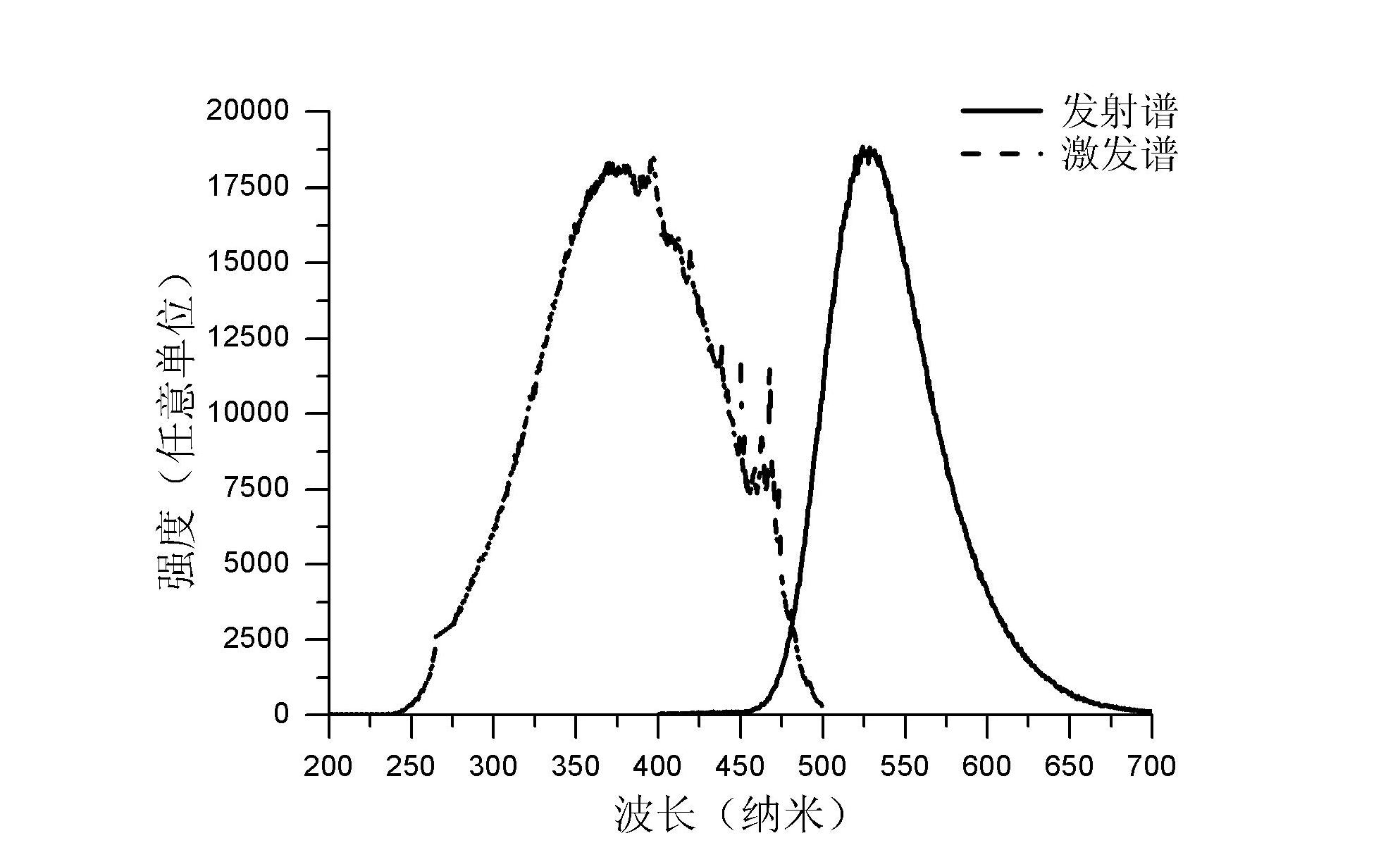
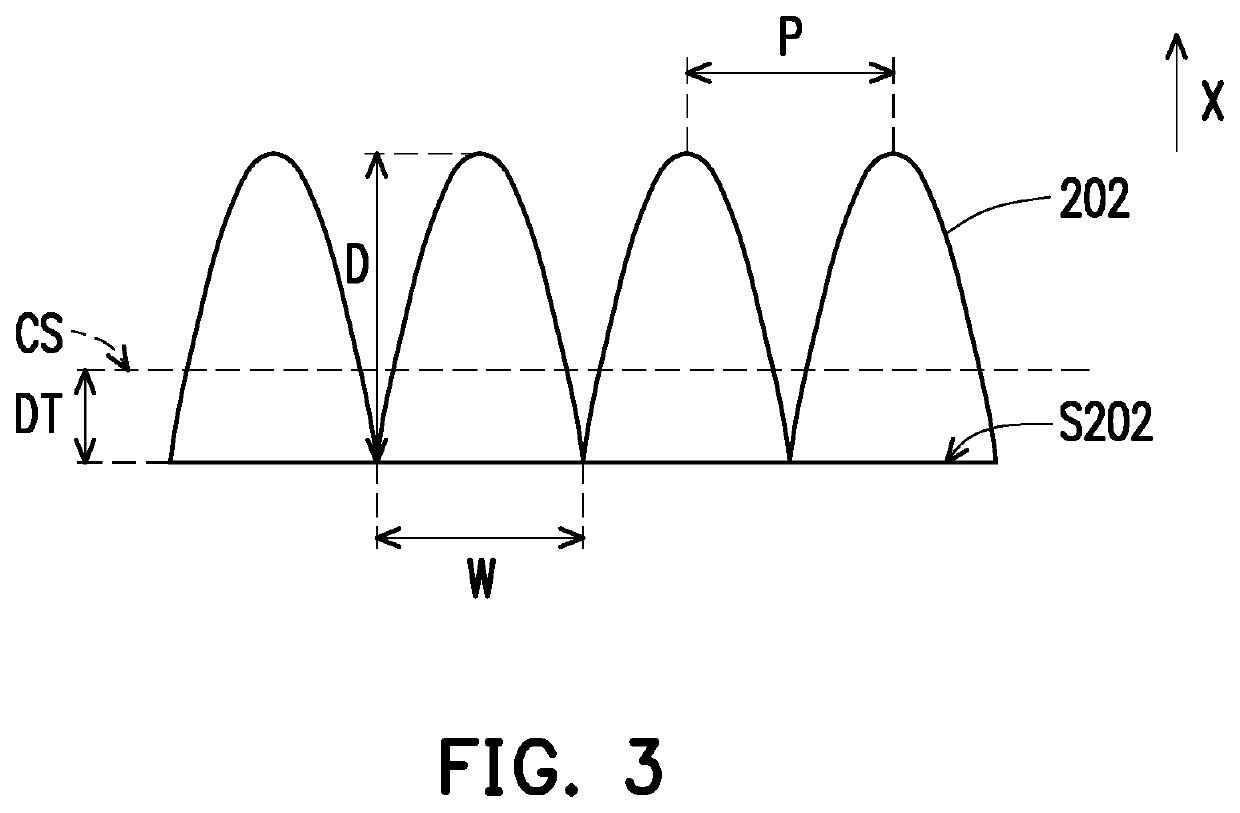
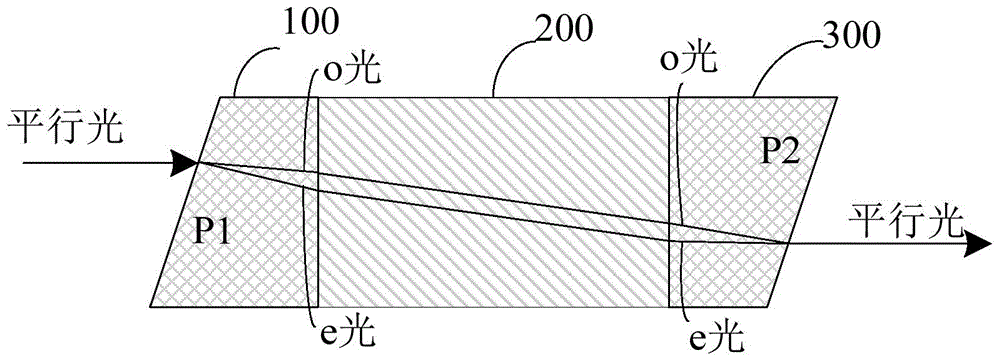
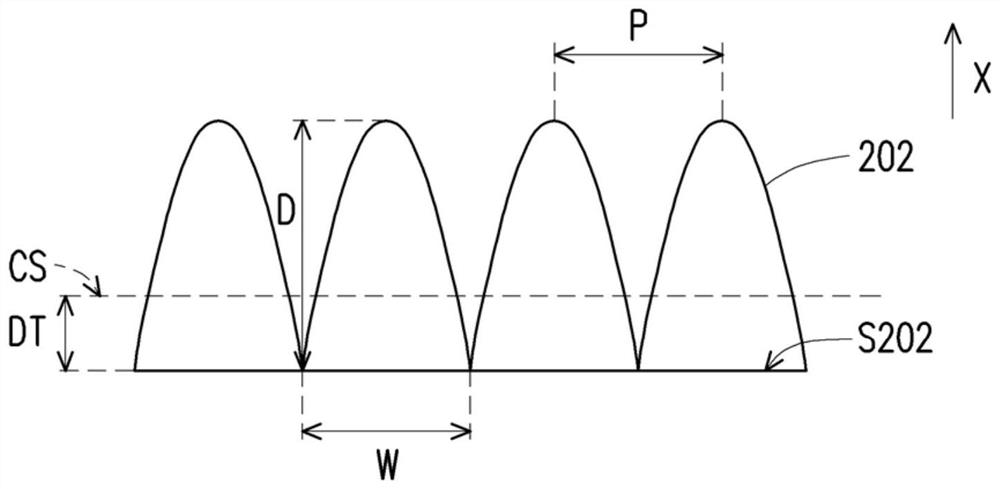
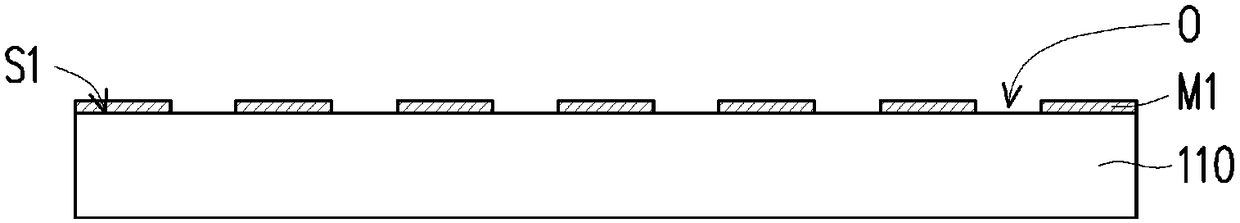
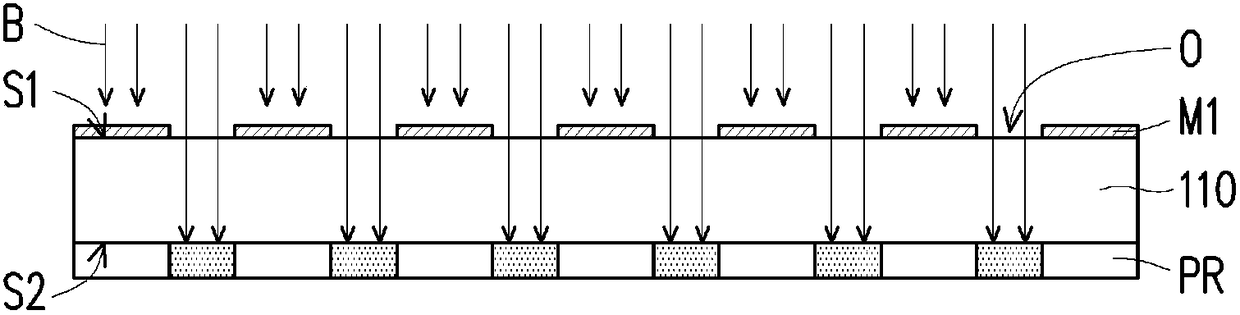
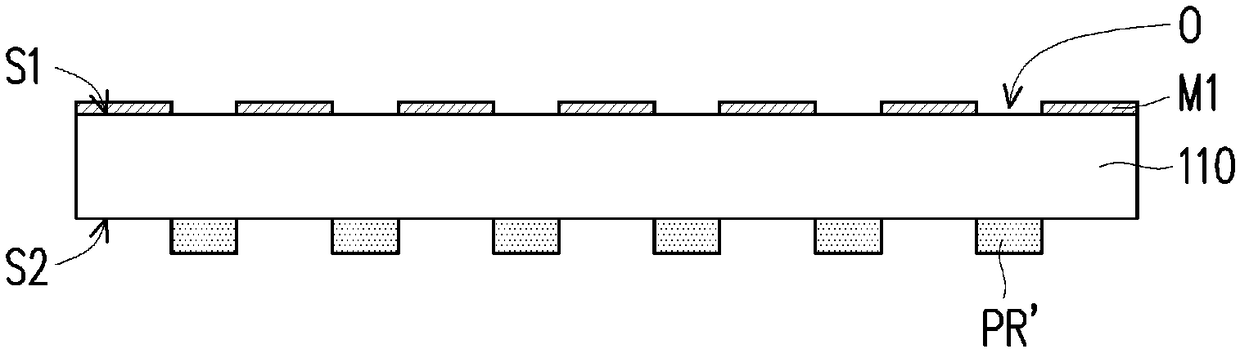
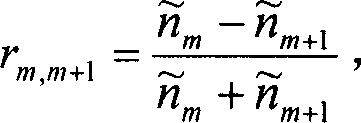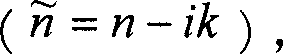Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56results about How to "Reduce interface reflection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
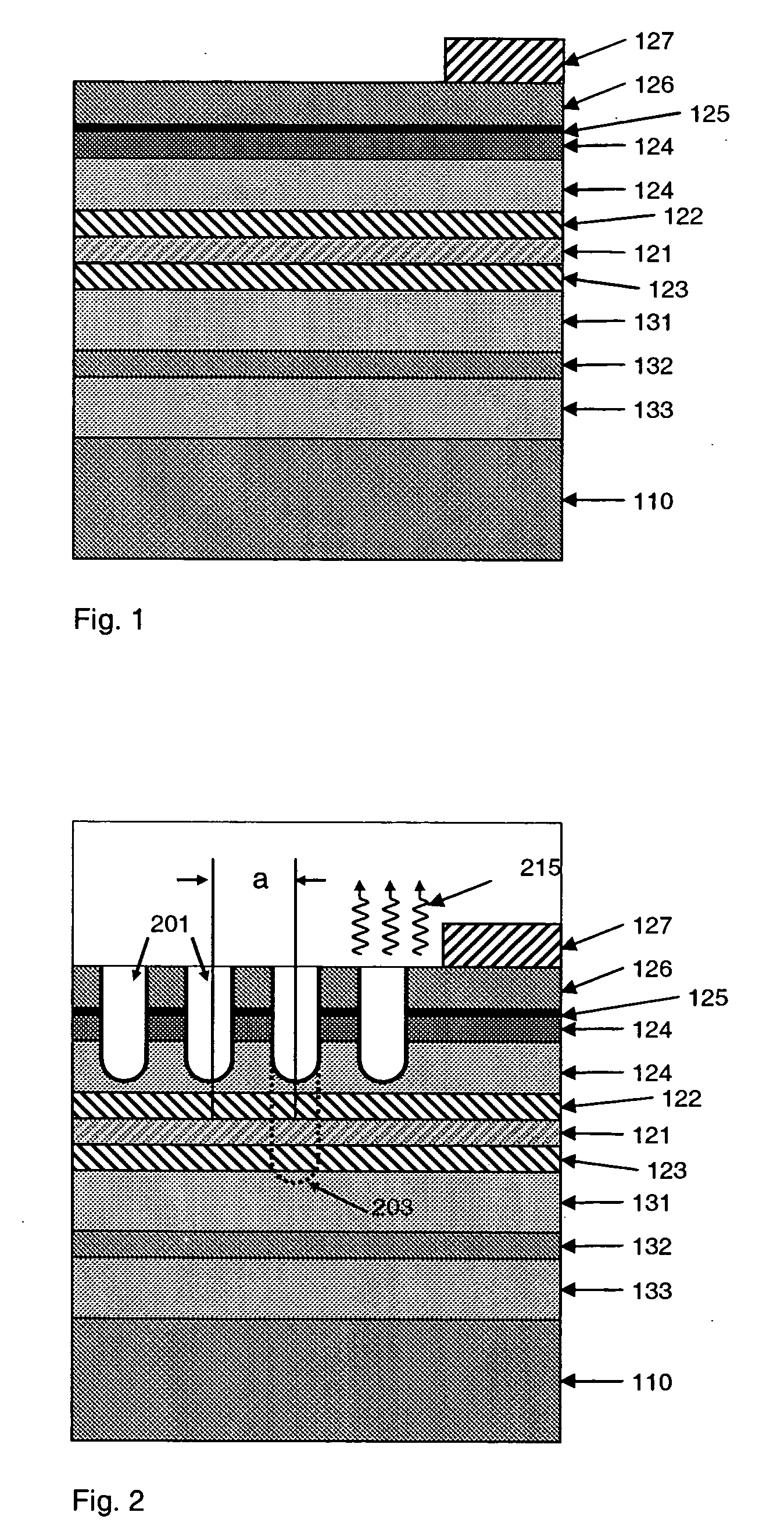
Lighting system with high and improved extraction efficiency
InactiveUS20050173714A1Efficient extractionImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotonic crystalPhoton emission
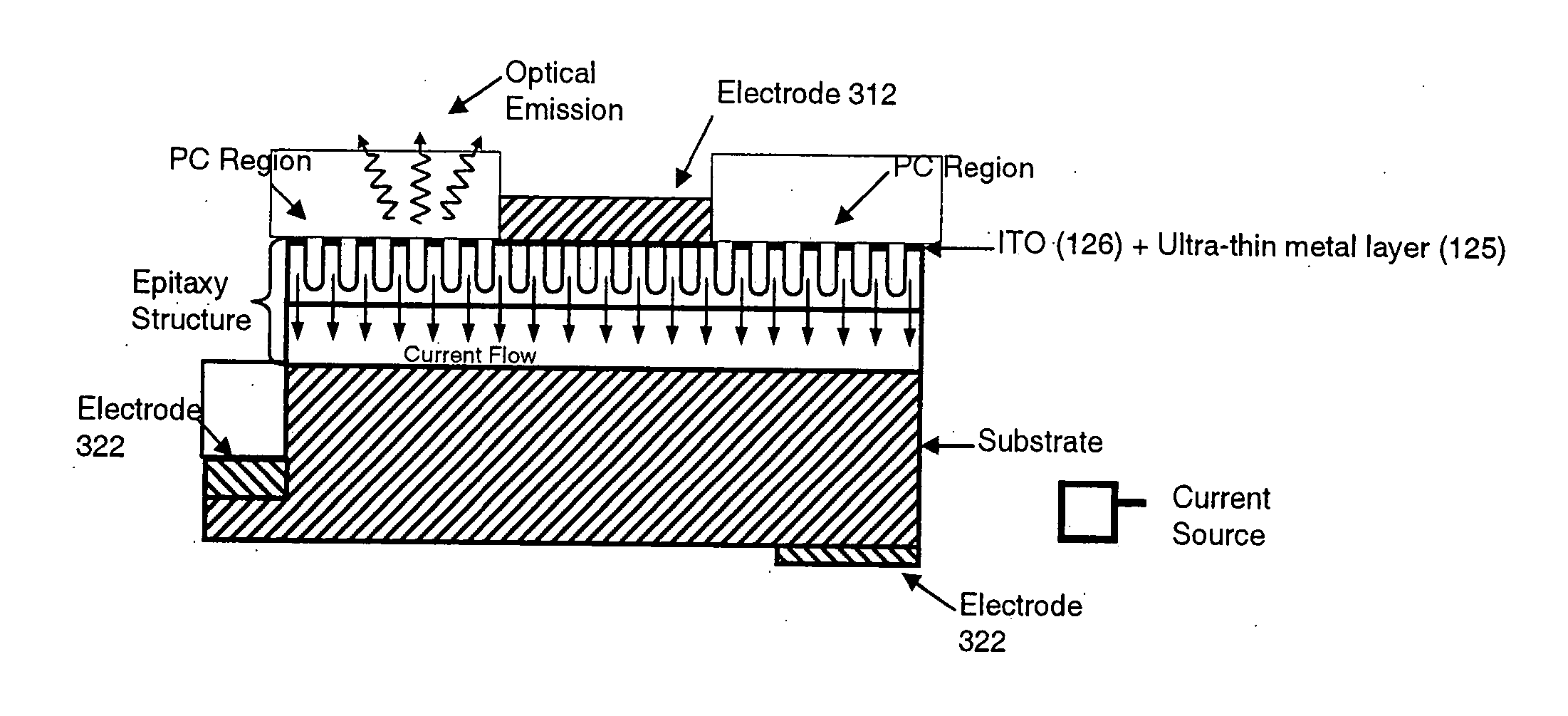
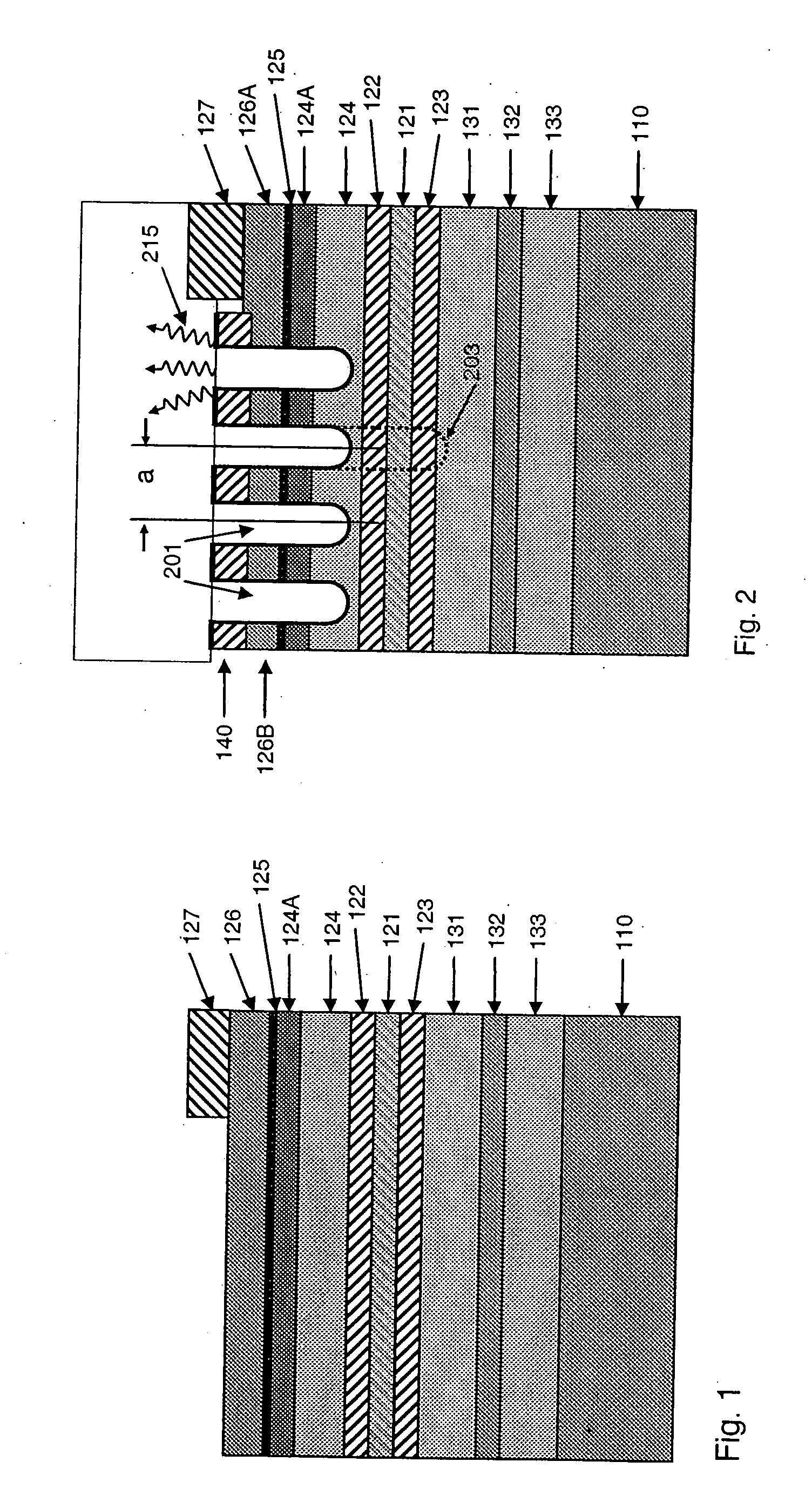
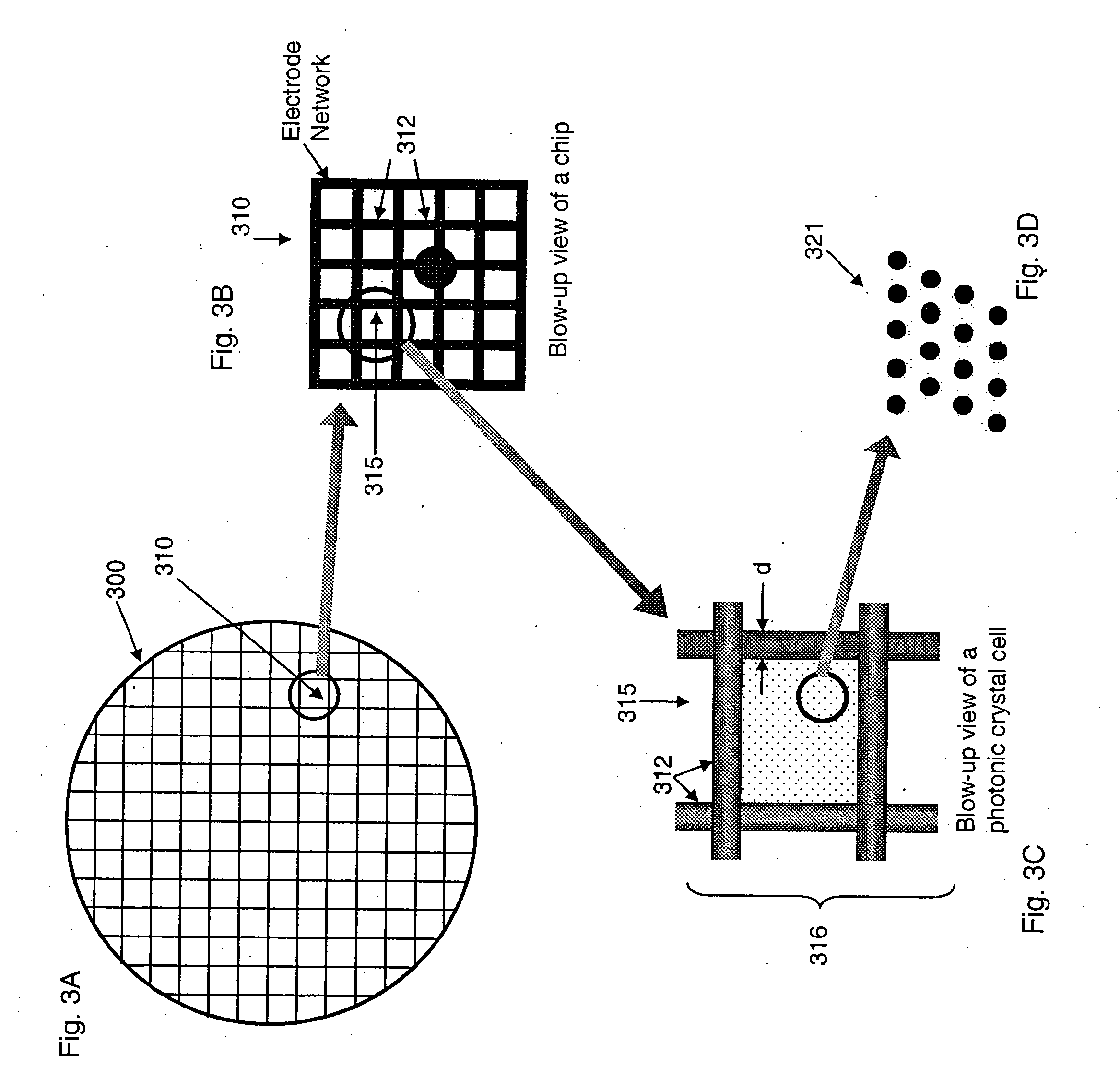
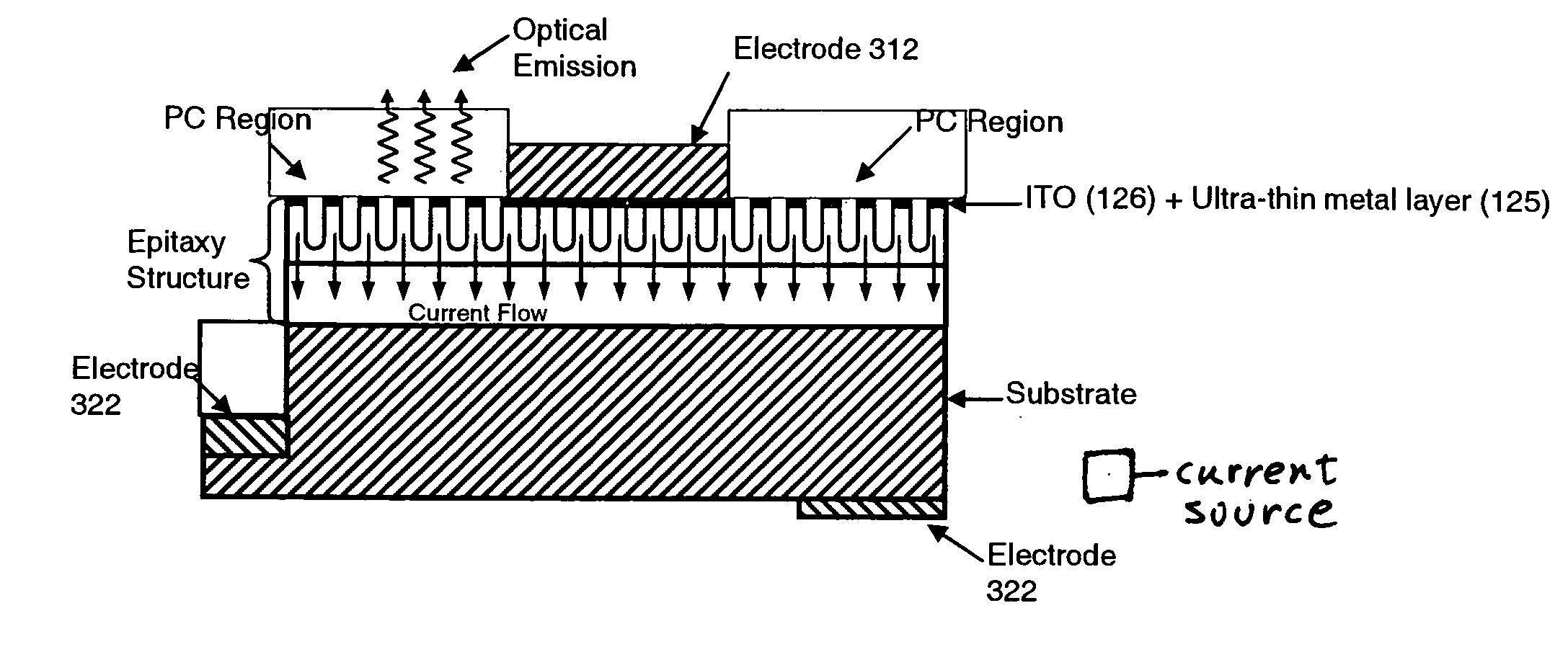
In an epitaxial structure of a solid state lighting system, electrical current injection into the active layer is used to excite the photon emission. The present invention employs a unique waveguide layer in the epitaxial structure for trapping the light generated by the active layer in the fundamental waveguide mode. Multiple photonic crystal regions with different characteristics located either outside or inside one or more current injection regions extract photons from the waveguide layer(s). The present invention creates solid state lighting with high optical output and high power efficiency.
Owner:DICON FIBEROPTICS
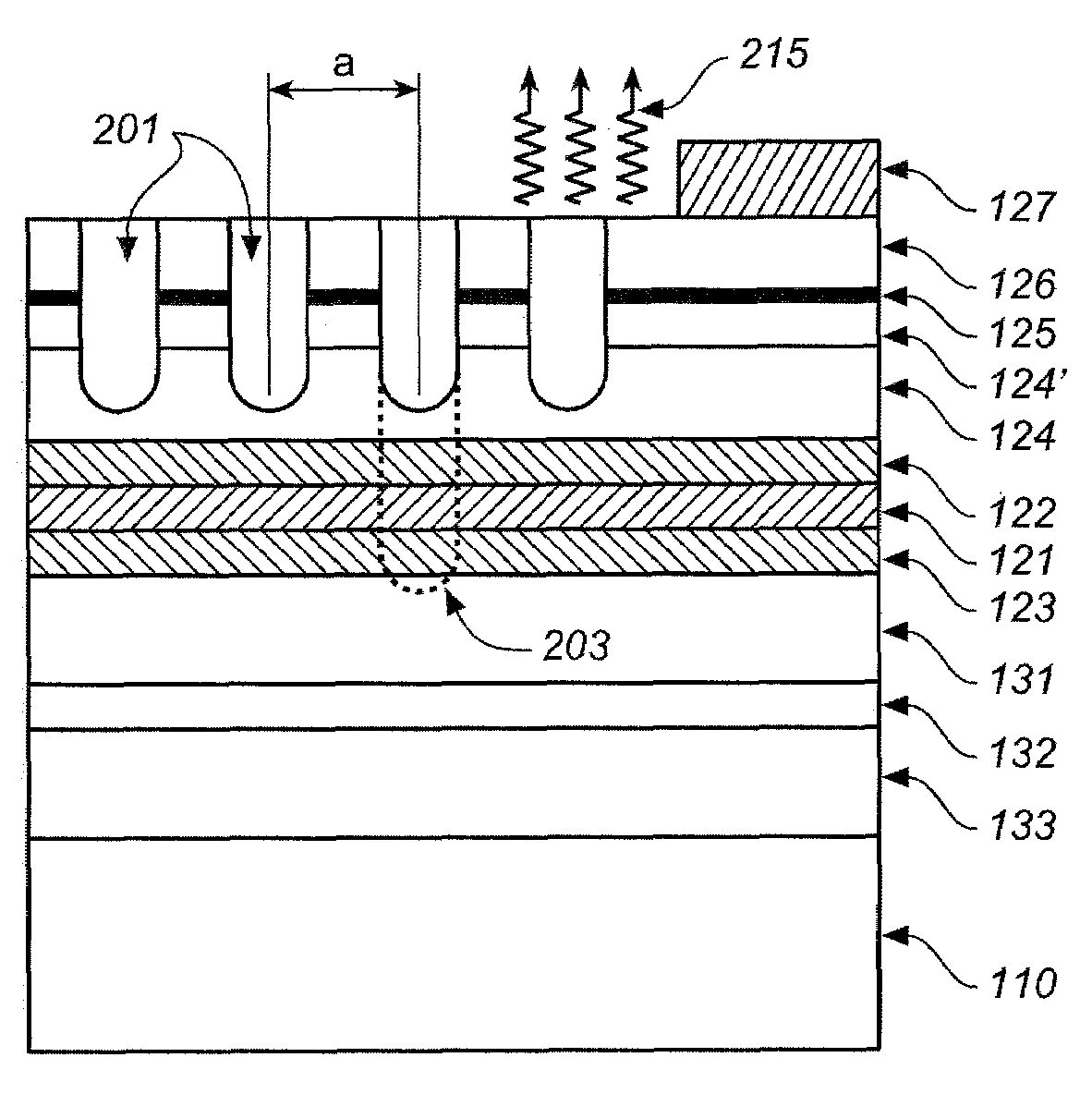
Light emitting system with high extraction efficency
ActiveUS20050173717A1Efficiently extractImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityRadiation
In an epitaxial structure of a solid state lighting system, electrical current injection into the active layer is used to excite the photon emission. The present invention employs a unique waveguide layer in the epitaxial structure for trapping the light generated by the active layer in the fundamental waveguide mode. Multiple photonic crystal regions located either outside or inside one or more current injection regions extract photons from the waveguide layer(s). This novel design optimizes the interplay of electrical pumping, radiation and optical extraction to increase the optical output to several times that of conventional LEDs. A transparent and conductive ITO layer is added to the surface of an epitaxial structure to reduce the interface reflection in addition to functioning as a current spreading layer. The present invention creates solid state lighting with high optical output and high power efficiency.
Owner:DICON FIBEROPTICS
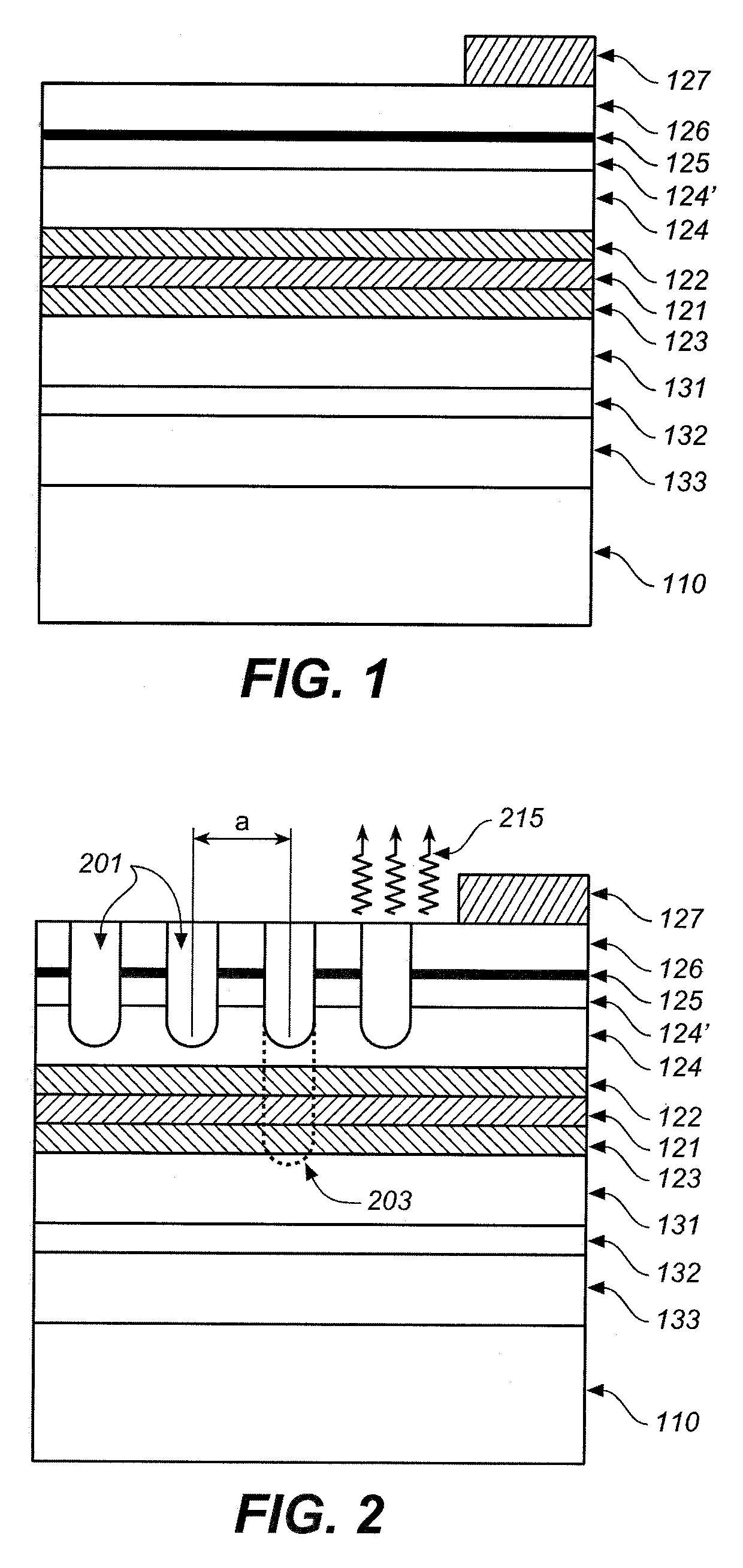
Light emitting system with high extraction efficency
ActiveUS7250635B2Improve performanceImprove light outputElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesElectricityPhoton emission
In an epitaxial structure of a solid state lighting system, electrical current injection into the active layer is used to excite the photon emission. The present invention employs a unique waveguide layer in the epitaxial structure for trapping the light generated by the active layer in the fundamental waveguide mode. Multiple photonic crystal regions located either outside or inside one or more current injection regions extract photons from the waveguide layer(s). This novel design optimizes the interplay of electrical pumping, radiation and optical extraction to increase the optical output to several times that of conventional LEDs. A transparent and conductive ITO layer is added to the surface of an epitaxial structure to reduce the interface reflection in addition to functioning as a current spreading layer. The present invention creates solid state lighting with high optical output and high power efficiency.
Owner:DICON FIBEROPTICS
Light emitting diode chip structure and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101582479AReduce crystal defectsQuality improvementSemiconductor devicesCrystallographic defectLight-emitting diode
The invention relates to a light emitting diode chip structure, comprising a sapphire substrate layer; wherein, the sapphire substrate layer is provided with triangular pyramid microstructures arranged periodically. The invention also relates to a manufacturing method of the light emitting diode chip structure, including the following steps: 1) a graph is transferred onto the sapphire substrate by applying dry etching technology; 2) the graph on the sapphire substrate is formed in periodically arranged triangular pyramid by applying wet etching. The invention can greatly reduce boundary reflection and internal absorption as periodically arranged high quality triangular pyramid microstructures are formed on the sapphire substrate; and crystal defect of the sapphire is greatly reduced after wet etching, thus high crystal quality epitaxial layer can be grown on the surface and the quality and luminous efficiency of the light emitting diode are greatly improved.
Owner:EPILIGHT TECH
Method for manufacturing LED chips
ActiveCN101515624AImprove luminous efficiencyImprovement of defects in epitaxial growthSemiconductor devicesLight-emitting diodeSemiconductor
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing LED chips, comprising the following steps: manufacturing convex-hull periodically arranged microstructures on the surface of a sapphire substrate, and forming a buffer layer on the upper surface of the substrate, an n-type semiconductor layer on the buffer layer, a luminous layer on one part of the n-type semiconductor layer, a p-type semiconductor layer on the luminous layer, and n-type and p-type electrodes on the other part of the n-type semiconductor layer and the p-type semiconductor layer respectively. The yurt-shaped periodically arranged microstructures on the substrate are capable of reducing boundary reflection and internal absorption, effectively improving the defect of epitaxial growth, thus increasing the luminous efficiency of the LED chips.
Owner:EPILIGHT TECH
Organic luminous component and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveCN101114697AImprove luminous efficiencyImprove luminous brightnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefractive indexMetal
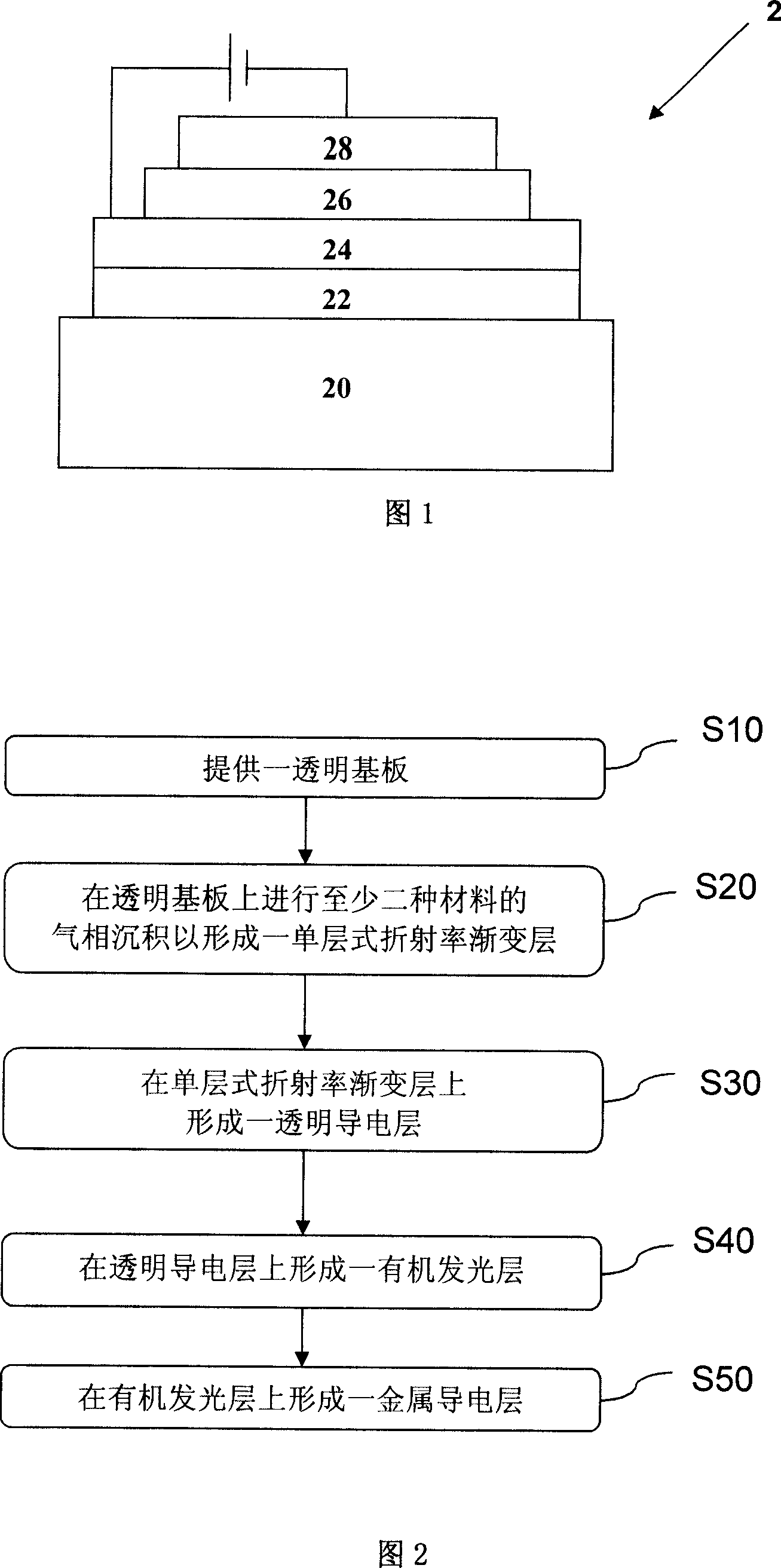
The invention provides an organic luminous component together with the related processing method, which is characterized in that on a transparent substrate, at least one dielectric material with low refractive index and a transparent conducting material or a dielectric material with high refractive index are in vapor deposition in order to form a single-layered gradual changing layer of refractive index on the transparent substrate and the gradual changing layer of refractive index is provided with a transparent conducting layer as anode that is provided with an organic luminous layer which is provided with a metal conducting layer as cathode. As the refractive index value of upper surface and lower surface of the gradual changing layer of refractive index is the same with that of the transparent substrate and the transparent conducting layer, and the refractive index value of lower surface of the gradual changing layer of refractive index increases following the vertical height and reaches the refractive index value of upper surface of the gradual changing layer of refractive index, the refractive index value of gradual changing layer of refractive index is a smoothing and continuous refractive index to effectively reduce interface reflection and improve luminous efficiency, luminous brightness, and prolong the service life of the organic luminous component.
Owner:GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
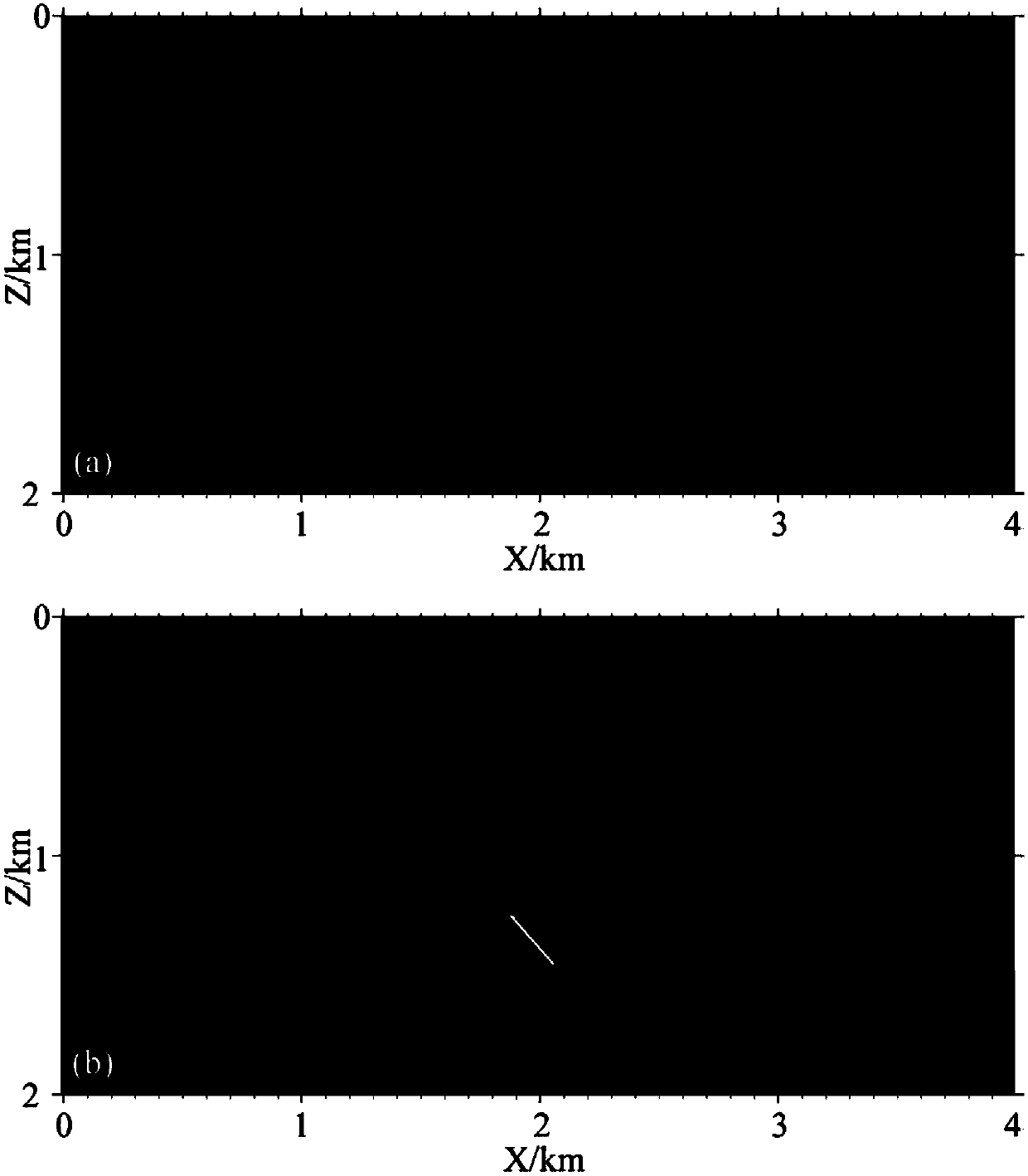
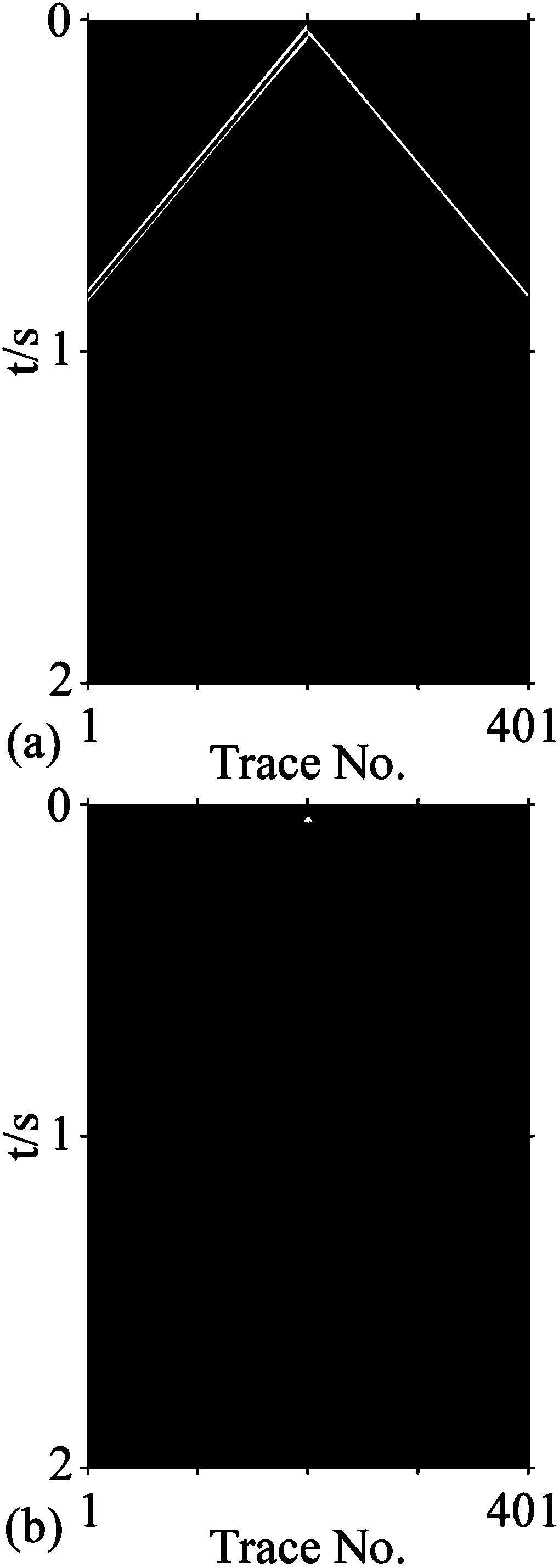
Quasi-spatial domain elastic wave equation-based finite difference calculation method
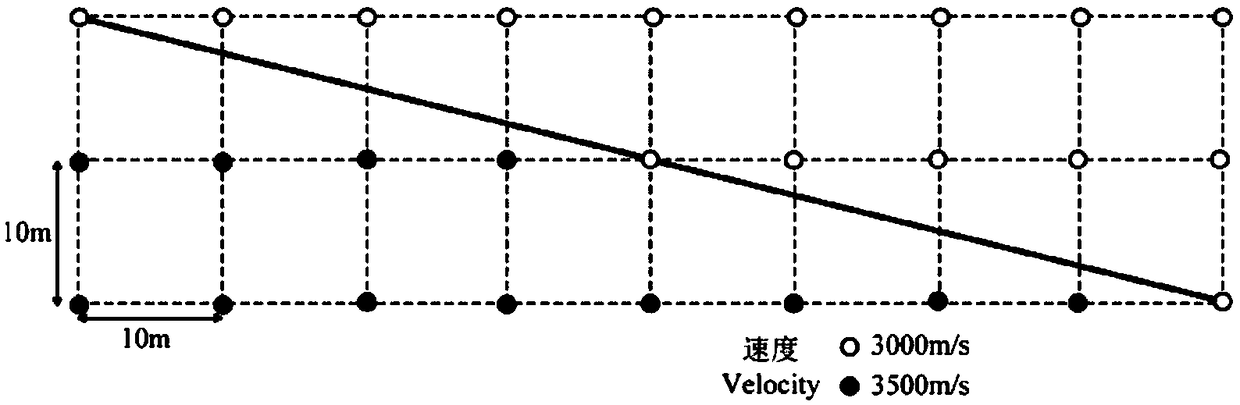
ActiveCN108108331AReduce the degree of mutationReduce the problem of speed interface shape distortionComplex mathematical operationsReverse timeImaging quality
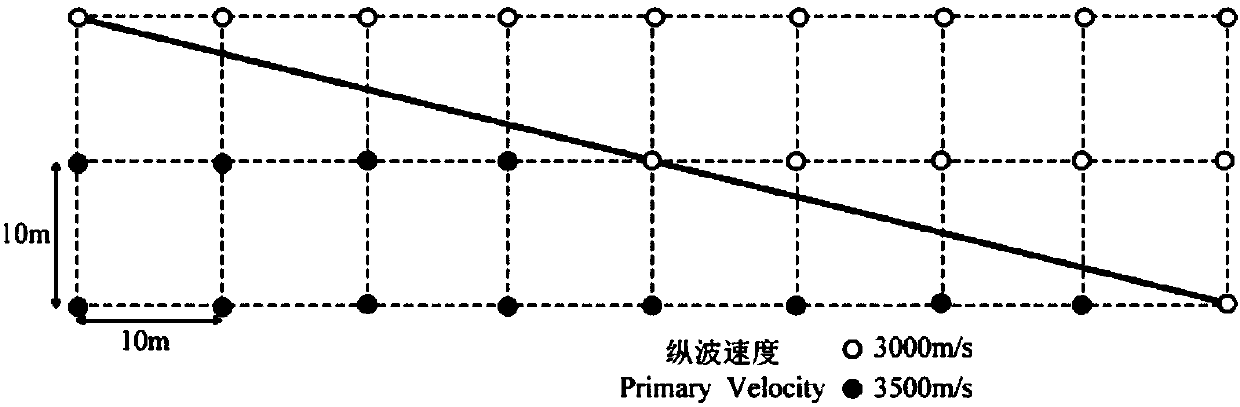
The invention discloses a quasi-spatial domain elastic wave equation-based finite difference calculation method, belongs to the field of seismic exploration, and mainly mains at converting a conventional elastic wave equation into a quasi-spatial domain elastic wave equation so as to convert equally spaced distance grid step lengths of spatial domains into non-equally spaced propagation time steplengths so that people can accurately calculate propagation times at two sides of speed interfaces on the basis of strictly defining speed models. On the basis, the equation and a 2N (N is a positiveinteger)-order precision finite different expression of a completely matched layer boundary condition are given, so that finite difference wave field prolongation of seismic waves in a reverse time migration process can be realized. According to the method, the problem that a speed interface, in a reverse time migration section, of the conventional elastic wave equation is distorted can be well solved; and moreover, through carrying out wave field prolongation on the basis of a quasi-spatial domain elastic wave equation, interface false scattering and inter-layer reflection waves can be obviously weakened, so that the migration imaging quality is further improved.
Owner:NAT DEEP SEA CENT +1
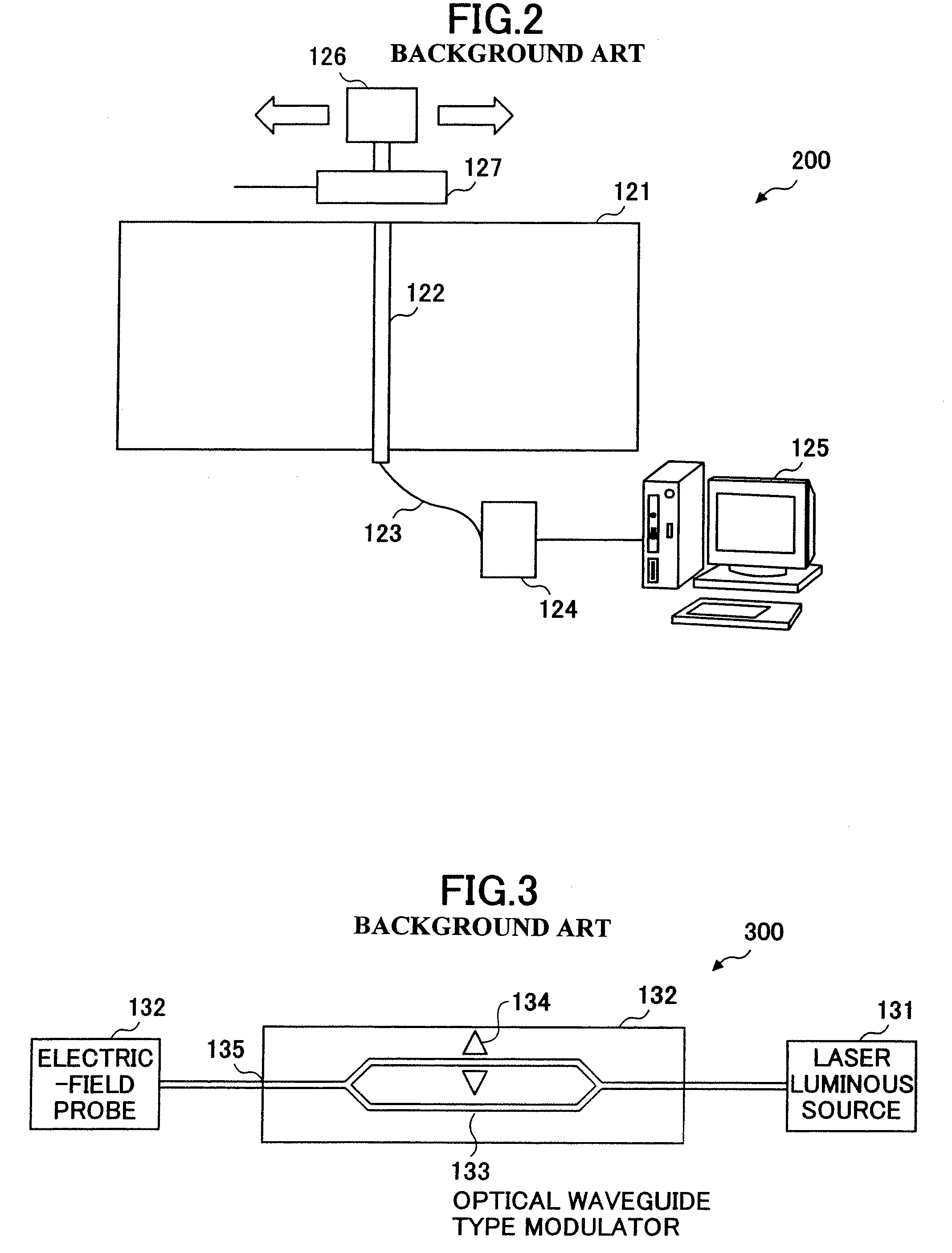
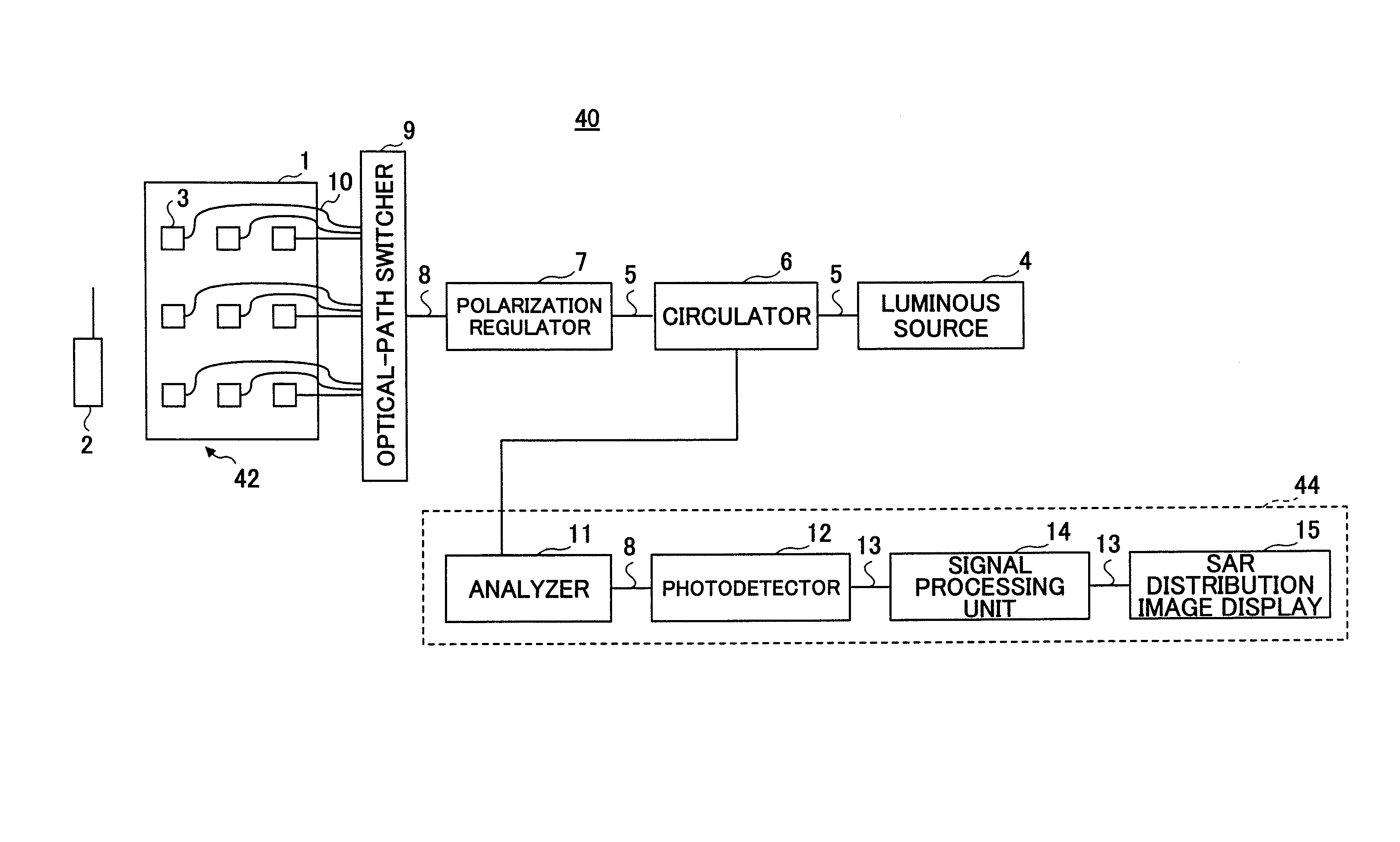
Specific absorption rate measuring system, and a method thereof
InactiveUS20070236229A1Accurate measurementReduce interface reflectionResistance/reactance/impedenceScattering properties measurementsMeasurement pointEnergy absorption
A biological tissue equivalent phantom unit to be used by the specific absorption rate measuring system for evaluating absorption of electromagnetic wave energy includes a biological tissue equivalent phantom for absorbing an electromagnetic wave. In addition, two or more electro-optical crystals are arranged at two or more measurement points in the biological tissue equivalent phantom. The electro-optical crystals have a dielectric constant that is approximately equal to that of the biological tissue equivalent phantom. Two or more optical fibers are laid in the biological tissue equivalent phantom for optically connecting each of the electro-optical crystals to an external destination.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC +1
OLED display panel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110993675AReduce the number of layersReduce interface reflectionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHemt circuitsDriver circuit
The invention provides an OLED display panel and a preparation method thereof. The OLED display panel comprises a display area and an electronic element setting area corresponding to the setting position of an electronic element, and the OLED display panel comprises a substrate, a driving circuit layer, a pixel definition layer, a blocking member, a first inorganic packaging layer, an organic packaging layer and a second inorganic packaging layer which are arranged in a stacked manner; wherein the pixel definition layer comprises a plurality of opening areas and a plurality of pixel definitionareas, and sub-pixels are formed in the opening areas; the blocking component is formed in the electronic element setting area and is arranged corresponding to the area without the sub-pixels; a first inorganic encapsulation layer formed on the sub-pixels and extending to cover the pixel definition layer and the blocking member; the organic packaging layer is formed on the first inorganic packaging layer and is arranged corresponding to the opening area in the electronic element arrangement area and the display area; the second inorganic packaging layer is formed on the organic encapsulationlayer and extends to cover the first inorganic packaging layer. By reducing the number of film layers above the pixel definition layer, the shooting effect of the under-screen camera is improved.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
Solar battery module
InactiveCN102683467AImprove efficiencyQuick responsePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHigh energyHigh energy photon
The invention provides a solar battery module comprising a solar battery cell, a wavelength conversion film, a glass layer and a rear panel, wherein the wavelength conversion film is manufactured on the solar battery cell; the glass layer is placed on the solar battery cell; and the rear panel is placed on the back face of the solar battery cell. The battery module utilizes the wavelength conversion film to change a solar spectrum so as to improve the efficiency of a solar battery. The wavelength conversion film is a rare-earth composite and has the function of converting high-energy photons including near-ultraviolet light, blue light and the like into one or more low-energy photons, such as green light, near-infrared photons and the like, so as to improve the efficiency of the solar battery. The absorption range of the wavelength conversion film is 200-500 nm and the emission range is 500-1100 nm. The thickness of the wavelength conversion film is in the range of 100 nanometers to 5 microns. The battery module also can utilize a DBR (Distributed Bragg Reflector) and / or an inversed-pyramid suede structure to reduce the reflectivity and improve the efficiency of the solar battery.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Fluid analysis device and related method
InactiveUS20140275863A1Easy to processWide applicabilityAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAuscultation instrumentsHerdComputer module
A device and method for analyzing characteristics of a fluid. The device is a bolus arranged to remain within the fluid for the analysis. The bolus includes a sensor module, a fluid analysis module, a fluid pumping module and a control and data transmission module. The sensor module includes a transducer element to generate acoustic signals and convert acoustic signals. The information derived from generating and receiving acoustic signals is used to obtain information about constituents and conditions of the fluid. That information may be transferred to a near or remote location for analysis. The device and analysis method are suitable for evaluating the health of animals. The device may be used in a telemedicine environment at an animal health facility. It may also be uploaded to a database for use in the analysis of a group of sources of fluid, such as a herd of cows.
Owner:VITAL HERD
Finite difference calculation method based on quasi-spatial domain acoustic wave equation
ActiveCN108051855AReduce the degree of mutationQuality improvementSeismic signal processingReverse timeWave field
The invention relates to a finite difference calculation method based on the quasi-spatial domain acoustic wave equation and belongs to the field of seismic exploration. The main idea of the method isto transform a conventional acoustic wave equation into a quasi-spatial domain acoustic wave equation so that the equally spaced 'distance' grid length steps in the spatial domain is transformed intonon-equally spaced 'propagation time' length steps. Thus, a user can accurately calculate the 'propagation time' on both sides of a velocity interface based on a strictly defined velocity model. Then, the equation of a 2N-order (N is a positive integer) precision finite difference expression for its perfectly matched layer boundary condition is given based on this. Accordingly, the finite difference wavefield extension of seismic waves in the process of reverse time migration can be realized. The method can well solve the problem of the shape distortion of the velocity interface in the reverse-time migration profile of a conventional acoustic wave equation. In addition, the wave field extension based on the quasi-spatial domain acoustic wave equation can significantly weaken the interfacepseudo-scattering and the inter-layer reflection wave so as to further improves the quality of offset imaging.
Owner:NAT DEEP SEA CENT +1
Liquid crystal display device
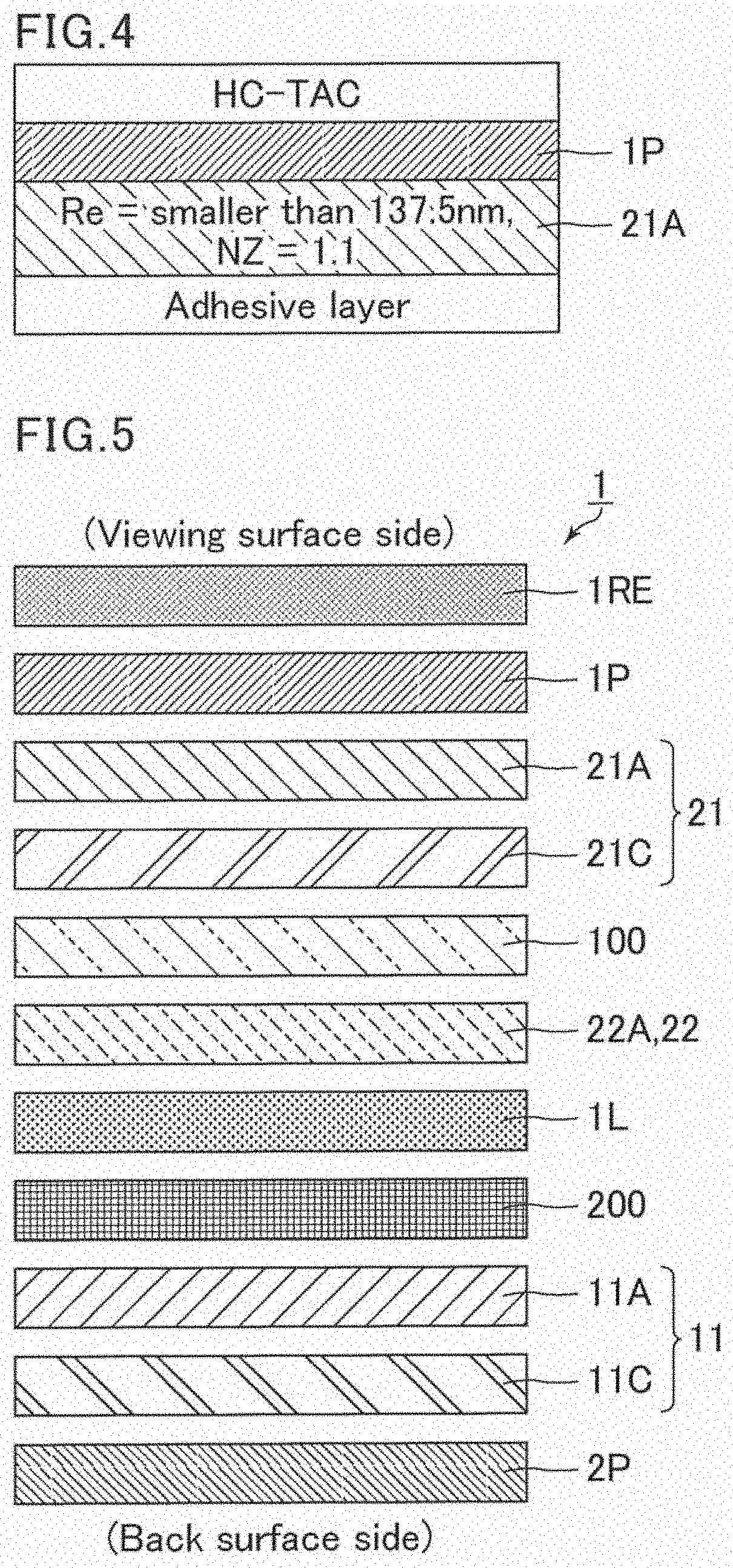
ActiveUS20200192165A1Prevent display defectsPoor recognitionPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A liquid crystal display device includes sequentially from a viewing surface side: a first polarizer; an out-cell retardation layer; a first substrate; an in-cell retardation layer; a horizontally aligned liquid crystal layer; a second substrate; and a second polarizer. The liquid crystal display device includes a viewing angle compensation film between the first polarizer and the out-cell retardation layer or between the second substrate and the second polarizer. The out-cell retardation layer is a laminate including sequentially from a viewing surface side: a first retardation layer having an NZ coefficient of 1.0-1.1 and an Re of 120 nm or greater and smaller than 137.5 nm; and a second retardation layer having an Re of 0-10 nm and an Rth of 80-150 nm. The in-cell retardation layer is a third retardation layer having an NZ coefficient of 0.7-1.4 and an Re of 120 nm or greater and smaller than 137.5 nm.
Owner:SHARP KK
Arthropod Repellent or Attractant Liquid Reservoir with Fill Indicator
ActiveUS20190090469A1Minimize surface area to volume ratioDecrease surface tension energyGaseous substancesAnimal repellantsSurface tension gradientDiffusion
A progressive liquid fill capacity indicator located inside a vapor diffusion membrane liquid reservoir that utilizes index refraction matching of liquid contact to components, dyes, and surface tension gradients. This fill capacity indicator is low cost and reliable. It enables users to visually assess readiness and remaining liquid capacity to deliver attraction, masking, and repulsion scent vapors from wearable and stationary devices to repel or attract mosquitos and arthropods.
Owner:ENERGY RELATED DEVICES
Specific absorption rate measuring system, and a method thereof
InactiveUS7511511B2Accurate measurementReduce interface reflectionResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis using microwave meansEnergy absorptionMeasurement point
A biological tissue equivalent phantom unit to be used by the specific absorption rate measuring system for evaluating absorption of electromagnetic wave energy includes a biological tissue equivalent phantom for absorbing an electromagnetic wave. In addition, two or more electro-optical crystals are arranged at two or more measurement points in the biological tissue equivalent phantom. The electro-optical crystals have a dielectric constant that is approximately equal to that of the biological tissue equivalent phantom. Two or more optical fibers are laid in the biological tissue equivalent phantom for optically connecting each of the electro-optical crystals to an external destination.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC +1
Touch display device and electronic apparatus
InactiveCN106484166ASolve the problem of poor outdoor visibilityReduce interface reflectionNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingVisibilityDisplay device
The invention provides a touch display device used for solving the problem that the outdoor visibility of a frame sticking type touch display device is poor under the influence of strong ambient light in the prior art. The invention relates to a touch display device comprising a first polarizer (2); a display panel (3) arranged on the first polarizer; a gap (4) arranged on the display panel; and a second polarizer (5) arranged on the gap. The touch display device further comprises a cover plate, wherein the cover plate is arranged on the outermost side face of the touch display device relative to the first polarizer. The invention further relates to an electronic apparatus comprising the touch display device described above.
Owner:TOP VICTORY INVESTMENTS
Medical needle
InactiveCN104219998AEasy to manufactureReduce interface reflectionDiagnostics using pressureSurgical needlesOptical measurementsBiomedical engineering
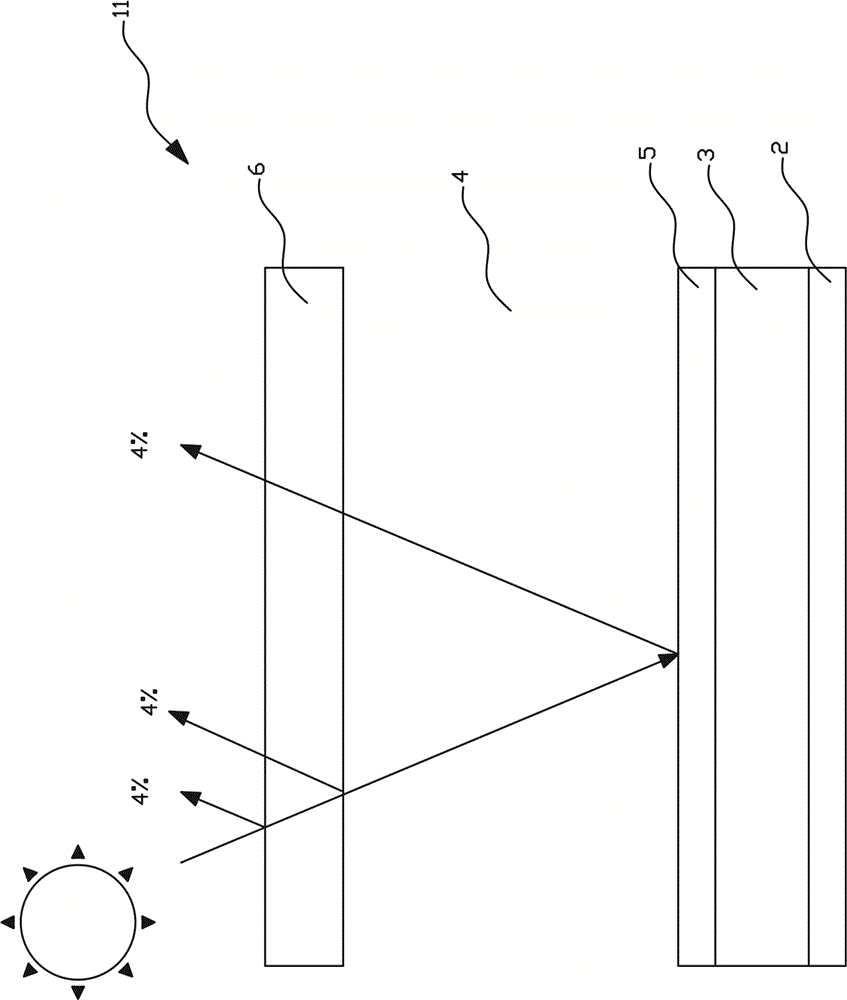
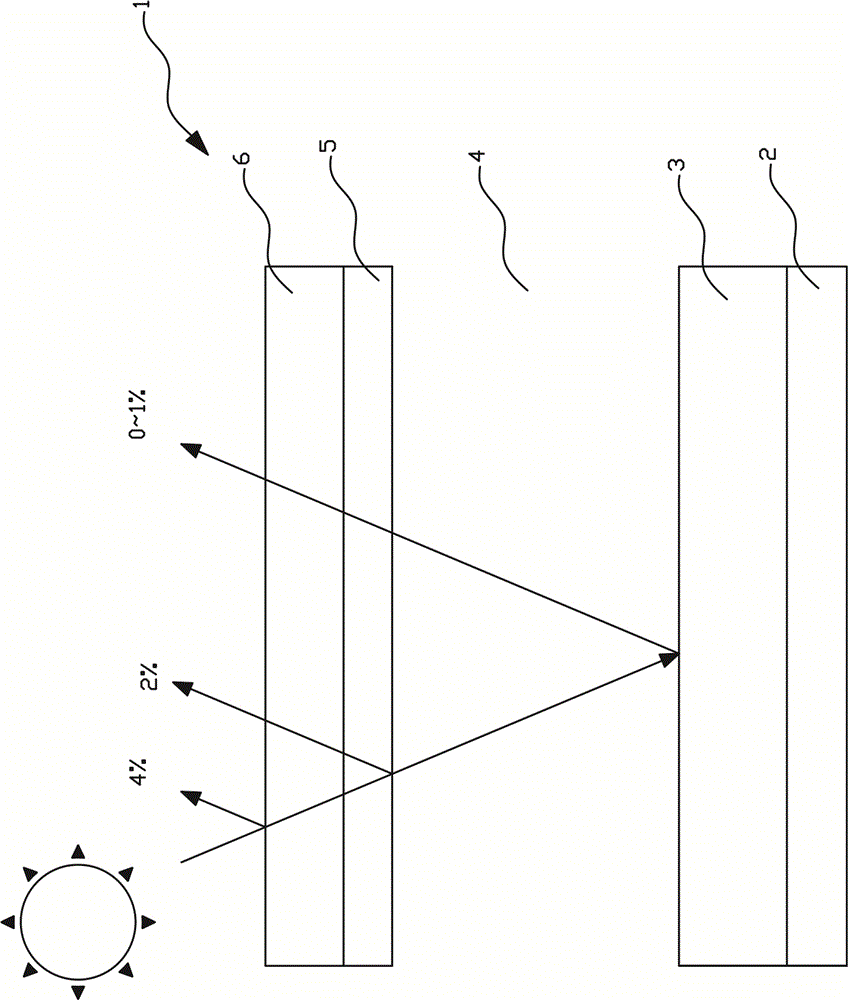
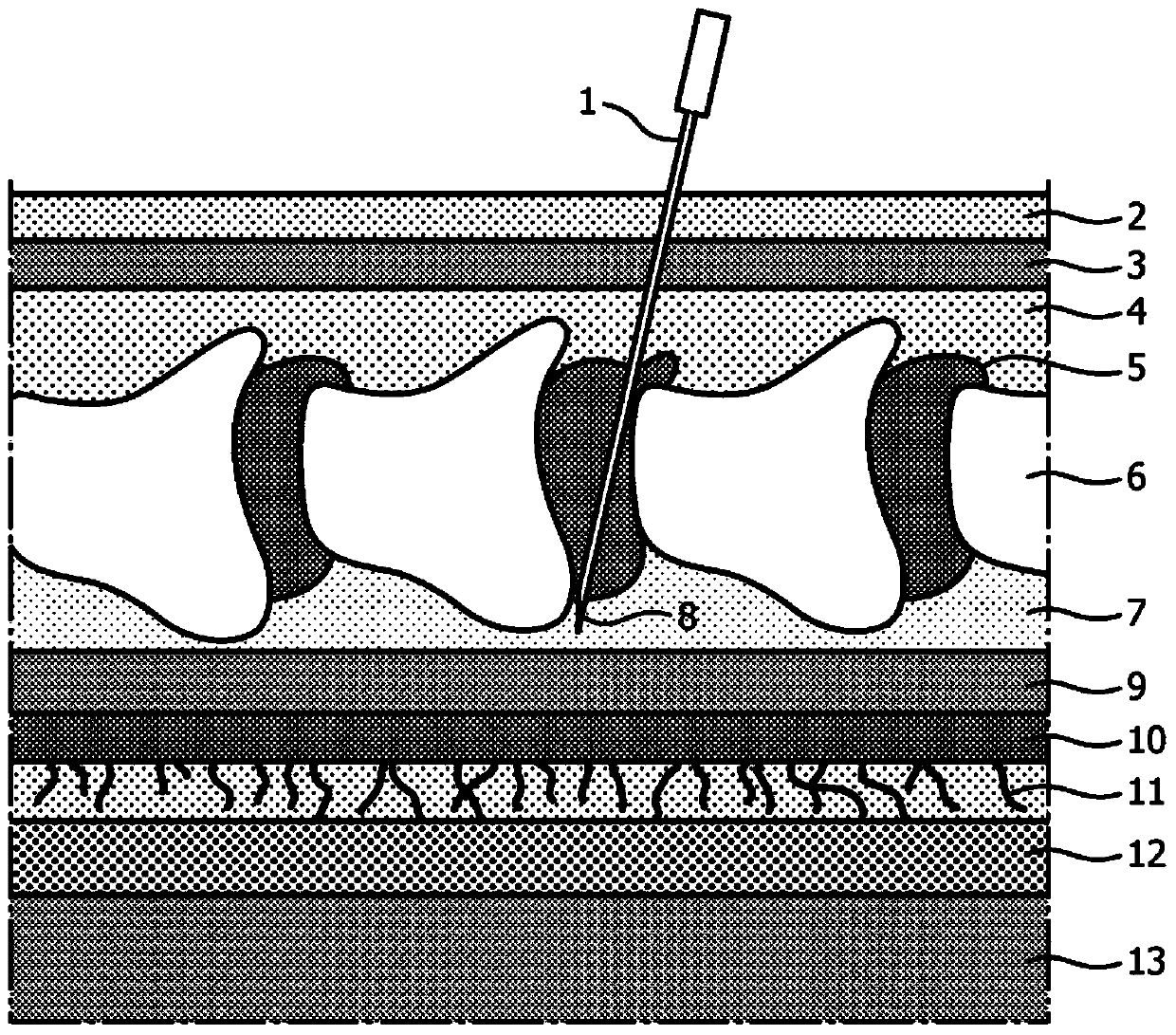
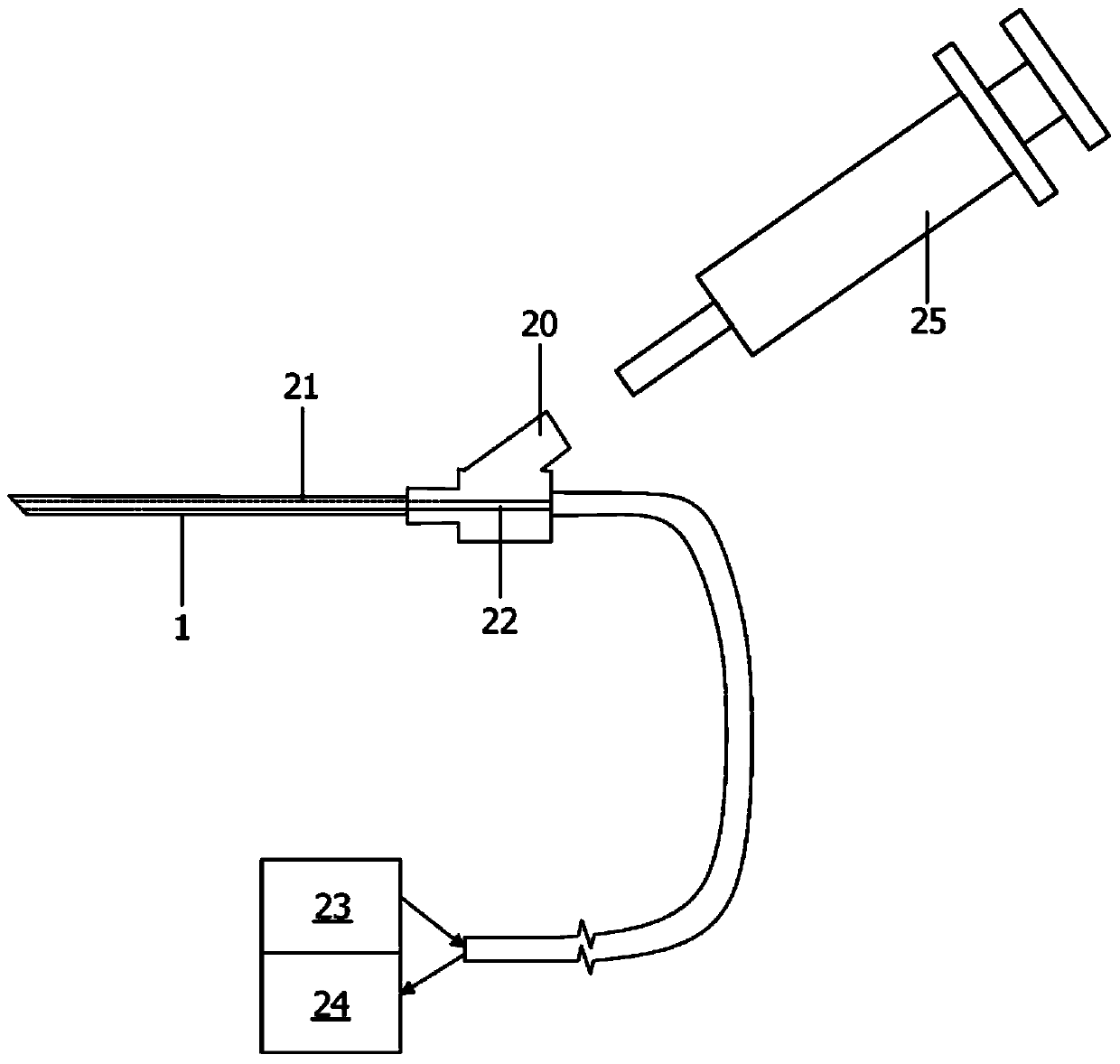
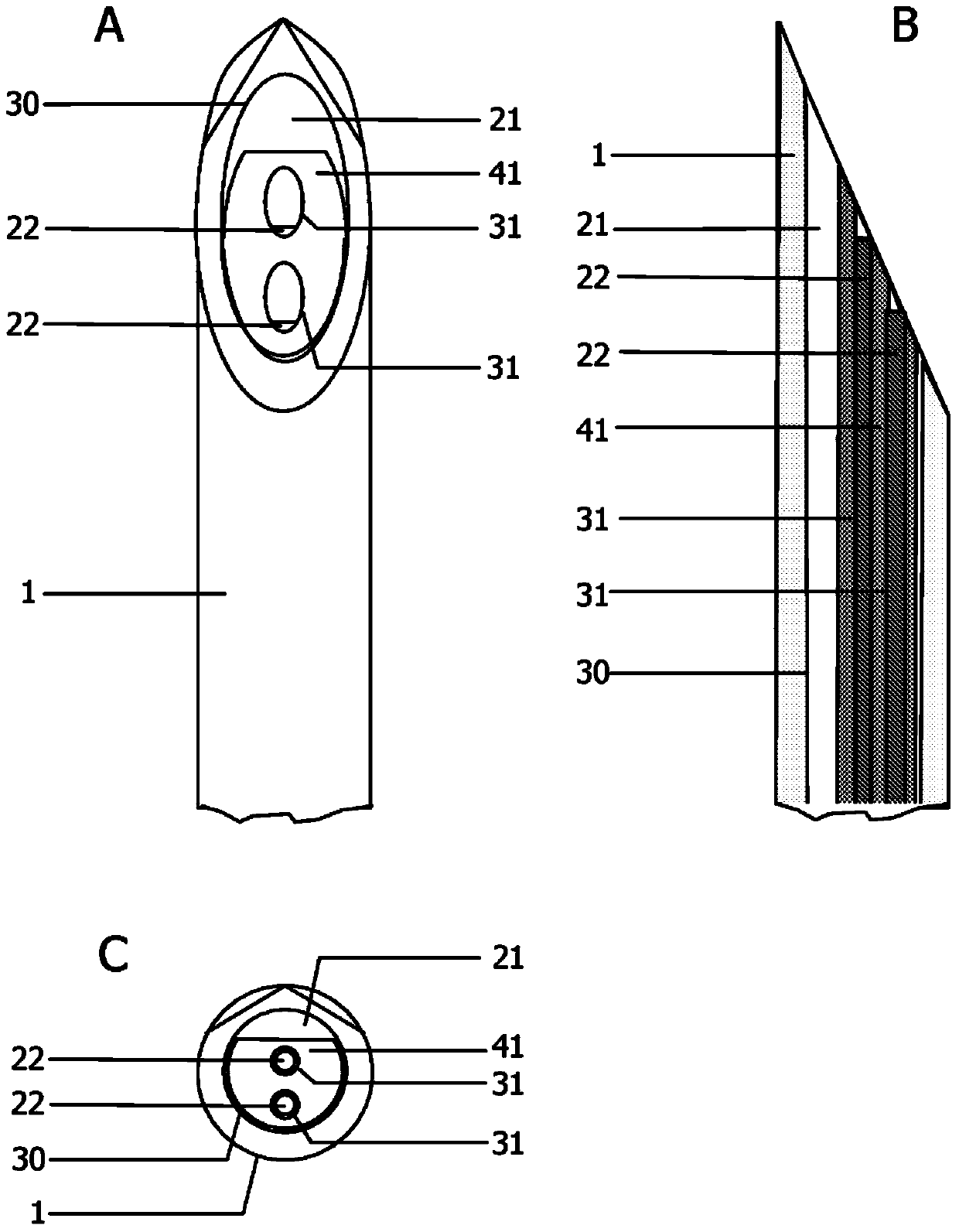
The present invention relates to a medical needle which comprises a needle (1) having at least one channel (21), at least one optical waveguide (22) and a syringe connector (20). The syringe connector (20) is in communication with the at least one channel (21) and permits further communication with an additional syringe (25), thereby permitting the correspondence of fluid between the syringe (25) and the tip of the needle (1). The optical waveguides (22) are arranged within the needle (1) in order to make optical measurements at the tip of the needle (1). The cross section of the distal end of the elongate tube (1) has a dividing line for each channel (21) which separates that channel (21) from the one or more optical waveguides (22).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Transparent uv-curable adhesive
InactiveUS20170166787A1Reduce interface reflectionPoor thicknessPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesGraft polymer adhesivesAdhesiveUltraviolet
A transparent ultraviolet curable adhesive is a solventless composition, based on a total weight of the composition, being composed of 35-65 wt % of a polyurethane (meth)acrylate resin, 30-60 wt % of a (meth)acrylate monomer, 0.1-5 wt % of an acrylate group-containing bisphenol fluorene derivative, 0.3-8 wt % of a photopolymerization initiator and 0.002-0.01 wt % of a vinyl silane coupling agent; and, the adhesive if cured has a refractive index of 1.52-1.56 very close to 1.52 for a glass thereof and has a visible light transmittance of 93-99 VLT (%) so suitable to be adhered to displays, transparent conductive film and touch panels.
Owner:NANYA PLASTICS CORP
Flexible intelligent dimming film with high visible light transmittance and heat insulation and preparation method of film
PendingCN111638610ASuppress interface reflectionHigh visible light transmittanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPhysicsElectrically conductive
The invention provides a flexible intelligent dimming film with visible light high transmittance and heat insulation. The flexible intelligent dimming film comprises a polymer dispersed liquid crystallayer and flexible transparent conductive electrodes symmetrically arranged at the two sides of the polymer dispersed liquid crystal layer. The flexible transparent conductive electrode comprises anoxide layer, an ultrathin metal layer and an oxide layer which are stacked in sequence, and the oxide layer is selected from TiO2 or Nb2O5. The flexible intelligent dimming film provided by the invention has high visible light transmittance and also has efficient heat insulation performance.
Owner:宁波材料所杭州湾研究院 +1
Noise reduction green belt constructed with photonic crystal
ActiveCN106416882AIncident EfficientPromote absorptionCultivating equipmentsCrystal structurePhotonic crystal structure
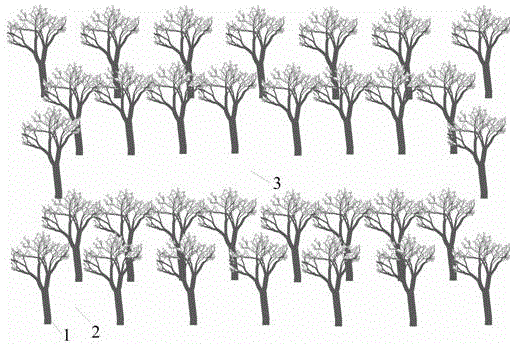
Provided is a noise reduction green belt constructed with photonic crystal, the green belt is constructed with a certain amount of trees planted according to a special array approach, and the array constitutes a definite photonic crystal structure. In the noise reduction green belt constructed with photonic crystal, the diffuser (1) is of green grass and trees, and the base (2) is air. The special array is a rectangular shape structure, and arranged in parallel by order using 2n rows of trees, the n rows of mutually parallel trees form a group, an empty row space of trees is left between two groups in n rows of trees, and a rectangular middle cavity (3) is formed, wherein n is 2-5. The said certain amount is 32-180. Crystal lattice coefficients are counted as coefficients of two type, three type, four type, and five type. The hollow cavity design effectively captures incident noise, reduces the out leakage of noise, thus strengthens sound insulation and noise reduction ability; the invention adopts grass and trees as the diffuser, to guarantee the function of green standardization and beautification, air purification, environment protection and energy saving; using air as the base can guarantee the smooth circulation of the air.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGXI ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD RES INST +1
Head mount display
A head mount display including two display units respectively disposed in front of eyes of a user is provided. Each of the display units includes a display device, a Fresnel lens, and a plurality of moth eye structures. The Fresnel lens is disposed between the display device and one of the eyes of the user. The plurality of moth eye structures are located on at least one surface between the display device and the one of the eyes of the user.
Owner:STARBREEZE AB
Polarization-independent type photo-isolator and magneto-optical crystal device manufacturing method
InactiveCN105044936AReduce interface reflectionLow insertion lossNon-linear opticsWedge angleOptical polarization
The invention relates to a polarization-independent type photo-isolator. The polarization-independent type photo-isolator comprises a first crystal wedge angle piece and a second crystal wedge angle piece. The first crystal wedge angle piece and the second crystal wedge angle piece are fixed to the two ends of a magneto-optical crystal device respectively in an optical cement mode. During forward transmission, the first crystal wedge angle piece divides parallel light from a first optical collimator into light o and light e. The magneto-optical crystal device rotates the polarization faces of the light o and the light e in the identical direction by 45 degrees, so that the light o and the light e are transmitted to the second crystal wedge angle piece, and the second crystal wedge angle piece refracts the light o and the light e to form two beams of parallel light; during reverse transmission, the second crystal wedge angle piece divides parallel light from the second optical collimator into light o and light e, and at the moment, a first included angle is formed between the light o and the light e. The magneto-optical crystal device rotates the polarization face of the light o and the light e in the identical direction and then transmits the light to the first crystal wedge angle piece, the first crystal wedge angle piece refracts the light o and the light e to form light e and light o, and at the moment, a second included angle is formed between the light e and the light o, wherein the second included angle is larger than the first included angle. The insertion loss of the polarization-independent type photo-isolator can be lowered.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
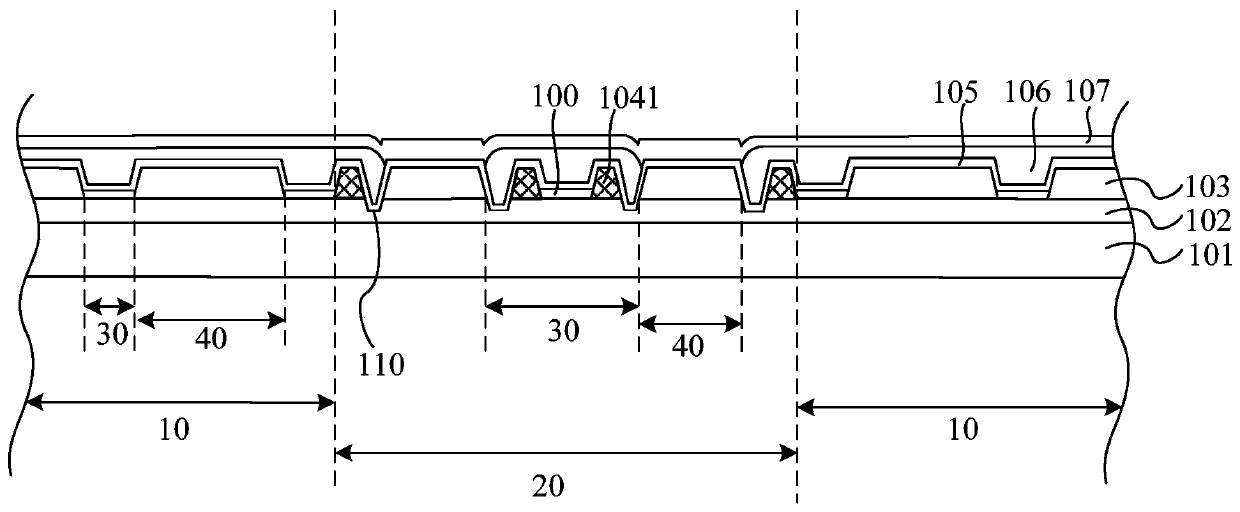
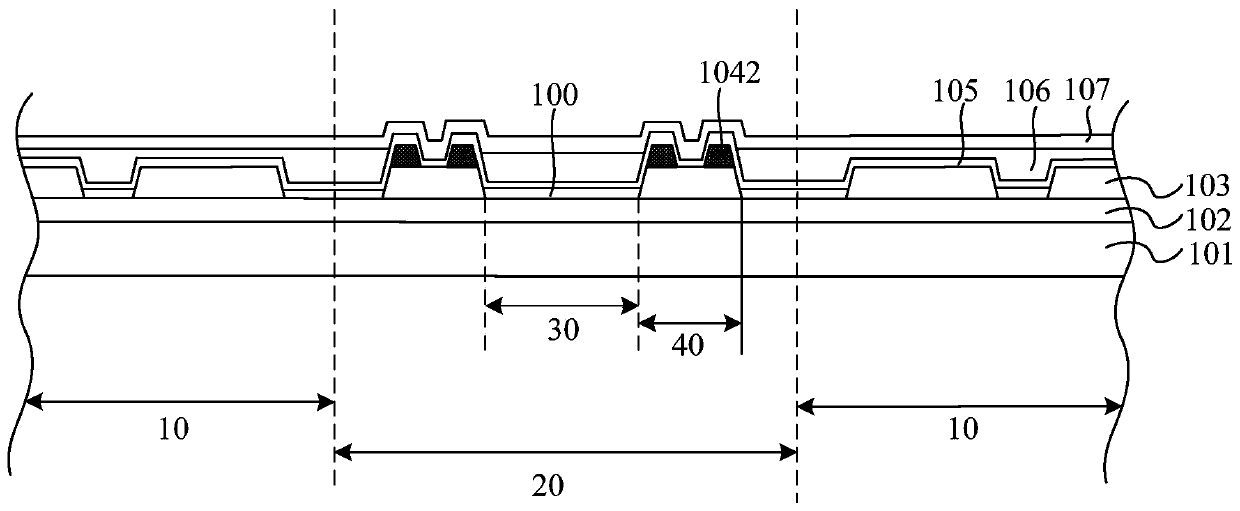
Microstructure glass substrate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113193059AReduce interface reflectionIncreased efficiency of access to photoemissive material layersFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesGratingSpectral sensitivity
The invention relates to a microstructure glass substrate and a preparation method thereof. The microstructure glass substrate comprises a glass substrate layer and a photoelectric emission material layer, and the glass substrate layer is provided with grating groove structures distributed in a grid shape; the grating groove structure is formed by mutually crossing a plurality of grooves in a first direction and a plurality of grooves in a second direction, openings of the grooves face the photon emergent surface, and the grooves are filled with oxide film layers. The size of the grooves and the thickness of the photoelectric emission material layer meet the following relation: W*(delta+W)=1000*D, W is the width of the grooves, delta is the distance between two adjacent grooves, and D is the thickness of the photoelectric emission material layer. The emergent surface of the glass substrate is subjected to microstructure processing to form a grating with a special material structure, so that the photon propagation path is increased, and the spectral sensitivity is improved.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Fluid analysis device and related method
InactiveUS20150241392A1Easy to processMonitor healthAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEndoradiosondesTransducerEngineering
A device and method for analyzing characteristics of a fluid. The device is a bolus arranged to remain within the fluid for the analysis. The bolus includes a sensor module, a fluid analysis module, a fluid pumping module and a control and data transmission module. The sensor module includes a transducer element to generate acoustic signals and convert acoustic signals. The information derived from generating and receiving acoustic signals is used to obtain information about constituents and conditions of the fluid. That information may be transferred to a near or remote location for analysis. The device and analysis method are suitable for evaluating the health of animals. The device may be used in a telemedicine environment at an animal health facility. It may also be uploaded to a database for use in the analysis of a group of sources of fluid, such as a herd of cows.
Owner:VITAL HERD
Head mounted display
InactiveCN113341563AReduce interface reflectionImprove display qualityOptical elementsFresnel lensOphthalmology
The invention provides a head mounted display. The head-mounted display comprises two display units which are respectively arranged in front of two eyes of a user. Each display unit comprises a display device, a Fresnel lens and a plurality of moth eye structures, the Fresnel lens is disposed between the display device and one eye of the user, and the plurality of moth eye structures are located on at least one surface between the display device and one of the eyes of the user.
Owner:STARVR CORP +1
Light collimator and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN108627994AReduce interface reflectionAvoid scratchesOptical elementsOptoelectronicsCollimator
The invention provides a light collimator and a manufacturing method thereof. The light collimator comprises a light transmitting substrate and a plurality of light absorbing patterns, wherein two opposite surfaces of the light transmitting substrate are respectively provided with a plurality of depressions which are arranged at intervals, and the depressions on the two surfaces are mutually aligned; and the light absorbing patterns are arranged in the depressions. The light collimator and the manufacturing method thereof provided by the invention can enable the light absorbing patterns on thetwo opposite surfaces of the light transmitting substrate to be mutually aligned, reduce the interface reflection and improve a problem of scratches.
Owner:FOCALTECH SMART SENSORS CO LTD
Component gradually changed alloy absorption layer of pyroelectric detector and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107359234ALow refractive indexSolve the problem of high reflectivityThermoelectric device with dielectric constant thermal changePyroelectric detectorsRefractive index
The invention discloses a component gradually changed alloy absorption layer of a pyroelectric detector and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of pyroelectric detectors. The aim of the invention is to provide the component gradually changed alloy absorption layer of the pyroelectric detector and the preparation method thereof, so as to solve the problem of high reflectivity in the infrared band of the absorption layer prepared by means of the nickel chromium or other alloy materials in the prior art. The component gradually changed alloy absorption layer of the pyroelectric detector comprises a bottom metal film, a middle layer metal film and a top layer metal film arranged on the top of the sensitive element successively from the bottom to the top, and the refractive indexes of which are gradually decreased. The preparation method of the component gradually changed alloy absorption layer of the pyroelectric detector comprises the following steps: preparing the bottom metal film on the top of sensitive element; preparing the middle layer metal film on the bottom metal film, and the refractive index of the middle layer metal film is smaller than the refractive index of the bottom metal film; and preparing the top layer metal film on the middle layer metal film, and the refractive index of the top metal film is smaller than that of the middle layer metal film. The invention is applied to the pyroelectric detector.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Manufacturing method for light-emitting diode chip substrate structure
ActiveCN101567415BOvercomes the inability to form high-quality microstructure patternsClear patternSemiconductor devicesEngineeringLight-emitting diode
The invention provides a manufacturing method for a light-emitting diode chip substrate structure, which comprises the following steps of: forming a metal layer on the surface of a substrate; forming a photoresist film layer on the obtained metal layer; back washing the obtained photoresist film layer by utilizing the backwash technology; irradiating the photoresist film layer by utilizing deep ultraviolet; causing the obtained photoresist film layer to back wash and volatilize the solvent in the photoresist film layer completely by utilizing the backwash technology; and transferring a patternon the photoresist film layer to a substrate by etching so as to form a plurality of convex microstructures on the surface of the substrate. The method can manufacture the substrate structure with good microstructure, thus reducing boundary reflection and internal absorption of the light-emitting diode chip, improving the defect of epitaxial growth and improing the chip luminous efficiency.
Owner:EPILIGHT TECH
Method for manufacturing LED chip substrate structure
ActiveCN101515626BOvercomes the inability to form high-quality microstructure patternsImprove luminous efficiencySemiconductor devicesBond energyInductively coupled plasma
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing an LED chip substrate structure, comprising the following steps: plating a layer of metal layer on the surface of a sapphire substrate, forming a layer of photoresist film layer on the metal layer, patterning the photoresist film layer using the photoetching technology to form the desirable patterns, melting the photoresist film layer using the reflux technology to form a plurality of convex hulls; and transmiting the profiles of the convex hulls on the substrate using the inductively coupled plasma etching process to form convex-hull microstructures on the substrate. By plating a layer of metal on the substrate, the influence from the bond energy of the sapphire substrate to the photoresist can be isolated, therefore, the photoresist iscapable of refluxing more ideal patterns on the surface of the metal layer to help make good-quality substrates with microstructural patterns, reduce the internal absorption and boundary reflection of the LED chips, improve the defect of epitaxial growth, and increase the luminous efficiency of chips.
Owner:EPILIGHT TECH
A Finite Difference Calculation Method Based on Pseudospace Domain Acoustic Wave Equation
ActiveCN108051855BReduce the degree of mutationQuality improvementSeismic signal processingReverse timeWave field
The invention relates to a finite difference calculation method based on the quasi-spatial domain acoustic wave equation and belongs to the field of seismic exploration. The main idea of the method isto transform a conventional acoustic wave equation into a quasi-spatial domain acoustic wave equation so that the equally spaced 'distance' grid length steps in the spatial domain is transformed intonon-equally spaced 'propagation time' length steps. Thus, a user can accurately calculate the 'propagation time' on both sides of a velocity interface based on a strictly defined velocity model. Then, the equation of a 2N-order (N is a positive integer) precision finite difference expression for its perfectly matched layer boundary condition is given based on this. Accordingly, the finite difference wavefield extension of seismic waves in the process of reverse time migration can be realized. The method can well solve the problem of the shape distortion of the velocity interface in the reverse-time migration profile of a conventional acoustic wave equation. In addition, the wave field extension based on the quasi-spatial domain acoustic wave equation can significantly weaken the interfacepseudo-scattering and the inter-layer reflection wave so as to further improves the quality of offset imaging.
Owner:NAT DEEP SEA CENT +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com