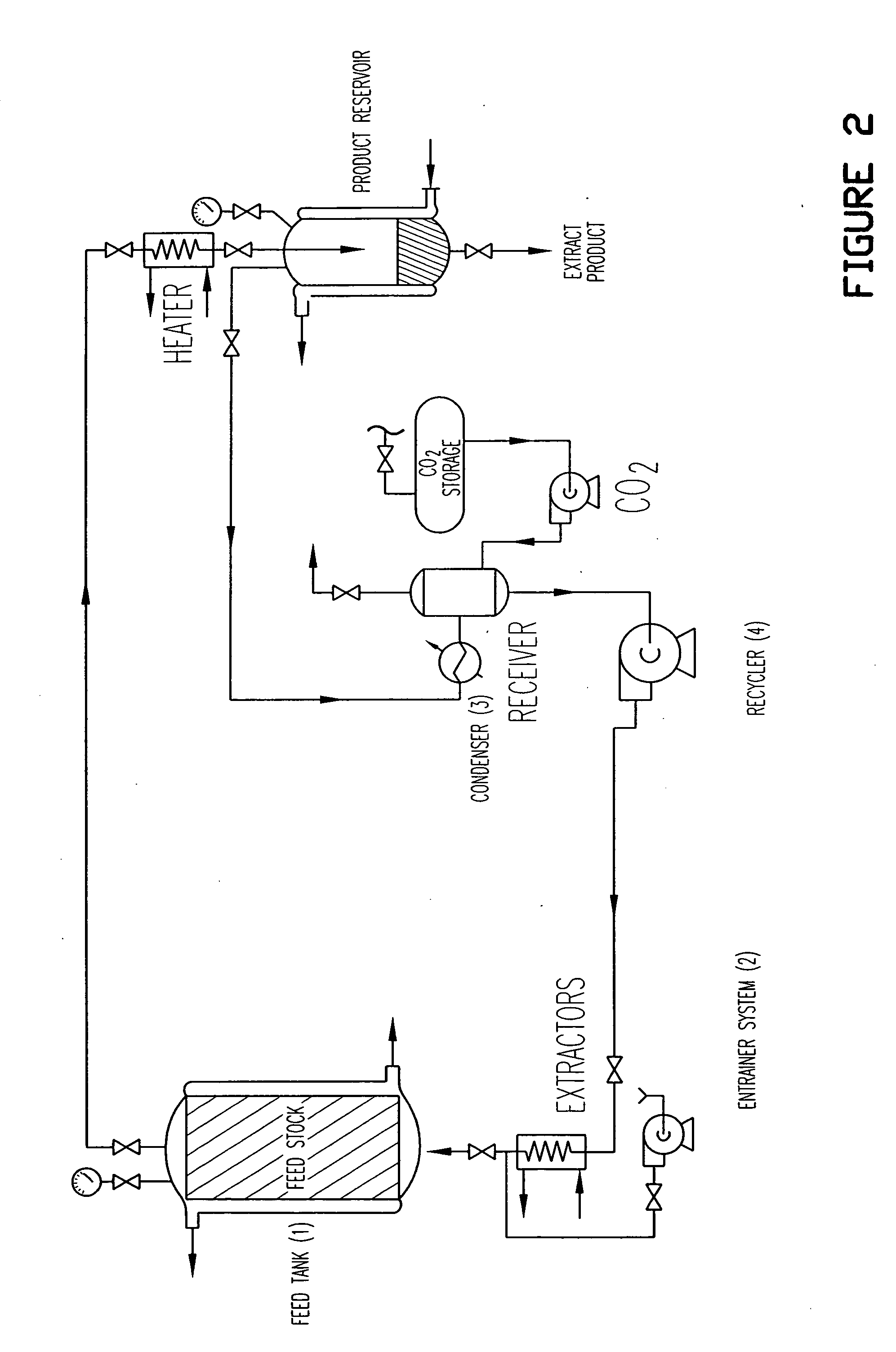
Method for extracting betulin from birch bark
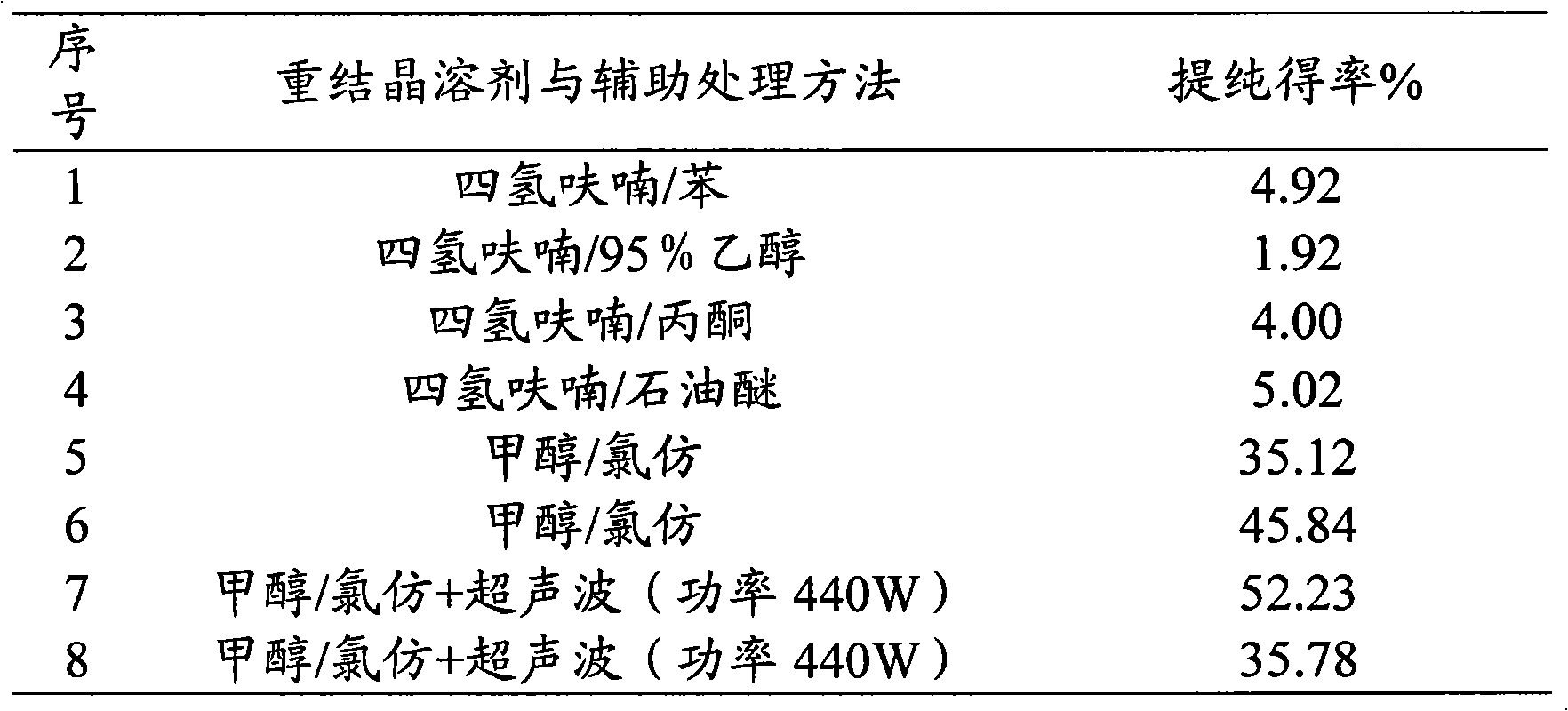
The invention discloses a method for extracting betulin from birch barks, comprising the following steps: firstly, crushed birch barks are added into an ethanol water solution, undergo reflux extraction under auxiliary processing of ultrasonic waves, and then are filtrated for removal of residue, and an extract is obtained; secondly, solid powder is separated out after decompression and concentration of the extract, and then dried to the constant weight so as to obtain betulin coarse products; and thirdly, the betulin coarse products are added into an organic solvent, undergo ultrasonic treatment and then stand, crystals are separated out, and the betulin is obtained after the separated crystals are dried to the constant weight. The method has a simple operation flow, short extraction time, low production cost and high safety, and provides a better method and a better platform for further development and utilization of natural products.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for abstracting and purifying betulin in birch bark
The invention relates to a method for extracting and purifying the betulin from birch bark. The invention comprises the following procedures, cutting the birch bark into the bark particles, heating, refluxing and extracting by aqueous ethanol solution, filtering, vacuum concentration of the filtrate, cooling, collecting and drying the separated crude betulin. The method of the invention can obtain the betulin with the purity of more than 90 percent, and has the advantages of simple process, lower cost and being suitable for the industrial production.
Owner:CHINA GATEWAY PHARMA DEV CO LTD
Birch bark processing and the isolation of natural products from birch bark
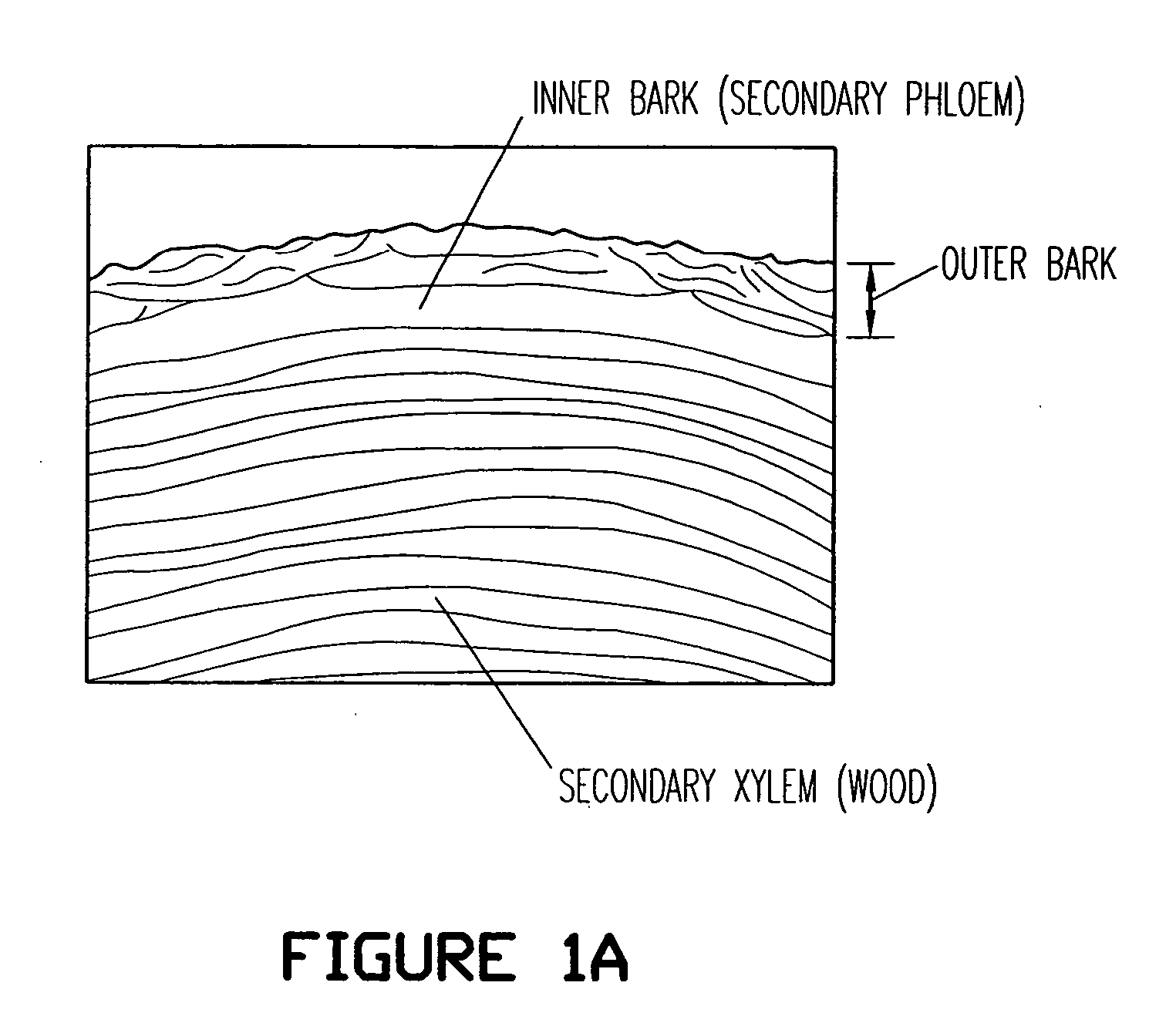
InactiveUS6815553B2Not costly and lengthy and dangerous procedureEasy to handleSolvent extractionOrganic compound preparationNatural productBetula platyphylla
The invention provides methods for separating outer birch bark from inner birch bark. The invention also provides methods for isolating betulin; lupeol; betulinic acid; 9,10-epoxy-18-hydroxyoctadecanoic acid; 9,10,18-trihydroxyoctadecanoic acid; polyphenolic polymers and fatty acids from birch bark.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Birch bark processing and the isolation of natural products from birch bark
InactiveUS20050158414A1Not costly and lengthy and dangerous procedureEasy to handleBiocideSolvent extractionNatural productBetula platyphylla
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Selective oxidation of triterpenes employing tempo
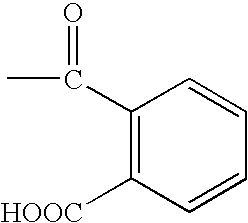
The present invention provides a process of preparing betulin-28-aldehyde from betulin. The process includes contacting betulin with a compound of formula (I), e.g., TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl) for a period of time effective to provide betulin-28-aldehyde. The present invention also provides a process of preparing betulinic acid. The process includes contacting betulin with a composition that includes: sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl); sodium chlorite (NaClO2), potassium chlorite (KClO2), or a combination thereof; and a compound of formula (I), e.g., TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl); for a period of time effective to provide betulinic acid.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Compound extract of common phellinus fungus and chaga, its preparing method and preparation
InactiveCN101023967AGood for healthGood treatment effectPowder deliveryNervous disorderLipid formationDisease
The present invention relates to a compound extract of fomes yucafensis and betulin, its preparation method and preparation. Said preparation method includes the following steps: (1), respectively pulverizing fomes yucafensis and betulin; (2), mixing (by weight portion) 2-8 portions of fomes yucafensis powder and 3.5-11.5 portions of betulin powder; soaking the obtained mixturein water, heating to make water extraction, taking out supernatant fluid to obtain the supernatant fluid A; (3), adding water into the mixture extracted by step 2 and making water extraction, taking out supernatant fluid to obtain supernatant fluid B; (4), mixing the above-mentioned two supernatant fluids to obtain their mixed liquor, removing protein, lipid and impurity; and (5), concentrating and drying said mixed liquor so as to obtain the invented compound extract of fomes yucafensis and belutin.
Owner:卢昶年 +1
Betulin derived compounds useful as antiprotozoal agents
InactiveUS20100190795A1Improve solubilityLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideProtozoaLeishmaniasis
The invention relates to betulin derivatives, and to the use thereof as agents against protozoa of the genus Leishmania and against leishmaniasis in applications of pharmaceutical industry.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
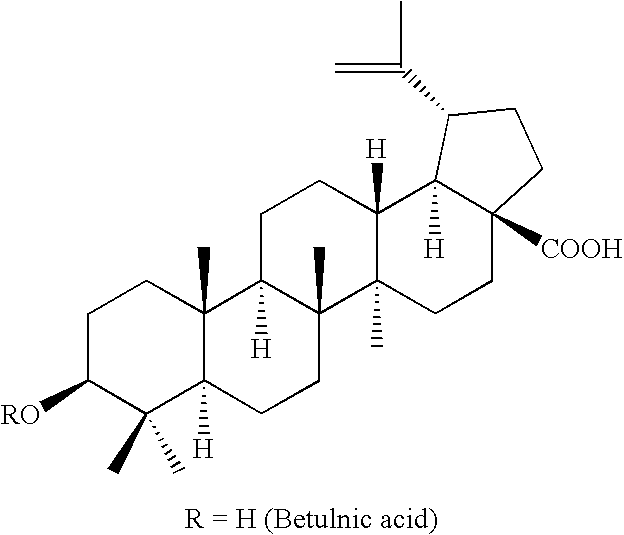
Bidesmosidic betulin and betulinic acid derivatives and uses thereof as antitumor agents
The instant application is directed to bidesmosidic betulin and betulinic acid saponin derivatives of formula (I), and use thereof as antitumor agents. In particular, said compounds are effective in treating lung carcinomas, colorectal adenocarcinomas, breast adenocarcinomas, and prostate adenocarcinomas. Methods of synthesizing said compounds through selective glycosylation of the C-28 and C-3 position, and diagnostic methods for identifying tumours suitable for treatment by said compounds are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV DU QUEBEC CHICOUTIMI
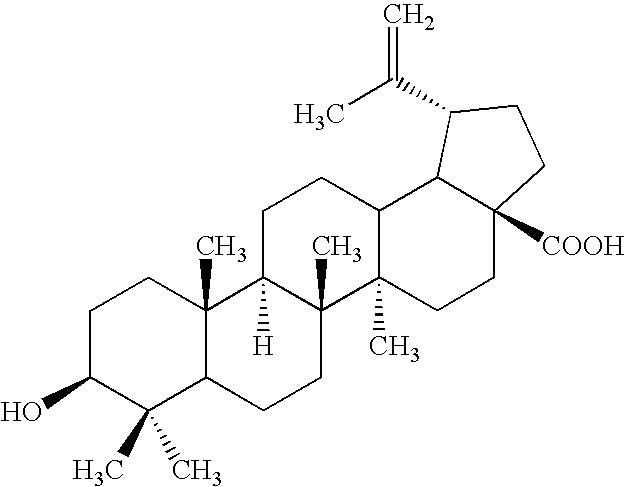
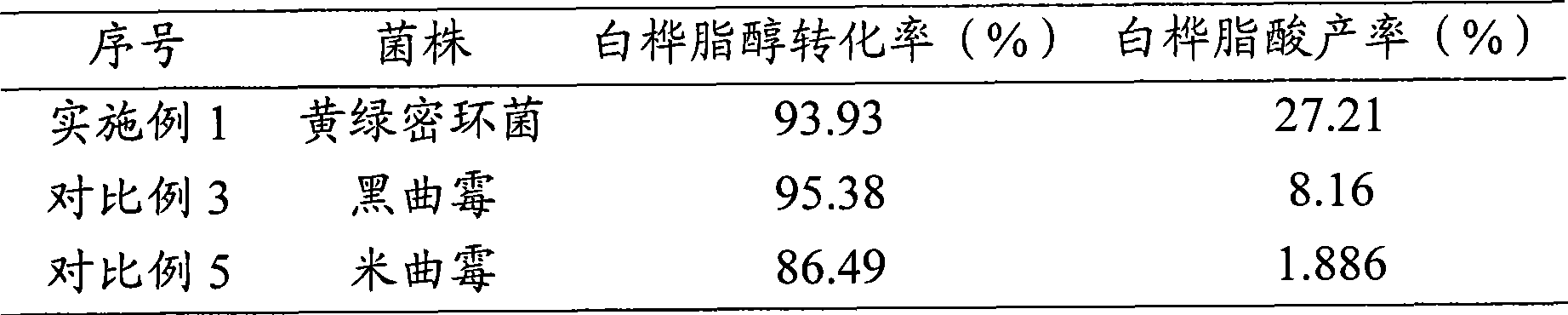
Method for synthesizing betulic acid from betulin through microbial cell bioconversion
InactiveCN101457250AImprove conversion rateShort training timeMicroorganism based processesFermentationChemical synthesisMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing betulic acid by microbial cell bioconversion of betulin comprising the following steps: inoculating an Armillaria luteo-virens Sacc. ZJUQH to sterilized culture solution and obtaining a pre reaction system; adding a substrate solution containing the betulin and reacting for 5-7 days at between 25 and 30 DEG C, processing the converted culture solution and obtaining the betulic acid, wherein the betulin dosage is 0. 01-0. 1 g per each litre of culture solution. Comparing with the direct plant extraction of the betulic acid method and the chemical synthesis of the betulic acid method The method of the invention has advantages of short microbial cell culture time, easy operation and control, short whole bioconversion period, safe and reliable conversion process, low cost and is suitable for the industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
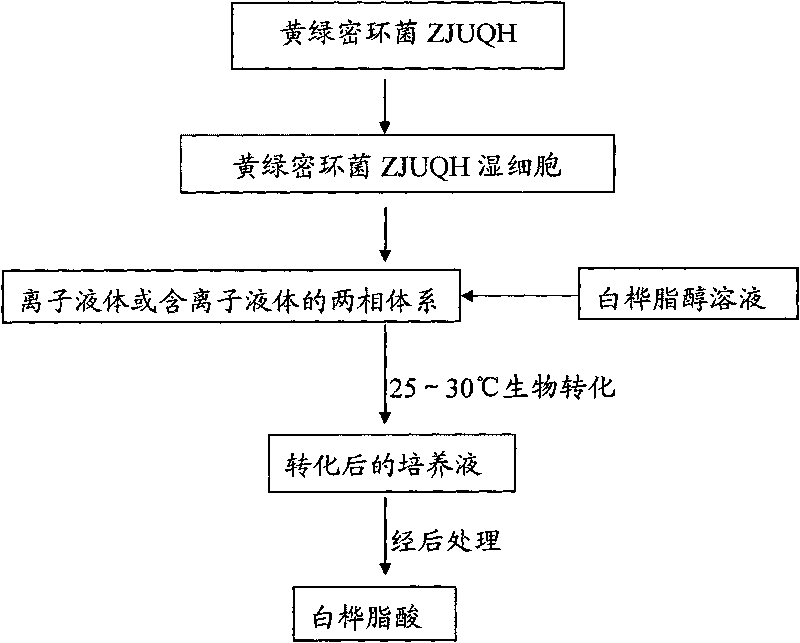
Method for synthesizing betulic acid by carrying out biocatalysis on betulin
InactiveCN101709322AEasy to separateEasy to operateMicroorganism based processesChemical recyclingBiocompatibility TestingPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing betulic acid by carrying out biocatalysis on betulin, comprising the following steps: (1) preparing armillaria luteo-uirens ZJUQH wet cells; (2) adding armillaria luteo-uirens ZJUQH wet cells into ionic liquid or a two-phase system for pre-culture to obtain a pre-culture system; (3) adding betulin solution in the pre-culture system for fermentation culture for 6-24 hours at 25-30 DEG C to obtain transformed culture solution; (4) processing the transformed culture solution to obtain betulic acid. The two-phase system is mixed solvent of ionic liquid and normal hexane, or mixed solvent of ionic liquid and phosphoric acid buffer solution. Compared with a conventional method, the inventive method has higher product yield, shorter catalytic reaction time, simple product separation, lower volatility of ionic liquid system, better biocompatibility and no pollution to the environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of betulin extract, application and its composition
The present invention relates to a preparation method of extract of downy leaf of white birch, its new medicine application and medicine composition containing said extract. It using water to repeatedly soak downy leaf ow hite birch to prepare the extract of downy leaf ow hite birch, and said extract can be used to prepare the medicine with the functions of transquilizing the mind, resisting anxiety and resisting depression.
Owner:王红红
Compositions that include a triterpene and a carrier
InactiveUS20060003948A1Inhibiting and killing fungusImprove skin appearanceCosmetic preparationsBiocideTriterpeneLanolin
The present invention provides for compositions that includes a triterpene (e.g., betulin) and a carrier (e.g., lanolin). The compositions are useful for skin care (e.g., as cosmetic formulations), and as therapeutic formulations, e.g., for treating topical fungal infections.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Bio-based hemodialysis membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106076126AImprove transmittanceHigh retention rateSemi-permeable membranesMembranesBiocompatibility TestingClelands Reagent
The invention discloses a bio-based hemodialysis membrane and a preparation method thereof. The hemodialysis membrane is prepared from polylactic acid, laminarin, thiolated chitosan, silk fibroin, sodium ascorbyl phosphate, cellulose acetate, dithiothreitol, stachyose, betulin caffeate, ammonium persulfate, ferulic acid, hydroxyethyl starch, N-benzyl glycine hydrochloride, deoxycholic acid, polyhydroxyalkanoate, hexamethylenediamine, hyaluronic acid, benzoperoxide and dimethyl sulfoxide. According to the prepared hemodialysis membrane, the tensile strength is not lower than 7.0 MPa, the transmittance of urea is higher than 86%, the transmittance of beta2 microglobulin is higher than 66%, the rejection rate of macromolecular protein is higher than 95%, the biocompatibility is good, coagulation, thrombus, inflammation, poisoning and other adverse reactions do not exist, and an application prospect is wide.
Owner:林春梅
Monoacylated betulin and dihydrobetulin derivatives, preparation thereof and use thereof
Betulin and dihydrobetulin acyl derivatives according to the present invention have been found to have potent anti-HIV activity. The compounds of the present invention have Formula I as described herein, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof; wherein R1 is a C2-C20 substituted or unsubstituted carboxyacyl or ester thereof; R2 is hydrogen, halogen, hydroxyl or —OR3, R3 is C2-C20 substituted or unsubstituted carboxyacyl; and R4 is hydrogen or C(C6H5)3; wherein the dashed line represents an optional double bond between C20 and C29.
Owner:MYREXIS INC +2
Method for improving content of betulin and oleanolic acid in birch cell by utilizing MeJA (methyl-jasmonate) and SA (salicyl acid)
InactiveCN102943104AShorten the production cycleNo pollution in the processFermentationBiologyCulture mediums
The invention belongs to the field of biological engineering, and particularly relates to a method for improving the content of betulin and oleanolic acid in a birch cell by utilizing MeJA (methyl-jasmonate) and SA (salicyl acid), which comprises the following steps of: inoculating a birch tissure culture seedling stem to NT + 0.1 mg / L of 6-BA and 0.01 mg / L of TDZ culture mediums to induce birch callus, and obtaining a birch suspension cell with high content of total triterpenes through multi-time subculture, screening and suspension culture; inoculating the screened cell into the same liquid culture medium, wherein the inoculation amount is 3g / 100ml; adding 100mu Mum / L of MeJA and 50mg / L of SA when the shake culture is performed at the seventh day; after 24-48h, obtaining the product; and detecting the content of total triterpenes, betulin and oleanolic acid in the cell. Through the comparison of the two kinds of processing methods, the content of total triterpenes is improved by 21.6-31.7%, the content of oleanolic acid is improved by 277.4-369.34%, and the content of betulin is improved by 44.42-179.58%. The application of the invention provides a new path for solving the problem of shortage of natural plant drug resources and realizing large-scale industrial production of betulin and oleanolic acid drugs.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +2
Exterior wall thermal insulation foaming putty
The invention discloses a novel external wall heat insulating foaming putty, which is mainly formed by the following materials with percentage by weight, 15-25% H2O, 0.05-0.15 preservative agent, 0.8-1.5% acrylate, 0.2-0.5% dispersing agent, 1-1.5% anti-freeze agent, 0.5-2% NH4 HCO3, 1-2% 12 carbon betulin, 3-5% wood fiber or polypropylene fiber, 0.4-0.6% water-loss reducer, 10-20% propyl benzene emulsion, 20-30% CaCO3 powder, 30-40% talcum powder, 3-5% polyphenylene particle and 0.5-1.5% wax emulsion. The external wall heat insulating foaming putty adopts the self-foaming principle, provides heat insulating effect through adding polyphenylene particle in heat-insulating mortar, has excellent heat insulating effect, and can be extensively applied on the external walls of buildings.
Owner:谭苏平
Foam Formulations Containing at Least One Triterpenoid
InactiveUS20120315315A1Pleasant applicabilityGood skin compatibilityBiocideCosmetic preparationsTriterpeneTriterpenoid
The invention relates to a foam formulation comprising an emulsion, comprising an oil phase and an aqueous phase, wherein the emulsion comprises at least one triterpenoid. Further the invention relates to anemulsion comprising an oil phase and an aqueous phase, wherein the emulsion comprises at least one triterpenoid selected from the group consisting of betulin, betulinic acid, lupeol, erythrodiol, oleanolic acid, (C1-C6) alkyl esters of the aforementioned acids, or mixtures thereof, and wherein the oil phase comprises at least one membrane-forming substance forming a lamellar arranged membrane in the emulsion.
Owner:NEUBOURG SKIN CARE GMBH & CO KG
Method for synthesizing betulic acid by carrying out biocatalysis on betulin
InactiveCN101709322BHigh yieldEasy to separateMicroorganism based processesChemical recyclingPhosphoric acidBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing betulic acid by carrying out biocatalysis on betulin, comprising the following steps: (1) preparing armillaria luteo-uirens ZJUQH wet cells; (2) adding armillaria luteo-uirens ZJUQH wet cells into ionic liquid or a two-phase system for pre-culture to obtain a pre-culture system; (3) adding betulin solution in the pre-culture system for fermentation culture for 6-24 hours at 25-30 DEG C to obtain transformed culture solution; (4) processing the transformed culture solution to obtain betulic acid. The two-phase system is mixed solvent of ionic liquid and normal hexane, or mixed solvent of ionic liquid and phosphoric acid buffer solution. Compared with a conventional method, the inventive method has higher product yield, shorter catalytic reaction time, simple product separation, lower volatility of ionic liquid system, better biocompatibility and no pollution to the environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for enriching and purifying betulin in birch barks
ActiveCN102093458AHigh adsorption selectivityParsing fastSteroidsHeat stabilityUltimate tensile strength
The invention belongs to the field of natural organic chemistry and relates to a method for enriching and purifying betulin in birch barks by utilizing a batch distillation-macroporous absorption resin method. The method has the advantages of good adsorption selectivity to betulin, quickness of adsorption and resolution, larger adsorption capacity, convenience and quickness of extraction, rich raw material source, low production cost, obvious separation effect and high extraction purity, can be used for obtaining a semi-finished betulin product with a content higher than 35 percent and a finished betulin product with a content higher than 98 percent and overcomes the defects of relatively lower conventional extraction ratio and low extraction purity. In the invention, macroporous absorption resin having stable physical and chemical properties, larger surface area, higher exchange speed, higher mechanical strength, strong antipollution capacity and good heat stability is used, which can selectively adsorb the betulin from the solution through physical adsorption, thus the invention has the advantages of quickness of adsorption and resolution and larger adsorption capacity.
Owner:DAXINGANLING LINGOBERRY BOREAL BIOTECH CO LTD
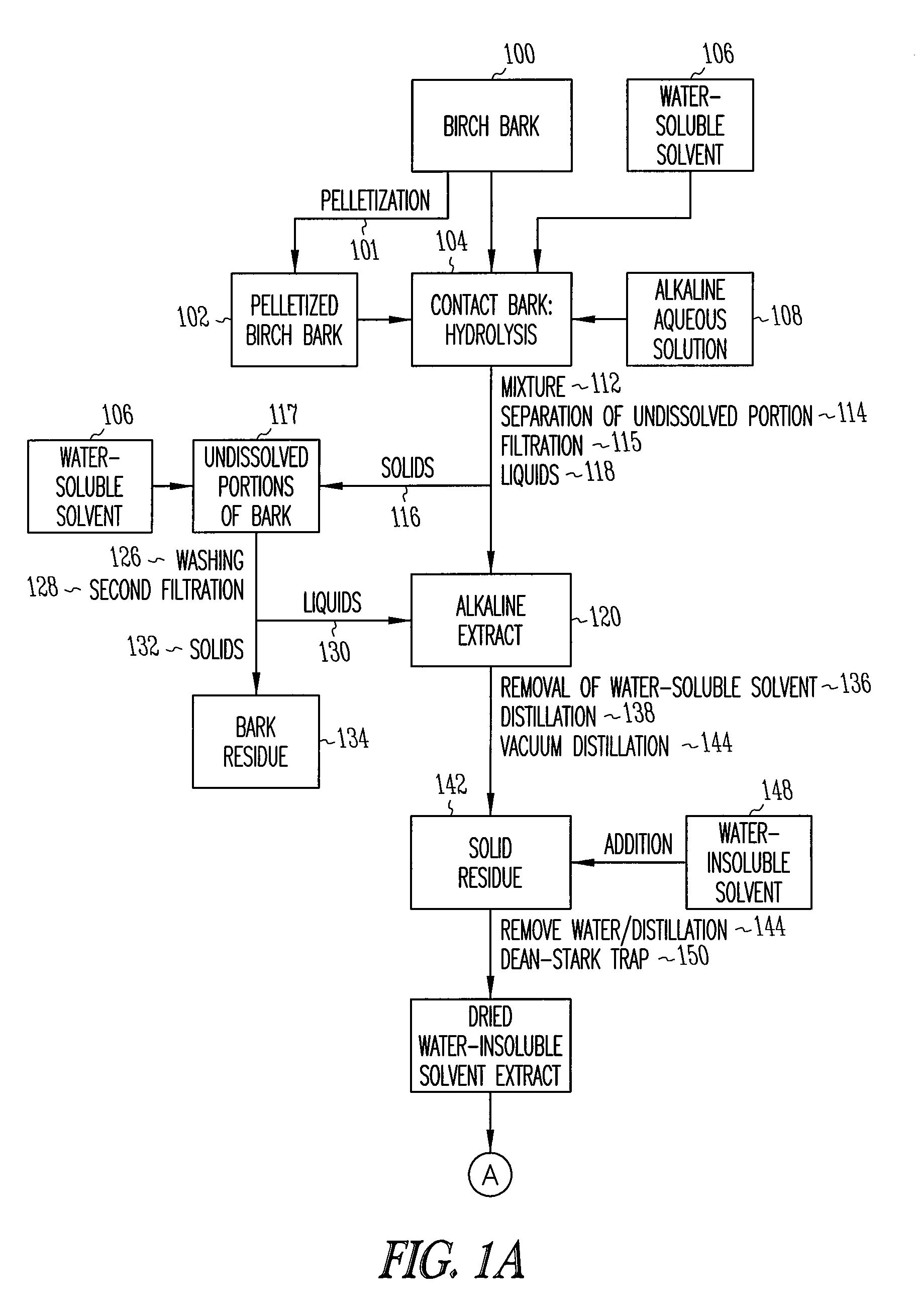
Depolymerization extraction of compounds from birch bark
ActiveUS20090182158A1Increase productionHigh yieldBiocideCosmetic preparationsSimple Organic CompoundsDepolymerization
The invention provides improved processes for the extraction of betulin, lupeol, betulinic acid, suberinic acids, and / or other organic compounds and compositions from birch bark. In some embodiments, the birch bark can be physically processed prior to the extraction process, which can further improve the yield of the extraction. The bark processing can include, but is not limited to, one or more of pelletizing the bark, baling the bark, pucking the bark, or compressing the bark, to a form that is more dense per volume unit than prior to the processing.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Triterpene quaternary salts as biologically active surfactants
InactiveUS20050059642A1Abundant and relatively inexpensive starting materialEasy to handleAntibacterial agentsBiocideTriterpeneMedicinal chemistry
The invention provides novel compounds that are quaternary amine derivatives of betulin and other triterpenes. The compounds have antibacterial, antifungal, and surfactant properties.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Process for extracting lupinol from betulin category plant
The invention discloses a method to distill lupeol from birch genus plant that includes the following steps: smashing the dry birch bark, using methylene chloride to take back flowing and distilling, recycling methylene chloride, placing for deposition, filtering, removing filtrate and the washing deposit by a little cyclohexane several time to remove the low polarity impurity; recrystallizing for three times by absolute ethyl alcohol and acetone, the lupeol would be gained. The invention has the advantage of low cost, common raw material, simple technology.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA +1
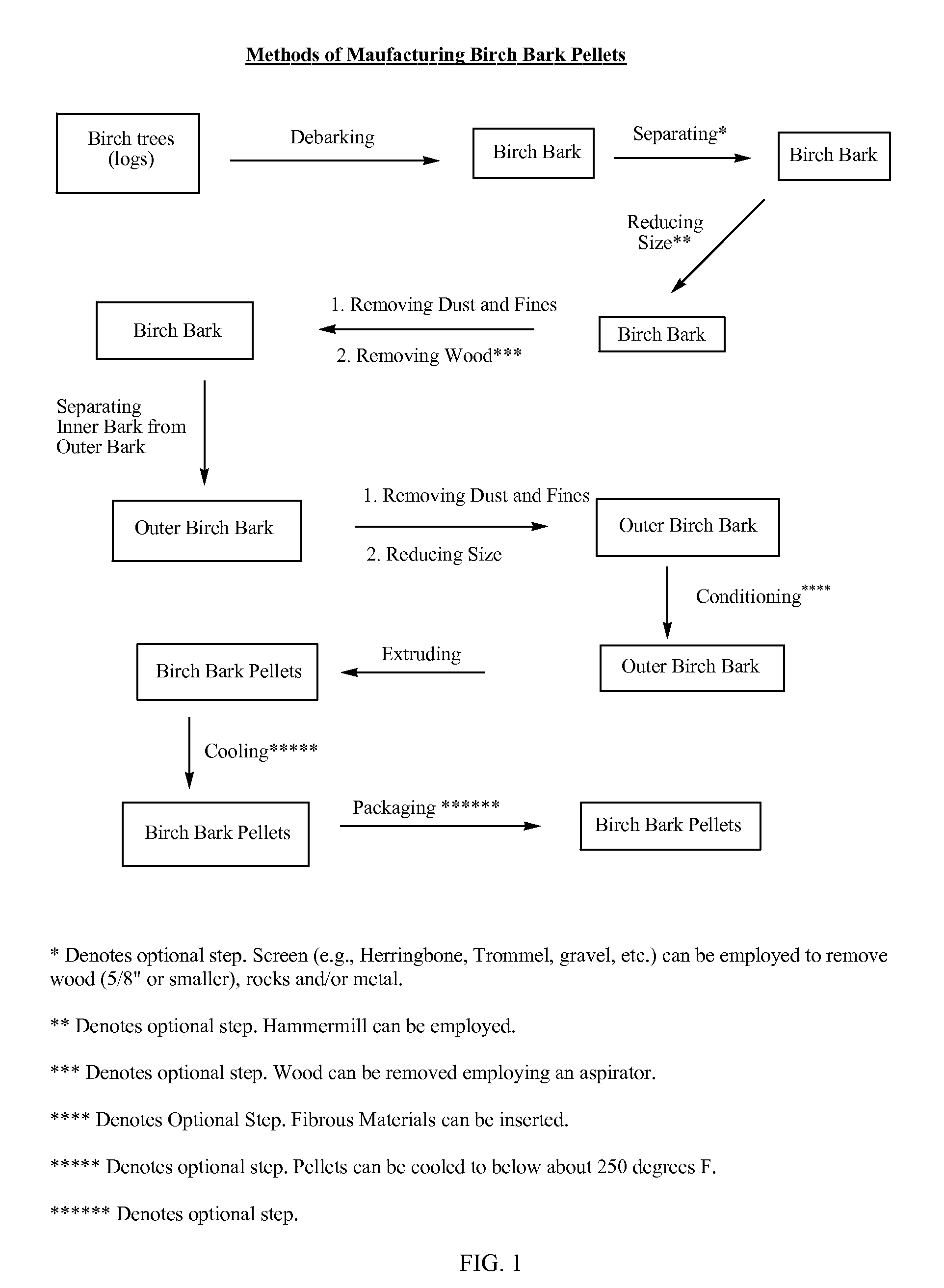
Birch bark pelletization and methods for obtaining natural products from birch bark pellets
InactiveUS20090253943A1Reduce shippingReduce processing costsDischarging arrangementMouldsNatural productMedicine
The present invention provides birch bark pellets that include outer birch bark. The present invention also provides methods of manufacturing birch bark pellets from outer birch bark. The present invention also provides methods for obtaining a natural product from birch bark pellets. The birch bark pellets are manufactured from outer birch bark that includes relatively low amounts of inner birch bark and wood. The birch bark pellets meet the requirement for extraction, to obtain e.g., betulin and / or lupeol from the pellets.
Owner:MYREXIS INC
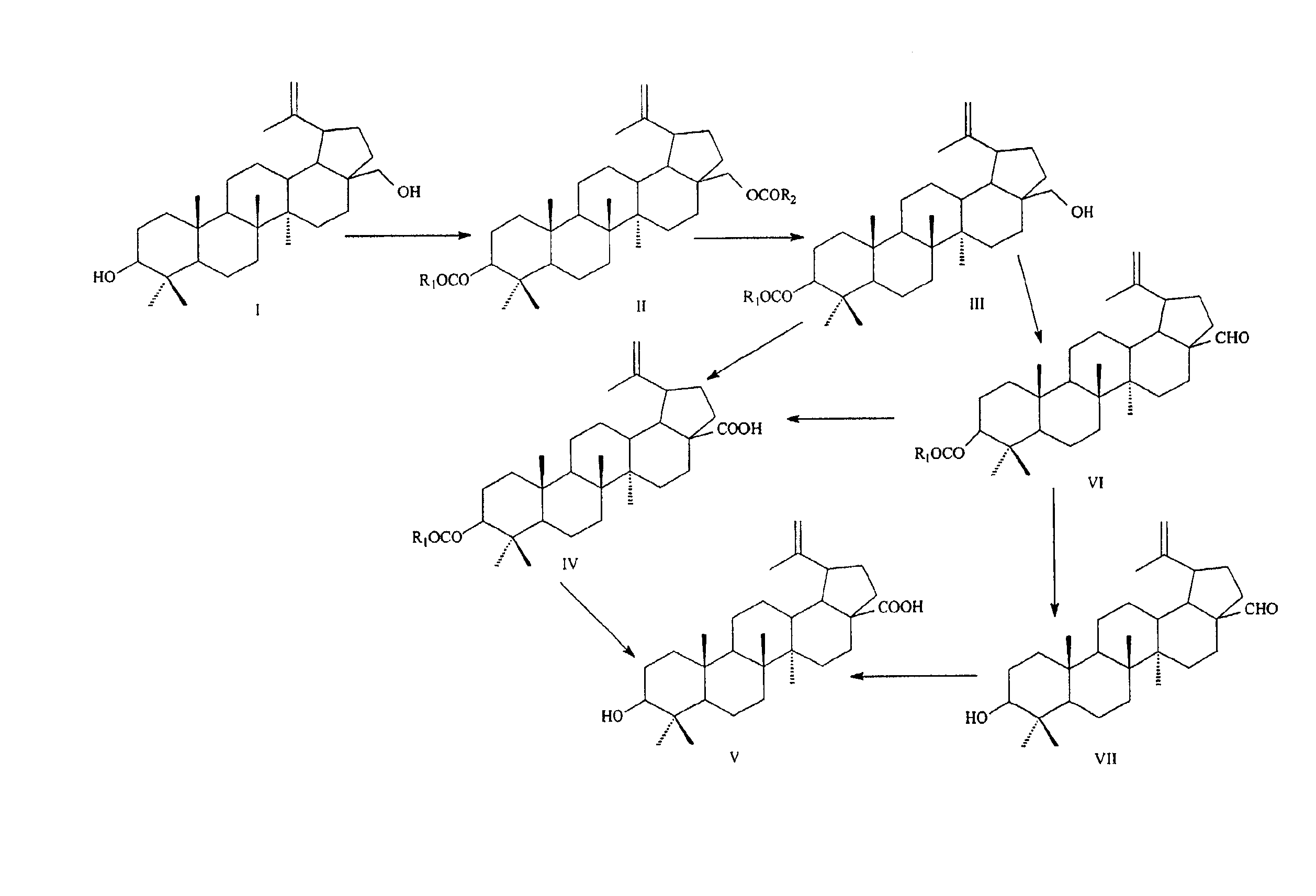
Methods for manufacturing betulinic acid
InactiveUS6867314B2Less timeLess expensiveFatty acid chemical modificationPreparation from carboxylic acid halidesAcetic acidAlcohol
The present invention provides a method for preparing an ester of betulin at the 3-position, e.g., betulin-3-acetate, including the selective alcoholysis of a betulin-3,28-diester, e.g., betulin-3,28-diacetate; a method for preparing betulin-3-acetate including (1) acetylating betulin to provide betulin-3,28-diacetate and (2) the alcoholysis of betulin-3,28-diacetate to provide betulin-3-acetate; and a method for preparing betulinic acid (1) acetylating betulin to provide betulin-3,28-diacetate, (2) the alcoholysis of betulin-3,28-diacetate to provide betulin-3-acetate, (3) oxidizing betulin-3-acetate to provide betulinic aldehyde-3-acetate, (4) oxidizing betulinic aldehyde-3-acetate to provide betulinic acid-3-acetate, and (5) deprotecting betulinic acid-3-acetate to provide betulinic acid.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Derivatives of Betulin
Owner:GLAXO SMITHKLINE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com