Quasi-spatial domain elastic wave equation-based finite difference calculation method
An elastic wave equation and finite difference technology, which is applied in the field of finite difference calculation based on the elastic wave equation in the quasi-space domain, can solve the problems of poor imaging effect, little research in the field of elastic wave equation, and large error in Poynting vector calculation.
Active Publication Date: 2018-06-01
NAT DEEP SEA CENT +1
View PDF8 Cites 8 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
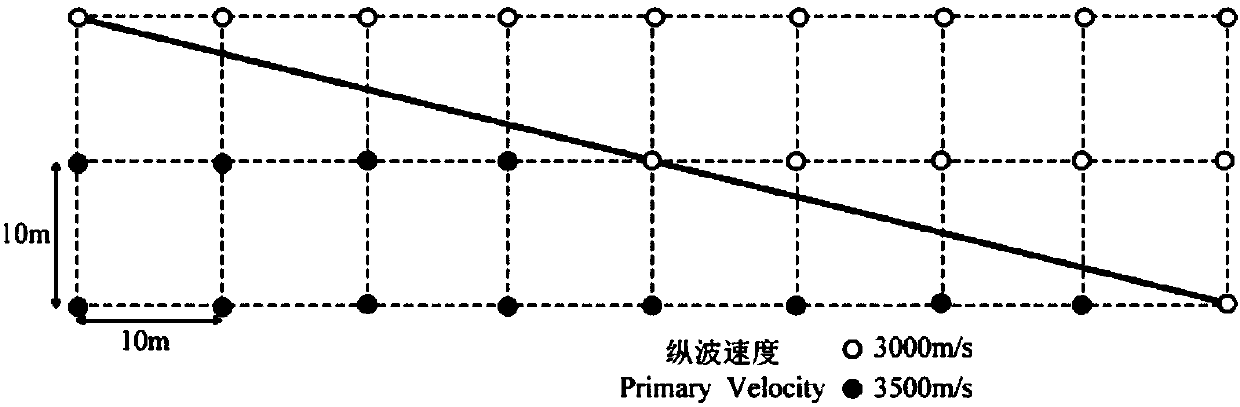
In order to reduce the influence of interlayer reflection waves, Baysal et al. derived the non-reflection acoustic wave equation under the assumption that the wave impedance of the underground medium is constant, and the effect of suppressing interlayer reflection is only good at vertical incidence; He Bingshou et al. Arbitrary wide-angle acoustic wave equation reverse time migration technology, but the imaging effect of this method is poor in shallow layers; Yoon et al. In the application of the structural area, the calculation error of the Poynting vector is relatively large
[0005] It can be seen that the current methods have limitations in solving interface distortion and suppressing interlayer reflection waves, and there is still little research in the field of elastic wave equations
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
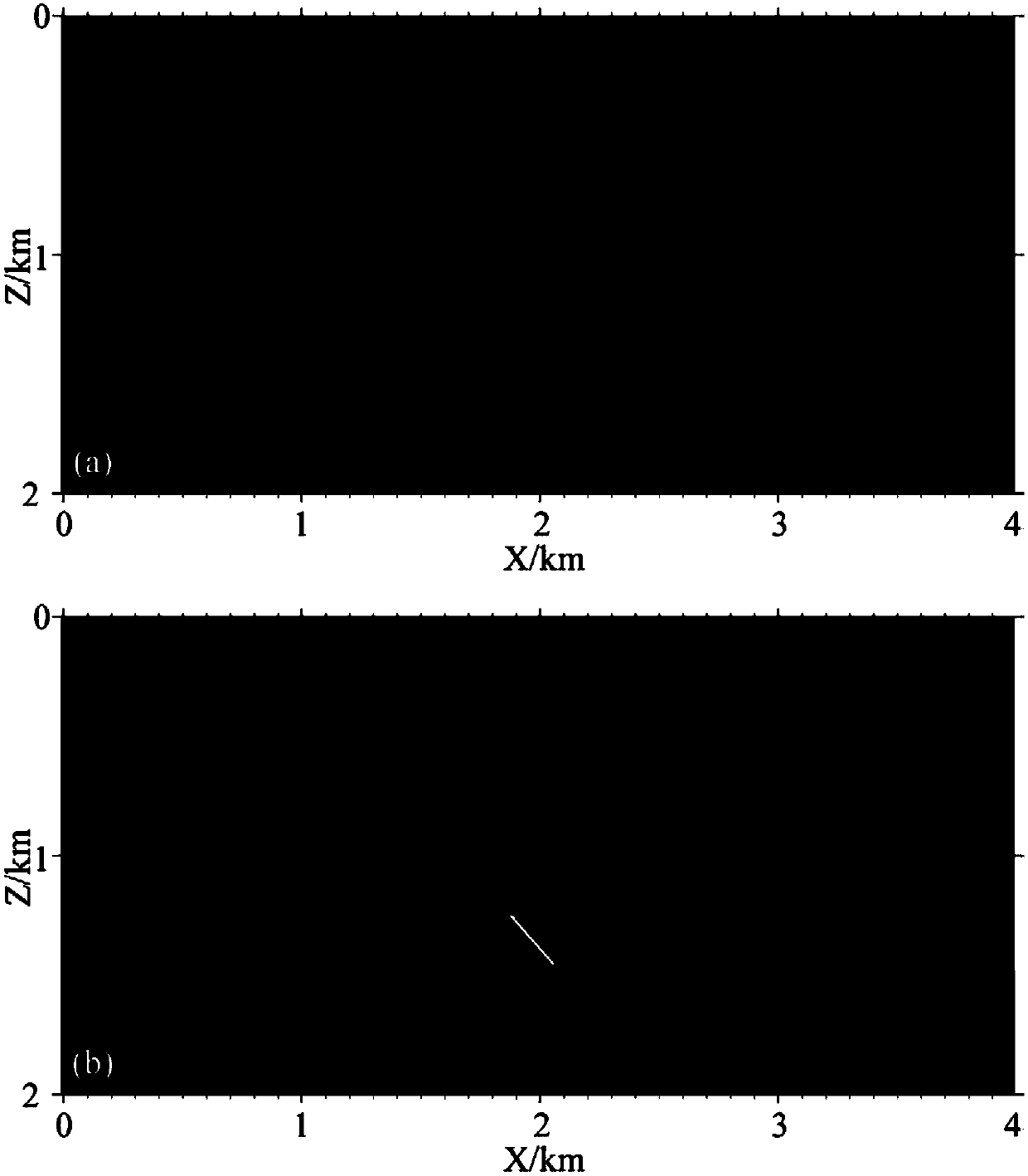
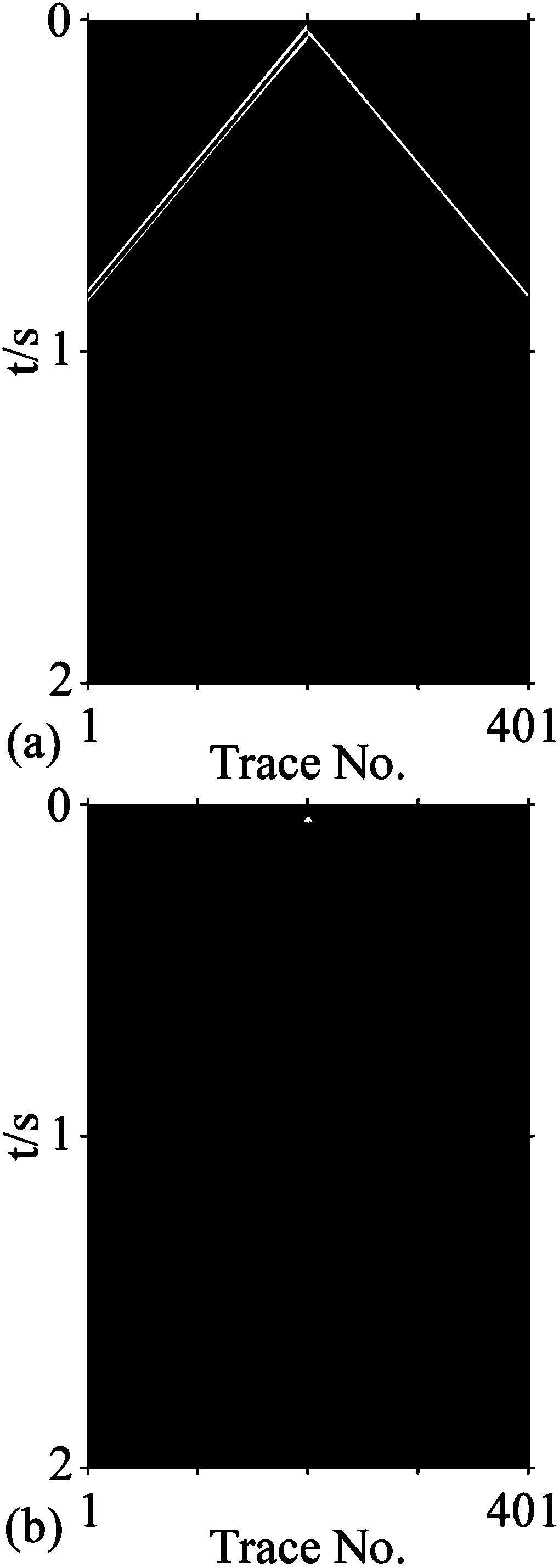
[0056] The main purpose of this experiment is to verify the effectiveness of the finite-difference calculation method for elastic wave equations in quasi-space domain in solving velocity interface distortion and suppressing interface false scattering and interlayer reflection waves in reverse time migration.
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Login to View More
Abstract
The invention discloses a quasi-spatial domain elastic wave equation-based finite difference calculation method, belongs to the field of seismic exploration, and mainly mains at converting a conventional elastic wave equation into a quasi-spatial domain elastic wave equation so as to convert equally spaced distance grid step lengths of spatial domains into non-equally spaced propagation time steplengths so that people can accurately calculate propagation times at two sides of speed interfaces on the basis of strictly defining speed models. On the basis, the equation and a 2N (N is a positiveinteger)-order precision finite different expression of a completely matched layer boundary condition are given, so that finite difference wave field prolongation of seismic waves in a reverse time migration process can be realized. According to the method, the problem that a speed interface, in a reverse time migration section, of the conventional elastic wave equation is distorted can be well solved; and moreover, through carrying out wave field prolongation on the basis of a quasi-spatial domain elastic wave equation, interface false scattering and inter-layer reflection waves can be obviously weakened, so that the migration imaging quality is further improved.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention belongs to the field of seismic exploration, and in particular relates to a finite difference calculation method based on an elastic wave equation in a quasi-space domain. Background technique [0002] Seismic exploration is currently the most effective geophysical method for proving underground geological structures, and it mainly includes three links: seismic information acquisition, data processing, and result interpretation. Seismic data processing is an important bridge connecting information acquisition and result interpretation. For a long time, precise subsurface structural migration imaging has been a research hotspot in seismic data processing. [0003] In the field of migration imaging, reverse time migration imaging based on the two-way wave equation theory is recognized as an accurate method. This technical method is generally applied to an important numerical calculation method - the finite difference method in the current...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): G06F17/11
CPCG06F17/11
Inventor 张晓波王修田宋鹏谭军夏冬明姜秀萍赵波李金山刘保华于凯本杨志国于盛齐宗乐贾永刚
Owner NAT DEEP SEA CENT
Features
- Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com