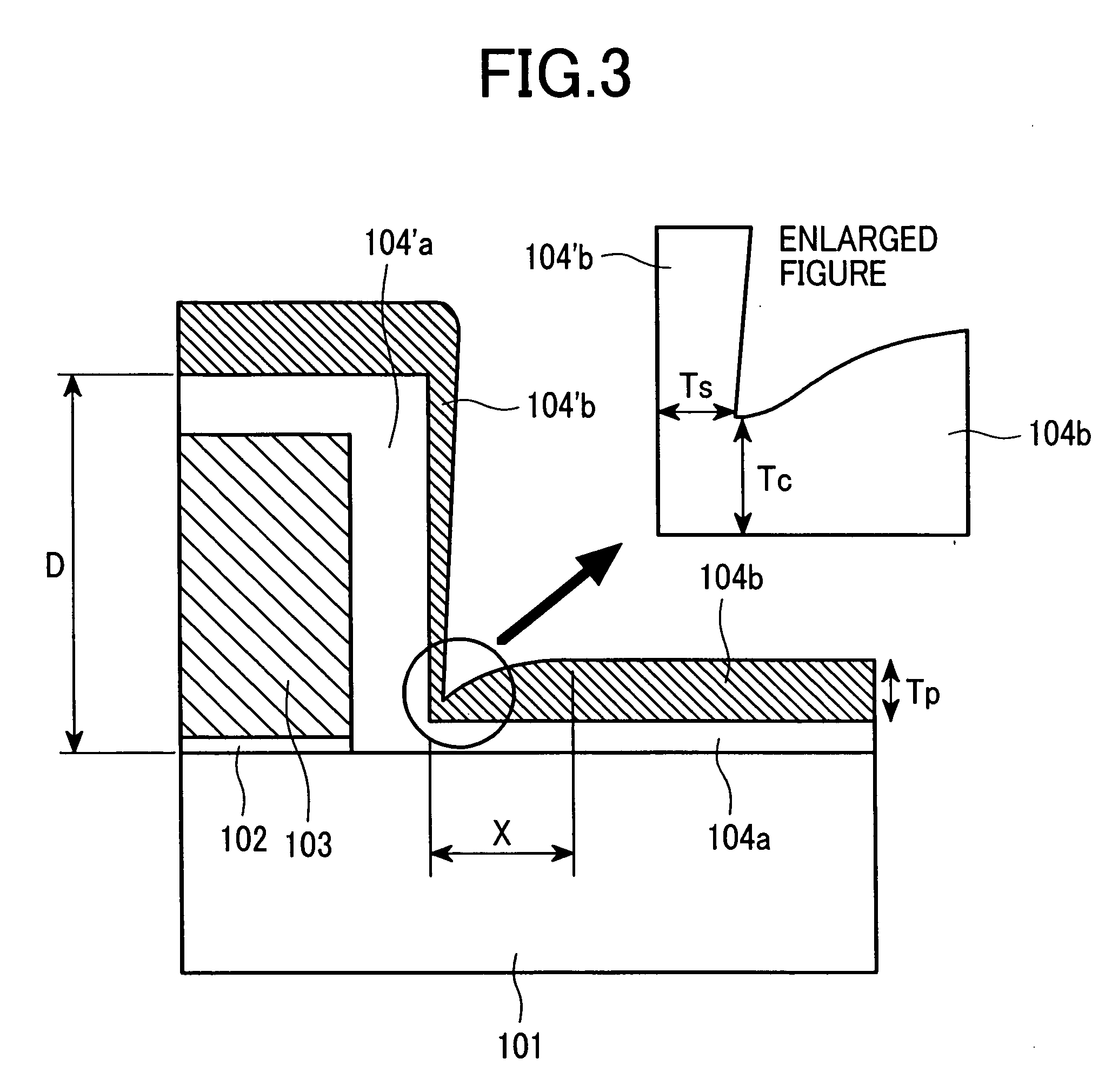
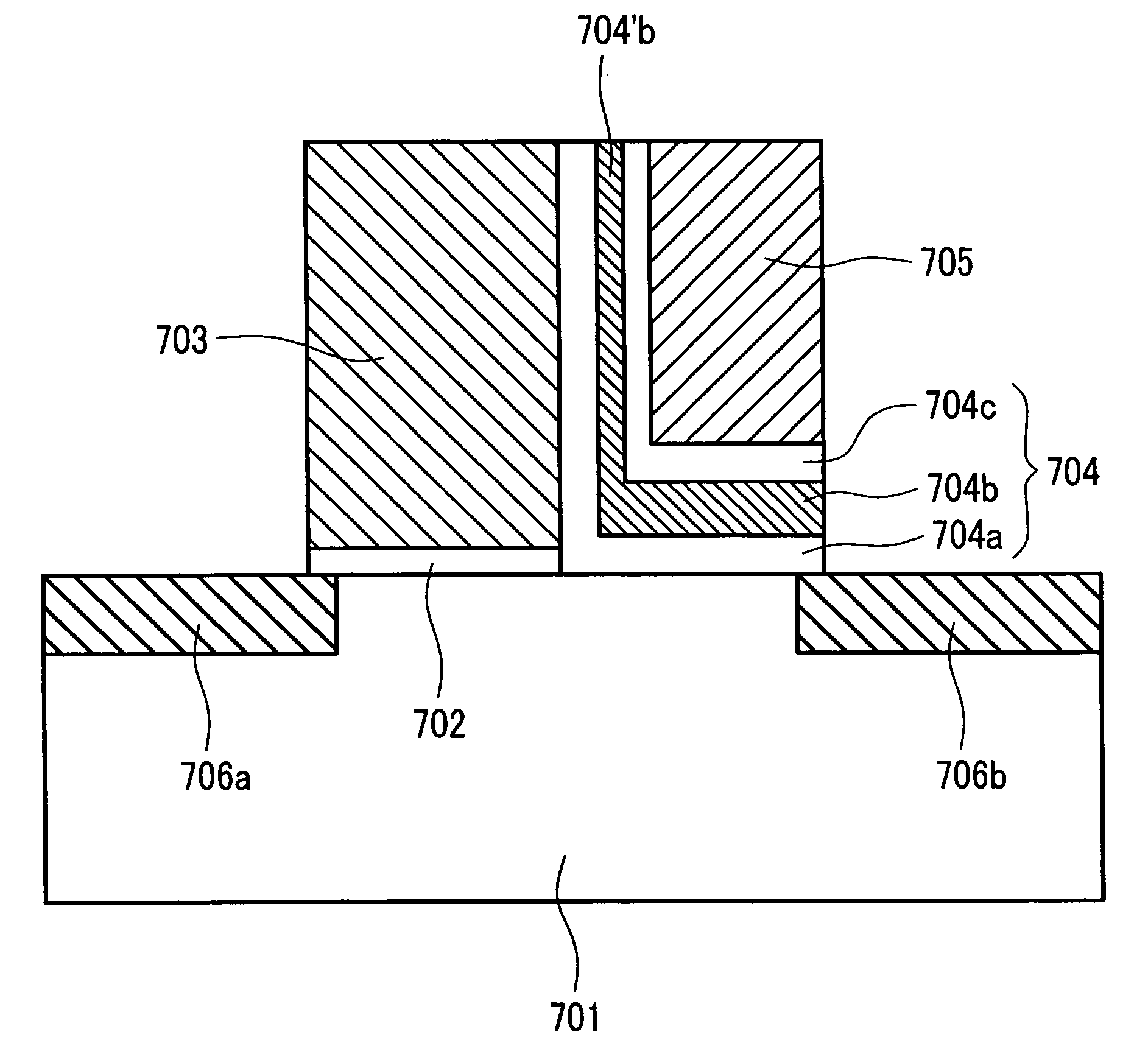
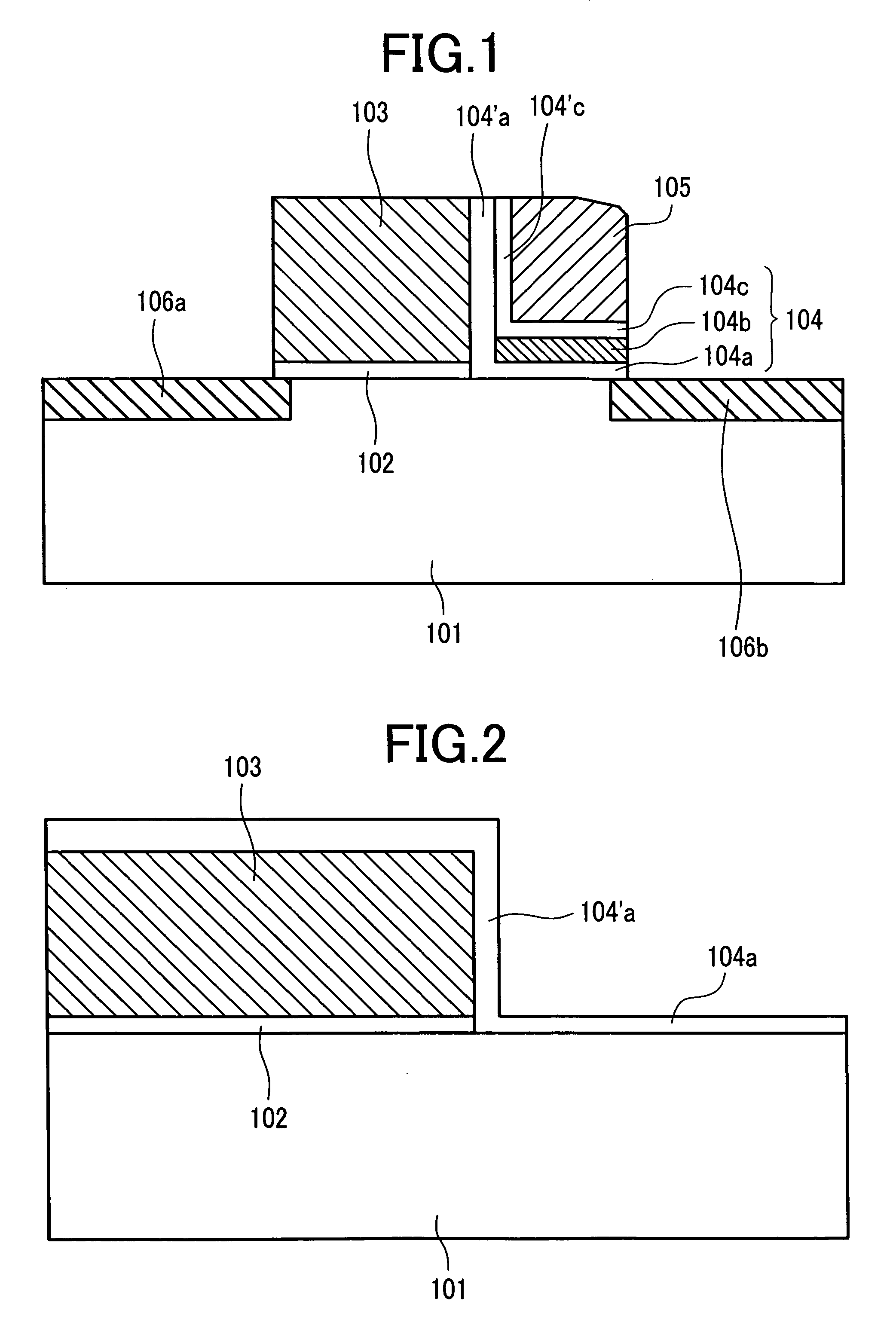
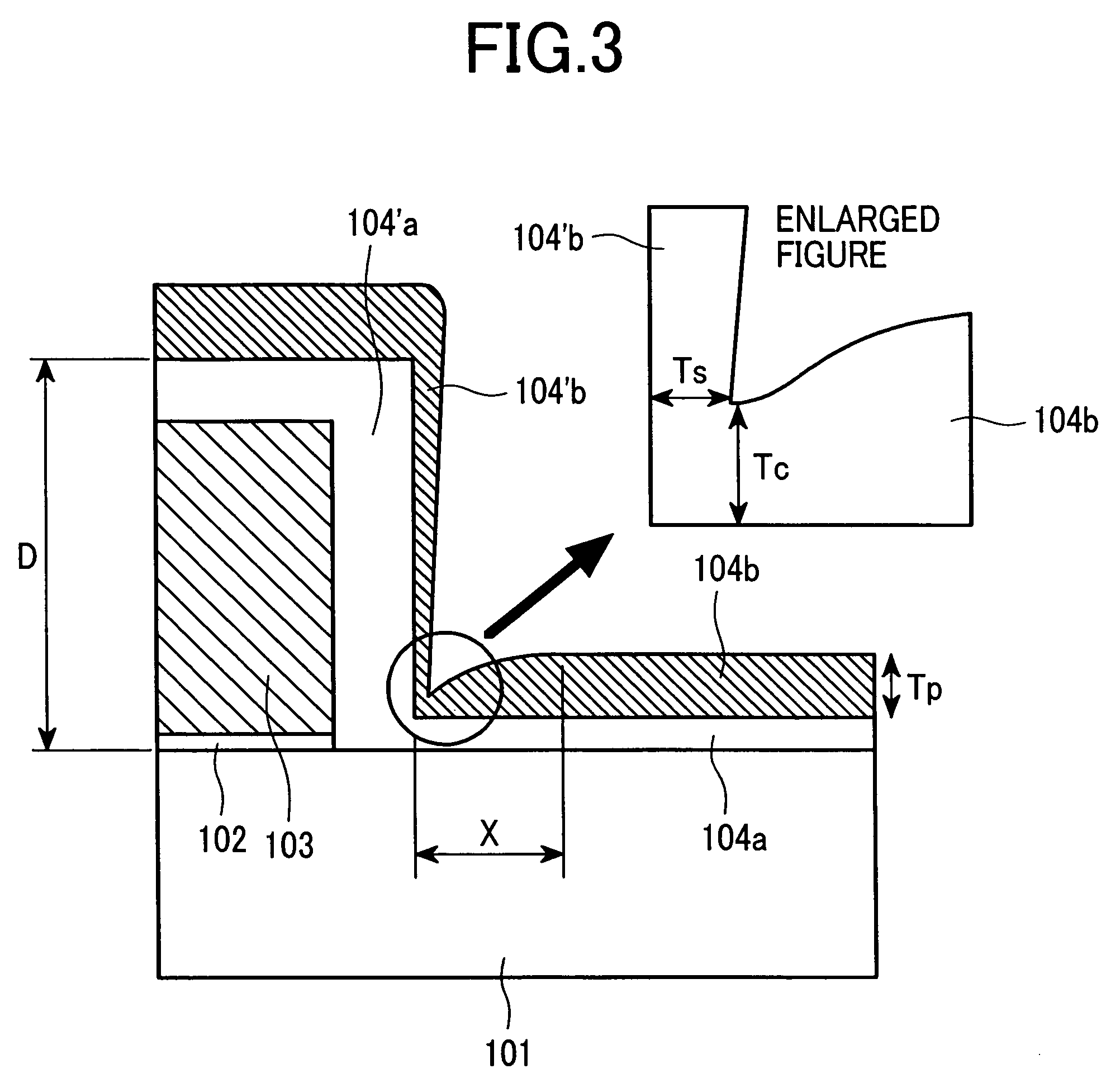
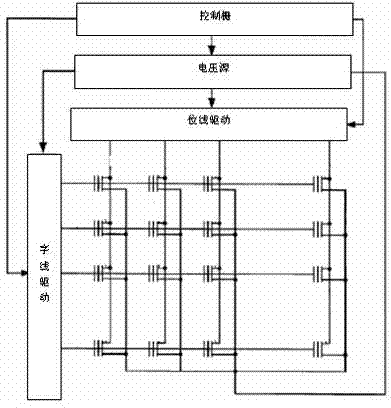
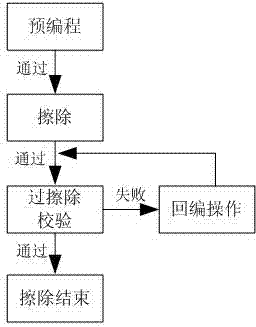
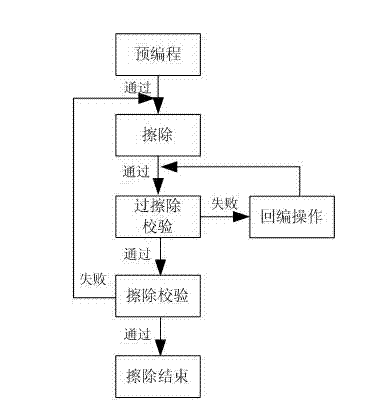
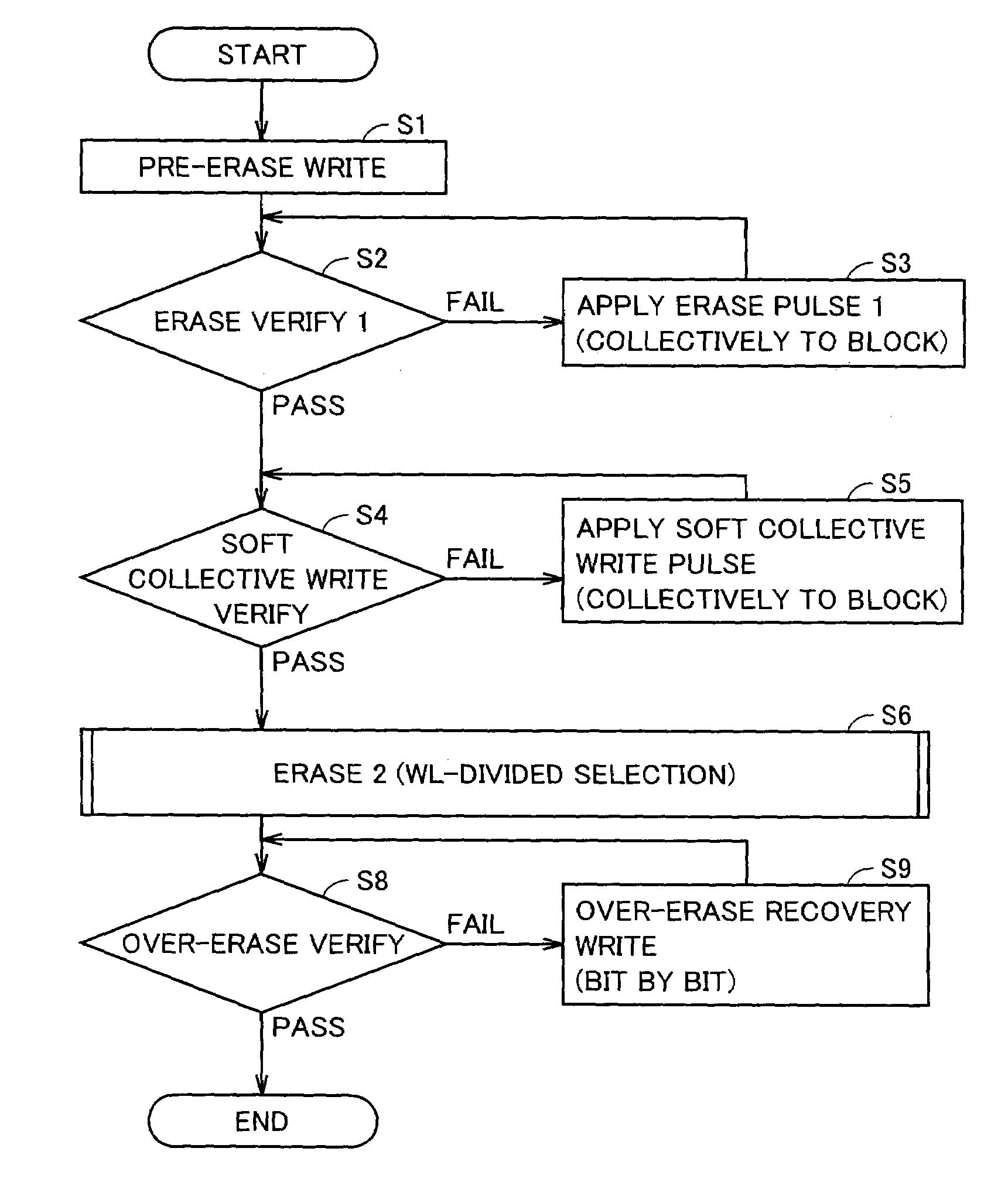
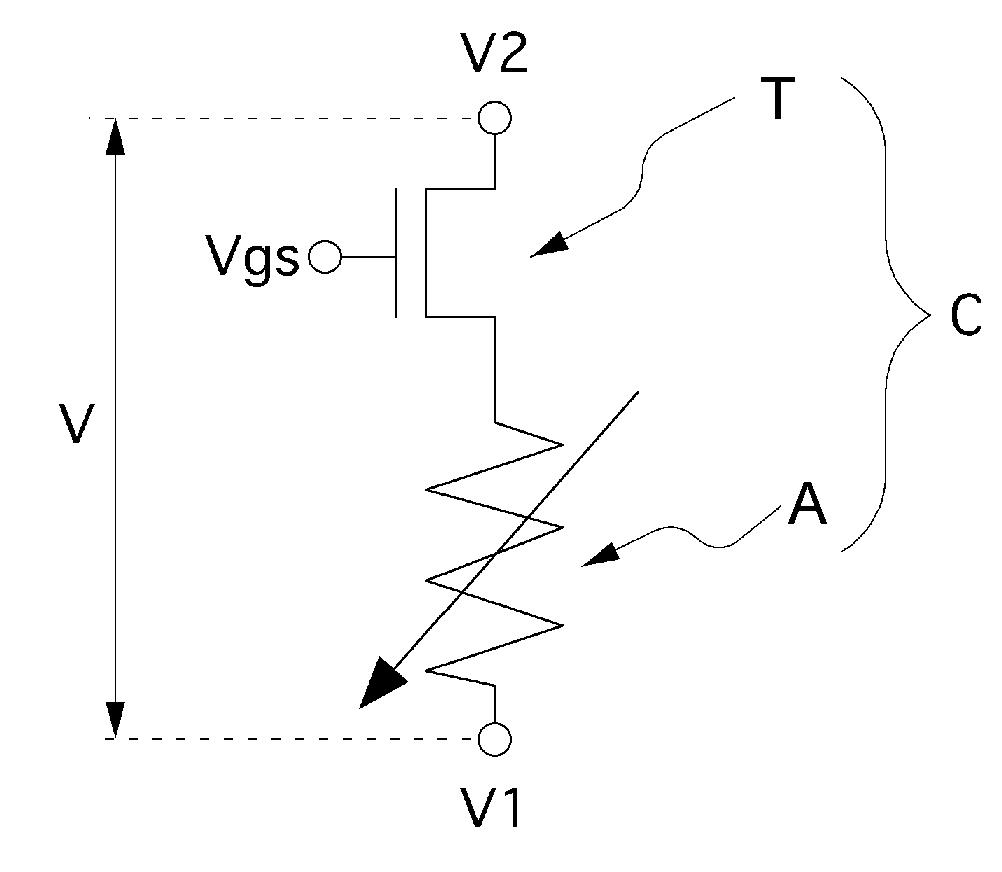
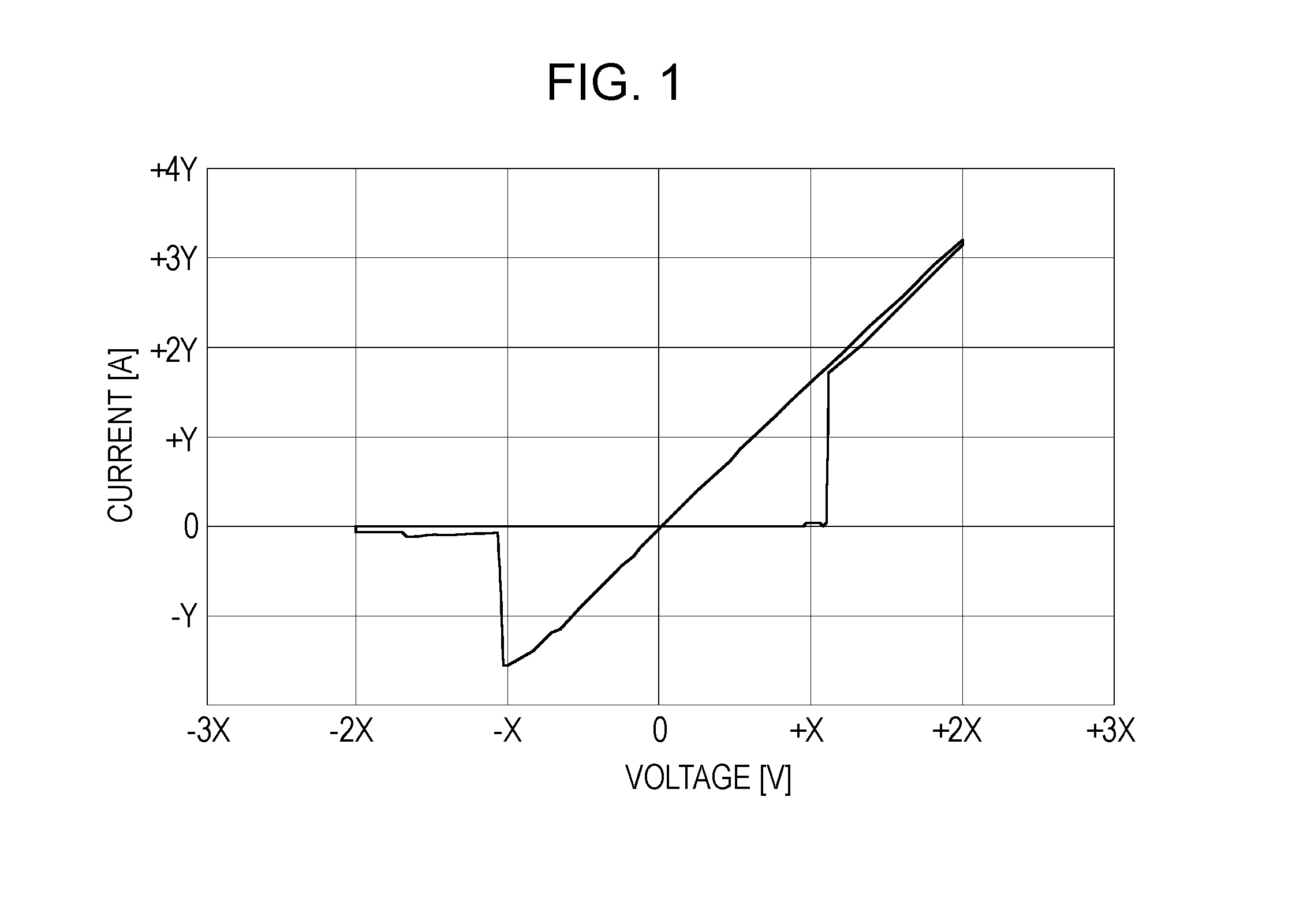
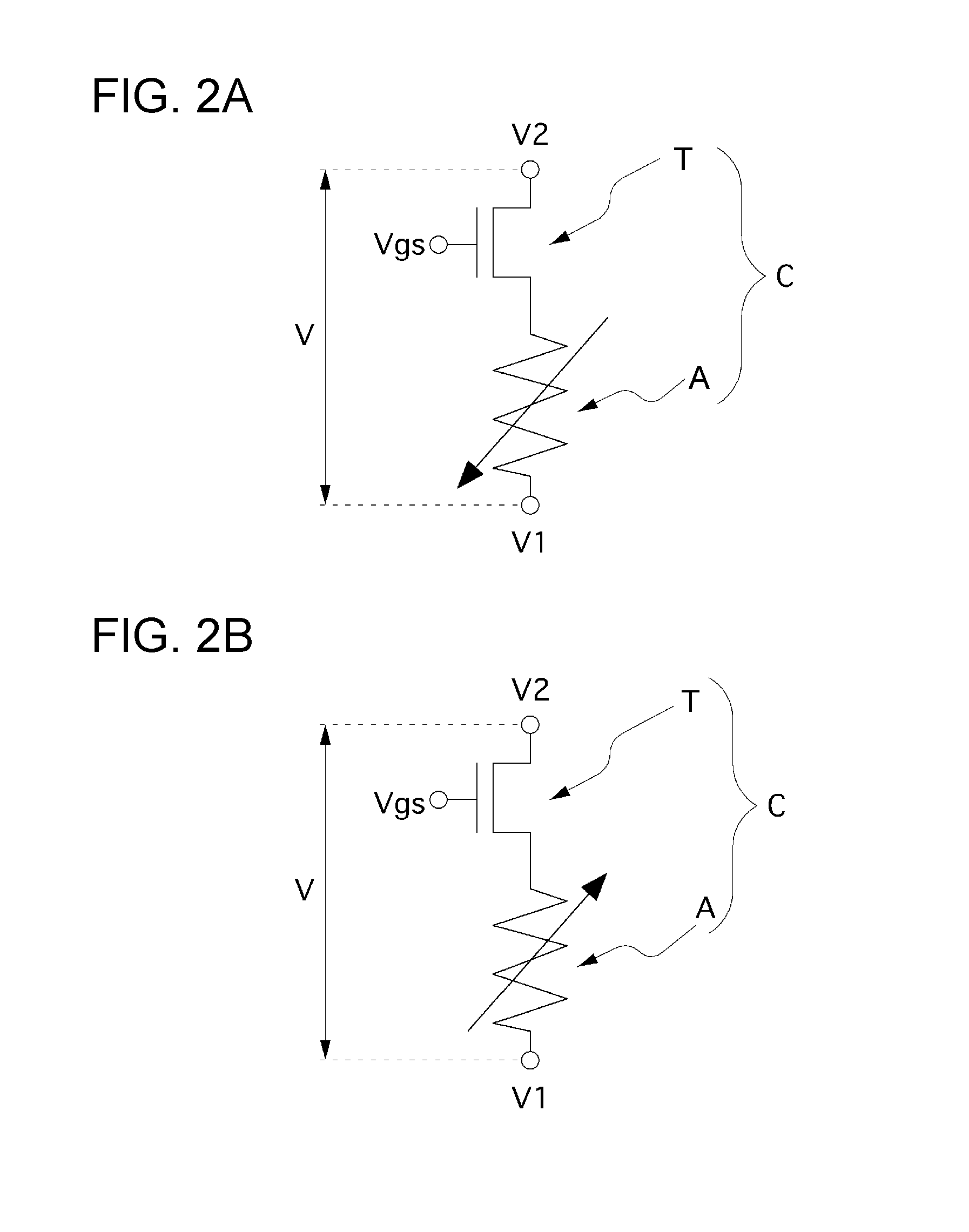
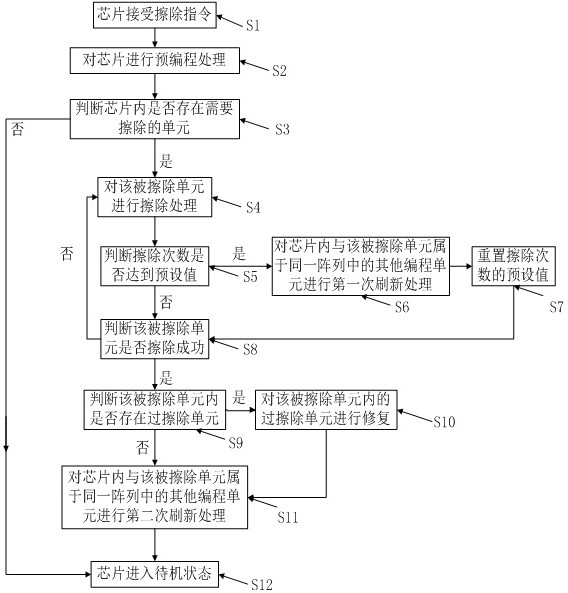
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
74results about How to "Reduce erasure time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
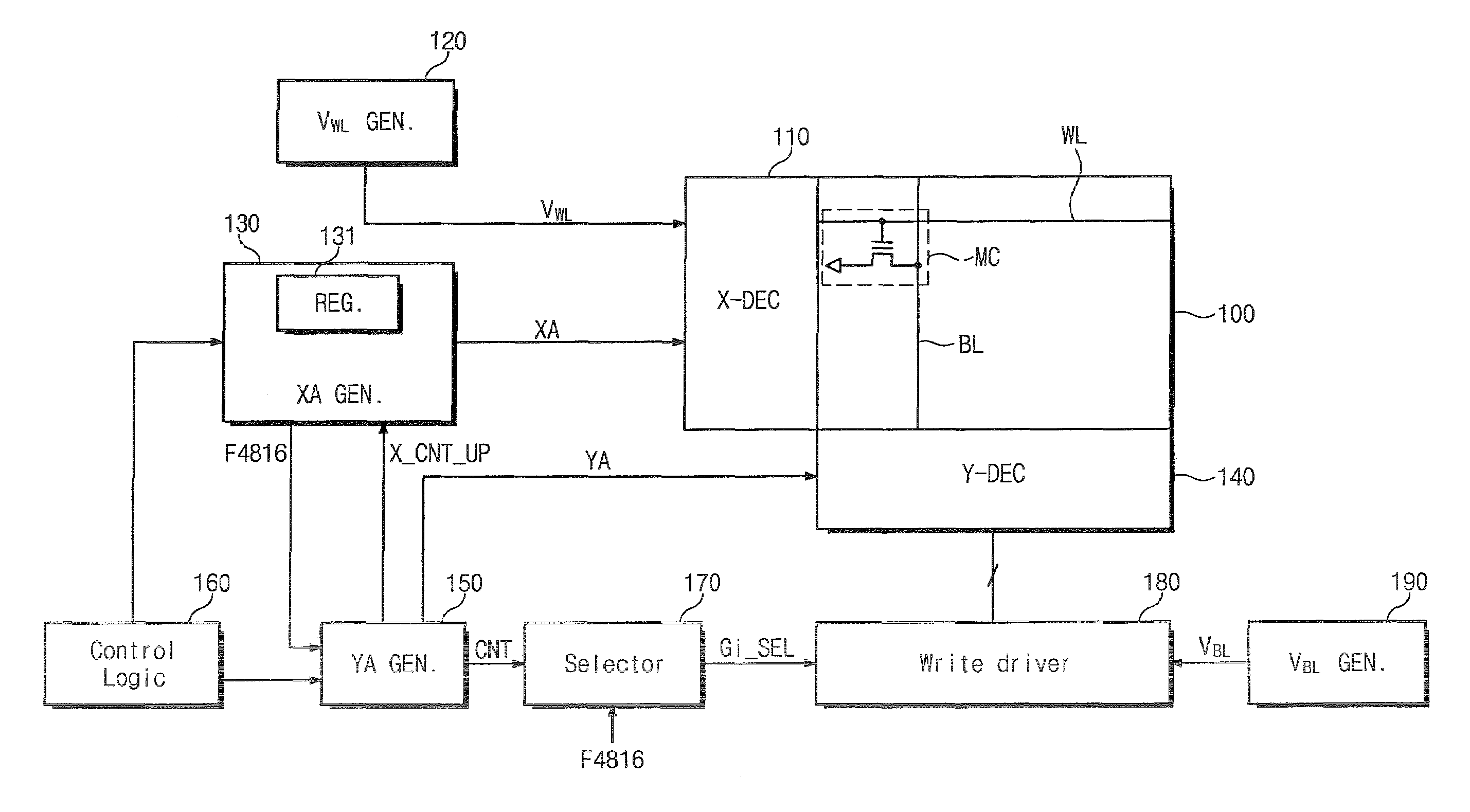
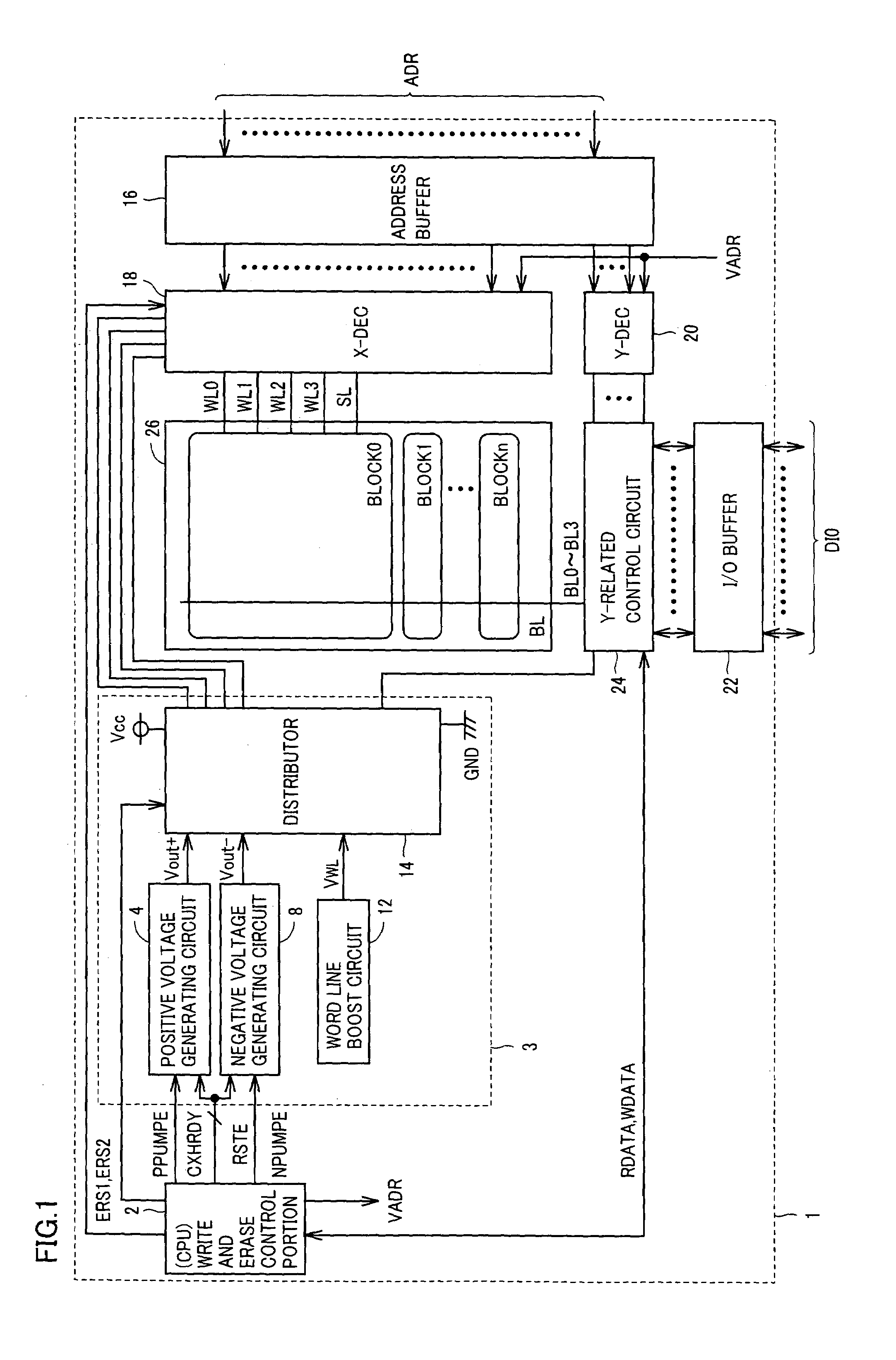
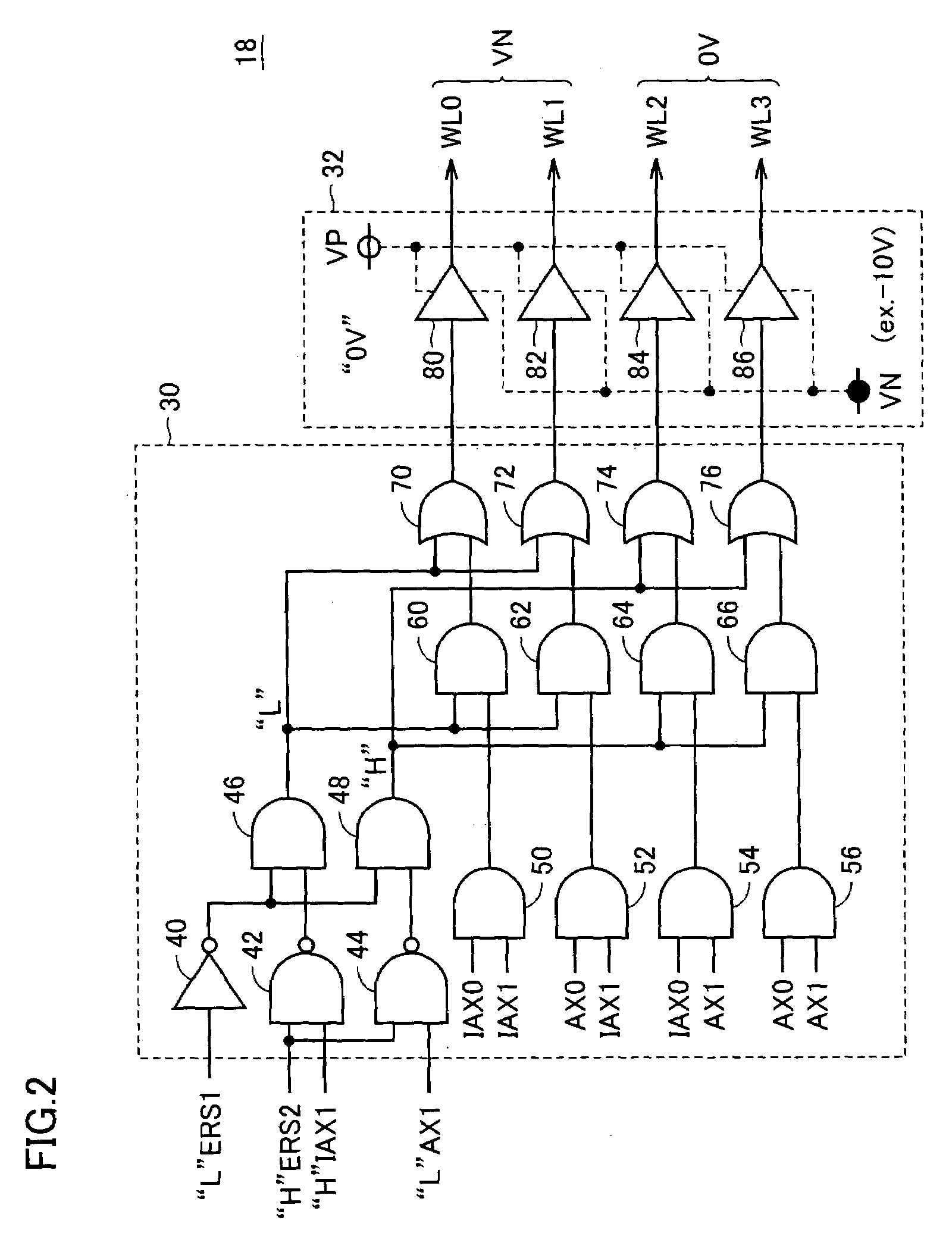
Flash memory device and erasing method thereof
InactiveUS7460412B2Reduce erasure timeShorten the timeRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer scienceStorage cell
A method of post-programming a flash memory device includes the steps of: post-programming memory cells of a selected word line in a predetermined unit; determining, after incrementing an address for selecting the next word line, whether the incremented address matches one of reference addresses; and varying the post-programming unit of the selected memory cells whenever the incremented address matches one of reference addresses.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
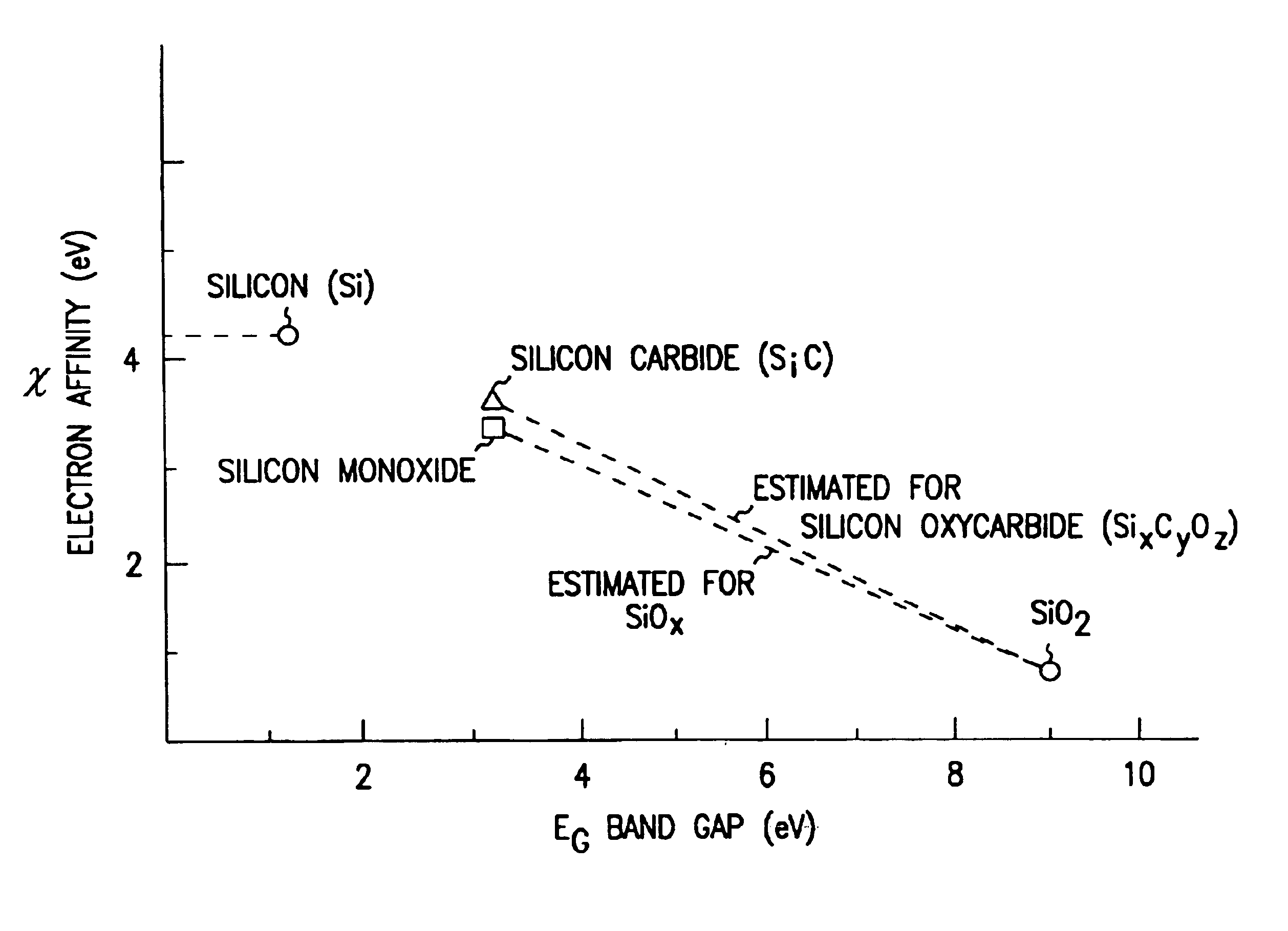
Graded composition gate insulators to reduce tunneling barriers in flash memory devices
InactiveUS6955968B2Reduce device erase timeLarge problemsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricComposite insulators
Flash memory cells are provided that include a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region separated by a channel region. A first gate opposes. A first gate insulator separates the first gate from the channel. The first gate insulator includes a graded composition gate insulator. A second gate is separated from the first gate insulator by a second gate insulator. The above memory cells produce gate insulators with less charging at the interface between composite insulator layers and provide gate insulators with low surface state densities. The memory cells substantially reduce large barrier heights or energy problems by using dielectrics having suitably, adjustably lower barrier heights in contact with the polysilicon floating gate. Such adjustable barrier heights of controlled thicknesses can be formed using a silicon suboxide and a silicon oxycarbide dielectrics prepared according to the process as described herein.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20050199940A1Reduce the impactReduce in quantityTransistorSolid-state devicesReactive plasmaSputter deposition
A MONOS nonvolatile memory of a split gate structure, wherein writing and erasing are performed by hot electrons and hot holes respectively, is prone to cause electrons not to be erased and to remain in an Si nitride film on a select gate electrode sidewall and that results in the deterioration of rewriting durability. When long time erasing is applied as a measure to solve the problem, drawbacks appear, such as the increase of a circuit area caused by the increase of the erasing current and the deterioration of retention characteristics. In the present invention, an Si nitride film is formed by the reactive plasma sputter deposition method that enables oriented deposition and the Si nitride film on a select gate electrode sidewall is removed at the time when a top Si oxide film is formed.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7115943B2Improve performanceReduce in quantityTransistorSolid-state devicesReactive plasmaSputter deposition
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
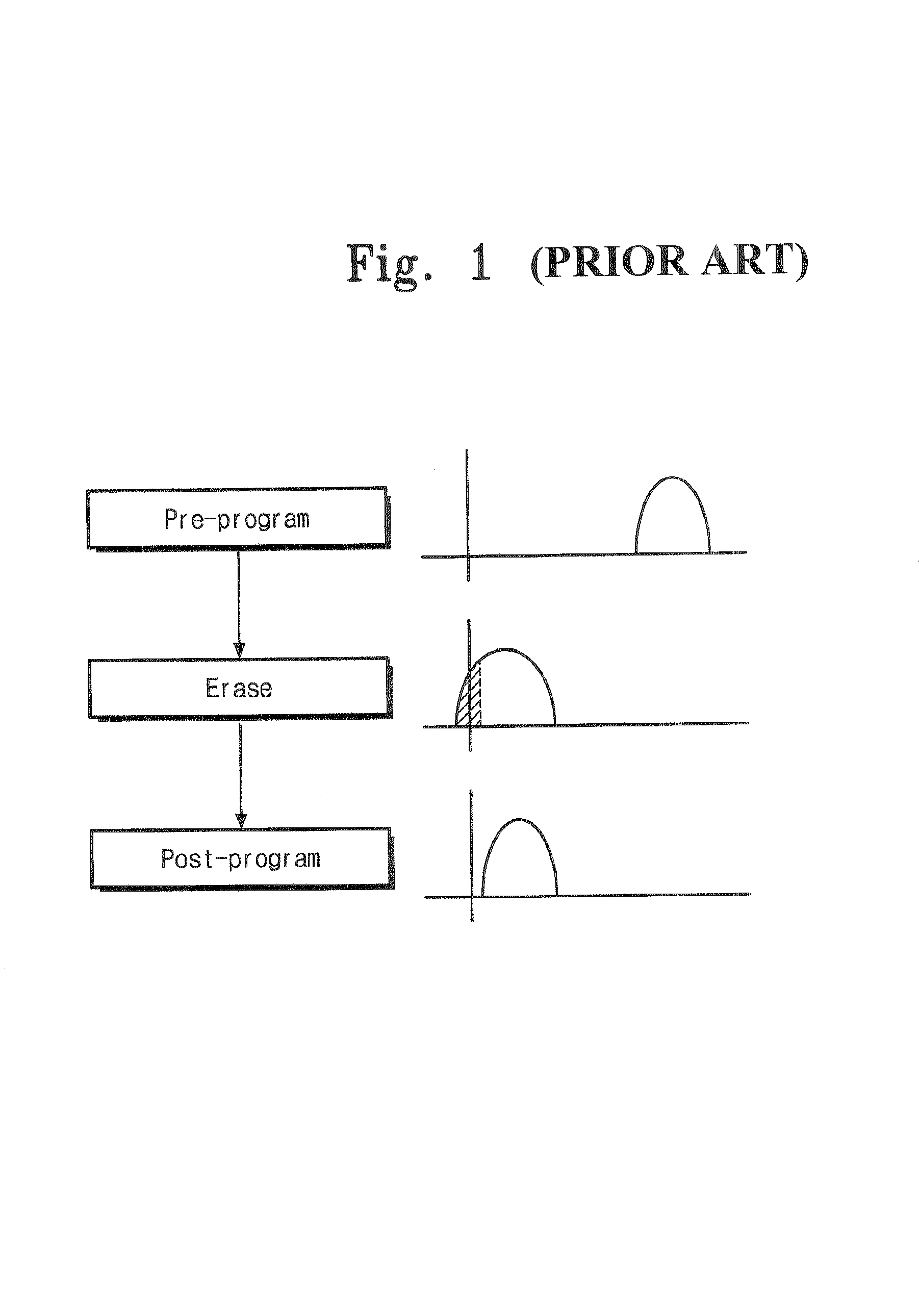
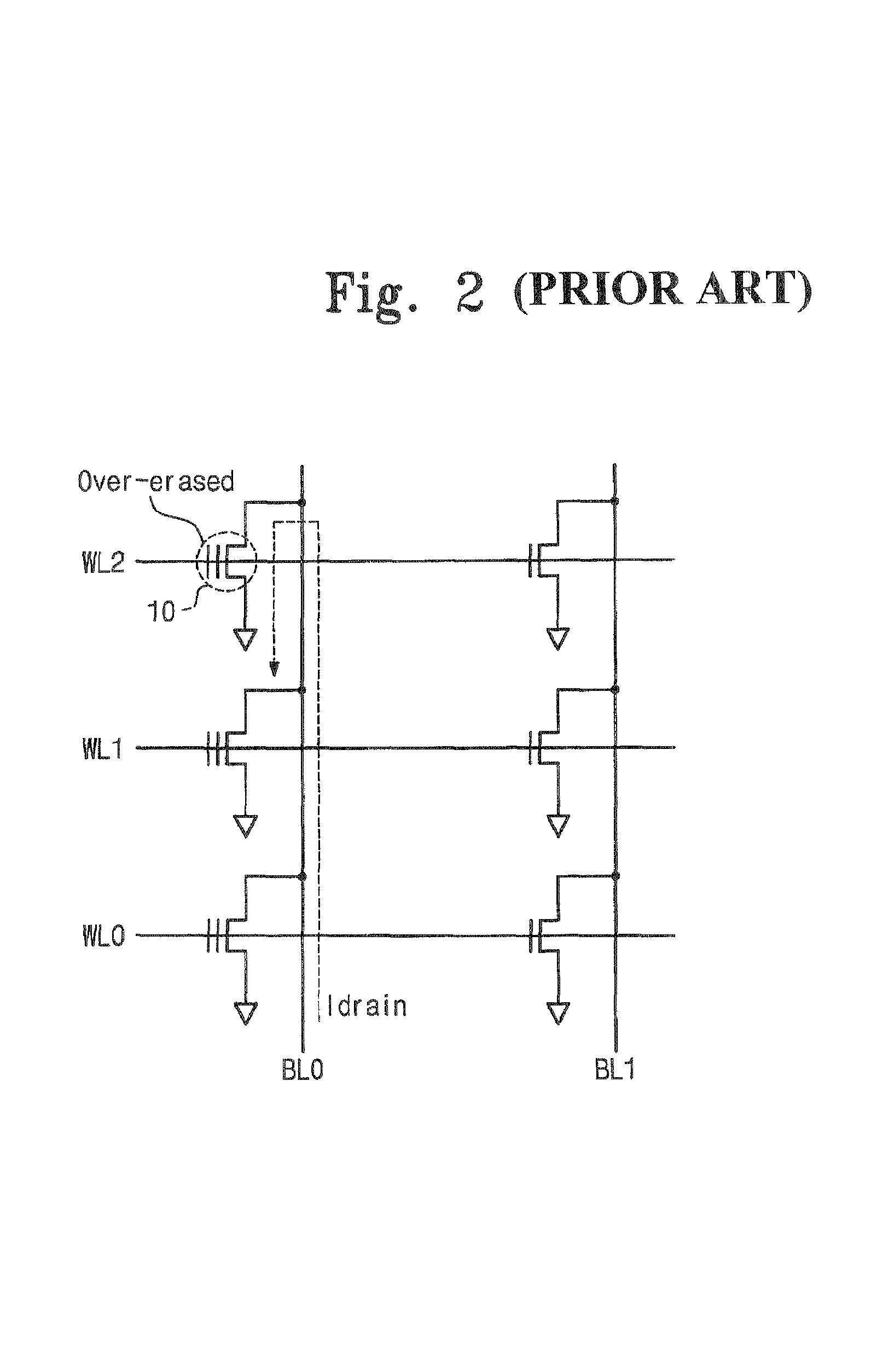
Erasing method for flash memory
The invention relates to an erasing method for a flash memory. The method comprises the following three operation steps: pre-programmed checking, i.e. pre-programming; erase checking, i.e. erasing; and over-erase checking, i.e. over-erase correction. In the method, two state zone bits comprising an erase zone bit and an over-erase zone bit are adopted; an erase and over-erase loop is adopted; and when the cycle index of the loop exceeds preset times, the erasing operation is stepped out. According to the invention, the erasing time is shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI FUDAN MICROELECTRONICS GROUP
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device having reduced erasing time
ActiveUS7050336B2Reduce erasure timeReduce in quantityRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer scienceMemory block
An operation of erasing data in a memory block of a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device employs an operation of collectively applying an erase pulse to the memory block, and an operation of collectively applying an erase pulse to a limited region in the memory block. Thereby, the number of the erase pulses excessively applied to the memory cells, which passed verify, can be reduced as compared with a conventional structure so that the number of the memory cells to be subjected to over-erase recovery write decreases, and the total block erase time can be short.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
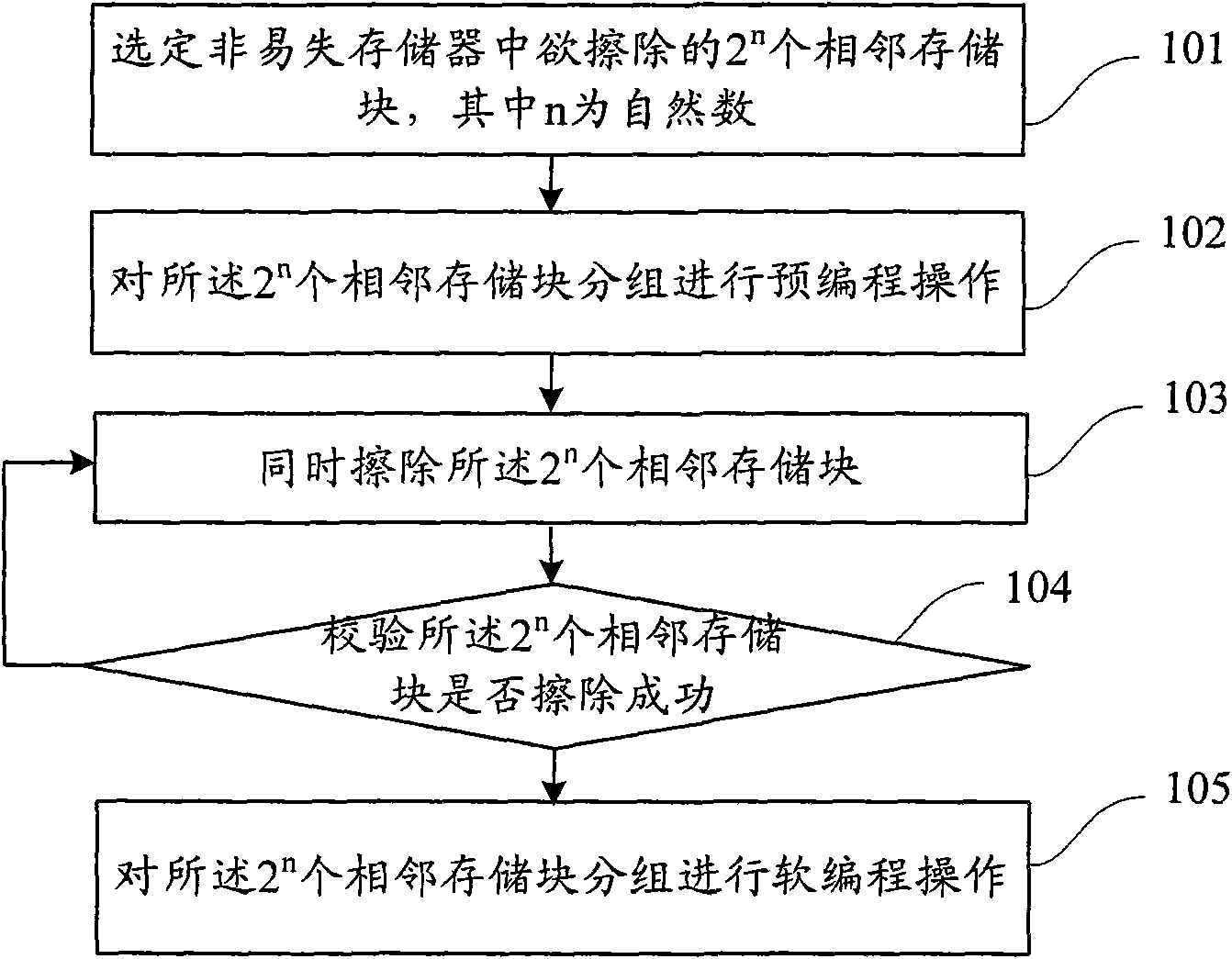
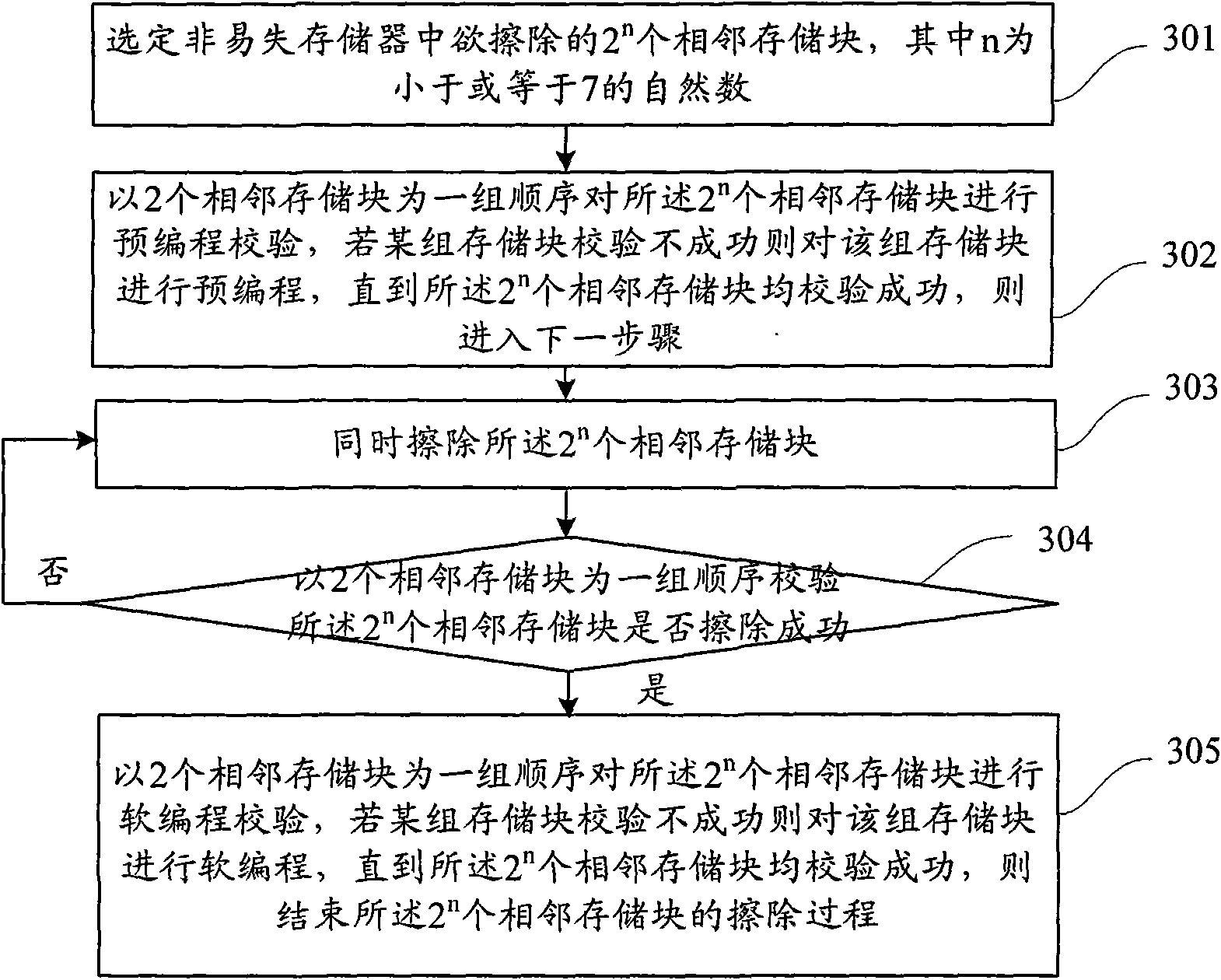
Erasing method and device for non-volatile memory
ActiveCN101923900AShorten the timeIncrease erasing speedRead-only memoriesNon-volatile memoryMemory block
The invention discloses an erasing method for a non-volatile memory. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a target, namely, selecting 2n to-be-erased adjacent memory blocks in the non-volatile memory, wherein n is a natural number; performing pre-programming operation, namely, pre-programming the 2n adjacent memory blocks in groups; erasing, namely, simultaneously erasing the 2n adjacent memory blocks; checking the erasing, namely, checking whether the 2n adjacent memory blocks are successfully erased in groups, if so, performing soft programming operation, and otherwise, returning to the erasing step; and performing the soft programming operation, namely, performing the soft programming operation on the adjacent memory blocks in groups. The method can save erasing time and improve erasing speed and erasing efficiency.
Owner:GIGADEVICE SEMICON (BEIJING) INC
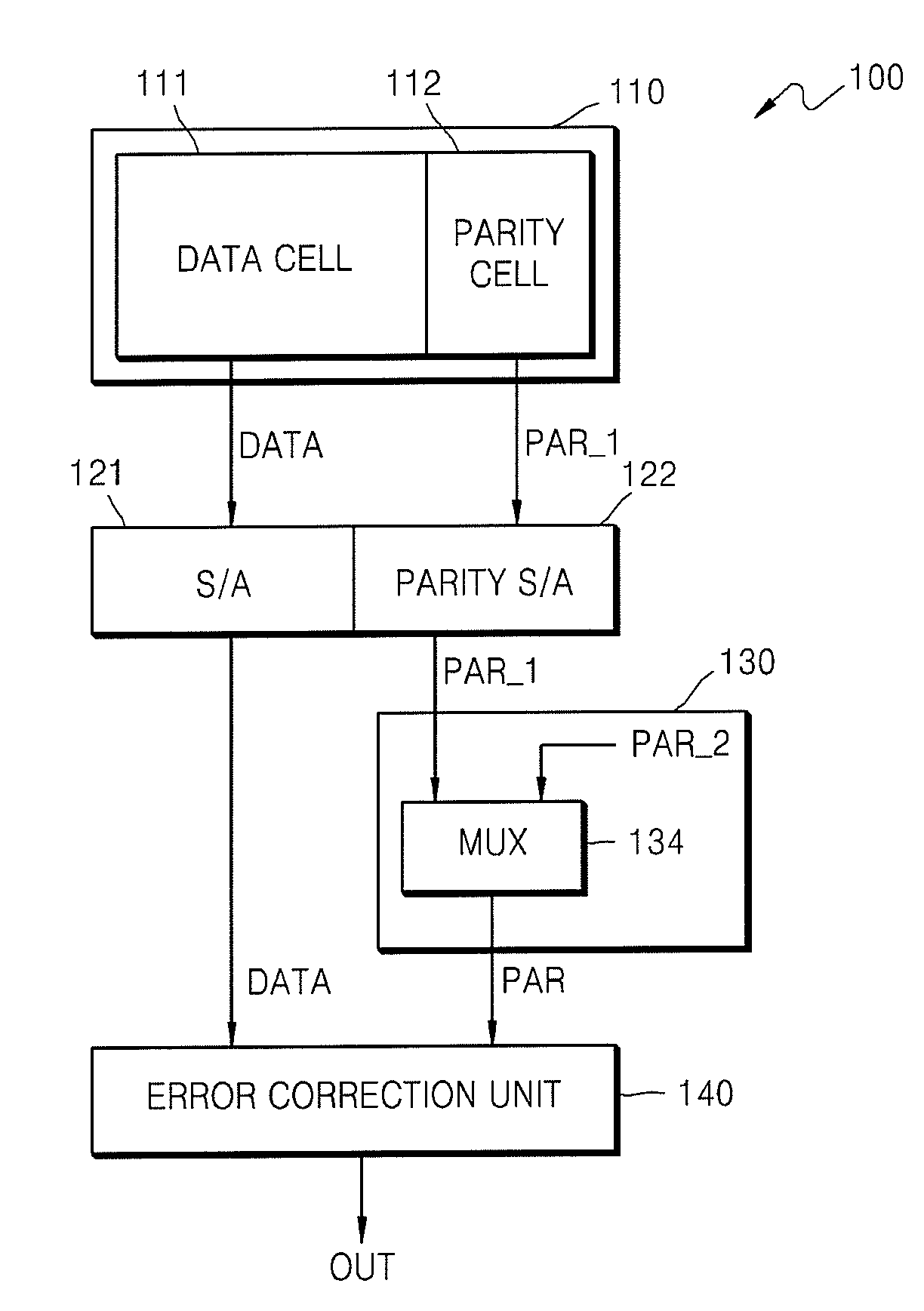
Flash memory device using ECC algorithm and method of operating the same
ActiveUS8347183B2Low failure rateReduce erasure timeError detection/correctionRead-only memoriesData memoryData storing
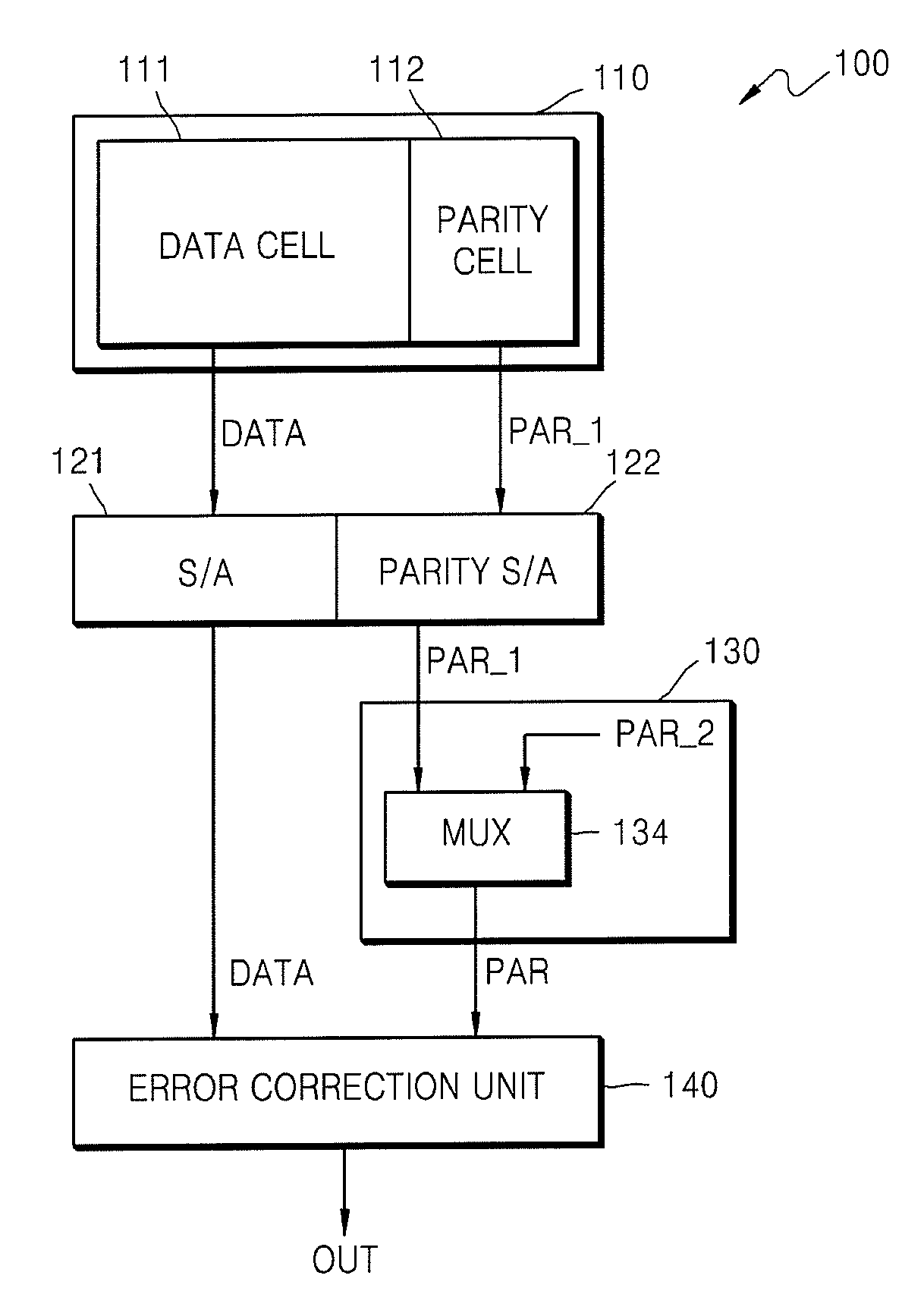
A flash memory device using an error correction code (ECC) algorithm and a method of operating the same. The device includes a memory cell array including a error correction code (ECC) block including data memory cells configured to store data and a parity cell configured to store a first parity code, a parity controller configured to generate a second parity code based on a the current operating mode of the flash memory device, and an error correction unit configured to receive one of the first and second parity codes and to perform an ECC algorithm on the data stored in the data memory cells using the received parity code. A control logic restarts an erase operation on an erroneously unerased data memory cell or prevents the erase operation from being restarted based on the number of erroneous bits per ECC block.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for erasing non-volatile memory
InactiveUS20070206424A1Shorten the timeImprove reliabilityRead-only memoriesDigital storageTrappingEngineering
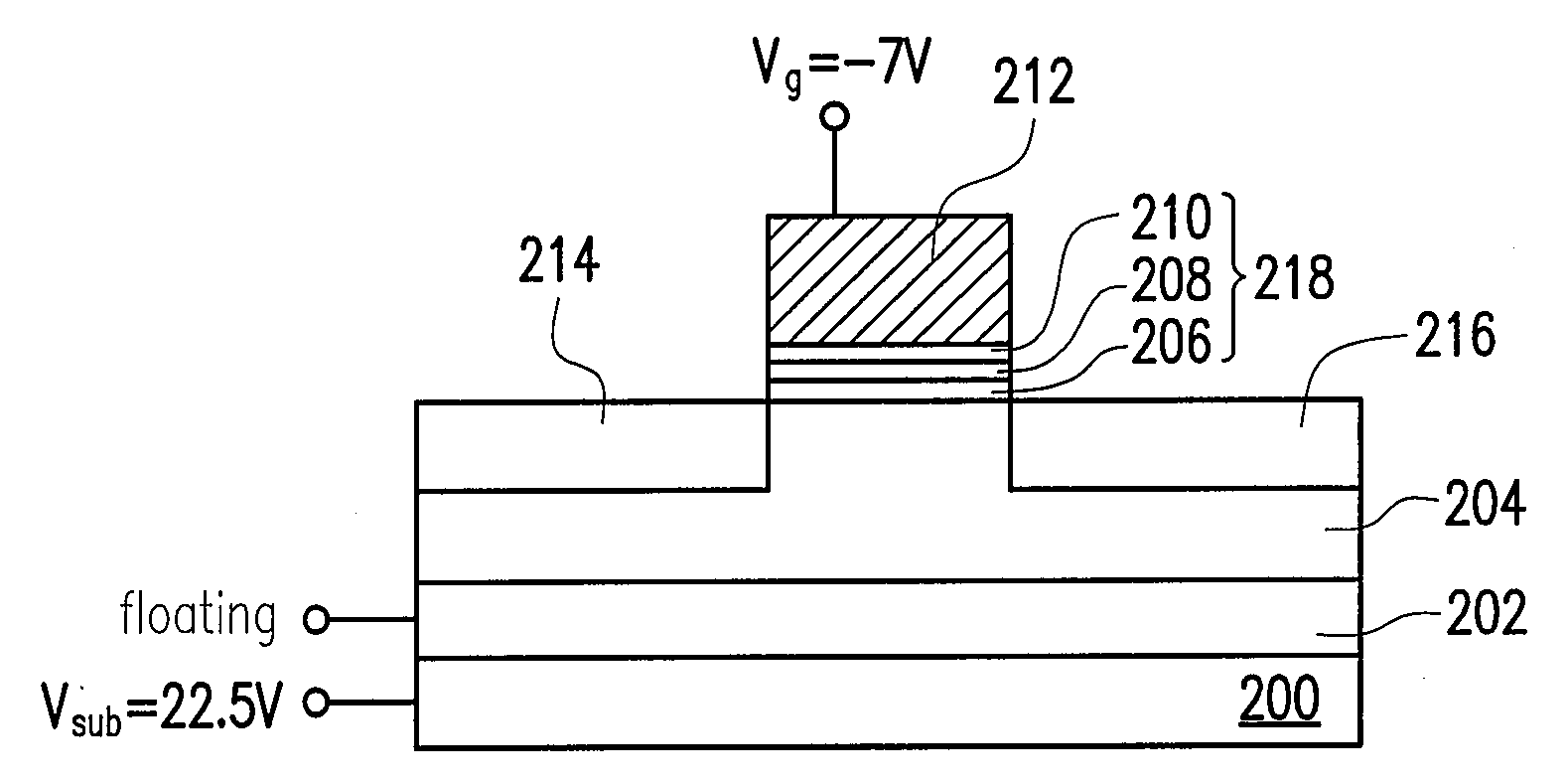
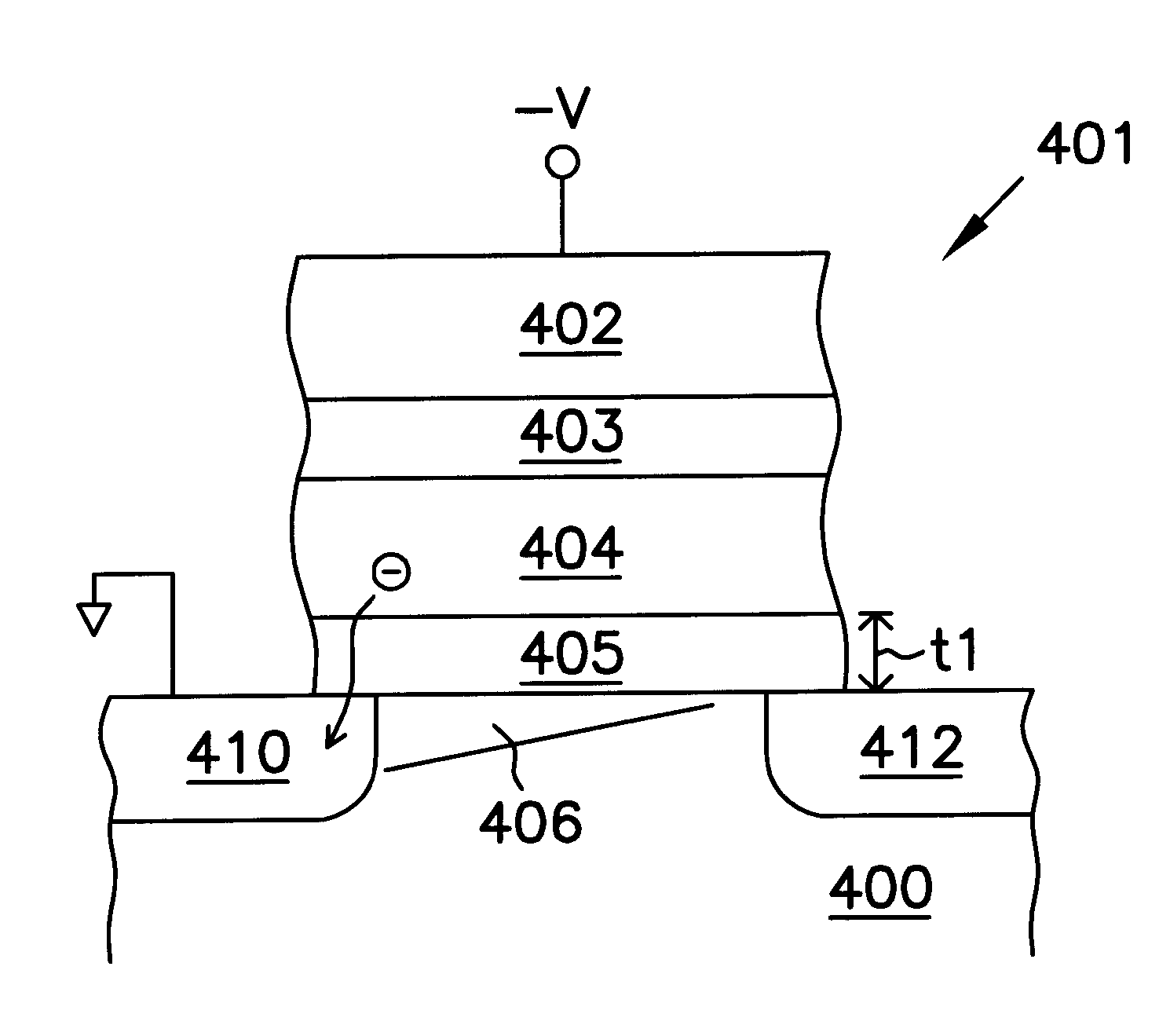
A method for erasing a non-volatile memory is provided. The non-volatile memory includes a first conductive type substrate, a second conductive type well disposed in the first conductive type substrate, a first conductive type well disposed on the second conductive type well, and a memory cell disposed on the first conductive type substrate. The memory cell includes a charge trapping layer and a gate. The erasing method includes the following steps. A first voltage is applied to the gate, a second voltage is applied to the first conductive type substrate, and the second conductive type well is floating. The second voltage is large enough to induce a substrate hot hole effect. The holes are injected into the charge trapping layer by applying the first voltage.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
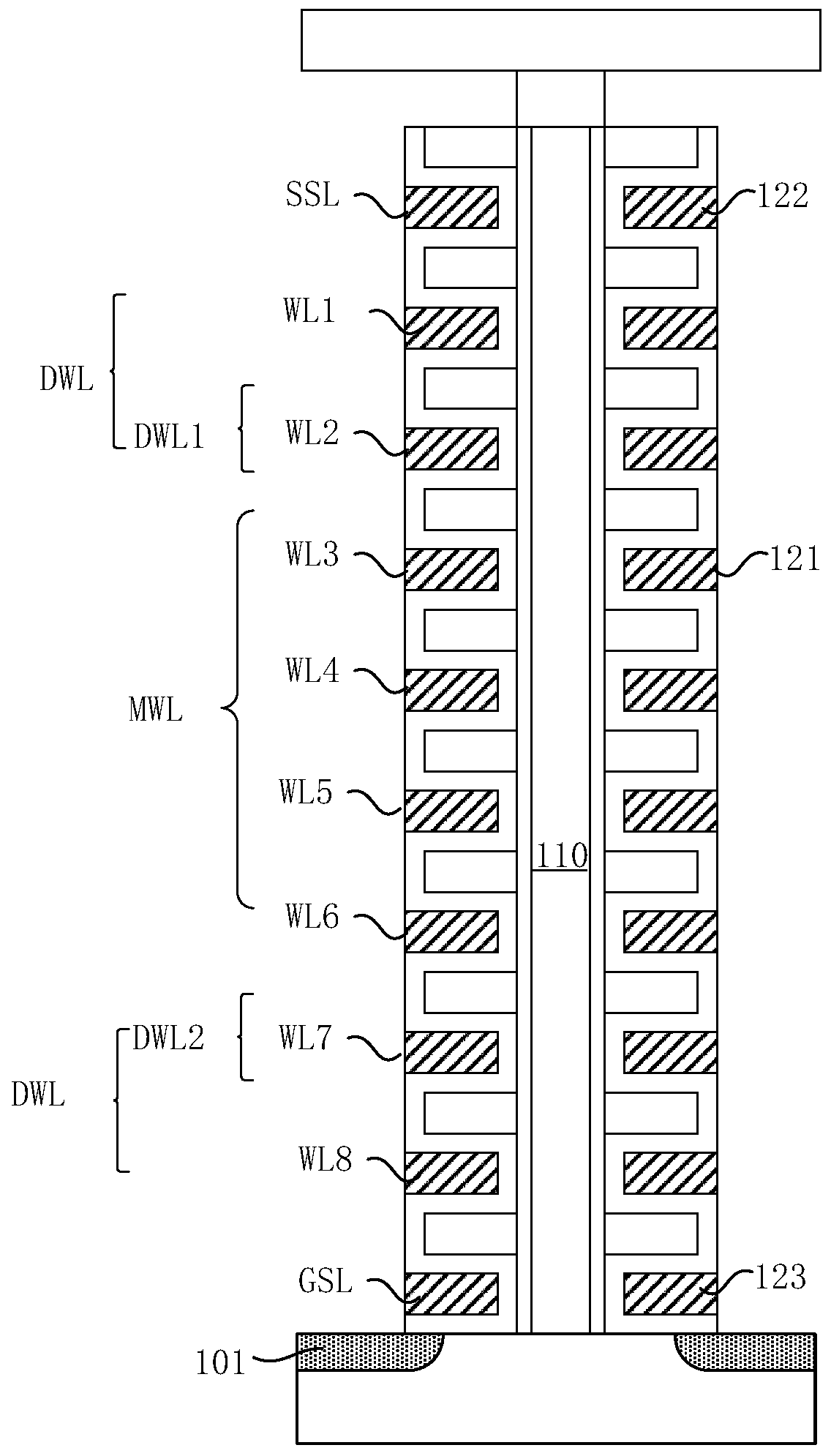
A 3D memory device and a data operation method thereof
ActiveCN109949835AImprove reliabilityImprove erase efficiencyRead-only memoriesComputer architectureData operations
The invention discloses a data operation method of a 3D storage device. The 3D memory device has a plurality of memory cell strings arranged in a direction perpendicular to a substrate, each memory cell string including a first select transistor, a first dummy memory cell, a plurality of main memory cells, a second dummy memory cell, and a second select transistor, including: receiving an erase instruction; executing an erase operation on the first pseudo storage unit, the plurality of main storage units and the second pseudo storage unit according to the erase instruction; verifying whether the plurality of main storage units are erased successfully or not after the erase operation is finished; when the plurality of main storage units are erased successfully, receiving a programming instruction; and executing programming operation on the first pseudo storage unit and the second pseudo storage unit according to the programming instruction. The pseudo storage unit and the storage unit are erased at the same time, and then the pseudo storage unit is programmed, so that the erasure efficiency of the edge storage unit is improved, the erasure frequency is reduced, and the reliability of the storage unit is improved.
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
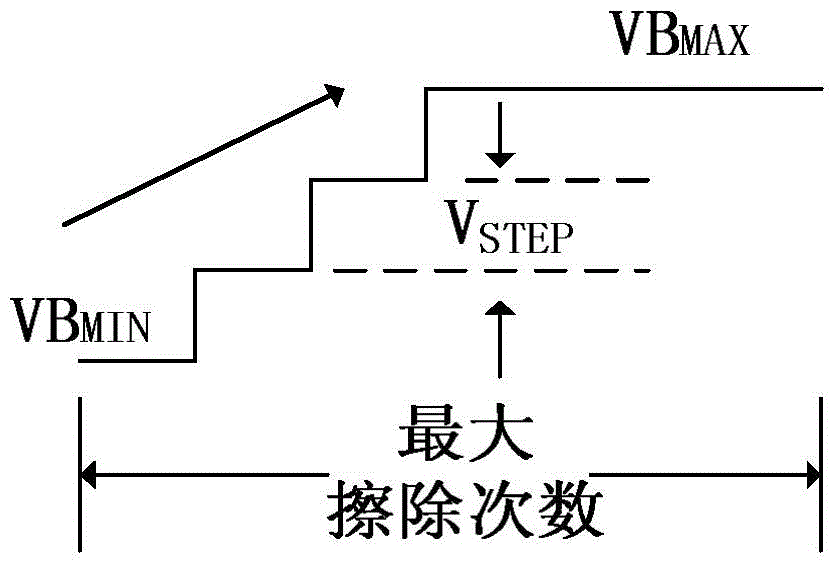
Method for accelerating erasing operation of flash memory, and system thereof
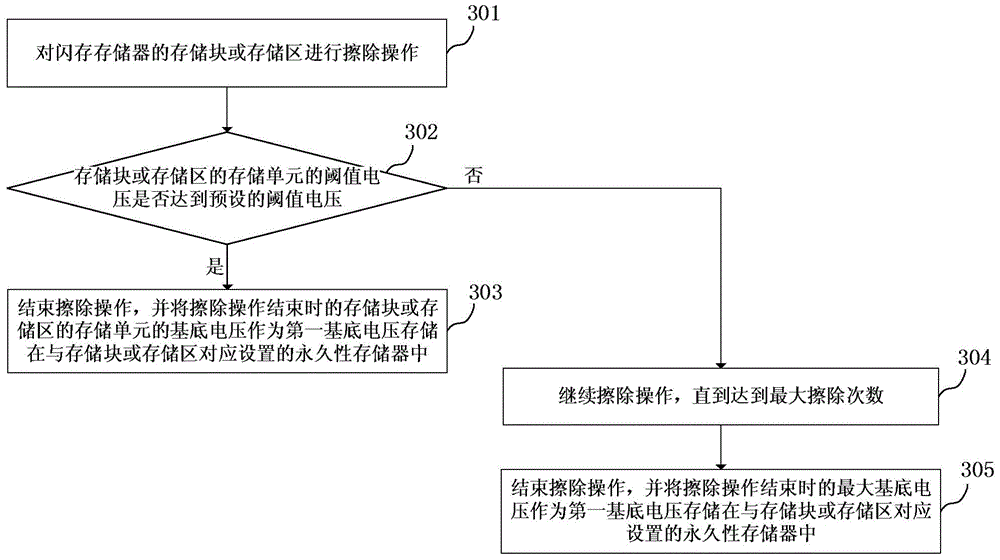
The invention discloses a method for accelerating the erasing operation of a flash memory, and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: erasing the memory block or memory area of the flash memory; and storing the substrate voltage of the memory cell of the memory block or the memory area when the erasing operation ends in a permanent memory arranged corresponding to the memory block or the memory area as a first substrate voltage, wherein the first substrate voltage is an initial substrate voltage of a next erasing operation of the memory block or the memory area. The method and the system can improve the erasing ability of the memory block or the memory area of the flash memory and shorten the erasing time.
Owner:GIGADEVICE SEMICON (BEIJING) INC
Data writing method, memory controller, and memory storage apparatus
ActiveUS20120079231A1Reduce erasure timeImprove memory performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwareMemory controller
A data writing method and a memory controller and a memory storage apparatus using the same are provided. The data writing method includes grouping a plurality of physical blocks into a plurality of physical units, grouping the physical units into at least a data area and a free area, and configuring a plurality of logical units for mapping to the physical units of the data area. The data writing method also includes getting a physical unit from the free area, writing data in at least one of the logical units into the gotten physical unit, and writing an end mark into the gotten physical unit, and in the gotten physical unit, the end mark follows the data belonging to the at least one logical unit. Thereby, the storage space of each physical unit can be effectively used, and the lifespan of the memory storage apparatus can be prolonged.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
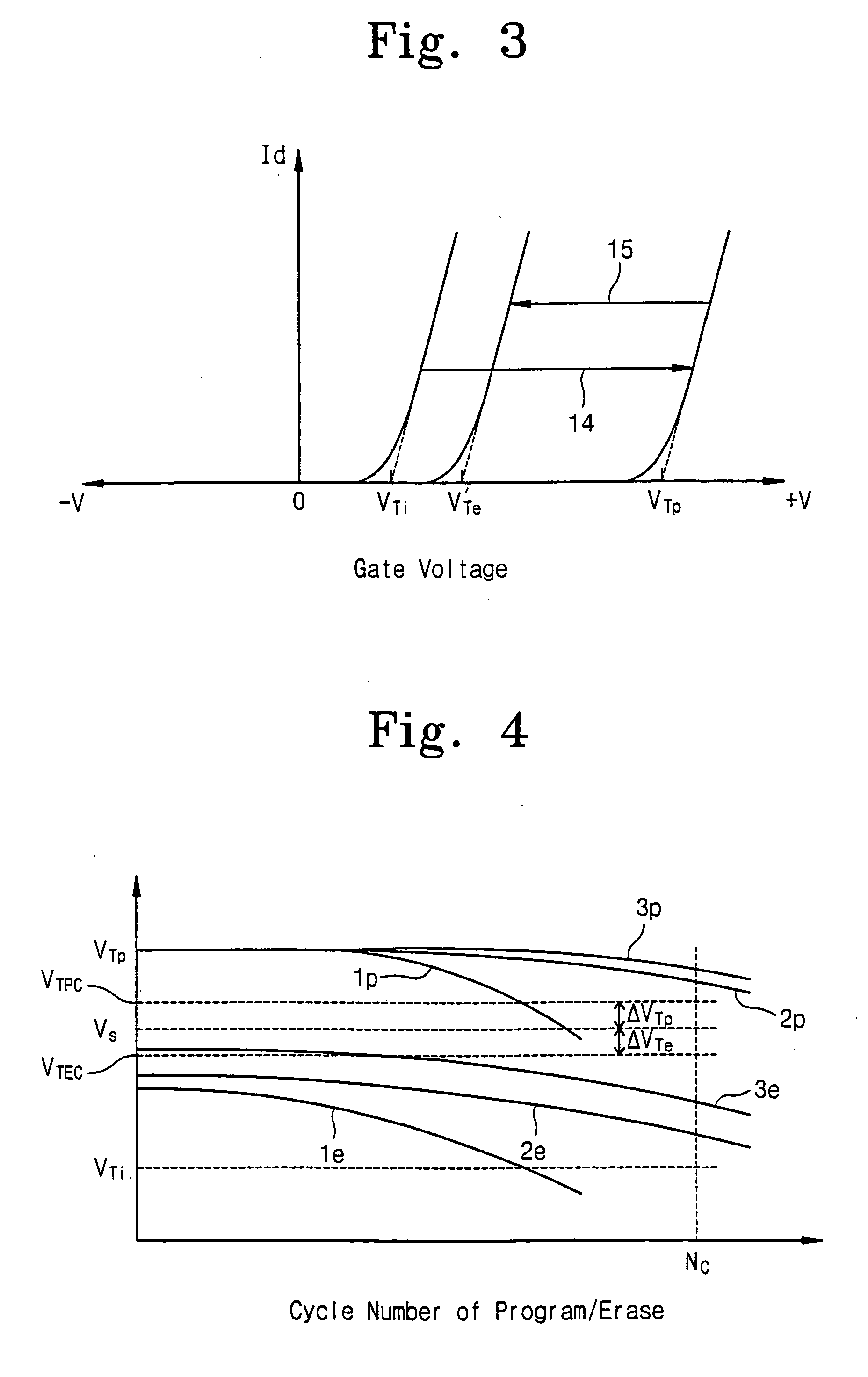
Electrically erasable charge trap nonvolatile memory cells having erase threshold voltage that is higher than an initial threshold voltage
InactiveUS6947330B2Reduce erasure timeCharge is trappedSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesThreshold voltageDurability testing
An electrically erasable charge trap nonvolatile memory cell has an initial threshold voltage, a program voltage that is higher than the initial threshold voltage, and an erase threshold voltage that is lower than the program threshold voltage but is higher than the initial threshold voltage. The programmed electrically erasable charge trap nonvolatile memory cells may be erased by applying an erase voltage for a time interval that is sufficient to lower the threshold voltage the transistor from a program threshold voltage to an erase threshold voltage that is lower than the program threshold voltage, but is higher than the initial threshold voltage. The time interval may be determined by repeatedly performing an endurance test using a time interval that is increased or decreased from an initial time interval, to obtain the time interval that meets an endurance specification, or allows a read to be performed successfully.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
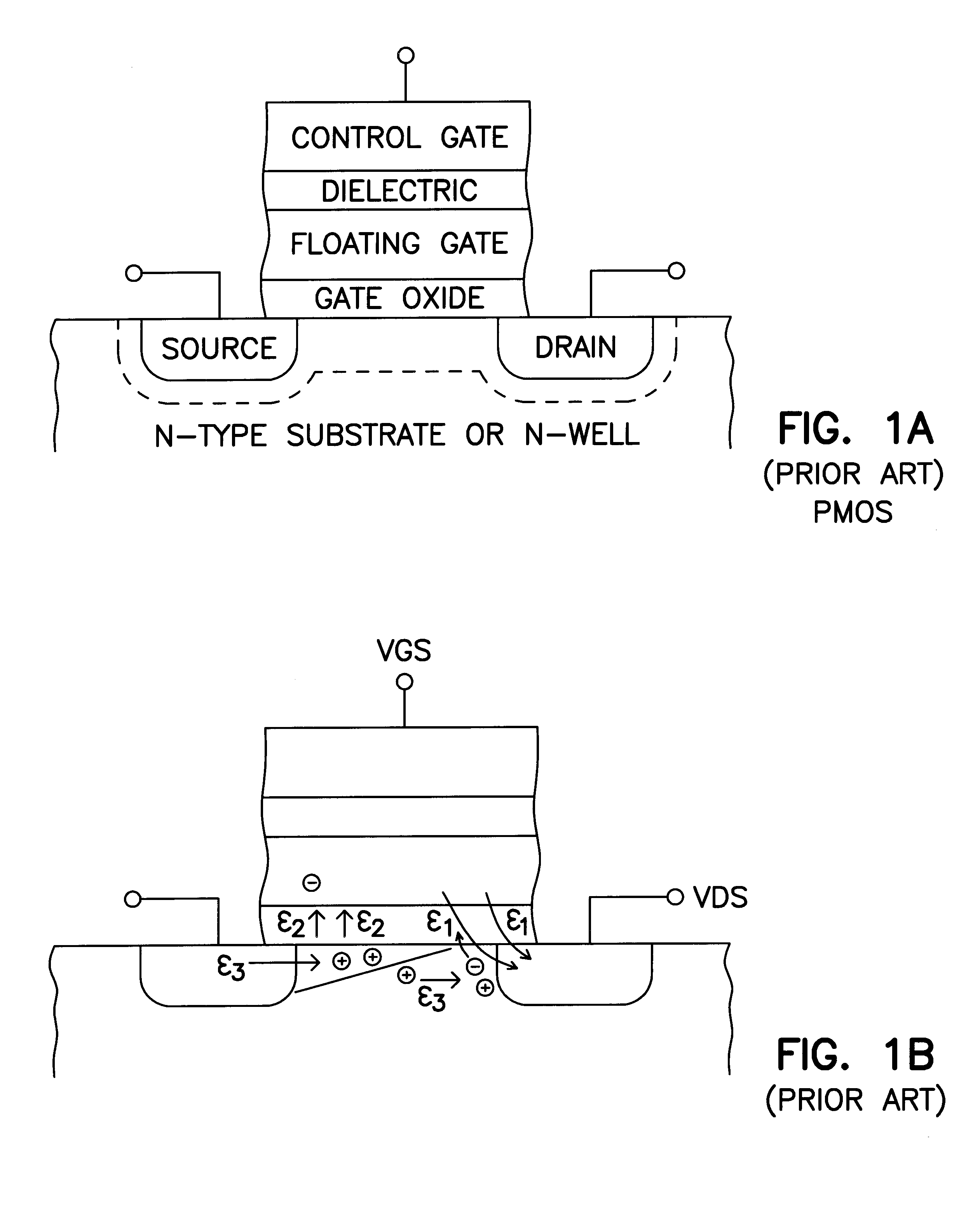
P-channel dynamic flash memory cells with ultrathin tunnel oxides
InactiveUS6909138B2Lower the barrierIncrease currentTransistorRead-only memoriesVoltage shiftP channel
Structures and methods involve dynamic enhancement mode p-channel flash memories with ultrathin tunnel oxide thicknesses. Both write and erase operations are performed by tunneling. The p-channel flash memory cell with thin tunnel oxides will operate on a dynamic basis. The stored data can be refreshed every few seconds as necessary. However, the write and erase operations will now be orders of magnitude faster than traditional p-channel flash memory. Structures and methods for p-channel floating gate transistors are provided that avoid p-channel threshold voltage shifts and achieve source side tunneling erase. The p-channel memory cell structure includes a floating gate separated from a channel region by an oxide layer of less than 50 Angstroms. The methods further include reading the p-channel memory cell by applying a potential to a control gate of the p-channel memory cell of less than 1.0 Volt.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Electrically erasable charge trap nonvolatile memory cells having erase threshold voltage that is higher than an initial threshold voltage
InactiveUS20050237783A1Reduce erasure timeCharge is trappedSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringThreshold voltage
An electrically erasable charge trap nonvolatile memory cell has an initial threshold voltage, a program voltage that is higher than the initial threshold voltage, and an erase threshold voltage that is lower than the program threshold voltage but is higher than the initial threshold voltage. The programmed electrically erasable charge trap nonvolatile memory cells may be erased by applying an erase voltage for a time interval that is sufficient to lower the threshold voltage the transistor from a program threshold voltage to an erase threshold voltage that is lower than the program threshold voltage, but is higher than the initial threshold voltage. The time interval may be determined by repeatedly performing an endurance test using a time interval that is increased or decreased from an initial time interval, to obtain the time interval that meets an endurance specification, or allows a read to be performed successfully.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
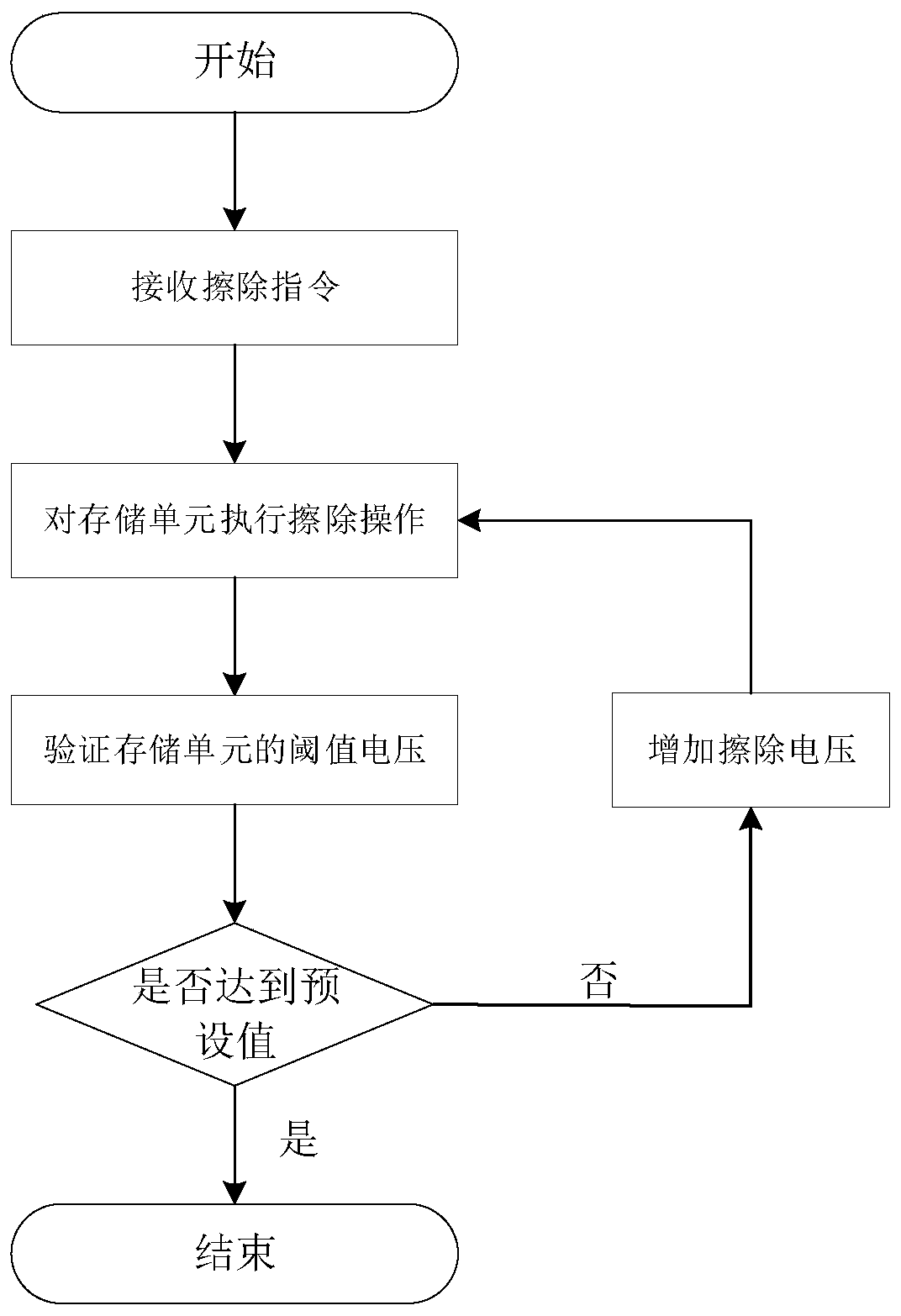
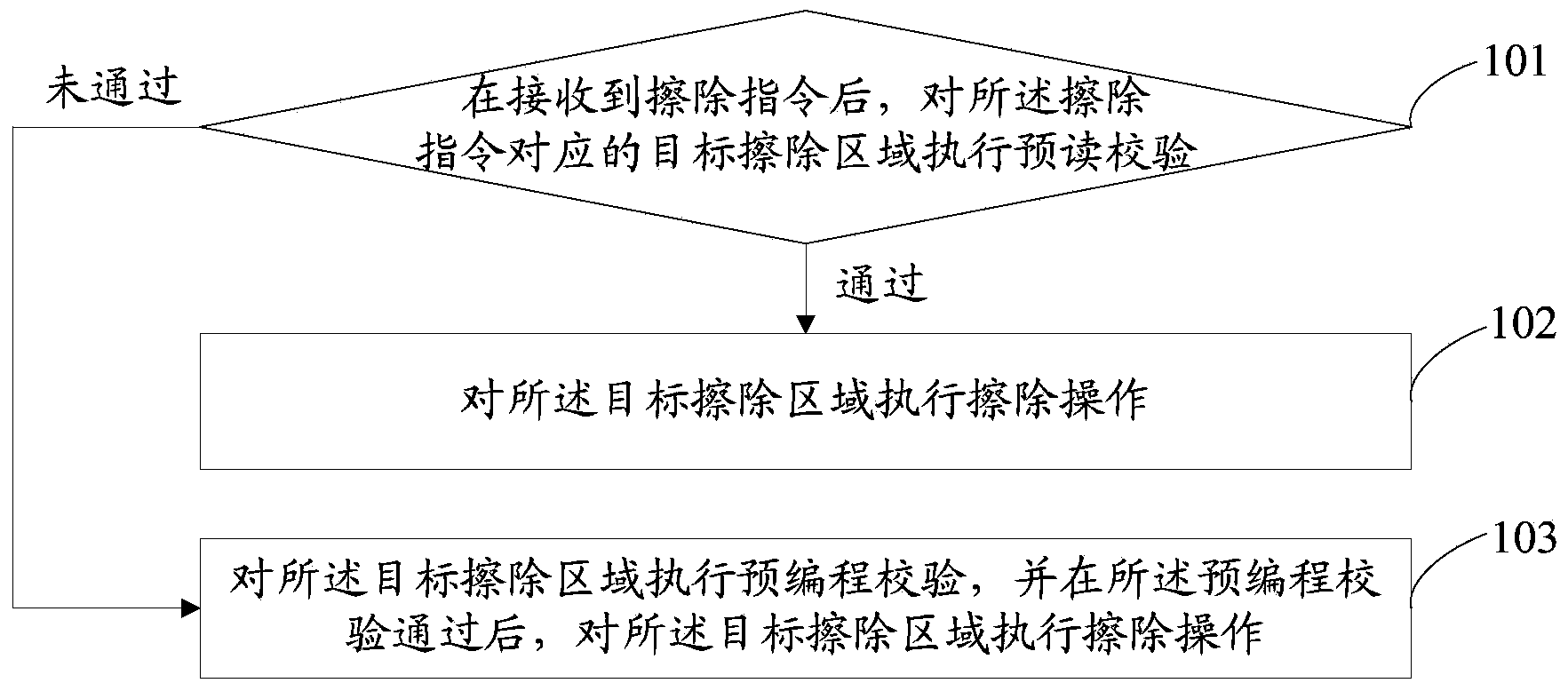
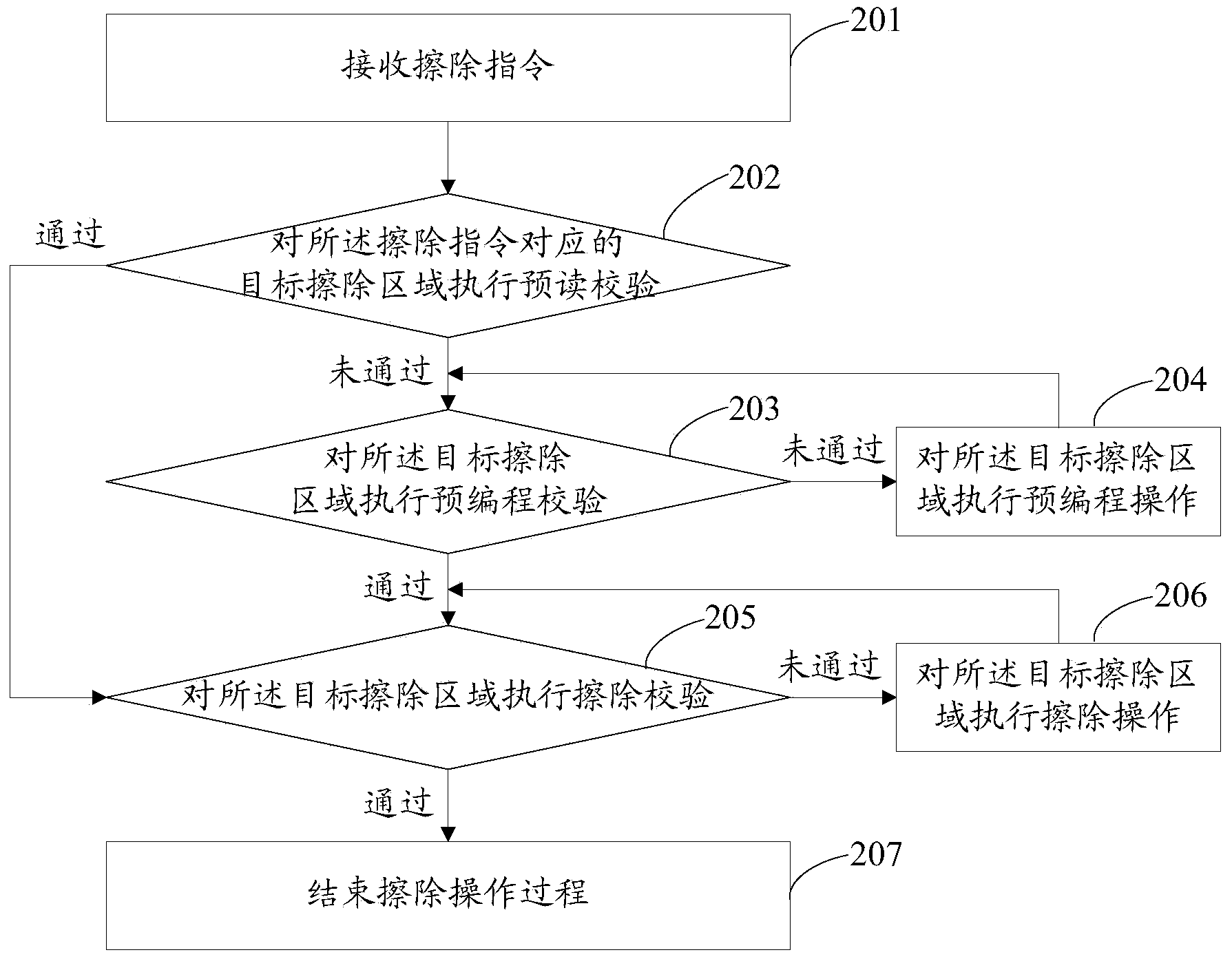
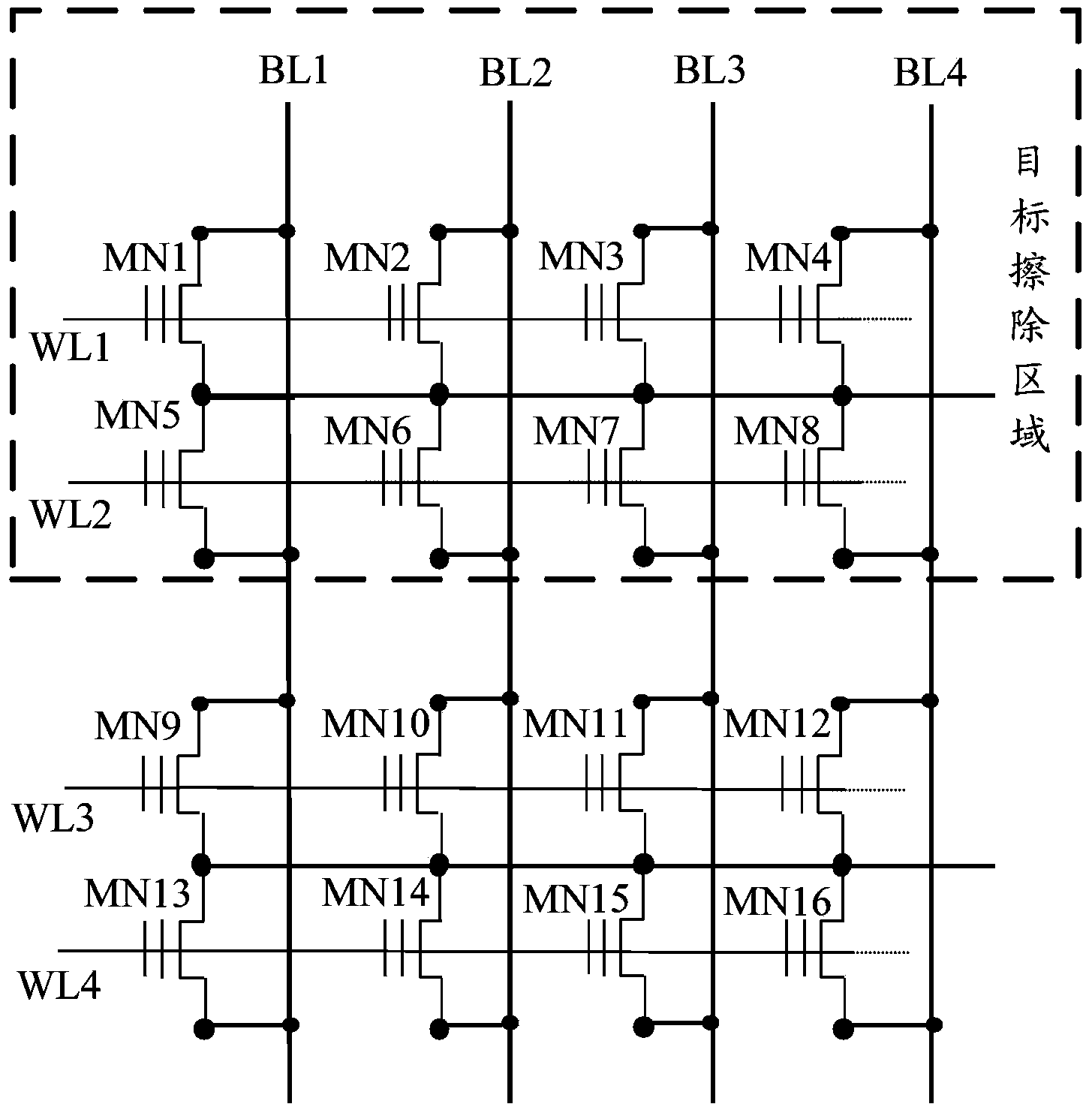
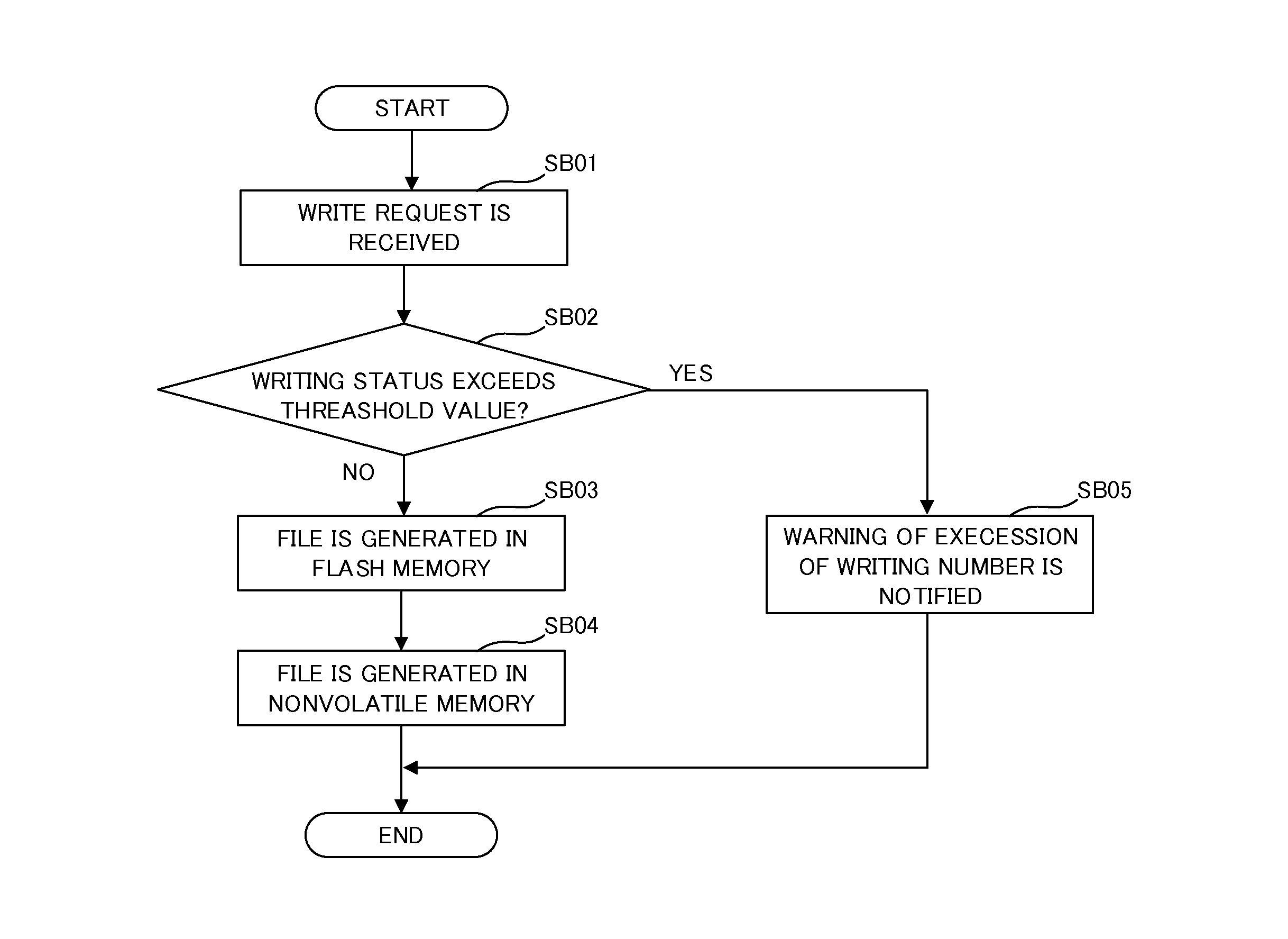
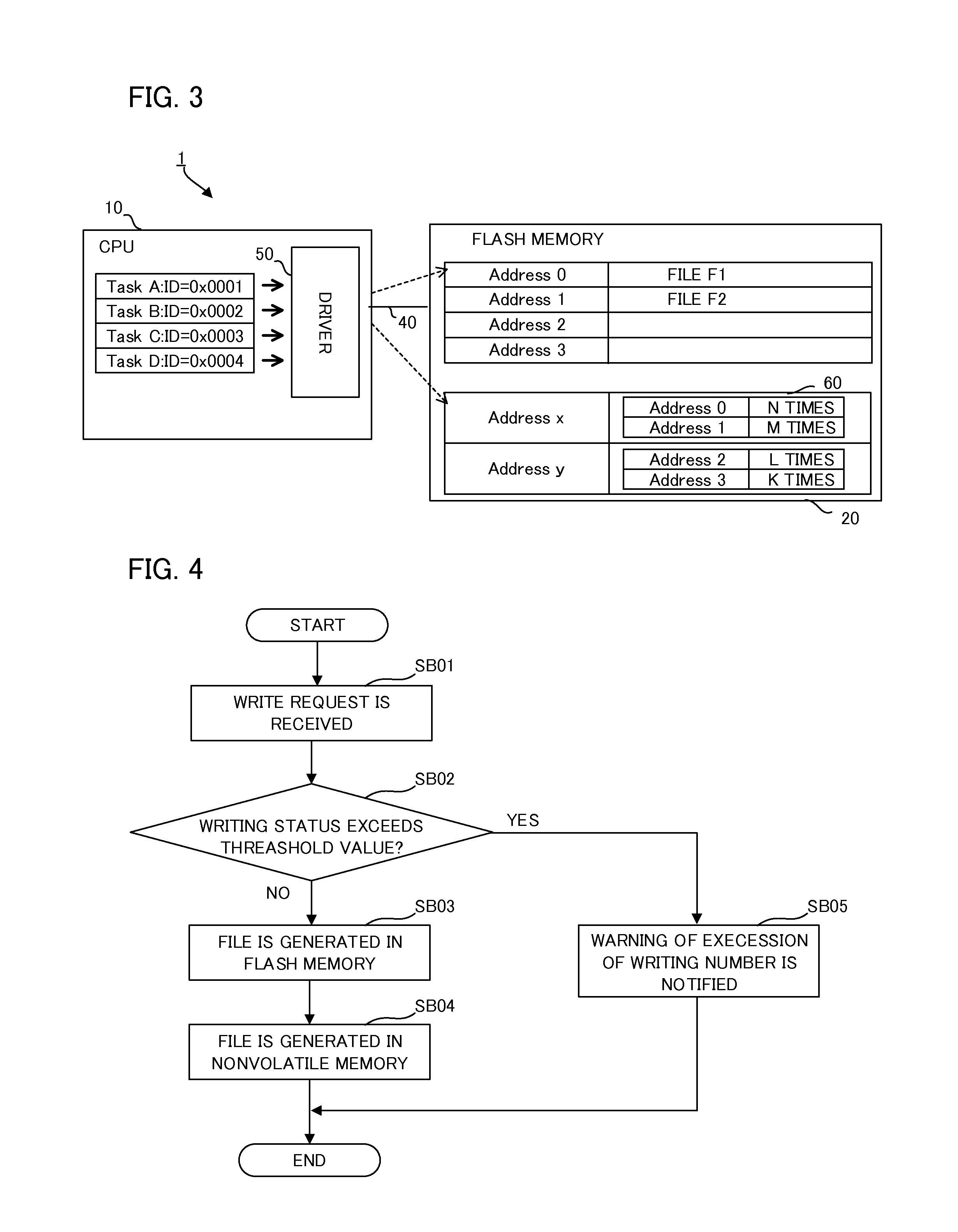
Erasure method and device for nonvolatile memory
The invention provides an erasure method and device for a nonvolatile memory, aiming at solving the problems that current erasure operation causes unnecessary time expenditure and has complicated process. The method comprises the steps of after receiving an erasure command, performing pre-reading check on a target erasure area corresponding to the erasure command; and if the pre-reading check is passed, erasing the target erasure area, but if not, performing pre-programming check on the target erasure area, and erasing the target erasure area after the pre-programming check is passed. Unnecessary pre-programming check processes are not needed before the erasure operation under the situation that the target erasure area is in all-erasure state, so that the erasure time can be saved, and the erasure process is simple.
Owner:GIGADEVICE SEMICON (BEIJING) INC
Nonvolatile memory erase control method capable of prolonging service life
InactiveCN110310692AReduce erasure timeExtended service lifeInput/output to record carriersRead-only memoriesMemory erasureSoftware
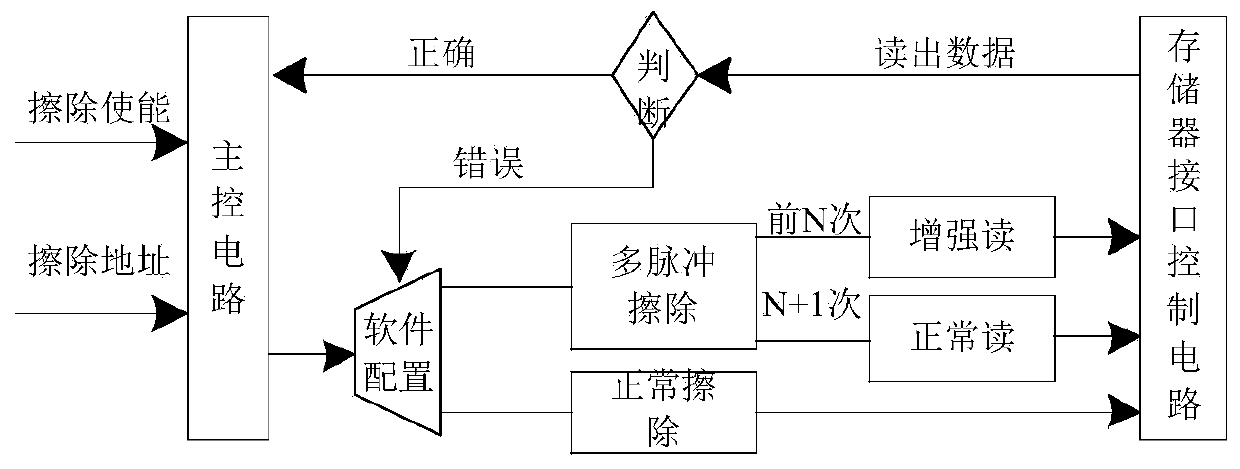
The invention discloses a software and hardware combined nonvolatile memory erasure control method capable of prolonging the service life. The method comprises the steps that first, a software is configured with and uses the multi-pulse erasure and enables the enhanced reading; then, the system initiates a request for erasing a nonvolatile memory, the hardware suspends the CPU clock, and the execution of other instructions is prevented; and after the erasing process is completed, the hardware reads the data of the erasing block by using a more strict standard, judges whether the erasing is successful, and informs the software of an erasing result flag bit; if the erase is successful, the CPU clock is turned on, and the subsequent instruction operation is executed continuously; if the erasefails, the software initiates a second erase instruction operation until the correct data is read; if the continuous N times of multi-pulse erase fails, the (N + 1)-th software enables the normal reading, and the data of the erase block is read; if the continuous N times of multi-pulse erase is successful, it is considered that the erase succeeds, otherwise, the erase process fails, wherein N canbe preset. According to the present invention, the service life of the nonvolatile memory can be effectively prolonged.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Flash memory device using ecc algorithm and method of operating the same
ActiveUS20090327839A1Low failure rateReducing erase timeRead-only memoriesCode conversionData memoryData storing
A flash memory device using an error correction code (ECC) algorithm and a method of operating the same. The device includes a memory cell array including a error correction code (ECC) block including data memory cells configured to store data and a parity cell configured to store a first parity code, a parity controller configured to generate a second parity code based on a the current operating mode of the flash memory device, and an error correction unit configured to receive one of the first and second parity codes and to perform an ECC algorithm on the data stored in the data memory cells using the received parity code. A control logic restarts an erase operation on an erroneously unerased data memory cell or prevents the erase operation from being restarted based on the number of erroneous bits per ECC block.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
P-channel dynamic flash memory cells with ultrathin tunnel oxides
InactiveUS6888749B2Lower the barrierIncrease currentTransistorRead-only memoriesVoltage shiftP channel
Structures and methods involve dynamic enhancement mode p-channel flash memories with ultrathin tunnel oxide thicknesses. Both write and erase operations are performed by tunneling. The p-channel flash memory cell with thin tunnel oxides will operate on a dynamic basis. The stored data can be refreshed every few seconds as necessary. However, the write and erase operations will now be orders of magnitude faster than traditional p-channel flash memory. Structures and methods for p-channel floating gate transistors are provided that avoid p-channel threshold voltage shifts and achieve source side tunneling erase. The p-channel memory cell structure includes a floating gate separated from a channel region by an oxide layer of less than 50 Angstroms. The methods further include reading the p-channel memory cell by applying a potential to a control gate of the p-channel memory cell of less than 1.0 Volt.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
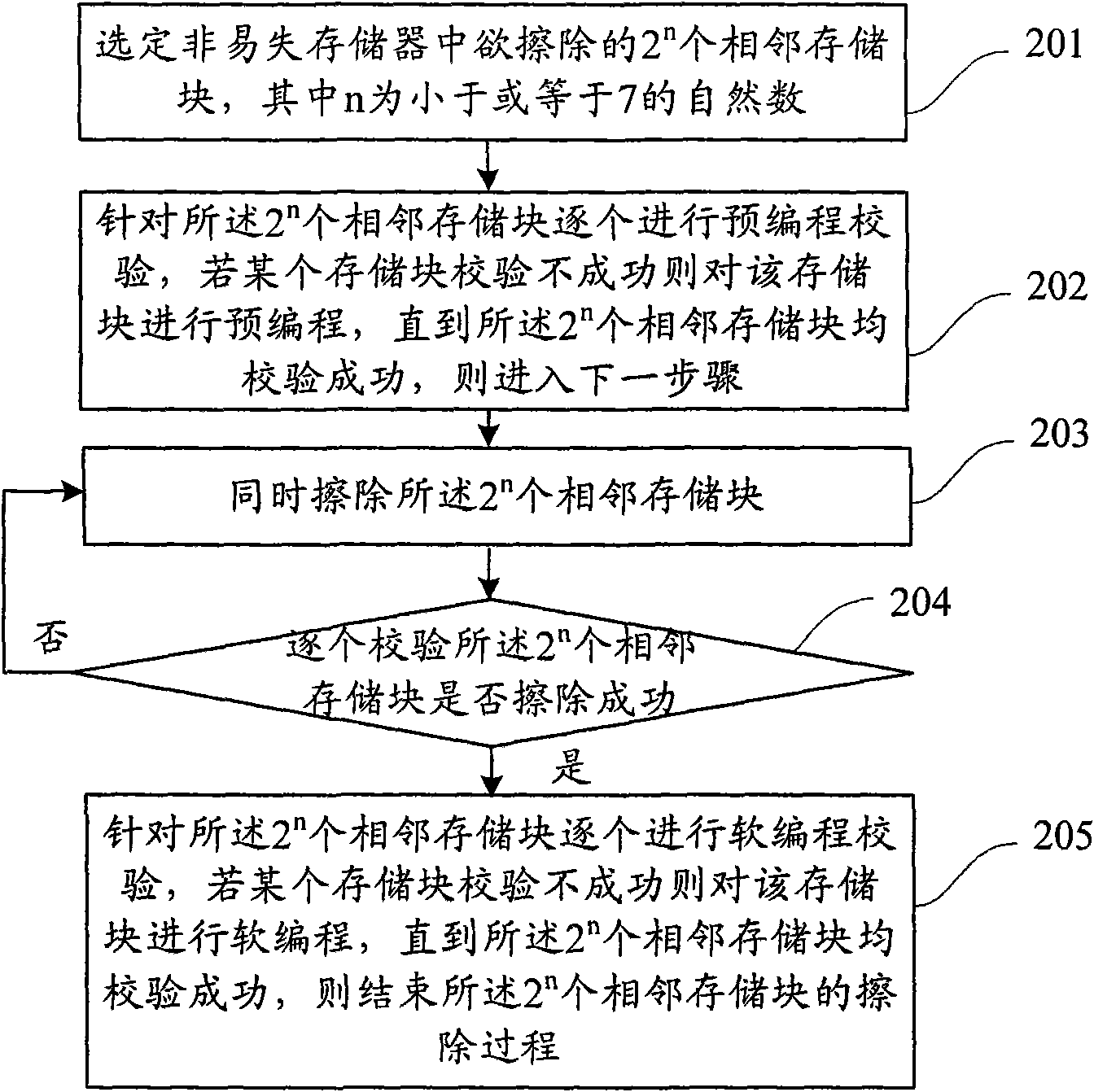
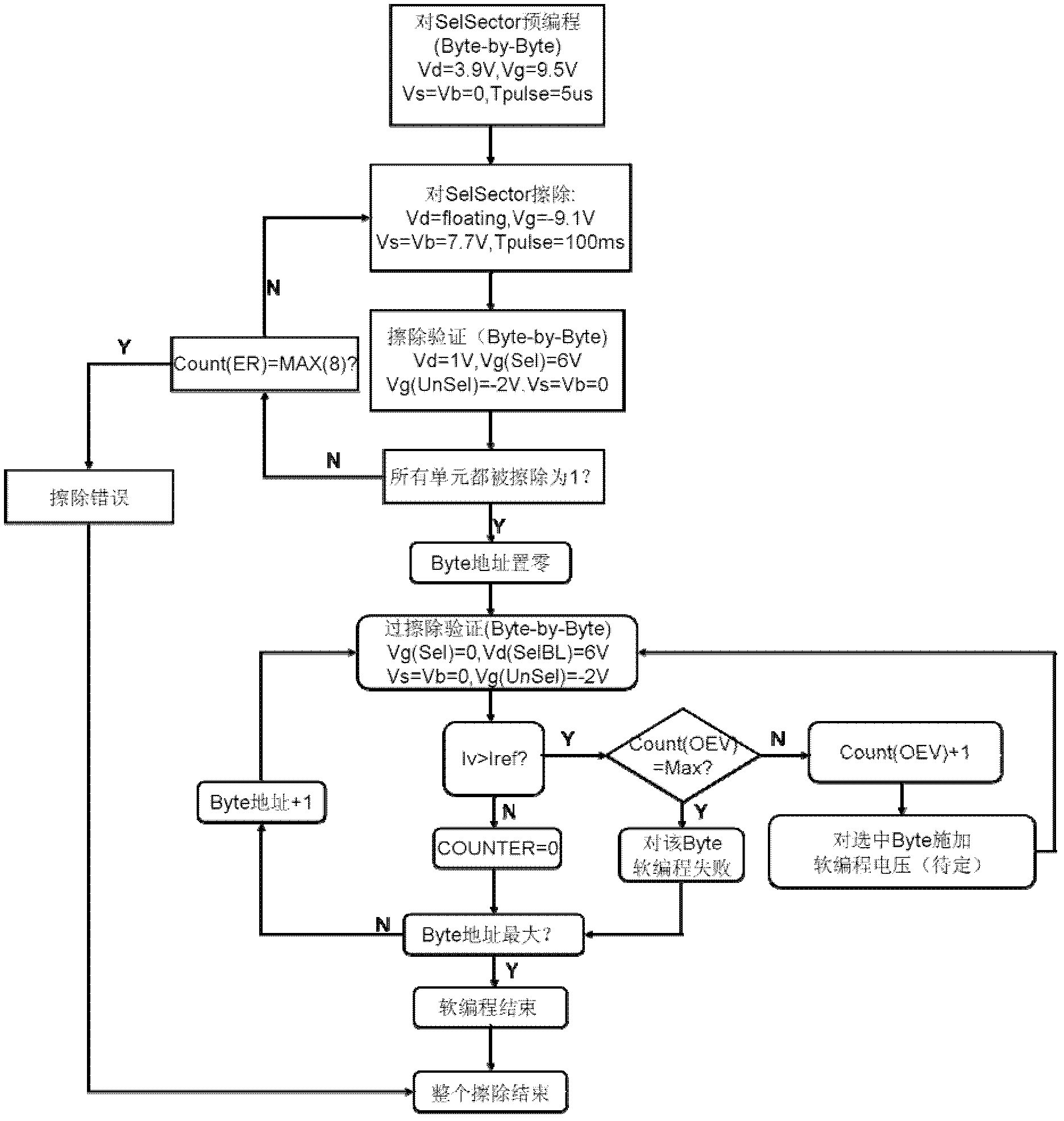
Memory chip erasing method
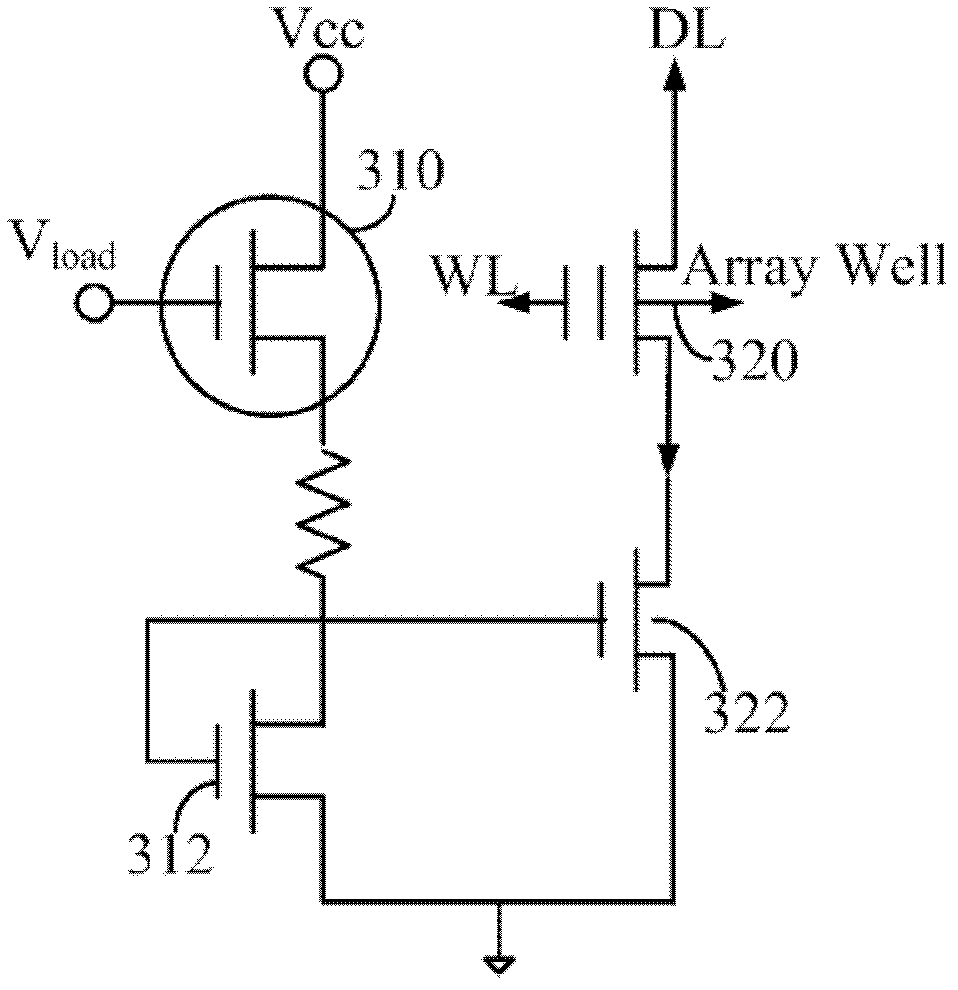
InactiveCN103000224AEasy to implementReduce erasure timeRead-only memoriesEmbedded systemCurrent limiting
The present invention discloses a memory chip erasing method, wherein a current limiting device connection manner of a common-source of a memory chip is changed into a ground connection manner. The method comprises: carrying out pre-programming on a block in a storage unit; erasing all storage units; verifying the erased storage unit; and adopting a bit line as a unit to carry out soft programming verification. With the method, an erasing time can be effectively shortened; due to use of the current limiting device, a plurality of the units are concurrently erased, and the current of the storage unit can not be too large, such that the storage unit can not be destroyed, and reliability of the erasing operation is ensured, such that the method is particularly applicable for large capacity memory chips.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Flash memory configuration method
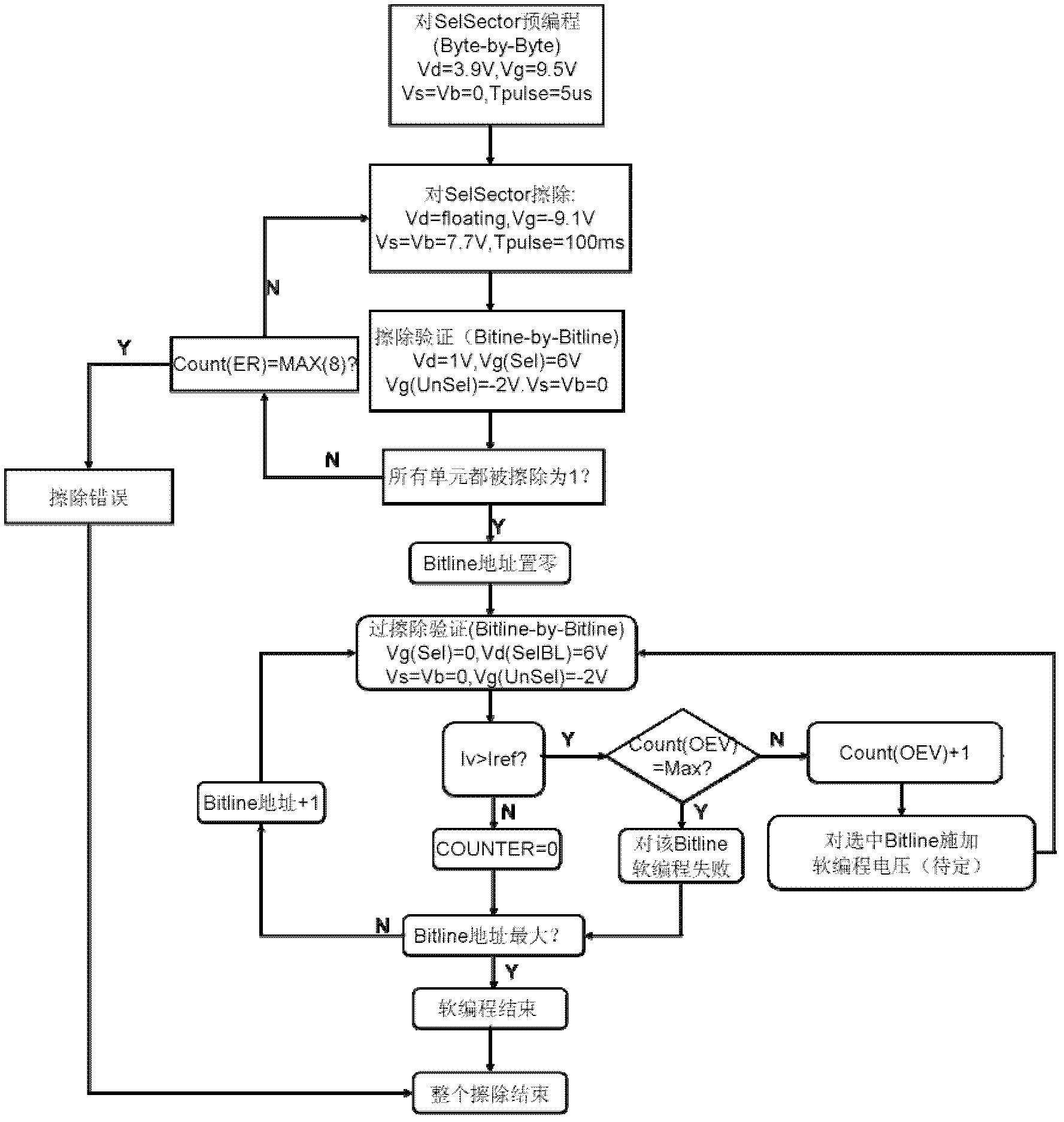
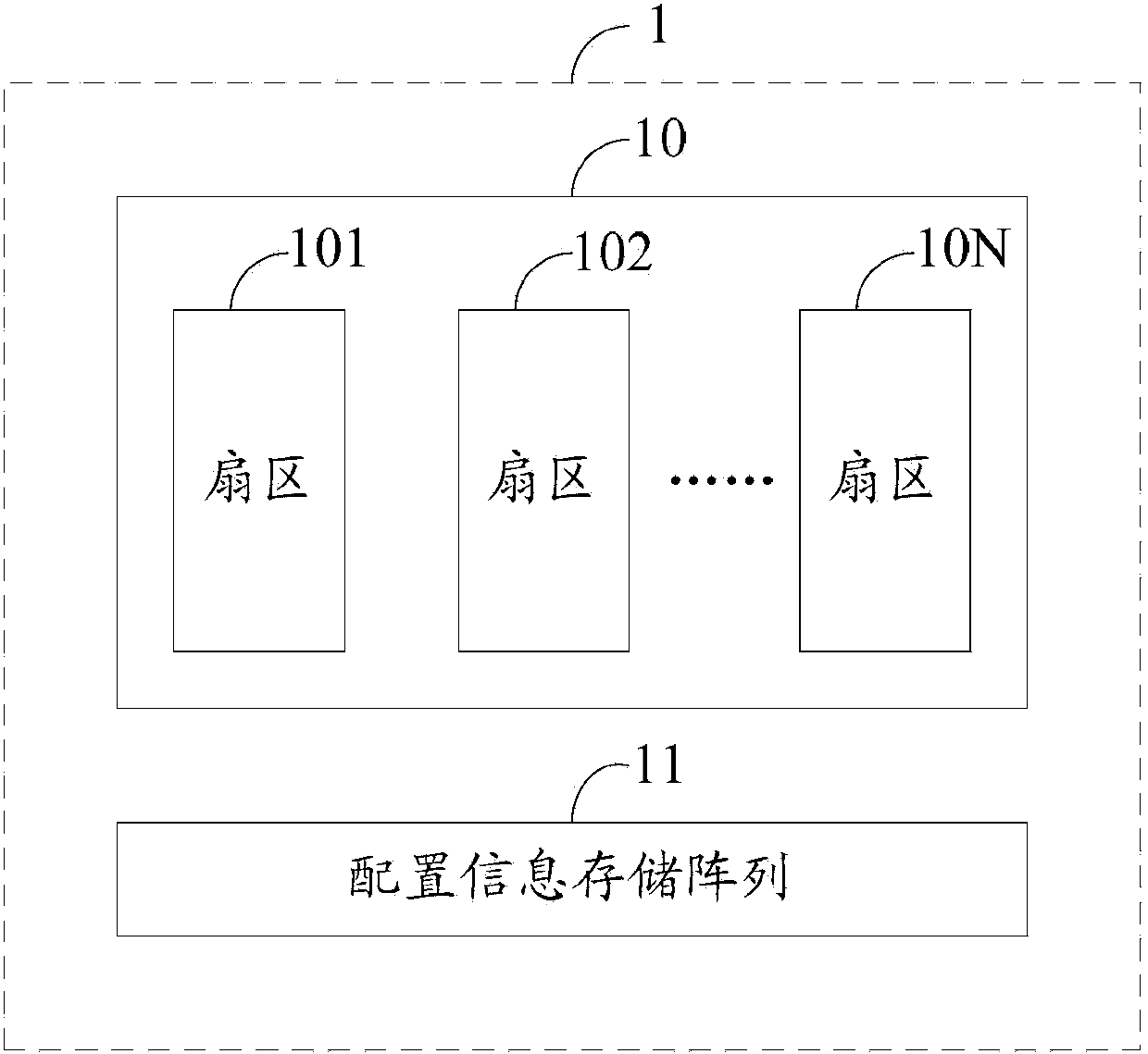
InactiveCN104217760AReduce erasure timeAvoid over-erasing effectsRead-only memoriesHigh pressureInformation storage
The invention discloses a flash memory configuration method. A flash memory comprises a data storage array and a configuration information storage array, wherein the data storage array comprises at least one sector. The flash memory configuration method comprises the following steps: a) carrying out an erasing operation to the sector; b) verifying whether the sector is successfully erased or not; c) if the sector is successfully erased, writing a binary code corresponding to sector erasing time into the configuration information storage array; d) if the sector fails to be erased, judging whether sector erasing operation frequencies reach an upper limit or not; e) if the sector erasing operation frequencies reach the upper limit, judging that the sector fails; and f) if the sector erasing operation frequencies do not reach the upper limit, repeating the step a). The flash memory can be protected from over-erasing, sector erasing time is shortened, time for a flash memory unit to bear high-pressure stress is shortened, and the reliability of the flash memory unit is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Data storage system
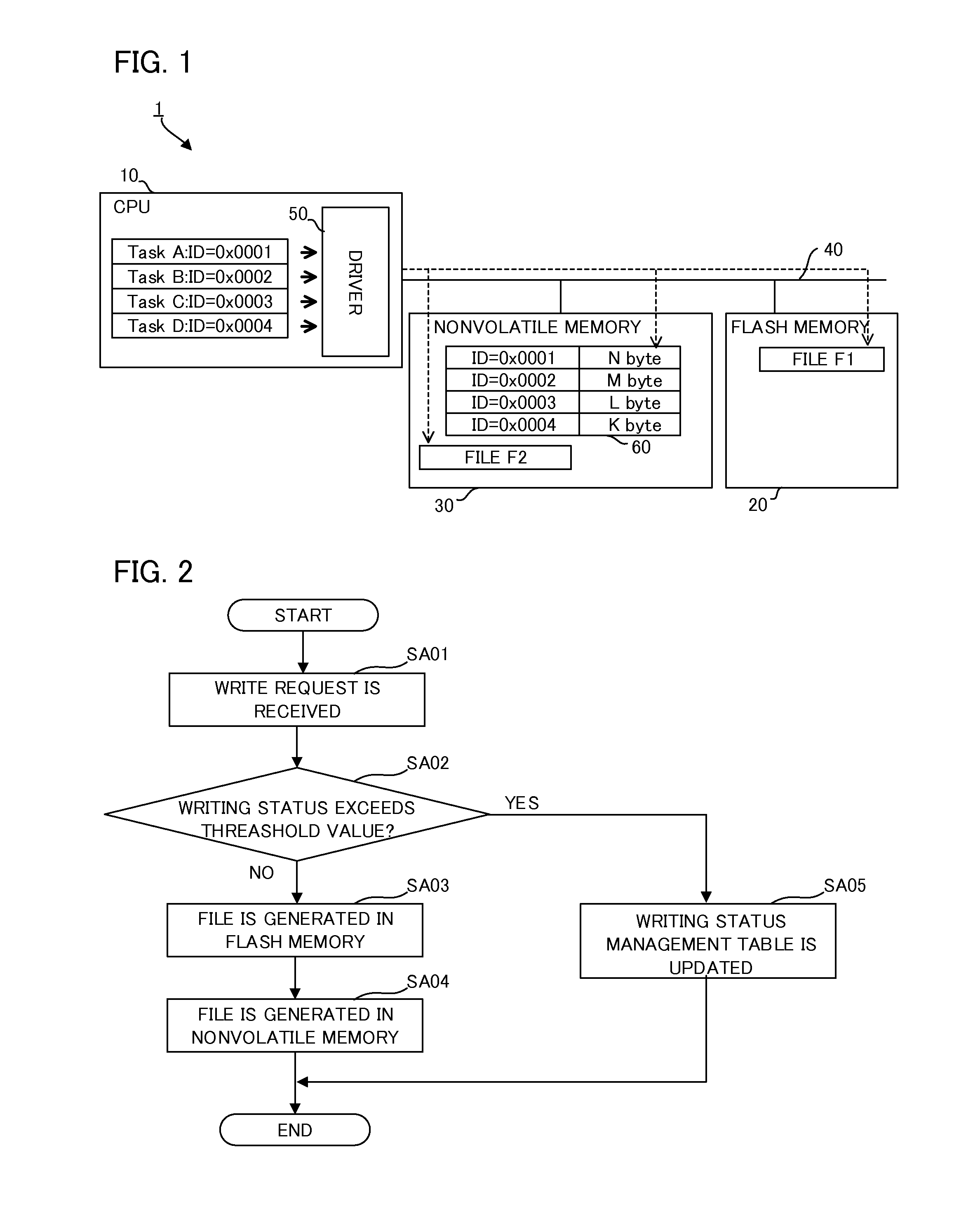
InactiveUS20160124682A1Reduce erasure timeReduce exchange frequencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersRelevant informationData store
A data storage system including a processor configured to execute a plurality of tasks, wherein the processor is configured to generate writing status information based on the data relevant information and otre the data relevant information and the writing status information in association with each other in the nonvolatile memory when the processor write data in the recording medium based on demand of the task and writing to the recording medium is configured to be controlled based on the data relevant information and the write-in status information stored in nonvolatile memory.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Non-volatile memory and manufacturing method and erasing method thereof
InactiveUS20080099818A1High speedReduce erasure timeTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringGate oxide
A non-volatile memory is provided, including a control gate, a floating gate, a gate oxide layer, a source region, a drain region, a first dielectric layer, a second dielectric layer, and an erase gate. The control gate is disposed in a substrate. The floating gate comprising a coupling part and a gate part is disposed over the control gate and located over a portion of the substrate with the gate oxide layer there-between. The source region adjoins with one side of the gate part, while the drain region adjoins with the other side of the gate part. The first dielectric layer is disposed on the floating gate. The second dielectric layer is disposed on the sidewalls of the floating gate. The erase gate is disposed over the coupling part of the floating gate and covers the first dielectric layer and the second dielectric layer.
Owner:EPISIL TECH INC
Storage device and semiconductor apparatus
InactiveUS7423902B2Reduce power consumptionReduce erasure timeElectric analogue storesDigital storageElectrical polarityElectric signal
A storage device includes memory cells disposed in a matrix. The memory cells each include a storage element whose resistance changes from a higher state to a lower state when an electric signal of a first threshold level or higher is applied and whose resistance changes from the lower state to the higher state when an electric signal of a second threshold level or higher whose polarity is different from the polarity of the electric signal of the first threshold level or higher is applied, and a circuit element connected in series with the storage element. In a state in which an erasing voltage is applied to at least one memory cell on which erasing is currently being performed, after the lapse of a predetermined time from the application, an erasing voltage is applied to at least one memory cell on which erasing is to be next performed.
Owner:SONY CORP
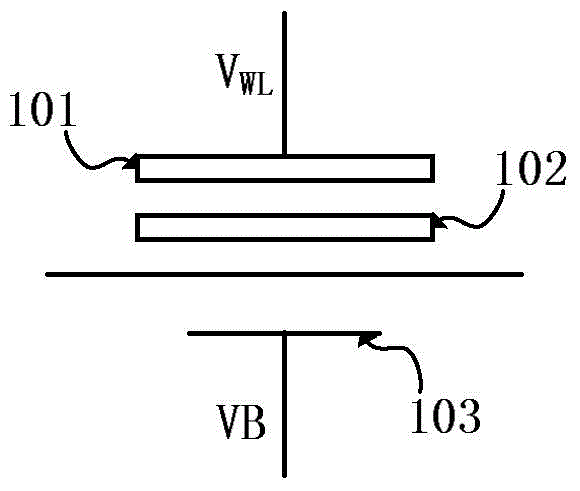
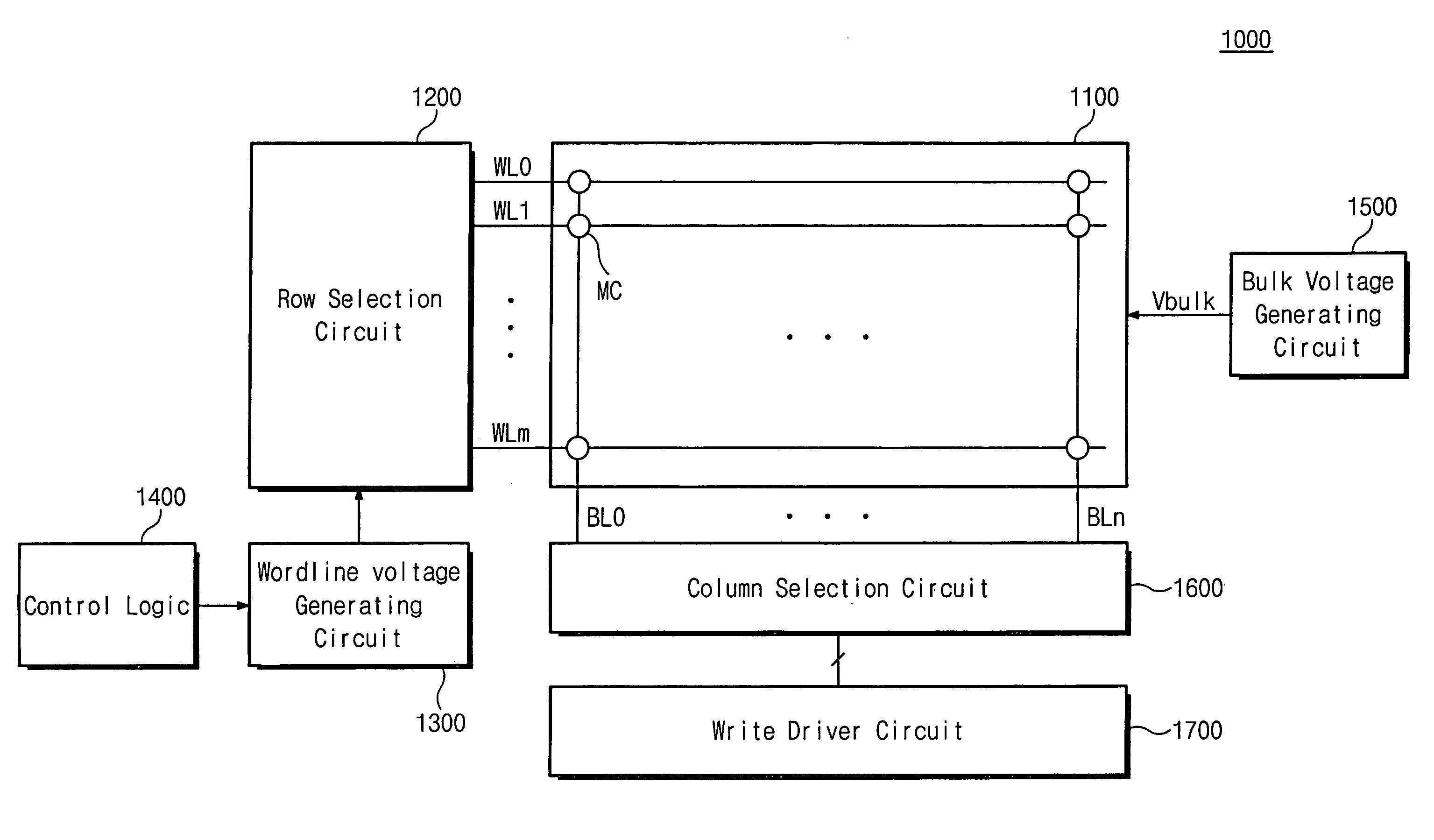
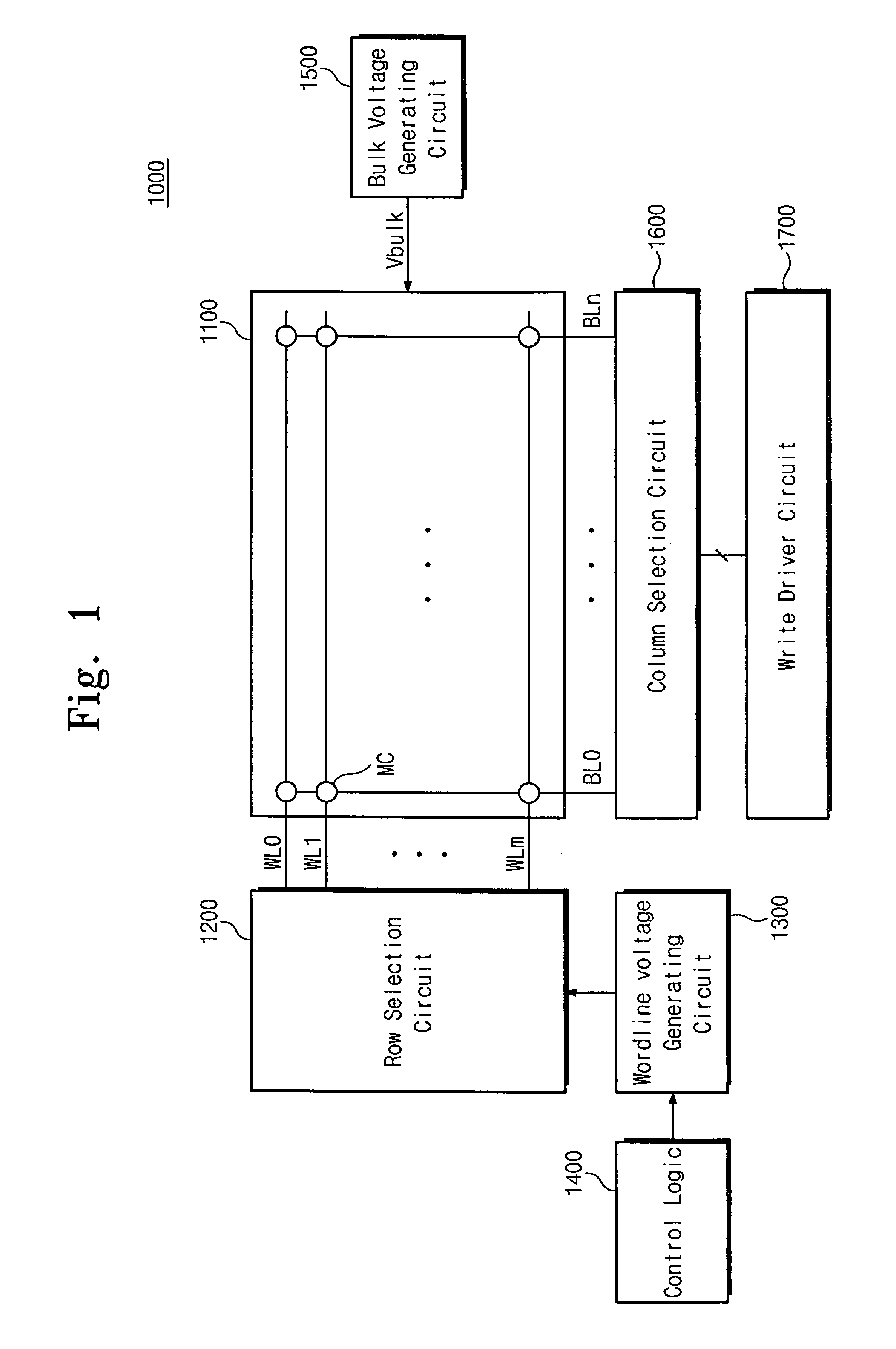
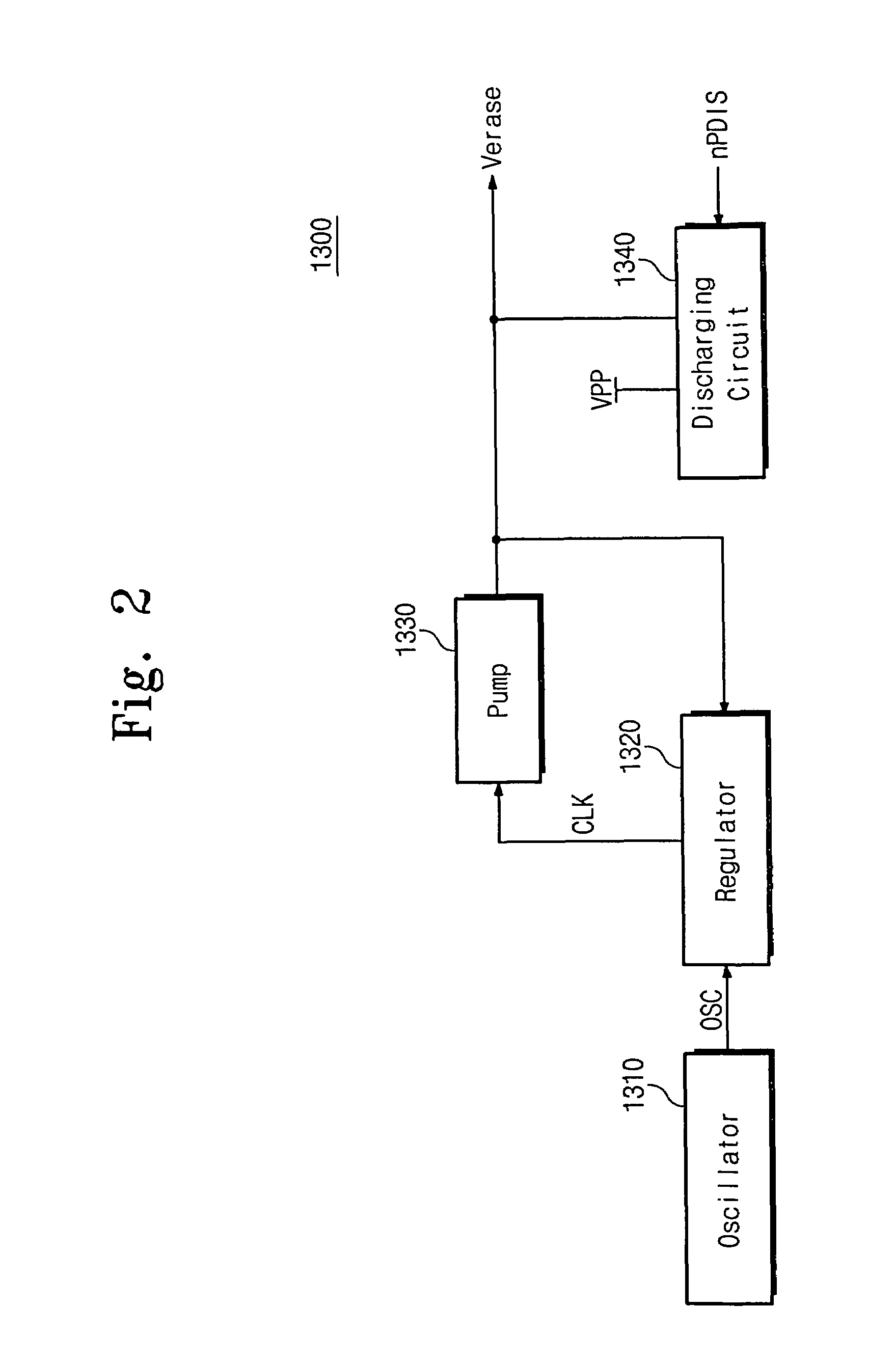
Flash memory device with reduced erase time
A NOR flash memory device comprises a memory cell array, a row selection circuit adapted to drive wordlines in the memory cell array with a wordline voltage during an erase operation, and an erase voltage generating circuit adapted to generate an erase voltage as the wordline voltage during the erase operation. The erase voltage generating circuit includes a discharging circuit receiving a high voltage that is regularly maintained irrespective of variations in a power voltage, and discharging the erase voltage supplied from the wordline during an erasing recovery period of the erase operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for writing data into flash memory and related control apparatus
ActiveUS20160148677A1Extended service lifeIncrease speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageParallel computingMulti-level cell
A method for writing data into a flash memory, wherein the flash memory includes a plurality multi-level cells, and each of the plurality of multi-level cells is capable of storing a plurality of bits. The method includes: storing a first bit into each of the plurality of multi-level cells respectively; determining if each of the plurality of multi-level cells stores the first bit respectively; and when each of the plurality of multi-level cells stores the first bit respectively, storing a second bit into each of the plurality of multi-level cells respectively.
Owner:SILICON MOTION INC (TW)
Storage device and semiconductor apparatus
InactiveUS20070153564A1Reduce power consumptionHigh speedElectric analogue storesDigital storageStorage cellSemiconductor
A storage device includes memory cells disposed in a matrix. The memory cells each include a storage element whose resistance changes from a higher state to a lower state when an electric signal of a first threshold level or higher is applied and whose resistance changes from the lower state to the higher state when an electric signal of a second threshold level or higher whose polarity is different from the polarity of the electric signal of the first threshold level or higher is applied, and a circuit element connected in series with the storage element. In a state in which an erasing voltage is applied to at least one memory cell on which erasing is currently being performed, after the lapse of a predetermined time from the application, an erasing voltage is applied to at least one memory cell on which erasing is to be next performed.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and system for reducing erase interference and erase time, storage medium and terminal
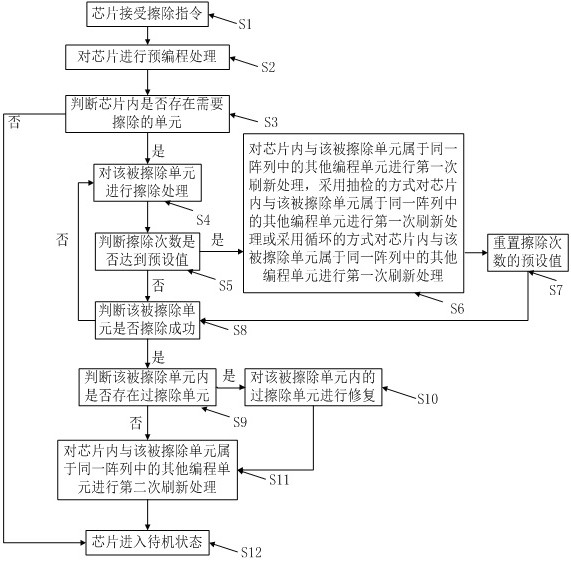
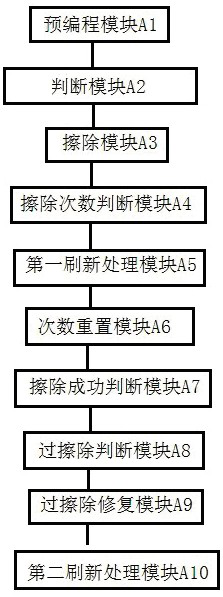
ActiveCN111785315AReduce erasure timeMeet the use requirementsRead-only memoriesComputer hardwareProcessing
The invention discloses a method and a system for reducing erasing interference and erasing time, a storage medium and a terminal. The method comprises the step of performing first refreshing processing on other programming units which belong to the same array as an erased unit in a chip by adopting a sampling inspection mode or performing first refreshing processing on other programming units which belong to the same array as the erased unit in the chip by adopting a circulating mode. Although certain reliability of the chip is sacrificed, the erasing time is greatly reduced, and the use requirements of products are met.
Owner:XTX TECH INC
Flash chip and erasing method thereof
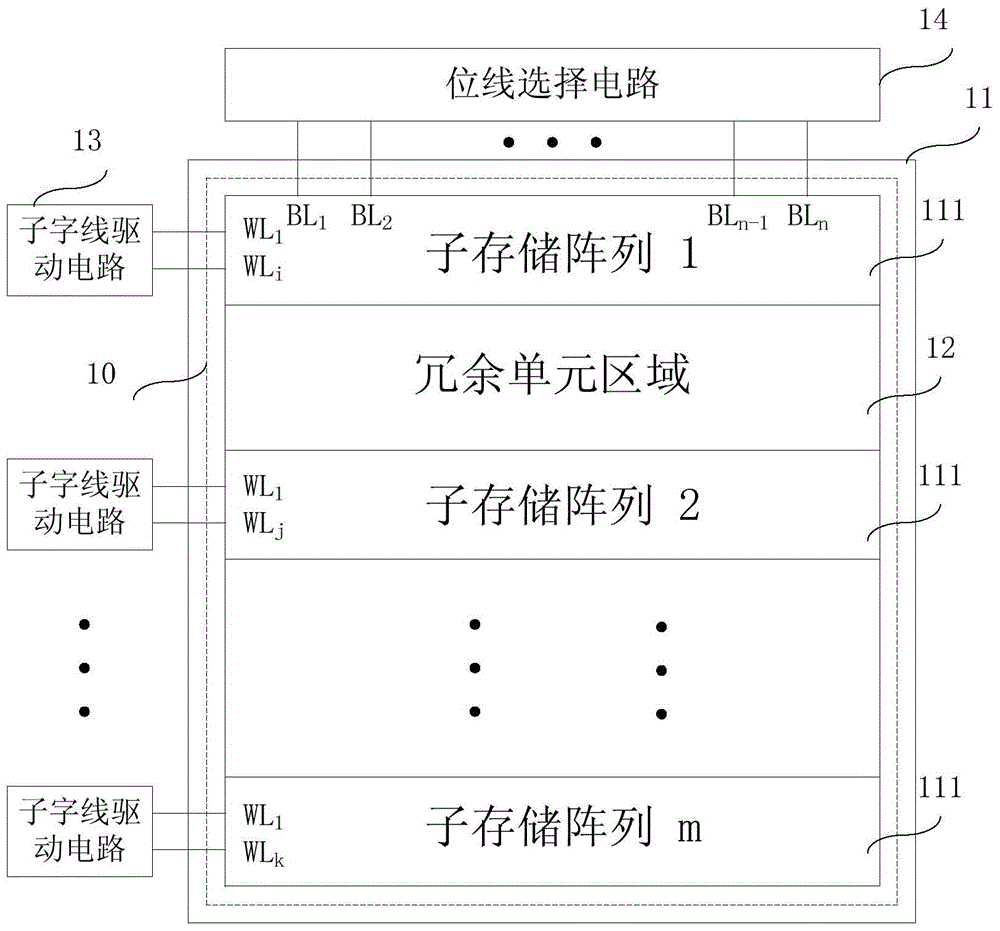
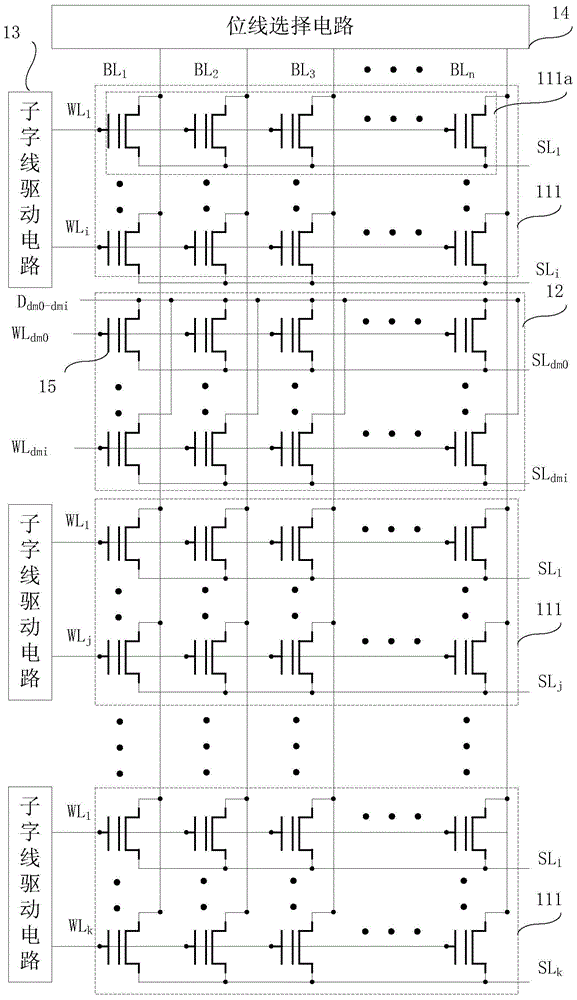
ActiveCN104882165AErase interference has little effectImprove erase effectRead-only memoriesBit lineHemt circuits
The invention relates to the technical field of memories and particularly relates to a flash chip and an erasing method thereof. The flash chip comprises a memory array, m word line driving sub-circuits and a bit line selecting circuit, wherein the memory array comprises m memory subarrays and a redundancy unit zone; the m memory subarrays are formed in one well region; the redundancy unit zone is formed between two adjacent memory subarrays; during erasing, a drain electrode of a memory unit in the redundancy unit zone is suspended in midair; the m word line driving sub-circuits are respectively connected to the m memory subarrays; each word line driving sub-circuit provides driving signal to the memory subarray connected to the corresponding word line driving sub-circuit; and the bit line selecting circuit provides a plurality of bit lines, is connected to drain electrodes of memory units of the memory subarrays in each row of the memory array and is used for selecting the memory units in the memory subarrays. Erasing performance of the flash chip provided by embodiments is improved and erasing time of the flash chip is shortened, thus increasing the erasing efficiency.
Owner:GIGADEVICE SEMICON (BEIJING) INC
Flash memory device and erase method using the same
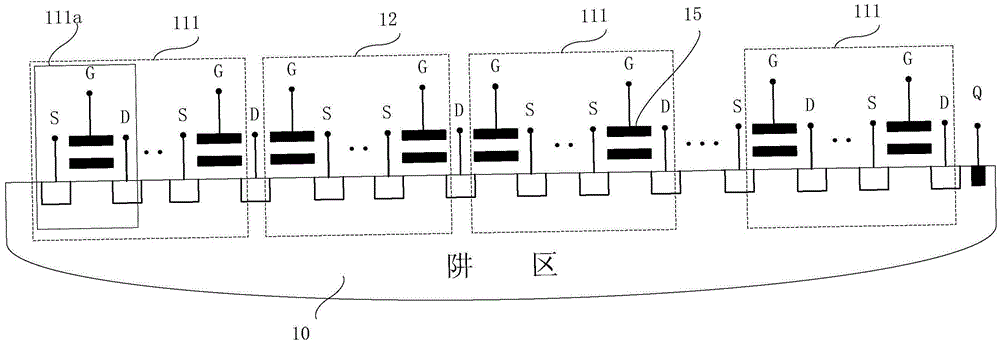
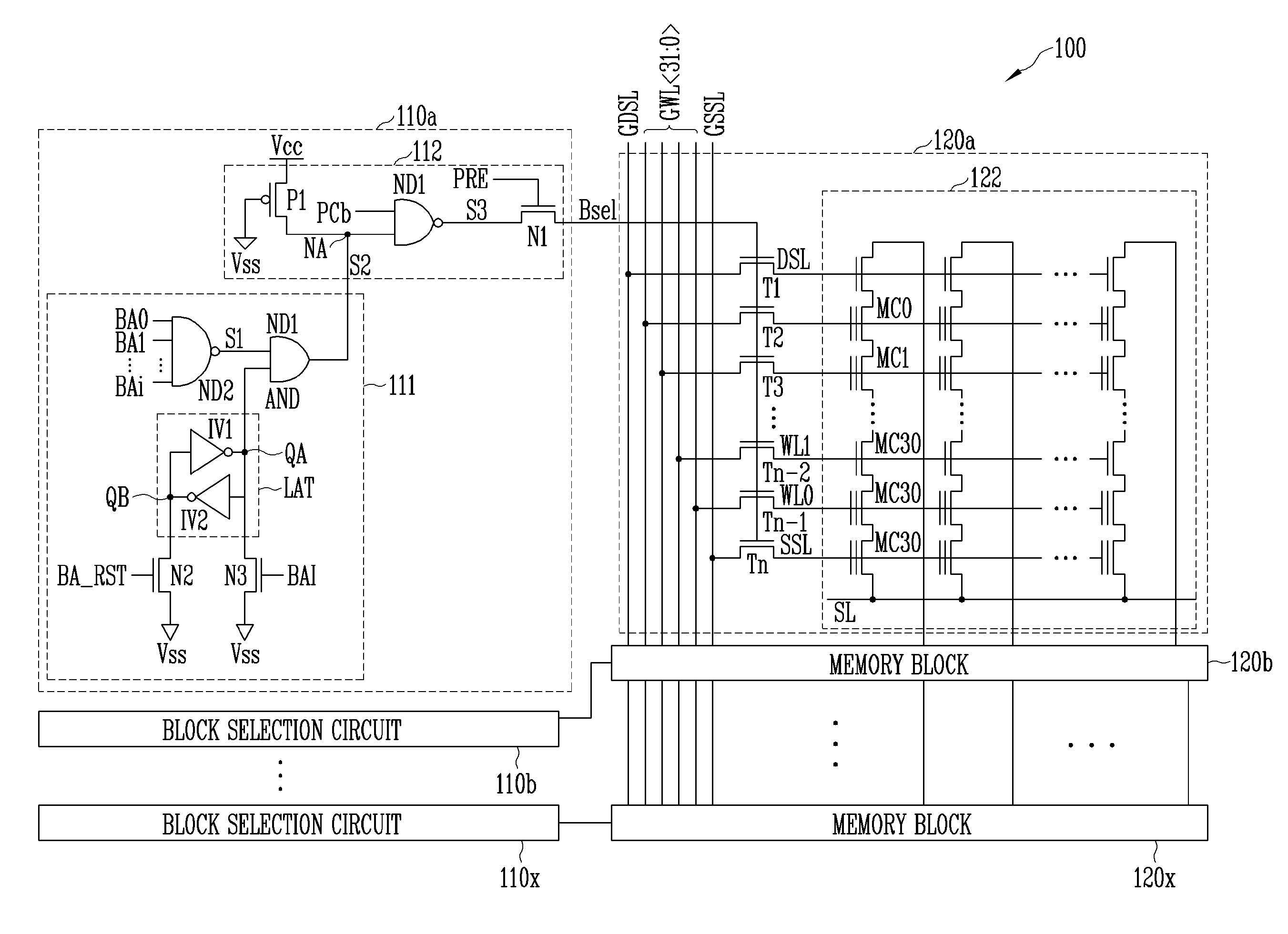
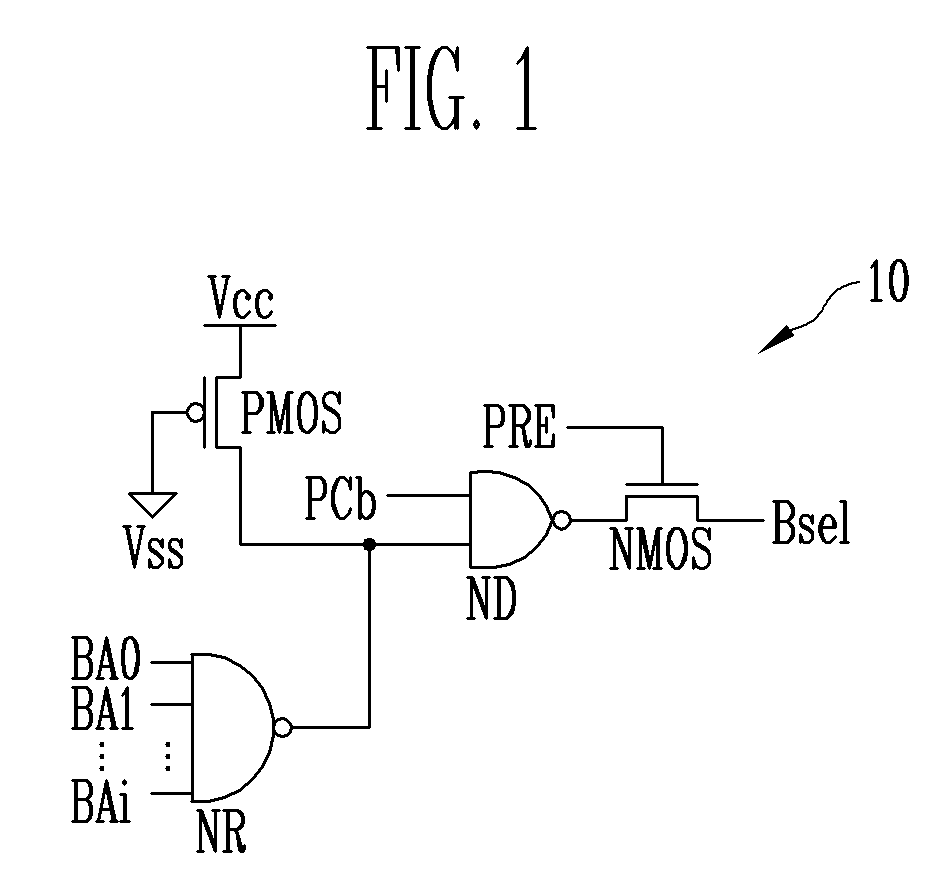
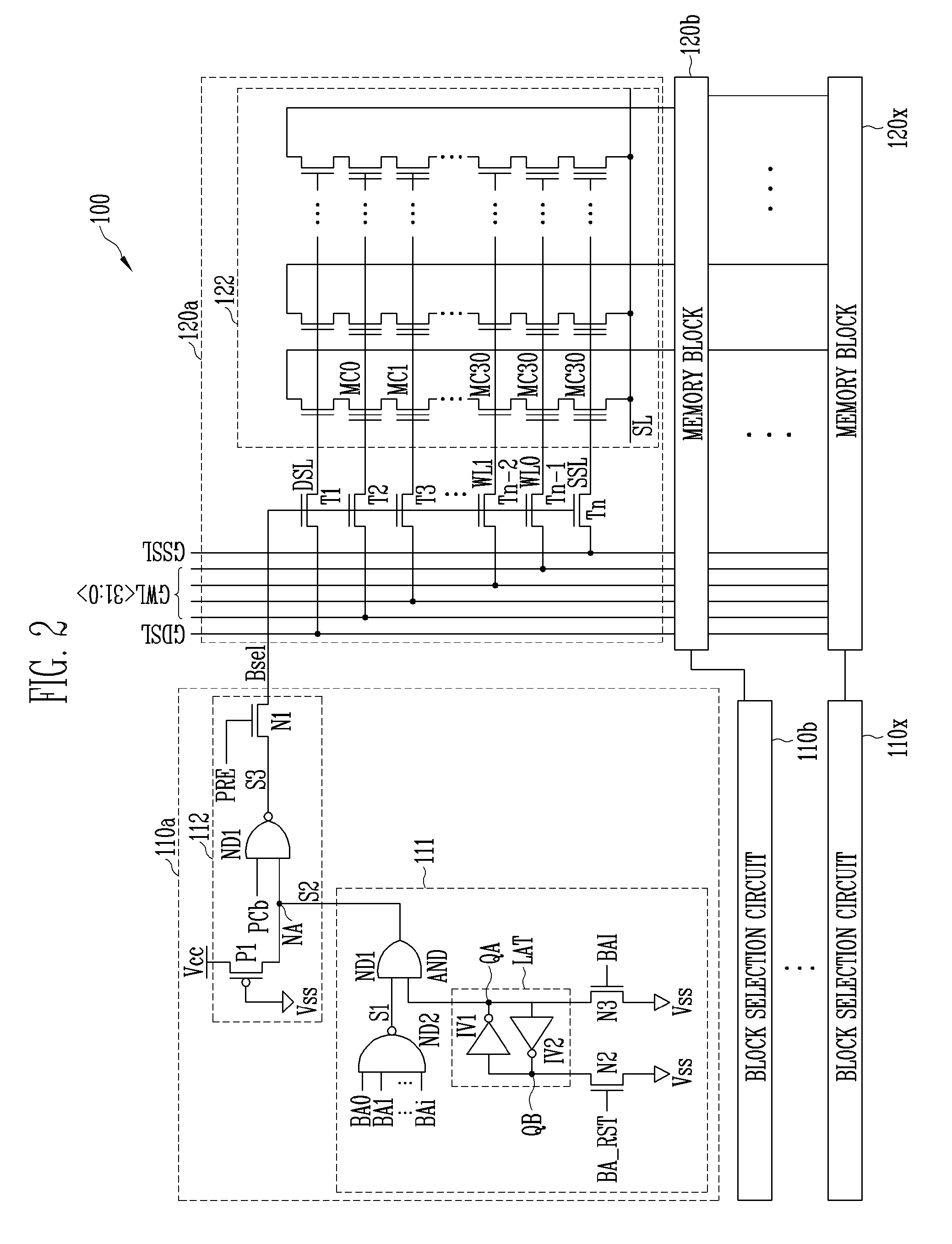
ActiveUS7760580B2Reduce erasure timeRead-only memoriesDigital storageControl signalParallel computing
A flash memory device includes a plurality of block selection circuits and a plurality of memory blocks. The plurality of block selection circuits generate a block select signal in response to a plurality of decoded block address signals and a block control signal. The plurality of memory blocks are connected to global lines in response to the block select signal, and include a plurality of memory cell arrays performing an erase operation in response to a well bias. Each of the block selection circuits generates the block select signal in response to the block control signal regardless of the plurality of decoded block address signals, or selects the block select signal to select a corresponding memory block in response to the plurality of decoded block address signals.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com