Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
104 results about "Absorption current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Absorption current. [əb′sȯrp·shən ′kər·ənt] (electricity) The component of a dielectric current that is proportional to the rate of accumulation of electric charges within the dielectric.
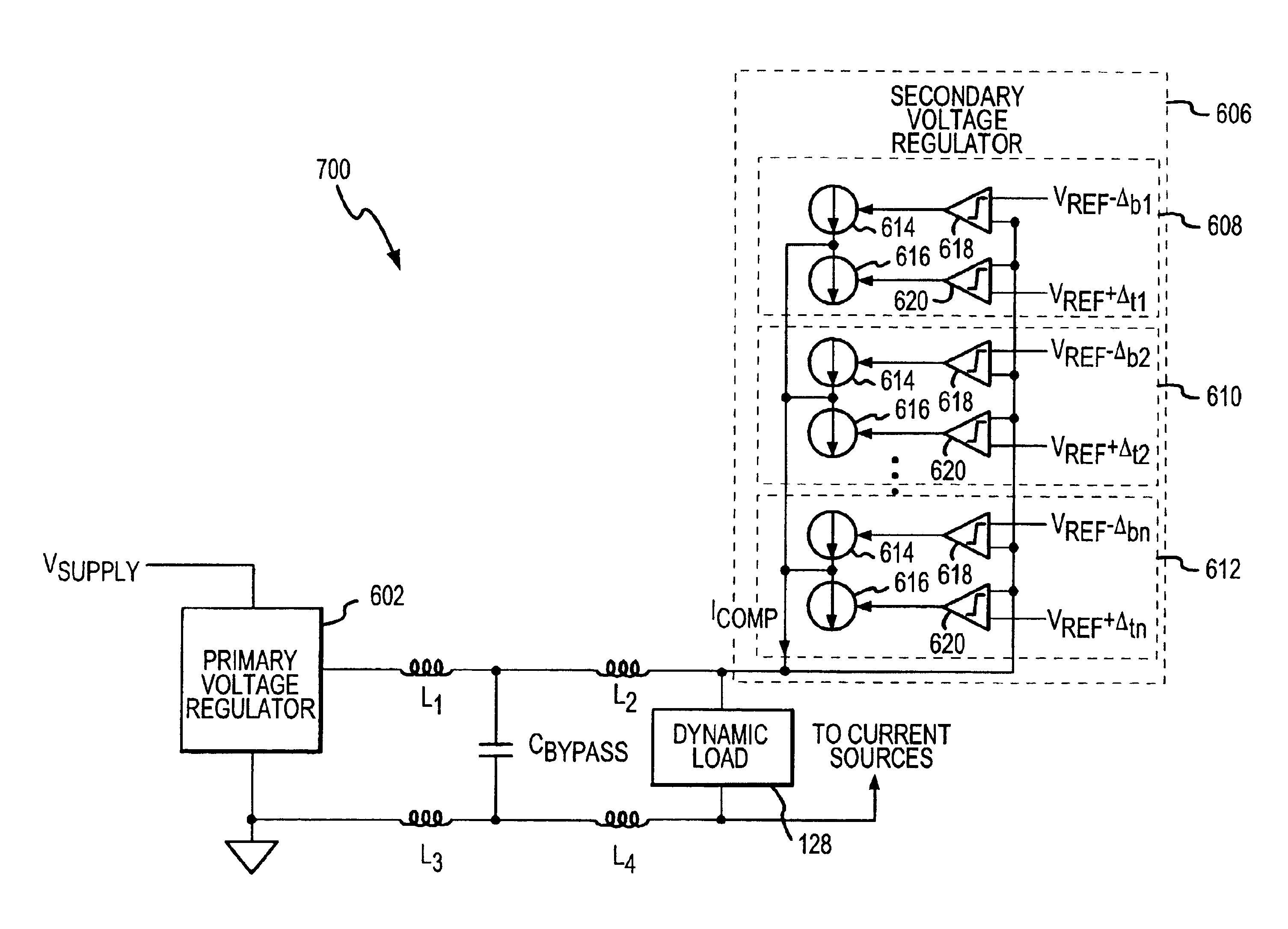
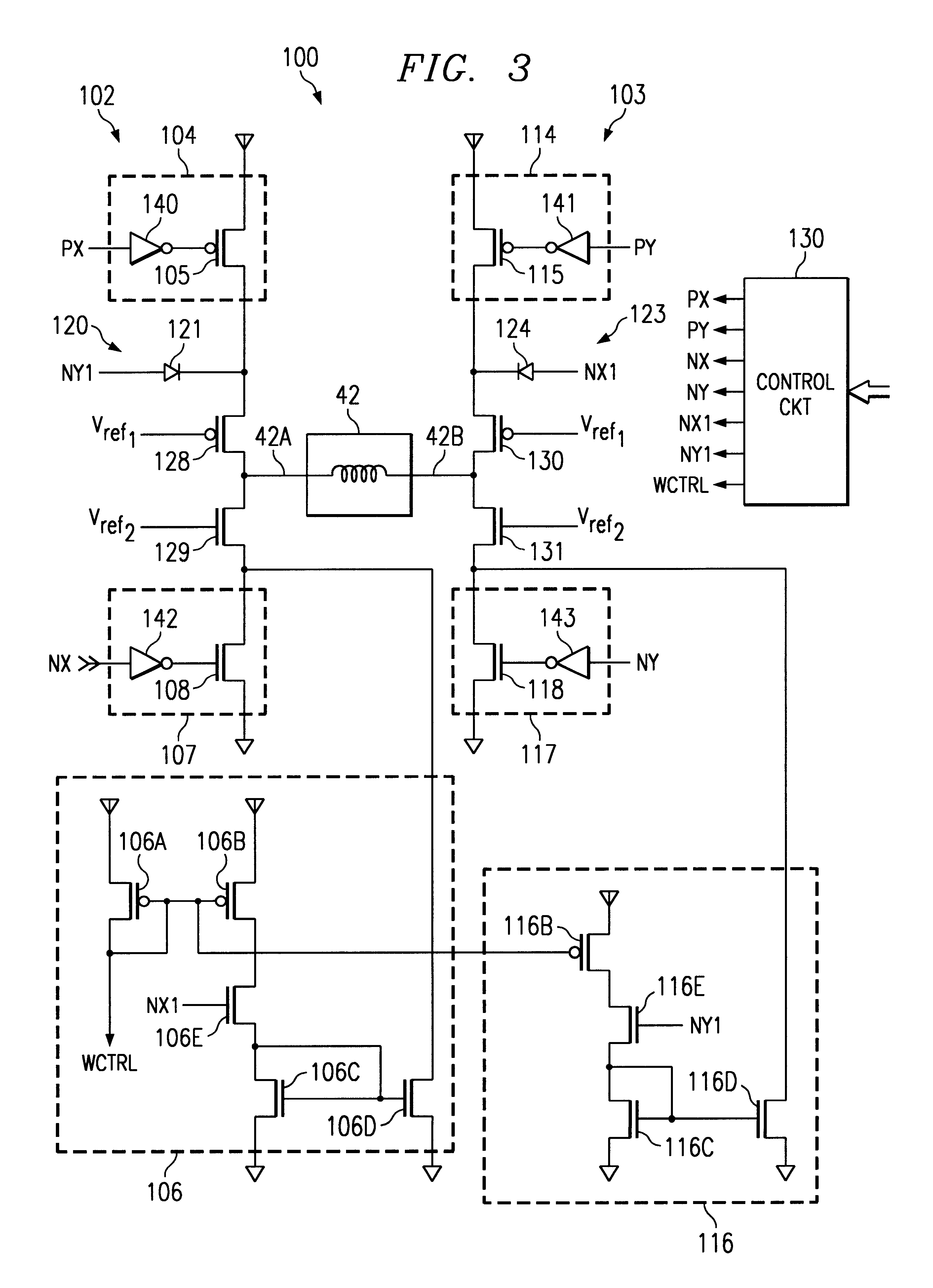
Method and apparatus for providing wideband power regulation to a microelectronic device
A method, apparatus, and system for providing operating power and transient suppression power to a microelectronic device are disclosed. The system includes a primary regulator to supply nominal operating power and to respond to relatively slow transient events and a transient suppression regulator to respond to fast transient power events. The system also includes a sense circuit to detect when a transient event occurs and to send a signal to the transient suppression regulator to supply or sink current to the load in response to a sensed transient power event.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
Voltage-activated, constant current sink circuit
InactiveUS20060049818A1Accurately sinking currentLow costMultiple-port networksOne-port networksZener diodeGrounding resistance
Voltage-activated and accurate current sink, and method of providing same. In one aspect, a circuit for accurately sinking current includes a zener diode coupled to a power source at the cathode of the zener diode, and first and second transistors, where the first transistor has its collector coupled to the power source and its base coupled to the cathode of the zener diode, and the second transistor has its base coupled to the anode of the zener diode and its emitter coupled to ground. A resistor is coupled between the emitter of the first transistor and the collector of the second transistor.
Owner:MICREL
Charge control apparatus and measurement apparatus equipped with the charge control apparatus
ActiveUS7683319B2Perform charge processingIncrease speedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesElectron sourceCarbon nanotube
The invention solves charge nonuniformity of a specimen surface resulting from emission variation of a carbon nanotube electron source and individual difference of emission characteristics. During charge control processing, charge of the specimen surface is measured in real time. As means for solving charge nonuniformity resulting from nonuniformity of electron illumination density, electrons illuminating the specimen and the specimen are moved relatively to average electron illumination density. Moreover, an absorption current flowing into the specimen and the numbers of secondary electrons emitted from the specimen and of backscattered electrons are measured as means for monitoring charge of the specimen surface in real time.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Voltage-activated, constant current sink circuit
InactiveUS7248097B2Accurate currentLow costMultiple-port networksOne-port networksZener diodeElectrical current
Voltage-activated and accurate current sink, and method of providing same. In one aspect, a circuit for accurately sinking current includes a zener diode coupled to a power source at the cathode of the zener diode, and first and second transistors, where the first transistor has its collector coupled to the power source and its base coupled to the cathode of the zener diode, and the second transistor has its base coupled to the anode of the zener diode and its emitter coupled to ground. A resistor is coupled between the emitter of the first transistor and the collector of the second transistor.
Owner:MICREL
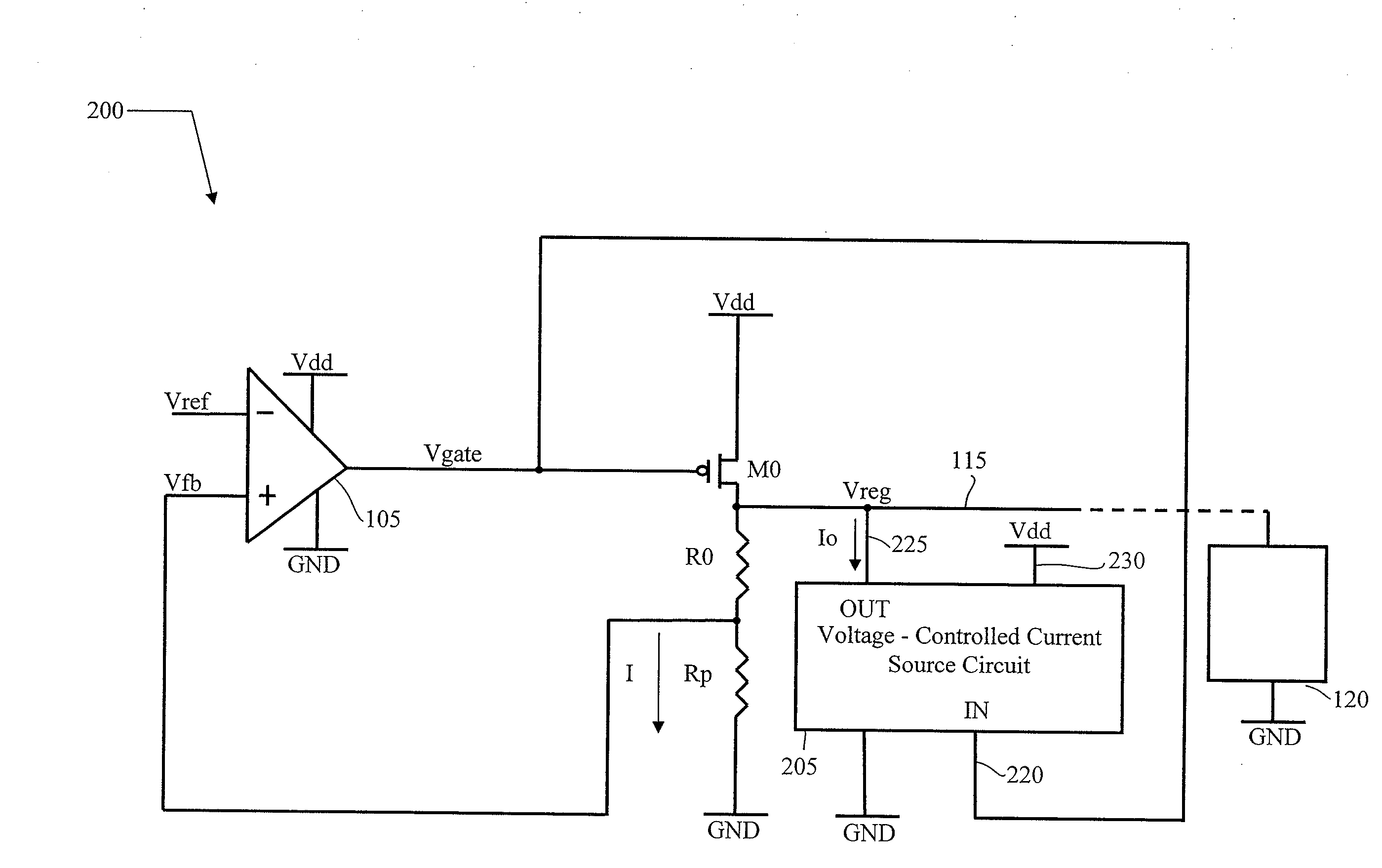
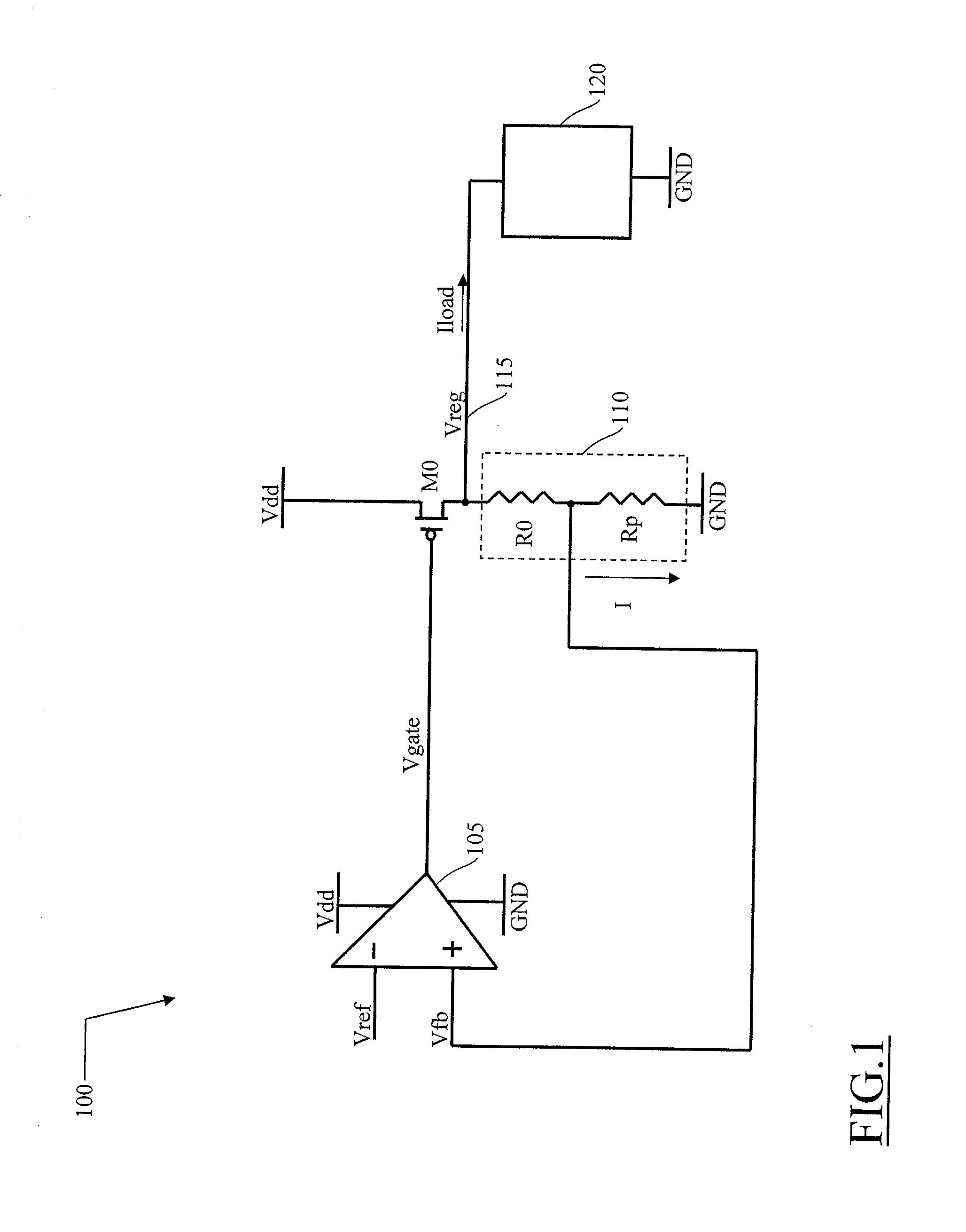
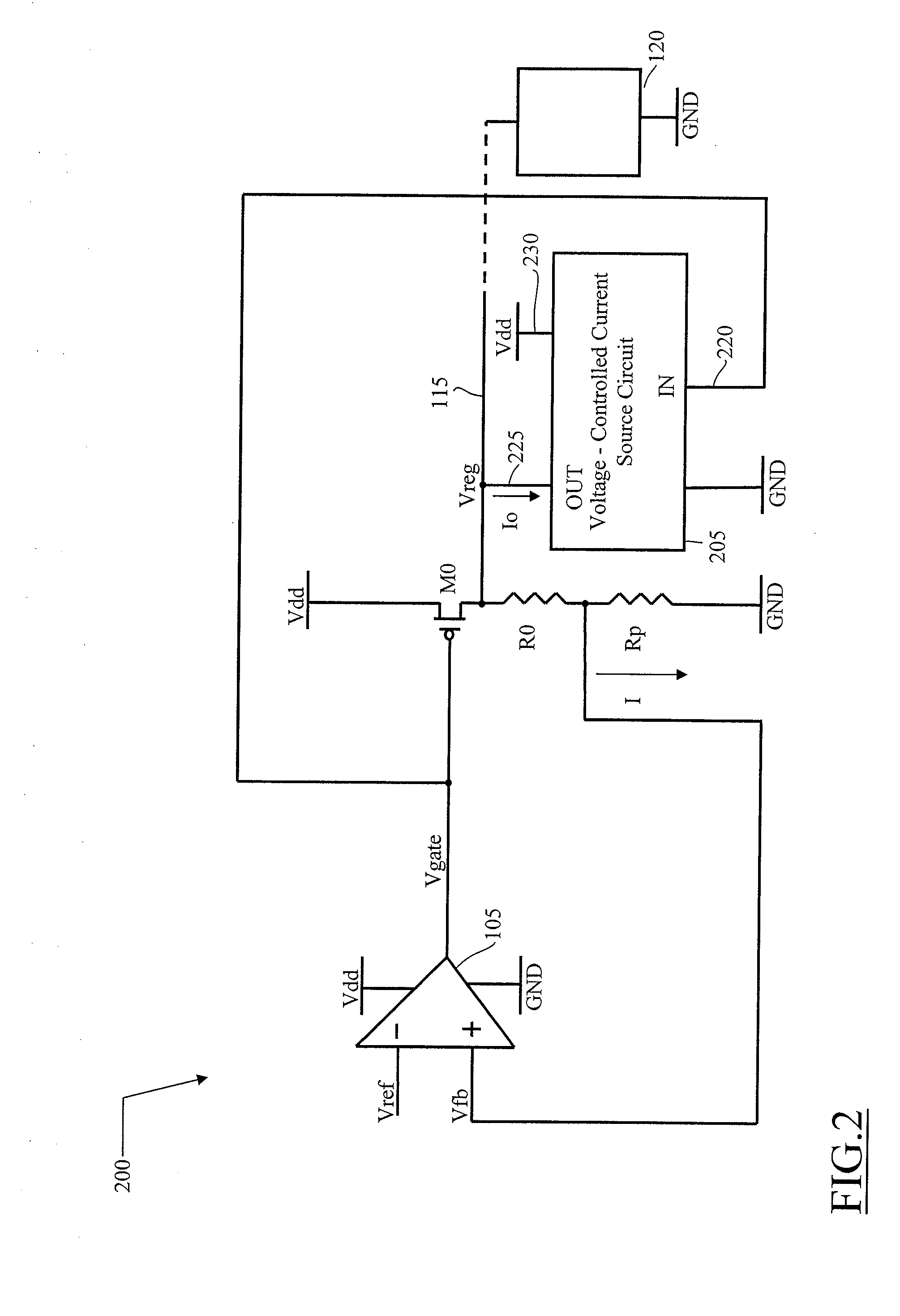
Voltage regulator with leakage current compensation
A voltage regulator having an input terminal for receiving an input voltage and an output terminal for providing a regulated voltage, the voltage regulator including: a differential amplifier configured for receiving a reference voltage and a feedback signal being a function of the regulated voltage, and for providing a regulation signal according to a comparison between the reference voltage and the feedback signal, a regulation transistor having a control terminal for receiving the regulation signal, a first terminal for receiving the first voltage and a second terminal coupled with the output terminal of the voltage regulator, wherein a voltage-controlled circuit coupled to the output terminal, responsive to a voltage difference between the first voltage and the regulation voltage and adapted to sink from the output terminal a current depending on said voltage difference between the supply voltage and the regulation voltage, said current being related to a leakage current of the regulation transistor.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
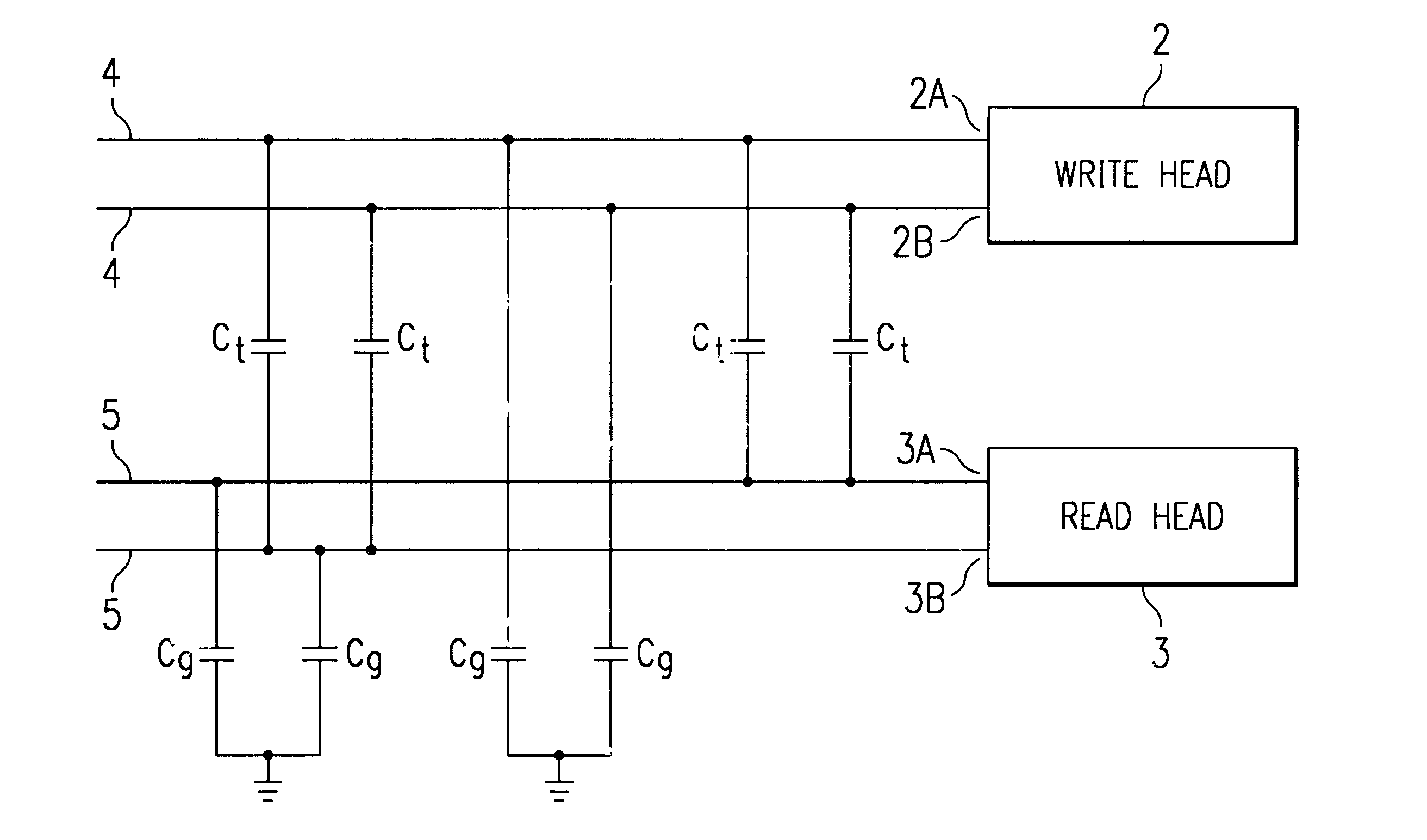
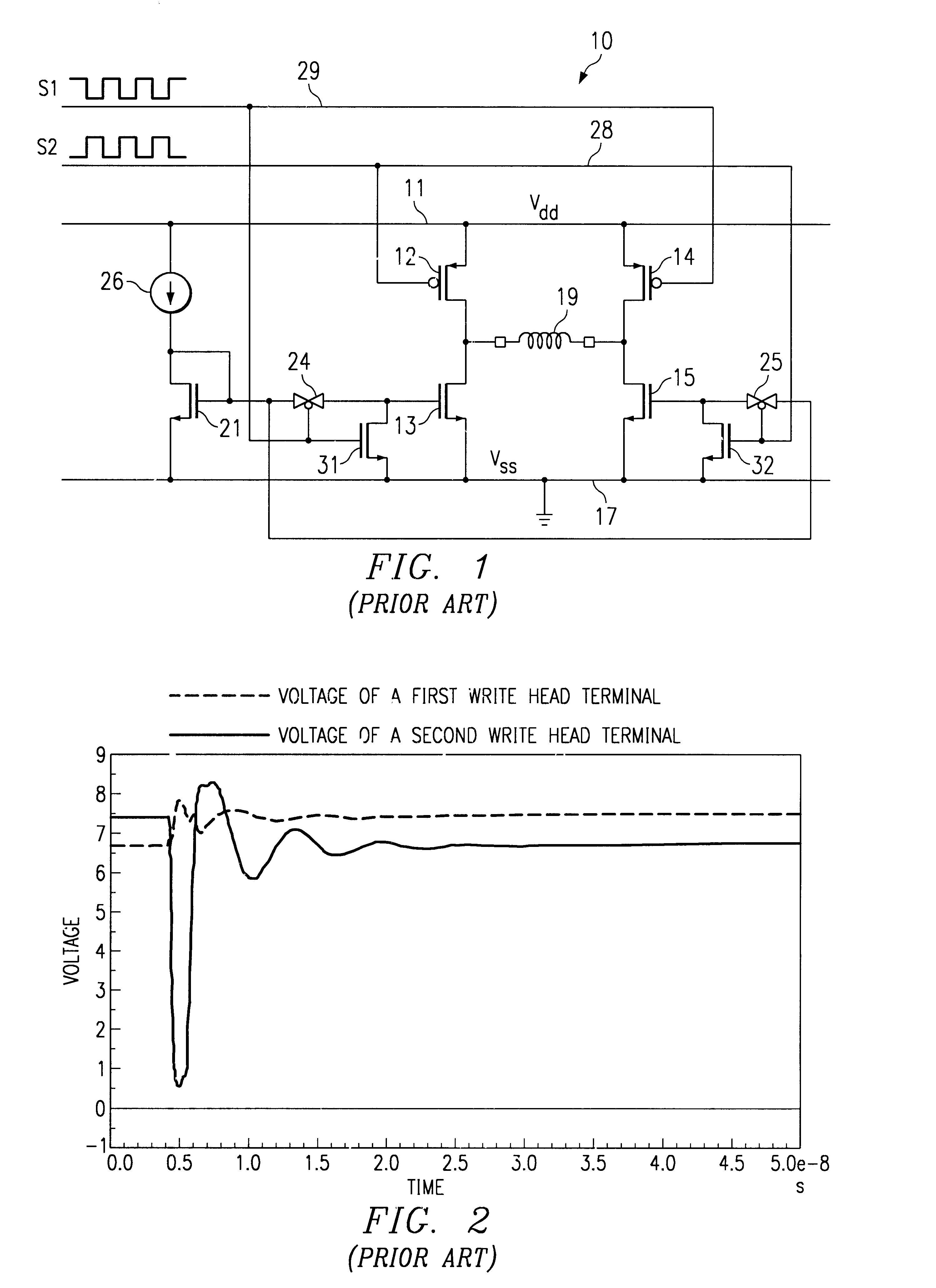
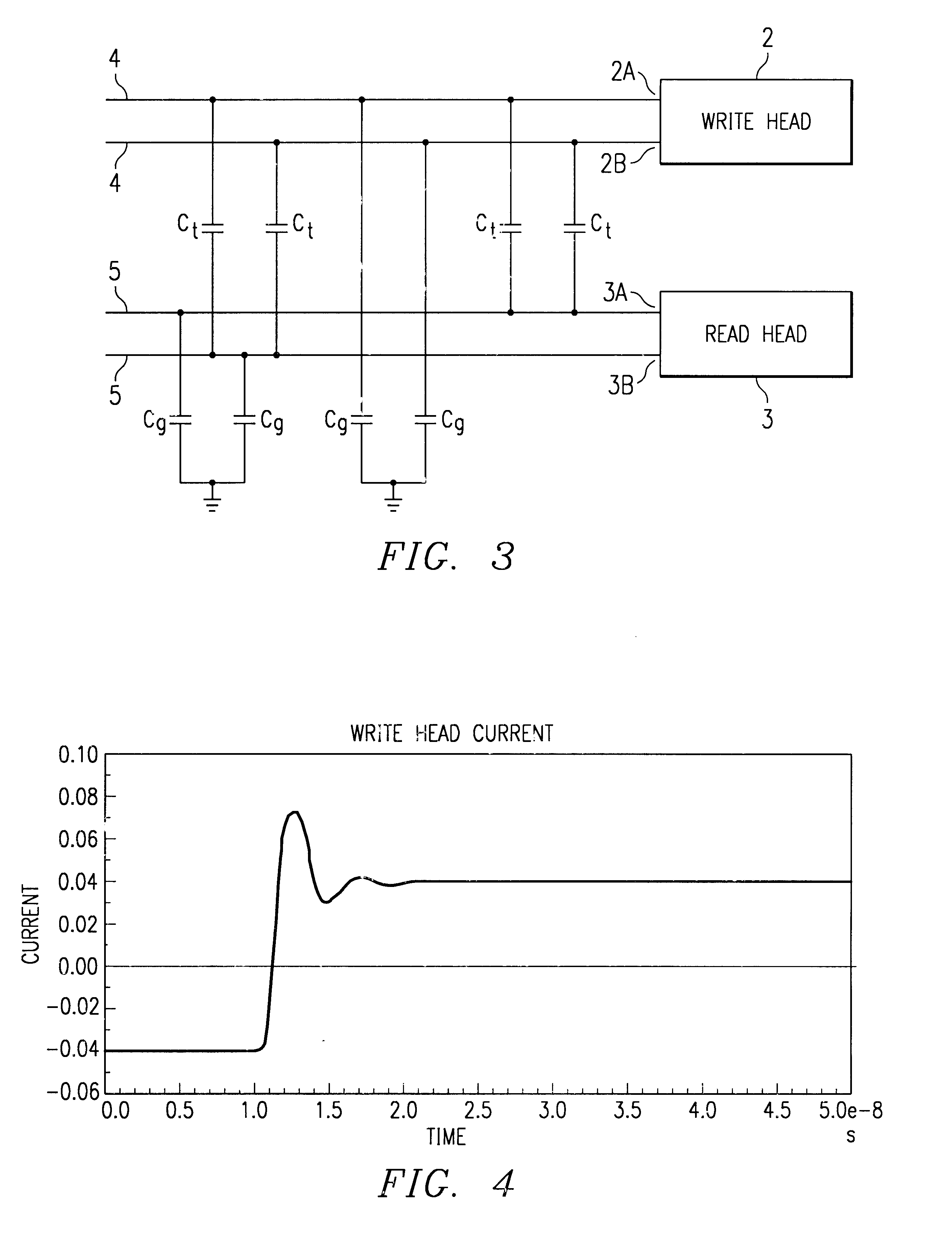
Write head driver circuit and method for writing to a memory disk
InactiveUS6504666B1H-bridge head driver circuitRecord information storageDriver circuitHemt circuits
A method and circuit are disclosed for controlling the write head of a magnetic disk storage device. The circuit includes a pull-up device and a current sink circuits coupled to each terminal of the write head, for selectively sourcing current to and sinking current from the write head, respectively. A clamp device is coupled to each write head terminal to selectively clamp the write head terminals to steady state intermediate voltage levels. The circuit further includes a control circuit for individually activating the pull-up devices, the current sink circuits and the clamp devices. In particular, when reversing the direction of current flow through the write head from a first direction in which current is provided to the write head via the write head terminal to a second direction in which current is drawn from the write head from the write head terminal, the appropriate pull-up device is activated for a predetermined period of time. The clamp device coupled to the temporarily activated pull-up device is thereafter activated to clamp the corresponding write head terminals to the steady state intermediate voltage levels.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
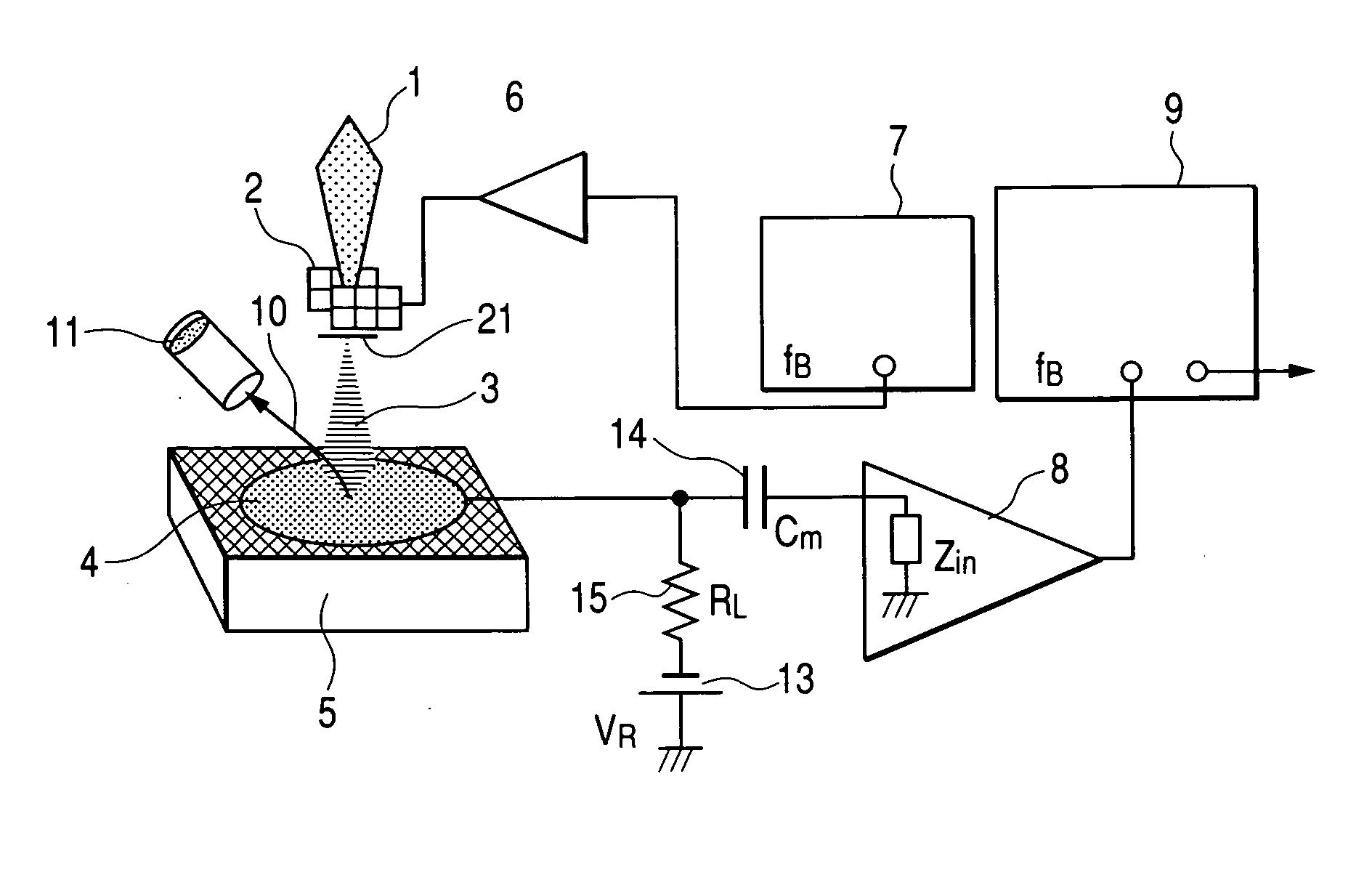
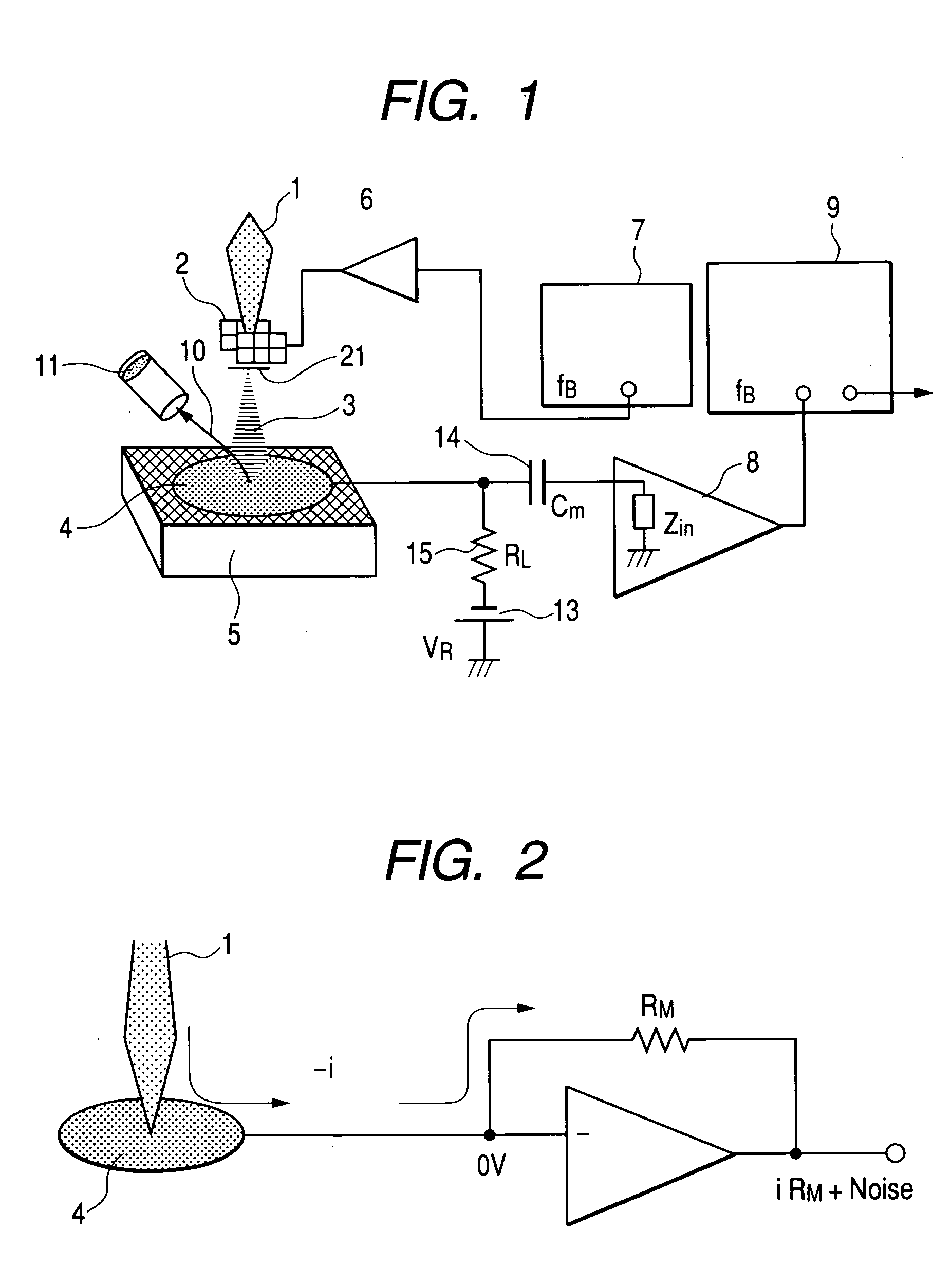
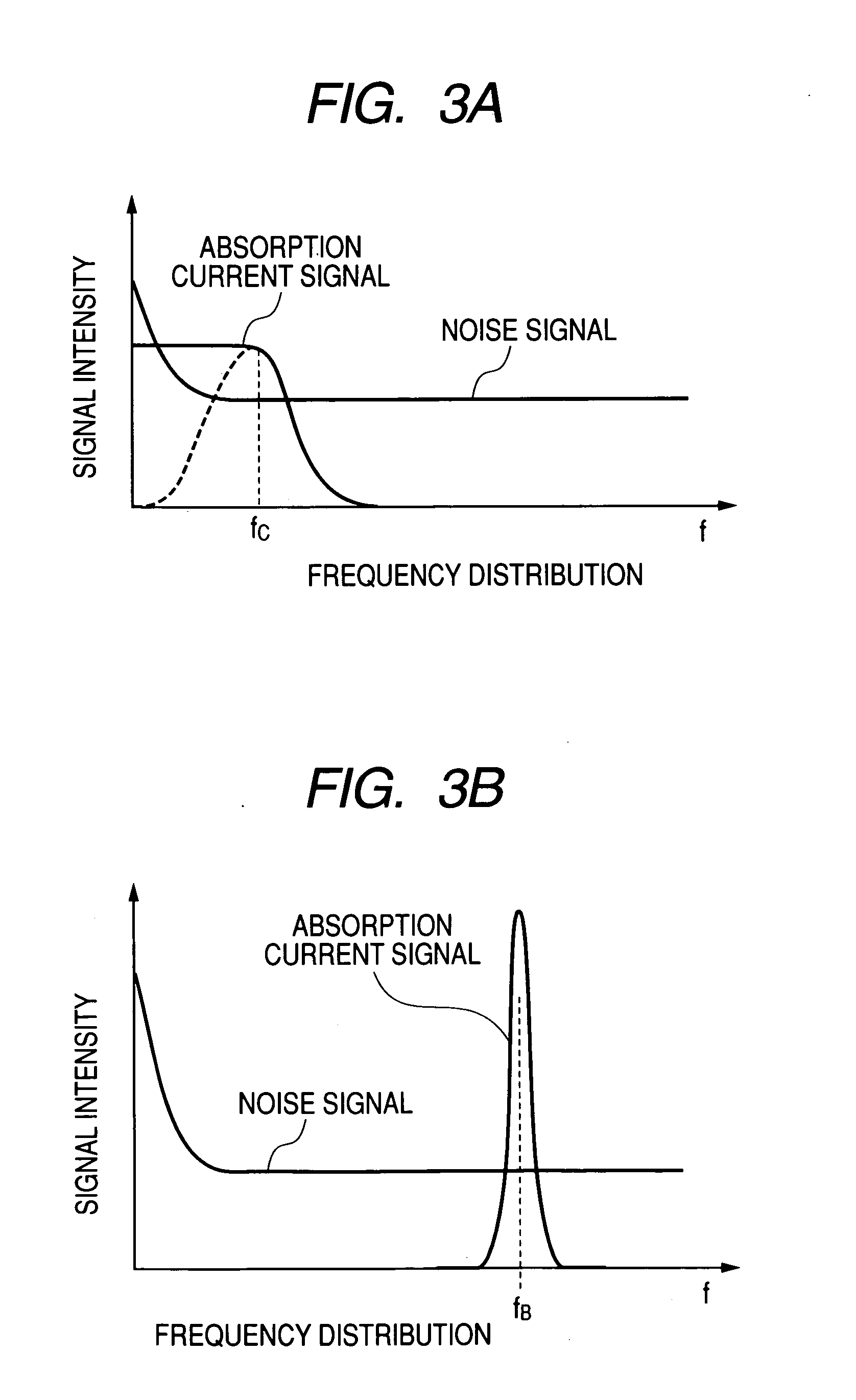
Absorption current image apparatus in electron microscope
ActiveUS20050045820A1Increase speedImprove accuracyThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron microscopeElectron
It was hard for conventional SEMs to take measurements at a high speed and take accurate measurements when an insulator exists between an object to probe and the detector, because the conventional SEMs used a continuous electron beam. Also, it was impossible to apply voltage to the sample during the measurement of current. By pulse-modulating the electron beam and extracting a high-frequency signal component from the sample, new SEM equipment disclosed herein detects electrons absorbed in the sample at a high speed and with precision. Precise and high-speed absorption current measurements can be achieved. High-functionality inspection apparatus can be provided.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
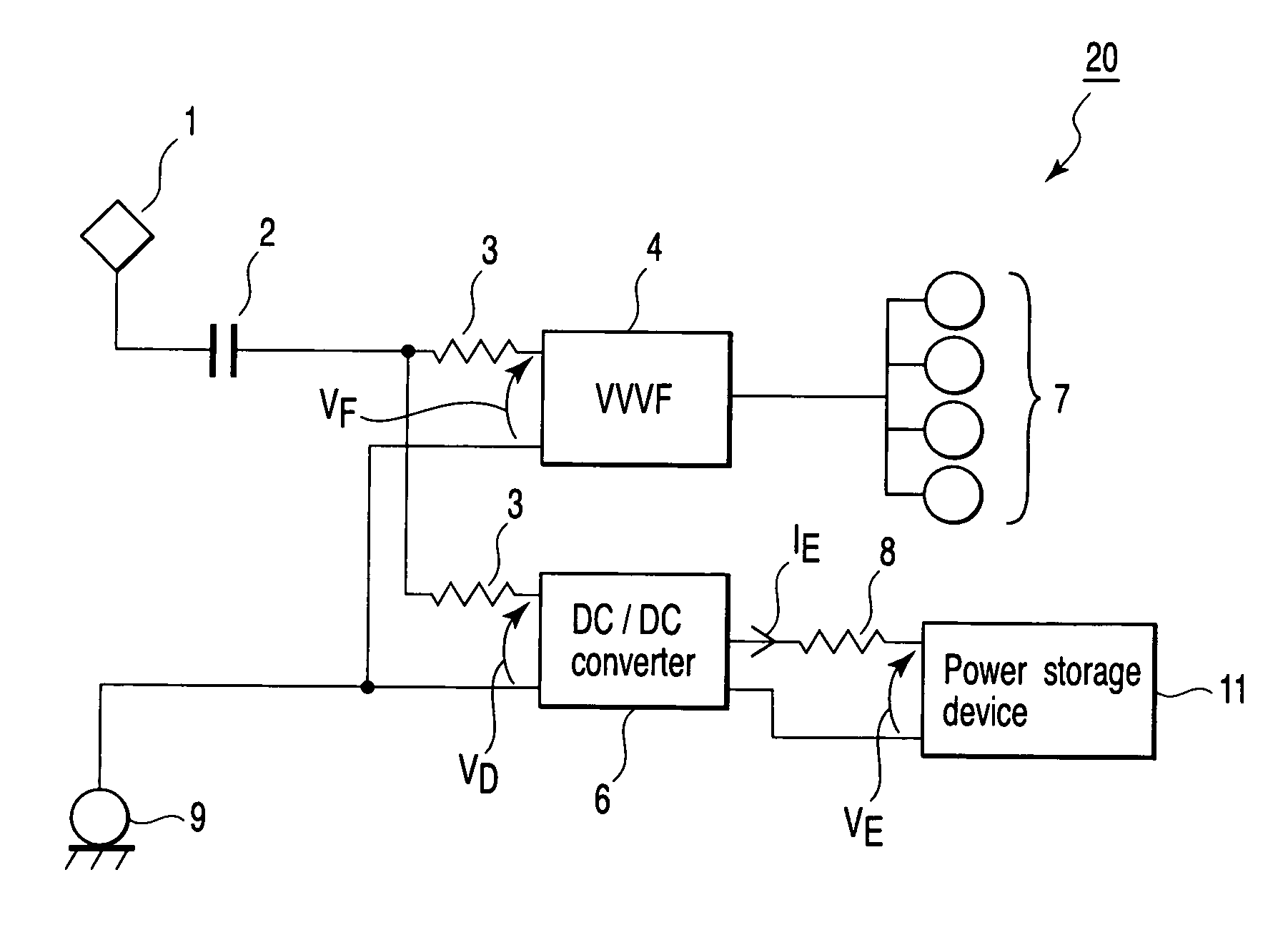
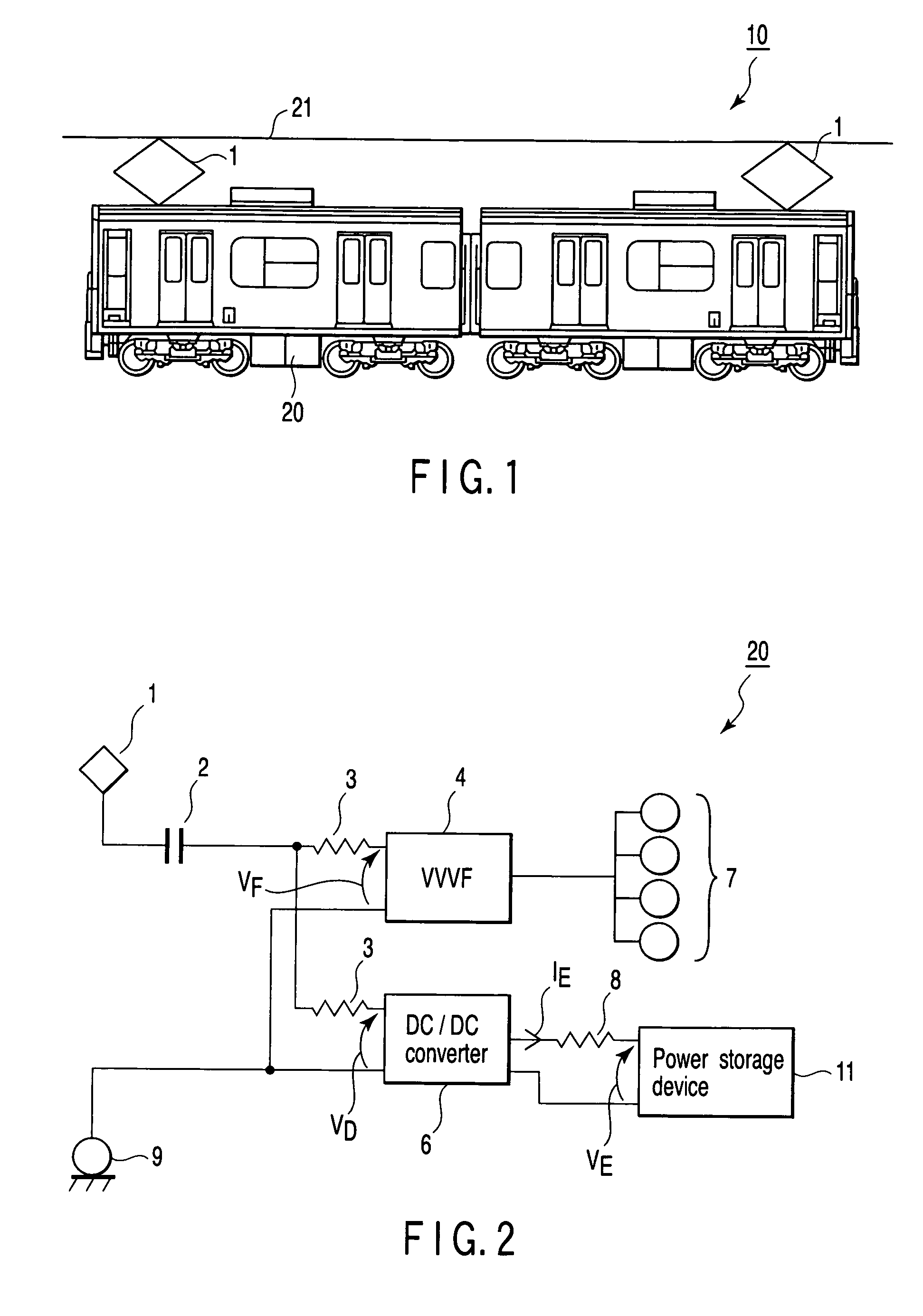
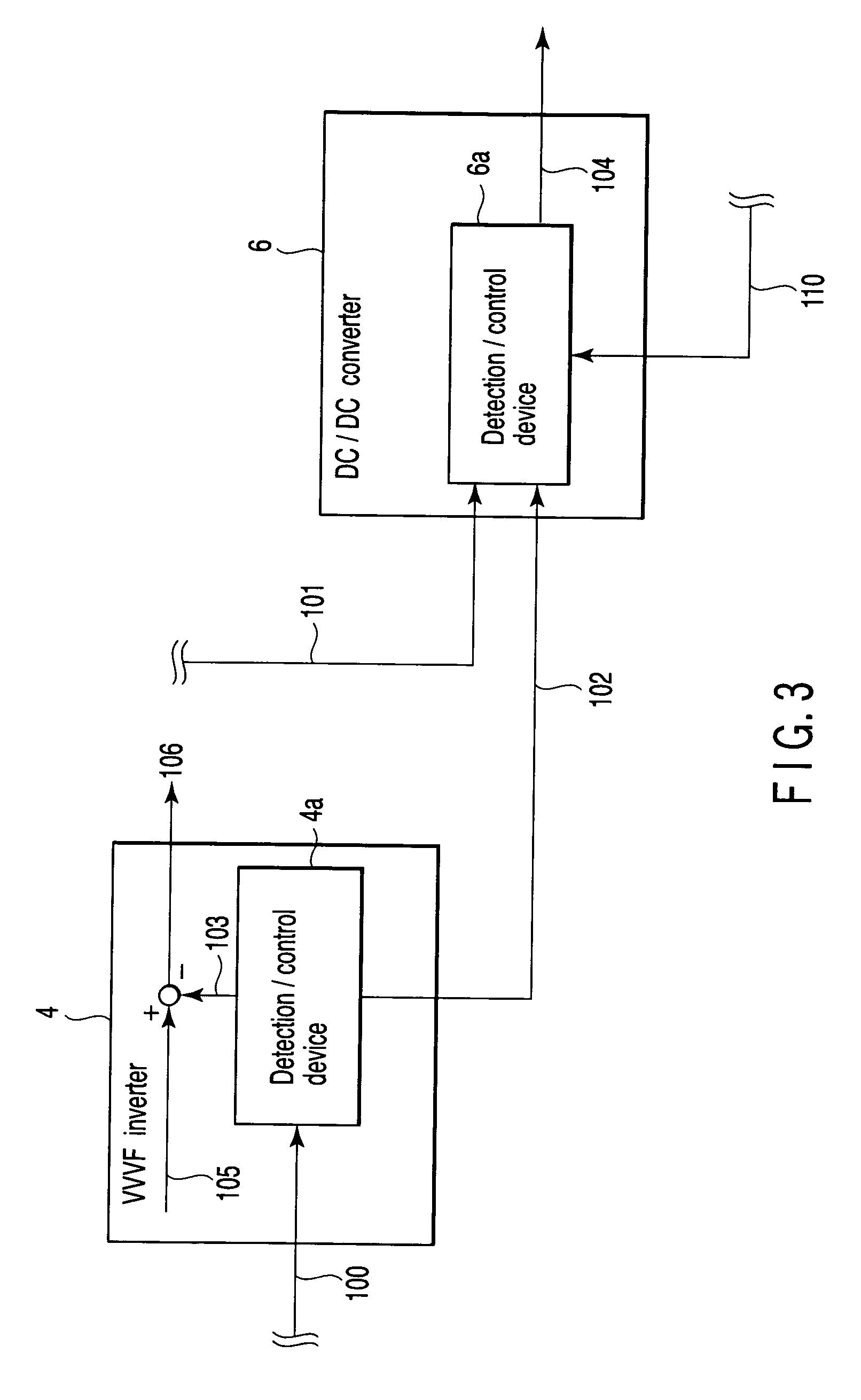
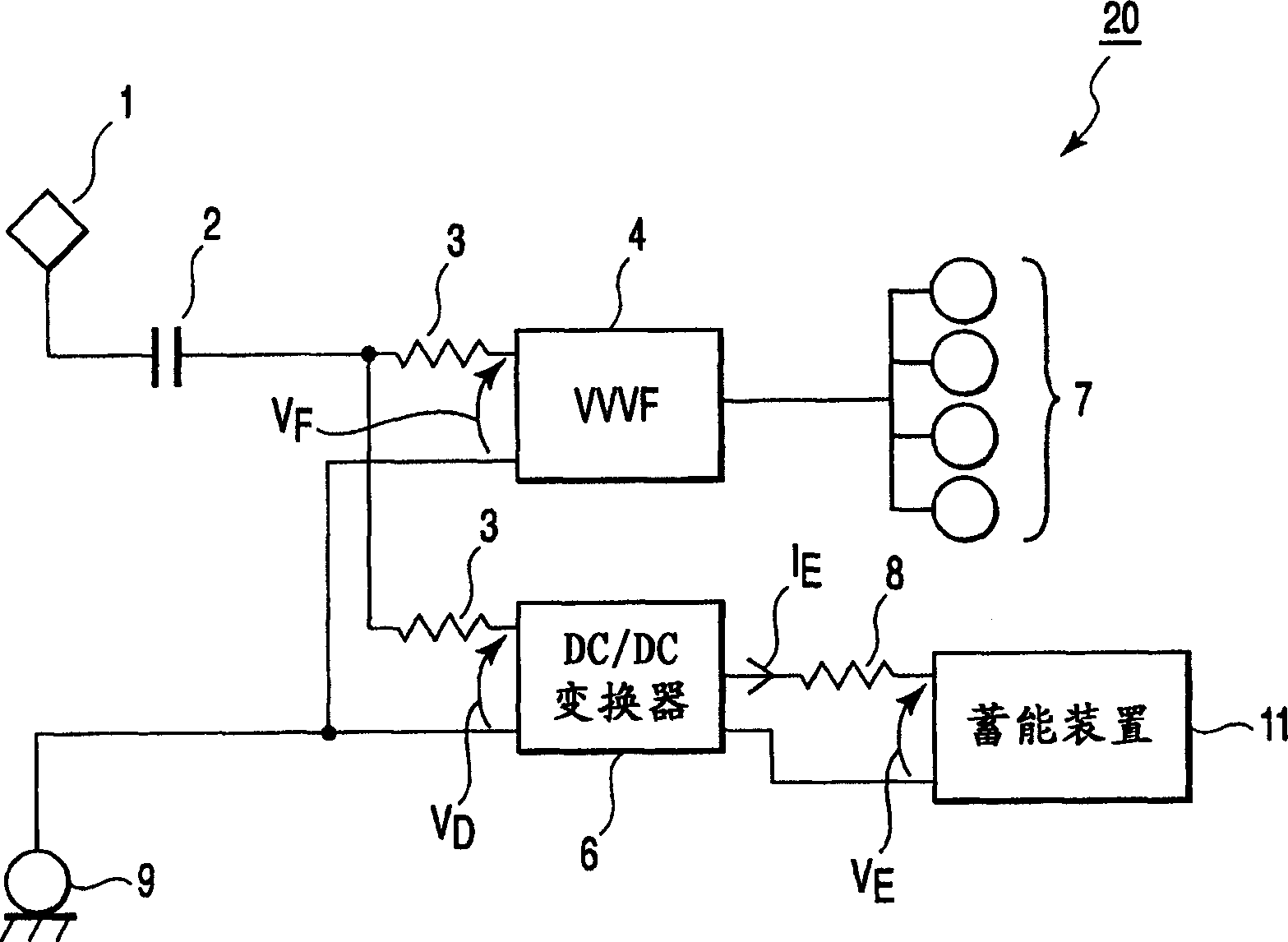
Electric motor car control apparatus
InactiveUS20060290318A1Effective energy absorptionMaintain balanceBatteries circuit arrangementsAC motor controlEngineeringCar controls
An electric motor control apparatus including an inverter which drives a motor of an electric motor car, storage unit for storing energy for the motor, and a converter which is connected to the storage unit, the inverter comprising detection unit for detecting a power value of the motor, and transmission unit for transmitting the power value detected by the detection unit to the converter, and the converter comprising calculation unit for receiving the power value transmitted by the transmission unit, and calculating an absorption current on the basis of the received power value, and control unit for controlling the storage unit on the basis of the absorption current calculated by the calculation unit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
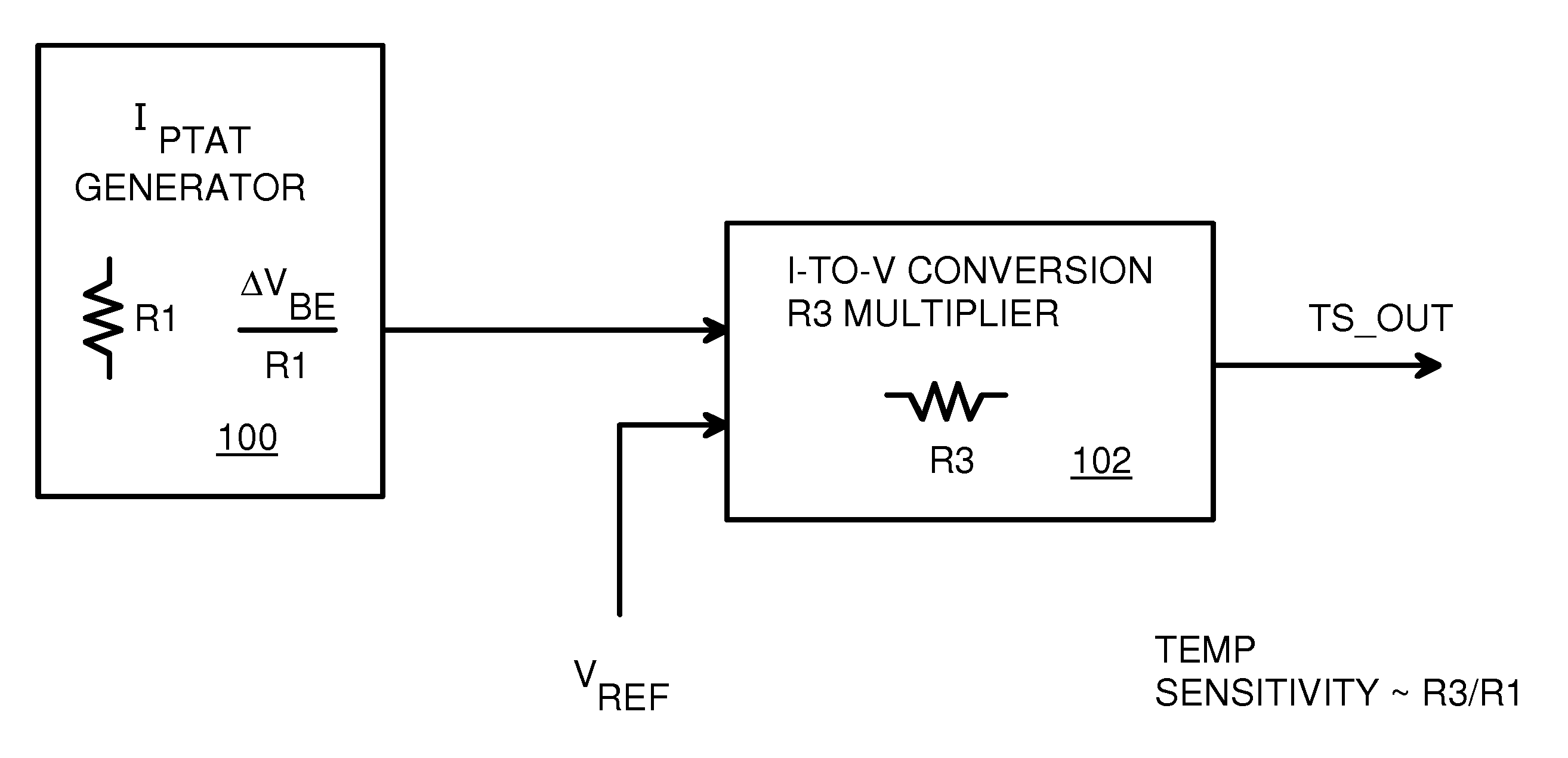
CMOS Temperature Sensor with Sensitivity Set by Current-Mirror and Resistor Ratios without Limiting DC Bias
InactiveUS20130235903A1Thermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsVoltage referenceEngineering
An on-chip temperature sensor circuit can be implemented in a standard complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) process using PNP transistors. A pair of transistors have collector currents that are sensitive to voltage, both directly and due to saturation currents. A scaling resistor connects to the emitter of one transistor and its voltage compared to the other transistor's emitter voltage by an error amplifier that generates a bias voltage to current sources that are proportional to absolute temperature since the saturation current sensitivity is subtracted out. The current is mirrored to sink current through a multiplier resistor from an output. An amplifier connected across the multiplier resistor compares a reference voltage to set the DC bias independent of temperature sensitivity. The temperature sensitivity is proportional to the ratio of the multiplier resistor and the scaling resistor, and is multiplied by a mirroring factor. A differential output may also be provided.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Threshold voltage method and apparatus for ESD protection
ActiveUS7760476B2TransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentShunt DeviceEngineering
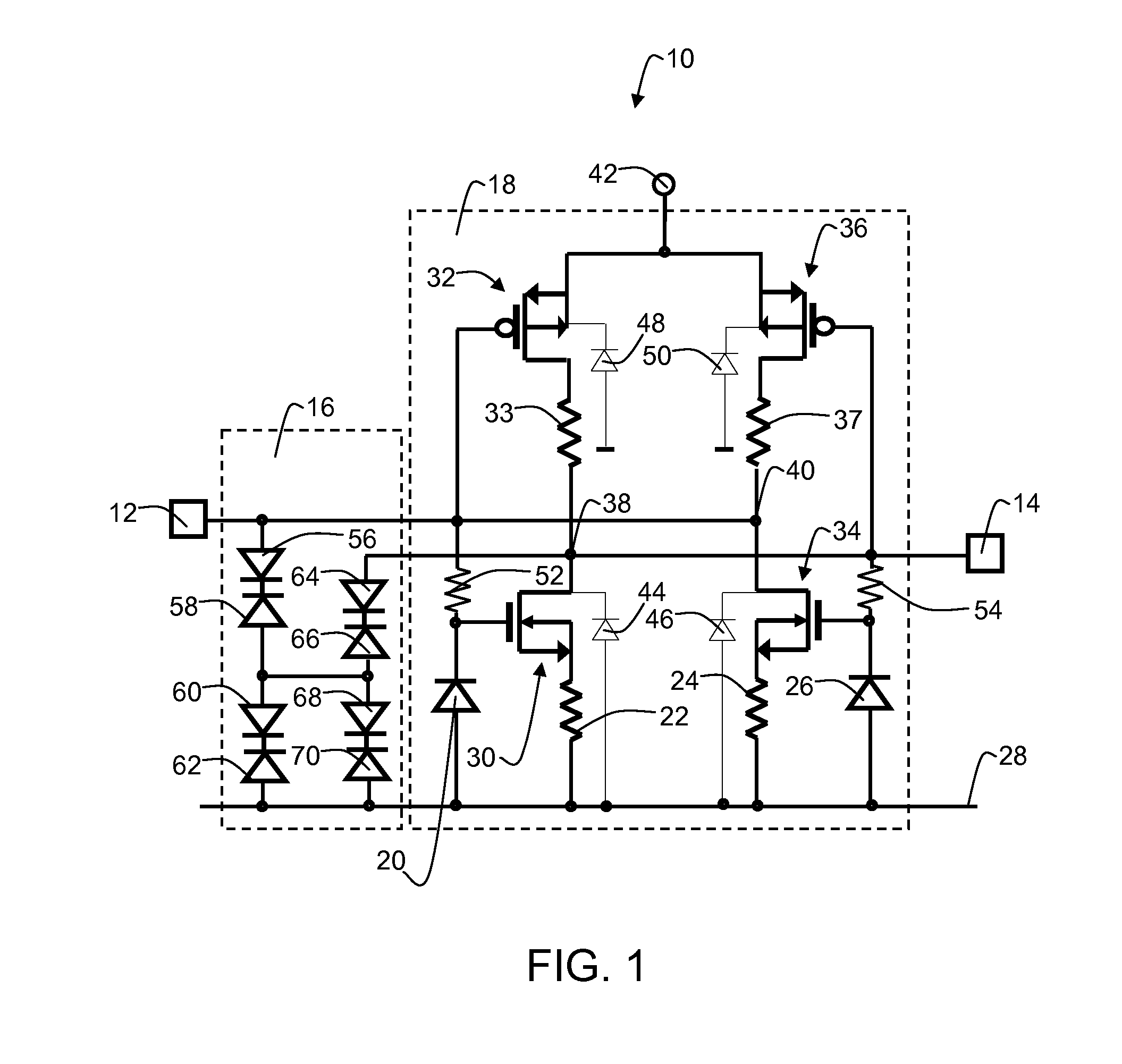
An electrostatic discharge protection circuit comprises a comparator coupled between a power supply terminal and ground. The comparator responds to an electrostatic discharge event producing a trigger signal at a comparator output. The comparator comprises a first and second current mirror. The first and second current mirrors each comprise a sense device and a mirror device. The mirror devices are coupled in series between the power supply terminal and ground. The first mirror device produces an incident current and the second mirror device receives an absorption current. With a supply voltage on the power supply terminal equal to or greater than a trigger supply voltage, the absorption current exceeds the incident current and produces a trigger signal at the comparator output. The trigger signal activates a shunt device that shunts current from the power supply terminal to ground.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Low latency combined clock data recovery logic network and charge pump circuit
ActiveUS20190377378A1Logic circuits characterised by logic functionPulse automatic controlProportional controlCarrier signal
Methods and systems are described for obtaining a sequence of data decisions and an error signal generated by one or more samplers operating on a received input signal according to a sampling clock, applying the sequence of data decisions and the error signal to each logic branch of a set of logic branches, and responsively selecting a logic branch from the set of logic branches, the logic branch selected responsive to (i) a detection of a transitional data pattern in the sequence of data decisions and (ii) the error signal, the selected logic branch generating an output current, and providing the output current to a local oscillator controller, the output current sourcing and sinking current to a capacitor through a resistive element to adjust an input voltage of a proportional control circuit relative to a voltage on the capacitor connected to the resistive element.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
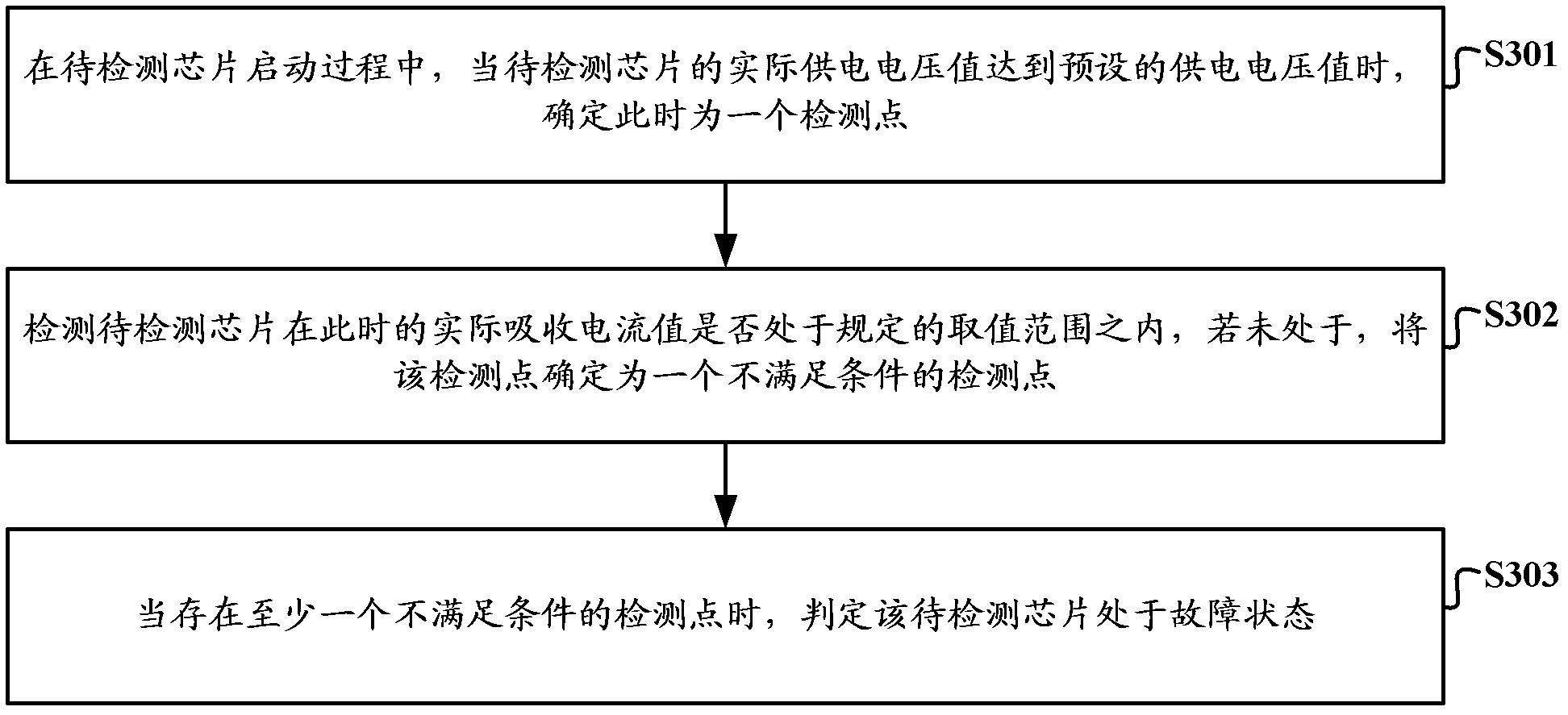
A chip fault detection method and device
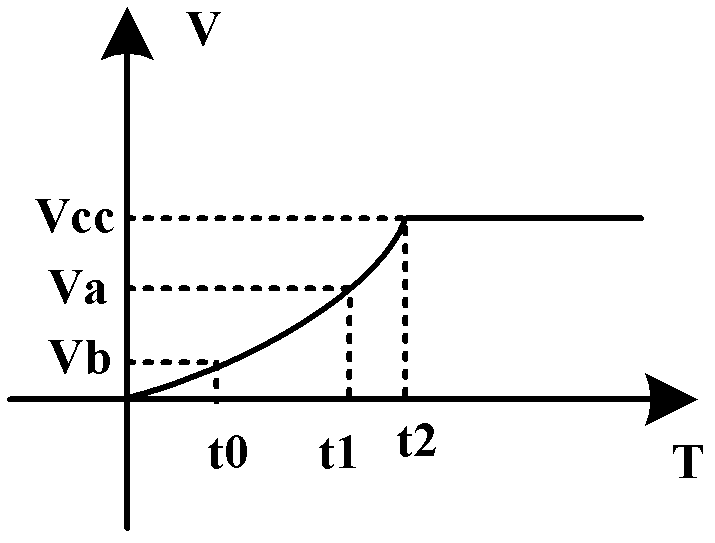
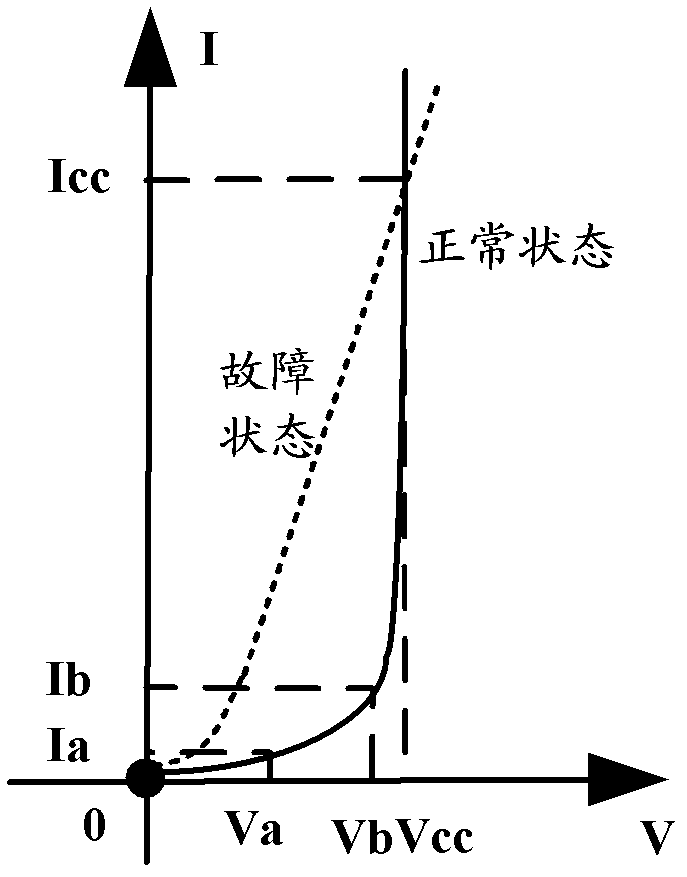
ActiveCN102288890ACurrent/voltage measurementIndividual semiconductor device testingAbsorption currentPower supply voltage
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting failures of a chip. The method and device disclosed by the invention are used for detecting whether the chip of an electronic product or electronic equipment is in a failure state or not under the premise that the electronic product or the electronic equipment is normally operated, wherein the method for detecting the failures of the chip comprises the following steps: when the actual power supply voltage value of the chip to be detected reaches the preset power supply voltage value, determining the moment as a detection point in the course of starting the chip to be detected; detecting whether the actual absorption current value of the chip to be detected at the moment is in the specified value range or not; if not, determining the detection point as a detection point which does not meet the conditions; and when at least one detection point which does not meet the conditions exists, judging that the chip to be detected is in the failure state.
Owner:RUIJIE NETWORKS CO LTD
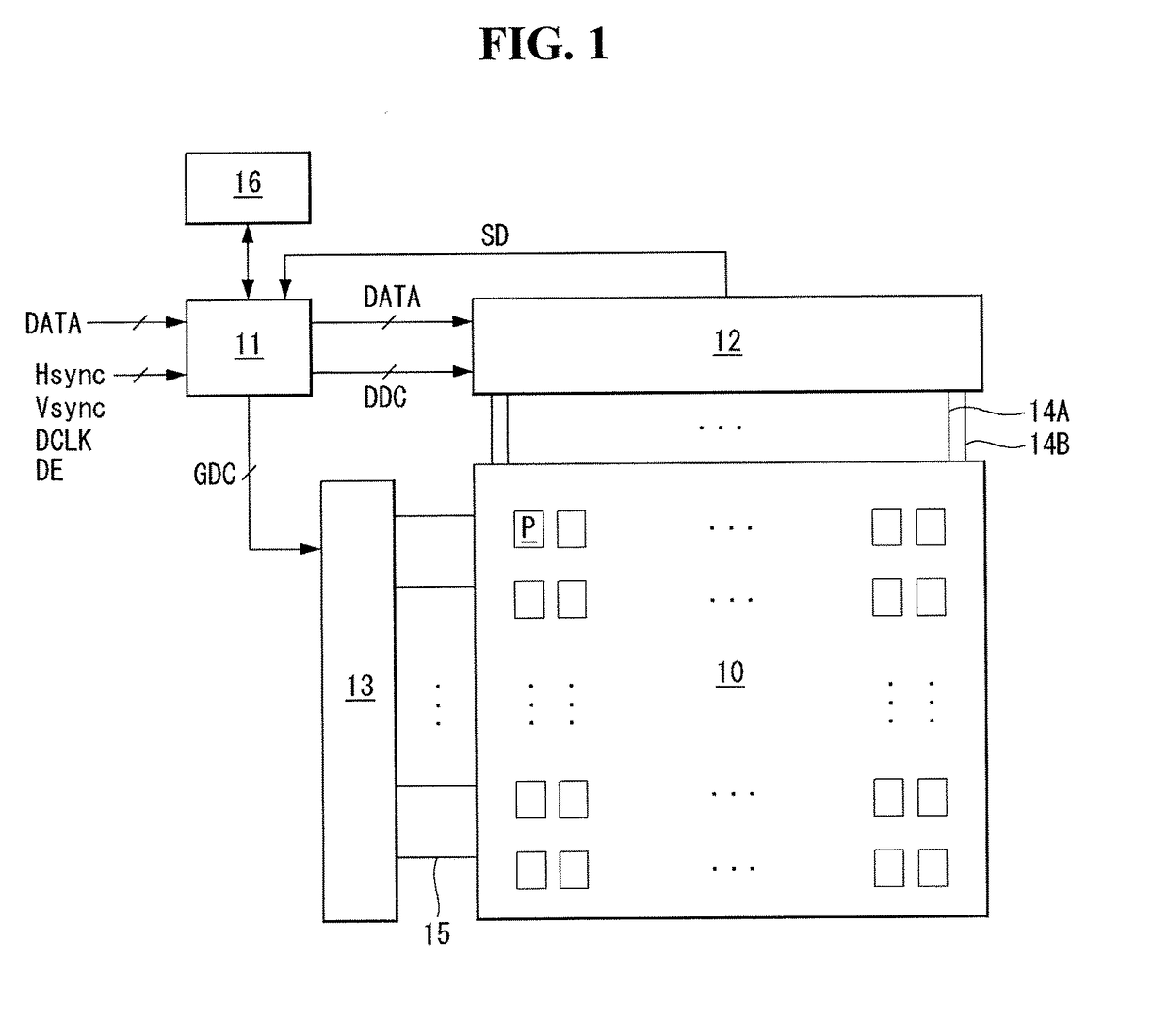
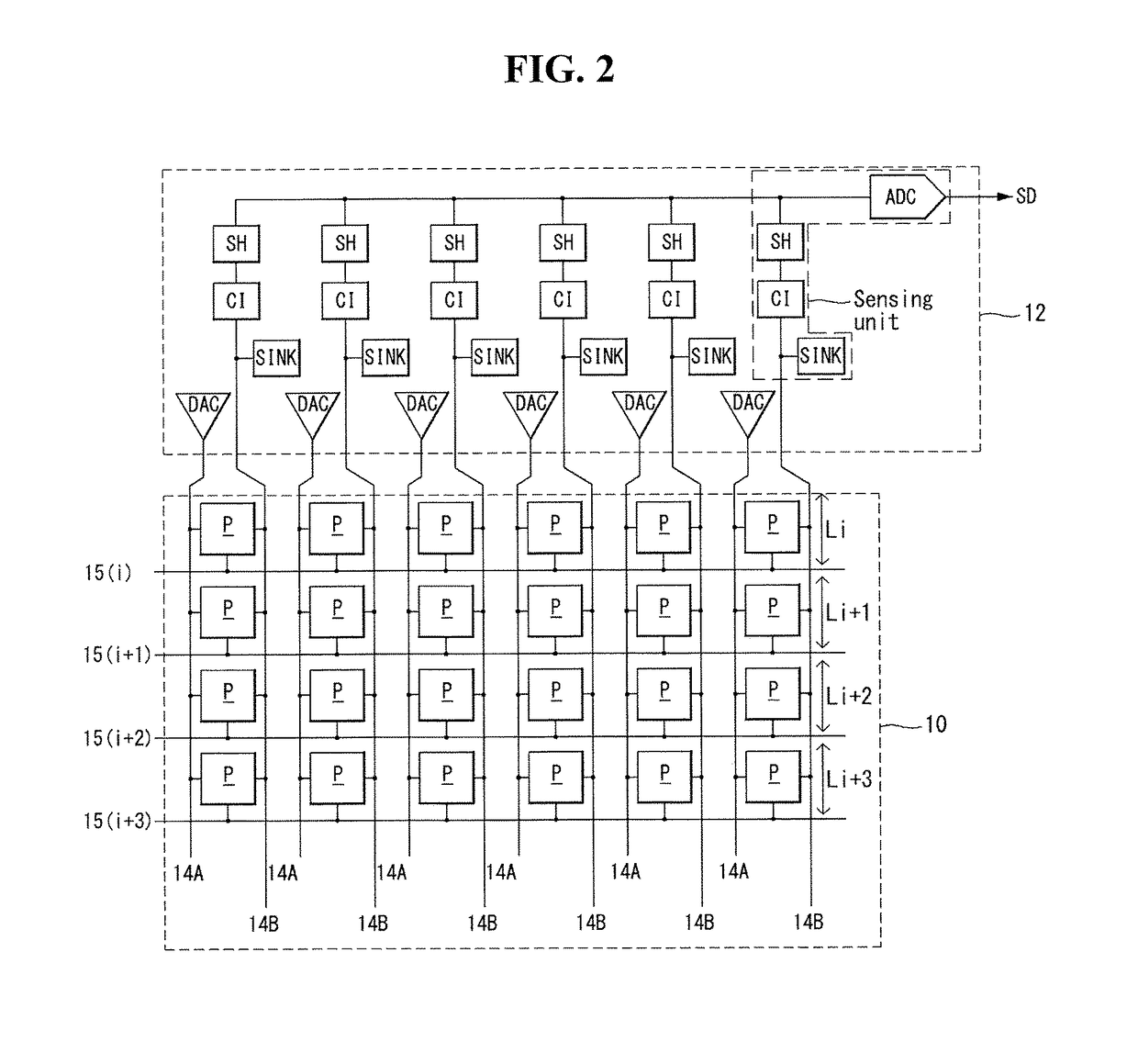
Current sensing type sensing unit and organic light-emitting display comprising the same
ActiveUS20170294159A1Improves current sensing capabilityIncrease in sizeStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesIntegratorAnalog-to-digital converter
A current sensing unit can include a current sink circuit connected to a sensing line, which reduces a pixel current fed via the sensing line by an amount equal to a sink current; a current integrator connected to the sensing line, which accumulates an adjusted current from the sensing line and outputs an integrated value based on the pixel current minus the sink current; a sampling part that samples and holds the integrated value; and an analog-to-digital converter that converts the integrated value from an analog value to a digital sensed value.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method for differentially writing to a memory disk
InactiveUS6512649B1H-bridge head driver circuitRecord information storageVoltage referenceEngineering
A method is disclosed for controlling the write head of a magnetic disk storage device. The method includes sinking current from the first terminal of the write head and sourcing current to the second terminal of the write head substantially simultaneously with sinking current from the first terminal so that a first steady state voltage level appears on the first terminal of the write head and a second steady state voltage level appears on the second terminal thereof that are approximately at a midpoint between a high reference voltage level and a low reference voltage level. The common mode voltage of the write head is substantially constant over time.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
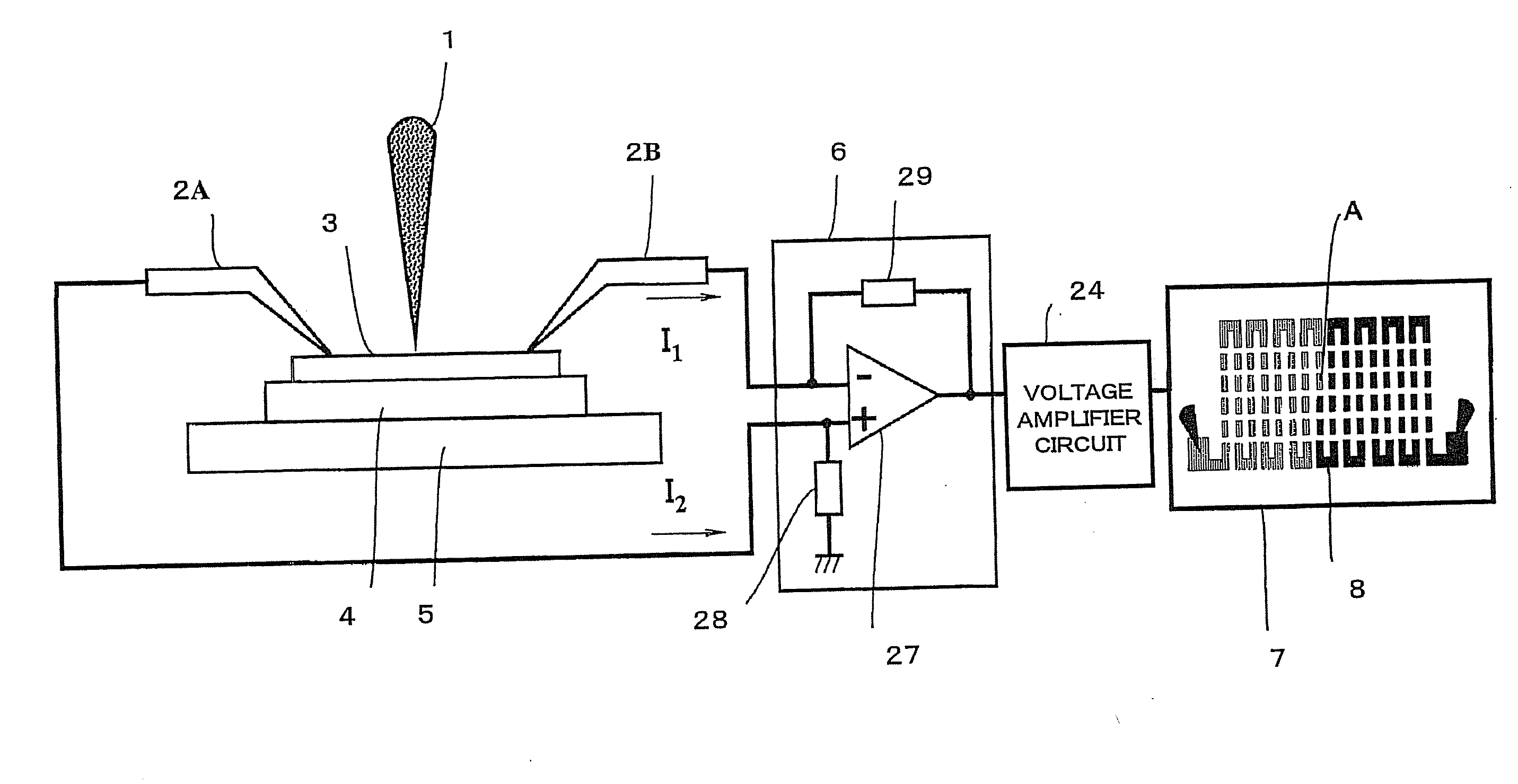
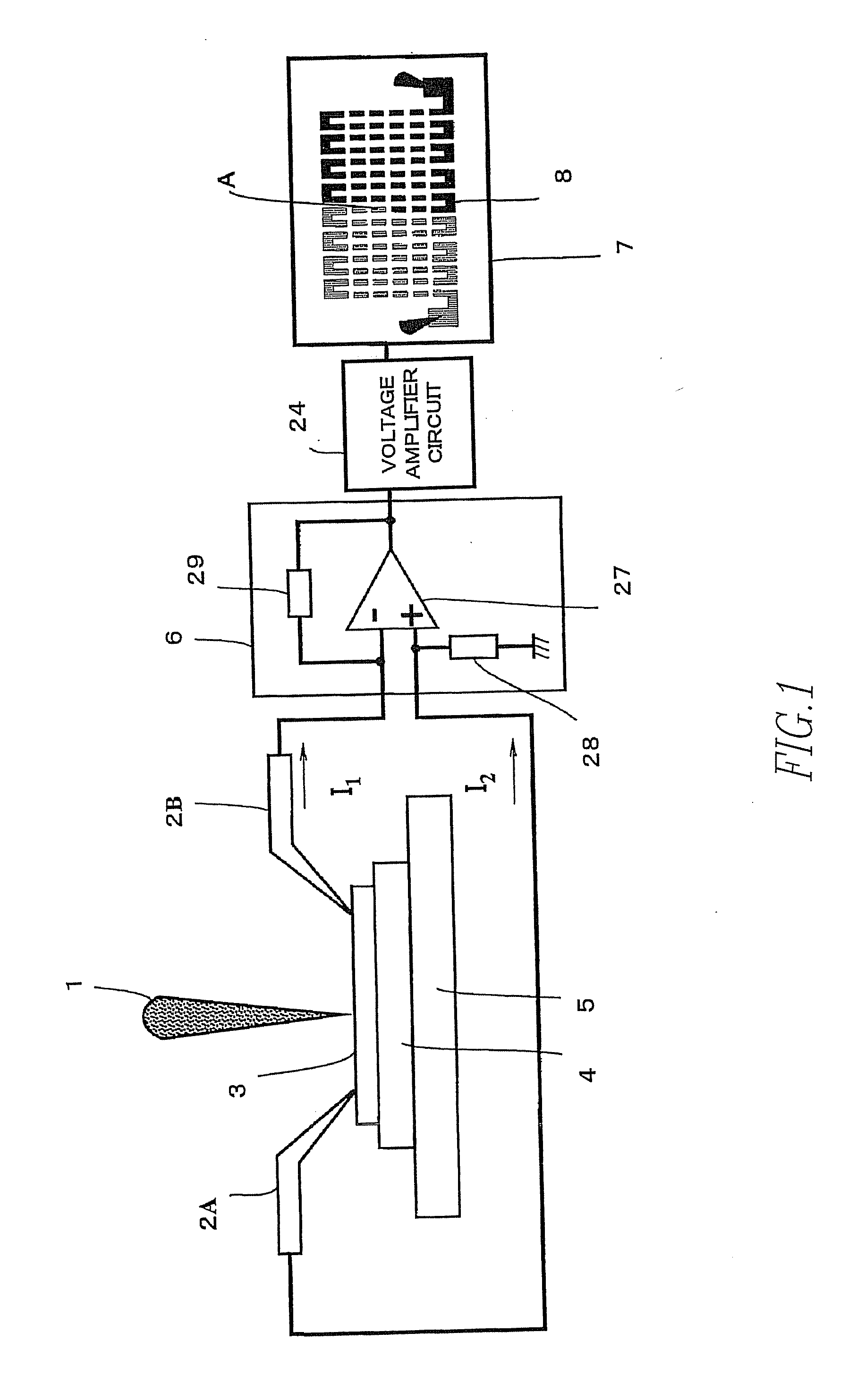
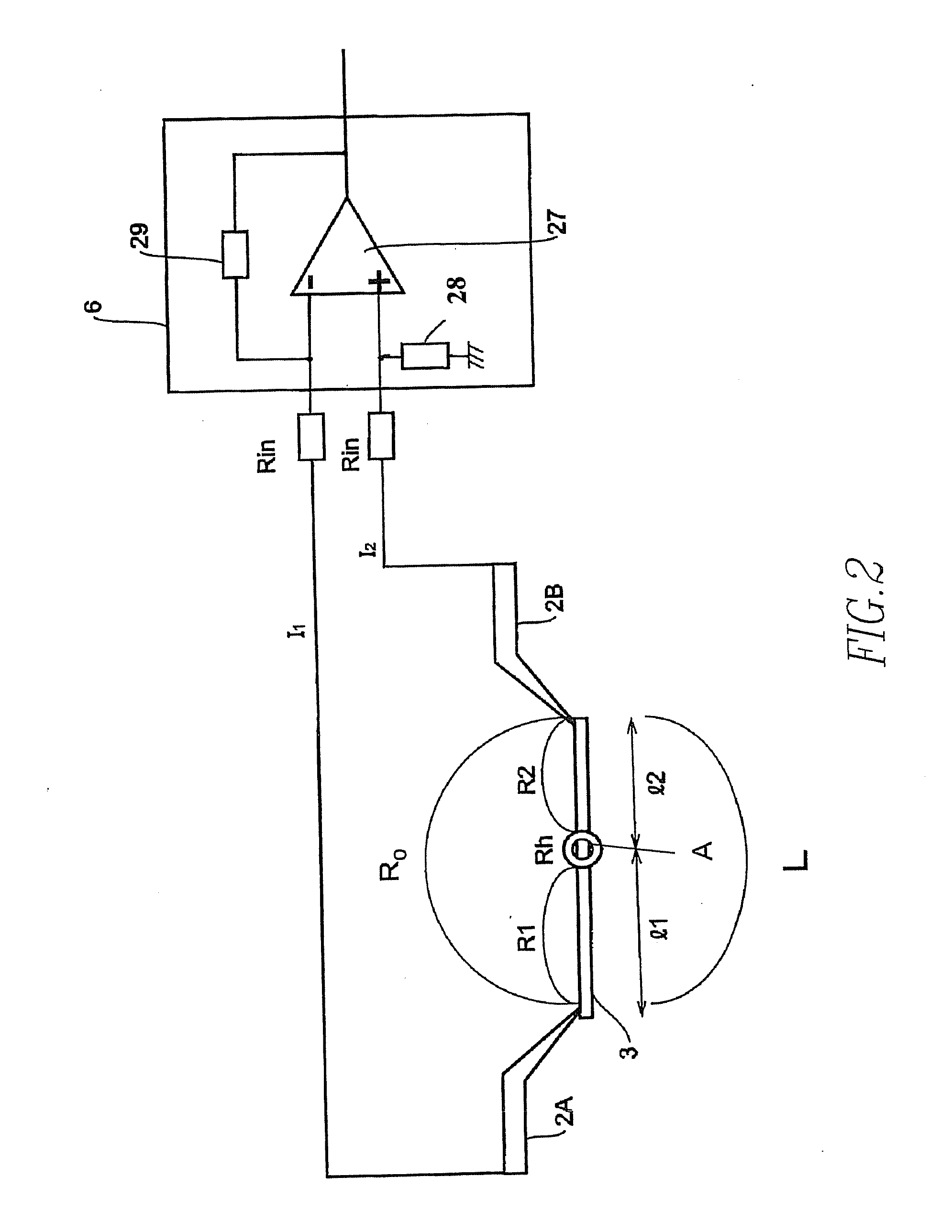
Charged-Particle Beam System
InactiveUS20080135754A1Reliable detectionSharp contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesVoltage converterElectron source
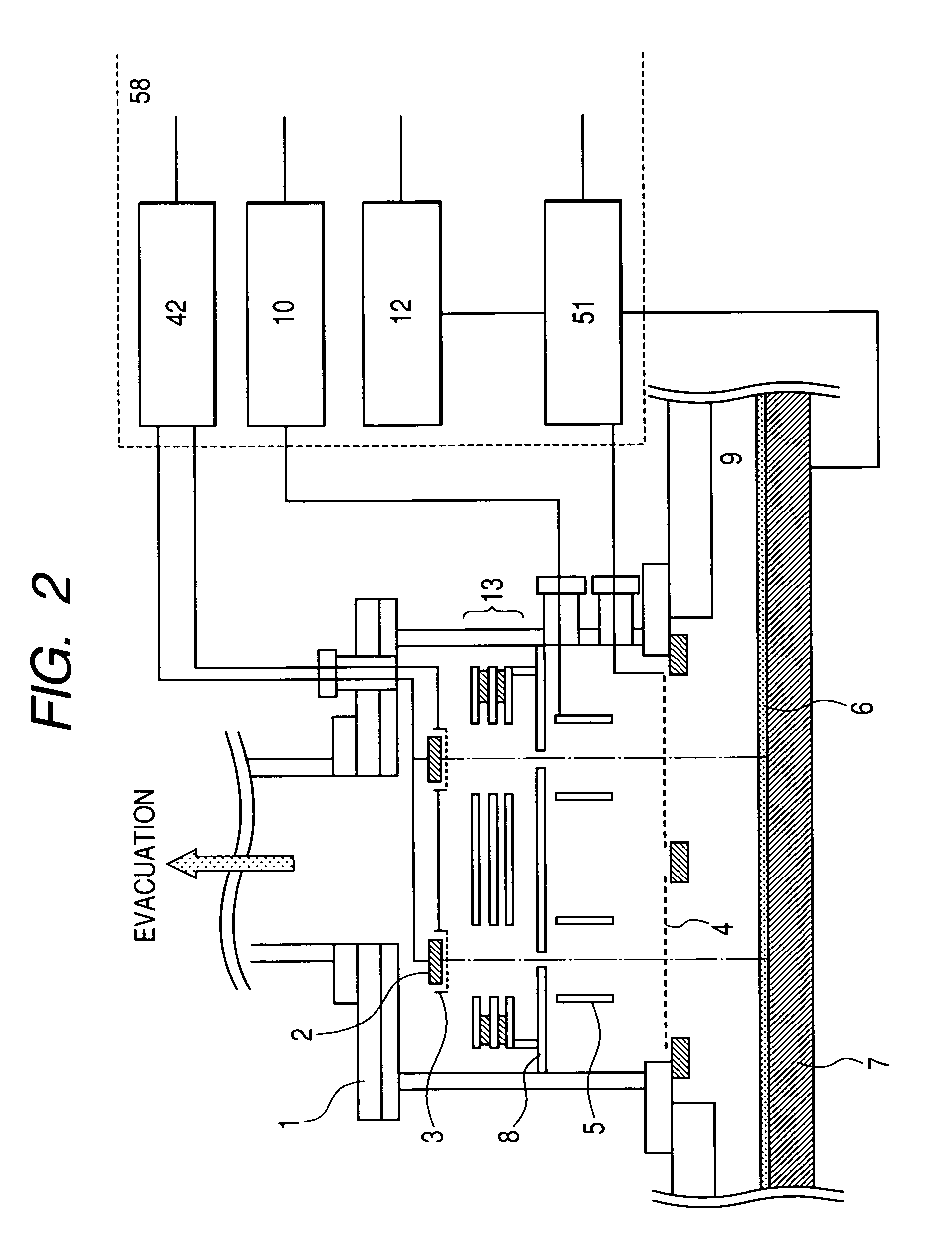
A charged-particle beam system capable of reliably detecting defects in an interconnect pattern, which is formed, for example, on a semiconductor device. The system uses an electron source for producing an electron beam. A specimen on which the interconnect pattern is formed is scanned with the electron beam in two dimensions. An image of the specimen is created based on a signal obtained from the specimen in response to the scanning, and the image is displayed on a display portion. Two probes are brought into contact with arbitrary locations on the interconnect pattern. Absorption currents obtained via the probes are applied to a differential current-voltage converter. Thus, the difference between the absorption currents is converted into a voltage signal. An absorption current image is created based on the voltage signal and displayed on the display portion.
Owner:JEOL LTD
LDO (linear voltage regulator) for internal electric source and with improved load transient performance
A voltage regulator includes a feedback regulation loop and a drive transistor configured to source current to a regulated output. A transient recovery circuit is coupled to the voltage regulator circuit and includes a first transistor coupled to source current into a control terminal of the drive transistor, wherein the source current is in addition to current sourced in response to operation of the feedback regulation loop. The first transistor is selectively actuated in response to a drop in voltage at the regulated output. The transient recovery circuit further includes a second transistor coupled to sink current from the regulated output. The sink current has a first non-zero magnitude in the quiescent operating mode of the regulator circuit. In response to an increase in voltage at the regulated output, the operation of the second transistor is modified to increase the sink current to a second, greater, non-zero magnitude.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (SHENZHEN) R&D CO LTD
Control apparatus for an eletric locomotive
InactiveCN1865038AEffective absorptionSpeed controllerBatteries circuit arrangementsEngineeringAbsorption current
An electric motor control apparatus including an inverter (4) which drives a motor of an electric motor car, storage unit (11) for storing energy for the motor (7), and a converter which is connected to the storage unit (11), the inverter (4) comprising detection unit for detecting a power value of the motor (7), and transmission unit for transmitting the power value detected by the detection unit to the converter (6), and the converter (6) comprising calculation unit for receiving the power value transmitted by the transmission unit, and calculating an absorption current on the basis of the received power value, and control unit for controlling the storage unit (11) on the basis of the absorption current calculated by the calculation unit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
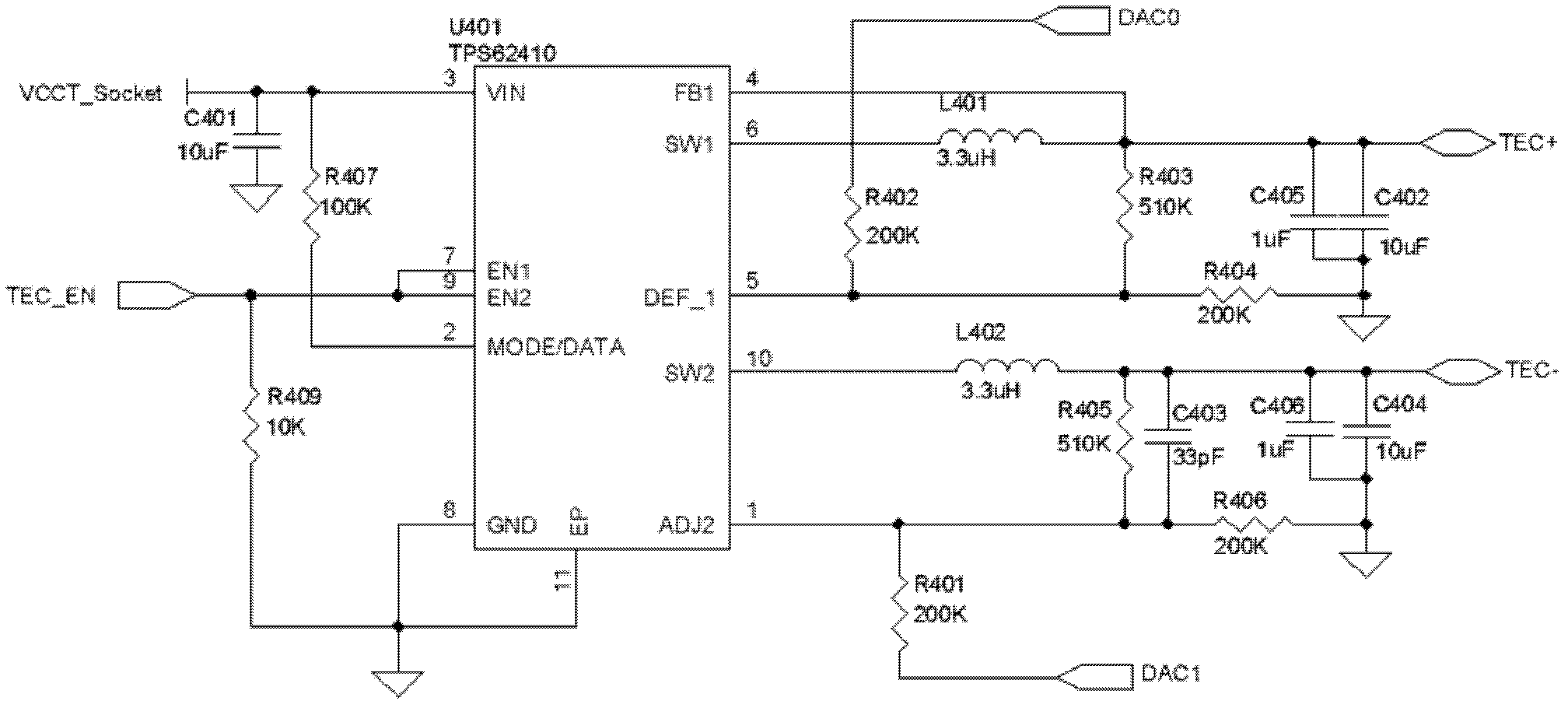
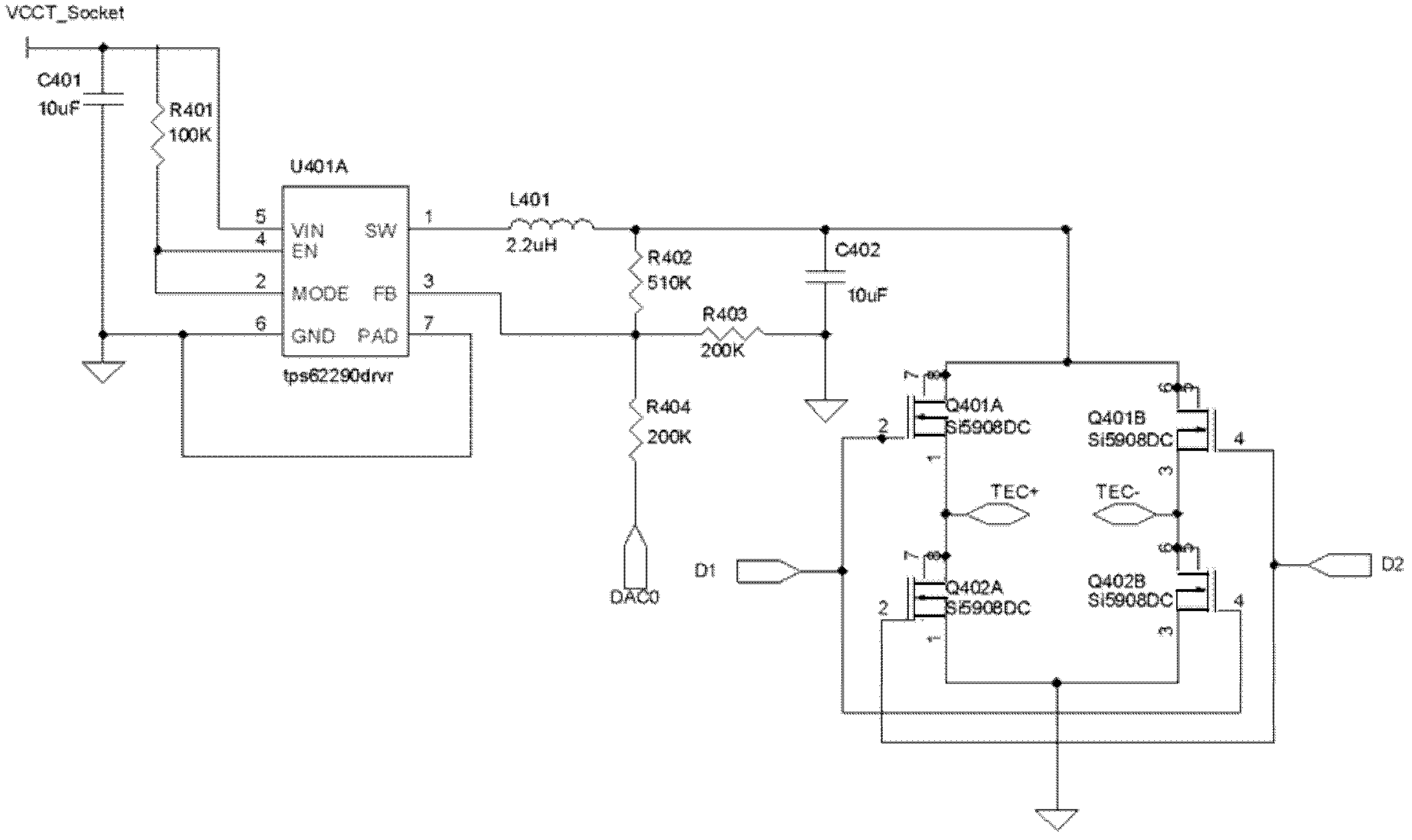
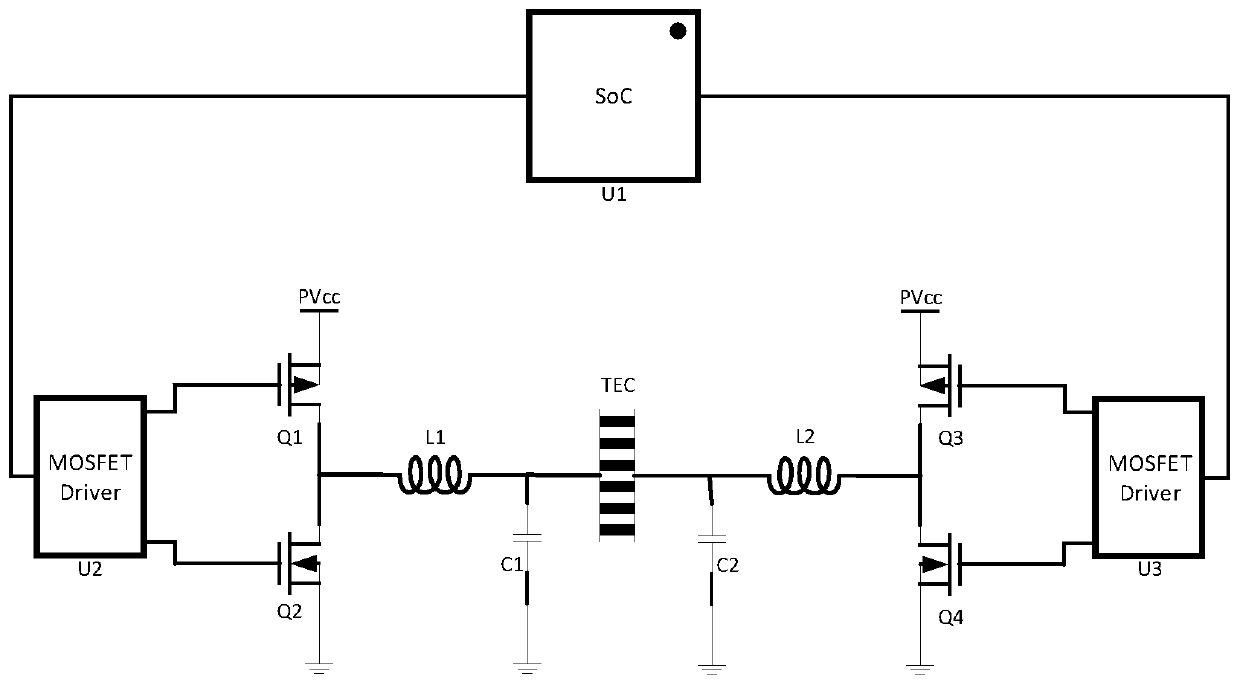
Driving circuit of thermal electric cooler (TEC)
ActiveCN102494433ASink current capability limitImproved ability to drive TECsMachines using electric/magnetic effectsRefrigeration safety arrangementSingle chipDirect current
The invention discloses a driving circuit of a thermal electric cooler (TEC), which comprises a single-channel DC-DC (direct current-direct current) conversion chip and a bridge circuit. The bridge circuit is connected with an output end of the single-channel DC-DC conversion chip, two output ends of the bridge circuit are respectively connected with two input ends of the TEC, and the bridge circuit is controlled by two channels of driving voltage. Current direction of the TEC can be controlled by controlling level of the two channels of driving voltage, so that running states of the TEC can be controlled. Since directions of current flowing through the TEC are switched by the bridge circuit, the output end of the single-chip DC-DC conversion chip keeps working in an output current state, limitation of current absorption capacity when in use of a double-channel DC-DC conversion chip is avoided, and the capacity of the DC-DC conversion chip for driving the TEC is improved.
Owner:SOURCE PHOTONICS CHENGDU
Current sink system based on sample and hold for source side sensing
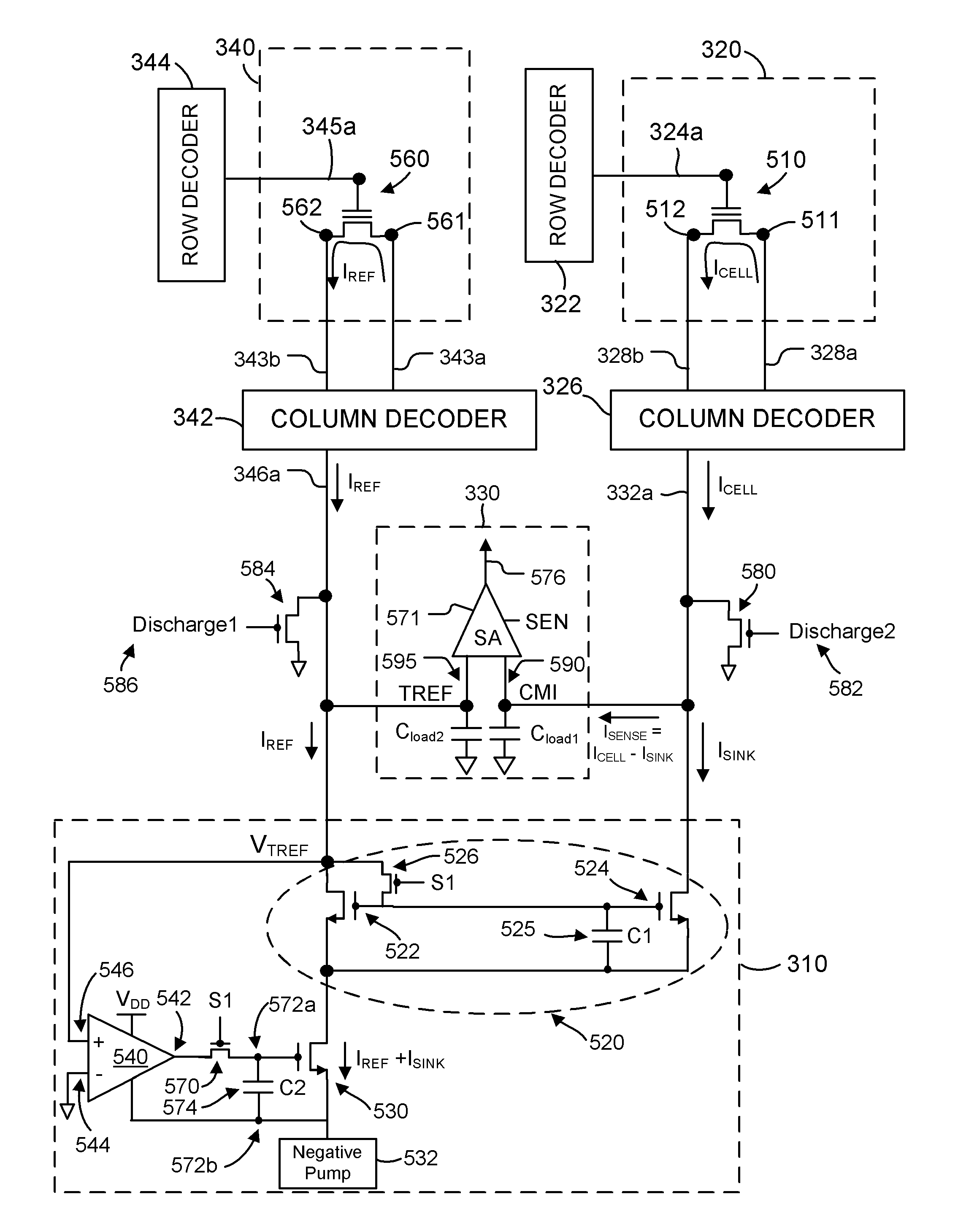
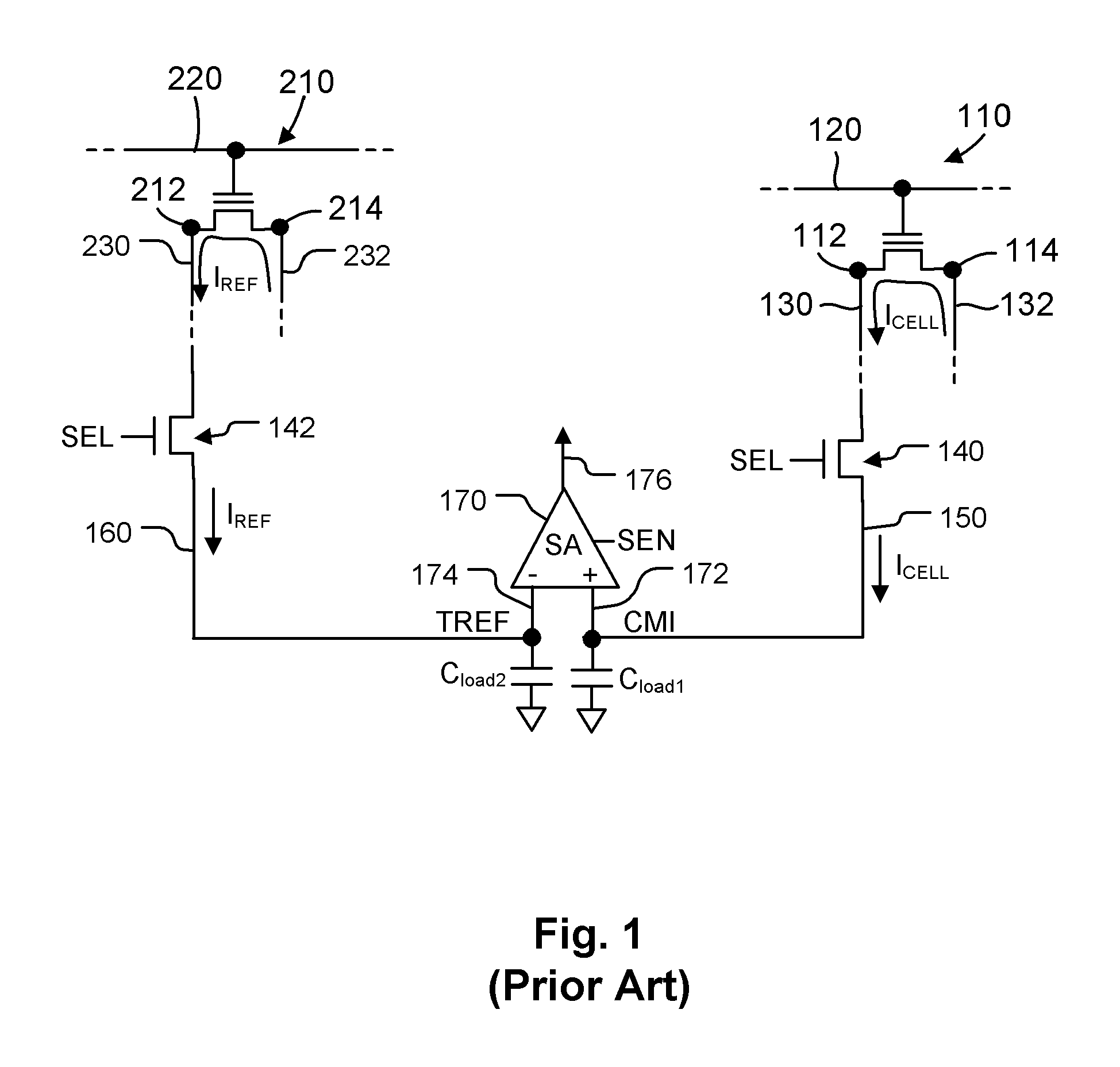
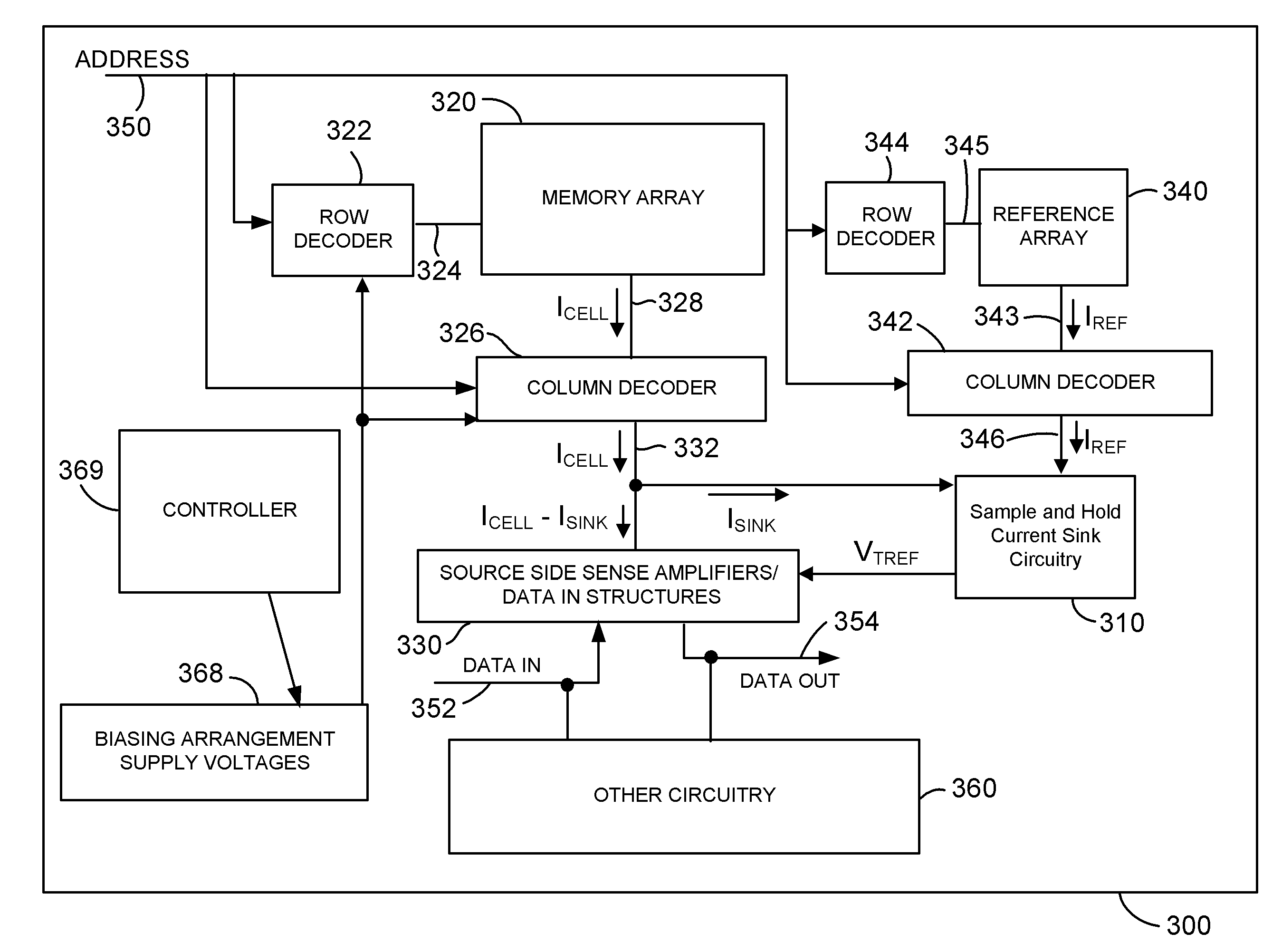
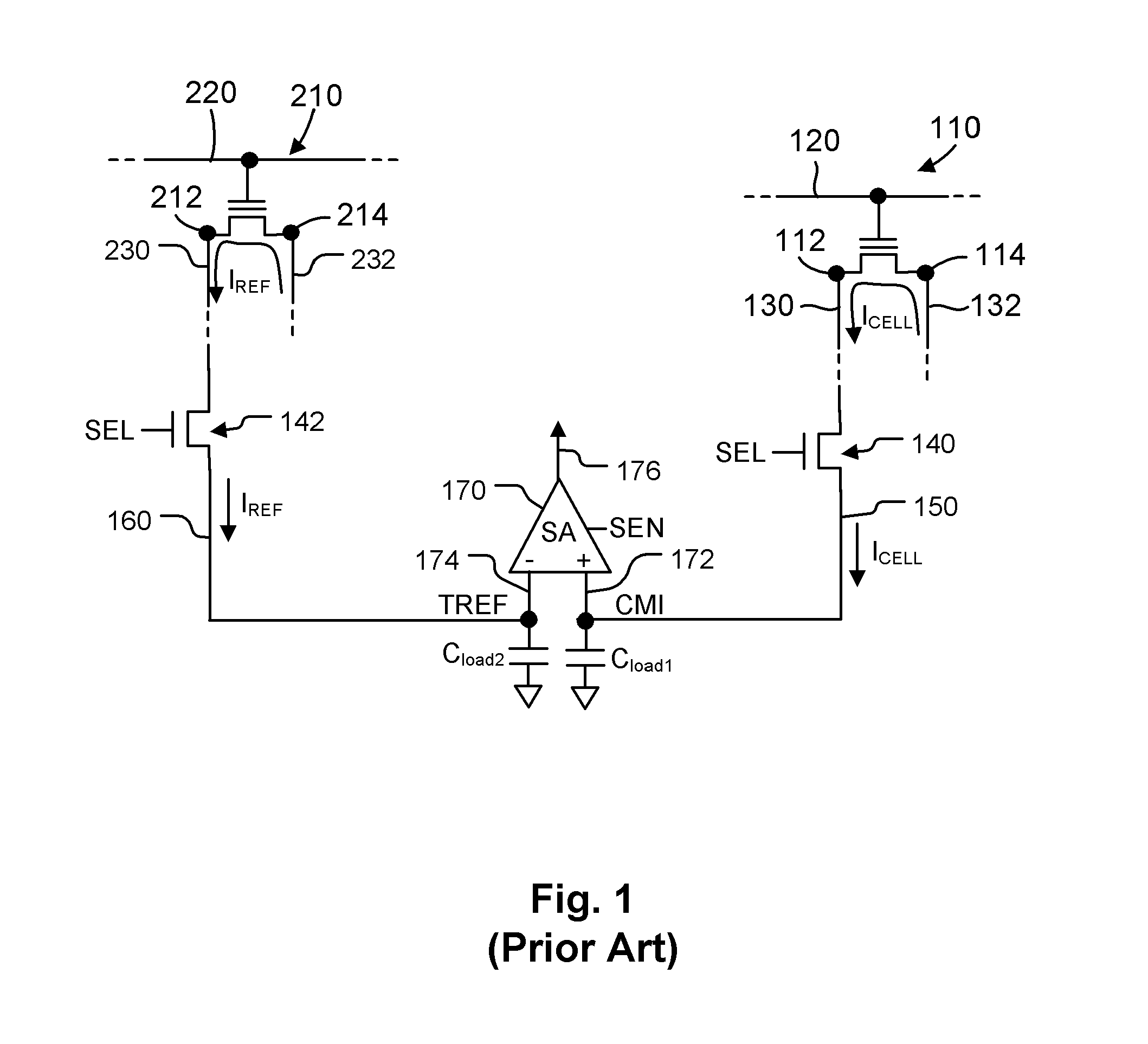
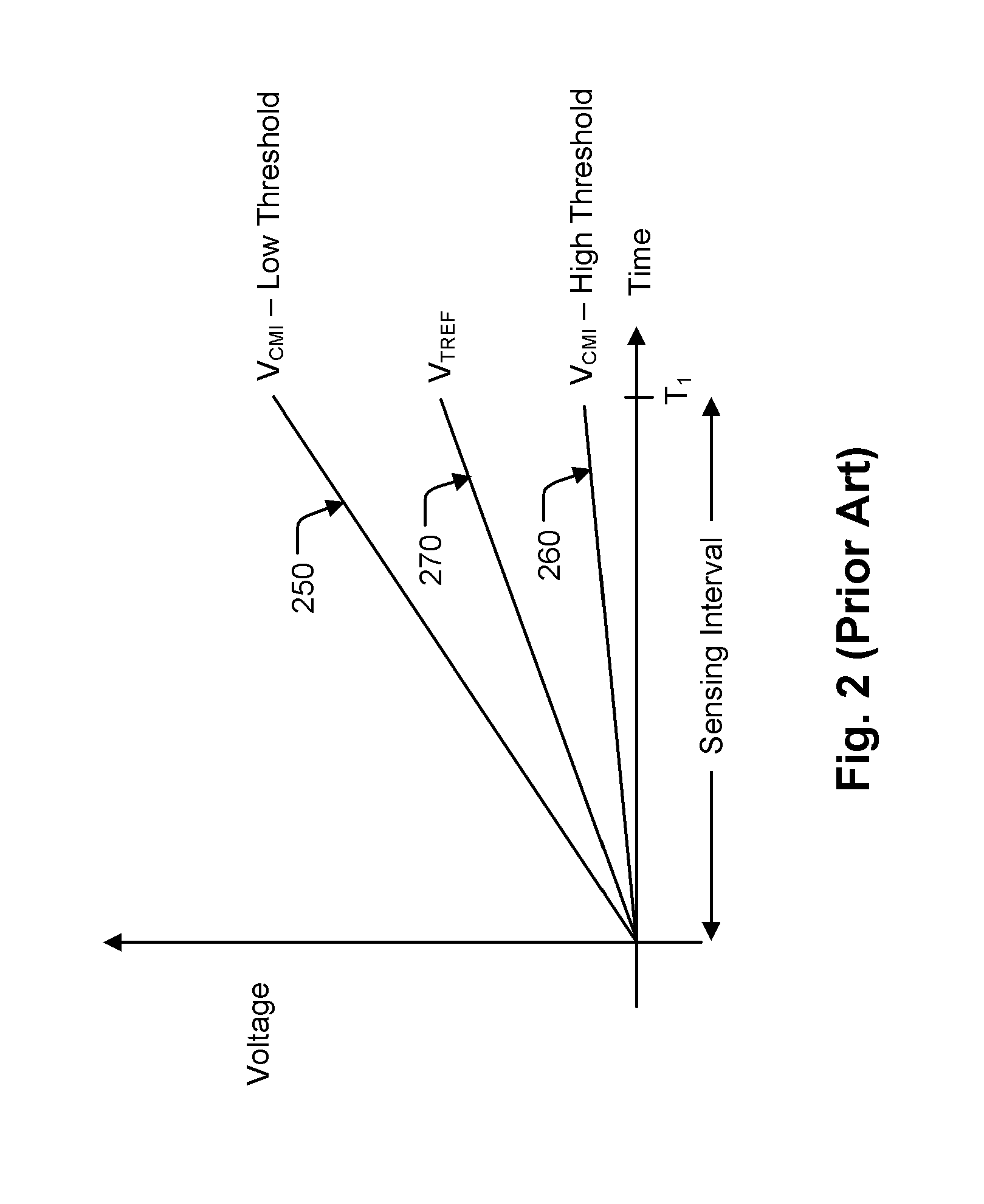
ActiveUS8149627B2Reduce amountReduce variationRead-only memoriesDigital storageReference currentComputer science
Source-side sensing techniques described herein determine the data value stored in a memory cell based on the difference in current between the read current from the source terminal of the memory cell and a sink current drawn from the read current. The sink current is drawn in response to a magnitude of an operating voltage between first and second nodes. During a first time interval, the operating voltage is set in response to a magnitude of the reference current using a feedback path. During a second time interval following the first time interval, the operating voltage is held independent of the feedback path. The data value stored in the memory cell is determined based on a difference in current between the read current and the sink current during the second time interval.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Current sink system based on sample and hold for source side sensing
ActiveUS20110216601A1Reduce amountReduce variationRead-only memoriesDigital storageReference currentData value
Source-side sensing techniques described herein determine the data value stored in a memory cell based on the difference in current between the read current from the source terminal of the memory cell and a sink current drawn from the read current. The sink current is drawn in response to a magnitude of an operating voltage between first and second nodes. During a first time interval, the operating voltage is set in response to a magnitude of the reference current using a feedback path. During a second time interval following the first time interval, the operating voltage is held independent of the feedback path. The data value stored in the memory cell is determined based on a difference in current between the read current and the sink current during the second time interval.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Electrostatic discharge protection circuit arrangement, electronic circuit and ESD protection method
An electrostatic discharge, ESD, protection circuit arrangement is connectable to a first pin and a second pin of an electronic circuit and arranged to at least partly absorb an ESD current entering the electronic circuit through at least one of the first pin or the second pin during an ESD stress event. The protection circuit arrangement comprises a first ESD protection circuit arranged to absorb a first portion of the ESD current during a first part of the ESD stress event during which first part a level of the ESD current exceeds a predetermined current threshold; and a second ESD protection circuit arranged to absorb a second portion of the ESD current, the second portion having a current level below the current threshold, at least during a second part of the ESD stress event. The second ESD protection circuit comprises a current limiting circuit arranged to limit a current through at least a portion of the second ESD protection circuit to the current threshold.
Owner:NXP USA INC
High-frequency current generating circuit and control device for controlling light intensity of laser diode
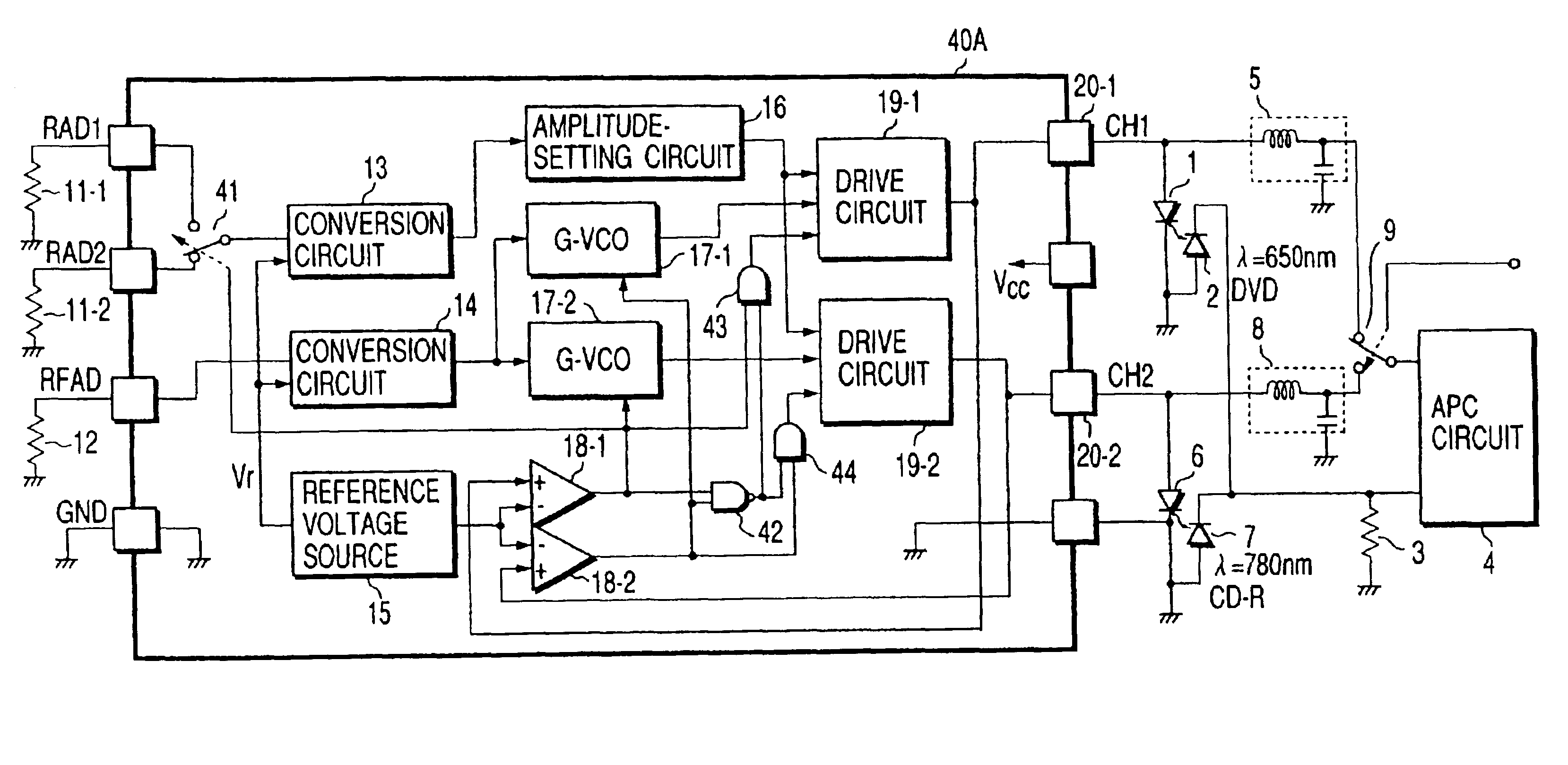
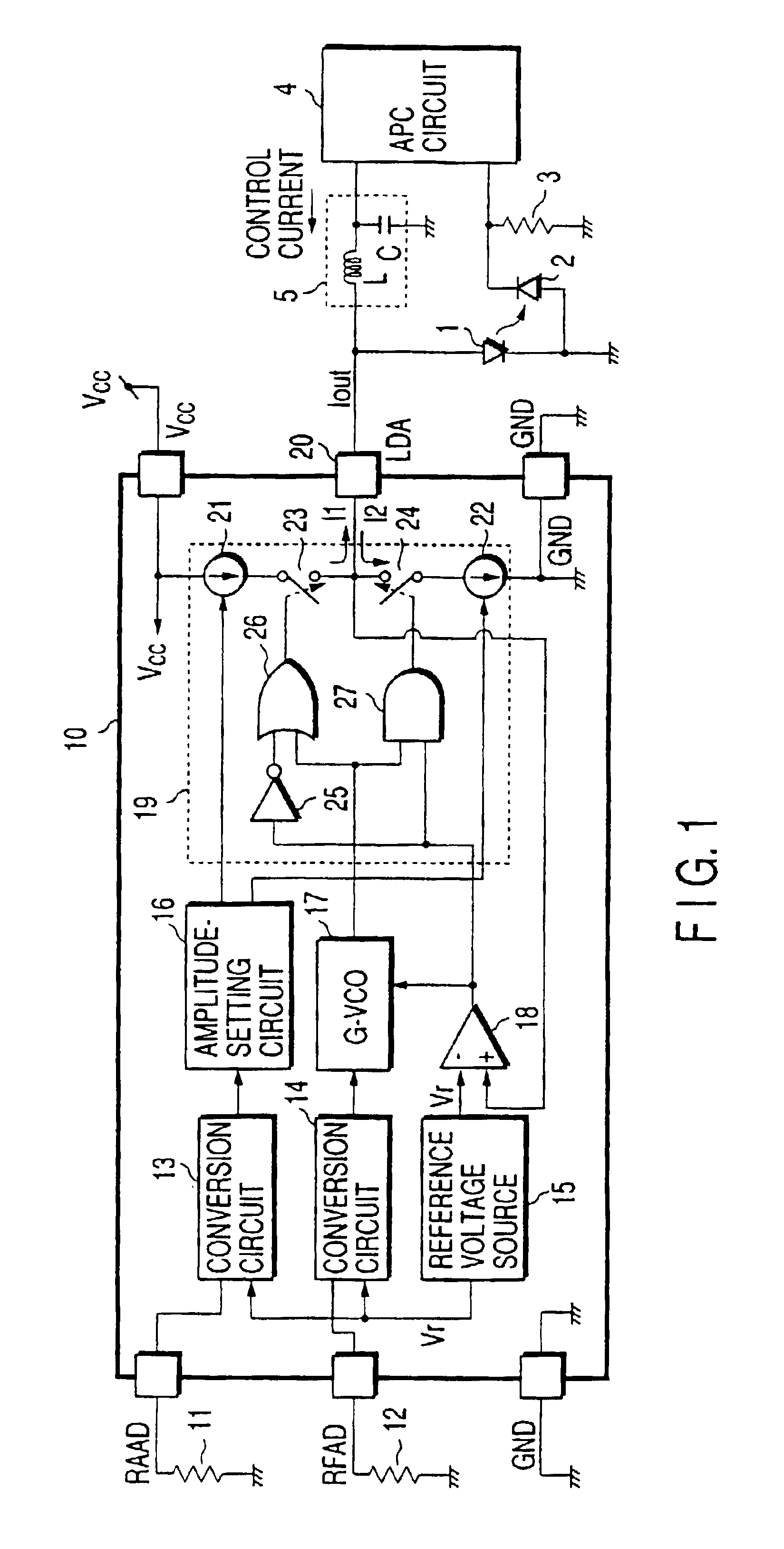
InactiveUS6855919B2Less heatSuppress power consumptionPhotometry using reference valueLaser detailsCurrent sourceLight intensity
In a laser-driving device including a high-frequency current generating circuit generating a high-frequency current superimposed on a control current output from a light intensity control circuit for light intensity control, and supplied to a laser diode as a drive current, the high-frequency current generating circuit has a sourcing current source, a sinking current source, current switches connected between the current sources and a drive output terminal respectively, a gated oscillation circuit oscillating with a desired frequency, and switch drive circuits complementarily on / off controlling the current switches by using a drive switching signal obtained by removing a high-frequency component from an output signal of the oscillation circuit. The present invention, therefore, provides a high-frequency current generating circuit which can increase the amplitude of the high-frequency current superimposed on the control current of the laser diode and which generates less heat while suppressing power consumption.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Variable gain amplifier, and am-modulated signal reception circuit and detection circuit
ActiveUS20070238432A1Improve linearityWide variable gain rangeGain controlAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
In order to provide a variable gain amplifier of enhanced linearity and wide variable gain range, an AM-modulated signal reception circuit in which the noise of an input portion is reduced so as to improve the follow-up characteristic of an AGC circuit, and an AM-modulated signal detection circuit which produces an output precisely corresponding to a peak value envelope, the variable gain amplifier comprises a differential input amplifier which includes transistors T1 and T2 (in FIG. 8) constituting a differential pair, and a constant current circuit Is operating as an absorption current circuit of the transistors T1 and T2, and a variable impedance which is connected between the sources of the respective transistors T1 and T2, wherein the gain of the differential input amplifier is made variable by variably controlling the value of the variable impedance.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
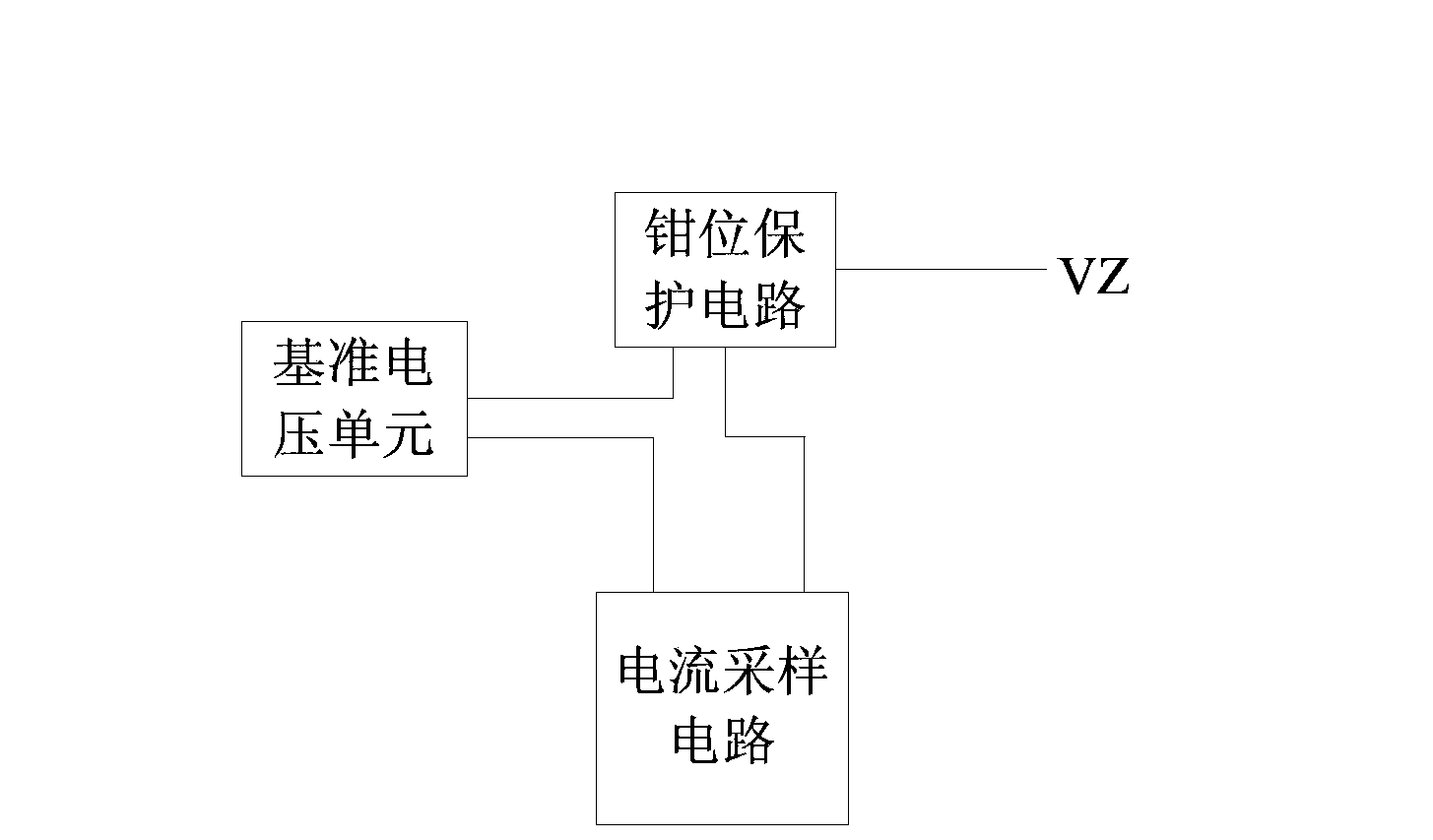
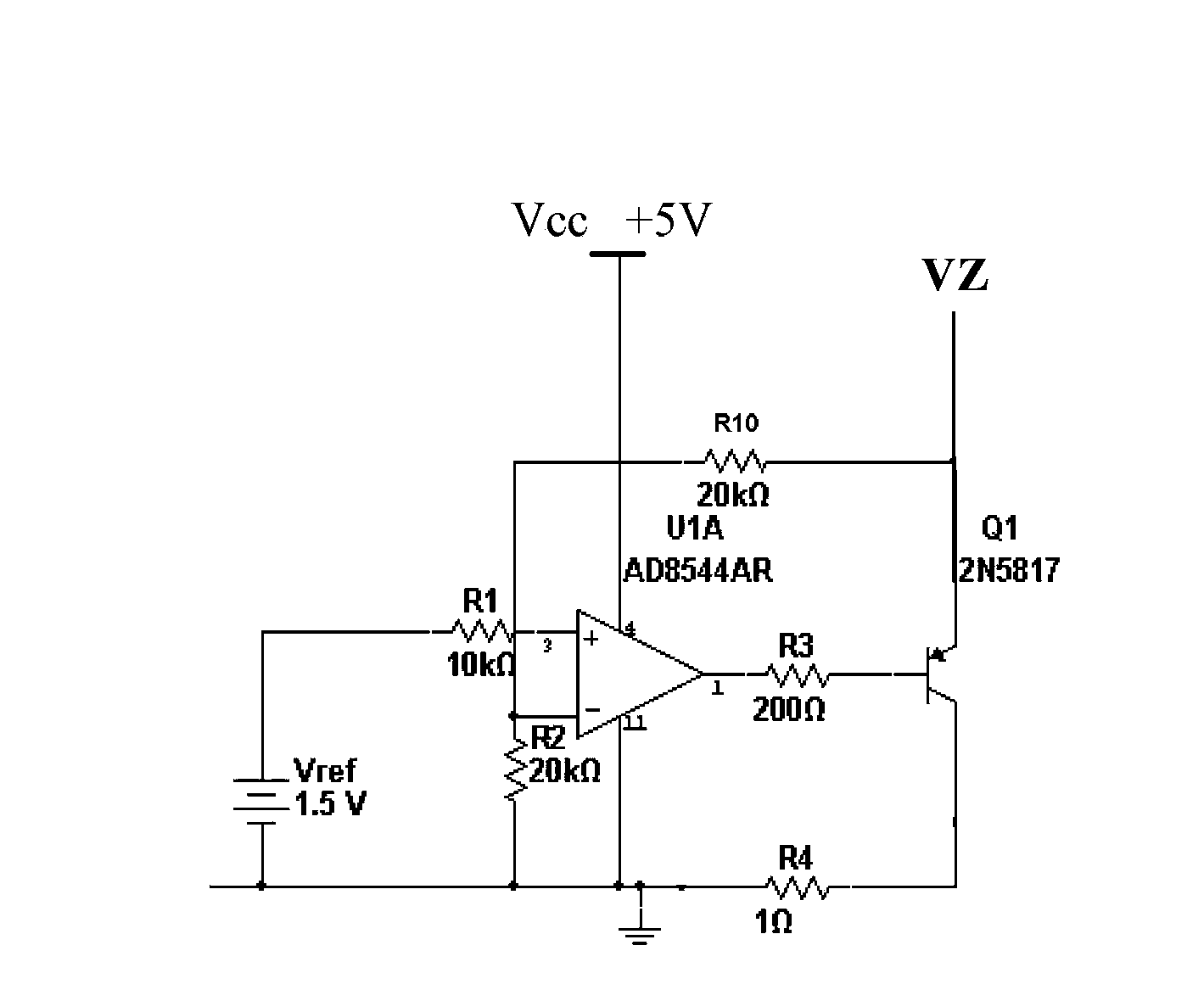
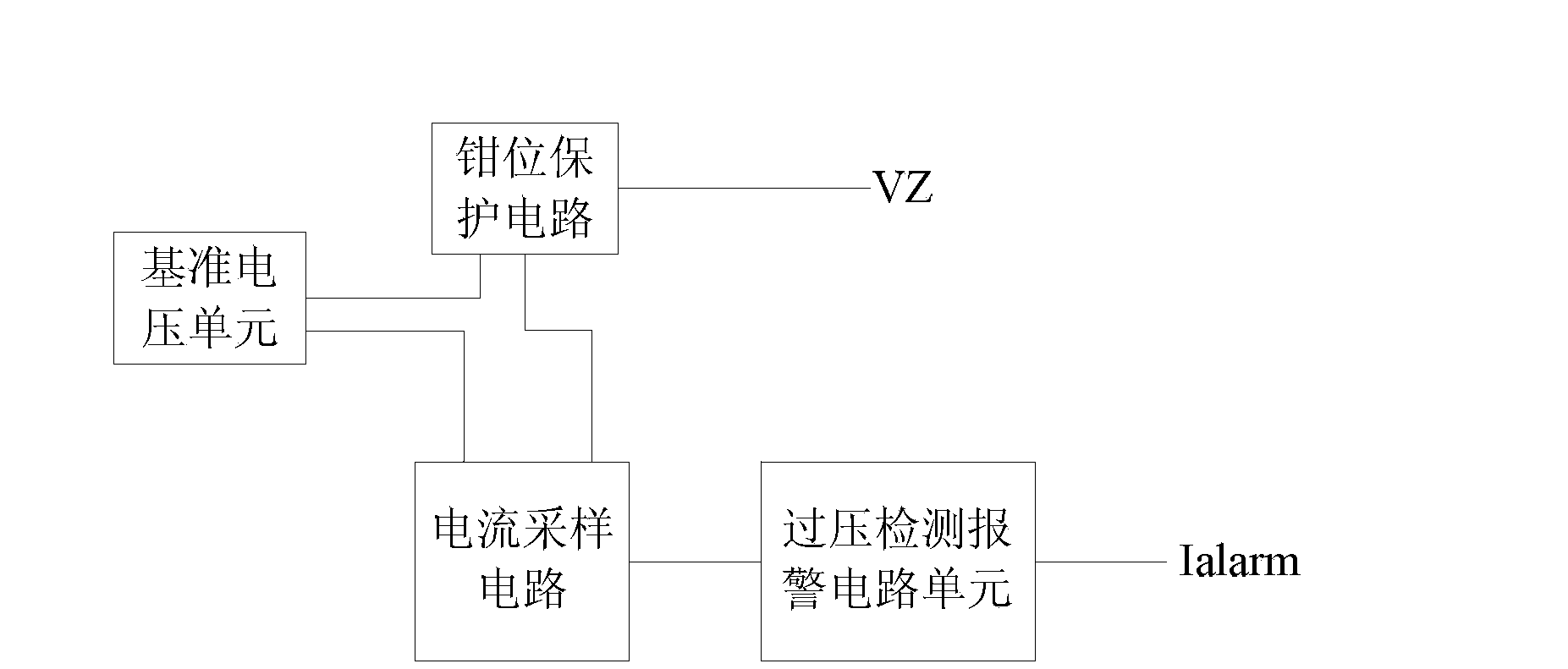
Overvoltage absorption protection circuit
ActiveCN103915829ASimple structureImprove stabilityEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentOvervoltagePower flow
The invention discloses an overvoltage absorption protection circuit. A clamping threshold and an overvoltage protection current alarm value are set through a pure analog circuit, and clamping protection and overvoltage absorption are performed on an MCU port when an overvoltage is input, and alarm is performed when the value of an absorption current which undergoes amplification processing reaches a current alarm value. At the same time, the circuit approaches a zero power consumption state under a condition that overvoltage does not exist. The overvoltage absorption protection circuit has the advantages of being simple in structure, great in stability and low in cost.
Owner:BEIJING AEONMED
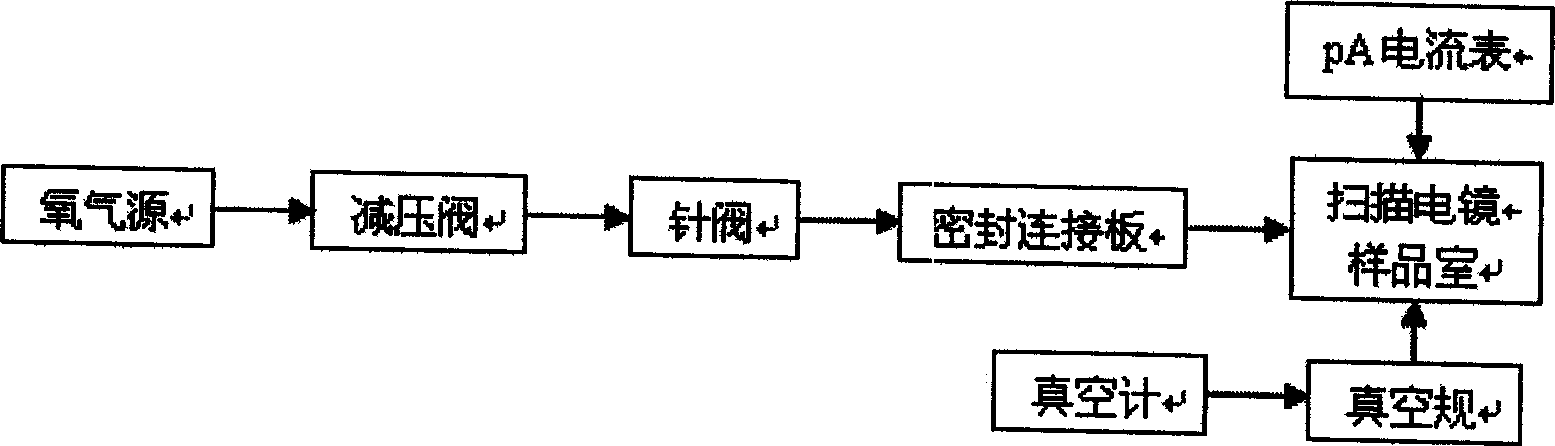
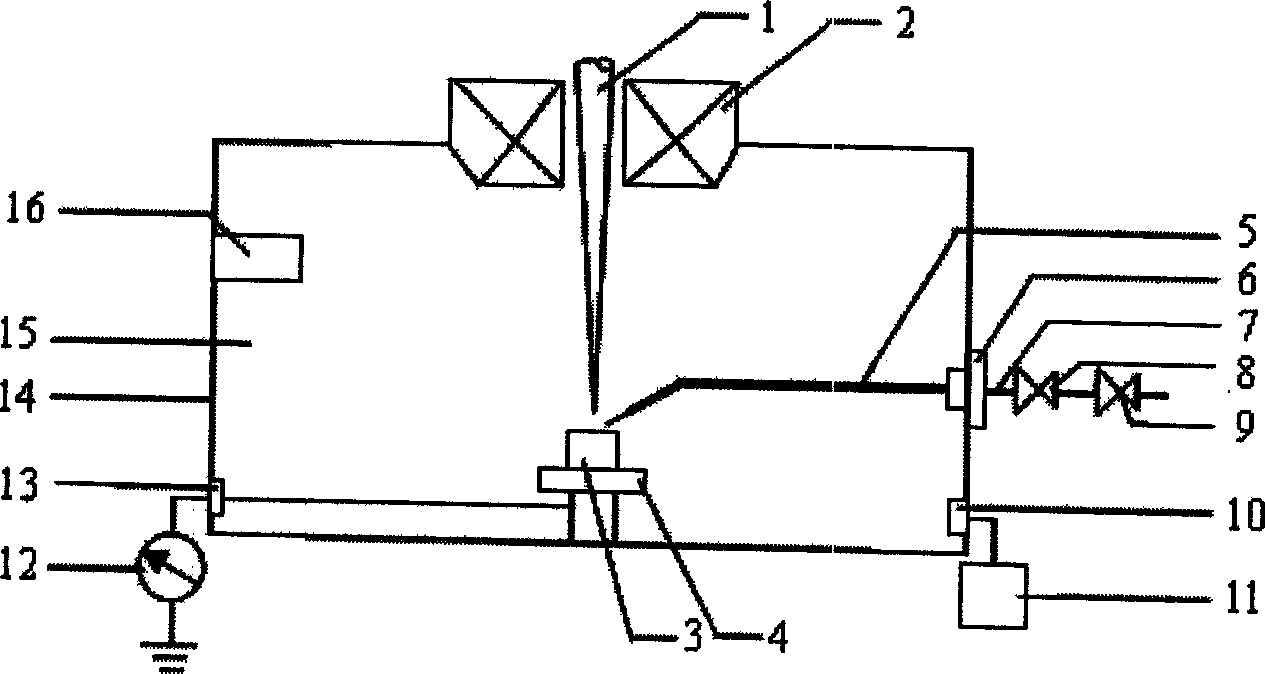
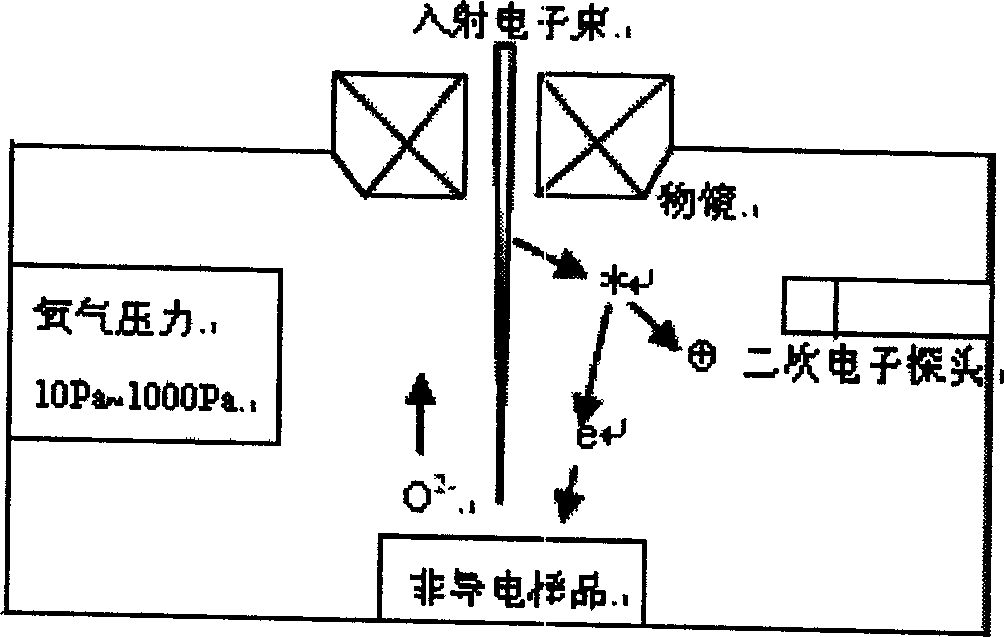
Oxygen environment scan electronic microscopic method and system
InactiveCN1587978ACompensation for charging effectsMaintain vacuum mode of operationSurface/boundary effectScanning probe techniquesScanning tunneling microscopeScanning electron microscope
The invention relates to a direct observing and analyzing method and system to non conducting material in oxygen atmosphere created by injecting oxygen in minute quantities into scanning electron microscope. It has the property that before, scanning sample, active oxygen in minute quantities is injected into sample chamber to decrease or eliminate charged phenomenon of non conducting sample. Vacuum model is chosen before injecting oxygen, whose pressure is decreased through pressure reducing valve, degree of vacuum of sample chamber is monitored by vacuometer and vacuum gauge, needle valve is used to decrease flux of oxygen right along. Oxygen injected has little influence to the degree of vacuum of scanning electron microscope system, realizing oxygen atmosphere observation condition under different vacuum model. Oxygen microinjection system is install on sidewall of sample chamber to coordinate with oxygen atmosphere scanning electron microscope method, consisted of air feed loop, vacuum checkout systems and absorption current checkout systems. The invention has reached the goal of effectively eliminating sample of non conducting like oxide and hydroxide which will generate charged effect when does electric electron microanalysis.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
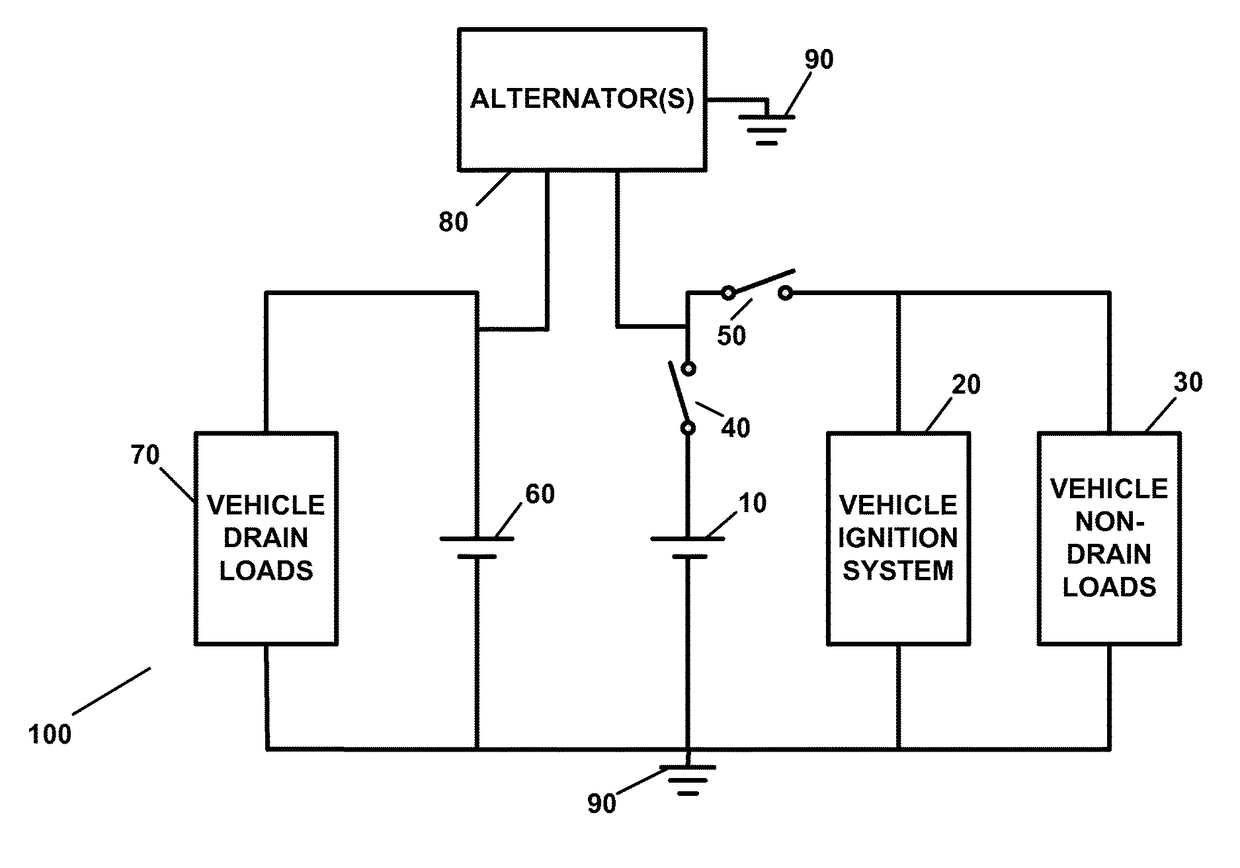
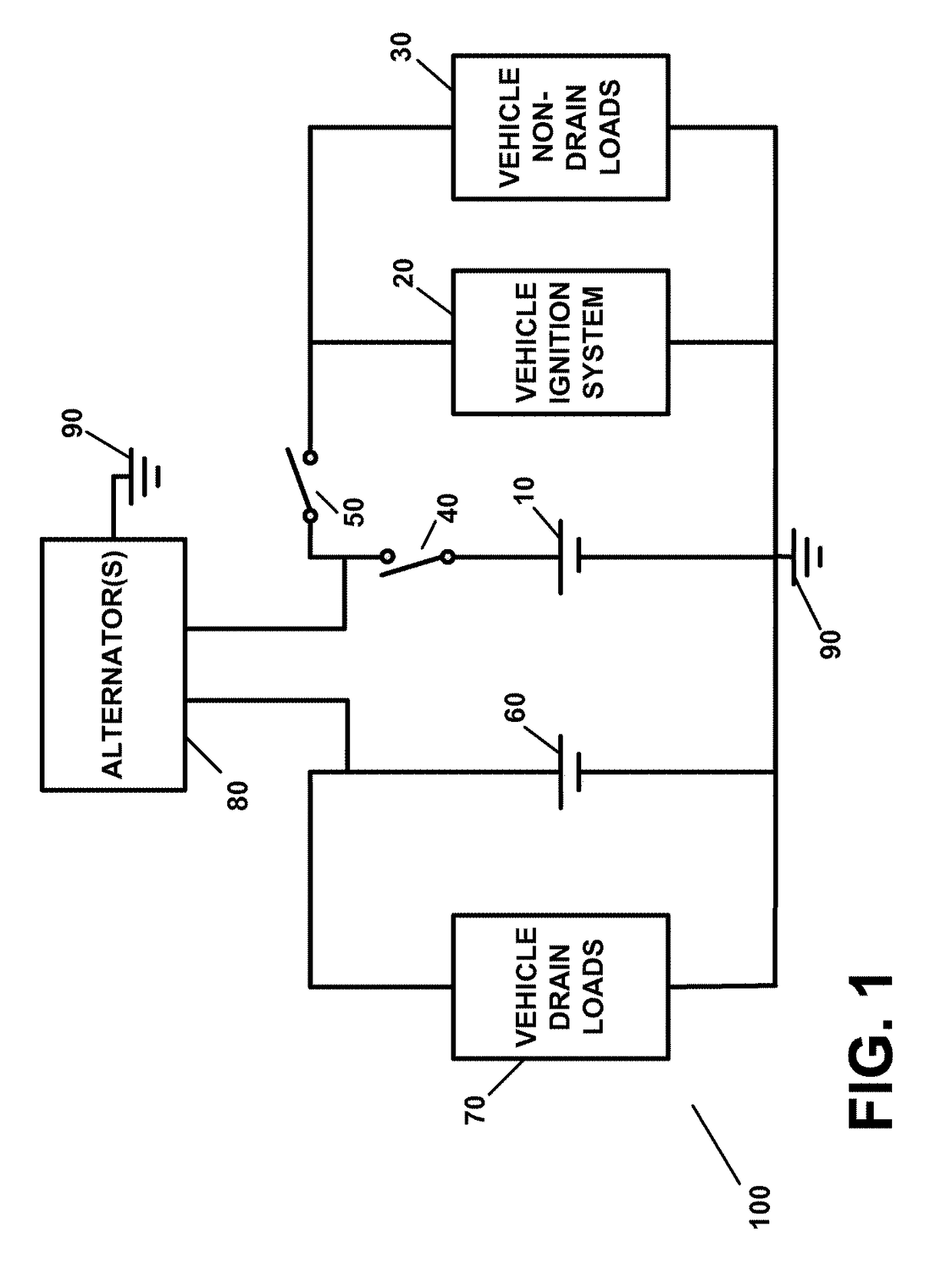
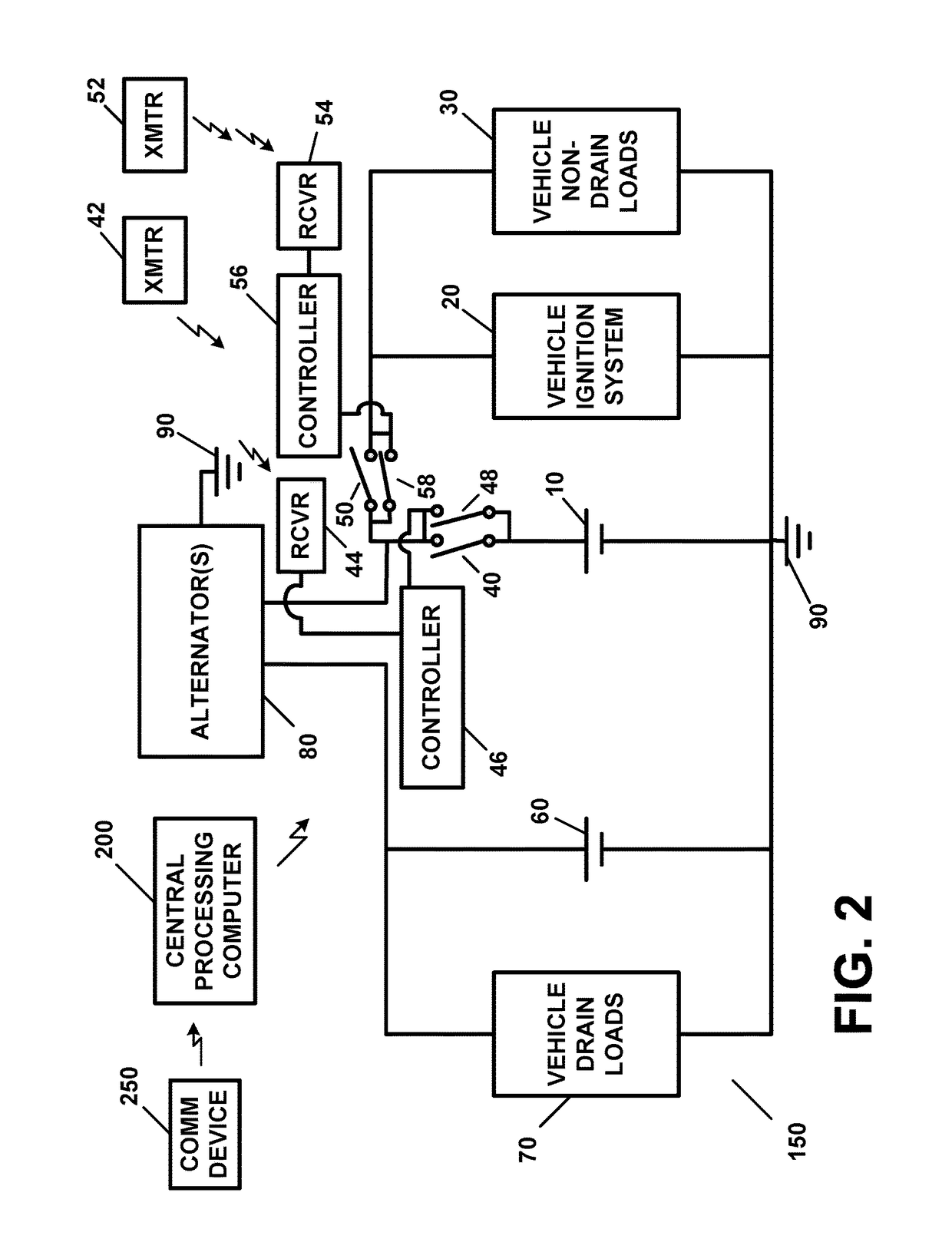
Battery power management apparatus and method
ActiveUS9821738B2Conserving charge level and electrical powerSufficient charge levelBatteries circuit arrangementsMachines/enginesAlternatorElectrical battery
A battery power management apparatus, including a first battery capable of providing electrical power to a first load of a vehicle at a selected time, wherein the first load does not draw current when an ignition system is not operating; a second battery capable of providing electrical power to a second load which draws current when the ignition system is not operating; a first switch capable of disconnecting the first battery from a first circuit containing the ignition system; a second switch capable of connecting the first battery to the first circuit containing the ignition system and is capable of connecting the first battery to a second circuit containing the first load; and an alternator which recharges both the first battery and second battery simultaneously when the ignition system is operating. The second battery provides electrical power to the second load when the alternator ceases to operate.
Owner:JOAO RAYMOND ANTHONY
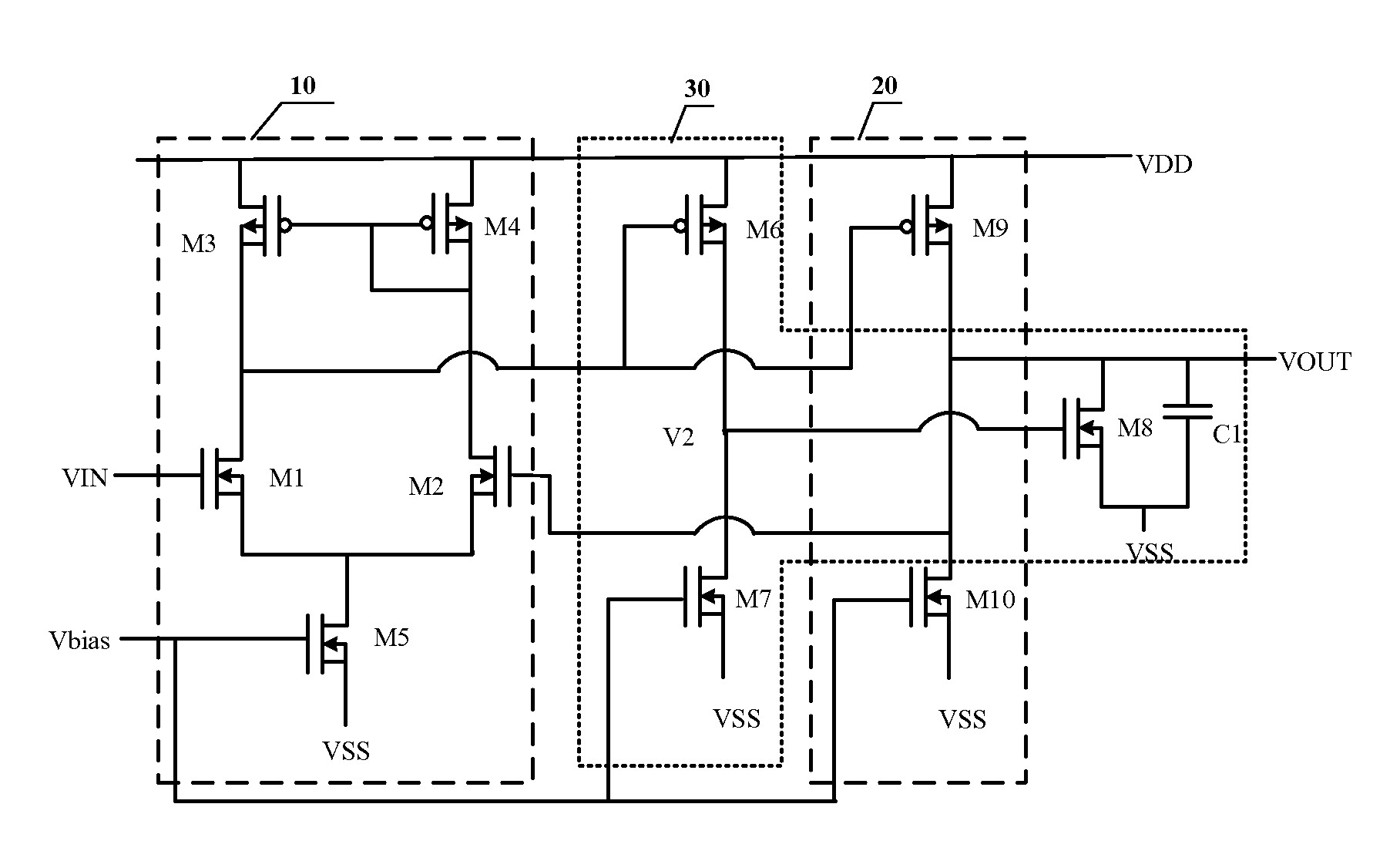
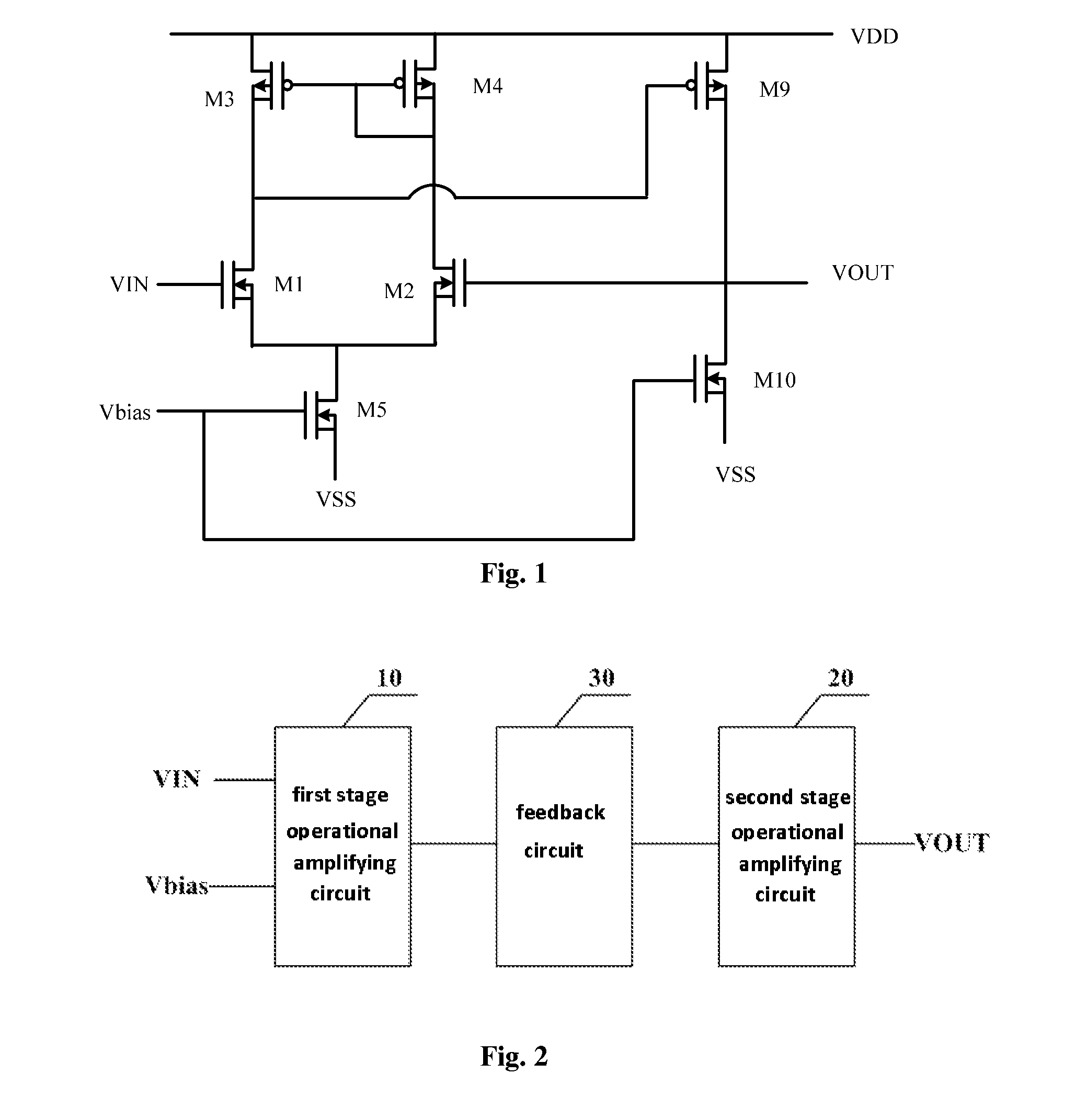
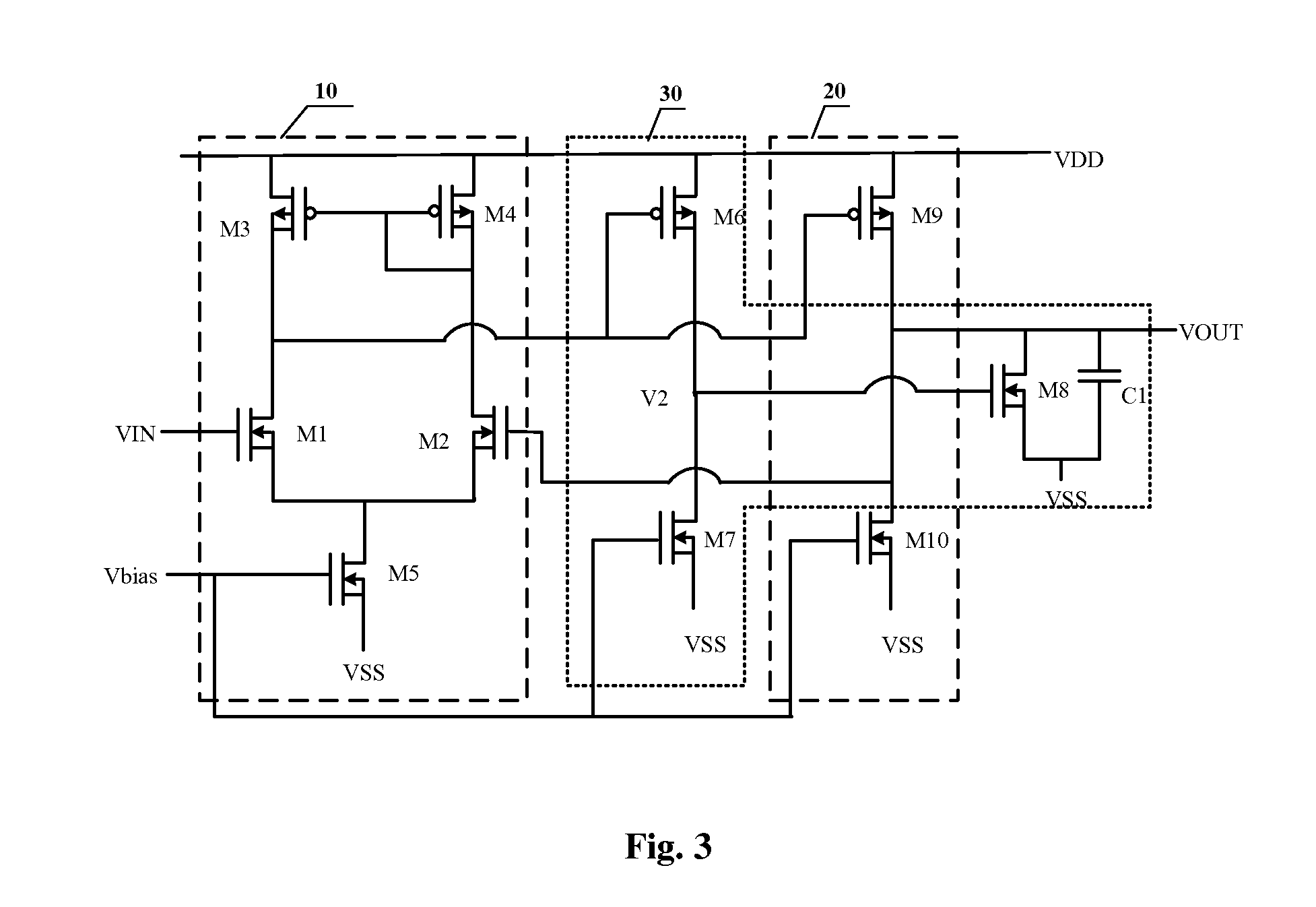
Output buffer circuit, array substrate and display device
ActiveUS20150229273A1Suppresses fluctuations in output voltageImprove stabilityStatic indicating devicesAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierDisplay device
The embodiments of the present invention provide a output buffer circuit, comprising: a first stage operational amplifying circuit configured as a differential input circuit; a second stage operational amplifying circuit configured as a common source amplifying circuit having an active load; and a feedback circuit provided between the first stage operational amplifying circuit and the second stage operational amplifying circuit and configured to have driving capability of providing source current and sink current alternately. By forming a unit gain amplifier comprising the first stage operational amplifying circuit, the second stage operational amplifying circuit and the feedback circuit connected therebetween, the output buffer circuit has the driving capability of providing source current and sink current alternately. No special voltage stabilizing circuit is needed, thus the circuit structure is simple and the chip area is decreased; since the power consumption can be reduced without a special voltage stabilizing circuit, the fluctuation of the output voltage is suppressed at the same time, the stability of the circuit is ensured in operation and offset is suppressed optimally, the output signal is more accurate and the quality of image displayed is improved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Memory with bit line current injection
Embodiments of a memory are disclosed that may allow for the detection of weak data storage cells or may allow operation of data storage cells under conditions that may represent the effects of transistor ageing. The memory may include data storage cells, a column multiplexer, a sense amplifier, and a current injector. The current injector may be configured to generate multiple current levels and may be operable to controllably select one of the current levels to either source current to or sink current from the input of the sense amplifier.
Owner:APPLE INC
Variable gain amplifier, and AM-modulated signal reception circuit and detection circuit
ActiveUS7761071B2Wide variable gain rangeImprove featuresGain controlAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
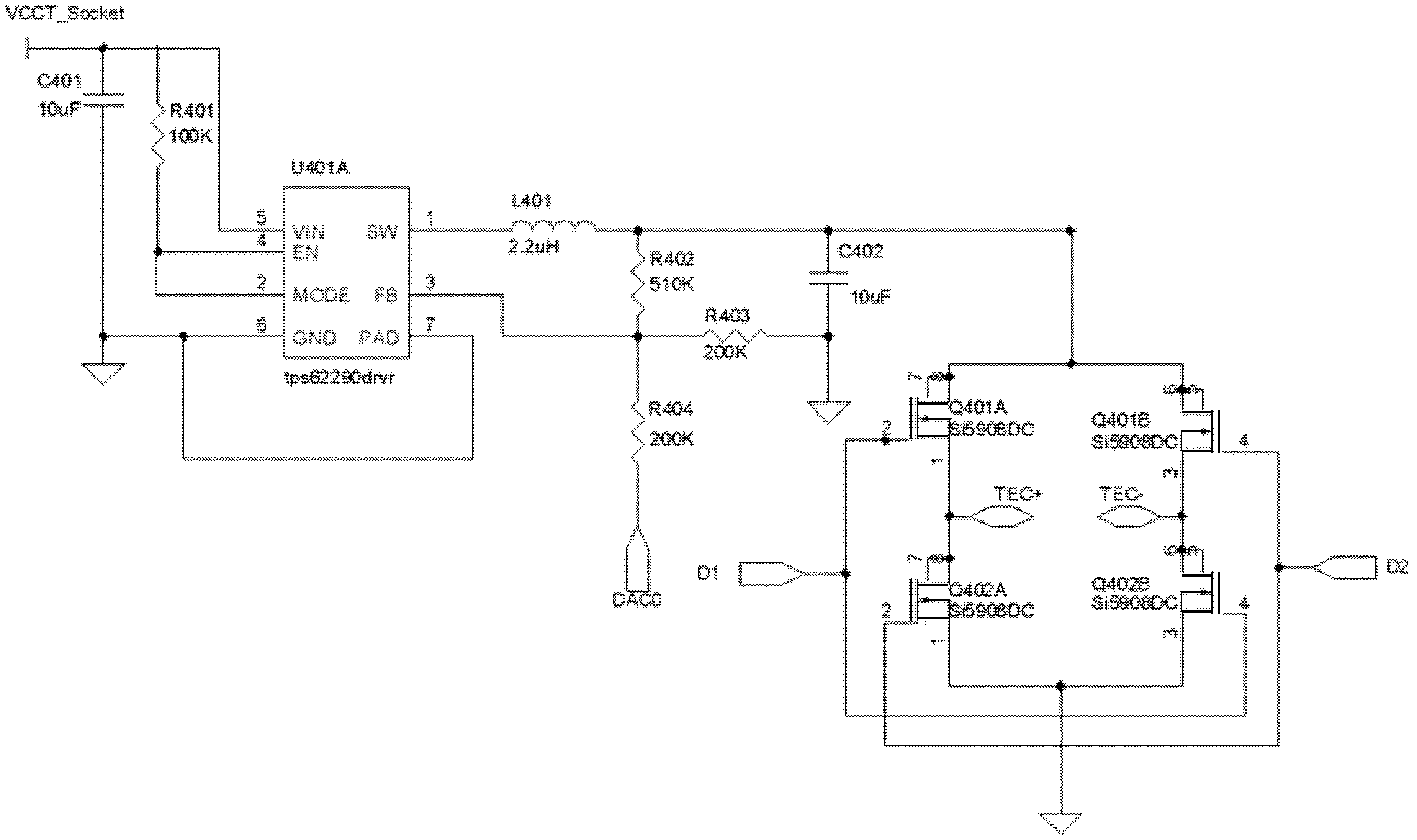
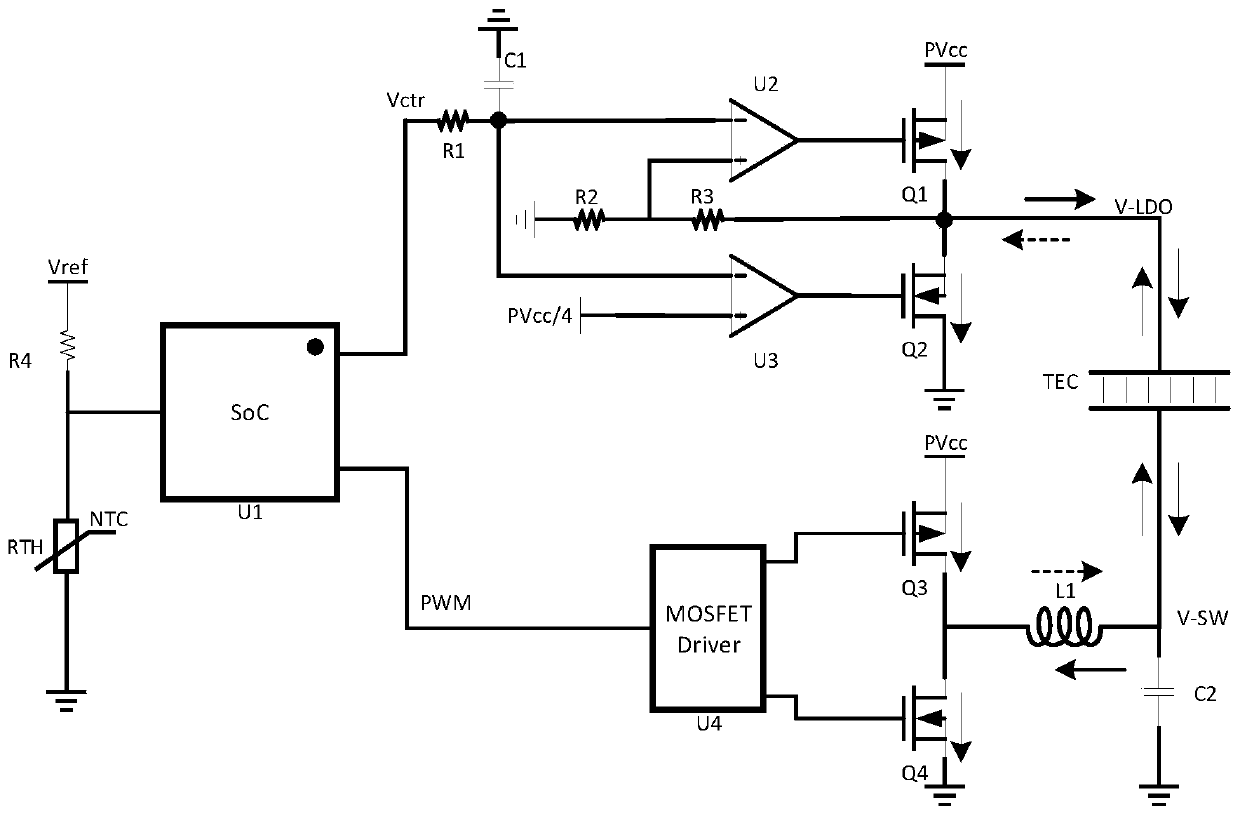
TEC temperature control driving circuit and control strategy thereof
The invention discloses a TEC temperature control driving circuit which is characterized in that the circuit comprises a linear regulator LDO, a current absorbing circuit and a switching power supply SW circuit. The output end of the linear regulator LDO is connected with the LDO terminal of a TEC to provide input voltage V-LDO. The output end of the switching power supply SW circuit is connected with the SW end of the TEC to provide input voltage V-SW. According to the current absorbing circuit, when V-LDO is greater than V-SW, disconnection is carried out, and current flows from the linear regulator LDO into the TEC; when V-LDO is less than V-SW, breakover is carried out, and current flows from the TEC to the current absorbing circuit. According to the invention, a new LDO+SW topology circuit structure is designed, and the advantages of small LDO ripple and high SW efficiency are combined; the current absorbing circuit is added on the LDO terminal, so that the LDO terminal can output current and absorb current; and the same circuit is used to drive the TEC to carry out heating or refrigeration.
Owner:NANJING MOVELASER TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com